Column internals. MTE Process technology
|
|
|
- Beatrice Henry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Table of contents 1. Internals for packed columns Liquid Distributors MLD11/MRD21 Pan type distributor/re-distributor MLD 112/212 Pan type distributor with raised orifices MLD121/MRD221 Riser deck distributor/re-distributor MLD122/MRD222 Riser deck distributor/re-distributor with raised orifices MLD141/MRD241 Trough type (re-)distributor with sump MLD142/MRD242 Trough type (re-)distributor with sump with raised holes MLD143 Trough type distributor with parting box & V-caps MLD161 Pipe Arm distributor MLD146 Trough type liquid distributor with orifice multipliers Bed Limiters MBL31 Bed limiter for random packing MHG32 Hold down grid for structured packing Support Plates MSP41 Support plate MSP42 Support plate MSP43 Support plate MSG44 Support grid Liquid collectors / Chimney trays MLC51 Liquid collector tray MLC52 Vane Type Collector MLC53 Trough Type Collector Feed devices Liquid only Mixed or flashing feeds Vapor only / 16
2 1. Internals for packed columns Introduction Columns packed with either random or structured packing must also include several additional key internal components that are necessary for the packing to function. These internals include vapor and liquid feed distributors, packing support and hold down plates, entrainment separators and liquid draw-off trays, all of which must be designed to suit the specific service requirements. MTE has developed basic engineering standards for the design and manufacture of high performance packed column internals based upon many years of installation experience and industry feedback. These standards are applied to custom design and manufactured internals to suit individual process and installation requirements resulting in consistent and reliable column performance. General Arrangement The typical arrangement of a packed column alongside shows indicative locations and space requirements for a range of internals. The internal clearances shown are the normal minimum required for access. Access manway locations should take account of future maintenance work which would typically include checking chimney trays and distributors and also possibly removal and replacement of the packing. MTE have considerable experience in retrofitting existing columns with new internals by using unique design variations to overcome space restrictions and to use existing welded-in attachments. 2 / 16
3 1.1 Liquid Distributors Packed tower design is based on the fundamental concept of equal liquid and gas superficial velocity across the column section. The pressure drop across the packing provides an impetus for the upward flowing gas to get uniformly distributed across the column area. The liquid flows down the packed bed by gravity and unlike a gas has poorer cross-mixing tendency. Hence it is imperative to manage a very uniform liquid distribution at the top of the bed. Distributors are internals installed above a packed bed which perform the job of providing a finite liquid distribution over the packed bed. It provides for liquid to be distributed over the packed bed in discrete streams, which could either be through orifices or V- weirs. It also provides for a separate passage for the upward flowing gas. On entering the bed the packing tend to redistribute the liquid by virtue of dispersion and after some height the liquid profile adapts to the natural distribution tendency of the packing which generally is worse than the initial liquid distribution provided by the distributor. Hence packed beds are broken down after fixed heights and liquid redistributors are provided to collect all the down flowing liquid and redirect it uniformly over the packing. A packed bed irrigated by a very good distributor helps one to realize the full separation potential (number of stages) of the packed bed. Distribution Quality Quantifying the uniformity of liquid distribution is done by calculating the distribution quality (DQ) of a distributor. It relates the liquid flux across the column area at the top of the packed bed by marking circles proportional to the liquid flow through that orifice and then considering the irrigated, overlapping and un-irrigated areas of the circles. An ideal distributor should have a DQ of 100%, but practical constructional difficulties restrict the DQ to about 96% maximum. A low DQ indicates a high degree of maldistribution and some parts of the column area may be receiving substantially different from the other parts of the cross sectional area. Also in large diameter columns proper irrigation of areas near the column wall becomes a very crucial factor in maintaining a good DQ. A distributor with a very good DQ helps in exploiting the full separation efficiency of the bed. As the DQ decreases the number of stages that can be realized from the packed bed decreases, consequently decreasing the separation efficiency. The effect of a poor DQ is depending on the number of theoretical stages generated by the packing. For packed beds with a high number of theoretical stages the effect of a poor DQ of the distributor is much larger compared to a bed with a low number of theoretical stages. Various factors considered in the design of liquid distributors / redistributors at MTE are: Drip points This indicates the irrigation points provided per square meter of the column area and are a function of mainly the size of the packing, the liquid load and the desired DQ. Smaller or highly efficient packing, that provide a very low HETP, needs a larger number of drip points and vice-versa. More important compared to the number of drip points is the drip point arrangement and equally pitch. To provide same liquid distribution across the column area. 3 / 16
4 Hydraulic Design This forms the most important aspect of the distributor design wherein the designer decides the various dimensional details of the distributor to ensure its efficiency over the range of working conditions. A distributor can feed the liquid to the packing top either under pressure, as in a pressure fed distributor where the liquid is fed to the distributor under pressure or due to gravity, as in a gravity flow distributor where the liquid falls thru the distributor by virtue of its head on the distributor deck. A pressure fed distributor is either of ladder arm type or of spray nozzle type, used for very specific applications, mainly for heat transfer services. As these distributors operate under pressure, the orifice sizes in these distributors are usually small. These distributors should not be used with flashing feed. Major advantage of using a pressure fed distributor is total wetting of the surface of the packed bed; while high point to point flow variation and high cost are some of the disadvantages. Unless otherwise requisitioned MTE always recommends a gravity flow distributor. These distributors, due to the several constructional variables available to the designer as discussed below, offer excellent uniformity and control of liquid flow to the packed bed. The gravity fed distributor could either use orifices or V-weirs to feed the liquid. Again the orifices could either be located on the floor of the deck/trough or on the side wall of a trough (single level or multilevel). Passage for gas rising upwards is either provided by riser boxes/pipes or through the gaps between the troughs. Orifices are sized to maintain a minimum liquid head in order to handle normal turn down conditions and also avoid distributor flooding during turn up conditions having maximum flow rates. Very small orifice diameters are avoided to prevent fouling. Distributor levelness, liquid gradient due to cross flow, aeration of the liquid due to falling liquid streams and the ledge/support ring levelness are factored for during the orifice sizing, so that even at very low flows the orifice to orifice flow variation is controlled to acceptable limits. Better resistant against fowling. For high fouling services, which can occur due to sedimentation, coking, debris, polymerization, etc. orifices on the deck floor are avoided. Depending on the service, V-weirs or orifices on the side wall are provided. The use of orifice multipliers also increases orifice size and makes the distributor. Multilevel orifices help in the distributor operation over a wide range of flows and are typically used whenever a very high turn-up / turn down ratio is required. Distribution Quality (DQ) Depending on the service and separation efficiency required from the packed bed, the size of the packing and the orifices, the drip points are laid out to meet the specific drip point requirements. During this stage allowances are made for the distributor constructional details like support beams, gas risers etc. so as to maintain the required DQ. 4 / 16
5 1.1.1 MLD11/MRD21 Pan type distributor/re-distributor This simple looking device for small towers up to 1200mm is actually a high performance distributor consisting of critically sized orifices uniformly laid on the base of the pan for liquid down flow and adequate open area for upward flow of vapor. Downwards of a certain size and under the corresponding operating conditions the gas risers are no longer necessary. Their absence in this case is not detrimental to the functioning of the unit. Column Diameter < 1200 mm Liquid Load m 3 /m 2.hr Turndown ratio 2,5:1 Fouling resistance Low to medium This distributor can be made in both single and multi-piece construction. In multi-piece construction, all joints are foreseen with gaskets. Attachment to the tower wall is mostly by bolting to cleats. It can also be mounted between body flanges or alternatively suspended from a ring sandwiched between the body flanges. The choice between these two arrangements will depend on the location of other internals and in revamp case, the type of attachments already available in the column. For columns with diameters up to 800 mm, the supply of liquid is effected by means of a pipe which is bent downwards onto the center of the distributor. For diameters over 800 mm, we recommend a sprinkler pipe which is perforated on the underside. In both cases the exit velocity of the liquid should not considerably exceed 1,5 m/s. The feed pipe is also available together with the distributor upon request. The re-distributor consists of riser caps and when attachment is to cleats, wall wiper is also required MLD 112/212 Pan type distributor with raised orifices This distributor is similar to model MLD111 only with raised orifices, created by constructing orifices with driptubes. With driptubes the distributor is able to be designed for larger T/D ratio and in combination with orifice multipliers it can be made better resistant to fouling as well. Column Diameter < 1200 mm Liquid Load m 3 /m 2.hr Turndown ratio 10:1 Fouling resistance Low to medium 5 / 16
6 1.1.3 MLD121/MRD221 Riser deck distributor/re-distributor This is a deck type distributor where orifices are located on the base of the distributor. Gas risers located between the orifices propagate liquid cross-flow thereby enhancing distribution quality. It is generally in multi-piece construction and all joints are sealed with gaskets. Attachment is by clamping to a ledge/support ring which is welded to the column wall. This distributor can be provided with anti-migration bars in the risers and thereby eliminating the use of bed limiters. Redistributor risers are capped to prevent short circuiting of liquid Column Diameter > 250 mm Liquid Load >2-150 m 3 /m 2.hr Turndown ratio 2,5:1 Fouling resistance Low to medium MLD122/MRD222 Riser deck distributor/re-distributor with raised orifices This is a deck type distributor where orifices are located on the walls of the risers of the distributor. Gas risers located between the orifices propagate liquid cross-flow thereby enhancing distribution quality. Deck types can also be designed with driptubes like MLD112 Column Diameter < 1200 mm Liquid Load > m 3 /m 2.hr Turndown ratio 10:1 Fouling resistance Low to medium 6 / 16
7 1.1.5 MLD141/MRD241 Trough type (re-)distributor with sump This distributor is constructed of multiple tunnels called troughs with a integrated parting box called a sump. The feed enters the sump which divides it proportionally to the troughs. Orifice for liquid are located on the base or of the troughs and the sump. Column Diameter > 800 mm Liquid Load 2 50 m 3 /m 2.hr Turndown ratio 2,5:1 Fouling resistance Low to medium Achieving adequate sealing is critical due to large number of joints at the sump to trough connection. All joints are gasketed for adequate sealing. This distributor is appropriate for applications with higher gas capacities, as a larger free area can be created between the troughs compared to deck types. This distributor rests on a ledge/support ring. The redistributor consists of riser caps and wall wiper. A construction with parting box can be considered for high liquid loads MLD142/MRD242 Trough type (re-)distributor with sump with raised holes This distributor is similar to model MLD141 only with raised orifices, created by constructing orifices on the trough walls or with driptubes. For low liquid loads, this type of distributor is constructed to hang below a support ring or support beams, so secure elevation of all troughs is possible for high distribution quality. Column Diameter > 800 mm Liquid Load 0,5 50 m 3 /m 2.hr Turndown ratio 10:1 Fouling resistance Medium 7 / 16
8 1.1.7 MLD143 Trough type distributor with parting box & V-caps This distributor is especially developed for application with high liquid load or high tendency for fouling, without high requirements for liquid distribution quality. It consists of long tunnels called troughs and one or more parting boxes for feeding liquid to the troughs. The parting box helps in controlling the feed velocity to the troughs and ensures proportional distribution of the li quid to the troughs. Column Diameter > 900 mm Liquid Load m 3 /m 2.hr Turndown ratio 5:1 Fouling resistance High The space between the troughs is available for vapor passage. Number and location of the parting box will depend on the column diameter. Rectangular or V-shaped notches are located on the trough walls. Notches can also be applied to deck type distributors MLD161 Pipe Arm distributor This is a very simple distributor consisting of a header and a lateral assembly. It requires very little column height and provides high open area resulting in very low vapor pressure drop. It does not provide very high distribution quality and therefore it has limited applications. The main header is flanged at one end and clamped to a column wall clip at the opposite end. Column Diameter > 500 mm Liquid Load m 3 /m 2.hr Turndown ratio 2:1 Fouling resistance Low 8 / 16
9 1.1.9 MLD146 Trough type liquid distributor with orifice multipliers The MLD146 is a modification of the MLD142 type where a second distribution stage is introduced below the troughs. In this distribution point the liquid flowing from a single drip tube is divided in 6 stream by an overflow principle. The liquid is guided through wells down to the fingers which are set to for the distribution points and create an uniform distribution across the columns area. Column Diameter > 250 mm Liquid Load 0,2 50 m 3 /m 2.hr Turndown ratio 20:1 Fouling resistance Medium to high The unique design of this distributor allows the designed to increase the orifice diameter in the drip tubes in case of low flows and achieve a device which is less sensitive to fouling by plugging of the orifices. This is the main principle which gave the starting point for the development of this distributor type. By implementing overflow notches in the driptubes, the distributor is proven to keep working over a huge range of flows and hardly sensitive for fouling. This distributor has proven performance in various systems varying ranging from m3/m2.hr. For very low flows this distributor is also used in high quality systems where distribution qualities of 95% and higher are achieved for flows of 0.5 m3/m2.hr with aqueousliquids and even lower in hydrocarbon systems. The new production methods also allow MTE to manufacture this device in any material, metal alloys as well as thermoplastics. All joints are gasketed and material thickness can be designed to suit your application. 9 / 16
10 1.2 Bed Limiters Bed limiters or Hold down plates are retaining devices used above the packed beds to prevent fluidization, which mainly occur during upset conditions and restrict packing movement. Bed limiters are designed to provide high free area and reduce interference to liquid flow. They should withstand upward forces acting on the packed bed MBL31 Bed limiter for random packing This bed limiter is normally recommended for metal and plastic random packing and is designed to withstand an up thrust. The openings sizes can be varied to suit various packing sizes and the beams can de designed to support man-load. The bed limiter can be clamped on to a support ring or rests on the tower packing where no tray support ring is available. The major advantage of using a movable anti-migration screen is reduction in crushing of tower packing during surges or bed expansions, certainly for beds with carbon or ceramic packing. The bed limiter is held in place by providing weight bars and does not require any type of clamping arrangement. Another option is to make the bed limiter construction expandable with jack screws provided to tighten on the column wall which obviates the need for ledge/support ring. This maintains good distribution near the column wall. The MBL31 bed limiter consists of a frame backed with a screen of expanded metal. The plates, which are divided into segments, are installed into the column through the manholes and then bolted together. The materials used are carbon steel, stainless steels and thermoplastics. Please note that plates made of carbon steel are normally backed with screens made of stainless steel. Versions made of special metals are also available MHG32 Hold down grid for structured packing The Hold Down plate is normally used for towers using structured packing. Fluidization does not occur with structured packing, but for large diameter columns, sections of packing may be dislodged during upset conditions. Hold Down grids for structured packing are designed to reduce interference with liquid distribution. They are bolted to the column wall by vertical clips. For smaller columns, the distributor is provided with an integral retention plate, thereby eliminating need for separate Hold down Grid. 10 / 16
11 1.3 Support Plates Support plates are provided for physically supporting the cumulative weight of the random and structured packing as well as operating liquid hold up. Support plates are shaped and designed to provide maximum open area such that there is minimum resistance to gas flow. The factors that influence the choice and design of the support plate are the column diameter, design load, packing type, liquid hold up and systems corrosivity. Gas injection support plates provide separate pathways for gas and liquid and therefore it reduces pressure drop across the support plate. These are the most preferred type and are used in the majority of applications. Light duty support plate is used only for very small columns and where hydraulic loading is not severe. All support plates rest directly on a support ring since the weight of the packing is sufficient to keep the support plate in place. If required however, they can be clamped to the ring MSP41 Support plate Model MSP41 is a support plate recommended for towers generally smaller than 900mm diameter. This type of support plate is designed using expanded metal and is constructed as a multi-piece or single piece unit depending on the column opening that will be available to install it. These support plates rest freely on, or can be clamped/bolted to, a ledge support ring MSP42 Support plate Model SP42 is a gas injection type support plate designed for towers generally smaller than 1200 mm diameter. These types of support beams are generally designed in multi piece or single piece construction that depends on the manhole sizing or installation through body flange. Under normal circumstances, the individual segments in the column are not bolted together. This can be provided for, however, on special request. The slot size is based on the size of packing to be supported. These support plates rest freely or can be bolted to the tray support ring. In all cases, the free cross section of the MSP42 is more than 80% of the cross sectional area of the column. 11 / 16
12 1.3.3 MSP43 Support plate Model MSP43 is a gas injection type support plate designed for towers generally greater than 1200 mm diameter. The design ensures a high degree of permeability for gas and liquids. In the standard version, permeability is more than 100%. The MSP43 is designed for higher mechanical strength. The beams are made in single units that pass through a manhole. Special variants are available to handle very tall beds and are also available in thermoplastic materials. The perforation of the plate elements is suitable for both rings-shaped and saddle-shaped packing. The minimum dimensions for the tower packing are d 15mm for rings and d > 1 for saddles. As a rule, all support plates are placed on a closed support ring. In order to prevent the support plates from being lifted when there are pressure surges in the column, the support plate is fixed to the support ring by means of special locking devices. Very tall beds together with larger column diameters results in higher load, in such cases support plates are supported using I-beams in conjunction with the tray support ring MSG44 Support grid Model MSG44 is a support grid used in towers for supporting structured packing. It is designed to allow free passage of gas and liquid. These support grids rest freely or can be clamped to a ledge/support ring. Very tall beds together with larger column diameters results in higher load, in such cases support plates are supported by support beams in con-junction with the tray support ring. 12 / 16
13 1.4 Liquid collectors / Chimney trays Liquid collection between packed beds is frequently required. Liquid collectors are used in three main applications:» For total draw-off of liquid as a product or to re-boiler or for pump-around sections» Partial draw-off of liquid with overflow continuing down the tower» Collection of liquid for mixing or redistributing Liquid collectors come in different design styles to meet the needs of specific applications. The factors considered in the design of the collector trays are: Height required/available for the collector tray Column pressure (Vacuum) and permissible pressure drop (to decide the open area) Liquid and vapor loads and densities Column diameter Liquid draw-off quantity Allowable leakage rate MLC51 Liquid collector tray This deck type liquid collector is a versatile one that can be used in all towers. Liquid volume and residence time can be controlled by having tall risers (round) on the deck. Sumps can be added on one side, both sides or across the centre to facilitate liquid withdrawal. This collector can provide 25 to 40% open area. This collector requires mid-span support beams in large columns (> 2000 mm ID). The deck and optional sump(s) rest on tower ledges / tray support ring and the plate is seal-welded. Gas risers can be made in sections / pieces to allow installation through manhole, later they are welded to the deck. 13 / 16
14 1.4.2 MLC52 Vane Type Collector The model MLC52 is used in towers which process high vapor loads and low liquid loads (vacuum service). The vanes collect the overhead liquid and direct it into the annular sump, which may then be drawn from the tower or fed to a distributor below using an appropriate feeding system. It offers the minimal pressure drop (as it can provide open areas from 40 75%) and it avoids entrainment even at high vapor rates which otherwise would cause entrainment from conventional gas risers. The vanes rest on an annular sump, and are fastened to cleats provided on the sump. The sump is welded to the tower wall and is generally provided for by the column vendor. For larger towers and high liquid rates, collection trough(s) are added, spanning across the annular sump to reduce liquid gradients MLC53 Trough Type Collector The model MLC53 is being used in a wide range of applications with column diameters larger than 1400mm. This type is normally used in applications where thermal expansion due to temperature fluctuations is of great importance. The trough type design reduces the number of welds with the column wall. The troughs can easily expand and are mounted on a support ring. An layout with a drip bar directs the liquid than into the troughs. The main collector trough in the center of the column carries the weight of the other troughs. At one side the main trough is connected to a pipeline where the liquid can be removed from the application. The other side is closed and can be used to give some additional space for expansion. The size of the main and side troughs is determined according the required hydraulic load in the column. In general this collector type has a open area between 25 and 40%. 14 / 16
15 1.5 Feed devices Piping systems inside the column are required to introduce feeds and in some cases to draw products. These need to be custom engineered in conjunction with all other column internals to suit the process and mechanical specifications of the column. MTE have developed a set engineering standards for the design of internal pipe work to ensure that liquid feeds are compatible with the proper functioning of liquid distributors and that inlet vapor velocities will not cause maldistribution. Processes demand various feed to be introduced into the column at appropriate locations. The feeds being introduced could be:» Liquid only» Liquid and Vapor above a packed bed (flashing or mixed feeds)» Vapor only Liquid only Liquid-only feed devices are required to introduce liquid into the column, either as feed or as reflux. The liquid is fed into the distributor and its design depends on the distributor type, liquid flow, operation range, degrees of sub-cooling etc. In most cases a liquid only feed pipe is a piping system of headers, lateral branches and down pipes, which is used to fed liquid from outside the column onto a distributor/redistributor. Each feed pipe meters flow to one or more appropriate feed areas, matching the hydraulic requirements of the distributor to prevent excessive turbulence and control the horizontal flow velocity in the distributor. A liquid only feed pipe can be attached to an internal column flange and further supported by the tower wall clips Mixed or flashing feeds For mixed or flashing feed devices above a distributor separating the two phases is the main concern. The various factors in design include the flow rate, the type of flow at feed (flashing or suppressed), turndown necessary, column height needed for flashing vapor distribution and mixing of the inlet liquid with overhead liquid. MTE is able to design and supply all different types of mixed and flashing feed devices like flash galleries, flash feed chambers and flashing feed pipes. 15 / 16
16 1.5.3 Vapor only Vapor only feed devices are required for re-boiler returns or to introduce vapor feed or gaseous feeds. If the column offers adequate pressure drop then the packing tends to mix the vapors. But in event of very low pressure drop across the packed beds, vapor channeling could become a serious problem. The kinetic energy of the vapor and its composition at the point of introduction are the two main factors considered in designing the vapor entry device. A vapor distributor can be a pipe distributor or a plate distributor. The pipe distributor is used when the feed requires uniform distribution over the tower area. This type of distributor is the most simple and therefore the most costeffective option for gas/vapor introduction. The inlet pipe is either perforated or slit on the underside or executed as an open pipe section. The gas exits downwards from the orifices, is deflected and flows into the packed bed. The arrangement of the orifices prevents the liquid from entering the gas/vapor inlet. This distributor works by creating a pressure drop on the gas ensuring equal amounts flowing from all orifices. Hence the inlet flow and the required pressure drop would decide the operating range, but 4:1 is generally achievable. A disadvantage of this design is that at high gas or vapor velocities the pressure drop increases with possible entrainment of the liquid drops. High velocities are caused by particularly large gas volume rates or when the inlet pipes cover a significant portion of the column cross-section. A plate distributor is a liquid collection base with gas risers permits effective and cost-effective gas distributor. This distributor plate is used when vapor enters the bottom of a column with a very high kinetic energy. This distributor will consume some pressure drop in the vapor, reduce its kinetic energy and ensure goods distribution below the packed bed. The pressure drop across this distributor could be 1-10 mbar. This model is available in any sheet metal and is supported by a ledge/support ring (mid-span beams may be required in large columns). It is provided with liquid down comers or a sump for removal of the liquid which makes it possible to handle high gas velocities. 16 / 16
Packed Tower Internals
 Packed Tower Internals Packed Tower Internals Guide Koch-Glitsch s dedication to provide state-of-the-art mass transfer equipment is demonstrated in a complete line of packed tower internals, developed
Packed Tower Internals Packed Tower Internals Guide Koch-Glitsch s dedication to provide state-of-the-art mass transfer equipment is demonstrated in a complete line of packed tower internals, developed
Optimization of Packed Tower Inlet Design by CFD Analysis. Dana Laird Koch-Glitsch, Inc.
 39e Optimization of Packed Tower Inlet Design by CFD Analysis Dana Laird Koch-Glitsch, Inc. Brian Albert ExxonMobil Research and Engineering (formerly with Koch-Glitsch, Inc.) Carol Schnepper John Zink
39e Optimization of Packed Tower Inlet Design by CFD Analysis Dana Laird Koch-Glitsch, Inc. Brian Albert ExxonMobil Research and Engineering (formerly with Koch-Glitsch, Inc.) Carol Schnepper John Zink
Combustion Equipment. Combustion equipment for. Solid fuels Liquid fuels Gaseous fuels
 Combustion Equipment Combustion equipment for Solid fuels Liquid fuels Gaseous fuels Combustion equipment Each fuel type has relative advantages and disadvantages. The same is true with regard to firing
Combustion Equipment Combustion equipment for Solid fuels Liquid fuels Gaseous fuels Combustion equipment Each fuel type has relative advantages and disadvantages. The same is true with regard to firing
Topical 2: Separations Session: 537. Glenn Shiveler, Sulzer Chemtech USA Inc. Tulsa, OK
 Meeting: Autumn AIChE National Meeting San Francisco, CA November 3 rd through November 7 th, 2013 Topical 2: Separations Session: 537 Title: "Modern Sieve Trays for Liquid-Liquid Extraction" Authors:
Meeting: Autumn AIChE National Meeting San Francisco, CA November 3 rd through November 7 th, 2013 Topical 2: Separations Session: 537 Title: "Modern Sieve Trays for Liquid-Liquid Extraction" Authors:
VFC-5 to VFC-500 FLO-COATER
 VFC-5 to VFC-500 FLO-COATER OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS Page -1- CONTENTS PAGE NUMBER System Description... 2 Flo-Coater Description... 4 Operation of a Flo-Coater... 8 Selective Operator Control... 9 Operating
VFC-5 to VFC-500 FLO-COATER OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS Page -1- CONTENTS PAGE NUMBER System Description... 2 Flo-Coater Description... 4 Operation of a Flo-Coater... 8 Selective Operator Control... 9 Operating
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES
 ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
NARVIK-YARWAY. Heavy Duty A.T. - Temp Desuperheater Model: 18/54 and 28/64
 NARVIK-YARWAY Narvik-Yarway covers requirements for Desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power-pulp &
NARVIK-YARWAY Narvik-Yarway covers requirements for Desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power-pulp &
Definitions of Technical Terms
 Definitions of Technical Terms ABSOLUTE A measure having as it s zero point of base the complete absence of the entity being measured. ABSOLUTE PRESSURE A pressure scale with zero point at a perfect vacuum.
Definitions of Technical Terms ABSOLUTE A measure having as it s zero point of base the complete absence of the entity being measured. ABSOLUTE PRESSURE A pressure scale with zero point at a perfect vacuum.
Mass Transfer Trays for - Refineries - Chemical and Petrochemical Industries - Environmental Applications
 Mass Transfer Trays for - Refineries - Chemical and Petrochemical Industries - Environmental Applications Our Program Products, Installation and Technical Support We Offer Solutions...... to increase the
Mass Transfer Trays for - Refineries - Chemical and Petrochemical Industries - Environmental Applications Our Program Products, Installation and Technical Support We Offer Solutions...... to increase the
Fouling tendency is a critical
 Balanced distillation equipment design Fouling resistance and efficiency requirements for distillation equipment are balanced and optimised for reliable unit performance SOUN HO LEE GTC Technology Fouling
Balanced distillation equipment design Fouling resistance and efficiency requirements for distillation equipment are balanced and optimised for reliable unit performance SOUN HO LEE GTC Technology Fouling
Lecture 27: Principles of Burner Design
 Lecture 27: Principles of Burner Design Contents: How does combustion occur? What is a burner? Mixing of air and gaseous fuel Characteristic features of jet Behavior of free (unconfined) and confined jet
Lecture 27: Principles of Burner Design Contents: How does combustion occur? What is a burner? Mixing of air and gaseous fuel Characteristic features of jet Behavior of free (unconfined) and confined jet
2. Hydraulic Valves, Actuators and Accessories. 24 Marks
 2. Hydraulic Valves, Actuators and Accessories 24 Marks Co related to chapter 602.2 Describe working principle of various components used in hydraulic & pneumatic systems. 602.3 Choose valves, actuators
2. Hydraulic Valves, Actuators and Accessories 24 Marks Co related to chapter 602.2 Describe working principle of various components used in hydraulic & pneumatic systems. 602.3 Choose valves, actuators
The gear boxes can be run at the same speeds as the actuator models. Do not exceed torque ratings.
 1. What is the lifting torque required? The lifting torque for a single actuator depends on the load, the worm gear ratio, type of screw (machine cut or ball screw) and the pitch of the lifting screw.
1. What is the lifting torque required? The lifting torque for a single actuator depends on the load, the worm gear ratio, type of screw (machine cut or ball screw) and the pitch of the lifting screw.
AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER
 AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER The Carter Model YH carbureter may be compared with a Carter YF downdraft carbureter with the circuits rearranged to operate
AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER The Carter Model YH carbureter may be compared with a Carter YF downdraft carbureter with the circuits rearranged to operate
Selection of Column Internals - Coker Unit
 Moving Ahead Selection of Column Internals - Coker Unit Sulzer Chemtech August 4, 2009 Presenter: Nina Prohorenko-Johnson Coker Main Fractionator Quench Feed: Bottom of Barrel GAS LPG GASOLINE COKE DRUMS
Moving Ahead Selection of Column Internals - Coker Unit Sulzer Chemtech August 4, 2009 Presenter: Nina Prohorenko-Johnson Coker Main Fractionator Quench Feed: Bottom of Barrel GAS LPG GASOLINE COKE DRUMS
YARWAY NARVIK STANDARD DUTY A.T.-TEMP DESUPERHEATER MODEL 38/48
 Yarway covers requirements for Desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power-pulp and paper industry and
Yarway covers requirements for Desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power-pulp and paper industry and
Chapter 4 ANALYTICAL WORK: COMBUSTION MODELING
 a 4.3.4 Effect of various parameters on combustion in IC engines: Compression ratio: A higher compression ratio increases the pressure and temperature of the working mixture which reduce the initial preparation
a 4.3.4 Effect of various parameters on combustion in IC engines: Compression ratio: A higher compression ratio increases the pressure and temperature of the working mixture which reduce the initial preparation
Silencers. Transmission and Insertion Loss
 Silencers Practical silencers are complex devices, which operate reducing pressure oscillations before they reach the atmosphere, producing the minimum possible loss of engine performance. However they
Silencers Practical silencers are complex devices, which operate reducing pressure oscillations before they reach the atmosphere, producing the minimum possible loss of engine performance. However they
Numerical simulation of detonation inception in Hydrogen / air mixtures
 Numerical simulation of detonation inception in Hydrogen / air mixtures Ionut PORUMBEL COMOTI Non CO2 Technology Workshop, Berlin, Germany, 08.03.2017 09.03.2017 Introduction Objective: Development of
Numerical simulation of detonation inception in Hydrogen / air mixtures Ionut PORUMBEL COMOTI Non CO2 Technology Workshop, Berlin, Germany, 08.03.2017 09.03.2017 Introduction Objective: Development of
Multilayer Energy Dissipating Inlet Column in Center-Feed Clarifiers 1
 Multilayer Energy Dissipating Inlet Column in Center-Feed Clarifiers 1 References 6,276,537 08/21/2001 Esler et al 210/519 6,800,209 10/05/2004 Wright 210/801 Field of Invention Clarifiers are tanks where
Multilayer Energy Dissipating Inlet Column in Center-Feed Clarifiers 1 References 6,276,537 08/21/2001 Esler et al 210/519 6,800,209 10/05/2004 Wright 210/801 Field of Invention Clarifiers are tanks where
BTX Extractive Distillation Capacity Increased by Enhanced Packing Distributors
 BTX Extractive Distillation Capacity Increased by Enhanced Packing Distributors Karl Kolmetz kkolmetz@yahoo.com Jeff Gray jeffngray@hotmail.com Mel Chua Sulzer Chemtech Raghu Desai Sulzer Chemtech AIChE
BTX Extractive Distillation Capacity Increased by Enhanced Packing Distributors Karl Kolmetz kkolmetz@yahoo.com Jeff Gray jeffngray@hotmail.com Mel Chua Sulzer Chemtech Raghu Desai Sulzer Chemtech AIChE
CH.4 Basic Components of Hydraulic and Pneumatic System/16 M HAP/17522/AE5G
 Content : 4.1 Hydraulic and Pneumatic actuators. 10 Marks Hydraulic Actuators - Hydraulic cylinders (single, double acting and telescopic) construction and working, Hydraulic motors (gear and piston type)
Content : 4.1 Hydraulic and Pneumatic actuators. 10 Marks Hydraulic Actuators - Hydraulic cylinders (single, double acting and telescopic) construction and working, Hydraulic motors (gear and piston type)
Chris Santner; Sr Director, Catalytic Cracking Technology. Coking and CatCracking Conference, New Delhi, October 2013
 Technip Stone & Webster Process Technology Offering FCC Revamp in RefiningSolutions Chris Santner; Sr Director, Catalytic Cracking Technology Technip Stone & Webster Process Technology Coking and CatCracking
Technip Stone & Webster Process Technology Offering FCC Revamp in RefiningSolutions Chris Santner; Sr Director, Catalytic Cracking Technology Technip Stone & Webster Process Technology Coking and CatCracking
Crispin Valves Operating Guide. Crispin
 Crispin Valves Operating Guide Crispin Since 1905 Crispin Multiplex Manufacturing Co. 600 Fowler Avenue Berwick, PA 18603 1-800-AIR-VALV T: (570) 752-4524 F: (570) 752-4962 www.crispinvalve.com sales@crispinvalve.com
Crispin Valves Operating Guide Crispin Since 1905 Crispin Multiplex Manufacturing Co. 600 Fowler Avenue Berwick, PA 18603 1-800-AIR-VALV T: (570) 752-4524 F: (570) 752-4962 www.crispinvalve.com sales@crispinvalve.com
Standard Duty A.T.S.A. - Temp Desuperheater Model 24 / 34
 Narvik-Yarway covers requirements for desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power, pulp & paper industry
Narvik-Yarway covers requirements for desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power, pulp & paper industry
The FCCU main fractionator is a key
 Benefit of revamping a main fractionator Additional FCCU capacity can often be achieved by implementing new packing and distributor designs, even if the main fractionator has already been revamped. The
Benefit of revamping a main fractionator Additional FCCU capacity can often be achieved by implementing new packing and distributor designs, even if the main fractionator has already been revamped. The
Cooling water. Reflux drum. Product drum. Boiler. Decant oil. feed. water. Revamp improves FCC performance at BP s Texas City refinery
 P ROCESSING PROCESS FLOW SCHEME BEFORE REVAMP Fig. 1 Steam Scott W. Golden Daryl W. Hanson Process Consulting Services Inc. Houston Joy Hansen Mike Brown BP Products Co. Texas City,Tex. LCCO product Gasoline-LCCO
P ROCESSING PROCESS FLOW SCHEME BEFORE REVAMP Fig. 1 Steam Scott W. Golden Daryl W. Hanson Process Consulting Services Inc. Houston Joy Hansen Mike Brown BP Products Co. Texas City,Tex. LCCO product Gasoline-LCCO
General Engineering Spray Nozzles & Accessories
 General Engineering Spray Nozzles & Accessories 3 GENERAL SPRAY NOZZLES & ACCESSORIES Clip On Spray Nozzles SWIVELING ANGLE ADJUSTMENT SPRAY CHARACTERISTICS : These nozzles simply clip over a pre-drilled
General Engineering Spray Nozzles & Accessories 3 GENERAL SPRAY NOZZLES & ACCESSORIES Clip On Spray Nozzles SWIVELING ANGLE ADJUSTMENT SPRAY CHARACTERISTICS : These nozzles simply clip over a pre-drilled
Yarway Narvik Desuperheater Model 18/54 and 28/64 Heavy Duty
 Yarway covers requirements for Desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide of models, sizes and materials to satisfy the specifications of the power, pulp and paper industries along with
Yarway covers requirements for Desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide of models, sizes and materials to satisfy the specifications of the power, pulp and paper industries along with
A GUIDE TO CLEAN AND EFFICIENT OPERATION COAL-STOKER-FIRED BOILERS
 A GUIDE TO CLEAN AND EFFICIENT OPERATION OF COAL-STOKER-FIRED BOILERS 2002 American Boiler Manufacturers Association 4001 North 9th Street, Suite 226 Arlington, VA 22203-1900 Copyright 2002 American Boiler
A GUIDE TO CLEAN AND EFFICIENT OPERATION OF COAL-STOKER-FIRED BOILERS 2002 American Boiler Manufacturers Association 4001 North 9th Street, Suite 226 Arlington, VA 22203-1900 Copyright 2002 American Boiler
ZEECO BURNER DIVISION
 ZEECO BURNER DIVISION Enhanced Jet Flat Flame Burners GLSF Series 22151 EAST 91ST STREET BROKEN ARROW OK 74014 USA +1-918-258-8551 SALES@ZEECO.COM ZEECO.COM INTRODUCTION: This document discusses the advantages
ZEECO BURNER DIVISION Enhanced Jet Flat Flame Burners GLSF Series 22151 EAST 91ST STREET BROKEN ARROW OK 74014 USA +1-918-258-8551 SALES@ZEECO.COM ZEECO.COM INTRODUCTION: This document discusses the advantages
Nomenclature. Nomenclature Distributing coil types
 STEAM COILS Contents and Nomenclature Distributing coil types Nomenclature... 1 Distributing Coil Types JA and GA... 1 DA and LA... 1 RA and TA... 2 Non-Distributing Coil Types SA and HA, SB and HB...
STEAM COILS Contents and Nomenclature Distributing coil types Nomenclature... 1 Distributing Coil Types JA and GA... 1 DA and LA... 1 RA and TA... 2 Non-Distributing Coil Types SA and HA, SB and HB...
Gauges, Sight Glasses and Vacuum Breakers
 Gauges, Sight Glasses and Vacuum Breakers Gauges, Sight Glasses and Vacuum Breakers Gauges Pressure gauges Pressure gauges should be installed in at least the following situations: Upstream of a pressure
Gauges, Sight Glasses and Vacuum Breakers Gauges, Sight Glasses and Vacuum Breakers Gauges Pressure gauges Pressure gauges should be installed in at least the following situations: Upstream of a pressure
Installation Procedures
 For the precision ball and roller bearings supplied by MRC Bearings, skill and cleanliness while handling, mounting and dismounting are necessary to ensure satisfactory bearing performance. As precision
For the precision ball and roller bearings supplied by MRC Bearings, skill and cleanliness while handling, mounting and dismounting are necessary to ensure satisfactory bearing performance. As precision
UniWine Pressure-compensating, Continuously Self-cleaning Dripper
 Applications Sub-surface and on-surface installation Drip irrigation technology comprises the following features: Solid set system: each vine has its own individual drippers always ready for operation.
Applications Sub-surface and on-surface installation Drip irrigation technology comprises the following features: Solid set system: each vine has its own individual drippers always ready for operation.
Experiment No.3: Flow through orifice meter. Background and Theory
 Experiment No.3: Flow through orifice meter Background and Theory Flow meters are used in the industry to measure the volumetric flow rate of fluids. Differential pressure type flow meters (Head flow meters)
Experiment No.3: Flow through orifice meter Background and Theory Flow meters are used in the industry to measure the volumetric flow rate of fluids. Differential pressure type flow meters (Head flow meters)
Mounting and Operating Instructions EB 5894 EN. Electric control valves with jet pump. Flanged version of valve with jet pump
 Electric control valves with jet pump Type 3267/5824, Type 3267/5825, Type 3267/3374, Type 3267/3274 Pneumatic control valves with jet pump Type 3267-1, Type 3267-7 Flanged version of valve with jet pump
Electric control valves with jet pump Type 3267/5824, Type 3267/5825, Type 3267/3374, Type 3267/3274 Pneumatic control valves with jet pump Type 3267-1, Type 3267-7 Flanged version of valve with jet pump
Monitoring, Mitigating g and Troubleshooting FCC Catalyst Losses
 Monitoring, Mitigating g and Troubleshooting FCC Catalyst Losses Bob Ludolph CatCracking.com League City, TX - April 12-16, 2010 Presentation Outline Loss Precursors & Warning Signs Catalyst Monitoring
Monitoring, Mitigating g and Troubleshooting FCC Catalyst Losses Bob Ludolph CatCracking.com League City, TX - April 12-16, 2010 Presentation Outline Loss Precursors & Warning Signs Catalyst Monitoring
Heavy Duty Que - Temp Desuperheater Model: 13 / 23
 Narvik covers requirements for Desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power, pulp & paper industry and
Narvik covers requirements for Desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power, pulp & paper industry and
Chapter 4 Membrane Equipment
 Chapter 4 Membrane Equipment The Components of Membrane Technology MEMBRANES MODULES Membrane Housing SYSTEMS Modules, Pumps, Piping, Tanks, Controls, Monitoring, Pretreatment t t Facilities, Cleaning
Chapter 4 Membrane Equipment The Components of Membrane Technology MEMBRANES MODULES Membrane Housing SYSTEMS Modules, Pumps, Piping, Tanks, Controls, Monitoring, Pretreatment t t Facilities, Cleaning
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
 UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
Series HCD Airfoil Control Damper
 Series HCD Airfoil Control Damper Model: HCD-1 The Holyoake HCD-1 is a precisely made volume and pressure control device with extremely low leakage when closed, (in the range of 0.003m 3 /s at 100 Pa).
Series HCD Airfoil Control Damper Model: HCD-1 The Holyoake HCD-1 is a precisely made volume and pressure control device with extremely low leakage when closed, (in the range of 0.003m 3 /s at 100 Pa).
FUNDAMENTAL SAFETY OVERVIEW VOLUME 2: DESIGN AND SAFETY CHAPTER E: THE REACTOR COOLANT SYSTEM AND RELATED SYSTEMS
 PAGE : 1 / 13 4. PRESSURISER 4.1. DESCRIPTION The pressuriser (PZR) is a pressurised vessel forming part of the reactor coolant pressure boundary (CPP) [RCPB]. It comprises a vertical cylindrical shell,
PAGE : 1 / 13 4. PRESSURISER 4.1. DESCRIPTION The pressuriser (PZR) is a pressurised vessel forming part of the reactor coolant pressure boundary (CPP) [RCPB]. It comprises a vertical cylindrical shell,
YARWAY NARVIK MODEL 33/43 STANDARD DUTY QUE-TEMP DESUPERHEATER
 Yarway covers requirements for desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power-pulp and paper industry and
Yarway covers requirements for desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power-pulp and paper industry and
03. Fuel and Air Feed System
 Page 11 of 03. Fuel and Air Feed System Content (16 Marks) 3.1 Petrol fuel supply system. 8 Marks Conventional Petrol Engine: Gravity feed, Pump feed (Layout,Function of Components and location). Construction
Page 11 of 03. Fuel and Air Feed System Content (16 Marks) 3.1 Petrol fuel supply system. 8 Marks Conventional Petrol Engine: Gravity feed, Pump feed (Layout,Function of Components and location). Construction
Oil discharge from vacuum pump exhaust possible causes and remedies
 Updated March 2013 Oil discharge from vacuum pump exhaust possible causes and remedies To obtain the reasonably high vacuum level required for the resin infusion process it is normal to use a single stage
Updated March 2013 Oil discharge from vacuum pump exhaust possible causes and remedies To obtain the reasonably high vacuum level required for the resin infusion process it is normal to use a single stage
Click on Warman Logo to go back to Menu WARMAN PUMPS ASSEMBLY, OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS PART 2Q SLURRY JET PUMPS TYPES JPC AND JPH PC2Q
 Click on Warman Logo to go back to Menu WARMAN PUMPS ASSEMBLY, OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS PART 2Q SLURRY JET PUMPS TYPES JPC AND JPH PC2Q WARMAN PUMPS ASSEMBLY, OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS
Click on Warman Logo to go back to Menu WARMAN PUMPS ASSEMBLY, OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS PART 2Q SLURRY JET PUMPS TYPES JPC AND JPH PC2Q WARMAN PUMPS ASSEMBLY, OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS
Introduction to Circuit Breaker. Working Principle of Circuit Breaker
 Definition of Circuit Breaker : - Electrical Circuit Breaker is a switching device which can be operated manually as well as automatically for controlling and protection of electrical power system respectively.
Definition of Circuit Breaker : - Electrical Circuit Breaker is a switching device which can be operated manually as well as automatically for controlling and protection of electrical power system respectively.
PROHEAT 35 Induction Heating Application Photos for PREHEAT and PWHT
 PROHEAT 35 Induction Heating Application Photos for PREHEAT and PWHT 2 PREHEAT APPLICATIONS and VARIOUS COIL CONFIGURATIONS FOR PREHEAT 3 Transmission Pipeline Construction - Preheat Transmission pipeline
PROHEAT 35 Induction Heating Application Photos for PREHEAT and PWHT 2 PREHEAT APPLICATIONS and VARIOUS COIL CONFIGURATIONS FOR PREHEAT 3 Transmission Pipeline Construction - Preheat Transmission pipeline
TRITON Underdrain Systems
 TRITON Underdrain Systems TRITON UNDERDRAINS: The solution Triton Underdrains exceptional performance as a filter underdrain system utilizes Johnson s world renowned Vee-Wire screen technology and our
TRITON Underdrain Systems TRITON UNDERDRAINS: The solution Triton Underdrains exceptional performance as a filter underdrain system utilizes Johnson s world renowned Vee-Wire screen technology and our
Tow-Bro Unitube Sludge Removers
 Tow-Bro Unitube Sludge Removers Water Technologies Tow-Bro for rapid,uniform removal of final clarifier sludges. Tow-Bro Unitube Header - Process Advantages 6 reasons why you ll get more from your final
Tow-Bro Unitube Sludge Removers Water Technologies Tow-Bro for rapid,uniform removal of final clarifier sludges. Tow-Bro Unitube Header - Process Advantages 6 reasons why you ll get more from your final
Separator Internals. Overview. AlphaPLUS DESIGN SHEET. Inlet Devices: Defoaming Internals: Coalescing Internals:
 Separator Internals Overview HAT supplies a large number of internals used in separation service from the various Alpha product ranges. Many of these have uses in other applications, but some have been
Separator Internals Overview HAT supplies a large number of internals used in separation service from the various Alpha product ranges. Many of these have uses in other applications, but some have been
Yarway Narvik Ven-Temp Desuperheater Model 25
 Yarway covers requirements for Desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power, pulp and paper industry and
Yarway covers requirements for Desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power, pulp and paper industry and
MNSD-V MULTIPLE NOZZLE SPRAY DESUPERHEATER BULLETIN 1144 SEPTEMBER 2001
 MNSD-V MULTIPLE NOZZLE SPRAY DESUPERHEATER BULLETIN 1144 SEPTEMBER 2001 MNSD V MULTIPLE NOZZLE SPRAY DESUPERHEATER Multiple Nozzle Spray Desuperheater Offers High Temperature Capabilities and Low Class
MNSD-V MULTIPLE NOZZLE SPRAY DESUPERHEATER BULLETIN 1144 SEPTEMBER 2001 MNSD V MULTIPLE NOZZLE SPRAY DESUPERHEATER Multiple Nozzle Spray Desuperheater Offers High Temperature Capabilities and Low Class
MNSD-V MULTIPLE NOZZLE SPRAY DESUPERHEATER BULLETIN 1144 APRIL 2004
 MNSD-V MULTIPLE NOZZLE SPRAY DESUPERHEATER BULLETIN 1144 APRIL 2004 MNSD V MULTIPLE NOZZLE SPRAY DESUPERHEATER Multiple Nozzle Spray Desuperheater Offers High Temperature Capabilities and Low Class V Leakage
MNSD-V MULTIPLE NOZZLE SPRAY DESUPERHEATER BULLETIN 1144 APRIL 2004 MNSD V MULTIPLE NOZZLE SPRAY DESUPERHEATER Multiple Nozzle Spray Desuperheater Offers High Temperature Capabilities and Low Class V Leakage
Mold Design. 7. Mold Design Runner & Gate. Bong-Kee Lee School of Mechanical Engineering Chonnam National University
 7. Runner & Gate Bong-Kee Lee Chonnam National University Delivery System Delivery System (Feed System) sprue (for a cold runner mold) cold slug well (for a cold runner mold) runner gate basic feed system
7. Runner & Gate Bong-Kee Lee Chonnam National University Delivery System Delivery System (Feed System) sprue (for a cold runner mold) cold slug well (for a cold runner mold) runner gate basic feed system
accqpulse Velocity Profiler Sensor Installation Guide
 accqpulse Velocity Profiler Sensor Installation Guide Instruction Sheet #69-7403-012 Released May 2016 Overview This instruction guide is for the installation of the accqpulse shallow water and deep water
accqpulse Velocity Profiler Sensor Installation Guide Instruction Sheet #69-7403-012 Released May 2016 Overview This instruction guide is for the installation of the accqpulse shallow water and deep water
FLANGE. Flanges used for
 FLANGE FLANGE Flanges with rating class designations 150, 300, 400, 600, 900, 1500, and 2500 in sizes NPS 1 2 through NPS 24 ASME B16.5: Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings (NPS 24 ) ASME B16.47: NPS 26
FLANGE FLANGE Flanges with rating class designations 150, 300, 400, 600, 900, 1500, and 2500 in sizes NPS 1 2 through NPS 24 ASME B16.5: Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings (NPS 24 ) ASME B16.47: NPS 26
CLOSED CIRCUIT HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSION
 Energy conservation and other advantages in Mobile Equipment Through CLOSED CIRCUIT HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSION C. Ramakantha Murthy Technical Consultant Various features/advantages of HST Hydrostatic transmissions
Energy conservation and other advantages in Mobile Equipment Through CLOSED CIRCUIT HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSION C. Ramakantha Murthy Technical Consultant Various features/advantages of HST Hydrostatic transmissions
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007026 1863A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0261863 A1 MACLEOD et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2007 (54) SEALING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 166/387: 166/202
(19) United States US 2007026 1863A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0261863 A1 MACLEOD et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2007 (54) SEALING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 166/387: 166/202
Direct Contact Desuperheaters
 Control Description Spirax Sarco direct contact desuperheaters reduce the temperature of superheated steam to produce steam temperatures approaching saturation temperature to cool the superheated steam,
Control Description Spirax Sarco direct contact desuperheaters reduce the temperature of superheated steam to produce steam temperatures approaching saturation temperature to cool the superheated steam,
Fire Cobra. AGD Design Presentation Winter 2012 Mec E 460. Jesse Moore Charles Weir Evrhetton Gold Chris Languedoc Alexander Dufour
 Fire Cobra AGD Design Presentation Winter 2012 Mec E 460 Jesse Moore Charles Weir Evrhetton Gold Chris Languedoc Alexander Dufour Background Information Irrigation sprinklers have long been used as a tool
Fire Cobra AGD Design Presentation Winter 2012 Mec E 460 Jesse Moore Charles Weir Evrhetton Gold Chris Languedoc Alexander Dufour Background Information Irrigation sprinklers have long been used as a tool
SERIES COOLING TOWER SINGLE-CELL UP TO 1500HRT COOLING CAPACITY
 TX-C SERIES COOLING TOWER SINGLE-CELL UP TO 1500HRT COOLING CAPACITY High Performance Crossflow Type PROVEN PERFORMANCE RELIABILITY EASY INSTALLATION TX-C Series is an induced draft cross-flow, film filled,
TX-C SERIES COOLING TOWER SINGLE-CELL UP TO 1500HRT COOLING CAPACITY High Performance Crossflow Type PROVEN PERFORMANCE RELIABILITY EASY INSTALLATION TX-C Series is an induced draft cross-flow, film filled,
Penn Valley Pump Company Design Information for Double Disc Pumps
 Penn Valley Pump Company Design Information for Double Disc Pumps INTRODUCTION The Penn Valley Double Disc Pump utilizes a unique principle of operation whereby the discs perform the duties of pumping
Penn Valley Pump Company Design Information for Double Disc Pumps INTRODUCTION The Penn Valley Double Disc Pump utilizes a unique principle of operation whereby the discs perform the duties of pumping
04. Ignition and Exhaust system
 New Polytechnic Kolhapur Page 1 of 10 04. Ignition and Exhaust system 4.1 Introduction to Ignition System 4 Marks Requirements of ignition system. Magneto and Battery Ignition systems (Working only). Firing
New Polytechnic Kolhapur Page 1 of 10 04. Ignition and Exhaust system 4.1 Introduction to Ignition System 4 Marks Requirements of ignition system. Magneto and Battery Ignition systems (Working only). Firing
Leading Tray Technology Reliability and Performance
 Leading Tray Technology Reliability and Performance Sulzer Chemtech Mass Transfer Technology Your partner in separation and mixing technology The highest level of application know-how Our team provides
Leading Tray Technology Reliability and Performance Sulzer Chemtech Mass Transfer Technology Your partner in separation and mixing technology The highest level of application know-how Our team provides
TempLowHT Steam Desuperheater Model: 59/69/79
 NARVIK-YARWAY The TempLowHT utilizes the fundamental design concepts of the standard Templow, designed for temperatures up to 1150 F (621 C). The TempLowHT is designed to eliminate sliding trim parts in
NARVIK-YARWAY The TempLowHT utilizes the fundamental design concepts of the standard Templow, designed for temperatures up to 1150 F (621 C). The TempLowHT is designed to eliminate sliding trim parts in
Increased recovery of straight-run
 Maximising diesel recovery from crude The CDU/DU process flow scheme is reviewed, including equipment design and operating fundamentals used to maximise straight-run diesel recovery. Factors important
Maximising diesel recovery from crude The CDU/DU process flow scheme is reviewed, including equipment design and operating fundamentals used to maximise straight-run diesel recovery. Factors important
HERCULES-2 Project. Deliverable: D8.8
 HERCULES-2 Project Fuel Flexible, Near Zero Emissions, Adaptive Performance Marine Engine Deliverable: D8.8 Study an alternative urea decomposition and mixer / SCR configuration and / or study in extended
HERCULES-2 Project Fuel Flexible, Near Zero Emissions, Adaptive Performance Marine Engine Deliverable: D8.8 Study an alternative urea decomposition and mixer / SCR configuration and / or study in extended
YARWAY NARVIK VEN-TEMP DESUPERHEATER MODEL 25
 Yarway covers requirements for Desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power, pulp and paper industry and
Yarway covers requirements for Desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power, pulp and paper industry and
VORTAB FLOW CONDITIONERS. For Flow Meters, Pumps and Other Flow Profile Critical Equipment
 VORTAB FLOW CONDITIONERS For Flow Meters, Pumps and Other Flow Profile Critical Equipment Reduce flow meter straight-run requirements into just a few diameters Balance pump inlet flow to eliminate premature
VORTAB FLOW CONDITIONERS For Flow Meters, Pumps and Other Flow Profile Critical Equipment Reduce flow meter straight-run requirements into just a few diameters Balance pump inlet flow to eliminate premature
Standard Duty Que - Temp Desuperheater Model: 33 / 43
 Model: 33 / 43 Narvik-Yarway covers requirements for desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power-pulp
Model: 33 / 43 Narvik-Yarway covers requirements for desuperheaters, pneumatic actuators, strainers with a wide range of models, sizes and materials to satisfy all the specifications of the power-pulp
2.6. Air Flow Control Valve Type PRD
 2.6. Air Flow Control Valve Type PRD Page 1/10 Air Flow Control Valve, Type PRD Page 2/10 Air Flow Control Valve Type PRD Description and Design The PRD remains the air valve of choice for critical heating,
2.6. Air Flow Control Valve Type PRD Page 1/10 Air Flow Control Valve, Type PRD Page 2/10 Air Flow Control Valve Type PRD Description and Design The PRD remains the air valve of choice for critical heating,
VXI Closed circuit cooling towers
 Closed circuit cooling towers Key benefits Reliable Quiet Compact characteristics Counter flow, centrifugal fan, forced draft Capacity range up to 2615 kw Maximum entering fluid temperature 82 C Typical
Closed circuit cooling towers Key benefits Reliable Quiet Compact characteristics Counter flow, centrifugal fan, forced draft Capacity range up to 2615 kw Maximum entering fluid temperature 82 C Typical
Regenerative Turbine Pumps
 Bulletin 0 0 2 0 2 170 270 Series Regenerative Turbine Pumps Capacities to 0 GPM Heads to Feet MTH PUMPS 0 2 0 2 170 270 Series Regenerative Turbine Pump MTH 0 2 0 2 170 270 Series regenerative turbine
Bulletin 0 0 2 0 2 170 270 Series Regenerative Turbine Pumps Capacities to 0 GPM Heads to Feet MTH PUMPS 0 2 0 2 170 270 Series Regenerative Turbine Pump MTH 0 2 0 2 170 270 Series regenerative turbine
LNR ENGINE CHAPTER - 5
 LHR ENGINE CHAPTER - 5 LNR ENGINE 5.0 INTRODUCTION The studies on the performance of the conventional engine are shown in Chapter - 4. The research is extended to conduct experiments so as to improve the
LHR ENGINE CHAPTER - 5 LNR ENGINE 5.0 INTRODUCTION The studies on the performance of the conventional engine are shown in Chapter - 4. The research is extended to conduct experiments so as to improve the
Direct Contact Desuperheaters
 Local regulations may restrict the use of this product to below the conditions quoted. In the interests of development and improvement of the product, we reserve the right to change the specification without
Local regulations may restrict the use of this product to below the conditions quoted. In the interests of development and improvement of the product, we reserve the right to change the specification without
Chapter 6. Supercharging
 SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
SIHI prime - Side Channel Pumps Self-priming, segmental type with very low NPSH
 SIHI prime - Side Channel Pumps Self-priming, segmental type with very low NPSH CEH-X 1201 3608 TECHICAL DATA Capacity: Delivery head: Speed: from 0.4 up to 7.5 m³/h from 10 up to 322 m 1450 rpm (max.
SIHI prime - Side Channel Pumps Self-priming, segmental type with very low NPSH CEH-X 1201 3608 TECHICAL DATA Capacity: Delivery head: Speed: from 0.4 up to 7.5 m³/h from 10 up to 322 m 1450 rpm (max.
THE CARBURETOR: THE ADDITIONAL SYSTEMS
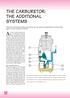 THE CARBURETOR: THE ADDITIONAL SYSTEMS From the acceleration pump to the power jet: the special configuration of circuits that apply to some carburetor models As stated in the previous article, a carburetor
THE CARBURETOR: THE ADDITIONAL SYSTEMS From the acceleration pump to the power jet: the special configuration of circuits that apply to some carburetor models As stated in the previous article, a carburetor
SERVICE & OPERATING MANUAL
 SERVICE & OPERATING MANUAL 8-4 Mud Cleaner (03-00-060) INTRODUCTION The Triflo 8-4 Mud Cleaner is capable of processing up to 520 gallons per minute and can get do to cut point of approximately 35 microns.
SERVICE & OPERATING MANUAL 8-4 Mud Cleaner (03-00-060) INTRODUCTION The Triflo 8-4 Mud Cleaner is capable of processing up to 520 gallons per minute and can get do to cut point of approximately 35 microns.
So how does a turbocharger get more air into the engine? Let us first look at the schematic below:
 How a Turbo System Works Engine power is proportional to the amount of air and fuel that can get into the cylinders. All things being equal, larger engines flow more air and as such will produce more power.
How a Turbo System Works Engine power is proportional to the amount of air and fuel that can get into the cylinders. All things being equal, larger engines flow more air and as such will produce more power.
Water Technologies. Tow-Bro Unitube Sludge Removers
 Water Technologies Tow-Bro Unitube Sludge Removers Tow-Bro Unitube Header - Process Advantages Tow-Bro for rapid,uniform removal of final clarifier sludges. 2 6 REASONS WHY YOU LL GET MORE FROM YOUR FINAL
Water Technologies Tow-Bro Unitube Sludge Removers Tow-Bro Unitube Header - Process Advantages Tow-Bro for rapid,uniform removal of final clarifier sludges. 2 6 REASONS WHY YOU LL GET MORE FROM YOUR FINAL
VAD Variable Area Desuperheaters
 Local regulations may restrict the use of this product to below the conditions quoted. In the interests of development and improvement of the product, we reserve the right to change the specification without
Local regulations may restrict the use of this product to below the conditions quoted. In the interests of development and improvement of the product, we reserve the right to change the specification without
78200/18200 Series LINCOLNLOG Valves Anti-cavitation High Pressure Control Valves
 LINCOLNLOG Valves Anti-cavitation High Pressure Control Valves Featuring High Resistance Multiple Stage LINCOLNLOG Trim Angle Configuration 78200 Globe Configuration 18200 Specification Data CP6020 10/97
LINCOLNLOG Valves Anti-cavitation High Pressure Control Valves Featuring High Resistance Multiple Stage LINCOLNLOG Trim Angle Configuration 78200 Globe Configuration 18200 Specification Data CP6020 10/97
On-Line Process Analyzers: Potential Uses and Applications
 On-Line Process Analyzers: Potential Uses and Applications INTRODUCTION The purpose of this report is to provide ideas for application of Precision Scientific process analyzers in petroleum refineries.
On-Line Process Analyzers: Potential Uses and Applications INTRODUCTION The purpose of this report is to provide ideas for application of Precision Scientific process analyzers in petroleum refineries.
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial Number 09/152.467 Filing Date 8 September 1998 Inventor Neil J. Dubois NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
Serial Number 09/152.467 Filing Date 8 September 1998 Inventor Neil J. Dubois NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
three different ways, so it is important to be aware of how flow is to be specified
 Flow-control valves Flow-control valves include simple s to sophisticated closed-loop electrohydraulic valves that automatically adjust to variations in pressure and temperature. The purpose of flow control
Flow-control valves Flow-control valves include simple s to sophisticated closed-loop electrohydraulic valves that automatically adjust to variations in pressure and temperature. The purpose of flow control
W91/W94 Series TEMPERATURE REGULATORS. Self-Operated Temperature Regulators. Design & Operation W91 Non-Indicating W94 Dial Thermometer
 Design & Operation W91 Non-Indicating W94 Dial Thermometer Watson McDaniel reserves the right to change the designs and/or materials of its products without notice. 2010 Watson McDaniel Company CAPILLARY
Design & Operation W91 Non-Indicating W94 Dial Thermometer Watson McDaniel reserves the right to change the designs and/or materials of its products without notice. 2010 Watson McDaniel Company CAPILLARY
Delayed Coking. Process Overview
 Process Overview Page 1 of 6 History of the Delayed Coking Process Petroleum coke was first made by the pioneer oil refineries in Northwestern Pennsylvania in the 1860 s. Primitive distillation techniques
Process Overview Page 1 of 6 History of the Delayed Coking Process Petroleum coke was first made by the pioneer oil refineries in Northwestern Pennsylvania in the 1860 s. Primitive distillation techniques
MNSD-V & MNSD-U. Multiple Nozzle Spray Desuperheater
 MNSD-V & MNSD-U Multiple Nozzle Spray Desuperheater Copes-Vulcan has been providing control valves and desuperheaters for the power, process and nuclear industries since 1903. SPX provides a wide range
MNSD-V & MNSD-U Multiple Nozzle Spray Desuperheater Copes-Vulcan has been providing control valves and desuperheaters for the power, process and nuclear industries since 1903. SPX provides a wide range
Section 10 Chapter 17
 Section 10 Chapter 17 24 Valve, 8.3 Liter Engine Air Intake System Note: All coding used in the 8.3 Liter and 9 Liter engine manuals are Cummins engine codes. These engine codes have no meaning to New
Section 10 Chapter 17 24 Valve, 8.3 Liter Engine Air Intake System Note: All coding used in the 8.3 Liter and 9 Liter engine manuals are Cummins engine codes. These engine codes have no meaning to New
TECHNICAL DATA. Table Standard Materials
 Page 1 of 8 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION Foam Chambers are suitable for the protection of fixed roof-mounted tanks and are to be used as low expansion Type II discharge devices (as defined by NFPA11) with approved
Page 1 of 8 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION Foam Chambers are suitable for the protection of fixed roof-mounted tanks and are to be used as low expansion Type II discharge devices (as defined by NFPA11) with approved
Factors to consider when selecting a diverter valve
 Factors to consider when selecting a diverter valve Selecting a diverter valve for your pneumatic conveying system can be a tough job, especially when you consider how many diverter valves are on the market.
Factors to consider when selecting a diverter valve Selecting a diverter valve for your pneumatic conveying system can be a tough job, especially when you consider how many diverter valves are on the market.
TURNING AIR INTO SOLUTIONS. AIR KITS. Model FC
 TURNING AIR INTO SOLUTIONS. AIR KITS Model FC CATALOG 150 June 2017 AIR KITS Overview FC Wheel Construction Air kit wheels are designed for speeds up to 7,000 ft/min. at 70 F. The blades are die-formed
TURNING AIR INTO SOLUTIONS. AIR KITS Model FC CATALOG 150 June 2017 AIR KITS Overview FC Wheel Construction Air kit wheels are designed for speeds up to 7,000 ft/min. at 70 F. The blades are die-formed
MONOVAR is the energy dissipating valve.
 MONOVAR is the energy dissipating valve. Features Extremely simple design (patented) Excellent cavitation characteristics Very accurate flow or pressure control Manual or automatic control Suitable for
MONOVAR is the energy dissipating valve. Features Extremely simple design (patented) Excellent cavitation characteristics Very accurate flow or pressure control Manual or automatic control Suitable for
PIPINGSOLUTIONS, INC.
 Piping Stress Analysis Where do I start? The following information will take you step-by-step through the logic of the data collection effort that should occur prior to beginning to model a piping system
Piping Stress Analysis Where do I start? The following information will take you step-by-step through the logic of the data collection effort that should occur prior to beginning to model a piping system
General TAHVIEH HAMOON Airfoil Centrifugal Fans Utilize the latest design techniques to product a quiet highly efficient air mover.
 General TAHVIEH HAMOON Airfoil Centrifugal Fans Utilize the latest design techniques to product a quiet highly efficient air mover. Aerodynamically designed blades and air passages allow more air to be
General TAHVIEH HAMOON Airfoil Centrifugal Fans Utilize the latest design techniques to product a quiet highly efficient air mover. Aerodynamically designed blades and air passages allow more air to be
Cylindrical Silencers
 Cylindrical Silencers A200 Series and 300 Series Installation and Operation Manual Rev. B (c) Copyright 2012, GT Exhaust, Inc. All Rights Reserved Published: April 30, 2012 NOTICE The instructions herein
Cylindrical Silencers A200 Series and 300 Series Installation and Operation Manual Rev. B (c) Copyright 2012, GT Exhaust, Inc. All Rights Reserved Published: April 30, 2012 NOTICE The instructions herein
2) Rich mixture: A mixture which contains less air than the stoichiometric requirement is called a rich mixture (ex. A/F ratio: 12:1, 10:1 etc.
 Unit 3. Carburettor University Questions: 1. Describe with suitable sketches : Main metering system and Idling system 2. Draw the neat sketch of a simple carburettor and explain its working. What are the
Unit 3. Carburettor University Questions: 1. Describe with suitable sketches : Main metering system and Idling system 2. Draw the neat sketch of a simple carburettor and explain its working. What are the
