Engine Belt System Overview
|
|
|
- Corey Lamb
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Engine Belt System Overview Note: The majority of new vehicles use Micro-V belts to power their front end accessories. However, V-belts (not shown in this engine illustration) are still used on some vehicles. 2
3 V-Belts & Micro-V Belts In modern cars, there are generally two types of belts used on front-end accessory drive systems: V-belts or Micro-V belts. The big difference between the two belts is in the profile. Micro-V belts are flatter and wider than V-belts, with multiple V-shaped ribs extending along the belt s length. Micro-V work better inside today s smaller, more complex engine compartments, where space is limited and one flexible Micro-V belt can do the job formerly carried out by several V-belts. The Micro-V belt was designed to transmit power via the backside of the belt as well as the ribs. This allows the belt to perform in serpentine drives drives that require one belt to power all accessories in the drive system. V-belts have a V -shaped profile designed to wedge into a corresponding pulley groove of similar profile. To accommodate small pulleys, the underside of the belt is notched, which allows greater flexibility and a decreased bend radius. The variable notch pattern used on NAPA Belts/Hose belts also reduces noise. 3
4 Front-end belts used on a car engine drive many critical parts and systems including these accessories: The alternator which supplies electrical power to the vehicle. The water pump which circulates coolant. The fan which draws in air to cool liquid flowing through the radiator. The air conditioning compressor which circulates the refrigerant in the air conditioning system. Any number of other accessories, from power steering pumps to air pumps, and other equipment. Without belts, or when a belt fails, the engine will not run long, or it may not run at all. A failed belt may also hinder the safe operation of other important vehicle systems. 4
5 Belt Construction Micro-V belts and V-belts consist of three bonded sections the undercord, the tensile cord, and the overcord. The overcord is made of advanced elastomeric composites and fabric. It protects the tensile cord from dirt, oil and other environmental contaminants. It also gives the cords additional transverse (side-to-side) support on the pulley by sustaining a firm gripping surface. 5
6 Tensile cords are what make the belt strong. Cords generally consist of twisted polyester bands. These bands allow flexibility while maintaining belt integrity by providing stretch resistance. The cords provide enough strength to stand up to the shock of high load-carrying and are exceptionally durable. The undercord ribbed section supports the other layers and transfers their load directly to the pulleys. Precision grinding assures a secure fit and consistent tension. The adhesive material used to join the belt sections consists of advanced bonding agents and liquid elastomers that provide protection and cushion for the tensile cords and prevent separation. These bonding agents and elastomers are adhered during the vulcanization process in which rubber is cured with the assistance of heat and chemical agents. Both Micro-V belts and V-belts are engineered to exact tolerances. Combined, all three layers act as one fully integrated component that is flexible enough to transmit power around small pulleys that rotate at thousands of revolutions per minute. They must also be structurally strong enough to handle the load under the proper tension. 6
7 Expected Belt Life Because today s belts operate under heavier loads, are exposed to greater heat and temperature fluctuations, as well as water, dirt, grease, oil and other environmental contaminants, normal failure may occur differently on different applications. For example, air conditioning and higher output alternator drives are more demanding; power steering and water pumps are less so. Also, it s not always possible to tell if a belt is still good by visual inspection alone. Statistics show that failures increase dramatically after the fourth year of service, so automotive experts recommend that all belts be replaced at least every four years, as part of routine maintenance. 7
8 Belts Can Fail Faster While the four-year replacement interval is a basic rule of thumb, it s not exact. Idling time in traffic takes a major toll on belt life. The engine runs hotter, and belts can break down much more rapidly in a car exposed to sustained periods of stop and go driving. Today s normal urban driving patterns constitute extreme operating conditions, exposing belts to excessive stress and wear. Sometimes, the first indication of a faulty belt is a squeaking noise coming from the engine compartment. While a warning of a possible malfunction, this noise is not a precise indicator. Therefore, it is imperative to periodically inspect belts even belts less than four years old whenever a vehicle comes in for service. If there is ever any doubt, recommend replacement of the belts. The alternative could be a customer stranded in the middle of rush hour with a broken belt and a disabled vehicle. To inspect a belt, first make sure the engine is off. If a belt exhibits any of the telltale signs of wear, it should be replaced. See Page 16 for belt wear guidelines. Belt failures increase dramatically after the fourth year of service. All belts should be replaced at least every four years. 8
9 Automotive Belt Tensioner/Pulley/Idler Assemblies Vehicles using a single serpentine belt often employ an automatic belt tensioning system. Designed to apply a constant force to a belt, the tensioner compensates for belt length changes due to wear or changes in accessory drive operating loads. The tension is supplied through a component consisting of a spring mechanism housed behind a pulley. 9
10 This automatic re-tensioning reduces maintenance by eliminating the need to re-tighten belts periodically, as the proper tension will be applied for the life of the belt. Also, when tension is maintained at an optimal level as belt wear occurs, the life of bearings and accessories, as well as the belt itself, is increased. Automatic tensioners are generally used with Micro-V belts only, though some have been effectively applied to V-belt drives. A specially designed V-belt may be required when a tensioner is applied to the backside of a belt since most V-belts are not designed to accommodate reverse bending. While these Special Application belts are ideal for backside idler drives, they are not recommended on traditional drives. These Special Application belts may also be required on those pulley applications that do not conform to SAE standards. These belts have the exact measurement as the OE belt. Because of the excellent performance of automatic belt tensioners, more and more vehicles are being built with this type of system. Like any other component, automatic belt tensioners wear out, and should be replaced periodically for the belt system to work properly. Constant predetermined tension increases the life of belts, bearings and accessories. 10
11 Pulleys and Idlers A pulley is a grooved wheel whose purpose is to transmit torque to driven components in the accessory drive system. In contrast, an idler is either flat for the backside of the belt or grooved for the bottom of the belt. It is generally free spinning and does not transmit torque to an accessory component. An idler s purpose can be to optimize belt routing, suppress belt span vibration, or provide a means for tensioning the belt. Periodic inspection of the accessory drive system should be performed at regularly scheduled maintenance intervals. 11
12 The important role of the pulley How the belt rides in the pulley groove is an important factor affecting a belt s life and ability to transmit power. The belt should ride slightly above the top of the pulley groove. If it rides too high, the edges of the pulley will wear into the belt sides and eventually cut through the cover (or into the exposed internal parts of the belt.) If the belt rides too low, it will soon bottom out in the pulley groove. The belt then acts like a flat belt and loses its wedging grip on the sides of the pulley groove. This will cause the belt to slip, accelerating belt wear, glazing the belt sidewalls and increasing pulley groove wear. Note: When components are replaced, be sure to check for the correct match. 12
13 Automotive Belt Tensioner/Pulley/Idler Assembly Components An automatic tensioner is a spring-loaded device consisting of eight basic parts. 13
14 Base The base is a stationary part, bolted to the engine block or other accessory. Each base design is different but they all usually feature a locating pin and mounting holes where the base is bolted to the engine. The locating pin and bolt holes position the entire tensioner assembly properly in relation to other pulleys. Damper or Bushing The damper is a plastic ring designed to reduce vibration in the tensioner. Often it will wear during operation and require tensioner replacement. Spring The spring is the core feature that makes the tensioner work, by providing tension to the belt. Tension is pre-loaded at the factory, so never try to disassemble a tensioner as a sudden release of the spring could cause injury. Arm The arm connects the spring to the tensioner pulley. It is usually an aluminum casting. 14
15 Pulley Pulleys transmit torque to driven components and come in a range of diameters, styles and materials. Materials include engineered plastic nylon or steel. Styles can be grooved, flat, or flat with flanges. Pulleys should be periodically inspected for damage or wear. Nylon pulleys are vulnerable to wear and should be replaced if wear is excessive. See the troubleshooting guide on page 25 for inspection guidelines. Pulley Bearing Do not attempt to replace a failed bearing in a used pulley, as proper alignment will be impossible. The entire pulley assembly should be replaced. NAPA Belts/Hose supplies premium replacement pulley and bearing assemblies that are factory assembled and ready to install. Dust Shield The dust shield is a small washer that protects the bearings from environmental contaminants. Pulley Center Bolt The pulley center bolt attaches the pulley to the arm. 15
16 Belt Length Variation Gauge Some tensioners have a belt length variation gauge (see page 23 for two-mark and three-mark type gauges), indicating the belt s length. It usually consists of a pointer and either two or three marks to show the range of tensioner movement. The marks are designed to indicate minimum, ideal, and full or maximum take-up length. The gauge window is located on or along the break between the base and arm of the tensioner assembly, or it may be in a position that is harder to see. Locate the gauge to determine the relative length of the belt. Premium NAPA Belts/Hose belts are designed for minimal stretching as the belt wears. Some competitive belts, however, stretch excessively, resulting in belt noise. If noise is a problem on older belts, check the tensioner gauge. If the gauge shows minimum take-up length, replace the belt with the correct size NAPA Belts/Hose XL belt. 16
17 Micro-V belts for the growing Sports Compact Tuner market are now available from NAPA Belts/Hose under the brand name Hyoshi Performance. Unlike traditional belt products, these performance belts are bright red and blue, colors popular with this growing market. NAPA Belts/Hose also offers Timing Component Kits, PowerGrip hose clamps, coolant hose kits, cam sprockets and silicone vacuum hoses. 17
18 NAPA Belts/Hose Provides Vehicle- Specific Replacement Tensioners A NAPA Belts/Hose DriveAlign replacement tensioner/pulley assembly is made specifically for each vehicle. Other aftermarket tensioner manufacturers try to use common base and tensioner arm assemblies that often do not fit on applications without filing, grinding or application of quick-drying cement to secure the locator pin and bushing. NAPA Belts/Hose DriveAlign tensioners look and fit like original equipment. More importantly, they perform like original equipment, with more than three times the service life of universal type tensioners. 18
19 System Component Problems Belt Noise Terms such as chirp, squeal, squeak, hoot and yelp have been used to describe noises caused by friction-induced vibration in engine accessory drive belts. These noises may indicate underlying damage to tensioners, bearings, pulleys and other components. Untended, they could lead to belt failure. The two major causes of belt noise are improper tension and misalignment. Improper tension is caused by a number of factors: Insufficient installation tension No run in and retension when the belt is new No continuing tension maintenance Insufficient installation allowance in the drive Insufficient take-up allowance in the drive Change in drive center distance Pulley groove wear Belt sidewall wear Belt permanent elongation 19
20 Without proper tension, a belt will slip, the sidewalls will wear smooth, and the belt will eventually harden through heataging, a process referred to as glazing. The more glazed the belt surface is, the more likely it is to be noisy and lack sufficient ability to transmit power. Note: Technicians often refer to belt stretch as a cause of belt noise. Use of the term stretch is actually an inaccurate identification for what is, in fact, a loss of tension caused by one of the factors listed above. Belt deformation is usually not a sufficient reason for loss of tension. See page 31 of the troubleshooting guide for proper corrective action. Note: Belts tensioned too high may not cause noise, but can shorten pulley bearing life from excessive hub loads. Too much tension can also result in excessive belt wear, increased belt temperatures, and premature belt failure. Because tension levels in a belt will normally decrease with use over time, new belts are typically installed with a higher degree of tension necessary to prevent slip. The tension decay properties of a belt are designed to provide minimal tension loss with a decay rate that is both gradual and predictable. Never use belt dressing or any type of substance to coat the belt to eliminate belt squeal or noise. Contamination from applying a substance on the belt will adversely affect belt life. 20
21 Misalignment generally refers to two types: parallel or angular Parallel misalignment refers to pulleys that are outside the plane of other pulleys in the drive system but whose shafts remain parallel with the other components. Proper positioning of a pulley on a shaft will help ensure all pulleys are in a common plane. Angular misalignment refers to pulleys which are within the drive system plane but are tilted because their shafts are not parallel. 21
22 Both misalignment conditions can create belt tracking problems, excessive wear, chirp noise and belt stability problems. Just a few degrees of misalignment can increase belt operating temperature by 30 F, reducing belt life by as much as 50 percent. Misalignment noise occurs most frequently on the shortest spans in a drive, which often arise between a backside pulley and an adjacent grooved accessory pulley. Proper pulley alignment is particularly critical in these locations. Misalignment noise is generally loudest at idle speed and diminishes with increasing engine rpm. The presence of high humidity (or a damp belt) often increases the likelihood for misalignment noise to occur. High output alternators used on today s cars can produce other noises and add extra stress to the belt system. These high-power alternators result in higher belt loads and a higher likelihood of belt slip. This can result in excessive heat, belt wear, premature belt and tensioner failure and noise. Misalignment noise occurs most frequently on the shortest spans in a drive, which most often arise between a backside pulley and an adjacent accessory pulley. 22
23 Low belt tension, contamination by grease or oil, and belt vibration are also sources of belt noise. Wet slip is another type of belt noise and can be aggravated by worn or glazed belts and/or worn pulleys that are water soaked. When the engine is idling, this situation can be checked and the noise can be replicated by misting the belt with water as it rotates. See the Water Spray Test on page 21 of this manual for more specific information on how to test for improper tension or misalignment problems. Also, a pebble or other foreign object can become imbedded in the belt, causing a tapping or grinding noise. Both the belt and pulley can be affected. If a foreign object has damaged a belt, it should be changed immediately. If bearings are noisy, the belt tensioner/pulley assembly should be replaced and the belt examined for replacement at the same time. Vibration and noise can develop over time as drive components such as pulleys, bearings, and spring tensioners wear out of tolerance, and brackets loosen, or as belts wear. In any case, noise from the belt system indicates a malfunction, and corrective action should be taken to eliminate the problem. Two major causes of belt failure are improper tension and misalignment. 23
24 NAPA Belts/Hose belts use new elastomeric compounds and fiber loads that are noise-resistant under various environmental and wear conditions. These new belts feature additives that enable them to slide easily into and out of the pulley. This low-noise construction helps eliminate belt noise from most misalignment situations. NAPA Belts/Hose tighter-than-oem Micro-V belt fit tolerances allow a properly functioning tensioner to maintain proper tension throughout the life of the belt. Improper belt tension can cause bearing failure on associated system components such as alternators, water pumps, etc. This chart compares NAPA Belts/Hose belts and competitive belts in regard to length differences between parts. The 0 on the chart represents the optimal OEM length. While NAPA Belts/Hose belts tested within.3 inches, competitive belts proved to be up to 1.2 inches longer than the OEM belt. 24
25 Pulley Incompatibility There are two forms of V-belt pulley incompatibility: pulley groove size mismatch and pulley groove spacing mismatch. Pulley groove size mismatch (Fig. 1) occurs when an original equipment accessory is replaced in the vehicle. The new or rebuilt accessory may come with a pulley attached or a new pulley may be used to replace the old pulley. The new pulley may be designed for a different belt cross section or a different number of V-ribs, thus leading to a pulley groove size mismatch. The belt will not seat properly and misalignment occurs. 25
26 Multiple groove V pulleys incorporate a ridge between the grooves to separate the belts. The groove spacing can vary from pulley to pulley around the accessory drive. Pulley groove spacing mismatch (Fig. 2) can occur during the design and manufacture of a vehicle when parts produced by different suppliers are combined. Often these suppliers used different standards to produce their pulleys, resulting in a mismatch between pulley dimensions on the various accessories. Pulley groove size mismatch and pulley groove spacing mismatch can both result in irregular belt wear, inefficient load transmission, belt turnover, improper span tensions, noise, and excessive bearing wear. 26
27 Diagnosing Belt Warranty Returns This chart indicates the difference between valid and invalid manufacturing warranty issues. Improper Installation/Uncontrollable Factors (Non-Warranty Issues) Misinstallation A belt rib begins separating from the joined strands. Repair Damage The belt is accidentally cut during underhood repair work. Note the existence of a clean cut in the edge or surface of the belt. 27
28 Gravel Penetration A pebble, sand or other foreign object became embedded in the bottom of the belt or the pulley grooves during vehicle operation. Example: Frayed portion of belt. Bearing Failure Often a belt is broken and shows excessive localized wear, where the belt has melted into a smaller diameter bend. Abrasion The backside of the belt appears shiny or glazed. When in motion, the belt makes contact with an object in its path such as a flange or bolt. 28
29 Uneven Rib Wear Damage to the side of the belt, a possible break in a tensile cord or jagged-edge ribs. Belt Turn-over (not shown) A condition that applies to V-belts only in which the belt twists out of its upright position as a result of pulley misalignment, excessive belt span vibration, or excessive pulley or belt wear. Normal Wear Factors (Non-Warranty Issues) Cold Cracking Excessive cracking after a period of severely cold weather of -20 F or below. 29
30 Normal Cracking Small, yet visible cracks along the length of a rib or ribs. Normal wear after more than 50,000 miles of service or under extreme operating conditions. Chunk-Out Pieces or chunks of rubber material have broken away from the belt. Generally another high-mileage condition. When chunk-out has occurred, a belt can fail at any moment. Glazing Friction, created by a loose belt slipping in the pulley, causes the belt sidewalls to become slick and shiny. This action accelerates belt degradation, leading to cracking and chunking. 30
31 Pilling Belt material is sheared off from the ribs and builds up in the belt grooves. This action makes the belt s grooved surface uneven, and causes vibration and belt noise, belt slip, or in severe cases allows the belt to walk off the drive. Oil Saturation Grease, oil, coolant solutions and other degrading engine fluids can soak the belt sidewalls, resulting in a glazed belt that slips. Prolonged contact with petroleum can lead to adhesion breakdown of belt materials and cause premature failure. Edge Cord/Sidewall Wear A foreign object, such as a pebble, can cut perpendicularly into the belt, causing the exposed tensile cord to separate or break away from the belt. 31
32 Manufacturing Defects (Warranty Issues) Rib Defect May be a smooth cut ground into the belt during manufacturing. Backside Defect Inconsistent appearance prior to installation. Grinder Defect Uniform indention left in belt ribs by the manufacturing grinder. Mispackaged Wrong sleeve on a belt that misidentifies it. Be sure to keep both the belt and the package for the NAPA Belts/Hose representative to verify. 32
33 Pulley Noise A grinding sound can also result from damaged bearings in the pulley assembly. Bearing damage can often be detected by continuous hissing or grinding noises that increase as engine rpm is increased. It can begin with a continuous growling noise, which changes to a whine with the increase in rpm. To locate the noise, turn off the engine, remove the belt, then hand spin all the pulleys to see if any are hard to turn, feel rough or rattle. A combination of growling, whining and hissing during engine operation usually means that a bearing has lost lubrication and is about to fail. 33
34 Tensioner Wear or Failure Automatic tensioners wear or fail in a number of ways as indicated below. See the troubleshooting guide for proper corrective action. Pulley wear/failure All Micro-V and V-belt pulleys will show wear with extended usage. Smaller pulleys usually will indicate wear first. Damage from stones is not uncommon and will appear as deep scratches or pits in the pulley grooves. Burns or pulley distortion will effect belt-to-pulley fit and, in severe cases, can cause excessive pilling, noise, belt slip, belt turn-over, irregular belt wear, and reduced belt life. Visible signs of wear or damage can contribute to tensioner failure. Use the troubleshooting guide at the end of this manual to determine proper corrective action. Pulley/bearing assembly wear or failure Pulley bearings can fail due to excessive use or loss of lubrication. Intermittent bearing irregularities are generally an early indication of eventual component failure. If the grease seal appears damaged, replacement is the best remedy. Also, rotate the pulley and feel for sticking, roughness, or unnatural vibration. There are no serviceable parts inside a tensioner. The entire tensioner/ pulley assembly should be replaced. 34
35 Pulley alignment Proper alignment is generally more critical to Micro-V belts than V-belts. Maximum recommended misalignment for Micro-V belts is 1/16 inch per 12 inches of belt span length (1/3 degree). Pulley alignment can be checked using a straightedge. (See NAPA Belts/Hose AutoSmarts Automotive Training Video ( ) for more information on checking pulley alignment.) Damping failure Excessive oscillation of the tensioner arm while the engine is running may indicate a worn out damper or bushing. The tensioner needs to be replaced. With the engine off, operate the tensioner through its entire range of motion. Sticking or roughness may indicate wear on the tensioner bearing surfaces. Tensioner rattle A rattling noise during operation indicates wear on the internal components. It could also indicate that the belt is too long and the free arm stop is being contacted. In either case, the tensioner should be replaced. Note: Heat Check marks on aluminum castings are sometimes mistaken for cracks. This is not a product defect, but a normal occurrence during the die casting process. Note: Some tensioners have no spring pre-load at the free arm position (i.e. belt not installed) and are sometimes returned as defective. For example, tensioner part number has no pre-load on the spring. This is not a No Load or weak spring condition. Tensioners often fail because of careless belt replacement. 35
36 Troubleshooting Methods Proper belt tension and pulley assembly operation depends on correct installation and maintenance. When experiencing any operational problems, use the following troubleshooting methods to resolve the problem. Determining Correct Part Application Always double-check all parts to ensure that the proper belt, tensioners, pulley assemblies, etc. are installed for the particular vehicle and engine in question. Incorrect parts or aftermarket parts that are not made to the proper specifications may cause the entire system to malfunction. Be certain that all parts are designed for the specific application and installed properly. If any component within the belt drive system has been recently replaced (power steering pumps, water pumps, compressors, etc.), check that part for correct installation and alignment. Any component installed improperly throws the entire belt circuit out of alignment, resulting in less than optimum performance. A misalignmentgenerated noise will not be corrected by increasing tension or simply replacing the belt. 36
37 Water Spray Test Noise caused by misalignment and/or improper tension may be diagnosed by using the Water Spray Test. Fill a spray bottle with water and spray the belt with a light mist, while the engine is running. If the noise occurs after misting, there may be problems with tension or misrouted belts. If the noise decreases for a few seconds, then returns even louder, the problem is likely to be misalignment. A misalignmentgenerated noise will not be corrected by increasing tension or simply replacing the belt. All pulleys and tensioner assemblies should be checked for proper installation and alignment to correct a misalignment problem. When re-installing a belt, clean the pulley groves. Dirt or paint on the pulleys may cause belt noise. If the noise increases immediately after misting the belt with water and the noise does not become louder, chances are it is a tension problem. The belt may be excessively worn and need replacement, the belt may be misrouted, or there may be a tensioner problem. 37
38 Removing and Re-Installing the Belt/ Changing Belt Direction Because misalignment noise is influenced by the direction of misalignment in the drive, removing the belt, turning it around, and re-installing it should eliminate or significantly reduce noise caused by misalignment temporarily. This action may confirm or disprove a misalignment problem. Replacing Tensioners Sometimes, tensioners fail because of careless belt replacement. The old belt must be removed properly and carefully to ensure that the tensioner does not spring down and crack. If the new belt is too short, it can snap the tensioner. If the belt is too long, it will slip or cause the tensioner to rattle. Some tensioners may be replaced by removing a single bolt, while others may have seals or gaskets that are integral parts of the cooling system. Others may involve removing several other components to access the tensioner base. Caution: The tensioner is manufactured containing a pre-loaded spring. Never try to disassemble the tensioner unit! Doing so could result in personal injury. Consult the vehicle s shop manual for specific instructions. 38
39 Every vehicle has tensioners designed for that particular engine assembly; there is no universal replacement procedure. Consult the proper vehicle shop manual for correct replacement procedures. In general, the proper guidelines are as follows: 1. Mark the rotation direction on the belt. 2. Unload the belt from the tensioner by rotating the tensioner as indicated (See Rotate to Load arrow). 3. Remove the old tensioner from the engine. 4. Place the new tensioner on the engine. 5. Torque the mounting bolts to 1/3 installation torque in a star pattern. 6. Retighten the bolts to 2/3 torque, then to full torque. 7. Install the belt in the same direction of rotation as the old belt. 8. Load the belt on the tensioner by rotating the tensioner as indicated (See Rotate to Load arrow). NOTE: Any time you replace a tensioner, replace the belt. Make sure it s the right belt for the application and the correct length. 39
40 Determining Correct Belt Length On either the two-mark type or three-mark type gauge, the indicator should point to a spot in the middle of the gauge, indicating ideal belt length. A worn belt will put the indicator toward the maximum belt length indicator mark. It is best to replace any belt that is worn beyond the ideal belt length indicator mark. 40
41 When a new belt is installed, the pointer should fall between the minimum belt length mark and half way through the gauge. As belts age, they wear, and the tensioner automatically moves to keep tension constant. When the pointer on the belt length variation gauge is within five percent of the full or maximum take-up mark, the belt should be replaced. At this point, the tensioner is out of its useful range, and the belt has worn to the point of failure. 41
42 If a new belt is outside the normal new belt range, it is too long for the application and may result in reduced belt life. A shorter belt should be used to bring the pointer into the proper range. 42
43 Using the Technical Service Bulletins Manual Sometimes problems are systematic or original equipment design flaws, and not due to belt tension, misalignment or excessive wear. It s a good idea to check the NAPA Belts/Hose Technical Service Bulletins manual (Part No. NBH129) or CD-ROM (Part No. NBH129CD) for any vehicle manufacturing defects or other problems that could cause noises within the front end accessory drive system. 43
44 Troubleshooting Accessory Belt Drive Systems Proper operation of accessory belt drive systems depends on locating and correcting operational problems. The following charts provide detailed directions on how to identify possible causes, conduct a proper and safe inspection, and take corrective action. To accurately check for the causes of noise, the system must be loaded: Air conditioner on full Air conditioner fan on full Head lights on high beam Rear window defroster on Wheels turned 3/4 to the left or right 44
45 45
46 46
47 47
48 48
49 49
50 50
51 51
52 52
53 53
54 54
55 55
56 56
57 Level 101 Review Quiz 1. Which of the following characteristics demonstrates the biggest difference between Micro-V belts and V-belts? a. belt construction b. profile c. variable notch pattern 2. Which critical parts and systems on a car engine can be affected by a failed belt? a. water pump b. fan c. alternator d. air conditioning compressor e. power steering pump f. all of the above 57
58 3. Which section of a Micro-V belt helps provide transverse support on the pulley? a. undercord b. tensile cord c. overcord 4. You can always determine if a belt is still good by visually inspecting it. True or False? 5. Automatic belt tensioners are designed to a. reduce maintenance b. apply a constant force to a belt c. reduce belt wear d. all of the above 58
59 6. An idler transmits torque to an accessory component. True or False? 7. Which part is the core feature that makes a tensioner work? a. pulley bearing b. pulley center bolt c. arm d. spring 8. The two major causes of belt noise are a. engine vibration and belt elongation b. belt slip and excessive hub loads c. improper tension and misalignment d. misalignment and glazing e. improper tension and vibration 59
60 9. Which condition exists when pulleys are outside the plane of other pulleys in the drive system but their shafts remain parallel? a. misalignment b. pulley incompatibility 10. Misalignment can reduce belt life by a. as much as 25 percent b. as much as 50 percent c. as much as 75 percent d. as much as 90 percent 11. Misalignment occurs most frequently on the longest spans in a drive. True or False? 60
61 12. List five sources of belt noise. a. b. c. d. e. 13. When parts produced by different suppliers are combined on a vehicle, pulley incompatibility can result from a. pulley groove spacing mismatch b. pulley groove size mismatch 14. Which of the following is not a result of pulley incompatibility? a. belt turnover b. excessive belt wear c. vibration d. improper span tensions e. inefficient load transmission f. irregular belt wear 61
62 15. Match the following descriptions with their correct names. a. gravel penetration b. bearing failure Damage to the side of the belt, tensile cord break or jagged edge ribs. Backside of belt appears shiny or glazed. c. misinstallation Belt is accidentally cut during repair work. d. repair damage Belt is broken and shows excesive wear. e. abrasion A belt rib begins separating from the joined strands. f. uneven rib wear A pebble, sand or other object was embedded in the belt. g. belt turnover Belt twists out of its upright position. 62
63 16. Match the following descriptions with their correct names. a. pilling Belt sidewalls soaked by degrading engine fluids. b. cold cracking Small, yet visible cracks along the length of a rib(s). c. glazing Slick or shiny belt sidewalls caused by friction. d. chunk-out Belt material sheared off from ribs and built up in belt grooves. e. normal cracking Pieces of rubber material broken away from belt. f. oil saturation Excessive cracking after a period of cold weather. g. edge cord/sidewall wear Damage from a foreign object that cuts into the belt. 63
64 17. A combination of growling, whining and hissing during engine operation usually means that a. a belt has lost its tension b. two pulleys are misaligned c. a bearing has lost its lubrication 18. A failed or worn tensioner should be disassembled and the non-serviceable part(s) replaced. True or False? 19. Proper alignment is generally more critical to V-belts than to Micro-V belts. True or False? 64
65 20. If any component within the belt drive system has been recently replaced, the best way to ensure optimum performance is to a. apply the water spray test b. check that part for correct installation and alignment c. consult the vehicle s shop manual 21. Any time you replace a tensioner you should replace the belt. True or False? 22. Belt dressing can improve belt life. True or False? 65
66 Answers 1. b. profile 2. f. all of the above 3. c. overcord 4. False 5. b. apply a constant force to a belt 6. False 7. d. spring 8. c. improper tension and misalignment 9. a. misalignment 10 b. as much as 50 percent 11. False 12. oil, grease, low belt tension, belt vibration, foreign objects 13. a. pulley groove spacing mismatch 14. c. vibration 15. f, e, d, b, c, a, g 16. f, e, c, a, d, b, g 17. c. a bearing has lost its lubrication 18. False 19. False 20. B. check that part for correct installation and alignment 21. True 22. False 66
Automotive Belts, Tensioners, Pulleys 101. Introduction to Front-End Accessory Drive Systems
 Automotive Belts, Tensioners, Pulleys 101 Introduction to Front-End Accessory Drive Systems Introduction to Front-End Accessory Drive and V-Belt Drive Systems Table of Contents Engine Belt System Overview...Page
Automotive Belts, Tensioners, Pulleys 101 Introduction to Front-End Accessory Drive Systems Introduction to Front-End Accessory Drive and V-Belt Drive Systems Table of Contents Engine Belt System Overview...Page
FOR MICRO-V XF MULTI-RIBBED BELTS
 E2/70407 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE FOR MICRO-V XF MULTI-RIBBED BELTS In older cars, the accessory belt drive system or fan belt system used V-belts. In 1982, Gates introduced the Micro-V multi-ribbed belt,
E2/70407 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE FOR MICRO-V XF MULTI-RIBBED BELTS In older cars, the accessory belt drive system or fan belt system used V-belts. In 1982, Gates introduced the Micro-V multi-ribbed belt,
Automatic Belt Tensioners:
 Automatic Belt Tensioners: Why cars have them and where to get them Over 100 million vehicles use automatic belt tensioners. Tensioners, like any other part, don t last forever, and automotive technicians
Automatic Belt Tensioners: Why cars have them and where to get them Over 100 million vehicles use automatic belt tensioners. Tensioners, like any other part, don t last forever, and automotive technicians
V-Belt Installation, Maintenance & Storage Installation
 V-Belt Installation, Maintenance & Storage Installation 1. Check pulleys for rust, oil, grease, dust, dirt and other foreign materials. Clean the pulleys. Foreign materials accelerate belt wear and dramatically
V-Belt Installation, Maintenance & Storage Installation 1. Check pulleys for rust, oil, grease, dust, dirt and other foreign materials. Clean the pulleys. Foreign materials accelerate belt wear and dramatically
Synchronous Belt Failure Analysis Guide
 Synchronous Belt Failure Analysis Guide Contents Part 1: Common Causes of Belt Failure Normal Belt Wear and Failure Belt Crimp Failures Shock Load Part 2: Improper Belt Installation Tension Introduction
Synchronous Belt Failure Analysis Guide Contents Part 1: Common Causes of Belt Failure Normal Belt Wear and Failure Belt Crimp Failures Shock Load Part 2: Improper Belt Installation Tension Introduction
SECTION Accessory Drive
 303-05-i Accessory Drive 303-05-i SECTION 303-05 Accessory Drive CONTENTS PAGE DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Accessory Drive... 303-05-2 Inspection and Verification... 303-05-2 Symptom Chart... 303-05-5 Component
303-05-i Accessory Drive 303-05-i SECTION 303-05 Accessory Drive CONTENTS PAGE DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Accessory Drive... 303-05-2 Inspection and Verification... 303-05-2 Symptom Chart... 303-05-5 Component
Jason Industrial Inc.
 Jason Industrial Inc. POWER TRANSMISSION V-BELTS Select Multi-Plus A & B Belts and Discontinue Your 4L & 5L Inventory! Dual Part Number System is more than just labeling. FHP & Classical have the same
Jason Industrial Inc. POWER TRANSMISSION V-BELTS Select Multi-Plus A & B Belts and Discontinue Your 4L & 5L Inventory! Dual Part Number System is more than just labeling. FHP & Classical have the same
Belt failure. Joseph Pandolfo PAPA 2016
 Belt failure Joseph Pandolfo joeboy@ptd.net 570 350 3359 PAPA 2016 Squealing sound: Belt slipping Chirping sound: Misalignment of an accessory drive pulley Frayed belt edge: Misalignment of an accessory
Belt failure Joseph Pandolfo joeboy@ptd.net 570 350 3359 PAPA 2016 Squealing sound: Belt slipping Chirping sound: Misalignment of an accessory drive pulley Frayed belt edge: Misalignment of an accessory
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
 303-05-1 Accessory Drive 303-05-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Accessory Drive Inspection and Verification CAUTION: Under no circumstances should the accessory drive belt, tensioner or pulleys be lubricated as
303-05-1 Accessory Drive 303-05-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Accessory Drive Inspection and Verification CAUTION: Under no circumstances should the accessory drive belt, tensioner or pulleys be lubricated as
GatesFacts Technical Information Library Gates Compass Power Transmission CD-ROM version 1.2 The Gates Rubber Company Denver, Colorado USA
 Gary L. Miller Plant Engineering November 7, 1991 DIFFERENCES IN SYNCHRONOUS BELTS All toothed belts are not the same; subtle differences in tooth profiles and construction affect performance. Synchronous
Gary L. Miller Plant Engineering November 7, 1991 DIFFERENCES IN SYNCHRONOUS BELTS All toothed belts are not the same; subtle differences in tooth profiles and construction affect performance. Synchronous
REMY TECHNICAL SERVICE BULLETIN
 June 2018 REMY TECHNICAL SERVICE BULLETIN Remy Power Products is continuously adding technical training and technical information. We welcome suggestions. If there is something technical you would like
June 2018 REMY TECHNICAL SERVICE BULLETIN Remy Power Products is continuously adding technical training and technical information. We welcome suggestions. If there is something technical you would like
2011 Focus Workshop Manual. DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 06/24/2010
 SECTION 303-05: Accessory Drive 2011 Focus Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 06/24/2010 Accessory Drive The accessory drive: has a single serpentine drive belt with 6 ribs.
SECTION 303-05: Accessory Drive 2011 Focus Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 06/24/2010 Accessory Drive The accessory drive: has a single serpentine drive belt with 6 ribs.
Mechanical Equipment - Course 230.1
 Mechanical Equipment - Course 230.1 BELT DRIVES A conunon method of transmitting power is a combination of belts and pulleys, There are many types of belts and pulleys used for the transmission of power
Mechanical Equipment - Course 230.1 BELT DRIVES A conunon method of transmitting power is a combination of belts and pulleys, There are many types of belts and pulleys used for the transmission of power
Pulley Alignment. Parallel Misalignment
 Pulley Alignment There are many different factors that contribute to machine downtime when considering Sheave/Pulley, Belt and Bearing wear. The single biggest factor that can impact the reliability of
Pulley Alignment There are many different factors that contribute to machine downtime when considering Sheave/Pulley, Belt and Bearing wear. The single biggest factor that can impact the reliability of
Timing Belt Installation
 Timing Belt Installation The following is an installation guideline designed to combat problems resulting from improper installation of timing belt drives. 1) Loosen Motor. Check to make sure that the
Timing Belt Installation The following is an installation guideline designed to combat problems resulting from improper installation of timing belt drives. 1) Loosen Motor. Check to make sure that the
Failures of Rolling Bearings in Bar and Rod Mill
 Case Study Failures of Rolling Bearings in Bar and Rod Mill by Christo Iliev University of Zimbabwe, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Harare, Zimbabwe INTRODUCTION Bar and rod mills can usually be found
Case Study Failures of Rolling Bearings in Bar and Rod Mill by Christo Iliev University of Zimbabwe, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Harare, Zimbabwe INTRODUCTION Bar and rod mills can usually be found
Engine Bearing Failure Analysis By Clevite 1965
 Engine Bearing Failure Analysis By Clevite 1965 RECOMMENDED BEARING INSTALLATION TOLERANCES CRANKCASE TOLERANCES Finish of main bores 80 micro inch or better. Bore Tolerance.001 " up to 10" bore,.002"
Engine Bearing Failure Analysis By Clevite 1965 RECOMMENDED BEARING INSTALLATION TOLERANCES CRANKCASE TOLERANCES Finish of main bores 80 micro inch or better. Bore Tolerance.001 " up to 10" bore,.002"
Power Transmission Belt Drive System Installation, Maintenance and Troubleshooting Guide
 Power Transmission Drive System Installation, Maintenance and Troubleshooting Guide www.contitech.us Table of Contents Installation Guide 2 Table of Contents Installation V-s V-s 3 Banded s Torque Team
Power Transmission Drive System Installation, Maintenance and Troubleshooting Guide www.contitech.us Table of Contents Installation Guide 2 Table of Contents Installation V-s V-s 3 Banded s Torque Team
Commissioning & Maintenance Instructions. for. COBRA linear stepping motors
 Commissioning & Maintenance Instructions for COBRA linear stepping motors ACP&D Limited. 86 Rose Hill Road, Ashton-under-Lyne, Lancashire, OL6 8NS. Tel : +44 (0)161 343 1884 Fax: +44 (0)161 343 7773 e-mail:
Commissioning & Maintenance Instructions for COBRA linear stepping motors ACP&D Limited. 86 Rose Hill Road, Ashton-under-Lyne, Lancashire, OL6 8NS. Tel : +44 (0)161 343 1884 Fax: +44 (0)161 343 7773 e-mail:
WARNING DO NOT USE THE PRODUCTS IN THIS GUIDE IN AIRCRAFT APPLICATIONS. THE PRODUCTS IN THIS GUIDE ARE NOT INTENDED FOR USE IN AIRCRAFT APPLICATIONS.
 P O W E R T R A N S M I S S I O N P R O D U C T S power transmission belt drive system Installation, Maintenance and Troubleshooting Guide WARNING DO NOT USE THE PRODUCTS IN THIS GUIDE IN AIRCRAFT APPLICATIONS.
P O W E R T R A N S M I S S I O N P R O D U C T S power transmission belt drive system Installation, Maintenance and Troubleshooting Guide WARNING DO NOT USE THE PRODUCTS IN THIS GUIDE IN AIRCRAFT APPLICATIONS.
PRECISION BELLOWS COUPLINGS
 PRECISION BELLOWS COUPLINGS Bellows couplings are used where precise rotation, high speeds, and dynamic motion must be transmitted. They exhibit zero backlash and a high level of torsional stiffness, offering
PRECISION BELLOWS COUPLINGS Bellows couplings are used where precise rotation, high speeds, and dynamic motion must be transmitted. They exhibit zero backlash and a high level of torsional stiffness, offering
Tyre Care & Safety for Agricultural Tires
 Tyre Care & Safety for Agricultural Tires Operating Instructions Some Points Worth Remembering; The BKT Agricultural tires are designed for Agricultural tractors, Trailers & Implements. Before using them
Tyre Care & Safety for Agricultural Tires Operating Instructions Some Points Worth Remembering; The BKT Agricultural tires are designed for Agricultural tractors, Trailers & Implements. Before using them
Poly-V-Belts February Description and Operation of the Poly-V- Belts. Removal of the Poly-V- Belts. Inspection of the Poly-V- Belts
 1 02 13-18 SUBJECT DATE Poly-V-Belts February 2018 Additions, Revisions, or Updates Publication Number / Title Platform Section Title Change Description and Operation of the Poly-V- Belts DDC-SVC-MAN-0190
1 02 13-18 SUBJECT DATE Poly-V-Belts February 2018 Additions, Revisions, or Updates Publication Number / Title Platform Section Title Change Description and Operation of the Poly-V- Belts DDC-SVC-MAN-0190
GATES POWERGRIP TIMING BELTS MENU
 GATES POWERGRIP TIMING BELTS MENU PowerGrip timing belt installation PowerGrip timing belt troubleshooting guide More about PowerGrip timing belts GATES POWERGRIP TIMING BELTS INSTALLATION Timing Belt
GATES POWERGRIP TIMING BELTS MENU PowerGrip timing belt installation PowerGrip timing belt troubleshooting guide More about PowerGrip timing belts GATES POWERGRIP TIMING BELTS INSTALLATION Timing Belt
GatesFacts Technical Information Library Gates Compass Power Transmission CD-ROM version 1.2 The Gates Rubber Company Denver, Colorado USA
 Timing Belt Selection And Troubleshooting David E. Roos Maintenance Technology September 1989 Evenly spaced teeth on the bottom surface of synchronous or timing belts mesh with grooves on the pulleys for
Timing Belt Selection And Troubleshooting David E. Roos Maintenance Technology September 1989 Evenly spaced teeth on the bottom surface of synchronous or timing belts mesh with grooves on the pulleys for
Troubleshooting Power Transmission Couplings
 Troubleshooting Power Transmission Couplings Introduction Power transmission couplings are used to connect two shafts that turn in the same direction on the same centerline. There are three principle types
Troubleshooting Power Transmission Couplings Introduction Power transmission couplings are used to connect two shafts that turn in the same direction on the same centerline. There are three principle types
Tyres OVERVIEW TYRE PRESSURES TYRE PRESSURES. R performance wheels
 Tyres OVERVIEW Tyres of the correct type, manufacturer and dimensions, with correct cold inflation pressures are an integral part of every vehicle s design. Regular maintenance of tyres contributes not
Tyres OVERVIEW Tyres of the correct type, manufacturer and dimensions, with correct cold inflation pressures are an integral part of every vehicle s design. Regular maintenance of tyres contributes not
Caterpillar Engine 01.00
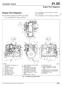 Caterpillar Engine 01.00 Engine Port Diagrams Engine Port Diagrams Use the following diagrams to identify engine ports: For a Caterpillar CFE engine, see Fig. 1. For a Caterpillar C-7/C-9 and C-11/C-13
Caterpillar Engine 01.00 Engine Port Diagrams Engine Port Diagrams Use the following diagrams to identify engine ports: For a Caterpillar CFE engine, see Fig. 1. For a Caterpillar C-7/C-9 and C-11/C-13
FTM-L SERIES SINGLE OR TWIN DIRECT STEAM MIXER KETTLE COMPLETE WITH HYDRAULIC POWER TILT BRIDGE PARTS AND SERVICE MANUAL
 FTM-L SERIES SINGLE OR TWIN DIRECT STEAM MIXER KETTLE COMPLETE WITH HYDRAULIC POWER TILT BRIDGE PARTS AND SERVICE MANUAL EFFECTIVE SEPTEMBER 19, 2014 Superseding All Previous Parts Lists. The Company reserves
FTM-L SERIES SINGLE OR TWIN DIRECT STEAM MIXER KETTLE COMPLETE WITH HYDRAULIC POWER TILT BRIDGE PARTS AND SERVICE MANUAL EFFECTIVE SEPTEMBER 19, 2014 Superseding All Previous Parts Lists. The Company reserves
Conditions requiring belt replacement are excessive wear, severe glazing, frayed cords, etc. Replace any belt exhibiting any of these conditions.
 REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Accessory Drive Belts Conditions requiring belt replacement are excessive wear, severe glazing, frayed cords, etc. Replace any belt exhibiting any of these conditions. NOTE: Minor
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION Accessory Drive Belts Conditions requiring belt replacement are excessive wear, severe glazing, frayed cords, etc. Replace any belt exhibiting any of these conditions. NOTE: Minor
ACCESSORY BELT DRIVE SYSTEM
 MICRO-V HORIZON Multi-Ribbed Belt ACCESSORY BELT DRIVE SYSTEM MICRO-V HORIZON The All-New Micro-V Horizon The Most Advanced Belt Ever Made Accessory belts are crucial to the function of modern cars. You
MICRO-V HORIZON Multi-Ribbed Belt ACCESSORY BELT DRIVE SYSTEM MICRO-V HORIZON The All-New Micro-V Horizon The Most Advanced Belt Ever Made Accessory belts are crucial to the function of modern cars. You
TIRE SELECTION GUIDE. u TIRE BASICS u CHOOSING THE RIGHT TIRE u PROPER TIRE CARE u WHEN TO REPLACE u REDUCING TIRE COSTS
 TIRE SELECTION GUIDE u TIRE BASICS u CHOOSING THE RIGHT TIRE u PROPER TIRE CARE u WHEN TO REPLACE u REDUCING TIRE COSTS www.forkliftsmi.com 616-455-2376 TIRE BASICS SECTION 1 Forklift tires are not all
TIRE SELECTION GUIDE u TIRE BASICS u CHOOSING THE RIGHT TIRE u PROPER TIRE CARE u WHEN TO REPLACE u REDUCING TIRE COSTS www.forkliftsmi.com 616-455-2376 TIRE BASICS SECTION 1 Forklift tires are not all
HORSTMAN GREASED LIGHTNING CLUTCH
 HORSTMAN GREASED LIGHTNING CLUTCH Horstman s Greased Lightning (GL) clutch is designed for ultra high performance, and requires expert setup and a serious commitment to maintenance. Warning!!! 1. Clutch
HORSTMAN GREASED LIGHTNING CLUTCH Horstman s Greased Lightning (GL) clutch is designed for ultra high performance, and requires expert setup and a serious commitment to maintenance. Warning!!! 1. Clutch
WARM ENGINE STARTING PROCEDURE
 saw starting COLD ENGINE STARTING PROCEDURE 1. Pull the choke lever out. 2. Lock the throttle in the start position by depressing and holding the throttle lock button (C) while releasing the trigger (A)
saw starting COLD ENGINE STARTING PROCEDURE 1. Pull the choke lever out. 2. Lock the throttle in the start position by depressing and holding the throttle lock button (C) while releasing the trigger (A)
GatesFacts Technical Information Library Gates Compass Power Transmission CD-ROM version 1.2 The Gates Rubber Company Denver, Colorado USA
 HOT AND COLD RUNNING BELTS James Shepherd Power Transmission Design Magazine October 1992 Temperature has a big influence on the life of V-belts, especially in very hot or cold environments. But, there
HOT AND COLD RUNNING BELTS James Shepherd Power Transmission Design Magazine October 1992 Temperature has a big influence on the life of V-belts, especially in very hot or cold environments. But, there
DIAMOND ROLLER CHAIN. For Agricultural and Construction Equipment
 DIAMOND ROLLER CHAIN For Agricultural and Construction Equipment FABRICATION While roller chain would appear to be a simple product, the number of components in a ten foot section of 40 pitch chain totals
DIAMOND ROLLER CHAIN For Agricultural and Construction Equipment FABRICATION While roller chain would appear to be a simple product, the number of components in a ten foot section of 40 pitch chain totals
Module 6: Air Foundation Brakes
 Air Brakes Terms and Definitions Basic Components That Make Up Air Foundation Brakes Types of Air Foundation Brakes Parts of a Cam Foundation Brake Parts of a Wedge Foundation Brake Parts of a Disc Foundation
Air Brakes Terms and Definitions Basic Components That Make Up Air Foundation Brakes Types of Air Foundation Brakes Parts of a Cam Foundation Brake Parts of a Wedge Foundation Brake Parts of a Disc Foundation
Electric Brakes. Braking Systems - Electric
 Electric Brakes The electric brakes on your trailer are similar to the drum brakes on your automobile. The basic difference is that your automotive brakes are actuated by hydraulic pressure while your
Electric Brakes The electric brakes on your trailer are similar to the drum brakes on your automobile. The basic difference is that your automotive brakes are actuated by hydraulic pressure while your
2.- HANDLING OF VALVES BEFORE ASSEMBLY 3.- FITTING THE VALVE TO THE REST OF THE ASSEMBLY 5.- PERIODICAL INSPECTION OF THE VALVE AND MAINTENANCE
 Page 1 of 16 CONTENTS 1.- INTRODUCTION 2.- HANDLING OF VALVES BEFORE ASSEMBLY 3.- FITTING THE VALVE TO THE REST OF THE ASSEMBLY 4.- OPERATION OF A BALL VALVE 5.- PERIODICAL INSPECTION OF THE VALVE AND
Page 1 of 16 CONTENTS 1.- INTRODUCTION 2.- HANDLING OF VALVES BEFORE ASSEMBLY 3.- FITTING THE VALVE TO THE REST OF THE ASSEMBLY 4.- OPERATION OF A BALL VALVE 5.- PERIODICAL INSPECTION OF THE VALVE AND
OPERATION SERVICE PARTS TUGIT2. Manually Operated Short Handle Lever Hoist A3140-XXX
 OPERATION SERVICE PARTS TUGIT2 Manually Operated Short Handle Lever Hoist A3140-XXX Sold & Serviced by Morgan Aero 1450 80 th Street SW Everett WA U.S.A. 425/438.9600 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS WARNING! Improper
OPERATION SERVICE PARTS TUGIT2 Manually Operated Short Handle Lever Hoist A3140-XXX Sold & Serviced by Morgan Aero 1450 80 th Street SW Everett WA U.S.A. 425/438.9600 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS WARNING! Improper
SECTION steering mechanism
 07-302.01/ 1 2011MR17 SECTION 07-302.01 GENERAL Description See Figure 1. The includes the steering wheel (1), the steering column, the miter box (3), the steering shafts (2 and 4), and the drag link (7).
07-302.01/ 1 2011MR17 SECTION 07-302.01 GENERAL Description See Figure 1. The includes the steering wheel (1), the steering column, the miter box (3), the steering shafts (2 and 4), and the drag link (7).
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR ROTATING UNIONS SEALING TECHNOLOGIES
 DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR ROTATING UNIONS SEALING TECHNOLOGIES Rotating unions convey fluid from a stationary supply line to equipment or a rotating tool. They are critical elements in a variety of applications
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR ROTATING UNIONS SEALING TECHNOLOGIES Rotating unions convey fluid from a stationary supply line to equipment or a rotating tool. They are critical elements in a variety of applications
SECTION 8 2 DO IT YOURSELF MAINTENANCE. Chassis
 DO IT YOURSELF MAINTENANCE Chassis SECTION 8 2 Checking the coolant level of the traction motor................ 184 Checking the radiator....................................... 185 Checking brake fluid........................................
DO IT YOURSELF MAINTENANCE Chassis SECTION 8 2 Checking the coolant level of the traction motor................ 184 Checking the radiator....................................... 185 Checking brake fluid........................................
DC MOTOR MAINTENANCE ALL ELECTRIC LIFT TRUCKS PART NO SRM 294
 DC MOTOR MAINTENANCE ALL ELECTRIC LIFT TRUCKS PART NO. 897076 620 SRM 294 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR When lifting parts or assemblies, make sure all slings, chains, or cables are correctly
DC MOTOR MAINTENANCE ALL ELECTRIC LIFT TRUCKS PART NO. 897076 620 SRM 294 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR When lifting parts or assemblies, make sure all slings, chains, or cables are correctly
Part 7 DO IT YOURSELF MAINTENANCE
 Part 7 DO IT YOURSELF MAINTENANCE Chapter 7 2 Engine and Chassis Checking the engine oil level Checking the engine coolant level Checking brake fluid Checking power steering fluid Checking tire pressure
Part 7 DO IT YOURSELF MAINTENANCE Chapter 7 2 Engine and Chassis Checking the engine oil level Checking the engine coolant level Checking brake fluid Checking power steering fluid Checking tire pressure
Sequoia power steering rack service Match-mounting wheels and tires Oxygen sensor circuit diagnosis
 In this issue: Sequoia power steering rack service Match-mounting wheels and tires Oxygen sensor circuit diagnosis PHASE MATCHING Often referred to as match mounting, phase matching involves mounting the
In this issue: Sequoia power steering rack service Match-mounting wheels and tires Oxygen sensor circuit diagnosis PHASE MATCHING Often referred to as match mounting, phase matching involves mounting the
Installation and Operational Instructions for EAS -Compact overload clutch, Type 49_. 4._ Sizes 4 and 5
 Please read these Operational Instructions carefully and follow them accordingly! Ignoring these Instructions may lead to malfunctions or to clutch failure, resulting in damage to other parts. Contents:
Please read these Operational Instructions carefully and follow them accordingly! Ignoring these Instructions may lead to malfunctions or to clutch failure, resulting in damage to other parts. Contents:
General Removal & Installation Procedures for Most Heavy Duty Alternators
 General Removal & Installation Procedures for Most Heavy Duty Alternators MAY 2012 A. Removal Procedures 1. Disconnect negative battery cable. Note: there may be more than one negative battery cable if
General Removal & Installation Procedures for Most Heavy Duty Alternators MAY 2012 A. Removal Procedures 1. Disconnect negative battery cable. Note: there may be more than one negative battery cable if
Timing Belt Design Hints A guide to Timing Belt drives
 Timing Belt Design Hints A guide to Timing Belt drives Properties This table is provided to assist in specifying an Optibelt drive element for a particular drive application. Ambient temperature Maximum/minimum
Timing Belt Design Hints A guide to Timing Belt drives Properties This table is provided to assist in specifying an Optibelt drive element for a particular drive application. Ambient temperature Maximum/minimum
Installation Tensioning Procedure
 Contents PARTICULARS Introduction PIX X treme HTD Belts Construction Features Designation Pitch range Length range Pulley Dimensions Length tolerances Width tolerances PIX X treme Classical Belts Construction
Contents PARTICULARS Introduction PIX X treme HTD Belts Construction Features Designation Pitch range Length range Pulley Dimensions Length tolerances Width tolerances PIX X treme Classical Belts Construction
GatesFacts Technical Information Library Gates Compass Power Transmission CD-ROM version 1.2 The Gates Rubber Company Denver, Colorado USA
 PREVENTING DRIVE BELT ALIGNMENT PROBLEMS Dan Parsons Plant Engineering July, 1993 Amount of angular and parallel misalignment determines what action to take. Misalignment is one of the most common causes
PREVENTING DRIVE BELT ALIGNMENT PROBLEMS Dan Parsons Plant Engineering July, 1993 Amount of angular and parallel misalignment determines what action to take. Misalignment is one of the most common causes
Installation Instructions Pro Bandit Shifter Fits: GM Powerglide Automatic Transmissions
 Installation Instructions Pro Bandit Shifter Fits: 1962-1973 GM Powerglide Automatic Transmissions Part # 80793 WORK SAFELY! For maximum safety, perform this installation on a clean, level surface and
Installation Instructions Pro Bandit Shifter Fits: 1962-1973 GM Powerglide Automatic Transmissions Part # 80793 WORK SAFELY! For maximum safety, perform this installation on a clean, level surface and
FAST BRAKE INDEX. trouble-shooting guide
 FAST BRAKE trouble-shooting guide INDEX INTRODUCTION 3 PRECAUTIONS 3 INSPECTION 4 Q&A Why does my spring brake have square air-inlet ports? 4 Why is the yoke welded to the service push-rod? 6 What do I
FAST BRAKE trouble-shooting guide INDEX INTRODUCTION 3 PRECAUTIONS 3 INSPECTION 4 Q&A Why does my spring brake have square air-inlet ports? 4 Why is the yoke welded to the service push-rod? 6 What do I
INSTALLATION, OPERATION, AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL RBK FRP FAN
 Bulletin 62-January-20-09 ROOF UPBLAST & SIDEWALL CENTRIFUGAL FIBERGLASS EXHAUST FAN INSTALLATION, OPERATION, AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL RBK FRP FAN The M.K. Plastics catalog on the above corrosion resistant
Bulletin 62-January-20-09 ROOF UPBLAST & SIDEWALL CENTRIFUGAL FIBERGLASS EXHAUST FAN INSTALLATION, OPERATION, AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL RBK FRP FAN The M.K. Plastics catalog on the above corrosion resistant
AIRCRAFT ENGINE MECHANIC, 8602
 May 2000 Federal Wage System Job Grading Standards FEDERAL WAGE SYSTEM JOB GRADING STANDARD FOR AIRCRAFT ENGINE MECHANIC, 8602 Theodore Roosevelt Building 1900 E Street, NW Washington, DC 20415-8330 Classification
May 2000 Federal Wage System Job Grading Standards FEDERAL WAGE SYSTEM JOB GRADING STANDARD FOR AIRCRAFT ENGINE MECHANIC, 8602 Theodore Roosevelt Building 1900 E Street, NW Washington, DC 20415-8330 Classification
Randy Recommends... If your bike has chain drive, here are some things you should know.
 Chains part 1: Sizing Motorcycle drive chains are made up of alternating internal links and external links, connected by pins. The internal links consist of two plates connected to each other through two
Chains part 1: Sizing Motorcycle drive chains are made up of alternating internal links and external links, connected by pins. The internal links consist of two plates connected to each other through two
Auger Belt Tension Adjustment DB7659
 Rev 1.0 3-23-13 Auger Belt Tension Adjustment DB7659 WARNING Entanglement Hazard - Before performing any adjustment procedures, make sure the engine is off and remove the spark plug wire from the spark
Rev 1.0 3-23-13 Auger Belt Tension Adjustment DB7659 WARNING Entanglement Hazard - Before performing any adjustment procedures, make sure the engine is off and remove the spark plug wire from the spark
 DRUM BRAKE RIMS Periodic inspection of drum brake rims is necessary to determine indications of uneven or excessive wear. In general, brake rim failures other that regular wear are caused by brake linings
DRUM BRAKE RIMS Periodic inspection of drum brake rims is necessary to determine indications of uneven or excessive wear. In general, brake rim failures other that regular wear are caused by brake linings
Straight Talk on Parts
 Topic: Recoated Fuser Rollers Revised February 1997 Q Some companies offer recoated ( remanufactured ) fuser rollers at extremely low prices. Are there quality sacrifices, potential performance problems,
Topic: Recoated Fuser Rollers Revised February 1997 Q Some companies offer recoated ( remanufactured ) fuser rollers at extremely low prices. Are there quality sacrifices, potential performance problems,
Diaphragm Valves Type 15
 Serial No. H-V031-E-8 Diaphragm Valves Type 15 User s Manual Contents (1) Be sure to read the following warranty clauses of our product 1 (2) General operating instructions 2 (3) General instructions for
Serial No. H-V031-E-8 Diaphragm Valves Type 15 User s Manual Contents (1) Be sure to read the following warranty clauses of our product 1 (2) General operating instructions 2 (3) General instructions for
Important Notes Note Recommended Equipment NOT included in kit
 Important Notes This helicopter is recommended for skilled intermediates and advanced RC helicopter flyers. Make sure to read and follow all the instructions in this manual, including all accessories.
Important Notes This helicopter is recommended for skilled intermediates and advanced RC helicopter flyers. Make sure to read and follow all the instructions in this manual, including all accessories.
Sediment strainer (Type Y)
 Installation,Operation and Maintenance Manual Serial No. H-V034-E-9 Sediment strainer (Type Y) Contents (1) Be sure to read the following warranty clauses of our product 1 User s Manual (2) General operating
Installation,Operation and Maintenance Manual Serial No. H-V034-E-9 Sediment strainer (Type Y) Contents (1) Be sure to read the following warranty clauses of our product 1 User s Manual (2) General operating
Motion System Components Diagram. Note: #2 Mirror Cover and X-Axis Motor Cover have been removed for visibility. Maintenance.
 Professional Laser System PLS3.75, PLS4.75, PLS6.75 and PLS6.150D Keeping the laser system clean will ensure the highest quality engraving. A clean laser system is the best performing laser system. The
Professional Laser System PLS3.75, PLS4.75, PLS6.75 and PLS6.150D Keeping the laser system clean will ensure the highest quality engraving. A clean laser system is the best performing laser system. The
TIRES AND WHEELS 22-1 TIRES AND WHEELS CONTENTS
 ZJ TIRES AND WHEELS 22-1 TIRES AND WHEELS CONTENTS TIRES... 1 WHEELS... 7 TIRES INDEX DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION RADIAL-PLY TIRES... 2 REPLACEMENT TIRES... 3 SPARE TIRE TEMPORARY... 2 TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES...
ZJ TIRES AND WHEELS 22-1 TIRES AND WHEELS CONTENTS TIRES... 1 WHEELS... 7 TIRES INDEX DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION RADIAL-PLY TIRES... 2 REPLACEMENT TIRES... 3 SPARE TIRE TEMPORARY... 2 TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES...
Plastic and Composite Repair Student Handouts
 Plastic and Composite Repair Student Handouts Version: 13.2 2011-2014 Inter-Industry Conference on Auto Collision Repair PLA03-STHO02-E This page is intentionally left blank. STEP Clean The Part Two-Sided
Plastic and Composite Repair Student Handouts Version: 13.2 2011-2014 Inter-Industry Conference on Auto Collision Repair PLA03-STHO02-E This page is intentionally left blank. STEP Clean The Part Two-Sided
Contents H-V034-E-12. Serial No. (page) (1) Be sure to read the following warranty clauses of our product 1. (2) General operating instructions 2
 Serial No. H-V034-E-12 Sediment strainer (Type Y) Contents (page) (1) Be sure to read the following warranty clauses of our product 1 User s Manual (2) General operating instructions 2 (3) General instructions
Serial No. H-V034-E-12 Sediment strainer (Type Y) Contents (page) (1) Be sure to read the following warranty clauses of our product 1 User s Manual (2) General operating instructions 2 (3) General instructions
WEAPONX CIRCUIT COMPRESSION
 WeaponX Ignition Coil Technology WeaponX designs and employs the greatest performance proven technologies available. The creation of a high quality ignition system has been a challenging process for OEMS
WeaponX Ignition Coil Technology WeaponX designs and employs the greatest performance proven technologies available. The creation of a high quality ignition system has been a challenging process for OEMS
Learn how rollers and web handling affect your 100% inspection system s performance
 Learn how rollers and web handling affect your 100% inspection system s performance The following article explains the many reasons why rollers (idlers) and web material properties can adversely affect
Learn how rollers and web handling affect your 100% inspection system s performance The following article explains the many reasons why rollers (idlers) and web material properties can adversely affect
SECTION 6 3 SERVICE PROCEDURES AND SPECIFICATIONS. Chassis
 SERVICE PROCEDURES AND SPECIFICATIONS Chassis SECTION 6 3 Specifications........................................... 208 Checking brake fluid...................................... 210 Checking power steering
SERVICE PROCEDURES AND SPECIFICATIONS Chassis SECTION 6 3 Specifications........................................... 208 Checking brake fluid...................................... 210 Checking power steering
Best Practice Guideline. Tyre Handling in Surface Operations
 Best Practice Guideline Tyre Handling in Surface Operations www.aspasa.co.za June 2018 Introduction The job of tyre servicing can be extremely hazardous. An inflated large vehicle tyre contains tremendous
Best Practice Guideline Tyre Handling in Surface Operations www.aspasa.co.za June 2018 Introduction The job of tyre servicing can be extremely hazardous. An inflated large vehicle tyre contains tremendous
Oil Pump. Features: AISIN aluminum die-casting technology allows for size and weight reduction.
 Oil Pump Engineered to exacting OE specifications, AISIN Oil Pumps deliver ideal oil pressure to the engine without creating excess load. Lubricating critical components to extend the life of the engine,
Oil Pump Engineered to exacting OE specifications, AISIN Oil Pumps deliver ideal oil pressure to the engine without creating excess load. Lubricating critical components to extend the life of the engine,
Why choose Bosch Timing Belts?
 Why choose Bosch Timing Belts? Bosch is one of the largest suppliers of automotive belts to the Australian and New Zealand market, offering a comprehensive range for Australian, Asian and European vehicle
Why choose Bosch Timing Belts? Bosch is one of the largest suppliers of automotive belts to the Australian and New Zealand market, offering a comprehensive range for Australian, Asian and European vehicle
Fig. 1: Remove the bolts which fasten the upper timing belt cover... Fig. 2:... and remove the cover
 Show Timing Belt and Covers REMOVAL & INSTALLATION 1983 87 626 NOTE: For access, safely support the car, then remove the right front wheel and splash shield. 1. Loosen the alternator mounting bolts and
Show Timing Belt and Covers REMOVAL & INSTALLATION 1983 87 626 NOTE: For access, safely support the car, then remove the right front wheel and splash shield. 1. Loosen the alternator mounting bolts and
LESSON Transmission of Power Introduction
 LESSON 3 3.0 Transmission of Power 3.0.1 Introduction Earlier in our previous course units in Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering, we introduced ourselves to the concept of support and process systems
LESSON 3 3.0 Transmission of Power 3.0.1 Introduction Earlier in our previous course units in Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering, we introduced ourselves to the concept of support and process systems
Installation and Operational Instructions for EAS -smartic synchronous clutch Type 48_. 5._ Sizes 01 2
 Please read these Operational Instructions carefully and follow them accordingly! Ignoring these Instructions may lead to malfunctions or to clutch failure, resulting in damage to other parts. Contents:
Please read these Operational Instructions carefully and follow them accordingly! Ignoring these Instructions may lead to malfunctions or to clutch failure, resulting in damage to other parts. Contents:
TIMING BELT AND SPROCKET(S) REMOVAL - TIMING BELT
 TIMING BELT AND SPROCKET(S) REMOVAL - TIMING BELT 1. Disconnect negative battery cable. 2. Raise vehicle on hoist. Remove right front wheel. 3. Remove belt splash shield. 4. Remove accessory drive belts.
TIMING BELT AND SPROCKET(S) REMOVAL - TIMING BELT 1. Disconnect negative battery cable. 2. Raise vehicle on hoist. Remove right front wheel. 3. Remove belt splash shield. 4. Remove accessory drive belts.
BRAKE SYSTEM Return To Main Table of Contents
 BRAKE SYSTEM Return To Main Table of Contents GENERAL... 2 BRAKE PEDAL... 10 MASTER CYLINDER... 13 BRAKE BOOSTER... 16 BRAKE LINE... 18 PROPORTIONING VALVE... 19 FRONT DISC BRAKE... 20 REAR DRUM BRAKE...
BRAKE SYSTEM Return To Main Table of Contents GENERAL... 2 BRAKE PEDAL... 10 MASTER CYLINDER... 13 BRAKE BOOSTER... 16 BRAKE LINE... 18 PROPORTIONING VALVE... 19 FRONT DISC BRAKE... 20 REAR DRUM BRAKE...
GatesFacts Technical Information Library Gates Compass Power Transmission CD-ROM version 1.2 The Gates Rubber Company Denver, Colorado USA
 MAKING THE RIGHT SHAFT CONNECTIONS Daniel Schwartz & Gary Porter Power Transmission Design August, 1996 Securing a belt pulley to a drive shaft often seems like such a routine task, that engineers and
MAKING THE RIGHT SHAFT CONNECTIONS Daniel Schwartz & Gary Porter Power Transmission Design August, 1996 Securing a belt pulley to a drive shaft often seems like such a routine task, that engineers and
JASON MULTI-PLUS DUAL BRAND V-BELTS LIGHT & HEAVY DUTY SHEAVES & BUSHINGS. For Heating. Air Conditioning. Ventilation. Refrigeration.
 JASON MULTI-PLUS DUAL BRAND V-BELTS LIGHT & HEAVY DUTY SHEAVES & BUSHINGS For Heating Air Conditioning Ventilation Refrigeration Industrial TABLE OF CONTENTS Product Type Page V-BELTS F.H.P./3L Section
JASON MULTI-PLUS DUAL BRAND V-BELTS LIGHT & HEAVY DUTY SHEAVES & BUSHINGS For Heating Air Conditioning Ventilation Refrigeration Industrial TABLE OF CONTENTS Product Type Page V-BELTS F.H.P./3L Section
CLUTCH 6-1 CLUTCH CONTENTS
 Z CLUTCH 6-1 CLUTCH CONTENTS page page CLUTCH DIAGNOSIS... 2 CLUTCH SERVICE... 9 CLUTCH COMPONENTS MECHANICAL COMPONENTS The clutch mechanism in Grand Cherokee models with manual transmission consists
Z CLUTCH 6-1 CLUTCH CONTENTS page page CLUTCH DIAGNOSIS... 2 CLUTCH SERVICE... 9 CLUTCH COMPONENTS MECHANICAL COMPONENTS The clutch mechanism in Grand Cherokee models with manual transmission consists
Brake Systems. Introduction
 Brake Systems Figure 1. A Typical Brake System Introduction The brake system (Figure 1) is designed to slow and halt the motion of a vehicle. To do that, various components within a hydraulic brake system
Brake Systems Figure 1. A Typical Brake System Introduction The brake system (Figure 1) is designed to slow and halt the motion of a vehicle. To do that, various components within a hydraulic brake system
Troubleshooting. Pull Type Clutches - Poor Release
 Troubleshooting Pull Type Clutches - Poor Release Complaint Possible Causes Corrective Action Poor Release Intermediate plate sticking on drive lugs due to cocked drive pins (AS and EP 1402 only) (see
Troubleshooting Pull Type Clutches - Poor Release Complaint Possible Causes Corrective Action Poor Release Intermediate plate sticking on drive lugs due to cocked drive pins (AS and EP 1402 only) (see
OPERATIONS MANUAL LEVER CHAIN HOIST
 OPERATIONS MANUAL LEVER CHAIN HOIST IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION Please read, understand and follow all safety information contained in these instructions prior to the use of this hoist. Retain these instructions
OPERATIONS MANUAL LEVER CHAIN HOIST IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION Please read, understand and follow all safety information contained in these instructions prior to the use of this hoist. Retain these instructions
CHESTER HOIST AIR LOW HEADROOM CHAIN HOISTS AL-680 SECTION A
 CHESTER HOIST AIR LOW HEADROOM CHAIN HOISTS AL-680 SECTION A OPERATING and MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS FOR AL SERIES HOISTS Users should refer to the ANSI B30.16 American National Standard and ASME HST-5M
CHESTER HOIST AIR LOW HEADROOM CHAIN HOISTS AL-680 SECTION A OPERATING and MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS FOR AL SERIES HOISTS Users should refer to the ANSI B30.16 American National Standard and ASME HST-5M
Module 1: Introduction to Drive Trains
 Introduction ÂÂ Basic Components of a Drive Train Operation of a Drive Train Working Applications Types of Drives Types of Gears Formula for Calculating Gear Ratio Determining Gear Rotation Introduction
Introduction ÂÂ Basic Components of a Drive Train Operation of a Drive Train Working Applications Types of Drives Types of Gears Formula for Calculating Gear Ratio Determining Gear Rotation Introduction
JASON MULTI-PLUS DUAL BRAND V-BELTS LIGHT & HEAVY DUTY SHEAVES & BUSHINGS. For Heating. Air Conditioning. Ventilation. Refrigeration.
 JASON MULTI-PLUS DUAL BRAND V-BELTS LIGHT & HEAVY DUTY SHEAVES & BUSHINGS For Heating Air Conditioning Ventilation Refrigeration Industrial TABLE OF CONTENTS Product Type Page V-BELTS F.H.P./3L Section
JASON MULTI-PLUS DUAL BRAND V-BELTS LIGHT & HEAVY DUTY SHEAVES & BUSHINGS For Heating Air Conditioning Ventilation Refrigeration Industrial TABLE OF CONTENTS Product Type Page V-BELTS F.H.P./3L Section
REAR SUSPENSION GROUP CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION TRAILING ARM REAR SUSPENSION DIAGNOSIS TOE CONTROL ARM...
 34-1 GROUP 34 CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 34-2 DIAGNOSIS 34-3 INTRODUCTION TO DIAGNOSIS 34-3 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 34-3 SYMPTOM CHART 34-3 SYMPTOM PROCEDURES 34-3 SPECIAL TOOLS 34-5 ON-VEHICLE
34-1 GROUP 34 CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 34-2 DIAGNOSIS 34-3 INTRODUCTION TO DIAGNOSIS 34-3 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 34-3 SYMPTOM CHART 34-3 SYMPTOM PROCEDURES 34-3 SPECIAL TOOLS 34-5 ON-VEHICLE
CHAPTER 14 PARKING BRAKE
 1 page INDEX1 PARKING BRAKE 14-1 14-143E-05 CHAPTER 14 PARKING BRAKE 1Models FA and FB with LF05S TROUBLESHOOTING...14-2 SPECIAL TOOLS...14-3 INSPECTION AND ADJUSTMENT...14-4 PARKING BRAKE...14-7 14 PARKING
1 page INDEX1 PARKING BRAKE 14-1 14-143E-05 CHAPTER 14 PARKING BRAKE 1Models FA and FB with LF05S TROUBLESHOOTING...14-2 SPECIAL TOOLS...14-3 INSPECTION AND ADJUSTMENT...14-4 PARKING BRAKE...14-7 14 PARKING
Seals Stretch Running Friction Friction Break-Out Friction. Build With The Best!
 squeeze, min. = 0.0035 with adverse tolerance build-up. If the O-ring is made in a compound that will shrink in the fluid, the minimum possible squeeze under adverse conditions then must be at least.076
squeeze, min. = 0.0035 with adverse tolerance build-up. If the O-ring is made in a compound that will shrink in the fluid, the minimum possible squeeze under adverse conditions then must be at least.076
Car Company Quality: A Vehicle Test Fit Study of 1,907 Car Company Service Parts
 Car Company Quality: A Vehicle Test Fit Study of 1,907 Car Company Service Study Dates: March 1999 March 2002 Prepared By Certified Automotive Association 1518 K Street NW, Suite 306 Washington, DC 20005
Car Company Quality: A Vehicle Test Fit Study of 1,907 Car Company Service Study Dates: March 1999 March 2002 Prepared By Certified Automotive Association 1518 K Street NW, Suite 306 Washington, DC 20005
Module 7: Cooling System Components
 Â ÂÂ Â Basic Cooling System Components Radiators Common Types of Radiators Coolant Hoses Water Pumps Centrifugal Force Types of Drives for Water Pumps Types of Drive Belts Basic Cooling System Components
 Â  Basic Cooling System Components Radiators Common Types of Radiators Coolant Hoses Water Pumps Centrifugal Force Types of Drives for Water Pumps Types of Drive Belts Basic Cooling System Components
Q&A Session for Advanced Linear Bearings and Guides 201 : Troubleshooting for Design Engineers
 Q&A Session for Advanced Linear Bearings and Guides 201 : Troubleshooting for Design Engineers Date: April 22, 2009 Q: We are currently looking into using Self Lubricating Bushings in a high-load Off-
Q&A Session for Advanced Linear Bearings and Guides 201 : Troubleshooting for Design Engineers Date: April 22, 2009 Q: We are currently looking into using Self Lubricating Bushings in a high-load Off-
Your Brakes. Fundamentals of Braking
 B U S S E R V I C E, I N C. Your Brakes Fundamentals of Braking There are a variety of mechanical forces and physical components that make up the braking system of your coach. The forces that effect your
B U S S E R V I C E, I N C. Your Brakes Fundamentals of Braking There are a variety of mechanical forces and physical components that make up the braking system of your coach. The forces that effect your
DESIGN. I. Loading and Speed
 DESIGN D.Wren designs Solid Rubber & Duramatic Tyres as per customer s requirements at its computer aided design facility based on the following data. Selection of Solid Tyres by the users should be based
DESIGN D.Wren designs Solid Rubber & Duramatic Tyres as per customer s requirements at its computer aided design facility based on the following data. Selection of Solid Tyres by the users should be based
COOLING SYSTEM. Return to Main Table of Contents
 COOLING SYSTEM Return to Main Table of Contents GENERAL... 2 COOLING SYSTEM... 7 RADIATOR... 9 ENGINE COOLANT PUMP... 12 THERMOSTAT... 14 ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENDER &, SENSOR... 15 ENGINE COOLANT
COOLING SYSTEM Return to Main Table of Contents GENERAL... 2 COOLING SYSTEM... 7 RADIATOR... 9 ENGINE COOLANT PUMP... 12 THERMOSTAT... 14 ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENDER &, SENSOR... 15 ENGINE COOLANT
Belt Drive Preventive Maintenance Manual
 VAC VAC VAC VAC VAC VAC Belt Drive Preventive Maintenance Manual VAC Belt Drive Preventive Maintenance Manual Preventive Maintenance Saves Time & Money Compared to the mechanical problems and costs incurred
VAC VAC VAC VAC VAC VAC Belt Drive Preventive Maintenance Manual VAC Belt Drive Preventive Maintenance Manual Preventive Maintenance Saves Time & Money Compared to the mechanical problems and costs incurred
LEADING THE WAY IN OE QUALITY
 LEADING THE WAY IN OE QUALITY THE OE STANDARD IN MULTI-RIBBED BELTS THE OE STANDARD IN MULTI-RIBBED BELTS Car manufacturers of even the top brands call in the experts when it s time to design a new multi-ribbed
LEADING THE WAY IN OE QUALITY THE OE STANDARD IN MULTI-RIBBED BELTS THE OE STANDARD IN MULTI-RIBBED BELTS Car manufacturers of even the top brands call in the experts when it s time to design a new multi-ribbed
SERVICE BULLETIN No. 1088
 SERVICE BULLETIN No. 1088 Circulate to listed addressees COACH MODEL BULLETIN TYPE MANUAL & SECTION : T800 Series; T900 Series; T 2100 Series; C2045 : Service Information : Maintenance Manual: Chapter
SERVICE BULLETIN No. 1088 Circulate to listed addressees COACH MODEL BULLETIN TYPE MANUAL & SECTION : T800 Series; T900 Series; T 2100 Series; C2045 : Service Information : Maintenance Manual: Chapter
Identify and understand the key components to the starting and charging system. Rotating Electrical Troubleshooting Guide. Battery.
 Rotating Electrical Troubleshooting Guide Battery Alternator Identify and understand the key components to the starting and charging system. Starter Motor TRUE SPECIALISTS CHOOSE EFEL 1 Efel_Trouble_Shooting_Guide_ENG_2016.indd
Rotating Electrical Troubleshooting Guide Battery Alternator Identify and understand the key components to the starting and charging system. Starter Motor TRUE SPECIALISTS CHOOSE EFEL 1 Efel_Trouble_Shooting_Guide_ENG_2016.indd
SECTION Wheels and Tires
 204-04-i Wheels and Tires 204-04-i SECTION 204-04 Wheels and Tires CONTENTS PAGE DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Wheels And Tires... 204-04-2 Inspection and Verification... 204-04-2 Tire Wear... 204-04-3 Symptom
204-04-i Wheels and Tires 204-04-i SECTION 204-04 Wheels and Tires CONTENTS PAGE DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Wheels And Tires... 204-04-2 Inspection and Verification... 204-04-2 Tire Wear... 204-04-3 Symptom
