Functional Description. Table of content
|
|
|
- Tracy Nash
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MY07 Vehicle: S80, XC90 Engine: B6324S Functional Description Table of content DISCLAIMER...2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW...3 Communication on the internal network...4 INPUT SIGNALS...5 OUTPUT SIGNALS...6 DIAGNOSE FUNCTIONS OVERVIEW...7 Catalytic converter diagnostic...8 Misfire diagnostic...10 Leakage diagnostic...12 Fuel system diagnosis...16 Heated oxygen sensors diagnostic...18 APPENDIX: CORRESPONDING MODE$06 DATA / DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTIONS 1
2 Disclaimer All information, illustrations and specifications contained herein are based on the latest production information available at the time of this publication. Volvo reserves the right to make changes in specifications and design at any time. June Volvo Customer Service 2
3 System overview - Design and function The following modules communicate with the Engine Control Module (ECM) via the network: - Electronic Throttle System (ETS) including Electronic Throttle Module (ETM) and Accelerator Pedal Module (APM) - Transmission Control Module (TCM) - Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) - Central Electronic Module (CEM) - Diagnostic Connector for connection to VADIS (Volvo Aftersales Diagnostic and Information System) - Driver Information Module (DIM), combined instrument panel - Climate Control Module (CCM) - Steering Wheel Module (SWM) - Central Electronic Module (CEM) is the central computer in the network, which handles the exchange between the network s high speed and low speed sections. The high-speed section covers the following modules: Engine Control Module (ECM), Electronic Throttle Module (ETM), Transmission Control Module (TCM), Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and the Central Electronic Module (CEM). - The Engine Management System contains a large number of sensors that send information by analog signals directly to the Engine Control Module (ECM). Communication on the internal network CAN communication ECM (Engine Control Module) sends out and receives the following signals via the network: Brake Control Monitoring (BCM) Provides information so that the Engine Control Module (ECM) can determine whether any misfiring is due to road condition or to a fault in the engine management system. Also provides a vehicle speed signal. Climate Control Module (CCM) Informs the Engine Control Module (ECM) about A/C selection and requests A/C activation. Central Electronic Module (CEM) Is the main computer in the network and coordinates required information between other modules. It also controls diagnostic function by connecting the Diagnostic Connector to the network for programming and reading off diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and parameters. The CEM also includes the Immobilizer. Steering Wheel Module (SWM) Provides information to the Engine Control Module (ECM) that the cruise control is selected and that the driver requests changing the cruise control speed. Transmission Control Module (TCM) The Transmission Control Module (TCM) is only implemented in automatic transmission cars. The following signals are being sent on the network from the Engine Control Module (ECM) and picked up by the Transmission Control Module (TCM): - Engine load - Throttle opening - Response to torque limiting - Accelerator and brake pedal position - Cruise control status. 3
4 The following signals are sent out on the network from the Transmission Control Module (TCM) and taken up by the Engine Control Module (ECM): - Request for torque limiting step I and II - Request to light Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) - Signal for constant idle speed compensation (P/N position) - Engaged gear. Diagnostic Connector The serial communication via the Diagnostic Connector is used when reading off the Volvo onboard diagnostic (OBD) system. Contact General allocation Contact General allocation 1 Discretionary 2 Not Connected 3 MS_CAN (Manufacturer spec) 4 Chassis ground 5 Signal ground 6 CAN_H line of ISO Not Connected 8 Discretionary 9 Discretionary 10 Not Connected 11 MS_CAN (Manufacturer spec) 12 Discretionary 13 Discretionary 14 CAN_L line of ISO Not Connected 16 Permanent positive voltage 4
5 Input signals Component A/C Linear High Pressure Sensors Accelerator Pedal Alternator, LIN (bus) Purpose Provides information using a linear signal about any pressure changes on the highpressure side of the A/C system. Not used by emission related functions. Senses the accelerator pedal position. The signal is used by the ECM. The pedal is designed with two independent signals, one with analogue and one with digital output (Pulse Width Modulated PWM). Exchange of information between the Engine Control Module (ECM) and the other units occurs as well with the use of LIN (Local Interconnect Network) serial communication. Not used by emission related functions. Ambient temperature sensor Brake light switch Camshaft sensor, inlet/outlet Coolant Level Switch Not EuCD CAN (bus) Engine Coolant Temp Sensor Flywheel/Crank Sensor Fuel Pressure/Temp. Sensor Heated Oxygen Sensors Front, UHEGO (One sensor for each bank) Heated Oxygen Sensors, HEGO (One sensor for each bank) Ignition Switch Knock sensors (One sensor for each bank) MAF Sensor MAP Sensor Oil Quality Sensor Starter Switch Wake Up Switch Provides information about ambient air temperature. The signal is used by the ECM. Informs Engine Control Module (ECM) that the car is braking. Not used by emission related functions. Provides the ECM information about the engine working cycle. Indicates low level in coolant water, the switch is open when the level is low. Reading out fault codes. Exchange of information between the ECM and the following units: CEM, BCM, TCM, Steering Angle Sensor (SAS), Differential Electronic Module (DEM) and Diagnostic Connector. To detect coolant temperature, which makes it necessary for the ECM to correct fuel injection. Provides the ECM information about the crankshaft position and engine speed To measure the fuel pressure and fuel temperature. UHEGO linear oxygen sensor detects oxygen concentration in the exhaus gas. (Universal HEGO) Detection of lambda = 1, where the catalyst function is optimal. Ignition starts the ECM) To detect harmful knocking combustions in the engine. Provides information about the quantity of air mass passing through into the engine, mainly under normal driving conditions. Provides information, about the engine load at rapid load changes, to the engine control unit. Provides information to the engine control unit, which will determine when to inform the driver about needed oil top-ups or required service. Not used by emission related functions. Starter switch activates the output for starter motor by the ECM Wake Up starts the ECM 5
6 Output signals Component Purpose A/C Compressor Control Valve A/C Relay Alternator, LIN (bus) Battery (Kl.30) Controlling the A/C compressor displacement. Not used by emission related functions. Connecting and disconnecting A/C compressor. Not used by emission related functions. Exchange of information between the ECM and the other units occurs as well with the use of LIN serial communication. Not used by emission related functions. Provides the ECM with RAM backup voltage. CAN Exchange of information between the ECM and other Control Units. CPS - Cam Profile Shifting Diagnose Module Tank Leakage (DMTL) ECM Power Electronic Throttle Module Electronic Fan Control Module (EFCM) EVAP Canister Purge Valve Ignition Coils/Power Stages (1-6) Instrument panel Is used to control the CPS valves for variable inlet valve lift. Detects leakages above 0.5 mm in tank using overpressure. Main ECM power supply To control the engine torque at all driving conditions by regulating the throttle plates, and hence air flow to the engine, with an electrical motor. The EFCM allows continuously variable control of the fan motor srotation rate. To control the purge flow from canister to engine. The ignition coils store energy from the battery and transform to a high voltage ignition pulse to the spark plugs out of a control signal from the ECM. Displays the MIL. Starter Motor Relay Relay to switch on and off starter motor. System relay VVT Control Valves, intake (One for each bank) Pump Electronic Module (PEM) Spark plugs (1-6) TCM (Automatic transmission only) VIS - Variable Intake System Controlled by the ECM. To switch on and off EMS components. Is used to control the Intake VVT valve for VVT Timing. The PEM is a component within a demand controlled fuel supply system (DECOS). It s a power stage that is used to control the flow rate and pressure of the fuel pump continuously. Transfer the high-tension ignition voltage generated within the coil into the cumbustion chamber. No output signal directly from the ECM. Receiving signals (through CAN) from ECM. Hard wired Park/Neutral signal from TCM to ECM. Is used to control the variable intake systems two electricaly controled tuning valves. 6
7 DIAGNOSE FUNCTIONS OVERVIEW The Engine Management System fuel/ignition system control module has an on-board diagnostic system for self- diagnosis, continuously monitoring input and output signals and several other functions. If the engine control module (ECM) detects a fault, some parameters will switch to predetermined, default values, to allow as normal as possible operation. At this time a pending diagnostic trouble code (DTC) will be stored together with a number of relevant parameters, to help the fault tracing operation. If the same fault occurs during the next driving cycle then the DTC will be set as permanent and if the fault is emission relevant the malfunction indicator (MIL) will be activated. If a fault disappears after the DTC has been stored, information about the fault is stored in the ECM. Every time the fault reoccurs a counter counts it. After three consecutive driving cycles without the fault it is allowed to turn off the MIL. For every warm-up cycle that is driven without the fault reoccurring a second counter counts down. It begins with 40 and counts down to 0. When the second counter has counted down to 0 the diagnostic trouble code can be erased from the ECM memory.if the fault reoccurs the second counter is reset to 40. The OnBoard Diagnostic (OBD) system also makes it possible to read out the values and status of a number of parameters through the diagnostic link connector (DLC) using standardized protocol and a standardized scan tool, or the manufacturers diagnostic tool. 7
8 Catalytic converter diagnostic General Description Exhaust system with a total of four sensors two-sensor method stereo. UHEGO CCC HEGO UFC Tailpipe HEGO = Universal Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor = Binary sensor UHEGO = Universal Heated Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor = Linear sensor CCC = Close Coupled Catalyst UFC = Under Floor Catalyst 8
9 The three-way catalytic converter (TWC) stores oxygen found in the exhaust gases and uses it to make toxic gases less dangerous. The catalytic converter is a TWC converter in which hydrocarbons (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO) are oxidized and oxides of nitrogen (NOx) are reduced. As the TWC ages its ability to store oxygen drops. This reduces the conversion capacity of the TWC. To avoid dangerous emissions the ECM checks TWC efficiency. This check is carried out as follows. The two-sensor method stereo makes use of one upstream and one downstream oxygen sensor for each cylinder bank, each bank has one sensor before the catalytic converter (UHEGO) and one after (HEGO). Rich and lean lambda pulses are sent through the TWC. For a TWC with good gas converter and large oxygen storage capacity, it will take a long time for the rich/lean pulse to reach the rear oxygen sensor. The rear oxygen sensor will then have long rich and lean pulses and a long time between switches. When the TWC detoriate and oxygen storage capacity drops will the rear oxygen sensor switching frequency increase. The rear oxygen sensor voltage will be used to calculate a test value of the TWC performance and a malfunctioning TWC will be detected by OBD II system. Catalytic Converter Monitor Operation DTCs Monitor Strategy description P Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) P Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2) High air flow monitoring Corresponding MonitorID Typical catalytic converter diagnostic enable conditions Enable condition Minimum Maximum Ambient pressure 74 kpa Vehicle speed 0 km/h 655 km/h Catalyst temperature 550 C 1000 C Typical catalytic converter malfunction thresholds Malfunction criteria Accumulated signal fluctuation on secondary O2 sensor during A/F modulation (shift from lean to rich /rich to lean) Threshold value Bank 1 > 22.5 Bank 2 >
10 Misfire diagnostic If the fuel/air mixture does not burn correctly, then the generated torque will be less than intended and the engine rpm will drop suddenly, (decelerate) the engine is said to be misfiring. The control module can detect misfiring by measuring the time between successive segments on the flywheel /carrier plate. If there is a misfire then there will be a stepchange in the size of these successive time measurements, if there is a misfire the lost torque will be noticed as a slowing down of the flywheel rotation. The prerequisite for reliable misfire detection is accurate segment period measurement. However, the period between two top dead centers (TDC), at constant speed, is also subject to variations due to manufacturing tolerances and off center installation. These inaccuracies are systematic, so they can be learned during fuel cut off periods and used for compensation. By this way, the systematic error introduced by the tolerances of the target flywheel is largely eliminated. The segment time can vary due to the following reasons: - Misfiring - Flywheel mechanical tolerances - Driveline oscillations - Normal variations caused by uneven combustion - Poor roads. Since mechanical tolerances and driveline oscillation interfere with the signal, it is difficult to ascertain whether or not this interference is due to misfiring. To eliminate mechanical faults in the flywheel the flywheel signal is adapted. Two crankshaft revolutions are divided into six periods, (on a 6 cylinder engine), if the engine has no external load all six periods should be equal. This is to even out the signal, so that a mechanical fault in the flywheel is not registeredas misfiring. After adaptation there is someinterference in the signal due to oscillations in the drive train and normal engine irregularities.the flywheel signal is adapted when: - Engine speed is between two targets - The fuel shut-off system is operating and has been active for 100 revolutions. A DTC is stored when misfiring leads to increased emissions and a DTC is stored when misfiring could cause damage to the TWC. The engine control module registers and stores the engine speed, load and warmup status in which the misfiring occurred. See part Diagnostic functions, Overview. If misfire exceeds catalyst damage threshold, the system will cut the fuel on those cylinders that experience misfire if one of the two following conditions are fulfilled: 1. Misfire on single cylinder 2. One or two cylinders misfiring all the time. 10
11 Misfire Diagnostic Operation DTCs Monitor Strategy description P0300 P0301 P0302 P0303 P0304 P0305 P0306 Emission related Catalyst damage Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected Cylinder 5 Misfire Detected Cylinder 6 Misfire Detected Corresponding MonitorID A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 Typical Misfire diagnostic enable conditions Enable condition Minimum Maximum Load 0.29 g/rev Depending on altitude and coolant temperature 0.65 g/rev Depending on altitude and coolant temperature Engine speed 500 rpm 6600 rpm Coolant temperature -20 C Typical Misfire malfunction thresholds Malfunction criteria Threshold value > 1.5 % (4th exceedance FTP Emission threshold or exceedance in first 1000 revolutions) Catalyst damage threshold 8-25 % 11
12 Leakage diagnostic Vapor that evaporates from the fuel in the fuel tank is routed to and stored in the EVAP canister from where it is introduced into the combustion process via the Canister Purge (CP) valve. A leak diagnostic has been introduced in certain markets to ensure that there are no leaks in the fuel tank system. The diagnostic is designed to detect leakage corresponding to a 0,20 inch or larger hole. The fuel tank system consists of fuel tank, fuel filler pipe, EVAP canister, CP valve and all pipes between these components. To be able to diagnose the fuel tank system, it is also equipped with a diagnostic module (DMTL = Diagnostic Module Tank Leakage) including the electrical driven air pump. To canister Reference Orifice Fresh air Leakage diagnostic (LD) is performed in after run mode, when key off. The diagnostic is divided into different phases as follow: Reference leak measurement, performed every LD Rough leak test, performed every DCY Small leak test performed every second DCY when enabling conditions are met. The diagnostic is performed by measuring the LD Pump Module Motor current and then compares it to a specified reference current. If a fault is detected in any of the phases the diagnostic is interrupted and the DTC for the component identified is stored. Diagnosis is carried out in the following stages: At the first engine stop after refueling, the module DMTL will start if conditions are met (conditions for soak time and fuel level are over ridden). When the fuel level sensors are working correctly and the fuel level is higher than 85 % or smaller than 15 % all leakage tests are aborted. Also, the test is aborted if the initial rate of change is higher than a calibrated level due to a combination of high fuel level and high evaporation. In case of healing attempt the test is aborted when the fuel level is too high, which is calibrated lower than 85 %. While the fuel level sensors are not working correctly the test only will be aborted if the initial rate of change is higher than a calibrated level. 12
13 1. Reference leak measurement phase For the reference current measurement, the motorpump is switched on. In this mode fresh air is pumped through a 0.02-inch reference orifice, situated internally in the module, and the pump motor current is measured. At some unusual operating conditions the pump current may not stabilize. In this case the leak check is aborted and a new leak check will be performed in the next after run. To prevent a permanent disablement of the leak check due to a DM-TL module problem, the number of subsequent irregular current measurements is counted and a module error is set as soon as the counter exceeds a calibrated value. 2. Rough leak test phase In this monitoring mode the changeover valve is switched over (the purge control valve remains closed). The motor current drops to a zero load level. Fresh air is now pumped through the canister into the tank. This creates a small overpressure at a tight evaporative system, which leads to a current increase. The rough leak check ( 0.04-inch) is performed by monitoring the pump motor current gradient. Relative pump motor current is created by using minimum pump motor current and reference pump motor current. Area ratio is created by dividing integrated relative current with ideal area, which is the linear integrated area from minimum pump current to current sample of the current. If the relative current has increased above an upper limit but not exceeded a calibrated area, within a calibrated time, the rough leak check has passed without a fault. If the calibrated area ratio is reached before the relative pump current limit, within the calibrated time, a rough leak fault code is set. The integrated relative pump current area Aint is defined by; Aint = A1 + A2 and the ideal area Aideal, Aideal = A2. See figure below. 13
14 3. Small leak test phase If the conditions for a small leak check (³0.02- inch) are set the pump motor remains on in monitoring mode until an elliptic combination of the relation pump current and area ratio are fulfilled, or a maximum time limit has been reached. The judgment is based on a test value which is a combination of the actual area ratio and gradient of area ratio with respect to relative pump current. If the estimated leak size is close to the fault limit (0.020 leaks) the monitor may decide to extend the run time of the pump to encrease the build up pressure. This will make the judgement of a small leak safer. If the test value is very near to set 0.02 inch leakage the reference leak measurement phase is performed again in order to compensate test value and make a final judgment. If the motor current decreases or increases too much during one of the tests, the test is aborted and a new leak test will be performed in the next after run. Monitoring conditions To carry out the leak diagnostic it is necessary that: - Engine-on time is at least 20 minutes and last engineoff time is more than 5 hours. - ECM (=Engine Control Module) is in after run mode - Engine speed is 0 rpm - Vehicle speed is 0 km/h - Altitude is less than (or equal to) 2500 meters - Engine coolant temperature is above (or equal to) +4 C - Ambient temperature is between +4 C and +35 C - Fuel level between 15% to 85% when no fuel level fault - Fuel level is not used if fault on fuel level - Rate of change of the initial relative pump current is low enough - Concentration of fuel vapor in the EVAP canister is not excessive - Battery voltage between 11.0 V and 14.5 V - Purge valve is closed. With the following errors the leakage detection monitoring can not be performed. These errors will therefore disable the leakage detection monitoring and the MIL (and the corresponding fault code) will be set. The disable conditions are: - Error on power stages DM-TL pump - Error on power stage purge valve - Error on purge valve - Error on change-over valve 14
15 Leakage diagnostic operation Leakage detection pump, mechanical error DTCs P043E P043F P2407 Monitor Strategy description Continuous, high Continuous, low Noisy during reference Typical Leakage diagnostic enable conditions Enable condition Minimum Maximum Ambient temperature 3 C 36 C Battery voltage 11.0 V 15.0 V Fuel level 0% 80% Atmospheric pressure 69 kpa Typical Leakage malfunction thresholds Malfunction criteria Reference current above limit for specified time Reference measurement could not be performed within specified TIME even though running conditions were satisfied Threshold value > 36 ma > 10 s > 200 s 15
16 Fuel system diagnosis The fuel system diagnosis monitor the long term fuel trim adaptions, to check if any of the adaption points has reached it s limits (rich or lean), and no more adaption is possible. This will not immediately lead to higher emissions, because the short-term fuel trim can take care of additional faults. The long term fuel trim is calculated from the front linear oxygen sensor, and there are 6 times 6 (depending on load and engine speed) different adaptation points. Each point is monitored in order to check if it is higher/lower than the threshold value. Below are some faults that illustrate cases, which could cause higher emissions: - Fault leading to lean A/F mixture. - Air leakage after MAF sensor. If there is an air leakage after the Maf sensor, this will lead to unmeasured air is added to the combustion. Short term and long term fuel trim will adjust fuel amount to homogenous A/F mixture, and if the leakage is large enough, the diagnosis will detect a lean fault. Greatest influence of this fault is at low load. Fault leading to low fuel pressure. If for example there is a fault which decreases the fuel pressure from required pressure, this could also affect the short term and long term fuel trim, and if this difference is a large deviation from the required fuel pressure, then the diagnosis will detect a lean fault. Greatest influence of this fault is at high load. - Fault leading to rich A/F mixture. - Maf sensor which is rich. If the Maf sensor measure more air than is actually passing the sensor, then this will result in a rich combustion, and the consequence if the fault is great enough, the diagnosis will detect a rich fault. Other fault leading to rich A/F mixture If the fuel pressure regulator is broken, injectors are broken or there is another fault that will result in a rich A/F mixture, then the diagnosis will detect rich. 16
17 Fuel system diagnostic operation DTCs Fuel system adaptation error P0171 P0172 P0174 P0175 Monitor Strategy description Lean fault, bank 1 Rich fault, bank 1 Lean fault, bank 2 Rich fault, bank 2 Corresponding MonitorID Typical Fuel System diagnosis enable conditions Enable condition Minimum Maximum After start delay 20 s Air flow 1.99 g/s Engine coolant temp 60 C 110 C Typical Fuel System diagnosis malfunction thresholds Malfunction criteria Threshold value Adaptive fuelling value above limit > 1.24 for specified time > 5 s Adaptive fuelling value below limit < 0.78 for specified time > 5 s Closed loop fuel trim To be able to activate closed-loop lambda control after engine start the following must be true: - Oxygen Sensor readiness detected (sensor heating must be completed). - No errors present for the Oxygen Sensor. - The engine start sequence must be completed (engine rpm risen close to idle). - No catalyst damaging misfire detected. - Not too big deviation of target lambda. - Engine load not too low. - No F/C (Fuel cut) recovery enrichment effect. - It is required that the engine is running. 17
18 Heated oxygen sensors diagnostic An S80 car with EMS system that meets ULEV2/EU- RO4 legal demands is fitted with two heated oxygen sensors per bank. The upper sensor is fitted before the CCC and the second sensor after the CCC and before the UFC (under floor catalyst). The upper sensor is linear type and the second is a binary type. The upper sensors have the following monitoring: - Slow activation (P-code P0134 and P0154). When the Oxygen sensor heater circuit start to heat up the element, a delay counter is activated. After a specified time of heating is a judgment done by evaluating sensor element impedance. Continues monitoring. - Slow response (P-code P0133 and P0153). A dither is added to target lambda. The diagnose will then check if the lambda value can follow this square wave. When the sensor is slow enough to give high emission it will be detected as malfunctioning. Performed once per driving cycle. - Heater circuit (P-code P0031, P0032 and P0051, P0052). The sensor heater is continuously monitored. Fault will be detected if circuit is: Open, short to ground or short to battery. - Sensor circuit (P-code P0131, P0132 and P0151 and P0152). The sensor circuit is continuously monitored. Fault will be detected if sensor circuit is: Open, short to ground or short to battery. - The second sensors have the following monitoring: - Sensor circuit (P-code P0137, P0138 and P0157, P0158). The sensor working range is checked to detect if sensor have an amplitude/range problem to work in its normal voltage range. Sensor must be able to work in catalyst monitoring area to be judged as normal and be close to 0V after fuel cut. Function also monitor if sensor is stuck in range. - Heater circuit (P-code P0037, P0038 and P0057, P0058). The sensor heater is continuously monitored. Fault will be detected if circuit is: Open, short to ground or short to battery. - Sensor out of range (P-code P1137, P1138 and P1157, P1158). If sensor doesn t work in its normal range, fault will be detected. Continuous monitoring. Typical Heated Oxygen Sensor diagnostic enable conditions Enable condition Minimum Maximum UHEGO heater On operation Duty Low Level 7.7 ms UHEGO heater On operation Duty High 120ms After start delay 30s Typical Heated Oxygen Sensor malfunction thresholds Malfunction criteria Threshold value O2 Sensor Heater fault flag. 5.12s Element impedance too high > 80 Ω during 10 s 18
19 Heated Oxygen Sensor operation Upper O2 Heater Control Circuit Monitor Strategy description Corresponding MonitorID P0031 P0032 P0051 P0052 Upper O2 Sensor Circuit P0131 P0132 P0151 P0152 Upper O2 Circuit Slow Response Heater low fault, bank 1 Heater high fault, bank 1 Heater low fault, bank 2 Heater high fault, bank 2 Element low fault, bank 1 Element high fault, bank 1 Element low fault, bank 2 Element high fault, bank P0133 P0153 UHEGO Slow response, bank 1 UHEGO Slow response, bank DTCs Upper O2 Circuit Slow Activation P0134 P0154 O2 Heater ControlCircuit P0037 P0038 P0057 P0058 O2 Sensor Circuit P0137 P0138 P0157 P0158 O2 Sensor Out Of Range P1137 P1138 P1157 P1158 UHEGO Slow activation, bank 1 UHEGO Slow activation, bank 2 Heater low fault, bank 1 Heater high fault, bank 1 Heater low fault, bank 2 Heater high fault, bank 2 Element low fault, bank 1 Element high fault, bank 1 Element low fault, bank 2 Element high fault, bank 2 Out of range high, bank 1 Out of range low, bank 1 Out of range high, bank 2 Out of range low, bank
20 Mode $06 Data MY07 Vehicle: S80, XC90 Engine: B6324S Request on-board monitoring test results for specific monitored systems The purpose of this service is to allow access to the results for on-board diagnostic monitoring tests of specific components / systems that are continuously monitored (e.g. misfire monitoring) and non-continuously monitored (e.g. catalyst system). The request message for test values includes an On-Board Diag ostic Monitor ID, see Annex D (ISO/DIS ) that indicates the information requested. Unit and Scaling information is included in Annex E (ISO/DIS ). The vehicle manufacturer is responsible for assigning Manufacturer Defined Test IDs for different tests of a monitored system. The latest test values (results) are to be retained, even over multiple ignitions OFF cycles, until replaced by more recent test values (results). Test values (results) are requested y On-Board Diagnostic Monitor ID. Test values (results) are always reported with the Minimum and Maximum Test Limits. The Unit and Scaling ID included in the response message defines the scaling and unit to be used by the external test equipment to display the test values (results), Minimum Test Limit, and Maximum Test Limit information. all systems. On-Board Diagnostic Monitor ID $00 is a bit-encoded value that indicates for each ECU which On-Board Diagnostic Monitor IDs are supported. On-Board Diagnostic Monitor ID $00 indicates support for On-Board Diagnostic Monitor IDs from $01 to $20. On-Board Diagnostic Monitor ID $20 indicates support for On-Board Diagnostic Monitor IDs $21 through $40, etc. This is the same concept for PIDs/TIDs/InfoTypes support in services $01, $02, $06, $08, and $09. On-Board Diagnostic Monitor ID $00 is required for those ECUs that respond to a corresponding service $06 request message as specified in Annex A ISO/DIS ). On-Board Diagnostic Monitor ID $00 is optional for those ECUs that do not respond to additional service $06 request messages. If an On-Board Diagnostic Monitor has not been completed at least once since Clear/reset emission-related diagnostic information or battery disconnect, then the parameters Test Value (Results), Minimum Test Limit, and Maximum Test Limit shall be set to zero $00) values. Not all On-Board Diagnostic Monitor IDs are applicable or supported by I
21 Mode $06 Data MY07 Vehicle: S80, XC90 Engine: B6324S The test values shows the distance to fault limit (normalized values) = normal deviation = aged system = close to faultlimit = fault 65535= not active Monitor ID Description Test ID DTCs Unit ID Min Max Unit Remarks 01 Oxygen Sensor Monitor Bank 1 - Sensor 1 80 P0132/P per bit hex to decimal unsigned Oxygen Sensor Monitor Bank 1 - Sensor 1 82 P per bit hex to decimal unsigned Oxygen Sensor Monitor Bank 1 - Sensor 1 83 P per bit hex to decimal unsigned 02 Oxygen Sensor Monitor Bank 1 - Sensor 2 84 P0137/P per bit hex to decimal unsigned 41 Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor Bank 1 - Sensor 1 90 P0031/P per bit hex to decimal unsigned 42 Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor Bank 1- Sensor 2 91 P0037/P per bit hex to decimal unsigned 05 Oxygen Sensor Monitor Bank 2 - Sensor 1 80 P0051/P per bit hex to decimal unsigned Oxygen Sensor Monitor Bank 2 - Sensor 1 82 P per bit hex to decimal unsigned Oxygen Sensor Monitor Bank 2 - Sensor 1 83 P per bit hex to decimal unsigned II
22 Mode $06 Data MY07 Vehicle: S80, XC90 Engine: B6324S The test values shows the distance to fault limit (normalized values) = normal deviation = aged system = close to faultlimit = fault 65535= not active Monitor ID Description Test ID DTCs Unit ID Min Max Unit Remarks 06 Oxygen Sensor Monitor Bank 2 - Sensor 2 84 P0157/P per bit hex to decimal unsigned 45 Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor Bank 2 - Sensor 1 90 P0051/P per bit hex to decimal unsigned 46 Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor Bank 2- Sensor 2 91 P0057/P per bit hex to decimal unsigned 42 Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor Bank 1- Sensor 2 86 P0036, P0037, P per bit hex to decimal unsigned 3B EVAP Monitor (0.040 ) 8B P per bit hex to decimal unsigned 3C EVAP Monitor (0.020 ) 8D P per bit hex to decimal unsigned 3D Purge Flow Monitor 8E P0458/P per bit hex to decimal unsigned Purge Flow Monitor 95 P per bit hex to decimal unsigned 21 Catalyst Monitor Bank 1 88 P per bit hex to decimal unsigned 22 Catalyst Monitor Bank 2 88 P per bit hex to decimal unsigned 81 Fuel System Monitor Bank 1 91 P0171/P per bit hex to decimal unsigned 82 Fuel System Monitor Bank 2 91 P0174/P per bit hex to decimal unsigned III
23 Mode $06 Data MY07 Vehicle: S80, XC90 Engine: B6324S IV The test values shows the distance to fault limit (normalized values) = normal deviation = aged system = close to faultlimit = fault 65535= not active Monitor ID Description Test ID DTCs Unit ID Min Max Unit Remarks A1 Misfire Monitor General Data 93 P count per bit Misfire Monitor General Data 94 P count per bit A2 Misfire Cylinder 1 Data 0B P count per bit Misfire Cylinder 1 Data 0C P count per bit A3 Misfire Cylinder 2 Data 0B P count per bit Misfire Cylinder 2 Data 0C P count per bit A4 Misfire Cylinder 3 Data 0B P count per bit Misfire Cylinder 3 Data 0C P count per bit A5 Misfire Cylinder 4 Data 0B P count per bit Misfire Cylinder 4 Data 0C P count per bit A6 Misfire Cylinder 5 Data 0B P count per bit Misfire Cylinder 5 Data 0C P count per bit A7 Misfire Cylinder 6 Data 0B P count per bit Misfire Cylinder 6 Data 0C P count per bit
Functional Description. Table of content
 MY04 Vehicle: S40 Engine: B5254T2 Functional Description Table of content DISCLAIMER...2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW...3 DIAGNOSE FUNCTIONS OVERVIEW...4 INPUT SIGNALS...5 OUTPUT SIGNALS...6 MISFIRE DIAGNOSTIC...8
MY04 Vehicle: S40 Engine: B5254T2 Functional Description Table of content DISCLAIMER...2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW...3 DIAGNOSE FUNCTIONS OVERVIEW...4 INPUT SIGNALS...5 OUTPUT SIGNALS...6 MISFIRE DIAGNOSTIC...8
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
L (LU4, LJ3, L88) used in Saab 9-5 ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC PARAMETERS
 Catalytic Converter Monitoring P0420 Front vs. Rear O2 sensor signal Evaluated data 1,75 times FTP std 80 (unitless) Coolant temp Throttle Delta load, positive Delta load, negative Engine speed, man. trans
Catalytic Converter Monitoring P0420 Front vs. Rear O2 sensor signal Evaluated data 1,75 times FTP std 80 (unitless) Coolant temp Throttle Delta load, positive Delta load, negative Engine speed, man. trans
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS ME7.2 Engine Management
 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS ME7.2 Engine Management Vehicle Coverage: New Range Rover 2005 MY Land Rover Revision Date: September 2004 Page 1 of 84 1 Contents 1 Contents 2 2 Introduction 5 2.1 Inputs and Outputs
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS ME7.2 Engine Management Vehicle Coverage: New Range Rover 2005 MY Land Rover Revision Date: September 2004 Page 1 of 84 1 Contents 1 Contents 2 2 Introduction 5 2.1 Inputs and Outputs
Powertrain DTC Summaries OBD II
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2002 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2002 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
L (LK9, LQ8) when use in: Saab 9-3
 NOTE: Printing this file may require 8.5" x 14" (legal size) paper, depending on your printer setup. Catalytic Converter Monitoring P0420 Time for Rear O2 sensor signal Time for rear O2 to go low. Value
NOTE: Printing this file may require 8.5" x 14" (legal size) paper, depending on your printer setup. Catalytic Converter Monitoring P0420 Time for Rear O2 sensor signal Time for rear O2 to go low. Value
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2001.5 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2001.5 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
ProECU Subaru BRZ Toyota GT86 Scion FR-S
 ProECU Subaru BRZ Toyota GT86 Scion FR-S DTC List 2012-onward Model Year v1.0 Engine DTC List P000A Camshaft Position "A" - Timing Slow Response Bank 1 P000B Camshaft Position "B" - Timing Slow Response
ProECU Subaru BRZ Toyota GT86 Scion FR-S DTC List 2012-onward Model Year v1.0 Engine DTC List P000A Camshaft Position "A" - Timing Slow Response Bank 1 P000B Camshaft Position "B" - Timing Slow Response
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar S-TYPE V6, V8 N/A and V8 SC 2002.5 Model Year Refer to pages 2 9 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries.
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar S-TYPE V6, V8 N/A and V8 SC 2002.5 Model Year Refer to pages 2 9 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing
 Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
2.8 Liter VR6 2V Fuel Injection & Ignition, Engine Code(s): AAA m.y
 2.8 Liter VR6 2V Fuel Injection & Ignition, Engine Code(s): AAA m.y. 1996-1997 01 - On Board Diagnostic (OBD) On Board Diagnostic (OBD II) Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) On Board Diagnostic (OBD II),
2.8 Liter VR6 2V Fuel Injection & Ignition, Engine Code(s): AAA m.y. 1996-1997 01 - On Board Diagnostic (OBD) On Board Diagnostic (OBD II) Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) On Board Diagnostic (OBD II),
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS V6 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS V6 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Vehicle Coverage: S-Type 2006 MY Onwards XJ 2006 MY Onwards Jaguar Cars Revision Date: May 2005 Page 1 of 113 1 Contents 1 Contents 2 2 Introduction 5 2.1
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS V6 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Vehicle Coverage: S-Type 2006 MY Onwards XJ 2006 MY Onwards Jaguar Cars Revision Date: May 2005 Page 1 of 113 1 Contents 1 Contents 2 2 Introduction 5 2.1
2UZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM
 160 2UZ-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM DTC P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1) DTC P0172 System Too Rich (Bank 1) DTC P0174 System Too Lean (Bank 2) DTC P0175 System Too Rich (Bank 2) DCRIPTION The fuel
160 2UZ-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM DTC P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1) DTC P0172 System Too Rich (Bank 1) DTC P0174 System Too Lean (Bank 2) DTC P0175 System Too Rich (Bank 2) DCRIPTION The fuel
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0430 AMPLITUDE RATIO OF POST AND PRE HEATED OXYGEN SENSORS BANK 2 (3.2L DOHC)
 1F366 ENGINE CONTROLS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0430 AMPLITUDE RATIO OF POST AND PRE HEATED OXYGEN SENSORS BANK 2 (3.2L DOHC) System Description The vehicle with 6 cylinder has two independent manifold
1F366 ENGINE CONTROLS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0430 AMPLITUDE RATIO OF POST AND PRE HEATED OXYGEN SENSORS BANK 2 (3.2L DOHC) System Description The vehicle with 6 cylinder has two independent manifold
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Description P1083 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1084 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1085 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank
 Code Description P1083 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1084 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1085 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 2 Sensor 1) P1086 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank
Code Description P1083 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1084 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1085 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 2 Sensor 1) P1086 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank
DTC P0171, P0172, P0174, or P0175
 Page 1 of 6 2009 Pontiac G8 G8 Service Manual Document ID: 2076050 DTC P0171, P0172, P0174, or P0175 Diagnostic Instructions Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle prior to using this diagnostic
Page 1 of 6 2009 Pontiac G8 G8 Service Manual Document ID: 2076050 DTC P0171, P0172, P0174, or P0175 Diagnostic Instructions Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle prior to using this diagnostic
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
11 OBDGS2 Engine Diagnostics MAIN SECTION 1 OF 1 SECTION
 Catalytic Converter Monitoring P0420 Time for Rear O2 sensor signal to Time for rear O2 to go go low. Catalyst monitoring low. Value corrected to performed at idle. Wait for throttle standard flow and
Catalytic Converter Monitoring P0420 Time for Rear O2 sensor signal to Time for rear O2 to go go low. Catalyst monitoring low. Value corrected to performed at idle. Wait for throttle standard flow and
9. Subaru Select Monitor
 9. A: OPERATION 1. HOW TO USE SUBARU SELECT MONI- TOR 1) Prepare the kit. CAUTION: Do not connect the scan tools except for Subaru Select
9. A: OPERATION 1. HOW TO USE SUBARU SELECT MONI- TOR 1) Prepare the kit. CAUTION: Do not connect the scan tools except for Subaru Select
Lotus Service Notes Section EMR
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMR Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMR.1 3 Component Function EMR.2 7 Component Location EMR.3 9 Diagnostic Guide EMR.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMR Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMR.1 3 Component Function EMR.2 7 Component Location EMR.3 9 Diagnostic Guide EMR.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
1GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM
 134 1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM DTC P0136 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (ank 1 Sensor ) DTC P0137 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (ank 1 Sensor ) DTC P0138 Oxygen Sensor Circuit High Voltage
134 1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM DTC P0136 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (ank 1 Sensor ) DTC P0137 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (ank 1 Sensor ) DTC P0138 Oxygen Sensor Circuit High Voltage
System overview ME 7.0
 "VCC106196 EN 20101130" 1(21) System overview ME 7.0 The ME 7.0 (Motronic, Electronic 7.0) is a development of the Motronic 4.4 but also has strong similarities with the DENSO engine management system
"VCC106196 EN 20101130" 1(21) System overview ME 7.0 The ME 7.0 (Motronic, Electronic 7.0) is a development of the Motronic 4.4 but also has strong similarities with the DENSO engine management system
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table
 Page 1 of 40 01-19 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table Note: When malfunctions occur in monitored sensors or components, Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are stored in DTC memory with a description of the
Page 1 of 40 01-19 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) table Note: When malfunctions occur in monitored sensors or components, Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are stored in DTC memory with a description of the
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS
 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS DTC Description P0010 Variable Valve Timing Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1) P0020 Variable Valve Timing Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2)
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS DTC Description P0010 Variable Valve Timing Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1) P0020 Variable Valve Timing Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2)
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS
 EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
EMISSION CONTROL EMISSION CONTROLS Emissions control systems on Land Rover vehicles work closely with fuel system controls to reduce airborne pollutants. Improper operation of these systems can lead to
Motronic September 1998
 The Motronic 1.8 engine management system was introduced with the 1992 Volvo 960. The primary difference between this Motronic system and the previous generation of Volvo LH-Jetronic engine management
The Motronic 1.8 engine management system was introduced with the 1992 Volvo 960. The primary difference between this Motronic system and the previous generation of Volvo LH-Jetronic engine management
Lotus Service Notes Section EMD
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMD Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMD.1 3 Component Function EMD.2 8 Component Location EMD.3 10 Diagnostic Guide EMD.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMD Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMD.1 3 Component Function EMD.2 8 Component Location EMD.3 10 Diagnostic Guide EMD.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ProECU Subaru DIT. DTC List 2012-onward Model Year. v1.0
 ProECU Subaru DIT DTC List 2012-onward Model Year v1.0 Engine DTC List P000A A CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE (BANK 1) P000B B CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE (BANK 1) P000C A CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE
ProECU Subaru DIT DTC List 2012-onward Model Year v1.0 Engine DTC List P000A A CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE (BANK 1) P000B B CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE (BANK 1) P000C A CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE
Emissions Theory and Diagnostics
 SECTION 1 Introduction 5-Gas Theory Emissions History OBD II SECTION 2 PCV System Function Failure Diagnosis Emissions Theory and Diagnostics SECTION 3 EGR EGR Theory Vacuum Systems Backpressure Systems
SECTION 1 Introduction 5-Gas Theory Emissions History OBD II SECTION 2 PCV System Function Failure Diagnosis Emissions Theory and Diagnostics SECTION 3 EGR EGR Theory Vacuum Systems Backpressure Systems
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle
 Document ID# 850406 2002 Pontiac Firebird Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle DTC DTC 021 and/or 031 DTC 022 and/or 032 DTC 023 or 033 DTC 24/34 DTC 025 and/or 035 DTC 041 DTC 042 DTC 043 DTC
Document ID# 850406 2002 Pontiac Firebird Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle DTC DTC 021 and/or 031 DTC 022 and/or 032 DTC 023 or 033 DTC 24/34 DTC 025 and/or 035 DTC 041 DTC 042 DTC 043 DTC
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: DI231 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your readings due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a malfunction code is displayed
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: DI231 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your readings due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a malfunction code is displayed
DATA LIST / ACTIVE TEST
 2UZFE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 43 DATA LIST / ACTIVE TT 1. DATA LIST HINT: Using the intelligent tester's DATA LIST allows switch, sensor, actuator and other item values to be read without removing
2UZFE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 43 DATA LIST / ACTIVE TT 1. DATA LIST HINT: Using the intelligent tester's DATA LIST allows switch, sensor, actuator and other item values to be read without removing
DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2)
 05498 DIAGNOSTICS DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) 05EXR06 DTC P0172 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2) DTC P0175 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 2) CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION The fuel trim is
05498 DIAGNOSTICS DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) 05EXR06 DTC P0172 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2) DTC P0175 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 2) CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION The fuel trim is
1 of 13 10/17/2016 1:36 PM
 1 of 13 10/17/2016 1:36 PM DTC P2195 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2196 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2197 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck
1 of 13 10/17/2016 1:36 PM DTC P2195 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2196 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2197 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck
DTC P0131 HO2S CIRCUIT LOW VOLTAGE (BANK 1/SENSOR 1)
 2008 Kia Sorento 3.3L Eng LX DTC P0131 HO2S CIRCUIT LOW VOLTAGE (BANK 1/SENSOR 1) COMPONENT LOCATION Fig 1: Identifying HO2S GENERAL DESCRIPTION In order to control emissions of the CO, HC and x components
2008 Kia Sorento 3.3L Eng LX DTC P0131 HO2S CIRCUIT LOW VOLTAGE (BANK 1/SENSOR 1) COMPONENT LOCATION Fig 1: Identifying HO2S GENERAL DESCRIPTION In order to control emissions of the CO, HC and x components
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT:
 DIAGNOSTICS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: SFI SYSTEM (1MZFE) 05241 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a
DIAGNOSTICS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: SFI SYSTEM (1MZFE) 05241 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a
DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) DTC P0172 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2) DTC P0175 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 2)
 05155 05NZ501 DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) DTC P0172 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2) DTC P0175 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 2) CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION These DTCs indicate that the
05155 05NZ501 DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) DTC P0172 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2) DTC P0175 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 2) CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION These DTCs indicate that the
DTC Summaries. NipponDenso V12 Engine Management
 DTC Summaries NipponDenso V12 Engine Management OBD II MONITORING CONDITIONS: When testing for DTC reoccurrence, it can be determined if the Service Drive Cycle was of sufficient length by performing a
DTC Summaries NipponDenso V12 Engine Management OBD II MONITORING CONDITIONS: When testing for DTC reoccurrence, it can be determined if the Service Drive Cycle was of sufficient length by performing a
DTC P0420 CATALYST SYSTEM EFFICIENCY BELOW THRESHOLD (BANK 1)
 DTC P0420 CATALYST SYSTEM EFFICIENCY BELOW THRESHOLD (BANK 1) 05195 05FNS02 MONITOR DESCRIPTION The ECM uses 2 sensors mounted before and after the threeway catalytic converter (TWC) to monitor its efficiency.
DTC P0420 CATALYST SYSTEM EFFICIENCY BELOW THRESHOLD (BANK 1) 05195 05FNS02 MONITOR DESCRIPTION The ECM uses 2 sensors mounted before and after the threeway catalytic converter (TWC) to monitor its efficiency.
Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim
 Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim Q: What is Lambda and Lambda Control? A: In the case of a gasoline engine, the optimal mixture of air to fuel for complete combustion is a ratio of 14.7 parts
Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim Q: What is Lambda and Lambda Control? A: In the case of a gasoline engine, the optimal mixture of air to fuel for complete combustion is a ratio of 14.7 parts
Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
 190 1NZ-FXE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM DTC P0420 Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) MONITOR DCRIPTION The ECM uses 2 sensors mounted before and after the three-way catalytic converter
190 1NZ-FXE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM DTC P0420 Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) MONITOR DCRIPTION The ECM uses 2 sensors mounted before and after the three-way catalytic converter
DTC P0420. Circuit Description. Conditions for Running the DTC.
 Page 1 of 5 DTC P0420 2003 Buick LeSabre LeSabre (VIN H) Service Manual Document ID: 792202 Circuit Description In order to control emissions of hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and oxides of nitrogen
Page 1 of 5 DTC P0420 2003 Buick LeSabre LeSabre (VIN H) Service Manual Document ID: 792202 Circuit Description In order to control emissions of hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and oxides of nitrogen
DATA LIST/ACTIVE TEST
 05-406 DATA LIST/ACTIVE TEST 1. DATA LIST HINT: DIAGNOSTICS - SFI SYSTEM (3MZ-FE)(From August, 2004) Using the hand-held tester DATA LIST allows switch, sensor, actuator and other item values to be read
05-406 DATA LIST/ACTIVE TEST 1. DATA LIST HINT: DIAGNOSTICS - SFI SYSTEM (3MZ-FE)(From August, 2004) Using the hand-held tester DATA LIST allows switch, sensor, actuator and other item values to be read
Fixed Right First Time. Volvo Technicians, Service and Parts Managers
 Tech-Net Notes Fixed Right First Time Volvo Technicians, Service and Parts Managers NO: 25-19 DATE: 6-30-2004 MODEL: 960-S/V90/850/S70/V70/C70 M. YEAR: 1996-1998 SUBJECT: Establishing Readiness for OBD
Tech-Net Notes Fixed Right First Time Volvo Technicians, Service and Parts Managers NO: 25-19 DATE: 6-30-2004 MODEL: 960-S/V90/850/S70/V70/C70 M. YEAR: 1996-1998 SUBJECT: Establishing Readiness for OBD
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
Evaporative Emissions
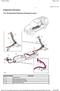 Page 1 of 6 Published : Apr 8, 2005 Evaporative Emissions 4.4L V8 Evaporative Emissions Component Layout Item Part Number 1 - Fuel filler head 2 - DMTL pump filter (NAS only) 3 - Fuel tank vent hose to
Page 1 of 6 Published : Apr 8, 2005 Evaporative Emissions 4.4L V8 Evaporative Emissions Component Layout Item Part Number 1 - Fuel filler head 2 - DMTL pump filter (NAS only) 3 - Fuel tank vent hose to
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART (SAE Controlled)
 1MZFE ENGINE EG2404 (SAE Controlled) HINT: Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. DTC No. Detection Item Diagnostic Trouble
1MZFE ENGINE EG2404 (SAE Controlled) HINT: Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. DTC No. Detection Item Diagnostic Trouble
DTC P0420 or P0430. Circuit Description. DTC Descriptors. Conditions for Running the DTC
 Page 1 of 5 2005 Cadillac STS STS (VIN D) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 4.6L (LH2) Diagnostic Information and Procedures DTC P0420 or P0430 Circuit Description A three-way catalytic converter
Page 1 of 5 2005 Cadillac STS STS (VIN D) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 4.6L (LH2) Diagnostic Information and Procedures DTC P0420 or P0430 Circuit Description A three-way catalytic converter
DTC P0420 CATALYST SYSTEM EFFICIENCY BELOW THRESHOLD (BANK 1) DTC P0430 CATALYST SYSTEM EFFICIENCY BELOW THRESHOLD (BANK 2)
 DIAGNOSTICS DTC P0420 CATALYST SYSTEM EFFICIENCY BELOW THRESHOLD (BANK 1) 05551 05BNU11 DTC P0430 CATALYST SYSTEM EFFICIENCY BELOW THRESHOLD (BANK 2) MONITOR DESCRIPTION The ECM uses sensors mounted before
DIAGNOSTICS DTC P0420 CATALYST SYSTEM EFFICIENCY BELOW THRESHOLD (BANK 1) 05551 05BNU11 DTC P0430 CATALYST SYSTEM EFFICIENCY BELOW THRESHOLD (BANK 2) MONITOR DESCRIPTION The ECM uses sensors mounted before
2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE. Self-Diagnostics - RAV4. Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs).
 2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Self-Diagnostics - RAV4 INTRODUCTION NOTE: Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). To properly diagnosis and repair this
2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Self-Diagnostics - RAV4 INTRODUCTION NOTE: Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). To properly diagnosis and repair this
GROUP 13Ab. 13Ab-2 CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-29 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS...
 13Ab-1 GROUP 13Ab CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. 13Ab-2 DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-29 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS..... 13Ab-2 FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION REFERENCE TABLE........................ 13Ab-20 DIAGNOSTIC
13Ab-1 GROUP 13Ab CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. 13Ab-2 DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-29 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS..... 13Ab-2 FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION REFERENCE TABLE........................ 13Ab-20 DIAGNOSTIC
Fuel Supply & ME-SFI Engine Management Emission Systems (Part 12) 508 HO Part 12 - Emission systems (WJB)
 Fuel Supply & ME-SFI Engine Management Emission Systems (Part 12) 508 HO Part 12 - Emission systems (WJB) 04-01-01 1 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials,
Fuel Supply & ME-SFI Engine Management Emission Systems (Part 12) 508 HO Part 12 - Emission systems (WJB) 04-01-01 1 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials,
Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review
 Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your own hand written notes may be used for the 1 st 10 minutes of the test Based on Chapters 25, 26, 32, 33, 34 and Lab Demonstrations Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your
Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your own hand written notes may be used for the 1 st 10 minutes of the test Based on Chapters 25, 26, 32, 33, 34 and Lab Demonstrations Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your
Alternative Fuel Engine Control Unit
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Cavalier (CNG) Alternative Fuel Engine Control Unit Table 1: AF ECU Function Parameters The (AF ECU) controls alternative fuel engine operation. The control unit monitors various engine
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Cavalier (CNG) Alternative Fuel Engine Control Unit Table 1: AF ECU Function Parameters The (AF ECU) controls alternative fuel engine operation. The control unit monitors various engine
ATASA 5 th. Engine Performance Systems. Please Read The Summary. ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 25 Pages Engine Performance Systems 100 Points
 ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 25 Pages 725 763 100 Points Please Read The Summary 1. Engine systems are those responsible for how an engine runs. Performance Emission Control Electronic 2. The correct
ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 25 Pages 725 763 100 Points Please Read The Summary 1. Engine systems are those responsible for how an engine runs. Performance Emission Control Electronic 2. The correct
Hyundai - Specific Trouble Codes
 Hyundai - Specific Trouble Codes P1100 Map Sensor - Malfunction P1101 Map Sensor - Abnormal P1102 Map Sensor - Low Input P1103 Map Sensor - High Input P1104 Air Flow P1105 Air Flow - Abnormal P1106 Air
Hyundai - Specific Trouble Codes P1100 Map Sensor - Malfunction P1101 Map Sensor - Abnormal P1102 Map Sensor - Low Input P1103 Map Sensor - High Input P1104 Air Flow P1105 Air Flow - Abnormal P1106 Air
DTC P20EE, P249D, P249E, or P2BAD
 Page 1 of 7 Document ID: 2614257 DTC P20EE, P249D, P249E, or P2BAD Diagnostic Instructions Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle prior to using this diagnostic procedure. Review Strategy Based
Page 1 of 7 Document ID: 2614257 DTC P20EE, P249D, P249E, or P2BAD Diagnostic Instructions Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle prior to using this diagnostic procedure. Review Strategy Based
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 DI158 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: ENGINE (2JZGTE) Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a malfunction code
DI158 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: ENGINE (2JZGTE) Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a malfunction code
L (L91) used on this vehicle: Aveo w / Manual trans DIAGNOSTIC PARAMETERS
 NOTE: Printing this file may require 8.5" x 14" (legal size) paper, depending on your printer setup. O2_11_HeaterShortLow O2_11_HeaterShortHigh O2_12_HeaterShortLow O2_12_HeaterShortHigh P0031 Detects
NOTE: Printing this file may require 8.5" x 14" (legal size) paper, depending on your printer setup. O2_11_HeaterShortLow O2_11_HeaterShortHigh O2_12_HeaterShortLow O2_12_HeaterShortHigh P0031 Detects
Lotus Service Notes Section EMQ
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Cylinder Numbering 2 Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Cylinder Numbering 2 Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11
COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENTS MONITORING
 Automobili Lamborghini s.p.a. OBDII MY 09 Section 16 Page 1 COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENTS MONITORING Automobili Lamborghini s.p.a. OBDII MY 09 Section 16 Page 2 Description Automobili Lamborghini s.p.a. OBDII
Automobili Lamborghini s.p.a. OBDII MY 09 Section 16 Page 1 COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENTS MONITORING Automobili Lamborghini s.p.a. OBDII MY 09 Section 16 Page 2 Description Automobili Lamborghini s.p.a. OBDII
Service Bulletin. DTC Detection Item Associated Monitor
 Service Bulletin 03-010 Applies To: All OBD II equipped models except SLX March 29, 2003 OBD II DTCs and Their Associated Monitors This is a list of all DTCs for all OBD II models. No one model has all
Service Bulletin 03-010 Applies To: All OBD II equipped models except SLX March 29, 2003 OBD II DTCs and Their Associated Monitors This is a list of all DTCs for all OBD II models. No one model has all
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G9>
 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
 3MZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 29 SFI SYSTEM PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE Symptom Suspected area See page 1. Starter ST-8 Engine does not crank (Does not start) 2. ST relay ST-2 3. Park/neutral position
3MZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 29 SFI SYSTEM PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE Symptom Suspected area See page 1. Starter ST-8 Engine does not crank (Does not start) 2. ST relay ST-2 3. Park/neutral position
L (L81) V-car Catera Engine Diagnostic Parameters. 98c30R_V ae.doc
 Component / System Fault Monitor Strategy Description Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value Secondary Parameters Enable Conditions Time Required MIL Illumination Mass Air P0100 range check low airmass
Component / System Fault Monitor Strategy Description Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value Secondary Parameters Enable Conditions Time Required MIL Illumination Mass Air P0100 range check low airmass
1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS
 09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (continued) GM Specific Codes
 85 GM Specific Codes P11XX Fuel and Air Metering P1106 MAP Sensor Circuit Intermittent High Voltage P1107 MAP Sensor Circuit Intermittent Low Voltage P1108 BARO to MAP Signal Comparison Too High P1111
85 GM Specific Codes P11XX Fuel and Air Metering P1106 MAP Sensor Circuit Intermittent High Voltage P1107 MAP Sensor Circuit Intermittent Low Voltage P1108 BARO to MAP Signal Comparison Too High P1111
Lotus Service Notes Section EMQ
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
SECONDARY PARAMETERS AND ENABLE CONDITIONS
 SECONDARY S AND Manifold Pressure Sensor Rationality Manifold Pressure Too Low Manifold Pressure Too High Intake Air Temperature Sensor Shorted Intake Air Temperature Sensor Open Coolant Temperature Sensor
SECONDARY S AND Manifold Pressure Sensor Rationality Manifold Pressure Too Low Manifold Pressure Too High Intake Air Temperature Sensor Shorted Intake Air Temperature Sensor Open Coolant Temperature Sensor
Malfunction Criteria and Threshold Value Adaptive value. Secondary Parameters with Enable Conditions. >50.8 S Engine load 9-45% Delta fuel adaptation
 DTC Error Message P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1) Diagnostic Procedure Check fuel pump delivery and quantity. Refer to page 126. Check Fuel pressure regulator and residual pressure. Refer to Fuel Injection
DTC Error Message P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1) Diagnostic Procedure Check fuel pump delivery and quantity. Refer to page 126. Check Fuel pressure regulator and residual pressure. Refer to Fuel Injection
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-27
 W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
Full list of fault codes and events
 Page 1/7 VIN Order number Model series/model designation License plate 203.747 Full list of fault codes and events P2001 - [1] M16/6 (Throttle valve actuator), Plausibility Position Throttle valve [P0638]
Page 1/7 VIN Order number Model series/model designation License plate 203.747 Full list of fault codes and events P2001 - [1] M16/6 (Throttle valve actuator), Plausibility Position Throttle valve [P0638]
ARTICLE BEGINNING INTRODUCTION SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM RETRIEVING DTCS ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Self-Diagnostics - Gasoline
 Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1996 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Self-Diagnostics - Gasoline Cabrio, Golf III, GTI, Jetta III, Passat INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing preliminary
Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1996 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Self-Diagnostics - Gasoline Cabrio, Golf III, GTI, Jetta III, Passat INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing preliminary
cylinder cars / trucks (except Saturn S-series cars) ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC PARAMETERS
 2001 4-cylinder cars / trucks (except Saturn S-series cars) ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC S SECONDARY S AND Manifold Pressure/Throttle Position Sensor Manifold Pressure/Throttle Position Sensor Manifold Pressure Too
2001 4-cylinder cars / trucks (except Saturn S-series cars) ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC S SECONDARY S AND Manifold Pressure/Throttle Position Sensor Manifold Pressure/Throttle Position Sensor Manifold Pressure Too
GM Enhanced Parameters
 GM Enhanced Parameters # of 4x Ref Pulses between CAM Counter # OF EGR ADAPTIVE LEARN MATRIX CELLS OUT OF RANGE High # OF EGR ADAPTIVE LEARN MATRIX CELLS OUT OF RANGE LOW 1-2 Adapt High Cell 1-2 Adapt
GM Enhanced Parameters # of 4x Ref Pulses between CAM Counter # OF EGR ADAPTIVE LEARN MATRIX CELLS OUT OF RANGE High # OF EGR ADAPTIVE LEARN MATRIX CELLS OUT OF RANGE LOW 1-2 Adapt High Cell 1-2 Adapt
Fuel Management...26 Principle of Operation...32 Workshop Hints...38 Tools and Equipment...42
 Table of Contents MS45 - E85 with M54 Engine Subject Page MS45........................................................2 Objectives of the Module.......................................2 Purpose of the System.........................................3
Table of Contents MS45 - E85 with M54 Engine Subject Page MS45........................................................2 Objectives of the Module.......................................2 Purpose of the System.........................................3
OBD System Declaration Materials for SGMW_CN200S_1.5T_MT_CN5
 OBD System Declaration Materials for SGMW_CN200S_1.5T_MT_CN5 Contents 1 Malfunction Indicator (MI)... 4 1.1 Description of the malfunction indicator (MI)... 4 1.2 Icon of MI... 4 2 All parts monitored
OBD System Declaration Materials for SGMW_CN200S_1.5T_MT_CN5 Contents 1 Malfunction Indicator (MI)... 4 1.1 Description of the malfunction indicator (MI)... 4 1.2 Icon of MI... 4 2 All parts monitored
Fuel control. The fuel injection system tasks. Starting fuel pump (FP)
 1 Fuel control The fuel injection system tasks - To provide fuel - To distribute the fuel between the cylinders - To provide the correct quantity of fuel Starting fuel pump (FP) The control module (1)
1 Fuel control The fuel injection system tasks - To provide fuel - To distribute the fuel between the cylinders - To provide the correct quantity of fuel Starting fuel pump (FP) The control module (1)
DTC P0174 Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 2
 2000 Chevrolet/Geo S10 Pickup - 4WD DTC P0174 Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 2 Circuit Description In order to provide the best possible combination of driveability, fuel economy, and emission control, the
2000 Chevrolet/Geo S10 Pickup - 4WD DTC P0174 Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 2 Circuit Description In order to provide the best possible combination of driveability, fuel economy, and emission control, the
Model Year: 2007 Model: Tacoma Doc ID: RM H800NX
 Page 1 of 12 Last Modified: 5-7-2008 5.1 C From: 200608 Model Year: 2007 Model: Tacoma Doc ID: RM0000013H800NX Title: 2TR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM: SFI SYSTEM: P2A00: A/F Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank
Page 1 of 12 Last Modified: 5-7-2008 5.1 C From: 200608 Model Year: 2007 Model: Tacoma Doc ID: RM0000013H800NX Title: 2TR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM: SFI SYSTEM: P2A00: A/F Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L
 G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
TroubleCodes.net- engine & OBD2 Trouble Codes and Technical info & Tool Store.
 Page 1 sur 8 advertisement Articles / SAFETY / TOOL STORE!! / BAT Support / Search / Help / Guestbook / About Us / Contact Us Forums Navigation Links & Technical Trouble Codes Sunday, January 23, 2005
Page 1 sur 8 advertisement Articles / SAFETY / TOOL STORE!! / BAT Support / Search / Help / Guestbook / About Us / Contact Us Forums Navigation Links & Technical Trouble Codes Sunday, January 23, 2005
MULTIPORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI) <3.0L ENGINE>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 13B-3 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 13B-6 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 13B-7 SEALANT AND ADHESIVE 13B-7 SPECIAL TOOL 13B-8 MULTIPORT
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 13B-3 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 13B-6 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 13B-7 SEALANT AND ADHESIVE 13B-7 SPECIAL TOOL 13B-8 MULTIPORT
Five-digit error code First position: P - is for powertrain codes B - is for body codes C - is for chassis codes
 https://www.automotive-manuals.net Five-digit error code First position: P - is for powertrain codes B - is for body codes C - is for chassis codes The second position: 0 - the total for the OBD-II code
https://www.automotive-manuals.net Five-digit error code First position: P - is for powertrain codes B - is for body codes C - is for chassis codes The second position: 0 - the total for the OBD-II code
Electronic Engine Controls
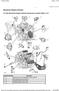 Page 1 of 28 Published : Oct 22, 2004 Electronic Engine Controls 4.0 Liter Electronic Engine Controls Component Location Sheet 1 of 2 Item Part Number Description 1 - Mass air flow/ inlet air temperature
Page 1 of 28 Published : Oct 22, 2004 Electronic Engine Controls 4.0 Liter Electronic Engine Controls Component Location Sheet 1 of 2 Item Part Number Description 1 - Mass air flow/ inlet air temperature
ProECU Nissan GT-R & Juke
 ProECU Nissan GT-R & Juke DTC List 2008-onward Model Year v1.23 1.1. Engine DTC List U0101 Lost communication with TCM U0164 Lost communication with HVAC U1001 CAN Communication Line Error P0011 Intake
ProECU Nissan GT-R & Juke DTC List 2008-onward Model Year v1.23 1.1. Engine DTC List U0101 Lost communication with TCM U0164 Lost communication with HVAC U1001 CAN Communication Line Error P0011 Intake
Short to Ground High Resistance Open P0132, P0131, P0132, P0133, P0134, P0131, P0132, P0133, P0134, P0137, P0140, P0151, P0152,
 Page 1 of 7 2008 Pontiac G8 DTC P0140,, P2270, or P2271 Diagnostic Instructions Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle prior to using this diagnostic procedure. Review Strategy Based Diagnosis for
Page 1 of 7 2008 Pontiac G8 DTC P0140,, P2270, or P2271 Diagnostic Instructions Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle prior to using this diagnostic procedure. Review Strategy Based Diagnosis for
DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected. DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected. DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected
 1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 169 DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire
1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 169 DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire
DTC P0134 OXYGEN SENSOR CIRCUIT NO ACTIVITY DETECTED (BANK 1 SENSOR 1)
 05 120 05CRQ 02 DTC P0134 OXYGEN SENSOR CIRCUIT NO ACTIVITY DETECTED (BANK 1 SENSOR 1) CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION Refer to DTC P0130 on page 05 101. DTC No. DTC Detecting Condition Trouble Area P0134 After engine
05 120 05CRQ 02 DTC P0134 OXYGEN SENSOR CIRCUIT NO ACTIVITY DETECTED (BANK 1 SENSOR 1) CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION Refer to DTC P0130 on page 05 101. DTC No. DTC Detecting Condition Trouble Area P0134 After engine
01 02B ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (FS)]
![01 02B ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (FS)] 01 02B ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (FS)]](/thumbs/80/80600627.jpg) ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (FS)] CONTROL SYSTEM WIRING DIAGRAM [FS]............................ 2 CONTROL SYSTEM DEVICE AND CONTROL RELATIONSHIP CHART [FS]........ 4 Engine Control System............
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (FS)] CONTROL SYSTEM WIRING DIAGRAM [FS]............................ 2 CONTROL SYSTEM DEVICE AND CONTROL RELATIONSHIP CHART [FS]........ 4 Engine Control System............
DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected. DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected. DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected
 1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 171 DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected DTC P030 Cylinder Misfire Detected DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected
1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 171 DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected DTC P030 Cylinder Misfire Detected DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected
ENGINE 01 02A 1. Toc of SCT ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE. Toc of SCT 01 02A ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (ZM)] 01 02A
![ENGINE 01 02A 1. Toc of SCT ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE. Toc of SCT 01 02A ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (ZM)] 01 02A ENGINE 01 02A 1. Toc of SCT ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE. Toc of SCT 01 02A ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (ZM)] 01 02A](/thumbs/90/103285807.jpg) ENGINE 01 SECTION Toc of SCT ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (ZM)]...01-02A ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (FS)]...01-02B ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM].......01-02C
ENGINE 01 SECTION Toc of SCT ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (ZM)]...01-02A ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (FS)]...01-02B ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC [CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM].......01-02C
DI 3 ENGINE DIAGNOSTICS DI00H 22 PRE CHECK
 PRECHECK DI3 DI00H22 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Description When troubleshooting OBD II vehicles, the only difference from the usual troubleshooting procedure is that you connect to the vehicle the OBD II
PRECHECK DI3 DI00H22 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Description When troubleshooting OBD II vehicles, the only difference from the usual troubleshooting procedure is that you connect to the vehicle the OBD II
If a single test is completed entirely, but indicated as "not OK", a DTC will be stored in DTC memory. Check DTC Memory Page
 Page 1 of 43 01-77 Readiness code The readiness code appears as an 8-digit display in measuring value block 086, display field 1. Each of the 8 digits is allocated to a specific exhaust related system.
Page 1 of 43 01-77 Readiness code The readiness code appears as an 8-digit display in measuring value block 086, display field 1. Each of the 8 digits is allocated to a specific exhaust related system.
DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
 162 DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected DTC P0304 Cylinder 4 Misfire
162 DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected DTC P0304 Cylinder 4 Misfire
3. Engine Control System Diagram
 ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 59 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Pump Resister Circuit Opening Fuel Relay Filter Intake Temp. Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Fuel Pump
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 59 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Pump Resister Circuit Opening Fuel Relay Filter Intake Temp. Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Fuel Pump
