5-speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B
|
|
|
- Ursula Bradley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Service. Self-Study Programme speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Design and Function
2 The new 5-speed automatic gearbox The new automatic gearbox is intended for installation in the Volkswagen and Audi platform for transversely mounted engines. 232_ _ _998 NEW Important Note The Self-Study Programme describes the design and the function of new developments! The contents are not updated! Please always refer to the relevant Service Literature for all inspection, adjustment and repair instructions.literature. 2
3 Table of Contents General information Basic configuration of gearbox Selector mechanism Torque curve System overview Electronic components - Control unit Output signals Sensors Actuators Function diagram Self-diagnosis Service Test your knowledge
4 General information As with the 4-speed automatic gearbox in the Polo and Lupo, the new 5-speed automatic gearbox is built by Jatco, the well-known automatic gearbox manufacturer. The gearbox was adapted to the vehicle and the control unit software in co-operation with Volkswagen's engineers. 232_021 This gearbox is notable for the following components and functions: - Automatic shifting of the five gears bydriver and situation dependent driving programs (fuzzy logic: see SSP No.172) - A drag-dependent driving program (recognises traction resistances when driving uphill and downhill, when towing a trailer and when driving into a headwind) - Tiptronic - Shift indicator in dash panel insert - Torque converter with torque converter lock-up clutch - Stationary decoupling When the vehicle stops and a forward drive position is engaged, the gearbox changes into neutral. Advantage: the vehicle shows no tendency to creep, which means higher fuel economy and lower emissions. - Ignition key removal lock 4
5 Specifications Designation Max. torque A-platform 09A/09B Sharan 350 Nm Weight unladen 89.5 kg filled with ATF oil kg ATF oil G Capacity Oil-change quantity 9 l 5 l 7 l when changing the converter The ATF oil is designed to last for the service life of the gearbox. It also lubricates the final drive. 232_997 5
6 General information The selector lever has two selector gates: one for automatic gearshifts and one for Tiptronic. 232_ _221 Automatic selector gate In»D«position, the gearbox automatically changes gears 1 to 5 depending on load. However, first gear cannot be selected directly by the driver - it is engaged by the control unit depending on vehicle load. 1st gear can only be engaged directly in the Tiptronic selector gate. In this case, 1st gear uses the engine brake. Tiptronic selector gate If the selector lever is engaged in the right selector gate, the gearbox is in the Tiptronic program. If the selector lever is moved forward or backward in this program, the gearbox shifts up or down a gear. Move selector lever towards "+", to select the next higher gear. Move selector lever towards " ", to select the next lower gear. The gear selected is displayed in the dash panel insert. 6
7 Selector lever mechanism 232_095 Selector lever lock solenoid N _ _094 The selector lever lock is implemented as described previously by means of the selector lever lock solenoid. The selector lever lock prevents accidental selection of a drive position while the engine is running. The solenoid does not cancel the interlock until the brake is operated. The ignition key removal lock only allows the ignition key to be withdrawn in selector lever position»p«. This stops the driver exiting the vehicle without applying the parking lock. Starting the engine The engine can only be started in»p«or»n«position. Push-starting and towing The conditions for push-starting or towing have not changed compared with other Group automatic gearboxes. For more information, refer to the vehicle Owner's Manual. 7
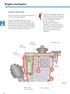
8 Basic configuration of gearbox External views Selector lever 232_ _081 Valve body cover and the valve body beneath Final drive Automatic gearbox control unit Automatic gearbox 232_021 The automatic gearbox system can be subdivided into the following main components: The selector lever - signals to the control unit in the Tiptronic selector range the gear the driver wishes to select and - positions the manual selector valve in the valve body in the desired selector range in the automatic gearbox. The automatic gearbox - This translates all hydraulic and electrical control commands into mechanical functions or gears. The control unit - is the brain of the automatic gearbox. It controls all electrical and hydraulic functions of the automatic gearbox. 8
9 Several components of the automatic gearbox are recognisable from the exterior. In the following we will show you the complex inner workings of the gearbox in the form of a simplified cut-away diagram so that you can see how the individual modules and components are arranged inside the gearbox. Final drive Planetary gear ATF oil filler opening 232_ _019 Valve body cover and the valve body beneath In this SSP we use schematic diagrams to explain the functional principle of the gearbox. These diagrams need not necessarily show the true installation position or dimensions. 9
10 Basic configuration of gearbox The torque curve To develop a 5-speed automatic gearbox for vehicles with transversely mounted engines it was necessary to arrange the three planetary gears on two planes due to the confined space. Planetary gears I and II are located directly on the turbine shaft. Planetary gear III is arranged below them on a separate shaft. Planetary gears I and II are coupled to planetary gear III via spur gears A and B. Torque is always output via the output gear on the shaft of planetary gear III. The torque is then transmitted from the output gear to the drive shaft via the differential. The ATF oil pump is driven by the input rotor of the torque converter. Spur gear A Spur gear B Output gear Differential 232_011 10
11 Spur gear A Planetary gear I ATF oil pump Planetary gear II Torque input Turbine shaft Spur gear B Output gear Planetary gear III Differential 232_067 11
12 Gearbox design The torque converter is equipped with a torque converter lock-up clutch which transmits the engine torque directly to the gearbox input shaft at high engine speeds. The control unit controls the closing movement of the torque converter lock-up clutch. Torque-converter housing Friction lining of torque converter lock-up clutch Input rotor Turbine rotor Gearbox side Engine side Gearbox housing 232_068 12
13 This is how it works: If the gearbox control unit decides, based on engine speed and engine torque, that it would be more economical to close the torque converter lock-up clutch, it activates solenoid valve N91. The oil chamber upstream of the torque converter lock-up clutch is opened by the solenoid valve to allow oil pressure to drop. This causes the oil pressure downstream of the clutch to increase. The clutch closes. 232_070 N91 Torque converter lock-up clutch closed Oil inflow via the rear end of the lock-up clutch Control unit When solenoid valve N91 shuts off the flow, the oil pressure upstream of the clutch builds up again. The clutch opens. 232_069 Torque converter lock-up clutch open N91 Valve Oil inflow via the front end of the lock-up clutch Control unit The ATF oil pump It is driven by the input rotor of the torque converter. Its tasks are to draw ATF oil out of the oil sump, build up oil pressure and transfer oil pressure to the valve body. 232_071 Outer rotor Inner rotor Drive Pressure side Suction side 13
14 Basic configuration of gearbox The planetary gear It comprises three individual planetary gears which engage the five forward gears and reverse gear. 232_140 Sun gear II Turbine shaft Planet carrier K3 Spur gear A Planetary gear I 232_125 Planetary gear II 232_124 Planetary gears I and II They are connected to the turbine shaft of the torque converter. Torque is applied to planetary gear I via clutch K3 (indirect connection). Torque can only be transmitted to planetary gear I when clutch K3 is closed. Planetary gear II is positively (directly) connected to the turbine shaft via the sun gear. Torque is always output from the planet carrier of planetary gear II to spur gear A. 14
15 Spur gear B Ring gear Planet carrier Output gear 232_141 to differential 232_128 Planetary gear III It receives torque via spur gears A and B onto the ring. The torque is output via the planet carrier to the differential output gear. 15
16 Basic configuration of gearbox The position of the clutches and brakes K3 K2 B2 K1 B1 Freewheel Freewheel K4 B3 In this illustration the clutches and brakes are highlighted in colour to give you an overview of how they are arranged in the automatic gearbox. 232_060 16
17 Gears are engaged by driving or arresting components of the planetary gear by opening and closing the clutches and brakes. Gears 1-4 and reverse gear are engaged via clutches K1, K2 and K3 and brakes B1 and B2. Drive-away engine torque is compensated by the freewheels on planetary gears I and III. 5th gear is engaged by clutch K4 on planetary gear III. Brake B3 is closed in all gears, except 5th gear. To give up a better idea of the interaction between mechanical and hydraulic components, we will explain the main components in simplified terms in the following chapters. B2 Planetary gear I Planetary gear II Freewheel B1 K1 Spur gear A K2 For reference purposes, compare this figure with the cut-away diagram opposite. K3 Drive Spur gear B Freewheel K4 B3 Planetary gear III to Differential 232_061 17
18 Basic configuration of gearbox Fixed connections Ring gear I Planet carrier II Planetary gears I and II are mechanically coupled by the ring gear of planetary gear I and the planet carrier of planetary gear II. Torque is also output to spur gear A via planet carrier II. Spur gear A There are also positive mechanical connections in planetary gear III. Spur gear B is positively connected to the ring gear of the planetary gear and the planet carrier, in turn, is connected to the output shaft. 232_153 Spur gear B Output shaft 232_154 Ring gear III Planet carrier III The clutches They are controlled by the valve body by applying ATF oil pressure. When closed, the clutches drive individual components of the planetary gear and this transfers engine torque to the final drive. 232_213 18
19 Clutch K1 It drives the ring gear of planetary gear II and the planet carrier of planetary gear I when closed. Clutch K1 is closed in first, second and third gear and has a centrifugal force equaliser (for function see SSP172). 232_ _100 K1 Planet carrier I Ring gear II Clutch K2 232_145 It drives the sun gear of planetary gear I. It is actuated by a ball valve and is closed in second gear (see SSP172). 232_ _126 Sun gear I 232_213 K2 232_146 19
20 Basic configuration of gearbox Clutch K3 232_101 It drives the planet carrier of planet gear I. Third, fourth and fifth gear are engaged via K3. This clutch also has a centrifugal force equaliser. 232_102 K3 232_147 Planet carrier I Clutch K4 It drives the sun gear of planetary gear III in fifth gear. This clutch is also actuated by a ball valve. 232_ _217 K4 232_148 Sun gear III 20
21 The brakes The brakes in the automatic gearbox have the task of controlling the gear ratios by arresting individual components of the planetary gear. Different types of brake are used in the 5-speed automatic gearbox: 232_006 - Two multi-disc brakes and - a singleband brake. Multi-disc brakes 232_007 They function according to the same principle as plate clutches. They also consist of two clutch plate sets which are pressed together hydraulically. Unlike the clutches, which drive the movable components of the planetary gear, the multi-disc brakes arrest these components. Example of multi-disc brake B1 Brake B1 is a clutch plate set connected to the gearbox housing and the planet carrier of planetary gear I. If the brake is required to arrest the planet carrier, the control unit sweeps the clutch plate set with ATF oil via the valve body. Band brakes They have the same function in the automatic gearbox as multi-disc brakes. However, the clutch plate sets are not pressed against each other. Instead, a brake band is tautened by a hydraulic cylinder. In this illustration you can see that the sun wheel of the planetary gear is arrested when the brake band is applied. 232_063 21
22 Basic configuration of gearbox Multi-disc brake B1 It arrests the planet carrier of planetary gear II in reverse gear and the first gear of the Tiptronic by means of the engine brake. 232_112 B1 Planet carrier II Multi-disc brake B2 232_151 It arrests the sun gear of planetary gear I in second, fourth and fifth gear. 232_105 Sun gear I B2 232_149 22
23 Band brake B3 It arrests the sun gear of planetary gear III. It is closed in all gears, except in fifth gear. 232_107 Sun gear III B3 232_150 23
24 Basic configuration of gearbox The pressure accumulator A pressure accumulator is located in the hydraulic circuits of clutches K1, K3 and K4 as well as multi-disc brake B2. Two additional pressure accumulators are located in the valve body and gearbox housing respectively. Their task is to ensure that the clutches and brake mentioned above close softly. Pressure accumulator in the gearbox housing for clutch K4 232_130 Pressure accumulators in the housing and housing cover for brake B2 232_129 K1 K3 232_131 Pressure accumulator on the valve body for clutches K1 and K3 24
25 This is how it works. Example: First gear, selector lever position "D". If one of the clutches or brakes mentioned in the introduction to this topic is closed, then pressurised ATF oil flows simultaneously from the valve body to the pressure accumulator and the clutch or brake to be closed. Controlled oil pressure Pressure accumulator with piston and piston spring Clutch 232_001 In the pressure accumulator, the oil presses against a chamber filled with oil under pressure and a spring-loaded piston. A portion of the oil pressure is used to counteract the spring and oil pressure. Therefore, the full oil pressure is not applied to the clutch. The clutch does not close completely yet. Controlled oil pressure The maximum oil pressure is not reached as the volume is expanding. Only when the piston has reached its limit position does the full pressure act upon the clutch to close it completely. This process follows exactly the same pattern as clutches K3 and K4 and brake B2, and is repeated during every gearshift. Controlled oil pressure 232_002 When the piston has reached its limit position, the volume can expand no further. The maximum pressure is reached and the clutch closes. 232_003 25
26 Selector mechanism The hydraulic control unit has the task of controlling the automatic upshifts and downshifts of the individual gears at the correct point in time. It comprises the following component parts: - the valve body with control valve and two pressure accumulators, - the solenoid valves and - the hand-operated change-over valve. The valve body 232_116 It has the task of adapting the oil pressure built up by the ATF pump to the shift pressure and distributing it to all gear shifting elements. Solenoid valves N88- N93 and N281-N283 are arranged in the valve body. They are activated by the control unit. They are responsible for all changes in oil pressure in the oil galleries and supply the clutches and brakes with oil pressure. 232_066 The hand-operated change-over valve It is actuated by the selector lever. The driver defines the desired drive position with the selector lever. Fourth gear and reverse gear are engaged directly via this valve without intervention by the control unit. 232_ _127
27 Selector mechanism To illustrate more clearly how the clutches and brakes on the planetary gear interact, we will now examine more closely what components are required to change gears. Let's recap on the component parts involved: B2 K2 K3 Roller freewheel B1 K1 Spur gear A Spur gear B Sprag clutch Output gear 232_061 B3 K4 Differential 27
28 Torque curve 1st gear selector lever position D Roller freewheel locked K1 Sun gear II Sprag clutch locked B3 232_156 Torque input Torque curve Torque output Arrested components N88 N89 N92 Valve body Solenoid valves energised In Tiptronic 1st gear, brake B1 is additionally closed. So the vehicle can be driven with the engine brake. 232_075 28
29 2nd gear B2 K1 Sprag clutch locked B3 232_157 Torque input Torque curve Torque output Arrested components N88 N89 Valve body Solenoid valves energised 232_076 29
30 Torque curve 3rd gear K3 K1 Sprag clutch locked B3 232_158 Torque input Torque curve Torque output Arrested components N89 Valve body Solenoid valves energised 232_077 30
31 4th gear B2 K3 Sprag clutch locked B3 232_159 Torque input Torque curve Torque output Arrested components N92 Valve body Solenoid valves energised If the solenoid valves cannot be activated (e.g. because the control unit has failed), fourth gear is engaged by the manual selector valve. 232_078 31
32 Torque curve 5th gear B2 K3 K4 232_160 Torque input Torque curve Torque output Arrested components N88 N92 Valve body Solenoid valves energised 232_079 32
33 Reverse gear K2 B1 B3 232_161 Torque input Torque curve Torque output Arrested components N88 N89 N92 Valve body Solenoid valves energised 232_080 33
34 System overview Sensors Automatic gearbox control unit J217 Gearbox input speed sender G182 Road speed sender G68 Intermediate shaft speed sender G265 Multi-function switch F125 Tiptronic switch F189 Gearbox oil (ATF) temperature sender G93 Brake pressure switch F270 34
35 Signal for cruise control system CAN bus Actuators Engine control unit Selector lever lock solenoid N110 Solenoid valves in the valve body N88, N89, N90, N92, N281 Ignition control signal to engine control unit Solenoid valves in the valve body N91, N93, N282 Engine torque, engine speed Starter inhibitor relay J226 Selector lever display illumination L101 Selector lever position P/N warning lamp K142 Road speed signal to control unit with display unit in dash panel insert J285 from the ABS control unit to the air conditioning system control unit (if fitted) 232_015 35
36 Electronic components - The control unit Automatic gearbox control unit J217 This is the brain of the gearbox. It controls the output signals as well as the actuators, based on the information received from the sensors. The driving programs The control unit has a driver/situation-dependent driving program based on the information processing fuzzy logic (refer to SSP172). An additional program recognises and makes allowance for tractive resistance, e.g. when driving uphill or downhill, as well as the influencing factors when driving into headwind or towing a trailer. 232_081 Emergency running mode If the gearbox control unit fails, - fourth gear and - reverse can still be selected. These gears are mechanically shifted in the valve body by the selector lever via the manual selector valve. 232_162 36
37 Torque signal from engine control unit In all vehicles with an electronic accelerator pedal control (EPC), the main input variable in the gearbox control unit is the torque signal from the engine control unit. The gearbox control unit receives this signal via the CAN bus. It replaces the signal from the throttle valve potentiometer used in previous automatic gearboxes. Due to the new functional structure the engine control units, where engine torque is used as the central reference variable, the signal from the engine control unit now refers directly to the actual torque. This allows the gearbox control unit to adapt the shift pressures to the actual engine torque with much greater accuracy and to execute gearshifts more precisely and smoothly. Automatic gearbox Control unit Engine control unit Engine speed, load signal, ignition advance angle 232_173 Signal utilisation Effects of signal failure On the basis of the torque signal, the gearbox control unit determines what shift pressures are required. The gearshift sequence is structured in such a way that the gearbox control unit first sends a signal to the engine control unit indicating that it wishes to execute a gearshift. The engine control unit then reduces engine torque so as to allow the gearbox control unit to close the clutches at low pressure. This results in soft, jolt-free gearshifts. Gearshifts are harsher as shift pressure cannot be adapted by the gearbox control unit. Electrical circuit CAN high CAN low This modification will also be made to the Polo with electronic accelerator pedal control and automatic gearbox. J _164 37
38 Electronic components - The sensors Data is transferred directly to the control unit (and not via the CAN bus) The engine speed sensor There are three engine speed sensors in the automatic gearbox. All three sensors are housed in the gearbox and are not accessible from outside. They are all inductive senders and are of identical design. Gearbox input speed sender G182 detects the speed of the gearbox input shaft by sampling the teeth on the outside of clutch K2. 232_ _ _209 Signal utilisation The control unit uses this signal to: - control the torque converter lock-up clutch and - calculate the slippage of the torque converter lock-up clutch Effects of signal failure The gearshifts are harsher. The stationary decoupling function is de-activated and the lock-up clutch can no longer be closed. 38
39 Intermediate shaft speed sender G _116 This sender picks up a signal corresponding to the number of teeth on spur gear A at the torque output of planetary gears I and II. 232_ _210 Signal utilisation The control unit requires this signal to determine the opening and closing times of the clutches. Effects of signal failure The stationary decoupling function is de-activated. The gearshifts are harsher. 39
40 Electronic components - The sensors Road speed sender G68 detects the speed of the parking lock gear. 232_ _207 Signal utilisation 232_211 The control unit requires this signal: - to calculate vehicle speed, - to select the gears and - to control the torque converter lock-up clutch Effects of signal failure 5th gear is no longer engaged. The gearshifts are harsh, the stationary decoupling function is de-activated and the shift points are displaced. Electrical circuit J217 G68 G182 G _180 The vehicle speed signal is sent to the control unit with a display unit in the dash panel. 40
41 Gearbox oil (ATF) temperature sender G93 It is also located inside the gearbox housing. It continuously monitors the temperature of the ATF oil and sends a temperature signal to the gearbox control unit. 232_ _174 Signal utilisation The gearbox control unit uses the ATF oil temperature to calculate a hot-engine shift program in order to regulate shift pressures as a factor of gear oil temperature. In simplified terms, a high shift pressure is applied at low oil temperature. This pressures is then continuously reduced as a function of rising ATF oil temperature. To prevent the ATF oil from overheating, the engine is revved for longer in the individual gears and the lock-up clutch is closed more frequently when the oil temperature exceeds 150 Celsius. These measures reduce friction and allow the oil to cool down. 41
42 Electronic components - The sensors Effects of signal failure If the signal from sender G93 fails, the hotengine shift program is no longer received, with the result that the gearbox performs gearshifts at higher pressures. The control unit utilises the signal from the coolant temperature sender up to a temperature of 70 C. It then utilises a fixed value of 110 C. Electrical circuit J217 G93 232_182 42
43 Multi-function switch F125 This is located on the exterior of the gearbox housing. It is actuated by the selector lever cable. 232_064 In previous automatic gearboxes, mechanical circuits were used in the multi-function switch. The mechanical circuits have now been replaced by Hall senders. The non-contact switches are wear free. For inspection and repair work, please refer to the relevant Workshop Manual. Signal utilisation The multi-function switch detects the position of the selector lever and passes this information on to the gearbox control unit. The control unit initiates the required gearshifts and activates the starter inhibitor relay if the selector lever is in»p«or»n«position. Effects of signal failure If the multi-function switch fails, the engine can only be started in selector lever position»p«. If it fails while travelling, the control unit reverts to automatically to selector lever position»d«. In both cases the control unit no longer accepts a forward selector lever position request from the driver. It shifts all forward gears electrically. The driver need only engage reverse gear. Electrical circuit S J217 F _178 43
44 Electronic components - The sensors Tiptronic switch F189 is located on the selector lever mechanism. If the driver engages the selector lever in the right selector gate, the Tiptronic switch is actuated and the automatic gearbox enters Tiptronic mode. 232_225 Signal utilisation Based on this signal, gears are selected as follows: Move selector lever forward (+) to change up one gear Move selector lever backward (-) to change down one gear. Effects of signal failure Tiptronic mode cannot be activated. Electrical circuit J217 F189 E20 Automatic gearbox control unit Tiptronic switch Switches and instruments - lighting control F189 E20 J _181
45 Brake pressure switch F270 This is integrated in the brake circuit. It supplies the automatic gearbox control unit with a signal indicating when brake pressure has been built up. Automatic gearbox Control unit Brake pressure switch 232_175 Signal utilisation The gearbox control unit utilises the signal from the brake pressure switch to control the stationary decoupling of the gearbox. At present, stationary decoupling is only performed on diesel engined vehicles. Stationary decoupling suppresses the vehicle's tendency to creep. This improves fuel economy and reduces exhaust emissions. When the vehicle stops (e.g. at traffic lights), the gearbox control unit disengages the gear. Effects of signal failure - No stationary decoupling 45
46 Electronic components - The sensors Data transfer via the CAN bus Engine speed This is detected by the engine speed sender and transferred to the engine control unit. The engine control unit sends this information to the automatic gearbox control unit via the CAN bus. Automatic gearbox Control unit Engine control unit Engine speed sender 232_163 Signal utilisation The gearbox control unit utilises the engine speed to control the torque converter lock-up clutch and stationary decoupling. Effects of signal failure - The lock-up clutch is no longer closed, - no stationary decoupling. 46
47 Brake light switch F For safety reasons, there are two brake light switches on the brake pedal. Both switches send a»brake operated«signal to the engine control unit. The engine control unit then sends this signal to the automatic gearbox control unit via the CAN bus. Automatic gearbox Control unit Engine control unit 232_172 Brake light switch Signal utilisation When the vehicle is stationary, the control unit releases the selector lever lock after it receives the corresponding signal from the brake light switch. If a travelling vehicle is braked while the lock-up clutch is closed, the gearbox control unit opens the torque converter lock-up clutch. Effects of signal failure If one of the two signals is received, the functions remain active. If both signals fail, then the selector lever can be operated without depressing the brake pedal. The engine control unit self-diagnostics stores the brake light switch fault. 47
48 Electronic components - The sensors Kick-down switch F8 This switch is only used in vehicles without electronic accelerator. By operating this switch, the driver indicates to the control unit that he wishes to accelerate at full throttle. The relevant data is transferred over the CAN bus. Automatic gearbox Control unit Engine control unit 232_176 Kick-down switch Signal utilisation After the»kick-down«command is given, the control unit selects a special shifting characteristic which revs the engine for longer in the individual gears. To accelerate the vehicle more quickly, a downshift is executed depending on actual engine speed after the kick-down command is given. Effects of signal failure If the signal fails, the engine control unit calculates a substitute signal from the position of the accelerator pedal. 48
49 Further CAN signals which are used as input variables for the gearbox control unit include: the signal from the ABS control unit If the driving situation requires the ABS control unit to employ the Traction Control System (TCS) or the Electronic Stability Program (ESP), then the ABS control unit passes this information on to the CAN bus. Automatic gearbox Control unit ABS control unit 232_177 Signal utilisation If the gearbox control unit is informed that the TCS or ESP have intervened to compensate for loss of traction or instability, the control unit performs no gearshifts during the intervention period. Effects of signal failure If the automatic control unit does not receive any signals from the ABS control unit, the gearbox continues to perform gearshifts even if TCS or ESP are activated. 49
50 Electronic components - The output signals The gearbox control unit receives data signals from other control units and sends the same information to the other control units. Signal for selector lever position to engine control unit The signal for selector lever position is an analogue signal and is supplied to the engine control unit over an electric wire. Automatic gearbox Control unit Engine control unit Multi-function switch F _222 Signal utilisation The engine control unit uses the selector lever position signal tode-activate the cruise control system in the»p«,»n«and»r«selector lever positions. Effects of signal failure The cruise control system is not functional. 50
51 The signal from the road speed sender The signal is sent to other control units via the CAN bus. Automatic gearbox Control unit Engine control unit Road speed sender G68 232_223 Signal utilisation The control unit in the dash panel insert uses the signal for the speedometer. Effects of signal failure The control unit in the dash panel insert calculates a substitute value from the gearbox speed sender G38 signal. 51
52 Electronic components - The actuators Solenoid valves Nine solenoid valves are located in the valve body of the automatic gearbox. They are activated for gear changing by the automatic gearbox control unit. There are two types of solenoid valve which have different operating mdoes: yes/no valves and modulation valves. Six of the nine solenoid valves are yes/no valves. They can either fully open or completely close an oil gallery. Intermediate settings are not possible. These valves are numbered N88, N89, N90, N92, N281 and N282. The other three solenoid valves are modulation valves. They not only have the circuit states»fully open«and»fully closed«but can also be steplessly adjusted. These valves are numbered N91, N93 and N283. Layout of solenoid valves in the valve body Solenoid valve N88 Solenoid valve N92 Solenoid valve N281 Solenoid valve N89 Solenoid valve N93 Solenoid valve N91 Solenoid valve N90 Solenoid valve N283 Solenoid valve N _082 52
53 The yes/no valves Solenoid valves N88, N89 and N92 They are responsible for gear changing N88 N92 N89 232_087 The table shows which of the three solenoid valves is activated in the individual gears by the control unit. (+) = activated Solenoid valve Gear N88 N89 N Tip R Electrical circuit N88 N89 N92 Even if a single valve fails, the gearbox control unit reverts to emergency mode. 53
54 Electronic components - The actuators Solenoid valve N90 is activated to open and close clutch K1 depending on driving conditions. Solenoid valve N90 is also activated if the reverse gear is engaged while the vehicle is moving forwards. This prevents clutch K2 for the reverse gear from closing. When driving away, the main ATF oil pressure is increased by this solenoid valve. N90 232_088 Effects of signal failure - The control unit does not select 5th gear. - Stationary decoupling is not carried out. Electrical circuit J217 N90 232_188 54
55 Solenoid valve N281 This maintains the ATF oil pressure on brake B3 in gears 1 to 4 and in reverse while the pressure on the other clutches and brakes is reduced during gear changes. N _089 Effects of signal failure If this solenoid valve fails, brake B3 is kept closed and this results in slightly harsher downshifts. Electrical circuit J217 N _192 55
56 Electronic components - The actuators Solenoid valve N282 This solenoid valve is activated by the control unit when brake B2 is opened or closed. It is closed in 2nd, 4th and 5th gear. Together with solenoid valve N90, this solenoid valve decouples the gearboxes of diesel-engined vehicles when stationary. N _090 Effects of signal failure - The vehicle can only be driven in 4th gear and in reverse. - Stationary decoupling is not carried out. Electrical circuit J217 N _190 56
57 The modulation valves Solenoid valve N93 This regulates the main oil pressure for the entire automatic gearbox depending on driving conditions. It ensures smooth running and joltfree gear changes. N93 232_091 Effects of signal failure - The main oil pressure is not regulated, resulting in harsh gearshifts, - no stationary decoupling. Electrical circuit J217 N93 232_191 57
58 Electronic components - The actuators Solenoid valve N283 This regulates the ATF oil pressure of brakes B2 and B3. Brake B2 is closed in 2nd, 4th and 5th gear while brake B3 is closed in 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th and reverse gear. N _092 Effects of signal failure - The maximum main oil pressure is applied to the brakes, resulting in harsh gearshifts - no stationary decoupling. Electrical circuit J217 N _189 58
59 Solenoid valve N91 This regulates the pressure during the opening and closing movements of the torque converter lock-up clutch. To close the torque converter lock-up clutch, the solenoid valve is energised by the control unit. N91 232_093 Effects of signal failure - The torque converter lock-up clutch is no longer closed. Electrical circuit J217 N91 232_193 59
60 Electronic components - The actuators Selector lever lock solenoid N110 It is located in the selector lever mechanism. It prevents the gear lever from being moved from selector lever positions P and N into other positions. The selector lever lock is cancelled when the brake is operated. The lock is activated when the driver turns on the ignition. 232_194 Effects of signal failure If the solenoid for selector lever lock fails, the selector lever can be engaged in a drive position without the driver having to depress the brake pedal. If both brake light switches fail, the selector lever can no longer be moved. If fault in the brake light switch is stored in the self-diagnostics of the engine control unit. 232_195 Electrical circuit J217 N _184 60
61 Selector lever display illumination L101 and selector lever position P/N warning lamp K142 are integrated in Tiptronic switch F189. The brightness of the selector lever display illumination can be adjusted by switches and instruments-lighting control E _ _197 The selector lever position P/N warning lamp indicates when the lever is in these two positions. It serves to remind the driver that the brake pedal has to be depressed in order to move the selector lever out of these positions. 232_198 Electrical circuit S J217 F189 E20 K142 L101 Automatic gearbox control unit Tiptronic switch Switches and instruments - lighting control Selector lever position P/N warning lamp Selector lever display illumination K142 N110 F189 L101 E20 J _196 61
62 Function diagram Components F125 F189 F270 Multi-function switch Tiptronic switch Brake pressure switch G68 Road speed sender G182 Gearbox input speed sender G265 Intermediate shaft speed sender J217 J226 Automatic gearbox control unit Starter inhibitor and reversing light relay B S S N110 K142 L101 Selector lever position P/N warning lamp Selector lever display illumination J226 N88 - N93 Solenoid valves N110 Selector lever lock solenoid N281- N283 Solenoid valves A C S Fuse Auxiliary signals A to the reversing lights B to the ignition switch C to the starter Terminal 50 D Road speed signal E Road speed signal F Self-diagnostics G CAN - high H CAN - low I Switches and instruments - lighting control K Selector lever position to engine control unit L Signal for cruise control system F125 62
63 S S S K142 L101 G68 G182 G265 F189 I F G H L J217 D E K F270 G93 N88 - N93 N281 - N _014 63
64 Self-diagnostics The self-diagnostic function of the automatic gearbox independently monitors the signals from the sensors as well as the actuator activation signals, and checks the control unit. If faults occur, substitute functions are made available and the fault is stored in the control unit's fault memory. The control unit has a non-volatile fault memory. The means that the contents of the fault memory are kept even if the control unit is temporarily disconnected from the power supply. The new vehicle diagnostic, testing and information system VAS 5051 is used for faultfinding and reading out the fault memory. This device includes all the tools required for fault-finding in electronic vehicle systems. The user can run the guided fault finding routine or carry out test procedures using the test instruments. 210_102 The following functions can be invoked in the self-diagnostics under the address word 02»Gearbox electronics«: 01»Interrogate control unit version«, 02»Read out fault memory«, 04»Start basic adjustment«, 05»Clear fault memory«, 06»End of output«and 08»Read data block«. 64
65 Function 01 Interrogate control unit version Spare part No. of control unit 09A Gearbox designation AG5 gearbox 09A Program version 0004 WSC 0000 Workshop code Function 02 Interrogate fault memory The colour-coded sensors and actuators are detected by the self-diagnosis function and stored in the fault memory. G265 G68 J217 G182 F125 F189 N110 N88, N89, N90, N92, N281 N91, N93, N282 G93 L101 K142 F _200 65
66 Self-diagnostics Function 04 Basic setting On completion of repair work on the accelerator pedal sender or after replacing the engine control unit, carry out a basic setting procedure. As with the 4-speed automatic gearbox, iyou must carry out the basic setting procedure after you replace the control unit. Function 08 Read data block Signals from the components highlighted in colour can be tested in the measured value block. G265 G68 J217 G182 F125 F189 N110 N88, N89, N90, N92, N281 N91, N93, N282 G93 F270 L101 K142 J285 ABS 210_199 66
67 Service Special tools In keeping with the care concept for the 5-speed automatic gearbox, the following new special tools are required to carry out repair work. Pressure piece T for installing the shaft oil seal 210_205 Pressure piece T10088 for installing the left and right flange shafts 210_204 Pressure piece T10089 for fitting the oil seal on the torque converter 210_203 Pressure piece T10090 for fitting the oil seal on the selector shaft 210_202 Adjustment plate 3282/32 210_201 for removing the gearbox from the vehicle T10091 for adjusting the multi-function switch 210_224 67
68 Test your knowledge 1. In what selector lever position does 1st gear use the engine brake? a) 1st gear always uses the engine brake. b) in selector lever position "D" only c) in the Tiptronic selector gate only 2. How many planetary gears are there in the AG5? a) 2 Ravignaux planet gear sets b) 3 planetary gears c) 4 planetary gears 3. Via which components is torque transmitted to the planetary gears? a) via the sun gear of planetary gear II and via clutch K3 b) via clutch K1 and clutch K2 c) via clutch K3 only 4. What clutches equalise centrifugal force in the AG5? a) clutch K4 only b) clutches K2 and K4 c) clutches K1 and K3 5. Are there different types of brake in the AG5? If yes, name them. a) no b) yes
69 6. Identify the components! 232_060 69
70 7. What is the task of the pressure accumulators? a) They regulate the main oil pressure of the automatic gearbox. b) They are responsible for ensuring the soft closing of clutches K1, K3 and K4 as well as brake B2. c) B3 is activated by the pressure accumulators. 8. How many solenoid valves are located in the valve body of the automatic gearbox? a) 7 b) 8 c) 9 9. Gearshifts are initiated by the different solenoid valve closing combinations. What are the electrical designations of the 3 solenoid valves? a) N88, N89 and N92 b) N91, N93 and N Three engine speed sensors with identical design and operating principles are located in the automatic gearbox. According to what electrical operating principle do they work? a) their function is based on the Hall principle. b) their function is based on the induction principle. 70
71 Solutions 1.) c 2.) b 3.) a 4.) c 5.) b 6.) see page 16 7.) b 8.) c 9.) a 10.) b 71
72 232 For internal use only VOLKSWAGEN AG, Wolfsburg All rights reserved. Technical specifications subject to change without notice Technical status: 5/00 This paper is produced from non-chlorine-bleached pulp.
6-speed automatic transmission 09D
 Service. Self-Study Programme 300 6-speed automatic transmission 09D Design and function Compared to the 5-speed automatic transmission, the 09D 6-speed automatic transmission provides: a reduction in
Service. Self-Study Programme 300 6-speed automatic transmission 09D Design and function Compared to the 5-speed automatic transmission, the 09D 6-speed automatic transmission provides: a reduction in
Service Training Edition Speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B. Trainer Information (GB)
 7.02 Edition 09.2000 5-Speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Trainer Information (GB) Contents Section Page General Information 2 Input and output signals 7 Control System Details 9 ATF Pressure Control 16 Lock-up
7.02 Edition 09.2000 5-Speed Automatic Gearbox 09A/09B Trainer Information (GB) Contents Section Page General Information 2 Input and output signals 7 Control System Details 9 ATF Pressure Control 16 Lock-up
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (5AT)
 (5AT) GENERAL 1. General To improve the dynamic performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle, a new 5-speed automatic transmission is developed. The features of this new automatic transmission are as
(5AT) GENERAL 1. General To improve the dynamic performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle, a new 5-speed automatic transmission is developed. The features of this new automatic transmission are as
6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53. VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: (040) 09/2003. Introduction
 VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: 24 24 01 03 (040) 6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53 weltweit Datum/Date: 09/2003 Introduction The 6-speed automatic transmissions GA6HP19Z and GA6HP26Z have been jointly
VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: 24 24 01 03 (040) 6-speed automatic transmission E60, E53 weltweit Datum/Date: 09/2003 Introduction The 6-speed automatic transmissions GA6HP19Z and GA6HP26Z have been jointly
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM. 1. General CH-16 CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
 CH-16 ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The electronic control system of the U340E automatic transaxle consists of the controls listed below. System Clutch Pressure Control (See page CH-20) Line Pressure
CH-16 ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The electronic control system of the U340E automatic transaxle consists of the controls listed below. System Clutch Pressure Control (See page CH-20) Line Pressure
6-speed Automatic Gearbox 09G/09K/09M
 Service Training Self-study Programme 309 6-speed Automatic Gearbox 09G/09K/09M The 6-speed automatic gearbox from the Japanese manufacturer AISIN is used in the following Volkswagen vehicles: Code Maximum
Service Training Self-study Programme 309 6-speed Automatic Gearbox 09G/09K/09M The 6-speed automatic gearbox from the Japanese manufacturer AISIN is used in the following Volkswagen vehicles: Code Maximum
6-speed manual gearbox 02M
 Service. Self-Study Programme 205 6-speed manual gearbox 02M Design and Function Adapting modern automobiles to meet the rapidly growing demands on driving comfort, environmental compatibility and driving
Service. Self-Study Programme 205 6-speed manual gearbox 02M Design and Function Adapting modern automobiles to meet the rapidly growing demands on driving comfort, environmental compatibility and driving
U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES
 ASSIS U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES -41 U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES DESCRIPTION The new model uses 2 types (U340E, U441E) of automatic transaxle. A U340E automatic transaxle is provided
ASSIS U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES -41 U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES DESCRIPTION The new model uses 2 types (U340E, U441E) of automatic transaxle. A U340E automatic transaxle is provided
Continuously Variable Transaxle Specification. Forward/Reverse Switching Mechanism Double Pinion Type Planetary Gear
 CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41B Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1nr-fe engine models. 2. The K41B CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41B Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1nr-fe engine models. 2. The K41B CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
CHASSIS AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE. Destination New Model Previous Model Change (from previous model)
 CHASSIS AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE CH-37 U341E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 1. General The compact and high-capacity 4-speed U341E automatic transaxle [Super ECT (Electronic Controlled Transaxle)] is used. The following
CHASSIS AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE CH-37 U341E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 1. General The compact and high-capacity 4-speed U341E automatic transaxle [Super ECT (Electronic Controlled Transaxle)] is used. The following
Continuously Variable Transaxle Specification. Forward/Reverse Switching Mechanism Double Pinion Type Planetary Gear
 CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41A Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1kr-fe engine models. 2. The K41A CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41A Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1kr-fe engine models. 2. The K41A CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion
 Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
Service Training Self-study programme 317 The electro-mechanical power steering with dual pinion Design and function The electro-mechanical power steering has many advantages over the hydraulic steering
CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION (CVT)
 23-1 GROUP 23 CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION () CONTENTS........................... 23-2 GENERAL INFORMATION............. 23-2 PRINCIPLE OF IMPROVEMENTS IN FUEL ECONOMY AND PERFORMANCE WITH......................................
23-1 GROUP 23 CONTINUOUSLY VARIABLE TRANSMISSION () CONTENTS........................... 23-2 GENERAL INFORMATION............. 23-2 PRINCIPLE OF IMPROVEMENTS IN FUEL ECONOMY AND PERFORMANCE WITH......................................
U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
 CH-125 U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE DESCRIPTI The 02 Camry line-up uses the following types of automatic transaxles: 2AZ-FE U241E 1MZ-FE U140E These automatic transaxles are compact and high-capacity
CH-125 U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE DESCRIPTI The 02 Camry line-up uses the following types of automatic transaxles: 2AZ-FE U241E 1MZ-FE U140E These automatic transaxles are compact and high-capacity
The electromechanical parking brake
 Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Module 5: Cooling Fundamentals
 Terms and Definitions Major Mechanical Parts of a Four Speed Auto Transmission Parts of a Planetary Gear System Planetary Gear System Operation Speed, Torque, and Directional Function Fluid Pump and Pressure
Terms and Definitions Major Mechanical Parts of a Four Speed Auto Transmission Parts of a Planetary Gear System Planetary Gear System Operation Speed, Torque, and Directional Function Fluid Pump and Pressure
DESCRIPTION. Chrysler NCV3 Service Info Section 08 > Electronic Modules > MODULE, Transmission Control Information
 DESCRIPTION The transmission control module (TCM) receives, processes and sends various digital and analog signals related to the automatic transmission. In addition, it processes information received
DESCRIPTION The transmission control module (TCM) receives, processes and sends various digital and analog signals related to the automatic transmission. In addition, it processes information received
LX AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATION TABLE OF CONTENTS
 LX AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATION 21-495 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATION TABLE OF CONTENTS page AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATION DESCRIPTION...496
LX AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATION 21-495 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATION TABLE OF CONTENTS page AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION NAG1 - SERVICE INFORMATION DESCRIPTION...496
6-Speed Automatic Transmission 09G/09M Design and Function
 6-Speed Automatic Transmission 09G/09M Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 851503 Volkswagen of America, Inc. Service Training Printed in U.S.A. Printed 04/05 Course Number 851503 2005
6-Speed Automatic Transmission 09G/09M Design and Function Self-Study Program Course Number 851503 Volkswagen of America, Inc. Service Training Printed in U.S.A. Printed 04/05 Course Number 851503 2005
Variable Valve Timing
 Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Service. Self-study programme 246 Variable Valve Timing with fluted variator Design and Function The demands on combustion engines continue to grow. On one hand, customers want more power and torque, while
Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine
 Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
Service. Self-Study Programme 250 Engine Management for the Phaeton W12 Engine Design and Function The Motronic engine management system for the W12 engine allows high engine performance with low fuel
V8 Vantage Sportshift Driving Guide
 LG/GE/10/03/2011 The V8 Vantage incorporates a 6-speed Sportshift automated manual transmission. There are two driving modes for V8 Vantage Sportshift. The first is Paddle Shift Mode This is the mode where
LG/GE/10/03/2011 The V8 Vantage incorporates a 6-speed Sportshift automated manual transmission. There are two driving modes for V8 Vantage Sportshift. The first is Paddle Shift Mode This is the mode where
12.Electrohydraulic Control System
 W1860BE.book Page 67 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 12.Electrohydraulic Control System A: DESCRIPTION The electrohydraulic system for the transmission and transfer consists of various sensors and switches,
W1860BE.book Page 67 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 12.Electrohydraulic Control System A: DESCRIPTION The electrohydraulic system for the transmission and transfer consists of various sensors and switches,
Transmission Description
 Page 1 of 23 Published: Feb 1, 2007 Transmission Description COMPONENT LOCATION Item Part Number Description 1 Transmission selector lever assembly 2 Cable bracket 3 Automatic transmission 4 Transmission
Page 1 of 23 Published: Feb 1, 2007 Transmission Description COMPONENT LOCATION Item Part Number Description 1 Transmission selector lever assembly 2 Cable bracket 3 Automatic transmission 4 Transmission
Mercedes Presented by Dr William (Bill) Henney PhD F.I.M.I
 Mercedes 722.9 Presented by Dr William (Bill) Henney PhD F.I.M.I Features Electronically Controlled Automatic Gearbox 7 Forward and 2 Reverse Gears Transmission Control Module is : Integrated into the
Mercedes 722.9 Presented by Dr William (Bill) Henney PhD F.I.M.I Features Electronically Controlled Automatic Gearbox 7 Forward and 2 Reverse Gears Transmission Control Module is : Integrated into the
Engine mechanics. Crankcase ventilation outlet
 Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
1. Cruise Control CRUISE CONTROL A: OPERATION CC-2
 W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Cruise Control A: OPERATION The cruise system automatically s the vehicle speed. It allows the vehicle to run at a constant speed without need
W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Cruise Control A: OPERATION The cruise system automatically s the vehicle speed. It allows the vehicle to run at a constant speed without need
Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function
 Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme Technology 507 Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function The 8-speed automatic gearbox in the Amarok With a combustion
Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme Technology 507 Amarok 2012 The 8-speed automatic gearbox 0CM Design and function The 8-speed automatic gearbox in the Amarok With a combustion
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
 368001 023 1. GENERAL INFORMATION DSI M78 Automatic Transmission is based on the transmission in the vehicle with D20DT engine for EURO III or EURO IV. Differences: changed some components (torque converter
368001 023 1. GENERAL INFORMATION DSI M78 Automatic Transmission is based on the transmission in the vehicle with D20DT engine for EURO III or EURO IV. Differences: changed some components (torque converter
GA6HP26Z Automatic Transmission Objectives of the Module...1 Purpose of the System...2 Technical Data...5
 Table of Contents Subject Page Objectives of the Module.....................................1 Purpose of the System.......................................2 Technical Data.............................................5
Table of Contents Subject Page Objectives of the Module.....................................1 Purpose of the System.......................................2 Technical Data.............................................5
Sequential manual transmission (SMG) E60. VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: (044) 10/2003. Introduction
 VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: 23 23 03 03 (044) Sequential manual transmission (SMG) E60 weltweit Datum/Date: 10/2003 Introduction The sequential manual transmission (SMG) has its origins in motor racing and
VS-22 je Baugruppe/Group: 23 23 03 03 (044) Sequential manual transmission (SMG) E60 weltweit Datum/Date: 10/2003 Introduction The sequential manual transmission (SMG) has its origins in motor racing and
Table of Contents. E70 Transmissions
 Table of Contents Subject Page New Transmissions for E70....................................5 Changes.......................................................5 Technical Data...............................................6
Table of Contents Subject Page New Transmissions for E70....................................5 Changes.......................................................5 Technical Data...............................................6
Phaeton Convenience and Safety Electronics
 Service. Self-Study Programme 273 Phaeton Convenience and Safety Electronics Design and Function Open sesame - thanks to a new system for entry and start authorisation, the Phaeton can be accessed without
Service. Self-Study Programme 273 Phaeton Convenience and Safety Electronics Design and Function Open sesame - thanks to a new system for entry and start authorisation, the Phaeton can be accessed without
Audi A6 Current Flow Diagram No. 63 / 1
 Page 1 of 8 Audi A6 Current Flow Diagram No. 63 / 1 Automatic gearbox (01V), (01L) From model year 2001 Fuse box Edition 06.2002 From fuse number 23 upwards the fuses in the fuse box are designated as
Page 1 of 8 Audi A6 Current Flow Diagram No. 63 / 1 Automatic gearbox (01V), (01L) From model year 2001 Fuse box Edition 06.2002 From fuse number 23 upwards the fuses in the fuse box are designated as
EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
 Service. Self-Study Programme 259 EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering Design and Function EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering 259_033 The EPHS = Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
Service. Self-Study Programme 259 EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering Design and Function EPHS Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering 259_033 The EPHS = Electrically Powered Hydraulic Steering
Service. Variable Automatic Gearbox multitronic 01J Design and Function. Self-Study Programme 228. For internal use only
 228 Service. Variable Automatic Gearbox multitronic 01J Design and Function Self-Study Programme 228 For internal use only multitronic The name multitronic stands for the new variable automatic gearbox
228 Service. Variable Automatic Gearbox multitronic 01J Design and Function Self-Study Programme 228 For internal use only multitronic The name multitronic stands for the new variable automatic gearbox
Electromechanical Steering with Parallel-axis Drive
 Service Training Self-study Programme 399 Electromechanical Steering with Parallel-axis Drive Design and Function The electromechanical power steering has many advantages compared with a hydraulic steering
Service Training Self-study Programme 399 Electromechanical Steering with Parallel-axis Drive Design and Function The electromechanical power steering has many advantages compared with a hydraulic steering
ATF (AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION FLUID) WS
 CH-8 CHASSIS - U250E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE ATF (AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION FLUID) WS ATF WS is used to reduce the resistance of the ATF and improve the fuel economy by reducing its viscosity in the practical
CH-8 CHASSIS - U250E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE ATF (AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION FLUID) WS ATF WS is used to reduce the resistance of the ATF and improve the fuel economy by reducing its viscosity in the practical
capacity due to increased traction; particularly advantageous on road surfaces
 42-800 Design and function of acceleration slip control (ASR I) A. General B. Driving with ASR I C. Overall function of ASR I D. Location of components E. Individual functions A. General The acceleration
42-800 Design and function of acceleration slip control (ASR I) A. General B. Driving with ASR I C. Overall function of ASR I D. Location of components E. Individual functions A. General The acceleration
ZF 6HP26 Automatic Transmission Component Location
 Published : Apr 8, 2005 ZF 6HP26 Automatic Transmission Component Location Item Part Number Description 1 - PRND LCD display 2 - M/S LCD display 3 - Selector lever assembly 4 - Instrument cluster 5 - Automatic
Published : Apr 8, 2005 ZF 6HP26 Automatic Transmission Component Location Item Part Number Description 1 - PRND LCD display 2 - M/S LCD display 3 - Selector lever assembly 4 - Instrument cluster 5 - Automatic
Onboard power supply management
 Onboard power supply management The onboard power supply J519 Functions of onboard power supply control unit Until now s and relays functioned at different locations in the vehicle. In the onboard power
Onboard power supply management The onboard power supply J519 Functions of onboard power supply control unit Until now s and relays functioned at different locations in the vehicle. In the onboard power
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC)
 VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM 1. Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) System A: GENERAL The vehicle dynamics control (VDC) system is a driver assist system which enhances vehicle s running stability
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM 1. Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) System A: GENERAL The vehicle dynamics control (VDC) system is a driver assist system which enhances vehicle s running stability
Cars Drivetrain 9-Speed Automatic Transmission (725.0) AKUBIS direct special Final Test Go Hand-outs for participants
 Global Training The finest automotive learning Cars Drivetrain 9-Speed Automatic Transmission (725.0) AKUBIS direct special Final Test Go Hand-outs for participants T0831E As at 06.09.2013 This document
Global Training The finest automotive learning Cars Drivetrain 9-Speed Automatic Transmission (725.0) AKUBIS direct special Final Test Go Hand-outs for participants T0831E As at 06.09.2013 This document
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control. Basics of the damping system
 Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
 Page 1 of 13 437: Transmission control module (TCM), TF-80SC AWD XC90, 2007, D5244T4, TF-80SC AWD, L.H.D, YV1CM714671338226, 338226 7/7/2016 PRINT 437: Transmission control module (TCM), TF-80SC AWD Adaptation
Page 1 of 13 437: Transmission control module (TCM), TF-80SC AWD XC90, 2007, D5244T4, TF-80SC AWD, L.H.D, YV1CM714671338226, 338226 7/7/2016 PRINT 437: Transmission control module (TCM), TF-80SC AWD Adaptation
Variable Automatic Transmission multitronic 01J Design and Function
 AKPPHELP.RU Руководство по ремонту АКПП Variable Automatic Transmission multitronic 01J Design and Function Audi of America, Inc. 3800 Hamlin Road Auburn Hills, MI 48326 Printed in U.S.A. August 2001 Self-Study
AKPPHELP.RU Руководство по ремонту АКПП Variable Automatic Transmission multitronic 01J Design and Function Audi of America, Inc. 3800 Hamlin Road Auburn Hills, MI 48326 Printed in U.S.A. August 2001 Self-Study
Automatic Transmission Basics
 Section 1 Automatic Transmission Basics Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the function of the torque converter. 2. Identify the three major components of the torque converter that contribute to the multiplication
Section 1 Automatic Transmission Basics Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the function of the torque converter. 2. Identify the three major components of the torque converter that contribute to the multiplication
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine
 1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
Convenience CAN databus
 Convenience CAN databus The convenience CAN databus operates with a transmission rate of 100 kbit/s. Onboard power supply control unit J519 with databus diagnostic interface J533 (gateway) CLIMAtronic
Convenience CAN databus The convenience CAN databus operates with a transmission rate of 100 kbit/s. Onboard power supply control unit J519 with databus diagnostic interface J533 (gateway) CLIMAtronic
6-speed manual gearbox 0A5
 Service Training Self-study programme 320 6-speed manual gearbox 0A5 Design and function S320_002 In addition to meeting increasing technical demands, modern cars also have to represent effective space
Service Training Self-study programme 320 6-speed manual gearbox 0A5 Design and function S320_002 In addition to meeting increasing technical demands, modern cars also have to represent effective space
The Touareg Electrical System
 Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
Service. Self-Study Programme 298 The Touareg Electrical System Design and Function Vehicles with off-road capability are no longer just utility vehicles for a limited group of people. At all levels in
Workbook. Transmission Technology. Transmission External ZF training P a g e 1
 Workbook Technology P a g e 1 Table of content 1. History... 3 2. 6HP Design... 4 3. Adaption... 25 3. Oil change Service and Mechatronic... 38 4. 6HP Overhaul... 60 6. 8 HP... 80 7. Identification of
Workbook Technology P a g e 1 Table of content 1. History... 3 2. 6HP Design... 4 3. Adaption... 25 3. Oil change Service and Mechatronic... 38 4. 6HP Overhaul... 60 6. 8 HP... 80 7. Identification of
44 - AUTOMATIC GEARBOX
 44 - AUTOMATIC GEARBOX CONTENTS Page ZF AUTO DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - DESCRIPTION... 4 OPERATION... 19 ADJUSTMENT SELECTOR CABLE... 1 GEARBOX - DRAIN AND REFILL - FROM 99MY...
44 - AUTOMATIC GEARBOX CONTENTS Page ZF AUTO DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - DESCRIPTION... 4 OPERATION... 19 ADJUSTMENT SELECTOR CABLE... 1 GEARBOX - DRAIN AND REFILL - FROM 99MY...
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Charts
 SECTION 307-01: Automatic Transaxle/Transmission 5R55S 2009 Mustang Workshop Manual DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 06/30/2009 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Charts DTC Chart **May also be
SECTION 307-01: Automatic Transaxle/Transmission 5R55S 2009 Mustang Workshop Manual DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Procedure revision date: 06/30/2009 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Charts DTC Chart **May also be
DSI M78 6-SPEED A/T / / / / / DSI M78 6-SPEED A/T GENERAL INFORMATION OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS
 DSI M78 6SPEED A/T 311001/365001/366001/368001/372101/921001 DSI M78 6SPEED A/T GENERAL INFORMATION 1. DSI M78 6SPEED AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION GENERAL... 2. STRUCTURE CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS...
DSI M78 6SPEED A/T 311001/365001/366001/368001/372101/921001 DSI M78 6SPEED A/T GENERAL INFORMATION 1. DSI M78 6SPEED AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION GENERAL... 2. STRUCTURE CHARACTERISTICS AND SPECIFICATIONS...
DC-5 SPEED AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
 01-3 DC-5 SPEED AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION GENERAL 1. SPECIFICATIONS 01-4 01-5 OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. OVERVIEW 2WD 4WD DC 5-Speed Automatic Transmission DCAG 5-speed automatic transmission is an
01-3 DC-5 SPEED AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION GENERAL 1. SPECIFICATIONS 01-4 01-5 OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. OVERVIEW 2WD 4WD DC 5-Speed Automatic Transmission DCAG 5-speed automatic transmission is an
SECTION : Automatic Transmission
 307-01-1 Automatic Transmission 307-01-1 SECTION : 307-01 Automatic Transmission VEHICLE APPLICATION : 2003.0 BA Falcon CONTENTS SPECIFICATIONS PAGE Specifications...307-01-3 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
307-01-1 Automatic Transmission 307-01-1 SECTION : 307-01 Automatic Transmission VEHICLE APPLICATION : 2003.0 BA Falcon CONTENTS SPECIFICATIONS PAGE Specifications...307-01-3 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ATF level, checking and changing, 01J, CVT A/T FWD. Special tools, testers and auxiliary items required
 ATF level, checking and changing, 01J, CVT A/T FWD Special tools, testers and auxiliary items required Vehicle Diagnostic, Testing and Information System VAS 5051 A with diagnostic cable VAS 5051/5A ATF
ATF level, checking and changing, 01J, CVT A/T FWD Special tools, testers and auxiliary items required Vehicle Diagnostic, Testing and Information System VAS 5051 A with diagnostic cable VAS 5051/5A ATF
Function description
 30-0006 Function description Electronic accelerator (EA) Block diagram Overvoltage protection EA control relay, Models 124, 202 (power supply) Idle speed control Base, Models (ISC) 129,140, 124.034/036
30-0006 Function description Electronic accelerator (EA) Block diagram Overvoltage protection EA control relay, Models 124, 202 (power supply) Idle speed control Base, Models (ISC) 129,140, 124.034/036
SECTION 1 7 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake
 SECTION 1 7 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake Ignition switch.............................................. 114 Automatic transmission.....................................
SECTION 1 7 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake Ignition switch.............................................. 114 Automatic transmission.....................................
Advanced Auto Tech Worksheet Auto Trans & Transaxle Chapter 40 Pages Points Due Date
 Advanced Auto Tech Worksheet Name Auto Trans & Transaxle Chapter 40 Pages 1173 1215 107 Points Due Date 1. Automatic transmissions are operated by hydraulics as well as electronics to select according
Advanced Auto Tech Worksheet Name Auto Trans & Transaxle Chapter 40 Pages 1173 1215 107 Points Due Date 1. Automatic transmissions are operated by hydraulics as well as electronics to select according
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (DC 5-SPEED) GENERAL 1. AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION OVERVIEW
 02-4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION () GENERAL 1. AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION OVERVIEW DC 5-speed Automatic Transmission Assembly T-Tronic DC 5-speed automatic transmission is an electronically controlled 5-speed transmission
02-4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION () GENERAL 1. AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION OVERVIEW DC 5-speed Automatic Transmission Assembly T-Tronic DC 5-speed automatic transmission is an electronically controlled 5-speed transmission
CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM
 CRUISE CONTROL 1. Cruise Control A: OPERATION The cruise control system automatically controls the vehicle speed. It allows the vehicle to run at a constant speed without need for the driver to keep the
CRUISE CONTROL 1. Cruise Control A: OPERATION The cruise control system automatically controls the vehicle speed. It allows the vehicle to run at a constant speed without need for the driver to keep the
SPECIFICATIONS kg (including oil) ATF DEXRON II or III. Major element Housing Part-time Bolt 11EA, M8 x 1.25
 3240-01 05-3 1. SPECIFICATIONS Description Specifications Total length 343 mm Weight 32.4 kg (including oil) Oil capacity 1.4 L Oil type ATF DEXRON II or III Location Transfer case Major element Housing
3240-01 05-3 1. SPECIFICATIONS Description Specifications Total length 343 mm Weight 32.4 kg (including oil) Oil capacity 1.4 L Oil type ATF DEXRON II or III Location Transfer case Major element Housing
Transmission Electronic Control System
 SECTION 307-01: Automatic Transaxle/Transmission 5R55S 2009 Mustang Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 05/23/2008 Transmission Electronic Control System Electronic System
SECTION 307-01: Automatic Transaxle/Transmission 5R55S 2009 Mustang Workshop Manual DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 05/23/2008 Transmission Electronic Control System Electronic System
Automatic Gearbox - Fundamentals -
 Automatic Gearbox - Fundamentals - The gearbox in a motorcar is the technical aid for converting the engine forces into the varying operating conditions. Operating the clutch and shifting gears make up
Automatic Gearbox - Fundamentals - The gearbox in a motorcar is the technical aid for converting the engine forces into the varying operating conditions. Operating the clutch and shifting gears make up
ABS, 4-ETS and EBP BRAKES ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 4-WHEEL ELECTRONIC TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (4-ETS) ELECTRONIC BRAKE PROPORTIONING (EBP)
 1 of 9 4/27/2008 7:52 AM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: METRO TOYOTA OK 2002 Mercedes Benz Truck ML 320 (163.154) V6-3.2L (112.942)
1 of 9 4/27/2008 7:52 AM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: METRO TOYOTA OK 2002 Mercedes Benz Truck ML 320 (163.154) V6-3.2L (112.942)
Transmissions. Service Training Course No. 200 WARNING: WHILE SERVICING AND TESTING VEHICLES AND VEHICLE SYSTEMS, TAKE ALL
 Service Training Course No. 200 Transmissions This publication is intended for instructional purposes only. Always refer to the appropriate Jaguar Service publication for specific details and procedures.
Service Training Course No. 200 Transmissions This publication is intended for instructional purposes only. Always refer to the appropriate Jaguar Service publication for specific details and procedures.
SECTION ZF TRANSMISSION
 10-103.04/ 1 2009JL16 SECTION 10-103.04 GENERAL DESCRIPTION See Figure 1. The ZF-Ecomat transmission consists of a hydrodynamic torque converter, with a lock-up clutch for direct drive, a hydrodynamic
10-103.04/ 1 2009JL16 SECTION 10-103.04 GENERAL DESCRIPTION See Figure 1. The ZF-Ecomat transmission consists of a hydrodynamic torque converter, with a lock-up clutch for direct drive, a hydrodynamic
The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
DRIVETRAIN 7.0 Introduction 7.1 Drivetrain configurations 7.2 Drivetrain elements 7.3 Clutch Operation
 DRIVETRAIN 7.0 Introduction Drivetrain is the assembly of all the components that are involved in the transmission of the power from the engine of the vehicle to its wheels. 7.1 Drivetrain configurations
DRIVETRAIN 7.0 Introduction Drivetrain is the assembly of all the components that are involved in the transmission of the power from the engine of the vehicle to its wheels. 7.1 Drivetrain configurations
CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM
 CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Toyota Motor Sales, U.S.A., Inc. - Cruise Control Systems Celica DESCRIPTION Cruise control system consists of Cruise Control Electronic
CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Toyota Motor Sales, U.S.A., Inc. - Cruise Control Systems Celica DESCRIPTION Cruise control system consists of Cruise Control Electronic
TWIN CLUTCH-SPORTRO NIC SHIFT TRANSMISSION (TC-SST)
 22B-1 GROUP 22B TWIN CLUTCH-SPORTRO NIC SHIFT TRANSMISSION (TC-SST) CONTENTS TWIN CLUTCH-SPORTRONIC SHIFT TRANSMISSION (TC-SST)........ 22B-2 GENERAL INFORMATION............. 22B-2 DESCRIPTION OF FUNCTION.........
22B-1 GROUP 22B TWIN CLUTCH-SPORTRO NIC SHIFT TRANSMISSION (TC-SST) CONTENTS TWIN CLUTCH-SPORTRONIC SHIFT TRANSMISSION (TC-SST)........ 22B-2 GENERAL INFORMATION............. 22B-2 DESCRIPTION OF FUNCTION.........
1. SPECIFICATIONS Part-time transfer case. Mating surface of front flange kg (including oil)
 3240-01 07-3 1. SPECIFICATIONS Type Total length Description Mating surface of front flange Weight Oil capacity Oil type Location Specifications Part-time transfer case 343 mm 40 mm 32.4 kg (including
3240-01 07-3 1. SPECIFICATIONS Type Total length Description Mating surface of front flange Weight Oil capacity Oil type Location Specifications Part-time transfer case 343 mm 40 mm 32.4 kg (including
Part 1 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS
 Part 1 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Chapter 1-6 Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake Ignition switch with steering lock Automatic transmission Manual transmission Four-wheel drive system
Part 1 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Chapter 1-6 Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake Ignition switch with steering lock Automatic transmission Manual transmission Four-wheel drive system
4 Spd. Automatic Transmission 096
 4 Spd. Automatic Transmission 096 00 - General, Technical data Transmission identification Code letters, model/engine applications, ratios, equipment Capacities Repair instructions 01 - On Board Diagnostic
4 Spd. Automatic Transmission 096 00 - General, Technical data Transmission identification Code letters, model/engine applications, ratios, equipment Capacities Repair instructions 01 - On Board Diagnostic
 Page 1 of 10 Main Components and Functions Torque Converter 1 Cover (Part of 7902) 2 Converter Damper Plate 3 O-Ring (Part of 7902) 4 Turbine Assembly (Part of 7902) 5 Selective Spacer 6 Thrust Washer
Page 1 of 10 Main Components and Functions Torque Converter 1 Cover (Part of 7902) 2 Converter Damper Plate 3 O-Ring (Part of 7902) 4 Turbine Assembly (Part of 7902) 5 Selective Spacer 6 Thrust Washer
2007 Dodge Nitro R/T
 1 - TURBINE 2 - IMPELLER 2007 Dodge Nitro R/T CONVERTER-TORQUE DESCRIPTION TORQUE CONVERTER Fig. 267: Cutaway View Of Torque Converter Fig. 268: Impeller 2007 Dodge Nitro R/T 3 - STATOR 4 - INPUT SHAFT
1 - TURBINE 2 - IMPELLER 2007 Dodge Nitro R/T CONVERTER-TORQUE DESCRIPTION TORQUE CONVERTER Fig. 267: Cutaway View Of Torque Converter Fig. 268: Impeller 2007 Dodge Nitro R/T 3 - STATOR 4 - INPUT SHAFT
The Brake Assist System
 Service. Self-study programme 264 The Brake Assist System Design and function Accident statistics show that in 1999 alone, 493,527 accidents in Germany were caused by driver error. Many accidents caused
Service. Self-study programme 264 The Brake Assist System Design and function Accident statistics show that in 1999 alone, 493,527 accidents in Germany were caused by driver error. Many accidents caused
CH-23 CHASSIS AA80E AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION. Function of Shift Solenoid Valves. Spool Valve. Hydraulic Pressure. Sleeve. Current. Shift Solenoid Valve
 CH-23 Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SL2 Current 036CH29TE Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SLU Current 036CH27TE Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SLT
CH-23 Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SL2 Current 036CH29TE Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SLU Current 036CH27TE Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SLT
DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND PROCEDURES > TRANSFER CASE SHIFT CONTROL SWITCH INOPERATIVE > CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
 Page 1 of 9 Service Manual: TRANSFER CASE - BW 4484 DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND PROCEDURES > TRANSFER CASE SHIFT CONTROL SWITCH INOPERATIVE > CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION The range/mode switch circuit consists of
Page 1 of 9 Service Manual: TRANSFER CASE - BW 4484 DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION AND PROCEDURES > TRANSFER CASE SHIFT CONTROL SWITCH INOPERATIVE > CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION The range/mode switch circuit consists of
1. Cruise Control CRUISE CONTROL A: OPERATION B: LOCATION OF COMPONENTS. CC(STi)-2
 W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Cruise Control A: OPERATION The cruise control system automatically controls the vehicle speed. It allows the vehicle to run at a constant speed
W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Cruise Control A: OPERATION The cruise control system automatically controls the vehicle speed. It allows the vehicle to run at a constant speed
ESCONDIDO FIRE DEPT TRAINING MANUAL Section DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 Pumps and Accessory Equipment Revised
 DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 PUMPS AND ACCESSORY EQUIPMENT Pumps are designed for many different purposes. In order to understand the proper application and operation of a pump in a given situation, firefighters
DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 PUMPS AND ACCESSORY EQUIPMENT Pumps are designed for many different purposes. In order to understand the proper application and operation of a pump in a given situation, firefighters
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine
 The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The 6-Speed Manual Gearbox 08D
 Service. Self-Study Programme 299 The 6-Speed Manual Gearbox 08D Design and Function The Touareg is an exclusive cross country vehicle with the driving properties and driving comfort of a sporty luxury
Service. Self-Study Programme 299 The 6-Speed Manual Gearbox 08D Design and Function The Touareg is an exclusive cross country vehicle with the driving properties and driving comfort of a sporty luxury
TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION CIRCUIT ACTYON
 311001 017 311001 TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION 018 311001 (3) DESCRIPTION A. ION (BTRA) M74 4WD AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION The ION (BTR) Four Speed
311001 017 311001 TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION 018 311001 (3) DESCRIPTION A. ION (BTRA) M74 4WD AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION The ION (BTR) Four Speed
DC 5-SPEED AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
 03 1. OVERVIEW 2WD 4WD DCAG 5speed automatic transmission is an electronically controlled 5speed transmission with a lockup clutch in the torque converter. The ratios for the gears are realized by three
03 1. OVERVIEW 2WD 4WD DCAG 5speed automatic transmission is an electronically controlled 5speed transmission with a lockup clutch in the torque converter. The ratios for the gears are realized by three
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (DIAGNOSTICS) AT
 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (DIAGNOSTICS) AT Page 1. Basic Diagnostic Procedure...2 2. Check List for Interview...4 3. General Description...5 4. Electrical Components Location...7 5. Transmission Control Module
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (DIAGNOSTICS) AT Page 1. Basic Diagnostic Procedure...2 2. Check List for Interview...4 3. General Description...5 4. Electrical Components Location...7 5. Transmission Control Module
The Transporter 2004 Electrical system
 Service. Self-study programme 311 The Transporter 2004 Electrical system Design and function The Transporter 2004 has an extensive network of electronic control units. Functions which were controlled in
Service. Self-study programme 311 The Transporter 2004 Electrical system Design and function The Transporter 2004 has an extensive network of electronic control units. Functions which were controlled in
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS Mitsubishi F3A20 Series TRANSMISSION APPLICATION TABLE
 Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS Mitsubishi F3A20 Series APPLICATION TRANSMISSION APPLICATION TABLE Vehicle Application Transmission Model Colt 3-Speed (1990-94)... F3A21 Colt Vista
Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS Mitsubishi F3A20 Series APPLICATION TRANSMISSION APPLICATION TABLE Vehicle Application Transmission Model Colt 3-Speed (1990-94)... F3A21 Colt Vista
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS II SYSTEM. 5. Specified Data. Signal (V) Ignition SW ON (Engine OFF)
 1. ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL OBD0092A Crankshaft Camshaft Mass air flow Throttle Signal (+) 8 0 7 +7 Sensor output waveform Signal ( ) 29 0 0 Shield 54 0 0 Signal (+) 7 0 7 +7 Sensor output
1. ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL OBD0092A Crankshaft Camshaft Mass air flow Throttle Signal (+) 8 0 7 +7 Sensor output waveform Signal ( ) 29 0 0 Shield 54 0 0 Signal (+) 7 0 7 +7 Sensor output
The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function
 Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
Service Training Self-study Programme 442 The 1.6ltr. TDI Engine with Common Rail Injection System Design and Function The 1.6l TDI engine with common rail injection system will form the basis for all
New Development of Highly Efficient Front-Wheel Drive Transmissions in the Compact Vehicle Segment
 New Development of Highly Efficient Front-Wheel Drive Transmissions in the Compact Vehicle Segment Introduction Dr. Ing. Ansgar Damm, Dipl.-Ing. Tobias Gödecke, Dr. Ing. Ralf Wörner, Dipl.-Ing. Gerhard
New Development of Highly Efficient Front-Wheel Drive Transmissions in the Compact Vehicle Segment Introduction Dr. Ing. Ansgar Damm, Dipl.-Ing. Tobias Gödecke, Dr. Ing. Ralf Wörner, Dipl.-Ing. Gerhard
FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 35B-2 35B-6 SENSOR 35B-6 ACTUATORS 35B-6 ABS-ECU 35B-7 35B-2 The ABS that ensures directional stability and controllability
35B-1 GROUP 35B FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 35B-2 35B-6 SENSOR 35B-6 ACTUATORS 35B-6 ABS-ECU 35B-7 35B-2 The ABS that ensures directional stability and controllability
Geo Prizm ( LSi) Toyota Celica 1.8L (1994)
 Page 1 of 140 ARTICLE BEGINNING APPLICATION TRANSMISSION APPLICATIONS Application Geo Prizm (1993-94 LSi) Toyota Celica 1.6L (1993) Celica 1.8L (1994) Celica 2.2L (1993) Corolla 1.8L MR2 Paseo Transaxle
Page 1 of 140 ARTICLE BEGINNING APPLICATION TRANSMISSION APPLICATIONS Application Geo Prizm (1993-94 LSi) Toyota Celica 1.6L (1993) Celica 1.8L (1994) Celica 2.2L (1993) Corolla 1.8L MR2 Paseo Transaxle
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition
 Стр. 1 из 11 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition 10.2001 Audi A4 (1.8 litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic (5-valve/turbo), 4-cylinder), engine codes APU/ANB From model year 2000 Audi
Стр. 1 из 11 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 4 / 1 Edition 10.2001 Audi A4 (1.8 litre fuel injection engine, 110 kw, Motronic (5-valve/turbo), 4-cylinder), engine codes APU/ANB From model year 2000 Audi
Automated Control Electronics (ACE ) System Operation and Diagnostics
 Commercial Products Automated Control Electronics (ACE ) System Operation and Diagnostics PART NO. 98962SL This page is intentionally blank. Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Controller Operation and
Commercial Products Automated Control Electronics (ACE ) System Operation and Diagnostics PART NO. 98962SL This page is intentionally blank. Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Controller Operation and
2.0l TDI engines in the T Design and function
 Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
Service Training Commercial Vehicles Self-Study Programme 455 2.0l TDI engines in the T5 2010 Design and function With the T5 2010, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is taking a new path in engine strategy.
ZF4HP16. Technical Bulletin # Signal Combination L1 L2 L3 L4 P R N D
 Transmission: Subject: Application: Issue Date: Technical Bulletin # 1308 ZF4HP16 Electronical Components Description 2005 Suzuki Forenza L4-2.0L February, 2010 ZF4HP16 Electronical Components Description
Transmission: Subject: Application: Issue Date: Technical Bulletin # 1308 ZF4HP16 Electronical Components Description 2005 Suzuki Forenza L4-2.0L February, 2010 ZF4HP16 Electronical Components Description
