Technology review. Design philosophy Engine performance... 5 CASS Engine block Crankshaft and bearings Connecting rod...
|
|
|
- Karen Scott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Technology review
2 2
3 Technology review This is a summary of the technicall features and performance of the Wärtsilä 46F engine. Design philosophy Engine performance CASS Engine block Crankshaft and bearings Connecting rod Piston & piston rings Cylinder liner and antipolishing ring Cylinder head Camshaft and valve gear Fuel injection system Turbocharging system Cooling system Lubrication oil system Automation system Maintenance Main technical data
4 Design philosophy The new Wärtsilä 46F engine offers outstanding power-to-weight and power-to-space ratios in its power range. With a bore of 46 cm and a stroke of 58 cm, the rated output of the new Wärtsilä 46F engine is 1250 kw/cyl at 600 rpm. Full advantage is taken of the proven solutions used in the earlier Wärtsilä 46-bore engine, while new features and customer benefits have been added. Reliability and total economy are the guiding principles, although emission control options and installation friendliness are strongly in focus. The main features of the Wärtsilä 46F are: Cylinder output 1250 kw Nominal speed 600 rpm High thermal efficiency and low emissions Common rail fuel injection Conventional fuel injection with twin plunger injection pumps, optional Integrated automation system including speed control; extent and features according to application Humidification of the combustion air for NOx reduction, optional (CASS - Combustion Air Saturation System) Water mist catcher in the charge air system High reliability and low maintenance costs Safe bearing technology Big end bearing and main bearing temperature monitoring Variable Inlet Valve Closing (VIC), optional All ancillaries are built on the engine in standard configuration Also available without built-on ancillaries, several intermediate options available All connections concentrated at a few points. Ancillary equipment such as pumps, thermostats and lubrication oil module can be either built on the engine or separate. All connections are concentrated at a few points to reduce installation work. Pressure control valves are Automation system, interface to external system Lube oil filter Lube oil module Charge air cooler and water mist catcher Lube oil thermostatic valve LT-water pump HT-water pump Charge air temperature control valve (LT-water by-pass) Control oil pump (Common Rail) Control oil, to filter LT-water, from standby pump LT-water, outlet LT-water, inlet Sludge, from lube oil filter Lube oil, from standby pump Fuel oil, inlet Fuel oil, outlet Control oil, inlet Main lube oil pump Lube oil, inlet to main pump Lube oil, inlet from external prelube pump 4
5 Engine configuration options built on the engine for proper control of fuel and lubricating oil pressure. When pumps and thermostats are built on, adjustable orifices are installed on the engine for easy tuning of the cooling water systems. The turbocharger can be located in either the free or in the driving end. Transversal turbocharger alignment makes it possible to incline the exhaust gas outlet in the longitudinal direction. The embedded control and monitoring system is modular and depending on configuration it offers either Ethernet communication or hardwired signals to external systems. The minimum configuration includes integrated speed control, fundamental safety functions and a local control panel. HT-water temperature control valve Leak oil drain HT pump N N HT thermostat N N LT pump N N N N LT thermostat N N N LO pump N LO pressure control valve N LO module* N N N N Pre-lube pump N N N N N N = equipment is built on to engine N = equipment not on engine *) including cooler, automatic filter and thermostats HT-water, outlet HT-water, inlet HT-water, from standby pump Leak oil drain Start air, inlet Engine performance The engine output has been achieved by increasing engine speed instead of mean effective pressure, and the latest developments in turbocharging technology have been fully available to make wider use of the Miller concept. At full-load operation, early closure of the inlet valves gives room for a low effective compression ratio, and thereby comparatively low temperatures at the end of the compression stroke. The charge air, being both somewhat expanded and cooled on its way through the receiver into the cylinders, contributes to creating the initial conditions favourable to an environmentally friendly combustion process, i.e. a low global temperature that is still high enough to guarantee reliable and stable ignition of the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber. In the Wärtsilä 46F engine, these advantageous initial conditions are combined with a higher engine speed and a high expansion ratio, i.e. with design parameters that make the combustion chamber expand quickly when the combustion process has started. Due to the quick expansion of the combustion gases, the temperatures most critical to intensive NOx formation in the combustion chamber are limited to the shortest time possible. This combination makes the combustion process not only environmentally friendly but efficient as well, since the high expansion ratio also creates the required conditions for efficient utilization of the heat energy released by combustion at the beginning of the power stroke. However, it is not only the choice of the compression/expansion ratio that makes the Wärtsilä 46F engine highly efficient. All versions of the engine are equipped with a fuel injection system that allows the operator to adjust the injection characteristics to the prevailing load conditions, fuel in use, etc. For example, the operator can freely fine-tune the injection process to enable full use of the engine loading potential over a wide power range in order to reach the best possible fuel economy. Alternatively, the operator can of course use the degrees of freedom offered by the flexible fuel injection equipment to adjust the engine to the existing limitations of exhaust gas emissions, to minimize smoke formation. Thermal load and mechanical stress levels are kept within the safety margins established by Wärtsilä over decades of engine development. 5
6 CASS The new NOx reduction technology developed by Wärtsilä is named CASS, for Combustion Air Saturation System. The principle of CASS is to introduce water with the intake air to reduce the combustion temperature and thereby the formation of NOx. Pressurized water is injected directly after the compressor of the turbocharger. The high temperature of the compressed air evaporates the water, which enters the cylinders as steam. A water mist catcher prevents water in liquid state from entering the cylinders. The anticipated NOx reduction is up to 50%, and the water consumption is expected to be about two times the fuel oil consumption. CASS is available as an option. Water injection Compressor Water mist catcher Saturated air C Engine block Nodular cast iron is the natural choice for engine blocks today because of its strength and stiffness properties. The Wärtsilä 46F engine block design makes optimum use of modern foundry technology. The charge air receiver and the HT water outlet channel are integrated into the engine block. The cooling water is distributed around the liners with water distribution rings at the lower end of the collar. Thus there is no wet space in the engine block around the cylinder liner. Resilient mounting is almost standard in many applications today and the engine block has been designed especially for this purpose. Main features of the engine block: Nodular cast iron Rigid and self-supporting design Dry cylinder liner Main bearing screws and side screws Hydraulically tightened main bearing and side screws Easy access also for large size service personnel. Heat Principle of CASS. 6
7 Engine foot Fixing rail Resilient element Foundation Main features of the crankshaft design: Clean steel technology minimizes the amount of slag forming elements and guarantees superior material properties Built up from three-pieces: crankshaft, gear and end piece. Crankshaft itself forged in one piece Each throw individually fully balanced for safe bearing function Main bearing temperature monitoring Patented crankpin bearing temperature monitoring Modest bearing loads thanks to generous bearing dimensions. Resilient mounting. Crankshaft and bearings The latest advances in combustion development require a crank gear which can operate reliably at high cylinder pressures. The crankshaft must be robust and the specific bearing loads kept at a safe level. This is achieved by careful optimization of crankthrow dimensions and fillets. The specific bearing loads are conservative and the cylinder spacing, which is important for the overall length of the engine, is minimized. Besides low bearing loads, the other crucial factor for safe bearing operation is oil film thickness. Ample oil film thickness in the main bearings is ensured by optimal balancing of the rotational masses. Crankpin bearing temperature monitoring. 7
8 Connecting rod The three-piece connecting rod is of the marine type, where combustion forces are distributed over a maximum bearing area and the relative movements between mating surfaces are minimized. The connecting rod is optimized for both strength and weight. The shank is fully machined. The three-piece design reduces the piston overhauling height as piston overhauling is possible without touching the big end bearing. The big end bearing can also be inspected without removing the piston. Main features of the connecting rod design: Three-piece marine type design Fully machined shank Hydraulically tightened bolts Strength- and weight-optimized Easy maintenance. Piston & piston rings For years, the outstanding piston concept for highly rated heavy fuel engines has been a rigid composite piston with a steel crown and nodular cast-iron skirt. More than twenty years of experience has fine-tuned this concept. When it comes to reliability, there is no real alternative today for modern engines with high cylinder pressures and combustion temperatures. Wärtsilä-patented skirt lubrication is applied to minimize frictional losses and ensure appropriate lubrication of both piston rings and the piston skirt. In Wärtsilä s three-ring concept each ring has a specific task. The rings are dimensioned and profiled for consistent performance throughout their operating lives. To avoid carbon deposits in the ring grooves of a heavy 8
9 fuel engine, the pressure balance above and below each ring is crucial. Experience has shown that this effect is most likely achieved with a three-ring pack. Finally, it is well known that most frictional losses in a reciprocating combustion engine originate from the rings. Thus a three-ring pack is the obvious choice in this respect, too. The piston ring package and ring grooves are optimized for long lifetime by special wear-resistant coating and groove treatment. Main features of the piston design: Two-piece composite structure Steel crown and nodular cast-iron skirt Two compression rings and one oil scraper ring in combination with pressure lubricated piston skirt give low friction and high seizure resistance Optimum temperature of the piston ring grooves prevents cold corrosion. lube oil consumption. The function of this ring is to calibrate the carbon deposits formed on the piston top land to a thickness small enough to prevent any contact between the liner wall and the deposits at any piston position. The absence of contact between the liner and piston top land deposits eliminates the risk of bore polishing. Nor can oil be scraped upwards by the piston. This significantly reduces liner wear and keeps the lube oil consumption stable for long periods of time. The high strength of the wear-resistant liner materials used for years in Wärtsilä engines has been further increased to cope with the high combustion pressures expected in the future. Main features of the cylinder liner design: Centrifugal casting with high strength and good wear resistance Bore cooled for optimum wall temperatures High-collar technology to ensure good cylinder head gasket tightness Antipolishing ring removes deposits from the piston top land, ensuring proper cylinder function, no bore polishing, stable lube oil consumption and low wear of the liner. Cylinder liner and antipolishing ring The thick high-collar type cylinder liner is designed to have the stiffness needed to withstand both pretension forces and combustion pressures with virtually no deformation. This gives the best cylinder function and ensures the tightness of the cylinder head gasket. Its temperature is controlled by bore cooling of the upper part of the collar to achieve a low thermal load and to avoid sulphuric acid corrosion. The cooling water is distributed around the liners with water distribution rings at the lower end of the collar. In the upper end the liner is equipped with an antipolishing ring to eliminate bore polishing and reduce 9
10 Cylinder head The cylinder head design features high reliability and easy maintenance. A stiff cone- / box-like design can cope with high combustion pressure, and is essential for obtaining both liner roundness and even contact between the exhaust valves and their seats. Wärtsilä s vast experience gained from heavy fuel operation all around the world has contributed greatly to exhaust valve design and development. The basic criterion for the exhaust valve design is correct temperature. This is achieved by optimized cooling and closed seat ring technology, which ensures long lifetimes for the valves and seats. The cylinder head design is based on the four-screw concept developed by Wärtsilä and used for many years. A four-screw cylinder head design also provides all the freedom needed for designing the inlet and exhaust ports with a minimum of flow losses. The port design has been optimized using computational fluid dynamics analysis in combination with full-scale flow measurements. Main features of the cylinder head design: Four cylinder head screws only, giving space for flow-efficient ports Inlet and exhaust gas ports on the same side Height and rigid design ensure even and sufficient surface pressure on the cylinder head gasket Bore-cooled flame plate for optimum temperature distribution Two inlet valves and two exhaust gas valves, all with valve rotators. Closed-type exhaust gas seats for efficient cooling of the valve seats and valves. Camshaft and valve gear The engine is available with either traditional mechanical valve actuation or variable inlet valve actuation. The camshaft is built of single cylinder sections with integrated cams. The camshaft sections are connected through separate bearing journals, which makes it possible to remove the shaft sections sideways from the camshaft compartment. The valve follower is of the roller tappet type, where the roller profile is slightly convex for good load distribution. The valve mechanism includes rocker arms working on yokes guided by pins. 10
11 VIC on engine. Both exhaust and inlet valves are equipped with valve rotators to ensure safe valve and seat function. The rotation provides for even temperature distribution and wear of the valves, and keeps the sealing surface free from deposits. Variable Inlet valve Closure (VIC), available as an option, offers the Main features of the camshaft and valve design: Each cylinder section of the camshaft is forged in one piece with integrated cams Separate bearing journals Valve follower is of the roller tappet type Traditional valve actuation Variable Inlet Valve Closing (VIC) as an option. flexibility to apply early inlet valve closure at high load for lowest NO x levels, while good part-load performance is ensured by completely removing the advanced inlet valve closure at part load. The achievable change in valve timing is up to 30 crank angle. The operating principle is based on a hydraulic device between the valve tappet and the pushrod. Briefly, the device can be described as two hydraulic cylinders connected through two passages. The flow through one passage is controlled by the position of the tappet, while the other passage is controlled with a valve. The tappet acts on one of the hydraulic pistons and the other piston acts on the pushrod. The pushrod can move only when oil is flowing between the two cylinders. When the VIC control valve is open, the pushrod follows the tappet immediately, which results in early valve closure. When the control valve is closed, the downward movement of the pushrod is delayed until the piston actuated by the tappet reveals the passage between the two cylinders. Engine oil is used as the hydraulic medium. Valve lift Crank angle VIC valve VIC control valve Principle layout of VIC. VIC air bleed valve VIC vent valve 11
12 Fuel injection system The patented Wärtsilä multihousing principle ensures outstanding safety of the low-pressure fuel system. The fuel line consists of channels drilled in cast parts, which are clamped firmly on the engine block. For easy assembly and disassembly these parts are connected to each other using slide connections. The engine is available with two different fuel injection systems: common rail fuel injection and conventional fuel injection with twin plunger injection pumps. Both systems are characterized by high injection pressures for low smoke emission. Common rail technology enables operation at any load without visible smoke. Housing both the entire low-pressure system and the high-pressure system in a fully covered compartment ensures an unbeatable standard of safety. Common rail technology offers almost unlimited possibilities to adjust the fuel injection process to Common rail architecture. The patented Multihousing with drilled channels for low pressure fuel oil. Common Rail fuel injection system. prevailing engine operating conditions, fuel characteristics and emission levels. The main components in the common rail injection system that are designed especially for the Wärtsilä 46F engine are the high-pressure pumps, balance accumulators, control oil pumps and fuel injection valves. The control oil is engine oil with 12
13 additional filtration. The control oil pump is built onto the engine. The system high-pressure pumps are camshaft-driven and amply dimensioned for supplying fuel to two cylinders. Each pump is connected to a fuel accumulator that evens out the pressure and feeds two cylinders. The accumulators are connected to each other through double-walled pipes, a detail that both guarantees continuous even pressure in all accumulators and allows the engine to operate with one or two disconnected high-pressure pumps, should this ever be necessary. From the accumulators fuel is supplied at the required pressure into the cylinders through injection valves controlled by electro-hydraulic actuators. The individual, and therefore cylinder-specific, control of injection timing and duration is an important feature made possible by this injection equipment. One safety detail worth mentioning here is that the injection valve design ensures totally unloaded injection nozzles between injection periods. This feature eliminates the risk of unintended fuel supply into cylinders caused, for example, by incomplete closure of the nozzle needle at the end of injection. The traditional twin-pump system, likewise, offers the possibility to adjust the fuel injection process to prevailing engine operating conditions, fuel characteristics and emission levels. The big difference is that common rail technology allows for individual (cylinder-specific) control of injection timing and duration and for keeping the injection pressure at a sufficiently high level over the whole load range. Main features of the fuel injection system design: Common rail fuel injection Conventional fuel injection with twin plunger injection pumps as option Both systems make it possible to adjust the fuel injection process to prevailing engine operating conditions. Even with conventional fuel injection precise control according to the prevailing conditions is possible, thanks to the twin plunger injection pumps. One plunger controls the quantity of fuel while the other controls the injection timing. injector delivery valve timing plunger quantity plunger - tappets on cam base circle - filling of injection pump - quantity plunger shuts off spill port - excessive fuel out to low pressure side through filling port - both ports are shut off - delivery valve lifts - start of injection - spill port opens - excessive fuel out to low pressure side through spill port - end of injection Functional sketch of the TWIN pump fuel injection system. 13
14 Turbocharging system Turbocharger technology has undergone intense design and performance development in recent years, resulting in high performance and high reliability. Only the best available charger technology is used on the Wärtsilä 46F. The engine is equipped with a one-stage turbocharging system that best fulfils the requirements of each application. The standard is a single-pipe exhaust gas (SPEX) system, with the option of exhaust wastegate or air bypass according to the application. The SPEX system is designed to apply the benefits of both pulse charging and constant pressure charging. SPEX is able to utilize the pressure pulses without disturbing the cylinder scavenging. Lube oil cooled chargers are used with inboard plain bearings lubricated from the engine s lube oil system. All this makes for longer intervals between overhauls and reduced maintenance. The charge air receiver is integrated into the engine block. The two-stage self-supporting charge air cooler consists of separate HT and LT water sections, which gives an advantage for heat recovery applications. The charge air temperature is controlled by an LT water temperature control valve (bypass valve). The engine has a water mist catcher as standard, enabling humidification of the air for reduced NOx emissions. Turbocharger. Main features of the turbocharging system: One-stage turbocharging Oil-cooled turbocharger with plain bearings lubricated by engine oil Two-stage charge air cooler LT water bypass valve for charge air temperature control Charge air receiver integrated into the engine block SPEX. 14
15 circuit. The lubricating oil cooler and the second stage in the charge air cooler are connected to the LT circuit. The amount of water passing through the LT stage in the charge air cooler is controlled by a thermostatic valve to maintain the desired intake air temperature, regardless of load level or variations in cooling water temperature. Engine-driven pumps and built-on thermostatic valves are standard. As an option the engine is also available without pumps and thermostats. Charge air system. Water mist catcher, enabling humidification of the air for reduced NOx emissions Air and exhaust waste gate functions for best engine performance Single-pipe exhaust gas system (SPEX) optimized for each cylinder configuration Cooling system The cooling system on the engine is split into two separate circuits: high-temperature (HT) and a low-temperature (LT). The cylinder liner, the cylinder head and the first stage in the charge air cooler are connected to the HT Water pumps. Lubricating oil cooler Charge air cooler LT Charge air cooler HT Cyl. Heat recovery Central cooler LT stand-by pump LT pump HT pump HT stand-by pump Preheater Principle layout of the cooling system. 15
16 Automatic filter Oil cooler Oil pump Electric stand-by oil pump Centrifugal filter Electric pre-lube oil pump Dry oil sump Suction strainer System oil tank Principle layout of the lubricating system. Lubricating oil system The engine is available either with a complete built-on lube oil system or with the lube oil pump, lube oil filter and lube oil cooler separately installed in the engine room. The oil sump is of the dry type, i.e. a separate system oil tank is needed. The built-on lube oil system comprises: Engine-driven main lube oil pump (screw type) with built-in safety valve Pressure regulating valve that keeps the pressure before the main bearings at a constant level Lubricating oil module including lube oil cooler, full flow automatic filter and thermostatic valves Special running-in filters before each main bearing, camshaft line and turbocharger Centrifugal filter for lube oil quality indication On in-line engines the lubricating oil module is always located at the opposite end to the turbocharger. The lube oil filtration is based on an automatic back-flushing filter. This requires a minimum of maintenance and needs no disposable filter cartridges Connections for stand-by auxiliaries. Lubricating oil system. 16
17 Automation system The Wärtsilä 46F engine is equipped with a scaleable embedded control system that can cover a wide range of engine applications. Reliability and serviceability were the main cornerstones of this system s design. The on-engine electronics are designed to match the harsh environment on a large diesel engine, while also allowing fault tracing and maintenance on board with commonly available tools. A non-repairable harness design is not used. The system is designed for use with common marine type cables. For fault tracing all connections points in the systems are easily accessible, and replacing the electronics is easy. Input Output Modules (IOM) take care of measurements of the engine instrumentation Cylinder Control Modules (CCM) independently handle the electronic fuel injection control. The architecture is based on CAN (controller area network) communication between the modules, and Ethernet communication to external automation systems. The system also internally implements redundancy on selected systems and components. The automation system is based on a number of hardware modules: Engine Safety Module (ESM) handles engine safety functions in a partly redundant hardware implementation Local Control Panel (LCP) collects the local engine instrumentation as well as local control functions for e.g. engine start and stop Main Control Module (MCM) handles the speed control and overall engine functionality 17
18 The following illustration describes the control system for the 46F common rail engine, with the EFIC control by the CCM modules, speed/load and main engine control by the MCM controller, and engine safety handled by the ESM module. As the engine is also available with conventional diesel injection equipment on request, the system can also be scaled to match systems where only the fundamental engine safety is handled by the ESM module and the speed/load control is handled by the MCM module. Other measurements are taken out to external automation systems. On request, an engine with conventional diesel injection can also be supplied with a fully embedded control system. LCP (Local control panel) Ethernet to external systems CCM (Cylinder control module) MCM (Speed controller) ESM (Engine safety module) IOM (Input output module) MCM (additional I/O) Hardwired measurements to external systems MCM (Speed controller) ESM (Engine safety module) 18
19 Main technical data Marine engines, In-line engine Cylinder bore: 460 mm Piston stroke: 580mm Speed: 600 rpm Mean effective pressure: 25.9 bar Piston speed: 11.6 m/s Output/cylinder: 1250 kw Fuel specification: Fuel oil 730 cst/50 C ISO 8217, category ISO-F-RMG-RMK 55 Maintenance During design and development the engine manufacturer emphasizes the necessity for easy maintenance by including tooling and easy access in the basic design and by providing easy-to-understand instructions. The Wärtsilä 46F maintenance principle is substantiated by the following: A cylinder head with four fixing studs and simultaneous hydraulic tightening of all four studs A hydraulic jack for overhaul of the main bearing Uniform one-cylinder camshaft pieces Slip-on fittings wherever possible Exhaust gas system insulation using easy-to remove panels on an engine-mounted frame The three-piece connecting rod allows inspection of the big end bearing without removal of the piston, and piston overhaul without dismantling the big end bearing Weight-optimized and user-friendly maintenance tools Rated Power: Propulsion engines Cylinder configuration kw* BHP* 6L46F L46F L46F L46F *At flywheel Principal engine dimensions (mm) and weights (tonnes)** Cylinder configuration A B C Weight (dry) 6L46F L46F L46F L46F ** Subject to revision without notice A = Total length B = Total breadth C = Total height (from the bottom of the oil sump to the exhaust gas outlet) 19
20 / Bock s Office / Wärtsilä is The Ship Power Supplier for builders, owners and operators of vessels and offshore installations. We are the only company with a global service network to take complete care of customers ship machinery at every lifecycle stage. Wärtsilä is a leading provider of power plants, operation and lifetime care services in decentralized power generation. The Wärtsilä Group includes Imatra Steel, which specializes in special engineering steels. For more information visit WÄRTSILÄ is a registered trademark. Copyright 2004 Wärtsilä Corporation. Wärtsilä Corporation P.O.Box 196 FIN Helsinki Tel: Fax:
Engine technology 16 and 20V34SG
 Engine technology 16 and 20V34SG 2 Engine technology Introduction............................. 4 Design philosophy........................ 5 The lean-burn concept..................... 6 Low emissions...........................
Engine technology 16 and 20V34SG 2 Engine technology Introduction............................. 4 Design philosophy........................ 5 The lean-burn concept..................... 6 Low emissions...........................
H35/40G(V) /7 Call Center. Engine Power Plant Sales Dep t Tel : 86)
 http://www.soarpower.com http://www.soarpower.com H35/40G(V) Copyright 2014 Hyundai Heavey Industries Engine Power Plant Sales Dep t Tel : 86) 4006-690 588 E-mail : sale@soar.hk 24/7 Call Center 9 +8-4008111308
http://www.soarpower.com http://www.soarpower.com H35/40G(V) Copyright 2014 Hyundai Heavey Industries Engine Power Plant Sales Dep t Tel : 86) 4006-690 588 E-mail : sale@soar.hk 24/7 Call Center 9 +8-4008111308
H35/40G(V) HHI-EMD Korean-English 24/7 Call Center
 www.hhi.co.kr www.hyundai-engine.com MACHINERY www.hyundai-engine.com ENGINE & H35/40G(V) 1000, Bangeojinsunhwan-doro, Dong-gu, Ulsan, Korea Copyright 2014 Hyundai Heavey Industries Marine Engine & Machinery
www.hhi.co.kr www.hyundai-engine.com MACHINERY www.hyundai-engine.com ENGINE & H35/40G(V) 1000, Bangeojinsunhwan-doro, Dong-gu, Ulsan, Korea Copyright 2014 Hyundai Heavey Industries Marine Engine & Machinery
WÄRTSILÄ 46 TECHNOLOGY REVIEW
 WÄRTSILÄ 46 TECHNOLOGY REVIEW 2 WÄRTSILÄ 46 TECHNOLOGY REVIEW This is a summary of Wärtsilä s approach to design and technology in the Wärtsilä 46 engine. DESIGN PHILOSOPHY... 4 DEVELOPMENT POLICY... 4
WÄRTSILÄ 46 TECHNOLOGY REVIEW 2 WÄRTSILÄ 46 TECHNOLOGY REVIEW This is a summary of Wärtsilä s approach to design and technology in the Wärtsilä 46 engine. DESIGN PHILOSOPHY... 4 DEVELOPMENT POLICY... 4
WÄRTSILÄ 34SG ENGINE TECHNOLOGY
 WÄRTSILÄ 34SG ENGINE TECHNOLOGY 2 ENGINE TECHNOLOGY This is a brief guide to the technical features and performance of the Wärtsilä 34SG engine. DESIGN PHILOSOPHY... 4 THE LEAN-BURN CONCEPT... 6 LOW EMISSIONS...
WÄRTSILÄ 34SG ENGINE TECHNOLOGY 2 ENGINE TECHNOLOGY This is a brief guide to the technical features and performance of the Wärtsilä 34SG engine. DESIGN PHILOSOPHY... 4 THE LEAN-BURN CONCEPT... 6 LOW EMISSIONS...
Bergen liquid fuel engines Sustainable and affordable power systems
 Bergen liquid fuel engines Sustainable and affordable power systems B32:40 powerful and reliable Rolls-Royce has supplied liquid fuel oil-burning engines for power generation and mechanical drive applications
Bergen liquid fuel engines Sustainable and affordable power systems B32:40 powerful and reliable Rolls-Royce has supplied liquid fuel oil-burning engines for power generation and mechanical drive applications
Bergen liquid fuel engines Sustainable and affordable power systems
 Bergen liquid fuel engines Sustainable and affordable power systems B32:40 powerful and reliable Rolls-Royce has supplied liquid fuel oil-burning engines for power generation and mechanical drive applications
Bergen liquid fuel engines Sustainable and affordable power systems B32:40 powerful and reliable Rolls-Royce has supplied liquid fuel oil-burning engines for power generation and mechanical drive applications
THE MOST EFFICIENT ENGINE IN THE WORLD. Risto Lejon, Product Management, Wärtsilä 31 Wärtsilä Marine Solutions, Business Line Engines 2017
 THE MOST EFFICIENT ENGINE IN THE WORLD Risto Lejon, Product Management, Wärtsilä 31 Wärtsilä Marine Solutions, Business Line Engines 2017 WHAT HAS BEEN THE DRIVERS FOR THIS ENGINE DEVELOPMENT ENERGY EFFICIENCY
THE MOST EFFICIENT ENGINE IN THE WORLD Risto Lejon, Product Management, Wärtsilä 31 Wärtsilä Marine Solutions, Business Line Engines 2017 WHAT HAS BEEN THE DRIVERS FOR THIS ENGINE DEVELOPMENT ENERGY EFFICIENCY
CONVENTIONAL ENGINE CONSTRUCTION
 CONVENTIONAL ENGINE CONSTRUCTION CYLINDER BLOCKS, HEADS, AND CRANKCASES The cylinder, or the engine block, is the basic foundation of virtually all liquid-cooled engines. The block is a solid casting made
CONVENTIONAL ENGINE CONSTRUCTION CYLINDER BLOCKS, HEADS, AND CRANKCASES The cylinder, or the engine block, is the basic foundation of virtually all liquid-cooled engines. The block is a solid casting made
Engine Services UD30 DIESEL ENGINE NEW COMBUSTION
 Engine Services UD30 DIESEL ENGINE NEW COMBUSTION UD30 V12 M4 ud30 diesel engine Reliable - Compact - Economical Source of power for applications: marine power plant railway industrial 1 MAIN TECHNICAL
Engine Services UD30 DIESEL ENGINE NEW COMBUSTION UD30 V12 M4 ud30 diesel engine Reliable - Compact - Economical Source of power for applications: marine power plant railway industrial 1 MAIN TECHNICAL
NZQA unit standard version 5 Page 1 of 6. Demonstrate knowledge of engine design factors and machining practices
 Page 1 of 6 Title Demonstrate knowledge of engine design factors and machining practices Level 4 Credits 20 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to demonstrate knowledge of engine design
Page 1 of 6 Title Demonstrate knowledge of engine design factors and machining practices Level 4 Credits 20 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to demonstrate knowledge of engine design
MAN B&W ME Engine Description. Page 1 of 6. Frame Box
 ME Engine Description Page 1 of 6 Please note that engines built by our licensees are in accordance with MAN Diesel & Turbo drawings and standards but, in certain cases, some local standards may be applied;
ME Engine Description Page 1 of 6 Please note that engines built by our licensees are in accordance with MAN Diesel & Turbo drawings and standards but, in certain cases, some local standards may be applied;
Handout Activity: HA170
 Basic diesel engine components Handout Activity: HA170 HA170-2 Basic diesel engine components Diesel engine parts are usually heavier or more rugged than those of similar output gasoline engines. Their
Basic diesel engine components Handout Activity: HA170 HA170-2 Basic diesel engine components Diesel engine parts are usually heavier or more rugged than those of similar output gasoline engines. Their
GE Marine. Seaworthy power. GE s new L250 inline diesel engine. imagination at work
 GE Marine Seaworthy power GE s new L250 inline diesel engine imagination at work GE s L250 Built by one of the world s largest manufacturers of medium-speed diesel engines Designed to save fuel and meet
GE Marine Seaworthy power GE s new L250 inline diesel engine imagination at work GE s L250 Built by one of the world s largest manufacturers of medium-speed diesel engines Designed to save fuel and meet
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES
 ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
R&D on Environment-Friendly, Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine
 20000 M4.2.2 R&D on Environment-Friendly, Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine (Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine Group) Nobuyasu Matsudaira, Koji Imoto, Hiroshi Morimoto, Akira Numata, Toshimitsu
20000 M4.2.2 R&D on Environment-Friendly, Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine (Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine Group) Nobuyasu Matsudaira, Koji Imoto, Hiroshi Morimoto, Akira Numata, Toshimitsu
 Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Page 1 of 9 303-01C Engine 6.0L Diesel 2004 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Procedure revision date: 08/06/2003 Engine Printable View Engine Description The 6.0L diesel engine
Name Date. True-False. Multiple Choice
 Name Date True-False T F 1. Oil film thickness increases with an increase in oil temperature. T F 2. Displacement is the volume that a piston displaces in an engine when it travels from top dead center
Name Date True-False T F 1. Oil film thickness increases with an increase in oil temperature. T F 2. Displacement is the volume that a piston displaces in an engine when it travels from top dead center
MAN Energy Solutions
 ME Engine Description Page 1 of 6 Please note that engines built by our licensees are in accordance with drawings and standards but, in certain cases, some local standards may be applied; however, all
ME Engine Description Page 1 of 6 Please note that engines built by our licensees are in accordance with drawings and standards but, in certain cases, some local standards may be applied; however, all
51/60G. Four-stroke gas engine
 51/60G Four-stroke gas engine MAN Diesel & Turbo is the world s leading designer and manufacturer of low and medium speed engines. Our involvement with electrical power generators goes back to 1904 when
51/60G Four-stroke gas engine MAN Diesel & Turbo is the world s leading designer and manufacturer of low and medium speed engines. Our involvement with electrical power generators goes back to 1904 when
SECTION D Engine 6.0L Diesel
 303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
303-01D-i Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-i SECTION 303-01D Engine 6.0L Diesel CONTENTS PAGE DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine... 303-01D-2 303-01D-2 Engine 6.0L Diesel 303-01D-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Engine
Pete Jacobs. Business Development Manager Wartsila North America, Inc. (281)
 Pete Jacobs Business Development Manager Wartsila North America, Inc. (281) 513-9836 Pete.Jacobs@wartsila.com Uniform and Integrated Solution Engines Propulsion Automation Power Distribution Power Drives
Pete Jacobs Business Development Manager Wartsila North America, Inc. (281) 513-9836 Pete.Jacobs@wartsila.com Uniform and Integrated Solution Engines Propulsion Automation Power Distribution Power Drives
2013. The engine for agricultural equipment kw at 2100 rpm
 2013. The engine for agricultural equipment. 81-118 kw at 2100 rpm... These are the characteristics of the 2013: Modern water-cooled 6-cylinder in-line engines. Turbocharging and turbocharging with charge
2013. The engine for agricultural equipment. 81-118 kw at 2100 rpm... These are the characteristics of the 2013: Modern water-cooled 6-cylinder in-line engines. Turbocharging and turbocharging with charge
Diesel Technology: Engines
 Diesel Technology: Engines NATEF Crosswalk The following NATEF Diesel Engines tasks (rev. 2004) are covered in this publication. The chart shows where each task is located within the publication. The first
Diesel Technology: Engines NATEF Crosswalk The following NATEF Diesel Engines tasks (rev. 2004) are covered in this publication. The chart shows where each task is located within the publication. The first
Scania at INTERMAT 2009: New engine range meets 2011 emission standards
 PRESS info P09101EN / Kristina Axelson 16 January 2009 Scania at INTERMAT 2009: New engine range meets 2011 emission standards Scania launches a range of engines that complies with the Stage IIIB and Tier
PRESS info P09101EN / Kristina Axelson 16 January 2009 Scania at INTERMAT 2009: New engine range meets 2011 emission standards Scania launches a range of engines that complies with the Stage IIIB and Tier
1013ec. The engine for construction equipment.
 1013ec. The engine for construction equipment. 92-235 kw at 2000-2300 rpm Engines with conventional cooling system. These are the characteristics of the 1013ec: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
1013ec. The engine for construction equipment. 92-235 kw at 2000-2300 rpm Engines with conventional cooling system. These are the characteristics of the 1013ec: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
Technology Review. Introduction 4. Development background 6. Exhaust emissions 7. Real in-service fuel economy 8. Piston-running behaviour 10
 Technology review 2 Technology Review This is a brief guide to the technical features and benefits of the Sulzer RTA84T-B and RTA84T-D low-speed marine diesel engines, herein collectively called Sulzer
Technology review 2 Technology Review This is a brief guide to the technical features and benefits of the Sulzer RTA84T-B and RTA84T-D low-speed marine diesel engines, herein collectively called Sulzer
PRESS info. Scania at ConExpo-Con/Agg 2011 Scania engines ready for Tier 4 final, Tier 4i and Stage IIIB compliant
 PRESS info P11302EN / Ann-Helen Tolleman March 2011 Scania at ConExpo-Con/Agg 2011 Scania engines ready for Tier 4 final, Tier 4i and Stage IIIB compliant Scania s range of industrial engines is compliant
PRESS info P11302EN / Ann-Helen Tolleman March 2011 Scania at ConExpo-Con/Agg 2011 Scania engines ready for Tier 4 final, Tier 4i and Stage IIIB compliant Scania s range of industrial engines is compliant
1 Name any 5stationary parts and moving partsof a large 2-stroke diesel engine?
 2 Marks question Bank for ME 802 General & Motor 1 Name any 5stationary parts and moving partsof a large 2-stroke diesel engine? 2 Why in certain engine the bottom half of crosshead bearing is of single
2 Marks question Bank for ME 802 General & Motor 1 Name any 5stationary parts and moving partsof a large 2-stroke diesel engine? 2 Why in certain engine the bottom half of crosshead bearing is of single
SNS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY (An Autonomous Institution) Department of Automobile Engineering
 SNS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY (An Autonomous Institution) Department of Automobile Engineering ACADEMIC YEAR 2015-16 FIFTH SEMESTER AU 302 AUTOMOTIVE ENGINE COMPONENTS DESIGN UNIT 2 CYLINDER, PISTON & CONNECTING
SNS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY (An Autonomous Institution) Department of Automobile Engineering ACADEMIC YEAR 2015-16 FIFTH SEMESTER AU 302 AUTOMOTIVE ENGINE COMPONENTS DESIGN UNIT 2 CYLINDER, PISTON & CONNECTING
HANS JENSEN LUBRICATORS A/S
 HANS JENSEN LUBRICATORS A/S Case study Cylinder oil consumption on Sulzer RT-flex engines Example of reduction in cylinder oil consumption on: Sulzer 7RT-flex68-B & Sulzer 12RT-flex96C Innovation through
HANS JENSEN LUBRICATORS A/S Case study Cylinder oil consumption on Sulzer RT-flex engines Example of reduction in cylinder oil consumption on: Sulzer 7RT-flex68-B & Sulzer 12RT-flex96C Innovation through
ENVIRONMENT. The Diesel Engine and the Environment
 ENVIRONMENT The Diesel Engine and the Environment David Steffens Wartsila North America, Inc. Session Chair Wayne Cole, Cole Engineering September 16-17, 2003 Houston, Texas Introduction The diesel engine
ENVIRONMENT The Diesel Engine and the Environment David Steffens Wartsila North America, Inc. Session Chair Wayne Cole, Cole Engineering September 16-17, 2003 Houston, Texas Introduction The diesel engine
1012. The engine for construction equipment kw at min -1
 1012. The engine for construction equipment. 41-123 kw at 1500-2500 min -1... Engines with integrated cooling system These are the characteristics of the 1012: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
1012. The engine for construction equipment. 41-123 kw at 1500-2500 min -1... Engines with integrated cooling system These are the characteristics of the 1012: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
Module 13: Mechanical Fuel Injection Diagnosis and Repair
 Terms and Definitions Parts of Injection Nozzles Types of Nozzle Valves Operation of an Injection Nozzle Fuel Flow Through the Unit Injector Optional Features on Fuel Injection Pumps Main Parts of a Distributor-Type
Terms and Definitions Parts of Injection Nozzles Types of Nozzle Valves Operation of an Injection Nozzle Fuel Flow Through the Unit Injector Optional Features on Fuel Injection Pumps Main Parts of a Distributor-Type
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
 UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
PRESSRELEASE. Technical Information. Optimization focus: Engine mechanics. Less friction in the engine reduces fuel consumption
 PRESSRELEASE Technical Information Optimization focus: Engine mechanics Less friction in the engine reduces fuel consumption Stuttgart/Germany, September 2009 In the combustion engine, an important engineering
PRESSRELEASE Technical Information Optimization focus: Engine mechanics Less friction in the engine reduces fuel consumption Stuttgart/Germany, September 2009 In the combustion engine, an important engineering
SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL
 IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
4 Stroke Diesel. Oil type SAE 15 W40/E 3
 MARCH 2006 TECHNICAL DATA 2.33 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS Cycle Air supply Injection 4 Stroke Diesel naturally aspirated direct Number of cylinders 4 in line 6 in line Bore mm 104 Stroke mm 132 Total displacement
MARCH 2006 TECHNICAL DATA 2.33 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS Cycle Air supply Injection 4 Stroke Diesel naturally aspirated direct Number of cylinders 4 in line 6 in line Bore mm 104 Stroke mm 132 Total displacement
1013. The engine for construction equipment.
 1013. The engine for construction equipment.... 63-190 kw at 1500-2300 min -1 Engines with integrated cooling system These are the characteristics of the 1013: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
1013. The engine for construction equipment.... 63-190 kw at 1500-2300 min -1 Engines with integrated cooling system These are the characteristics of the 1013: Modern water-cooled 4- and 6-cylinder in-line
Scania at INTERMAT 2012 in Paris: Scania engines ready for Stage IV and Tier 4 final
 PRESS info P12401EN / Ann-Helen Tolleman April 2012 Scania at INTERMAT 2012 in Paris: Scania engines ready for Stage IV and Tier 4 final Scania industrial engines will manage Stage IV and Tier 4 final
PRESS info P12401EN / Ann-Helen Tolleman April 2012 Scania at INTERMAT 2012 in Paris: Scania engines ready for Stage IV and Tier 4 final Scania industrial engines will manage Stage IV and Tier 4 final
Technological breakthrough for Scania: Euro 5 without aftertreatment or fuel penalty
 PRESS info P07901EN / Per-Erik Nordström 5 September 2007 Technological breakthrough for Scania: Euro 5 without aftertreatment or fuel penalty As the first heavy vehicle manufacturer, Scania achieves Euro
PRESS info P07901EN / Per-Erik Nordström 5 September 2007 Technological breakthrough for Scania: Euro 5 without aftertreatment or fuel penalty As the first heavy vehicle manufacturer, Scania achieves Euro
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting
 Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting 3176C and 3196 Engines for Caterpillar Built Machines S/N: 4SS00001-UP (Excavators 345B) S/N: 7ZR01004 (ENGINE) Use the bookmarks for navigation inside of the manual
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 13 & 14 Pages Engine Construction 52 Points
 Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 13 & 14 Pages 182-216 Engine Construction 52 Points Automotive Service 1. The engine top end includes the cylinder, valve cover and intake & exhaust. Head, Manifolds
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 13 & 14 Pages 182-216 Engine Construction 52 Points Automotive Service 1. The engine top end includes the cylinder, valve cover and intake & exhaust. Head, Manifolds
Ship Power Systems edition
 Ship Power Systems 2005 2. edition 2 Wärtsilä offers the most effective solutions to all marine power and propulsion needs, supported by being the most responsive and efficient partner from first concepts
Ship Power Systems 2005 2. edition 2 Wärtsilä offers the most effective solutions to all marine power and propulsion needs, supported by being the most responsive and efficient partner from first concepts
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, August 2003
 9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, 24. 28. August 2003 Recent Developments in BMW s Diesel Technology Fritz Steinparzer, BMW Motoren, Austria 1. Introduction The image
9 th Diesel Engine Emission Reduction Conference Newport, Rhode Island, 24. 28. August 2003 Recent Developments in BMW s Diesel Technology Fritz Steinparzer, BMW Motoren, Austria 1. Introduction The image
Reducing emissions using 2-stage turbo charging
 WÄRTSILÄ TECHNICAL JOURNAL 1. Reducing emissions using -stage turbo charging AUTHORS: Christer Wik, Engine Performance Technologies, Wärtsilä Global R&D and Björn Hallbäck, Engine Performance Technologies
WÄRTSILÄ TECHNICAL JOURNAL 1. Reducing emissions using -stage turbo charging AUTHORS: Christer Wik, Engine Performance Technologies, Wärtsilä Global R&D and Björn Hallbäck, Engine Performance Technologies
Technical Specification
 Technical Specification including performance data Project 3 x 9CM25 rev 2. consisting of 3 Caterpillar Diesel Generator sets Type 9CM25 with site output of: 2475 bkw at each engine flywheel rated 750
Technical Specification including performance data Project 3 x 9CM25 rev 2. consisting of 3 Caterpillar Diesel Generator sets Type 9CM25 with site output of: 2475 bkw at each engine flywheel rated 750
Powertrain Efficiency Technologies. Turbochargers
 Powertrain Efficiency Technologies Turbochargers Turbochargers increasingly are being used by automakers to make it possible to use downsized gasoline engines that consume less fuel but still deliver the
Powertrain Efficiency Technologies Turbochargers Turbochargers increasingly are being used by automakers to make it possible to use downsized gasoline engines that consume less fuel but still deliver the
REDESIGNED MODULES FOR THE SECTOR AUTOMOBILE UNDER MODULAR EMPLOYABLE SKILLS (MES)
 REDESIGNED MODULES FOR THE SECTOR OF AUTOMOBILE UNDER MODULAR EMPLOYABLE SKILLS (MES) Redesigned in - 2014 By Government of India Directorate General of Employment & Training Ministry of Labour & Employment
REDESIGNED MODULES FOR THE SECTOR OF AUTOMOBILE UNDER MODULAR EMPLOYABLE SKILLS (MES) Redesigned in - 2014 By Government of India Directorate General of Employment & Training Ministry of Labour & Employment
The Construction Equipment Engine kw hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim
 The Construction Equipment Engine 50 85 kw 67 114 hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim Starting January 2011, diesel engines of mobile construction machines with power classes ranging
The Construction Equipment Engine 50 85 kw 67 114 hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim Starting January 2011, diesel engines of mobile construction machines with power classes ranging
Copyright by WÄRTSILÄ FINLAND Oy
 Copyright by WÄRTSILÄ FINLAND Oy All rights reserved. No part of this booklet may be reproduced or copied in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, graphic, photocopying, recording, taping or
Copyright by WÄRTSILÄ FINLAND Oy All rights reserved. No part of this booklet may be reproduced or copied in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, graphic, photocopying, recording, taping or
Less Emissions Through Waste Heat Recovery
 Summary Less Emissions Through Waste Heat Recovery Heinrich Schmid Manager, Application Technology, Ship Power Wärtsilä Switzerland Ltd, Winterthur Current interest in reducing emissions and reducing engine
Summary Less Emissions Through Waste Heat Recovery Heinrich Schmid Manager, Application Technology, Ship Power Wärtsilä Switzerland Ltd, Winterthur Current interest in reducing emissions and reducing engine
MAN 51/60DF. Dual-fuel flexibility and reliability
 MAN 51/60DF Dual-fuel flexibility and reliability MAN Diesel & Turbo Powering the world responsibly MAN Diesel & Turbo is the world s leading provider of large-bore diesel engines and turbomachinery.
MAN 51/60DF Dual-fuel flexibility and reliability MAN Diesel & Turbo Powering the world responsibly MAN Diesel & Turbo is the world s leading provider of large-bore diesel engines and turbomachinery.
Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting
 M0064276 (en-us) December 2015 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 4008-30 Industrial Engine SD8 (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and
M0064276 (en-us) December 2015 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 4008-30 Industrial Engine SD8 (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and
Diesel Engine Fundamentals Part 1 Course# ME4061
 Diesel Engine Fundamentals Part 1 Course# ME4061 EZpdh.com All Rights Reserved Diesel Engine Fundamentals DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF FIGURES... ii LIST OF TABLES...
Diesel Engine Fundamentals Part 1 Course# ME4061 EZpdh.com All Rights Reserved Diesel Engine Fundamentals DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF FIGURES... ii LIST OF TABLES...
National Maritime Center
 National Maritime Center Providing Credentials to Mariners U.S.C.G. Merchant Marine Exam (Sample Examination) Page 1 of 20 U.S.C.G. Merchant Marine Exam Illustrations: 9 Choose the best answer to the following
National Maritime Center Providing Credentials to Mariners U.S.C.G. Merchant Marine Exam (Sample Examination) Page 1 of 20 U.S.C.G. Merchant Marine Exam Illustrations: 9 Choose the best answer to the following
SPECIFICATIONS TEST AND ADJUSTMENT SPECIFICATIONS SPECIFICATIONS ENGINE FD620D, K SERIES
 ENGINE FD620D, K SERIES SPECIFICATIONS SPECIFICATIONS TEST AND ADJUSTMENT SPECIFICATIONS Engine Oil Pressure Sensor Activates............................... 98 kpa (14.2 psi) Oil Pressure While Cranking
ENGINE FD620D, K SERIES SPECIFICATIONS SPECIFICATIONS TEST AND ADJUSTMENT SPECIFICATIONS Engine Oil Pressure Sensor Activates............................... 98 kpa (14.2 psi) Oil Pressure While Cranking
Engine for Industrial Applications kw hp at 2200 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim
 Engine for Industrial Applications 160-250 kw 214-335 hp at 2200 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim Modern, water-cooled 6-cyclinder in-line engine Turbocharged with intercooler (air/air),
Engine for Industrial Applications 160-250 kw 214-335 hp at 2200 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim Modern, water-cooled 6-cyclinder in-line engine Turbocharged with intercooler (air/air),
NUMBER: S.M. REF.: Refer to 2.5 ENGINE: 60 DATE: January 2007
 NUMBER: 1 60 07 S.M. REF.: Refer to 2.5 ENGINE: 60 DATE: January 2007 SUBJECT: N3 ELECTRONIC INJECTOR PUBLICATION: 6SE483 The Series 60 Service Manual has been revised. Engine models built from December
NUMBER: 1 60 07 S.M. REF.: Refer to 2.5 ENGINE: 60 DATE: January 2007 SUBJECT: N3 ELECTRONIC INJECTOR PUBLICATION: 6SE483 The Series 60 Service Manual has been revised. Engine models built from December
Air Management System Components
 AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
Engine Systems. Basic Engine Operation. Firing Order. Four Stroke Cycle. Overhead Valves - OHV. Engine Design. AUMT Engine Systems 4/4/11
 Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting
 KENR6931 May 2007 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 1106C Genset PK (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and repair are caused by failure
KENR6931 May 2007 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 1106C Genset PK (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and repair are caused by failure
CREATING POWER SOLUTIONS. 4H50TIC The new generation. Hatz Diesel Engines Made in Germany.
 CREATING POWER SOLUTIONS. 4H50TIC The new generation Hatz Diesel Engines Made in Germany EN www.hatz-diesel.com The new generation of water-cooled Hatz diesel engines From 2014 a new engine family will
CREATING POWER SOLUTIONS. 4H50TIC The new generation Hatz Diesel Engines Made in Germany EN www.hatz-diesel.com The new generation of water-cooled Hatz diesel engines From 2014 a new engine family will
SPECIFICATIONS TEST AND ADJUSTMENT SPECIFICATIONS SPECIFICATIONS ENGINE FD620D, K SERIES
 TEST AND ADJUSTMENT Engine Oil Pressure Sensor Activates............................... 98 kpa (14.2 psi) Oil Pressure While Cranking (Minimum).......................... 28 kpa (4 psi) Oil Pressure.....................................
TEST AND ADJUSTMENT Engine Oil Pressure Sensor Activates............................... 98 kpa (14.2 psi) Oil Pressure While Cranking (Minimum).......................... 28 kpa (4 psi) Oil Pressure.....................................
Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 250 34 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D13F Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 12.2006 250 34 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D13F Intake and Exhaust System, Design and Function
The engine company. The Engine for Construction Equipment ,9 kw hp at rpm
 The engine company. The Engine for Construction Equipment. 23 74,9 kw 31 100 hp at 1600 2800 rpm Engine description Type of cooling: Crankcase: Crankcase breather: Cylinder head: Valve arrangement/ Timing:
The engine company. The Engine for Construction Equipment. 23 74,9 kw 31 100 hp at 1600 2800 rpm Engine description Type of cooling: Crankcase: Crankcase breather: Cylinder head: Valve arrangement/ Timing:
Internal Combustion Engine
 Internal Combustion Engine The development of the internal combustion engine was made possible by the earlier development of the STEAM ENGINE. Both types of engines burn fuel, releasing energy from it
Internal Combustion Engine The development of the internal combustion engine was made possible by the earlier development of the STEAM ENGINE. Both types of engines burn fuel, releasing energy from it
6 cylinder turbocharged diesel engines for industrial applications
 Perkins 2800 Models 2806C-E16 WORKSHOP MANUAL 6 cylinder turbocharged diesel engines for industrial applications Publication TSD3450E, Issue 1 Proprietary information of Perkins Engines Company Limited,
Perkins 2800 Models 2806C-E16 WORKSHOP MANUAL 6 cylinder turbocharged diesel engines for industrial applications Publication TSD3450E, Issue 1 Proprietary information of Perkins Engines Company Limited,
Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1-3 ENGINE CLASSIFICATIONS Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition 1 (a) Spark Ignition (SI). An SI engine starts the combustion
Chapter 1 Introduction 1-3 ENGINE CLASSIFICATIONS Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition 1 (a) Spark Ignition (SI). An SI engine starts the combustion
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) Maybach Engine M285
 512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
Slow Steaming. Benefiting retrofit solutions from MAN PrimeServ
 Slow Steaming Benefiting retrofit solutions from MAN PrimeServ 2 Slow Steaming Slow Steaming Introduction Out of the total operational costs of a ship, fuel costs account for by far the highest proportion.
Slow Steaming Benefiting retrofit solutions from MAN PrimeServ 2 Slow Steaming Slow Steaming Introduction Out of the total operational costs of a ship, fuel costs account for by far the highest proportion.
Power Generation Stability and Response in DP Applications An Overview of Modern Diesel Engine Performance
 DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE September 16-17, 2003 Power Session Power Generation Stability and Response in DP Applications An Overview of Modern Diesel Engine Performance Magnus Miemois Wärtsilä Finland
DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE September 16-17, 2003 Power Session Power Generation Stability and Response in DP Applications An Overview of Modern Diesel Engine Performance Magnus Miemois Wärtsilä Finland
Wärtsilä 46F PRODUCT GUIDE
 Wärtsilä 46F PRODUCT GUIDE Copyright by WÄRTSILÄ FINLAND Oy All rights reserved. No part of this booklet may be reproduced or copied in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, graphic, photocopying,
Wärtsilä 46F PRODUCT GUIDE Copyright by WÄRTSILÄ FINLAND Oy All rights reserved. No part of this booklet may be reproduced or copied in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, graphic, photocopying,
Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly January Removal of the Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly
 1 18-13 1 1 18-13 SUBJECT DATE Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly January 2013 Additions, Revisions, or Updates Publication Number / Title Platform Section Title Change Removal of the Piston and Connecting
1 18-13 1 1 18-13 SUBJECT DATE Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly January 2013 Additions, Revisions, or Updates Publication Number / Title Platform Section Title Change Removal of the Piston and Connecting
Engine for Industrial Applications kw hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim
 Engine for Industrial Applications 28-55.9 kw 38-75 hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim 4 cylinder in-line engines turbocharged, with or without charge air cooler Water-cooled
Engine for Industrial Applications 28-55.9 kw 38-75 hp at 2600 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim 4 cylinder in-line engines turbocharged, with or without charge air cooler Water-cooled
1.2 For the purpose of this UR, the following definitions apply: Low-Speed Engines means diesel engines having a rated speed of less than 300 rpm.
 (Feb 2015) (Corr.1 June 2016) Type Testing of I.C. Engines 1. General 1.1 Type approval of I.C. engine types consists of drawing approval, specification approval, conformity of production, approval of
(Feb 2015) (Corr.1 June 2016) Type Testing of I.C. Engines 1. General 1.1 Type approval of I.C. engine types consists of drawing approval, specification approval, conformity of production, approval of
Auramarine fuel supply units PIONEERING FUEL SUPPLY SOLUTIONS FOR POWER INDUSTRY
 Auramarine fuel supply units PIONEERING FUEL SUPPLY SOLUTIONS FOR POWER INDUSTRY Critical roles in power plant performance Power plants are an essential asset of today s global infrastructures, generating
Auramarine fuel supply units PIONEERING FUEL SUPPLY SOLUTIONS FOR POWER INDUSTRY Critical roles in power plant performance Power plants are an essential asset of today s global infrastructures, generating
Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly August Removal of the Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly
 1 8 17-13 SUBJECT DATE Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly August 2013 Additions, Revisions, or Updates Publication Number / Title Platform Section Title Change Removal of the Piston DDC-SVC-MAN-0081 DD
1 8 17-13 SUBJECT DATE Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly August 2013 Additions, Revisions, or Updates Publication Number / Title Platform Section Title Change Removal of the Piston DDC-SVC-MAN-0081 DD
Crankcase scavenging.
 Software for engine simulation and optimization www.diesel-rk.bmstu.ru The full cycle thermodynamic engine simulation software DIESEL-RK is designed for simulating and optimizing working processes of two-
Software for engine simulation and optimization www.diesel-rk.bmstu.ru The full cycle thermodynamic engine simulation software DIESEL-RK is designed for simulating and optimizing working processes of two-
Bunker Summit Greece. Monique Vermeire Athens. 10 May, 2007
 Bunker Summit Greece Monique Vermeire Athens 10 May, 2007 Chevron 2005 Efficient engine operation in a world of changing fuel oil quality Driving factors influencing today s and future fuel oil quality
Bunker Summit Greece Monique Vermeire Athens 10 May, 2007 Chevron 2005 Efficient engine operation in a world of changing fuel oil quality Driving factors influencing today s and future fuel oil quality
Essential Wear Parts. MAN PrimeServ
 MAN PrimeServ 2 Introduction Certain spare parts for the two-stroke engine are considered to be Essential Wear Parts as they are key components that have a critical effect on the performance of the engine.
MAN PrimeServ 2 Introduction Certain spare parts for the two-stroke engine are considered to be Essential Wear Parts as they are key components that have a critical effect on the performance of the engine.
The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle
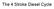 The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle Nickolaus Otto invented the 4 stroke cycle in 1862. More details of how the four stroke spark ignition cycle works, together with pictures of Otto's first engines can be found
The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle Nickolaus Otto invented the 4 stroke cycle in 1862. More details of how the four stroke spark ignition cycle works, together with pictures of Otto's first engines can be found
A technology factsheet on Volvo Cars T8 Twin Engine AWD powertrain technology ELECTRIFICATION CLEAN EFFICIENCY RESPONSIVE POWER
 A technology factsheet on Volvo Cars T8 Twin Engine AWD powertrain technology ELECTRIFICATION CLEAN EFFICIENCY RESPONSIVE POWER Contents Twin Engine (PHEV) Technology 3 - Introducing Twin Engine Technology
A technology factsheet on Volvo Cars T8 Twin Engine AWD powertrain technology ELECTRIFICATION CLEAN EFFICIENCY RESPONSIVE POWER Contents Twin Engine (PHEV) Technology 3 - Introducing Twin Engine Technology
MAINTENANCE STANDARDS TABLE
 TABLE 4 MAINTENANCE STANDARDS TABLE Unit: mm [in.] ( Maximum rpm, (no-load) Minimum rpm, (no-load) According to engine specification Adjust governor setting. Compression pressure MPa (kgf/cm 2 ) [psi]
TABLE 4 MAINTENANCE STANDARDS TABLE Unit: mm [in.] ( Maximum rpm, (no-load) Minimum rpm, (no-load) According to engine specification Adjust governor setting. Compression pressure MPa (kgf/cm 2 ) [psi]
GAS/PETROL THE ALTERNATIVE: ENGINES LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER AND MORE COMPACT ENVIRONMENTALLY FRIENDLY 22,0 6,6 431,1
 THE ALTERNATIVE: GAS/PETROL ENGINES MARINE ENERGY INDUSTRY GAS/PETROL ENGINES BY FORD 22,0 6,6 AUTOMOTIVE OEM COMPONENTS CLASSIC 7,1 SERVICE PARTS LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER
THE ALTERNATIVE: GAS/PETROL ENGINES MARINE ENERGY INDUSTRY GAS/PETROL ENGINES BY FORD 22,0 6,6 AUTOMOTIVE OEM COMPONENTS CLASSIC 7,1 SERVICE PARTS LOWER COST OF PURCHASE AFFORDABLE MAINTENANCE LIGHTER
MAN-B&W 6S70 ME-C diesel engines concept, specifics of maintenance and repair in service.
 MAN-B&W 6S70 ME-C diesel engines concept, specifics of maintenance and repair in service. Subject presentation will briefly include the following: General concept and advantages of ME-C towards other MC-/ME-B
MAN-B&W 6S70 ME-C diesel engines concept, specifics of maintenance and repair in service. Subject presentation will briefly include the following: General concept and advantages of ME-C towards other MC-/ME-B
2. Turbocharger System
 INTAKE (INDUCTION) 2. Turbocharger System A: GENERAL The turbocharger system consists of a water-cooled turbocharger, air-cooled intercooler, wastegate control solenoid valve, etc. The turbine rotated
INTAKE (INDUCTION) 2. Turbocharger System A: GENERAL The turbocharger system consists of a water-cooled turbocharger, air-cooled intercooler, wastegate control solenoid valve, etc. The turbine rotated
Reliability in detail: technology highlights of the new MAN D3876 engine
 Reliability in detail: technology highlights of the new MAN D3876 engine Up to 640 HP and 3000 Newton metres from 15.2 litres Full torque from 930 rpm New design concepts in the cylinder head, cooling
Reliability in detail: technology highlights of the new MAN D3876 engine Up to 640 HP and 3000 Newton metres from 15.2 litres Full torque from 930 rpm New design concepts in the cylinder head, cooling
DISASSEMBLED VIEWS. Disassembled Views. Engine Covers and Component Assemblies (1 of 2) (LF1, LFW or LFX)
 2012 Cadillac CTS Wagon AWD V6-3.0L Vehicle > Engine, Cooling and Exhaust > Engine > Locations > Components DISASSEMBLED VIEWS Disassembled Views Engine Covers and Component Assemblies (1 of 2) (LF1, LFW
2012 Cadillac CTS Wagon AWD V6-3.0L Vehicle > Engine, Cooling and Exhaust > Engine > Locations > Components DISASSEMBLED VIEWS Disassembled Views Engine Covers and Component Assemblies (1 of 2) (LF1, LFW
Bi-Fuel Conversion for High Speed Diesel Engins
 Bi-Fuel Conversion for High Speed Diesel Engins Introduction The bi-fuel system modifies standard heavy-duty diesel engines to operate on diesel and gas simultaneously. The gas is used as main fuel and
Bi-Fuel Conversion for High Speed Diesel Engins Introduction The bi-fuel system modifies standard heavy-duty diesel engines to operate on diesel and gas simultaneously. The gas is used as main fuel and
The Construction Equipment Engine kw hp at 2100 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim
 The Construction Equipment Engine 300 520 kw 402 697 hp at 2100 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim Starting January 2011, diesel engines of mobile construction machines with power classes
The Construction Equipment Engine 300 520 kw 402 697 hp at 2100 min -1 rpm EU Stage III B / US EPA Tier 4 interim Starting January 2011, diesel engines of mobile construction machines with power classes
PAPER NO.: 221 Development of Electronically Controlled Engine Mitsubishi UEC Eco-Engine
 CONSEIL INTERNATIONAL DES MACHINES A COMBUSTION INTERNATIONAL COUNCIL ON COMBUSTION ENGINES PAPER NO.: 221 Development of Electronically Controlled Engine Mitsubishi UEC Eco-Engine Katsuhiko Sakaguchi,
CONSEIL INTERNATIONAL DES MACHINES A COMBUSTION INTERNATIONAL COUNCIL ON COMBUSTION ENGINES PAPER NO.: 221 Development of Electronically Controlled Engine Mitsubishi UEC Eco-Engine Katsuhiko Sakaguchi,
MAN 175D. 100 % Marine. 100 % High Speed.
 MAN 175D 100 % Marine. 100 % High Speed. 2 3 Ever since we steered the marine industry out of the steam age, MAN has been setting the standard for diesel engines. It s a history of undisputed reliability,
MAN 175D 100 % Marine. 100 % High Speed. 2 3 Ever since we steered the marine industry out of the steam age, MAN has been setting the standard for diesel engines. It s a history of undisputed reliability,
AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER
 AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER The Carter Model YH carbureter may be compared with a Carter YF downdraft carbureter with the circuits rearranged to operate
AN EXPLANATION OF CIRCUITS CARTER YH HORIZONTAL CLIMATIC CONTROL CARBURETER The Carter Model YH carbureter may be compared with a Carter YF downdraft carbureter with the circuits rearranged to operate
INTERNATIONAL A26. DISPLACEMENT HORSEPOWER TORQUE lb.-ft. 12.4L INTERNATIONAL A26 ENGINE
 INTERNATIONAL A26 DISPLACEMENT HORSEPOWER TORQUE lb.-ft. 12.4L 370-475 1350-1750 INTERNATIONAL A26 ENGINE PROJECT ALPHA BORN FROM A NEW WAY OF THINKING. HOW A DEDICATION TO UPTIME LED TO THE INTERNATIONAL
INTERNATIONAL A26 DISPLACEMENT HORSEPOWER TORQUE lb.-ft. 12.4L 370-475 1350-1750 INTERNATIONAL A26 ENGINE PROJECT ALPHA BORN FROM A NEW WAY OF THINKING. HOW A DEDICATION TO UPTIME LED TO THE INTERNATIONAL
Bronze Level Training
 Bronze Level Training Engine Principles of Operation While not everyone at the dealership needs to be a top rated service technician, it is good for all the employees to have a basic understanding of engine
Bronze Level Training Engine Principles of Operation While not everyone at the dealership needs to be a top rated service technician, it is good for all the employees to have a basic understanding of engine
This information covers the design and function of the intake and exhaust systems for the Volvo D16F engine.
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA Intake and Exhaust System DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 2.2007 250 35 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D16F W2005773 This
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA Intake and Exhaust System DService Bulletin Trucks Date Group No. Page 2.2007 250 35 1(6) Intake and Exhaust System Design and Function D16F W2005773 This
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS 2.1 INTRODUCTION 2.2 CLASSIFICATION OF IC ENGINES. Objectives. Structure. 2.1 Introduction
 UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
ENGINE 1ZZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION EG-1 ENGINE - 1ZZ-FE ENGINE
 EG-1 ENGINE - 1ZZ-FE ENGINE ENGINE 1ZZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-intelligent) system, the DIS (Direct Ignition System), and a plastic intake manifold have been used on the
EG-1 ENGINE - 1ZZ-FE ENGINE ENGINE 1ZZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-intelligent) system, the DIS (Direct Ignition System), and a plastic intake manifold have been used on the
