TOPIS: Seoul s Intelligent Traffic System (ITS)
|
|
|
- Amanda McDaniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TOPIS: Seoul s Intelligent Traffic System (ITS) Prepared by: Shin Lee 1 Seoul TOPIS (Seoul Transport Operation & Information Service) is an integrated traffic management center that operates and manages Seoul s traffic situation and collects traffic information from traffic-related organizations these include Bus Management System (BS), traffic card system, unmanned enforcement systems and traffic broadcasting, the National Policy Agency, and the Korea Expressway Corporation. Seoul TOPIS (Seoul Transport Operation and Information Services) refers to an integrated traffic center that plans, constructs, and operates Seoul s Intelligent Transport System (ITS). The Korean name can be literally translated as Seoul Traffic Information Center. However, the English name of Seoul TOPIS is more familiar to the public. The traffic information situation control room, which is an important part of Seoul TOPIS, is sometimes easily mistaken for the entire Seoul TOPIS. However, Seoul TOPIS actually refers to the intangible functional organization that manages Seoul city s ITS, which applies advanced IT to traffic, as a practical department of Seoul city composed of 4 divisions and 90 employees. Over its evolution of the past 15 years, Seoul TOPIS has come to obtain various functions and equipment. In 2015, the functions of Seoul TOPIS were systematized to launch a new platform. Its components include the six platforms of center platform (the traffic information control room), the bus platform (BIS/BS), the unmanned enforcement platform, the freeway traffic management system (FTMS), the advanced traffic management system (ATMS), and the big data platform (traffic predictions, information support). Seoul TOPIS continually collects a wide variety of traffic information: information such as highways and freeways, 9000 buses, current traffic situations from public traffic card systems, vehicle violations (parking and stopping, speeding, driving on bus lanes), and accidents. Then, based on these platforms, it analyzes the traffic demands or causes of traffic congestion and provides real-time traffic information required by traffic facility users and public transportation operation managers. With respect to unmanned enforcement, it has an automatic penalty management system that collectively manages the imposition and collection of penalties and bills. 1 Translation by ESL 1
2 With the use of advanced IT, detailed information on the massive Seoul traffic system can be collected in real-time and a remarkable amount of data can be gathered and analyzed by the one center of Seoul TOPIS. This is done to increase the accuracy of the information. Furthermore, by sharing such analysis results with private corporations and the people, it allows for the development of various derived information products. Ultimately, Seoul TOPIS works toward the goal of constructing a traffic system having maximized satisfaction by the users and enhanced safety of traffic users, as well as minimizing traffic congestion by optimizing the efficiency of existing traffic facilities. Figure 1: Seoul TOPIS Platform Seoul Traffic Information Division (2016) 1. Policy Implementation Period Here, a summary of the historical process for Seoul city s building of the current ITS system is provided. It was not planned and developed as a single system, but each part was gradually initiated based on the formation of the conditions and needs. Based on these individual experiences, the entire process and system was integrated and consequently reconstructed into six platforms. As a result, the temporary construction of each of the six platforms was possible in different geological and spatial contexts. Institution of Namsan region traffic management system (10.6km): 1998 Institution and expansion of he urban highway traffic management system: 2000 Inauguration of Seoul TOPIS (the situation control room) and introduction of traffic card system: 2004 Introduction of the unmanned enforcement system: 2005 Pilot installation and expansion of the bus information terminal (BIT): 2008 Launching mobile traffic information service: 2009 Traffic data open to the public: 2010 Introduction of Standard design (VMS, VDS) of the ITS facility 2
3 Launching combined (traffic + disaster + general affairs) urban management situation control room: 2013 Launching Seoul TOPIS platform (ITS Solution): 2015 Figure 2: History of Seoul TOPIS Source: Seoul Traffic Information Division (2016) 2. Background Information Before 2004 In the 1950s and 1960s, before Korea s economic development had officially begun, the traffic facilities and infrastructure in Seoul city were very weak. It was difficult even to catch buses and the roads had no traffic signals, which resulted in a dependency on hand signals. The surface car (also known as a streetcar or tram) constructed in the early 20th century was almost the only form of public transportation. In addition to the expansion of the city, the route network gradually extended. However, there were restrictions to handling the increasing number of users along with the rapid economic growth. In addition, with the remarkable increase in the use of motor vehicles and the introduction of buses, which allowed free movement, the surface car whose installation and expansion was a relatively difficult naturally began to decline. In 1968, the last route of the surface car was terminated. At the time of the termination of the surface car, Seoul s public transportation comprised of the surface car and buses, each of which transported half of the population. The official growth of Seoul began at this time, and it began to section and compartmentalizes itself by gradually constructing roads from the nearest regions from the heart of the city using buses as the main form of transportation. 3
4 Throughout the era of high speed urban growth after the 1970s, road construction was performed for the expansion of bus services and the infrastructure of Seoul s road systems was formed by constructing the Gangbyeonbuk-ro and Hangang bridges as a series of expanding the weak traffic facilities. Furthermore, in 1974, Seoul s subway era began along with the opening of subway line number 1. However, the continual increase in income of the Seoul citizens, due to the rapid industrialization, resulted in a surge in the use of vehicles. The increase in road transport facilities actually further caused increases in the operation of vehicles and this resulted in a lack of roads. At the time, therefore, there was no seemingly practical resolution of the road congestion. In a situation where the general role of public transportation was decreasing and the use of personal vehicle increasing, the status of the subway rose in comparison to buses in the public transportation market in early 2000s. This is not irrelevant to the institutional support of setting the subway as the main axis of Seoul transportation. However, due to the excessive use of vehicles, the level of road services declined, and the service competitiveness of buses, which depends on roads, weakened in relative terms. This then caused an outflow of users to other mode of transportation and the allocated rate of passengers on buses continually decreased from 30.1% in 1996 to 26% in 2002 (Seoul Statistics 2016). Figure 3: Trends of Allocated Passengers for each Method of Transportation Source: Seoul City 2004; The Seoul Institute
5 After 2004 Together with the notion that the supply of roads cannot resolve traffic problems, particularly the problem of traffic congestion, the public found the role of public transportation ever more important. Seoul needed to revitalize a bus industry which was visibly declining. There were several attempts by the city to partially improve the operation of buses. However, the extensive reformation of the public transportation system was finally conducted in The two main essence of this reformation are as follows: 1) The public transportation service was unified by combining the subway and bus systems in order to reinforce the competitiveness of public transportation. 2) The bus industry at the time was privatized, but a so-called semipublic bus management system was established to control the market price in areas of operation and management. This was determined as essential to meet the strategic goal of combining public transportation. In order to obtain competitiveness of public transportation, the qualitative of public transportation services needed to be enhanced. The central bus lane, smart traffic card, and the public transportation information system (BMS/BIS) were introduced as a part of the reformation inthe public transportation system, which all composed Seoul TOPIS. 3. The Importance of the Policy Seoul TOPIS is a management system that ties Seoul transportation with advanced technology and plays two significant roles in terms of traffic policy. The first significant role is that it grants competitiveness to public transportation by providing convenience and allows communication through bus lanes, smart traffic cards, and the public transportation information system. This greatly helps maintain the allocated number of passengers in public transportation at a consistent level. The second role is that a reasonable level of service throughout the entire road traffic system can be maintained by helping the communication of vehicles through various road management systems, automatic illegal parking control systems, and unexpected situation control systems. The result is a generally higher level of user satisfaction with no relation to the suitable allocation of passengers or method of transportation. 4. Relevance with Other Policies As displayed in the platform composition of Seoul TOPIS, the following policies provided as a part of the current manual series are each a platform that handles the operation of the real-time traffic system of Seoul TOPIS. 5
6 1) Bus information system (BMS/BIS) 2) Unmanned enforcement system 3) Freeway Traffic Management System (FTMS) 4) Advanced Traffic Management System (ATMS) 5. Policy Objectives The goal is to provide a forum for sharing an advanced traffic system or public transportation operation management and, from this, provide scientific traffic administrative support, real-time communication management and citizen traffic information services through the connection and combination of traffic information and traffic systems. As specific achievements, the following are to be achieved through optimized efficiency of the existing traffic facilities, including the roads. 1) Improved urban traffic speed by minimizing traffic congestion 2) Reduce traffic accidents 3) Reduction of negative effects arising from unexpected situations 4) Prediction of traffic situations and support of other traffic policies by analyzing traffic big data 5) Enhanced consumer satisfaction through punctuality of public transportation and the sharing of traffic information 6) Maximized road utilization through unmanned enforcement and contribution to the right parking cultrue 7) Enhanced profits based on the imposition of penalties and fines (Used for the construction of parking lots) 6. Main Policy Contents Seoul TOPIS is an integrated traffic center that plans, constructs, and operates the advanced traffic of Seoul city and is operated by 150 employees and 4 teams. The main functions of Seoul TOPIS can be largely categorized as follows: First, a wide variety of information from the urban highways and freeways is collected and analyzed through advanced IT devices. And then, real-time traffic surveillance and management on traffic situations is performed to increase the efficiency of road use. In view of the types and scales of IT devices used by Seoul TOPIS, speed information is collected in real-time from roads reaching 1,268 km through 1,181 video and loop detectors installed on site and 35,000 GPS devices installed in taxis. Further, 832 surveillance cameras 6
7 installed for traffic and disaster monitoring are operated, as well as 326 virtual memory systems (VMS) 3,600 real-time signal controllers, local control stations (LCS) installed in 33 areas, and remote manipulator systems (RMS) installed in 13 areas are used to operate road communication, along with information collection. The drawing below displays the statistics related to the types and quantity of various IT devices obtained by TOPIS. Figure 4: Current state of Seoul TOPIS road traffic management devices Seoul Traffic Information Division (2016) After processing the traffic information collected from these devices, Seoul TOPIS provides the data to drivers and manages the traffic situation. First, a whole host of different technologies are employed to collect speed, traffic volume, unexpected situations, weather, and other necessary and relevant information. Fundamentally, the locational information of taxis installed with GPSs is collected in real-time to calculate the passing speed on the roads. This is collected through wireless communication between the GPS in standard vehicles, wireless communication devices, and road-side base stations. Advanced vehicle detection systems, such as loop detectors and video detectors, are installed every 250m to 500m on highways, and thus, the traffic speed and volume are collected from these on-site systems. Surveillance cameras allow the monitoring of communication and unexpected situations, and the road weather information system collects and provides climate information, such as the road state, temperature, and visibility. Moreover, information on traffic situations or unexpected situations is obtained through the National Police Agency, the Meteorological Administration, and citizen reports. The road and traffic information collected through these various channels is gathered at Seoul TOPIS, processed in real-time, and then provided to traffic users in real-time through various media channels, such as mobile applications, ARS, navigation, SNS, the TOPIS website, road electronic displays, and traffic broadcasts. Upon occurrence of an unexpected situation on the road, the situation is detected by a video or 7
8 automatic detector and automatically displayed on an electronic dis play. The road control system controls, operates the roads based on the needs, and provides bypass roads so as to control the traffic flow. Furthermore, the connection road control system is operated upon need to prevent any increase in traffic congestion, and the signal control system assists in smoothing the traffic by prolonging the duration of green signals and lights on roads with severe congestion. Seoul TOPIS also has the function of preparing for the full closure of a road due to any unexpected situation, such as a large scale rally or bad weather, by carrying out various simulations. Second, Seoul TOPIS manages approximately 9,000 Seoul buses in real-time, and operates a public transportation information system that provides assistance with public transportation information to the users. Bus-related information is collected in real-time by installing bus information collection terminals that use bus management systems (BMS) and traffic card functions on all buses in Seoul. Through the combined terminals installed on 9,334 buses, all detailed information related to buses is collected - such as all bus operating situations from the point of departure to the point of arrival, real-time speed, location of buses, sudden acceleration, sudden stops, no-stop passing, breaking away from the route, and driving with the door open. Furthermore, these bus information collection terminals also checks traffic card information, and thus, can collect the information of passengers in real-time. The terminals collect approximately 85 million cases of traffic card information each day. The collected information is provided to the citizens by automatically calculating the bus arrival times and returning passengers by the Seoul TOPIC bus information processing technology. The bus operation management records (including various operation acts that may harm the safety of the citizens) are systematically stored, analyzed, and managed to be used as an important index in the regular evaluation of bus corporations, and the bus route is managed by adjusting unreasonable routes and constructing new routes to support the establishment of the optimum public transportation policy. There are diverse means of providing bus information. First, bus information terminals (BIT) are installed at 52% of bus stations in Seoul, to assist the passengers with the bus arrival time in real-time and provide bus information, as well as subway arrival information. The bus passengers are provided with a wealth of information, such as the predicted bus arrival time, information related to buses for the disabled, the last bus of the day, congestion due to accidents, and the predicted time of arrival of the nearest subway through bus information terminals installed at these bus stations. Furthermore, all information at Seoul TOPIS is 100% open, where 24 million cases of information is provided to the public in an open API method. Private corporations may reprocess this information to suit different types of consumers to directly provide public transportation information to the users. Currently, a significant number of public transportation users that use the internet or smart phones receive public transportation information through portals, websites or mobile applications of communications companies or mobile applications 8
9 launched by personal developers. Thus, the users do not depend only on bus information terminals installed at bus stations, but can plan the ir use of public transportation anywhere and at any time. All of this bus information, as well as the user-customized information (such as a safe arrival service which helps accompany vulnerable pedestrians to their destination via text, and an alarm function notifying the arrival at a destination) can be provided on smart phones. Detailed information and websites can be used by accessing a QR code attached to bus stops, as well as an automatic response service for bus passengers who are unfamiliar with smart phones. Such bus information collected and provided through advanced devices displays an accuracy of 98%. The accuracy of this information is evident by the use of the combined public transportation information that surpasses 1.4 million hits, and achieves satisfaction levels of 96%. Fig. 4 below displays the number and statistics related to the information collected at terminals by the public transportation information system. Figure 5: Current status of Seoul TOPIS bus information system Seoul Traffic Information Division (2016) The electronic payment system, which allows the payment of various public transportation fares with a single card, is also linked with Seoul TOPIS. The bus information collection terminal previously explained is constructed so that it combines the bus operation information system and the traffic card system. The traffic card information collected thereby is becoming an important element of the public traffic information system of Seoul TOPIS. Traffic cards are used by almost all public transportation users, including 100% of subway users and 98.7% of bus users. Taxi passengers also display an increasing use of traffic cards each year and currently stand at 53.5%. Seoul s combined electronic payment system follows the distance proportion system within the metropolitan area: a distance within 10km can be transferred to for free using any method of public transportation within a time limit of 30 minutes. The distribution of the fare is calculated based on the basic fare for each method of transportation. 9
10 The usage of the traffic card is expanded to distribution, dining, culture, and traffic safety services, and thus, is breaking the boundary of the electronic payment system, and can also be used via pre-paid card, credit card, or the mobile phone. The traffic card was previously only available for use in Seoul, but the use of the traffic card is now permitted and functional in most regions of Korea. In addition, the mobile payment compatibility service is also operated in Singapore. There are plans for it to be expanded to other countries, including Japan, Hong Kong, Thailand, and Malaysia. Seoul TOPIS controls illegally parked or stood vehicles in bus lanes, which cause traffic congestion through the unmanned enforcement system. Since 2005, Seoul TOPIS has been constructing and operating an unmanned enforcement system, which automatically controls illegally parked or stopped in bus lanes and thus is not reliant on any labor force. Currently, the automatic unmanned enforcement system uses two types of devices. First, the fixed unmanned enforce system installed on roads uses a detector which can automatically control vehicles illegally parked or stopped or vehicles that drive in bus or bicycle lanes within 200m of the detection device. The portable unmanned enforce system is simply a camera equipped on buses or monitoring vehicles that records the number plate of a vehicle in violation when such vehicle is detected during the running of the relevant buses or monitoring vehicles. This information is then transferred to Seoul TOPIS. The fixed unmanned enforcement system is restricted, however, in not being able to control vehicles in violation outside of the installed point of the device, whereas the portable unmanned enforcement system can supplement this weakness as drivers are unaware of the point of installation. 10
11 Figure 6: Seoul TOPIS unmanned enforce system Source: Seoul Traffic Information Division (2016) The unmanned enforcement system not only exposes vehicles in violation, but is the world s first automatic penalty management system that automatically transfers a penalty notice to the owner of the vehicle in violation. First, when a vehicle in violation is detected, the registration of the vehicle is searched to automatically record the owner and address of the vehicle. It then sends a penalty report providing photograph evidence and ownership information of the vehicle to the post office in electronic form. The electronic penalty notice is then automatically delivered to the address of the owner of the vehicle. All processes from the detection of violation to the delivery of the penalty notice are automatically performed, and thus, only takes two to three days. Before the successful automation of this process, it often took 10 to 15 days to complete. Thus, the amount 11
12 of labor force and resources saved is evident by the automation of this process. Figure 7: Seoul TOPIS automatic penalty imposition system Source: Seoul Traffic Information Division (2016) Seoul TOPIS operates 308 unmanned enforcement systems, and enforces approximately 1.8 million illegally parked or stood vehicles as well as vehicles in bus lanes through this system. Fourth, Seoul TOPIS is constructing and operating a traffic prediction system that prevents traffic congestion. Currently, traffic prediction is conducted in the 157km highway region, and is scheduled to expand to the main freeways. In addition to real-time traffic information services, data related to the traffic flow on each road, weather, and accidents, accumulated over the past five years is analyzed to predict the traffic situation of each road in 15 minute, 1 hour, and 1 day units. Furthermore, if or when an unexpected situation arises, such as an accident, the traffic simulation is used to predict the outcome of the situation. A congestion alarm is used to allow the citizens to know both the region and times of congestion in advance. This helps drivers avoid using certain roads at certain times and provides great benefits. The traffic prediction technology was developed by the Korea Transport Institute, and an accuracy of 90% of the traffic prediction was verified based on the urban highways. Seoul TOPIS intends to expand the traffic prediction system on the main roads of Seoul for the citizens to use traffic predictions in a similar way to how they use weather forecasts in everyday lives. Furthermore, the traffic prediction system can be used to prevent accidents that may occur, based on communication between vehicles, i.e., the V2V technology, and bilateral wireless communication can be used between a vehicle and a communication-based infrastructure (V2I) to provide roadside assistance reflecting real-time road situations, signal changes, and the prediction of crosswalks. 12
13 Seoul TOPIS: Organization and Operation Seoul TOPIS is an organization that plans, constructs, and operates intelligent traffic. It is composed of 32 public servants in 4 divisions. A total of 150 employees work at Seoul TOPIS where they monitor, control, provide maintenance, and carry out the management of the traffic situation. The operation of Seoul TOPIS requires an annual budget of 17 trillion won. Most of the budget is used for site facilities and the maintenance and management of the labor force. Fig. 8 below provides a summary of the statistics related to the operation of Seoul TOPIS, the unmanned enforce system and other related aspects. Figure 8: Seoul TOPIS organization and operation, and other related statistics Source: Seoul Traffic Information Division (2016) 8. Technical Details 1) Main system of Seoul TOPIS The center system accounting to the brain of TOPIS collects, combines and processes all information in real-time and then allows for an immediate response by providing the information to the operator. The operator is supported and able to control all traffic and disaster situations from the center by providing the necessary information to the citizens and taking all relevant precautions these include detecting the symptoms of unexpected situations and disasters by monitoring all information, and controlling the on-site equipment such as the traffic signals and electronic 13
14 displays. Furthermore, the system is constructed so as to allow rapid contact and cooperation with related organizations. Figure 9: Seoul TOPIS center system Source: Seoul Traffic Information Division (2016) 14
15 2) Bus Information System Figure 10: Seoul TOPIS bus information system Source: Seoul Traffic Information Division (2016) Operation of all 9334 buses in Seoul, from the point of departure and arrival, is collected in realtime through the Seoul TOPIS bus information system. Each bus has an integrated bus terminal installed therein combining bus operation information and the traffic card function. It collects all bus-related information, such as the passengers and running of the bus (including factors such as sudden accelerations, sudden stops, and nonstop passing) in addition to real-time speeds and locations. The collected information is provided to the citizens by automatically calculating the number of returning passengers and the arrival time of buses based on the Seoul TOPIS bus processing technology. From this, various actions that may cause harm to the safety of citizens are stored and analyzed for use in the evaluation of bus corporations. Bus Management System (BMS) Through the construction of the BMS center for real-time public transportation operation management, the enhancement of bus competitiveness was initiated by enhancing bus punctuality, improved operation orders, providing a wider range of bus information, and promoting a rational public traffic policy bill based on operational historical precedents. The combined bus control room is in charge of the role as the main body in relation to the majority of strategies and is in the center of all bus operation management strategies. The BMS collects bus operation information using location tracking technology and processes the information as bus operation policy data in order to provide the data to operators, bus companies, and drivers. 15
16 Bus Information System (BIS) This system collects bus location information to process bus arrival predictions using algorithms and to provide the information to users and related organizations. To achieve this, personal information services, such as internet websites, ARS and mobile services, were initiated and the bus information terminals (BIT) were installed. Thereafter, bus information is fully disclosed to the public. This led to the introduction of various products focused on internet and mobile applications, and a selection of services that better suit the consumer s needs and preferences. 3) Unmanned enforcement system The advanced unmanned enforcement system constructed for the management of the communicative situation by Seoul TOPIS detects and punishes illegally parked or stopped vehicles on urban highways as well as vehicles driving in bus lanes through the use of unmanned enforcement cameras. The unmanned enforcement cameras cover all vehicles within a 200m radius in all directions on all roads. Vehicles captured by the unmanned enforcement camera are confirmed in as little as five minutes. Portable or bus-equipped unmanned enforcement systems have the advantage of detecting vehicles on all roads of the pertinent route. Of the four cameras equipped on buses, two cameras equipped at a 45 degree angle detect illegally parked vehicles on the shoulder of the road. Currently, fixed enforcement cameras are installed in all regions of Seoul, and the bus-equipped cameras are able to detect vehicles on main freeways in real-time. Enforcement can also be confirmed by the public in real-time. When a search is performed on the owner of the vehicle and the penalty is imposed using t he number plate and photograph sent to the traffic violation management system, the notice is printed and sent to the post office. Here, it is automatically connected to the nearest post office of the owner of the vehicle and duly sent out. All phases of Seoul s unmanned enforcement system are automatically performed, from the enforcement to the receipt of the penalty. A sum of approximately 120 billion won, from 3 million cases of enforcement each year, is used for the maintenance and operation of public parking lots. Accordingly, the unmanned enforcement system contributes to the relief of urban traffic congestion as well as a lack of parking spaces. 16
17 8. Policy Effects Figure 11: Current status of Seoul TOPIS information in use Source: Seoul Traffic Information Division (2016) The usage of the combined public transportation information is 1.4 million cases each day. The total accuracy of the bus information is approximately 98% and the satisfaction rate of public transportation is 96%. Traffic cards are used by almost all public transportation users, including 100% of subway users and 98.7% of bus users. Taxi passengers also display an increased use of traffic cards each year and 59% of the taxi passengers use traffic cards. (Seoul Urban Traffic Division 2016). Increase in the Bus Allocation Rate Table 2: Increasing Rate of Public Transportation Use Each Year, Subway 4,567 4,540 4,533 4,532 4,577 4,730 4,835 Bus 4,782 5,451 5,662 5,603 5,647 5,681 5,719 Total 9,349 9,991 10,195 10,135 10,224 10,411 10,554 Source: Seoul City % increase in the accuracy of bus arrival times (from 87.3% in 2006 to 91.4% in 2013) 26% increase in the average speed of buses (15 km/h to 19 km/h) 2.6% increase in the average daily bus passengers by 150 thousand passengers (from 5.6 million in 2007 to 5.75 million in 2013) Source: Seoul Traffic Information Division (2016) 17
18 9. Challenges and Solutions At the time of policy implementation, there was an increase in the general understanding and interest on ITS due to the national initiation of the ITS project. With respect to the policy plan and implementation process, there were no obstacles or technical difficulties related to the interest group that may be recorded as direct beneficiaries, such as Seoul city, bus companies, drivers, or bus passengers. 18
19 Reference TOPIS 5%EC%A0%95%EB%B3%B4%EC%84%BC%ED%84%B0topis Pucher, J., H. Park, M. Han Kim and J. Song (2005) Public transport reforms in Seoul: Innovations motivated by funding crisis, Journal of Public Transportation 8 (5):41 62 Park, Y-W (2010) BRT system in Seoul and integrated e-ticketing, UITP Asia Pacific Symposium on Public Transport (with special focus on BRT), January, Delhi Cited in Heather Allen(2013) Global Report on Human Settlements 2013 (Available from Seo, B. M., Cho, J. S. (2012) Seoul Bus Information System (BIS) Case Study: Focused on the Analysis of the Effect from the User s Perspective, Global Management Study Vol. 24, No. 2, p Seoul Statistics (searched on August 23, 2016) Seoul Traffic Information Division (2016) Seoul TOPIS Presentation Seoul Urban Traffic Division (as of 2016) People-prioritized safe and convenient traffic 19
- Need for an integrated information system seamlessly linking demand for diverse means of transportation
 Policies TOPIS: Seoul s Intelligent Traffic System (ITS) Date 2014-10-16 Category Transportation Updater scaadmin Writer Ph.d JoonHo Ko, Shin Lee Date 2014-10-16 Last Update 2017-04-26 Policy Overview
Policies TOPIS: Seoul s Intelligent Traffic System (ITS) Date 2014-10-16 Category Transportation Updater scaadmin Writer Ph.d JoonHo Ko, Shin Lee Date 2014-10-16 Last Update 2017-04-26 Policy Overview
Seoul. (Area=605, 10mill. 23.5%) Capital Region (Area=11,730, 25mill. 49.4%)
 Seoul (Area=605, 10mill. 23.5%) Capital Region (Area=11,730, 25mill. 49.4%) . Major changes of recent decades in Korea Korea s Pathways at a glance 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s Economic Development
Seoul (Area=605, 10mill. 23.5%) Capital Region (Area=11,730, 25mill. 49.4%) . Major changes of recent decades in Korea Korea s Pathways at a glance 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s Economic Development
Smart Green Transportation of LG CNS. Seoul Case
 Smart Green Transportation of LG CNS Seoul Case about Seoul Seoul Was about Seoul about Seoul - 1/22 Economic Growth of Korea Item 1970 2004 Differences Population 5,433,198 10,297,004 2 times Vehicles
Smart Green Transportation of LG CNS Seoul Case about Seoul Seoul Was about Seoul about Seoul - 1/22 Economic Growth of Korea Item 1970 2004 Differences Population 5,433,198 10,297,004 2 times Vehicles
Sustainable Urban Transport Policy : Experience of Daejeon city
 Expert Group Meeting, Kathmandu, Sep. 22, 2016 Sustainable Urban Transport Policy : Experience of Daejeon city Daehee Han / Ph.D. Senior researcher of Department Policy Division Daejeon Metropolitan City
Expert Group Meeting, Kathmandu, Sep. 22, 2016 Sustainable Urban Transport Policy : Experience of Daejeon city Daehee Han / Ph.D. Senior researcher of Department Policy Division Daejeon Metropolitan City
Seoul Transportation
 Seoul Transportation September 2014 Joonho Ko, Ph.D. Director, Megacity Research Center The Seoul Institute Contents Ⅰ. Past & Now 3 Ⅱ. Vision 1 5 Ⅲ. Implementation 1 9 Ⅰ. Past & Now 1. Past & Now Seoul
Seoul Transportation September 2014 Joonho Ko, Ph.D. Director, Megacity Research Center The Seoul Institute Contents Ⅰ. Past & Now 3 Ⅱ. Vision 1 5 Ⅲ. Implementation 1 9 Ⅰ. Past & Now 1. Past & Now Seoul
Smart systems. Smart traffic. Siemens Intelligent Traffic Systems
 Smart systems. Smart traffic. Siemens Intelligent Traffic Systems Unrestricted Siemens AG 2019 siemens.com/traffic The world of mobility is facing tremendous challenges We are facing the next mobility
Smart systems. Smart traffic. Siemens Intelligent Traffic Systems Unrestricted Siemens AG 2019 siemens.com/traffic The world of mobility is facing tremendous challenges We are facing the next mobility
Build a Green, Harmonious and Integrated Public Transport System
 Build a Green, Harmonious and Integrated Public Transport System Three stages for reform and development of in : 1. Overall reform in 1996, with system, mechanism and ticketing system as the breach 2.
Build a Green, Harmonious and Integrated Public Transport System Three stages for reform and development of in : 1. Overall reform in 1996, with system, mechanism and ticketing system as the breach 2.
Ex-Ante Evaluation (for Japanese ODA Loan)
 Japanese ODA Loan Ex-Ante Evaluation (for Japanese ODA Loan) 1. Name of the Project Country: India Project: Delhi Mass Rapid Transport System Project Phase 2 (V) Loan Agreement: March 31, 2010 Loan Amount:
Japanese ODA Loan Ex-Ante Evaluation (for Japanese ODA Loan) 1. Name of the Project Country: India Project: Delhi Mass Rapid Transport System Project Phase 2 (V) Loan Agreement: March 31, 2010 Loan Amount:
Urban Transport Development Investment Program (RRP MON 39256) SECTOR ROAD MAP
 Urban Transport Development Investment Program (RRP MON 39256) SECTOR ROAD MAP 1. The government s vision for urban transport in Ulaanbaatar provides the basis for the sector roadmap to be implemented
Urban Transport Development Investment Program (RRP MON 39256) SECTOR ROAD MAP 1. The government s vision for urban transport in Ulaanbaatar provides the basis for the sector roadmap to be implemented
The Strategies and Revelation of Free Buses in Chengdu
 The Strategies and Revelation of Free Buses in Chengdu Chen,She ChengduAcademyofSocial Sciences,Sichuan,China November6,2014 The Introduction of Chengdu Buses Chengdu, located in the central area of Sichuan
The Strategies and Revelation of Free Buses in Chengdu Chen,She ChengduAcademyofSocial Sciences,Sichuan,China November6,2014 The Introduction of Chengdu Buses Chengdu, located in the central area of Sichuan
C-ITS in Taiwan. Michael Li
 C-ITS in Taiwan Michael Li (hhli@itri.org.tw) Deputy Division Director Division for Telematics and Vehicular Control System Information and Communication Lab. (ICL) Industrial Technology Research Institute
C-ITS in Taiwan Michael Li (hhli@itri.org.tw) Deputy Division Director Division for Telematics and Vehicular Control System Information and Communication Lab. (ICL) Industrial Technology Research Institute
Fujitsu Intelligent Mobility Solution
 Fujitsu Intelligent Mobility Solution 20 th February, 2018 Global Business Division, Public Sector & Regional Sales Group, Fujitsu Limited Contents 1. About Fujitsu 2. Intelligent Mobility Solution 1 Contents
Fujitsu Intelligent Mobility Solution 20 th February, 2018 Global Business Division, Public Sector & Regional Sales Group, Fujitsu Limited Contents 1. About Fujitsu 2. Intelligent Mobility Solution 1 Contents
Building smart transport in Moscow
 Building smart transport in Moscow Moscow addressed its road and public transit congestion problems and developed one of the world s smartest and most-used public transportation systems. Here s how. Maksim
Building smart transport in Moscow Moscow addressed its road and public transit congestion problems and developed one of the world s smartest and most-used public transportation systems. Here s how. Maksim
* Presented at 2011 World Bank Transport Forum, March Jaehak Oh. Director, Global Research Office for Green Growth & Convergence
 * Presented at 2011 World Bank Transport Forum, March 2011 Jaehak Oh Director, Global Research Office for Green Growth & Convergence I. Green Growth and Transport II. Future Trend III. Innovative Technologies
* Presented at 2011 World Bank Transport Forum, March 2011 Jaehak Oh Director, Global Research Office for Green Growth & Convergence I. Green Growth and Transport II. Future Trend III. Innovative Technologies
Strategic Plan
 2005-2015 Strategic Plan SUMMARY OF THE REVISED PLAN IN 2011 A decade focused on developing mass transit in the Outaouais A updated vision of mass transit in the region The STO is embracing the future
2005-2015 Strategic Plan SUMMARY OF THE REVISED PLAN IN 2011 A decade focused on developing mass transit in the Outaouais A updated vision of mass transit in the region The STO is embracing the future
Car Sharing at a. with great results.
 Car Sharing at a Denver tweaks its parking system with great results. By Robert Ferrin L aunched earlier this year, Denver s car sharing program is a fee-based service that provides a shared vehicle fleet
Car Sharing at a Denver tweaks its parking system with great results. By Robert Ferrin L aunched earlier this year, Denver s car sharing program is a fee-based service that provides a shared vehicle fleet
2. Big Data Big Data in Seoul s Transportation Policy: Designing Late Night Bus Routes Based on Big 2. 빅데이터 빅데이터를활용한서울시교통계획 : 빅데이터를이용한심야버스노선설계
 2. Big Data Big Data in Seoul s Transportation Policy: Designing Late Night Bus Routes Based on Big Data 2. 빅데이터 빅데이터를활용한서울시교통계획 : 빅데이터를이용한심야버스노선설계 A city that never sleeps, Seoul is a place where economic
2. Big Data Big Data in Seoul s Transportation Policy: Designing Late Night Bus Routes Based on Big Data 2. 빅데이터 빅데이터를활용한서울시교통계획 : 빅데이터를이용한심야버스노선설계 A city that never sleeps, Seoul is a place where economic
Bus System Reform and Social Cohesion
 Toronto Visit 15 th June Bus System Reform and Social Cohesion by Dr. Ma, Kookjun Table of of Contents Ⅰ. Introduction Ⅱ. The Weak, and Concepts of Seoul Public Transportation System Ⅲ. Seoul Public Transportation
Toronto Visit 15 th June Bus System Reform and Social Cohesion by Dr. Ma, Kookjun Table of of Contents Ⅰ. Introduction Ⅱ. The Weak, and Concepts of Seoul Public Transportation System Ⅲ. Seoul Public Transportation
Innovation and Transformation of Urban Mobility Role of Smart Demand Responsive Transport (DRT) service
 Innovation and Transformation of Urban Mobility Role of Smart Demand Responsive Transport (DRT) service Eng. Mohammed Abubaker Al Hashimi Director of Planning & Business Development, Public Transport Agency
Innovation and Transformation of Urban Mobility Role of Smart Demand Responsive Transport (DRT) service Eng. Mohammed Abubaker Al Hashimi Director of Planning & Business Development, Public Transport Agency
Roundtable New Delhi, India
 Roundtable New Delhi, India Dept. of Railway Research Division for Rail Policy and Industry Research Associate Research Fellow LEE, JUN 1 Q-1 Reason of Investment for HSR? Beginning: Serious Congestion
Roundtable New Delhi, India Dept. of Railway Research Division for Rail Policy and Industry Research Associate Research Fellow LEE, JUN 1 Q-1 Reason of Investment for HSR? Beginning: Serious Congestion
Mobility on Demand, Mobility as a Service the new transport paradigm. Richard Harris, Xerox
 Mobility on Demand, Mobility as a Service the new transport paradigm Richard Harris, Xerox Xerox Transport Services 37 billion 100 million transit fare transactions processed annually and more public transport
Mobility on Demand, Mobility as a Service the new transport paradigm Richard Harris, Xerox Xerox Transport Services 37 billion 100 million transit fare transactions processed annually and more public transport
Back ground Founded in 1887, and has expanded rapidly Altitude about 2500 meters above MSL Now among the ten largest cities in Sub Saharan Africa
 Back ground Founded in 1887, and has expanded rapidly Altitude about 2500 meters above MSL Now among the ten largest cities in Sub Saharan Africa Annual growth rate is 3.8% By 2020 population growth would
Back ground Founded in 1887, and has expanded rapidly Altitude about 2500 meters above MSL Now among the ten largest cities in Sub Saharan Africa Annual growth rate is 3.8% By 2020 population growth would
National Road Safety Action Plan in China
 Sixth SHRP 2 Safety Research Symposium National Road Safety Action Plan in China Dr. Yan Wang July 14, 2011 Washington DC, USA Outline 1 Initiative of Road Safety Action Plan 2 Phase I 3 For Next Phase?
Sixth SHRP 2 Safety Research Symposium National Road Safety Action Plan in China Dr. Yan Wang July 14, 2011 Washington DC, USA Outline 1 Initiative of Road Safety Action Plan 2 Phase I 3 For Next Phase?
Our mission is to be the best public service transporter for passengers in the city of Kigali using modern, clean and safe urban city buses.
 Kigali Bus Services Ltd. was incorporated in January 2006 in Kigali Rwanda. The Company started operations in March 2007 with just a few buses! We now operate a fleet of 50 Buses throughout Kigali City
Kigali Bus Services Ltd. was incorporated in January 2006 in Kigali Rwanda. The Company started operations in March 2007 with just a few buses! We now operate a fleet of 50 Buses throughout Kigali City
Toward the Realization of Sustainable Mobility
 GIES 2008 Toward the Realization of Sustainable Mobility March 13, 2008 Toyota Motor Corporation Senior Technical Executive Hiroyuki Watanabe 1 CO 2 Emission from Transportation Sector Distribution by
GIES 2008 Toward the Realization of Sustainable Mobility March 13, 2008 Toyota Motor Corporation Senior Technical Executive Hiroyuki Watanabe 1 CO 2 Emission from Transportation Sector Distribution by
Connected Vehicles. The rise of safety innovations and intelligent mobility
 Connected Vehicles The rise of safety innovations and intelligent mobility 1 Global Trends Growing world population Between now and 2050 the global population is expected to increase from 6.9 billion to
Connected Vehicles The rise of safety innovations and intelligent mobility 1 Global Trends Growing world population Between now and 2050 the global population is expected to increase from 6.9 billion to
Transport Demand Management Policies in Beijing. CAI Jing Beijing Transport Energy and Environment Center April 2016 in New Delhi
 Transport Demand Management Policies in Beijing CAI Jing Beijing Transport Energy and Environment Center April 2016 in New Delhi Contents I. Beijing Basics II. Transport demand management policies Beijing
Transport Demand Management Policies in Beijing CAI Jing Beijing Transport Energy and Environment Center April 2016 in New Delhi Contents I. Beijing Basics II. Transport demand management policies Beijing
actsheet Car-Sharing
 actsheet Car-Sharing This paper was prepared by: SOLUTIONS project This project was funded by the Seventh Framework Programme (FP7) of the European Commission Solutions project www.uemi.net The graphic
actsheet Car-Sharing This paper was prepared by: SOLUTIONS project This project was funded by the Seventh Framework Programme (FP7) of the European Commission Solutions project www.uemi.net The graphic
Submission to Greater Cambridge City Deal
 What Transport for Cambridge? 2 1 Submission to Greater Cambridge City Deal By Professor Marcial Echenique OBE ScD RIBA RTPI and Jonathan Barker Introduction Cambridge Futures was founded in 1997 as a
What Transport for Cambridge? 2 1 Submission to Greater Cambridge City Deal By Professor Marcial Echenique OBE ScD RIBA RTPI and Jonathan Barker Introduction Cambridge Futures was founded in 1997 as a
One City, One System: Integrating Public Urban Transportation in Coimbra
 One City, One System: Integrating Public Urban Transportation in Coimbra CIVITAS MODERN Study Tour Luis Santos, SMTUC Luis da Vinha, Municipality of Coimbra 8-9 November 2012 Coimbra Situation before CIVITAS
One City, One System: Integrating Public Urban Transportation in Coimbra CIVITAS MODERN Study Tour Luis Santos, SMTUC Luis da Vinha, Municipality of Coimbra 8-9 November 2012 Coimbra Situation before CIVITAS
Road Tolls and Road Pricing Innovative Methods to Charge for the Use of Road Systems
 Road Tolls and Road Pricing Innovative Methods to Charge for the Use of Road Systems by Daphnée Benayoun & René P. Cousin The Louis Berger Group, Inc. Introduction Major challenges facing now the road
Road Tolls and Road Pricing Innovative Methods to Charge for the Use of Road Systems by Daphnée Benayoun & René P. Cousin The Louis Berger Group, Inc. Introduction Major challenges facing now the road
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 2018 What is the More MARTA Atlanta program? The More MARTA Atlanta program is a collaborative partnership between MARTA and the City of Atlanta to develop and implement a program
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 2018 What is the More MARTA Atlanta program? The More MARTA Atlanta program is a collaborative partnership between MARTA and the City of Atlanta to develop and implement a program
Doubling the Market Share of Public Transport Worldwide by 2025: A Smart Future for Cities
 Doubling the Market Share of Public Transport Worldwide by 2025: A Smart Future for Cities Dawn CHUI International Association of Public Transport (UITP) Contents 1. What would happen in 2025 if current
Doubling the Market Share of Public Transport Worldwide by 2025: A Smart Future for Cities Dawn CHUI International Association of Public Transport (UITP) Contents 1. What would happen in 2025 if current
GOVERNMENT STATUS REPORT OF JAPAN
 GOVERNMENT STATUS REPORT OF JAPAN Hidenobu KUBOTA Director, Policy Planning Office for Automated Driving Technology, Engineering Policy Division, Road Transport Bureau, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure,
GOVERNMENT STATUS REPORT OF JAPAN Hidenobu KUBOTA Director, Policy Planning Office for Automated Driving Technology, Engineering Policy Division, Road Transport Bureau, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure,
Opportunities to Leverage Advances in Driverless Car Technology to Evolve Conventional Bus Transit Systems
 Opportunities to Leverage Advances in Driverless Car Technology to Evolve Conventional Bus Transit Systems Podcar City 7 Symposium Emerging Transportation Technologies R&D George Mason University, October
Opportunities to Leverage Advances in Driverless Car Technology to Evolve Conventional Bus Transit Systems Podcar City 7 Symposium Emerging Transportation Technologies R&D George Mason University, October
History of Subway in Kyoto
 TO: Board Members FROM: Yasuyo Tsukamoto DATE: May 6, 2016 SUBJECT: Alternative Plan to Increasing Fares in Kyoto City I am strongly against the idea that the (KMTB) increase the subway fare. Although
TO: Board Members FROM: Yasuyo Tsukamoto DATE: May 6, 2016 SUBJECT: Alternative Plan to Increasing Fares in Kyoto City I am strongly against the idea that the (KMTB) increase the subway fare. Although
Transportation Demand Management Element
 Transportation Demand Management Element Over the years, our reliance on the private automobile as our primary mode of transportation has grown substantially. Our dependence on the automobile is evidenced
Transportation Demand Management Element Over the years, our reliance on the private automobile as our primary mode of transportation has grown substantially. Our dependence on the automobile is evidenced
Recent Transportation Projects
 Dr. Dazhi Sun Associate Professor Director of Texas Transportation Institute Regional Division Department of Civil & Architectural Engineering Texas A&M University-Kingsville 1 Recent Transportation Projects
Dr. Dazhi Sun Associate Professor Director of Texas Transportation Institute Regional Division Department of Civil & Architectural Engineering Texas A&M University-Kingsville 1 Recent Transportation Projects
FENEBUS POSITION PAPER ON REDUCING CO2 EMISSIONS FROM ROAD VEHICLES
 FENEBUS POSITION PAPER ON REDUCING CO2 EMISSIONS FROM ROAD VEHICLES The Spanish Federation of Transport by Bus (Fenebús) is aware of the importance of the environmental issues in order to fully achieve
FENEBUS POSITION PAPER ON REDUCING CO2 EMISSIONS FROM ROAD VEHICLES The Spanish Federation of Transport by Bus (Fenebús) is aware of the importance of the environmental issues in order to fully achieve
The Experience of Vienna City
 Examples from key cities and public transport operators: The Experience of Vienna City DI Isabella Kossina, MBA Wiener Stadtwerke, Vienna, Austria Wiener Stadtwerke Sustainability Report 2008 and Sustainability
Examples from key cities and public transport operators: The Experience of Vienna City DI Isabella Kossina, MBA Wiener Stadtwerke, Vienna, Austria Wiener Stadtwerke Sustainability Report 2008 and Sustainability
Braking Performance Improvement Method for V2V Communication-Based Autonomous Emergency Braking at Intersections
 , pp.20-25 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.86.05 Braking Performance Improvement Method for V2V Communication-Based Autonomous Emergency Braking at Intersections Sangduck Jeon 1, Gyoungeun Kim 1,
, pp.20-25 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.86.05 Braking Performance Improvement Method for V2V Communication-Based Autonomous Emergency Braking at Intersections Sangduck Jeon 1, Gyoungeun Kim 1,
Urban Transport systems in major cities in China. Sun Kechao Senior Engineer China Academy of Transportation Sciences, Beijing, China
 Urban Transport systems in major cities in China Sun Kechao Senior Engineer China Academy of Transportation Sciences, Beijing, China Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 Part 4 Introduction Urban transport policies Urban
Urban Transport systems in major cities in China Sun Kechao Senior Engineer China Academy of Transportation Sciences, Beijing, China Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 Part 4 Introduction Urban transport policies Urban
Urban Mobility. Story how to build the urban mobility of Seoul. Kim, Sangbum Visiting Professor University of Seoul
 Urban Mobility Story how to build the urban mobility of Seoul Kim, Sangbum Visiting Professor University of Seoul I. Introduction 1. Civilization has closely been related to mobility of human activities
Urban Mobility Story how to build the urban mobility of Seoul Kim, Sangbum Visiting Professor University of Seoul I. Introduction 1. Civilization has closely been related to mobility of human activities
January 18, ZERO-SUM,LTD. TOYOTA InfoTechnology Center Co., Ltd.
 January 18, 2019 Demonstration of an Emergency Vehicle Priority System using Japanese originated international standard V2X communication technology that has been undertaken in Ahmedabad city, INDIA ZERO-SUM,LTD.
January 18, 2019 Demonstration of an Emergency Vehicle Priority System using Japanese originated international standard V2X communication technology that has been undertaken in Ahmedabad city, INDIA ZERO-SUM,LTD.
building liveable cities
 N 3-2016 building liveable cities + Combatting climate change North american mobility renaissance Holger Mette / El Panecillo hill and bus station, Quito Ecuador Deposit at 1080 Brussels - Price per copy
N 3-2016 building liveable cities + Combatting climate change North american mobility renaissance Holger Mette / El Panecillo hill and bus station, Quito Ecuador Deposit at 1080 Brussels - Price per copy
Smart City/Smart Mobility Strategy. Hans Larsen, Fremont Public Works Director May 2, 2018
 Smart City/Smart Mobility Strategy Hans Larsen, Fremont Public Works Director May 2, 2018 About Fremont 230,000 Population; 4 th Largest City in Bay Area About Fremont #1 Happiest Place to Live in America
Smart City/Smart Mobility Strategy Hans Larsen, Fremont Public Works Director May 2, 2018 About Fremont 230,000 Population; 4 th Largest City in Bay Area About Fremont #1 Happiest Place to Live in America
The City of Toronto s Transportation Strategy July 2007
 The City of Toronto s Transportation Strategy July 2007 Presentation Outline Transportation Statistics Transportation Building Blocks Toronto s Official Plan Transportation and City Building Vision Projects
The City of Toronto s Transportation Strategy July 2007 Presentation Outline Transportation Statistics Transportation Building Blocks Toronto s Official Plan Transportation and City Building Vision Projects
Autonomous Driving, Tohoku University Sendai - Review of the Excursion
 Autonomous Driving, Tohoku University Sendai - Review of the Excursion 17.07.2017 (Report about my assigned site visit during the Japan Excursion - TU Vienna 2017) The Excursion to the Tohoku University
Autonomous Driving, Tohoku University Sendai - Review of the Excursion 17.07.2017 (Report about my assigned site visit during the Japan Excursion - TU Vienna 2017) The Excursion to the Tohoku University
Kathrine Wilson-Ellis Strategic Safety Team. Phil Proctor Future Technologies
 Kathrine Wilson-Ellis Strategic Safety Team Phil Proctor Future Technologies Who are we? 1 st April 2015 Highways England is a public sector company, owned by the Government Primary role of Highways England
Kathrine Wilson-Ellis Strategic Safety Team Phil Proctor Future Technologies Who are we? 1 st April 2015 Highways England is a public sector company, owned by the Government Primary role of Highways England
VIETNAM TRAFFIC SAFETY FOR 2 WHEELERS: CHALLENGES AND STRATEGIES. Trinh Thu Ha Deputy Chief Office National Traffic Safety Committee Vietnam
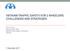 VIETNAM TRAFFIC SAFETY FOR 2 WHEELERS: CHALLENGES AND STRATEGIES Trinh Thu Ha Deputy Chief Office National Traffic Safety Committee Vietnam 7 December 2017 12/7/2017 2 Content Vietnam Demographic-Society
VIETNAM TRAFFIC SAFETY FOR 2 WHEELERS: CHALLENGES AND STRATEGIES Trinh Thu Ha Deputy Chief Office National Traffic Safety Committee Vietnam 7 December 2017 12/7/2017 2 Content Vietnam Demographic-Society
SAFE DRIVING USING MOBILE PHONES
 SAFE DRIVING USING MOBILE PHONES PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S0527 COLLEGE : SKSVMA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, GADAG BRANCH : COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING GUIDE : NAGARAJ TELKAR STUDENTS
SAFE DRIVING USING MOBILE PHONES PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S0527 COLLEGE : SKSVMA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, GADAG BRANCH : COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING GUIDE : NAGARAJ TELKAR STUDENTS
Proposed FY Capital Improvement Program (CIP) March 5, 2018 Capital Planning Committee 1
 Proposed FY 2019-2023 Capital Improvement Program (CIP) March 5, 2018 Capital Planning Committee 1 The Capital Improvement Program is: A fiscally constrained, 5-year program of capital projects An implementation
Proposed FY 2019-2023 Capital Improvement Program (CIP) March 5, 2018 Capital Planning Committee 1 The Capital Improvement Program is: A fiscally constrained, 5-year program of capital projects An implementation
Finance Operation Plan on Transportation Sector
 :: Metropolis Commissions 4 and 2 Meeting in Seoul Finance Operation Plan on Transportation Sector 0 SMG l. OverviewO view of Seoul Overview Area : 605km 2-0.6% of the national territoryg (Seoul Metropolitan
:: Metropolis Commissions 4 and 2 Meeting in Seoul Finance Operation Plan on Transportation Sector 0 SMG l. OverviewO view of Seoul Overview Area : 605km 2-0.6% of the national territoryg (Seoul Metropolitan
Introduction of Electronic Tolling Collection system in Japan
 Introduction of Electronic Tolling Collection system in Japan November 2014 ICT SOLUTION HEADQUARTERS 2013 MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD. All Rights Reserved. 2014 MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD.
Introduction of Electronic Tolling Collection system in Japan November 2014 ICT SOLUTION HEADQUARTERS 2013 MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD. All Rights Reserved. 2014 MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD.
Amman Green Policies Projects and Challenges. Prepared by: Eng. Sajeda Alnsour Project coordinator Sept. 20, 2017
 Amman Green Policies Projects and Challenges Prepared by: Eng. Sajeda Alnsour Project coordinator Sept. 20, 2017 Amman: Demographics Greater AMMAN Municipality GAM Amman is the capital of Jordan with a
Amman Green Policies Projects and Challenges Prepared by: Eng. Sajeda Alnsour Project coordinator Sept. 20, 2017 Amman: Demographics Greater AMMAN Municipality GAM Amman is the capital of Jordan with a
That sweet toll sound
 That sweet toll sound casestudy In the US state of Washington, a traffic control project that is unique in North America will be given the green light to start at the beginning of 2005. The project in
That sweet toll sound casestudy In the US state of Washington, a traffic control project that is unique in North America will be given the green light to start at the beginning of 2005. The project in
HOW TO DELIVER PUBLIC TRANSPORT ON REDUCED BUDGET
 LONDON MAY 25, 2011 HOW TO DELIVER PUBLIC TRANSPORT ON REDUCED BUDGET Marc Le Tourneur Direction de l Innovation et du Développement Sinotropher Conference London - May 25, 2011 - SUMMARY PART - 1 Climate
LONDON MAY 25, 2011 HOW TO DELIVER PUBLIC TRANSPORT ON REDUCED BUDGET Marc Le Tourneur Direction de l Innovation et du Développement Sinotropher Conference London - May 25, 2011 - SUMMARY PART - 1 Climate
An Introduction to Automated Vehicles
 An Introduction to Automated Vehicles Grant Zammit Operations Team Manager Office of Technical Services - Resource Center Federal Highway Administration at the Purdue Road School - Purdue University West
An Introduction to Automated Vehicles Grant Zammit Operations Team Manager Office of Technical Services - Resource Center Federal Highway Administration at the Purdue Road School - Purdue University West
Applicability for Green ITS of Heavy Vehicles by using automatic route selection system
 Applicability for Green ITS of Heavy Vehicles by using automatic route selection system Hideyuki WAKISHIMA *1 1. CTI Enginnering Co,. Ltd. 3-21-1 Nihonbashi-Hamacho, Chuoku, Tokyo, JAPAN TEL : +81-3-3668-4698,
Applicability for Green ITS of Heavy Vehicles by using automatic route selection system Hideyuki WAKISHIMA *1 1. CTI Enginnering Co,. Ltd. 3-21-1 Nihonbashi-Hamacho, Chuoku, Tokyo, JAPAN TEL : +81-3-3668-4698,
Park Smart. Parking Solution for Smart Cities
 Park Smart Parking Solution for Smart Cities Finding a car parking often becomes a real problem that causes loss of time, increasing pollution and traffic. According to the insurer Allianz in industrialized
Park Smart Parking Solution for Smart Cities Finding a car parking often becomes a real problem that causes loss of time, increasing pollution and traffic. According to the insurer Allianz in industrialized
PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION
 PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION An Overview of the Industry, Key Federal Programs, and Legislative Processes American Public Transportation Association 1 The Public Transportation Industry: What is "public transportation"?
PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION An Overview of the Industry, Key Federal Programs, and Legislative Processes American Public Transportation Association 1 The Public Transportation Industry: What is "public transportation"?
Welcome to the world of electromobility!
 www.siemens.com/drivergy Welcome to the world of electromobility! Drivergy puts electricity on the road Answers for the environment. Contents The future has begun 3 Convenient and economical: Home charging
www.siemens.com/drivergy Welcome to the world of electromobility! Drivergy puts electricity on the road Answers for the environment. Contents The future has begun 3 Convenient and economical: Home charging
Intelligent Mobility for Smart Cities
 Intelligent Mobility for Smart Cities A/Prof Hussein Dia Centre for Sustainable Infrastructure CRICOS Provider 00111D @HusseinDia Outline Explore the complexity of urban mobility and how the convergence
Intelligent Mobility for Smart Cities A/Prof Hussein Dia Centre for Sustainable Infrastructure CRICOS Provider 00111D @HusseinDia Outline Explore the complexity of urban mobility and how the convergence
Metropolitan Freeway System 2013 Congestion Report
 Metropolitan Freeway System 2013 Congestion Report Metro District Office of Operations and Maintenance Regional Transportation Management Center May 2014 Table of Contents PURPOSE AND NEED... 1 INTRODUCTION...
Metropolitan Freeway System 2013 Congestion Report Metro District Office of Operations and Maintenance Regional Transportation Management Center May 2014 Table of Contents PURPOSE AND NEED... 1 INTRODUCTION...
UITP PTx2 Strategy: What Role for Busses and Recommendations from UITP Istanbul Bus Declaration
 International Seminar on the renewal of Public Transport Bus Fleets 17 September 2012, Skopje, Macedonia UITP PTx2 Strategy: What Role for Busses and Recommendations from UITP Istanbul Bus Declaration
International Seminar on the renewal of Public Transport Bus Fleets 17 September 2012, Skopje, Macedonia UITP PTx2 Strategy: What Role for Busses and Recommendations from UITP Istanbul Bus Declaration
Appendix C. Parking Strategies
 Appendix C. Parking Strategies Bremerton Parking Study Introduction & Project Scope Community concerns regarding parking impacts in Downtown Bremerton and the surrounding residential areas have existed
Appendix C. Parking Strategies Bremerton Parking Study Introduction & Project Scope Community concerns regarding parking impacts in Downtown Bremerton and the surrounding residential areas have existed
Moscow International Transport Experts Council. Laurence A. Bannerman
 Moscow International Transport Experts Council 4 th Meeting, 29 30 September 2016 Laurence A. Bannerman President EPA - European Parking Association THE URBAN MOBILITY SYSTEMS - EU PUBLIC MOBILITY INFRASTRUCTURES
Moscow International Transport Experts Council 4 th Meeting, 29 30 September 2016 Laurence A. Bannerman President EPA - European Parking Association THE URBAN MOBILITY SYSTEMS - EU PUBLIC MOBILITY INFRASTRUCTURES
Application of Autonomous Vehicle Technology to Public Transit
 Application of Autonomous Vehicle Technology to Public Transit University Transportation Research Center 2014 Ground Transportation Technology Symposium November 19, 2014 Jerome M. Lutin, Ph.D., P.E. Senior
Application of Autonomous Vehicle Technology to Public Transit University Transportation Research Center 2014 Ground Transportation Technology Symposium November 19, 2014 Jerome M. Lutin, Ph.D., P.E. Senior
state, and federal levels, complete reconstruction and expansion of I35 in the near future is not likely.
 Project Summary Johnson County is an economic engine for the Kansas City metropolitan area and the State of Kansas. It s the fastest growing county in the state of Kansas and has the nation s third highest
Project Summary Johnson County is an economic engine for the Kansas City metropolitan area and the State of Kansas. It s the fastest growing county in the state of Kansas and has the nation s third highest
Automated Driving System
 2014 Global Symposium on Connected Vehicles and Infrastructure Automated Driving System up to date information from Japan April 23, 2014 Hiroyuki Watanabe Chairman, ITS Japan ITS WORLDCONGRESS TOKYO 2013
2014 Global Symposium on Connected Vehicles and Infrastructure Automated Driving System up to date information from Japan April 23, 2014 Hiroyuki Watanabe Chairman, ITS Japan ITS WORLDCONGRESS TOKYO 2013
Green and Inclusive Urban Transport
 Green and Inclusive Urban Transport ATF 2015 AfDB Transport Forum Stefanie Holzwarth Urban Mobility Unit Urban Basic Services Branch UN-Habitat The Global Urban Context Cities today occupy approximately
Green and Inclusive Urban Transport ATF 2015 AfDB Transport Forum Stefanie Holzwarth Urban Mobility Unit Urban Basic Services Branch UN-Habitat The Global Urban Context Cities today occupy approximately
Smart cities & effective mobility management solutions - 25 th March, San Paulo ViajeoPLUS Latin American Innovation week.
 Smart cities & effective mobility management solutions - 25 th March, San Paulo ViajeoPLUS Latin American Innovation week. SWARCO AG Content Global changes & Challenges Smart City Effective Mobility solutions
Smart cities & effective mobility management solutions - 25 th March, San Paulo ViajeoPLUS Latin American Innovation week. SWARCO AG Content Global changes & Challenges Smart City Effective Mobility solutions
Policy Note. Vanpools in the Puget Sound Region The case for expanding vanpool programs to move the most people for the least cost.
 Policy Note Vanpools in the Puget Sound Region The case for expanding vanpool programs to move the most people for the least cost Recommendations 1. Saturate vanpool market before expanding other intercity
Policy Note Vanpools in the Puget Sound Region The case for expanding vanpool programs to move the most people for the least cost Recommendations 1. Saturate vanpool market before expanding other intercity
Share with the GHSEA. Smart Energy Initiatives. Collaboration and a partner eco-system to achieve results
 Share with the GHSEA on behalf of the DSEA - learning and experience Color variant: Siemens Cool Gray Smart Energy Initiatives Collaboration and a partner eco-system to achieve results Realizing a Community-centric
Share with the GHSEA on behalf of the DSEA - learning and experience Color variant: Siemens Cool Gray Smart Energy Initiatives Collaboration and a partner eco-system to achieve results Realizing a Community-centric
Steering Actuator for Autonomous Driving and Platooning *1
 TECHNICAL PAPER Steering Actuator for Autonomous Driving and Platooning *1 A. ISHIHARA Y. KUROUMARU M. NAKA The New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) is running a "Development
TECHNICAL PAPER Steering Actuator for Autonomous Driving and Platooning *1 A. ISHIHARA Y. KUROUMARU M. NAKA The New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) is running a "Development
The fact that SkyToll is able to deliver quality results has been proven by its successful projects.
 www.skytoll.com At present, an efficient and well-functioning transport sector and the quality of transport infrastructure itself are a prerequisite for the further growth of the economy and ensure the
www.skytoll.com At present, an efficient and well-functioning transport sector and the quality of transport infrastructure itself are a prerequisite for the further growth of the economy and ensure the
Electric Vehicle Adoption in the South African Context
 Electric Vehicle Adoption in the South African Context Policy, Pilot Projects and Awareness Creation Challenges and Opportunities Sustainability Week CSIR ICC Transport Seminar 7 June 2018 Context 1. Transport
Electric Vehicle Adoption in the South African Context Policy, Pilot Projects and Awareness Creation Challenges and Opportunities Sustainability Week CSIR ICC Transport Seminar 7 June 2018 Context 1. Transport
Road fatalities in 2012
 Lithuania 1 Inhabitants Vehicles/1 000 inhabitants Road fatalities in 2012 Fatalities /100 000 inhabitants in 2012 2.98 million 751 301 10.1 1. Road safety data collection Definitions Road fatality: person
Lithuania 1 Inhabitants Vehicles/1 000 inhabitants Road fatalities in 2012 Fatalities /100 000 inhabitants in 2012 2.98 million 751 301 10.1 1. Road safety data collection Definitions Road fatality: person
Leading the way to seamless mobility November th, 2017 Tampa, Florida
 Leading the way to seamless mobility November 14-15 th, 2017 Tampa, Florida usa.siemens.com/intelligenttraffic Urban mobility challenges A view on safety and congestion Trend Challenges + 2 Cities grow
Leading the way to seamless mobility November 14-15 th, 2017 Tampa, Florida usa.siemens.com/intelligenttraffic Urban mobility challenges A view on safety and congestion Trend Challenges + 2 Cities grow
Findings from the Limassol SUMP study
 5 th European Conference on Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans 14-15 May 2018 Nicosia, Cyprus Findings from the Limassol SUMP study Apostolos Bizakis Deputy PM General Information The largest city in the
5 th European Conference on Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans 14-15 May 2018 Nicosia, Cyprus Findings from the Limassol SUMP study Apostolos Bizakis Deputy PM General Information The largest city in the
METI Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. METI s Automated driving Demo
 METI Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry METI s Automated driving Demo Table of contents 1.Background 2.Roadmap 3.Demonstration projects 1Mobility service in rural area 2Providing information for operators
METI Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry METI s Automated driving Demo Table of contents 1.Background 2.Roadmap 3.Demonstration projects 1Mobility service in rural area 2Providing information for operators
DSRC Roadside Unit INFOBEACON and Solutions Utilizing ETC On-Board Units
 DSRC Roadside Unit INFOBEACON and Solutions Utilizing ETC On-Board Units YOSHIMOTO Masahiro, KONDO Toshiya, NOGI Yoshinori OKANISHI Shogo, ISSHIKI Naoki, SUGAWA Kunihiko Abstract The ETC (Electronic Toll
DSRC Roadside Unit INFOBEACON and Solutions Utilizing ETC On-Board Units YOSHIMOTO Masahiro, KONDO Toshiya, NOGI Yoshinori OKANISHI Shogo, ISSHIKI Naoki, SUGAWA Kunihiko Abstract The ETC (Electronic Toll
The Status of Transportation Funding, Road Charge and Vehicle Miles Traveled in California
 The Status of Transportation Funding, Road Charge and Vehicle Miles Traveled in California Long-Term Policy Options for Sustainable Transportation Options NCSL State Transportation Leaders Symposium October
The Status of Transportation Funding, Road Charge and Vehicle Miles Traveled in California Long-Term Policy Options for Sustainable Transportation Options NCSL State Transportation Leaders Symposium October
UNINTENDED CONSEQUENCE OF THE ELECTRIC VEHICLE REVOLUTION
 UNINTENDED CONSEQUENCE OF THE ELECTRIC VEHICLE REVOLUTION By Tom Grahamslaw and Paul Marsh THROUGH THE NEWS AND MEDIA, ROAD USERS ARE BECOMING MORE AWARE THAT WE ARE NOW SEEING A TRANSITION FROM THE TRADITIONAL
UNINTENDED CONSEQUENCE OF THE ELECTRIC VEHICLE REVOLUTION By Tom Grahamslaw and Paul Marsh THROUGH THE NEWS AND MEDIA, ROAD USERS ARE BECOMING MORE AWARE THAT WE ARE NOW SEEING A TRANSITION FROM THE TRADITIONAL
Transportation Policy for Reducing GHG Emissions in Korea. Junhaeng Jo
 Transportation Policy for Reducing GHG Emissions in Korea Junhaeng Jo Contents Transportation Policy for Reducing GHG Emissions in Korea CO 2 Emissions in Transportation Sector Transportation Policy Measures
Transportation Policy for Reducing GHG Emissions in Korea Junhaeng Jo Contents Transportation Policy for Reducing GHG Emissions in Korea CO 2 Emissions in Transportation Sector Transportation Policy Measures
BMW GROUP DIALOGUE. HANGZHOU 2017 TAKE AWAYS.
 BMW GROUP DIALOGUE. HANGZHOU 2017 TAKE AWAYS. BMW GROUP DIALOGUE. CONTENT. A B C Executive Summary: Top Stakeholder Expert Perceptions & Recommendations from Hangzhou Background: Mobility in Hangzhou 2017,
BMW GROUP DIALOGUE. HANGZHOU 2017 TAKE AWAYS. BMW GROUP DIALOGUE. CONTENT. A B C Executive Summary: Top Stakeholder Expert Perceptions & Recommendations from Hangzhou Background: Mobility in Hangzhou 2017,
CHANGE IN DRIVERS PARKING PREFERENCE AFTER THE INTRODUCTION OF STRENGTHENED PARKING REGULATIONS
 CHANGE IN DRIVERS PARKING PREFERENCE AFTER THE INTRODUCTION OF STRENGTHENED PARKING REGULATIONS Kazuyuki TAKADA, Tokyo Denki University, takada@g.dendai.ac.jp Norio TAJIMA, Tokyo Denki University, 09rmk19@dendai.ac.jp
CHANGE IN DRIVERS PARKING PREFERENCE AFTER THE INTRODUCTION OF STRENGTHENED PARKING REGULATIONS Kazuyuki TAKADA, Tokyo Denki University, takada@g.dendai.ac.jp Norio TAJIMA, Tokyo Denki University, 09rmk19@dendai.ac.jp
Urban Mobility Systems - Regulation Across Modes
 1st European Intermodal Transport Regulation Forum Urban Mobility Systems - Regulation Across Modes Florence 7 December 12 UITP - The basics - UITP is the global organisation for urban, suburban and regional
1st European Intermodal Transport Regulation Forum Urban Mobility Systems - Regulation Across Modes Florence 7 December 12 UITP - The basics - UITP is the global organisation for urban, suburban and regional
Intelligent Vehicle Systems
 Intelligent Vehicle Systems Southwest Research Institute Public Agency Roles for a Successful Autonomous Vehicle Deployment Amit Misra Manager R&D Transportation Management Systems 1 Motivation for This
Intelligent Vehicle Systems Southwest Research Institute Public Agency Roles for a Successful Autonomous Vehicle Deployment Amit Misra Manager R&D Transportation Management Systems 1 Motivation for This
Structure. Transport and Sustainability. Lessons from Past. The Way Forward
 1 Structure Transport and Sustainability Lessons from Past The Way Forward 2 Transport and Sustainability Consequences for fuel demand By 2025 more than half of the population in SSA will be living in
1 Structure Transport and Sustainability Lessons from Past The Way Forward 2 Transport and Sustainability Consequences for fuel demand By 2025 more than half of the population in SSA will be living in
2.1 TRANSIT VISION 2040 FROM VISION TO ACTION. Expand regional rapid transit networks STRATEGIC DIRECTION
 TRANSIT VISION 2040 FROM VISION TO ACTION TRANSIT VISION 2040 defines a future in which public transit maximizes its contribution to quality of life with benefits that support a vibrant and equitable society,
TRANSIT VISION 2040 FROM VISION TO ACTION TRANSIT VISION 2040 defines a future in which public transit maximizes its contribution to quality of life with benefits that support a vibrant and equitable society,
Public Transportation Problems and Solutions in the Historical Center of Quito
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1266 205 Public Transportation Problems and Solutions in the Historical Center of Quito JACOB GREENSTEIN, Lours BERGER, AND AMIRAM STRULOV Quito, the capital of Ecuador,
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1266 205 Public Transportation Problems and Solutions in the Historical Center of Quito JACOB GREENSTEIN, Lours BERGER, AND AMIRAM STRULOV Quito, the capital of Ecuador,
More persons in the cars? Status and potential for change in car occupancy rates in Norway
 Author(s): Liva Vågane Oslo 2009, 57 pages Norwegian language Summary: More persons in the cars? Status and potential for change in car occupancy rates in Norway Results from national travel surveys in
Author(s): Liva Vågane Oslo 2009, 57 pages Norwegian language Summary: More persons in the cars? Status and potential for change in car occupancy rates in Norway Results from national travel surveys in
How can parking policy change the city?
 How can parking policy change the city? Outcomes from new parking policies in Madrid EPA POLIS SEMINAR Krakow, September 15th, 2016 Sergio Fernandez Balaguer Empresa Municipal de INDEX How can parking
How can parking policy change the city? Outcomes from new parking policies in Madrid EPA POLIS SEMINAR Krakow, September 15th, 2016 Sergio Fernandez Balaguer Empresa Municipal de INDEX How can parking
Chapter 4. Design and Analysis of Feeder-Line Bus. October 2016
 Chapter 4 Design and Analysis of Feeder-Line Bus October 2016 This chapter should be cited as ERIA (2016), Design and Analysis of Feeder-Line Bus, in Kutani, I. and Y. Sado (eds.), Addressing Energy Efficiency
Chapter 4 Design and Analysis of Feeder-Line Bus October 2016 This chapter should be cited as ERIA (2016), Design and Analysis of Feeder-Line Bus, in Kutani, I. and Y. Sado (eds.), Addressing Energy Efficiency
Car-pooling : ways to promote its development
 Car-pooling : ways to promote its development Presented by Christophe Saroli CERTU - Département Déplacements Durables 1 Certu in brief Agency of the French Ministry of Ecology, Sustainable Development
Car-pooling : ways to promote its development Presented by Christophe Saroli CERTU - Département Déplacements Durables 1 Certu in brief Agency of the French Ministry of Ecology, Sustainable Development
Telematics Service for Commercial Vehicles to Realize Safe Traffic Society
 Telematics Service for Commercial Vehicles to Realize Safe Traffic Society Makoto Koike Masatsugu Isogai As operation management for commercial vehicles, services that use digital tachograph-based devices
Telematics Service for Commercial Vehicles to Realize Safe Traffic Society Makoto Koike Masatsugu Isogai As operation management for commercial vehicles, services that use digital tachograph-based devices
STRATEGIC PRIORITIES AND POLICY COMMITTEE MAY 5, 2016
 STRATEGIC PRIORITIES AND POLICY COMMITTEE MAY 5, 2016 Shift Rapid Transit Initiative Largest infrastructure project in the city s history. Rapid Transit initiative will transform London s public transit
STRATEGIC PRIORITIES AND POLICY COMMITTEE MAY 5, 2016 Shift Rapid Transit Initiative Largest infrastructure project in the city s history. Rapid Transit initiative will transform London s public transit
Smart Cities Around the Country
 Smart Cities Around the Country Robert James Date 11/09/2017 Contact rojames@hntb.com (732) 689-1989 2 Automated Intersection https://youtu.be/4smjp8tdwtu Smart Cities A Smart City utilizes innovative
Smart Cities Around the Country Robert James Date 11/09/2017 Contact rojames@hntb.com (732) 689-1989 2 Automated Intersection https://youtu.be/4smjp8tdwtu Smart Cities A Smart City utilizes innovative
ASIAN DEVELOPMENT FUND (ADF) ADF XI REPLENISHMENT MEETING 7 9 March 2012 Manila, Philippines. Post-Conflict Assistance to Afghanistan
 ASIAN DEVELOPMENT FUND (ADF) ADF XI REPLENISHMENT MEETING 7 9 March 2012 Manila, Philippines Post-Conflict Assistance to Afghanistan February 2012 ABBREVIATIONS ADB Asian Development Bank ADF Asian Development
ASIAN DEVELOPMENT FUND (ADF) ADF XI REPLENISHMENT MEETING 7 9 March 2012 Manila, Philippines Post-Conflict Assistance to Afghanistan February 2012 ABBREVIATIONS ADB Asian Development Bank ADF Asian Development
