iii Professional Technician Series Part of Updates to the Fifth Edition Text was updated Supplements Package All Professional Technician
|
|
|
- Laurence Owens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Preface Professional Technician Series Part of Pearson Automotive s Professional Technician Series, the fifth edition of Automotive Engine Performance represents the future of automotive textbooks. The series is a full-color, media-integrated solution for today s students and instructors. The series includes textbooks that cover all eight areas of ASE certification, plus additional titles covering common courses. The series is also peer reviewed for technical accuracy. Updates to the Fifth Edition Text was updated with the following features: Many new full color line drawings and photos were added to this edition to help bring the subject to life. Updated throughout and correlated to the latest ASE/ NATEF tasks. New Case Studies included in this edition that includes the three Cs (Complaint, cause and correction). New OSHA hazardous chemical labeling requirements added to Chapter 2. Atkinson Cycle engine design added to Chapter 3. Scope testing of MAF sensors added to Chapter 23. Additional content on gasoline direct injection (GDI) added to Chapter 28. Fiat Chrysler Multiair System information added to Chapter 30. Tier 3 Emission Standards added to Chapter 31. Unlike other textbooks, this book is written so that the ASE and NATEF Correlated NATEF-certified programs need to demonstrate that they use course material that covers NATEF and ASE tasks. All Professional Technician textbooks have been correlated to the appropriate ASE and NATEF task lists. These correlations can be found in two locations: As an appendix to each book. At the beginning of each chapter in the Instructor s Manual. A Complete Instructor and Student Supplements Package All Professional Technician textbooks are accompanied by a full set of instructor and student supplements. Please see page vi for a detailed list of supplements. A Focus on Diagnosis and Problem Solving The Professional Technician Series has been developed to satisfy the need for a greater emphasis on problem diagnosis. Automotive instructors and service managers agree that students and beginning technicians need more training in diagnostic procedures and skill development. To meet this need and demonstrate how real-world problems are solved, Real World Fix features are included throughout and highlight how real-life problems are diagnosed and repaired. The following pages highlight the unique core features that set the Professional Technician Series book apart from other automotive textbooks. theory, construction, diagnosis, and service of a particular component or system are presented in one location. There is no need to search through the entire book for other references to the same topic. iii A01_HALD4917_05_SE_FM.indd 3 9/14/15 8:08 PM
2 In-Text Features Safety Tip Shop Cloth Disposal Always dispose of oily shop cloths in an enclosed container to prevent a fire. See Figure Whenever oily cloths are thrown together on the floor or workbench, a chemical reaction can occur, which can ignite the cloth even without an open flame. This process of ignition without an open flame is called spontaneous combustion. Safety Tips alert students to possible hazards on the job and how to avoid them. case study There Is No Substitute for a Thorough Visual Inspection An intermittent check engine light and a randommisfire diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P0300 was being diagnosed. A scan tool did not provide any help because all systems seemed to be functioning normally. Finally, the technician removed the engine cover and discovered a mouse nest. See Figure LEARNING Objectives and Key Terms appear at the beginning of each chapter to help students and instructors focus on the most important material in each chapter. The chapter objectives are based on specific ASE and NATEF tasks. Summary: Complaint Customer stated that the Check Engine light was on. Cause A stored P0300 DTC was stored indicating a random misfire had been detected caused by an animal that had partially eaten some fuel injector wires. Correction The mouse nest was removed and the wiring was repaired. CASE STUDY present students with actual automotive scenarios and show how these common (and sometimes uncommon) problems were diagnosed and repaired. Tech Tip It Just Takes a Second Whenever removing any automotive component, it is wise to screw the bolts back into the holes a couple of threads by hand. This ensures that the right bolt will be used in its original location when the component or part is put back on the vehicle.? Frequently Asked Question How Many Types of Screw Heads Are Used in Automotive Applications? There are many, including Torx, hex (also called Allen), plus many others used in custom vans and motor homes. See Figure 1 9. Tech Tips feature real-world advice and tricks of the trade from ASE-certified master technicians. Frequently Asked Questions are based on the author s own experience and provide answers to many of the most common questions asked by students and beginning service technicians. iv In-Text Features A01_HALD4917_05_SE_FM.indd 4 9/14/15 8:08 PM
3 Note: Most of these locking nuts are grouped together and are commonly referred to as prevailing torque nuts. This means that the nut will hold its tightness or torque and not loosen with movement or vibration. Notes provide students with additional technical information to give them a greater understanding of a specific task or procedure. CAUTION: Never use hardware store (nongraded) bolts, studs, or nuts on any vehicle steering, suspension, or brake component. Always use the exact size and grade of hardware that is specified and used by the vehicle manufacturer. Cautions alert students about potential damage to the vehicle that can occur during a specific task or service procedure. Warning Do not use incandescent trouble lights around gasoline or other flammable liquids. The liquids can cause the bulb to break and the hot filament can ignite the flammable liquid, which can cause personal injury or even death. The Summary, Review Questions, and Chapter Quiz at the end of each chapter help students review the material presented in the chapter and test themselves to see Warnings alert students to potential dangers to how much they ve learned. themselves during a specific task or service procedure. Step-by-Step photo sequences show in detail the steps involved in performing a specific task or service procedure. In- T ext F eatures A01_HALD4917_05_SE_FM.indd 5 v 9/14/15 8:08 PM
4 Supplements Resources in Print and Online Automotive Engine Performance NAME OF SUPPLEMENT PRINT ONLINE AUDIENCE DESCRIPTION Instructor Resource Manual TestGen PowerPoint Presentation Image Bank NATEF Correlated Task Sheets - For Instructors NATEF Correlated Task Sheets - For Students CourseSmart etext Instructors NEW! The Ultimate teaching aid: Chapter summaries, key terms, chapter learning objectives, lecture resources, discuss/demonstrate classroom activities, and answers to the in text review and quiz questions. Instructors Test generation software and test bank for the text. Instructors Slides include chapter learning objectives, lecture outline of the test, and graphics from the book. Instructors All of the images and graphs from the textbook to create customized lecture slides. Instructors Downloadable NATEF task sheets for easy customization and development of unique task sheets. Students Study activity manual that correlates NATEF Automobile Standards to chapters and pages numbers in the text. Available to students at a discounted price when packaged with the text. Students An alternative to purchasing the print textbook, students can subscribe to the same content online and save up to 50% off the suggested list price of the print text. Visit All online resources can be downloaded from the Instructor s Resource Center: vi Supplements A01_HALD4917_05_SE_FM.indd 6 9/14/15 8:08 PM
5 chapter 28 Gasoline Direct-Injection Systems Learning Objectives Key Terms After studying this chapter, the reader will be able to: 1. Discuss how to troubleshoot a gasoline directinjection system. 2. Explain how a gasoline direct-injection system works. 3. Describe the differences between port fuelinjection and gasoline direct-injection systems. 4. List the various modes of operation of a gasoline direct-injection system. This chapter will help you prepare for Engine Repair (A8) ASE certification test content area C (Fuel, Air Induction, and Exhaust Systems Diagnosis and Repair). Gasoline direct injection (GDI) 436 Homogeneous mode 438 Spark ignition direct injection (SIDI) 436 Stratified mode M28_HALD4917_05_SE_C28.indd 435
6 PCM B+ IC IC 12 V FUEL PUMP SPEED MODULE FUEL RAIL HIGH- PRESSURE SENSOR LOW- PRESSURE SENSOR Figure 28 1 A gasoline direct-injection system injects fuel under high pressure directly into the combustion chamber. HIGH-PRESSURE PUMP FUEL PUMP GDI INJECTORS FUEL TANK Figure 28 2 A GDI system uses a low-pressure pump in the gas tank similar to other types of fuel-injection systems. The PCM controls the pressure of the high-pressure pump using sensor inputs. Direct Fuel Injection Several vehicle manufacturers such as Audi, Mitsubishi, Mercedes, BMW, Toyota/Lexus, Mazda, Ford, and General Motors are using gasoline direct injection (GDI) systems, which General Motors refers to as a spark ignition direct injection (SIDI) system. A direct-injection system sprays highpressure fuel, up to 2,900 PSI, into the combustion chamber as the piston approaches the top of the compression stroke. With the combination of high-pressure swirl injectors and modified combustion chamber, almost instantaneous vaporization occurs. This combined with a higher compression ratio allows a direct-injected engine to operate using a leaner-than-normal air fuel ratio, which results in improved fuel economy with higher power output and reduced exhaust emissions. See Figure Advantages of Gasoline Direct Injection The use of direct injection compared with port fuel injection has many advantages including: Improved fuel economy due to reduced pumping losses and heat loss Allows a higher compression ratio for higher engine efficiency Allows the use of lower-octane gasoline The volumetric efficiency is higher Less need for extra fuel for acceleration Improved cold starting and throttle response Allows the use of greater percentage of EGR to reduce exhaust emissions Up to 25% improvement in fuel economy 12% to 15% reduction in exhaust emissions Disadvantages of Gasoline Direct Injection Higher cost due to high-pressure pump and injectors More components compared with port fuel injection Due to the high compression, a NOx storage catalyst is sometimes required to meet emission standards, especially in Europe. ( See Figure 28 2.) Uses up to six operating modes depending on engine load and speed, which requires more calculations to be performed by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). 436 chapter 28 M28_HALD4917_05_SE_C28.indd 436
7 FUEL TANK HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL PUMP PRESSURE REGULATOR COMMON RAIL THE HIGH-PRESSURE PUMP DRIVE LOBE IS LOCATED ON THE ENGINE CAMSHAFT Figure 28 3 A typical directinjection system uses two pumps one low-pressure electric pump in the fuel tank and the other a high-pressure pump driven by the camshaft. The high pressure fuel system operates at a pressure as low as 500 PSI during light load conditions and as high as 2,900 PSI under heavy loads. INJECTOR LOW-PRESSURE FUEL PUMP Direct-Injection Fuel Delivery System PRESSURE REGULATOR SPRING Low-Pressure Supply Pump The fuel pump in the fuel tank supplies fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump at a pres sure of approximately 60 PSI. The fuel filter is located in the fuel tank and is part of the fuel pump assembly. It is not usu ally serviceable as a separate component; the engine control module (ECM) controls the output of the high-pressure pump, which has a range between 500 PSI (3,440 kpa) and 2,900 PSI (15,200 kpa) during engine operation. See Figures 28 2 and High-Pressure Pump In a General Motors system, the engine control module (ECM) controls the output of the high-pressure pump, which has a range between 500 PSI (3,440 kpa) and 2,900 PSI (15,200 kpa) during engine operation. The high-pressure fuel pump connects to the pump in the fuel tank through the low-pressure fuel line. The pump consists of a single-barrel piston pump, which is driven by the engine camshaft. The pump plunger rides on a three-lobed cam on the camshaft. The high-pressure pump is cooled and lubricated by the fuel itself. See Figure Fuel Rail The fuel rail stores the fuel from the highpressure pump and stores high-pressure fuel for use to each injector. All injectors get the same pressure fuel from the fuel rail. Fuel Pressure Regulator An electric pressurecontrol valve is installed between the pump inlet and outlet valves. The fuel rail pressure sensor connects to the PCM with three wires: 5 volt reference ground signal PISTON CHECK BALL CAMSHAFT Figure 28 4 A typical camshaft-driven high-pressure pump used to increase fuel pressure to 2,000 PSI or higher. The sensor signal provides an analog signal to the PCM that varies in voltage as fuel rail pressure changes. Low pressure results in a low-voltage signal and high pressure results in a high-voltage signal. Gasoline Direct-Injection Systems 437 M28_HALD4917_05_SE_C28.indd 437
8 HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL PUMP ELECTRIC PRESSURE CONTROL VALVE FUEL RAIL FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR FUEL INJECTOR Figure 28 5 A gasoline direct-injection (GDI) fuel rail and pump assembly with the electric pressure control valve. The PCM uses internal drivers to control the power feed and ground for the pressure control valve. When both PCM drivers are deactivated, the inlet valve is held open by spring pressure. This causes the high pressure fuel pump to default to low-pressure mode. The fuel from the high-pressure fuel pump flows through a line to the fuel rail and injectors. The actual operating pressure can vary from as low as 500 PSI (3,440 kpa) at idle to over 2,000 PSI (13,800 kpa) during high speed or heavy load conditions. See Figure Note: Unlike a port fuel-injection system, a gasoline direct injection system varies the fuel pressure to achieve greater fuel delivery using a very short pulse time, which is usually less than one millisecond. To summarize: Port Fuel Injection constant fuel pressure but variable injector pulse-width. GDI almost constant injector pulse-width with varying fuel pressure. Gasoline Direct- Injection Fuel Injectors Each high-pressure fuel injector assembly is an electrically magnetic injector mounted in the cylinder head. In the GDI system, the PCM controls each fuel injector with 50 to 90 volts (usually 60 to 70 volts), depending on the system, which is created by a boost capacitor in the PCM. During the high-voltage boost phase, the capacitor is discharged through an injector, allowing for initial injector opening. The injector is then held open with 12 volts. The high-pressure fuel injector has a small slit or six precision-machined holes that generate the desired spray pattern. The injector also has an extended tip to allow for cooling from a water jacket in the cylinder head. See Chart 28 1 for an overview of the differences between a port fuel-injection system and a gasoline directinjection system. Port Fuel-Injection System Compared With Gdi System PORT FUEL INJECTION GASOLINE DIRECT INJECTION Fuel pressure PSI Lift pump 50 to 60 PSI High-pressure pump 500 to 2,900 PSI Injection pulse ms About 0.4 ms (400 μs) width at idle Injector resistance ohms 1 3 ohms Injector voltage 6 V for low V resistance injectors, 12 V for most injectors Number of injections One 1 3 per event Engine compression ratio 8:1 11:1 11:1 13:1 Chart 28 1 A comparison chart showing the major differences between a port fuel-injection system and a gasoline direct-injection system. Modes of Operation The two basic modes of operation include: 1. Stratified mode. In this mode of operation, the air fuel mixture is richer around the spark plug than it is in the rest of the cylinder. 2. Homogeneous mode. In this mode of operation, the air fuel mixture is the same throughout the cylinder. There are variations of these modes that can be used to fine-tune the air fuel mixture inside the cylinder. For example, Bosch, a supplier to many vehicle manufacturers, uses the following six modes of operation: Homogeneous mode. In this mode, the injector is pulsed one time to create an even air fuel mixture in the cylinder. The injection occurs during the intake stroke. This mode is used during high-speed and/or high-torque conditions. Homogeneous lean mode. Similar to the homogeneous mode except that the overall air fuel mixture is slightly lean for better fuel economy. The injection occurs during the intake stroke. This mode is used under steady, lightload conditions. Stratified mode. In this mode of operation, the injection occurs just before the spark occurs resulting in lean combustion, reducing fuel consumption. Homogeneous stratified mode. In this mode, there are two injections of fuel: 438 chapter 28 M28_HALD4917_05_SE_C28.indd 438
9 SPRAY-GUIDED COMBUSTION INJECTOR INJECTOR WALL-GUIDED (SWIRL) COMBUSTION SPARK PLUG Figure 28 7 The side injector combines with the shape of the piston to create a swirl as the piston moves up on the compression stroke. SPARK PLUG Figure 28 6 In this design, the fuel injector is at the top of the cylinder and sprays fuel into the cavity of the piston. WALL-GUIDED (TUMBLE) COMBUSTION SPARK PLUG Figure 28 8 The piston creates a tumbling force as it moves upward. The first injection is during the intake stroke. The second injection is during the compression stroke. As a result of these double injections, the rich air fuel mixture around the spark plug is ignited first. Then, the rich mixture ignites the leaner mixture. The advantages of this mode include lower exhaust emissions than the stratified mode and less fuel consumption than the homogeneous lean mode. INJECTOR Homogeneous knock protection mode. The purpose of this mode is to reduce the possibility of spark knock from occurring under heavy loads at low engine speeds. There are two injections of fuel: The first injection occurs on the intake stroke. The second injection occurs during the compression stroke with the overall mixture being stoichiometric. As a result of this mode, the PCM does not need to retard ignition timing as much to operate knock-free. Stratified catalyst heating mode. In this mode, there are two injections: The first injection is on the compression stroke just before combustion. The second injection is after combustion occurs to heat the exhaust. This mode is used to quickly warm the catalytic converter and to burn the sulfur from the NO x catalyst. Piston Top Designs Gasoline direct-injection (GDI) systems use a variety of shapes of piston and injector locations depending on make and model of engine. Three of the most commonly used designs include: Spray-guided combustion. In this design, the injector is placed in the center of the combustion chamber and injects fuel into the dished-out portion of the piston. The shape of the piston helps guide and direct the mist of fuel in the combustion chamber. See Figure Swirl combustion. This design uses the shape of the piston and the position of the injector at the side of the combustion chamber to create turbulence and swirl of the air fuel mixture. See Figure Tumble combustion. Depending on when the fuel is injected into the combustion chamber helps determine how the air fuel mixture is moved or tumbled. See Figure Gasoline Direct-Injection Systems 439 M28_HALD4917_05_SE_C28.indd 439
10 HIGH DIRECT INJECTION ONLY TORQUE DIRECT INJECTION AND PORT INJECTION ENGINE SPEED (RPM) HIGH Figure 28 9 Notice that there are conditions when the port fuel-injector, located in the intake manifold, and the gasoline direct injector, located in the cylinder, both operate to provide the proper air fuel mixture. Engine Start System Lexus Port- and Direct- Injection Systems Overview Many Lexus vehicles use gasoline direct injection and in some engines they also use a conventional port fuel-injection system. The Lexus D-4S system combines directinjection injectors located in the combustion chamber with port fuel-injectors in the intake manifold near the intake valve. The two injection systems work together to supply the fuel needed by the engine. See Figure 28 9 for how the two systems are used throughout the various stages of engine operation. An engine equipped with gasoline direct injection could use the system to start the engine. This is most useful during idle stop mode when the engine is stopped while the vehicle is at a traffic light to save fuel. The steps used in the Mazda startstop system, called the smart idle stop system (SISS), allow the engine to be started without a starter motor and include the following steps: step 1 The engine is stopped. The normal stopping position of an engine when it stops is 70 degrees before top dead center, plus or minus 20 degrees. This is because the engine stops with one cylinder on the compression stroke and the PCM can determine the cylinder position, using the crankshaft and camshaft position sensors. Cold-Start Warm-up To help reduce exhaust emissions after a cold start, the fuel system uses a stratified change mode. This results in a richer air fuel mixture near the spark plug and allows for the spark to be retarded to increase the temperature of the exhaust. As a result of the increased exhaust temperature, the catalytic converter rapidly reaches operating temperature, which reduces exhaust emissions. step 2 step 3 step 4 step 5 When a command is made to start the engine by the PCM, fuel is injected into the cylinder that is on the compression stroke and ignited by the spark plug. The piston on the compression stroke is forced downward forcing the crankshaft to rotate counterclockwise or in the opposite direction to normal operation. The rotation of the crankshaft then forces the companion cylinder toward the top of the cylinder. Fuel is injected and the spark plug is fired, forcing the piston down, causing the crankshaft to rotate in the normal (clockwise) direction. Normal combustion events continue allowing the engine to keep running. 440 chapter 28 M28_HALD4917_05_SE_C28.indd 440
11 Gasoline DirectInjection Service Noise Issues FUEL INJECTOR INTAKE VALVES Gasoline direct-injection systems operate at high pressure and the injectors can often be heard with the engine running and the hood open. This noise can be a customer SPARK PLUG concern because the clicking sound is similar to noisy valves. If a noise issue is the customer concern, check the following: Check a similar vehicle to determine if the sound is louder or more noticeable than normal. Check that nothing under the hood is touching the fuel rail. If another line or hose is in contact with the fuel rail, the sound of the injectors clicking can be transmitted throughout the engine, making the sound more noticeable. Check for any technical service bulletins (TSBs) that may include new clips or sound insulators to help reduce EXHAUST VALVES Figure There may become a driveability issue because the gasoline direct-injection injector is exposed to combustion carbon and fuel residue. the noise. Carbon Issues that the engine will start and idle, but lack power to accelcarbon is often an issue in engines equipped with gasoline direct-injection systems. Carbon can erate the vehicle. The carbon deposits restrict the airflow into the cylinder enough to decrease engine power. affect engine operation by accumulating in two places: On the injector itself. Because the injector tip is in the combustion chamber, fuel residue can accumulate on the injector, reducing its ability to provide the proper spray pattern and amount of fuel. Some injector designs line direct-injection injectors do not show intake valve deposits. It is thought that the fuel being sprayed onto the intake valve from the port injector helps keep the are more likely to be affected by carbon than others. For intake valve clean. example, if the injector uses small holes, these tend to Carbon Cleaning. Most experts recommend the use of become clogged more than an injector that uses a single slit opening where the fuel being sprayed out tends to blast away any carbon. See Figure Note: Lexus engines that use both port and gaso- The backside of the intake valve. This is a common place for fuel residue and carbon to accumulate on en- Techron, a fuel system dispersant, to help keep carbon from accumulating. The use of a dispersant every six months or every 6,000 miles has proven to help prevent injector and intake valve deposits. If the lack of power is discovered and there are no stored gines equipped with gasoline direct injection. The accumu- diagnostic trouble codes, a conventional carbon cleaning pro- lation of carbon on the intake valve can become so severe cedure will likely restore power if the intake valves are coated. Summary 1. A gasoline direct-injection system uses a fuel injector that delivers a short squirt of fuel directly into the combustion chamber rather than in the intake manifold, near the intake valve on a port fuel-injection system. 2. The advantages of using gasoline direct injection instead of port fuel injection include: Improved fuel economy Reduced exhaust emissions Greater engine power 3. Some of the disadvantages of gasoline direct-injection systems compared with a port fuel-injection system include: Higher cost The need for NOx storage catalyst in some applications More components 4. The operating pressure can vary from as low as 500 PSI dur ing some low-demand conditions to as high as 2,900 PSI. G asoline D irect -I n j ection S y stems M28_HALD4917_05_SE_C28.indd
12 5. The fuel injectors are open for a very short period of time and are pulsed using a 50 to 90 volt pulse from a capacitor circuit. 6. GDI systems can operate in many modes, which are separated into the two basic modes: Stratified mode Homogeneous mode 7. GDI can be used to start an engine without the use of a starter motor for idle-stop functions. 8. GDI does create a louder clicking noise from the fuel injectors than port fuel-injection injectors. 9. Carbon deposits on the injector and the backside of the intake valve are a common problem with engines equipped with gasoline direct-injection systems. Review Questions 1. What are two advantages of gasoline direct injection compared with port fuel injection? 2. What are two disadvantages of gasoline direct injection compared with port fuel injection? 3. How is the fuel delivery system different from a port fuelinjection system? 4. What are the basic modes of operation of a GDI system? Chapter Quiz 1. Where is the fuel injected in an engine equipped with gasoline direct injection? a. Into the intake manifold near the intake valve b. Directly into the combustion chamber c. Above the intake port d. In the exhaust port 2. The fuel pump inside the fuel tank on a vehicle equipped with gasoline direct injection produces about what fuel pressure? a. 5 to 10 PSI b. 10 to 20 PSI c. 20 to 40 PSI d. 50 to 60 PSI 3. The high-pressure fuel pumps used in gasoline directinjection (GDI) systems are powered by. a. Electricity (DC motor) b. Electricity (AC motor) c. The camshaft d. The crankshaft 4. The high-pressure fuel pump pressure is regulated by using. a. An electric pressure-control valve b. A vacuum-biased regulator c. A mechanical regulator at the inlet to the fuel rail d. A non-vacuum biased regulator 5. The fuel injectors operate under a fuel pressure of about. a. 35 to 45 PSI c. 500 to 2,900 PSI b. 90 to 150 PSI d. 2,000 to 5,000 PSI 6. The fuel injectors used on a gasoline direct-injection system are pulsed on using what voltage? a. 12 to 14 volt c. 100 to 110 volt b. 50 to 90 volt d. 200 to 220 volt 7. Which mode of operation results in a richer air fuel mixture near the spark plug? a. Stoichiometric c. Stratified b. Homogeneous d. Knock protection 8. Some engines that use a gasoline direct-injection system also have port injection. a. True b. False 9. A gasoline direct-injection system can be used to start an engine without the need for a starter. a. True b. False 10. A lack of power from an engine equipped with gasoline direct injection could be due to. a. Noisy injectors b. Carbon on the injectors c. Carbon on the intake valves d. Both b and c 442 chapter 28 M28_HALD4917_05_SE_C28.indd 442
Automotive Fuel and Emissions Control Systems 4/E
 Automotive Fuel and Emissions Control Systems 4/E Opening Your Class KEY ELEMENT Introduce Content Motivate Learners State the learning objectives for the chapter or course you are about to cover and explain
Automotive Fuel and Emissions Control Systems 4/E Opening Your Class KEY ELEMENT Introduce Content Motivate Learners State the learning objectives for the chapter or course you are about to cover and explain
Module7:Advanced Combustion Systems and Alternative Powerplants Lecture 32:Stratified Charge Engines
 ADVANCED COMBUSTION SYSTEMS AND ALTERNATIVE POWERPLANTS The Lecture Contains: DIRECT INJECTION STRATIFIED CHARGE (DISC) ENGINES Historical Overview Potential Advantages of DISC Engines DISC Engine Combustion
ADVANCED COMBUSTION SYSTEMS AND ALTERNATIVE POWERPLANTS The Lecture Contains: DIRECT INJECTION STRATIFIED CHARGE (DISC) ENGINES Historical Overview Potential Advantages of DISC Engines DISC Engine Combustion
iii Professional Technician Series Part of Pearson Updates to the Seventh Edition Based on Package All Professional Technician textbooks
 Preface Professional Technician Series Part of Pearson Automotive s Professional Technician Series, the seventh edition of Automotive Steering, Suspension, and Alignment represents the future of automotive
Preface Professional Technician Series Part of Pearson Automotive s Professional Technician Series, the seventh edition of Automotive Steering, Suspension, and Alignment represents the future of automotive
Sensors & Controls. Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask.
 Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01
 Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01 Notice Due to the wide range of vehicles makes and models, the information given during the class will be general in nature and
Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01 Notice Due to the wide range of vehicles makes and models, the information given during the class will be general in nature and
GASOLINE DIRECT INJECTION IN SI ENGINES B. PAVAN VISWANADH P. ASHOK KUMAR. Mobile No : Mobile No:
 GASOLINE DIRECT INJECTION IN SI ENGINES SUBMIT TED BY B. PAVAN VISWANADH P. ASHOK KUMAR Y06ME011, III/IV B. Tech Y06ME003, III/IV B. Tech Pavan.visu@gmail.com ashok.me003@gmail.com Mobile No :9291323516
GASOLINE DIRECT INJECTION IN SI ENGINES SUBMIT TED BY B. PAVAN VISWANADH P. ASHOK KUMAR Y06ME011, III/IV B. Tech Y06ME003, III/IV B. Tech Pavan.visu@gmail.com ashok.me003@gmail.com Mobile No :9291323516
LONG BEACH CITY COLLEGE AUTO MECHANICS 233 AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRICAL & FUEL SYSTEMS SPRING 2005
 LONG BEACH CITY COLLEGE AUTO MECHANICS 233 AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRICAL & FUEL SYSTEMS SPRING 2005 SUBJECT MATTER AREA Automotive Technology COURSE NUMBER AMECH 233 SECTION NUMBER 31377 ROOM # MM128A/MM130 COURSE
LONG BEACH CITY COLLEGE AUTO MECHANICS 233 AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRICAL & FUEL SYSTEMS SPRING 2005 SUBJECT MATTER AREA Automotive Technology COURSE NUMBER AMECH 233 SECTION NUMBER 31377 ROOM # MM128A/MM130 COURSE
Chapter 20 OBD-II Diesel Monitors
 Light Vehicle Diesel Engines First Edition Chapter 20 OBD-II Diesel Monitors LEARNING OBJECTIVES (1 of 2) 20.1 Prepare for the Light Vehicle Diesel Engine (A9) ASE certification fuel system diagnosis and
Light Vehicle Diesel Engines First Edition Chapter 20 OBD-II Diesel Monitors LEARNING OBJECTIVES (1 of 2) 20.1 Prepare for the Light Vehicle Diesel Engine (A9) ASE certification fuel system diagnosis and
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
3. At sea level, the atmosphere exerts psi of pressure on everything.
 41 Chapter Gasoline Injection Fundamentals Name Instructor Date Score Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to explain the construction, operation, and classifications of modern gasoline
41 Chapter Gasoline Injection Fundamentals Name Instructor Date Score Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to explain the construction, operation, and classifications of modern gasoline
Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Lecture 14:Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions
 Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions The Lecture Contains: SI Engine Variables and Emissions Compression
Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions The Lecture Contains: SI Engine Variables and Emissions Compression
DTC P0420 or P0430. Circuit Description. DTC Descriptors. Conditions for Running the DTC
 Page 1 of 5 2005 Cadillac STS STS (VIN D) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 4.6L (LH2) Diagnostic Information and Procedures DTC P0420 or P0430 Circuit Description A three-way catalytic converter
Page 1 of 5 2005 Cadillac STS STS (VIN D) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 4.6L (LH2) Diagnostic Information and Procedures DTC P0420 or P0430 Circuit Description A three-way catalytic converter
2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components
 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Fuel Delivery and Air Induction > Description and Operation
2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Fuel Delivery and Air Induction > Description and Operation
Troubleshooting A Vintage Distributor Ignition System
 Troubleshooting A Vintage Distributor Ignition System -Henry P. Olsen When the owners of vintage carburetor- and distributor-equipped vehicles see that a shop has a big-box engine analyzer, they believe
Troubleshooting A Vintage Distributor Ignition System -Henry P. Olsen When the owners of vintage carburetor- and distributor-equipped vehicles see that a shop has a big-box engine analyzer, they believe
A. Perform a vacuum gauge test to determine engine condition and performance.
 ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSIS, REMOVAL, AND INSTALLATION LESSON 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC TESTS NOTE: Testing the engine s mechanical condition is required when the cause of a problem is not located
ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSIS, REMOVAL, AND INSTALLATION LESSON 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC TESTS NOTE: Testing the engine s mechanical condition is required when the cause of a problem is not located
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When preparing for a compression test, technician A disables the ignition system. Technician
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When preparing for a compression test, technician A disables the ignition system. Technician
16.01 Theory Module INPUTS
 16.01 Theory Module INPUTS Crankshaft position sensor Camshaft position sensor Knock sensor (some engine types) Barometric pressure sensor Intake air temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature sensor
16.01 Theory Module INPUTS Crankshaft position sensor Camshaft position sensor Knock sensor (some engine types) Barometric pressure sensor Intake air temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature sensor
Oregon Fuel Injection
 2001 2006 Dodge Mercedes - Freightliner Sprinter Diagnostics In order to do proper diagnostics you will need a scan tool and some special tools available from Mopar Special Tools http://mopar.snapon.com.
2001 2006 Dodge Mercedes - Freightliner Sprinter Diagnostics In order to do proper diagnostics you will need a scan tool and some special tools available from Mopar Special Tools http://mopar.snapon.com.
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Fuel System Diagnosis
 1996 Chevrolet Impala Caprice, Impala, Roadmaster (VIN B) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 4.3L (Caprice Only) and 5.7L Diagnostic Information and Procedures Document ID: 37723 Fuel System Diagnosis
1996 Chevrolet Impala Caprice, Impala, Roadmaster (VIN B) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 4.3L (Caprice Only) and 5.7L Diagnostic Information and Procedures Document ID: 37723 Fuel System Diagnosis
H - TESTS W/O CODES Nissan 240SX INTRODUCTION TROUBLE SHOOTING SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS WILL NOT START
 H - TESTS W/O CODES 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Trouble Shooting - No Codes Nissan; 240SX, Axxess, Maxima, Pathfinder, Pickup, Pulsar, Sentra, Van, INTRODUCTION Before diagnosing symptoms
H - TESTS W/O CODES 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Trouble Shooting - No Codes Nissan; 240SX, Axxess, Maxima, Pathfinder, Pickup, Pulsar, Sentra, Van, INTRODUCTION Before diagnosing symptoms
Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim
 Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim Q: What is Lambda and Lambda Control? A: In the case of a gasoline engine, the optimal mixture of air to fuel for complete combustion is a ratio of 14.7 parts
Lambda Control Fuel Adaptation and Fuel Trim Q: What is Lambda and Lambda Control? A: In the case of a gasoline engine, the optimal mixture of air to fuel for complete combustion is a ratio of 14.7 parts
ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION
 ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION Because the most widely used piston engine is the four-stroke cycle type, it will be used as the example for this section, Engine Operation and as the basis for comparison in the
ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION Because the most widely used piston engine is the four-stroke cycle type, it will be used as the example for this section, Engine Operation and as the basis for comparison in the
ACTUAL CYCLE. Actual engine cycle
 1 ACTUAL CYCLE Actual engine cycle Introduction 2 Ideal Gas Cycle (Air Standard Cycle) Idealized processes Idealize working Fluid Fuel-Air Cycle Idealized Processes Accurate Working Fluid Model Actual
1 ACTUAL CYCLE Actual engine cycle Introduction 2 Ideal Gas Cycle (Air Standard Cycle) Idealized processes Idealize working Fluid Fuel-Air Cycle Idealized Processes Accurate Working Fluid Model Actual
Automotive Technology. Resources
 Automotive Technology Resources Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach Third Canadian Edition Jack Erjavec, Martin Restoule, Stephen Leroux, Rob Thompson 9780176531522 Advancing technology continues
Automotive Technology Resources Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach Third Canadian Edition Jack Erjavec, Martin Restoule, Stephen Leroux, Rob Thompson 9780176531522 Advancing technology continues
Engine Systems. Basic Engine Operation. Firing Order. Four Stroke Cycle. Overhead Valves - OHV. Engine Design. AUMT Engine Systems 4/4/11
 Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Fuel System Diagnosis
 Page 1 of 8 Document ID# 104786 1997 Chevrolet Corvette Feedback Print Fuel Diagnosis (1) Fuel Pressure Gauge Bleed Hose (2) J 37287 Fuel Line Shut-off Adapters (3) Return Pipe (4) Feed
Page 1 of 8 Document ID# 104786 1997 Chevrolet Corvette Feedback Print Fuel Diagnosis (1) Fuel Pressure Gauge Bleed Hose (2) J 37287 Fuel Line Shut-off Adapters (3) Return Pipe (4) Feed
IGNITION SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND OPERATION
 69 IGNITION SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND OPERATION Figure 69-1 A point-type distributor from a hot rod being tested on a distributor machine. WARNING: The spark from an ignition coil is strong enough to cause
69 IGNITION SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND OPERATION Figure 69-1 A point-type distributor from a hot rod being tested on a distributor machine. WARNING: The spark from an ignition coil is strong enough to cause
DTC P0174 Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 2
 2000 Chevrolet/Geo S10 Pickup - 4WD DTC P0174 Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 2 Circuit Description In order to provide the best possible combination of driveability, fuel economy, and emission control, the
2000 Chevrolet/Geo S10 Pickup - 4WD DTC P0174 Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 2 Circuit Description In order to provide the best possible combination of driveability, fuel economy, and emission control, the
Powertrain DTC Summaries OBD II
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2002 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2002 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE. General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L
 INTRODUCTION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem. This is also where to begin
INTRODUCTION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem. This is also where to begin
Vacuum Readings for Tuning and Diagnosis
 Vacuum Readings for Tuning and Diagnosis -Henry P. Olsen Once you learn to properly interpret its readings, a vacuum gauge can be one of the most useful tools in your toolbox. 22 FEATURE Some people consider
Vacuum Readings for Tuning and Diagnosis -Henry P. Olsen Once you learn to properly interpret its readings, a vacuum gauge can be one of the most useful tools in your toolbox. 22 FEATURE Some people consider
2002 Chevrolet Silverado 1500
 For the specific DTCs required for each system, see table. Systems such as fuel delivery, misfire, and comprehensive components may not be listed in a system status list. These tests run continuously on
For the specific DTCs required for each system, see table. Systems such as fuel delivery, misfire, and comprehensive components may not be listed in a system status list. These tests run continuously on
CH. 48 ENGINE MECHANICAL PROBLEMS TEST
 TERRY FOX AUTOMOTIVE CH. 48 ENGINE MECHANICAL PROBLEMS TEST WHEN YOU ARE DONE THIS TEST GUESS WHAT YOU THINK YOU WILL RECEIVE FOR A MARK BELOW. IF YOU ARE WITHIN 2 MARKS YOU WILL RECEIVE 2 BONUS MARKS.
TERRY FOX AUTOMOTIVE CH. 48 ENGINE MECHANICAL PROBLEMS TEST WHEN YOU ARE DONE THIS TEST GUESS WHAT YOU THINK YOU WILL RECEIVE FOR A MARK BELOW. IF YOU ARE WITHIN 2 MARKS YOU WILL RECEIVE 2 BONUS MARKS.
Engine Design Classifications
 Chapter 12 Engine Design Classifications Name: Date: Instructor: Score: Textbook pages 158-175 Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to describe and explain basic automotive engine designs
Chapter 12 Engine Design Classifications Name: Date: Instructor: Score: Textbook pages 158-175 Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to describe and explain basic automotive engine designs
Fuel System Diagnosis
 2000 Chevrolet Corvette Corvette (VIN Y) Service Manual Document ID: 609667 Page 1 of 7 Fuel Diagnosis (1) Fuel Feed Pipe (2) Auxiliary Fuel Feed Rear Pipe (left tank to jet pump) (3) Auxiliary Fuel Return
2000 Chevrolet Corvette Corvette (VIN Y) Service Manual Document ID: 609667 Page 1 of 7 Fuel Diagnosis (1) Fuel Feed Pipe (2) Auxiliary Fuel Feed Rear Pipe (left tank to jet pump) (3) Auxiliary Fuel Return
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar S-TYPE V6, V8 N/A and V8 SC 2002.5 Model Year Refer to pages 2 9 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries.
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar S-TYPE V6, V8 N/A and V8 SC 2002.5 Model Year Refer to pages 2 9 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries.
EVENING PROGRAM DESCRIPTIONS. California State Smog Repair Technician
 EVENING PROGRAM DESCRIPTIONS California State Smog Repair Technician School Name: Smog Tech Institute Course Name: Smog Repair Technician Course Number: TBA Program Title: Californian State Smog Repair
EVENING PROGRAM DESCRIPTIONS California State Smog Repair Technician School Name: Smog Tech Institute Course Name: Smog Repair Technician Course Number: TBA Program Title: Californian State Smog Repair
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
User s Guide For Control Pressure Gauge
 User s Guide For Note: The fuel system should be under pressure even when the car is off. ALWAYS follow these precautions: 1. Always wear safety glasses. 2. When the fuel lines are first loosened about
User s Guide For Note: The fuel system should be under pressure even when the car is off. ALWAYS follow these precautions: 1. Always wear safety glasses. 2. When the fuel lines are first loosened about
CAUTION: CAREFULLY READ INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE PROCEEDING
 Daytona Sensors LLC Engine Controls and Instrumentation Systems Installation Instructions for Wide-Band Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor Interface CAUTION: CAREFULLY READ INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE PROCEEDING OVERVIEW
Daytona Sensors LLC Engine Controls and Instrumentation Systems Installation Instructions for Wide-Band Exhaust Gas Oxygen Sensor Interface CAUTION: CAREFULLY READ INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE PROCEEDING OVERVIEW
Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines
 Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines Use the Textbook Pages 321 349 to help answer the questions Why You Learn So Well in Tech & Engineering Classes 1. Internal combustion make heat by burning a fuel & air mixture
Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines Use the Textbook Pages 321 349 to help answer the questions Why You Learn So Well in Tech & Engineering Classes 1. Internal combustion make heat by burning a fuel & air mixture
THE witech SOFTWARE IS REQUIRED TO BE AT THE LATEST RELEASE BEFORE PERFORMING THIS PROCEDURE.
 NUMBER: 18-094-15 GROUP: Vehicle Performance DATE: November 25, 2015 This bulletin is supplied as technical information only and is not an authorization for repair. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
NUMBER: 18-094-15 GROUP: Vehicle Performance DATE: November 25, 2015 This bulletin is supplied as technical information only and is not an authorization for repair. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE. Self-Diagnostics - RAV4. Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs).
 2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Self-Diagnostics - RAV4 INTRODUCTION NOTE: Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). To properly diagnosis and repair this
2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Self-Diagnostics - RAV4 INTRODUCTION NOTE: Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). To properly diagnosis and repair this
NOTE: This bulletin applies to CS models built after February 1, 2004 (MDH 0201XX) equipped with a 3.5L engine (Sales Code EGN).
 NUMBER: 09-010-06 GROUP: Engine DATE: September 16, 2006 THIS BULLETIN SUPERSEDES TECHNICAL SERVICE BULLETIN 09-005-05, DATED DECEMBER 2, 2005, WHICH SHOULD BE REMOVED FROM YOUR FILES. THIS IS A COMPLETE
NUMBER: 09-010-06 GROUP: Engine DATE: September 16, 2006 THIS BULLETIN SUPERSEDES TECHNICAL SERVICE BULLETIN 09-005-05, DATED DECEMBER 2, 2005, WHICH SHOULD BE REMOVED FROM YOUR FILES. THIS IS A COMPLETE
Feature. The MR16DDT. Small Displacement, Big Output. 4 Nissan TechNews
 Feature The MR16DDT Small Displacement, Big Output 4 Nissan TechNews A look at the MR16DDT turbocharged, direct-injection gasoline engine in the JUKE, covering the engine design, direct injection system,
Feature The MR16DDT Small Displacement, Big Output 4 Nissan TechNews A look at the MR16DDT turbocharged, direct-injection gasoline engine in the JUKE, covering the engine design, direct injection system,
Fuel System Diagnosis
 Page 1 of 9 1999 Chevrolet Express Express, Savana (VIN G) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 5.0L and 5.7L Diagnostic Information and Procedures Document ID: 412957 Fuel System Diagnosis Circuit
Page 1 of 9 1999 Chevrolet Express Express, Savana (VIN G) Service Manual Engine Engine Controls - 5.0L and 5.7L Diagnostic Information and Procedures Document ID: 412957 Fuel System Diagnosis Circuit
Module 12 Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
 Module 12 Throttle Position (TP) Sensor Author: Grant Swaim E-mail: sureseal@nr.infi.net URL: www.tech2tech.net Phone: (336) 632-9882 Fax: (336) 632-9688 Postal Address: Tech-2-Tech Website PO Box 18443
Module 12 Throttle Position (TP) Sensor Author: Grant Swaim E-mail: sureseal@nr.infi.net URL: www.tech2tech.net Phone: (336) 632-9882 Fax: (336) 632-9688 Postal Address: Tech-2-Tech Website PO Box 18443
Oregon Fuel Injection
 2003 2007 Dodge 5.9L Diesel Diagnostics In order to do proper diagnostics you will need a scan tool and some special tools available from Miller Special Tools http://millerspecialtools.spx.com. High Pressure
2003 2007 Dodge 5.9L Diesel Diagnostics In order to do proper diagnostics you will need a scan tool and some special tools available from Miller Special Tools http://millerspecialtools.spx.com. High Pressure
Catalytic Failures. Engine running too hot.
 Catalytic Failures It is not uncommon for technicians to misdiagnose a driveability or emissions issue by blaming the converter. In many cases, it s not the converter s fault, but rather one of the engine
Catalytic Failures It is not uncommon for technicians to misdiagnose a driveability or emissions issue by blaming the converter. In many cases, it s not the converter s fault, but rather one of the engine
NATEF ENGINE PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST Name Date Period
 NATEF ENGINE PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST Name Period For every task in Engine Performance the following safety requirement must be strictly enforced: Comply with personal and environmental safety practices associated
NATEF ENGINE PERFORMANCE CHECKLIST Name Period For every task in Engine Performance the following safety requirement must be strictly enforced: Comply with personal and environmental safety practices associated
 Page 1 of 18 2004 PCED On Board Diagnostics SECTION 5: Pinpoint Tests Procedure revision date: 10/26/2007 H: Fuel Control H: Introduction H1 PERFORM THE KOER SELF-TEST Engine at normal operating temperature.
Page 1 of 18 2004 PCED On Board Diagnostics SECTION 5: Pinpoint Tests Procedure revision date: 10/26/2007 H: Fuel Control H: Introduction H1 PERFORM THE KOER SELF-TEST Engine at normal operating temperature.
2002 Buick Rendezvous - AWD
 2002 Buick Rendezvous - AWD DTC P0410 Description The control module activates the secondary air injection (AIR) system by grounding both the pump relay and the vacuum control solenoid control circuits.
2002 Buick Rendezvous - AWD DTC P0410 Description The control module activates the secondary air injection (AIR) system by grounding both the pump relay and the vacuum control solenoid control circuits.
Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps
 Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
(P0135/P0155), (P0141/P0161), (P1131/P1151), (P1132/P1152). To further clarify this, see the more detailed scenario as follows:
 1. Always reset KAM after performing a repair: After performing a repair on a vehicle with the MIL on, and/or DTCs present, always clear KAM. When a malfunction is present, the PCM adapts (attempts to
1. Always reset KAM after performing a repair: After performing a repair on a vehicle with the MIL on, and/or DTCs present, always clear KAM. When a malfunction is present, the PCM adapts (attempts to
COMBUSTION CHEMISTRY & EMISSION ANALYSIS
 Section 3 COMBUSTION CHEMISTRY & EMISSION ANALYSIS Introduction to Combustion Chemistry The gasoline powered internal combustion engine takes air from the atmosphere and gasoline, a hydrocarbon fuel, and
Section 3 COMBUSTION CHEMISTRY & EMISSION ANALYSIS Introduction to Combustion Chemistry The gasoline powered internal combustion engine takes air from the atmosphere and gasoline, a hydrocarbon fuel, and
BASIC DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
 BASIC DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES 2001 Chevrolet Camaro 2001 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Basic Diagnostic Procedures - Cars Except Metro & Prizm MODEL IDENTIFICATION MODEL IDENTIFICATION Body Code (1) Model C... Park
BASIC DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES 2001 Chevrolet Camaro 2001 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Basic Diagnostic Procedures - Cars Except Metro & Prizm MODEL IDENTIFICATION MODEL IDENTIFICATION Body Code (1) Model C... Park
Description and Operation. Fig. 13 Electro-Hydraulic Actuator
 1 of 3 10/17/2008 12:35 PM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help METRO TOYOTA Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: 1989 Mercedes Benz 420SEL (126 Chassis) V8-4196cc 4.2L
1 of 3 10/17/2008 12:35 PM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help METRO TOYOTA Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: 1989 Mercedes Benz 420SEL (126 Chassis) V8-4196cc 4.2L
Module 11 Thermistor Inputs
 Module 11 Thermistor Inputs Author: Grant Swaim E-mail: sureseal@nr.infi.net URL: www.tech2tech.net Phone: (336) 632-9882 Fax: (336) 632-9688 Postal Address: Tech-2-Tech Website PO Box 18443 Greensboro,
Module 11 Thermistor Inputs Author: Grant Swaim E-mail: sureseal@nr.infi.net URL: www.tech2tech.net Phone: (336) 632-9882 Fax: (336) 632-9688 Postal Address: Tech-2-Tech Website PO Box 18443 Greensboro,
THE witech SOFTWARE IS REQUIRED TO BE AT THE LATEST RELEASE BEFORE PERFORMING THIS PROCEDURE.
 NUMBER: GROUP: 18-021-15 REV. C Vehicle Performance DATE: June 10, 2015 This bulletin is supplied as technical information only and is not an authorization for repair. No part of this publication may be
NUMBER: GROUP: 18-021-15 REV. C Vehicle Performance DATE: June 10, 2015 This bulletin is supplied as technical information only and is not an authorization for repair. No part of this publication may be
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
Glossary. 116
 Sequential Fuel Injection Sequential means that each injector for each cylinder is triggered only one time during the engine s cycle. Typically the injector is triggered only during the intake stroke.
Sequential Fuel Injection Sequential means that each injector for each cylinder is triggered only one time during the engine s cycle. Typically the injector is triggered only during the intake stroke.
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited
 Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited WG1605 Engine Training: System Overviews Mechanical Components Electronic Components and Sensors Operation Service Tool Fuel System Overview: Fuel System Overview:
Kubota Engine Training: WG1605, spark ignited WG1605 Engine Training: System Overviews Mechanical Components Electronic Components and Sensors Operation Service Tool Fuel System Overview: Fuel System Overview:
Rough Idle Crank No Start Extended Crank Or Misfire Due to Excessive Carbon On Top of the Valves or Sticking Valves
 Rough Idle Crank No Start Extended Crank Or Misfire Due to Excessive Carbon On Top of the Valves or Sticking Valves 2000-2015 All Passenger Cars with Gasoline Engines 2000-2015 All Light Duty Trucks with
Rough Idle Crank No Start Extended Crank Or Misfire Due to Excessive Carbon On Top of the Valves or Sticking Valves 2000-2015 All Passenger Cars with Gasoline Engines 2000-2015 All Light Duty Trucks with
Lab #5 4-Cylinder Single Overhead Cam Engine Dissection
 Engr 3 Mission College Faculty: Kate Disney TA: Andrew Dina Lab #5 4-Cylinder Single Overhead Cam Engine Dissection Equipment: 4-Cylinder Mazda 16 Valve SOHC 92 (Manual Transmission) Ratchet with 2 and
Engr 3 Mission College Faculty: Kate Disney TA: Andrew Dina Lab #5 4-Cylinder Single Overhead Cam Engine Dissection Equipment: 4-Cylinder Mazda 16 Valve SOHC 92 (Manual Transmission) Ratchet with 2 and
Task 4: Read the texts, look at the illustrations and do the activities below.
 Task 4: Read the texts, look at the illustrations and do the activities below. 4 BASIC OPERATIONS The Induction Stroke On the induction stroke, the inlet valve opens and the piston, moving down, creates
Task 4: Read the texts, look at the illustrations and do the activities below. 4 BASIC OPERATIONS The Induction Stroke On the induction stroke, the inlet valve opens and the piston, moving down, creates
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM. 1. General ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE
 ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE 69 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 3VZ FE engine has the same basic construction and operation as for the 2VZ FE engine. However, the sequential
ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE 69 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 3VZ FE engine has the same basic construction and operation as for the 2VZ FE engine. However, the sequential
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2001.5 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2001.5 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
EMISSION SUB SYSTEMS - Closed Loop Feedback Control System
 Emission Control Sub-Systems Closed Loop Feedback Control System The heart of the emissions control system is the closed loop fuel feedback control system. It is responsible for controlling the content
Emission Control Sub-Systems Closed Loop Feedback Control System The heart of the emissions control system is the closed loop fuel feedback control system. It is responsible for controlling the content
Technician Turbocharger Guide for the L Power Stroke Engine
 Technician Turbocharger Guide for the 2003.25 6.0L Power Stroke Engine Vanes VGT Actuator Piston Turbine Wheel Shaft Seal Compressor Wheel VGT Control Valve TURBOCHARGER DESCRIPTION AND BASIC OPERATION
Technician Turbocharger Guide for the 2003.25 6.0L Power Stroke Engine Vanes VGT Actuator Piston Turbine Wheel Shaft Seal Compressor Wheel VGT Control Valve TURBOCHARGER DESCRIPTION AND BASIC OPERATION
Using Multiple Cylinder Engines
 Lesson A6 6 Using Multiple Cylinder Engines Unit A. Mechanical Systems and Technology Problem Area 6. Agricultural Power Systems Lesson 6. Using Multiple Cylinder Engines New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway
Lesson A6 6 Using Multiple Cylinder Engines Unit A. Mechanical Systems and Technology Problem Area 6. Agricultural Power Systems Lesson 6. Using Multiple Cylinder Engines New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway
Basic Requirements. ICE Fuel Metering. Mixture Quality Requirements. Requirements for Metering & Mixing
 Basic Requirements ICE Fuel Metering Dr. M. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET) Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Basic Requirements ICE Fuel Metering Dr. M. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET) Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Gasoline Direct Injection
 INTRODUCTION In recent years, legislative and market requirements have driven the need to reduce fuel consumption while meeting increasingly stringent exhaust emissions. This trend has dictated increasing
INTRODUCTION In recent years, legislative and market requirements have driven the need to reduce fuel consumption while meeting increasingly stringent exhaust emissions. This trend has dictated increasing
ATASA 5 th. Engine Performance Systems. Please Read The Summary. ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 25 Pages Engine Performance Systems 100 Points
 ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 25 Pages 725 763 100 Points Please Read The Summary 1. Engine systems are those responsible for how an engine runs. Performance Emission Control Electronic 2. The correct
ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 25 Pages 725 763 100 Points Please Read The Summary 1. Engine systems are those responsible for how an engine runs. Performance Emission Control Electronic 2. The correct
Focus on Training Section: Unit 2
 All Pump Types Page 1 1. Title Page Learning objectives Become familiar with the 4 stroke cycle Become familiar with diesel combustion process To understand how timing affects emissions To understand the
All Pump Types Page 1 1. Title Page Learning objectives Become familiar with the 4 stroke cycle Become familiar with diesel combustion process To understand how timing affects emissions To understand the
2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview. Study Guide. Course Code: 8777
 2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview Study Guide Course Code: 8777 1 2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview Study Guide 2015 Navistar, Inc. 2701 Navistar Drive, Lisle, IL 60532. All rights reserved. No part of
2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview Study Guide Course Code: 8777 1 2015 PSI 8.8L LPG Engine Overview Study Guide 2015 Navistar, Inc. 2701 Navistar Drive, Lisle, IL 60532. All rights reserved. No part of
The Basics of Four-Stroke Engines
 Youth Explore Trades Skills Description Students will be introduced to basic engine parts, theory and terminology. Understanding how an engine works and knowing some key related parts and terminology is
Youth Explore Trades Skills Description Students will be introduced to basic engine parts, theory and terminology. Understanding how an engine works and knowing some key related parts and terminology is
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
 EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
Chapter 4 ANALYTICAL WORK: COMBUSTION MODELING
 a 4.3.4 Effect of various parameters on combustion in IC engines: Compression ratio: A higher compression ratio increases the pressure and temperature of the working mixture which reduce the initial preparation
a 4.3.4 Effect of various parameters on combustion in IC engines: Compression ratio: A higher compression ratio increases the pressure and temperature of the working mixture which reduce the initial preparation
The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control
 The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control actuators. The PCM has various memories within it. These
The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control actuators. The PCM has various memories within it. These
DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Rich
 Page 1 of 6 1997 Chevrolet Cavalier Cavalier, Sunfire (VIN J) Service Manual Document ID: 47788 DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Rich System Description A Closed Loop air/fuel metering system is used to provide
Page 1 of 6 1997 Chevrolet Cavalier Cavalier, Sunfire (VIN J) Service Manual Document ID: 47788 DTC P0172 Fuel Trim System Rich System Description A Closed Loop air/fuel metering system is used to provide
3GR-FSE FUEL. Fuel Pump (High Pressure) Cold Start Fuel Injector *
 ENGINE EG 75 General This engine uses the D-4 (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine) system. A (low pressure) fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump located
ENGINE EG 75 General This engine uses the D-4 (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine) system. A (low pressure) fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump located
Alternative Fuel Engine Control Unit
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Cavalier (CNG) Alternative Fuel Engine Control Unit Table 1: AF ECU Function Parameters The (AF ECU) controls alternative fuel engine operation. The control unit monitors various engine
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Cavalier (CNG) Alternative Fuel Engine Control Unit Table 1: AF ECU Function Parameters The (AF ECU) controls alternative fuel engine operation. The control unit monitors various engine
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION AND SECONDARY AIR- INJECTION SYSTEMS
 85 POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION AND SECONDARY AIR- INJECTION SYSTEMS Figure 85-1 A PCV valve in a cutaway valve cover, showing the baffles that prevent liquid oil from being drawn into the intake manifold.
85 POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION AND SECONDARY AIR- INJECTION SYSTEMS Figure 85-1 A PCV valve in a cutaway valve cover, showing the baffles that prevent liquid oil from being drawn into the intake manifold.
6.0L BUILT ON OR BEFORE 9/29/2003 DTCS P006A TSB OR P132B LACKS POWER, SURGE, OR FLUTTER AFTER FIELD SERVICE ACTION 06E17
 6.0L BUILT ON OR BEFORE 9/29/2003 DTCS P006A TSB 06-24-6 OR P132B LACKS POWER, SURGE, OR FLUTTER AFTER FIELD SERVICE ACTION 06E17 FORD: 2003-2004 Excursion, F-Super Duty ISSUE 3. Using IDS datalogger,
6.0L BUILT ON OR BEFORE 9/29/2003 DTCS P006A TSB 06-24-6 OR P132B LACKS POWER, SURGE, OR FLUTTER AFTER FIELD SERVICE ACTION 06E17 FORD: 2003-2004 Excursion, F-Super Duty ISSUE 3. Using IDS datalogger,
EMS & OBD Engine Testing and Instrumentation 1
 EMS & OBD Engine Management System (EMS) It consists of ECU, various sensors and actuators in the engine. It uses the information acquired from sensors to control the fuel injection, ignition systems,
EMS & OBD Engine Management System (EMS) It consists of ECU, various sensors and actuators in the engine. It uses the information acquired from sensors to control the fuel injection, ignition systems,
Stop Lamp Switch. STP or BRK. Stop Lamps
 WORKSHEET 2 1 Position/Mode Switches and Circuits (Instructor Copy) Vehicle Year/Prod. Date Engine Transmission Technician Objectives With this worksheet, you will learn to test position/mode circuits
WORKSHEET 2 1 Position/Mode Switches and Circuits (Instructor Copy) Vehicle Year/Prod. Date Engine Transmission Technician Objectives With this worksheet, you will learn to test position/mode circuits
1 of 13 10/17/2016 1:36 PM
 1 of 13 10/17/2016 1:36 PM DTC P2195 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2196 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2197 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck
1 of 13 10/17/2016 1:36 PM DTC P2195 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2196 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2197 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck
Part 1. Reduced fuel flow due to a restricted inlet screen. Sluggish plunger movement due to contamination.
 http://www.datec.us/instructor/ More about the author http://www.datec.us /instructor SCREEN Part 1 There is not a good way to check the fuel distribution per cylinder. The intention of this session is
http://www.datec.us/instructor/ More about the author http://www.datec.us /instructor SCREEN Part 1 There is not a good way to check the fuel distribution per cylinder. The intention of this session is
UNDERSTANDING 5 GAS DIAGNOSIS
 UNDERSTANDING 5 GAS DIAGNOSIS AND EMISSIONS Gas Diagnostic Steps This procedure will help in your efforts to figure out what the five-gas reading are telling you. In order for five gas analyses to be conclusive
UNDERSTANDING 5 GAS DIAGNOSIS AND EMISSIONS Gas Diagnostic Steps This procedure will help in your efforts to figure out what the five-gas reading are telling you. In order for five gas analyses to be conclusive
DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2)
 05498 DIAGNOSTICS DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) 05EXR06 DTC P0172 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2) DTC P0175 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 2) CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION The fuel trim is
05498 DIAGNOSTICS DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) 05EXR06 DTC P0172 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2) DTC P0175 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 2) CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION The fuel trim is
ATASA 5 th. ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 31 Pages EFI Diagnosis & Service 47 Points. Please Read The Summary
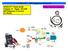 ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 31 Pages 922 948 47 Points Please Read The Summary 1. Troubleshooting EFI systems requires step by step test procedures mostly due to the many interrelated components and
ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 31 Pages 922 948 47 Points Please Read The Summary 1. Troubleshooting EFI systems requires step by step test procedures mostly due to the many interrelated components and
Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting
 RENR1271-11 February 2006 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 3126B and 3126E Truck Engine BKD1-Up (Engine) G3E1-Up (Engine) DPF1-Up (Engine) 1AJ1-Up (Engine) 8YL1-Up (Engine) CKM1-Up (Engine) CRP1-Up
RENR1271-11 February 2006 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 3126B and 3126E Truck Engine BKD1-Up (Engine) G3E1-Up (Engine) DPF1-Up (Engine) 1AJ1-Up (Engine) 8YL1-Up (Engine) CKM1-Up (Engine) CRP1-Up
2) Rich mixture: A mixture which contains less air than the stoichiometric requirement is called a rich mixture (ex. A/F ratio: 12:1, 10:1 etc.
 Unit 3. Carburettor University Questions: 1. Describe with suitable sketches : Main metering system and Idling system 2. Draw the neat sketch of a simple carburettor and explain its working. What are the
Unit 3. Carburettor University Questions: 1. Describe with suitable sketches : Main metering system and Idling system 2. Draw the neat sketch of a simple carburettor and explain its working. What are the
Scan Tool Test Procedures Steve Zack Technical Instructor Bosch AA-AS
 Scan Tool Test Procedures Steve Zack Technical Instructor Bosch AA-AS Steve Zack 8.10.15 1 This class will develop the technician skills to use their scan tool to resolve difficult technical issues efficiently.
Scan Tool Test Procedures Steve Zack Technical Instructor Bosch AA-AS Steve Zack 8.10.15 1 This class will develop the technician skills to use their scan tool to resolve difficult technical issues efficiently.
Module 22 Ignition Systems - Outputs
 Module 22 Ignition Systems - Outputs Author: Grant Swaim E-mail: sureseal@nr.infi.net URL: www.tech2tech.net Phone: (336) 632-9882 Fax: (336) 632-9688 Postal Address: Tech-2-Tech Website PO Box 18443 Greensboro,
Module 22 Ignition Systems - Outputs Author: Grant Swaim E-mail: sureseal@nr.infi.net URL: www.tech2tech.net Phone: (336) 632-9882 Fax: (336) 632-9688 Postal Address: Tech-2-Tech Website PO Box 18443 Greensboro,
APPLIED MECHANICS 40/50
 APPLIED MECHANICS 40/50 Description (Combined Course- 2 periods) Applied Mechanics 40 introduces students to automobile servicing and the maintenance/repair field. Work is performed on operational vehicles.
APPLIED MECHANICS 40/50 Description (Combined Course- 2 periods) Applied Mechanics 40 introduces students to automobile servicing and the maintenance/repair field. Work is performed on operational vehicles.
IDENTIFICATION OF FUEL INJECTION CONTROL SYSTEM IN A GDI ENGINE
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 17, No. 4 21 IDENTIFICATION OF FUEL INJECTION CONTROL SYSTEM IN A GDI ENGINE Zbigniew Wo czy ski Technical University of Radom Chrobrego Av. 45, 26-6 Radom,
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 17, No. 4 21 IDENTIFICATION OF FUEL INJECTION CONTROL SYSTEM IN A GDI ENGINE Zbigniew Wo czy ski Technical University of Radom Chrobrego Av. 45, 26-6 Radom,
