Transient Control of Combustion Phasing and Lambda in a 6- Cylinder Port-Injected Natural-gas Engine
|
|
|
- Delphia Palmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proceedings of the ASME Internal Combustion Engine Division 29 Spring Technical Conference ICES29 May 3-, 29, Milwaukee, Wisconsin, USA ICES29-7 Transient Control of Combustion Phasing and Lambda in a - Cylinder Port-Injected Natural-gas Engine Mehrzad Kaiadi, Magnus Lewander, Patrick Borgqvist, Per Tunestal, Bengt Johansson Division of Combustion Engines, Lund University, Faculty of Engineering Copyright 29 ASME International ABSTRACT Fuel economy and emissions are the two central parameters in heavy duty engines. High EGR rates combined with turbocharging has been identified as a promising way to increase the maximum load and efficiency of heavy duty spark ignition engines. With stoichiometric conditions a three way catalyst can be used which keeps the regulated emissions at very low levels. The Lambda window which results in very low emissions is very narrow. This issue is more complex with transient operation resulting in losing brake efficiency and also catalyst converting efficiency. This paper presents different control strategies to maximize the reliability for maintaining efficiency and emissions levels under transient conditions. Different controllers are developed and tested successfully on a heavy duty -cylinder port injected natural gas engine. Model Predictive Control (MPC) was used to control lambda which was modeled using System Identification. Furthermore, a Proportional Integral (PI) regulator combined with a feedforward map for obtaining Maximum Brake Torque (MBT) timing was applied. The results show that excellent steady-state and transient performance can be achieved. INTRODUCTION Recently, environmental improvement and energy issues have become increasingly important as worldwide concerns. Road transport is one of the biggest energy consuming sectors which have a great impact on the environment. The fuels mainly used in internal combustion engines are petroleum products namely gasoline and diesel. One way for reducing these impacts is to use alternative fuels. Natural gas consisting mainly of methane (~9%) is a good alternative fuel to improve environmental problems because of its plentiful availability and clean burning characteristics. Heavy duty spark ignited (SI) natural gas engines can be operated either lean or stoichiometric. Recent work at the department of energy sciences at Lund University has shown better results with stoichiometric operation X[X] since stoichiometric operation with a three way catalyst results in very low emissions while keeping efficiency at a reasonable level. A reliable and sophisticated control strategy is essential for achieving good catalyst efficiency and hence low emissions. Accurate stationary and transient lambda control is very important for maintaining good catalyst efficiency and consequently low emissions. A lot of research on controlling lambda and Air/Fuel Ratio (AFR) has been performed; some of it is reported in X[2X-XX]. Model Predictive Control (MPC) is a model based control strategy that uses prediction to optimize future control actions with respect to a cost function [XX]. The optimization cost function is given by: J w ( r x ) w u 2 2 xi i i ui i where x i is the control variable, r i the reference variable, u i the manipulated variable and w is a weighting coefficient. The main reasons for applying MPC control are its capability to handle multivariable control problems
2 for and account for actuator constraints. Use of MPC for controlling lambda has not been reported previously. fuel, air and EGR. The controllers can be activated from the Graphical User Interface (GUI). The objective of this work is to develop a MPC controller to control the overall AFR. For being able To use MPC a model is needed for capturing the dynamics between fuel injection, throttle position and measured lambda. System identification tools were used for modeling. Furthermore a Maximum Brake Torque (MBT) Timing control was developed for increasing the reliability of ignition timing during transient operation. EXPERIMENTAL SETUP In this section the specification of the experimental engine and its control system, the measurement system and gas data are described. THE ENGINE The experimental engine was originally a diesel engine from Volvo which has been converted to a natural gas engine, see XTable X specification. The engine is equipped with a short route cooled EGR system and also turbocharger with wastegate. Number of Cylinder Displacement 9, Liter Bore 2 mm Stroke 38 mm Compression ratio, : Fuel Natural gas Table : Specification of the engine Originally the engine has single point injection system which is replaced by a multi-port injection system. The main idea with this modification is to control the fuel injection of each cylinder individually and also to get rapid engine response to change throttle position. ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM A master PC based on GNU/Linux operating system is used as a control system. It communicates with three Cylinder-Control-Modules (CCM) for cylinder-individual control of ignition and fuel injection via Controller Area Network (CAN) communication, see XFigure X. Crank and cam information are used to synchronize the CCMs with the crank rotation. Flexible controller implementation is achieved using Simulink and C-code is generated using the automatic code generation tool of Real Time Workshop. The C- code is then compiled to an executable program which communicates with the main control program. The controllers used for this experiment are lambda, load and EGR controller which determine the offset amount of 2 Figure : The Engine and its control system MEASUREMENT SYSTEM Each cylinder head is equipped with a piezo electric pressure transducer of type Kistler 7B to monitor cylinder pressures for heat release calculations. Cylinder pressure and ion-current data are sampled by a Microstar A data acquisition processor. EGR was calculated by measuring CO2 at inlet and exhaust. Emissions (HC, CO, NO, NO2, NOx, CO2, O2) are measured before and after catalyst. Also, temperatures at inlet/exhaust, pressures at inlet/exhaust, fuel and air flow, lambda, torque and engine speed are measured. GAS DATA The composition of the natural gas, which varies slightly over time, is shown in XTable 2X. The lower heating value is 8, MJ/kg. Composition % Structure Methane 89,8 CH Ethane,82 C2H Propane 2,33 C3H8 I-Butane,38 CH N-Butane,2 CH I-Pentane, CH2 N-Pentane,7 CH2 Hexane, CH Nitrogen,27 N2 CO2, CO2 Table 2: The natural gas composition
3 shows named CONTROL APPROACH Two main controllers are developed in this work, namely Lambda Controller and Maximum Brake Torque Timing controller. The control approach used for each controller is discussed below. LAMBDA CONTROL This part is divided into three different parts: system identification and modeling, validation of the model and finally design of the controller. USystem identification and Modeling A dynamic model is essential to a MPC controller. A model is needed to be able to predict the future behavior of the system. Injection duration and throttle position are used as input parameters and lambda is an output parameter of the model. System identification is used to obtain a black box model. The system was excited with Pseudo-Random Binary Sequence (PRBS) signals for injection duration and throttle position and data was collected. The system Identification Toolbox in Matlab named Ident was used to construct a model of the dynamic system from measured input-output data. It uses a combination of subspace-based identification and optimization of prediction error which proved to generate a good model. A 3rd order discrete time state space model was designed. The injection duration is between 3- ms and throttle position between - % (opening) at RPM. XFigure 2X how the modeled lambda follows the measured lambda. Offset is removed from the data..3.2 and simulated model output Simulated UModel Validation The dynamic model must be validated before using in a controller. The model was designed at RPM and -% throttle opening. It is validated by data from 8 RPM 3- % opening (see XFigure 3X). The result shows that the model can capture the lambda dynamics with very good precision Time Figure 3: Validation of the lambda model UDesign of the Lambda Controller data Silumated model Throttle position is used as a measured disturbance and injection duration as manipulated variable (see XFigure X). When a parameter is defined as measured disturbance it means that the controller should provide feedforward compensation based on the measurement. A manipulated variable is a signal that will be adjusted by the controller, i.e., in this case injection duration which will by controlled by injectors. An input parameter in XFigure X Unmeasured is a disturbance for which the controller will provide feedback compensation. An Unmeasured can be some parameters like engine speed or EGR rate Time (Sec) Figure 2: System identification of lambda by PRBS signals Figure : MPC Controller structure There are a number of tuning parameters to be used when designing a MPC controller, such as: weights, constraints, estimation gain etc. The proper constraints on manipulated variables e.g. injection duration were set. The output constraints were chosen between [-..3] from the set value which is. This means that the lambda is allowed to be between [.3.9]. This interval was chosen in order to prevent high level of NOX or HC emissions. 3
4 shows shows also MBT TIMING CONTROL For each operating condition of the engine optimal spark timing can be obtained. This optimal spark timing is called maximum brake torque (MBT) timing, which maximizes the output load and the efficiency of the engine and thereby lowers the fuel consumption. CA is an engine crank position in Crank Angle Degree (CAD) at % heat release. XFigure X how changes in CA position affect load, efficiency and thereby the Specific Fuel Consumption (SFC). MBT is obtained roughly when CA is degrees After Top Dead Center (ATDC). Figure : Effect of ignition timing on Brake efficiency and SFC CA is almost unique for each operating condition (see XFigure X). It means that it is essential to have control of MBT timing during the transients in order to achieve the lowest SFC. Traditionally MBT timing is implemented as an open-loop control where the ignition timing is found by using a static lookup tables. Ignition MBT [CAD BTDC] BMEP [Bar] SFC [g/kwh] CA [CAD ATDC] BMEP [Bar] Figure : MBT timing for different loads and speeds RPM 9 RPM RPM 3 RPM RPM Brake Efficiency [%] UDesign of the MBT Controller A PI regulator was designed to control the MBT timing. The closed loop MBT control evaluates the calculated CA. The error signal is based on the difference between the calculated CA and a predefined CA (i.e. CA=) and, an ignition offset was generated from that for each cylinder. The individual ignition timing was adjusted by the regulator to keep the CA at the same level as the desired CA. Bumpless transfer and Anti-Windup algorithms were applied during the design of the regulator. RESULTS This section is divided into two parts because of the two developed controllers. In the first part the results during development of the MBT controller is discussed and in the second part the results for the lambda controller are discussed. MBT CONTROLLER The engine is operated at different operating condition (different speeds and loads) and during these tests the MBT controller was active and performed well. XFigure 7X shows how a PI regulator can improve CA balancing in all cylinders. The engine is operated at engine speed 2 RPM and 8 bar Brake Mean Effective Pressure (BMEP). CA of Different Cylinders With and Without Regulator 2 CA [CAD] 8 2 Without Regulator With Regulator Cylinder Cylinder 2 Cylinder 3 Cylinder Cylinder Cylinder Figure 7: CA of all cylinder with and without MBT Controller Step changes in load are performed in order to investigate the performance of the MBT controller. XFigure 8X that when opening the throttle position from 3 to % (which corresponds roughly to 3 to BMEP at 2 RPM), the ignition timing of each cylinder is adjusted by the MBT controller in order to keep CA equal to. XFigure 8X shows that an overshoot occurs in CA which is a result of the sudden change in throttle. The controller tries to compensate the error
5 shows immediately which results in an overshoot. This overshoot can be minimized by using a lookup table as a feedforward map coupled with the feedback controller. Feedforward is a control technique that can be measured but not controlled. The disturbance (i.e. throttle changes) is measured and fed forward to an earlier part of the control loop so that corrective action can be initiated in advance of the disturbance having an adverse effect on the system response. Data for creating the feedforward map is collected from running the engine at different operating conditions (see XFigure X). XFigure 9X that the overshoot is minimized by using the feedforward map. It is also obvious in the figure that the controller with feedforward responds more quickly to the disturbance. CA [CAD ATDC] 2 3 CA-Regulator Without FeedForward-map 2 2 Cyl Cyl2 Cyl3 Cyl Cyl Cyl 2 Figure 8: Individual ignition control (Feedback control) with load step 2 RPM 8 2 Ignition Start [CAD BTDC] CA [CAD ATDC] 2 3 Figure 9: Individual ignition control (Feedforward + Feedback control) with load step 2 RPM LAMBDA REGULATION CA-Regulator With FeedForward-map The performance of the developed MPC lambda controller is tested by generating different disturbances. These disturbances are step changes and ramp changes in throttle position i.e. load transients, step changes in speed and EGR are also made to investigate the quality of the MPC lambda controller. The lambda controller is also tested with step changes outside the range of the designed model. The results of these tests are presented in the following subsections. The reference lambda in these tests is,99 which represent the best trade-off for the catalyst used in these tests. THROTTLE DISTURBANCE XFigure X shows the response of the controller and the emissions of HC and NOX when applying step change in throttle position. Since the emission measuring system is not fast, some delay is seen in the plot. The emissions are measured after the catalyst. Lambda is close to the defined constraints but it does not exceed. In XFigure X ramp changes in throttle are applied and the controller follows the changes very well. In order to see how the controller works outside of the range of the model, some tests are also performed. The model is designed at RPM, throttle [ %] and injection duration [3 ] millisecond. In XFigure 2X a wider throttle change than the model validation range is applied. The emissions do not exceed the limits. XFigure 3X shows throttle changes at 8 2 Ignition Start [CAD BTDC]
6 lower engine speed i.e. 8 RPM. It shows that lambda exceeds somewhat the constraint for some cycles. This can be solved by introducing engine speed as another input into the model and apply feedforward based on the measurement. This is planned as future work Figure : Results of the MPC lambda controller with step change of the throttle inside the model range Figure : Results of the MPC lambda controller with ramp change of the throttle in the model range Measurd NOX NOX Euro V Figure 2: Results of the MPC lambda controller with step change of the throttle outside of the model range [3 %] HC HC Euro V 2 HC Euro V Figure 3: Results of the MPC lambda controller with step change of the throttle out of the model 8 RPM 3....
7 SPEED DISTURBANCE In XFigure X a rapid decrease in engine speed is applied. The controller manages this transient well and the emissions are not affected significantly. Again, further improvement is possible by including engine speed as a measured disturbance. Speed [RPM] Figure : Results of the MPC lambda controller with step change of the speed in the model range EGR DISTURBANCE In XFigure X a rapid change in EGR level is applied in order to see if the lambda controller can manage this kind of disturbance. Since the EGR measurement is slow and takes a couple of seconds it is decided to plot only the changes in EGR valve position. At this point the amount of EGR was increased from to percent. XFigure X shows that lambda exceeds slightly the constraints and thereby HC emission exceeds slightly the limit for some cycles. This can be improved by using a model which has the EGR valve position as input parameter EGR Valve[%] 8 2 HC Euro V Figure : Results of the lambda MPC regulator with step change of the EGR in the model range ( % EGR rate) PI VERSUS MPC LAMBDA CONTROLLER Before using the MPC lambda controller a traditional PI lambda controller was used for controlling the overall Air/Fuel ratio. In this part the same tests which were performed with the MPC controller are applied with the PI controller. In XFigure X a rapid but not too big throttle change is applied. The results show that the lambda goes up to, which results in a big increase in NOX emissions. XFigure X shows the results of the same experiment performed with the MPC regulator. By using an MPC regulator the feedforward calculation helps to find the right amount of fuel injection faster. In XFigure 7X a bigger change is applied to the throttle. Comparing XFigure 2X with XFigure 7X shows how much better the MPC controller manages this type of transient than the PI controller... 7
8 Figure : Results of the lambda PI regulator with step change of the throttle Lambda NOX NOX Euro V HC HC Euro V Figure 7: Results of the lambda PI regulator with step change of the throttle CONCLUSION Two main controllers are developed in this study. A combination of a feedforward map coupled with a PI closed loop controller is developed to control MBT timing. Model Predictive Control is also developed to control the overall Air/Fuel ratio. The main conclusions obtained from this study are as follows:. Using a static feedforward map coupled with a PI closed loop controller showed excellent performance for controlling MBT Timing. 2. System identification made it possible to make a reliable dynamic model of lambda. Injection duration and throttle position were the two input parameters of this model. 3. Model Predictive Control was shown to be a suitable method for controlling lambda.. MPC lambda controller is compared with PI lambda controller and MPC showed to be a better choice than PI for controlling lambda.. The results show that rapid increase in engine speed and EGR rate makes the quality of lambda control deteriorate. Including engine speed and EGR rate as input parameters to the model can improve the results. ERENCES [] Patrik Einewall, Per Tunestål and Bengt Johansson., Lean Burn Natural Gas Operation vs. Stoichiometric Operation with EGR and a Three Way Catalyst. Lund Institute of Technology, SAE Paper 2--2 [2] A. D. Noble, A. J. Beaumont Control System for a Low Emissions Natural Gas Engine for Urban Vehicles, Ricardo Consulting Engineers, SAE Paper 92 [3] P. Kaidantzis, P. Rasmussen, M. Jensen, T. Vesterholm, T, Hendricks Robust, Self-Calibrating Lambda Feedback for SI Engines Technical University of Denmark, SAE Paper 938 [] H. Takubo, T. Umeno New Lambda - Lambda Air-Fuel Ratio Feedback Control Mitsubishi Electric Corp, SAE Paper [] Maciejowski, J. M. Predictive Control with Constraints, Pearson Education, Essex, 22. CONTACT Mehrzad Kaiadi Mehrzad.kaiadi@energy.lth.se 8
Closed-Loop Combustion Control Using Ion-Current Signals in a 6-Cylinder PortInjected Natural-gas Engine
 Closed-Loop Combustion Control Using Ion-Current Signals in a 6-Cylinder PortInjected Natural-gas Engine Kaiadi, Mehrzad; Tunestål, Per; Johansson, Bengt Published in: SAE technical paper series Published:
Closed-Loop Combustion Control Using Ion-Current Signals in a 6-Cylinder PortInjected Natural-gas Engine Kaiadi, Mehrzad; Tunestål, Per; Johansson, Bengt Published in: SAE technical paper series Published:
Developing New Methods, Techniques to Improve Heavy-Duty Natural Gas Engine Performance
 Developing New Methods, Techniques to Improve Heavy-Duty Natural Gas Engine Performance By: Mehrzad Kaiadi Supervisor: Associate Prof. Per Tunestål GERG ACADEMIC NETWORK EVENT - 2010 Division of Combustion
Developing New Methods, Techniques to Improve Heavy-Duty Natural Gas Engine Performance By: Mehrzad Kaiadi Supervisor: Associate Prof. Per Tunestål GERG ACADEMIC NETWORK EVENT - 2010 Division of Combustion
Gasoline Engine Performance and Emissions Future Technologies and Optimization
 Gasoline Engine Performance and Emissions Future Technologies and Optimization Paul Whitaker - Technical Specialist - Ricardo 8 th June 2005 RD. 05/52402.1 Contents Fuel Economy Trends and Drivers USA
Gasoline Engine Performance and Emissions Future Technologies and Optimization Paul Whitaker - Technical Specialist - Ricardo 8 th June 2005 RD. 05/52402.1 Contents Fuel Economy Trends and Drivers USA
Experimental Investigation of Performance and Emissions of a Stratified Charge CNG Direct Injection Engine with Turbocharger
 MATEC Web of Conferences 1, 7 (17 ) DOI:1.11/matecconf/1717 ICTTE 17 Experimental Investigation of Performance and Emissions of a Stratified Charge CNG Direct Injection Engine with charger Hilmi Amiruddin
MATEC Web of Conferences 1, 7 (17 ) DOI:1.11/matecconf/1717 ICTTE 17 Experimental Investigation of Performance and Emissions of a Stratified Charge CNG Direct Injection Engine with charger Hilmi Amiruddin
Variations of Exhaust Gas Temperature and Combustion Stability due to Changes in Spark and Exhaust Valve Timings
 Variations of Exhaust Gas Temperature and Combustion Stability due to Changes in Spark and Exhaust Valve Timings Yong-Seok Cho Graduate School of Automotive Engineering, Kookmin University, Seoul, Korea
Variations of Exhaust Gas Temperature and Combustion Stability due to Changes in Spark and Exhaust Valve Timings Yong-Seok Cho Graduate School of Automotive Engineering, Kookmin University, Seoul, Korea
Control of Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engine Dynamics
 Control of Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engine Dynamics Johan Bengtsson, Petter Strandh, Rolf Johansson, Per Tunestål and Bengt Johansson Dept. Automatic Control, Lund University, PO
Control of Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) Engine Dynamics Johan Bengtsson, Petter Strandh, Rolf Johansson, Per Tunestål and Bengt Johansson Dept. Automatic Control, Lund University, PO
The MathWorks Crossover to Model-Based Design
 The MathWorks Crossover to Model-Based Design The Ohio State University Kerem Koprubasi, Ph.D. Candidate Mechanical Engineering The 2008 Challenge X Competition Benefits of MathWorks Tools Model-based
The MathWorks Crossover to Model-Based Design The Ohio State University Kerem Koprubasi, Ph.D. Candidate Mechanical Engineering The 2008 Challenge X Competition Benefits of MathWorks Tools Model-based
Ignition- and combustion concepts for lean operated passenger car natural gas engines
 Ignition- and combustion concepts for lean operated passenger car natural gas engines Patrik Soltic 1, Thomas Hilfiker 1 Severin Hänggi 2, Richard Hutter 2 1 Empa, Automotive Powertrain Technologies Laboratory,
Ignition- and combustion concepts for lean operated passenger car natural gas engines Patrik Soltic 1, Thomas Hilfiker 1 Severin Hänggi 2, Richard Hutter 2 1 Empa, Automotive Powertrain Technologies Laboratory,
Closed-Loop Combustion Control of a Multi Cylinder HCCI Engine using Variable Compression Ratio and Fast Thermal Management
 Closed-Loop Combustion Control of a Multi Cylinder HCCI Engine using Variable Compression Ratio and Fast Thermal Management Haraldsson, Göran 2005 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
Closed-Loop Combustion Control of a Multi Cylinder HCCI Engine using Variable Compression Ratio and Fast Thermal Management Haraldsson, Göran 2005 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
GT-POWER/SIMULINK SIMULATION AS A TOOL TO IMPROVE INDIVIDUAL CYLINDER AFR CONTROL IN A MULTICYLINDER S.I. ENGINE
 1 GT-Suite Users International Conference Frankfurt a.m., October 30 th 2000 GT-POWER/SIMULINK SIMULATION AS A TOOL TO IMPROVE INDIVIDUAL CYLINDER CONTROL IN A MULTICYLINDER S.I. ENGINE F. MILLO, G. DE
1 GT-Suite Users International Conference Frankfurt a.m., October 30 th 2000 GT-POWER/SIMULINK SIMULATION AS A TOOL TO IMPROVE INDIVIDUAL CYLINDER CONTROL IN A MULTICYLINDER S.I. ENGINE F. MILLO, G. DE
Institutionen för systemteknik
 Institutionen för systemteknik Department of Electrical Engineering Examensarbete Investigation of Correlations Between COV of Ion Integral and COV of IMEP in a Port-Injected Natural-Gas Engine Examensarbete
Institutionen för systemteknik Department of Electrical Engineering Examensarbete Investigation of Correlations Between COV of Ion Integral and COV of IMEP in a Port-Injected Natural-Gas Engine Examensarbete
Crankcase scavenging.
 Software for engine simulation and optimization www.diesel-rk.bmstu.ru The full cycle thermodynamic engine simulation software DIESEL-RK is designed for simulating and optimizing working processes of two-
Software for engine simulation and optimization www.diesel-rk.bmstu.ru The full cycle thermodynamic engine simulation software DIESEL-RK is designed for simulating and optimizing working processes of two-
Five Cool Things You Can Do With Powertrain Blockset The MathWorks, Inc. 1
 Five Cool Things You Can Do With Powertrain Blockset Mike Sasena, PhD Automotive Product Manager 2017 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 FTP75 Simulation 2 Powertrain Blockset Value Proposition Perform fuel economy
Five Cool Things You Can Do With Powertrain Blockset Mike Sasena, PhD Automotive Product Manager 2017 The MathWorks, Inc. 1 FTP75 Simulation 2 Powertrain Blockset Value Proposition Perform fuel economy
Control of Charge Dilution in Turbocharged CIDI Engines via Exhaust Valve Timing
 Control of Charge Dilution in Turbocharged CIDI Engines via Exhaust Valve Timing Anna Stefanopoulou, Hakan Yilmaz, David Rausen University of Michigan, Ann Arbor Extended Summary ABSTRACT Stringent NOx
Control of Charge Dilution in Turbocharged CIDI Engines via Exhaust Valve Timing Anna Stefanopoulou, Hakan Yilmaz, David Rausen University of Michigan, Ann Arbor Extended Summary ABSTRACT Stringent NOx
Published in: First Biennial Meeting of the Scandinavian-Nordic Section of the Combustion Institute
 HCCI Operation of a Multi-Cylinder Engine Tunestål, Per; Olsson, Jan-Ola; Johansson, Bengt Published in: First Biennial Meeting of the Scandinavian-Nordic Section of the Combustion Institute 21 Link to
HCCI Operation of a Multi-Cylinder Engine Tunestål, Per; Olsson, Jan-Ola; Johansson, Bengt Published in: First Biennial Meeting of the Scandinavian-Nordic Section of the Combustion Institute 21 Link to
Transient Control of a Multi Cylinder HCCI Engine During a Drive Cycle. Haraldsson, Göran; Tunestål, Per; Johansson, Bengt; Hyvönen, Jari
 Transient Control of a Multi Cylinder HCCI Engine During a Drive Cycle Haraldsson, Göran; Tunestål, Per; Johansson, Bengt; Hyvönen, Jari Published in: SAE Special Publications Published: 5-1-1 Link to
Transient Control of a Multi Cylinder HCCI Engine During a Drive Cycle Haraldsson, Göran; Tunestål, Per; Johansson, Bengt; Hyvönen, Jari Published in: SAE Special Publications Published: 5-1-1 Link to
Module7:Advanced Combustion Systems and Alternative Powerplants Lecture 32:Stratified Charge Engines
 ADVANCED COMBUSTION SYSTEMS AND ALTERNATIVE POWERPLANTS The Lecture Contains: DIRECT INJECTION STRATIFIED CHARGE (DISC) ENGINES Historical Overview Potential Advantages of DISC Engines DISC Engine Combustion
ADVANCED COMBUSTION SYSTEMS AND ALTERNATIVE POWERPLANTS The Lecture Contains: DIRECT INJECTION STRATIFIED CHARGE (DISC) ENGINES Historical Overview Potential Advantages of DISC Engines DISC Engine Combustion
Development of Bi-Fuel Systems for Satisfying CNG Fuel Properties
 Keihin Technical Review Vol.6 (2017) Technical Paper Development of Bi-Fuel Systems for Satisfying Fuel Properties Takayuki SHIMATSU *1 Key Words:, NGV, Bi-fuel add-on system, Fuel properties 1. Introduction
Keihin Technical Review Vol.6 (2017) Technical Paper Development of Bi-Fuel Systems for Satisfying Fuel Properties Takayuki SHIMATSU *1 Key Words:, NGV, Bi-fuel add-on system, Fuel properties 1. Introduction
Model-Based Engine Calibration
 Model-Based Engine Calibration International Automotive Conference 15 June 2004 Dr David Sampson The MathWorks 2003 The MathWorks, Inc. Model-Based Calibration: Outline The concept Example applications
Model-Based Engine Calibration International Automotive Conference 15 June 2004 Dr David Sampson The MathWorks 2003 The MathWorks, Inc. Model-Based Calibration: Outline The concept Example applications
Calibration. DOE & Statistical Modeling
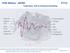 ETAS Webinar - ASCMO Calibration. DOE & Statistical Modeling Injection Consumption Ignition Torque AFR HC EGR P-rail NOx Inlet-cam Outlet-cam 1 1 Soot T-exhaust Roughness What is Design of Experiments?
ETAS Webinar - ASCMO Calibration. DOE & Statistical Modeling Injection Consumption Ignition Torque AFR HC EGR P-rail NOx Inlet-cam Outlet-cam 1 1 Soot T-exhaust Roughness What is Design of Experiments?
DF-PCCI: Concept Development of New Diesel Dual Fuel Technology for Diesel Common-Rail Light Duty Pickup Truck
 DF-PCCI: Concept Development of New Diesel Dual Fuel Technology for Diesel Common-Rail Light Duty Pickup Truck Krisada Wannatong, Somchai Siengsanorh and Nirod Akarapanyavit PTT Research and Technology
DF-PCCI: Concept Development of New Diesel Dual Fuel Technology for Diesel Common-Rail Light Duty Pickup Truck Krisada Wannatong, Somchai Siengsanorh and Nirod Akarapanyavit PTT Research and Technology
Hydrogen Addition For Improved Lean Burn Capability of Slow and Fast Burning Natural Gas Combustion Chambers
 Hydrogen Addition For Improved Lean Burn Capability of Slow and Fast Burning Natural Gas Combustion Chambers Tunestål, Per; Christensen, Magnus; Einewall, Patrik; Andersson, Tobias; Johansson, Bengt; Jönsson,
Hydrogen Addition For Improved Lean Burn Capability of Slow and Fast Burning Natural Gas Combustion Chambers Tunestål, Per; Christensen, Magnus; Einewall, Patrik; Andersson, Tobias; Johansson, Bengt; Jönsson,
Saud Bin Juwair, Taib Iskandar Mohamad, Ahmed Almaleki, Abdullah Alkudsi, Ibrahim Alshunaifi
 The effects of research octane number and fuel systems on the performance and emissions of a spark ignition engine: A study on Saudi Arabian RON91 and RON95 with port injection and direct injection systems
The effects of research octane number and fuel systems on the performance and emissions of a spark ignition engine: A study on Saudi Arabian RON91 and RON95 with port injection and direct injection systems
8 th International Symposium TCDE Choongsik Bae and Sangwook Han. 9 May 2011 KAIST Engine Laboratory
 8 th International Symposium TCDE 2011 Choongsik Bae and Sangwook Han 9 May 2011 KAIST Engine Laboratory Contents 1. Background and Objective 2. Experimental Setup and Conditions 3. Results and Discussion
8 th International Symposium TCDE 2011 Choongsik Bae and Sangwook Han 9 May 2011 KAIST Engine Laboratory Contents 1. Background and Objective 2. Experimental Setup and Conditions 3. Results and Discussion
66RHMLPD ([DPSOHVRIXVDJHDQGVSUHDGRI'\PROD ZLWKLQ7R\RWD 0RGHOLFD:RUNVKRS3URFHHGLQJVSS
 66RHMLPD ([DPSOHVRIXVDJHDQGVSUHDGRI'\PROD ZLWKLQ7R\RWD 0RGHOLFD:RUNVKRS3URFHHGLQJVSS 3DSHUSUHVHQWHGDWWKH0RGHOLFD:RUNVKRS2FW/XQG6ZHGHQ $OOSDSHUVRIWKLVZRUNVKRSFDQEHGRZQORDGHGIURP KWWSZZZ0RGHOLFDRUJPRGHOLFDSURFHHGLQJVKWPO
66RHMLPD ([DPSOHVRIXVDJHDQGVSUHDGRI'\PROD ZLWKLQ7R\RWD 0RGHOLFD:RUNVKRS3URFHHGLQJVSS 3DSHUSUHVHQWHGDWWKH0RGHOLFD:RUNVKRS2FW/XQG6ZHGHQ $OOSDSHUVRIWKLVZRUNVKRSFDQEHGRZQORDGHGIURP KWWSZZZ0RGHOLFDRUJPRGHOLFDSURFHHGLQJVKWPO
Fuel Effects in Advanced Combustion -Partially Premixed Combustion (PPC) with Gasoline-Type Fuels. William Cannella. Chevron
 Fuel Effects in Advanced Combustion -Partially Premixed Combustion (PPC) with Gasoline-Type Fuels William Cannella Chevron Acknowledgement Work Done In Collaboration With: Vittorio Manente, Prof. Bengt
Fuel Effects in Advanced Combustion -Partially Premixed Combustion (PPC) with Gasoline-Type Fuels William Cannella Chevron Acknowledgement Work Done In Collaboration With: Vittorio Manente, Prof. Bengt
Influence of Fuel Injector Position of Port-fuel Injection Retrofit-kit to the Performances of Small Gasoline Engine
 Influence of Fuel Injector Position of Port-fuel Injection Retrofit-kit to the Performances of Small Gasoline Engine M. F. Hushim a,*, A. J. Alimin a, L. A. Rashid a and M. F. Chamari a a Automotive Research
Influence of Fuel Injector Position of Port-fuel Injection Retrofit-kit to the Performances of Small Gasoline Engine M. F. Hushim a,*, A. J. Alimin a, L. A. Rashid a and M. F. Chamari a a Automotive Research
Using MATLAB/ Simulink in the designing of Undergraduate Electric Machinery Courses
 Using MATLAB/ Simulink in the designing of Undergraduate Electric Machinery Courses Mostafa.A. M. Fellani, Daw.E. Abaid * Control Engineering department Faculty of Electronics Technology, Beni-Walid, Libya
Using MATLAB/ Simulink in the designing of Undergraduate Electric Machinery Courses Mostafa.A. M. Fellani, Daw.E. Abaid * Control Engineering department Faculty of Electronics Technology, Beni-Walid, Libya
INFLUENCE OF INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE AND EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION ON HCCI COMBUSTION PROCESS USING BIOETHANOL
 ENGINEERING FOR RURAL DEVELOPMENT Jelgava, 2.-27..216. INFLUENCE OF INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE AND EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION ON HCCI COMBUSTION PROCESS USING BIOETHANOL Kastytis Laurinaitis, Stasys Slavinskas
ENGINEERING FOR RURAL DEVELOPMENT Jelgava, 2.-27..216. INFLUENCE OF INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE AND EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION ON HCCI COMBUSTION PROCESS USING BIOETHANOL Kastytis Laurinaitis, Stasys Slavinskas
Steady-State Engine Modeling for Calibration: A Productivity and Quality Study
 Steady-State Engine Modeling for Calibration: A Productivity and Quality Study MathWorks Automotive Conference 2007 Hyatt Regency, Dearborn, MI Ulrike Schoop John Reeves Satoru Watanabe Ken Butts IAV GmbH
Steady-State Engine Modeling for Calibration: A Productivity and Quality Study MathWorks Automotive Conference 2007 Hyatt Regency, Dearborn, MI Ulrike Schoop John Reeves Satoru Watanabe Ken Butts IAV GmbH
Setup Tabs. Basic Setup: Advanced Setup:
 Setup Tabs Basic Setup: Password This option sets a password that MUST be entered to re-enter the system. Note: ProEFI can NOT get you into the calibration if you lose this password. You will have to reflash
Setup Tabs Basic Setup: Password This option sets a password that MUST be entered to re-enter the system. Note: ProEFI can NOT get you into the calibration if you lose this password. You will have to reflash
Improving Fuel Efficiency with Fuel-Reactivity-Controlled Combustion
 ERC Symposium 2009 1 Improving Fuel Efficiency with Fuel-Reactivity-Controlled Combustion Rolf D. Reitz, Reed Hanson, Derek Splitter, Sage Kokjohn Engine Research Center University of Wisconsin-Madison
ERC Symposium 2009 1 Improving Fuel Efficiency with Fuel-Reactivity-Controlled Combustion Rolf D. Reitz, Reed Hanson, Derek Splitter, Sage Kokjohn Engine Research Center University of Wisconsin-Madison
Towards High Efficiency Engine THE Engine
 Towards High Efficiency Engine THE Engine Bengt Johansson Div. of Combustion Engines Director of KCFP, Lund University, Sweden What is a high efficiency? Any text book on ICE: Ideal cycle with heat addition
Towards High Efficiency Engine THE Engine Bengt Johansson Div. of Combustion Engines Director of KCFP, Lund University, Sweden What is a high efficiency? Any text book on ICE: Ideal cycle with heat addition
Embedded Torque Estimator for Diesel Engine Control Application
 2004-xx-xxxx Embedded Torque Estimator for Diesel Engine Control Application Peter J. Maloney The MathWorks, Inc. Copyright 2004 SAE International ABSTRACT To improve vehicle driveability in diesel powertrain
2004-xx-xxxx Embedded Torque Estimator for Diesel Engine Control Application Peter J. Maloney The MathWorks, Inc. Copyright 2004 SAE International ABSTRACT To improve vehicle driveability in diesel powertrain
INFLUENCE OF FUEL TYPE AND INTAKE AIR PROPERTIES ON COMBUSTION CHARACTERISTICS OF HCCI ENGINE
 ENGINEERING FOR RURAL DEVELOPMENT Jelgava, 23.-24.5.213. INFLUENCE OF FUEL TYPE AND INTAKE AIR PROPERTIES ON COMBUSTION CHARACTERISTICS OF HCCI ENGINE Kastytis Laurinaitis, Stasys Slavinskas Aleksandras
ENGINEERING FOR RURAL DEVELOPMENT Jelgava, 23.-24.5.213. INFLUENCE OF FUEL TYPE AND INTAKE AIR PROPERTIES ON COMBUSTION CHARACTERISTICS OF HCCI ENGINE Kastytis Laurinaitis, Stasys Slavinskas Aleksandras
Electronic Engine Controls Subscription Methods of Pressure Cycle Processing for Engine Control Nonlinear Analysis of
 Electronic Engine Controls Subscription 2003-01-0352 Methods of Pressure Cycle Processing for Engine Control 2003-01-0354 Nonlinear Analysis of Combustion Engine Vibroacoustic Signals for Misfire Detection
Electronic Engine Controls Subscription 2003-01-0352 Methods of Pressure Cycle Processing for Engine Control 2003-01-0354 Nonlinear Analysis of Combustion Engine Vibroacoustic Signals for Misfire Detection
BOOSTED HCCI OPERATION ON MULTI CYLINDER V6 ENGINE
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 13, No. 2 BOOSTED HCCI OPERATION ON MULTI CYLINDER V6 ENGINE Jacek Misztal, Mirosław L Wyszyński*, Hongming Xu, Athanasios Tsolakis The University of Birmingham,
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 13, No. 2 BOOSTED HCCI OPERATION ON MULTI CYLINDER V6 ENGINE Jacek Misztal, Mirosław L Wyszyński*, Hongming Xu, Athanasios Tsolakis The University of Birmingham,
GT-Suite Users International Conference Frankfurt a.m., October 22 nd 2012
 GT-Suite Users International Conference Frankfurt a.m., October 22 nd 2012 Computational Analysis of Internal and External EGR Strategies combined with Miller Cycle Concept for a Two Stage Turbocharged
GT-Suite Users International Conference Frankfurt a.m., October 22 nd 2012 Computational Analysis of Internal and External EGR Strategies combined with Miller Cycle Concept for a Two Stage Turbocharged
Application of WAVE 1-D Engine Models with Vehicle. Simulation Tools to Investigate Efficiency, Performance, and
 Application of WAVE 1-D Engine Models with Vehicle Simulation Tools to Investigate Efficiency, Performance, and Emission Impacts of Advanced Engine Operation. Presented at the Ricardo Software 9 th Annual
Application of WAVE 1-D Engine Models with Vehicle Simulation Tools to Investigate Efficiency, Performance, and Emission Impacts of Advanced Engine Operation. Presented at the Ricardo Software 9 th Annual
Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition combustion and fuel composition
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition combustion and fuel composition This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition combustion and fuel composition This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by
IDENTIFICATION OF FUEL INJECTION CONTROL SYSTEM IN A GDI ENGINE
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 17, No. 4 21 IDENTIFICATION OF FUEL INJECTION CONTROL SYSTEM IN A GDI ENGINE Zbigniew Wo czy ski Technical University of Radom Chrobrego Av. 45, 26-6 Radom,
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 17, No. 4 21 IDENTIFICATION OF FUEL INJECTION CONTROL SYSTEM IN A GDI ENGINE Zbigniew Wo czy ski Technical University of Radom Chrobrego Av. 45, 26-6 Radom,
Lean burn versus stoichiometric operation with EGR and 3-way catalyst of an engine fueled with natural gas and hydrogen enriched natural gas
 Lean burn versus stoichiometric operation with EGR and 3-way catalyst of an engine fueled with natural gas and hydrogen enriched natural gas Saanum, Inge; Bysveen, Marie; Tunestål, Per; Johansson, Bengt
Lean burn versus stoichiometric operation with EGR and 3-way catalyst of an engine fueled with natural gas and hydrogen enriched natural gas Saanum, Inge; Bysveen, Marie; Tunestål, Per; Johansson, Bengt
Study of Performance and Emission Characteristics of a Two Stroke Si Engine Operated with Gasoline Manifold Injectionand Carburetion
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(37), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i37/101984, October 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Study of Performance and Emission Characteristics
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(37), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i37/101984, October 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Study of Performance and Emission Characteristics
NEW DIESEL EMISSIONS CONTROL STRATEGY for US TIER 2
 NEW DIESEL EMISSIONS CONTROL STRATEGY for US TIER 2 Jeffrey A. Leet Shizuo Sasaki, PhD. Yiqun Huang, PhD. Gary Neely Department of Engine and Emissions Research Southwest Research Institute 24 Diesel Engine
NEW DIESEL EMISSIONS CONTROL STRATEGY for US TIER 2 Jeffrey A. Leet Shizuo Sasaki, PhD. Yiqun Huang, PhD. Gary Neely Department of Engine and Emissions Research Southwest Research Institute 24 Diesel Engine
Experimental Investigation of Acceleration Test in Spark Ignition Engine
 Experimental Investigation of Acceleration Test in Spark Ignition Engine M. F. Tantawy Basic and Applied Science Department. College of Engineering and Technology, Arab Academy for Science, Technology
Experimental Investigation of Acceleration Test in Spark Ignition Engine M. F. Tantawy Basic and Applied Science Department. College of Engineering and Technology, Arab Academy for Science, Technology
Development of Variable Geometry Turbocharger Contributes to Improvement of Gasoline Engine Fuel Economy
 Development of Variable Geometry Turbocharger Contributes to Improvement of Gasoline Engine Fuel Economy 30 MOTOKI EBISU *1 YOSUKE DANMOTO *1 YOJI AKIYAMA *2 HIROYUKI ARIMIZU *3 KEIGO SAKAMOTO *4 Every
Development of Variable Geometry Turbocharger Contributes to Improvement of Gasoline Engine Fuel Economy 30 MOTOKI EBISU *1 YOSUKE DANMOTO *1 YOJI AKIYAMA *2 HIROYUKI ARIMIZU *3 KEIGO SAKAMOTO *4 Every
Evaluation of Exhaust Emissions Reduction of a Retrofitted Bi-Fuel Spark Ignition Engine
 M. A. Kalam et al./journal of Energy & Environment, Vol. 5, May 2006 101 Evaluation of Exhaust Emissions Reduction of a Retrofitted Bi-Fuel Spark Ignition Engine M. A. Kalam, H. H. Masjuki and I. I. Yaacob
M. A. Kalam et al./journal of Energy & Environment, Vol. 5, May 2006 101 Evaluation of Exhaust Emissions Reduction of a Retrofitted Bi-Fuel Spark Ignition Engine M. A. Kalam, H. H. Masjuki and I. I. Yaacob
PIEZO ELECTRIC CONTROL HYDRAULIC STACKS FOR THE CAMLESS ENGINE
 PIEZO ELECTRIC CONTROL HYDRAULIC STACKS FOR THE CAMLESS ENGINE PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S0751 COLLEGE : BASAVAKALYAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, BIDAR BRANCH : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING GUIDE : SANTOSH PATIL STUDENTS
PIEZO ELECTRIC CONTROL HYDRAULIC STACKS FOR THE CAMLESS ENGINE PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S0751 COLLEGE : BASAVAKALYAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, BIDAR BRANCH : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING GUIDE : SANTOSH PATIL STUDENTS
Dual Fuel Combustion an Applicable Technology for Mobile Application?
 1 S C I E N C E P A S S I O N T E C H N O L O G Y Dual Fuel Combustion an Applicable Technology for Mobile Application? 10 th Conference Eco Mobility 2025plus Univ.Prof. Dr. Helmut Eichlseder Institute
1 S C I E N C E P A S S I O N T E C H N O L O G Y Dual Fuel Combustion an Applicable Technology for Mobile Application? 10 th Conference Eco Mobility 2025plus Univ.Prof. Dr. Helmut Eichlseder Institute
2.61 Internal Combustion Engines
 Due: Thursday, February 19, 2004 2.61 Internal Combustion Engines Problem Set 2 Tuesday, February 10, 2004 1. Several velocities, time, and length scales are useful in understanding what goes on inside
Due: Thursday, February 19, 2004 2.61 Internal Combustion Engines Problem Set 2 Tuesday, February 10, 2004 1. Several velocities, time, and length scales are useful in understanding what goes on inside
Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Lecture 14:Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions
 Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions The Lecture Contains: SI Engine Variables and Emissions Compression
Module 3: Influence of Engine Design and Operating Parameters on Emissions Effect of SI Engine Design and Operating Variables on Emissions The Lecture Contains: SI Engine Variables and Emissions Compression
DEUTZ Corporation 914 Gas. Customer / Event DEUTZ Corporation Presentation DATE, 2010
 DEUTZ Corporation 914 Gas Customer / Event DEUTZ Corporation Presentation DATE, 2010 914 Gas Content Target Market General Product Features Performance Data Dimensions and Weight Emissions Gas Train and
DEUTZ Corporation 914 Gas Customer / Event DEUTZ Corporation Presentation DATE, 2010 914 Gas Content Target Market General Product Features Performance Data Dimensions and Weight Emissions Gas Train and
EGR Transient Simulation of a Turbocharged Diesel Engine using GT-Power
 GT-SUITE USERS CONFERENCE FRANKFURT, OCTOBER 4 TH 2004 EGR Transient Simulation of a Turbocharged Diesel Engine using GT-Power TEAM OF WORK: G. GIAFFREDA, C. VENEZIA RESEARCH CENTRE ENGINE ENGINEERING
GT-SUITE USERS CONFERENCE FRANKFURT, OCTOBER 4 TH 2004 EGR Transient Simulation of a Turbocharged Diesel Engine using GT-Power TEAM OF WORK: G. GIAFFREDA, C. VENEZIA RESEARCH CENTRE ENGINE ENGINEERING
Split Injection for CNG Engines
 Willkommen Welcome Bienvenue Split Injection for CNG Engines Patrik Soltic, Hannes Biffiger Empa, Automotive Powertrain Technologies Laboratory Motivation CNG engines are gaining on importance in the stationary
Willkommen Welcome Bienvenue Split Injection for CNG Engines Patrik Soltic, Hannes Biffiger Empa, Automotive Powertrain Technologies Laboratory Motivation CNG engines are gaining on importance in the stationary
IC Engine Control - the Challenge of Downsizing
 IC Engine Control - the Challenge of Downsizing Dariusz Cieslar* 2nd Workshop on Control of Uncertain Systems: Modelling, Approximation, and Design Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge 23-24/9/2013
IC Engine Control - the Challenge of Downsizing Dariusz Cieslar* 2nd Workshop on Control of Uncertain Systems: Modelling, Approximation, and Design Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge 23-24/9/2013
LECTURE NOTES INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION
 LECTURE NOTES on INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION Integrated Master Course on Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department November 2015 Approach SI _ indirect injection
LECTURE NOTES on INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES SI AN INTEGRATED EVALUATION Integrated Master Course on Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department November 2015 Approach SI _ indirect injection
Gasoline HCCI engine with DME (Di-methyl Ether) as an Ignition Promoter
 Gasoline HCCI engine with DME (Di-methyl Ether) as an Ignition Promoter Kitae Yeom, Jinyoung Jang, Choongsik Bae Abstract Homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) combustion is an attractive way
Gasoline HCCI engine with DME (Di-methyl Ether) as an Ignition Promoter Kitae Yeom, Jinyoung Jang, Choongsik Bae Abstract Homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) combustion is an attractive way
Introduction of Current Clean Diesel Technology and Subjects for Passenger Car, Application for Thailand
 Introduction of Current Clean Diesel Technology and Subjects for Passenger Car, Application for Thailand Norio Suzuki Thai-Nichi Institute of Technology ABSTRACT Diesel emission regulations have become
Introduction of Current Clean Diesel Technology and Subjects for Passenger Car, Application for Thailand Norio Suzuki Thai-Nichi Institute of Technology ABSTRACT Diesel emission regulations have become
Objectives / Expected Results
 Objectives / Expected Results WP Leader: Dr. M. Moser, T. Moeller Cut operating, maintenance and deployment costs Develop systems, methods an processes for improved engine lifetime performance Reduction
Objectives / Expected Results WP Leader: Dr. M. Moser, T. Moeller Cut operating, maintenance and deployment costs Develop systems, methods an processes for improved engine lifetime performance Reduction
Effects of Pre-injection on Combustion Characteristics of a Single-cylinder Diesel Engine
 Proceedings of the ASME 2009 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition IMECE2009 November 13-19, Lake Buena Vista, Florida, USA IMECE2009-10493 IMECE2009-10493 Effects of Pre-injection
Proceedings of the ASME 2009 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition IMECE2009 November 13-19, Lake Buena Vista, Florida, USA IMECE2009-10493 IMECE2009-10493 Effects of Pre-injection
Which are the four important control loops of an spark ignition (SI) engine?
 151-0567-00 Engine Systems (HS 2017) Exercise 1 Topic: Lecture 1 Johannes Ritzmann (jritzman@ethz.ch), Raffi Hedinger (hraffael@ethz.ch); October 13, 2017 Problem 1 (Control Systems) Why do we use control
151-0567-00 Engine Systems (HS 2017) Exercise 1 Topic: Lecture 1 Johannes Ritzmann (jritzman@ethz.ch), Raffi Hedinger (hraffael@ethz.ch); October 13, 2017 Problem 1 (Control Systems) Why do we use control
PPC FOR LOW LOAD CONDITIONS IN MARINE ENGINE USING COMPUTATIONAL AND EXPERIMENTAL TECHNIQUES
 PPC FOR LOW LOAD CONDITIONS IN MARINE ENGINE USING COMPUTATIONAL AND EXPERIMENTAL TECHNIQUES Presented By:Kendra Shrestha Authors: K.Shrestha, O.Kaario, M. Imperato, T. Sarjovaara, M. Larmi Internal Combusion
PPC FOR LOW LOAD CONDITIONS IN MARINE ENGINE USING COMPUTATIONAL AND EXPERIMENTAL TECHNIQUES Presented By:Kendra Shrestha Authors: K.Shrestha, O.Kaario, M. Imperato, T. Sarjovaara, M. Larmi Internal Combusion
Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine Trends to Meet Future Emissions Standards (Euro VI)
 Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine Trends to Meet Future Emissions Standards (Euro VI) Andrew Nicol AECC Technical Seminar on Heavy-Duty Vehicle Emissions (Euro VI) Brussels 25 October 2007 Contents Emissions Legislation
Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine Trends to Meet Future Emissions Standards (Euro VI) Andrew Nicol AECC Technical Seminar on Heavy-Duty Vehicle Emissions (Euro VI) Brussels 25 October 2007 Contents Emissions Legislation
Direct Injection Ethanol Boosted Gasoline Engines: Biofuel Leveraging For Cost Effective Reduction of Oil Dependence and CO 2 Emissions
 Direct Injection Ethanol Boosted Gasoline Engines: Biofuel Leveraging For Cost Effective Reduction of Oil Dependence and CO 2 Emissions D.R. Cohn* L. Bromberg* J.B. Heywood Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Direct Injection Ethanol Boosted Gasoline Engines: Biofuel Leveraging For Cost Effective Reduction of Oil Dependence and CO 2 Emissions D.R. Cohn* L. Bromberg* J.B. Heywood Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The control of a free-piston engine generator. Part 2: engine dynamics and piston motion control
 The control of a free-piston engine generator. Part 2: engine dynamics and piston motion control R. Mikalsen, A.P. Roskilly Sir Joseph Swan Institute for Energy Research, Newcastle University, Newcastle
The control of a free-piston engine generator. Part 2: engine dynamics and piston motion control R. Mikalsen, A.P. Roskilly Sir Joseph Swan Institute for Energy Research, Newcastle University, Newcastle
Experimental Researches of Fuelling Systems and Alcohol Blends on Combustion and Emissions in a Two Stroke Si Engine
 Experimental Researches of Fuelling Systems and Alcohol Blends on Combustion and Emissions in a Two Stroke Si Engine MIHAI ALEONTE, CORNELIU COFARU, RADU COSGAREA, MARIA LUMINITA SCUTARU, LIVIU JELENSCHI,
Experimental Researches of Fuelling Systems and Alcohol Blends on Combustion and Emissions in a Two Stroke Si Engine MIHAI ALEONTE, CORNELIU COFARU, RADU COSGAREA, MARIA LUMINITA SCUTARU, LIVIU JELENSCHI,
Internal Combustion Optical Sensor (ICOS)
 Internal Combustion Optical Sensor (ICOS) Optical Engine Indication The ICOS System In-Cylinder Optical Indication 4air/fuel ratio 4exhaust gas concentration and EGR 4gas temperature 4analysis of highly
Internal Combustion Optical Sensor (ICOS) Optical Engine Indication The ICOS System In-Cylinder Optical Indication 4air/fuel ratio 4exhaust gas concentration and EGR 4gas temperature 4analysis of highly
Effects of ethanol unleaded gasoline blends on cyclic variability and emissions in an SI engine
 Applied Thermal Engineering 25 (2005) 917 925 www.elsevier.com/locate/apthermeng Effects of ethanol unleaded gasoline blends on cyclic variability and emissions in an SI engine M.A. Ceviz *,F.Yüksel Department
Applied Thermal Engineering 25 (2005) 917 925 www.elsevier.com/locate/apthermeng Effects of ethanol unleaded gasoline blends on cyclic variability and emissions in an SI engine M.A. Ceviz *,F.Yüksel Department
COMPARISON OF VARIABLE VALVE ACTUATION, CYLINDER DEACTIVATION AND INJECTION STRATEGIES FOR LOW-LOAD RCCI OPERATION OF A LIGHT-DUTY ENGINE
 COMPARISON OF VARIABLE VALVE ACTUATION, CYLINDER DEACTIVATION AND INJECTION STRATEGIES FOR LOW-LOAD RCCI OPERATION OF A LIGHT-DUTY ENGINE Anand Nageswaran Bharath, Yangdongfang Yang, Rolf D. Reitz, Christopher
COMPARISON OF VARIABLE VALVE ACTUATION, CYLINDER DEACTIVATION AND INJECTION STRATEGIES FOR LOW-LOAD RCCI OPERATION OF A LIGHT-DUTY ENGINE Anand Nageswaran Bharath, Yangdongfang Yang, Rolf D. Reitz, Christopher
EURO 4-5 Diesel Exhaust Pollutant. After-Threatment
 EURO4-5 Common Rail EURO 4-5 Diesel Exhaust Pollutant After-Threatment 1 Exhaust gas recirculation EGR fundamentals: AFR: Air to Fuel Ratio. This parameter is used to define the ratio between fuel (petrol,
EURO4-5 Common Rail EURO 4-5 Diesel Exhaust Pollutant After-Threatment 1 Exhaust gas recirculation EGR fundamentals: AFR: Air to Fuel Ratio. This parameter is used to define the ratio between fuel (petrol,
X4v2 Testing Update 19 th November 2007
 X4v2 Testing Update 19 th November 2007 Copyright 2007 Revetec Holdings Limited Contents Forward 2 Economy and Driving 2 Advances in Engine Technology to Increase/Widen Torque Bands 3 Variable Length Intake
X4v2 Testing Update 19 th November 2007 Copyright 2007 Revetec Holdings Limited Contents Forward 2 Economy and Driving 2 Advances in Engine Technology to Increase/Widen Torque Bands 3 Variable Length Intake
System Simulation for Aftertreatment. LES for Engines
 System Simulation for Aftertreatment LES for Engines Christopher Rutland Engine Research Center University of Wisconsin-Madison Acknowledgements General Motors Research & Development Caterpillar, Inc.
System Simulation for Aftertreatment LES for Engines Christopher Rutland Engine Research Center University of Wisconsin-Madison Acknowledgements General Motors Research & Development Caterpillar, Inc.
Virtual Testing and Simulation Environment [Micro-HiL] for Engine and Aftertreatment Calibration and Development -Part 2
![Virtual Testing and Simulation Environment [Micro-HiL] for Engine and Aftertreatment Calibration and Development -Part 2 Virtual Testing and Simulation Environment [Micro-HiL] for Engine and Aftertreatment Calibration and Development -Part 2](/thumbs/89/98656646.jpg) Copyright 2012 SAE International SAE Paper 2012-01-0928 This paper is posted on this website with permission from SAE Further use or distribution is not permitted without permission from SAE Virtual Testing
Copyright 2012 SAE International SAE Paper 2012-01-0928 This paper is posted on this website with permission from SAE Further use or distribution is not permitted without permission from SAE Virtual Testing
REDUCTION OF EMISSIONS BY ENHANCING AIR SWIRL IN A DIESEL ENGINE WITH GROOVED CYLINDER HEAD
 REDUCTION OF EMISSIONS BY ENHANCING AIR SWIRL IN A DIESEL ENGINE WITH GROOVED CYLINDER HEAD Dr.S.L.V. Prasad 1, Prof.V.Pandurangadu 2, Dr.P.Manoj Kumar 3, Dr G. Naga Malleshwara Rao 4 Dept.of Mechanical
REDUCTION OF EMISSIONS BY ENHANCING AIR SWIRL IN A DIESEL ENGINE WITH GROOVED CYLINDER HEAD Dr.S.L.V. Prasad 1, Prof.V.Pandurangadu 2, Dr.P.Manoj Kumar 3, Dr G. Naga Malleshwara Rao 4 Dept.of Mechanical
Potential of the Mild HCCI Combustion for Worldwide Applications
 Potential of the Mild HCCI Combustion for Worldwide Applications Future Fuels for IC Engines ERC Research Symposium Madison June 6-7, 2007 P.Gastaldi M.Besson JP.Hardy Renault Powertrain Division Overview
Potential of the Mild HCCI Combustion for Worldwide Applications Future Fuels for IC Engines ERC Research Symposium Madison June 6-7, 2007 P.Gastaldi M.Besson JP.Hardy Renault Powertrain Division Overview
Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset
 Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset Vikas Kumar Agarwal Deputy Manager Mahindra Two Wheelers Ltd. MIDC Chinchwad Pune 411019 India Abbreviations:
Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset Vikas Kumar Agarwal Deputy Manager Mahindra Two Wheelers Ltd. MIDC Chinchwad Pune 411019 India Abbreviations:
A Novel Method of Data Synchronization during Transient Engine Testing for ECU Development
 Speakers Information- Controls, Measurement & Calibration Congress A Novel Method of Data Synchronization during Transient Engine Testing for ECU Development Jensen Samuel J, Paul Pramod S, Ramesh A IIT
Speakers Information- Controls, Measurement & Calibration Congress A Novel Method of Data Synchronization during Transient Engine Testing for ECU Development Jensen Samuel J, Paul Pramod S, Ramesh A IIT
The Effect of Clean and Cold EGR on the Improvement of Low Temperature Combustion Performance in a Single Cylinder Research Diesel Engine
 The Effect of Clean and Cold EGR on the Improvement of Low Temperature Combustion Performance in a Single Cylinder Research Diesel Engine C. Beatrice, P. Capaldi, N. Del Giacomo, C. Guido and M. Lazzaro
The Effect of Clean and Cold EGR on the Improvement of Low Temperature Combustion Performance in a Single Cylinder Research Diesel Engine C. Beatrice, P. Capaldi, N. Del Giacomo, C. Guido and M. Lazzaro
Experimental investigation on influence of EGR on combustion performance in SI Engine
 - 1821 - Experimental investigation on influence of EGR on combustion performance in SI Engine Abstract M. Božić 1*, A. Vučetić 1, D. Kozarac 1, Z. Lulić 1 1 University of Zagreb, Faculty of Mechanical
- 1821 - Experimental investigation on influence of EGR on combustion performance in SI Engine Abstract M. Božić 1*, A. Vučetić 1, D. Kozarac 1, Z. Lulić 1 1 University of Zagreb, Faculty of Mechanical
CONTROLLING COMBUSTION IN HCCI DIESEL ENGINES
 CONTROLLING COMBUSTION IN HCCI DIESEL ENGINES Nicolae Ispas *, Mircea Năstăsoiu, Mihai Dogariu Transilvania University of Brasov KEYWORDS HCCI, Diesel Engine, controlling, air-fuel mixing combustion ABSTRACT
CONTROLLING COMBUSTION IN HCCI DIESEL ENGINES Nicolae Ispas *, Mircea Năstăsoiu, Mihai Dogariu Transilvania University of Brasov KEYWORDS HCCI, Diesel Engine, controlling, air-fuel mixing combustion ABSTRACT
Development and performance analysis of a Miller cycle in a modified using diesel engine
 에너지공학, 제 17 권제 4 호 (2008) Journal of Energy Engineering, Vol. 17, No. 4, pp. 198~203 (2008) Development and performance analysis of a Miller cycle in a modified using diesel engine Gyeung Ho Choi*, Chedthawut
에너지공학, 제 17 권제 4 호 (2008) Journal of Energy Engineering, Vol. 17, No. 4, pp. 198~203 (2008) Development and performance analysis of a Miller cycle in a modified using diesel engine Gyeung Ho Choi*, Chedthawut
POSSIBLE SHORT-TERM INTRODUCTION OF HYDROGEN AS VEHICLE FUEL / FUEL ADDITIVE
 Which Fuels For Low CO 2 Engines? P. Duret (Editor) and Editions Technip, Paris, 24, pp. 27 rue Ginoux, 7 Paris POSSIBLE SHORT-TERM INTRODUCTION OF HYDROGEN AS VEHICLE FUEL / FUEL ADDITIVE Per Tunestål,
Which Fuels For Low CO 2 Engines? P. Duret (Editor) and Editions Technip, Paris, 24, pp. 27 rue Ginoux, 7 Paris POSSIBLE SHORT-TERM INTRODUCTION OF HYDROGEN AS VEHICLE FUEL / FUEL ADDITIVE Per Tunestål,
Problem 1 (ECU Priority)
 151-0567-00 Engine Systems (HS 2016) Exercise 6 Topic: Optional Exercises Raffi Hedinger (hraffael@ethz.ch), Norbert Zsiga (nzsiga@ethz.ch); November 28, 2016 Problem 1 (ECU Priority) Use the information
151-0567-00 Engine Systems (HS 2016) Exercise 6 Topic: Optional Exercises Raffi Hedinger (hraffael@ethz.ch), Norbert Zsiga (nzsiga@ethz.ch); November 28, 2016 Problem 1 (ECU Priority) Use the information
Comparative performance and emissions study of a lean mixed DTS-i spark ignition engine operated on single spark and dual spark
 26 IJEDR Volume 4, Issue 2 ISSN: 232-9939 Comparative performance and emissions study of a lean mixed DTS-i spark ignition engine operated on single spark and dual spark Hardik Bambhania, 2 Vijay Pithiya,
26 IJEDR Volume 4, Issue 2 ISSN: 232-9939 Comparative performance and emissions study of a lean mixed DTS-i spark ignition engine operated on single spark and dual spark Hardik Bambhania, 2 Vijay Pithiya,
Project Summary Fuzzy Logic Control of Electric Motors and Motor Drives: Feasibility Study
 EPA United States Air and Energy Engineering Environmental Protection Research Laboratory Agency Research Triangle Park, NC 277 Research and Development EPA/600/SR-95/75 April 996 Project Summary Fuzzy
EPA United States Air and Energy Engineering Environmental Protection Research Laboratory Agency Research Triangle Park, NC 277 Research and Development EPA/600/SR-95/75 April 996 Project Summary Fuzzy
The Effect of Volume Ratio of Ethanol Directly Injected in a Gasoline Port Injection Spark Ignition Engine
 10 th ASPACC July 19 22, 2015 Beijing, China The Effect of Volume Ratio of Ethanol Directly Injected in a Gasoline Port Injection Spark Ignition Engine Yuhan Huang a,b, Guang Hong a, Ronghua Huang b. a
10 th ASPACC July 19 22, 2015 Beijing, China The Effect of Volume Ratio of Ethanol Directly Injected in a Gasoline Port Injection Spark Ignition Engine Yuhan Huang a,b, Guang Hong a, Ronghua Huang b. a
COMBUSTION CONTROLLER DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATION USING MODEL-BASED DESIGN
 COMBUSTION CONTROLLER DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATION USING MODEL-BASED DESIGN Klaus Rothbart April, 7th 00 AGENDA Introduction Development Application on engine test bed Results Summary INTRODUCTION AVL The
COMBUSTION CONTROLLER DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATION USING MODEL-BASED DESIGN Klaus Rothbart April, 7th 00 AGENDA Introduction Development Application on engine test bed Results Summary INTRODUCTION AVL The
Vehicle simulation with cylinder deactivation
 Vehicle simulation with cylinder deactivation Potential analysis of cylinder deactivation using a detailed Cyrille Frottier, Lars Böttcher, GT-SUITE Users Conference, October 2011 Vehicle simulation with
Vehicle simulation with cylinder deactivation Potential analysis of cylinder deactivation using a detailed Cyrille Frottier, Lars Böttcher, GT-SUITE Users Conference, October 2011 Vehicle simulation with
Effect of hydrogen and gasoline fuel blend on the performance of SI engine
 Vol. 4(7), pp. 125-130, November 2013 DOI: 10.5897/JPTAF2013.0095 2013 Academic Journals http://www.academicjournals.org/jptaf Journal of Petroleum Technology and Alternative Fuels Full Length Research
Vol. 4(7), pp. 125-130, November 2013 DOI: 10.5897/JPTAF2013.0095 2013 Academic Journals http://www.academicjournals.org/jptaf Journal of Petroleum Technology and Alternative Fuels Full Length Research
R&D on Environment-Friendly, Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine
 20000 M4.2.2 R&D on Environment-Friendly, Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine (Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine Group) Nobuyasu Matsudaira, Koji Imoto, Hiroshi Morimoto, Akira Numata, Toshimitsu
20000 M4.2.2 R&D on Environment-Friendly, Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine (Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine Group) Nobuyasu Matsudaira, Koji Imoto, Hiroshi Morimoto, Akira Numata, Toshimitsu
Combustion Performance
 Analysis of Crankshaft Speed Fluctuations and Combustion Performance Ramakrishna Tatavarthi Julian Verdejo GM Powertrain November 10, 2008 Overview introduction definition of operating map speed-load d
Analysis of Crankshaft Speed Fluctuations and Combustion Performance Ramakrishna Tatavarthi Julian Verdejo GM Powertrain November 10, 2008 Overview introduction definition of operating map speed-load d
Potential of Large Output Power, High Thermal Efficiency, Near-zero NOx Emission, Supercharged, Lean-burn, Hydrogen-fuelled, Direct Injection Engines
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 29 (2012 ) 455 462 World Hydrogen Energy Conference 2012 Potential of Large Output Power, High Thermal Efficiency, Near-zero NOx Emission, Supercharged,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 29 (2012 ) 455 462 World Hydrogen Energy Conference 2012 Potential of Large Output Power, High Thermal Efficiency, Near-zero NOx Emission, Supercharged,
ProECU EVO X. Tuning Guide 2008-onward Model Year. v1.8
 ProECU EVO X Tuning Guide 2008-onward Model Year v1.8 Contents ECU Map Descriptions... 3 3D Maps... 3 Fuel Maps Shown in Live Data as Injector % and Injector ms... 3 High Octane... 3 Low Octane... 3 Ignition
ProECU EVO X Tuning Guide 2008-onward Model Year v1.8 Contents ECU Map Descriptions... 3 3D Maps... 3 Fuel Maps Shown in Live Data as Injector % and Injector ms... 3 High Octane... 3 Low Octane... 3 Ignition
Decision & abrupt change detection
 Decision & abrupt change Statistical tools P. pierre.granjon@grenoble-inp.fr Grenoble INP, ense3, gipsa-lab 2013-2014 The estimation problem p X θ (x) f ( ) Physical system unknown parameter θ Measurements
Decision & abrupt change Statistical tools P. pierre.granjon@grenoble-inp.fr Grenoble INP, ense3, gipsa-lab 2013-2014 The estimation problem p X θ (x) f ( ) Physical system unknown parameter θ Measurements
Digital Shaping and Optimization of Fuel Injection Pattern for a Common Rail Automotive Diesel Engine through Numerical Simulation
 Digital Shaping and Optimization of Fuel Injection Pattern for a Common Rail Automotive Diesel Engine through Numerical Simulation European GT Conference 2017 - Frankfurt am Main Politecnico di Torino:
Digital Shaping and Optimization of Fuel Injection Pattern for a Common Rail Automotive Diesel Engine through Numerical Simulation European GT Conference 2017 - Frankfurt am Main Politecnico di Torino:
EFFECT OF H 2 + O 2 GAS MIXTURE ADDITION ON EMISSONS AND PERFORMANCE OF AN SI ENGINE
 EFFECT OF H 2 + O 2 GAS MIXTURE ADDITION ON EMISSONS AND PERFORMANCE OF AN SI ENGINE M.Sc. Karagoz Y. 1, M.Sc. Orak E. 1, Assist. Prof. Dr. Sandalci T. 1, B.Sc. Uluturk M. 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
EFFECT OF H 2 + O 2 GAS MIXTURE ADDITION ON EMISSONS AND PERFORMANCE OF AN SI ENGINE M.Sc. Karagoz Y. 1, M.Sc. Orak E. 1, Assist. Prof. Dr. Sandalci T. 1, B.Sc. Uluturk M. 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Air Charge Control for Turbocharged Spark Ignition Engines with Internal Exhaust Gas Recirculation
 Air Charge Control for Turbocharged Spark Ignition Engines with Internal Exhaust Gas Recirculation Donghoon Lee, Li Jiang, Hakan Yilmaz and Anna G. Stefanopoulou Abstr This paper presents the design of
Air Charge Control for Turbocharged Spark Ignition Engines with Internal Exhaust Gas Recirculation Donghoon Lee, Li Jiang, Hakan Yilmaz and Anna G. Stefanopoulou Abstr This paper presents the design of
THE FKFS 0D/1D-SIMULATION. Concepts studies, engineering services and consulting
 THE FKFS 0D/1D-SIMULATION Concepts studies, engineering services and consulting r e s e a r c h i n m o t i o n. VEHICLE IN MOTION On the basis of constant engine speeds and loads, the combustion engine
THE FKFS 0D/1D-SIMULATION Concepts studies, engineering services and consulting r e s e a r c h i n m o t i o n. VEHICLE IN MOTION On the basis of constant engine speeds and loads, the combustion engine
Combining Optimisation with Dymola to Calibrate a 2-zone Predictive Combustion Model.
 Combining Optimisation with Dymola to Calibrate a 2-zone Predictive Combustion Model. Mike Dempsey Optimised Engineering Design Conference 2016 Claytex Services Limited Software, Consultancy, Training
Combining Optimisation with Dymola to Calibrate a 2-zone Predictive Combustion Model. Mike Dempsey Optimised Engineering Design Conference 2016 Claytex Services Limited Software, Consultancy, Training
COMBUSTION ANALYSIS OF A CNG DIRECT INJECTION SPARK IGNITION ENGINE. A. Rashid A. Aziz, Firmansyah and Raja Shahzad ABSTRACT
 International Journal of Automotive and Mechanical Engineering (IJAME) ISSN: 2229-8649 (Print); ISSN: 218-166 (Online); Volume 2, pp. 157-17, July-December 21 Universiti Malaysia Pahang DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.15282/ijame.2.21.5.13
International Journal of Automotive and Mechanical Engineering (IJAME) ISSN: 2229-8649 (Print); ISSN: 218-166 (Online); Volume 2, pp. 157-17, July-December 21 Universiti Malaysia Pahang DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.15282/ijame.2.21.5.13
