Standard Test Method for Cold Filter Plugging Point of Diesel and Heating Fuels 1
|
|
|
- Dortha May
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Designation: D An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Cold Filter Plugging Point of Diesel and Heating Fuels 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6371; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval. 1. Scope 1.1 This test method covers the determination of the cold filter plugging point (CFPP) temperature of diesel and domestic heating fuels using either manual or automated apparatus. NOTE 1 This test method is technically equivalent to test methods IP 309 and EN The manual apparatus and automated apparatus are both suitable for referee purposes. 1.3 This test method is applicable to distillate fuels, including those containing a flow-improving or other additive, intended for use in diesel engines and domestic heating installations. 1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section Referenced Documents 2.1 ASTM Standards: D 2500 Test Method for Cloud Point of Petroleum Oils 2 D 4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products 3 D 4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products 3 D 5771 Test Method for Cloud Point of Petroleum Products (Optical Detection Stepped Cooling Method) 4 D 5772 Test Method for Cloud Point of Petroleum Products (Linear Cooling Rate Method) 4 D 5773 Test Method for Cloud Point of Petroleum Products (Constant Cooling Rate Method) 4 E 1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers IP Standards: 6 IP 309 Diesel and domestic heating fuels - Determination of cold filter plugging point Specifications for IP Standard Thermometers 2.3 ISO Standards: 7 IP 3310 Test sieves - Technical requirements and testing - Part 1: Metal cloth 2.4 European Standards: 8 EN 116 Diesel and domestic heating fuels - Determination of cold filter plugging point 3. Terminology 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard: cold filter plugging point, n highest temperature, expressed in multiples of 1 C, at which a given volume of fuel fails to pass through a standardized filtration device in a specified time when cooled under the conditions prescribed in this test method certified reference material, n a stable petroleum product with a method-specific nominal CFPP value established by a method-specific interlaboratory study following RR:D guidelines or ISO Guides 34 and Summary of Test Method 4.1 A specimen of the sample is cooled under specified conditions and, at intervals of 1 C, is drawn into a pipet under a controlled vacuum through a standardized wire mesh filter. The procedure is repeated, as the specimen continues to cool, for each 1 C below the first test temperature. Testing is continued until the amount of wax crystals that have separated out of solution is sufficient to stop or slow down the flow so that the time taken to fill the pipet exceeds 60 s or the fuel fails to return completely to the test jar before the fuel has cooled by a further 1 C. 1 This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-2 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D D on Wax-Related Viscometric Properties of Fuels and Oils. Current edition approved Feb. 10, Published April Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol Available from Institute of Petroleum, 61 New Cavendish St., London, W. I., England. 7 Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., New York, Available from European Committee for Standardization, Central Secretariat, Rue Bréderode 2, B-1000, Brussels, Belgium. 9 Available from ASTM Headquarters. Copyright ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA , United States. 1
2 4.2 The indicated temperature at which the last filtration was commenced is recorded as the CFPP. 5. Significance and Use 5.1 The CFPP of a fuel is suitable for estimating the lowest temperature at which a fuel will give trouble-free flow in certain fuel systems. 5.2 In the case of diesel fuel used in European light duty trucks, the results are usually close to the temperature of failure in service except when the fuel system contains, for example, a paper filter installed in a location exposed to the weather or if the filter plugging temperature is more than 12 C below the cloud point value in accordance with Test Method D 2500, D 5771, D 5772, or D Domestic heating installations are usually less critical and often operate satisfactorily at temperatures somewhat lower than those indicated by the test results. 5.3 The difference in results obtained from the sample as received and after heat treatment at 45 C for 30 min can be used to investigate complaints of unsatisfactory performance under low temperature conditions. 6. Apparatus 6.1 Manual Apparatus: The apparatus, as detailed in , shall be arranged as shown in Fig Test Jar, cylindrical, of clear glass, flat bottomed, with an internal diameter of mm, a wall thickness of mm and a height of mm. The jar shall have a permanent mark at the ml level. NOTE 2 Test jars of the required dimensions may be obtained by selection from jars conforming to Test Method D 2500, which specifies a wider diameter tolerance Jacket, brass, watertight, cylindrical, flat bottomed, to be used as an air bath. It shall have an inside diameter of mm, outside diameter of mm, and a height of mm (see Fig. 2) Insulating Ring, made from oil-resistant plastics or other suitable material, to be placed in the bottom of the jacket (see 6.1.3) to provide insulation for the bottom of the test jar. It shall fit closely inside the jacket and have a thickness of mm Spacers (two), approximately 5-mm thick, made of oil-resistant plastics or other suitable material, to be placed as shown in Fig. 1 around the test jar (see 6.1.2) to provide insulation for the test jar from the sides of the jacket. The spacers shall fit closely to the test jar and closely inside the jacket. The use of incomplete rings, each with a 2-mm circumferential gap, will accommodate variations in test jar diameter. The spacers and insulating ring may be made as a single part as shown in Fig Supporting Ring, of oil resistant plastics or other suitable non-metallic, non-absorbent, oil-resistant material, used to suspend the jacket (see 6.1.3) in a stable and upright position in the cooling bath and to provide a concentric location for the stopper (see 6.1.7). A design is shown in Fig. 4 for guidance, but this design may be modified to suit the cooling bath Stopper, of oil-resistant plastics or other suitable non-metallic, non-absorbent, oil-resistant material, to fit the test jar and the support ring as shown in Fig. 5. It shall have three holes to accommodate the pipet (see 6.1.8) and the thermometer (see 6.1.9) and to allow venting of the system. If necessary, when using the high-range thermometer (see 6.1.9), FIG. 1 Arrangement of Manual CFPP Apparatus FIG. 2 Watertight Brass Jacket 2
3 FIG. 3 Spacers FIG. 5 Stopper with Holes for Thermometer, Pipet, and Vent FIG. 4 Supporting Ring the upper part of the stopper shall have an indentation to permit the thermometer (see (a)) to be read down to a temperature of -30 C. A pointer shall be fitted to the upper surface of the stopper to facilitate location of the thermometer in relation to the bottom of the test jar. A spring wire clip shall be used to retain the thermometer in the correct position Pipet with Filter Unit: A Pipet,, of clear glass with a calibration mark corresponding to a contained volume of ml at a point mm from the bottom of the pipet (see Fig. 6). It shall be connected to the filter unit (see ) A Filter Unit (see Fig. 7), containing the following elements: (a) A Brass Body, with a threaded cavity that houses the wire mesh holder. The cavity shall be fitted with an O-ring of oil-resistant plastics. The internal diameter of the central tube shall be mm; (b) A Brass Screw Cap, to connect the upper part of the body of the filter unit (see ) to the lower part of the pipet (see ) to ensure a leak-free joint. An example of satisfactory connection is shown in Fig. 7. (c) A Disc, mm diameter, of plain weave stainless steel wire mesh gauze with a nominal aperture size of 45 µm. The nominal diameter of the wire shall be 32 µm, and the tolerance for the size of an individual aperture shall be as follows: (1) No aperture size shall exceed the nominal size by more than 22 µm; (2) The average aperture size shall be within µm of the nominal size; (3) Not more than 6 % of the apertures shall be above the nominal size by more than 13 µm. NOTE 3 The requirements for the wire mesh are taken from ISO 3310, to which reference may be made for methods for testing the gauze. 3
4 FIG. 6 Pipet FIG. 7 Filter Unit (d) A Filter Holder of Brass, in which the disc of wire mesh gauze (see (c)) is firmly clamped by a retaining ring pressed into the filter holder. The diameter of the exposed part of the gauze shall be mm (see Fig. 8); (e) A Brass Cylinder, threaded on the outside, that can be screwed into the cavity of the body (see (a)) to clamp the filter holder (see (d)) against the O-ring ( (a)), The lower end shall have four slots to allow the specimen to flow into the filter unit Thermometers, having ranges shown below and conforming to the requirements prescribed in Specification E 1 or Specifications for IP Standard Thermometers. Thermometer Number Thermometer Temperature Range ASTM IP High-range for CFPP down to 38 C to +50 C 5C 1C 30 C Low-range from CFPP below 80 C to +20 C 6C 2C 30 C Cooling bath 80 C to +20 C 6C 2C Cooling Bath: The type of cooling bath is optional, but it shall be of a shape and size suitable for containing the jacket (see 6.1.3) in a stable and upright position at the required depth The bath shall be fitted with a cover with one or more holes in it to accommodate the supporting ring (see 6.1.6). The jacket (see 6.1.3) may be permanently mounted in the cover. FIG. 8 Brass Filter Holder The bath temperature shall be maintained at the required value and tolerance by a refrigeration unit or by the use of suitable freezing mixtures, ensuring a homogenous temperature in the bath by stirring or other means of agitation. Table 1 lists the bath temperature set-points required in the CFPP procedure. If only one bath is utilized, it must have the ability to change down to the next lower set-point temperature in a time period not exceeding 2 min 30 s. 4
5 TABLE 1 Cooling Bath Temperatures Expected CFPP Required Cooling Bath Temperature(s) Down to 20 C C Between 20 C and 35 C C then C Below 35 C C then C then C Stopcock, glass, with double oblique bore of 3-mm diameter Vacuum Source, vacuum pump or water pump powerful enough to ensure an air flow rate in the vacuum regulator of L/h for the duration of the test Vacuum Regulator, consisting of a glass bottle, at least 350-mm high, not less than 5 L capacity, partially filled with water. It shall be closed by a stopper with three holes of convenient diameters for glass tubes. Two tubes shall be short and shall not go below the water level. The third tube, with an internal diameter of mm, shall be long enough for one end to be approximately 200 mm beneath the surface of the water while the other end reaches a few centimetres above the stopper. The depth of the immersed part shall then be adjusted to obtain a depression of mm of water ( kpa) on the manometer, which shall contain water. A second empty 5 L bottle shall be fitted in the line to serve as a vacuum reservoir to ensure a constant depression. The arrangement is shown in Fig Stopwatch, with a graduation or reading of 0.2 s or lower, with an accuracy of 0.1 % over a period of 10 min. 6.2 Automated Apparatus: The automated apparatus shall include elements conforming to , platinum resistance thermometers, cooling bath(s), vacuum pump, and suitable electronic control and measurement devices Cooling Bath, a refrigeration unit capable of maintaining the cooling bath at the required temperature and also of automatically changing the bath temperature within 2 min 30 s at the appropriate stage (see ) Vacuum Pump, powerful enough to ensure an air flow rate in the vacuum regulator of a minimum of L/h, and to maintain a constant vacuum of mm( kpa) for the duration of the test. For multi-position testers using the same vacuum pump, the flow rate shall be checked when several positions are operating simultaneously. 7. Reagents and Materials 7.1 Heptane, clean commercial or reagent grade. NOTE 4 Warning: Flammable. Harmful if inhaled. 7.2 Acetone, clean commercial or reagent grade. NOTE 5 Warning: Extremely flammable. 7.3 Lintless Filter Paper, (5 6 1 µm retention). 7.4 Certified Reference Materials. 8. Sampling 8.1 Unless otherwise specified in the commodity specification, samples shall be taken as described in Practice D 4057 or D 4177 in accordance with the requirements of national standards or regulation for the sampling of the product under test, or both. 9. Preparation of Test Specimen 9.1 Filter approximately 50 ml of the sample (see 8.1) at laboratory ambient temperature, but in any case not at a temperature less than 15 C, through dry filter paper (see 7.3). 10. Preparation of Apparatus 10.1 Prepare the manual apparatus or the automated apparatus for operation in accordance with the manufacturer s instructions for calibrating, checking, and operating the equipment. See Fig. 1 for manual apparatus Before each test, dismantle the filter unit (see ) and wash the pieces and the test jar (see 6.1.2), the pipet (see ) and the thermometer (see for manual apparatus and 6.2 for platinum resistance used in automated equipment) with heptane (see 7.1), then rinse with acetone (see 7.2) and dry in a stream of filtered air. Check the cleanliness and dryness of all elements, including the jacket (see 6.1.3). Examine the wire mesh (see (c)) and the joints (see (a) and (b) for damage; if necessary renew them Check that the screw cap (see (b) is tight enough to prevent leakage. 11. Calibration and Standardization 11.1 Adjust the automated CFPP apparatus (when used) in accordance with the manufacturer s instructions Calibrate the temperature measuring device in accordance with the manufacturer s instructions Periodically verify the correct functioning of manual and automated apparatus using a certified reference material or in-house secondary reference material, such as fuel of known CFPP value. NOTE 6 It is preferable that verification be carried out at least two times a year, where possible, using certified reference materials. The apparatus should be checked more frequently (for example, weekly) using a secondary verification material When the CFPP values obtained using a verification material deviate by more than the test repeatability (see 15.2), or an unacceptable statistical quality control bias is observed, check the condition and operation of the apparatus to ensure conformity with the specification as stated in this test method. The manufacturer s instruction manual should provide guidance on ensuring that the apparatus is correctly set up and calibrated. 12. Procedure 12.1 Manual Apparatus: Establish the cooling bath temperature at C Place the insulating ring (see 6.1.4) on the bottom of the jacket (see 6.1.3). If spacers (see 6.1.5) are not mounted on the insulating ring (see 6.1.4), position them approximately 15 and 75 mm above the bottom of the test jar (see 6.1.2) Pour the filtered specimen (see Section 9) into the clean and dry test jar to the mark (45 ml) Close the test jar with the stopper (see 6.1.7) carrying the pipet with filter unit (see 6.1.8) and the appropriate thermometer (see 6.1.9). Use a low-range thermometer if the expected CFPP is below 30 C. Thermometers shall not be 5
6 changed during the test. Adjust the apparatus in such a way that the bottom of the filter unit (see (e)) rests on the bottom of the test jar, and position the thermometer so that its lower end is mm above the bottom of the test jar. Take care to ensure that no part of the thermometer is not in contact with the side of the test jar or the filter body. NOTE 7 The precise positioning of the thermometer in the test jar is a critical parameter of this test method. The position of the lower end of the thermometer above the bottom of the test jar can be indirectly measured by marking the stem of the thermometer flush with the stopper (see 6.1.7) when the lower end of the thermometer is just touching the bottom of the test jar, and then pulling the thermometer up such that the reference line is mm above the top of the stopper If the jacket is not an integral part of the cooling bath, place the jacket vertically to a depth of mminthe cooling bath (see ), which is maintained at the temperature of C Insert the test jar assembly in a stable vertical position into the jacket With the stopcock (see ) open to atmosphere, connect the pipet to the vacuum system (see and ) by means of flexible tubing attached to the stopcock (see Fig. 1). Switch on the vacuum source and regulate to ensure an air flow rate of 15 L/h in the vacuum regulator (see ). Before starting a test, check that the U-tube manometer indicates a mm of water depression ( kpa) Start the test immediately after inserting the test jar assembly into the jacket, but if the cloud point of the sample is known, it is permitted to wait until the specimen has cooled to a temperature of not less than 5 C above its cloud point When the specimen temperature reaches a suitable integer value, turn the stopcock (see ) so that the filter assembly is connected to the vacuum source, causing the specimen to be drawn through the wire mesh into the pipet; simultaneously start the stopwatch When the specimen reaches the mark on the pipet, stop the stopwatch and turn the stopcock to its initial position to vent the pipet and so allow the specimen to return to the test jar If the time taken to reach the mark exceeds 60 s on the first filtration, abandon the test and repeat it on a fresh portion, starting at a higher temperature Repeat the operations (see to ) for each 1 C decrease of the specimen temperature until the temperature is reached at which the pipet is not filled to the 20 ml mark within 60 s. Record the temperature at which this last filtration was commenced as CFPP (see Section 13). NOTE 8 A small minority of samples may exhibit anomalous aspiration behavior, which can be detected by examining the observed aspiration times. This behavior is marked by an unexpected reduction in the time taken to fill the pipet, after which aspiration time again continues to increase progressively, until the failure limit of 60 s is reached If the filter has not plugged when the temperature of the specimen reaches 20 C, continue the test by using a second cooling bath maintained at C, quickly transferring the test jar and filtration assembly to a new jacket placed on the second cooling bath. Alternatively, for single bath apparatus, adjust the refrigeration unit to C. The new temperature must be reached within 2 min 30 s of the adjustment. Repeat the operations to to each 1 C decrease of the specimen temperature If the filter has not plugged when the temperature of the specimen reaches 35 C, continue the test by using a third cooling bath maintained at C by quickly transferring the test jar and filtration assembly to a new jacket placed on the second cooling bath. Alternatively, for single bath apparatus, adjust the refrigeration unit to C. The new temperature must be reached within 2 min 30 s of the adjustment. Repeat the operations to at each 1 C decrease of the specimen temperature If the filter has not plugged when the temperature of the specimen reaches 51 C, discontinue the test (see Section 13) If, after cooling in accordance with , , and , the specimen fills the pipet to the mark in less than 60 s, but does not flow back completely into the test jar when the pipet is vented to atmosphere through the stopcock (see ) before the start of the next aspiration, record the temperature at the commencement of the filtration as the CFPP (see Section 13) Automated Apparatus: Check that the cooling bath is operating and has reached the temperature required as specified in the manufacturer s instructions Pour the filtered specimen (see Section 9) into the clean and dry test jar to the 45 ml mark Close the test jar with the stopper (see 6.1.7) carrying the pipet with filter unit (see 6.1.8) and the platinum resistance thermometer. Adjust the apparatus in such a way that the bottom of the filter unit (see (e)) rests on the bottom of the test jar, and position the thermometer so that its lower end is mm above the bottom of the test jar. Take care to ensure that no part of the thermometer is in contact with the side of the test jar or the filter body. NOTE 9 The precise positioning of the thermometer in the test jar is a critical parameter of this test method. The position of the lower end of the thermometer above the bottom of the test jar can be indirectly measured by marking the stem of the thermometer flush with the stopper (see 6.1.7) when the lower end of the thermometer is just touching the bottom of the test jar, and then pulling the thermometer up such that the reference line is mm above the top of the stopper If necessary, reconnect the pipet to the vacuum system. Switch on the vacuum source and regulate to ensure an air flow rate of 15 L/h in the vacuum regulator. Check that the U-tube manometer (if used) indicates a mm depression ( kpa) or that the electronic vacuum regulator indicates a pressure of kpa Press the start button immediately after insertion of the test jar assembly. If the cloud point is known, aspiration of the specimen through the filter may be set to start when it has cooled to a temperature not less than 5 C above the cloud point. The apparatus will carry out the test procedure filtering the specimen at each 1 C decrease if temperature and measuring the filtering time. If the time to reach the 20 ml mark exceeds 60 s on the first filtration, the test is to be abandoned and repeated on a fresh specimen starting at a higher temperature. The apparatus will record the first temperature at which 6
7 the specimen fails to reach the 20 ml mark in less than 60 s or fails to flow back into the test jar when the vacuum is cut off as CFPP (see Section 13). The test will be discontinued if the specimen reaches 51 C without plugging (see Section 13). During the procedure, the apparatus will automatically change the cooling bath temperature as indicated below. Bath Temperature Start of test C When (if) specimen reaches 20 C C When (if) specimen reaches 35 C C NOTE 10 A small minority of samples may exhibit anomalous aspiration behavior, which can be detected by examining the aspiration times recorded in the test printout for signs of an unexpected reduction in the time taken to fill the pipet, after which aspiration time again continues to increase progressively until the failure limit of 60 s is reached If the automated CFPP apparatus used does not incorporate a lower light sensor, it shall only be used if the test sequence is observed as in the manual procedure (see ), so that any fuels not flowing back into the test jar as described are detected and reported accordingly. 13. Report 13.1 Report the temperature read or indicated at the beginning of the last filtration to the nearest 1 C (see , , and ) as the CFPP If the specimen has reached 51 C without plugging (see and ) report as Not plugged at 51 C The report shall contain at least the following information: The type and identification of the product under test; A reference to this test method; The sampling procedure used (see Section 8); The result of the test (13.1 or 13.2); Any deviation from the procedure described (see Note 8 and Note 10); and the date of the test. 14. Precision and Bias 14.1 The precision of this procedure as determined by the statistical examination of the interlaboratory test results is as follows: 14.2 Repeatability The difference between results obtained on the same day by the same operator with the same apparatus under constant operating conditions on identical test material, would in the long run, with normal and correct operation of the test method, exceed 1.76 C only in one case in twenty Reproducibility The difference between two single and independent results obtained by different operators working in different laboratories on identical test material, would in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of the test method, exceed the values indicated by the formula: (25 X) C where: X is the average of the two results being compared, only in one case in twenty. NOTE 11 The interlaboratory test program used to determine the precision of this test method was carried out in 1988 by the IP. The program involved 46 laboratories and 5 samples, ranging in CFPP values from 0 C to 33 C. Extrapolations to measurements more than a few degrees outside this range are unsupported by the data. The raw data from the 1988 program was re-analyzed in 1997 using the ASTM D2PP program. The report of the re-evaluation is available from ASTM Headquarters RR:D Bias The procedure in this test method has no bias because the value of CFPP can be defined only in terms of a test method Relative Bias The current interlaboratory tests confirm that there is no relative bias between the manual and automated apparatuses. Both apparatuses are suitable for reference purposes. 15. Keywords 15.1 automated cold filter plugging point; cold filter plugging point (CFPP); diesel; domestic heating fuels; filterability; manual cold filter plugging point ASTM International takes no position respecting the validity of any patent rights asserted in connection with any item mentioned in this standard. Users of this standard are expressly advised that determination of the validity of any such patent rights, and the risk of infringement of such rights, are entirely their own responsibility. This standard is subject to revision at any time by the responsible technical committee and must be reviewed every five years and if not revised, either reapproved or withdrawn. Your comments are invited either for revision of this standard or for additional standards and should be addressed to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend. If you feel that your comments have not received a fair hearing you should make your views known to the ASTM Committee on Standards, at the address shown below. This standard is copyrighted by ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA , United States. Individual reprints (single or multiple copies) of this standard may be obtained by contacting ASTM at the above address or at (phone), (fax), or service@astm.org ( ); or through the ASTM website ( 7
Standard Test Method for Pour Point of Petroleum Products (Automatic Air Pressure Method) 1
 Designation: D 6749 02 An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Pour Point of Petroleum Products (Automatic Air Pressure Method) 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6749;
Designation: D 6749 02 An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Pour Point of Petroleum Products (Automatic Air Pressure Method) 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6749;
Standard Test Method for Freezing Point of Aviation Fuels (Automated Optical Method) 1
 This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because it may not be technically
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because it may not be technically
Standard Test Method for Dropping Point of Lubricating Grease 1
 Designation: D 566 02 An American National Standard British Standard 2877 Designation: 132/96 Standard Test Method for Dropping Point of Lubricating Grease 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation
Designation: D 566 02 An American National Standard British Standard 2877 Designation: 132/96 Standard Test Method for Dropping Point of Lubricating Grease 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation
Standard Specification for ASTM Hydrometers 1
 Designation: E 100 03 Standard Specification for ASTM s 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 100; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original adoption
Designation: E 100 03 Standard Specification for ASTM s 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 100; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original adoption
Standard Test Methods for Determining the Compatibility of Resin/Solvent Mixtures by Precipitation Temperature (Cloud Point) 1
 Designation: D 6038 05 Standard Test Methods for Determining the Compatibility of Resin/Solvent Mixtures by Precipitation Temperature (Cloud Point) 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation
Designation: D 6038 05 Standard Test Methods for Determining the Compatibility of Resin/Solvent Mixtures by Precipitation Temperature (Cloud Point) 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation
Standard Test Method for Distillation of Industrial Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Materials 1
 Designation: D 850 02 e1 Standard Test Method for Distillation of Industrial Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Materials 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 850; the number immediately
Designation: D 850 02 e1 Standard Test Method for Distillation of Industrial Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Materials 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 850; the number immediately
Standard Test Method for Determination of Vapor Pressure of Crude Oil: VPCR x (Expansion Method) 1
 Designation: D6377 14 Standard Test Method for Determination of Vapor Pressure of Crude Oil: VPCR x (Expansion Method) 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6377; the number immediately
Designation: D6377 14 Standard Test Method for Determination of Vapor Pressure of Crude Oil: VPCR x (Expansion Method) 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6377; the number immediately
Standard Test Methods for Rubber Property Adhesion to Flexible Substrate 1
 Designation: D 413 98 (Reapproved 2002) e1 Standard Test Methods for Rubber Property Adhesion to Flexible Substrate 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 413; the number immediately following
Designation: D 413 98 (Reapproved 2002) e1 Standard Test Methods for Rubber Property Adhesion to Flexible Substrate 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 413; the number immediately following
Standard Test Method for Water and Sediment in Fuel Oils by the Centrifuge Method (Laboratory Procedure) 1
 Designation: D1796 11 Designation: Manual of Petroleum Measurement Standards (MPMS), Chapter 10.6 Standard Test Method for Water and Sediment in Fuel Oils by the Centrifuge Method (Laboratory Procedure)
Designation: D1796 11 Designation: Manual of Petroleum Measurement Standards (MPMS), Chapter 10.6 Standard Test Method for Water and Sediment in Fuel Oils by the Centrifuge Method (Laboratory Procedure)
Standard Specification for Threaded Couplings, Steel, Black or Zinc-Coated (Galvanized) Welded or Seamless, for Use in Steel Pipe Joints 1
 Designation: A 865 97 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS 00 Barr Harbor Dr., est Conshohocken, PA 9428 Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM Standard Specification for
Designation: A 865 97 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS 00 Barr Harbor Dr., est Conshohocken, PA 9428 Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM Standard Specification for
Standard Test Method for Flash Point by Modified Continuously Closed Cup (MCCCFP) Tester 1
 Designation: D7094 12 1 Standard Test Method for Flash Point by Modified Continuously Closed Cup (MCCCFP) Tester 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7094; the number immediately following
Designation: D7094 12 1 Standard Test Method for Flash Point by Modified Continuously Closed Cup (MCCCFP) Tester 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7094; the number immediately following
Standard Classification System for Carbon Blacks Used in Rubber Products 1
 Designation: D 1765 04 Standard Classification System for Carbon Blacks Used in Rubber Products 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 1765; the number immediately following the designation
Designation: D 1765 04 Standard Classification System for Carbon Blacks Used in Rubber Products 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 1765; the number immediately following the designation
Standard Test Method for Carbon Black Oil Absorption Number (OAN) 1
 Designation: D 2414 04 Standard Test Method for Carbon Black Oil Absorption Number (OAN) 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2414; the number immediately following the designation indicates
Designation: D 2414 04 Standard Test Method for Carbon Black Oil Absorption Number (OAN) 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2414; the number immediately following the designation indicates
Standard Specification for Bearing, Roller, Tapered, Single Row of Rollers (Metric Series) 1
 Designation: Standard Specification for Bearing, Roller, Tapered, Single Row of Rollers (Metric Series) 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2591; the number iediately following the designation
Designation: Standard Specification for Bearing, Roller, Tapered, Single Row of Rollers (Metric Series) 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2591; the number iediately following the designation
Standard Test Method for Measuring Wear Properties of Fluid Lubricants (Falex Pin and Vee Block Method) 1
 Designation: 95 (Reapproved 1999) An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Measuring Wear Properties of Fluid Lubricants (Falex Pin and Vee Block Method) 1 This standard is issued under the
Designation: 95 (Reapproved 1999) An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Measuring Wear Properties of Fluid Lubricants (Falex Pin and Vee Block Method) 1 This standard is issued under the
Standard Practice for Conversion of Kinematic Viscosity to Saybolt Universal Viscosity or to Saybolt Furol Viscosity 1
 Designation: D 2161 05 An American National Standard Standard Practice for Conversion of Kinematic Viscosity to Saybolt Viscosity or to Saybolt Furol Viscosity 1 This standard is issued under the fixed
Designation: D 2161 05 An American National Standard Standard Practice for Conversion of Kinematic Viscosity to Saybolt Viscosity or to Saybolt Furol Viscosity 1 This standard is issued under the fixed
Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Leather (Rotary Platform, Abraser Method) 1
 Designation: D7255 14 Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Leather (Rotary Platform, Abraser Method) 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7255; the number immediately following
Designation: D7255 14 Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Leather (Rotary Platform, Abraser Method) 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7255; the number immediately following
Standard Test Methods for Flash-Point by Pensky-Martens Closed Cup Tester 1
 Designation: D 93 99c An American National Standard Designation: D 34/99 Standard Test Methods for Flash-Point by Pensky-Martens Closed Cup Tester 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation
Designation: D 93 99c An American National Standard Designation: D 34/99 Standard Test Methods for Flash-Point by Pensky-Martens Closed Cup Tester 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation
Standard Test Method for Flash Point by Tag Closed Cup Tester 1
 Designation: D 56 05 An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Flash Point by Tag Closed Cup Tester 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 56; the number immediately following
Designation: D 56 05 An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Flash Point by Tag Closed Cup Tester 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 56; the number immediately following
Callisto 100. Cold Filter Plugging Point Tester
 Callisto 100 Cold Filter Plugging Point Tester Cold Filter Plugging Point The Cold Filter Plugging Point (CFPP) method is used to determine the low-temperature operability of diesel fuel, biodiesel, blends
Callisto 100 Cold Filter Plugging Point Tester Cold Filter Plugging Point The Cold Filter Plugging Point (CFPP) method is used to determine the low-temperature operability of diesel fuel, biodiesel, blends
Standard Test Methods for Mechanical-Shock Fragility of Products, Using Shock Machines 1
 Designation: D 3332 99 Standard Test Methods for Mechanical-Shock Fragility of Products, Using Shock Machines 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3332; the number immediately following
Designation: D 3332 99 Standard Test Methods for Mechanical-Shock Fragility of Products, Using Shock Machines 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3332; the number immediately following
Standard Test Methods for Flash Point by Pensky-Martens Closed Cup Tester 1
 Designation: D93 12 Designation: 34/99 Standard Test Methods for Flash Point by Pensky-Martens Closed Cup Tester 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D93; the number immediately following
Designation: D93 12 Designation: 34/99 Standard Test Methods for Flash Point by Pensky-Martens Closed Cup Tester 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D93; the number immediately following
Standard Specification and Test Method for Rear-Mounted Bicycle Child Carriers 1
 Designation: F 1625 00 An American National Standard Standard Specification and Test Method for Rear-Mounted Bicycle Child Carriers 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1625; the number
Designation: F 1625 00 An American National Standard Standard Specification and Test Method for Rear-Mounted Bicycle Child Carriers 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1625; the number
Standard Test Method for Measuring Viscosity at High Shear Rate and High Temperature by Tapered Bearing Simulator 1
 Designation: D 4683 04 An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Measuring Viscosity at High Shear Rate and High Temperature by Tapered Bearing Simulator 1 This standard is issued under the
Designation: D 4683 04 An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Measuring Viscosity at High Shear Rate and High Temperature by Tapered Bearing Simulator 1 This standard is issued under the
Standard Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products at Atmospheric Pressure 1
 Designation: D 86 03 An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products at Atmospheric Pressure 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 86; the number
Designation: D 86 03 An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products at Atmospheric Pressure 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 86; the number
Standard Specification for ASTM Thermometers 1
 Contact International (www.astm.org) for the latest information. Designation: Method 9501 Federal Test Method Standard No. 791b Standard Specification for Thermometers 1 This standard is issued under the
Contact International (www.astm.org) for the latest information. Designation: Method 9501 Federal Test Method Standard No. 791b Standard Specification for Thermometers 1 This standard is issued under the
Standard Test Method for Measurement of Extreme-Pressure Properties of Lubricating Fluids (Four-Ball Method) 1
 Designation: D 2783 03 An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Measurement of Extreme-Pressure Properties of Lubricating Fluids (Four-Ball Method) 1 This standard is issued under the fixed
Designation: D 2783 03 An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Measurement of Extreme-Pressure Properties of Lubricating Fluids (Four-Ball Method) 1 This standard is issued under the fixed
ISO 3679 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Determination of flash point Rapid equilibrium closed cup method
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 3679 Third edition 2004-04-01 Determination of flash point Rapid equilibrium closed cup method Détermination du point d'éclair Méthode rapide à l'équilibre en vase clos Reference
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 3679 Third edition 2004-04-01 Determination of flash point Rapid equilibrium closed cup method Détermination du point d'éclair Méthode rapide à l'équilibre en vase clos Reference
FINAL DRAFT UGANDA STANDARD
 FINAL DRAFT UGANDA STANDARD FDUS 1727 First Edition 2017-mm-dd Standard Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Products by Thermohydrometer Method
FINAL DRAFT UGANDA STANDARD FDUS 1727 First Edition 2017-mm-dd Standard Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Products by Thermohydrometer Method
Standard Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types in Liquid Petroleum Products by Fluorescent Indicator Adsorption 1
 Designation: D 1319 98 An American National Standard Designation: 156/97 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS 100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428 Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM
Designation: D 1319 98 An American National Standard Designation: 156/97 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS 100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428 Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM
Standard Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity) 1
 Designation: D 445 06 An American National Standard British Standard 2000: Part 71:1990 Designation: 71/1/97 Standard Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation
Designation: D 445 06 An American National Standard British Standard 2000: Part 71:1990 Designation: 71/1/97 Standard Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation
Standard Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products and Liquid Fuels at Atmospheric Pressure 1
 Designation: D86 15 Standard Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products and Liquid Fuels at Atmospheric Pressure 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D86; the number immediately
Designation: D86 15 Standard Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products and Liquid Fuels at Atmospheric Pressure 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D86; the number immediately
FINAL DRAFT UGANDA STANDARD
 FDUS 1696 FINAL DAFT UGANDA STANDAD First Edition 2017-mm-dd D AF T FO PU BL IC EV IE W Standard Test Method for Pour Point of Crude Oils eference number FDUS 1696: 2017 This Final Draft Uganda Standard,
FDUS 1696 FINAL DAFT UGANDA STANDAD First Edition 2017-mm-dd D AF T FO PU BL IC EV IE W Standard Test Method for Pour Point of Crude Oils eference number FDUS 1696: 2017 This Final Draft Uganda Standard,
Environmental Protection Agency
 Environmental Protection Agency Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products This method is written for the Environmental Protection Agency, National Vehicle and Fuel Emissions Laboratory (NVFEL) internal
Environmental Protection Agency Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products This method is written for the Environmental Protection Agency, National Vehicle and Fuel Emissions Laboratory (NVFEL) internal
Standard Test Method for Distillation Range of Volatile Organic Liquids 1
 Designation: D 1078 03 Designation: 195/98 Standard Test Method for Distillation Range of Volatile Organic Liquids 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 1078; the number immediately following
Designation: D 1078 03 Designation: 195/98 Standard Test Method for Distillation Range of Volatile Organic Liquids 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 1078; the number immediately following
Metallic materials Rockwell hardness test. Part 2: Verification and calibration of testing machines and indenters
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 6508-2 Third edition 2015-03-01 Metallic materials Rockwell hardness test Part 2: Verification and calibration of testing machines and indenters
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 6508-2 Third edition 2015-03-01 Metallic materials Rockwell hardness test Part 2: Verification and calibration of testing machines and indenters
ISO 3405 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Petroleum products Determination of distillation characteristics at atmospheric pressure
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 3405 Fourth edition 2011-01-15 Petroleum products Determination of distillation characteristics at atmospheric pressure Produits pétroliers Détermination des caractéristiques
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 3405 Fourth edition 2011-01-15 Petroleum products Determination of distillation characteristics at atmospheric pressure Produits pétroliers Détermination des caractéristiques
CLASSIFICATION NOTES. Type Testing Procedure for. Crankcase Explosion Relief Valves
 CLASSIFICATION NOTES Type Testing Procedure for Crankcase Explosion Relief Valves Contents 1. Scope, Application 2. Recognized Standards 3. Purpose 4. Test Facilities 5. Explosion Test Process 6. Testing
CLASSIFICATION NOTES Type Testing Procedure for Crankcase Explosion Relief Valves Contents 1. Scope, Application 2. Recognized Standards 3. Purpose 4. Test Facilities 5. Explosion Test Process 6. Testing
ISBN SANS 342:2006 Edition 4 SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL STANDARD Automotive diesel fuel Published by Standards South Africa 1 dr lategan roa
 ISBN 0-626-18752-4 SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL STANDARD Automotive diesel fuel Published by Standards South Africa 1 dr lategan road groenkloof private bag x191 pretoria 0001 tel: 012 428 7911 fax: 012 344
ISBN 0-626-18752-4 SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL STANDARD Automotive diesel fuel Published by Standards South Africa 1 dr lategan road groenkloof private bag x191 pretoria 0001 tel: 012 428 7911 fax: 012 344
Standard Test Method for Sulfur in Liquefied Petroleum Gases (Oxy-Hydrogen Burner or Lamp) 1
 Designation: D 2784 98 (Reapproved 2003) e1 An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Sulfur in Liquefied Petroleum Gases (Oxy-Hydrogen Burner or Lamp) 1 This standard is issued under the
Designation: D 2784 98 (Reapproved 2003) e1 An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Sulfur in Liquefied Petroleum Gases (Oxy-Hydrogen Burner or Lamp) 1 This standard is issued under the
Last date for sending comments : 30 November 2011
 For comments only Draft Indian Standard AUTOMOTIVE VEHICLES METHODS OF MEASUREMENT OF BRAKING COEFFICIENT OF ROAD SURFACES Part 2 Pendulum Method Not to be reproduced or used as a standard without the
For comments only Draft Indian Standard AUTOMOTIVE VEHICLES METHODS OF MEASUREMENT OF BRAKING COEFFICIENT OF ROAD SURFACES Part 2 Pendulum Method Not to be reproduced or used as a standard without the
Standard Practice for Rubber Materials, Equipment, and Procedures for Mixing Standard Compounds and Preparing Standard Vulcanized Sheets 1
 Designation: D 3182 07 Standard Practice for Rubber Materials, Equipment, and Procedures for Mixing Standard Compounds and Preparing Standard Vulcanized Sheets 1 This standard is issued under the fixed
Designation: D 3182 07 Standard Practice for Rubber Materials, Equipment, and Procedures for Mixing Standard Compounds and Preparing Standard Vulcanized Sheets 1 This standard is issued under the fixed
IEA SHC Task 27: Accelerated Aging of IG units: North American Test Methods
 IEA SHC Task 27: Accelerated Aging of IG units: North American Test Methods Hakim Elmahdy, Ph. D., MBA, P. Eng. Institute for Research in Construction National Research Council of Canada Introduction There
IEA SHC Task 27: Accelerated Aging of IG units: North American Test Methods Hakim Elmahdy, Ph. D., MBA, P. Eng. Institute for Research in Construction National Research Council of Canada Introduction There
BQ-9000 Quality Management System Testing Laboratory Requirements
 Quality Management System Testing Laboratory Requirements Revision 0 Effective Date: March 1, 2009 2009 National Biodiesel Board This requirements document has been prepared by the National Biodiesel Accreditation
Quality Management System Testing Laboratory Requirements Revision 0 Effective Date: March 1, 2009 2009 National Biodiesel Board This requirements document has been prepared by the National Biodiesel Accreditation
CFPP Process Analyzer
 Norms and standards CFPP ASTM D 6371 DIN EN 116 IP 309 Application The BARTEC BENKE CFPP (CFPP-4) is suited to analyze the standardized value of Cold Filter Plugging Point (CFPP) in a process stream online
Norms and standards CFPP ASTM D 6371 DIN EN 116 IP 309 Application The BARTEC BENKE CFPP (CFPP-4) is suited to analyze the standardized value of Cold Filter Plugging Point (CFPP) in a process stream online
Temperature Life with or without Electrical Load Test Procedure for Electrical Connectors and Sockets
 ANSI/EIA-364-17B-1999 Approved: April 23, 1999 EIA STANDARD EIA-364-17B TP-17B Temperature Life with or without Electrical Load Test Procedure for Electrical Connectors and Sockets EIA-364-17B (Revision
ANSI/EIA-364-17B-1999 Approved: April 23, 1999 EIA STANDARD EIA-364-17B TP-17B Temperature Life with or without Electrical Load Test Procedure for Electrical Connectors and Sockets EIA-364-17B (Revision
Standard Specification for Tensile Testing Machines for Textiles 1
 Designation: D 76 99 Standard Specification for Tensile Testing Machines for Textiles 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 76; the number immediately following the designation indicates
Designation: D 76 99 Standard Specification for Tensile Testing Machines for Textiles 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 76; the number immediately following the designation indicates
Determination of flash point Pensky-Martens closed cup method
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 2719 Fourth edition 2016-06-15 Determination of flash point Pensky-Martens closed cup method Détermination du point d éclair Méthode Pensky-Martens
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 2719 Fourth edition 2016-06-15 Determination of flash point Pensky-Martens closed cup method Détermination du point d éclair Méthode Pensky-Martens
Standard Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Gasoline Automotive Engine Oils by Thin-Film Oxygen Uptake (TFOUT) 1
 Designation: D 4742 02a An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Gasoline Automotive Engine Oils by Thin-Film Oxygen Uptake (TFOUT) 1 This standard is issued under
Designation: D 4742 02a An American National Standard Standard Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Gasoline Automotive Engine Oils by Thin-Film Oxygen Uptake (TFOUT) 1 This standard is issued under
Cold Vapor Mercury Apparatus* Purpose Figure 1 Cold Vapor Mercury Apparatus Assembly Overview
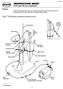 26744-88 Cold Vapor Mercury Apparatus* Purpose This instruction sheet shows how to assemble the apparatus set (26744-00) necessary for performing the Hach Cold Vapor Mercury Method (method 10065). Figure
26744-88 Cold Vapor Mercury Apparatus* Purpose This instruction sheet shows how to assemble the apparatus set (26744-00) necessary for performing the Hach Cold Vapor Mercury Method (method 10065). Figure
Tex-614-J, Testing Epoxy Materials
 Overview Effective: August 1999 May 2000. This method covers various test procedures for epoxy materials specified under the TxDOT Material Specification DMS-6100, Epoxies and Adhesives. The test to be
Overview Effective: August 1999 May 2000. This method covers various test procedures for epoxy materials specified under the TxDOT Material Specification DMS-6100, Epoxies and Adhesives. The test to be
RESOLUTION MEPC.205(62) Adopted on 15 July GUIDELINES AND SPECIFICATIONS FOR ADD-ON EQUIPMENT FOR UPGRADING RESOLUTION
 MEPC.60(33)-COMPLIANT OIL FILTERING EQUIPMENT MEPC.60(33)-COMPLIANT OIL FILTERING EQUIPMENT MEPC 62/24/Add.1 Annex 24, page 1 ANNEX 24 RESOLUTION MEPC.205(62) 2011 GUIDELINES AND SPECIFICATIONS FOR ADD-ON
MEPC.60(33)-COMPLIANT OIL FILTERING EQUIPMENT MEPC.60(33)-COMPLIANT OIL FILTERING EQUIPMENT MEPC 62/24/Add.1 Annex 24, page 1 ANNEX 24 RESOLUTION MEPC.205(62) 2011 GUIDELINES AND SPECIFICATIONS FOR ADD-ON
Operation Manual BOTTLE TOP DISPENSER
 Operation Manual BOTTLE TOP DISPENSER TABLE OF CONTENTS Page No. Intended Use Of The Instrument 1 Safety Instructions 1 Functions and Limitations of Use 2 Operating Exclusions 3 Storage Conditions 3 Chemical
Operation Manual BOTTLE TOP DISPENSER TABLE OF CONTENTS Page No. Intended Use Of The Instrument 1 Safety Instructions 1 Functions and Limitations of Use 2 Operating Exclusions 3 Storage Conditions 3 Chemical
BQ-9000 Quality Management System. Accredited Producer Requirements
 BQ-9000 Quality Management System Accredited Producer Requirements Revision 4 Effective Date: February 1, 2007 This requirements document has been prepared by the National Biodiesel Accreditation Commission,
BQ-9000 Quality Management System Accredited Producer Requirements Revision 4 Effective Date: February 1, 2007 This requirements document has been prepared by the National Biodiesel Accreditation Commission,
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 18752 First edition 2006-07-15 Rubber hoses and hose assemblies Wire- or textile-reinforced single-pressure types for hydraulic applications Specification Tuyaux et flexibles
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 18752 First edition 2006-07-15 Rubber hoses and hose assemblies Wire- or textile-reinforced single-pressure types for hydraulic applications Specification Tuyaux et flexibles
ISO 8710 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Motorcycles Brakes and brake systems Tests and measurement methods
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 8710 Second edition 2010-04-15 Motorcycles Brakes and brake Tests and measurement methods Motocyles Freins et systèmes de freinage Méthodes d'essai et de mesure Reference number
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 8710 Second edition 2010-04-15 Motorcycles Brakes and brake Tests and measurement methods Motocyles Freins et systèmes de freinage Méthodes d'essai et de mesure Reference number
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 10100 Second edition 2001-08-01 Hydraulic fluid power Cylinders Acceptance tests Transmissions hydrauliques Vérins Essais de réception Reference number ISO 10100:2001(E) ISO
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 10100 Second edition 2001-08-01 Hydraulic fluid power Cylinders Acceptance tests Transmissions hydrauliques Vérins Essais de réception Reference number ISO 10100:2001(E) ISO
2 ADAPTERS. Bushing / Connecting. Glass Bushing Adapters. Straight Connecting Adapters. PTFE Bushing Adapters. Offset Connecting Adapters
 ADAPTERS Whether converting joint types, reducing or enlarging joints, or creating connections in a distillation apparatus, Kimble offers a comprehensive selection of adapters including bushing adapters,
ADAPTERS Whether converting joint types, reducing or enlarging joints, or creating connections in a distillation apparatus, Kimble offers a comprehensive selection of adapters including bushing adapters,
Instruments for the Analysis of Petroleum Products. Oxidation Stability
 Instruments for the Analysis of Petroleum Products Oxidation Stability What is Oxidation Stability? Oxidation stability describes the resistance of a material towards oxygen. This is a basic requirement
Instruments for the Analysis of Petroleum Products Oxidation Stability What is Oxidation Stability? Oxidation stability describes the resistance of a material towards oxygen. This is a basic requirement
*** DRAFT *** Lubricant Service Designations for Automotive Manual Transmissions, Manual Transaxles, and Axles
 *** DRAFT *** Lubricant Service Designations for Automotive Manual Transmissions, Manual Transaxles, and Axles API PUBLICATION 1560 EIGHTH EDITION, 2011 American Petroleum Institute 1220 L Street, Northwest
*** DRAFT *** Lubricant Service Designations for Automotive Manual Transmissions, Manual Transaxles, and Axles API PUBLICATION 1560 EIGHTH EDITION, 2011 American Petroleum Institute 1220 L Street, Northwest
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Pneumatic fluid power Cylinders Final examination and acceptance criteria
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 10099 Second edition 2001-05-01 Pneumatic fluid power Cylinders Final examination and acceptance criteria Transmissions pneumatiques Vérins Critères de réception et de vérification
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 10099 Second edition 2001-05-01 Pneumatic fluid power Cylinders Final examination and acceptance criteria Transmissions pneumatiques Vérins Critères de réception et de vérification
A SURVEY OF OUR KNOW-HOW : PETROLEUM GLASSWARE VISCOMETER TUBES
 N O R M A L A B A N A L I S A SURVEY OF OUR KNOW-HOW : PETROLEUM GLASSWARE VISCOMETER TUBES NORMALAB ANALIS FRANCE S.A. 14, rue des Lilas 76210 LINTOT - FRANCE Tel : (33) 02 35 38 59 59 Fax : (33) 02 35
N O R M A L A B A N A L I S A SURVEY OF OUR KNOW-HOW : PETROLEUM GLASSWARE VISCOMETER TUBES NORMALAB ANALIS FRANCE S.A. 14, rue des Lilas 76210 LINTOT - FRANCE Tel : (33) 02 35 38 59 59 Fax : (33) 02 35
ISO 659 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Oilseeds Determination of oil content (Reference method)
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 659 Fourth edition 2009-07-01 Oilseeds Determination of oil content (Reference method) Graines oléagineuses Détermination de la teneur en huile
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 659 Fourth edition 2009-07-01 Oilseeds Determination of oil content (Reference method) Graines oléagineuses Détermination de la teneur en huile
Lorri Grainawi Steel Tank Institute. PA NISTM April 25, 2013 Harrisburg, PA
 Lorri Grainawi Steel Tank Institute PA NISTM April 25, 2013 Harrisburg, PA PEI/RP1200-12 ------------------------------------------------------ 1. Introduction 2. Definitions 3. Safety 4. Tank Secondary
Lorri Grainawi Steel Tank Institute PA NISTM April 25, 2013 Harrisburg, PA PEI/RP1200-12 ------------------------------------------------------ 1. Introduction 2. Definitions 3. Safety 4. Tank Secondary
FEDERAL SPECIFICATION ETHER, PETROLEUM; TECHNICAL GRADE. 1.1 Scope. This specification covers technical grade petroleum ether to be used as a solvent.
 METRIC 4 May 2015 SUPERSEDING O-E-751C 10 January 2003 FEDERAL SPECIFICATION ETHER, PETROLEUM; TECHNICAL GRADE The General Services Administration has authorized the use of this federal specification by
METRIC 4 May 2015 SUPERSEDING O-E-751C 10 January 2003 FEDERAL SPECIFICATION ETHER, PETROLEUM; TECHNICAL GRADE The General Services Administration has authorized the use of this federal specification by
THERMOELECTRIC SAMPLE CONDITIONER SYSTEM (TESC)
 THERMOELECTRIC SAMPLE CONDITIONER SYSTEM (TESC) FULLY AUTOMATED ASTM D2983 CONDITIONING AND TESTING ON THE CANNON TESC SYSTEM WHITE PAPER A critical performance parameter for transmission, gear, and hydraulic
THERMOELECTRIC SAMPLE CONDITIONER SYSTEM (TESC) FULLY AUTOMATED ASTM D2983 CONDITIONING AND TESTING ON THE CANNON TESC SYSTEM WHITE PAPER A critical performance parameter for transmission, gear, and hydraulic
ADU 5. Automatic Distillation Unit
 ADU 5 Automatic Distillation Unit Atmospheric Distillation Distillation tests are used to characterize the volatility of petrochemical products. These volatility characteristics are a critical measurement
ADU 5 Automatic Distillation Unit Atmospheric Distillation Distillation tests are used to characterize the volatility of petrochemical products. These volatility characteristics are a critical measurement
M-11 MARINE DIESEL ENGINE FUEL INJECTOR
 Guideline No.M-11(201510) M-11 MARINE DIESEL ENGINE FUEL INJECTOR Issued date: 20 October 2015 China Classification Society Foreword This Guideline constitutes the CCS rules, and establishes the applicable
Guideline No.M-11(201510) M-11 MARINE DIESEL ENGINE FUEL INJECTOR Issued date: 20 October 2015 China Classification Society Foreword This Guideline constitutes the CCS rules, and establishes the applicable
ASTM B117 Testing Quality Control
 ASTM B117 Testing Quality Control ASTM B117 Testing, also known as a Standard Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog), is used to analyze relative corrosion for specimens of metals and coated metals exposed
ASTM B117 Testing Quality Control ASTM B117 Testing, also known as a Standard Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog), is used to analyze relative corrosion for specimens of metals and coated metals exposed
Tex-614-J, Testing Epoxy Materials
 Overview Effective Date: January 2001 - July 2002. This method covers various test procedures for epoxy materials specified under the TxDOT Material Specification "DMS-6100, Epoxies and Adhesives." The
Overview Effective Date: January 2001 - July 2002. This method covers various test procedures for epoxy materials specified under the TxDOT Material Specification "DMS-6100, Epoxies and Adhesives." The
Phase Technology CPA-70Xi Cloud Point Analyzer
 Phase Technology CPA-70Xi Cloud Point Analyzer About Phase Technology Expertise: Design & manufacture of analyzers to test cloud, pour and freeze point Cold Flow is All We Do! Scientific Background: 29
Phase Technology CPA-70Xi Cloud Point Analyzer About Phase Technology Expertise: Design & manufacture of analyzers to test cloud, pour and freeze point Cold Flow is All We Do! Scientific Background: 29
Innovation in cold behavior
 Innovation in cold behavior Cold Filter Plugging Point testing by Orbis BV discover the new way of CFPP testing About AirSTAR CFPP Analyzer Cooling. The ColdBlock integrated cooling unit is friendly to
Innovation in cold behavior Cold Filter Plugging Point testing by Orbis BV discover the new way of CFPP testing About AirSTAR CFPP Analyzer Cooling. The ColdBlock integrated cooling unit is friendly to
Product Loss During Retail Motor Fuel Dispenser Inspection
 Product Loss During Retail Motor Fuel Dispenser Inspection By: Christian Lachance, P. Eng. Senior Engineer - ment Engineering and Laboratory Services ment Canada Date: Product Loss During Retail Motor
Product Loss During Retail Motor Fuel Dispenser Inspection By: Christian Lachance, P. Eng. Senior Engineer - ment Engineering and Laboratory Services ment Canada Date: Product Loss During Retail Motor
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Metallic tube connections for fluid power and general use Part 2: 37 flared connectors
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 8434-2 Second edition 2007-09-01 Metallic tube connections for fluid power and general use Part 2: 37 flared connectors Raccordements de tubes métalliques pour transmissions
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 8434-2 Second edition 2007-09-01 Metallic tube connections for fluid power and general use Part 2: 37 flared connectors Raccordements de tubes métalliques pour transmissions
Digital Copper Corrosion Measurement Vs. Visual Rating _ Incorporating New Technologies To Method Development
 Digital Copper Corrosion Measurement Vs. Visual _ Incorporating New Technologies To Method Development Aaron Mendez Ph.D. and Juan Ayala Ayalytical Instruments Inc. 2787 W Fulton St, Chicago, IL 60612
Digital Copper Corrosion Measurement Vs. Visual _ Incorporating New Technologies To Method Development Aaron Mendez Ph.D. and Juan Ayala Ayalytical Instruments Inc. 2787 W Fulton St, Chicago, IL 60612
ASTM Consensus Standards The Latest in Packaging Testing. Presented by: Dhuanne Dodrill President Rollprint Packaging Products, Inc.
 ASTM Consensus Standards The Latest in Packaging Testing Presented by: Dhuanne Dodrill President Rollprint Packaging Products, Inc. ASTM Overview Established in 1898 Voluntary, Full-Consensus Standards
ASTM Consensus Standards The Latest in Packaging Testing Presented by: Dhuanne Dodrill President Rollprint Packaging Products, Inc. ASTM Overview Established in 1898 Voluntary, Full-Consensus Standards
Why You Need Tank and Fuel Quality Management Service Programs?
 Why You Need Tank and Fuel Quality Management Service Programs? Dr. Ron F. Sickels PhD (The Fuel Doctor) Mechanical, Chemical and Environmental Engineering Clean Tanks and Fuel Mean Reliable and Efficient
Why You Need Tank and Fuel Quality Management Service Programs? Dr. Ron F. Sickels PhD (The Fuel Doctor) Mechanical, Chemical and Environmental Engineering Clean Tanks and Fuel Mean Reliable and Efficient
Guideline No.M-10(201510) M-10 Marine Diesel Engine Fuel Injection Pump
 Guideline No.M-10(201510) M-10 Marine Diesel Engine Fuel Injection Pump Issued date: 20 th October, 2015 China Classification Society Foreword This Guideline is a part of CCS Rules, which contains technical
Guideline No.M-10(201510) M-10 Marine Diesel Engine Fuel Injection Pump Issued date: 20 th October, 2015 China Classification Society Foreword This Guideline is a part of CCS Rules, which contains technical
ISO/TC 131/SC Pneumatic fluid power Cylinders, kpa (10 bar) series Mounting dimensions of rod-end clevises
 DRAFT INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/DIS 8140 ISO/TC 131/SC 3 Secretariat: DIN Voting begins on: Voting terminates on: 2017-06-07 2017-08-29 Pneumatic fluid power Cylinders, 1 000 kpa (10 bar) series Mounting
DRAFT INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/DIS 8140 ISO/TC 131/SC 3 Secretariat: DIN Voting begins on: Voting terminates on: 2017-06-07 2017-08-29 Pneumatic fluid power Cylinders, 1 000 kpa (10 bar) series Mounting
INSTITUTE OF PETROLEUM TESTING OF VAPOUR CONTAINMENT ON PETROLEUM ROAD TANKERS
 INSTITUTE OF PETROLEUM TESTING OF VAPOUR CONTAINMENT ON PETROLEUM ROAD TANKERS INSTITUTE OF PETROLEUM TESTING OF VAPOUR CONTAINMENT ON PETROLEUM ROAD TANKERS April 2001 Published by The Institute of Petroleum,
INSTITUTE OF PETROLEUM TESTING OF VAPOUR CONTAINMENT ON PETROLEUM ROAD TANKERS INSTITUTE OF PETROLEUM TESTING OF VAPOUR CONTAINMENT ON PETROLEUM ROAD TANKERS April 2001 Published by The Institute of Petroleum,
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Lubricants, industrial oils and related products (Class L) Family X (Greases) Specification
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 12924 First edition 2010-05-01 Lubricants, industrial oils and related products (Class L) Family X (Greases) Specification Lubrifiants, huiles industrielles et produits connexes
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 12924 First edition 2010-05-01 Lubricants, industrial oils and related products (Class L) Family X (Greases) Specification Lubrifiants, huiles industrielles et produits connexes
STANDARD PNEUMATIC RAM TEST METHOD AND EQUIPMENT USED IN EVALUATING THE PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTECTIVE HEADGEAR AND FACE GUARDS
 STANDARD PNEUMATIC RAM TEST METHOD AND EQUIPMENT USED IN EVALUATING THE PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTECTIVE HEADGEAR AND FACE GUARDS NOCSAE DOC (ND) 081-14m15 Prepared By NATIONAL OPERATING COMMITTEE
STANDARD PNEUMATIC RAM TEST METHOD AND EQUIPMENT USED IN EVALUATING THE PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTECTIVE HEADGEAR AND FACE GUARDS NOCSAE DOC (ND) 081-14m15 Prepared By NATIONAL OPERATING COMMITTEE
Lubricant Service Designations for Automotive Manual Transmissions, Manual Transaxles, and Axles
 Lubricant Service Designations for Automotive Manual Transmissions, Manual Transaxles, and Axles API PUBLICATION 1560 EIGHTH EDITION, 2012 SPECIAL NOTES 1. API PUBLICATIONS NECESSARILY ADDRESS PROBLEMS
Lubricant Service Designations for Automotive Manual Transmissions, Manual Transaxles, and Axles API PUBLICATION 1560 EIGHTH EDITION, 2012 SPECIAL NOTES 1. API PUBLICATIONS NECESSARILY ADDRESS PROBLEMS
Evaluation of Digital Refractometers for Field Determination of FSII Concentration in JP-5 Fuel
 Evaluation of Digital Refractometers for Field Determination of FSII Concentration in JP-5 Fuel NAVAIRSYSCOM REPORT 441/13-011 Prepared By: JOHN KRIZOVENSKY Chemist AIR 4.4.5 NAVAIR Public Release 2013-867
Evaluation of Digital Refractometers for Field Determination of FSII Concentration in JP-5 Fuel NAVAIRSYSCOM REPORT 441/13-011 Prepared By: JOHN KRIZOVENSKY Chemist AIR 4.4.5 NAVAIR Public Release 2013-867
68-253/Issue 1 (DERD 2491) 1 August 1997
 Ministry of Defence Defence Standard 68-25/Issue 1 (DERD 2491) 1 August 1997 FLUIDS, AVIATION, THRUST AUGMENTATION JOINT SERVICE DESIGNATION: AL-28 AND WTA This Defence Standard supersedes DERD 2491 Issue
Ministry of Defence Defence Standard 68-25/Issue 1 (DERD 2491) 1 August 1997 FLUIDS, AVIATION, THRUST AUGMENTATION JOINT SERVICE DESIGNATION: AL-28 AND WTA This Defence Standard supersedes DERD 2491 Issue
SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL STANDARD
 ISBN 0-626-18752-4 SANS 342:2006 SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL STANDARD Automotive diesel fuel Published by Standards South Africa 1 dr lategan road groenkloof private bag x191 pretoria 0001 tel: 012 428 7911
ISBN 0-626-18752-4 SANS 342:2006 SOUTH AFRICAN NATIONAL STANDARD Automotive diesel fuel Published by Standards South Africa 1 dr lategan road groenkloof private bag x191 pretoria 0001 tel: 012 428 7911
Urinuppsamlingspåsar - Del 2: Krav och provningsmetoder (ISO :1996) Urine collection bags - Part 2: Requirements and test methods :1996)
 Urine collection bags - Part 2: Requirements and test methods 8669-2:1996) Urinuppsamlingspåsar - Del 2: Krav och provningsmetoder (ISO 8669-2:1996) The European Standard EN ISO 8669-2:1996 has the status
Urine collection bags - Part 2: Requirements and test methods 8669-2:1996) Urinuppsamlingspåsar - Del 2: Krav och provningsmetoder (ISO 8669-2:1996) The European Standard EN ISO 8669-2:1996 has the status
Technical Procedure for Gas Chromatography (GC-FID)
 Technical Procedure for Gas Chromatography (GC-FID) 1.0 Purpose This technical procedure shall be followed for the operation of the gas chromatograph (GC- FID). 2.0 Scope This procedure applies to all
Technical Procedure for Gas Chromatography (GC-FID) 1.0 Purpose This technical procedure shall be followed for the operation of the gas chromatograph (GC- FID). 2.0 Scope This procedure applies to all
8.1.4 The 175 ml, 250 ml, or 500 ml unit may be used for static filtration testing up to and including 175 C (350 F).
 8 Static Filtration 8.1 Principle 8.1.1 Measurement of the filtration behavior and the filter cake characteristics of an oil-based drilling fluid are fundamental to the treatment and control of a drilling
8 Static Filtration 8.1 Principle 8.1.1 Measurement of the filtration behavior and the filter cake characteristics of an oil-based drilling fluid are fundamental to the treatment and control of a drilling
Draft Indian Standard FUSIBLE PLUG FOR DISSOLVED ACETYLENE GAS CYLINDER SPECIFICATION (first revision of IS 13497) (ICS )
 DRAFT STANDARD IN WIDE CIRCULATION DOCUMENT DESPATCH ADVICE Ref: MED 16 :3/T- 14 Date: 06-01-2015 Gas Cylinders, Sectional Committee, MED 16 TO: a) The interested members of Mechanical Engineering Division
DRAFT STANDARD IN WIDE CIRCULATION DOCUMENT DESPATCH ADVICE Ref: MED 16 :3/T- 14 Date: 06-01-2015 Gas Cylinders, Sectional Committee, MED 16 TO: a) The interested members of Mechanical Engineering Division
Foaming of Lubricating Oils (manual)
 Foaming of Lubricating Oils (manual) ASTM D 892, ASTM D 6082 sequence IV, ISO 6247, DIN 51566, IP 146, JIS K2518, BS 5092 (obs.) Product group(s): User group(s): Scope: Lubricant Testing Automotive, Engine
Foaming of Lubricating Oils (manual) ASTM D 892, ASTM D 6082 sequence IV, ISO 6247, DIN 51566, IP 146, JIS K2518, BS 5092 (obs.) Product group(s): User group(s): Scope: Lubricant Testing Automotive, Engine
JADE Bottle Top Dispenser
 Accrediting Certifying Bodies S C B A (E) ASCB(E) UK ISO 13485 JADE Bottle Top Dispenser Re-Circulation Valve Operation Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS Page No. Intended Use Of The Instrument 1 Safety Instruction
Accrediting Certifying Bodies S C B A (E) ASCB(E) UK ISO 13485 JADE Bottle Top Dispenser Re-Circulation Valve Operation Manual TABLE OF CONTENTS Page No. Intended Use Of The Instrument 1 Safety Instruction
COMMISSION REGULATION (EU)
 30.11.2011 Official Journal of the European Union L 317/17 COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) No 1235/2011 of 29 November 2011 amending Regulation (EC) No 1222/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council
30.11.2011 Official Journal of the European Union L 317/17 COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) No 1235/2011 of 29 November 2011 amending Regulation (EC) No 1222/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council
7 The revised IS 8034:2002 and revised STI be implemented w.e.f. 1 Feb 2005.
 BUREAU OF INDIAN STANDARDS (CENTRAL MARKS DEPARTMENT-III) Our Ref: CMD-III/16:8034 25 Oct 2004 Subject: Implementation of revised IS 8034:2002 Submersible Pump Sets and revised STI (Doc:STI/8034/5 ) IS
BUREAU OF INDIAN STANDARDS (CENTRAL MARKS DEPARTMENT-III) Our Ref: CMD-III/16:8034 25 Oct 2004 Subject: Implementation of revised IS 8034:2002 Submersible Pump Sets and revised STI (Doc:STI/8034/5 ) IS
UPDATING OF THE GLOBALLY HARMONIZED SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION AND LABELLING OF CHEMICALS (GHS) Physical hazards
 UNITED NATIONS Secretariat Distr. GENERAL ST ST/SG/AC.10/C.3/2007/11 12 April 2007 Original: ENGLISH COMMITTEE OF EXPERTS ON THE TRANSPORT OF DANGEROUS GOODS AND ON THE GLOBALLY HARMONIZED SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION
UNITED NATIONS Secretariat Distr. GENERAL ST ST/SG/AC.10/C.3/2007/11 12 April 2007 Original: ENGLISH COMMITTEE OF EXPERTS ON THE TRANSPORT OF DANGEROUS GOODS AND ON THE GLOBALLY HARMONIZED SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION
User Guide. Pall Laboratory Manifold. For laboratory use. Not for use in a manner other than indicated. Introduction. Regulatory References
 www.pall.com/lab User Guide Pall Laboratory Manifold For laboratory use. Not for use in a manner other than indicated. Introduction Application and Intended Use The membrane filtration (MF) technique is
www.pall.com/lab User Guide Pall Laboratory Manifold For laboratory use. Not for use in a manner other than indicated. Introduction Application and Intended Use The membrane filtration (MF) technique is
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 8178-2 Second edition 2008-04-15 Reciprocating internal combustion engines Exhaust emission measurement Part 2: Measurement of gaseous and particulate exhaust emissions under
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 8178-2 Second edition 2008-04-15 Reciprocating internal combustion engines Exhaust emission measurement Part 2: Measurement of gaseous and particulate exhaust emissions under
532: 2006 Bicycle tube valves and valve tubing Specification (third revision) 2414: 2005 Cycle and rickshaw pneumatic tyres (fourth revision)
 For BIS use only Draft Indian Standard CYCLE RUBBER TUBES (MOULDED/JOINTED) SPECIFICATION (fourth revision of IS 2415) Not to be reproduced without the permission Last date for receipt of comments is of
For BIS use only Draft Indian Standard CYCLE RUBBER TUBES (MOULDED/JOINTED) SPECIFICATION (fourth revision of IS 2415) Not to be reproduced without the permission Last date for receipt of comments is of
Bioprocessing Equipment
 ASME BPE-2007 (Revision of ASME BPE-2005) Bioprocessing Equipment A N I N T E R N A T I O N A L S T A N D A R D ASME BPE-2007 (Revision of ASME BPE-2005) Bioprocessing Equipment AN AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD
ASME BPE-2007 (Revision of ASME BPE-2005) Bioprocessing Equipment A N I N T E R N A T I O N A L S T A N D A R D ASME BPE-2007 (Revision of ASME BPE-2005) Bioprocessing Equipment AN AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD
ISO :2015/DAM 1
 DRAFT AMENDMENT ISO 19973-2:2015/DAM 1 ISO/TC 131 Voting begins on: 2018-01-15 Secretariat: ANSI Voting terminates on: 2018-04-09 Pneumatic fluid power Assessment of component reliability by testing Part
DRAFT AMENDMENT ISO 19973-2:2015/DAM 1 ISO/TC 131 Voting begins on: 2018-01-15 Secretariat: ANSI Voting terminates on: 2018-04-09 Pneumatic fluid power Assessment of component reliability by testing Part
