Three 3-Axis Accelerometers on the Inner Liner of a Tyre for Finding the Tyre-Road Contact Friction Indicators
|
|
|
- Liliana Austin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
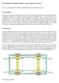
1 12th International Symposium on Advanced Vehicle Control September 22-26, 2014 AVEC Three 3-Axis Accelerometers on the Inner Liner of a Tyre for Finding the Tyre-Road Contact Friction Indicators Arto J. Niskanen, Ari J. Tuononen Aalto University, School of Engineering PO Box Espoo, 00076, FINLAND Phone: (+358) arto.niskanen@aalto.fi Direct tyre-road contact friction estimation is essential for future active safety systems. Friction estimation methods were proposed earlier for driving conditions in the presence of a slip angle or slip ratio. However, the estimation of friction from a freely rolling tyre is still an unsolved topic. This study uses three 3-axis accelerometers on the inner liner of a tyre to detect friction potential indicators on two equally smooth surfaces with different friction levels. The acceleration data before the contact is used to differentiate the two friction levels between the tyre and the road. In addition, the contact lengths from the three accelerometers are used to validate the acceleration data. A method to differentiate the friction levels on the basis of the acceleration signal is also introduced. Topics / Vehicle dynamics: steering, brake, tyre, suspension 1. INTRODUCTION Safe transportation is one of the main goals in vehicle-related research. Current Electronic Stability Control (ESC) and active safety systems such as Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) and Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) are relatively effective and they have increased traffic safety significantly. However, the systems still lack direct tyre-road contact information such as the maximum friction coefficient between the tyre and the road. If the friction could be estimated directly in the contact, the active safety systems could adapt to different friction situations and e.g. optimise the parameters of the brake system and adjust the appropriate safety gap. The lack of direct contact patch information has led to research on tyre sensors. A wide variety of sensors has been used to measure and predict different kinds of phenomena in tyre-road contact. Accelerometers have been found to be robust and they have potential as production tyre sensors in the near future. Since the Tyre Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) is already mandatory in new vehicles, tyre sensors are no longer only research and development tools. Acceleration signals have previously been used to examine the forces [1] and the progress of aquaplaning in the contact [2,3] and to determine the road surface conditions [4 6]. An accelerometer has also been used to study the energy harvesting needs for an intelligent tyre [7]. In the presence of a slip angle or slip ratio, friction estimation methods have been proposed [8,9] as well as a possible regressor for tyre force estimation [10]. However, the estimation of the friction potential from a freely rolling tyre is still an unsolved topic. Most of the time, the tyre is rolling without a considerable slip angle or slip ratio. Knowing the friction in these cases might prevent the need for extreme driving manoeuvres (e.g. late ESC or AEB intervention) to prevent collisions. This would be beneficial for traffic safety and essential for the autonomous cars of the future. In this study the measurements were performed on equally smooth concrete and ice surfaces. The smooth concrete surface was chosen instead of a typical asphalt road in order to eliminate the effect of the surface roughness on the acceleration signals and so that the pure friction phenomena could be researched. 2. RESEARCH METHODS 2.1 Accelerometers The tyre sensors used in this research were 3-axis integrated electronic piezoelectric accelerometers. The measurement range for the acceleration was ±1000 G, which has been proved to cover the possible accelerations at normal driving speeds. The size of the accelerometers was 6.35 x 6.35 x 7.62 mm and their weight was 1.1 gram. The tyre sensors should not affect the properties of the tyre, such as its stiffness and the inertia of the contact patch and the carcass. Such small sensors as those used in the research should not have a significant effect on the behaviour of the tyre. The accelerometers were attached to the inner liner (see Fig. 1) with cyanoacrylate adhesive. The accelerometer coordinate system is shown in Fig. 1. When the accelerometer on the inner liner is on the road surface, the longitudinal direction is the x-axis, the 529
2 lateral direction is the y-axis, and the vertical direction is the z-axis. In the tyre coordinate system, the x-axis measures circumferential, the y-axis lateral, and the z-axis radial acceleration. sensors and a data acquisition box. A sampling rate of 25.6 khz was used, which gives a resolution of ~0.3 mm between samples at a driving velocity of 30 km/h. The driving velocity was measured with an optical velocity sensor. Two different surfaces were used to compare low-μ and high-μ conditions. These surfaces were ice and smooth concrete (see Fig. 3). The surface roughness was similar in both cases, which eliminates the acceleration signal variation resulting from the surface texture and the pure friction phenomena can be determined from the signal. In the event of a comparison between ice and asphalt, it would be difficult to state if certain vibrations were caused by friction or road roughness. Thus, a macroscopically smooth high-μ surface was selected for this study. Fig. 1 Accelerometers attached to the inner liner of the tyre The accelerometers were positioned side by side so as to cover half of the contact area in the lateral direction (see Fig. 2). The positions were selected in such a way that the accelerometers were placed behind the contact patch ribs, except accelerometer 3, which was behind a separate tread block. This allowed the accelerometer to indicate the direct rubber-road contact. Figure 3 a) Low-μ ice surface on the left, b) high-μ concrete surface on the right The measurement routine was identical on both surfaces. The car was accelerated to the measurement velocity and the clutch was disengaged before the data logging. The data logging was stopped after several tyre rotations. The data that was collected thus presents the freely rolling tyre without any applied torque or steering. Three different driving velocities and three different tyre pressures were used. The velocities were 10, 20, and 30 km/h and the tyre pressures were 2.2, 2.4, and 2.6 bar. Fig. 2 Accelerometer positions in the tyre (accelerometers attached to the inside) 2.2 Measurements The data for this research was collected with an instrumented passenger car (with tyre sensors). The measuring equipment in the car consisted of a typical passenger car summer tyre with the three 3-axis accelerometers introduced above. A slip ring was used to transmit the accelerometer data from the tyre and to provide the rotational speed and position of the wheel. Data acquisition (DAQ) was handled with NI DAQ devices which included an amplifier for the IEPE 3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 3.1 Contact lengths Tyre-road contact length measurements were performed in the previous research to determine the aquaplaning progress in the contact [3]. The same concept was applied in this research. The contact length is the distance between the two peaks in the longitudinal x-axis acceleration, which occurs at the leading and trailing edges. The distance is the time between the peaks (the number of samples divided by the sampling rate) times the accelerometer velocity (the measured driving velocity). Fig. 4 presents the contact lengths on 530
3 ice for five consecutive tyre rotations. The contact lengths are consistent throughout the measurements and thus the reliability of the method can be verified. The contact lengths calculated with accelerometer 1, which is located in the centre rib, are the longest as a result of the elliptical shape of the contact patch. Additionally, the camber angle increases the contact length in the centre compared to the outer accelerometers. The second longest contact lengths are measured with accelerometer 2, which is located one rib further than the centre one. The shortest contact lengths are in the shoulder part of the tyre. The tyre pressure has an obvious effect on the contact lengths. The lower the pressure, the longer the contact length. The length of the contact decreases by almost 1.5 cm when the pressure is increased from 2.2 to 2.6 bar. 10 km/h 20 km/h 30 km/h Contact length (m) 2.2 bar 2.4 bar Tyre rotations 2.6 bar Accelerometer 1 Accelerometer 2 Accelerometer 3 vibration in the leading edge can be seen from the acceleration signals. The lower friction between the rubber and the surface enables the contact patch to vibrate more as a result of the increased local slip in the contact patch. The increase in the vibration on ice is more distinct in the circumferential and radial acceleration than in the lateral y-axis acceleration. One reason is that the excitation in the radial and circumferential directions resulting from contact deformation is greater, which can also be recognised from the maximum amplitude of the acceleration signals. Fig. 6 presents the x- and z-axis acceleration signals from accelerometer 3. The vibration level does not vary between the surfaces as much as in the case of accelerometer 1. Sensor 3 is placed in the shoulder part of the tyre, which contains separate tread blocks (Fig 2.). The vibration resulting from the tread blocks hitting the surface obviously covers the friction-related vibration. Accelerometers 1 and 2 were attached behind solid ribs which do not produce the same kind of vibration as the separate tread blocks. The signal from accelerometer 2 was similar to that from accelerometer 1, but the acceleration levels were lower. Thus it can be concluded that the best position for the accelerometer is behind a solid rib close to the centre of the contact patch. Fig. 4 Calculated contact lengths on ice for the three accelerometers Contact lengths can also be used to verify the accuracy of the acceleration signal. If the contact length that is acquired is not in the expected range, the signal can be ignored or classified as an outlier and the information can be used in other applications. For example, if the contact length is too long, it can be assumed that the tyre pressure is too low and with the help of TPMS the vehicle can detect the problem. Or if the camera in the vehicle detects bumps on the road, it can inform the tyre sensor about an upcoming disturbance in the acceleration signal. This data can then be ignored during the determination of the contact length. 3.2 Friction potential indicators For the friction estimation, one of the most interesting parts of the acceleration signal is the section before the contact. In the leading edge, different vibration levels can be seen under different friction conditions (see Fig. 5). In the figure, the signal from all three axes of one accelerometer is shown. With the high-μ concrete surface, it is assumed that the acceleration signals which vibrate less are due to the stabilising effect of the friction between the rubber and the surface. On the ice surface, an increase in the Fig. 5 Acceleration signals from accelerometer 1 on ice and on concrete 531
4 In order to use the acceleration signal for friction estimation, signal processing must be conducted. A method to determine the different friction levels is introduced. It was discovered that the vibration in the leading edge was in a specific frequency range. By forming a frequency spectrum, the assumed friction-related vibration was found to exist above 2000 Hz. Since the noise is more dominant at the higher frequencies, band-pass filtering was applied to the acceleration signal. the information from sensor 1 was used in the following results. Fig. 6 x- and z-axis acceleration signals from accelerometer 3 on ice and on concrete The vibration frequency is obviously velocity-dependent, but with the measurement velocities in this research (10, 20, and 30 km/h), no significant change in the frequency band needed was found. With higher driving velocities, a moving band-pass filter might be needed. Fig. 7 Power spectrum of the band-pass ( Hz) filtered x-axis acceleration signal before contact (from accelerometer 1) Since accelerometers 2 and 3 do not provide information as useful as that from accelerometer 1, only Fig. 8 Mean value for area under the band-pass filtered acceleration (from accelerometer 1) power curve on ice (blue) and on concrete (grey) for five consecutive tyre rotations First, the acceleration data in the leading edge (framed in Fig. 5) was band-pass ( Hz) 532
5 filtered and then a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) was conducted to find a power spectrum in that frequency range. Fig. 7 shows a typical power spectrum for the band-pass filtered x-axis acceleration on ice and on concrete. The area under each power spectrum curve was integrated and the mean value for the area for five tyre rotations was calculated. This mean value was then used to compare the different surfaces. From Fig. 8 it can be seen that the area under the power curve is larger in the case of the low-μ ice than in that of the high-μ concrete. The vibration in the tyre resulting from the lower friction level is greater and thus the power curve area is larger. For a velocity of 10 km/h the differences are not as clear as in the case of higher velocities. The area under the power curve of y-axis acceleration does not indicate the friction difference as clearly as the two other axes. That was already discovered from the raw signal shown in Fig. 5. For the x- and z-axes the area under the power spectrum curve is at least twice as large on ice as on concrete. Interestingly, the radial z-axis acceleration provides the most noticeable difference between the two surfaces. The large excitation in the radial direction is one of the reasons, as mentioned earlier. 4. CONCLUSION Knowing the friction potential in the tyre-road contact would benefit the active safety and stability control systems of vehicles. Friction estimation methods based on the applied slip angle and slip ratio have been proposed earlier, but in the case of a freely rolling tyre, the friction estimation is still an unsolved topic. In this research, three 3-axis accelerometers on the inner liner of the tyre were used to find friction indicators on smooth ice and concrete surfaces. The surfaces were chosen to have equal roughness to eliminate the effect of the surface texture on the acceleration signals. The contact lengths calculated from the acceleration signals were used to verify the acceleration data. The contact length information can be very useful for active safety systems in addition to the sensor information that is currently provided in the vehicle. The determination of the contact length was found to be reliable on the two surfaces used in this research. For friction estimation, the acceleration data before the contact was discovered to contain friction-related information. The vibration level on the lower-friction ice surface was higher. It is assumed that the local slip in the leading edge enables the tyre carcass to vibrate before contact. On the higher-friction concrete surface the vibration level was significantly lower. The friction between the rubber and the surface stabilises the vibration in the tyre carcass. The friction itself is a dissipative process as well, and thus it is reasonable that a high-μ surface dissipates tyre vibrations more than a low-μ one (under similar macro-roughness conditions). The radial z-axis and circumferential x-axis accelerations provided the greatest difference in vibration between the two friction levels. The lateral y-axis acceleration did not contain as great a difference in vibration levels as the other two. This is due to the lower excitation in the lateral direction. The use of three accelerometers did not offer any benefit for friction-related vibration measurement. The vibration from the separate tread blocks hitting the surface was found to cover the vibration caused by the local slip in the leading edge and thus the accelerometer should be positioned behind a solid rib. As a result of the higher vibration level on a low-μ surface, the area under the acceleration power spectrum curve was larger. The use of the area under the power curve was found to be an effective way to classify the two different friction levels. This could also be implemented in a real-time friction estimation algorithm to evaluate the method on different surfaces with various friction levels. It can be concluded that the area under the acceleration power curve can be used to differentiate two equally smooth surfaces with different friction levels. REFERENCES [1] Braghin F, Brusarosco M, Cheli F, Cigada A, Manzoni S, Mancosu F. Measurement of Contact Forces and Patch Features by Means of Accelerometers Fixed Inside the Tire to Improve Future Car Active Control, Veh Syst Dyn 2006; 44:3 13. [2] Matilainen M, Tuononen A. Intelligent Tire to Measure Contact Length in Dry Asphalt and Wet Concrete Conditions, Int. Symp. Adv. Veh. Control, [3] Niskanen A, Tuononen A. Three 3-Axial Accelerometers Fixed Inside the Tyre for Studying Contact Patch Deformations in Wet Conditions, 23rd Int. Symp. Dyn. Veh. Roads Tracks, Quingdao, China, August 19-23: 2013, 1 8. [4] Morinaga H, Wakao Y, Hanatsuka Y, Kobayakawa A. The Possibility of Intelligent Tire (Technology of Contact Area Information Sensing), FISITA World Automot. Congr., [5] Morinaga H, Hanatsuka Y, Wakao Y, Bridgestone Corporation. Sensing Technology Tire System for Road Surface Condition Judgement, FISITA World Automot. Congr., Budapest, Hungary, [6] Morinaga H, Manager G, Corporation B. CAIS Technology for Detailed Classification of Road Surface Condition, Tire Technology Expo, [7] Singh K B, Taheri S. Piezoelectric Vibration- Based Energy Harvesters for Next-Generation Intelligent Tires, Tire Science and Technology 2013; 4: [8] Hong S, Erdogan G, Hedrick K, Borrelli F. Tyre-Road Friction Coefficient Estimation Based on Tyre Sensors and Lateral Tyre Deflection: Modelling, Simulations and Experiments, Veh Syst Dyn 2013;51:
6 [9] Rajamani R, Phanomchoeng G, Piyabongkarn D, Lew JY. Algorithms for Real-Time Estimation of Individual Wheel Tire-Road Friction Coefficients, IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatronics 2012;17: [10] Savaresi S M, Tanelli M, Langthaler P, Del Re L. New Regressors for the Direct Identification of Tire Deformation in Road Vehicles Via In-Tire Accelerometers, IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 2008;16:
EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF A CONTACT PATCH FORM OF A ROLLING TIRE: INFLUENCE OF SPEED, WHEEL LOAD, CAMBER AND SLIP ANGLE
 EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF A CONTACT PATCH FORM OF A ROLLING TIRE: INFLUENCE OF SPEED, WHEEL LOAD, CAMBER AND SLIP ANGLE Pavel Sarkisov *, Günther Prokop, Steffen Drossel Technische Universität Dresden,
EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF A CONTACT PATCH FORM OF A ROLLING TIRE: INFLUENCE OF SPEED, WHEEL LOAD, CAMBER AND SLIP ANGLE Pavel Sarkisov *, Günther Prokop, Steffen Drossel Technische Universität Dresden,
Modeling tire vibrations in ABS-braking
 Modeling tire vibrations in ABS-braking Ari Tuononen Aalto University Lassi Hartikainen, Frank Petry, Stephan Westermann Goodyear S.A. Tag des Fahrwerks 8. Oktober 2012 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Review
Modeling tire vibrations in ABS-braking Ari Tuononen Aalto University Lassi Hartikainen, Frank Petry, Stephan Westermann Goodyear S.A. Tag des Fahrwerks 8. Oktober 2012 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Review
Cornering & Traction Test Rig MTS Flat-Trac IV CT plus
 Testing Facilities Cornering & Traction Test Rig MTS Flat-Trac IV CT plus s steady-state force and moment measurement dynamic force and moment measurement slip angel sweeps tests tractive tests sinusoidal
Testing Facilities Cornering & Traction Test Rig MTS Flat-Trac IV CT plus s steady-state force and moment measurement dynamic force and moment measurement slip angel sweeps tests tractive tests sinusoidal
I. Tire Heat Generation and Transfer:
 Caleb Holloway - Owner calebh@izzeracing.com +1 (443) 765 7685 I. Tire Heat Generation and Transfer: It is important to first understand how heat is generated within a tire and how that heat is transferred
Caleb Holloway - Owner calebh@izzeracing.com +1 (443) 765 7685 I. Tire Heat Generation and Transfer: It is important to first understand how heat is generated within a tire and how that heat is transferred
Analysis and evaluation of a tyre model through test data obtained using the IMMa tyre test bench
 Vehicle System Dynamics Vol. 43, Supplement, 2005, 241 252 Analysis and evaluation of a tyre model through test data obtained using the IMMa tyre test bench A. ORTIZ*, J.A. CABRERA, J. CASTILLO and A.
Vehicle System Dynamics Vol. 43, Supplement, 2005, 241 252 Analysis and evaluation of a tyre model through test data obtained using the IMMa tyre test bench A. ORTIZ*, J.A. CABRERA, J. CASTILLO and A.
Intelligent Tire to Measure Contact Length in Dry Asphalt and Wet Concrete Conditions
 Intelligent Tire to Measure Contact Length in Dr Asphalt and Wet Concrete Conditions Mika J. Matilainen, Ari J. Tuononen Aalto Universit School of Engineering Puumiehenkuja 5 A Espoo, FI-76, FINLAND Phone:
Intelligent Tire to Measure Contact Length in Dr Asphalt and Wet Concrete Conditions Mika J. Matilainen, Ari J. Tuononen Aalto Universit School of Engineering Puumiehenkuja 5 A Espoo, FI-76, FINLAND Phone:
Study of the Performance of a Driver-vehicle System for Changing the Steering Characteristics of a Vehicle
 20 Special Issue Estimation and Control of Vehicle Dynamics for Active Safety Research Report Study of the Performance of a Driver-vehicle System for Changing the Steering Characteristics of a Vehicle
20 Special Issue Estimation and Control of Vehicle Dynamics for Active Safety Research Report Study of the Performance of a Driver-vehicle System for Changing the Steering Characteristics of a Vehicle
AEB System for a Curved Road Considering V2Vbased Road Surface Conditions
 , pp.8-13 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.86.03 AEB System for a Curved Road Considering V2Vbased Road Surface Conditions Hyeonggeun Mun 1, Gyoungeun Kim 1, Byeongwoo Kim 2 * 1 Graduate School of
, pp.8-13 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.86.03 AEB System for a Curved Road Considering V2Vbased Road Surface Conditions Hyeonggeun Mun 1, Gyoungeun Kim 1, Byeongwoo Kim 2 * 1 Graduate School of
Optical position detection sensor to measure tyre carcass deflections in aquaplaning. Ari Tuononen* and Lassi Hartikainen
 Int. J. Vehicle Systems Modelling and Testing, Vol. 3, No. 3, 2008 189 Optical position detection sensor to measure tyre carcass deflections in aquaplaning Ari Tuononen* and Lassi Hartikainen Helsinki
Int. J. Vehicle Systems Modelling and Testing, Vol. 3, No. 3, 2008 189 Optical position detection sensor to measure tyre carcass deflections in aquaplaning Ari Tuononen* and Lassi Hartikainen Helsinki
Shimmy Identification Caused by Self-Excitation Components at Vehicle High Speed
 Shimmy Identification Caused by Self-Excitation Components at Vehicle High Speed Fujiang Min, Wei Wen, Lifeng Zhao, Xiongying Yu and Jiang Xu Abstract The chapter introduces the shimmy mechanism caused
Shimmy Identification Caused by Self-Excitation Components at Vehicle High Speed Fujiang Min, Wei Wen, Lifeng Zhao, Xiongying Yu and Jiang Xu Abstract The chapter introduces the shimmy mechanism caused
Extracting Tire Model Parameters From Test Data
 WP# 2001-4 Extracting Tire Model Parameters From Test Data Wesley D. Grimes, P.E. Eric Hunter Collision Engineering Associates, Inc ABSTRACT Computer models used to study crashes require data describing
WP# 2001-4 Extracting Tire Model Parameters From Test Data Wesley D. Grimes, P.E. Eric Hunter Collision Engineering Associates, Inc ABSTRACT Computer models used to study crashes require data describing
Skid against Curb simulation using Abaqus/Explicit
 Visit the SIMULIA Resource Center for more customer examples. Skid against Curb simulation using Abaqus/Explicit Dipl.-Ing. A. Lepold (FORD), Dipl.-Ing. T. Kroschwald (TECOSIM) Abstract: Skid a full vehicle
Visit the SIMULIA Resource Center for more customer examples. Skid against Curb simulation using Abaqus/Explicit Dipl.-Ing. A. Lepold (FORD), Dipl.-Ing. T. Kroschwald (TECOSIM) Abstract: Skid a full vehicle
Research on Skid Control of Small Electric Vehicle (Effect of Velocity Prediction by Observer System)
 Proc. Schl. Eng. Tokai Univ., Ser. E (17) 15-1 Proc. Schl. Eng. Tokai Univ., Ser. E (17) - Research on Skid Control of Small Electric Vehicle (Effect of Prediction by Observer System) by Sean RITHY *1
Proc. Schl. Eng. Tokai Univ., Ser. E (17) 15-1 Proc. Schl. Eng. Tokai Univ., Ser. E (17) - Research on Skid Control of Small Electric Vehicle (Effect of Prediction by Observer System) by Sean RITHY *1
Fuzzy Architecture of Safety- Relevant Vehicle Systems
 Fuzzy Architecture of Safety- Relevant Vehicle Systems by Valentin Ivanov and Barys Shyrokau Automotive Engineering Department, Ilmenau University of Technology (Germany) 1 Content 1. Introduction 2. Fuzzy
Fuzzy Architecture of Safety- Relevant Vehicle Systems by Valentin Ivanov and Barys Shyrokau Automotive Engineering Department, Ilmenau University of Technology (Germany) 1 Content 1. Introduction 2. Fuzzy
OPTICAL MEASUREMENT OF TREAD DEFORMATION FOR ROLLING RESISTANCE STUDIES
 Abstract OPTICAL MEASUREMENT OF TREAD DEFORMATION FOR ROLLING RESISTANCE STUDIES Yi Xiong, Ari Tuononen Vehicle Engineering, Department of Engineering Design and Production Aalto University P.O. Box 14300
Abstract OPTICAL MEASUREMENT OF TREAD DEFORMATION FOR ROLLING RESISTANCE STUDIES Yi Xiong, Ari Tuononen Vehicle Engineering, Department of Engineering Design and Production Aalto University P.O. Box 14300
Racing Tires in Formula SAE Suspension Development
 The University of Western Ontario Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering MME419 Mechanical Engineering Project MME499 Mechanical Engineering Design (Industrial) Racing Tires in Formula SAE
The University of Western Ontario Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering MME419 Mechanical Engineering Project MME499 Mechanical Engineering Design (Industrial) Racing Tires in Formula SAE
Technical Report Lotus Elan Rear Suspension The Effect of Halfshaft Rubber Couplings. T. L. Duell. Prepared for The Elan Factory.
 Technical Report - 9 Lotus Elan Rear Suspension The Effect of Halfshaft Rubber Couplings by T. L. Duell Prepared for The Elan Factory May 24 Terry Duell consulting 19 Rylandes Drive, Gladstone Park Victoria
Technical Report - 9 Lotus Elan Rear Suspension The Effect of Halfshaft Rubber Couplings by T. L. Duell Prepared for The Elan Factory May 24 Terry Duell consulting 19 Rylandes Drive, Gladstone Park Victoria
How and why does slip angle accuracy change with speed? Date: 1st August 2012 Version:
 Subtitle: How and why does slip angle accuracy change with speed? Date: 1st August 2012 Version: 120802 Author: Brendan Watts List of contents Slip Angle Accuracy 1. Introduction... 1 2. Uses of slip angle...
Subtitle: How and why does slip angle accuracy change with speed? Date: 1st August 2012 Version: 120802 Author: Brendan Watts List of contents Slip Angle Accuracy 1. Introduction... 1 2. Uses of slip angle...
Experimental Investigation of Effects of Shock Absorber Mounting Angle on Damping Characterstics
 Experimental Investigation of Effects of Shock Absorber Mounting Angle on Damping Characterstics Tanmay P. Dobhada Tushar S. Dhaspatil Prof. S S Hirmukhe Mauli P. Khapale Abstract: A shock absorber is
Experimental Investigation of Effects of Shock Absorber Mounting Angle on Damping Characterstics Tanmay P. Dobhada Tushar S. Dhaspatil Prof. S S Hirmukhe Mauli P. Khapale Abstract: A shock absorber is
FEASIBILITY STYDY OF CHAIN DRIVE IN WATER HYDRAULIC ROTARY JOINT
 FEASIBILITY STYDY OF CHAIN DRIVE IN WATER HYDRAULIC ROTARY JOINT Antti MAKELA, Jouni MATTILA, Mikko SIUKO, Matti VILENIUS Institute of Hydraulics and Automation, Tampere University of Technology P.O.Box
FEASIBILITY STYDY OF CHAIN DRIVE IN WATER HYDRAULIC ROTARY JOINT Antti MAKELA, Jouni MATTILA, Mikko SIUKO, Matti VILENIUS Institute of Hydraulics and Automation, Tampere University of Technology P.O.Box
Study on V2V-based AEB System Performance Analysis in Various Road Conditions at an Intersection
 , pp. 1-10 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2015.9.7.01 Study on V2V-based AEB System Performance Analysis in Various Road Conditions at an Intersection Sangduck Jeon 1, Gyoungeun Kim 1 and Byeongwoo
, pp. 1-10 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2015.9.7.01 Study on V2V-based AEB System Performance Analysis in Various Road Conditions at an Intersection Sangduck Jeon 1, Gyoungeun Kim 1 and Byeongwoo
SPMM OUTLINE SPECIFICATION - SP20016 issue 2 WHAT IS THE SPMM 5000?
 SPMM 5000 OUTLINE SPECIFICATION - SP20016 issue 2 WHAT IS THE SPMM 5000? The Suspension Parameter Measuring Machine (SPMM) is designed to measure the quasi-static suspension characteristics that are important
SPMM 5000 OUTLINE SPECIFICATION - SP20016 issue 2 WHAT IS THE SPMM 5000? The Suspension Parameter Measuring Machine (SPMM) is designed to measure the quasi-static suspension characteristics that are important
Preliminary Study on Quantitative Analysis of Steering System Using Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) Simulator
 TECHNICAL PAPER Preliminary Study on Quantitative Analysis of Steering System Using Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) Simulator M. SEGAWA M. HIGASHI One of the objectives in developing simulation methods is to
TECHNICAL PAPER Preliminary Study on Quantitative Analysis of Steering System Using Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) Simulator M. SEGAWA M. HIGASHI One of the objectives in developing simulation methods is to
Simulation of Collective Load Data for Integrated Design and Testing of Vehicle Transmissions. Andreas Schmidt, Audi AG, May 22, 2014
 Simulation of Collective Load Data for Integrated Design and Testing of Vehicle Transmissions Andreas Schmidt, Audi AG, May 22, 2014 Content Introduction Usage of collective load data in the development
Simulation of Collective Load Data for Integrated Design and Testing of Vehicle Transmissions Andreas Schmidt, Audi AG, May 22, 2014 Content Introduction Usage of collective load data in the development
SPMM OUTLINE SPECIFICATION - SP20016 issue 2 WHAT IS THE SPMM 5000?
 SPMM 5000 OUTLINE SPECIFICATION - SP20016 issue 2 WHAT IS THE SPMM 5000? The Suspension Parameter Measuring Machine (SPMM) is designed to measure the quasi-static suspension characteristics that are important
SPMM 5000 OUTLINE SPECIFICATION - SP20016 issue 2 WHAT IS THE SPMM 5000? The Suspension Parameter Measuring Machine (SPMM) is designed to measure the quasi-static suspension characteristics that are important
Modification of IPG Driver for Road Robustness Applications
 Modification of IPG Driver for Road Robustness Applications Alexander Shawyer (BEng, MSc) Alex Bean (BEng, CEng. IMechE) SCS Analysis & Virtual Tools, Braking Development Jaguar Land Rover Introduction
Modification of IPG Driver for Road Robustness Applications Alexander Shawyer (BEng, MSc) Alex Bean (BEng, CEng. IMechE) SCS Analysis & Virtual Tools, Braking Development Jaguar Land Rover Introduction
Proposal for amendments to Regulation No.79 (Steering equipment)
 Submitted by the experts from Germany and the Republic of Korea Informal document GRRF-86-13 86 th GRRF, 12-16 February 2018 Agenda item 9(b) Proposal for amendments to Regulation No.79 (Steering equipment)
Submitted by the experts from Germany and the Republic of Korea Informal document GRRF-86-13 86 th GRRF, 12-16 February 2018 Agenda item 9(b) Proposal for amendments to Regulation No.79 (Steering equipment)
Structural Dynamic Behaviour of Tyres
 XIX CNIM 15-16/11 Castellón Structural Dynamic Behaviour of Tyres Paul Sas Noise & Vibration Engineering Research Group KU.Leuven, Dept. Mechanical Engineering, Div. PMA Road traffic noise Vehicle noise:
XIX CNIM 15-16/11 Castellón Structural Dynamic Behaviour of Tyres Paul Sas Noise & Vibration Engineering Research Group KU.Leuven, Dept. Mechanical Engineering, Div. PMA Road traffic noise Vehicle noise:
Development of Noise-reducing Wheel
 Introduction of new technologies Development of Noise-reducing Wheel Development of Noise-reducing Wheel Youichi KAMIYAMA* Hisamitsu TAKAGI* Katsushi ISHII* Mikio KASHIWAI** ABSTRACT Tire cavity noise
Introduction of new technologies Development of Noise-reducing Wheel Development of Noise-reducing Wheel Youichi KAMIYAMA* Hisamitsu TAKAGI* Katsushi ISHII* Mikio KASHIWAI** ABSTRACT Tire cavity noise
Dynamic characteristics of railway concrete sleepers using impact excitation techniques and model analysis
 Dynamic characteristics of railway concrete sleepers using impact excitation techniques and model analysis Akira Aikawa *, Fumihiro Urakawa *, Kazuhisa Abe **, Akira Namura * * Railway Technical Research
Dynamic characteristics of railway concrete sleepers using impact excitation techniques and model analysis Akira Aikawa *, Fumihiro Urakawa *, Kazuhisa Abe **, Akira Namura * * Railway Technical Research
Article A Novel Strain-Based Method to Estimate Tire Conditions Using Fuzzy Logic for Intelligent Tires
 Article A Novel Strain-Based Method to Estimate Tire Conditions Using Fuzzy Logic for Intelligent Tires Daniel Garcia-Pozuelo 1, Oluremi Olatunbosun 2, Jorge Yunta 1, *, Xiaoguang Yang 3 and Vicente Diaz
Article A Novel Strain-Based Method to Estimate Tire Conditions Using Fuzzy Logic for Intelligent Tires Daniel Garcia-Pozuelo 1, Oluremi Olatunbosun 2, Jorge Yunta 1, *, Xiaoguang Yang 3 and Vicente Diaz
inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering August 2000, Nice, FRANCE
 Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 7.6 ROLLING NOISE FROM
Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 7.6 ROLLING NOISE FROM
CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL SHOCK TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY
 135 CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL SHOCK TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY 6.1 INTRODUCTION Shock is often defined as a rapid transfer of energy to a mechanical system, which results in a significant increase in the stress,
135 CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL SHOCK TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY 6.1 INTRODUCTION Shock is often defined as a rapid transfer of energy to a mechanical system, which results in a significant increase in the stress,
Collaborative vehicle steering and braking control system research Jiuchao Li, Yu Cui, Guohua Zang
 4th International Conference on Mechatronics, Materials, Chemistry and Computer Engineering (ICMMCCE 2015) Collaborative vehicle steering and braking control system research Jiuchao Li, Yu Cui, Guohua
4th International Conference on Mechatronics, Materials, Chemistry and Computer Engineering (ICMMCCE 2015) Collaborative vehicle steering and braking control system research Jiuchao Li, Yu Cui, Guohua
VR-Design Studio Car Physics Engine
 VR-Design Studio Car Physics Engine Contents Introduction I General I.1 Model I.2 General physics I.3 Introduction to the force created by the wheels II The Engine II.1 Engine RPM II.2 Engine Torque II.3
VR-Design Studio Car Physics Engine Contents Introduction I General I.1 Model I.2 General physics I.3 Introduction to the force created by the wheels II The Engine II.1 Engine RPM II.2 Engine Torque II.3
Design and Analysis of Hydrostatic Bearing Slide Used Linear Motor Direct-drive. Guoan Hou 1, a, Tao Sun 1,b
 Advanced Materials Research Vols. 211-212 (2011) pp 666-670 Online available since 2011/Feb/21 at www.scientific.net (2011) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.211-212.666
Advanced Materials Research Vols. 211-212 (2011) pp 666-670 Online available since 2011/Feb/21 at www.scientific.net (2011) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.211-212.666
Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers
 Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers U. Bin-Nun FLIR Systems Inc. Boston, MA 01862 ABSTRACT Cryocooler self induced vibration is a major consideration in the design of IR
Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers U. Bin-Nun FLIR Systems Inc. Boston, MA 01862 ABSTRACT Cryocooler self induced vibration is a major consideration in the design of IR
The possibility to use a vibration signal to estimate friction processes in sliding couplings
 The possibility to use a vibration signal to estimate friction processes in sliding couplings Wojciech Napadłek 1, Grzegorz Trawiński 2, Grzegorz Boruta 3, Chrzanowski Wojciech 4 1, 2, 4 Military University
The possibility to use a vibration signal to estimate friction processes in sliding couplings Wojciech Napadłek 1, Grzegorz Trawiński 2, Grzegorz Boruta 3, Chrzanowski Wojciech 4 1, 2, 4 Military University
Cyber TM Tyre for Vehicle Active Safety Giorgio Audisio 1, Federico Cheli 2, Stefano Melzi 2, Mauro Velardocchia 3
 Cyber TM Tyre for Vehicle Active Safety Giorgio Audisio 1, Federico Cheli 2, Stefano Melzi 2, Mauro Velardocchia 3 1 Pirelli Tyre, Italy E-mail: giorgio.audisio@pirelli.com 2 Dipartimento di Meccanica,
Cyber TM Tyre for Vehicle Active Safety Giorgio Audisio 1, Federico Cheli 2, Stefano Melzi 2, Mauro Velardocchia 3 1 Pirelli Tyre, Italy E-mail: giorgio.audisio@pirelli.com 2 Dipartimento di Meccanica,
Application of Airborne Electro-Optical Platform with Shock Absorbers. Hui YAN, Dong-sheng YANG, Tao YUAN, Xiang BI, and Hong-yuan JIANG*
 2016 International Conference on Applied Mechanics, Mechanical and Materials Engineering (AMMME 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-409-7 Application of Airborne Electro-Optical Platform with Shock Absorbers Hui YAN,
2016 International Conference on Applied Mechanics, Mechanical and Materials Engineering (AMMME 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-409-7 Application of Airborne Electro-Optical Platform with Shock Absorbers Hui YAN,
METHOD FOR TESTING STEERABILITY AND STABILITY OF MILITARY VEHICLES MOTION USING SR60E STEERING ROBOT
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 18, No. 1 11 METHOD FOR TESTING STEERABILITY AND STABILITY OF MILITARY VEHICLES MOTION USING SR6E STEERING ROBOT Wodzimierz Kupicz, Stanisaw Niziski Military
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 18, No. 1 11 METHOD FOR TESTING STEERABILITY AND STABILITY OF MILITARY VEHICLES MOTION USING SR6E STEERING ROBOT Wodzimierz Kupicz, Stanisaw Niziski Military
REDUCING THE OCCURRENCES AND IMPACT OF FREIGHT TRAIN DERAILMENTS
 REDUCING THE OCCURRENCES AND IMPACT OF FREIGHT TRAIN DERAILMENTS D-Rail Final Workshop 12 th November - Stockholm Monitoring and supervision concepts and techniques for derailments investigation Antonella
REDUCING THE OCCURRENCES AND IMPACT OF FREIGHT TRAIN DERAILMENTS D-Rail Final Workshop 12 th November - Stockholm Monitoring and supervision concepts and techniques for derailments investigation Antonella
A dream? Dr. Jürgen Bredenbeck Tire Technology Expo, February 2012 Cologne
 Rolling resistance measurement on the road: A dream? Dr. Jürgen Bredenbeck Tire Technology Expo, 14.-16. February 2012 Cologne Content Motivation Introduction of the used Measurement Equipment Introduction
Rolling resistance measurement on the road: A dream? Dr. Jürgen Bredenbeck Tire Technology Expo, 14.-16. February 2012 Cologne Content Motivation Introduction of the used Measurement Equipment Introduction
IMPROVED EMERGENCY BRAKING PERFORMANCE FOR HGVS
 IMPROVED EMERGENCY BRAKING PERFORMANCE FOR HGVS Dr Leon Henderson Research Associate University of Cambridge, UK lmh59@cam.ac.uk Prof. David Cebon University of Cambridge, UK dc@eng.cam.ac.uk Abstract
IMPROVED EMERGENCY BRAKING PERFORMANCE FOR HGVS Dr Leon Henderson Research Associate University of Cambridge, UK lmh59@cam.ac.uk Prof. David Cebon University of Cambridge, UK dc@eng.cam.ac.uk Abstract
Study on Braking Energy Recovery of Four Wheel Drive Electric Vehicle Based on Driving Intention Recognition
 Open Access Library Journal 2018, Volume 5, e4295 ISSN Online: 2333-9721 ISSN Print: 2333-9705 Study on Braking Energy Recovery of Four Wheel Drive Electric Vehicle Based on Driving Intention Recognition
Open Access Library Journal 2018, Volume 5, e4295 ISSN Online: 2333-9721 ISSN Print: 2333-9705 Study on Braking Energy Recovery of Four Wheel Drive Electric Vehicle Based on Driving Intention Recognition
APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE
 Colloquium DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 2012 Prague, February 7 8, 2011 CzechNC APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE Jiří Šimek Abstract: New type of aerodynamic
Colloquium DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 2012 Prague, February 7 8, 2011 CzechNC APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE Jiří Šimek Abstract: New type of aerodynamic
Estimation of Friction Force Characteristics between Tire and Road Using Wheel Velocity and Application to Braking Control
 Estimation of Friction Force Characteristics between Tire and Road Using Wheel Velocity and Application to Braking Control Mamoru SAWADA Eiichi ONO Shoji ITO Masaki YAMAMOTO Katsuhiro ASANO Yoshiyuki YASUI
Estimation of Friction Force Characteristics between Tire and Road Using Wheel Velocity and Application to Braking Control Mamoru SAWADA Eiichi ONO Shoji ITO Masaki YAMAMOTO Katsuhiro ASANO Yoshiyuki YASUI
Braking Performance Improvement Method for V2V Communication-Based Autonomous Emergency Braking at Intersections
 , pp.20-25 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.86.05 Braking Performance Improvement Method for V2V Communication-Based Autonomous Emergency Braking at Intersections Sangduck Jeon 1, Gyoungeun Kim 1,
, pp.20-25 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.86.05 Braking Performance Improvement Method for V2V Communication-Based Autonomous Emergency Braking at Intersections Sangduck Jeon 1, Gyoungeun Kim 1,
Forced vibration frequency response for a permanent magnetic planetary gear
 Forced vibration frequency response for a permanent magnetic planetary gear Xuejun Zhu 1, Xiuhong Hao 2, Minggui Qu 3 1 Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Parallel Robot and Mechatronic System, Yanshan
Forced vibration frequency response for a permanent magnetic planetary gear Xuejun Zhu 1, Xiuhong Hao 2, Minggui Qu 3 1 Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Parallel Robot and Mechatronic System, Yanshan
Damping Ratio Estimation of an Existing 8-story Building Considering Soil-Structure Interaction Using Strong Motion Observation Data.
 Damping Ratio Estimation of an Existing -story Building Considering Soil-Structure Interaction Using Strong Motion Observation Data by Koichi Morita ABSTRACT In this study, damping ratio of an exiting
Damping Ratio Estimation of an Existing -story Building Considering Soil-Structure Interaction Using Strong Motion Observation Data by Koichi Morita ABSTRACT In this study, damping ratio of an exiting
CHAPTER 4 : RESISTANCE TO PROGRESS OF A VEHICLE - MEASUREMENT METHOD ON THE ROAD - SIMULATION ON A CHASSIS DYNAMOMETER
 CHAPTER 4 : RESISTANCE TO PROGRESS OF A VEHICLE - MEASUREMENT METHOD ON THE ROAD - SIMULATION ON A CHASSIS DYNAMOMETER 1. Scope : This Chapter describes the methods to measure the resistance to the progress
CHAPTER 4 : RESISTANCE TO PROGRESS OF A VEHICLE - MEASUREMENT METHOD ON THE ROAD - SIMULATION ON A CHASSIS DYNAMOMETER 1. Scope : This Chapter describes the methods to measure the resistance to the progress
Simulating Rotary Draw Bending and Tube Hydroforming
 Abstract: Simulating Rotary Draw Bending and Tube Hydroforming Dilip K Mahanty, Narendran M. Balan Engineering Services Group, Tata Consultancy Services Tube hydroforming is currently an active area of
Abstract: Simulating Rotary Draw Bending and Tube Hydroforming Dilip K Mahanty, Narendran M. Balan Engineering Services Group, Tata Consultancy Services Tube hydroforming is currently an active area of
The research on gearshift control strategies of a plug-in parallel hybrid electric vehicle equipped with EMT
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(6):1647-1652 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The research on gearshift control strategies of
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(6):1647-1652 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The research on gearshift control strategies of
Transmitted by the expert from the European Commission (EC) Informal Document No. GRRF (62nd GRRF, September 2007, agenda item 3(i))
 Transmitted by the expert from the European Commission (EC) Informal Document No. GRRF-62-31 (62nd GRRF, 25-28 September 2007, agenda item 3(i)) Introduction of Brake Assist Systems to Regulation No. 13-H
Transmitted by the expert from the European Commission (EC) Informal Document No. GRRF-62-31 (62nd GRRF, 25-28 September 2007, agenda item 3(i)) Introduction of Brake Assist Systems to Regulation No. 13-H
Multi-axial fatigue life assessment of high speed car body based on PDMR method
 MATEC Web of Conferences 165, 17006 (018) FATIGUE 018 https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/01816517006 Multi-axial fatigue life assessment of high speed car body based on PDMR method Chaotao Liu 1,*, Pingbo
MATEC Web of Conferences 165, 17006 (018) FATIGUE 018 https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/01816517006 Multi-axial fatigue life assessment of high speed car body based on PDMR method Chaotao Liu 1,*, Pingbo
Mathematical Modelling and Simulation Of Semi- Active Suspension System For An 8 8 Armoured Wheeled Vehicle With 11 DOF
 Mathematical Modelling and Simulation Of Semi- Active Suspension System For An 8 8 Armoured Wheeled Vehicle With 11 DOF Sujithkumar M Sc C, V V Jagirdar Sc D and MW Trikande Sc G VRDE, Ahmednagar Maharashtra-414006,
Mathematical Modelling and Simulation Of Semi- Active Suspension System For An 8 8 Armoured Wheeled Vehicle With 11 DOF Sujithkumar M Sc C, V V Jagirdar Sc D and MW Trikande Sc G VRDE, Ahmednagar Maharashtra-414006,
WET GRIP TEST METHOD IMPROVEMENT for Passenger Car Tyres (C1) GRBP 68 th session
 Transmitted by the expert from ETRTO Informal document GRB-68-15 (68 th GRB, 12-14 September 2018, agenda item 6) WET GRIP TEST METHOD IMPROVEMENT for Passenger Car Tyres (C1) Overview of Tyre Industry
Transmitted by the expert from ETRTO Informal document GRB-68-15 (68 th GRB, 12-14 September 2018, agenda item 6) WET GRIP TEST METHOD IMPROVEMENT for Passenger Car Tyres (C1) Overview of Tyre Industry
Estimation of tire road friction coefficient and its application in chassis control systems
 Systems Science & Control Engineering An Open Access Journal ISSN: (Print) 2164-2583 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tssc20 Estimation of tire road friction coefficient and its
Systems Science & Control Engineering An Open Access Journal ISSN: (Print) 2164-2583 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tssc20 Estimation of tire road friction coefficient and its
Study on Tractor Semi-Trailer Roll Stability Control
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 238 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 214, 8, 238-242 Study on Tractor Semi-Trailer Roll Stability Control Shuwen Zhou *,1 and Siqi Zhang
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 238 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 214, 8, 238-242 Study on Tractor Semi-Trailer Roll Stability Control Shuwen Zhou *,1 and Siqi Zhang
Water influence on skid resistance. Standardisation: input of the HERMES programme
 Water influence on skid resistance Standardisation: input of the HERMES programme Research Director LRPC de Lyon France Presentation outline Water influence on skid resistance - influence of the surface
Water influence on skid resistance Standardisation: input of the HERMES programme Research Director LRPC de Lyon France Presentation outline Water influence on skid resistance - influence of the surface
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF IMPACT BETWEEN SHUNTING LOCOMOTIVE AND SELECTED ROAD VEHICLE
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 21, No. 4 2014 ISSN: 1231-4005 e-issn: 2354-0133 ICID: 1130437 DOI: 10.5604/12314005.1130437 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF IMPACT BETWEEN SHUNTING LOCOMOTIVE AND
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 21, No. 4 2014 ISSN: 1231-4005 e-issn: 2354-0133 ICID: 1130437 DOI: 10.5604/12314005.1130437 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF IMPACT BETWEEN SHUNTING LOCOMOTIVE AND
Analysis of Torsional Vibration in Elliptical Gears
 The The rd rd International Conference on on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES Pilsen, Czech Pilsen, Republic, Czech August Republic, September -, Analysis of Torsional Vibration in Elliptical Gears
The The rd rd International Conference on on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES Pilsen, Czech Pilsen, Republic, Czech August Republic, September -, Analysis of Torsional Vibration in Elliptical Gears
Simulation and Analysis of Vehicle Suspension System for Different Road Profile
 Simulation and Analysis of Vehicle Suspension System for Different Road Profile P.Senthil kumar 1 K.Sivakumar 2 R.Kalidas 3 1 Assistant professor, 2 Professor & Head, 3 Student Department of Mechanical
Simulation and Analysis of Vehicle Suspension System for Different Road Profile P.Senthil kumar 1 K.Sivakumar 2 R.Kalidas 3 1 Assistant professor, 2 Professor & Head, 3 Student Department of Mechanical
Hybrid Architectures for Automated Transmission Systems
 1 / 5 Hybrid Architectures for Automated Transmission Systems - add-on and integrated solutions - Dierk REITZ, Uwe WAGNER, Reinhard BERGER LuK GmbH & Co. ohg Bussmatten 2, 77815 Bühl, Germany (E-Mail:
1 / 5 Hybrid Architectures for Automated Transmission Systems - add-on and integrated solutions - Dierk REITZ, Uwe WAGNER, Reinhard BERGER LuK GmbH & Co. ohg Bussmatten 2, 77815 Bühl, Germany (E-Mail:
Engineering Integrity Society What s that horrible road noise? It s the tyres S d!
 Engineering Integrity Society What s that horrible road noise? It s the tyres S d! 4-5 November 15 NEC, Birmingham Understanding how tire construction affects contact patch acceleration and noise Radiated
Engineering Integrity Society What s that horrible road noise? It s the tyres S d! 4-5 November 15 NEC, Birmingham Understanding how tire construction affects contact patch acceleration and noise Radiated
TNO Science and Industry P.O. Box 756, 5700 AT Helmond, The Netherlands Honda R&D Co., Ltd.
 Proceedings, Bicycle and Motorcycle Dynamics 2010 Symposium on the Dynamics and Control of Single Track Vehicles, 20-22 October 2010, Delft, The Netherlands Application of the rigid ring model for simulating
Proceedings, Bicycle and Motorcycle Dynamics 2010 Symposium on the Dynamics and Control of Single Track Vehicles, 20-22 October 2010, Delft, The Netherlands Application of the rigid ring model for simulating
KINEMATICAL SUSPENSION OPTIMIZATION USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENT METHOD
 Jurnal Mekanikal June 2014, No 37, 16-25 KINEMATICAL SUSPENSION OPTIMIZATION USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENT METHOD Mohd Awaluddin A Rahman and Afandi Dzakaria Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti
Jurnal Mekanikal June 2014, No 37, 16-25 KINEMATICAL SUSPENSION OPTIMIZATION USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENT METHOD Mohd Awaluddin A Rahman and Afandi Dzakaria Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti
Design of Suspension and Steering system for an All-Terrain Vehicle and their Interdependence
 Design of Suspension and Steering system for an All-Terrain Vehicle and their Interdependence Saurabh Wanganekar 1, Chinmay Sapkale 2, Priyanka Chothe 3, Reshma Rohakale 4,Samadhan Bhosale 5 1 Student,Department
Design of Suspension and Steering system for an All-Terrain Vehicle and their Interdependence Saurabh Wanganekar 1, Chinmay Sapkale 2, Priyanka Chothe 3, Reshma Rohakale 4,Samadhan Bhosale 5 1 Student,Department
Optimization of Seat Displacement and Settling Time of Quarter Car Model Vehicle Dynamic System Subjected to Speed Bump
 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347-5161 2014 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Optimization
Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347-5161 2014 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Optimization
inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering August 2000, Nice, FRANCE
 Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 1.3 CURVE SQUEAL OF
Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 1.3 CURVE SQUEAL OF
Dynamic Behavior Analysis of Hydraulic Power Steering Systems
 Dynamic Behavior Analysis of Hydraulic Power Steering Systems Y. TOKUMOTO * *Research & Development Center, Control Devices Development Department Research regarding dynamic modeling of hydraulic power
Dynamic Behavior Analysis of Hydraulic Power Steering Systems Y. TOKUMOTO * *Research & Development Center, Control Devices Development Department Research regarding dynamic modeling of hydraulic power
SIMULATING A CAR CRASH WITH A CAR SIMULATOR FOR THE PEOPLE WITH MOBILITY IMPAIRMENTS
 International Journal of Modern Manufacturing Technologies ISSN 2067 3604, Vol. VI, No. 1 / 2014 SIMULATING A CAR CRASH WITH A CAR SIMULATOR FOR THE PEOPLE WITH MOBILITY IMPAIRMENTS Waclaw Banas 1, Krzysztof
International Journal of Modern Manufacturing Technologies ISSN 2067 3604, Vol. VI, No. 1 / 2014 SIMULATING A CAR CRASH WITH A CAR SIMULATOR FOR THE PEOPLE WITH MOBILITY IMPAIRMENTS Waclaw Banas 1, Krzysztof
Vehicle Dynamic Simulation Using A Non-Linear Finite Element Simulation Program (LS-DYNA)
 Vehicle Dynamic Simulation Using A Non-Linear Finite Element Simulation Program (LS-DYNA) G. S. Choi and H. K. Min Kia Motors Technical Center 3-61 INTRODUCTION The reason manufacturers invest their time
Vehicle Dynamic Simulation Using A Non-Linear Finite Element Simulation Program (LS-DYNA) G. S. Choi and H. K. Min Kia Motors Technical Center 3-61 INTRODUCTION The reason manufacturers invest their time
Assemblies for Parallel Kinematics. Frank Dürschmied. INA reprint from Werkstatt und Betrieb Vol. No. 5, May 1999 Carl Hanser Verlag, München
 Assemblies for Parallel Kinematics Frank Dürschmied INA reprint from Werkstatt und Betrieb Vol. No. 5, May 1999 Carl Hanser Verlag, München Assemblies for Parallel Kinematics Frank Dürschmied Joints and
Assemblies for Parallel Kinematics Frank Dürschmied INA reprint from Werkstatt und Betrieb Vol. No. 5, May 1999 Carl Hanser Verlag, München Assemblies for Parallel Kinematics Frank Dürschmied Joints and
BALL BEARING TESTS TO EVALUATE DUROID REPLACEMENTS
 BALL BEARING TESTS TO EVALUATE DUROID REPLACEMENTS M J Anderson, ESTL, AEA Technology Space, RD1/164 Birchwood Technology Park, Warrington, UK WA3 6AT Tel: +44 1925 253087 Fax: +44 1925 252415 e-mail:
BALL BEARING TESTS TO EVALUATE DUROID REPLACEMENTS M J Anderson, ESTL, AEA Technology Space, RD1/164 Birchwood Technology Park, Warrington, UK WA3 6AT Tel: +44 1925 253087 Fax: +44 1925 252415 e-mail:
The Multibody Systems Approach to Vehicle Dynamics
 The Multibody Systems Approach to Vehicle Dynamics A Short Course Lecture 4 Tyre Characteristics Professor Mike Blundell Phd, MSc, BSc (Hons), FIMechE, CEng Course Agenda Day 1 Lecture 1 Introduction to
The Multibody Systems Approach to Vehicle Dynamics A Short Course Lecture 4 Tyre Characteristics Professor Mike Blundell Phd, MSc, BSc (Hons), FIMechE, CEng Course Agenda Day 1 Lecture 1 Introduction to
HVE Vehicle Accelerometers: Validation and Sensitivity
 WP#-2015-3 HVE Vehicle Accelerometers: Validation and Sensitivity Kent W. McKee, M.E.Sc., P.Eng., Matthew Arbour, B.A.Sc., Roger Bortolin, P.Eng., and James R. Hrycay, M.A.Sc., P.Eng. HRYCAY Consulting
WP#-2015-3 HVE Vehicle Accelerometers: Validation and Sensitivity Kent W. McKee, M.E.Sc., P.Eng., Matthew Arbour, B.A.Sc., Roger Bortolin, P.Eng., and James R. Hrycay, M.A.Sc., P.Eng. HRYCAY Consulting
Robustness Analysis in Vehicle Ride Comfort
 Mercedes-Benz Research and Development India Robustness Analysis in Vehicle Ride Comfort Ragish Kalathil, Johannes Schaffner, Srikanth Kethu Date: 3 rd December, 2012 Mercedes-Benz Research and Development
Mercedes-Benz Research and Development India Robustness Analysis in Vehicle Ride Comfort Ragish Kalathil, Johannes Schaffner, Srikanth Kethu Date: 3 rd December, 2012 Mercedes-Benz Research and Development
WHITE PAPER Autonomous Driving A Bird s Eye View
 WHITE PAPER www.visteon.com Autonomous Driving A Bird s Eye View Autonomous Driving A Bird s Eye View How it all started? Over decades, assisted and autonomous driving has been envisioned as the future
WHITE PAPER www.visteon.com Autonomous Driving A Bird s Eye View Autonomous Driving A Bird s Eye View How it all started? Over decades, assisted and autonomous driving has been envisioned as the future
Comparison of Braking Performance by Electro-Hydraulic ABS and Motor Torque Control for In-wheel Electric Vehicle
 ES27 Barcelona, Spain, November 7-2, 23 Comparison of Braking Performance by Electro-Hydraulic ABS and Motor Torque Control for In-wheel Electric ehicle Sungyeon Ko, Chulho Song, Jeongman Park, Jiweon
ES27 Barcelona, Spain, November 7-2, 23 Comparison of Braking Performance by Electro-Hydraulic ABS and Motor Torque Control for In-wheel Electric ehicle Sungyeon Ko, Chulho Song, Jeongman Park, Jiweon
Development and validation of a vibration model for a complete vehicle
 Development and validation of a vibration for a complete vehicle J.W.L.H. Maas DCT 27.131 External Traineeship (MW Group) Supervisors: M.Sc. O. Handrick (MW Group) Dipl.-Ing. H. Schneeweiss (MW Group)
Development and validation of a vibration for a complete vehicle J.W.L.H. Maas DCT 27.131 External Traineeship (MW Group) Supervisors: M.Sc. O. Handrick (MW Group) Dipl.-Ing. H. Schneeweiss (MW Group)
Noise Reduction in Railway Traffic Noise Abatement at Source
 Noise Reduction in Railway Traffic Noise Abatement at Source Dipl.-Ing. Harald Willrich, FUCHS LUBRITECH GmbH, D-67685 Weilerbach 1 The Problem Many railway companies throughout the world are increasingly
Noise Reduction in Railway Traffic Noise Abatement at Source Dipl.-Ing. Harald Willrich, FUCHS LUBRITECH GmbH, D-67685 Weilerbach 1 The Problem Many railway companies throughout the world are increasingly
From the Lohner-Porsche to the 911 Turbo
 newsroom History Mar 14, 2018 From the Lohner-Porsche to the 911 Turbo One of the first cars to feature all-wheel drive was a Porsche, and it was a sports car: Ferdinand Porsche designed and built the
newsroom History Mar 14, 2018 From the Lohner-Porsche to the 911 Turbo One of the first cars to feature all-wheel drive was a Porsche, and it was a sports car: Ferdinand Porsche designed and built the
Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train
 Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train A.R.Mokate 1, R.R.Navthar 2 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, PDVVP COE, A. Nagar, Maharashtra, India 1 Assistance Professor,
Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train A.R.Mokate 1, R.R.Navthar 2 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, PDVVP COE, A. Nagar, Maharashtra, India 1 Assistance Professor,
Performance of Rear Differential Depending on Vehicle Driving Mode
 TECHNICAL REPORT Performance of Rear Differential Depending on Vehicle Driving Mode K. KAWAGUCHI A. UEMURA H. MATSUYAMA T. AIDA JTEKT has developed a tapered roller bearing with super-low-friction torque
TECHNICAL REPORT Performance of Rear Differential Depending on Vehicle Driving Mode K. KAWAGUCHI A. UEMURA H. MATSUYAMA T. AIDA JTEKT has developed a tapered roller bearing with super-low-friction torque
Active Suspensions For Tracked Vehicles
 Active Suspensions For Tracked Vehicles Y.G.Srinivasa, P. V. Manivannan 1, Rajesh K 2 and Sanjay goyal 2 Precision Engineering and Instrumentation Lab Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 1 PEIL
Active Suspensions For Tracked Vehicles Y.G.Srinivasa, P. V. Manivannan 1, Rajesh K 2 and Sanjay goyal 2 Precision Engineering and Instrumentation Lab Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 1 PEIL
Feature Article. Wheel Slip Simulation for Dynamic Road Load Simulation. Bryce Johnson. Application Reprint of Readout No. 38.
 Feature Article Feature Wheel Slip Simulation Article for Dynamic Road Load Simulation Application Application Reprint of Readout No. 38 Wheel Slip Simulation for Dynamic Road Load Simulation Bryce Johnson
Feature Article Feature Wheel Slip Simulation Article for Dynamic Road Load Simulation Application Application Reprint of Readout No. 38 Wheel Slip Simulation for Dynamic Road Load Simulation Bryce Johnson
BEHAVIOUR OF ELECTRIC FUSES IN AUTOMOTIVE SYSTEMS UNDER INTERMITTENT FAULT
 BEHAVIOUR OF ELECTRIC FUSES IN AUTOMOTIVE SYSTEMS UNDER INTERMITTENT FAULT B. Dilecce, F. Muzio Centro Ricerche FIAT, Orbassano (Torino), Italy A. Canova, M. Tartaglia Dipartimento Ingegneria Elettrica
BEHAVIOUR OF ELECTRIC FUSES IN AUTOMOTIVE SYSTEMS UNDER INTERMITTENT FAULT B. Dilecce, F. Muzio Centro Ricerche FIAT, Orbassano (Torino), Italy A. Canova, M. Tartaglia Dipartimento Ingegneria Elettrica
Chapter 2 Dynamic Analysis of a Heavy Vehicle Using Lumped Parameter Model
 Chapter 2 Dynamic Analysis of a Heavy Vehicle Using Lumped Parameter Model The interaction between a vehicle and the road is a very complicated dynamic process, which involves many fields such as vehicle
Chapter 2 Dynamic Analysis of a Heavy Vehicle Using Lumped Parameter Model The interaction between a vehicle and the road is a very complicated dynamic process, which involves many fields such as vehicle
Application of Steering Robot in the Test of Vehicle Dynamic Characteristics
 3rd International Conference on Mechatronics, Robotics and Automation (ICMRA 2) Application of Steering Robot in the Test of Vehicle Dynamic Characteristics Runqing Guo,a *, Zhaojuan Jiang 2,b and Lin
3rd International Conference on Mechatronics, Robotics and Automation (ICMRA 2) Application of Steering Robot in the Test of Vehicle Dynamic Characteristics Runqing Guo,a *, Zhaojuan Jiang 2,b and Lin
Gearbox Fault Detection
 Gearbox Fault Detection At the University of Iowa, detecting wind turbine gearbox faults based on vibration acceleration data provided by NREL is augmented by data mining techniques. By Andrew Kusiak and
Gearbox Fault Detection At the University of Iowa, detecting wind turbine gearbox faults based on vibration acceleration data provided by NREL is augmented by data mining techniques. By Andrew Kusiak and
Development of Seamless Shift for Formula One Car
 Development of Seamless Shift for Formula One Car Takashi YOSHIOKA* Katsumi KUBO* Takeshi UCHIYAMA* Ryo MATSUI* ABSTRACT Honda focused on gearbox development during its third Formula One era. The reduction
Development of Seamless Shift for Formula One Car Takashi YOSHIOKA* Katsumi KUBO* Takeshi UCHIYAMA* Ryo MATSUI* ABSTRACT Honda focused on gearbox development during its third Formula One era. The reduction
Steering Actuator for Autonomous Driving and Platooning *1
 TECHNICAL PAPER Steering Actuator for Autonomous Driving and Platooning *1 A. ISHIHARA Y. KUROUMARU M. NAKA The New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) is running a "Development
TECHNICAL PAPER Steering Actuator for Autonomous Driving and Platooning *1 A. ISHIHARA Y. KUROUMARU M. NAKA The New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) is running a "Development
FRICTION POTENTIAL AND SAFETY : PREDICTION OF
 BRITE EURAM PROJECT BRPR CT97 0461 2 ND INTERNATIONAL COLLOQUIUM ON VEHICLE TYRE ROAD INTERACTION FRICTION POTENTIAL AND SAFETY : PREDICTION OF HANDLING BEHAVIOR FLORENCE, FEBRUARY 23 rd 2001 Guidelines
BRITE EURAM PROJECT BRPR CT97 0461 2 ND INTERNATIONAL COLLOQUIUM ON VEHICLE TYRE ROAD INTERACTION FRICTION POTENTIAL AND SAFETY : PREDICTION OF HANDLING BEHAVIOR FLORENCE, FEBRUARY 23 rd 2001 Guidelines
ISSN: SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS OF PASSIVE SUSPENSION SYSTEM FOR DIFFERENT ROAD PROFILES WITH VARIABLE DAMPING AND STIFFNESS PARAMETERS S.
 Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Sciences www.jchps.com ISSN: 974-2115 SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS OF PASSIVE SUSPENSION SYSTEM FOR DIFFERENT ROAD PROFILES WITH VARIABLE DAMPING AND STIFFNESS PARAMETERS
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Sciences www.jchps.com ISSN: 974-2115 SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS OF PASSIVE SUSPENSION SYSTEM FOR DIFFERENT ROAD PROFILES WITH VARIABLE DAMPING AND STIFFNESS PARAMETERS
Identification of tyre lateral force characteristic from handling data and functional suspension model
 Identification of tyre lateral force characteristic from handling data and functional suspension model Marco Pesce, Isabella Camuffo Centro Ricerche Fiat Vehicle Dynamics & Fuel Economy Christian Girardin
Identification of tyre lateral force characteristic from handling data and functional suspension model Marco Pesce, Isabella Camuffo Centro Ricerche Fiat Vehicle Dynamics & Fuel Economy Christian Girardin
CONNECTED AUTOMATION HOW ABOUT SAFETY?
 CONNECTED AUTOMATION HOW ABOUT SAFETY? Bastiaan Krosse EVU Symposium, Putten, 9 th of September 2016 TNO IN FIGURES Founded in 1932 Centre for Applied Scientific Research Focused on innovation for 5 societal
CONNECTED AUTOMATION HOW ABOUT SAFETY? Bastiaan Krosse EVU Symposium, Putten, 9 th of September 2016 TNO IN FIGURES Founded in 1932 Centre for Applied Scientific Research Focused on innovation for 5 societal
Relative ride vibration of off-road vehicles with front-, rear- and both axles torsio-elastic suspension
 Relative ride vibration of off-road vehicles with front-, rear- and both axles torsio-elastic suspension Mu Chai 1, Subhash Rakheja 2, Wen Bin Shangguan 3 1, 2, 3 School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,
Relative ride vibration of off-road vehicles with front-, rear- and both axles torsio-elastic suspension Mu Chai 1, Subhash Rakheja 2, Wen Bin Shangguan 3 1, 2, 3 School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,
VALMONT MITIGATOR TR1
 VALMONT MITIGATOR TR1 Research Verification of the Valmont TR1 Damper Performance MITIGATOR TR1 VIBRATION DAMPER The Valmont TR1 damper has been specifically designed using vibration theory and innovative
VALMONT MITIGATOR TR1 Research Verification of the Valmont TR1 Damper Performance MITIGATOR TR1 VIBRATION DAMPER The Valmont TR1 damper has been specifically designed using vibration theory and innovative
Chapter 2 Analysis on Lock Problem in Frontal Collision for Mini Vehicle
 Chapter 2 Analysis on Lock Problem in Frontal Collision for Mini Vehicle Ce Song, Hong Zang and Jingru Bao Abstract To study the lock problem in the frontal collision test on a kind of mini vehicle s sliding
Chapter 2 Analysis on Lock Problem in Frontal Collision for Mini Vehicle Ce Song, Hong Zang and Jingru Bao Abstract To study the lock problem in the frontal collision test on a kind of mini vehicle s sliding
