Introduction. Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines. Involute profile. 7. Gears
|
|
|
- Baldwin Parks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction The kinematic function of gears is to transfer rotational motion from one shaft to another Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines 7. Gears Since these shafts may be parallel, perpendicular, or at any other angle with respect to each other, gears designed for any of these cases take different forms and have different names: spur, helical, bevel, worm, The fundamental requirement in most applications is that the coefficient of motion transformation (called the gear ratio) remains constant. What is needed to meet this requirement follows from Kennedy s theorem. The important point is that this requirement imposes a constraint on the suitable geometry of gear teeth profiles. Herein only one such profile is considered, called the involute profile. Involute profile An involute is generated by a tracing point on a cord as it is unwrapped from a circle (called a base circle) starting at T0 and ending at T1. It is seen that points A and B are the instantaneous centers of rotation of the cord. It follows that the cord is normal to the involute at each point. Consider two circular disks with centers at O2 and O3. To each disk a plate with an involute profile is attached. The involutes on these plates are different since they are generated for different base circles, starting at points D2 and D3. The two plates have a common point C and a common normal AB. This common normal is tangential to both base circles at any moment during the rotation while the two involutes are engaged. Line AB intersects the line of centers O2O3 at point P (pitch point). It then follows from Kennedy s theorem that this point is the instantaneous center for the two circular disks. And since this point remains the same while the disks rotate, it follows also that the kinematic ratio (called the transmission ratio) w2/w3 remains constant. Note that the common normal AB is called the line of action because the force is transmitted from one disk to another along this line.
2 The distance between any two similar points on the adjacent teeth along the pitch circle is called the circular pitch, and it is equal to where N is the number of teeth. Since circular pitch is equal for the two meshing gears, one finds that the transmission ratio can be expressed through the ratio of teeth numbers: The two gears are kinematically compatible only if they have the same circular pitch. Thus, to meet the requirement of interchangeability of gears produced by different manufacturers they should agree on a specific set of numbers for the circular pitches. In other words, the circular pitch should be standardized. In practice, instead of circular pitch, the ratio D/N is standardized. This ratio is called the module in the metric system. If the pitch radius of one of the gears becomes infinitely large, then its pitch circle, as well as the base and addendum circles, are transformed into lines (imagine unfolding an infinite cord with respect to an infinite base circle). Such a gear is called an involute rack.
3 Types Of Involute Gears The concept of an involute profile is used to design various types of gears having different functional and performance properties. Here, spur, helical, bevel, and worm gears will be briefly discussed. 1. Spur Gears This is the most common and most fundamental type of gear. The involute surface of the gear tooth is a cylindrical surface. 2. Helical Gears The helical gear is an extension of a spur gear to a more complex involute surface geometry. Since the involute helicoid is generated from the base cylinder, the two meshing helical gears will have the transmission ratio defined by the radii of these cylinders, and, correspondingly, by the radii of the pitch cylindrical surfaces, exactly in the same way as in the case of spur gears. Thus, kinematically, from the point of view of motion transfer, helical gears are not different from spur gears. They have, however, other properties that make them attractive. The basic one is the increase in the socalled contact ratio. Benefits of this are smaller contact stresses and smoother motion transfer. Also, a helical gear, due to its geometry, is stronger in withstanding bending forces. This leads to one of the drawbacks of helical gears, the generation of parasitic axial forces.
4 3. Bevel Gears The spur gears transmit motion only between the parallel shafts, so that the gear planes of rotation are parallel. The helical gears can be used to transmit motion between the shafts that can be either parallel or crossed, and thus the gear planes of rotation can vary from being parallel to perpendicular, but their axes do not intersect. The bevel gears transmit motion between the shafts whose axes intersect while their planes of rotation may vary. Instead of a cylindrical surface, as in the case of spur and helical gears, serving as a base for an involute surface, in this case the base surface is conical. The corresponding pitch surface is also conical and is called the pitch cone. From the equivalency of bevel and spur gears it follows that the transmission ratio for a pair of bevel gears is given by: 4. Worm Gears Worm gears are usually used when there is a need to transfer motion between perpendicular shafts and a large transmission ratio, from 10:1 to 15:1, is required. The worm has a screw like thread and is always a driver. The teeth profiles are not involutes (since an involute profile for a tooth gives a point contact with the gear). To ensure a line contact of the interfacing teeth, they are cut using the same hob.
5 for the shafts at 90 the axial pitch for the worm is equal to the circular pitch for the gear. Therefore, If N2 is the number of threads (teeth) on the worm and N3 is the number of teeth on the worm gear, then, the transmission ratio for the worm worm gear pair is defined as: Parallel-Axis Gear Trains Very often a single gear pair transferring motion between two parallel shafts cannot meet the needed transmission ratio requirement. For example, if this requirement is 10:1, then the diameter of the gear must be 10 times larger then the diameter of the pinion. This is usually unacceptable from the design specifications concerning product size. The solution is achieved by arranging a series of gear pairs. Such series is called a gear train. A train may comprise different type of gears: spur, helical, bevel, and worm. The gears in a train are functionally in series with each other. If a system comprises a few trains, they are functionally in parallel with each other. Usually a system of gears arranged physically in one case (box), whether in series or in parallel, is called a transmission box. In the below figure gears 3 and 4 can be shifted along the shaft so that the following trains are obtained: First: Second: Third: Train Transmission Ratio It is customary to define the transmission ratio of a pair as the ratio of driven to driving angular velocities. It is known that if the gears have external meshing, the sense of rotation changes to the opposite, while for gears with internal meshing it remains the same. Thus, for any pair in the train with external meshing the transmission ratio is And thus the train transmission ratio is An example of a transmission box with parallel gear trains where K is the number of pairs. It is clear that for gears with external meshing, if K is even, the sense of the rotation of the output is the same as that of the input, and, if K is odd, the sense of rotation changes to the opposite.
6 Substituting the first equation in the second one, the train transmission ratio is obtained as a ratio of angular velocities of last and first gears in the train, i.e., Consider the transmission ratio of the first train in the sample automobile gearbox. Recalling that the transmission ratio of a gear pair can be expressed through the ratio of gear teeth numbers, one can write Similarly, the transmission ratios of the second and third trains are Design Considerations In designing a gear box, the input information is the required transmission ratios for each speed. Thus, the problem is, given transmission ratios (ei, eii, ), find gears with teeth numbers that will meet other transmission box design requirements, such as, for example, specific center distances between the shafts and the teeth strength, among others. In the previous example, gear pairs 2 5, 3 6, and 4 7 are mounted on two parallel shafts. This fact gives additional equations in the form of the requirement that the center distance for each pair be the same. It is worth mentioning that the number of teeth for each gear, must be an integer. Considering this fact and other limitations, the process of gear train (box) design is an iterative one. Planetary Gear Trains An elementary planetary gear train is shown in the below figure. It comprises two gears, 2 and 4, each mounted on its own shaft. The new element here is the link 3 connecting these shafts and able to rotate around the fixed axis O1. This system has two degrees of freedom, which means that if only the input velocity is given, the motion of the two other elements cannot be determined. Input gear 2 is called the sun. (or central) gear, gear 4 is called the planetary (or epicyclic) gear, and link 3 is called the planet carrier (or crank arm).
7 Planetary gear trains allow obtaining high transmission ratios in a compact design, which makes them suitable for applications in, for example, machine tools, hoists, and automatic transmissions. An example of a simple planetary gear box is the following figure, where in addition to the elements in the previous figure, an additional annular gear 5 is added, so that the planetary gear 4 is now interfacing both the sun and the annular gears. Note that the annular gear is fixed. The number of degrees of freedom of this system is 1, which means that for a given input there is a unique output. Transmission Ratio In Planetary Trains Suppose that arm 3 rotates with angular velocity ω3. Then, if an observer is sitting on this arm, for this observer the rotation of gears 2 and 4 will not be different from that for a parallel fixed-shaft system, and the corresponding transmission ratio will be ω4/ ω2. One realizes that an observer on the arm sees rotation in a moving (rotating) coordinate system. Now if the observer is standing on the frame, then the observer will see that the arm rotates with ω3. The question is what will be the angular velocities of gears 2 and 4 with respect to the observer on a frame. The answer is given by a general rule for summation of angular velocities in the case when a body rotates with respect to its own axis with velocity ω1, while the axis itself rotates with respect to another axis with the velocity ω. In the case when the two axes are parallel, the total angular velocity equals the algebraic sum of velocities of two rotations. Thus, the total angular velocity will be: The above rule is directly applicable to the planetary gear trains. Indeed, the axes of gears 2 and 4 are parallel and one of them rotates with respect to the other with ω3. Now, the transmission ratio in a coordinate system rotating with ω3 is known. It is equal to e42 = N2/N4. Thus, if one applies a counter-rotation with ω3 to the entire system, then the gear velocities (according to the rule of summation) will be and, and link 3 becomes fixed. Thus, the transmission ratio is given by The above equation confirms that the system shown in the first figure has two degrees of freedom. Indeed, if only ω2 is given, two unknown velocities remain, ω3 and ω4, while the gears are defined. The example of the first figure described by above equation is equivalent to a one-pair system in conventional gear trains. In this respect, the system in the second figure is equivalent to a two-pair system where the pairs are functionally in series with each other. Thus, in this case there are two transmission ratios: first, from the sun gear 2 to the planetary gear 4, which is described by the above equation, and, second, from the planetary gear 4 to the annular gear 5. The latter is equal to (in a rotating coordinate system): If ω5 = 0 (annular gear is fixed) and ω2 is known, then ω3 and ω4 are found from the first and the second equations. And, finally, it should be noted that the planetary gear plays the role of an idle gear in the second figure. Indeed, the total transmission ratio for a system in series is equal to the product of transmission ratios of its subsystems. In the case of the second figure the total transmission ratio is the product of the first and the second equations. The result is
8 Differential Differentials are planetary trains made out of bevel gears and having two degrees of freedom. An example of an automotive differential is shown in the following figure. The rotation from the engine is transferred through bevel gears 2 and 3 to the system of bevel gears 4, 5, and 6. Gears 4 are mounted on the carrier and are the planetary gears, whereas gears 5 and 6 are two independent sun gears. The transmission ratio from 2 to 3 is independent from the rest of the system (in fact, gear 3 could be considered an input gear with known angular velocity). Thus, the transmission through system will be considered. The important distinction of the bevel planetary mechanism is that the rule of summation of velocities for the planetary and sun gears is not applicable in the sense discussed above since in this case the axes of gears 5 and 4 and gears 6 and 4 are not parallel. Thus, if gear 5 rotates clockwise, when viewed along its axis from the right, gear 6 will be rotating counterclockwise from the same point of view (next figure). However, the rotation of the gears 3 and 5 and gears 3 and 6 is around parallel axes, and so the rule of summation discussed for planar trains is applicable. Thus, if one applies a counter-rotation ω3 to the entire system, one will have the system shown in the following figure in which gear 5 rotates with angular velocity ω5- ω3 and gear 6 with ω6- ω3. The transmission ratio between gears 5 and 6 in a rotating coordinate system is equal to One equation with two unknowns, ω5 and ω6, is obtained. Thus, the system has two degrees of freedom. In practical terms this means that the left axle can rotate independently of the right axle. From the above equation it follows that The latter relationship means that while ω3 remains constant, the values of ω5 and ω6 may change. In the automotive applications w5 and ω6 are the angular velocities of two wheels, and w3 can be considered the angular velocity of the engine. So when the vehicle turns, the angular velocities ω5 and ω6 become unequal, but it does not affect the engine speed. In other words, the engine maintains its speed during turns. Note also that when the vehicle moves straight, ω5 = ω6, the planetary gear 4 does not rotate because ω5 = ω6 = ω3. Otherwise, the planetary gear will be rotating, allowing relative motion between gears 5 and 6. One more comment concerning the latter equation should be made. In the case of an inverse mechanism, when gears 5 and 6 provide input, while gear 3 is the output, the mechanism performs an operation of summation. If the sign of one of the rotations changes, then it will show the result of subtraction. This property of the differential (the reason it is so named) is used in mechanical calculators.
CH#13 Gears-General. Drive and Driven Gears 3/13/2018
 CH#13 Gears-General A toothed wheel that engages another toothed mechanism in order to change the speed or direction of transmitted motion The gear set transmits rotary motion and force. Gears are used
CH#13 Gears-General A toothed wheel that engages another toothed mechanism in order to change the speed or direction of transmitted motion The gear set transmits rotary motion and force. Gears are used
GEAR CONTENTS POWER TRANSMISSION GEAR TYPES OF GEARS NOMENCLATURE APPLICATIONS OF GEARS VELOCITY RATIO GEAR TRAINS EXAMPLE PROBLEMS AND QUESTIONS
 GEAR CONTENTS POWER TRANSMISSION GEAR TYPES OF GEARS NOMENCLATURE APPLICATIONS OF GEARS VELOCITY RATIO GEAR TRAINS EXAMPLE PROBLEMS AND QUESTIONS GEAR.. Power transmission is the movement of energy from
GEAR CONTENTS POWER TRANSMISSION GEAR TYPES OF GEARS NOMENCLATURE APPLICATIONS OF GEARS VELOCITY RATIO GEAR TRAINS EXAMPLE PROBLEMS AND QUESTIONS GEAR.. Power transmission is the movement of energy from
Chapter seven. Gears. Laith Batarseh
 Chapter seven Gears Laith Batarseh Gears are very important in power transmission between a drive rotor and driven rotor What are the functions of gears? - Transmit motion and torque (power) between shafts
Chapter seven Gears Laith Batarseh Gears are very important in power transmission between a drive rotor and driven rotor What are the functions of gears? - Transmit motion and torque (power) between shafts
What are the functions of gears? What is gear?
 8//0 hapter seven Laith atarseh are very important in power transmission between a drive rotor and driven rotor What are the functions of gears? - Transmit motion and torque (power) between shafts - Maintain
8//0 hapter seven Laith atarseh are very important in power transmission between a drive rotor and driven rotor What are the functions of gears? - Transmit motion and torque (power) between shafts - Maintain
Part VII: Gear Systems: Analysis
 Part VII: Gear Systems: Analysis This section will review standard gear systems and will provide the basic tools to perform analysis on these systems. The areas covered in this section are: 1) Gears 101:
Part VII: Gear Systems: Analysis This section will review standard gear systems and will provide the basic tools to perform analysis on these systems. The areas covered in this section are: 1) Gears 101:
(POWER TRANSMISSION Methods)
 UNIT-5 (POWER TRANSMISSION Methods) It is a method by which you can transfer cyclic motion from one place to another or one pulley to another pulley. The ways by which we can transfer cyclic motion are:-
UNIT-5 (POWER TRANSMISSION Methods) It is a method by which you can transfer cyclic motion from one place to another or one pulley to another pulley. The ways by which we can transfer cyclic motion are:-
11/23/2013. Chapter 13. Gear Trains. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhiba, PE
 Chapter 13 Gear Trains 1 2 13.2. Types of Gear Trains 1. Simple gear train 2. Compound gear train 3. Reverted gear train 4. Epicyclic gear train: axes of shafts on which the gears are mounted may move
Chapter 13 Gear Trains 1 2 13.2. Types of Gear Trains 1. Simple gear train 2. Compound gear train 3. Reverted gear train 4. Epicyclic gear train: axes of shafts on which the gears are mounted may move
Chapter 3. Transmission Components
 Chapter 3. Transmission Components The difference between machine design and structure design An important design problem in a mechanical system is how to transmit and convert power to achieve required
Chapter 3. Transmission Components The difference between machine design and structure design An important design problem in a mechanical system is how to transmit and convert power to achieve required
11. GEAR TRANSMISSIONS
 11. GEAR TRANSMISSIONS 11.1. GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS Gears are one of the most important elements used in machinery. There are few mechanical devices that do not have the need to transmit power and motion
11. GEAR TRANSMISSIONS 11.1. GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS Gears are one of the most important elements used in machinery. There are few mechanical devices that do not have the need to transmit power and motion
KINEMATICS OF MACHINARY UBMC302 QUESTION BANK UNIT-I BASICS OF MECHANISMS PART-A
 KINEMATICS OF MACHINARY UBMC302 QUESTION BANK UNIT-I BASICS OF MECHANISMS PART-A 1. Define the term Kinematic link. 2. Classify kinematic links. 3. What is Mechanism? 4. Define the terms Kinematic pair.
KINEMATICS OF MACHINARY UBMC302 QUESTION BANK UNIT-I BASICS OF MECHANISMS PART-A 1. Define the term Kinematic link. 2. Classify kinematic links. 3. What is Mechanism? 4. Define the terms Kinematic pair.
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad
 St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: Kinematics of Machines Class : MECH-II Group A (Short Answer Questions) UNIT-I 1 Define link, kinematic pair. 2 Define mechanism
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: Kinematics of Machines Class : MECH-II Group A (Short Answer Questions) UNIT-I 1 Define link, kinematic pair. 2 Define mechanism
Catalog Q Conversion For those wishing to ease themselves into working with metric gears
 1.3.4 Conversion For those wishing to ease themselves into working with metric gears by looking at them in terms of familiar inch gearing relationships and mathematics, Table 1-5 is offered as a means
1.3.4 Conversion For those wishing to ease themselves into working with metric gears by looking at them in terms of familiar inch gearing relationships and mathematics, Table 1-5 is offered as a means
ME6401 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY UNIT- I (Basics of Mechanism)
 ME6401 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY UNIT- I (Basics of Mechanism) 1) Define resistant body. 2) Define Link or Element 3) Differentiate Machine and Structure 4) Define Kinematic Pair. 5) Define Kinematic Chain.
ME6401 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY UNIT- I (Basics of Mechanism) 1) Define resistant body. 2) Define Link or Element 3) Differentiate Machine and Structure 4) Define Kinematic Pair. 5) Define Kinematic Chain.
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05310304 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2007 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile Engineering)
Code No: R05310304 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2007 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile Engineering)
GEARING. Theory of. Stephen. Kinetics, Geometry, and Synthesis. P. Radzevich. /Ov CRC Press yc*** J Taylor& Francis Croup Boca Raton
 Theory of GEARING Kinetics, Geometry, and Synthesis Stephen P. Radzevich /Ov CRC Press yc*** J Taylor& Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an
Theory of GEARING Kinetics, Geometry, and Synthesis Stephen P. Radzevich /Ov CRC Press yc*** J Taylor& Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an
Bevel Gears. Fig.(1) Bevel gears
 Bevel Gears Bevel gears are cut on conical blanks to be used to transmit motion between intersecting shafts. The simplest bevel gear type is the straighttooth bevel gear or straight bevel gear as can be
Bevel Gears Bevel gears are cut on conical blanks to be used to transmit motion between intersecting shafts. The simplest bevel gear type is the straighttooth bevel gear or straight bevel gear as can be
Instantaneous Centre Method
 Instantaneous Centre Method The combined motion of rotation and translation of the link AB may be assumed to be a motion of pure rotation about some centre I, known as the instantaneous centre of rotation.
Instantaneous Centre Method The combined motion of rotation and translation of the link AB may be assumed to be a motion of pure rotation about some centre I, known as the instantaneous centre of rotation.
Simple Gears and Transmission
 Simple Gears and Transmission Simple Gears and Transmission page: of 4 How can transmissions be designed so that they provide the force, speed and direction required and how efficient will the design be?
Simple Gears and Transmission Simple Gears and Transmission page: of 4 How can transmissions be designed so that they provide the force, speed and direction required and how efficient will the design be?
Effect of Geometry Factor I & J Factor Multipliers in the performance of Helical Gears
 Effect of Geometry Factor I & J Factor Multipliers in the performance of Helical Gears 1 Amit D. Modi, 2 Manan B. Raval, 1 Lecturer, 2 Lecturer, 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, 2 Department of
Effect of Geometry Factor I & J Factor Multipliers in the performance of Helical Gears 1 Amit D. Modi, 2 Manan B. Raval, 1 Lecturer, 2 Lecturer, 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, 2 Department of
Gear Tooth Geometry - This is determined primarily by pitch, depth and pressure angle
 Gear Tooth Geometry - This is determined primarily by pitch, depth and pressure angle Addendum: The radial distance between the top land and the pitch circle. Addendum Circle: The circle defining the outer
Gear Tooth Geometry - This is determined primarily by pitch, depth and pressure angle Addendum: The radial distance between the top land and the pitch circle. Addendum Circle: The circle defining the outer
2. a) What is pantograph? What are its uses? b) Prove that the peaucellier mechanism generates a straight-line motion. (5M+10M)
 Code No: R22032 R10 SET - 1 1. a) Define the following terms? i) Link ii) Kinematic pair iii) Degrees of freedom b) What are the inversions of double slider crank chain? Describe any two with neat sketches.
Code No: R22032 R10 SET - 1 1. a) Define the following terms? i) Link ii) Kinematic pair iii) Degrees of freedom b) What are the inversions of double slider crank chain? Describe any two with neat sketches.
Copyright Notice. Small Motor, Gearmotor and Control Handbook Copyright Bodine Electric Company. All rights reserved.
 Copyright Notice Small Motor, Gearmotor and Control Handbook Copyright 1993-2003 Bodine Electric Company. All rights reserved. Unauthorized duplication, distribution, or modification of this publication,
Copyright Notice Small Motor, Gearmotor and Control Handbook Copyright 1993-2003 Bodine Electric Company. All rights reserved. Unauthorized duplication, distribution, or modification of this publication,
428 l Theory of Machines
 428 l heory of Machines 13 Fea eatur tures es 1. Introduction. 2. ypes of Gear rains. 3. Simple Gear rain. 4. ompound Gear rain. 5. Design of Spur Gears. 6. Reverted Gear rain. 7. picyclic Gear rain. 8.
428 l heory of Machines 13 Fea eatur tures es 1. Introduction. 2. ypes of Gear rains. 3. Simple Gear rain. 4. ompound Gear rain. 5. Design of Spur Gears. 6. Reverted Gear rain. 7. picyclic Gear rain. 8.
12/6/2013 9:09 PM. Chapter 13. Gears General. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 13 Gears General 1 2 Chapter Outline 1. Types of Gears 2. Nomenclature 3. Conjugate Action 4. Involute Properties 5. Fundamentals 6. Contact Ratio 7. Interference 8. The Forming of Gear Teeth 9.
Chapter 13 Gears General 1 2 Chapter Outline 1. Types of Gears 2. Nomenclature 3. Conjugate Action 4. Involute Properties 5. Fundamentals 6. Contact Ratio 7. Interference 8. The Forming of Gear Teeth 9.
1/2/2015 2:04 PM. Chapter 13. Gears General. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 13 Gears General 1 2 Chapter Outline 1. Types of Gears 2. Nomenclature 3. Conjugate Action 4. Involute Properties 5. Fundamentals 6. Contact Ratio 7. Interference 8. The Forming of Gear Teeth 9.
Chapter 13 Gears General 1 2 Chapter Outline 1. Types of Gears 2. Nomenclature 3. Conjugate Action 4. Involute Properties 5. Fundamentals 6. Contact Ratio 7. Interference 8. The Forming of Gear Teeth 9.
Chapter 8 Kinematics of Gears
 Chapter 8 Kinematics of Gears Gears! Gears are most often used in transmissions to convert an electric motor s high speed and low torque to a shaft s requirements for low speed high torque: Speed is easy
Chapter 8 Kinematics of Gears Gears! Gears are most often used in transmissions to convert an electric motor s high speed and low torque to a shaft s requirements for low speed high torque: Speed is easy
Basic Fundamentals of Gear Drives
 Basic Fundamentals of Gear Drives Course No: M06-031 Credit: 6 PDH A. Bhatia Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877) 322-4774
Basic Fundamentals of Gear Drives Course No: M06-031 Credit: 6 PDH A. Bhatia Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877) 322-4774
Simple Gears and Transmission
 Simple Gears and Transmission Contents How can transmissions be designed so that they provide the force, speed and direction required and how efficient will the design be? Initial Problem Statement 2 Narrative
Simple Gears and Transmission Contents How can transmissions be designed so that they provide the force, speed and direction required and how efficient will the design be? Initial Problem Statement 2 Narrative
1. (a) Discuss various types of Kinematic links with examples. (b) Explain different types of constrained motions with examples.
 Code No: RR310304 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, February 2007 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics and Production Engineering) Time: 3
Code No: RR310304 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, February 2007 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics and Production Engineering) Time: 3
Lecture (7) on. Gear Measurement. By Dr. Emad M. Saad. Industrial Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering. Fayoum University.
 1 Lecture (7) on Gear Measurement Fayoum University By Dr. Emad M. Saad Industrial Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Engineering Dept. 2015-2016
1 Lecture (7) on Gear Measurement Fayoum University By Dr. Emad M. Saad Industrial Engineering Dept. Faculty of Engineering Fayoum University Faculty of Engineering Industrial Engineering Dept. 2015-2016
CHENDU COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK IV SEMESTER
 CHENDU COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK IV SEMESTER Sub Code: ME 6401 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY UNIT-I PART-A 1. Sketch and define Transmission angle
CHENDU COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK IV SEMESTER Sub Code: ME 6401 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY UNIT-I PART-A 1. Sketch and define Transmission angle
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6401- KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY QUESTION BANK Part-A Unit 1-BASICS OF MECHANISMS 1. Define degrees of freedom. 2. What is meant by spatial mechanism? 3. Classify the
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6401- KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY QUESTION BANK Part-A Unit 1-BASICS OF MECHANISMS 1. Define degrees of freedom. 2. What is meant by spatial mechanism? 3. Classify the
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6401- KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY QUESTION BANK PART-A Unit 1-BASICS OF MECHANISMS 1. Define degrees of freedom. BT1 2. Describe spatial
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6401- KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY QUESTION BANK PART-A Unit 1-BASICS OF MECHANISMS 1. Define degrees of freedom. BT1 2. Describe spatial
1.6 Features of common gears
 1.6 Features of common gears Chapter 1.2 covered briefly on types of gear. The main gear features are explained here. Helical gear Helical gear has characteristics of transferability of larger load, less
1.6 Features of common gears Chapter 1.2 covered briefly on types of gear. The main gear features are explained here. Helical gear Helical gear has characteristics of transferability of larger load, less
Unit IV GEARS. Gallery
 Gallery Components of a typical, four stroke cycle, DOHC piston engine. (E) Exhaust camshaft, (I) Intake camshaft, (S) Spark plug, (V) Valves, (P) Piston, (R) Connecting rod, (C) Crankshaft, (W) Water
Gallery Components of a typical, four stroke cycle, DOHC piston engine. (E) Exhaust camshaft, (I) Intake camshaft, (S) Spark plug, (V) Valves, (P) Piston, (R) Connecting rod, (C) Crankshaft, (W) Water
Different types of gears. Spur gears. Idler gears. Worm gears. Bevel gears. Belts & Pulleys
 GEARS Robot Gears By using different gear diameters, you can exchange between rotational (or translation) velocity and torque. by looking at the motor datasheet you can determine the output velocity and
GEARS Robot Gears By using different gear diameters, you can exchange between rotational (or translation) velocity and torque. by looking at the motor datasheet you can determine the output velocity and
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Subject code: ME6601 Subject Name: DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS UNIT-I DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR FLEXIBLE ELEMENTS 1. What is the effect of centre distance
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Subject code: ME6601 Subject Name: DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS UNIT-I DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS FOR FLEXIBLE ELEMENTS 1. What is the effect of centre distance
SECTION 4 SPUR GEAR CALCULATIONS
 Function of α, or invα, is known as involute function. Involute function is very important in gear design. Involute function values can be obtained from appropriate tables. With the 3.1 Contact Ratio center
Function of α, or invα, is known as involute function. Involute function is very important in gear design. Involute function values can be obtained from appropriate tables. With the 3.1 Contact Ratio center
UNIT -I. Ans: They are specified by the no. of strands & the no. of wires in each strand.
 VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, THOTTIAM, NAMAKKAL-621215. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SIXTH SEMESTER / III YEAR ME6601 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEM (Regulation-2013) UNIT
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, THOTTIAM, NAMAKKAL-621215. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SIXTH SEMESTER / III YEAR ME6601 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEM (Regulation-2013) UNIT
Spur Gears. Helical Gears. Bevel Gears. Worm Gears
 Spur s General: Spur gears are the most commonly used gear type. They are characterized by teeth which are perpendicular to the face of the gear. Spur gears are by far the most commonly available, and
Spur s General: Spur gears are the most commonly used gear type. They are characterized by teeth which are perpendicular to the face of the gear. Spur gears are by far the most commonly available, and
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub Code/Name: ME 1352 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS Year/Sem: III / VI UNIT-I (Design of transmission systems for flexible
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub Code/Name: ME 1352 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS Year/Sem: III / VI UNIT-I (Design of transmission systems for flexible
Mechanism Feasibility Design Task
 Mechanism Feasibility Design Task Dr. James Gopsill 1 Contents 1. Last Week 2. Types of Gear 3. Gear Definitions 4. Gear Forces 5. Multi-Stage Gearbox Example 6. Gearbox Design Report Section 7. This Weeks
Mechanism Feasibility Design Task Dr. James Gopsill 1 Contents 1. Last Week 2. Types of Gear 3. Gear Definitions 4. Gear Forces 5. Multi-Stage Gearbox Example 6. Gearbox Design Report Section 7. This Weeks
Session #3 Gears: Force Transmission & Gear Trains. Dan Frey
 Session #3 Gears: Force Transmission & Gear Trains Dan Frey Today s Agenda Pass out second reading packet Pass out loaner laptops Introduce project teams Gears Force Transmission Gear Trains Survey HW
Session #3 Gears: Force Transmission & Gear Trains Dan Frey Today s Agenda Pass out second reading packet Pass out loaner laptops Introduce project teams Gears Force Transmission Gear Trains Survey HW
GEARBOXES. Gearboxes. Gearboxes. Gearbox is a mechanical device utilized to increase the output torque or change
 GEARBOXES Gearboxes Gearboxes Gearbox is a mechanical device utilized to increase the output torque or change the speed of a motor. The motor's shaft is attached to one end of the gearbox and through the
GEARBOXES Gearboxes Gearboxes Gearbox is a mechanical device utilized to increase the output torque or change the speed of a motor. The motor's shaft is attached to one end of the gearbox and through the
ME6601 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS
 SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
Graphical representation of a gear
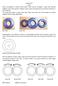 Homework 4 Gears Gears are designed to transmit rotary motion. Often they are arranged in a gear train (meshed together). Gear trains provide a change in speed, torque (turning force) and direction (clockwise
Homework 4 Gears Gears are designed to transmit rotary motion. Often they are arranged in a gear train (meshed together). Gear trains provide a change in speed, torque (turning force) and direction (clockwise
Subject with Code: Kinematic of Machinery (16ME304)Course & Branch: B. Tech - ME Year &Sem : II-B. Tech &I-Sem Regulation: R16
 SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING &TECHNOLOGY:: PUTTUR (Approved by AICTE, New Delhi & Affiliated to JNTUA, Anantapuramu) (Accredited by NBA & Accredited by NAAC with A Grade) (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified
SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING &TECHNOLOGY:: PUTTUR (Approved by AICTE, New Delhi & Affiliated to JNTUA, Anantapuramu) (Accredited by NBA & Accredited by NAAC with A Grade) (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified
INVOLUTE SPIRAL FACE COUPLINGS AND GEARS: DESIGN APPROACH AND MANUFACTURING TECHNIQUE
 УДК 621.9.015 Dr. Alexander L. Kapelevich, Stephen D. Korosec 38 INVOLUTE SPIRAL FACE COUPLINGS AND GEARS: DESIGN APPROACH AND MANUFACTURING TECHNIQUE This paper presents spiral face gears with an involute
УДК 621.9.015 Dr. Alexander L. Kapelevich, Stephen D. Korosec 38 INVOLUTE SPIRAL FACE COUPLINGS AND GEARS: DESIGN APPROACH AND MANUFACTURING TECHNIQUE This paper presents spiral face gears with an involute
Paper Number: DETC
 Proceedings of the th ASME International Power Transmission and Gearing Conference DETC20 August 28-3, 20, Washington, DC, USA Paper Number: DETC20-48494 THE DYNAMIC SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS OF A CYCLOIDAL
Proceedings of the th ASME International Power Transmission and Gearing Conference DETC20 August 28-3, 20, Washington, DC, USA Paper Number: DETC20-48494 THE DYNAMIC SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS OF A CYCLOIDAL
CHAPTER 5 PREVENTION OF TOOTH DAMAGE IN HELICAL GEAR BY PROFILE MODIFICATION
 90 CHAPTER 5 PREVENTION OF TOOTH DAMAGE IN HELICAL GEAR BY PROFILE MODIFICATION 5.1 INTRODUCTION In any gear drive the absolute and the relative transmission error variations normally increases with an
90 CHAPTER 5 PREVENTION OF TOOTH DAMAGE IN HELICAL GEAR BY PROFILE MODIFICATION 5.1 INTRODUCTION In any gear drive the absolute and the relative transmission error variations normally increases with an
Bevel Gears n A Textbook of Machine Design
 080 n A Textbook of Machine Design C H A P T E R 30 Bevel Gears. Introduction.. Classification of Bevel Gears. 3. Terms used in Bevel Gears. 4. Determination of Pitch Angle for Bevel Gears. 5. Proportions
080 n A Textbook of Machine Design C H A P T E R 30 Bevel Gears. Introduction.. Classification of Bevel Gears. 3. Terms used in Bevel Gears. 4. Determination of Pitch Angle for Bevel Gears. 5. Proportions
Lecture 13 BEVEL GEARS
 Lecture 13 BEVEL GEARS CONTENTS 1. Bevel gear geometry and terminology 2. Bevel gear force analysis 3. Bending stress analysis 4. Contact stress analysis 5. Permissible bending fatigue stress 6. Permissible
Lecture 13 BEVEL GEARS CONTENTS 1. Bevel gear geometry and terminology 2. Bevel gear force analysis 3. Bending stress analysis 4. Contact stress analysis 5. Permissible bending fatigue stress 6. Permissible
Theory of Machines. CH-1: Fundamentals and type of Mechanisms
 CH-1: Fundamentals and type of Mechanisms 1. Define kinematic link and kinematic chain. 2. Enlist the types of constrained motion. Draw a label sketch of any one. 3. Define (1) Mechanism (2) Inversion
CH-1: Fundamentals and type of Mechanisms 1. Define kinematic link and kinematic chain. 2. Enlist the types of constrained motion. Draw a label sketch of any one. 3. Define (1) Mechanism (2) Inversion
Engineering Information
 Engineering nformation Gear Nomenclature ADDENDUM (a) is the height by which a tooth projects beyond the pitch circle or pitch line. BASE DAMETER (D b ) is the diameter of the base cylinder from which
Engineering nformation Gear Nomenclature ADDENDUM (a) is the height by which a tooth projects beyond the pitch circle or pitch line. BASE DAMETER (D b ) is the diameter of the base cylinder from which
MECHANISMS. AUTHORS: Santiago Camblor y Pablo Rivas INDEX
 MECHANISMS AUTHORS: Santiago Camblor y Pablo Rivas INDEX 1 INTRODUCTION 2 LEVER 3 PULLEYS 4 BELT AND PULLEY SYSTEM 5 GEARS 6 GEARS WITH CHAIN 7 WORM GEAR 8 RACK AND PINION 9 SCREW AND NUT 10 CAM 11 ECCENTRIC
MECHANISMS AUTHORS: Santiago Camblor y Pablo Rivas INDEX 1 INTRODUCTION 2 LEVER 3 PULLEYS 4 BELT AND PULLEY SYSTEM 5 GEARS 6 GEARS WITH CHAIN 7 WORM GEAR 8 RACK AND PINION 9 SCREW AND NUT 10 CAM 11 ECCENTRIC
A Study on Noncircular Gears with Non-Uniform Teeth
 A Study on Noncircular Gears with Non-Uniform Teeth Kazushi Kumagai* 1 and Tetsuya Oizumi* *1 Department of Infomation System, Sendai National College of Technology 4-16-1 Ayashi-Chuo, Aoba-ku, Sendai
A Study on Noncircular Gears with Non-Uniform Teeth Kazushi Kumagai* 1 and Tetsuya Oizumi* *1 Department of Infomation System, Sendai National College of Technology 4-16-1 Ayashi-Chuo, Aoba-ku, Sendai
Title Objective Scope LITERATURE REVIEW
 Title Objective Scope : Car Gear System : Investigate the force conversion in the gear system : Low rev engine match with five speed manual transmission Low rev engine match with four speed-auto transmission
Title Objective Scope : Car Gear System : Investigate the force conversion in the gear system : Low rev engine match with five speed manual transmission Low rev engine match with four speed-auto transmission
FIRSTRANKER. 2. (a) Distinguish (by neat sketches) betweenpeaucellier mechanism and Hart mechanism.
 Code No: 07A51404 R07 Set No. 2 IIIB.Tech I Semester Examinations,May 2011 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY Mechatronics Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks 1.
Code No: 07A51404 R07 Set No. 2 IIIB.Tech I Semester Examinations,May 2011 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY Mechatronics Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks 1.
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05222106 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Supplimentary Examinations, Aug/Sep 2007 MECHANISMS AND MECHANICAL DESIGN (Aeronautical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Code No: R05222106 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Supplimentary Examinations, Aug/Sep 2007 MECHANISMS AND MECHANICAL DESIGN (Aeronautical Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
ME3200Practice Questions
 ME3200Practice Questions 5.(15 pts) esign an active low-pass filter with a gain of 5 and a time constant of 50 msec. Use realistic values as were used in lab. 6. (8 pts) A pressure sensor is made by gluing
ME3200Practice Questions 5.(15 pts) esign an active low-pass filter with a gain of 5 and a time constant of 50 msec. Use realistic values as were used in lab. 6. (8 pts) A pressure sensor is made by gluing
FIRSTRANKER. Code No: R R09 Set No. 2
 Code No: R09220302 R09 Set No. 2 IIB.Tech IISemester Examinations,APRIL 2011 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering, Automobile Engineering Time:
Code No: R09220302 R09 Set No. 2 IIB.Tech IISemester Examinations,APRIL 2011 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering, Automobile Engineering Time:
Program Internal Gear Set Profile Shift Coefficients With Zero Backlash Introduction
 Program 60-107 Internal Gear Set Profile Shift Coefficients With Zero Backlash Introduction The purpose of this model is to provide data for a gear set when the tooth thickness and/or the center distance
Program 60-107 Internal Gear Set Profile Shift Coefficients With Zero Backlash Introduction The purpose of this model is to provide data for a gear set when the tooth thickness and/or the center distance
Design of Helical Gear and Analysis on Gear Tooth
 Design of Helical Gear and Analysis on Gear Tooth Indrale Ratnadeep Ramesh Rao M.Tech Student ABSTRACT Gears are mainly used to transmit the power in mechanical power transmission systems. These gears
Design of Helical Gear and Analysis on Gear Tooth Indrale Ratnadeep Ramesh Rao M.Tech Student ABSTRACT Gears are mainly used to transmit the power in mechanical power transmission systems. These gears
Model Library Power Transmission
 Model Library Power Transmission The Power Transmission libraries in SimulationX support the efficient modeling and analysis of mechanical powertrains as well as the simulation-based design of controlled
Model Library Power Transmission The Power Transmission libraries in SimulationX support the efficient modeling and analysis of mechanical powertrains as well as the simulation-based design of controlled
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 Course Name Course Code Class Branch MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK 2015 2016 : KINEMATICS OF MACHINES : A40309
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 Course Name Course Code Class Branch MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK 2015 2016 : KINEMATICS OF MACHINES : A40309
1 135 teeth to rack
 1. A spur gear with 46 teeth, 2.5 module has to be cut on a column and knee type horizontal milling machine with a rotary disc type form gear milling cutter. The 2.5 module cutter no. 3 is used on a blank
1. A spur gear with 46 teeth, 2.5 module has to be cut on a column and knee type horizontal milling machine with a rotary disc type form gear milling cutter. The 2.5 module cutter no. 3 is used on a blank
Gearless Power Transmission for Skew Shafts (A SRRS Mechanism)
 , pp.61-72 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijast.2015.79.06 Gearless Power Transmission for Skew Shafts (A SRRS Mechanism) Amit Kumar 1 and Mukesh Kumar 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,Baba Saheb Dr.
, pp.61-72 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijast.2015.79.06 Gearless Power Transmission for Skew Shafts (A SRRS Mechanism) Amit Kumar 1 and Mukesh Kumar 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,Baba Saheb Dr.
A CAD Design of a New Planetary Gear Transmission
 A CAD Design of a New Planetary Gear Transmission KONSTANTIN IVANOV AIGUL ALGAZIEVA ASSEL MUKASHEVA GANI BALBAYEV Abstract This paper presents the design and characteriation of a new planetary transmission
A CAD Design of a New Planetary Gear Transmission KONSTANTIN IVANOV AIGUL ALGAZIEVA ASSEL MUKASHEVA GANI BALBAYEV Abstract This paper presents the design and characteriation of a new planetary transmission
we will learn how to conduct force and torque analysis on gears in order to calculate bearing
 8.1 Introduction to Gears Gears are used to transmit motion and torque from one shaft to another. In this section we will discuss the kinematics of gears; that is, the motion relationships between gears.
8.1 Introduction to Gears Gears are used to transmit motion and torque from one shaft to another. In this section we will discuss the kinematics of gears; that is, the motion relationships between gears.
FRICTION DEVICES: DYNAMOMETER. Presented by: RONAK D. SONI Assistant Professor Parul Institute of Technology, Parul University
 FRICTION DEVICES: DYNAMOMETER Presented by: RONAK D. SONI Assistant Professor Parul Institute of Technology, Parul University DYNAMOMETER A dynamometer is a brake but in addition it has a device to measure
FRICTION DEVICES: DYNAMOMETER Presented by: RONAK D. SONI Assistant Professor Parul Institute of Technology, Parul University DYNAMOMETER A dynamometer is a brake but in addition it has a device to measure
T25 T25 T25 T27 T27 T28 T28 T28 T28 T29 T29 T29 T31 T37 T37 T38 T T T48
 1.0 INTRODUCTION 2.0 BASIC GEOMETRY OF SPUR GEARS 2.1 Basic Spur Gear Geometry 2.2 The Law of Gearing 2.3 The Involute Curve 2.4 Pitch Circles 2.5 Pitch 2.5.1 Circular Pitch 2.5.2 Diametral Pitch 2.5.3
1.0 INTRODUCTION 2.0 BASIC GEOMETRY OF SPUR GEARS 2.1 Basic Spur Gear Geometry 2.2 The Law of Gearing 2.3 The Involute Curve 2.4 Pitch Circles 2.5 Pitch 2.5.1 Circular Pitch 2.5.2 Diametral Pitch 2.5.3
Introduction to Gear Design
 Introduction to Gear Design Course No: M03-016 Credit: 3 PDH Robert P. Tata, P.E. Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877) 322-4774
Introduction to Gear Design Course No: M03-016 Credit: 3 PDH Robert P. Tata, P.E. Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877) 322-4774
BRCM COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY BAHAL, BHIWANI Practical Experiment Instructions Sheet
 BRCM COLLEGE OF KOM ME- 212 F KINEMATICS OF MACHINES LAB BRANCH-ME List of Experiments : 1. To study various types of Kinematic links, pairs, chains and Mechanisms. 2. To study inversions of 4 Bar Mechanisms,
BRCM COLLEGE OF KOM ME- 212 F KINEMATICS OF MACHINES LAB BRANCH-ME List of Experiments : 1. To study various types of Kinematic links, pairs, chains and Mechanisms. 2. To study inversions of 4 Bar Mechanisms,
SECTION 8 BEVEL GEARING
 SECTION 8 BEVEL GEARING For intersecting shafts, bevel gears offer a good means of transmitting motion and power. Most transmissions occur at right angles, Figure 8-1, but the shaft angle can be any value.
SECTION 8 BEVEL GEARING For intersecting shafts, bevel gears offer a good means of transmitting motion and power. Most transmissions occur at right angles, Figure 8-1, but the shaft angle can be any value.
DUDLEY'S" HANDBOOK OF PRACTICAL GEAR DESIGN AND MANUFACTURE. Stephen P. Radzevich
 Second Edition DUDLEY'S" HANDBOOK OF PRACTICAL GEAR DESIGN AND MANUFACTURE Stephen P. Radzevich LßP) CRC Press VV J Taylors Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor
Second Edition DUDLEY'S" HANDBOOK OF PRACTICAL GEAR DESIGN AND MANUFACTURE Stephen P. Radzevich LßP) CRC Press VV J Taylors Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor
Theory of Mechanisms and Machines
 Theory of Mechanisms and Machines Theory of Mechanisms and Machines C.S. SHARMA Formerly Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Jai Narain Vyas University Jodhpur KAMLESH PUROHIT Professor Department
Theory of Mechanisms and Machines Theory of Mechanisms and Machines C.S. SHARMA Formerly Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Jai Narain Vyas University Jodhpur KAMLESH PUROHIT Professor Department
CHAPTER 6 GEARS CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 CHAPTER 6 GEARS CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to do the following: Compare the types of gears and their advantages. Did you ever take a clock apart to
CHAPTER 6 GEARS CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to do the following: Compare the types of gears and their advantages. Did you ever take a clock apart to
CHAPTER 3 page 35 PRINCIPLES OF GEAR-TOOTH GENERATION. .1 Angular Velocity Ratio
 CHAPTER 1 page 1..., ATURE, NOTATION AND CONVENTIONS TYPES OF GEAR 1.1 Spur 1.2 Helical 1.3 Double-Helical 1.4 Crossed Helical 1.5 Conical Involute 1.6 Bevel 1.7 Spiral Bevel 1.8 Hypoid 1.9 Worm NOMENCLATURE
CHAPTER 1 page 1..., ATURE, NOTATION AND CONVENTIONS TYPES OF GEAR 1.1 Spur 1.2 Helical 1.3 Double-Helical 1.4 Crossed Helical 1.5 Conical Involute 1.6 Bevel 1.7 Spiral Bevel 1.8 Hypoid 1.9 Worm NOMENCLATURE
Sheet 1 Variable loading
 Sheet 1 Variable loading 1. Estimate S e for the following materials: a. AISI 1020 CD steel. b. AISI 1080 HR steel. c. 2024 T3 aluminum. d. AISI 4340 steel heat-treated to a tensile strength of 1700 MPa.
Sheet 1 Variable loading 1. Estimate S e for the following materials: a. AISI 1020 CD steel. b. AISI 1080 HR steel. c. 2024 T3 aluminum. d. AISI 4340 steel heat-treated to a tensile strength of 1700 MPa.
Moments. It doesn t fall because of the presence of a counter balance weight on the right-hand side. The boom is therefore balanced.
 Moments The crane in the image below looks unstable, as though it should topple over. There appears to be too much of the boom on the left-hand side of the tower. It doesn t fall because of the presence
Moments The crane in the image below looks unstable, as though it should topple over. There appears to be too much of the boom on the left-hand side of the tower. It doesn t fall because of the presence
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6401- KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY QUESTION BANK
 1 BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6401- KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY QUESTION BANK Unit 1-BASICS OF MECHANISMS PART-A 1) Differentiate between a machine and a structure?
1 BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6401- KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY QUESTION BANK Unit 1-BASICS OF MECHANISMS PART-A 1) Differentiate between a machine and a structure?
UNIT III TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS CONTENTS: Clutch-types and construction Gear boxes- manual and automatic Gear shift mechanisms Over drive Transfer box
 UNIT III TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS CONTENTS: Clutch-types and construction Gear boxes- manual and automatic Gear shift mechanisms Over drive Transfer box Fluid flywheel Torque converter Propeller shaft Slip
UNIT III TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS CONTENTS: Clutch-types and construction Gear boxes- manual and automatic Gear shift mechanisms Over drive Transfer box Fluid flywheel Torque converter Propeller shaft Slip
Machines and mechanisms
 Machines and mechanisms Contents: 1. Basics and Kinematics of Mechanism 2. Cam and Follower 3. Governor 4. Gear and Gear Train 5. Inertia Force Analysis Basics and Kinematics Mechanism: 1. A rigid body
Machines and mechanisms Contents: 1. Basics and Kinematics of Mechanism 2. Cam and Follower 3. Governor 4. Gear and Gear Train 5. Inertia Force Analysis Basics and Kinematics Mechanism: 1. A rigid body
Gearheads H-51. Gearheads for AC Motors H-51
 Technical Reference H-51 for AC Since AC motor gearheads are used continuously, primarily for transmitting power, they are designed with priority on ensuring high permissible torque, long life, noise reduction
Technical Reference H-51 for AC Since AC motor gearheads are used continuously, primarily for transmitting power, they are designed with priority on ensuring high permissible torque, long life, noise reduction
CH16: Clutches, Brakes, Couplings and Flywheels
 CH16: Clutches, Brakes, Couplings and Flywheels These types of elements are associated with rotation and they have in common the function of dissipating, transferring and/or storing rotational energy.
CH16: Clutches, Brakes, Couplings and Flywheels These types of elements are associated with rotation and they have in common the function of dissipating, transferring and/or storing rotational energy.
TECHNOLOGY MECHANISMS
 TECHNOLOGY MECHANISMS 3º ESO IES CHAN DO MONTE URTAZA 1 WHAT IS A MECHANISM? Mechanism are devices that have been designed to make jobs easier. They all have certain things in common: They involve some
TECHNOLOGY MECHANISMS 3º ESO IES CHAN DO MONTE URTAZA 1 WHAT IS A MECHANISM? Mechanism are devices that have been designed to make jobs easier. They all have certain things in common: They involve some
SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2000 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2000 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
Gear Engineering Data. Spur Gear Gear Formulas Drive Selection Horsepower and Torque Tables
 Engineering Gear Engineering Data Spur Gear Gear Formulas Drive Selection Horsepower and Torque Tables G-79 Gear Selection Stock Spur Gear Drive Selection When designing a stock gear drive using the horsepower
Engineering Gear Engineering Data Spur Gear Gear Formulas Drive Selection Horsepower and Torque Tables G-79 Gear Selection Stock Spur Gear Drive Selection When designing a stock gear drive using the horsepower
bearing to conform to the same elliptical shape as the wave generator plug.
 32 Gear Product News April 2006 t h e b a s i c s o f H a r m o n i c D r i v e G e a r i n g Anthony Lauletta H armonic drives were invented in the late 1950s and have been a major part of the motion
32 Gear Product News April 2006 t h e b a s i c s o f H a r m o n i c D r i v e G e a r i n g Anthony Lauletta H armonic drives were invented in the late 1950s and have been a major part of the motion
CHENDU COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 CHENDU COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub Code: ME 2342 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEM UNIT - I 1. How the bevel gears are classified? Explain with
CHENDU COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub Code: ME 2342 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEM UNIT - I 1. How the bevel gears are classified? Explain with
Siddhant Dange 1, Saket Sant 2, Anish Sali 3, Parthan Pethodam 4, Mr. Sandeep Belgamwar 5
 International Journal of Latest Research in Engineering and Technology (IJLRET) ISSN: 2454-5031 ǁ Volume 2 Issue 4ǁ April 2016 ǁ PP 41-45 Design and Analysis of Planetary Gearbox for Industrial Concrete
International Journal of Latest Research in Engineering and Technology (IJLRET) ISSN: 2454-5031 ǁ Volume 2 Issue 4ǁ April 2016 ǁ PP 41-45 Design and Analysis of Planetary Gearbox for Industrial Concrete
Spiroid High Torque Skew Axis Gearing A TECHNICAL PRIMER F. EVERTZ, M. GANGIREDDY, B. MORK, T. PORTER & A. QUIST
 2016 Spiroid High Torque Skew Axis Gearing A TECHNICAL PRIMER F. EVERTZ, M. GANGIREDDY, B. MORK, T. PORTER & A. QUIST Table of Contents INTRODUCTION PAGE 02 SPIROID GEAR SET CHARACTERISTICS PAGE 03 BASIC
2016 Spiroid High Torque Skew Axis Gearing A TECHNICAL PRIMER F. EVERTZ, M. GANGIREDDY, B. MORK, T. PORTER & A. QUIST Table of Contents INTRODUCTION PAGE 02 SPIROID GEAR SET CHARACTERISTICS PAGE 03 BASIC
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING
 Name Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK : KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY : A40309 : II B. Tech II Semester : Mechanical Engineering
Name Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK : KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY : A40309 : II B. Tech II Semester : Mechanical Engineering
Address for Correspondence
 Research Article DESIGN AND STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF DIFFERENTIAL GEAR BOX AT DIFFERENT LOADS C.Veeranjaneyulu 1, U. Hari Babu 2 Address for Correspondence 1 PG Student, 2 Professor Department of Mechanical
Research Article DESIGN AND STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF DIFFERENTIAL GEAR BOX AT DIFFERENT LOADS C.Veeranjaneyulu 1, U. Hari Babu 2 Address for Correspondence 1 PG Student, 2 Professor Department of Mechanical
Thermal Analysis of Helical and Spiral Gear Train
 International Journal for Ignited Minds (IJIMIINDS) Thermal Analysis of Helical and Spiral Gear Train Dr. D V Ghewade a, S S Nagarale b & A N Pandav c a Principal, Department of Mechanical, GENESIS, Top-Kolhapur,
International Journal for Ignited Minds (IJIMIINDS) Thermal Analysis of Helical and Spiral Gear Train Dr. D V Ghewade a, S S Nagarale b & A N Pandav c a Principal, Department of Mechanical, GENESIS, Top-Kolhapur,
Bibliography. [1] Buckingham, Earle: "Analytical Mechanics of Gears", McGraw-Hill, New York, 1949, and republished by Dover, New York, 1963.
![Bibliography. [1] Buckingham, Earle: Analytical Mechanics of Gears, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1949, and republished by Dover, New York, 1963. Bibliography. [1] Buckingham, Earle: Analytical Mechanics of Gears, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1949, and republished by Dover, New York, 1963.](/thumbs/87/96820687.jpg) Bibliography The first five references listed are books on gearing. Some of them deal not only with the geometry, but also with many other aspects of gearing. However, the books are included in this bibliography
Bibliography The first five references listed are books on gearing. Some of them deal not only with the geometry, but also with many other aspects of gearing. However, the books are included in this bibliography
Gearhead Construction and Use
 Gearhead Construction and Use Spur Gear Type Gearheads Direction of Rotation Planetary Gears Spur Gear Type Gearheads Spur gear type gearheads are probably the best possible choice for relatively low torque
Gearhead Construction and Use Spur Gear Type Gearheads Direction of Rotation Planetary Gears Spur Gear Type Gearheads Spur gear type gearheads are probably the best possible choice for relatively low torque
Design and Analysis of Six Speed Gear Box
 Design and Analysis of Six Speed Gear Box Ujjayan Majumdar 1, Sujit Maity 2, Gora Chand Chell 3 1,2 Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Jalpaiguri Government Engineering College, Jalpaiguri,
Design and Analysis of Six Speed Gear Box Ujjayan Majumdar 1, Sujit Maity 2, Gora Chand Chell 3 1,2 Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Jalpaiguri Government Engineering College, Jalpaiguri,
AP Physics B: Ch 20 Magnetism and Ch 21 EM Induction
 Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B: Ch 20 Magnetism and Ch 21 EM Induction MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the north poles of
Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B: Ch 20 Magnetism and Ch 21 EM Induction MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the north poles of
 Lecture plan UNIT I Basics of Mechanisms SYLLABUS Introduction: Definitions : Link or Element, Pairing of Elements with degrees of freedom, Grubler s criterion (without derivation), Kinematic chain, Mechanism,
Lecture plan UNIT I Basics of Mechanisms SYLLABUS Introduction: Definitions : Link or Element, Pairing of Elements with degrees of freedom, Grubler s criterion (without derivation), Kinematic chain, Mechanism,
