COMPARISON OF AIRFOIL AND RIBBON FAIRINGS FOR SUPPRESSION OF FLOW-INDUCED VIBRATIONS
|
|
|
- Zoe Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) COMPARISON OF AIRFOIL AND RIBBON FAIRINGS FOR SUPPRESSION OF FLOW-INDUCED VIBRATIONS S. M. FANG & J. M. NIEDZWECKI Zachry Department of Civil Engineering, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, USA. ABSTRACT Cables and various subsea product flow-lines are often subjected to flow-induced vibrations as a consequence of wave or wave and current flow excitation. An experimental study that explores the comparative suppression effectiveness of airfoil and ribbon fairings is presented. In the experimental investigation, an instrumented tensioned 29 m horizontal composite cylinder with a length to diameter ratio of 760 is subjected to a range of uniform current and combined current and regular wave conditions. In the analysis of the cross-flow response amplitude ratios, modal parameters, such as mode shape, damping ratio were extracted. The analytical procedures were performed using a modified time domain decomposition technique. The analysis illustrated the amplified response behavior for bare cylinders, and illustrated that full coverage by airfoil and ribbon fairings could effectively suppress flow-induced vibrations in current only conditions, but both fairings were ineffective when regular wave conditions were superimposed on the uniform current conditions, even though the airfoil provided larger damping than ribbon fairings. Under combined wave and current conditions, the response behavior of either suppression device was found to be insensitive to coverage densities. Keywords: Airfoil fairing, combined loads of current and waves, coverage density, fl ow-induced vibration, ribbon fairing, Time domain decomposition, vortex-induced vibration. 1 INTRODUCTION Subsea cables, free-spanning pipelines and a variety of slender structural components are often subjected to current and wave conditions that may lead to damage due to vortex-induced vibrations (VIV). Nielsen, Soreide and Kvarme [1] reported on a free-spanning pipeline designed for the Ormen Lange field, located off the western coast of Norway, which had a length to diameter ratio (L/D) of 846, which is much larger than the typical limit value of 120, proposed by Det Norske Veritas [2]. The complexity of offshore installations involving combined environmental loads on large-scale structures supports the need of experimental study to investigate the system response behavior and the potential requirement for VIV suppression in certain design conditions. A brief summary of some VIV experiments studying the response of horizontally mounted cylinders is presented in Table 1. The studies presented can logically be grouped into three categories based upon their L/D ratio and the type of VIV suppression device used in the tests. The first group focused on the VIV suppression performance for small L/D ratios (<30), where such experimental setup facilitated testing devices with multiple geometries in high Reynolds number flow [3, 4]. Allen, Henning and Lee [3] tested five different airfoil fairings with chord to thickness ratio (c/t) values ranging from 1 to 2 at super-critical flow regime. It was determined that an airfoil fairing with chord to thickness ratio (c/t) of 1.18 was overall the best choice for it was both cost effective and efficient in reducing the root-mean-squared (RMS) cross-flow responses from 0.43D to 0.13D. The second group that focused on experiments studied VIV for flexible cylinders with intermediate or large L/D ratios. And these research studies were especially focused on multi-modal motions, the effect of pretension and the coupling effect between in-line and cross-flow vibrations. The experimental studies reported by Li et al. [5], Prastianto, Otsuka and Ikeda [6] and Wilde and Huijsmans [7] are included in Table WIT Press, ISSN: (paper format), ISSN: (online), DOI: /CMEM-V2-N
2 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) 31 Table 1: Summary of laboratory experiments using horizontal cylinder configurations. Recent Studies Year L/D Range of Re 10 3 Flow Regime 1 Mass Ratio VIV Suppression Devices Suppression Coverage % Environmental Loads Allen ,500 super-critical 1.39 Airfoil Fairings 100 Uniform Current Brown sub-critical 1.15 Ventilated Trouser 100 Uniform Current Li sub-critical None Uniform Current Prastianto sub-critical None Shared Current Wilde sub-critical None Uniform Current Allen sub-critical Airfoil Fairings 40 Uniform Current to critical Helical Strakes Trim sub-critical 1.60 Helical Strakes Uniform Current Chitwood sub-critical 0.91 None Uniform Current Regular Wave Irregular Wave Current + Irregular Wave 0.91 Airfoil Fairings Uniform Current Regular Wave Current + Regular Wave 0.91 Ribbons Uniform Current Regular Wave Current + Regular Wave Notes: 1 Flow Regime: sub-critical, Re < 2*10 5 ; critical, 2*10 5 < Re < 6*10 5 ; super-critical, Re > 6* The mass ratio here is for the bare cylinders without any fairings.
3 32 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) In these studies, the L/D ratios were 213, 269 and 788 respectively, and each of those experiments were performed in the sub-critical flow regime. Li et al. tested a bare cylinder for 27 different current velocities ranging from 0.1 to 1.5 m/s with pretensions of 200 N and 600 N, however no frequency lock-in or resonance was observed. Prastianto et al. reported an experiment at a relatively low uniform current velocity of 0.2 m/s, at which both the 3rd and 9th mode were excited with the lower mode being dominant. Similarly, Wilde and Huijsmans showed that in a test with current velocity of 1.0 m/s and pretension of 900 N, the 5th or 6th mode was dominant and the 11th or 12th mode participated. As studies by group two demonstrated, multi-modal responses were frequently observed in VIV for these L/D ratios and both current velocities and pretensions affected the dominant modes. Strong coupling effects between in-line and cross-flow responses were also observed in these studies. The third grouping of research studies focuses on the performance of various VIV suppression devices on long flexible cylinders. Allen and Henning [8] conducted experiments using a cylinder with an L/D ratio of 463 in sub-critical to critical flow regime, and compared the performance of helical strakes (17.5D pitch, 0.25D height) and short fairings (c/t ratio 1.5). Both devices were in 40% partial coverage and deployed from one end. The results revealed strakes and fairings can both effectively suppress the responses in the covered end, but that airfoil fairings outperformed strakes by providing more damping overall to the system. Trim et al. [9] compared helical strakes with 2 geometries, 17.5D pitch, 0.25D height versus 5D pitch, 0.14D height. The cylinder with an L/D ratio of 1407 was towed in sub-critical flow regime. The experiments demonstrated that the first strake design was more effective in mitigating VIV than the second, and reduced the estimated fatigue damage by one-order-of-magnitude. Coverage of 91%, 82%, 62% and 41% of strakes were studied and the results clearly showed that strake performance declined rapidly when coverage was smaller than 82%. The experimental results reported here fit with the third grouping of research studies and expand upon the initial research reported on ribbon fairings by Niedzwecki and Fang [10]. The study provides a comparison of airfoil fairings and ribbon fairings with both complete and partial coverage. Ribbon fairings are generally used to suppress VIV on cables, but have shown some advantages over airfoil fairings when applied to very flexible systems [11]. Tests comparing the response behavior of the two fairing types were conducted for a range of various uniform current conditions, and combined loads of uniform current and regular waves were also investigated. The multi-modal response behavior of the various test configurations was analyzed using the VIV analysis program developed by Niedzwecki and Fang [10] that incorporates the time domain decomposition technique [12] and the needed practical considerations to recover modal response envelopes and modal parameters. 2 EXPERIMENT PARTICULARS The experiments were conducted with the purpose of investigating the performance of airfoil and ribbon fairings in varying coverage subjected to uniform current or combined loads of current and regular waves. Figure 1 provides an illustration of the test configuration used for the experiments as reported by Chitwood [13]. The composite cylinder used in the tests was 29-m long, with an outside diameter of 38 mm and an inside diameter of 22 mm. It was estimated to have a unit weight of N/m, and submerged 0.61 m below the mean water surface. Thus, the composite test cylinder was very light with a mass ratio of 0.91 and quite flexible with an L/D ratio of 760. As shown in the figure, three wave probes were suspended from the bridge to measure the wave properties, and six bi-axial accelerometers were located
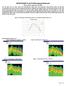
4 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) 33 Figure 1: Schematic of the model and instrumentation locations. at unequal spacing internal to the cylinder. Special care was taken to orient and seal the sensors inside the composite cylinder. Displacement time series were obtained from the recorded acceleration time series through a double integration procedure and the results were compared with the mid-span displacement measured using a string-potentiometer sensor. The bi-axial acceleration measurements enabled estimation of both cross-flow and in-line displacements. The towing speeds varied between 0.18 and 0.43 m/s and simulated uniform current conditions. For the combined uniform current and wave conditions tested, regular waves with the wave height 0.24 m and the peak period 3.2 s were introduced. Considering the maximum horizontal wave kinematic velocity, the Reynolds number was estimated to vary between 7*10 3 and 2.3*10 4, corresponding to sub-critical flow regime. Photographs in Fig. 2 present side-by-side photos of the airfoil and ribbon fairings used in the study. The airfoil fairings were made of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene plastic (ABS), with a width of mm (1 ft), a chord length of mm (6.5 in) and a thickness of 44.5 mm (1.75 in) resulting in a c/t ratio of 3.7. The airfoil fairings were attached to the cylinder with zip-ties to ensure free rotation. The ribbon fairings were made of soft compliant vinyl, with the same width as the airfoil fairings, and trailing length of 127 mm (5 in). The ribbon fairings were secured around the cylinder by zippers on the leading edge. The unit weight of the airfoil and ribbon fairings in air was N/m and N/m. Note that since the airfoil fairings were not watertight the water trapped inside needs to be counted when considering the total mass. The unit weight for the trapped water was estimated to be N/m.
5 34 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) Figure 2: Photographs of the airfoil (left) and ribbon (right) fairings used in the experiments. The airfoil fairings were tested at 100% 40% coverage in 10% decrements. The fairings were removed from the left end (accelerometer 6). The ribbon fairings were studied at the same coverage range but the reduction from 100% was done in 20% decrements. 3 DATA ANALYSIS USING TIME DOMAIN DECOMPOSITION The analysis of the time series data from the towed composite cylinder experiments required a rethinking of the time domain decomposition technique implementation to address subtleties of the phenomena and recorded data. Consequently, the analysis of the data was divided into several interrelated well-defined tasks. First, the cross-flow and in-line displacements were obtained through double integration of the acceleration time series data measured using the bi-axial accelerometers. In addition, the statistical characteristics that included the maximum, minimum and standard deviations of the displacements, measured tension, and current and wave data were obtained. The next major task was to perform a modified time domain decomposition of the displacement time series to recover information on the dominant modes that included the natural frequency, mode shape, modal contribution factor and modal damping. In evaluation of multi-modal vortex-induced vibration behavior one needs to be careful as the various modes can have the same lock-in range, and the mode of interest might be blended in with other possible modes and might not be correctly recognized. Chung [14] analyzed experimental data from a variety of sources and demonstrated the lock-in range could vary significantly depending upon the mass ratio, in particular cylinders with low mass ratios had a much broader lock-in range than those with higher mass ratios. Figure 3 presents data from this study illustrating the mode number versus the reduced velocity, which is defined here as the ratio of the current velocity to the product of the cylinder s natural frequency times its diameter. The figure presents information for the bare cylinder subjected to three different uniform current velocities (0.18, 0.27 and 0.43 m/s). The data suggests that as the uniform current velocities increase so that the corresponding modes 1 3, 2 4, 3 7 might be excited. This type of figure provides some guidance for the various configuration scenarios for the evaluation procedures regarding the expected mode behavior in this study.
6 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) 35 Figure 3: Mode number versus reduced velocity at varied current velocities for bare cylinder. The key aspects of the time domain decomposition technique include selective isolation of data from time histories, extraction of a certain mode shape from constructed energy matrix using singular value decomposition technique, and calculation of mode contribution factors, damping ratio and other modal parameters for each mode. In order to point out some of the subtleties and modifications associated with the implementation of the time domain decomposition technique for offshore structure applications, the important equations from the original formulation by Kim, Stubbs and Park [12] are included in the discussion for clarity. So beginning with a simple one-dimensional array of P unequally spaced sensors, the acceleration time history of vibrations in cross-flow direction can be assumed as the summation of infinite modes () Y&& t = c && ( i, ) j i = 1 where, Ÿ (t) is the cross-flow acceleration and (i,t) and j (i) are the modal contribution factor and the mode shape at the ith mode respectively. If N samples are recorded, Ÿ (t) is a p N matrix. Accordingly for P sensors one can only extract up to the p th modal parameters without aliasing. The first equation can then be expressed as p Y&& () t = c && ( i, t ) ()+ i 1 t i = 1 where, 1 ()= t && c( i t) () i denotes a truncation error due to higher modes. i= p (1) (2)
7 36 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) Spectral analysis and filter theory are applied to isolate the signal of the ith mode Ÿ (i,t) from the array signals. The power spectral densities at all sensors are generated and overlapped to find the energy concentration bandwidth for the targeted mode. Digital filters are designed and used to create a mode-isolated discrete-time response within the appropriate bandwidth. In this analysis a 20th order Butterworth band-pass filter was selected, but for implementation one can choose the optimal filter for the mode isolation process. Utilizing the orthogonality between components of the signal in modal space and the noise space, an energy matrix can be formulated as T T E() i = Y&& ( i, t ) Y&& ( i, t ) = UΩU (4) where, U = j() i, y() 1, y( 2),..., y p 1 (5) () si Ω= s () 1 s ( 2) K s p 1 (6) The singular value decomposition technique (SVD) is then utilized to decompose the constructed energy matrix, and from eqn (5), the mode shape can be deduced from the first column of U. The modal contribution factor with the mode shape obtained previously can be evaluated from the following equation: ( ) c && i t j i 1 j i T j i Y&& i t = T () () () For the targeted mode, the modal value of the critical damping ratio can be estimated using the Half-Power Bandwidth method applied to eqn (7). Bendat and Piersol [15] in their discussion of the Half-Power Bandwidth method expressed that to obtain accurate estimates, the power spectral density resolution B e requires to be much smaller than the half-power point bandwidth B i, specifically B e < 0.2B i. When the power spectral density resolution is quite coarse due to the short data lengths, as was the case of the data analyzed in this study, a non-destructive zoom technique can be implemented [16]. This technique is specifically designed to increase the power spectral density resolution near targeted modes by zooming in on the interested frequency range and concentrating all the spectral lines into a narrower band. Consider for example the case of 100% ribbon faired coverage of the test cylinder in regular waves with a current speed of 0.38 m/s. For this case the B e resolution was Hz while B i for the first mode was Hz, yielding B e = 1.24B i which clearly did not meet the criteria. Applying non-destructive zoom technique, the PSD resolution was reduced to Hz, resulting in B e = 0.2B i and a more accurate estimation of the critical damping ratio was achieved. As part of the software implementation, a wave-induced vibration simulation model was incorporated in order to estimate the role of the regular wave excitation in the total responses of the bare cylinder configuration, which was subjected to combined uniform current and (7)
8 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) 37 wave loading conditions. The Morison wave force model was adopted to simulate the wave force excitation with a linearized drag term. The derivation of the modal solution is based on results of Niedzwecki and Liagre [17], where string behavior of the model is assumed consistent with the large L/D ratio. The dynamic tension variation was assumed to be negligible to the pretension of the test cylinder. 4.1 Base case of bare cylinder tests 4 NUMERICAL RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Prior to the introduction of any fairings, bare cylinder tests were conducted first for a uniform current speed of 0.38 m/s, and then for the same current speed with the addition of regular waves with 0.24 m wave height and 3.2 s period. The normalized maximum and minimum cross-flow displacement envelopes for the cylinder under these conditions are presented in Fig. 4. Upon comparison of the envelopes it is quite evident that regular waves significantly amplify and dominate the bare cylinder response behavior. The targeted 3rd mode vibration behavior can be recognized for both environmental loading conditions. The results also indicate one possibility: the total responses in combined current and wave loads are composed of two components, a fundamental mode dominated by regular waves and a 3rd mode from the vortex shedding forces mainly due to current. Both components of the responses are significant for the bare cylinder cases. Figure 4: Bare cylinder response in current only (0.38 m/s) and combined current (0.38 m/s) and waves (0.24 m wave height, 3.2 s wave period) conditions.
9 38 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) 4.2 Response behavior with complete airfoil and ribbon fairing coverage The next cases of interest involve the comparison of the cylinder with full coverage of airfoil or ribbon fairings. For the bare cylinder tested at current velocities of 0.18, 0.24, 0.38 and 0.43 m/s, the root-mean-square (rms) amplitude ratios at mid-span of the cylinder were measured as 0.12D, 0.19D, 0.23D and 0.71D, respectively. For the cylinder test runs with complete coverage by the airfoil fairings, the reduction of the corresponding ratios was found to be 0.04D, 0.08D, 0.12D and 0.13D. By way of comparison, for complete coverage of the test cylinder by ribbon fairings the ratios were further reduced over the range of the two middle current speeds. Specifically, the corresponding rms amplitude ratios were determined to be 0.05D, 0.06D, 0.07D and 0.13D. Based upon the measured data available the results suggest that the rms responses of the cylinder at mid-span increase with current velocity, and that both airfoil and ribbon fairings significantly suppress the vibrations in the uniform current cases tested. An example of the cross-flow response behavior for the cases of complete coverage by either airfoil or ribbon fairings when the regular waves were introduced is presented in Fig. 5. For comparison the corresponding bare cylinder case is included in the figure. Clearly the wave kinematics dominated the response behavior and neither fairing type was able to suppress motions. In fact the cylinder equipped with airfoil fairings significantly amplified the vibrations and the one with ribbon fairings somehow kept the responses in similar scale or slightly increased the responses compared with the bare cylinder. The airfoil fairings although free to rotate seemed to accentuate the motion as they followed the wave kinematic motion Figure 5: Bare, full airfoil and ribbon faired cylinder response behavior in combined current and waves.
10 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) 39 resulting in increased maximum and minimum rms values especially at the mid-span of the test cylinder. The ribbon fairings were completely compliant and seemed to also respond to the fundamental mode induced by the wave motion, although one could observe the influence of an additional mode in the envelopes. The bare cylinder surface was not completely smooth as the surface reflected the construction of the composite material and had minor indentions and protrusions. Though the fairings tested were originally designed to mitigate flow-induced vibrations in current only situations, the results in Fig. 5 indicate the significantly reduced functionality of both fairings when regular waves were present. The amplification effect of airfoil and ribbon fairings can be partially explained by comparing the wave peak period and the natural period of the system. For a slightly damped system, the closer the excitation peak frequency approaches one of the natural periods within certain range, the larger the response will be. Considering structure mass, added mass and the mass of possibly trapped water especially for airfoil fairings, the natural periods of the 1st mode for full airfoil, ribbon faired and bare cylinders are estimated to be 2.8, 1.9 and 1.8 s, respectively. Since the wave peak period in the current study is 3.2 s, airfoil faired cylinder has the closest natural period to the waves, followed by ribbon faired and bare cylinder. The rank of this closeness matches well with the actual response envelopes. The amplification effect is also verified by the wave-induced vibration simulated results. Assuming the cylinders with and without fairings are uniform, the wave-induced response amplitude ratios at mid-span were estimated to be 4.8D, 3.5D and 2.0D for full airfoil, ribbon faired and bare cylinders. By way of comparison the measured cross-flow total responses ratios were 5.5D, 4.5D and 3.3D as shown in Fig. 5, confirming the dominance of the wave kinematics in the observed response behavior. The power spectral densities for the three cylinder configurations are presented in Fig. 6. The bare cylinder is subject to energy over a large range of frequencies and the effectiveness of the both fairings in reducing this to a few frequencies can be observed. The first peak for each case is centered around the wave frequency with the sequence of peak values Figure 6: Power spectral densities of bare, fully airfoil and fully ribbon faired cylinders.
11 40 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) corresponding to the airfoil followed in reduced amplitudes of the ribbon fairing and bare cylinder cases. The few remaining higher frequencies clearly influenced the ribbon fairings envelope when compared with the airfoil fairings, which was even more effective in reducing the effects of higher frequency contributions. The first three dominant mode shapes of airfoil and ribbon fairings, extracted from measured data using the time domain decomposition technique are presented in Fig. 7a and b, and (a) (b) Figure 7: (a) The three dominant mode shapes for fully airfoil faired cylinder coverage. (b) The three dominant mode shapes for fully ribbon faired cylinder coverage.
12 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) 41 further validate the noted observations. In particular, the mode shapes corresponding to airfoil fairing coverage appear to be strongly controlled by the fundamental mode, and meanwhile, the multiple mode shapes for the ribbon fairings are explicit and clear, corresponding to the 1st, 2nd and 3rd mode. This is another indicator that in ribbon faired cases, waves were not as dominant as that in airfoil cases, and vortex shedding forces were still significant to excite response in higher mode numbers. The damping ratios of the first three modes using non-destructive zoom technique and Half-Power Bandwidth method were estimated to be 8.4%, 4.4% and 3.2% for complete coverage by the airfoil fairings, and 7.7%, 2.4%, 2.3% for the comparable ribbon fairing case. These results illustrate that the airfoil fairings provide larger damping for the system when compared with the ribbon fairings. 4.3 Response behavior with partial airfoil and ribbon fairing coverage There was a range of coverage configurations as noted in the discussion of the experiment particulars. A comparison of 40% and 100% coverage was selected as being representative and is presented in Fig. 8. The results suggest in the combined loading condition, the response magnitudes are not sensitive to coverage, i.e. neither of the suppression devices is effective in mitigating the response behavior. This is consistent with the previous discussion, as the responses are dominated by waves and coverage of VIV suppression devices only affects the less important current-induced vibrations. Figure 8: Response envelopes for airfoil and ribbon faired cylinders with 100% and 40% coverage.
13 42 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) Figure 9: Power spectral densities of bare, 60%, 100% ribbon faired cylinders. The modal responses of partial coverage tests in the combined loading condition further explained the phenomena that though ineffective around the wave frequency, fairings could suppress the higher order modes. For illustrative purpose, power spectral densities of bare, 60% and 100% ribbon coverage at accelerometer 4 in the middle of the cylinder are presented in Fig. 9, which showed that the higher order mode components of the vibrations were gradually suppressed by the increased coverage while the responses near the wave frequency at 0.31 Hz remained significant. The total energy of the responses became smaller and moved toward lower frequencies as the coverage increased. The trend of energy shifting was similar in the case of airfoil faired cylinders. The different behaviors of the suppression devices at low and high frequencies were also reflected in the mode shapes, as shown in Fig. 10a, for the fundamental modes of 0%, 60% and 100% ribbon coverage and Fig. 10b for the second modes of 40% airfoil and ribbon coverage. In Fig. 10a, the near symmetry of the mode shapes confirmed the insensitivities of coverage density in wave dominated responses. In Fig. 10b, both mode shapes at partial coverage were asymmetric and unbalanced, with larger values on the bare right end, which was similar to a normal 2nd mode shape, and with reduced values on the left faired end. Moreover, the reduction effect of the mode shape from the airfoil fairing seemed stronger than that from the ribbon fairing, which suggested the airfoil fairing may provide larger damping than the ribbon fairing. It was further confirmed by the estimations of the damping ratios of the excited modes, 2.3% for airfoil and 1.5% for ribbon. A possible explanation for the unbalanced mode shapes is partial coverage affected distribution of structural and added mass, as well as hydrodynamic damping across the cylinder.
14 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) 43 (a) (b) Figure 10: (a) Recovered fundamental mode shapes of bare, 60% and 100% ribbon faired cylinder. (b) Recovered unbalanced mode shape of 40% airfoil and ribbon faired cylinder test. 5 SUMMARY Several featu res of time domain decomposition technique approach make it especially suitable for the analysis of data from a wide variety of offshore science and engineering applications, such as the analysis of flow-induced vibrations. First, the technique can be utilized to analyze measurements of system response due to ambient or controlled force excitation to resolve the modal characteristics. This is an important point as the laboratory
15 44 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) experiments were conducted at relatively low sub-critical Reynolds numbers, and field data will typically be in the super-critical flow regime. Thus, the methodology presented is valid for the analysis of laboratory or field data. Secondly, the computation of single value decomposition process is only dependent on the number of sensors, but as noted the subsequent frequency resolution is important. Finally, the technique allows direct estimates of the mode shape from the measured data without making assumptions or idealizations. The current study noted the practical implementation issues regarding optimal filter selection and subsequent solutions and the need for use of the zoom technique in some cases in order to more accurately estimate the modal critical damping ratios. The experiments reported here were conducted to investigate the effectiveness of VIV suppression performance of variable coverage of airfoil and ribbon fairings on a horizontally mounted flexible cylinder with an L/D ratio of 760. The various cylinder configurations were towed at several different speeds to simulate uniform current velocities, and for some cases regular wave conditions were superimposed. The VIV analysis program developed for this ongoing study was employed to conduct time series analysis, modal analysis and numerical simulation, and to extract useful response information in space and modal domain. The study presented in this paper confirmed the effectiveness of both fairings in suppressing VIV in uniform current conditions only. For the experiments where regular waves were introduced as the test cylinder was being towed, the response behavior was dominated by the orbital nature of the wave kinematics, and the functionality of both fairings types was greatly disturbed. The research findings serve to illustrate the challenges faced by offshore engineers when designing long flexible cylindrical offshore structures and flow-induced suppression devices when both currents and waves are present. Based upon the analysis of the data, it was shown that the ribbon fairings provided less average damping compared to the airfoil fairings, and that the airfoil fairings had a strong affinity to amplify the horizontal response behavior when subject to the combined current and wave conditions. It should be noted that in design practice ribbon fairings are typically used to suppress the flow-induced vibration of long vertically oriented slender cylinders or cables. The experiments also demonstrated the response behavior of test cylinder when subject to combined loads, which was not as sensitive to coverage density of fairings as might be expected, though higher modes and unbalanced mode shapes were observed in the partial coverage cases. The asymmetric response observed for the combined wave and current loading cases, which is inclusive of the bare cylinder and symmetric or asymmetric fairing coverage, might reflect the superposition effects and modal damping of the various dominant modes. Further investigation is warranted to further resolve this and other interesting observations from this study. REFERENCES [1] Nielsen, G.F., Soreide, T.H. & Kvarme, S.O., VIV response of long free spanning pipelines. Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Artic Engineering, OMAE 28075, [2] Det Norske Veritas (DNV), Free Spanning Pipelines, Guideline No. 14, DNV: Høvik, Norway, [3] Allen, D.W., Henning, D.L. & Lee, L., Drilling riser fairing tests at prototype Reynolds numbers. Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Artic Engineering, OMAE 29219, [4] Brown, A.J. & King, R., Tests with a flexible quasi-fairing to reduce riser drag, suppress VIV and limit drilling down-time. Offshore Technology Conference, OTC 19161, 2008.
16 S. M. Fang & J. M. Niedzwecki, Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) 45 [5] Li, X., Bose, N., Zhu, L. & Spencer, D., Multi-modal VIV tests for a highly flexible model riser. International Symposium on Technology of Ultra Deep Ocean Engineering, Tokyo, Japan, [6] Prastianto, R.W., Otsuka, K. & Ikeda, Y., A small scale experiment for multi-modal VIV response of a long flexible horizontal cylinder. Proceedings of the 17th International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, ISOPE, Lisbon, Portugal, [7] Wilde, I.J.J.D. & Huijsmans, R.H.M., Laboratory investigation of long riser VIV response. Proceedings of the 14th International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, ISOPE, Toulon, France, [8] Allen, D.W. & Henning, D.L., Fairings versus helical strakes for suppression of vortex-induced vibration: technical comparisons. Offshore Technology Conference, OTC 19373, [9] Trim, A.D., Braaten, H., Lie, H. & Tognarelli, M.A., Experimental investigation of vortex-induced vibration of long marine risers. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 21, , doi: [10] Niedzwecki, J.M. & Fang, S.M., Suppression of flow-induced vibrations using ribbon fairings. Journal of Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements, in press. [11] Every, M.J., King, R. & Weaver, D.S., Vortex-excited vibrations of cylinders and cables and their suppression. Ocean Engineering, 9(2), , doi: org/ / (82) [12] Kim, B.H., Stubbs, N. & Park, T., A new method to extract modal parameters using output-only responses. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 282, , doi: dx.doi.org/ /j.jsv [13] Chitwood, J.S., Vortex-induced vibration of a slender horizontal cylinder in currents and waves. OTRCreport No. 2/98-A9575, [14] Chung, T.Y., Vortex-induced vibration of flexible cylinders in sheared flows. Ph.D. dissertation, MIT Department of Ocean Engineering, Cambridge, Mass, USA, [15] Bendat, J.S. & Piersol, A.G., Engineering Applications of Correlation and Spectral Analysis, Wiley: New York, [16] Randall, R.B., Frequency Analysis, Bruel & Kjaer: Denmark, [17] Niedzwecki, J.M. & Liagre, P.-Y.F., System identification of distributed-parameter marine riser models. Ocean Engineering, 30, , doi: org/ /s (02)
Laboratory Tests for VIV Prediction of Deepwater Risers
 Laboratory Tests for VIV Prediction of Deepwater Risers Ir. Jaap J. de Wilde, MARIN (Maritime Research Institute Netherlands), E-mail: j.dewilde@marin.nl Abstract One of the great challenges in the offshore
Laboratory Tests for VIV Prediction of Deepwater Risers Ir. Jaap J. de Wilde, MARIN (Maritime Research Institute Netherlands), E-mail: j.dewilde@marin.nl Abstract One of the great challenges in the offshore
Research activities in the Norwegian Deepwater Programme Conference on CeSOS Highlights and AMOS Visions. Rolf Baarholm, Statoil
 Research activities in the Norwegian Deepwater Programme Conference on CeSOS Highlights and AMOS Visions Rolf Baarholm, Statoil Outline of presentation Norwegian Deepwater Programme VIV characterization
Research activities in the Norwegian Deepwater Programme Conference on CeSOS Highlights and AMOS Visions Rolf Baarholm, Statoil Outline of presentation Norwegian Deepwater Programme VIV characterization
Comprehensive Riser VIV Model Tests in Uniform and Sheared Flow
 Comprehensive Riser VIV Model Tests in Uniform and Sheared Flow The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Lie, Halvor,
Comprehensive Riser VIV Model Tests in Uniform and Sheared Flow The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Lie, Halvor,
Dynamic characteristics of railway concrete sleepers using impact excitation techniques and model analysis
 Dynamic characteristics of railway concrete sleepers using impact excitation techniques and model analysis Akira Aikawa *, Fumihiro Urakawa *, Kazuhisa Abe **, Akira Namura * * Railway Technical Research
Dynamic characteristics of railway concrete sleepers using impact excitation techniques and model analysis Akira Aikawa *, Fumihiro Urakawa *, Kazuhisa Abe **, Akira Namura * * Railway Technical Research
Matrix-LGS VIV AND DRAG REDUCTION DRILLING RISER BUOYANCY SYSTEMS
 Matrix-LGS VIV AND DRAG REDUCTION DRILLING RISER BUOYANCY SYSTEMS Keep drilling when others stop The premise is simple: use Matrix-LGS and you can keep drilling when you would normally have to stop. Based
Matrix-LGS VIV AND DRAG REDUCTION DRILLING RISER BUOYANCY SYSTEMS Keep drilling when others stop The premise is simple: use Matrix-LGS and you can keep drilling when you would normally have to stop. Based
Development of Rattle Noise Analysis Technology for Column Type Electric Power Steering Systems
 TECHNICAL REPORT Development of Rattle Noise Analysis Technology for Column Type Electric Power Steering Systems S. NISHIMURA S. ABE The backlash adjustment mechanism for reduction gears adopted in electric
TECHNICAL REPORT Development of Rattle Noise Analysis Technology for Column Type Electric Power Steering Systems S. NISHIMURA S. ABE The backlash adjustment mechanism for reduction gears adopted in electric
Shimmy Identification Caused by Self-Excitation Components at Vehicle High Speed
 Shimmy Identification Caused by Self-Excitation Components at Vehicle High Speed Fujiang Min, Wei Wen, Lifeng Zhao, Xiongying Yu and Jiang Xu Abstract The chapter introduces the shimmy mechanism caused
Shimmy Identification Caused by Self-Excitation Components at Vehicle High Speed Fujiang Min, Wei Wen, Lifeng Zhao, Xiongying Yu and Jiang Xu Abstract The chapter introduces the shimmy mechanism caused
FLOW AND HEAT TRANSFER ENHANCEMENT AROUND STAGGERED TUBES USING RECTANGULAR VORTEX GENERATORS
 FLOW AND HEAT TRANSFER ENHANCEMENT AROUND STAGGERED TUBES USING RECTANGULAR VORTEX GENERATORS Prabowo, Melvin Emil S., Nanang R. and Rizki Anggiansyah Department of Mechanical Engineering, ITS Surabaya,
FLOW AND HEAT TRANSFER ENHANCEMENT AROUND STAGGERED TUBES USING RECTANGULAR VORTEX GENERATORS Prabowo, Melvin Emil S., Nanang R. and Rizki Anggiansyah Department of Mechanical Engineering, ITS Surabaya,
Forced vibration frequency response for a permanent magnetic planetary gear
 Forced vibration frequency response for a permanent magnetic planetary gear Xuejun Zhu 1, Xiuhong Hao 2, Minggui Qu 3 1 Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Parallel Robot and Mechatronic System, Yanshan
Forced vibration frequency response for a permanent magnetic planetary gear Xuejun Zhu 1, Xiuhong Hao 2, Minggui Qu 3 1 Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Parallel Robot and Mechatronic System, Yanshan
Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers
 Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers U. Bin-Nun FLIR Systems Inc. Boston, MA 01862 ABSTRACT Cryocooler self induced vibration is a major consideration in the design of IR
Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers U. Bin-Nun FLIR Systems Inc. Boston, MA 01862 ABSTRACT Cryocooler self induced vibration is a major consideration in the design of IR
Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset
 Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset Vikas Kumar Agarwal Deputy Manager Mahindra Two Wheelers Ltd. MIDC Chinchwad Pune 411019 India Abbreviations:
Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset Vikas Kumar Agarwal Deputy Manager Mahindra Two Wheelers Ltd. MIDC Chinchwad Pune 411019 India Abbreviations:
Active Control of Sheet Motion for a Hot-Dip Galvanizing Line. Dr. Stuart J. Shelley Dr. Thomas D. Sharp Mr. Ronald C. Merkel
 Active Control of Sheet Motion for a Hot-Dip Galvanizing Line Dr. Stuart J. Shelley Dr. Thomas D. Sharp Mr. Ronald C. Merkel Sheet Dynamics, Ltd. 1776 Mentor Avenue, Suite 17 Cincinnati, Ohio 45242 Active
Active Control of Sheet Motion for a Hot-Dip Galvanizing Line Dr. Stuart J. Shelley Dr. Thomas D. Sharp Mr. Ronald C. Merkel Sheet Dynamics, Ltd. 1776 Mentor Avenue, Suite 17 Cincinnati, Ohio 45242 Active
CFD Investigation of Influence of Tube Bundle Cross-Section over Pressure Drop and Heat Transfer Rate
 CFD Investigation of Influence of Tube Bundle Cross-Section over Pressure Drop and Heat Transfer Rate Sandeep M, U Sathishkumar Abstract In this paper, a study of different cross section bundle arrangements
CFD Investigation of Influence of Tube Bundle Cross-Section over Pressure Drop and Heat Transfer Rate Sandeep M, U Sathishkumar Abstract In this paper, a study of different cross section bundle arrangements
TURBOGENERATOR DYNAMIC ANALYSIS TO IDENTIFY CRITICAL SPEED AND VIBRATION SEVERITY
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series D, Vol. 77, Iss. 3, 2015 ISSN 1454-2358 TURBOGENERATOR DYNAMIC ANALYSIS TO IDENTIFY CRITICAL SPEED AND VIBRATION SEVERITY Claudiu BISU 1, Florian ISTRATE 2, Marin ANICA 3 Vibration
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series D, Vol. 77, Iss. 3, 2015 ISSN 1454-2358 TURBOGENERATOR DYNAMIC ANALYSIS TO IDENTIFY CRITICAL SPEED AND VIBRATION SEVERITY Claudiu BISU 1, Florian ISTRATE 2, Marin ANICA 3 Vibration
Analysis on natural characteristics of four-stage main transmission system in three-engine helicopter
 Article ID: 18558; Draft date: 2017-06-12 23:31 Analysis on natural characteristics of four-stage main transmission system in three-engine helicopter Yuan Chen 1, Ru-peng Zhu 2, Ye-ping Xiong 3, Guang-hu
Article ID: 18558; Draft date: 2017-06-12 23:31 Analysis on natural characteristics of four-stage main transmission system in three-engine helicopter Yuan Chen 1, Ru-peng Zhu 2, Ye-ping Xiong 3, Guang-hu
Characteristic Analysis on Energy Waveforms of Point Sparks and Plamas Applied a Converting Device of Spark for Gasoline Engines
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(24), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i24/95986, June 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Characteristic Analysis on Energy Waveforms of Point
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(24), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i24/95986, June 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Characteristic Analysis on Energy Waveforms of Point
VALMONT MITIGATOR TR1
 VALMONT MITIGATOR TR1 Research Verification of the Valmont TR1 Damper Performance MITIGATOR TR1 VIBRATION DAMPER The Valmont TR1 damper has been specifically designed using vibration theory and innovative
VALMONT MITIGATOR TR1 Research Verification of the Valmont TR1 Damper Performance MITIGATOR TR1 VIBRATION DAMPER The Valmont TR1 damper has been specifically designed using vibration theory and innovative
THE LONGITUDINAL VIBRATION OF COMPOSITE DRIVE SHAFT
 THE LONGITUDINAL VIBRATION OF COMPOSITE DRIVE SHAFT Tongtong Zhang, Yongsheng Li, Weibo Wang National Key Laboratory on Ship Vibration and Noise, China Ship Scientific Research Centre, Wuxi, China email:
THE LONGITUDINAL VIBRATION OF COMPOSITE DRIVE SHAFT Tongtong Zhang, Yongsheng Li, Weibo Wang National Key Laboratory on Ship Vibration and Noise, China Ship Scientific Research Centre, Wuxi, China email:
Comparing FEM Transfer Matrix Simulated Compressor Plenum Pressure Pulsations to Measured Pressure Pulsations and to CFD Results
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 Comparing FEM Transfer Matrix Simulated Compressor Plenum Pressure Pulsations to Measured
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 Comparing FEM Transfer Matrix Simulated Compressor Plenum Pressure Pulsations to Measured
Application of Simulation-X R based Simulation Technique to Notch Shape Optimization for a Variable Swash Plate Type Piston Pump
 Application of Simulation-X R based Simulation Technique to Notch Shape Optimization for a Variable Swash Plate Type Piston Pump Jun Ho Jang 1, Won Jee Chung 1, Dong Sun Lee 1 and Young Hwan Yoon 2 1 School
Application of Simulation-X R based Simulation Technique to Notch Shape Optimization for a Variable Swash Plate Type Piston Pump Jun Ho Jang 1, Won Jee Chung 1, Dong Sun Lee 1 and Young Hwan Yoon 2 1 School
Research on vibration reduction of multiple parallel gear shafts with ISFD
 Research on vibration reduction of multiple parallel gear shafts with ISFD Kaihua Lu 1, Lidong He 2, Wei Yan 3 Beijing Key Laboratory of Health Monitoring and Self-Recovery for High-End Mechanical Equipment,
Research on vibration reduction of multiple parallel gear shafts with ISFD Kaihua Lu 1, Lidong He 2, Wei Yan 3 Beijing Key Laboratory of Health Monitoring and Self-Recovery for High-End Mechanical Equipment,
KINEMATICAL SUSPENSION OPTIMIZATION USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENT METHOD
 Jurnal Mekanikal June 2014, No 37, 16-25 KINEMATICAL SUSPENSION OPTIMIZATION USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENT METHOD Mohd Awaluddin A Rahman and Afandi Dzakaria Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti
Jurnal Mekanikal June 2014, No 37, 16-25 KINEMATICAL SUSPENSION OPTIMIZATION USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENT METHOD Mohd Awaluddin A Rahman and Afandi Dzakaria Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti
Passive Vibration Reduction with Silicone Springs and Dynamic Absorber
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 19 (2011 ) 431 435 International Conference on Optics in Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology 2011 Passive Vibration Reduction with Silicone
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 19 (2011 ) 431 435 International Conference on Optics in Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology 2011 Passive Vibration Reduction with Silicone
Relative ride vibration of off-road vehicles with front-, rear- and both axles torsio-elastic suspension
 Relative ride vibration of off-road vehicles with front-, rear- and both axles torsio-elastic suspension Mu Chai 1, Subhash Rakheja 2, Wen Bin Shangguan 3 1, 2, 3 School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,
Relative ride vibration of off-road vehicles with front-, rear- and both axles torsio-elastic suspension Mu Chai 1, Subhash Rakheja 2, Wen Bin Shangguan 3 1, 2, 3 School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia CIRP 33 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia CIRP 33 (2015 ) 581 586 9th CIRP Conference on Intelligent Computation in Manufacturing Engineering - CIRP ICME '14 Magnetic fluid seal
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia CIRP 33 (2015 ) 581 586 9th CIRP Conference on Intelligent Computation in Manufacturing Engineering - CIRP ICME '14 Magnetic fluid seal
Influence of Cylinder Bore Volume on Pressure Pulsations in a Hermetic Reciprocating Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Influence of Cylinder Bore Volume on Pressure Pulsations in a Hermetic Reciprocating
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Influence of Cylinder Bore Volume on Pressure Pulsations in a Hermetic Reciprocating
Advanced Design of a Ducted Propeller with High Bollard Pull Performance
 First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 009 Advanced Design of a Ducted Propeller with High Bollard Pull Performance Tadashi Taketani 1, Koyu Kimura 1, Norio
First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 009 Advanced Design of a Ducted Propeller with High Bollard Pull Performance Tadashi Taketani 1, Koyu Kimura 1, Norio
Estimation of Unmeasured DOF s on a Scaled Model of a Blade Structure
 Estimation of Unmeasured DOF s on a Scaled Model of a Blade Structure Anders Skafte 1, Rune Brincker 2 ABSTRACT This paper presents a new expansion technique which enables to predict mode shape coordinates
Estimation of Unmeasured DOF s on a Scaled Model of a Blade Structure Anders Skafte 1, Rune Brincker 2 ABSTRACT This paper presents a new expansion technique which enables to predict mode shape coordinates
MODELING SUSPENSION DAMPER MODULES USING LS-DYNA
 MODELING SUSPENSION DAMPER MODULES USING LS-DYNA Jason J. Tao Delphi Automotive Systems Energy & Chassis Systems Division 435 Cincinnati Street Dayton, OH 4548 Telephone: (937) 455-6298 E-mail: Jason.J.Tao@Delphiauto.com
MODELING SUSPENSION DAMPER MODULES USING LS-DYNA Jason J. Tao Delphi Automotive Systems Energy & Chassis Systems Division 435 Cincinnati Street Dayton, OH 4548 Telephone: (937) 455-6298 E-mail: Jason.J.Tao@Delphiauto.com
Enhance the Performance of Heat Exchanger with Twisted Tape Insert: A Review
 Enhance the Performance of Heat Exchanger with Twisted Tape Insert: A Review M.J.Patel 1, K.S.Parmar 2, Umang R. Soni 3 1,2. M.E. Student, department of mechanical engineering, SPIT,Basna, Gujarat, India,
Enhance the Performance of Heat Exchanger with Twisted Tape Insert: A Review M.J.Patel 1, K.S.Parmar 2, Umang R. Soni 3 1,2. M.E. Student, department of mechanical engineering, SPIT,Basna, Gujarat, India,
Design and Test of Transonic Compressor Rotor with Tandem Cascade
 Proceedings of the International Gas Turbine Congress 2003 Tokyo November 2-7, 2003 IGTC2003Tokyo TS-108 Design and Test of Transonic Compressor Rotor with Tandem Cascade Yusuke SAKAI, Akinori MATSUOKA,
Proceedings of the International Gas Turbine Congress 2003 Tokyo November 2-7, 2003 IGTC2003Tokyo TS-108 Design and Test of Transonic Compressor Rotor with Tandem Cascade Yusuke SAKAI, Akinori MATSUOKA,
Dynamic Behavior Analysis of Hydraulic Power Steering Systems
 Dynamic Behavior Analysis of Hydraulic Power Steering Systems Y. TOKUMOTO * *Research & Development Center, Control Devices Development Department Research regarding dynamic modeling of hydraulic power
Dynamic Behavior Analysis of Hydraulic Power Steering Systems Y. TOKUMOTO * *Research & Development Center, Control Devices Development Department Research regarding dynamic modeling of hydraulic power
EFFECTIVENESS OF THE ACTIVE PNEUMATIC SUSPENSION OF THE OPERATOR S SEAT OF THE MOBILE MACHINE IN DEPEND OF THE VIBRATION REDUCTION STRATEGIES
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 25, No. 3 2018 EFFECTIVENESS OF THE ACTIVE PNEUMATIC SUSPENSION OF THE OPERATOR S SEAT OF THE MOBILE MACHINE IN DEPEND OF THE VIBRATION REDUCTION STRATEGIES
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 25, No. 3 2018 EFFECTIVENESS OF THE ACTIVE PNEUMATIC SUSPENSION OF THE OPERATOR S SEAT OF THE MOBILE MACHINE IN DEPEND OF THE VIBRATION REDUCTION STRATEGIES
Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train
 Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train A.R.Mokate 1, R.R.Navthar 2 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, PDVVP COE, A. Nagar, Maharashtra, India 1 Assistance Professor,
Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train A.R.Mokate 1, R.R.Navthar 2 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, PDVVP COE, A. Nagar, Maharashtra, India 1 Assistance Professor,
Influence of Parameter Variations on System Identification of Full Car Model
 Influence of Parameter Variations on System Identification of Full Car Model Fengchun Sun, an Cui Abstract The car model is used extensively in the system identification of a vehicle suspension system
Influence of Parameter Variations on System Identification of Full Car Model Fengchun Sun, an Cui Abstract The car model is used extensively in the system identification of a vehicle suspension system
Experimental Study Of Effect Of Tilt Angle Of The Flap On Transverse Vibration Of Plate
 Experimental Study Of Effect Of Tilt Angle Of The Flap On Transverse Vibration Of Plate P. Mahadevaswamy a*, B.S. Suresh b a Department of Mechanical Engineering, Acharya Institute of Technology, Bangalore.
Experimental Study Of Effect Of Tilt Angle Of The Flap On Transverse Vibration Of Plate P. Mahadevaswamy a*, B.S. Suresh b a Department of Mechanical Engineering, Acharya Institute of Technology, Bangalore.
Interrelation between Wavelengths of Track Geometry Irregularities and Rail Vehicle Dynamic Properties
 THE ARCHIVES OF TRANSPORT VOL. XXV-XXVI NO 1-2 213 Interrelation between Wavelengths of Track Geometry Irregularities and Rail Vehicle Dynamic Properties Bogdan Sowinski Received January 213 Abstract The
THE ARCHIVES OF TRANSPORT VOL. XXV-XXVI NO 1-2 213 Interrelation between Wavelengths of Track Geometry Irregularities and Rail Vehicle Dynamic Properties Bogdan Sowinski Received January 213 Abstract The
Optimization of Seat Displacement and Settling Time of Quarter Car Model Vehicle Dynamic System Subjected to Speed Bump
 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347-5161 2014 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Optimization
Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347-5161 2014 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Optimization
Application of Reverse Engineering and Impact Analysis of Motor Cycle Helmet
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(34), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i34/100989, September 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Application of Reverse Engineering and Impact
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(34), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i34/100989, September 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Application of Reverse Engineering and Impact
Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Compression Loads in Twin Screw Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Compression Loads in Twin Screw Compressor
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Compression Loads in Twin Screw Compressor
Experimental Investigations on Board Level Electronic Packages Subjected to Sinusoidal Vibration Loads
 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347-5161 2014 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Experimental
Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347-5161 2014 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Experimental
Shock tube based dynamic calibration of pressure sensors
 Shock tube based dynamic calibration of pressure sensors C. E. Matthews, S. Downes, T.J. Esward, A. Wilson (NPL) S. Eichstädt, C. Elster (PTB) 23/06/2011 1 Outline Shock tube as a basis for calibration
Shock tube based dynamic calibration of pressure sensors C. E. Matthews, S. Downes, T.J. Esward, A. Wilson (NPL) S. Eichstädt, C. Elster (PTB) 23/06/2011 1 Outline Shock tube as a basis for calibration
EFFECTIVE SOLUTIONS FOR SHOCK AND VIBRATION CONTROL
 EFFECTIVE SOLUTIONS FOR SHOCK AND VIBRATION CONTROL Part 1 Alan Klembczyk TAYLOR DEVICES, INC. North Tonawanda, NY Part 2 Herb LeKuch Shocktech / 901D Monsey, NY SAVIAC Tutorial 2009 Part 1 OUTLINE Introduction
EFFECTIVE SOLUTIONS FOR SHOCK AND VIBRATION CONTROL Part 1 Alan Klembczyk TAYLOR DEVICES, INC. North Tonawanda, NY Part 2 Herb LeKuch Shocktech / 901D Monsey, NY SAVIAC Tutorial 2009 Part 1 OUTLINE Introduction
Oscillator Experiment of Simple Girder Bridge coupled with Vehicle
 The 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM 12) Seoul, Korea, August 26-30, 2012 Oscillator Experiment of Simple Girder Bridge coupled with Vehicle Mitsuo
The 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM 12) Seoul, Korea, August 26-30, 2012 Oscillator Experiment of Simple Girder Bridge coupled with Vehicle Mitsuo
Transmission Error in Screw Compressor Rotors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Transmission Error in Screw Compressor Rotors Jack Sauls Trane Follow this and additional
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Transmission Error in Screw Compressor Rotors Jack Sauls Trane Follow this and additional
Seismic Capacity Test of Overhead Crane under Horizontal and Vertical Excitation - Element Model Test Results on Nonlinear Response Behavior-
 2th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 2) Espoo, Finland, August 9-14, 29 SMiRT 2-Division, Paper Seismic Capacity Test of Overhead Crane under Horizontal and
2th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 2) Espoo, Finland, August 9-14, 29 SMiRT 2-Division, Paper Seismic Capacity Test of Overhead Crane under Horizontal and
Effect of Stator Shape on the Performance of Torque Converter
 16 th International Conference on AEROSPACE SCIENCES & AVIATION TECHNOLOGY, ASAT - 16 May 26-28, 2015, E-Mail: asat@mtc.edu.eg Military Technical College, Kobry Elkobbah, Cairo, Egypt Tel : +(202) 24025292
16 th International Conference on AEROSPACE SCIENCES & AVIATION TECHNOLOGY, ASAT - 16 May 26-28, 2015, E-Mail: asat@mtc.edu.eg Military Technical College, Kobry Elkobbah, Cairo, Egypt Tel : +(202) 24025292
Chapter 4. Vehicle Testing
 Chapter 4 Vehicle Testing The purpose of this chapter is to describe the field testing of the controllable dampers on a Volvo VN heavy truck. The first part of this chapter describes the test vehicle used
Chapter 4 Vehicle Testing The purpose of this chapter is to describe the field testing of the controllable dampers on a Volvo VN heavy truck. The first part of this chapter describes the test vehicle used
CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL SHOCK TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY
 135 CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL SHOCK TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY 6.1 INTRODUCTION Shock is often defined as a rapid transfer of energy to a mechanical system, which results in a significant increase in the stress,
135 CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL SHOCK TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY 6.1 INTRODUCTION Shock is often defined as a rapid transfer of energy to a mechanical system, which results in a significant increase in the stress,
Seismic-upgrading of Existing Stacks of Nuclear Power Station using Structural Control Oil Dampers
 October 12-17, 28, Beijing, China ABSTRACT : Seismic-upgrading of Existing Stacks of Nuclear Power Station using Structural Control Oil Dampers Ryu Shimamoto 1, Fukashi Mori 2, Tomonori Kitaori 2, Satoru
October 12-17, 28, Beijing, China ABSTRACT : Seismic-upgrading of Existing Stacks of Nuclear Power Station using Structural Control Oil Dampers Ryu Shimamoto 1, Fukashi Mori 2, Tomonori Kitaori 2, Satoru
A CASE STUDY OF A FLOW-INDUCED TORSIONAL RESONANCE
 A CASE STUDY OF A FLOW-INDUCED TORSIONAL RESONANCE William F. Eckert, P.Eng., Ph.D. Field Services Manager Brian C. Howes, M.Sc., P.Eng. Chief Engineer Beta Machinery Analysis Ltd., Calgary, AB, Canada,
A CASE STUDY OF A FLOW-INDUCED TORSIONAL RESONANCE William F. Eckert, P.Eng., Ph.D. Field Services Manager Brian C. Howes, M.Sc., P.Eng. Chief Engineer Beta Machinery Analysis Ltd., Calgary, AB, Canada,
HELICOPTER TAIL ROTOR ANALYSIS: EXPERIENCE IN AGUSTA WITH ADAMS
 HELICOPTER TAIL ROTOR ANALYSIS: EXPERIENCE IN AGUSTA WITH ADAMS Bianchi F., Agusta Sp.a. Via G.Agusta, 520 - Cascina Costa di Samarate,Varese - Italy - e-mail: atr@agusta.it Abstract The purpose of the
HELICOPTER TAIL ROTOR ANALYSIS: EXPERIENCE IN AGUSTA WITH ADAMS Bianchi F., Agusta Sp.a. Via G.Agusta, 520 - Cascina Costa di Samarate,Varese - Italy - e-mail: atr@agusta.it Abstract The purpose of the
Damping Ratio Estimation of an Existing 8-story Building Considering Soil-Structure Interaction Using Strong Motion Observation Data.
 Damping Ratio Estimation of an Existing -story Building Considering Soil-Structure Interaction Using Strong Motion Observation Data by Koichi Morita ABSTRACT In this study, damping ratio of an exiting
Damping Ratio Estimation of an Existing -story Building Considering Soil-Structure Interaction Using Strong Motion Observation Data by Koichi Morita ABSTRACT In this study, damping ratio of an exiting
AXLE HOUSING AND UNITIZE BEARING PACK SET MODAL CHARACTERISATION
 F2004F461 AXLE HOUSING AND UNITIZE BEARING PACK SET MODAL CHARACTERISATION 1 Badiola, Virginia*, 2 Pintor, Jesús María, 3 Gainza, Gorka 1 Dana Equipamientos S.A., España, 2 Universidad Pública de Navarra,
F2004F461 AXLE HOUSING AND UNITIZE BEARING PACK SET MODAL CHARACTERISATION 1 Badiola, Virginia*, 2 Pintor, Jesús María, 3 Gainza, Gorka 1 Dana Equipamientos S.A., España, 2 Universidad Pública de Navarra,
RELIABILITY IMPROVEMENT OF ACCESSORY GEARBOX BEVEL DRIVES Kozharinov Egor* *CIAM
 RELIABILITY IMPROVEMENT OF ACCESSORY GEARBOX BEVEL DRIVES Kozharinov Egor* *CIAM egor@ciam.ru Keywords: Bevel gears, accessory drives, resonance oscillations, Coulomb friction damping Abstract Bevel gear
RELIABILITY IMPROVEMENT OF ACCESSORY GEARBOX BEVEL DRIVES Kozharinov Egor* *CIAM egor@ciam.ru Keywords: Bevel gears, accessory drives, resonance oscillations, Coulomb friction damping Abstract Bevel gear
A CONTRIBUTION TO PASSIVE SHOCK ABSORBER FORCE INVESTIGATION
 Original Scientific Paper doi:10.5937/jaes12-5445 Paper number: 12(2014)3, 295, 217-226 A CONTRIBUTION TO PASSIVE SHOCK ABSORBER FORCE INVESTIGATION Dr Miroslav Demić* Faculty of Engineering Sciences,
Original Scientific Paper doi:10.5937/jaes12-5445 Paper number: 12(2014)3, 295, 217-226 A CONTRIBUTION TO PASSIVE SHOCK ABSORBER FORCE INVESTIGATION Dr Miroslav Demić* Faculty of Engineering Sciences,
FLOW CONTROL THROUGH VORTEX SHEDDING INTERACTION OF ONE CYLINDER DOWNSTREAM OF ANOTHER. Jonathan Payton 1, and *Sam M Dakka 2
 International Journal of GEOMATE, May, 2017, Vol.12, Issue 33, pp. 53-59 Geotec., Const. Mat. &Env., ISSN:2186-2990, Japan, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21660/2017.33.2565 FLOW CONTROL THROUGH VORTEX SHEDDING
International Journal of GEOMATE, May, 2017, Vol.12, Issue 33, pp. 53-59 Geotec., Const. Mat. &Env., ISSN:2186-2990, Japan, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21660/2017.33.2565 FLOW CONTROL THROUGH VORTEX SHEDDING
1874. Effect predictions of star pinion geometry phase adjustments on dynamic load sharing behaviors of differential face gear trains
 1874. Effect predictions of star pinion geometry phase adjustments on dynamic load sharing behaviors of differential face gear trains Zhengminqing Li 1, Wei Ye 2, Linlin Zhang 3, Rupeng Zhu 4 Nanjing University
1874. Effect predictions of star pinion geometry phase adjustments on dynamic load sharing behaviors of differential face gear trains Zhengminqing Li 1, Wei Ye 2, Linlin Zhang 3, Rupeng Zhu 4 Nanjing University
Cross flow and in-line damping measurements from forced excitations of a flexible cylinder in a uniform flow
 Proceedings of OMAE04 23rd International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering June 20-25, 2004, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada OM AE2004-51397 Cross flow and in-line damping measurements
Proceedings of OMAE04 23rd International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering June 20-25, 2004, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada OM AE2004-51397 Cross flow and in-line damping measurements
DYNAMIC TESTS ON A CONCRETE SLAB WITH A TUNED MASS DAMPER
 MATEC Web of Conferences, 6 ( 15) DOI: 1.151/ matecconf/ 15 6 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 15 DYNAMIC TESTS ON A CONCRETE SLAB WITH A TUNED MASS DAMPER Jorge Eliécer Campuzano Carmona
MATEC Web of Conferences, 6 ( 15) DOI: 1.151/ matecconf/ 15 6 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 15 DYNAMIC TESTS ON A CONCRETE SLAB WITH A TUNED MASS DAMPER Jorge Eliécer Campuzano Carmona
Modeling and Vibration Analysis of a Drum type Washing Machine
 Modeling and Vibration Analysis of a Drum type Washing Machine Takayuki KOIZUMI, Nobutaka TSUJIUCHI, Yutaka NISHIMURA Department of Engineering, Doshisha University, 1-3, Tataramiyakodani, Kyotanabe, Kyoto,
Modeling and Vibration Analysis of a Drum type Washing Machine Takayuki KOIZUMI, Nobutaka TSUJIUCHI, Yutaka NISHIMURA Department of Engineering, Doshisha University, 1-3, Tataramiyakodani, Kyotanabe, Kyoto,
Full Scale Experimental Evaluation for Cable Dampers
 Full Scale Experimental Evaluation for Cable Dampers Liang Dong, Tian Jingxian, Du Chuang, Ma Jinlong Abstract One of the key techniques for building long span cable-stayed bridge is the mitigation of
Full Scale Experimental Evaluation for Cable Dampers Liang Dong, Tian Jingxian, Du Chuang, Ma Jinlong Abstract One of the key techniques for building long span cable-stayed bridge is the mitigation of
MARINE FOUR-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING OIL FILM LUBRICATION CHARACTERISTIC ANALYSIS
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH Special Issue 2018 S2 (98) 2018 Vol. 25; pp. 30-34 10.2478/pomr-2018-0070 MARINE FOUR-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING OIL FILM LUBRICATION CHARACTERISTIC ANALYSIS
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH Special Issue 2018 S2 (98) 2018 Vol. 25; pp. 30-34 10.2478/pomr-2018-0070 MARINE FOUR-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING OIL FILM LUBRICATION CHARACTERISTIC ANALYSIS
Modeling of 17-DOF Tractor Semi- Trailer Vehicle
 ISSN 2395-1621 Modeling of 17-DOF Tractor Semi- Trailer Vehicle # S. B. Walhekar, #2 D. H. Burande 1 sumitwalhekar@gmail.com 2 dhburande.scoe@sinhgad.edu #12 Mechanical Engineering Department, S.P. Pune
ISSN 2395-1621 Modeling of 17-DOF Tractor Semi- Trailer Vehicle # S. B. Walhekar, #2 D. H. Burande 1 sumitwalhekar@gmail.com 2 dhburande.scoe@sinhgad.edu #12 Mechanical Engineering Department, S.P. Pune
Static And Modal Analysis of Tractor Power Take Off (PTO) Gearbox Housing
 Static And Modal Analysis of Tractor Power Take Off (PTO) Gearbox Housing Gopali S Lamani 1, Prof: S.R.Basavaraddi 2, Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, JSPM NTC RSSOER,India1 Professor,
Static And Modal Analysis of Tractor Power Take Off (PTO) Gearbox Housing Gopali S Lamani 1, Prof: S.R.Basavaraddi 2, Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, JSPM NTC RSSOER,India1 Professor,
Noise Reduction of Accumulators for R410A Rotary Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Noise Reduction of Accumulators for R410A Rotary Compressors Ling Li Guangdong Meizhi
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Noise Reduction of Accumulators for R410A Rotary Compressors Ling Li Guangdong Meizhi
Dynamic performance of flow control valve using different models of system identification
 Dynamic performance of flow control valve using different models of system identification Ho Chang, Po-Kai Tzenog and Yun-Min Yeh Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Taipei University of Technology
Dynamic performance of flow control valve using different models of system identification Ho Chang, Po-Kai Tzenog and Yun-Min Yeh Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Taipei University of Technology
ISSN: SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS OF PASSIVE SUSPENSION SYSTEM FOR DIFFERENT ROAD PROFILES WITH VARIABLE DAMPING AND STIFFNESS PARAMETERS S.
 Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Sciences www.jchps.com ISSN: 974-2115 SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS OF PASSIVE SUSPENSION SYSTEM FOR DIFFERENT ROAD PROFILES WITH VARIABLE DAMPING AND STIFFNESS PARAMETERS
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Sciences www.jchps.com ISSN: 974-2115 SIMULATION AND ANALYSIS OF PASSIVE SUSPENSION SYSTEM FOR DIFFERENT ROAD PROFILES WITH VARIABLE DAMPING AND STIFFNESS PARAMETERS
Improvements of Existing Overhead Lines for 180km/h operation of the Tilting Train
 Improvements of Existing Overhead Lines for 180km/h operation of the Tilting Train K. Lee, Y.H. Cho, Y. Park, S. Kwon Korea Railroad Research Institute, Uiwang-City, Korea Abstract The purpose of this
Improvements of Existing Overhead Lines for 180km/h operation of the Tilting Train K. Lee, Y.H. Cho, Y. Park, S. Kwon Korea Railroad Research Institute, Uiwang-City, Korea Abstract The purpose of this
Analysis and evaluation of a tyre model through test data obtained using the IMMa tyre test bench
 Vehicle System Dynamics Vol. 43, Supplement, 2005, 241 252 Analysis and evaluation of a tyre model through test data obtained using the IMMa tyre test bench A. ORTIZ*, J.A. CABRERA, J. CASTILLO and A.
Vehicle System Dynamics Vol. 43, Supplement, 2005, 241 252 Analysis and evaluation of a tyre model through test data obtained using the IMMa tyre test bench A. ORTIZ*, J.A. CABRERA, J. CASTILLO and A.
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S 2900 MIXER TO BE USED BY CNRL FOR BITUMEN VISCOSITY CONTROL Report R0. By Kimbal A.
 COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S 2900 MIXER TO BE USED BY CNRL FOR BITUMEN VISCOSITY CONTROL Report 412509-1R0 By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY May 2012 ALDEN RESEARCH
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S 2900 MIXER TO BE USED BY CNRL FOR BITUMEN VISCOSITY CONTROL Report 412509-1R0 By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY May 2012 ALDEN RESEARCH
CFD on Cavitation around Marine Propellers with Energy-Saving Devices
 63 CFD on Cavitation around Marine Propellers with Energy-Saving Devices CHIHARU KAWAKITA *1 REIKO TAKASHIMA *2 KEI SATO *2 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (MHI) has developed energy-saving devices that
63 CFD on Cavitation around Marine Propellers with Energy-Saving Devices CHIHARU KAWAKITA *1 REIKO TAKASHIMA *2 KEI SATO *2 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (MHI) has developed energy-saving devices that
Noise Reduction in a Reciprocating Compressor by Optimizing the Suction Muffler
 Noise Reduction in a Reciprocating Compressor by Optimizing the Suction Muffler Katakama Nagarjuna ¹ K.Sreenivas² ¹ M.tech student, ²Professor, dept of mechanical engineering kits, markapur, A.P, INDIA
Noise Reduction in a Reciprocating Compressor by Optimizing the Suction Muffler Katakama Nagarjuna ¹ K.Sreenivas² ¹ M.tech student, ²Professor, dept of mechanical engineering kits, markapur, A.P, INDIA
Enhanced Heat Transfer Surface Development for Exterior Tube Surfaces
 511 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 2013 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
511 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 2013 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
Special edition paper
 Countermeasures of Noise Reduction for Shinkansen Electric-Current Collecting System and Lower Parts of Cars Kaoru Murata*, Toshikazu Sato* and Koichi Sasaki* Shinkansen noise can be broadly classified
Countermeasures of Noise Reduction for Shinkansen Electric-Current Collecting System and Lower Parts of Cars Kaoru Murata*, Toshikazu Sato* and Koichi Sasaki* Shinkansen noise can be broadly classified
ASTM D4169 Truck Profile Update Rationale Revision Date: September 22, 2016
 Over the past 10 to 15 years, many truck measurement studies have been performed characterizing various over the road environment(s) and much of the truck measurement data is available in the public domain.
Over the past 10 to 15 years, many truck measurement studies have been performed characterizing various over the road environment(s) and much of the truck measurement data is available in the public domain.
Chapter 2 Dynamic Analysis of a Heavy Vehicle Using Lumped Parameter Model
 Chapter 2 Dynamic Analysis of a Heavy Vehicle Using Lumped Parameter Model The interaction between a vehicle and the road is a very complicated dynamic process, which involves many fields such as vehicle
Chapter 2 Dynamic Analysis of a Heavy Vehicle Using Lumped Parameter Model The interaction between a vehicle and the road is a very complicated dynamic process, which involves many fields such as vehicle
Analysis of Torsional Vibration in Elliptical Gears
 The The rd rd International Conference on on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES Pilsen, Czech Pilsen, Republic, Czech August Republic, September -, Analysis of Torsional Vibration in Elliptical Gears
The The rd rd International Conference on on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES Pilsen, Czech Pilsen, Republic, Czech August Republic, September -, Analysis of Torsional Vibration in Elliptical Gears
Effect of concave plug shape of a control valve on the fluid flow characteristics using computational fluid dynamics
 Effect of concave plug shape of a control valve on the fluid flow characteristics using computational fluid dynamics Yasser Abdel Mohsen, Ashraf Sharara, Basiouny Elsouhily, Hassan Elgamal Mechanical Engineering
Effect of concave plug shape of a control valve on the fluid flow characteristics using computational fluid dynamics Yasser Abdel Mohsen, Ashraf Sharara, Basiouny Elsouhily, Hassan Elgamal Mechanical Engineering
Mohit Law. Keywords: Machine tools, Active vibration isolation, Electro-hydraulic actuator, Design guidelines, Sensitivity analysis
 College of Engineering., Pune, Maharashtra, INDIA. Design Guidelines for an Electro-Hydraulic Actuator to Isolate Machines from Vibrations Mohit Law Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute
College of Engineering., Pune, Maharashtra, INDIA. Design Guidelines for an Electro-Hydraulic Actuator to Isolate Machines from Vibrations Mohit Law Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute
Traffic Signal Volume Warrants A Delay Perspective
 Traffic Signal Volume Warrants A Delay Perspective The Manual on Uniform Traffic Introduction The 2009 Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD) Control Devices (MUTCD) 1 is widely used to help
Traffic Signal Volume Warrants A Delay Perspective The Manual on Uniform Traffic Introduction The 2009 Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD) Control Devices (MUTCD) 1 is widely used to help
Experimental Study on Flutter Performance of a 1700m Long Truss Girder Suspension Bridge
 Experimental Study on Flutter Performance of a 1700m Long Truss Girder Suspension Bridge *Yanguo Sun 1), Haili Liao 2) and Mingshui Li 3) 1), 2), 3) Research Centre for Wind Eng., Southwest Jiaotong University,
Experimental Study on Flutter Performance of a 1700m Long Truss Girder Suspension Bridge *Yanguo Sun 1), Haili Liao 2) and Mingshui Li 3) 1), 2), 3) Research Centre for Wind Eng., Southwest Jiaotong University,
Driver roll speed influence in Ring Rolling process
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 207 (2017) 1230 1235 International Conference on the Technology of Plasticity, ICTP 2017, 17-22 September 2017, Cambridge, United
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 207 (2017) 1230 1235 International Conference on the Technology of Plasticity, ICTP 2017, 17-22 September 2017, Cambridge, United
Thermal Hydraulics Design Limits Class Note II. Professor Neil E. Todreas
 Thermal Hydraulics Design Limits Class Note II Professor Neil E. Todreas The following discussion of steady state and transient design limits is extracted from the theses of Carter Shuffler and Jarrod
Thermal Hydraulics Design Limits Class Note II Professor Neil E. Todreas The following discussion of steady state and transient design limits is extracted from the theses of Carter Shuffler and Jarrod
CHAPTER 4: EXPERIMENTAL WORK 4-1
 CHAPTER 4: EXPERIMENTAL WORK 4-1 EXPERIMENTAL WORK 4.1 Preamble 4-2 4.2 Test setup 4-2 4.2.1 Experimental setup 4-2 4.2.2 Instrumentation, control and data acquisition 4-4 4.3 Hydro-pneumatic spring characterisation
CHAPTER 4: EXPERIMENTAL WORK 4-1 EXPERIMENTAL WORK 4.1 Preamble 4-2 4.2 Test setup 4-2 4.2.1 Experimental setup 4-2 4.2.2 Instrumentation, control and data acquisition 4-4 4.3 Hydro-pneumatic spring characterisation
Dynamic Coefficients in Hydrodynamic Bearing Analysis Steven Pasternak C.O. Engineering Sleeve and Sleevoil Bearings 8/10/18 WP0281
 Dynamic Coefficients in Hydrodynamic Bearing Analysis Steven Pasternak C.O. Engineering Sleeve and Sleevoil Bearings 8/10/18 WP0281 Hydrodynamic Bearing Basics Hydrodynamic journal bearings operate by
Dynamic Coefficients in Hydrodynamic Bearing Analysis Steven Pasternak C.O. Engineering Sleeve and Sleevoil Bearings 8/10/18 WP0281 Hydrodynamic Bearing Basics Hydrodynamic journal bearings operate by
On the prediction of rail cross mobility and track decay rates using Finite Element Models
 On the prediction of rail cross mobility and track decay rates using Finite Element Models Benjamin Betgen Vibratec, 28 Chemin du Petit Bois, 69130 Ecully, France. Giacomo Squicciarini, David J. Thompson
On the prediction of rail cross mobility and track decay rates using Finite Element Models Benjamin Betgen Vibratec, 28 Chemin du Petit Bois, 69130 Ecully, France. Giacomo Squicciarini, David J. Thompson
STIFFNESS CHARACTERISTICS OF MAIN BEARINGS FOUNDATION OF MARINE ENGINE
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 23, No. 1 2016 STIFFNESS CHARACTERISTICS OF MAIN BEARINGS FOUNDATION OF MARINE ENGINE Lech Murawski Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 23, No. 1 2016 STIFFNESS CHARACTERISTICS OF MAIN BEARINGS FOUNDATION OF MARINE ENGINE Lech Murawski Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
Sport Shieldz Skull Cap Evaluation EBB 4/22/2016
 Summary A single sample of the Sport Shieldz Skull Cap was tested to determine what additional protective benefit might result from wearing it under a current motorcycle helmet. A series of impacts were
Summary A single sample of the Sport Shieldz Skull Cap was tested to determine what additional protective benefit might result from wearing it under a current motorcycle helmet. A series of impacts were
Design of Piston Ring Surface Treatment for Reducing Lubricating Oil Consumption
 The 3rd International Conference on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES 2014 Pilsen, Czech Republic, August 31 September 3, 2014 Design of Piston Ring Surface Treatment for Reducing Lubricating Consumption
The 3rd International Conference on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES 2014 Pilsen, Czech Republic, August 31 September 3, 2014 Design of Piston Ring Surface Treatment for Reducing Lubricating Consumption
Suppression of chatter vibration of boring tools using impact dampers
 International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture 40 (2000) 1141 1156 Suppression of chatter vibration of boring tools using impact dampers Satoshi Ema a,*, Etsuo Marui b a Faculty of Education, Gifu
International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture 40 (2000) 1141 1156 Suppression of chatter vibration of boring tools using impact dampers Satoshi Ema a,*, Etsuo Marui b a Faculty of Education, Gifu
Analysis and control of vehicle steering wheel angular vibrations
 Analysis and control of vehicle steering wheel angular vibrations T. LANDREAU - V. GILLET Auto Chassis International Chassis Engineering Department Summary : The steering wheel vibration is analyzed through
Analysis and control of vehicle steering wheel angular vibrations T. LANDREAU - V. GILLET Auto Chassis International Chassis Engineering Department Summary : The steering wheel vibration is analyzed through
Effects of Boundary Conditions on Vibration Characteristics of Planetary Ring Gear
 The 14th IFToMM World Congress, Taipei, Taiwan, October 25-3, 215 DOI Number: 1.6567/IFToMM.14TH.WC.OS6.31 Effects of Boundary Conditions on Vibration Characteristics of Planetary Ring Gear Jun Zhang 1
The 14th IFToMM World Congress, Taipei, Taiwan, October 25-3, 215 DOI Number: 1.6567/IFToMM.14TH.WC.OS6.31 Effects of Boundary Conditions on Vibration Characteristics of Planetary Ring Gear Jun Zhang 1
Semi-Active Suspension for an Automobile
 Semi-Active Suspension for an Automobile Pavan Kumar.G 1 Mechanical Engineering PESIT Bangalore, India M. Sambasiva Rao 2 Mechanical Engineering PESIT Bangalore, India Abstract Handling characteristics
Semi-Active Suspension for an Automobile Pavan Kumar.G 1 Mechanical Engineering PESIT Bangalore, India M. Sambasiva Rao 2 Mechanical Engineering PESIT Bangalore, India Abstract Handling characteristics
Study on Mechanism of Impact Noise on Steering Gear While Turning Steering Wheel in Opposite Directions
 Study on Mechanism of Impact Noise on Steering Gear While Turning Steering Wheel in Opposite Directions Jeong-Tae Kim 1 ; Jong Wha Lee 2 ; Sun Mok Lee 3 ; Taewhwi Lee 4 ; Woong-Gi Kim 5 1 Hyundai Mobis,
Study on Mechanism of Impact Noise on Steering Gear While Turning Steering Wheel in Opposite Directions Jeong-Tae Kim 1 ; Jong Wha Lee 2 ; Sun Mok Lee 3 ; Taewhwi Lee 4 ; Woong-Gi Kim 5 1 Hyundai Mobis,
A Comparison of the Effectiveness of Elastomeric Tuned Mass Dampers and Particle Dampers
 003-01-1419 A Comparison of the Effectiveness of Elastomeric Tuned Mass Dampers and Particle Dampers Copyright 001 Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc. Allan C. Aubert Edward R. Green, Ph.D. Gregory Z.
003-01-1419 A Comparison of the Effectiveness of Elastomeric Tuned Mass Dampers and Particle Dampers Copyright 001 Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc. Allan C. Aubert Edward R. Green, Ph.D. Gregory Z.
Siemens PLM Software develops advanced testing methodologies to determine force distribution and visualize body deformation during vehicle handling.
 Automotive and transportation Product LMS LMS Engineering helps uncover the complex interaction between body flexibility and vehicle handling performance Business challenges Gain insight into the relationship
Automotive and transportation Product LMS LMS Engineering helps uncover the complex interaction between body flexibility and vehicle handling performance Business challenges Gain insight into the relationship
Active Suspensions For Tracked Vehicles
 Active Suspensions For Tracked Vehicles Y.G.Srinivasa, P. V. Manivannan 1, Rajesh K 2 and Sanjay goyal 2 Precision Engineering and Instrumentation Lab Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 1 PEIL
Active Suspensions For Tracked Vehicles Y.G.Srinivasa, P. V. Manivannan 1, Rajesh K 2 and Sanjay goyal 2 Precision Engineering and Instrumentation Lab Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 1 PEIL
The Reduction of the Noise/Vibration Generated by the Discharge Valve System in Hermetic Compressor for Refrigerator
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2000 The Reduction of the Noise/Vibration Generated by the Discharge Valve System in Hermetic
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2000 The Reduction of the Noise/Vibration Generated by the Discharge Valve System in Hermetic
CHARACTERISTICS OF FLOWS AROUND A RECTANGULAR CYLINDER OF WHICH VIBRATION IS SUPPRESSED BY PULSATING JETS FROM THE LEADING EDGES
 BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics & Applications Milano, Italy, July, 20-2 2008 CHARACTERISTICS OF FLOWS AROUND A RECTANGULAR CYLINDER OF WHICH VIBRATION IS SUPPRESSED BY PULSATING
BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics & Applications Milano, Italy, July, 20-2 2008 CHARACTERISTICS OF FLOWS AROUND A RECTANGULAR CYLINDER OF WHICH VIBRATION IS SUPPRESSED BY PULSATING
