The Impact upon Durability of Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine using Low Percentage Biodiesel (B2)
|
|
|
- Dominick Holt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Impact upon Durability of Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine using Low Percentage Biodiesel (B2) Yong-Yuan Ku 1*, Ching-Fu Liao 1, Yu-Tsen Shih 1, Min-Tsang Chang 2 1 Automotive Research and Testing Center 2 Energy Technology Division, Bureau of Energy, Ministry of Economic Affairs Abstract Due to the increasing price of crude oil, biofuel as an alternative of fossil fuels is sought to be a global wide solution to reduce the emission of green house gas. A long-term operation with blended biodiesel (B2) by standard engine test is evaluated in this study. The results can be referred to the consideration of marketing promotion strategy as well as government policy in Taiwan. Both B2 diesel fuel (2 vol biodiesel) and diesel fuel were employed to the same type of three new heavy-duty diesel engines for testing purpose. The engines are equipped with an electronically controlled common-rail fuel injection system. After 5 hours full load test or 1 hours transient cycle operation, the key components of the engines were analyzed and characterized by a series of inspections to identify the degree of decay and wear behavior. In addition, the engine performance and emission were also determined at each maintenance stage. The results indicated that the engine components including piston rings, cylinder liners and needle valves of injector were less difference in sizes comparison before and after durability tests. According to microscopic characterization and engine oil analyses, the wear loss of the key components was insignificant and tribological performance of the biodiesel (B2) was slightly better than that of diesel fuel. It was found that the performance and emissions were varied under ±3 when diesel engine was fueled with B2 biodiesel. Keywords: biodiesel, engine, durability test, wear. *Corresponding author: tom@artc.org.tw (Yong-Yuan Ku) 1. Introduction The biofuel used in diesel engines is mostly produced from animal fats or vegetable oils via transesterification process. Compared with fossil diesel, biodiesel produces lower engine emissions of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), particular matter (PM), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), which significantly reduce the impact of greenhouse effect on the earth [1~3]. Biodiesel is composed of methyl esters and has higher oxygen content, about 11 of total composition, lower emission of the particles and CO during the burning process. Besides, biodiesel contains low sulfur and is renewable energy to be one of solutions in oil market and reducing impact on economy [4]. Most researches found that the fretting wear performance of biodiesel was better than that of diesel fuel. The engine oil, used in a compression ignition engine fueled with linseed oil methyl ester (LOME) for durability test, was analyzed by atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS). The results showed that the wear debris of metal in the engine oils was significant decreased than that with the traditional diesel fuel. Moreover, according to the size difference of the engine component before and after durability test, the difference in size of engine component test with biodiesel is smaller than that with traditional diesel. These results imply that biodiesel can reduce the wear of engine components [5~7]. However, some researches indicated that biodiesel could cause more wear on some engine components and affect engine operation. S. Kaul et al. presented the study of using non-edible oils for corrosion tests. It soaked the diesel engine components in four kinds of oils chronically. Only salvadora oil caused dramatically corrosion on engine components. It is attributed to the high content of sulfur while the others had the same results as that of petro-diesel [8]. Japanese Automobile Manufacturers Association (JAMA) also pointed out that using biodiesel over a long period of time possibly caused negative influence on vehicles. For instance, the components of common-rail system may tend to wear, which caused poor atomizing during injection period and unexpectedly engine burning. Biodiesel may also corrode fuel tank and pipes for long-term operation [9]. In June 27, Taiwan government has legislated 1572 as national biodiesel standard and 1471 which allowed blends up to 5 of fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) in diesel fuel. B1 biodiesel is now widely used in Taiwan from July 28. However, the biodiesel percentage will be increased to B2 in market from 21 to achieve the goal of at least one hundred million liters of biodiesel used for one year. In order to confirm the influence of nationally-made biodiesel on vehicle, the effects on engine components, including cylinders, piston rings, needle valves, pistons and fuel injection nozzles were examined in this paper to explore the differences of wear with microscopic analysis. The compositions of carbon deposits in engines were observed and the exhaust emissions, performance and fuel consumption of test engines were also evaluated during durability tests. 2. Methods Three new diesel engines of the same type were used for durability tests. The engine equipped with common rail fuel injection system was a 2977 c.c. MITSUBISHI 4M42-4AT2 diesel engine, complied with the environmental protection regulations in Taiwan. The basic specifications of the test engine are shown in
2 Table 1. The test fuels complied with 1471 were 1 diesel (D1) and B2 biodiesel, which was blended with 2 vol biodiesel and 98 vol diesel. The biodiesel (B1) was made from spent edible oils by local manufacturers and complied with the biodiesel standard The properties of biodiesel are different from fossil diesel fuel, such as cetane index and viscosity are higher, lower content of sulfur, and no aromatic hydrocarbon. The lubricity of engine can be improved with adequate amount of biodiesel. Table 2 shows the properties of the test fuels and it indicated that except the lubricity, the difference between B2 and D1 can be neglected. The durability test with both full-load operation and US FTP transient cycle were performed in the present of study. At each maintenance stage (125hr or 25hr), the engine performance was determined using SAE J1995 test method and the measurement of emission was conducted by engine dynamometer under US FTP transient cycle. Table 3 shows the test methods in this study. Figure 1 is the running mode of full-load operation for durability test, where each cycle takes 2 hours and is repeated for 5 hours [1]. As for the wear of engine components in detailed inspection, the 3D coordinate measuring machine (CMM), profile meter and other measuring rigs were used to measure the size of specific parts and calculate the size variation for each component before and after durability tests. After the tests, the engine components were cut into appropriate sizes and characterized by Field-Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FESEM) to identify the wear characteristics of each part of the components. In addition, the test methods of standard were also employed to probe into the change of the composition in the engine oils and fuel hoses to interpret the difference on the wear of components. 3. Results and Discussion 3.1 Wear on Engine Components The wear analysis of the diesel engine components, including cylinders, piston rings, and needle valves is accomplished as shown in following sections. The size variation for the specific positions and detailed cut view on worn components were examined Cylinder For engine operation, the friction loss between the piston ring and cylinder is 8 of the total loss. The cylinders are made of cast iron with acceptable damping ability which is one of the best materials used to make cylinder walls. Table 4 is the change of average measurement values for the diameter (Dy) in the impinging direction, side diameter (Dx), and overall change of average diameter (D) of the cylinder in all test conditions. In general, after the engines run for a long-term operation, the surface of the cylinder will be worn and the material will be lost. However, the durability test results (see Table 4) depicted a significant reduction in Dy of the engine due to burning substances and reactants in the oil adhered to the impact surface or the contrast surface. Meanwhile, the size variation of Dx bore diameter is insignificant, which means the biodiesel makes no difference on the wear of cylinder. SEM analysis was performed in order to evaluate the wear behavior on the cylinder. As shown in Table 5, three samples for SEM analysis were cut from the cylinder which was located in top dead center, middle point of the stoke, and bottom dead center, separately. On the cylinder wall, there are many dents which are the marks left after the graphite peel off. The artificial oil-containing line is evident, meaning that after the durability test, there was no critical wear on the cylinder wall for detailed size measurement. For the three engines examined, the dents in the D1 cylinder is significant, showing that B2 has better performance on wearing tests for other two engines. In addition, the smoothness of the cylinder using B2 for 5 hours is better than that of 1 hours as the surface wear is promotional to the running period Piston Ring Piston rings, consists of compression ring and oil ring, prevent the air leakage from the clearance between piston and cylinder wall. The experimental results indicate that piston rings of all tested engines have slight decrease of the size due to the wear during durability test process. The decrease of size is mainly due to the polishing effect on the surface of the piston ring under normal operation. However, the size of piston ring is probably increased when the carbon deposits are not easily washed. Table 6 shows the present of carbon deposits obviously between the contact surface of piston and the first compression ring. The wear of the first ring is due to the abrasive wear and surface fatigue. Depending on the operation duration and modes, the surfaces conditions are different. It can be concluded that the wear loss of 1 hours testing is worse than that of 5 hours testing, but there is no serious wear found on the surface. For second piston ring in D1 engine, the accumulation of carbon deposits is evidence and the surface of the carbon deposits show the considerable protuberance and cracks. In contrast, the carbon deposits exist in B2 engine as well, but the surface is more uneven and has peeled off. Comparing the contact surface between the piston ring and cylinder, it was observed fretting wear behavior on the surface in D1 engine which is more than that in the B2 engine. Finally, both the contact surfaces of the third piston ring on the D1 and B2 engine are very smooth and there are no clear wear reviewed as the surfaces are protected by oil between the surfaces of the piston ring Needle Valve The function of the nozzle is to nebulize and inject the fuel into the combustion chamber for the diesel engine. The solenoid valve and spring control the movement of needle valve. According to the experimental results, the outer diameters of needle valves decrease insignificant without excess the tolerance range for three engines. Table 7 shows the inspected surfaces at X1, X2 and X3 position before and after the 1 hours test,
3 respectively. Due to the surfaces of X1 and X2 do not contact with the inner wall of nozzle directly, the surface wear is not evident. The single contacted area for the nozzle, as shown by X3, the surface has little abrasive wear with ignorable depth. Examined with detailed measurement for the outer diameter, there is no serious wear on the surface of X Carbon Deposits on Engine Components The subsections below show the weight and microscopic observation of the accumulated carbon deposits around piston and the analysis of the surface composition of the components Piston The carbon deposits accumulated on the piston is extracted for weight measurement. The piston is immersed in acetone and washed by the ultrasonic cleaner. The carbon particle is then filtered from the acetone solution. Table 8 shows the weight of carbon particles extracted from the tested pistons. The weight of carbon deposit from the piston of B2 engine, both at the full-load 5 hours test and FTP 1 hours test, are larger than the D1 engine by 2 to 34. The result implies that the amount of carbon deposits adhered to the piston of B2 engine is more than that of D1 engine. The amount of carbon deposits is different according to the fuel quality, and the operation modes, such as full-load operation and US FTP transient cycle operation. The composition of the carbon deposit particles is analyzed by Energy Dispersive Spectrometer (EDS), qualitative and semi-quantitative method. Figure 2 shows the results of composition analysis of the carbon deposit particles of Engine3-B2 after 1 hours test. Five areas of carbon deposit, extracted from the piston, are randomly picked for analysis. It is shown that the edges of the particles are mostly blunt. The comparison of the composition of the carbon deposits from the three engines is shown in Figure 3. The piston carbon deposits are mostly composed of carbon, and oxygen, while there is more oxygen in the carbon deposits from the B2 engine. This is because the methyl ester in the biodiesel contains more oxygen elements. As a result, the oxygen elements in the deposits are more than those in the D1 engine after the burning process. Besides, due to the additives used in diesel fuel and engine oil, EDS also inspects some zinc, phosphorous, sulfur, and calcium. For B2 engine, the fewer above elements found in the carbon deposits is produced, as the amount of the engine oil consumed is less than the others during the burning process Fuel Injection Nozzle Table 9 shows the nozzle appearance by the SEM, where all the seven spray orifices at the same level. As shown in this table, the nozzle of the engine for B2 biodiesel is not blocked by the carbon deposits after the 5 hours test or the 1 hours test as the carbon deposits around the spray orifices are loose and unstacked. In contrast, more carbon deposit is found around the nozzle orifices in D1 engine. 3.3 The Influence on Engine Oil At each engine maintenance stage during the process of durability tests, the engine oils were changed and assayed the composition to interpret the wear on the B2 engine. The replacement cycle of Engine3-B2 is 25 hours while that of Engine1-D1 and Engine2-B2 is 125 hours. The test results are shown in Table 1 and the description is as follows: (a) Viscosity Fuel dilution or deterioration of the engine oil can be obtained through examining viscosity. Comparing the viscosity before and after the durability tests, the deterioration of Engine3-B2 was more evident. The viscosity indexes showed less difference indicating there was no obvious deterioration in the engine oils. (b) Total Base Number and Total Acid Number These two items reflect the concentration of the cleanness of the fuel, anti-oxidation, and part of the anti-wear additive to determine if the alkalinity was decreased and the lubricant should be replaced. The test result showed that B2 biodiesel influenced less on the total base number. And the total acid number is lower than that of diesel whether under stable durability tests or transient durability tests. The reason is that biodiesel contains anti-oxidant additives. (c) Additives In general, engine oil containing 1 to 25 additives increases the performance of lubrication. The results showed that the difference content of P, Zn, Ca, Ba between new and used oils was within the reasonable range, indicating that the engine ran smoothly. (d) Metallic Debris The elemental analyses of Al and Fe reflect the wearing of the engine components. Cr reflects the wearing of piston ring and cylinder liners while Tin, copper and lead reflect that of bearing and titled pads. Comparing between the new and used lubricants, there was more Fe in the oils of Engine1-D1 and Engine2-B2 under full-load durability tests than that in the Engine3-B2. The results showed that under full-load operation, the components, such as cylinder, crank, and piston rings, were worn more seriously. 3.4 Fuel Supply System The fuel supply system of the diesel engine consists of a fuel tank, fuel pipes, fuel filters, and a low pressure pump. During the durability tests, the fuel supply simulated as the way of on-road vehicles. Diesel fuel and B2 biodiesel were supplied respectively for the durability tests. The pressure and temperature were measured at the inlet and outlet of the filters and the outlet temperature remained within 4±5. After the durability tests, the fuel tanks and fuel pipes were dissected to evaluate the corrosion of the tanks, pipes and filters caused by biodiesel. Table 11 shows the dissection of the tanks, pipes, and filters of the three engines after the durability tests. It was observed that the test fuels (D1 and B2) made no corrosion to both the fuel tanks and the fuel pipes. Furthermore, there were not many impurities on the filters. The pressure between inlet and outlet of the filter of Engine3-B2 was 443mmH 2 O. Compared with that of
4 Engine1-D1 and Engine2-B2 under full-load durability test for 5 hours, the differential pressure was smaller after the US transient cycle durability test for 1 hours. Minor obstruction of the filter is due to the lower fuel rate under US transient cycle than that of full-load operation. In this paper, the rubber fuel hoses of Engine3-B2 under hour and 1 hours were inspected following test standards in Taiwan. Table 12 shows the change of hardness for the inlet and return hoses, percentage change in elongation rate and volume. It was found there was no evident difference caused by the low pressure operation. For the tensile strength, the properties of biodiesel increased the change in hardness after 1hr operation. In brief, there were no breaks, leaks, or deformation on rubber fuel hoses. The research posted in literature also indicated that using B2 biodiesel for 5 hours operation did not cause the fuel hoses hardening or broken [11]. 3.5 Engine Performance The engine performance was evaluated by the test procedure for SAE J1995 requirement. Figure 4 shows the engine torque variation both for B2 and D1 fuels and the corresponding durability tests with respect to engine speed. The torque variation for B2 biodiesel at full speed is under ±2 compared with using D1 fuel. For the speed under 12 rpm, however, the variation is more than ±2 but in the range of ±3. This shows that B2 biodiesel has little influence on engine torque and durability performance. Figure 5 shows the change of fuel consumption, having the same conclusion as engine performance. For example, with speed lower than 7 rpm, the difference of fuel consumption of Engine3 in B2 biodiesel before and after the durability tests, hour and 5 hours, is about 2.5. For other speed, the variation is within ±2. In summary, the engine performance and fuel consumption in B2 biodiesel for various durability tests are within ± Exhaust Emissions and Fuel Consumption The main pollutants emitted by diesel vehicles are nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particular matter (PM). Figure 6 shows the diesel emissions analyzed in this paper. The amounts of CO, HC, and NMHC from the diesel engine were much lower, about 1 of the emission standard. However, the NOx emission was 92 of the standard and the emission of PM is 95 compared with the standard. Based on the emissions of engine1-d1, Figure 7 shows the percentage changes of using B2 biodiesel under different durability tests. From the figure, it was found that the NOx and PM of Engine2-B2 for hour and 5 hours increased slightly and there was no obvious difference on CO 2 and fuel consumption. The NOx emission of Engine3-B2 for hour and 1 hours increased a little and there was no obvious difference on PM, CO 2, and fuel consumption. These results indicate that B2 biodiesel affected the emissions of diesel engines slightly under different durability tests. The emission of CO and HC was decreased, gains little effect on the improvement of pollutant emission. There was limited effort of the low percentage biodiesel on the emissions of PM and NOx. According to past researches, the decrease of emissions due to biodiesel was related with the percentage of the biodiesel and the emission control strategy. Using B1 biodiesel and old diesel vehicles fueled with biodiesel have the best effect upon the decrease of the exhaust emission [12]. 4. Conclusion The results obtained in this work indicate the influence of B2 biodiesel on diesel engines and answer the public s concerns in order to gain more trust and support for the use of biodiesel. The conclusions are detailed as follows. After the durability tests, either for the full-load operation or FTP transient cycle, B2 biodiesel did not have obvious influence on the sizes of the engine components. From the microscopic observation, on the other hand, the wear behavior of the piston ring of the engine using B2 biodiesel was slightly better than that of using diesel fuel. More carbon deposits on the top of piston were observed for B2 fuel. However, the results of fewer carbon deposits on the cylinder wall and nozzle for using B2 were as in contrast. Such outcome showed that the carbon deposits on the top of the piston of D1 engine were looser and could be easily peeled off because of generated from burning of engine oil. The amounts of phosphorous, sulfur and zinc of carbon deposits for B2 biodiesel were fewer than those of D1 and the deterioration of lubricant was slower. This showed that the less wear loss for the engine components than those of D1. With respect to the engine emission and performance, B2 biodiesel has slight effects on the exhaust emission under different durability tests. The changes of engine performance and fuel consumption were within ±3. 5. Acknowledgements The authors would like to acknowledge the financical support by Bureau of Energy, Ministry of Economic Affairs (R.O.C.) under contract 98-D14 and 99-D14, which has made this report successful. The authors gratefully thank Professor Yuan-Ching Lin from Taiwan University of Science and Technology and Professor Chi-Wei Lan from Yuan Ze University for their insightful discussions. 6. Reference 1. C.A. Sharp, S.A. Howell, J. Jobe, 2, The Effect of Biodiesel Fuels on Transient Emissions from Modern Diesel Engines, Part I Regulated Emissions and Performance, SAE paper V. Camobreco, J. Sheehan, J. Duffield, M. Graboski, 2, Understanding the Life-Cycle Costs and Environmental Profile of Biodiesel and Petroleum Diesel Fuel, SAE paper M.A. Kalam, H.H. Masjuki, 22, Biodiesel from palmoil - An analysis of its properties and potential,
5 Biomass Bioenergy, Vol. 23, pp K.S. Wain, J.M. Perez, E. Chapman, A.L. Boehman, 25, Alternative and low sulfur fuel options: Boundary lubrication performance and potential problems, Tribol. Int., Vol. 38, pp A.K. Agarwal, J. Bijwe, L.M. Das, 23, Wear assessment in a biodiesel fueled compression ignition engine, J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power, Vol. 125, pp A.K. Agarwal, J. Bijwe, L.M. Das, 23, Effect of biodiesel utilization of wear of vital parts in compression ignition engine, J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power, Vol. 125, pp A.K. Agarwal, 25, Experimental investigations of the effect of biodiesel utilization on lubricating oil tribology in diesel engines, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng., Vol. 219, pp S. Kaul, R.C. Saxena, A. Kumar, M.S. Negi, A.K. Bhatnagar, H.B. Goyal, A.K. Gupta, 27, Corrosion behavior of biodiesel from seed oils of Indian origin on diesel engine parts, Fuel Process. Technol., Vol. 88, pp Yasunori TAKEI, 27, JAMA s Recommendation on Bio Diesel Specification, The Fourth Meeting of the APEC Biofuels Task Force, Oct , Bangkok, Thailand. 1. Automotive Research & Testing Center, 28, The Durability Test of Biodiesel Engine (B2) Final Report, authorized by Industrial Technology Research Institute. 11. Industrial Technology Research Institute, 26, Development & Dissemination of Bio-fuel Technologies, final report, 95-D Industrial Technology Research Institute, 26, The Environmental Benefits and Strategy Analysis of the Biodiesel Vehicles, final report, EPA-95-FA1-3-A124. Engine speed (rpm) Time (hr) Figure 1. Full-load operating procedure for engine durability test Torque difference () Figure 2. Composition and appearance of carbon deposits on piston head (Engine3-B2) Content() Engine1-D1 Engine2-B2 Engine3-B2 C O P S Zn Ca Al Elements Figure 3. Comparison between test engines for the composition of carbon deposits on piston head Engine2-B2_hr vs. Engine1-D1_hr Engine3-B2_hr vs. Egnine1-D1_hr Engine2-B2_5hr vs. Engine1-D1_5hr Engine3-B2_1hr vs. Engine1-D1_5hr Engine speed (rpm) Figure 4. The effect on engine torque using different fuels under durability tests (SAE J1995) FC difference () Engine2-B2_hr vs. Engine1-D1_hr Engine3-B2_hr vs. Egnine1-D1_hr Engine2-B2_5hr vs. Engine1-D1_5hr Engine3-B2_1hr vs. Engine1-D1_5hr Engine speed (rpm) Figure 5. The effect on fuel consumption using different fuels under durability tests (SAE J1995)
6 Emission (g/bhp-hr) CO standard = 1. Engine1-D1-hr Engine2-B2-hr Engine3-B2-hr Engine1-D1-5hr Engine2-B2-5hr Engine3-B2-1hr CO HC NMHC Emission (g/bhp-hr) CO2 Engine1-D1-hr Engine2-B2-hr Engine3-B2-hr Engine1-D1-5hr Engine2-B2-5hr Engine3-B2-1hr Figure 6. Emissions of test engines before and after durability tests (FTP Transient Cycle) FC Emission (g/bhp-hr) NMHC+NOx standard = 2.4 (2.5) NOx Engine1-D1-hr Engine2-B2-hr Engine3-B2-hr Engine1-D1-5hr Engine2-B2-5hr Engine3-B2-1hr PM standard =.1 PM Emission difference () Engine2-B2_hr vs. Engine1-D1_hr Engine2-B2_5hr vs. Engine1-D1_5hr Engine3-B2_hr vs. Egnine1-D1_hr Engine3-B2_1hr vs. Engine1-D1_5hr CO HC NMHC Emission difference () Engine2-B2_hr vs. Engine1-D1_hr Engine2-B2_5hr vs. Engine1-D1_5hr Engine3-B2_hr vs. Egnine1-D1_hr Engine3-B2_1hr vs. Engine1-D1_5hr CO2 FC NOx PM Figure 7. The effect on engine emissions using different fuels under durability tests (FTP Transient Cycle) Table 1. Test engine specifications Item Specification Engine Type MITSUBISHI 4M42-4AT2 Displacement 2977 c.c. Rated Power 92. kw/32rpm Rated Torque 294 Nm/17rpm Cylinders In-line 4 Cylinder/4 Stroke Compression Ratio 17:1 Fuel System Common Rail (Direct Injection) Injection Pressure 16 bar max. Nozzle Hole Air Intake System Turbocharged with intercooler Emission Control System DOC, PCV, EGR Table 3. Test methods of engine operation and components Item Durability FTP Transient Full loading Full loading operation Cycle Emission test cycle FTP Transient Cycle Engine performance SAE J1995 Wear of Engine Components Size, microscopic observation (Cylinder liner, piston ring, needle valve) Carbon Deposits Weight, composition, microscopic observation (Piston, nozzle) Engine Oils Replaced oil during maintenance period ( test method) Fuel Supply System Fuel tank, fuel pipe, filter, rubber hose ( test method) Test item Table 2. Fuel properties Engine 1-D1 Engine 2-B2 Engine 3-B2 Unit Test method 1471 Cetane index min Density, g/ml report Copper strip corrosion (3hr at 1a 1a 1a rating No ) Flash point min Kinematic viscosity, cst Carbon residue (on 1 distillation residue) <.1 <.1 <.1 (m/m) Distillation, IBP Distillation, T Distillation, FBP Ash <.1.1 <.1 (m/m) Sulfur content ppm Polyaromatics content (m/m) Lubricity, corrected wear scar diameter μm (1.4 wsd, 6 ) Fatty acid methyl ester content (v/v) Water and sediment -.5 (v/v) Water content ppm max max max. 5 max max max max max max.
7 Total contaminant ppm 24 max Pour point * max Cold filtration plug point (CFPP) * max Oxidation stability, g/m 3 25 max Heating value kcal/kg D24 - * Diesel fuel blended with fatty acid methyl ester must conform to at least one of the above requirements. Table 4. The Size difference of cylinder liner before and after durability test (mm) (hr vs. 5hr) (hr vs. 5hr) (hr vs. 1hr) Dx Dy D D (Roundness) Remark Table 5. The microscopic surfaces of cylinder wall Top dead center Middle Bottom dead center Table 6. The microscopic surfaces of the piston rings after durability tests Ring NO.1 (outside) Ring NO.2 (inside) Ring NO.2 (outside) Ring NO.3 (outside) * Right side (outside) of the piston ring is contacted with cylinder wall. Table 7. The microscopic surfaces of the needle valves X1 X2 X3 hr (New) 1 hr (After durability test) Machining direction Machining direction Slide direction Remark
8 Table 8. Weight of carbon deposit on piston surfaces Weight (g) Surface of piston Table 11. Components of the fuel supply system (after durability test) Fuel tank Table 9. The microscopic observation of fuel injection nozzle orifices (after durability tests) Fuel pipe Nozzle tip Spray orifice Fuel filter Inlet/Outlet PD 792mmH 2 O Inlet/Outlet PD 785mmH 2 O Inlet/Outlet PD 443mmH 2 O * PD: pressure difference Table 1. Test result of the engine oils Oil sample New Test item (at hr) (at 125hr) (at 125hr) (at 25hr) Viscosity, cst, Viscosity, cst, Viscosity Index Total Acid Number, mgkoh/g Total Basic Number, mgkoh/g Fuel Dilution, wt <.7 <.7 <.7 <.7 N-pentane Insoluble, wt Toluene Insoluble, wt P, wt, XRF Zn, wt, XRF Ca, wt, XRF Ba, wt, XRF N.D<.11 N.D<.11 N.D<.11 N.D<.11 Mg, ppm, ICP Cr, ppm, ICP N.D<3 N.D<3 N.D<3 N.D<3 Cu, ppm, ICP N.D<3 5.1 N.D<3 N.D<3 Fe, ppm, ICP N.D< Al, ppm, ICP N.D<3 N.D<3 N.D<3 N.D<3 Sn, ppm, ICP N.D<3 N.D<3 N.D<3 N.D<3 Pb, ppm, ICP N.D<3 4.3 N.D<3 5.5 Remark D445 D664 D2896 D3524 D893 D4927 D5185 Table 12. Comparison of the rubber fuel hoses before and after 1hr durability test Test item Inlet Hose Return hose Remark Change in Hardness (Type A/1 sec) (28) Percentage Change in Tensile Strength () (1999) Percentage Change in Elongation Rate () Percentage Change in Volume () Test sample Fuel inlet hose Fuel return hose (1999) 3556 (27)
The Impact upon Durability of Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine using 5 Percentage Biodiesel
 13PFL-0370 The Impact upon Durability of Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine using 5 Percentage Biodiesel Author, co-author (Do NOT enter this information. It will be pulled from participant tab in MyTechZone) Affiliation
13PFL-0370 The Impact upon Durability of Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine using 5 Percentage Biodiesel Author, co-author (Do NOT enter this information. It will be pulled from participant tab in MyTechZone) Affiliation
2016 International Conference on Engineering Tribology and Applied Technology
 Tribological Performance Evaluation of Biodiesel Distilled Residues Blended with Fossil Diesel Yang-Ching Lin 1,a, Hung-Shiau Chen 1,b, Chun-Ching Hsu 1,c, YONG-YUAN KU 2,d, KE-WEI LIN 2,e 1 Department
Tribological Performance Evaluation of Biodiesel Distilled Residues Blended with Fossil Diesel Yang-Ching Lin 1,a, Hung-Shiau Chen 1,b, Chun-Ching Hsu 1,c, YONG-YUAN KU 2,d, KE-WEI LIN 2,e 1 Department
Experimental Investigations on a Four Stoke Diesel Engine Operated by Jatropha Bio Diesel and its Blends with Diesel
 International Journal of Manufacturing and Mechanical Engineering Volume 1, Number 1 (2015), pp. 25-31 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental Investigations on a
International Journal of Manufacturing and Mechanical Engineering Volume 1, Number 1 (2015), pp. 25-31 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental Investigations on a
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-issn: Volume: 04 Issue: 11 Nov p-issn:
 International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-issn: 2395-56 Performance and emission characteristics of a constant speed diesel engine fueled with Rubber seed oil and Jatropha
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-issn: 2395-56 Performance and emission characteristics of a constant speed diesel engine fueled with Rubber seed oil and Jatropha
Chandra Prasad B S, Sunil S and Suresha V Asst. Professor, Dept of Mechanical Engineering, SVCE, Bengaluru
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 9, Issue 7, July 2018, pp. 997 1004, Article ID: IJMET_09_07_106 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=9&itype=7
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 9, Issue 7, July 2018, pp. 997 1004, Article ID: IJMET_09_07_106 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=9&itype=7
ASTM D Standard Specification for Biodiesel Fuel (B 100) Blend Stock for Distillate Fuels
 ASTM D 6751 02 Standard Specification for Biodiesel Fuel (B 100) Blend Stock for Distillate Fuels Summary This module describes the key elements in ASTM Specifications and Standard Test Methods ASTM Specification
ASTM D 6751 02 Standard Specification for Biodiesel Fuel (B 100) Blend Stock for Distillate Fuels Summary This module describes the key elements in ASTM Specifications and Standard Test Methods ASTM Specification
BIODIESEL IMPROVES LUBRICITY OF LOW-SULFUR PETRO-DIESELS. De-Xing Peng
 DOI 10.1007/s10553-017-0762-1 Chemistry and Technology of Fuels and Oils, Vol. 52, No. 6, January, 2017 (Russian Original No.6, November December, 2016) BIODIESEL IMPROVES LUBRICITY OF LOW-SULFUR PETRO-DIESELS
DOI 10.1007/s10553-017-0762-1 Chemistry and Technology of Fuels and Oils, Vol. 52, No. 6, January, 2017 (Russian Original No.6, November December, 2016) BIODIESEL IMPROVES LUBRICITY OF LOW-SULFUR PETRO-DIESELS
ABSTRACT I. INTRODUCTION II. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS OF THE ENGINE III. MATERIAL & METHODS
 2015 IJSRSET Volume 1 Issue 2 Print ISSN: 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section : Engineering and Technology Experimental Investigations on a Four Stoke Die Engine Operated by Neem Bio Blended
2015 IJSRSET Volume 1 Issue 2 Print ISSN: 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section : Engineering and Technology Experimental Investigations on a Four Stoke Die Engine Operated by Neem Bio Blended
Performance and Emission Analysis of Diesel Engine using palm seed oil and diesel blend
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 2 Ver. VIII (Mar- Apr. 2014), PP 29-33 Performance and Emission Analysis of Diesel Engine
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 2 Ver. VIII (Mar- Apr. 2014), PP 29-33 Performance and Emission Analysis of Diesel Engine
Power Performance and Exhaust Gas Analyses of Palm Oil and Used Cooking Oil Methyl Ester as Fuel for Diesel Engine
 ICCBT28 Power Performance and Exhaust Gas Analyses of Palm Oil and Used Cooking Oil Methyl Ester as Fuel for Diesel Engine R. Adnan *, Universiti Tenaga Nasional, MALAYSIA I. M. Azree, Universiti Tenaga
ICCBT28 Power Performance and Exhaust Gas Analyses of Palm Oil and Used Cooking Oil Methyl Ester as Fuel for Diesel Engine R. Adnan *, Universiti Tenaga Nasional, MALAYSIA I. M. Azree, Universiti Tenaga
Material Science Research India Vol. 7(1), (2010)
 Material Science Research India Vol. 7(1), 201-207 (2010) Influence of injection timing on the performance, emissions, combustion analysis and sound characteristics of Nerium biodiesel operated single
Material Science Research India Vol. 7(1), 201-207 (2010) Influence of injection timing on the performance, emissions, combustion analysis and sound characteristics of Nerium biodiesel operated single
Production of Biodiesel from Used Groundnut Oil from Bosso Market, Minna, Niger State, Nigeria
 Production of Biodiesel from Used Groundnut Oil from Bosso Market, Minna, Niger State, Nigeria Alabadan B.A. Department of Agricultural and Bioresources Engineering, Federal University, Oye Ekiti. Ajayi
Production of Biodiesel from Used Groundnut Oil from Bosso Market, Minna, Niger State, Nigeria Alabadan B.A. Department of Agricultural and Bioresources Engineering, Federal University, Oye Ekiti. Ajayi
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF HYDROGEN BLENDING ON THE CONCENTRATION OF POLLUTANTS EMITTED FROM A FOUR STROKE DIESEL ENGINE
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF HYDROGEN BLENDING ON THE CONCENTRATION OF POLLUTANTS EMITTED FROM A FOUR STROKE DIESEL ENGINE Haroun A. K. Shahad hakshahad@yahoo.com Department of mechanical
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF HYDROGEN BLENDING ON THE CONCENTRATION OF POLLUTANTS EMITTED FROM A FOUR STROKE DIESEL ENGINE Haroun A. K. Shahad hakshahad@yahoo.com Department of mechanical
POLLUTION CONTROL AND INCREASING EFFICIENCY OF DIESEL ENGINE USING BIODIESEL
 POLLUTION CONTROL AND INCREASING EFFICIENCY OF DIESEL ENGINE USING BIODIESEL Deepu T 1, Pradeesh A.R. 2, Vishnu Viswanath K 3 1, 2, Asst. Professors, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Ammini College of
POLLUTION CONTROL AND INCREASING EFFICIENCY OF DIESEL ENGINE USING BIODIESEL Deepu T 1, Pradeesh A.R. 2, Vishnu Viswanath K 3 1, 2, Asst. Professors, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Ammini College of
ISSN: [Sirivella, 6(10): October, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116
![ISSN: [Sirivella, 6(10): October, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116 ISSN: [Sirivella, 6(10): October, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116](/thumbs/95/122785940.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY EVALUATION ON INFLUENCE OF FUEL INJECTION PRESSURE ON EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF CIDI ENGINE USING JATROPHA OIL METHYL ESTER
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY EVALUATION ON INFLUENCE OF FUEL INJECTION PRESSURE ON EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF CIDI ENGINE USING JATROPHA OIL METHYL ESTER
Ester (KOME)-Diesel blends as a Fuel
 International Research Journal of Environment Sciences E-ISSN 2319 1414 Injection Pressure effect in C I Engine Performance with Karanja Oil Methyl Ester (KOME)-Diesel blends as a Fuel Abstract Venkateswara
International Research Journal of Environment Sciences E-ISSN 2319 1414 Injection Pressure effect in C I Engine Performance with Karanja Oil Methyl Ester (KOME)-Diesel blends as a Fuel Abstract Venkateswara
Study of viscosity - temperature characteristics of rapeseed oil biodiesel and its blends
 Study of viscosity - temperature characteristics of rapeseed oil biodiesel and its blends Li Kong 1, Xiu Chen 1, a, Xiaoling Chen 1, Lei Zhong 1, Yongbin Lai 2 and Guang Wu 2 1 School of Chemical Engineering,
Study of viscosity - temperature characteristics of rapeseed oil biodiesel and its blends Li Kong 1, Xiu Chen 1, a, Xiaoling Chen 1, Lei Zhong 1, Yongbin Lai 2 and Guang Wu 2 1 School of Chemical Engineering,
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17043:2010. ASTM INTERNATIONAL 100 Barr Harbor Drive West Conshohocken, PA Amy Meacock
 SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17043:2010 ASTM INTERNATIONAL 100 Barr Harbor Drive West Conshohocken, PA 19428 Amy Meacock 610 832 9688 PROFICIENCY TESTING PROVIDER Valid To: May 31, 2021 Certificate
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION TO ISO/IEC 17043:2010 ASTM INTERNATIONAL 100 Barr Harbor Drive West Conshohocken, PA 19428 Amy Meacock 610 832 9688 PROFICIENCY TESTING PROVIDER Valid To: May 31, 2021 Certificate
SYNERGISTIC EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL- BASED RENEWABLE FUELS: FUEL PROPERTIES AND EMISSIONS
 SYNERGISTIC EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL- BASED RENEWABLE FUELS: FUEL PROPERTIES AND EMISSIONS by EKARONG SUKJIT School of Mechanical Engineering 1 Presentation layout 1. Rationality 2. Research aim 3. Research
SYNERGISTIC EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL- BASED RENEWABLE FUELS: FUEL PROPERTIES AND EMISSIONS by EKARONG SUKJIT School of Mechanical Engineering 1 Presentation layout 1. Rationality 2. Research aim 3. Research
Mechatronics, Electrical Power, and Vehicular Technology
 Mechatronics, Electrical Power, and Vehicular Technology 05 (2014) 59-66 Mechatronics, Electrical Power, and Vehicular Technology e-issn:2088-6985 p-issn: 2087-3379 Accreditation Number: 432/Akred-LIPI/P2MI-LIPI/04/2012
Mechatronics, Electrical Power, and Vehicular Technology 05 (2014) 59-66 Mechatronics, Electrical Power, and Vehicular Technology e-issn:2088-6985 p-issn: 2087-3379 Accreditation Number: 432/Akred-LIPI/P2MI-LIPI/04/2012
Investigation on PM Emissions of a Light Duty Diesel Engine with 10% RME and GTL Blends
 Investigation on PM Emissions of a Light Duty Diesel Engine with 10% RME and GTL Blends Hongming Xu Jun Zhang University of Birmingham Philipp Price Ford Motor Company International Particle Meeting, Cambridge
Investigation on PM Emissions of a Light Duty Diesel Engine with 10% RME and GTL Blends Hongming Xu Jun Zhang University of Birmingham Philipp Price Ford Motor Company International Particle Meeting, Cambridge
Automotive Technology
 International Conference on Automotive Technology An Experimental Study on the Performance and Emission Characteristics of a Single Cylinder Diesel Engine Using CME- Diesel Blends. Hari Vasudevan a*,sandip
International Conference on Automotive Technology An Experimental Study on the Performance and Emission Characteristics of a Single Cylinder Diesel Engine Using CME- Diesel Blends. Hari Vasudevan a*,sandip
Experimental Investigation of Emission Reduction by Blending Methanol, Ethanol and Biodiesel with diesel on C.I. Engine
 Experimental Investigation of Emission Reduction by Blending Methanol, Ethanol and Biodiesel with diesel on C.I. Engine V. Veeraragavan1, M. Sathiyamoorthy 2 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical
Experimental Investigation of Emission Reduction by Blending Methanol, Ethanol and Biodiesel with diesel on C.I. Engine V. Veeraragavan1, M. Sathiyamoorthy 2 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical
S S Ragit a *, S K Mohapatra a & K Kundu b. Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 18, June 2011, pp
 Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 18, June 2011, pp. 204-210 Comparative study of engine performance and exhaust emission characteristics of a single cylinder 4-stroke CI engine operated
Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 18, June 2011, pp. 204-210 Comparative study of engine performance and exhaust emission characteristics of a single cylinder 4-stroke CI engine operated
Prediction of Performance and Emission of Palm oil Biodiesel in Diesel Engine
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) ISSN: 2278-1684, PP: 16-20 www.iosrjournals.org Prediction of Performance and Emission of Palm oil Biodiesel in Diesel Engine Sumedh Ingle 1,Vilas
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) ISSN: 2278-1684, PP: 16-20 www.iosrjournals.org Prediction of Performance and Emission of Palm oil Biodiesel in Diesel Engine Sumedh Ingle 1,Vilas
National Journal on Advances in Building Sciences and Mechanics, Vol. 1, No.2, October
 National Journal on Advances in Building Sciences and Mechanics, Vol. 1, No.2, October 2010 34 EFFECT OF COMPRESSION RATIO, INJECTION TIMING AND INJECTION PRESSURE ON A DIESEL ENGINE FOR BETTER PERFORMANCE
National Journal on Advances in Building Sciences and Mechanics, Vol. 1, No.2, October 2010 34 EFFECT OF COMPRESSION RATIO, INJECTION TIMING AND INJECTION PRESSURE ON A DIESEL ENGINE FOR BETTER PERFORMANCE
Biodiesel Business Environment
 Biodiesel Business Environment By Patum Vegetable Oil co., ltd. February 12, 2008 Innovation on Biofuel in Thailand, Century Park Hotel Agenda Company Profile Biodiesel Technology Country Policy & Regulation
Biodiesel Business Environment By Patum Vegetable Oil co., ltd. February 12, 2008 Innovation on Biofuel in Thailand, Century Park Hotel Agenda Company Profile Biodiesel Technology Country Policy & Regulation
Project Reference No.: 40S_B_MTECH_007
 PRODUCTION OF BIODIESEL FROM DAIRY WASH WATER SCUM THROUGH HETEROGENEOUS CATALYST AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF TBC DIESEL ENGINE FOR DIFFERENT DIESEL AND METHANOL BLEND RATIOS Project Reference No.: 40S_B_MTECH_007
PRODUCTION OF BIODIESEL FROM DAIRY WASH WATER SCUM THROUGH HETEROGENEOUS CATALYST AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF TBC DIESEL ENGINE FOR DIFFERENT DIESEL AND METHANOL BLEND RATIOS Project Reference No.: 40S_B_MTECH_007
Effects of Biodiesel and Jatropha oil on Performance, Black Smoke and Durability of Single-Cylinder Diesel Engine
 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals. Vol.18 No.2 pp.181-185, 2008 Effects of Biodiesel and Jatropha oil on Performance, Black Smoke and Durability of Single-Cylinder Diesel Engine Teerapong BAITIANG
Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals. Vol.18 No.2 pp.181-185, 2008 Effects of Biodiesel and Jatropha oil on Performance, Black Smoke and Durability of Single-Cylinder Diesel Engine Teerapong BAITIANG
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: Vol.7, No.5, pp ,
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: 0974-4290 Vol.7, No.5, pp 2355-2360, 2014-2015 Performance, Combustion and Emission Analysis on A Diesel Engine Fueled with Methyl Ester
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: 0974-4290 Vol.7, No.5, pp 2355-2360, 2014-2015 Performance, Combustion and Emission Analysis on A Diesel Engine Fueled with Methyl Ester
Study of Performance and Emission Characteristics of a Two Stroke Si Engine Operated with Gasoline Manifold Injectionand Carburetion
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(37), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i37/101984, October 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Study of Performance and Emission Characteristics
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(37), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i37/101984, October 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Study of Performance and Emission Characteristics
PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF DIESEL ENGINE USING RICE BRAN OIL METHYL ESTER BLEND WITH ADITIVE DIETHYL ETHER (DEE)
 International Journal of Science, Engineering and Technology Research (IJSETR), Volume 3, Issue 2, February 214 PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF DIESEL ENGINE USING RICE BRAN OIL METHYL ESTER
International Journal of Science, Engineering and Technology Research (IJSETR), Volume 3, Issue 2, February 214 PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF DIESEL ENGINE USING RICE BRAN OIL METHYL ESTER
Performance and Emission Characteristics of 4 S DI diesel Engine fueled with Calophyllum Inophyllum Biodiesel Blends
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal ISSN: 2249-6645 Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Performance and Emission Characteristics of 4 S DI diesel Engine fueled with Calophyllum Inophyllum Biodiesel Blends
International OPEN ACCESS Journal ISSN: 2249-6645 Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Performance and Emission Characteristics of 4 S DI diesel Engine fueled with Calophyllum Inophyllum Biodiesel Blends
The Impact of Oil Consumption Mechanisms on Diesel Exhaust Particle Size Distributions and Detailed Exhaust Chemical Composition
 The Impact of Oil Consumption Mechanisms on Diesel Exhaust Particle Size Distributions and Detailed Exhaust Chemical Composition John Stetter, Nate Forster Jaal Ghandhi, David Foster University of Wisconsin-Madison
The Impact of Oil Consumption Mechanisms on Diesel Exhaust Particle Size Distributions and Detailed Exhaust Chemical Composition John Stetter, Nate Forster Jaal Ghandhi, David Foster University of Wisconsin-Madison
R&D on a Medium-speed, Four-cycle Diesel Engine Using Heavy fuel oil
 1999C.4.1.11 R&D on a Medium-speed, Four-cycle Diesel Engine Using Heavy fuel oil 1. R&D contents 1.1 Background and R&D objectives In order to meet increasing demand for light oil and intermediate fraction,
1999C.4.1.11 R&D on a Medium-speed, Four-cycle Diesel Engine Using Heavy fuel oil 1. R&D contents 1.1 Background and R&D objectives In order to meet increasing demand for light oil and intermediate fraction,
Container MBW12K90MC Thursday 25 Jan 2007
 Cylinder Oil Drain Analysis & Engine Performance Report Samples Landed : SINGAPORE - 26 Jan 7 Received at Analysis Labs : 29 Jan 7 Engine :SAMSUNG MAN B&W 12K9MC MCR : 74,64 bhp @ 94 rpm Next Samples Due
Cylinder Oil Drain Analysis & Engine Performance Report Samples Landed : SINGAPORE - 26 Jan 7 Received at Analysis Labs : 29 Jan 7 Engine :SAMSUNG MAN B&W 12K9MC MCR : 74,64 bhp @ 94 rpm Next Samples Due
Further Challenges in Automobile and Fuel Technologies For Better Air Quality. 5 th JCAP Conference. Diesel WG Report.
 Further Challenges in Automobile and Fuel Technologies For Better Air Quality 5 th JCAP Conference Diesel WG Report February 22, 2007 Research Objectives Objectives To study effects of fuel properties
Further Challenges in Automobile and Fuel Technologies For Better Air Quality 5 th JCAP Conference Diesel WG Report February 22, 2007 Research Objectives Objectives To study effects of fuel properties
STUDY ON ENTREPRENEURIAL OPPORTUNITIES IN BIODIESEL PRODUCTION FROM WASTE COCONUT OIL AND ITS UTILIZATION IN DIESEL ENGINE
 STUDY ON ENTREPRENEURIAL OPPORTUNITIES IN BIODIESEL PRODUCTION FROM WASTE COCONUT OIL AND ITS UTILIZATION IN DIESEL ENGINE Project Reference No.: 4S_B_BE_4 COLLEGE BRANCH GUIDE STUDENTS : KALPATARU INSTITUTE
STUDY ON ENTREPRENEURIAL OPPORTUNITIES IN BIODIESEL PRODUCTION FROM WASTE COCONUT OIL AND ITS UTILIZATION IN DIESEL ENGINE Project Reference No.: 4S_B_BE_4 COLLEGE BRANCH GUIDE STUDENTS : KALPATARU INSTITUTE
Copyright Statement FPC International, Inc
 Copyright Statement All rights reserved. All material in this document is, unless otherwise stated, the property of FPC International, Inc. Copyright and other intellectual property laws protect these
Copyright Statement All rights reserved. All material in this document is, unless otherwise stated, the property of FPC International, Inc. Copyright and other intellectual property laws protect these
Impact of Biodiesel Fuel on Engine Parts
 Impact of Biodiesel Fuel on Engine Parts Presented by Prof. Dr.Liaquat Ali Memon Department of Mechanical Engineering, Quaid-e-Awam University of Engineering, Science & Technology, Nawabshah, Sindh, PAKISTAN
Impact of Biodiesel Fuel on Engine Parts Presented by Prof. Dr.Liaquat Ali Memon Department of Mechanical Engineering, Quaid-e-Awam University of Engineering, Science & Technology, Nawabshah, Sindh, PAKISTAN
GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 1 Issue 12 November 2016 ISSN:
 GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 1 Issue 12 November 2016 ISSN: 2455-5703 Effect of Brake Thermal Efficiency of a Variable Compression Ratio Diesel Engine Operating
GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 1 Issue 12 November 2016 ISSN: 2455-5703 Effect of Brake Thermal Efficiency of a Variable Compression Ratio Diesel Engine Operating
Analysis of Straight Vegetable Oil (SVO) Spray Characteristics. and Droplets Distribution By Using. Nano-Spark Shadowgraph Photography Technique
 nalysis of Straight Vegetable Oil (SVO) Spray haracteristics and Droplets Distribution y Using Nano-Spark Shadowgraph Photography Technique bdullah dam 1, Mamat Rizalman 1, Yoshiyuki Kidoguchi 2 and Tomoaki
nalysis of Straight Vegetable Oil (SVO) Spray haracteristics and Droplets Distribution y Using Nano-Spark Shadowgraph Photography Technique bdullah dam 1, Mamat Rizalman 1, Yoshiyuki Kidoguchi 2 and Tomoaki
PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF DIESEL ENGINE WITH MUSTARD OIL-DIESEL BLENDS AS FUEL
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 14(S2), 216, 655-664 ISSN 972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF DIESEL ENGINE WITH MUSTARD OIL-DIESEL BLENDS AS FUEL M. PRABHAHAR a*, K. RAJAN
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 14(S2), 216, 655-664 ISSN 972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF DIESEL ENGINE WITH MUSTARD OIL-DIESEL BLENDS AS FUEL M. PRABHAHAR a*, K. RAJAN
Experimental studies for the role of piston rings face profiles on performance of a diesel engine fueled with diesel and jatropha based biodiesel
 Journal SINGH of Scientific et al: PERFORMANCE & Industrial Research OF A DIESEL ENGINE FUELED WITH DIESEL AND JATROPHA BASED BIODIESEL Vol. 71, January 2012, pp. 57-62 57 Experimental studies for the
Journal SINGH of Scientific et al: PERFORMANCE & Industrial Research OF A DIESEL ENGINE FUELED WITH DIESEL AND JATROPHA BASED BIODIESEL Vol. 71, January 2012, pp. 57-62 57 Experimental studies for the
Evaluation of Thailand Existing Motorcycle Fueled with Ethanol Blended Gasoline on Tailpipe Emissions
 The 7 th International Conference on Automotive Engineering (ICAE-7) March 28 April 1, 211, Challenger, Impact, Muang Thong Thani, Bangkok, Thailand Evaluation of Thailand Existing Motorcycle Fueled with
The 7 th International Conference on Automotive Engineering (ICAE-7) March 28 April 1, 211, Challenger, Impact, Muang Thong Thani, Bangkok, Thailand Evaluation of Thailand Existing Motorcycle Fueled with
Effects of several biofuels on the particle size distributions of an off-road diesel engine
 13 th ETH Conference on, Zürich, 22 nd 24 th June 2009 SUMMARY, June 9, 2009 Effects of several biofuels on the particle size distributions of an off-road diesel engine Authors: Niemi, S. 1, 2), Vauhkonen,
13 th ETH Conference on, Zürich, 22 nd 24 th June 2009 SUMMARY, June 9, 2009 Effects of several biofuels on the particle size distributions of an off-road diesel engine Authors: Niemi, S. 1, 2), Vauhkonen,
EXPERIMENTAL INVETIGATIONN ON PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF DI- CI ENGINE FUELED WITH PREHEATED SHEA OLEIN BIODIESEL
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 9, Issue 11, November 2018, pp. 2006 2014, Article ID: IJMET_09_11 211 Available online at http://www.ia aeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 9, Issue 11, November 2018, pp. 2006 2014, Article ID: IJMET_09_11 211 Available online at http://www.ia aeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=
Mack T-11 D EGR Engine Oil Test. Report Packet Version No. Conducted For
 Report Packet Version No. Conducted For V = I = N = Valid; The reference oil/non-reference oil was evaluated in accordance with the test procedure. Invalid; The reference oil/non-reference oil was not
Report Packet Version No. Conducted For V = I = N = Valid; The reference oil/non-reference oil was evaluated in accordance with the test procedure. Invalid; The reference oil/non-reference oil was not
Experimental Investigation on Performance Characteristic of Diesel Engine by Using Methyl Ester of Linseed and Neem oil
 B. KESAVA RAO et al. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN Experimental Investigation on Performance Characteristic of Diesel Engine by Using Methyl Ester of Linseed
B. KESAVA RAO et al. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN Experimental Investigation on Performance Characteristic of Diesel Engine by Using Methyl Ester of Linseed
Influence of the Biodiesel Tempura Oil on Diesel Vehicles
 JGSEE and Kyoto University 2nd Joint Int. Conference on "Sustainable Energy and Environment" swissotel NAI LERT PARK, Bangkok, Thailand Nov. 21-23, 2006 Influence of the Biodiesel Tempura Oil on Diesel
JGSEE and Kyoto University 2nd Joint Int. Conference on "Sustainable Energy and Environment" swissotel NAI LERT PARK, Bangkok, Thailand Nov. 21-23, 2006 Influence of the Biodiesel Tempura Oil on Diesel
COST-STSM-CM SCIENTIFIC REPORT STSM Topic: Regular (SMARTCATS)
 COST-STSM-CM144-3267 SCIENTIFIC REPORT STSM Topic: Regular (SMARTCATS) Visiting PhD Student: Dimitriadis Athanasios Chemical Process and Energy Resources Institute (CPERI) Centre for Research and Technology
COST-STSM-CM144-3267 SCIENTIFIC REPORT STSM Topic: Regular (SMARTCATS) Visiting PhD Student: Dimitriadis Athanasios Chemical Process and Energy Resources Institute (CPERI) Centre for Research and Technology
Production and Properties of Biodistillate Transportation Fuels
 Production and Properties of Biodistillate Transportation Fuels AWMA International Specialty Conference: Leapfrogging Opportunities for Air Quality Improvement May 10-14, 2010 Xi an, Shaanxi Province,
Production and Properties of Biodistillate Transportation Fuels AWMA International Specialty Conference: Leapfrogging Opportunities for Air Quality Improvement May 10-14, 2010 Xi an, Shaanxi Province,
Optimization of Neem and Niger Oil Blends and IOP Used for Diesel Engine Using Taguchi Method
 ISSN : 25-915 Vol-3, Issue-, July 217 Optimization of Neem and Niger Oil Blends and Used for Diesel Engine Using Taguchi Method 1 Mr. Kadam S. S., 2 Mr. Burkul R.M, 3 Mr. Andhale Y. S. 1 M.E. Heat Power,
ISSN : 25-915 Vol-3, Issue-, July 217 Optimization of Neem and Niger Oil Blends and Used for Diesel Engine Using Taguchi Method 1 Mr. Kadam S. S., 2 Mr. Burkul R.M, 3 Mr. Andhale Y. S. 1 M.E. Heat Power,
R&D on Environment-Friendly, Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine
 20000 M4.2.2 R&D on Environment-Friendly, Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine (Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine Group) Nobuyasu Matsudaira, Koji Imoto, Hiroshi Morimoto, Akira Numata, Toshimitsu
20000 M4.2.2 R&D on Environment-Friendly, Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine (Electronically Controlled Diesel Engine Group) Nobuyasu Matsudaira, Koji Imoto, Hiroshi Morimoto, Akira Numata, Toshimitsu
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF FOUR STROKE SINGLE CYLINDER DIESEL ENGINE WITH OXYGENATED FUEL ADDITIVES
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF FOUR STROKE SINGLE CYLINDER DIESEL ENGINE WITH OXYGENATED FUEL ADDITIVES 1 Bhavin Mehta, 2 Hardik B. Patel 1,2 harotar University of Science & Technology, Changa, Gujarat,
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF FOUR STROKE SINGLE CYLINDER DIESEL ENGINE WITH OXYGENATED FUEL ADDITIVES 1 Bhavin Mehta, 2 Hardik B. Patel 1,2 harotar University of Science & Technology, Changa, Gujarat,
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CI ENGINE USING PALM OIL METHYL ESTER
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CI ENGINE USING PALM OIL METHYL ESTER Prof. Hitesh Muthiyan 1, Prof. Sagar Rohanakar 2, Bidgar Sandip 3, Saurabh Biradar 4 1,2,3,4 Department of Mechanical Engineering, PGMCOE,
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CI ENGINE USING PALM OIL METHYL ESTER Prof. Hitesh Muthiyan 1, Prof. Sagar Rohanakar 2, Bidgar Sandip 3, Saurabh Biradar 4 1,2,3,4 Department of Mechanical Engineering, PGMCOE,
THE EFFECTS OF OXYGENATED ADDITIVE AND EGR IN A DIESEL ENGINE
 THE EFFECTS OF OXYGENATED ADDITIVE AND EGR IN A DIESEL ENGINE Seung-Hun, Choi Department of Automatic Mechanical Engineering, VISION University of Jeonju,Cheonjam-ro, Wansan-gu, Jeonju-si, Republic of
THE EFFECTS OF OXYGENATED ADDITIVE AND EGR IN A DIESEL ENGINE Seung-Hun, Choi Department of Automatic Mechanical Engineering, VISION University of Jeonju,Cheonjam-ro, Wansan-gu, Jeonju-si, Republic of
Use of Alternative Fuel in Lower Heat Rejection Engine with Different Insulation Levels
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 4 (2013), pp. 499-506 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Use of Alternative Fuel
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 4 (2013), pp. 499-506 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Use of Alternative Fuel
AN INVESTIGATION INTO HOW DIFFERENT BLENDS OF BIO-DIESEL AT A RANGE OF TEMPERATURES AFFECT ENGINE HORSEPOWER, TORQUE AND EMISSIONS
 Scientific Papers, USAMV Bucharest, Series A, Vol. LII, 2009, ISSN 1222-5359 AN INVESTIGATION INTO HOW DIFFERENT BLENDS OF BIO-DIESEL AT A RANGE OF TEMPERATURES AFFECT ENGINE HORSEPOWER, TORQUE AND EMISSIONS
Scientific Papers, USAMV Bucharest, Series A, Vol. LII, 2009, ISSN 1222-5359 AN INVESTIGATION INTO HOW DIFFERENT BLENDS OF BIO-DIESEL AT A RANGE OF TEMPERATURES AFFECT ENGINE HORSEPOWER, TORQUE AND EMISSIONS
Research Article. Effect of exhaust gas recirculation on NOx emission of a annona methyl ester operated diesel engine
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):723-728 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Effect of exhaust gas recirculation on NOx emission
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):723-728 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Effect of exhaust gas recirculation on NOx emission
Effect of Jatropha Biodiesel Blend with Diesel Fuel on Performance of Four Stroke Single Cylinder Diesel Engine
 Effect of Jatropha Biodiesel Blend with Diesel Fuel on Performance of Four Stroke Single Cylinder Diesel Engine Deep patel a, Amit shah b, Vijay Dhiman c a PG Student, Mechanical Engineering Department,
Effect of Jatropha Biodiesel Blend with Diesel Fuel on Performance of Four Stroke Single Cylinder Diesel Engine Deep patel a, Amit shah b, Vijay Dhiman c a PG Student, Mechanical Engineering Department,
EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF A COMPRESSION IGNITION ENGINE USING METHYL ESTERS OF RICE BRAN OIL AND DIESEL BLENDS
 EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF A COMPRESSION IGNITION ENGINE USING METHYL ESTERS OF RICE BRAN OIL AND DIESEL BLENDS R. Senthilraja Department of Mechanical Engineering, Institute of Road and Transport Technology,
EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF A COMPRESSION IGNITION ENGINE USING METHYL ESTERS OF RICE BRAN OIL AND DIESEL BLENDS R. Senthilraja Department of Mechanical Engineering, Institute of Road and Transport Technology,
Government Engineering College, Bhuj.
 Research Paper THE PERFORMANCE OF MULTI CYLINDER DIESEL ENGINE FUELLED WITH BLEND OF DIESEL AND NEEM OIL BIODIESEL Suthar Dinesh Kumar L. a*, Dr. Rathod Pravin P. b, Prof. Patel Nikul K. c Address for
Research Paper THE PERFORMANCE OF MULTI CYLINDER DIESEL ENGINE FUELLED WITH BLEND OF DIESEL AND NEEM OIL BIODIESEL Suthar Dinesh Kumar L. a*, Dr. Rathod Pravin P. b, Prof. Patel Nikul K. c Address for
Impact of Cold and Hot Exhaust Gas Recirculation on Diesel Engine
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Impact of Cold and Hot Exhaust Gas Recirculation on Diesel Engine P. Saichaitanya 1, K. Simhadri 2, G.Vamsidurgamohan 3 1, 2, 3 G M R Institute of Engineering and Technology,
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Impact of Cold and Hot Exhaust Gas Recirculation on Diesel Engine P. Saichaitanya 1, K. Simhadri 2, G.Vamsidurgamohan 3 1, 2, 3 G M R Institute of Engineering and Technology,
EXPERIMENTAL AND THEORETICAL INVESTIGATION ON PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF DIESEL FUEL BLENDS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 14(4), 2016, 2967-2972 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com EXPERIMENTAL AND THEORETICAL INVESTIGATION ON PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF DIESEL FUEL BLENDS M. VENKATRAMAN
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 14(4), 2016, 2967-2972 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com EXPERIMENTAL AND THEORETICAL INVESTIGATION ON PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF DIESEL FUEL BLENDS M. VENKATRAMAN
Combustion and Injection Characteristics of a Common Rail Direct Injection Diesel Engine Fueled with Methyl and Ethyl Esters
 Combustion and Injection Characteristics of a Common Rail Direct Injection Engine Fueled with Methyl and s Ertan Alptekin 1,,*, Huseyin Sanli,3, Mustafa Canakci 1, 1 Kocaeli University, Department of Automotive
Combustion and Injection Characteristics of a Common Rail Direct Injection Engine Fueled with Methyl and s Ertan Alptekin 1,,*, Huseyin Sanli,3, Mustafa Canakci 1, 1 Kocaeli University, Department of Automotive
ANALYSIS OF EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
 ANALYSIS OF EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM,, ABSTRACT Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is a way to control in-cylinder NOx and carbon production and is used on most modern high-speed direct injection
ANALYSIS OF EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM,, ABSTRACT Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is a way to control in-cylinder NOx and carbon production and is used on most modern high-speed direct injection
Biomass Fuel Applications in IC Engines
 The Energy Institute Biomass Fuel Applications in IC Engines André Boehman Professor of of Fuel Fuel Science and and Materials Science and and Engineering Department of of Energy and and Mineral Engineering
The Energy Institute Biomass Fuel Applications in IC Engines André Boehman Professor of of Fuel Fuel Science and and Materials Science and and Engineering Department of of Energy and and Mineral Engineering
Test Method D5967 Mack T-8. Version. Method: Conducted For
 Method D5967 Mack T-8 Version Method: Conducted For T-8A: T-8: T-8E: V = Valid I = Invalid N = Not Interpretable The Reference Oil/Non-Reference Oil was evaluated in accordance with the test procedure.
Method D5967 Mack T-8 Version Method: Conducted For T-8A: T-8: T-8E: V = Valid I = Invalid N = Not Interpretable The Reference Oil/Non-Reference Oil was evaluated in accordance with the test procedure.
PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT OF A DI DIESEL ENGINE WITH TURBOCHARGING USING BIOFUEL
 ISSN: 3159-4 Vol. 2 Issue 1, January - 215 PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT OF A DI DIESEL ENGINE WITH CHARGING USING BIOFUEL Rasik S. Kuware, Ajay V. Kolhe Heat Power Engineering, Mechanical Department, Kavikulguru
ISSN: 3159-4 Vol. 2 Issue 1, January - 215 PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT OF A DI DIESEL ENGINE WITH CHARGING USING BIOFUEL Rasik S. Kuware, Ajay V. Kolhe Heat Power Engineering, Mechanical Department, Kavikulguru
The influence of thermal regime on gasoline direct injection engine performance and emissions
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The influence of thermal regime on gasoline direct injection engine performance and emissions To cite this article: C I Leahu
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The influence of thermal regime on gasoline direct injection engine performance and emissions To cite this article: C I Leahu
Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology,Chennai ,Tamilnadu,India. JSPM s,college of Engineering,Hadapsar,Pune ,Maharashtra,India.
 INVESTIGATION OF COTTONSEED OIL BIO WITH ETHANOL AS AN ADDITIVE ON FUEL PROPERTIES, ENGINE PERFORMANCE, COMBUSTION AND EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF A ENGINE Shrikant MADIWALE 1*, Karthikeyan ALAGU 2 and
INVESTIGATION OF COTTONSEED OIL BIO WITH ETHANOL AS AN ADDITIVE ON FUEL PROPERTIES, ENGINE PERFORMANCE, COMBUSTION AND EMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF A ENGINE Shrikant MADIWALE 1*, Karthikeyan ALAGU 2 and
Palm Oil Methyl Ester and Its Emulsions Effect on Lubricant Performance and Engine Components Wear
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 14 (2012) 1748 1753 2011 2nd International Conference on Advances in Energy Engineering (ICAEE 2011) Palm Oil Methyl Ester and Its Emulsions Effect
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 14 (2012) 1748 1753 2011 2nd International Conference on Advances in Energy Engineering (ICAEE 2011) Palm Oil Methyl Ester and Its Emulsions Effect
Government Engineering College, Bhuj.
 Suthar et al., International Journal of Advanced Engineering Technology E-ISSN 0976-3945 Research Paper EFFECT OF FUEL ADDITIVE ON PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION FOR DIESEL ENGINE FUELLED WITH BLEND OF NEEM
Suthar et al., International Journal of Advanced Engineering Technology E-ISSN 0976-3945 Research Paper EFFECT OF FUEL ADDITIVE ON PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION FOR DIESEL ENGINE FUELLED WITH BLEND OF NEEM
D ISB Lubricant Performance Test. Report Packet Version No. Method. Conducted For:
 D 7484 - ISB Lubricant Performance Test Report Packet Version No. Method Conducted For: V = I = N = Valid; The reference oil / non-reference oil was evaluated in accordance with the test procedure. Invalid;
D 7484 - ISB Lubricant Performance Test Report Packet Version No. Method Conducted For: V = I = N = Valid; The reference oil / non-reference oil was evaluated in accordance with the test procedure. Invalid;
Performance and Emission Characteristics of Direct Injection Diesel Engine Running On Canola Oil / Diesel Fuel Blend
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-03, Issue-08, pp-202-207 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Performance and Emission Characteristics of
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-03, Issue-08, pp-202-207 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Performance and Emission Characteristics of
Comparative Analysis of Jatropha-Methanol Mixture and Diesel on Direct Injection Diesel Engine
 Volume 119 No. 16 218, 4947-4961 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ Comparative Analysis of Jatropha-Methanol Mixture and on Direct Injection
Volume 119 No. 16 218, 4947-4961 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ Comparative Analysis of Jatropha-Methanol Mixture and on Direct Injection
MAGNETIC FIELD EFFECT ON COMPRESSION IGNITION ENGINE PERFORMANCE
 MAGNETIC FIELD EFFECT ON COMPRESSION IGNITION ENGINE PERFORMANCE Hayder J. Kurji and Murtdha S. Imran Kerbala University, Engineering College, Mechanical Engineering Department, Kerbala, Iraq E-Mail: hayderkurji@gmail.com
MAGNETIC FIELD EFFECT ON COMPRESSION IGNITION ENGINE PERFORMANCE Hayder J. Kurji and Murtdha S. Imran Kerbala University, Engineering College, Mechanical Engineering Department, Kerbala, Iraq E-Mail: hayderkurji@gmail.com
PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION TEST OF CANOLA AND NEEM BIO-OIL BLEND WITH DIESEL
 PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION TEST OF CANOLA AND NEEM BIO-OIL BLEND WITH DIESEL MR.N.BALASUBRAMANI 1, M.THANASEGAR 2, R.SRIDHAR RAJ 2, K.PRASANTH 2, A.RAJESH KUMAR 2. 1Asst. Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering,
PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION TEST OF CANOLA AND NEEM BIO-OIL BLEND WITH DIESEL MR.N.BALASUBRAMANI 1, M.THANASEGAR 2, R.SRIDHAR RAJ 2, K.PRASANTH 2, A.RAJESH KUMAR 2. 1Asst. Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering,
Characteristics of PM Emissions of an Automotive Diesel Engine Under Cold Start and Transient Operating Conditions
 Characteristics of PM Emissions of an Automotive Diesel Engine Under Cold Start and Transient Operating Conditions Dai Liu, Jianyi Tian and Hongming Xu School of Mechanical Engineering 24 May 2014 Cambridge
Characteristics of PM Emissions of an Automotive Diesel Engine Under Cold Start and Transient Operating Conditions Dai Liu, Jianyi Tian and Hongming Xu School of Mechanical Engineering 24 May 2014 Cambridge
Analysis of Emission characteristics on Compression Ignition Engine using Dual Fuel Mode for Variable Speed
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 4, Issue 3 (October 2012), PP. 23-27 Analysis of Emission characteristics on Compression
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 4, Issue 3 (October 2012), PP. 23-27 Analysis of Emission characteristics on Compression
Study on the compatibility of rubber materials in biodiesel derived from cottonseed oil
 Study on the compatibility of rubber materials in biodiesel derived from cottonseed oil Guang Wu 1, Yongbin Lai 1, a, Li Kong 2, Lei Zhong 2 and Xiu Chen 2 1 School of Mechanical Engineering, Anhui University
Study on the compatibility of rubber materials in biodiesel derived from cottonseed oil Guang Wu 1, Yongbin Lai 1, a, Li Kong 2, Lei Zhong 2 and Xiu Chen 2 1 School of Mechanical Engineering, Anhui University
PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION ANALYSIS OF DIESEL ENGINE BY INJECTING DIETHYL ETHER WITH AND WITHOUT EGR USING DPF
 PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION ANALYSIS OF DIESEL ENGINE BY INJECTING DIETHYL ETHER WITH AND WITHOUT EGR USING DPF PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1036 COLLEGE BRANCH GUIDES : KS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, BANGALORE
PERFORMANCE AND EMISSION ANALYSIS OF DIESEL ENGINE BY INJECTING DIETHYL ETHER WITH AND WITHOUT EGR USING DPF PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1036 COLLEGE BRANCH GUIDES : KS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, BANGALORE
Biodistillate Fuels and Emissions in the U.S.
 Biodistillate Fuels and Emissions in the U.S. Presented to the Institute of Medicine Roundtable on Environmental Health Sciences, Research, and Medicine The Nexus of Biofuels, Energy, Climate Change, and
Biodistillate Fuels and Emissions in the U.S. Presented to the Institute of Medicine Roundtable on Environmental Health Sciences, Research, and Medicine The Nexus of Biofuels, Energy, Climate Change, and
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Arguments Against The Use Of FAME Biodiesel In Modern Diesel Engines Rich Cregar Fellow, Institute for Emerging Issues, NCSU White House Champion of Change APWA Fueling the Conversation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Arguments Against The Use Of FAME Biodiesel In Modern Diesel Engines Rich Cregar Fellow, Institute for Emerging Issues, NCSU White House Champion of Change APWA Fueling the Conversation
Biodiesel and Renewable Fuels
 National Renewable Energy Laboratory Biodiesel and Renewable Fuels Bob McCormick Denver, Colorado June 11, 2003 robert_mccormick@nrel.gov 303-275-4432 Operated for the U.S. Department of Energy by Midwest
National Renewable Energy Laboratory Biodiesel and Renewable Fuels Bob McCormick Denver, Colorado June 11, 2003 robert_mccormick@nrel.gov 303-275-4432 Operated for the U.S. Department of Energy by Midwest
EFFECT OF EGR AND CYCLONIC SEPARATOR ON EMISSIONS IN DI DIESEL ENGINES
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 27 (ICME27) 29-31 December 27, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME7-TH-9 EFFECT OF EGR AND CYCLONIC SEPARATOR ON EMISSIONS IN DI DIESEL ENGINES
Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 27 (ICME27) 29-31 December 27, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME7-TH-9 EFFECT OF EGR AND CYCLONIC SEPARATOR ON EMISSIONS IN DI DIESEL ENGINES
Biodiesel from Various Vegetable Oils as the Lubricity Additive for Ultra Low Sulphur Diesel (ULSD)
 AMM-5 The 2 st Conference of Mechanical Engineering Network of Thailand 7-9 October 27, Chonburi, Thailand Biodiesel from Various Vegetable Oils as the Lubricity Additive for Ultra Low Sulphur (ULSD) Subongkoj
AMM-5 The 2 st Conference of Mechanical Engineering Network of Thailand 7-9 October 27, Chonburi, Thailand Biodiesel from Various Vegetable Oils as the Lubricity Additive for Ultra Low Sulphur (ULSD) Subongkoj
Experimental Investigation on Performance of karanjaand mustard oil: Dual Biodiesels Blended with Diesel on VCR Diesel engine
 Experimental Investigation on Performance of karanjaand mustard oil: Dual Biodiesels Blended with Diesel on VCR Diesel engine Umesh Chandra Pandey 1, Tarun Soota 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Experimental Investigation on Performance of karanjaand mustard oil: Dual Biodiesels Blended with Diesel on VCR Diesel engine Umesh Chandra Pandey 1, Tarun Soota 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION
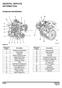 GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION Component Identification Figure 31 Reference Description Number 1 Lifting Eye (Flywheel End) 2 Turbocharger* 3 Lifting Eye ( Cooling Fan End) 4 Coolant Pump 5 Cooling Fan 6
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION Component Identification Figure 31 Reference Description Number 1 Lifting Eye (Flywheel End) 2 Turbocharger* 3 Lifting Eye ( Cooling Fan End) 4 Coolant Pump 5 Cooling Fan 6
FUEL QUALITY HAS DECLINED
 FUEL QUALITY HAS DECLINED Fuel Quality has Deteriorated because... Over the last two decades, the cetane number and the API gravity, the basic measures of crude oil quality have declined Diesel fuel quality
FUEL QUALITY HAS DECLINED Fuel Quality has Deteriorated because... Over the last two decades, the cetane number and the API gravity, the basic measures of crude oil quality have declined Diesel fuel quality
Experimental investigations on the performance characteristic of diesel engine using n- butyl alcohols
 Experimental investigations on the performance characteristic of diesel engine using n- butyl alcohols M. Karthe Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, M.KumarasamyCollege of Engineering,
Experimental investigations on the performance characteristic of diesel engine using n- butyl alcohols M. Karthe Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, M.KumarasamyCollege of Engineering,
CHAPTER 8 EFFECTS OF COMBUSTION CHAMBER GEOMETRIES
 112 CHAPTER 8 EFFECTS OF COMBUSTION CHAMBER GEOMETRIES 8.1 INTRODUCTION Energy conservation and emissions have become of increasing concern over the past few decades. More stringent emission laws along
112 CHAPTER 8 EFFECTS OF COMBUSTION CHAMBER GEOMETRIES 8.1 INTRODUCTION Energy conservation and emissions have become of increasing concern over the past few decades. More stringent emission laws along
Study on Stability of Ethanol/Diesel Fuel Blend
 Study on Stability of Ethanol/Diesel Fuel Blend Proceedings of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16- September 7 Study on Stability of Ethanol/Diesel Fuel Blend Gábor Nagy,
Study on Stability of Ethanol/Diesel Fuel Blend Proceedings of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16- September 7 Study on Stability of Ethanol/Diesel Fuel Blend Gábor Nagy,
ScienceDirect. Effect of bio-lubricant on tribological characteristics of steel
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 90 (2014 ) 740 745 10th International Conference on Mechanical Engineering, ICME 2013 Effect of bio-lubricant on tribological
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 90 (2014 ) 740 745 10th International Conference on Mechanical Engineering, ICME 2013 Effect of bio-lubricant on tribological
Inturi Vamsi et al. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications ISSN : , Vol. 5, Issue 5, ( Part -4) May 2015, pp.
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Investigations on the Engine Performance and Characteristics of Compression Ignition (CI) Engine Using Dual Bio Fuel Methyl Ester As Alternate Fuel With Exhaust
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Investigations on the Engine Performance and Characteristics of Compression Ignition (CI) Engine Using Dual Bio Fuel Methyl Ester As Alternate Fuel With Exhaust
Performance and Emission Characteristics of a Kirloskar HA394 Diesel Engine Operated on Mahua Oil Methyl Ester
 Performance and Emission Characteristics of a Kirloskar HA394 Diesel Engine Operated on Mahua Oil Methyl Ester Sharanappa Godiganur Department of Mechanical Engineering, Reva Institute of Technology and
Performance and Emission Characteristics of a Kirloskar HA394 Diesel Engine Operated on Mahua Oil Methyl Ester Sharanappa Godiganur Department of Mechanical Engineering, Reva Institute of Technology and
Louis Dreyfus Claypool Holdings, LLC. Biodiesel Production Plant Claypool, Indiana
 Louis Dreyfus Claypool Holdings, LLC Biodiesel Production Plant Claypool, Indiana Soybeans 163,000 Bu. = 48 Railcars = 172 Trucks Electricity 156,695 Kwh Natural Gas 3,049 Dth Claypool Inputs/Outputs Per
Louis Dreyfus Claypool Holdings, LLC Biodiesel Production Plant Claypool, Indiana Soybeans 163,000 Bu. = 48 Railcars = 172 Trucks Electricity 156,695 Kwh Natural Gas 3,049 Dth Claypool Inputs/Outputs Per
Experimental Study on Performance and Emission of Diesel Engine using Sunflower Oil-Diesel Blends as Fuel
 Experimental Study on Performance and Emission of Diesel Engine using Sunflower Oil-Diesel Blends as Fuel B. V. Krishnaiah Associate Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Narayana Engineering
Experimental Study on Performance and Emission of Diesel Engine using Sunflower Oil-Diesel Blends as Fuel B. V. Krishnaiah Associate Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Narayana Engineering
ENVO DIESEL TEST ON AUTOMOTIVE ENGINE AN ANALYSIS OF ITS PERFORMANCE AND EMISSIONS RESULTS
 International Journal of Mechanical and Materials Engineering (IJMME), Vol. 3 (2008), No.1, 55-60. ENVO DIESEL TEST ON AUTOMOTIVE ENGINE AN ANALYSIS OF ITS PERFORMANCE AND EMISSIONS RESULTS M.A. Kalam,
International Journal of Mechanical and Materials Engineering (IJMME), Vol. 3 (2008), No.1, 55-60. ENVO DIESEL TEST ON AUTOMOTIVE ENGINE AN ANALYSIS OF ITS PERFORMANCE AND EMISSIONS RESULTS M.A. Kalam,
