Main Gearbox Testing for Light Utility Helicopter of HAL
|
|
|
- Merry Strickland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 8 th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace, November 3-5, 2016 Main Gearbox Testing for Light Utility Helicopter of HAL MURALIDHAR B.S. 1, Bhawani Singh RATHORE 1 More info about this article: 1 Ground Testing Design Group, Rotary Wing Research and Design Centre, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), Bengaluru, India Phone: , muralidhar.bs@hal-india.com Abstract Non-destructive testing forms a very important part of development of systems during the design and development phase of a helicopter. Helicopter gearboxes are considered critical systems, as they transmit power from the engines to the rotors and accessories of the helicopter at the required speed and direction. The individual components of the gearboxes like gears, shafts, housings are subjected to various NDT techniques in HAL such as Magnetic particle inspection, X-ray and liquid penetrate checks. Final checks on the components include checking of all dimensions, surface finish, checking of special features such as splines, hardness checks, ensuring compliance to the specified manufacturing processes and finishing, prior to the subsequent release of acceptance tags for the accepted components. While the above activities take care of the checks at the component level, checks at the assembly level are essential in order to ensure that the gearbox, as an assembly, meets the design requirements with regard to its performance under loads at the rated speed. The design and development of special test stands plays a crucial role in the assembly level testing of gearboxes. The tests are carried out at the development stage, wherein loads at the rated speeds are applied to check the proper functioning of the gearboxes, as well as in the prototype acceptance stage, wherein each gearbox identified for ground runs and prototype flight testing undergoes Nondestructive testing on the gearbox test stands. This paper presents the details of Main Gear Box tests performed for HAL s Light Utility Helicopter on special test stands developed and commissioned at Ground Test Centre, RWR&DC, HAL. Keywords: Main Gear Box, Closed Loop Torques, Mast loads, Test stands 1. Introduction Power transmission from engine to rotors and accessories in helicopters is carried out by the Main Gearbox (MGB) via interconnecting shafts and gears. The MGB typically consists of the gearbox housing, gears and pinions, support bearings, freewheels, lubrication and cooling systems, accessory drive tap offs, monitoring sensors, and some of the components of rotor control mechanisms that are integral with gearboxes, such as swash plate mechanisms and control linkages [1]. MGB : Main Gearbox MR RB TR : Main Rotor : Rotor Brake : Tail Rotor TGB : Tail Gearbox Figure 1 : General schematic arrangement of gearboxes in a helicopter
2 The MGB in a helicopter is designed based on : - Engine Installation Features & Adequate Engine-to-Tail Drive Clearance - Required power capability - Suspension on Vibration Isolation System (VIS) - Drive for Accessories - Mounting of Main Rotor Actuators for Main rotor controls The individual components of the gearboxes like gears, shafts, housings are subjected to various NDT techniques such as Magnetic particle inspection, X-ray and liquid penetrant checks. Final checks on the components include checking of all dimensions, surface finish, checking of special features such as splines, hardness checks, ensuring compliance to the specified manufacturing processes and finishing, prior to the subsequent release of acceptance tags for the accepted components. While these activities take care of the checks at the component level, checks at the assembly level are essential in order to ensure that the gearbox, as an assembly, meets the design requirements with regard to its performance under loads at the rated speed. Towards this, special tests were carried out on the MGB as follows. 2. Tests carried out on Main Gearbox of Light Utility Helicopter (LUH) The LUH MGB has a single engine input, with outputs for main and tail rotor and accessories. Development and prototype Main Gear Boxes were designed and built by HAL for its LUH program, and tests carried were out as follows, for checking the conformance to design [3]. 2.1 MGB Oil distribution checks Oil distribution checks are necessary for checking the adequacy of the oil flow rates at the various gear meshes of the MGB. The Oil distribution checks set up comprised of an oil reservoir and an oil pump to feed the oil at the required flow rate to the MGB. The resulting oil pressure and flow at MGB inlet, TPTO (Tail Power Take-off) oil pressure, oil quantity collected from each jet, and the oil temperature were measured during the checks. Figure 2 : Views of the MGB specimen with cut outs for Oil Distribution Checks
3 Apart from measurement of oil flow rates, the Oil Distribution Checks were carried out for determination of direction of oil jets and determination of pressure drop within the gearbox unit. The tests carried out were : Determination of oil flow rate at the outlet of each oil jet Determination of effect on oil flow rate and pressure by blocking of any one oil jet hole PRESSURE INLET POINT OIL SUPPLY TO FILTER INLET AUXILIARY TANK TPTO PRESSURE POINT MGB SPECIMEN FLOWMETER FOR OIL FLOW RATE MEAS- UREMENT MGB OIL INLET HOSE CONNECTION POINT HOSE CONNECTION TO AUXILIARY TANK EXTERNAL OIL PUMP FOR OIL DELIVERY TO MGB MAIN TANK Figure 3 : Test Set-up for Oil Distribution Checks
4 The Oil Distribution Checks test set-up comprised of a Main tank filled with oil. The oil was fed to the inlet of MGB (at MGB filter) by using an external oil pump. The MGB was placed on an Auxiliary tank which was inter-connected with the Main tank. Photographs of test setup are shown in figure 3. The oil was fed to the inlet of MGB, sprayed out from the MGB oil jets to the MGB internals, and got collected in the Auxiliary tank. This oil flowed back to the Main oil tank by gravity, thus completing the oil circuit. During the test, Oil Flow rate, MGB inlet pressure, MGB TPTO pressure, Oil temperature and ambient temperatures were measured. There were a total of over a dozen oil jets in the MGB. The oil used was JSD OX- 38 oil as per DERD For the test, the external oil pump was switched on, and the flow rate was adjusted in steps as per the minimum flow rating of the MGB oil pump. After completion of the tests at minimum flow, the oil flow rate was increased to mean flow, and the directions of spray were observed for each case. The oil temperature was then increased using the oil heater for the high temperature checks. The pressure drop within the MGB was determined at different inlet oil flow rates by adjusting the flow and measuring the pressures at the MGB inlet and TPTO. The difference between the inlet pressure and TPTO pressure gives the required pressure drop. For the oil flow rate measurement at still higher temperature, the test was carried out with alternate oil simulating the viscosity of OX-38 oil at 120 C, in order to avoid hazards of handling hot oil. The MGB inlet oil flow rate was then adjusted to the maximum flow, and oil from various branches spraying out from the oil jets were collected one by one to measure the oil flow rate for the respective jet. 2.2 Wipe tests for contact pattern development of the spiral bevel gear mesh Iterations of contact pattern tests were carried out till the achieving of satisfactory contact pattern with the required shimming and grinding corrections. The Tooth contact pattern development test (Wipe Test) was conducted in Quasi Static conditions, to arrive at the acceptable contact pattern. The objective of the test was to arrive at the acceptable contact pattern for gear & pinion in terms of size & location, and to establish the required machine setting data for production of pinion for gear pair. This was a pre-requisite for further dynamic and endurance load tests. The contact patterns were checked for each step after disassembly of the gearboxes from the rig. No-load contact pattern for the gear teeth was prepared at the assembly shop at the gearbox build stage. After this, the MGB was subjected to quasi-static wipe tests on Wipe Test Rig (see figure 4). The test rig was designed for application of and measurement of torques (at quasi-static speed by using a motor with speed reduction stage), as well as rotor load application and measurement for the various steps as per test requirements. The test rig set up consisted of a Rotor mast loading block, Input and TPTO Bracket assemblies, Brake Motor with speed reduction gear box, Pulley arrangement and Specimen mounting fixture (Test cart). A variable speed drive motor was integrated with the speed reduction gear box connected to a flexible cardan shaft which in turn connected the rotor mast loading unit of the rig. The specimen MGB was assembled on the trolley with pylon struts and tie rods. The trolley with MGB specimen was assembled with rotor mast loading block, input bracket and TPTO bracket of the Wipe test rig.
5 LOADING PULLEY WITH WIRE ROPE MGB SPECIMEN STRUCTURAL FRAME Figure 4 : Wipe Test set-up fpr LUH MGB contact pattern checks The torque loading system consisted of rope & pulley arrangement assembled on the Input bracket and TPTO brackets of the Wipe test rig. The ropes on Input and TPTO were locked with wire lock adapters assembled on Input and TPTO brackets. The other end of the wire ropes of Input and TPTO brackets were hung with weighing pans and calibrated weights were added to apply the required torque, after which the drive motor was switched on for slow speed/quasi-static rotation. Torque transducers were connected at flanges of Input, TPTO and Hydraulic pinion for Torque measurement on MGB. Strain gauging was done on four pylon struts & three Tie rods, and load calibration was carried out in in both directions. Strain values were measured by means of strain measurement system using data acquisition software. Moments & thrust loads were applied using hydraulic jacks. The applied moments & thrust loads were measured through load cells attached to the hydraulic actuators of the Rotor mast loading block. After completion of each load case, the MGB was sent to the gearbox assembly shop for modular level disassembly and recording of the contact pattern. 2.3 Functional tests for establishing the lube oil parameters A functional test rig was designed and fabricated for functional testing of the MGB as per requirements of measuring the basic parameters like oil pressures, oil flow rate, gearbox housing and sump oil temperatures and vibrations, before subjecting the MGB to full load tests. The rig comprised structural items, speed step up rig gearbox, drive system and motor. The test rig also comprised of a flushing unit for MGB, rig lubrication tank and a structure to mount AC Drive motor and speed step up rig gearbox. The structure was isolated from floor by providing shock mounts. The required power to MGB input was obtained from the AC Drive motor and speed increasing adapter gearbox. The Test rig Lubrication system provided lubrication to the speed increasing adapter gearbox through hydraulic hose connections. A
6 high speed helicopter flexible shaft was assembled in between the speed increasing adapter Gearbox shaft to MGB Input shaft. The test set up sketch is shown in figure 5. Figure 5 : Schematic arrangement for MGB Functional Test Rig The measurement set up consisted of Flow meter, Thermocouples, accelerometers and Pressure sensors for the measurement of Flow, Temperatures, Vibrations and Pressures on the MGB respectively. Virtual instruments via software on PC monitor were used as indicators to measure the following parameters during the test - Body temperatures on Conical housing Bearing locations on Freewheel housing, Input and TPTO housing, MGB housing, Accessory housing, Cooler fan, Temperature at inlet to the Oil Cooler unit, Sump oil temperature, Temperature at outlet to the Oil Cooler unit, Flow measurement at inlet to cooler unit, pressure at Outlet of the Lube oil Pump, Tail Power Take off, Input to MGB, Oil cooler inlet, Oil cooler outlet, Vibration Pickups on Conical housing in X,Y,Z directions, Input housing in Radial directions, TPTO housing in Radial directions, Accessory housing in Radial directions, Cooler fan Bearing in Radial directions and RPM at MGB input. A PC based data acquisition system was installed to acquire and save the test data continuously during the run. As a safety measure for the test rig and the specimen under test, all the test rig parameters and specimen parameters were interlocked with the drive system to safely trip the test when the parameters exceed the limits specified. First the speed increasing test was carried out wherein the MGB was filled with oil and run by increasing the speed in steps of 5%, 10% to reach 100% speed. Both Flow and Pressure started building simultaneously with increase in speed. During the test run the absence of leakages at all interfaces, and the MGB parameters were monitored and recorded. After achieving satisfactory initial conditions, MGB was run at 100% speed for 1 hour. During the run all MGB parameters were monitored and recorded for every 2 minutes of interval till the temperature reached stabilization. The MGB parameters like temperature of housing surfaces
7 at various bearing locations, sump & ambient temperatures, Vibrations, Time trace and FFT, oil flow rate and pressures were recorded. Subsequently an accelerated cycle test run was carried out wherein the MGB was accelerated to 125% speed and held for 30 seconds. Then, it was decelerated to 100% and held for 60 seconds. A total 50 cycles of test run was carried out and parameters were recorded. During the test, the MGB was observed for any abnormal noise. During the run, the leakages at all interfaces and MGB parameters were monitored and recorded. Further, an oil quantity optimization test was carried out on the MGB with inclinations of forward tilt, rear tilt, right tilt and left tilt with reference to the Rotor axis. For each of the above inclinations, the MGB was run till the stabilization of sump oil temperature was reached. During the run, the leakages at all interfaces and MGB parameters were monitored and recorded for every 2 minutes. The test was further continued for determination of undrainable volume and unused oil quantity in MGB housing, oil filter, cooler and hoses. 2.4 Endurance Load Testing of MGB The test was carried out on an MGB test stand specially designed for conduction of load test by application of closed loop torques, mast loads and accessory loads at the required rpm. The rig was housed in a separate test facility, and comprised of the Test Rig Structure, a Multidrive system, Rig Gear boxes, Rotor Mast loading block, Hydraulic Actuators, Accessory loading systems, Control & monitoring system, Data acquisition system, Sensors for pressures, flow, temperatures, mast loads, torque, speed & vibration measurements. Initially, static strain survey tests & dynamic wipe tests were conducted on MGB assembly to evaluate the strain values on MGB with the actual mounting plates and Torque reaction parts. During the test, various combinations of mast loads and thrust loads were applied on MGB. The test stand sketch is shown in figure 6. During the endurance load test the MGB speed was increased gradually in steps by increasing the speed of an AC motor used as prime mover. Prior to applying loads on the MGB, a warm up run was carried at no load to observe functional parameters of MGB. The rotor mast loads, torques and accessory loads were applied as per the load spectrum to carry out the endurance runs. For running the MGB, an AC induction motor controlled by variable frequency drive (VFD) was used as a prime mover. The AC motor was mechanically coupled to the MGB input flange via suitable flexible couplings and Engine line test rig gearbox. By varying the input frequency to the motor, speed was varied from 0 RPM to the required RPM. The torque application on Input and TPTO was through an electrically closed loop [2] loading system where the electrical energy is re-circulated in a closed loop. For this, two AC induction generators were mechanically coupled to MGB main rotor shaft & Tail power output shaft via suitable flexible couplings, and controlled by separate AC drives connected to a common DC bus used for producing electrical power proportional to the torque required by regenerative braking, where mechanical energy was converted into electrical energy. The powers thus generated by regenerative braking during the test were fed back to the mains/grid, thus constituting an electrically closed loop system. Hence, the power drawn from the mains during testing is required only to overcome frictional losses in the mechanical system, thereby significantly reducing mains power demand and operating cost of the testing. Since the test rig is of electrically closed loop type, it can accommodate changes in teeth ratios in the Main
8 Gearbox during the development phase, thus making it flexible in nature. The torques were measured by torque sensors mounted in line with input & TPTO shafts. The speed increasing/ decreasing test rig gear boxes with suitable gear ratios ensured that required RPMs at MGB input and at AC generators were obtained. A specimen fixing carriage used for MGB assembly, thus completing the test set up. The generators used for application of torque at TPTO were mechanically coupled to the MGB flanges via flexible cardan shafts. The specimen carriage was used to assemble and prepare the MGB outside the rig. After assembly the carriage was pushed inside to align the MGB shafts with test rig gear box shafts (input & TPTO) and the cardan shaft connecting to upper gear box. The entire structure was isolated from ground by providing mechanical shock mounts. The test stand was positioned inside sound proof room with sound proof sliding doors and viewing windows. The lubrication system for intermediate gear boxes, hydraulic system for application of rotor mast loads & for loading hydraulic accessory pumps were placed at basement below the test rig for easy return of rig gearbox oil by gravity flow. External forced air cooling was used to cool the specimen under test during the load test to maintain the MGB temperatures within the specified limit. Figure 6 : Schematic arrangement for MGB Load Test Rig
9 For rotor mast load & thrust loads electronic pressure controllers were used, which regulated the proportional pressure valves mounted in hydraulic lines for each hydraulic jacks so that each jack was controlled independently such that any combination of loads could be applied on each jack. A programmable logic controller (PLC) was used in order to automate/control the sequence of activities up to the readiness to start the actual run. These activities included starting of cooling pumps for motor & generators, switching on lubrications for intermediate gearboxes, switching on hydraulic system for MGB accessory pumps, switching on hydraulic pumps for Rotor Mast Loading system, confirming the on-line status of the data acquisition system and bringing the multi-drive system to the ready mode. The PLC ensured that the drive ready status was reached only after the switching on all the motors, pumps, pressure & flow switches and ensuring the online status, the data acquisition system etc. The current feedback from generators to the drives maintained the torques always steady during the test. The encoder feedback from the motor to the drive always maintained constant speeds without fluctuations. As a safety factor, the control section also included protective functions such as over current, over voltage & over temperature protection circuitry. During the load test all the flight conditions were simulated as per the load spectrum. Since the testing involved the loading of MGB under dynamic conditions, a variable speed AC motor was used to rotate the MGB in the required speed and direction. The speed at the MGB input & TPTO were measured by speed sensor mounted at MGB input & TPTO shafts. Simulation of rotor mast loads & moments: Simulation of rotor loads & moments involves designing of a mechanical system to make the application of loads on a rotating part possible with the help of loading device fixed onto the static test rig structure. This rotor mast loading system was therefore visualized in the form of rotor mast loading block with thrust bearings, having four lugs at which hydraulic jacks are attached. By having independent control over the hydraulic jack load, it became possible to apply the required combination of rotor mast loads & also the moments. The rotor mast loads were measured by the jack load cells. Simulation of accessories loads: The accessories loads like alternator, two hydraulic pumps and oil cooler fan were simulated during the test. For this the original helicopter items were used on the MGB. The alternator was loaded by using external resistance load bank, where the energy was dissipated in the form of heat. The hydraulic pumps were loaded by using an external pump loading system. Safety features: An interlocking system was provided for each of the measured parameters for tripping the drive and releasing all the loads in case of safety limit of any parameter exceeds during the test. Also a video monitoring system was provided to monitor & record the run continuously during test. All the sensors, conditioners & data acquisition systems were connected to UPS power to take care of power fluctuations as well as to prevent loss of important test data in the event of power failures. As a safety factor, the control section also included protective functions such as over current, over voltage & over temperature protection circuitry. A shear neck flange with supporting bracket assembly was introduced between MGB flange and the rig gearbox. This shear neck flange acted as a mechanical fuse to prevent sudden load spikes or over load, if any. The MGB load test called for continuous monitoring of the following various parameters during the test: RPM of MGB specimen, Pressures at inlet, TPTO & outlet, Oil flow rate, Strain values at different locations on housing & MGB mounting parts like Z plates, Torque
10 strips, Temperatures at various locations like bearings, housings and oil sump areas, Vibration levels at various locations, Rotor mast loads applied by each of the 4 rotor mast loading jacks, Torque values at MGB input & TPTO, Loads on Tie-rods, pylon struts, and FFT & Time trace for vibration parameters. In addition to the parameters called for the test specifications, it was equally important to continuously monitor the satisfactory performance of the test rig by monitoring various key parameters. In view of the large number of parameters involved a PC based data acquisition system was used to monitor and acquire data continuously by means of data acquisition via Lab-view program. For the safety of test rig and specimen, all the instruments/sensors were calibrated prior to the start of tests. Following the above endurance tests, acceptance functional and load testing was carried out on new gearboxes made to the final configuration for the prototype tests. The typical gear tooth contact patterns obtained are shown in figure 7. Contact pattern for gear tooth - at no load Contact pattern for pinion tooth - at no load Contact pattern for gear tooth Contact pattern for pinion tooth after load test after load test Figure 7 : Typical gear tooth contact patterns obtained The endurance load tests were carried out according to a load spectrum comprising of steps corresponding to the loads experienced by the MGB during flight, including maximum continuous power (MCP) and take off power (TOP) steps. After passing these tests, the MGB was assembled onto the LUH prototypes for further helicopter system and flight tests. 3.0 Conclusion Special test set ups were prepared for the testing of the Main Gearbox of Light Utility Helicopter as per the test programs, and extensive testing was carried out in the various test stands indigenously developed at HAL. The feedback from all these tests was used to finalise the design of the helicopter main gearbox for use during the prototype testing phase of the helicopter. References: 1. DEF STAN (Transmission system) 2. (Gearbox testing) 3. FAR 27 document
Development Of A Power Re-Circulating Gear Test Rig
 Development Of A Power Re-Circulating Gear Test Rig V. Manoj, K. Gopinath and G.Muthuveerappan Dept. of Mech. Engg. IIT Madras, Chennai-600 036 manoj_v98@yahoo.com / gopinath@iitm.ac.in ABSTRACT In order
Development Of A Power Re-Circulating Gear Test Rig V. Manoj, K. Gopinath and G.Muthuveerappan Dept. of Mech. Engg. IIT Madras, Chennai-600 036 manoj_v98@yahoo.com / gopinath@iitm.ac.in ABSTRACT In order
Review Paper on Design and Development of Coupling Torque Endurance Test Machine with Variable Torque and Chamber Adjustment
 Review Paper on Design and Development of Coupling Torque Endurance Test Machine with Variable Torque and Chamber Adjustment 1. Mr. Borude S.C.(P.G. Student, JSPM s ICOER, Pune), 2.Prof. Biradar N.S.(HOD
Review Paper on Design and Development of Coupling Torque Endurance Test Machine with Variable Torque and Chamber Adjustment 1. Mr. Borude S.C.(P.G. Student, JSPM s ICOER, Pune), 2.Prof. Biradar N.S.(HOD
Finite Element and Experimental Validation of Stiffness Analysis of Precision Feedback Spring and Flexure Tube of Jet Pipe Electrohydraulic Servovalve
 Finite Element and Experimental Validation of Stiffness Analysis of Precision Feedback Spring and Flexure Tube of Jet Pipe Electrohydraulic Servovalve M. Singaperumal*, Somashekhar. S. Hiremath* R. Krishna
Finite Element and Experimental Validation of Stiffness Analysis of Precision Feedback Spring and Flexure Tube of Jet Pipe Electrohydraulic Servovalve M. Singaperumal*, Somashekhar. S. Hiremath* R. Krishna
CHAPTER 5 SINGLE-ROTOR POWER TRAIN SYSTEM MAIN DRIVE SHAFT FM 1-514
 CHAPTER 5 SINGLE-ROTOR POWER TRAIN SYSTEM A typical single-rotor power tram system (Figure 5-1) consists of a main transmission (main gearbox), a main drive shaft, and a series of tail rotor drive shafts
CHAPTER 5 SINGLE-ROTOR POWER TRAIN SYSTEM A typical single-rotor power tram system (Figure 5-1) consists of a main transmission (main gearbox), a main drive shaft, and a series of tail rotor drive shafts
AGE 222. Introduction to Farm Machinery Dr. O. U. Dairo. Farm Machinery and Power
 AGE 222 Introduction to Farm Machinery Dr. O. U. Dairo Farm Machinery and Power Equipment in the farm are classified as farm power and farm machinery Power provides pull/force required tom operate implements
AGE 222 Introduction to Farm Machinery Dr. O. U. Dairo Farm Machinery and Power Equipment in the farm are classified as farm power and farm machinery Power provides pull/force required tom operate implements
PNEUMATIC HIGH SPEED SPINDLE WITH AIR BEARINGS
 PNEUMATIC HIGH SPEED SPINDLE WITH AIR BEARINGS Terenziano RAPARELLI, Federico COLOMBO and Rodrigo VILLAVICENCIO Department of Mechanics, Politecnico di Torino Corso Duca degli Abruzzi 24, Torino, 10129
PNEUMATIC HIGH SPEED SPINDLE WITH AIR BEARINGS Terenziano RAPARELLI, Federico COLOMBO and Rodrigo VILLAVICENCIO Department of Mechanics, Politecnico di Torino Corso Duca degli Abruzzi 24, Torino, 10129
M-04 TRANSMISSION GEARS
 Guideline No.: M-04(201510) M-04 TRANSMISSION GEARS Issued date: October 20,2015 China Classification Society Foreword: This Guide is a part of CCS Rules, which contains technical requirements, inspection
Guideline No.: M-04(201510) M-04 TRANSMISSION GEARS Issued date: October 20,2015 China Classification Society Foreword: This Guide is a part of CCS Rules, which contains technical requirements, inspection
CLOSED CIRCUIT HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSION
 Energy conservation and other advantages in Mobile Equipment Through CLOSED CIRCUIT HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSION C. Ramakantha Murthy Technical Consultant Various features/advantages of HST Hydrostatic transmissions
Energy conservation and other advantages in Mobile Equipment Through CLOSED CIRCUIT HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSION C. Ramakantha Murthy Technical Consultant Various features/advantages of HST Hydrostatic transmissions
INVOLUTE TOOLING CORPORATION
 MANUFACTURERS OF DRIVES AND TRANSMISSIONS OFFICE: 13, JORBAGH, NEW DELHI - 110 003, INDIA, TEL: +91(011)24621453 FAX: +91(011) 24603609 WORKS: PLOT-65, SEC-27C, FARIDABAD - 121 003. INDIA, TEL: +91(0129)
MANUFACTURERS OF DRIVES AND TRANSMISSIONS OFFICE: 13, JORBAGH, NEW DELHI - 110 003, INDIA, TEL: +91(011)24621453 FAX: +91(011) 24603609 WORKS: PLOT-65, SEC-27C, FARIDABAD - 121 003. INDIA, TEL: +91(0129)
Analysis of Eclipse Drive Train for Wind Turbine Transmission System
 ISSN 2395-1621 Analysis of Eclipse Drive Train for Wind Turbine Transmission System #1 P.A. Katre, #2 S.G. Ganiger 1 pankaj12345katre@gmail.com 2 somu.ganiger@gmail.com #1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
ISSN 2395-1621 Analysis of Eclipse Drive Train for Wind Turbine Transmission System #1 P.A. Katre, #2 S.G. Ganiger 1 pankaj12345katre@gmail.com 2 somu.ganiger@gmail.com #1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Table of Content 1 Technical Description... 3
 Page: 2 of 15 Table of Content 1 Technical Description... 3 1.1 General Description... 3 1.2 Swivel & Gearbox Assembly... 4 1.3 Suspension System... 5 1.4 Drilling Motor Assembly... 6 1.4.1 AC Drilling
Page: 2 of 15 Table of Content 1 Technical Description... 3 1.1 General Description... 3 1.2 Swivel & Gearbox Assembly... 4 1.3 Suspension System... 5 1.4 Drilling Motor Assembly... 6 1.4.1 AC Drilling
IJESRT. Scientific Journal Impact Factor: (ISRA), Impact Factor: 2.114
 IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY SIMULATION AND VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF GEAR BOX USED IN COOLING TOWER FAN K.G.Patel*, S.U.Patil, H.G.Patil D.N.Patel College of
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY SIMULATION AND VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF GEAR BOX USED IN COOLING TOWER FAN K.G.Patel*, S.U.Patil, H.G.Patil D.N.Patel College of
Universal Fluid Power Trainer (UFPT)
 Universal Fluid Power Trainer (UFPT) The UFPT is a modular, smart and unique fluid power and motion control training unit. It contains an excellent integration of industrial-graded hardware and builtin
Universal Fluid Power Trainer (UFPT) The UFPT is a modular, smart and unique fluid power and motion control training unit. It contains an excellent integration of industrial-graded hardware and builtin
FANS. By- T.M.JOARDAR
 FANS By- T.M.JOARDAR Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 2. PRINCIPLE OF WORKING 3. CLASSIFICATION OF FANS 4. FAN DESIGNATION 5. CONSTRUCTIONAL FEATURES 6. PARAMETERS FOR FANS 7. CONTROLS 8. ACCESSORIES 9. INTERLOCK
FANS By- T.M.JOARDAR Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 2. PRINCIPLE OF WORKING 3. CLASSIFICATION OF FANS 4. FAN DESIGNATION 5. CONSTRUCTIONAL FEATURES 6. PARAMETERS FOR FANS 7. CONTROLS 8. ACCESSORIES 9. INTERLOCK
SPMM OUTLINE SPECIFICATION - SP20016 issue 2 WHAT IS THE SPMM 5000?
 SPMM 5000 OUTLINE SPECIFICATION - SP20016 issue 2 WHAT IS THE SPMM 5000? The Suspension Parameter Measuring Machine (SPMM) is designed to measure the quasi-static suspension characteristics that are important
SPMM 5000 OUTLINE SPECIFICATION - SP20016 issue 2 WHAT IS THE SPMM 5000? The Suspension Parameter Measuring Machine (SPMM) is designed to measure the quasi-static suspension characteristics that are important
29th European Rotorcraft Forum, Friedrichshafen, 1618 September 2003 AlfredColsmannSaal HighSpeed Forward Flight (6) New General Code for Helicopter D
 29th European Rotorcraft Forum, Friedrichshafen, 1618 September 2003 AlfredColsmannSaal HighSpeed Forward Flight (6) New General Code for Helicopter Dy(3) AirfoilVortex Interaction Simulation TheodorKoberSaal
29th European Rotorcraft Forum, Friedrichshafen, 1618 September 2003 AlfredColsmannSaal HighSpeed Forward Flight (6) New General Code for Helicopter Dy(3) AirfoilVortex Interaction Simulation TheodorKoberSaal
TE 73 TWO ROLLER MACHINE
 TE 73 TWO ROLLER MACHINE Background The TE 73 family of machines dates back to original Plint and Partners Ltd designs from the 1960s. These machines are all to the overhung roller design in which test
TE 73 TWO ROLLER MACHINE Background The TE 73 family of machines dates back to original Plint and Partners Ltd designs from the 1960s. These machines are all to the overhung roller design in which test
Design of Self-Adjusting Strainer Assembly for Off-road Conditions used in Diesel Engine
 Design of Self-Adjusting Strainer Assembly for Off-road Conditions used in Diesel Engine #1 Aditya C. Zod, #2 Dr. A. B. Kanase-Patil 1 PG Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sinhgad College
Design of Self-Adjusting Strainer Assembly for Off-road Conditions used in Diesel Engine #1 Aditya C. Zod, #2 Dr. A. B. Kanase-Patil 1 PG Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sinhgad College
Measuring equipment for the development of efficient drive trains using sensor telemetry in the 200 C range
 News Measuring equipment for the development of efficient drive trains using sensor telemetry in the 200 C range Whether on the test stand or on the road MANNER Sensortelemetrie, the expert for contactless
News Measuring equipment for the development of efficient drive trains using sensor telemetry in the 200 C range Whether on the test stand or on the road MANNER Sensortelemetrie, the expert for contactless
Universal Fluid Power Trainer (UFPT)
 Universal Fluid Power Trainer (UFPT) Milwaukee School of Engineering Applied Technology Center TM Department of Professional Education The UFPT is a modular, smart and unique fluid power and motion control
Universal Fluid Power Trainer (UFPT) Milwaukee School of Engineering Applied Technology Center TM Department of Professional Education The UFPT is a modular, smart and unique fluid power and motion control
PERFORMANCE THROUGH REVOLUTION
 PERFORMANCE THROUGH REVOLUTION Dynamatic has a complete range of gear pumps for both mobile and industrial market segments. Dynamatic developed these pumps in technical collaboration with DOWTY Hydraulic
PERFORMANCE THROUGH REVOLUTION Dynamatic has a complete range of gear pumps for both mobile and industrial market segments. Dynamatic developed these pumps in technical collaboration with DOWTY Hydraulic
LECTURE-23: Basic concept of Hydro-Static Transmission (HST) Systems
 MODULE-6 : HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS LECTURE-23: Basic concept of Hydro-Static Transmission (HST) Systems 1. INTRODUCTION The need for large power transmissions in tight space and their control
MODULE-6 : HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS LECTURE-23: Basic concept of Hydro-Static Transmission (HST) Systems 1. INTRODUCTION The need for large power transmissions in tight space and their control
Steering Test Rigs. The World of Steering Test Machines. A world of experience TEST AND MOTION SIMULATION 2
 Steering Test Rigs The World of Steering Test Machines Steering column assemblies, are by their nature extremely safety critical, thus the ability to test them accurately and repeatedly is extremely important.
Steering Test Rigs The World of Steering Test Machines Steering column assemblies, are by their nature extremely safety critical, thus the ability to test them accurately and repeatedly is extremely important.
COOLING SYSTEM - V8. Cooling system component layout DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
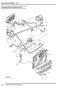 Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
Cooling system component layout 26-2-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 1 Heater matrix 2 Heater return hose 3 Heater inlet hose 4 Heater inlet pipe 5 Throttle housing 6 Connecting hose 7 Throttle housing inlet
Copyright Notice. Small Motor, Gearmotor and Control Handbook Copyright Bodine Electric Company. All rights reserved.
 Copyright Notice Small Motor, Gearmotor and Control Handbook Copyright 1993-2003 Bodine Electric Company. All rights reserved. Unauthorized duplication, distribution, or modification of this publication,
Copyright Notice Small Motor, Gearmotor and Control Handbook Copyright 1993-2003 Bodine Electric Company. All rights reserved. Unauthorized duplication, distribution, or modification of this publication,
SPMM OUTLINE SPECIFICATION - SP20016 issue 2 WHAT IS THE SPMM 5000?
 SPMM 5000 OUTLINE SPECIFICATION - SP20016 issue 2 WHAT IS THE SPMM 5000? The Suspension Parameter Measuring Machine (SPMM) is designed to measure the quasi-static suspension characteristics that are important
SPMM 5000 OUTLINE SPECIFICATION - SP20016 issue 2 WHAT IS THE SPMM 5000? The Suspension Parameter Measuring Machine (SPMM) is designed to measure the quasi-static suspension characteristics that are important
Procurement Specification for a High Security Lift Arm Barrier (HSLAB) EB950 CR Armstrong High Security Lift Arm Barrier
 Procurement Specification for a High Security Lift Arm Barrier (HSLAB) EB950 CR Armstrong High Security Lift Arm Barrier A. Requirement This document is to be used to specify the physical and operational
Procurement Specification for a High Security Lift Arm Barrier (HSLAB) EB950 CR Armstrong High Security Lift Arm Barrier A. Requirement This document is to be used to specify the physical and operational
Tilting Pad Journal Bearings
 Tilting Pad Journal Bearings Types W140 and W141 Diameter Range 40 355 mm Standard GTW Tilting Pad Journal Bearings type W140 with 4-pads and W141 with 5-pads. These bearings are used in high speed machines,
Tilting Pad Journal Bearings Types W140 and W141 Diameter Range 40 355 mm Standard GTW Tilting Pad Journal Bearings type W140 with 4-pads and W141 with 5-pads. These bearings are used in high speed machines,
MODELING SUSPENSION DAMPER MODULES USING LS-DYNA
 MODELING SUSPENSION DAMPER MODULES USING LS-DYNA Jason J. Tao Delphi Automotive Systems Energy & Chassis Systems Division 435 Cincinnati Street Dayton, OH 4548 Telephone: (937) 455-6298 E-mail: Jason.J.Tao@Delphiauto.com
MODELING SUSPENSION DAMPER MODULES USING LS-DYNA Jason J. Tao Delphi Automotive Systems Energy & Chassis Systems Division 435 Cincinnati Street Dayton, OH 4548 Telephone: (937) 455-6298 E-mail: Jason.J.Tao@Delphiauto.com
SHREE RAMCHANDRA EDUCATION SOCIETY S LONIKAND, PUNE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LAB MANUAL. Applied Thermodynamics (ATD) Semester-IV
 SHREE RAMCHANDRA EDUCATION SOCIETY S SHREE RAMCHANDRA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, LONIKAND, PUNE 412 216 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LAB MANUAL Applied Thermodynamics (ATD) Semester-IV Prepared by
SHREE RAMCHANDRA EDUCATION SOCIETY S SHREE RAMCHANDRA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, LONIKAND, PUNE 412 216 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LAB MANUAL Applied Thermodynamics (ATD) Semester-IV Prepared by
AN ELECTRICAL FUEL PUMPING AND METERING SYSTEM FOR MORE ELECTRICAL AERO-ENGINES
 25 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES AN ELECTRICAL FUEL PUMPING AND METERING SYSTEM FOR MORE ELECTRICAL AERO-ENGINES Jean-Yves ROUTEX HISPANO-SUIZA, SAFRAN GROUP Keywords: Fuel, pumping,
25 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES AN ELECTRICAL FUEL PUMPING AND METERING SYSTEM FOR MORE ELECTRICAL AERO-ENGINES Jean-Yves ROUTEX HISPANO-SUIZA, SAFRAN GROUP Keywords: Fuel, pumping,
Simulating Rotary Draw Bending and Tube Hydroforming
 Abstract: Simulating Rotary Draw Bending and Tube Hydroforming Dilip K Mahanty, Narendran M. Balan Engineering Services Group, Tata Consultancy Services Tube hydroforming is currently an active area of
Abstract: Simulating Rotary Draw Bending and Tube Hydroforming Dilip K Mahanty, Narendran M. Balan Engineering Services Group, Tata Consultancy Services Tube hydroforming is currently an active area of
ROTARY MODULES. Rotary modules
 Rotary modules Rotary modules ROTARY MODULES Series Size Page Rotary modules RM swivel unit 156 RM 08 160 RM 10 162 RM 12 164 RM 15 168 RM 21 172 RM rotor 176 RM 50 180 RM 110 182 RM 200 184 RM 310 186
Rotary modules Rotary modules ROTARY MODULES Series Size Page Rotary modules RM swivel unit 156 RM 08 160 RM 10 162 RM 12 164 RM 15 168 RM 21 172 RM rotor 176 RM 50 180 RM 110 182 RM 200 184 RM 310 186
6-speed manual gearbox 0A5
 Service Training Self-study programme 320 6-speed manual gearbox 0A5 Design and function S320_002 In addition to meeting increasing technical demands, modern cars also have to represent effective space
Service Training Self-study programme 320 6-speed manual gearbox 0A5 Design and function S320_002 In addition to meeting increasing technical demands, modern cars also have to represent effective space
Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train
 Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train A.R.Mokate 1, R.R.Navthar 2 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, PDVVP COE, A. Nagar, Maharashtra, India 1 Assistance Professor,
Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train A.R.Mokate 1, R.R.Navthar 2 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, PDVVP COE, A. Nagar, Maharashtra, India 1 Assistance Professor,
Figure1: Kone EcoDisc electric elevator drive [2]
![Figure1: Kone EcoDisc electric elevator drive [2] Figure1: Kone EcoDisc electric elevator drive [2]](/thumbs/77/75088735.jpg) Implementation of an Elevator s Position-Controlled Electric Drive 1 Ihedioha Ahmed C. and 2 Anyanwu A.M 1 Enugu State University of Science and Technology Enugu, Nigeria 2 Transmission Company of Nigeria
Implementation of an Elevator s Position-Controlled Electric Drive 1 Ihedioha Ahmed C. and 2 Anyanwu A.M 1 Enugu State University of Science and Technology Enugu, Nigeria 2 Transmission Company of Nigeria
TECHNICAL PAPER 1002 FT. WORTH, TEXAS REPORT X ORDER
 I. REFERENCE: 1 30 [1] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80504 Sheet 21, Hydraulic Schematic [2] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 60445, Sheet 21 Control Logic Flow Chart [3] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80577,
I. REFERENCE: 1 30 [1] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80504 Sheet 21, Hydraulic Schematic [2] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 60445, Sheet 21 Control Logic Flow Chart [3] Snow Engineering Co. Drawing 80577,
INTRODUCTION: Rotary pumps are positive displacement pumps. The rate of flow (discharge) of rotary pump remains constant irrespective of the
 INTRODUCTION: Rotary pumps are positive displacement pumps. The rate of flow (discharge) of rotary pump remains constant irrespective of the pressure. That is, even at very high pressure, these pumps can
INTRODUCTION: Rotary pumps are positive displacement pumps. The rate of flow (discharge) of rotary pump remains constant irrespective of the pressure. That is, even at very high pressure, these pumps can
HIGH LOAD LOW SHOCK RELEASE UNIT (30 kn)
 HIGH LOAD LOW SHOCK RELEASE UNIT (30 kn) Jens Müller (1), Christian Anderau (2) (1) Astrium GmbH, 81663 München (Germany), Email: Jens.mueller@astrium.eads.net (2) RUAG Aerospace AG, Widenholzstr. 1, 8304
HIGH LOAD LOW SHOCK RELEASE UNIT (30 kn) Jens Müller (1), Christian Anderau (2) (1) Astrium GmbH, 81663 München (Germany), Email: Jens.mueller@astrium.eads.net (2) RUAG Aerospace AG, Widenholzstr. 1, 8304
HMV Variable Motors Data and Specifications
 Data and Specifications Specifications HMR 55 HMR 75 HMR 105 HMR 135 cm 3/rev in 3/rev 55 3.36 75 4.57 105 6.40 135 8.23 Pressure Ratings Nominal 5000 PSIG Maximum 6090PSIG Peak 7250 PSIG Rated Speed 4000
Data and Specifications Specifications HMR 55 HMR 75 HMR 105 HMR 135 cm 3/rev in 3/rev 55 3.36 75 4.57 105 6.40 135 8.23 Pressure Ratings Nominal 5000 PSIG Maximum 6090PSIG Peak 7250 PSIG Rated Speed 4000
Camshaft Torque Analysis of Diesel Engine
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2017 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Swapnil
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2017 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Swapnil
X-Series Engine Dynamometer
 X-Series Engine Dynamometer Technical Specifications Metric May 2011 B N60 W22700 Silver Spring Drive Sussex, WI 53089 phone: (262) 252-4301 fax: (262) 246-0436 www.pwrtst.com Table of Contents 1.0 Power
X-Series Engine Dynamometer Technical Specifications Metric May 2011 B N60 W22700 Silver Spring Drive Sussex, WI 53089 phone: (262) 252-4301 fax: (262) 246-0436 www.pwrtst.com Table of Contents 1.0 Power
CH.4 Basic Components of Hydraulic and Pneumatic System/16 M HAP/17522/AE5G
 Content : 4.1 Hydraulic and Pneumatic actuators. 10 Marks Hydraulic Actuators - Hydraulic cylinders (single, double acting and telescopic) construction and working, Hydraulic motors (gear and piston type)
Content : 4.1 Hydraulic and Pneumatic actuators. 10 Marks Hydraulic Actuators - Hydraulic cylinders (single, double acting and telescopic) construction and working, Hydraulic motors (gear and piston type)
Design and Analysis of Six Speed Gear Box
 Design and Analysis of Six Speed Gear Box Ujjayan Majumdar 1, Sujit Maity 2, Gora Chand Chell 3 1,2 Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Jalpaiguri Government Engineering College, Jalpaiguri,
Design and Analysis of Six Speed Gear Box Ujjayan Majumdar 1, Sujit Maity 2, Gora Chand Chell 3 1,2 Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Jalpaiguri Government Engineering College, Jalpaiguri,
Design and Analysis of suspension system components
 Design and Analysis of suspension system components Manohar Gade 1, Rayees Shaikh 2, Deepak Bijamwar 3, Shubham Jambale 4, Vikram Kulkarni 5 1 Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, D Y Patil college
Design and Analysis of suspension system components Manohar Gade 1, Rayees Shaikh 2, Deepak Bijamwar 3, Shubham Jambale 4, Vikram Kulkarni 5 1 Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, D Y Patil college
VOLUME 9, FIRST ISSUE
 Editor INTEC GmbH, Argelsrieder Feld 13, 82234 Wessling, Germany VOLUME 9, FIRST ISSUE JULY 2005» CUSTOMER APPLICATION...01 Gearshift-Comfort Oriented Transmission and Drive Train Simulation at BMW» SOFTWARE...
Editor INTEC GmbH, Argelsrieder Feld 13, 82234 Wessling, Germany VOLUME 9, FIRST ISSUE JULY 2005» CUSTOMER APPLICATION...01 Gearshift-Comfort Oriented Transmission and Drive Train Simulation at BMW» SOFTWARE...
Test Which component has the highest Energy Density? A. Accumulator. B. Battery. C. Capacitor. D. Spring.
 Test 1 1. Which statement is True? A. Pneumatic systems are more suitable than hydraulic systems to drive powerful machines. B. Mechanical systems transfer energy for longer distances than hydraulic systems.
Test 1 1. Which statement is True? A. Pneumatic systems are more suitable than hydraulic systems to drive powerful machines. B. Mechanical systems transfer energy for longer distances than hydraulic systems.
Analysis of Spur Gear Box Using Software tool Ansys
 Analysis of Spur Gear Box Using Software tool Ansys K.G.Patel D.N.Patel College of Engineering, Shahada (Maharashtra) S.U.Patil D.N.Patel College of Engineering, Shahada (Maharashtra) H.G.Patil D.N.Patel
Analysis of Spur Gear Box Using Software tool Ansys K.G.Patel D.N.Patel College of Engineering, Shahada (Maharashtra) S.U.Patil D.N.Patel College of Engineering, Shahada (Maharashtra) H.G.Patil D.N.Patel
HOLINGER SF GEARBOX MANUAL
 HOLINGER SF GEARBOX MANUAL Approved By: Leigh Nash Date: 26/05/2011 Rev: D Date: 11/11 Holinger Engineering Gearbox Manual Page 1 FOREWORD The Holinger SF is a sequential-shift transaxle designed for use
HOLINGER SF GEARBOX MANUAL Approved By: Leigh Nash Date: 26/05/2011 Rev: D Date: 11/11 Holinger Engineering Gearbox Manual Page 1 FOREWORD The Holinger SF is a sequential-shift transaxle designed for use
Sheet 1 Variable loading
 Sheet 1 Variable loading 1. Estimate S e for the following materials: a. AISI 1020 CD steel. b. AISI 1080 HR steel. c. 2024 T3 aluminum. d. AISI 4340 steel heat-treated to a tensile strength of 1700 MPa.
Sheet 1 Variable loading 1. Estimate S e for the following materials: a. AISI 1020 CD steel. b. AISI 1080 HR steel. c. 2024 T3 aluminum. d. AISI 4340 steel heat-treated to a tensile strength of 1700 MPa.
three different ways, so it is important to be aware of how flow is to be specified
 Flow-control valves Flow-control valves include simple s to sophisticated closed-loop electrohydraulic valves that automatically adjust to variations in pressure and temperature. The purpose of flow control
Flow-control valves Flow-control valves include simple s to sophisticated closed-loop electrohydraulic valves that automatically adjust to variations in pressure and temperature. The purpose of flow control
Multilayer Energy Dissipating Inlet Column in Center-Feed Clarifiers 1
 Multilayer Energy Dissipating Inlet Column in Center-Feed Clarifiers 1 References 6,276,537 08/21/2001 Esler et al 210/519 6,800,209 10/05/2004 Wright 210/801 Field of Invention Clarifiers are tanks where
Multilayer Energy Dissipating Inlet Column in Center-Feed Clarifiers 1 References 6,276,537 08/21/2001 Esler et al 210/519 6,800,209 10/05/2004 Wright 210/801 Field of Invention Clarifiers are tanks where
Design and Fabrication of Automated Hacksaw Machine
 Design and Fabrication of Automated Hacksaw Machine D.V.Sabariananda 1, V.Siddhartha 1, B.Sushil Krishnana 1, T.Mohanraj 2 UG Student [Mechatronics], Dept. of Mechatronics Engineering, Kongu Engineering
Design and Fabrication of Automated Hacksaw Machine D.V.Sabariananda 1, V.Siddhartha 1, B.Sushil Krishnana 1, T.Mohanraj 2 UG Student [Mechatronics], Dept. of Mechatronics Engineering, Kongu Engineering
GÝROL FLUID DRIVES GÝROL FLUID DRIVES SAVE ENERGY HOW GÝROL FLUID DRIVES WORK
 GÝROL FLUID DRIVES Gýrol Fluid Drives are used to control speed and to absorb shock and torsional vibration. These extremely robust variable speed hydraulic drives provide a reliable, low maintenance,
GÝROL FLUID DRIVES Gýrol Fluid Drives are used to control speed and to absorb shock and torsional vibration. These extremely robust variable speed hydraulic drives provide a reliable, low maintenance,
Standard VVMC-1000 or VFMC-1000 controls, dispatched by an M3 Group System, allow group configurations with 64 landings and as many as 12 cars.
 General In This Section PTC PTC-SCR PTC-AC PTC-MG VVMC-1000 SCR VFMC-1000 AC VVMC-1000 MG Traction Controllers, PTC, VVMC, VFMC General Systems described in this section can be used for geared traction
General In This Section PTC PTC-SCR PTC-AC PTC-MG VVMC-1000 SCR VFMC-1000 AC VVMC-1000 MG Traction Controllers, PTC, VVMC, VFMC General Systems described in this section can be used for geared traction
Gdansk University of Technology Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Machine Design and Maintance Department. PG-II 1L Test rig for journal bearings
 Gdansk University of Technology Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Machine Design and Maintance Department PG-II 1L Test rig for journal bearings 1. INTRODUCTION The stand PG II-1 L is one of the many test
Gdansk University of Technology Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Machine Design and Maintance Department PG-II 1L Test rig for journal bearings 1. INTRODUCTION The stand PG II-1 L is one of the many test
WB 23 & WB 27. High-Speed Eddy-Current Dynamometers WB 23 & WB 27. Features. Description. Operating principles
 WB 23 & WB 27 High-Speed Eddy-Current Dynamometers Magtrol offers 3 types of dynamometer brakes to absorb load: Hysteresis, Eddy-Current and Magnetic Powder. Each type of Dynamometer has advantages and
WB 23 & WB 27 High-Speed Eddy-Current Dynamometers Magtrol offers 3 types of dynamometer brakes to absorb load: Hysteresis, Eddy-Current and Magnetic Powder. Each type of Dynamometer has advantages and
Ultrasonic Inspection Equipment for Al-Fin Insert Diesel Pistons
 A Paper By Mark Willcox Telephone +44 (0)1981 541122 Fax +44 (0)1981 541133 Email Sales@InsightNDT.com Web Site www.insightndt.com Insight NDT Equipment Ltd The Old Cider Mill Kings Thorn Herefordshire
A Paper By Mark Willcox Telephone +44 (0)1981 541122 Fax +44 (0)1981 541133 Email Sales@InsightNDT.com Web Site www.insightndt.com Insight NDT Equipment Ltd The Old Cider Mill Kings Thorn Herefordshire
Automated Seat Belt Switch Defect Detector
 pp. 10-16 Krishi Sanskriti Publications http://www.krishisanskriti.org/publication.html Automated Seat Belt Switch Defect Detector Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Sri Lanka Institute
pp. 10-16 Krishi Sanskriti Publications http://www.krishisanskriti.org/publication.html Automated Seat Belt Switch Defect Detector Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Sri Lanka Institute
Ultrasonic and Magnetic Particle Testing of New Railway Wheels
 19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 Ultrasonic and Magnetic Particle Testing of New Railway Wheels Wolfram A. Karl DEUTSCH 1, Wolfgang WEBER 1, Klaus MAXAM 1, Mathias RAZENG 1, Frank
19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 Ultrasonic and Magnetic Particle Testing of New Railway Wheels Wolfram A. Karl DEUTSCH 1, Wolfgang WEBER 1, Klaus MAXAM 1, Mathias RAZENG 1, Frank
SHOCK ABSORBER/DAMPER TESTING MACHINE
 SHOCK ABSORBER/DAMPER TESTING MACHINE Dampening force of a shock absorber is directly proportional to velocity and this parameter needs to be precisely controlled. A small variation of 1mm in a stroke
SHOCK ABSORBER/DAMPER TESTING MACHINE Dampening force of a shock absorber is directly proportional to velocity and this parameter needs to be precisely controlled. A small variation of 1mm in a stroke
AN INTEGRATED MODULAR TEST RIG FOR LANDING GEAR FATIGUE AND STRENGTH TESTING
 ICAS2002 CONGRESS AN INTEGRATED MODULAR TEST RIG FOR LANDING GEAR FATIGUE AND STRENGTH TESTING R. Kyle Schmidt, P. Eng. Messier-Dowty Inc., Ajax, Ontario, Canada Keywords: landing gear, fatigue, strength,
ICAS2002 CONGRESS AN INTEGRATED MODULAR TEST RIG FOR LANDING GEAR FATIGUE AND STRENGTH TESTING R. Kyle Schmidt, P. Eng. Messier-Dowty Inc., Ajax, Ontario, Canada Keywords: landing gear, fatigue, strength,
ZX6 INTRODUCTION ZX6 HOIST 2 : 1 4 : 1. Rope Reeving. Speeds 4/1.3 m/min 5/1.6 m/min 6/2 m/min 8/2.6 m/min. Lift 6.5m 10m 15m
 ZX HOIST ZX6 INTRODUCTION ZX6 HOIST The ZX6 Model is available with 4 gearbox ratio s, 3 drum lengths & 2 different reeving arrangements. These options combine to provide a comprehensive range of hoists
ZX HOIST ZX6 INTRODUCTION ZX6 HOIST The ZX6 Model is available with 4 gearbox ratio s, 3 drum lengths & 2 different reeving arrangements. These options combine to provide a comprehensive range of hoists
Design & Development of Regenerative Braking System at Rear Axle
 International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 2250-3234 Volume 8, Number 2 (2018), pp. 165-172 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Design & Development of Regenerative
International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 2250-3234 Volume 8, Number 2 (2018), pp. 165-172 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Design & Development of Regenerative
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1
 26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
26 - COOLING SYSTEM CONTENTS Page LAND ROVER V8 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE COOLING - DESCRIPTION... 3 ENGINE COOLING - OPERATION... 9 FAULT DIAGNOSIS COOLING SYSTEM FAULTS... 1 REPAIR COOLANT - DRAIN
Interface Webinar Wednesday. with Keith Skidmore
 Interface Webinar Wednesday Torque 101 with Keith Skidmore www.interfaceforce.com 480 948 5555 Definitions What is a Torque Transducer? Rotary vs. Reaction Shaft vs. Flange Couplings Floating vs. Fixed
Interface Webinar Wednesday Torque 101 with Keith Skidmore www.interfaceforce.com 480 948 5555 Definitions What is a Torque Transducer? Rotary vs. Reaction Shaft vs. Flange Couplings Floating vs. Fixed
Torque Sensors, Torque Transducers
 Torque Sensors, Torque Transducers Rotating with Slipring DR-2 1..500 0.1 - Cylindrical Shaft with Keyway DR-20 1..500 0.1 Standard Cylindrical Shaft with Keyway Sensors for Screw Driving Systems DR-1
Torque Sensors, Torque Transducers Rotating with Slipring DR-2 1..500 0.1 - Cylindrical Shaft with Keyway DR-20 1..500 0.1 Standard Cylindrical Shaft with Keyway Sensors for Screw Driving Systems DR-1
Chapter. Steering System Technology
 Chapter 78 Steering System Technology Objectives After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Explain the operating principles of steering systems. Identify the major parts of a steering system. Compare
Chapter 78 Steering System Technology Objectives After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Explain the operating principles of steering systems. Identify the major parts of a steering system. Compare
RE-EQUIPPING OF GEAR HOBBING MACHINE: NUMERICAL CONTROL INNOVATION BASED ON PLC AND SERVOMECHANISM
 RE-EQUIPPING OF GEAR HOBBING MACHINE: NUMERICAL CONTROL INNOVATION BASED ON PLC AND SERVOMECHANISM 1 OMKAR KADAM, 2 BALIRAM JADHAV, 3 SHRIKANT PAWAR 1 M.Tech, Production Engineering, Mechanical Engineering
RE-EQUIPPING OF GEAR HOBBING MACHINE: NUMERICAL CONTROL INNOVATION BASED ON PLC AND SERVOMECHANISM 1 OMKAR KADAM, 2 BALIRAM JADHAV, 3 SHRIKANT PAWAR 1 M.Tech, Production Engineering, Mechanical Engineering
Gear Drives. A third gear added to the system will rotate in the same direction as the drive gear Equal diameters = Equal number of teeth = Same speed
 Gear Drive Systems Gear Drives Gear Drive: Synchronous mechanical drive that uses gears to transfer power Gear: A toothed wheel that meshes with other toothed wheels to transfer rotational power Pinion
Gear Drive Systems Gear Drives Gear Drive: Synchronous mechanical drive that uses gears to transfer power Gear: A toothed wheel that meshes with other toothed wheels to transfer rotational power Pinion
Cooling Enhancement of Electric Motors
 Cooling Enhancement of Electric Motors Authors : Yasser G. Dessouky* and Barry W. Williams** Dept. of Computing & Electrical Engineering Heriot-Watt University Riccarton, Edinburgh EH14 4AS, U.K. Fax :
Cooling Enhancement of Electric Motors Authors : Yasser G. Dessouky* and Barry W. Williams** Dept. of Computing & Electrical Engineering Heriot-Watt University Riccarton, Edinburgh EH14 4AS, U.K. Fax :
Topic 1. Basics of Oil Hydraulic Systems
 Topic 1. Basics of Oil Hydraulic Systems Fluid power Fluid power is the technology that deals with the generation, control and transmission of forces and movement of mechanical element or system with the
Topic 1. Basics of Oil Hydraulic Systems Fluid power Fluid power is the technology that deals with the generation, control and transmission of forces and movement of mechanical element or system with the
Shock wave assisted removal of micron size dust. particles from silicon wafer surfaces.
 Shock wave assisted removal of micron size dust particles from silicon wafer surfaces G. Jagadeesh 1, M. Mizunaga 2, K. Shibasaki 2, S. Shibasaki 2, T. Saito 3 and K. Takayama 4 1 Dept. of Aerospace Engineering,Indian
Shock wave assisted removal of micron size dust particles from silicon wafer surfaces G. Jagadeesh 1, M. Mizunaga 2, K. Shibasaki 2, S. Shibasaki 2, T. Saito 3 and K. Takayama 4 1 Dept. of Aerospace Engineering,Indian
TECHNICAL MANUAL AVIATION UNIT AND INTERMEDIATE MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS ARMY MODEL UH-1H/V/EH-1H/X HELICOPTERS
 TECHNICAL MANUAL AVIATION UNIT AND INTERMEDIATE MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS ARMY MODEL UH-1H/V/EH-1H/X HELICOPTERS This manual supersedes TM 55-1520-210-23-2, 20 February 1979, including all changes. HEADQUARTERS,
TECHNICAL MANUAL AVIATION UNIT AND INTERMEDIATE MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS ARMY MODEL UH-1H/V/EH-1H/X HELICOPTERS This manual supersedes TM 55-1520-210-23-2, 20 February 1979, including all changes. HEADQUARTERS,
Power Jacks have taken time, engineering excellence and the best people to produce the ultra compact Neeter Drive gearbox.
 202 www.powerjacks.com Power Jacks have taken time, engineering excellence and the best people to produce the ultra compact Neeter Drive gearbox. Our expertise has been built on a history of engineering
202 www.powerjacks.com Power Jacks have taken time, engineering excellence and the best people to produce the ultra compact Neeter Drive gearbox. Our expertise has been built on a history of engineering
Gearbox, Bearings and Lubrication
 Chapter 4 Gearbox, Bearings and Lubrication Typical small gas turbine reduction gear train Small gas turbine engines spin at very high speed in the order of 25,000-85,000 rpm. A reduction gearbox is normally
Chapter 4 Gearbox, Bearings and Lubrication Typical small gas turbine reduction gear train Small gas turbine engines spin at very high speed in the order of 25,000-85,000 rpm. A reduction gearbox is normally
Skid against Curb simulation using Abaqus/Explicit
 Visit the SIMULIA Resource Center for more customer examples. Skid against Curb simulation using Abaqus/Explicit Dipl.-Ing. A. Lepold (FORD), Dipl.-Ing. T. Kroschwald (TECOSIM) Abstract: Skid a full vehicle
Visit the SIMULIA Resource Center for more customer examples. Skid against Curb simulation using Abaqus/Explicit Dipl.-Ing. A. Lepold (FORD), Dipl.-Ing. T. Kroschwald (TECOSIM) Abstract: Skid a full vehicle
Finite Element Modeling and Analysis of Vehicle Space Frame with Experimental Validation
 Finite Element Modeling and Analysis of Vehicle Space Frame with Experimental Validation Assoc. Prof Dr. Mohammed A.Elhaddad Mechanical Engineering Department Higher Technological Institute, Town of 6
Finite Element Modeling and Analysis of Vehicle Space Frame with Experimental Validation Assoc. Prof Dr. Mohammed A.Elhaddad Mechanical Engineering Department Higher Technological Institute, Town of 6
AUTOMATIC VEHICLE STABILIZATION SYSTEM Gaurav Pednekar 1, Raunak Borwankar 2 and Purva Sawant 3 1, 2, 3
 AUTOMATIC VEHICLE STABILIZATION SYSTEM Gaurav Pednekar 1, Raunak Borwankar 2 and Purva Sawant 3 1, 2, 3 Students, Department of Electronics & Telecommunication, Don Bosco Institute of Technology, University
AUTOMATIC VEHICLE STABILIZATION SYSTEM Gaurav Pednekar 1, Raunak Borwankar 2 and Purva Sawant 3 1, 2, 3 Students, Department of Electronics & Telecommunication, Don Bosco Institute of Technology, University
Wire Rope Hoist
 Wire Rope Hoist c a t a l o g Discover the power of technology Founded in 1991 Guralp is the first R&D centre in Turkeys overhead crane industry With Branches on 3 continents and service providers, worldwide
Wire Rope Hoist c a t a l o g Discover the power of technology Founded in 1991 Guralp is the first R&D centre in Turkeys overhead crane industry With Branches on 3 continents and service providers, worldwide
GENERAL The Honeywell model TFE731-40AR turbofan engine is a lightweight, two-spool, geared-stage, front-fan, jet engine.
 ENGINE GENERAL The Honeywell model TFE731-40AR turbofan engine is a lightweight, two-spool, geared-stage, front-fan, jet engine. The cross section of the engine is shown in Figure 7-71-1, page VII-71-3.
ENGINE GENERAL The Honeywell model TFE731-40AR turbofan engine is a lightweight, two-spool, geared-stage, front-fan, jet engine. The cross section of the engine is shown in Figure 7-71-1, page VII-71-3.
Vibration studies and on-site balancing of GT-1 assembly
 Page 1 of 32 Fig-1 showing the bump test measurements made on exciter rear end. A predominant frequency at 220 Hz was seen in the spectrum Page 2 of 32 Fig-2 showing bump test measurements made on generator
Page 1 of 32 Fig-1 showing the bump test measurements made on exciter rear end. A predominant frequency at 220 Hz was seen in the spectrum Page 2 of 32 Fig-2 showing bump test measurements made on generator
Axial-radial cylindrical roller bearings
 Axial-radial cylindrical roller bearings Designs and variants.............. 320 Bearing data..................... 321 (Boundary dimensions, tolerances) Product table 5.1 Axial-radial cylindrical roller
Axial-radial cylindrical roller bearings Designs and variants.............. 320 Bearing data..................... 321 (Boundary dimensions, tolerances) Product table 5.1 Axial-radial cylindrical roller
Vehicle Dynamic Simulation Using A Non-Linear Finite Element Simulation Program (LS-DYNA)
 Vehicle Dynamic Simulation Using A Non-Linear Finite Element Simulation Program (LS-DYNA) G. S. Choi and H. K. Min Kia Motors Technical Center 3-61 INTRODUCTION The reason manufacturers invest their time
Vehicle Dynamic Simulation Using A Non-Linear Finite Element Simulation Program (LS-DYNA) G. S. Choi and H. K. Min Kia Motors Technical Center 3-61 INTRODUCTION The reason manufacturers invest their time
Torque Sensors Force Sensors Multi-Component Sensors
 Torque Sensors Force Sensors Multi-Component Sensors Sensor Interfaces DIN Mounting Rail Devices Built-In Measuring Devices Portable Measuring Systems Tabletop and Laboratory Measuring Devices Highly precise
Torque Sensors Force Sensors Multi-Component Sensors Sensor Interfaces DIN Mounting Rail Devices Built-In Measuring Devices Portable Measuring Systems Tabletop and Laboratory Measuring Devices Highly precise
Fabrication and Automation of Solvent less Packaging Machine
 Fabrication and Automation of Solvent less Packaging Machine Masood Nazir*, Prof Rashmi Ranjan Das# * M.tech Student at School of Electrical Engineering, VIT University Vellore, Tamilnadu-632014 India
Fabrication and Automation of Solvent less Packaging Machine Masood Nazir*, Prof Rashmi Ranjan Das# * M.tech Student at School of Electrical Engineering, VIT University Vellore, Tamilnadu-632014 India
HANATEK FRICTION TESTER. MODEL 6010 (Obsolete) INSTRUCTION MANUAL. Replaced by:
 HANATEK FRICTION TESTER MODEL 6010 (Obsolete) INSTRUCTION MANUAL Replaced by: http://www.hanatekinstruments.com/advanced-friction-tester.html March 2004 2 CONTENTS SECTION No. Page No. 1 Contents 2 2 Introduction
HANATEK FRICTION TESTER MODEL 6010 (Obsolete) INSTRUCTION MANUAL Replaced by: http://www.hanatekinstruments.com/advanced-friction-tester.html March 2004 2 CONTENTS SECTION No. Page No. 1 Contents 2 2 Introduction
Cross Flow Heat Exchanger H352
 Cross Flow Heat Exchanger H352 H352 Shown With Optional Plain Tube of H352A fitted. Allows Investigation Of Plain And Finned Cross Flow Heat Exchangers. Expandable Free & Forced Convection Heat Transfer
Cross Flow Heat Exchanger H352 H352 Shown With Optional Plain Tube of H352A fitted. Allows Investigation Of Plain And Finned Cross Flow Heat Exchangers. Expandable Free & Forced Convection Heat Transfer
Lecture- 9: Load Equalization and Two Mark Questions. Load Equalization
 Lecture- 9: Load Equalization and Two Mark Questions Load Equalization In many industrial drives, such as in rolling mills, planning machines, electric hammers, reciprocating pumps, the load fluctuates
Lecture- 9: Load Equalization and Two Mark Questions Load Equalization In many industrial drives, such as in rolling mills, planning machines, electric hammers, reciprocating pumps, the load fluctuates
M-18 Controllable-Pitch Propeller
 Guideline No.M-18(201510) M-18 Controllable-Pitch Propeller Issued date: 20 th October, 2015 China Classification Society Foreword This Guideline is a part of CCS Rules, which contains technical requirements,
Guideline No.M-18(201510) M-18 Controllable-Pitch Propeller Issued date: 20 th October, 2015 China Classification Society Foreword This Guideline is a part of CCS Rules, which contains technical requirements,
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE. On Industrial Automation and Control
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE On Industrial Automation and Control By Prof. S. Mukhopadhyay Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Kharagpur Topic Lecture
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE On Industrial Automation and Control By Prof. S. Mukhopadhyay Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Kharagpur Topic Lecture
SECTION B1: MACHINE COMPONENTS
 SECTION B1: MACHINE COMPONENTS The machine portion of the Injected Metal Assembly system provides the means for: holding, heating and injecting the alloy; distributing and controlling electrical, pneumatic,
SECTION B1: MACHINE COMPONENTS The machine portion of the Injected Metal Assembly system provides the means for: holding, heating and injecting the alloy; distributing and controlling electrical, pneumatic,
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Seal-less rotodynamic pumps Class II Specification
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 15783 First edition 2002-02-01 Seal-less rotodynamic pumps Class II Specification Pompes rotodynamiques sans dispositif d'étanchéité d'arbre Classe II Spécifications Reference
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 15783 First edition 2002-02-01 Seal-less rotodynamic pumps Class II Specification Pompes rotodynamiques sans dispositif d'étanchéité d'arbre Classe II Spécifications Reference
KISSsys Application 008: Gearbox Concept Analysis
 KISSsoft AG Frauwis 1 CH - 8634 Hombrechtikon Telefon: +41 55 264 20 30 Calculation Software for Machine Design Fax: +41 55 264 20 33 www.kisssoft.ch info@kisssoft.ch 1. Abstract KISSsys: Efficient Drivetrain
KISSsoft AG Frauwis 1 CH - 8634 Hombrechtikon Telefon: +41 55 264 20 30 Calculation Software for Machine Design Fax: +41 55 264 20 33 www.kisssoft.ch info@kisssoft.ch 1. Abstract KISSsys: Efficient Drivetrain
AVL Media Conditioning Systems
 SIMULATION SOLUTIONS TEST SYSTEM SOLUTIONS Electrification TESTING Battery EQUIPMENT E-Motor Dynamometers and Actuators Power Electronics Test Vehicle Systems Testbeds Component Test Cell Mechanics Test
SIMULATION SOLUTIONS TEST SYSTEM SOLUTIONS Electrification TESTING Battery EQUIPMENT E-Motor Dynamometers and Actuators Power Electronics Test Vehicle Systems Testbeds Component Test Cell Mechanics Test
SECTION B: SYSTEM OPERATING COMPONENTS
 SECTION B: SYSTEM OPERATING COMPONENTS A brief description of the machine, Cable Processor Module and tooling will provide a better understanding of the various functions of the IMA system. SECTION B1:
SECTION B: SYSTEM OPERATING COMPONENTS A brief description of the machine, Cable Processor Module and tooling will provide a better understanding of the various functions of the IMA system. SECTION B1:
Improving predictive maintenance with oil condition monitoring.
 Improving predictive maintenance with oil condition monitoring. Contents 1. Introduction 2. The Big Five 3. Pros and cons 4. The perfect match? 5. Two is better than one 6. Gearboxes, for example 7. What
Improving predictive maintenance with oil condition monitoring. Contents 1. Introduction 2. The Big Five 3. Pros and cons 4. The perfect match? 5. Two is better than one 6. Gearboxes, for example 7. What
M-11 MARINE DIESEL ENGINE FUEL INJECTOR
 Guideline No.M-11(201510) M-11 MARINE DIESEL ENGINE FUEL INJECTOR Issued date: 20 October 2015 China Classification Society Foreword This Guideline constitutes the CCS rules, and establishes the applicable
Guideline No.M-11(201510) M-11 MARINE DIESEL ENGINE FUEL INJECTOR Issued date: 20 October 2015 China Classification Society Foreword This Guideline constitutes the CCS rules, and establishes the applicable
Radial piston motor for integrated drives MCR-H
 Radial piston motor for integrated drives MCR-H RE 15199 Edition: 03.2017 Replaces: 12.2013 Frame size MCR3, MCR5, MCR10, MCR15, MCR20 Displacement 160 cc to 3000 cc Differential pressure up to 450 bar
Radial piston motor for integrated drives MCR-H RE 15199 Edition: 03.2017 Replaces: 12.2013 Frame size MCR3, MCR5, MCR10, MCR15, MCR20 Displacement 160 cc to 3000 cc Differential pressure up to 450 bar
Hopkinsons Fig 9052 VALVE ACTUATOR
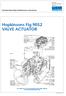 Excellent Power & Industrial Solutions Standard Operating & Maintenance Instructions Hopkinsons Fig 9052 VALVE ACTUATOR CUT-AWAY OF FIG. 9052 GEAR BOX, WITH LIMIT SWITCH & VALVE POSITION INDICATOR HOP
Excellent Power & Industrial Solutions Standard Operating & Maintenance Instructions Hopkinsons Fig 9052 VALVE ACTUATOR CUT-AWAY OF FIG. 9052 GEAR BOX, WITH LIMIT SWITCH & VALVE POSITION INDICATOR HOP
