Methodologies and Examples for Efficient Short and Long Duration Integrated Occupant-Vehicle Crash Simulation
|
|
|
- Monica Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Automotive Methodologies and Examples for Efficient Short and Long Duration Integrated Occupant-Vehicle Crash Simulation R. Reichert, C.-D. Kan, D. Marzougui, U. Mahadevaiah, R. Morgan, C.-K. Park, F. Tahan Center for Collision Safety and Analysis, George Mason University Abstract This paper describes efficient methodologies for fully integrated occupant-vehicle simulations as well as sub-system evaluations using prescribed motion in LS-DYNA. Examples include different short duration impacts such as frontal and side impact configurations with termination times of less than 200 milliseconds, and long duration impacts such as rollover events with termination times of 400 to 2500 milliseconds. A frontal offset and a frontal oblique impact was simulated using a Toyota Yaris model, side impact simulations were conducted with a Ford Taurus model, and a Ford Explorer model was used for rollover evaluations. Occupant models used include a Hybrid III, a THOR (Test device for Human Occupant Restraint), a US side impact, and a WorldSID dummy, as well as a THUMS (Total HUman Model for Safety) human model. Simulation results are compared to available full-scale crash test data. Parametric studies have been conducted to examine the influence of different input and output parameters when using sub-models with prescribed motion. Introduction Integrated occupant-vehicle analysis plays an important role in vehicle and occupant safety developments. Car manufacturers are using detailed full system models consisting of vehicle structure, interior, restraint systems, barrier, and occupant to develop safety measures and assure compliance with legal requirements, good rating results in consumer information tests, and vehicle safety in real life crash configurations. Suppliers are using sub-system models with to design and optimize interior and restraint system components with respect to various component and system requirements. While computer resources are becoming increasingly powerful, simulation models are becoming more detailed at the same time. Well organized modeling and simulation techniques are necessary in order to take full advantage of the numerical capabilities regarding meaningful occupant risk analysis. While full models are best suited to evaluate occupant risks in complex crash configurations taking the interaction of all participating components into account, reduced models can be useful for developing new restraint system or other component models. Depending on the purpose of a study, parts that directly interact with the occupant, such as the door trim in a side impact can be defined and applied with prescribed motion. In case the behavior of the door trim itself and its interaction with the occupant, seat, and airbag is the subject of interest, the vehicle door structure can be applied with prescribed motion and a model of the "deformable" door trim can be included in the sub-model, for example. 1-1
2 Session: Automotive 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference 1. Methodologies Fully Integrated Occupant-Vehicle Simulation All examples presented in this paper use a modular LS-DYNA [1] input deck, as illustrated in Figure 1. The vehicle structure model, barrier, occupant, airbag, seat belt, and other interior components are included into a main input file. Using this technique the various components can be replaced or modified in an efficient manner without having to rebuild the entire integrated occupant-vehicle model. Figure 1: Modular input deck Sub-Model Evaluations Sub-model techniques were used for model development. Defined output from a full vehicle run is used to create a reduced model with prescribed motion of the occupant environment. Occupant and restraint systems are included in the sub-model in a similar manner as in the full occupant-vehicle model. The reduced model replicates the intrusion behavior and vehicle kinematics from the full model, and can therefore be used for optimization of interior components and for validation purposes. The sub-model technique is illustrated in Figure 2. Figure 2: Sub-model technique 1-2
3 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Automotive IIHS Frontal Offset Impact with Hybrid III 2. Frontal Impact Examples A 2010 Toyota Yaris model with a 50th percentile Hybrid III [2] dummy in the driver seat was developed and used to simulate the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) 64 km/h, 40% offset impact into a fixed deformable barrier. Simulation results were evaluated with available full-scale crash test data [3] according to the IIHS normalized body region criteria. Simulation results match the "Acceptable" rating for the head and the "Good" rating for the other body regions when compared to the test results, as shown in Figure 3. Figure 3: IIHS frontal offset impact The described sub-model technique was used to develop and validate the fully integrated occupant-vehicle model [4]. Table 1 compares the full model on the left and the sub-model on the right regarding model size and time to complete the simulations. The turn-around time of the reduced model was about 20% when compared to the time required to run the full model. Absolute run times depend on the computer platform and number of cores and are used in this paper to outline the required run time of the sub-models relative to the full models. Table 1: Comparison of full and sub-model in IIHS load case Model size ~ Elements ~ Elements Run time ~ 5h ~ 1h 1-3
4 Session: Automotive 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Frontal Oblique Impact with THOR The same Toyota Yaris model with a 50th percentile THOR dummy [5] has been used to simulate a NHTSA oblique impact, where a research moving deformable barrier travels at 90 km/h into a stationary vehicle, configured at a 15 degree angle with a 35% overlap. Figure 4 compares the results of the integrated occupant-vehicle simulation with an available full-scale crash test [6]. Test and simulation show similar values for femur, chest, and neck criteria, as well as a distinct head acceleration peak with comparable timing. Figure 4: NHTSA oblique impact The described sub-model technique was used to develop and validate the fully integrated occupant-vehicle model [4]. Table 2 compares the full and sub-model regarding model size and required time to complete the simulations. The turn-around time of the reduced model was about 27% when compared to the time required to run the full model. Table 2: Comparison of full and sub-model in oblique load case Model size ~ Elements ~ Elements Run time ~ 22 h ~ 6h 1-4
5 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Automotive 3. Side Impact Examples SINCAP load case with US Side Impact Dummy A 2001 Ford Taurus 4-door vehicle model and two US side impact dummy models [2] were used to simulate a NHTSA Side Impact New Car Assessment Program (SINCAP) load case, where a moving deformable barrier strikes a stationary vehicle in a 27 degree crabbed position at a velocity of 62 km/h. Figure 5 compares chest and pelvis injury criteria from the simulation with an available full-scale crash test [7] for the front and rear occupant. The difference of test and simulation results is less than 10% for both body regions for the driver as well as the rear passenger. Figure 5: Ford Taurus Side Impact The described sub-model technique was used to develop and validate the fully integrated occupant-vehicle model. Table 3 compares the full model with front and rear passenger and a sub-model with driver dummy regarding model size and required time to complete the simulations. The turn-around time of the reduced model was about 17% when compared to the time necessary to run the full model. Table 3: Comparison of full and sub-model in SINCAP load case with USSID Model size Run time ~ Elements ~ Elements ~ 3 h ~ 0.5 h 1-5
6 Session: Automotive 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference SINCAP load case with World-SID The same Ford Taurus model that has been validated with an available full-scale crash test and the respective driver and passenger occupant models was used to analyze a WorldSID model [8], which is being developed in cooperation of the Center for Collision Safety and Analysis (CCSA) and the Livermore Software Technology Corporation (LSTC). Kinematics and numerical stability was evaluated for an early version of the WorldSID model under SINCAP loading conditions with seatbelt and side airbag interaction. The fully integrated occupant-vehicle model is shown in Figure 6. Figure 6: Ford Taurus Side Impact with WorldSID Table 4 compares the full model and a sub-model with a 50th percentile WorldSID in the driver seat regarding model size and necessary time to complete the simulations. The turn-around time of the reduced model was about 25% when compared to the time required to run the full model. Table 4: Comparison of full and sub-model in SINCAP load case with WorldSID Model size ~ Elements ~ Elements Run time ~ 3 h ~ 0.75h 1-6
7 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Automotive 4. Rollover Examples Integrated full and sub-model simulation with THUMS till 400 milliseconds A 2003 Ford Explorer vehicle model was used to simulate a rollover event together with a detailed 50th percentile THUMS [9] human occupant model. This example describes the results where initial conditions were applied to simulate the second quarter turn of a rollover configuration. Table 5 compares the full model and the sub-model regarding model size and required time to complete the simulations with a termination time of 400 milliseconds. The turnaround time for the reduced model was about 57% when compared to the time required to run the full model. Table 5: Comparison of full and sub-model in a rollover with THUMS Model size ~ Elements ~ Elements Run time ~ 35 h ~ 20 h Vehicle and integrated occupant sub-model simulation with THUMS till 2500 milliseconds Another way of using the reduced model technique is to first conduct a simulation of the vehicle structure without occupant. The occupant is then included in the reduced model that has been generated from the first simulation. Table 7 below shows pictures from a rollover simulation with the same Ford explorer vehicle model with termination time of 2500 milliseconds, which is more than ten times the time necessary to capture relevant occupant risks in a typical frontal or side impact configuration. Initial conditions were applied to capture the second, third, and fourth quarter turn of a rollover event with a detailed THUMS human model in the driver seat. The left column shows a sequence of the simulation where the vehicle structure has been run by itself. The middle column depicts the reduced model together with the THUMS occupant and relevant interior. The right column illustrates the same sequence of the reduced model using a tracked view as it would be seen from an on-board camera. 1-7
8 Session: Automotive 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Table 6: Simulation sequences of a 2500 milliseconds rollover event 1-8
9 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Automotive 5. Parametric Studies The described sub-model technique is based on the motion of defined nodes from relevant parts which is taken from a full model simulation. Two parameters are being examined in this section. One is the output frequency which describes the time interval that is used to record the motion of specified nodes. The second parameter is the output quantity which defines the number of nodes that are being recorded for relevant parts. Theoretically one could use every single node of all parts that are relevant for a sub-model and the motion of these nodes could be recorded at every single time step of a simulation. This would result in a motion of the defined parts that is identical in the full and sub-model. Since this is neither practical nor necessary, different values for the two parameters have been exercised and the effect on selected occupant results is described using a frontal impact and a side impact example. Sensitivity regarding output frequency The frontal impact IIHS load case with Hybrid III dummy was used to evaluate how the output frequency of defined nodes influenced the occupant results in a sub-model when compared to the outcome in the full occupant-vehicle model. In a first simulation the motion of defined nodes has been recorded every 1 millisecond in a full model run and applied as prescribed motion in the reduced model. In a second simulation nodal information that was recorded every 4 milliseconds and in a third simulation prescribed motion that was recorded every 8 milliseconds has been used in the reduced model analysis. Table 7: Comparison of full and sub-model using varying output frequency Nodal information was recorded every 1ms Nodal information was recorded every 4ms Nodal information was recorded every 8ms Chest Acceleration Neck Axial Force 1-9
10 Session: Automotive 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Table 7 exemplarily compares the chest acceleration and the neck axial force of the full occupant-vehicle simulation with the results of the respective sub-model runs. Close correlation can be noticed when prescribed motion that was recorded every millisecond was applied in the reduced model. More distinct differences between the sub-model and full model results can especially be noticed when an output frequency of 8 milliseconds has been used. Sensitivity regarding output quantity The side impact example with World-SID was used to evaluate how the number of nodes defined for the sub-model influenced the occupant results when compared to the outcome in the full model. In the first simulation the motion of every other node of the door and b-pillar trim has been recorded in a full model run and applied as prescribed motion in the reduced model. In the second simulation every 5th node, and in the third run every 10th node has been used. Table 8 exemplarily compares the maximum thorax rib deflection and the pelvis acceleration of the full occupant-vehicle and the respective reduced model simulations. It can be noticed that the time history plots compare well when every other node is applied with prescribed motion and that the discrepancy between full and sub-model is similar when every fifth and every tenth node is applied with prescribed motion. Table 8: Comparison of full and sub-model using varying output quantity Thorax Rib Deflection Pelvis Acceleration 1-10
11 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Automotive Methodologies 6. Summary and Conclusion Efficient methodologies for integrated occupant vehicle crash simulations were described. Modular input decks provide a proficient way of setting up different crash configurations with varying vehicle, barrier, interior, restraint system, and occupant models. The sub-model technique uses only parts that are relevant regarding occupant interaction, for example. By using prescribed motion for defined parts, comparable kinematics and intrusion behavior of the occupant environment can be achieved in the full vehicle and sub-model simulation. Reduced models are useful for efficiently setting up occupant-vehicle simulations, evaluating and optimizing interior, restraint system, and occupant models. Due to the same input structure, the developed, optimized or tested component models can be easily transferred from the sub-model and integrated into the full occupant-vehicle analysis. Examples Application examples for frontal impact, side impact, and rollover crash configurations were outlined and occupant results were compared to available full-scale crash test data. They include a frontal offset impact configuration with a Toyota Yaris with a Hybrid III dummy, a frontal offset oblique impact with the same vehicle and a THOR dummy, a side impact configuration of a Ford Taurus with an US side impact and a WorldSID dummy, and a long duration rollover crash event of a Ford Explorer with a detailed THUMS human model. Fully integrated occupant-vehicle models as well as reduced models with termination times that ranged from 100 to 2500 milliseconds for the various load cases were described. Comparisons of the required computer "turn around time" show that the reduced models needed 17 to 57 % time to complete the simulations when compared to the fully integrated occupant-vehicle models, depending on their respective sizes. Parametric study Two parameters that are relevant when using sub-models were evaluated. The output quantity defines, for how many nodes (of a relevant part) prescribed motion is being applied. The output frequency defines, which time interval is being used to record the motion of these nodes in the full vehicle simulation. In the first study, selected occupant results in full occupant-vehicle and respective sub-model simulations were compared using every second, every fifth, and every tenth node as output quantity. In the second study varying output frequencies of 1, 4, and 8 milliseconds were evaluated and their effect on selected occupant results was demonstrated. Choosing the appropriate values depends on the application, the purpose of the reduced model analysis, and the material properties of the relevant parts. Acknowledgment The authors would like to thank all organizations that provided funding and simulation models to make this work possible, especially the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA). 1-11
12 Session: Automotive 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference References [1] LS-DYNA Keyword User's Manual Version 971, Livermore Software Technology Corporation, Livermore, California, 2013 [2] Maurath, C., Guha, S., Updates to LSTC's LS-DYNA Anthropomorphic Models, 12th International LS-DYNA Users Conference, Dearborn, Michigan, 2012 [3] Crash Test Report, 2007 Toyota Yaris (CEF0610), Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), Arlington, Virginia, 2006 [4] Reichert, R., Park, C.-K., Morgan, R., Development of Integrated Vehicle-Occupant Model for Crashworthiness Safety Analysis, NHTSA report, Washington DC, 2014 [5] UNTAROIU, C., et al, Evaluation of a finite element model of the THOR dummy in frontal crash environment, 21st ESV Conference, Stuttgart, Germany, 2009 [6] Report for Frontal Oblique Offset Program, Testing on a 2011 Toyota Yaris, NHTSA No. RB5136, Calspan Corporation, Buffalo, NY, 2011 [7] New Car Assessment Program, Side Impact Test on a 2000 Ford Taurus, Report Nr. 214D-MGA , Burlington, Wisconsin, 2000 [8] Mahadevaiah, U., Maurath, C., Kan, C.-D., Marzougui, D., Development of a World Side Impact Dummy (WorldSID) Finite Element Model, 13th International LS-DYNA Users Conference, 2014 [9] Toyota Motor Corporation, Total HUman Model for Safety (THUMS), AM50 Pedestrian/Occupant Model, Academic Version 4.0, October
Development of a 2015 Mid-Size Sedan Vehicle Model
 Development of a 2015 Mid-Size Sedan Vehicle Model Rudolf Reichert, Steve Kan George Mason University Center for Collision Safety and Analysis 1 Abstract A detailed finite element model of a 2015 mid-size
Development of a 2015 Mid-Size Sedan Vehicle Model Rudolf Reichert, Steve Kan George Mason University Center for Collision Safety and Analysis 1 Abstract A detailed finite element model of a 2015 mid-size
Overview of LSTC s LS-DYNA Anthropomorphic Models
 Overview of LSTC s LS-DYNA Anthropomorphic Models Christoph Maurath, Sarba Guha, Dilip Bhalsod, Mike Burger, Jacob Krebs, Suri Bala Livermore Software Technology Corporation Sebastian Stahlschmidt, Reuben
Overview of LSTC s LS-DYNA Anthropomorphic Models Christoph Maurath, Sarba Guha, Dilip Bhalsod, Mike Burger, Jacob Krebs, Suri Bala Livermore Software Technology Corporation Sebastian Stahlschmidt, Reuben
IIHS Side Impact Evaluations. Sonja Arnold-Keifer 10/15/ th German LS-DYNA Forum
 IIHS Side Impact Evaluations Sonja Arnold-Keifer 10/15/2018 15 th German LS-DYNA Forum Motivation Passenger deaths in the US per year in multiple-vehicle side impact crashes: [IIHS2015_1] 2 IIHS side impact
IIHS Side Impact Evaluations Sonja Arnold-Keifer 10/15/2018 15 th German LS-DYNA Forum Motivation Passenger deaths in the US per year in multiple-vehicle side impact crashes: [IIHS2015_1] 2 IIHS side impact
Potential Effects of Deceleration Pulse Variations on Injury Measures Computed in Aircraft Seat HIC Analysis Testing
 Potential Effects of Deceleration Pulse Variations on Injury Measures Computed in Aircraft Seat HIC Analysis Testing K Friedman, G Mattos, K Bui, J Hutchinson, and A Jafri Friedman Research Corporation
Potential Effects of Deceleration Pulse Variations on Injury Measures Computed in Aircraft Seat HIC Analysis Testing K Friedman, G Mattos, K Bui, J Hutchinson, and A Jafri Friedman Research Corporation
Design Evaluation of Fuel Tank & Chassis Frame for Rear Impact of Toyota Yaris
 International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-issn: 2395-0056 Volume: 03 Issue: 05 May-2016 p-issn: 2395-0072 www.irjet.net Design Evaluation of Fuel Tank & Chassis Frame for Rear
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-issn: 2395-0056 Volume: 03 Issue: 05 May-2016 p-issn: 2395-0072 www.irjet.net Design Evaluation of Fuel Tank & Chassis Frame for Rear
An Evaluation of Active Knee Bolsters
 8 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Crash/Safety (1) An Evaluation of Active Knee Bolsters Zane Z. Yang Delphi Corporation Abstract In the present paper, the impact between an active knee bolster
8 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Crash/Safety (1) An Evaluation of Active Knee Bolsters Zane Z. Yang Delphi Corporation Abstract In the present paper, the impact between an active knee bolster
THUMS User Community
 THUMS User Community Therese Fuchs, Biomechanics Group, Institute of Legal Medicine, University of Munich therese.fuchs@med.uni-muenchen.de, tel. +49 89 2180 73365 Munich, 9th of April 2014 Agenda 1. What
THUMS User Community Therese Fuchs, Biomechanics Group, Institute of Legal Medicine, University of Munich therese.fuchs@med.uni-muenchen.de, tel. +49 89 2180 73365 Munich, 9th of April 2014 Agenda 1. What
STUDY ON CAR-TO-CAR FRONTAL OFFSET IMPACT WITH VEHICLE COMPATIBILITY
 STUDY ON CAR-TO-CAR FRONTAL OFFSET IMPACT WITH VEHICLE COMPATIBILITY Chang Min, Lee Jang Ho, Shin Hyun Woo, Kim Kun Ho, Park Young Joon, Park Hyundai Motor Company Republic of Korea Paper Number 17-0168
STUDY ON CAR-TO-CAR FRONTAL OFFSET IMPACT WITH VEHICLE COMPATIBILITY Chang Min, Lee Jang Ho, Shin Hyun Woo, Kim Kun Ho, Park Young Joon, Park Hyundai Motor Company Republic of Korea Paper Number 17-0168
Comparison of HVE simulations to NHTSA full-frontal barrier testing: an analysis of 3D and 2D stiffness coefficients in SIMON and EDSMAC4
 Comparison of HVE simulations to NHTSA full-frontal barrier testing: an analysis of 3D and 2D stiffness coefficients in SIMON and EDSMAC4 Jeffrey Suway Biomechanical Research and Testing, LLC Anthony Cornetto,
Comparison of HVE simulations to NHTSA full-frontal barrier testing: an analysis of 3D and 2D stiffness coefficients in SIMON and EDSMAC4 Jeffrey Suway Biomechanical Research and Testing, LLC Anthony Cornetto,
Advances in Simulating Corrugated Beam Barriers under Vehicular Impact
 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Automotive Advances in Simulating Corrugated Beam Barriers under Vehicular Impact Akram Abu-Odeh Texas A&M Transportation Institute Abstract W-beam
13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Automotive Advances in Simulating Corrugated Beam Barriers under Vehicular Impact Akram Abu-Odeh Texas A&M Transportation Institute Abstract W-beam
Development of a Finite Element Model of a Motorcycle
 Development of a Finite Element Model of a Motorcycle N. Schulz, C. Silvestri Dobrovolny and S. Hurlebaus Texas A&M Transportation Institute Abstract Over the past years, extensive research efforts have
Development of a Finite Element Model of a Motorcycle N. Schulz, C. Silvestri Dobrovolny and S. Hurlebaus Texas A&M Transportation Institute Abstract Over the past years, extensive research efforts have
WorldSID 50 th Update
 Informal Document No. GRSP-44-33 (44th session, 10-12 December 2008, agenda item 5(a)) PDB - Partnership for Dummy Technology and Biomechanics on behalf of the WorldSID Task Group 44 th GRSP Session Geneva,
Informal Document No. GRSP-44-33 (44th session, 10-12 December 2008, agenda item 5(a)) PDB - Partnership for Dummy Technology and Biomechanics on behalf of the WorldSID Task Group 44 th GRSP Session Geneva,
Study on the Influence of Seat Adjustment on Occupant Head Injury Based on MADYMO
 5th International Conference on Advanced Engineering Materials and Technology (AEMT 2015) Study on the Influence of Seat Adjustment on Occupant Head Injury Based on MADYMO Shucai Xu 1, a *, Binbing Huang
5th International Conference on Advanced Engineering Materials and Technology (AEMT 2015) Study on the Influence of Seat Adjustment on Occupant Head Injury Based on MADYMO Shucai Xu 1, a *, Binbing Huang
Study concerning the loads over driver's chests in car crashes with cars of the same or different generation
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Study concerning the loads over driver's chests in car crashes with cars of the same or different generation Related content -
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Study concerning the loads over driver's chests in car crashes with cars of the same or different generation Related content -
Statement before Massachusetts Auto Damage Appraiser Licensing Board. Institute Research on Cosmetic Crash Parts. Stephen L. Oesch.
 Statement before Massachusetts Auto Damage Appraiser Licensing Board Institute Research on Cosmetic Crash Parts Stephen L. Oesch INSURANCE INSTITUTE FOR HIGHWAY SAFETY 1005 N. GLEBE RD. ARLINGTON, VA 22201-4751
Statement before Massachusetts Auto Damage Appraiser Licensing Board Institute Research on Cosmetic Crash Parts Stephen L. Oesch INSURANCE INSTITUTE FOR HIGHWAY SAFETY 1005 N. GLEBE RD. ARLINGTON, VA 22201-4751
EFFECTIVENESS OF COUNTERMEASURES IN RESPONSE TO FMVSS 201 UPPER INTERIOR HEAD IMPACT PROTECTION
 EFFECTIVENESS OF COUNTERMEASURES IN RESPONSE TO FMVSS 201 UPPER INTERIOR HEAD IMPACT PROTECTION Arun Chickmenahalli Lear Corporation Michigan, USA Tel: 248-447-7771 Fax: 248-447-1512 E-mail: achickmenahalli@lear.com
EFFECTIVENESS OF COUNTERMEASURES IN RESPONSE TO FMVSS 201 UPPER INTERIOR HEAD IMPACT PROTECTION Arun Chickmenahalli Lear Corporation Michigan, USA Tel: 248-447-7771 Fax: 248-447-1512 E-mail: achickmenahalli@lear.com
Australian Pole Side Impact Research 2010
 Australian Pole Side Impact Research 2010 A summary of recent oblique, perpendicular and offset perpendicular pole side impact research with WorldSID 50 th Thomas Belcher (presenter) MarkTerrell 1 st Meeting
Australian Pole Side Impact Research 2010 A summary of recent oblique, perpendicular and offset perpendicular pole side impact research with WorldSID 50 th Thomas Belcher (presenter) MarkTerrell 1 st Meeting
Development of a Simplified Finite Element Approach for Investigation of Heavy Truck Occupant Protection in Frontal Impacts and Rollover Scenarios
 14 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session Automotive Development of a Simplified Finite Element Approach for Investigation of Heavy Truck Occupant Protection in Frontal Impacts and Rollover
14 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session Automotive Development of a Simplified Finite Element Approach for Investigation of Heavy Truck Occupant Protection in Frontal Impacts and Rollover
New Side Impact Dummy Developments
 New Side Impact Dummy Developments Bhavik Shah & Jennifer Tang First Technology Safety Systems Inc. 47460 Galleon Drive Plymouth MI 48170 USA Tel: +1 734 451 7878 Email: bshah@ftss.com & jzhou@ftss.com
New Side Impact Dummy Developments Bhavik Shah & Jennifer Tang First Technology Safety Systems Inc. 47460 Galleon Drive Plymouth MI 48170 USA Tel: +1 734 451 7878 Email: bshah@ftss.com & jzhou@ftss.com
VOLKSWAGEN. Volkswagen Safety Features
 Volkswagen Safety Features Volkswagen customers recognize their vehicles are designed for comfort, convenience and performance. But they also rely on vehicles to help protect them from events they hope
Volkswagen Safety Features Volkswagen customers recognize their vehicles are designed for comfort, convenience and performance. But they also rely on vehicles to help protect them from events they hope
Full Width Test ECE-R 94 Evaluation of test data Proposal for injury criteria Way forward
 Full Width Test ECE-R 94 Evaluation of test data Proposal for injury criteria Way forward Andre Eggers IWG Frontal Impact 19 th September, Bergisch Gladbach Federal Highway Research Institute BASt Project
Full Width Test ECE-R 94 Evaluation of test data Proposal for injury criteria Way forward Andre Eggers IWG Frontal Impact 19 th September, Bergisch Gladbach Federal Highway Research Institute BASt Project
AUTOMOTIVE SIDE-IMPACT SIMULATIONS AND COMPARISON OF DUMMY AND HUMAN BODY MODEL CRASH DYNAMIC RESPONSES ACCORDING TO REGULATORY STANDARDS.
 AUTOMOTIVE SIDE-IMPACT SIMULATIONS AND COMPARISON OF DUMMY AND HUMAN BODY MODEL CRASH DYNAMIC RESPONSES ACCORDING TO REGULATORY STANDARDS A Thesis by Durga Venkata Suresh Koppisetty Master of Technology,
AUTOMOTIVE SIDE-IMPACT SIMULATIONS AND COMPARISON OF DUMMY AND HUMAN BODY MODEL CRASH DYNAMIC RESPONSES ACCORDING TO REGULATORY STANDARDS A Thesis by Durga Venkata Suresh Koppisetty Master of Technology,
Development of Advanced HIII Abaqus dummies
 Visit the SIMULIA Resource Center for more customer examples. Development of Advanced HIII Abaqus dummies W. Li, J. Rasico, F. Zhu, M. Li, R. Kant, B. Aljundi First Technology Safety System Inc. Abstract:
Visit the SIMULIA Resource Center for more customer examples. Development of Advanced HIII Abaqus dummies W. Li, J. Rasico, F. Zhu, M. Li, R. Kant, B. Aljundi First Technology Safety System Inc. Abstract:
Crash test facility simulates frontal, rear-end and side collision with acceleration pulses of up to 65 g and 85 km/h (53 mph)
 Johnson Controls invests 3 million Euro (2.43 million GBP) in state-of-theart crash test facility Crash test facility simulates frontal, rear-end and side collision with acceleration pulses of up to 65
Johnson Controls invests 3 million Euro (2.43 million GBP) in state-of-theart crash test facility Crash test facility simulates frontal, rear-end and side collision with acceleration pulses of up to 65
Crashworthiness Evaluation of an Impact Energy Absorber in a Car Bumper for Frontal Crash Event - A FEA Approach
 Crashworthiness Evaluation of an Impact Energy Absorber in a Car Bumper for Frontal Crash Event - A FEA Approach Pravin E. Fulpagar, Dr.S.P.Shekhawat Department of Mechanical Engineering, SSBTS COET Jalgaon.
Crashworthiness Evaluation of an Impact Energy Absorber in a Car Bumper for Frontal Crash Event - A FEA Approach Pravin E. Fulpagar, Dr.S.P.Shekhawat Department of Mechanical Engineering, SSBTS COET Jalgaon.
Influence of Different Platen Angles and Selected Roof Header Reinforcements on the Quasi Static Roof Strength of a 2003 Ford Explorer FE Model
 Influence of Different Platen Angles and Selected Roof Header Reinforcements on the Quasi Static Roof Strength of a 2003 Ford Explorer FE Model Joachim Scheub, Fadi Tahan, Kennerly Digges, Cing Dao Kan
Influence of Different Platen Angles and Selected Roof Header Reinforcements on the Quasi Static Roof Strength of a 2003 Ford Explorer FE Model Joachim Scheub, Fadi Tahan, Kennerly Digges, Cing Dao Kan
Real World Accident Reconstruction with the Total Human Model for Safety (THUMS) in Pam-Crash
 Real World Accident Reconstruction with the Total Human Model for Safety (THUMS) in Pam-Crash R Segura 1,2, F Fürst 2, A Langner 3 and S Peldschus 4 1 Arbeitsgruppe Biomechanik, Institute of Legal Medicine,
Real World Accident Reconstruction with the Total Human Model for Safety (THUMS) in Pam-Crash R Segura 1,2, F Fürst 2, A Langner 3 and S Peldschus 4 1 Arbeitsgruppe Biomechanik, Institute of Legal Medicine,
Frontal Crash Simulation of Vehicles Against Lighting Columns in Kuwait Using FEM
 International Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering 2013, 2(5): 101-105 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijtte.20130205.02 Frontal Crash Simulation of Vehicles Against Lighting Columns in Kuwait Using FEM Yehia
International Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering 2013, 2(5): 101-105 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijtte.20130205.02 Frontal Crash Simulation of Vehicles Against Lighting Columns in Kuwait Using FEM Yehia
THE INFLUENCE OF THE SAFETY BELT ON THE DECISIVE INJURY ASSESSMENT VALUES IN THE NEW US-NCAP
 THE INFLUENCE OF THE SAFETY BELT ON THE DECISIVE INJURY ASSESSMENT VALUES IN THE NEW US-NCAP Burkhard Eickhoff*, Harald Zellmer*, Martin Meywerk** *Autoliv B.V. & Co. KG, Elmshorn, Germany **Helmut-Schmidt-Universität,
THE INFLUENCE OF THE SAFETY BELT ON THE DECISIVE INJURY ASSESSMENT VALUES IN THE NEW US-NCAP Burkhard Eickhoff*, Harald Zellmer*, Martin Meywerk** *Autoliv B.V. & Co. KG, Elmshorn, Germany **Helmut-Schmidt-Universität,
FINITE ELEMENT METHOD IN CAR COMPATIBILITY PHENOMENA
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 18, No. 4 2011 FINITE ELEMENT METHOD IN CAR COMPATIBILITY PHENOMENA Marcin Lisiecki Technical University of Warsaw Faculty of Power and Aeronautical Engineering
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 18, No. 4 2011 FINITE ELEMENT METHOD IN CAR COMPATIBILITY PHENOMENA Marcin Lisiecki Technical University of Warsaw Faculty of Power and Aeronautical Engineering
Potential Use of Crash Test Data for Crashworthiness Research
 Potential Use of Crash Test Data for Crashworthiness Research M Paine* and M Griffiths** * Vehicle Design and Research Pty Ltd, Beacon Hill NSW, Australia. ** Road Safety Solutions Pty Ltd, Caringbah NSW,
Potential Use of Crash Test Data for Crashworthiness Research M Paine* and M Griffiths** * Vehicle Design and Research Pty Ltd, Beacon Hill NSW, Australia. ** Road Safety Solutions Pty Ltd, Caringbah NSW,
REDUCING RIB DEFLECTION IN THE IIHS TEST BY PRELOADING THE PELVIS INDEPENDENT OF INTRUSION
 REDUCING RIB DEFLECTION IN THE IIHS TEST BY PRELOADING THE PELVIS INDEPENDENT OF INTRUSION Greg Mowry David Shilliday Zodiac Automotive US. Inc. United States Paper Number 5-422 ABSTRACT A cooperative
REDUCING RIB DEFLECTION IN THE IIHS TEST BY PRELOADING THE PELVIS INDEPENDENT OF INTRUSION Greg Mowry David Shilliday Zodiac Automotive US. Inc. United States Paper Number 5-422 ABSTRACT A cooperative
Working Paper. Development and Validation of a Pick-Up Truck Suspension Finite Element Model for Use in Crash Simulation
 Working Paper NCAC 2003-W-003 October 2003 Development and Validation of a Pick-Up Truck Suspension Finite Element Model for Use in Crash Simulation Dhafer Marzougui Cing-Dao (Steve) Kan Matthias Zink
Working Paper NCAC 2003-W-003 October 2003 Development and Validation of a Pick-Up Truck Suspension Finite Element Model for Use in Crash Simulation Dhafer Marzougui Cing-Dao (Steve) Kan Matthias Zink
NEW CRASH TESTS: SMALL CARS IMPROVE AND THE TOP PERFORMERS ALSO ARE FUEL SIPPERS
 NEWS RELEASE May 26, 2011 Contact: Russ Rader at 703/247-1500 (office) or at 202/257-3591 (cell) VNR: Thurs. 5/26/2011 10:30-11 am EDT (C) GALAXY 19/Trans. 15 (dl4000v) repeat 1:30-2 pm EDT (C) GALAXY
NEWS RELEASE May 26, 2011 Contact: Russ Rader at 703/247-1500 (office) or at 202/257-3591 (cell) VNR: Thurs. 5/26/2011 10:30-11 am EDT (C) GALAXY 19/Trans. 15 (dl4000v) repeat 1:30-2 pm EDT (C) GALAXY
A SLED TEST METHOD FOR SMALL OVERLAP CRASHES AND FATAL HEAD INJURIES
 A SLED TEST METHOD FOR SMALL OVERLAP CRASHES AND FATAL HEAD INJURIES Ola Bostrom Dion Kruse Autoliv Research Sweden Paper Number 11-0369 ABSTRACT A large portion of fatal crashes are characterized by passenger
A SLED TEST METHOD FOR SMALL OVERLAP CRASHES AND FATAL HEAD INJURIES Ola Bostrom Dion Kruse Autoliv Research Sweden Paper Number 11-0369 ABSTRACT A large portion of fatal crashes are characterized by passenger
ADVANCED RESTRAINT SY S STEM (ARS) Y Stephen Summers St NHTSA Ve NHTSA V hi hhicle S Saf t e y t R Resear R h c 1
 ADVANCED RESTRAINT SYSTEM (ARS) Stephen Summers NHTSA Vehicle Safety Research 1 CRASH AVOIDANCE METRICS PARTNERSHIP (CAMP) ARS 4 year Cooperative research program Demonstrate restraint systems that can
ADVANCED RESTRAINT SYSTEM (ARS) Stephen Summers NHTSA Vehicle Safety Research 1 CRASH AVOIDANCE METRICS PARTNERSHIP (CAMP) ARS 4 year Cooperative research program Demonstrate restraint systems that can
Benchmark Study on the AIRBAG_PARTICLE Method for Out-Of-Position Applications
 10 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Crash/Safety (3) Benchmark Study on the AIRBAG_PARTICLE Method for Out-Of-Position Applications Wenyu Lian General Motors Dilip Bhalsod Livermore Software Technology
10 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Crash/Safety (3) Benchmark Study on the AIRBAG_PARTICLE Method for Out-Of-Position Applications Wenyu Lian General Motors Dilip Bhalsod Livermore Software Technology
CURRENT WORLDWIDE SIDE IMPACT ACTIVITIES DIVERGENCE VERSUS HARMONISATION AND THE POSSIBLE EFFECT ON FUTURE CAR DESIGN
 CURRENT WORLDWIDE SIDE IMPACT ACTIVITIES DIVERGENCE VERSUS HARMONISATION AND THE POSSIBLE EFFECT ON FUTURE CAR DESIGN A. McNeill, J. Haberl, BMW AG Dr. M Holzner, Audi AG Dr. R. Schoeneburg, Daimler Chrysler
CURRENT WORLDWIDE SIDE IMPACT ACTIVITIES DIVERGENCE VERSUS HARMONISATION AND THE POSSIBLE EFFECT ON FUTURE CAR DESIGN A. McNeill, J. Haberl, BMW AG Dr. M Holzner, Audi AG Dr. R. Schoeneburg, Daimler Chrysler
Correlation of Occupant Evaluation Index on Vehicle-occupant-guardrail Impact System Guo-sheng ZHANG, Hong-li LIU and Zhi-sheng DONG
 07 nd International Conference on Computer, Mechatronics and Electronic Engineering (CMEE 07) ISBN: 978--60595-53- Correlation of Occupant Evaluation Index on Vehicle-occupant-guardrail Impact System Guo-sheng
07 nd International Conference on Computer, Mechatronics and Electronic Engineering (CMEE 07) ISBN: 978--60595-53- Correlation of Occupant Evaluation Index on Vehicle-occupant-guardrail Impact System Guo-sheng
Assessing Options for Improving Roadside Barrier Crashworthiness
 13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Simulation Assessing Options for Improving Roadside Barrier Crashworthiness D. Marzougui, C.D. Kan, and K.S. Opiela Center for Collision Safety and
13 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Simulation Assessing Options for Improving Roadside Barrier Crashworthiness D. Marzougui, C.D. Kan, and K.S. Opiela Center for Collision Safety and
Finite Element Modeling and Analysis of Crash Safe Composite Lighting Columns, Contact-Impact Problem
 9 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Impact Analysis (3) Finite Element Modeling and Analysis of Crash Safe Composite Lighting Columns, Contact-Impact Problem Alexey Borovkov, Oleg Klyavin and Alexander
9 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Impact Analysis (3) Finite Element Modeling and Analysis of Crash Safe Composite Lighting Columns, Contact-Impact Problem Alexey Borovkov, Oleg Klyavin and Alexander
Pre impact Braking Influence on the Standard Seat belted and Motorized Seat belted Occupants in Frontal Collisions based on Anthropometric Test Dummy
 Pre impact Influence on the Standard Seat belted and Motorized Seat belted Occupants in Frontal Collisions based on Anthropometric Test Dummy Susumu Ejima 1, Daisuke Ito 1, Jacobo Antona 1, Yoshihiro Sukegawa
Pre impact Influence on the Standard Seat belted and Motorized Seat belted Occupants in Frontal Collisions based on Anthropometric Test Dummy Susumu Ejima 1, Daisuke Ito 1, Jacobo Antona 1, Yoshihiro Sukegawa
Simulation of Structural Latches in an Automotive Seat System Using LS-DYNA
 Simulation of Structural Latches in an Automotive Seat System Using LS-DYNA Tuhin Halder Lear Corporation, U152 Group 5200, Auto Club Drive Dearborn, MI 48126 USA. + 313 845 0492 thalder@ford.com Keywords:
Simulation of Structural Latches in an Automotive Seat System Using LS-DYNA Tuhin Halder Lear Corporation, U152 Group 5200, Auto Club Drive Dearborn, MI 48126 USA. + 313 845 0492 thalder@ford.com Keywords:
ARE SMALL FEMALES MORE VULNERABLE TO LOWER NECK INJURIES WHEN SEATED SUFFICIENTLY AWAY FROM THE STEERING WHEEL IN A FRONTAL CRASH?
 ARE SMALL FEMALES MORE VULNERABLE TO LOWER NECK INJURIES WHEN SEATED SUFFICIENTLY AWAY FROM THE STEERING WHEEL IN A FRONTAL CRASH? Chandrashekhar Simulation Technologies LLC United States Paper Number
ARE SMALL FEMALES MORE VULNERABLE TO LOWER NECK INJURIES WHEN SEATED SUFFICIENTLY AWAY FROM THE STEERING WHEEL IN A FRONTAL CRASH? Chandrashekhar Simulation Technologies LLC United States Paper Number
Digges 1 INJURIES TO RESTRAINED OCCUPANTS IN FAR-SIDE CRASHES. Kennerly Digges The Automotive Safety Research Institute Charlottesville, Virginia, USA
 INJURIES TO RESTRAINED OCCUPANTS IN FAR-SIDE CRASHES Kennerly Digges The Automotive Safety Research Institute Charlottesville, Virginia, USA Dainius Dalmotas Transport Canada Ottawa, Canada Paper Number
INJURIES TO RESTRAINED OCCUPANTS IN FAR-SIDE CRASHES Kennerly Digges The Automotive Safety Research Institute Charlottesville, Virginia, USA Dainius Dalmotas Transport Canada Ottawa, Canada Paper Number
SLED TEST PROCEDURE FOR ASSESSING KNEE IMPACT AREAS
 EUROPEAN NEW CAR ASSESSMENT PROGRAMME (Euro NCAP) SLED TEST PROCEDURE FOR ASSESSING KNEE IMPACT AREAS CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION...2 2 PREREQUISITES FOR KNEE MAPPING...3 3 HARDWARE SETUP...4 4 VALIDATION
EUROPEAN NEW CAR ASSESSMENT PROGRAMME (Euro NCAP) SLED TEST PROCEDURE FOR ASSESSING KNEE IMPACT AREAS CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION...2 2 PREREQUISITES FOR KNEE MAPPING...3 3 HARDWARE SETUP...4 4 VALIDATION
REAR SEAT OCCUPANT PROTECTION IN FAR SIDE CRASHES
 REAR SEAT OCCUPANT PROTECTION IN FAR SIDE CRASHES Jörg Hoffmann Toyoda Gosei Europe N.V. Germany Kenji Hayakawa Takaki Fukuyama TOYODA GOSEI CO., LTD. Japan Paper Number 9-475 ABSTRACT The risk of being
REAR SEAT OCCUPANT PROTECTION IN FAR SIDE CRASHES Jörg Hoffmann Toyoda Gosei Europe N.V. Germany Kenji Hayakawa Takaki Fukuyama TOYODA GOSEI CO., LTD. Japan Paper Number 9-475 ABSTRACT The risk of being
The THUMS User Community Harmonisation of THUMS in Different Crash Codes
 The THUMS User Community Harmonisation of THUMS in Different Crash Codes Steffen Peldschus 1,2, Therese Fuchs 1, Torsten Gärtner 3, Christian Mayer 4, Bengt Pipkorn 5, Jens Weber 6, Philipp Wernicke 7,
The THUMS User Community Harmonisation of THUMS in Different Crash Codes Steffen Peldschus 1,2, Therese Fuchs 1, Torsten Gärtner 3, Christian Mayer 4, Bengt Pipkorn 5, Jens Weber 6, Philipp Wernicke 7,
*Friedman Research Corporation, 1508-B Ferguson Lane, Austin, TX ** Center for Injury Research, Santa Barbara, CA, 93109
 Analysis of factors affecting ambulance compartment integrity test results and their relationship to real-world impact conditions. G Mattos*, K. Friedman*, J Paver**, J Hutchinson*, K Bui* & A Jafri* *Friedman
Analysis of factors affecting ambulance compartment integrity test results and their relationship to real-world impact conditions. G Mattos*, K. Friedman*, J Paver**, J Hutchinson*, K Bui* & A Jafri* *Friedman
Effectiveness of ECP Brakes in Reducing the Risks Associated with HHFT Trains
 Effectiveness of ECP Brakes in Reducing the Risks Associated with HHFT Trains Presented To The National Academy of Sciences Review Committee October 14, 2016 Slide 1 1 Agenda Background leading to HM-251
Effectiveness of ECP Brakes in Reducing the Risks Associated with HHFT Trains Presented To The National Academy of Sciences Review Committee October 14, 2016 Slide 1 1 Agenda Background leading to HM-251
Development and Validation of a Finite Element Model of an Energy-absorbing Guardrail End Terminal
 Development and Validation of a Finite Element Model of an Energy-absorbing Guardrail End Terminal Yunzhu Meng 1, Costin Untaroiu 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering and Virginia Tech, Blacksburg,
Development and Validation of a Finite Element Model of an Energy-absorbing Guardrail End Terminal Yunzhu Meng 1, Costin Untaroiu 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering and Virginia Tech, Blacksburg,
EMBARGOED NEWS RELEASE
 NEWS RELEASE July 21, 2009 Contact: Russ Rader at 703/247-1500 or home at 202/785-0267 VNR: Tues. 7/21/2009 at 10:30-11 am EDT (C) AMC 3/Trans. 3 (dl3760h) repeat at 1:30-2 pm EDT (C) AMC 3/Trans. 3 (dl3760h);
NEWS RELEASE July 21, 2009 Contact: Russ Rader at 703/247-1500 or home at 202/785-0267 VNR: Tues. 7/21/2009 at 10:30-11 am EDT (C) AMC 3/Trans. 3 (dl3760h) repeat at 1:30-2 pm EDT (C) AMC 3/Trans. 3 (dl3760h);
Simulation of Occupant Posture Changes due to Evasive Manoeuvres and Injury Predictions in Vehicle Frontal and Side Collisions.
 Simulation of Occupant Posture Changes due to Evasive Manoeuvres and Injury Predictions in Vehicle Frontal and Side Collisions. Takao Matsuda, Katsunori Yamada, Shigeki Hayashi, Yuichi Kitagawa Abstract
Simulation of Occupant Posture Changes due to Evasive Manoeuvres and Injury Predictions in Vehicle Frontal and Side Collisions. Takao Matsuda, Katsunori Yamada, Shigeki Hayashi, Yuichi Kitagawa Abstract
Vehicle Seat Bottom Cushion Clip Force Study for FMVSS No. 207 Requirements
 14 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Automotive Vehicle Seat Bottom Cushion Clip Force Study for FMVSS No. 207 Requirements Jaehyuk Jang CAE Body Structure Systems General Motors Abstract
14 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Session: Automotive Vehicle Seat Bottom Cushion Clip Force Study for FMVSS No. 207 Requirements Jaehyuk Jang CAE Body Structure Systems General Motors Abstract
HEAD AND NECK INJURY POTENTIAL IN INVERTED IMPACT TESTS
 HEAD AND NECK INJURY POTENTIAL IN INVERTED IMPACT TESTS Steve Forrest Steve Meyer Andrew Cahill SAFE Research, LLC United States Brian Herbst SAFE Laboratories, LLC United States Paper number 07-0371 ABSTRACT
HEAD AND NECK INJURY POTENTIAL IN INVERTED IMPACT TESTS Steve Forrest Steve Meyer Andrew Cahill SAFE Research, LLC United States Brian Herbst SAFE Laboratories, LLC United States Paper number 07-0371 ABSTRACT
The Evolution of Side Crash Compatibility Between Cars, Light Trucks and Vans
 2003-01-0899 The Evolution of Side Crash Compatibility Between Cars, Light Trucks and Vans Hampton C. Gabler Rowan University Copyright 2003 SAE International ABSTRACT Several research studies have concluded
2003-01-0899 The Evolution of Side Crash Compatibility Between Cars, Light Trucks and Vans Hampton C. Gabler Rowan University Copyright 2003 SAE International ABSTRACT Several research studies have concluded
Attenuating Head Impact with Vehicular (Including Heavy Truck) Interiors
 Attenuating Head Impact with Vehicular (Including Heavy Truck) Interiors S E Meyer*, B Herbst**, A O Nelson*, S Forrest* *Safety Analysis & Forensic Engineering (S.A.F.E.), 6775 Hollister Ave, Ste 100,
Attenuating Head Impact with Vehicular (Including Heavy Truck) Interiors S E Meyer*, B Herbst**, A O Nelson*, S Forrest* *Safety Analysis & Forensic Engineering (S.A.F.E.), 6775 Hollister Ave, Ste 100,
Evaluation of Advance Compatibility Frontal Structures Using the Progressive Deformable Barrier
 Informal document No. GRSP-45-16 (45th GRSP, 25-29 May 2009 agenda item 6(a)) Evaluation of Advance Compatibility Frontal Structures Using the Progressive Deformable Barrier 45th GRSP May 2009 Susan MEYERSON,
Informal document No. GRSP-45-16 (45th GRSP, 25-29 May 2009 agenda item 6(a)) Evaluation of Advance Compatibility Frontal Structures Using the Progressive Deformable Barrier 45th GRSP May 2009 Susan MEYERSON,
Simulation of proposed FMVSS 202 using LS-DYNA Implicit
 4 th European LS-DYNA Users Conference Occupant II / Pedestrian Safety Simulation of proposed FMVSS 202 using LS-DYNA Implicit Vikas Patwardhan Babushankar Sambamoorthy Tuhin Halder Lear Corporation 21557
4 th European LS-DYNA Users Conference Occupant II / Pedestrian Safety Simulation of proposed FMVSS 202 using LS-DYNA Implicit Vikas Patwardhan Babushankar Sambamoorthy Tuhin Halder Lear Corporation 21557
Joint Australian and Canadian Pole Side Impact Research
 Joint Australian and Canadian Pole Side Impact Research Thomas Belcher Australian Government Department of Infrastructure and Transport Suzanne Tylko Transport Canada 7 th Meeting - GRSP Informal Group
Joint Australian and Canadian Pole Side Impact Research Thomas Belcher Australian Government Department of Infrastructure and Transport Suzanne Tylko Transport Canada 7 th Meeting - GRSP Informal Group
Application and CAE Simulation of Over Molded Short and Continuous Fiber Thermoplastic Composites: Part II
 12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Simulation(3) Application and CAE Simulation of Over Molded Short and Continuous Fiber Thermoplastic Composites: Part II Prasanna S. Kondapalli BASF Corp.,
12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Simulation(3) Application and CAE Simulation of Over Molded Short and Continuous Fiber Thermoplastic Composites: Part II Prasanna S. Kondapalli BASF Corp.,
REPORT NUMBER: 214P-MGA SAFETY COMPLIANCE TESTING FOR FMVSS 214 DYNAMIC SIDE IMPACT PROTECTION RIGID POLE
 REPORT NUMBER: 214P-MGA-21-3 SAFETY COMPLIANCE TESTING FOR FMVSS 214 DYNAMIC SIDE IMPACT PROTECTION RIGID POLE FORD MOTOR COMPANY 21 FORD F-15 4x2 REGULAR CAB NHTSA NUMBER: CA28 PREPARED BY: MGA RESEARCH
REPORT NUMBER: 214P-MGA-21-3 SAFETY COMPLIANCE TESTING FOR FMVSS 214 DYNAMIC SIDE IMPACT PROTECTION RIGID POLE FORD MOTOR COMPANY 21 FORD F-15 4x2 REGULAR CAB NHTSA NUMBER: CA28 PREPARED BY: MGA RESEARCH
Injury Risk and Seating Position for Fifth-Percentile Female Drivers Crash Tests with 1990 and 1992 Lincoln Town Cars. Michael R. Powell David S.
 Injury Risk and Seating Position for Fifth-Percentile Female Drivers Crash Tests with 1990 and 1992 Lincoln Town Cars Michael R. Powell David S. Zuby July 1997 ABSTRACT A series of 35 mi/h barrier crash
Injury Risk and Seating Position for Fifth-Percentile Female Drivers Crash Tests with 1990 and 1992 Lincoln Town Cars Michael R. Powell David S. Zuby July 1997 ABSTRACT A series of 35 mi/h barrier crash
EVALUATION OF MOVING PROGRESSIVE DEFORMABLE BARRIER TEST METHOD BY COMPARING CAR TO CAR CRASH TEST
 EVALUATION OF MOVING PROGRESSIVE DEFORMABLE BARRIER TEST METHOD BY COMPARING CAR TO CAR CRASH TEST Shinsuke, Shibata Azusa, Nakata Toru, Hashimoto Honda R&D Co., Ltd. Automobile R&D Center Japan Paper
EVALUATION OF MOVING PROGRESSIVE DEFORMABLE BARRIER TEST METHOD BY COMPARING CAR TO CAR CRASH TEST Shinsuke, Shibata Azusa, Nakata Toru, Hashimoto Honda R&D Co., Ltd. Automobile R&D Center Japan Paper
INVESTIGATING POTENTIAL CHANGES TO THE IIHS SIDE IMPACT CRASHWORTHINESS EVALUATION PROGRAM
 INVSTIGATING POTNTIAL CHANGS TO TH IIHS SID IMPACT CRASHWORTHINSS VALUATION PROGRAM Matthew L. Brumbelow Becky Mueller Raul A. Arbelaez Insurance Institute for Highway Safety USA Matthias Kuehn GDV German
INVSTIGATING POTNTIAL CHANGS TO TH IIHS SID IMPACT CRASHWORTHINSS VALUATION PROGRAM Matthew L. Brumbelow Becky Mueller Raul A. Arbelaez Insurance Institute for Highway Safety USA Matthias Kuehn GDV German
Wheelchair Transportation Principles I: Biomechanics of Injury
 Wheelchair Transportation Principles I: Biomechanics of Injury Gina Bertocci, Ph.D. & Douglas Hobson, Ph.D. Department of Rehabilitation Science and Technology University of Pittsburgh This presentation
Wheelchair Transportation Principles I: Biomechanics of Injury Gina Bertocci, Ph.D. & Douglas Hobson, Ph.D. Department of Rehabilitation Science and Technology University of Pittsburgh This presentation
The SIPS (Side Impact Protection System) includes side airbags and an Inflatable Curtain (IC) airbag that protects both front and rear occupants.
 VOLVO XC70 SAFETY Like all Volvo models, the XC70 has been developed and extensively crash tested in the Volvo Safety Centre in Gothenburg, Sweden, and features a comprehensive safety package designed
VOLVO XC70 SAFETY Like all Volvo models, the XC70 has been developed and extensively crash tested in the Volvo Safety Centre in Gothenburg, Sweden, and features a comprehensive safety package designed
Small Overlap Frontal Crashworthiness Evaluation Rating Protocol (Version II)
 Small Overlap Frontal Crashworthiness Evaluation Rating Protocol (Version II) Rating Guidelines for Restraints and Dummy Kinematics, Injury Measures, and Vehicle Structural Performance Weighting Principles
Small Overlap Frontal Crashworthiness Evaluation Rating Protocol (Version II) Rating Guidelines for Restraints and Dummy Kinematics, Injury Measures, and Vehicle Structural Performance Weighting Principles
Petition for Rulemaking; 49 CFR Part 571 Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards; Rear Impact Guards; Rear Impact Protection
 The Honorable David L. Strickland Administrator National Highway Traffic Safety Administration 1200 New Jersey Avenue, SE Washington, D.C. 20590 Petition for Rulemaking; 49 CFR Part 571 Federal Motor Vehicle
The Honorable David L. Strickland Administrator National Highway Traffic Safety Administration 1200 New Jersey Avenue, SE Washington, D.C. 20590 Petition for Rulemaking; 49 CFR Part 571 Federal Motor Vehicle
Simulation and Validation of FMVSS 207/210 Using LS-DYNA
 7 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Simulation Technology (2) Simulation and Validation of FMVSS 207/210 Using LS-DYNA Vikas Patwardhan Tuhin Halder Frank Xu Babushankar Sambamoorthy Lear Corporation
7 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Simulation Technology (2) Simulation and Validation of FMVSS 207/210 Using LS-DYNA Vikas Patwardhan Tuhin Halder Frank Xu Babushankar Sambamoorthy Lear Corporation
COMPARISON OF THE IMPACT PERFORMANCE OF THE G4(1W) AND G4(2W) GUARDRAIL SYSTEMS UNDER NCHRP REPORT 350 TEST 3-11 CONDITIONS
 Paper No. 00-0525 COMPARISON OF THE IMPACT PERFORMANCE OF THE G4(1W) AND G4(2W) GUARDRAIL SYSTEMS UNDER NCHRP REPORT 350 TEST 3-11 CONDITIONS by Chuck A. Plaxico Associate Research Engineer Worcester Polytechnic
Paper No. 00-0525 COMPARISON OF THE IMPACT PERFORMANCE OF THE G4(1W) AND G4(2W) GUARDRAIL SYSTEMS UNDER NCHRP REPORT 350 TEST 3-11 CONDITIONS by Chuck A. Plaxico Associate Research Engineer Worcester Polytechnic
Side Impact Protection. Technical perfection, automotive passion.
 Side Impact Protection Agenda Improved Concepts for Side Impact Protection Traffic Accidents and Side Crashes General Characteristics of Side Crashes Typical Injuries in Side Crashes Protection Strategy
Side Impact Protection Agenda Improved Concepts for Side Impact Protection Traffic Accidents and Side Crashes General Characteristics of Side Crashes Typical Injuries in Side Crashes Protection Strategy
Investigation of Potential Mitigation of Driver Injury in Heavy Truck Frontal and Rollover Crashes
 Investigation of Potential Mitigation of Driver Injury in Heavy Truck Frontal and Rollover Crashes Nathan Schulz, M.S.C.E. Chiara Silvestri Dobrovolny, Ph.D. Texas A&M Transportation Institute TRB IRSC
Investigation of Potential Mitigation of Driver Injury in Heavy Truck Frontal and Rollover Crashes Nathan Schulz, M.S.C.E. Chiara Silvestri Dobrovolny, Ph.D. Texas A&M Transportation Institute TRB IRSC
Front Bumper Crashworthiness Optimization
 9 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Crash/Safety (3) Front Bumper Crashworthiness Optimization Shokri El Houssini Daan Engineering s.n.c Abstract During a vehicles frontal crash, passengers jeopardize
9 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Crash/Safety (3) Front Bumper Crashworthiness Optimization Shokri El Houssini Daan Engineering s.n.c Abstract During a vehicles frontal crash, passengers jeopardize
Design and Validation of a Crash Rated Bollard as per SD-STD Rev. A (2003) Standard using LS-DYNA
 Design and Validation of a Crash Rated Bollard as per SD-STD-02.01 Rev. A (2003) Standard using LS-DYNA Saurabh R. Deshpande 1, Santosh E. Chopade 1, Maj. Amitava Mittra 2, and N. V. Karanth 1 1 Automotive
Design and Validation of a Crash Rated Bollard as per SD-STD-02.01 Rev. A (2003) Standard using LS-DYNA Saurabh R. Deshpande 1, Santosh E. Chopade 1, Maj. Amitava Mittra 2, and N. V. Karanth 1 1 Automotive
STATUS OF NHTSA S EJECTION MITIGATION RESEARCH. Aloke Prasad Allison Louden National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
 STATUS OF NHTSA S EJECTION MITIGATION RESEARCH Aloke Prasad Allison Louden National Highway Traffic Safety Administration United States of America Stephen Duffy Transportation Research Center United States
STATUS OF NHTSA S EJECTION MITIGATION RESEARCH Aloke Prasad Allison Louden National Highway Traffic Safety Administration United States of America Stephen Duffy Transportation Research Center United States
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 SIMULATION OF TRUCK REAR UNDERRUN BARRIER IMPACT Roger Zou*, George Rechnitzer** and Raphael Grzebieta* * Department of Civil Engineering, Monash University, ** Accident Research Centre, Monash University,
SIMULATION OF TRUCK REAR UNDERRUN BARRIER IMPACT Roger Zou*, George Rechnitzer** and Raphael Grzebieta* * Department of Civil Engineering, Monash University, ** Accident Research Centre, Monash University,
REPORT NUMBER: 214P-MGA SAFETY COMPLIANCE TESTING FOR FMVSS 214 DYNAMIC SIDE IMPACT PROTECTION RIGID POLE
 REPORT NUMBER: 214P-MGA-211-9 SAFETY COMPLIANCE TESTING FOR FMVSS 214 DYNAMIC SIDE IMPACT PROTECTION RIGID POLE TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION 211 SCION TC 3-DR LIFTBACK NHTSA NUMBER: CB517 PREPARED BY: MGA
REPORT NUMBER: 214P-MGA-211-9 SAFETY COMPLIANCE TESTING FOR FMVSS 214 DYNAMIC SIDE IMPACT PROTECTION RIGID POLE TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION 211 SCION TC 3-DR LIFTBACK NHTSA NUMBER: CB517 PREPARED BY: MGA
Improvement Design of Vehicle s Front Rails for Dynamic Impact
 5 th European LS-DYNA Users Conference Crash Technology (1) Improvement Design of Vehicle s Front Rails for Dynamic Impact Authors: Chien-Hsun Wu, Automotive research & testing center Chung-Yung Tung,
5 th European LS-DYNA Users Conference Crash Technology (1) Improvement Design of Vehicle s Front Rails for Dynamic Impact Authors: Chien-Hsun Wu, Automotive research & testing center Chung-Yung Tung,
ANALYTICAL EVALUATION OF AN ADVANCED INTEGRATED SAFETY SEAT DESIGN IN FRONTAL, REAR, SIDE, AND ROLLOVER CRASHES
 ANALYTICAL EVALUATION OF AN ADVANCED INTEGRATED SAFETY SEAT DESIGN IN FRONTAL, REAR, SIDE, AND ROLLOVER CRASHES Mostafa Rashidy, Balachandra Deshpande, Gunasekar T.J., Russel Morris EASi Engineering Robert
ANALYTICAL EVALUATION OF AN ADVANCED INTEGRATED SAFETY SEAT DESIGN IN FRONTAL, REAR, SIDE, AND ROLLOVER CRASHES Mostafa Rashidy, Balachandra Deshpande, Gunasekar T.J., Russel Morris EASi Engineering Robert
A Case Study on Design and Analysis of Automotive Body for Crashworthiness
 ISSN 2395-1621 A Case Study on Design and Analysis of Automotive Body for Crashworthiness #1 M.M.Pande, #2 Dr. G.V.Shah 1 mrunalmuley@gmail.com 2 gvscfd@gmail.com #12 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
ISSN 2395-1621 A Case Study on Design and Analysis of Automotive Body for Crashworthiness #1 M.M.Pande, #2 Dr. G.V.Shah 1 mrunalmuley@gmail.com 2 gvscfd@gmail.com #12 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
A Thesis by. Amirmasoud Moghaddami. Bachelor of Science, University of Kansas, 2015
 MODELING AND SIMULATIONS OF THE 50TH PERCENTILE HYBRID III AND EUROSID-2RE DUMMIES ON OBLIQUE-FACING RIGID AIRCRAFT SEATS UNDER FAR TEST-2 DYNAMIC CONDITIONS A Thesis by Amirmasoud Moghaddami Bachelor
MODELING AND SIMULATIONS OF THE 50TH PERCENTILE HYBRID III AND EUROSID-2RE DUMMIES ON OBLIQUE-FACING RIGID AIRCRAFT SEATS UNDER FAR TEST-2 DYNAMIC CONDITIONS A Thesis by Amirmasoud Moghaddami Bachelor
Summary briefing on four major new mass-reduction assessment for light-duty vehicles
 Summary briefing on four major new mass-reduction assessment for light-duty vehicles In 2010-2012, in the development of US passenger vehicle standards for model years 2017-2025, there were many questions
Summary briefing on four major new mass-reduction assessment for light-duty vehicles In 2010-2012, in the development of US passenger vehicle standards for model years 2017-2025, there were many questions
Vehicle Safety Research in TGGS
 Vehicle Safety Research in TGGS Core Knowledge of Automotive Safety and Assessment Engineer Program and Research in TGGS Vehicle fundamentals and manufacturing process Vehicle and part Assessment Crash
Vehicle Safety Research in TGGS Core Knowledge of Automotive Safety and Assessment Engineer Program and Research in TGGS Vehicle fundamentals and manufacturing process Vehicle and part Assessment Crash
Design and analysis of door stiffener using finite element analysis against FMVSS 214 pole impact test
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 14, Issue 6 Ver. I (Nov. - Dec. 2017), PP 79-84 www.iosrjournals.org Design and analysis of door
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 14, Issue 6 Ver. I (Nov. - Dec. 2017), PP 79-84 www.iosrjournals.org Design and analysis of door
Automobile Body, Chassis, Occupant and Pedestrian Safety, and Structures Track
 Automobile Body, Chassis, Occupant and Pedestrian Safety, and Structures Track These sessions are related to Body Engineering, Fire Safety, Human Factors, Noise and Vibration, Occupant Protection, Steering
Automobile Body, Chassis, Occupant and Pedestrian Safety, and Structures Track These sessions are related to Body Engineering, Fire Safety, Human Factors, Noise and Vibration, Occupant Protection, Steering
ROLLOVER CRASHWORTHINESS OF A RURAL TRANSPORT VEHICLE USING MADYMO
 ROLLOVER CRASHWORTHINESS OF A RURAL TRANSPORT VEHICLE USING MADYMO S. Mukherjee, A. Chawla, A. Nayak, D. Mohan Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi INDIA ABSTRACT In this work a full vehicle model
ROLLOVER CRASHWORTHINESS OF A RURAL TRANSPORT VEHICLE USING MADYMO S. Mukherjee, A. Chawla, A. Nayak, D. Mohan Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi INDIA ABSTRACT In this work a full vehicle model
JRS Dynamic Rollover Test Toyota Prius
 Page 1 of 62 JRS Dynamic Rollover Test 2010 Toyota Prius Sponsored By: Automotive Safety Research Institute Charlottesville, VA. Vehicle Donated by: State Farm Insurance Company Chicago, IL. Introduction
Page 1 of 62 JRS Dynamic Rollover Test 2010 Toyota Prius Sponsored By: Automotive Safety Research Institute Charlottesville, VA. Vehicle Donated by: State Farm Insurance Company Chicago, IL. Introduction
FIMCAR Accident Analysis Report to GRSP frontal impact IWG Summary of findings
 FIMCAR Accident Analysis Report to GRSP frontal impact IWG Summary of findings Mervyn Edwards, Alex Thompson, Thorsten Adolph, Rob Thomson, Aleksandra Krusper October 14 th 2010 Objectives Determine if
FIMCAR Accident Analysis Report to GRSP frontal impact IWG Summary of findings Mervyn Edwards, Alex Thompson, Thorsten Adolph, Rob Thomson, Aleksandra Krusper October 14 th 2010 Objectives Determine if
Abaqus Technology Brief. Abaqus BioRID-II Crash Dummy Model
 Abaqus Technology Brief TB-09-BIORID-1 Revised: January 2009 Abaqus BioRID-II Crash Dummy Model Summary The Biofidelic Rear Impact Dummy (BioRID-II) hardware model has been developed to measure automotive
Abaqus Technology Brief TB-09-BIORID-1 Revised: January 2009 Abaqus BioRID-II Crash Dummy Model Summary The Biofidelic Rear Impact Dummy (BioRID-II) hardware model has been developed to measure automotive
EVALUATION OF VEHICLE-BASED CRASH SEVERITY METRICS USING EVENT DATA RECORDERS
 EVALUATION OF VEHICLE-BASED CRASH SEVERITY METRICS USING EVENT DATA RECORDERS Grace Wusk Hampton Gabler Virginia Tech United States Paper Number 17-0407 ABSTRACT Injury risk in real world crashes is often
EVALUATION OF VEHICLE-BASED CRASH SEVERITY METRICS USING EVENT DATA RECORDERS Grace Wusk Hampton Gabler Virginia Tech United States Paper Number 17-0407 ABSTRACT Injury risk in real world crashes is often
STUDY OF VEHICLE DYNAMICS AND OCCUPANT RESPONSE IN SIDE IMPACT CRASH TESTS
 STUDY OF VEHICLE DYNAMICS AND OCCUPANT RESPONSE IN SIDE IMPACT CRASH TESTS Brock Watson Duane Cronin Brett Campbell University of Waterloo Canada Paper Number 09-0016 ABSTRACT Side impact crash is a leading
STUDY OF VEHICLE DYNAMICS AND OCCUPANT RESPONSE IN SIDE IMPACT CRASH TESTS Brock Watson Duane Cronin Brett Campbell University of Waterloo Canada Paper Number 09-0016 ABSTRACT Side impact crash is a leading
VERTICAL IMPACT SIMULATIONS OF A FULL-SIZE AND SIMPLIFIED SCALED MODELS OF AN AIRCRAFT FUSELAGE SECTION
 VERTICAL IMPACT SIMULATIONS OF A FULL-SIZE AND SIMPLIFIED SCALED MODELS OF AN AIRCRAFT FUSELAGE SECTION A Thesis by Vishal Krishna Prasad Bachelor of Engineering, Visvesvaraya Technological University,
VERTICAL IMPACT SIMULATIONS OF A FULL-SIZE AND SIMPLIFIED SCALED MODELS OF AN AIRCRAFT FUSELAGE SECTION A Thesis by Vishal Krishna Prasad Bachelor of Engineering, Visvesvaraya Technological University,
An Analysis of Less Hazardous Roadside Signposts. By Andrei Lozzi & Paul Briozzo Dept of Mechanical & Mechatronic Engineering University of Sydney
 An Analysis of Less Hazardous Roadside Signposts By Andrei Lozzi & Paul Briozzo Dept of Mechanical & Mechatronic Engineering University of Sydney 1 Abstract This work arrives at an overview of requirements
An Analysis of Less Hazardous Roadside Signposts By Andrei Lozzi & Paul Briozzo Dept of Mechanical & Mechatronic Engineering University of Sydney 1 Abstract This work arrives at an overview of requirements
Ford Mustang (reassessment)
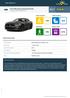 Ford Mustang (reassessment) Standard Safety Equipment 2017 Adult Occupant Child Occupant 72% 32% Pedestrian Safety Assist 78% 61% SPECIFICATION Tested Model Body Type Ford Mustang 5.0 Fastback, LHD - 2
Ford Mustang (reassessment) Standard Safety Equipment 2017 Adult Occupant Child Occupant 72% 32% Pedestrian Safety Assist 78% 61% SPECIFICATION Tested Model Body Type Ford Mustang 5.0 Fastback, LHD - 2
DESIGN FOR CRASHWORTHINESS
 - The main function of the body structure is to protect occupants in a collision - There are many standard crash tests and performance levels - For the USA, these standards are contained in Federal Motor
- The main function of the body structure is to protect occupants in a collision - There are many standard crash tests and performance levels - For the USA, these standards are contained in Federal Motor
Integrated. Safety Handbook. Automotive. Ulrich Seiffert and Mark Gonter. Warrendale, Pennsylvania, USA INTERNATIONAL.
 Integrated Automotive Safety Handbook Ulrich Seiffert and Mark Gonter INTERNATIONAL. Warrendale, Pennsylvania, USA Table of Contents Preface ix Chapter 1 The Need to Increase Road Safety 1 1.1 Introduction
Integrated Automotive Safety Handbook Ulrich Seiffert and Mark Gonter INTERNATIONAL. Warrendale, Pennsylvania, USA Table of Contents Preface ix Chapter 1 The Need to Increase Road Safety 1 1.1 Introduction
REPORT NUMBER: 301-MGA SAFETY COMPLIANCE TESTING FOR FMVSS 301R FUEL SYSTEM INTEGRITY REAR IMPACT
 REPORT NUMBER: 301-MGA-2010-007 SAFETY COMPLIANCE TESTING FOR FMVSS 301R FUEL SYSTEM INTEGRITY REAR IMPACT NISSAN MOTOR COMPANY LTD 2010 NISSAN CUBE NHTSA NUMBER: CA5205 PREPARED BY: MGA RESEARCH CORPORATION
REPORT NUMBER: 301-MGA-2010-007 SAFETY COMPLIANCE TESTING FOR FMVSS 301R FUEL SYSTEM INTEGRITY REAR IMPACT NISSAN MOTOR COMPANY LTD 2010 NISSAN CUBE NHTSA NUMBER: CA5205 PREPARED BY: MGA RESEARCH CORPORATION
SPCT Method. The SPCT Method - Testing of Dog Crates. Utskrivet dokument är ostyrt, dvs inte säkert gällande.
 Kvalitetsdokument Författare, enhet Mikael Videby Bygg och Mekanik Hållfasthet och konstruktion Utgåva 1 (7) Godkännare 2 The Testing of Dog Crates Application Area... 2 References... 2 1 Test Sample Selection...
Kvalitetsdokument Författare, enhet Mikael Videby Bygg och Mekanik Hållfasthet och konstruktion Utgåva 1 (7) Godkännare 2 The Testing of Dog Crates Application Area... 2 References... 2 1 Test Sample Selection...
Virtual human body model for fast safety assessment
 Virtual human body model for fast safety assessment Luděk Hynčík et al. Luděk Kovář el al. University of West Bohemia MECAS ESI s.r.o. Plzeň (Pilsen), Czech Republic AUTOSYMPO 2017 31 October 2 November
Virtual human body model for fast safety assessment Luděk Hynčík et al. Luděk Kovář el al. University of West Bohemia MECAS ESI s.r.o. Plzeň (Pilsen), Czech Republic AUTOSYMPO 2017 31 October 2 November
