(12) United States Patent
|
|
|
- Daniel McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
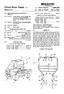
1 (12) United States Patent Nakajima et al. USOO B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 14, 2001 (54) AUTOMATIC ENGINE STOP AND RESTART SYSTEM FOR WEHICLE (75) Inventors: Yuki Nakajima, Yokohama; Masaaki Uchida, Kanagawa; Hiroaki Ogane, Kanagawa; Takahiro Yoshino, Kanagawa, all of (JP) (73) Assignee: Nissan Motor Co., Ltd., Yokohama (JP) (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by 0 days. (21) Appl. No.: 09/484,443 (22) Filed: Jan. 18, 2000 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar. 19, 1999 (JP) (51) Int. Cl.... F02D 29/02; B60K 41/00; B6OK 1/OO (52) U.S. Cl /54; 290/34; 123/179.4 (58) Field of Search /1,54; 290/38 E, 290/40 A, 34; 477/116; 123/179.3, 1794; 180/65.2 (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,286,683 * 9/1981 Zeigner et al /54.1 4,364,343 12/1982 Malik / ,482,812 11/1984 Hori et al /38 R 4,630,577 * 12/1986 Cornacchia / ,653,659 8/1997 Kunibe et al /111 6, * 7/2000 Tabata et al /40R 6,149,544 * 11/2000 Masberg et al /13 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS /1996 (JP). * cited by examiner Primary Examiner Michael J. Zanelli (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Foley & Lardner (57) ABSTRACT An automatic engine Stop and restart System includes an engine, a Starting motor, a transmission, a Vehicle operating condition Sensor and a controller. The controller monitors the vehicle operating condition to produce an automatic engine restart request Signal during an automatic engine Stop operation, calculates a target engine Speed for the automatic engine restart operation, and drives the motor in accordance with the target Speed to perform the automatic engine restart operation in response to the engine restart request signal. During the automatic engine restart operation, the transmis Sion is held in a drive State or in a non-drive State invariably. 18 Claims, 5 Drawing Sheets WEHICLE SPEED SENSOR ACC SENSOR BRAKE SENSOR CONTROL UNT 12 BATTERY
2 U.S. Patent Aug. 14, 2001 Sheet 1 of 5 WEHICLE SPEED SENSOR 6b BRAKE SENSOR CONTROL UNIT 12 BATTERY
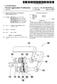
3 U.S. Patent Aug. 14, 2001 Sheet 2 of 5 FIG.2 SET DELAY TIME FRFST=1 ENG STOP MODE FSTPFST=O MOTOR TORQUE=0 TERMINATEFUEL NJECTION FSTPFST=0? ENG RESTART MODE FENGSTRT-02 SET DELAY TIME FENGSTRT-1 SET /S PERMISSION TIME FSTPFST-1 FENGSTRT-O ACC OFF TARGET SPEED-OLE SPEED T ME END? FUEL NJECTION S25 S33 0 S34 {ESSXN EXPLOSON? SET TARGE SPEED MOTOR TORQUE=0 FUEL NJECTION RETURN
4 U.S. Patent Aug. 14, 2001 Sheet 3 of 5 FIG.3 TARGET SPEED ACCELERATOR OPENING N TME -
5 U.S. Patent Aug. 14, 2001 Sheet 4 of 5 FIG.4 DLNG STOP - ACCELERATOR OPENING closed -1 TORQUE (Nm) O M/G TORQUE ENG TORQUE Y ASU-RESULTANT TORQUE s E)MOTOR TORQUE=0 ENGINE 600 SPEED Ne(rpm) O TORQUE ----PRESSURE o CONVERTER a rew mys rews OUTPUT SHAFT LINE TORQUE PRESSURE (Nm) O BOOST (mmhg) O -600 ENER" RES O ENGINE STARTING Time (msec) , SWITCH NORMAL FROM STATE MOTOR TO ENGINE
6 U.S. Patent Aug. 14, 2001 Sheet 5 of 5 FIG.5 SET DELAY TIME FCOND=1 R RANGE? NO FRFST=0 ENG STOP2 ENG STOP2 NO ENG STOP2 NO PERMISSION T ME END NONE YES SET DELAY TME ENG STOP MODE DELAY TIME END? TERMINATEFUEL NECTION FENGSRT-02 FSTPFST=O2 SET DELAY TIME FENGSTRT-1 SET /S PERMISSION TIME FSTPFST-1 NP RANGE ACC OFF FENGSTRT-O TARGET SPEED-DLE SPEED SEARET T ME END2 MOTOR TORQUEO FUEL NJECTION FUEL NJECT ON RETURN
7 1 AUTOMATIC ENGINE STOP AND RESTART SYSTEM FOR WEHICLE BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates to an automatic engine Stop and restart System. Japanese Patent Kokai Publication No. H8(1996) shows a conventional automatic engine Stop and restart System. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION When a vehicle is stopped with an automatic transmission in the drive range, this conventional Stop and restart System restarts the engine by forcibly holding the automatic trans mission in the neutral range, and Shifts the automatic trans mission from the neutral range to the drive range when the engine Speed reaches an idle Speed. Therefore, this System tends to arouse unnatural feeling in the driver by a delay in producing the creep force of the automatic transmission, and produces a torque Shock unexpectedly by allowing a torque converter to transmit, to a drive shaft, a torque proportional to the Square of the engine Speed when the transmission is shifted from the neutral range to the drive range. The torque shock is increased when the vehicle is restarted with the accelerator pedal being depressed. It is therefore an object of the present invention to provide automatic engine Stop and restart apparatus and method for reducing an undesired torque Shock in an automatic engine restart operation, and for producing a driving force as demanded by a driver. According to the present invention, a vehicle comprises: an engine; a motor for Starting the engine; an automatic transmission; a Sensing device for Sensing a vehicle oper ating condition; and a controller for performing an automatic engine Stop operation for automatically Stopping the engine and an automatic engine restart operation for terminating the automatic engine Stop operation and instead automatically restarting the engine in accordance with the vehicle operat ing condition. The controller produces an engine restart request Signal to request a restart of the engine during the automatic engine Stop operation, determines a target engine Speed for the automatic engine restart operation, and per forms the automatic engine restart operation, in response to the engine restart request Signal, by driving the motor in accordance with the target Speed while holding a transmis Sion State of the automatic transmission unchanged. According to one aspect of the present invention, an automatic engine Stop and restart control apparatus com prises: first means for automatically Stopping the engine in a predetermined vehicle situation; Second means for pro ducing an automatic restart request Signal in accordance with a vehicle operating condition in the predetermined vehicle Situation; third means for monitoring a driving condition of an automatic transmission connected with the engine; fourth means for determining a target engine Speed for an automatic engine restart operation in accordance with the driving condition of the automatic transmission; and fifth means for restarting the engine in response to the automatic engine restart request Signal, by controlling the Starting motor in accordance with the target engine Speed. According to one aspect of the present invention, an automatic engine Stop and restart control process comprises: putting the engine in an automatic Stop State in a predeter mined vehicle Situation; producing an automatic restart request signal in accordance with a vehicle operating con dition in the predetermined vehicle situation; detecting a driving condition of an automatic transmission connected with the engine; determining a target engine Speed for an automatic engine restart operation in accordance with the driving condition of the automatic transmission; and initi ating the automatic engine restart operation for restarting the engine in response to the automatic engine restart request Signal, by controlling the Starting motor in accordance with the target engine Speed. According to one aspect of the present invention, the controller Sets the target engine Speed for the automatic engine restart operation equal to an idle Speed when the transmission is in a non-driving state (Such as the N range and the Prange) in which a driving torque is not transmitted through the transmission. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a Schematic view showing a vehicle equipped with an automatic engine Stop and restart System according to one embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a flowchart for showing a control process performed by the automatic engine Stop and restart System of FIG. 1. FIG. 3 is a graph showing a characteristic of a target engine speed used in the system of FIGS. 1 and 2. FIG. 4 is a time chart for illustrating operations of the automatic engine Stop and restart System of FIGS. 1 and 2. FIG. 5 is a flowchart for showing a control process according to another embodiment of the present invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION FIG. 1 shows a vehicle equipped with an automatic engine Stop and restart System according to one embodiment of the present invention. Between an engine 1 and an automatic transmission 3, there is provided a motor/generator (or motor) 2. The automatic transmission 3 of this example is a continuously variable transmission (CVT). Rotation of the engine 1 or the motor/generator 2 is transmitted through the automatic transmission 3 to a drive shaft 7 for driving drive wheels of the vehicle. The engine 1 of this example may be a gasoline engine or a diesel engine. The automatic transmission 3 may be a multi-speed automatic transmission having a torque con verter or a start clutch, instead of the CVT transmission. The automatic transmission 3 of this example includes a torque converter 4, a forward-reverse changeover mecha nism 5 and a belt type CVT unit 6 having variable pulleys 6a and 6b and a metal belt 6c connecting the pulleys 6a and 6b. The CVT unit 6 can vary the speed ratio between the input Speed and the output Speed continuously by varying the pulley ratio. The control System determines a target Speed ratio in accordance with an operating condition, and controls primary and Secondary oil pressures for driving the pulleys 6a and 6b So as to make the actual Speed ratio equal to the target Speed ratio. An external electric oil pump 14 Supplies an oil pressure required for varying the Speed ratio. The oil pump 14 can produce the oil pressure and Supply the oil pressure to the automatic transmission 3 even when the engine 1 Stops rotation. In this example, the oil pump 14 is a motor-driven pump external to the automatic transmission 3. The forward and reverse changeover mechanism 5 is arranged to change the direction of the output rotation
8 3 between the forward rotation and the reverse rotation to move the vehicle forwards and backwards. The torque converter 4 transmits torque from the input member to the output member by dynamic fluid action. When the input Speed is very low, the torque converter 4 allows the output member to Stop rotation. The motor/generator 2 of this example is directly con nected with the crankshaft of the engine 1. Alternatively, it is optional to connect the motor/generator 2 with the engine 1 through a belt drive or a chain drive. The motor/generator 2 rotates in Synchronism with the engine 1. The motor/ generator 2 can function as an electric motor or a Starter motor and as an electric generator. A power control unit 12 controls the operating mode, the Speed (rpm) and the power generation quantity of the motor/generator 2. When the motor/generator 2 Serves as a motor to add assisting torque to the output of the engine 1, or to crank the engine 1, current is Supplied from a battery 13 through the power control unit 12 to the motor/generator 2. When the motor/generator 2 Serves as a generator to absorb running energy of the vehicle, generated current is Supplied through the power control unit 12 to charge the battery 13. An automatic Stop and restart controller 10 is a main component of the automatic engine Stop and restart System for automatically stopping the engine 1 when the vehicle is Stopped temporarily and for automatically restarting the engine 1 to restart the vehicle. The Stop and restart controller 10 Stops the engine 1 when the vehicle comes to a halt, and restarts the engine 1 with the motor/generator 2 to restart the vehicle. The stop and restart controller 10 receives input informa tion on vehicle operating conditions from an engine Speed Sensor 9, a brake Sensor 11, an accelerator Sensor 15, a Select position Sensor 17 for Sensing a Select position of the automatic transmission 3, and a vehicle Speed Sensor 18. In accordance with Signals from these Sensors, the Stop and restart controller 10 performs the automatic engine Stop and restart control. Specifically, the stop and restart controller 10 according to this embodiment of the invention performs an automatic engine restart operation with the motor/generator 2 while the automatic transmission 3 is in the State capable of transmitting engine rotation therethrough. By So doing, this restart System produces the driving force and the creep force as expected by the driver in restarting So as to avoid unnatural feeling, and reduces a shock in restarting. FIG.2 shows an automatic Stop and restart control process performed by the stop and restart controller 10. This process is performed after the warm-up operation of the engine. When, for example, the vehicle is stopped at a crossing, this System automatically stops the engine 1 and restarts the engine 1. At a step S1, the controller 10 checks if the engine warm-up operation is completed and the engine 1 is in a warmed-up state. Then, at steps S2-S5, the controller 10 further checks the conditions of the brake pedal, the vehicle Speed, the accelerator pedal and the engine Speed. The controller 10 proceeds to a step S6 if the engine 1 is in the warmed-up State, the brake pedal is depressed, the vehicle Speed is Zero, the accelerator pedal is released, and the engine speed is in an idling range (for example, equal to or lower than 800 rpm). At the step S6, the controller 10 checks if these conditions are Satisfied for the first time, by checking if FCONDO. When FCOND=0, the controller 10 sets a stop delay time for delaying a stoppage of the engine 1, and Sets FCOND to one (FCOND=1) at a step S7. After the step S7, the controller 10 proceeds to a step 58. For example, the stop delay time is equal to 2 Seconds. This System Stops the engine 1 at the end of the delay time starting from the time point at which all the conditions are first satisfied. When FCOND=1, the controller 10 proceeds from the step S6 directly to the step S8. At the step S8, the controller 10 examines the shift position of the automatic transmission 3. When the shift position is not the R range, then the controller 10 resets a flag FRFST to zero (FRFST=0) at a step S9 to initiate an automatic Stop operation. Then, the controller 10 checks, at a step S10, whether the engine 1 is in a stop State, or not. In this example, the automatic Stop and restart operation is performed not only in the D range, but in the L range, S range, N (neutral) range and P (parking) range as well. If the engine 1 is not stopped, the controller 10 proceeds from the step S10 to a step S11, and checks, at the step S11, if the delay time has elapsed. When the delay time has elapsed from the time point at which all the conditions of the steps S1-S5 become satisfied, the controller 10 enters the program Section S12-S17 for the automatic engine Stop operation. In the engine Stop mode for automatically stopping the engine 1, the controller 10 reduces the torque of the motor/ generator 2 to Zero at the Step S13, and stops the fuel injection for the engine 1 at the Step S14. Then, at the Step S15, the controller 10 checks if FISTPFST=0, to examine whether this is the first operation in the automatic engine Stop mode. When the current execution is the first execution of the engine Stop mode, the controller 10 proceeds from the step S15 to the step S16, at which the controller 10 sets an idling stop permission time, and sets the flag FISTPFST to one (FISTPFST=1) to indicate the setting of the idling stop permission time. At the step S17, the controller 10 resets a flag FENGSTRT to zero (FENGSTRT=0) to indicate that the engine 1 is in the automatic Stop State. Thus, the engine 1 is put in the Stop State. When any one or more of the conditions of the steps S1-S4 become unsatisfied, the controller proceeds to a step S18. That is, the controller proceeds to the step S18 if the engine 1 is not in the warmed-up State, or if the brake pedal is released, or if the accelerator pedal is depressed, or if the vehicle speed becomes greater than Zero. The controller 10 resets the flag FCOND to zero (FCOND=0) to indicate that the engine Stop condition becomes unsatisfied at the Step S18, and checks, at a step S19, whether the engine 1 is in the Stop State. When the engine 1 is in the Stop State, the controller 10 proceeds from the step S19 to a step S22 to restart the engine 1. When the engine 1 is not in the stop state, the controller 10 proceeds from the step S19 to a step S20, and resets the idling stop permission flag FISTPFST to zero (FISTPFST= 0) at the step S20. When the engine Stop condition is Satisfied, and the engine 1 is already in the Stop State, the controller 10 proceeds from the step S10 to a step S21, and examines if the idling stop permission time (set at the Step S16) has elapsed. When the idling Stop permission time has elapsed, the controller 10 initiates the automatic engine restart opera tion of steps S and S33-S36. The controller 10 initiates the automatic engine restart operation at the step 522, and checks whether this is the first operation in the automatic engine restart mode, by checking whether FENGSTRT=0 at the step S23. In the case of the first operation (FENGSTRT=0), the controller 10 sets a restart delay time and sets FENGSTRT to one
9 S (FENGSTRT=1) at the step S24. The restart delay time is set equal to a time (1.5 second, for example) required to develop an intake boost to a level of about -400 mmhg (s48 kpa) in restarting. During this restart delay time, the System cranks the engine 1 without injecting fuel, and thereby obtains a Smooth engine Starting operation. At the step 525, the controller 10 checks if the accelerator pedal is in the off (non-depressed) state. In the case of a restart with the accelerator pedal being in the non-depressed State, the controller 10 Sets a target engine Speed at an idle Speed (the target speed=the idle Speed) at the step S26, and waits for the elapse of the restart delay time at the step 527. Then, the control System Starts the fuel injection at the Step S28. When the accelerator pedal is depressed, the controller 10 proceeds from the step S25 to the step 533 and checks if the engine 1 is in a complete explosion State. When the engine 1 is in the complete explosion state, the controller 10 proceeds to the step S35, and performs the torque control of the motor/generator 2 to reduce the motor torque to Zero. It is possible to detect the complete explosion State of the engine, for example, by examining if the engine Speed reaches a predetermined level. When the engine 1 is not in the complete explosion State, the controller 10 proceeds to the step S34, sets the target engine Speed, and cranks the engine 1 with the motor/ generator 2. In this case, the control System determines the target engine Speed from a target driving force, or from the accelerator opening (degree) and the time from a start of an engine Starting operation, as a function of the accelerator opening and the time from the Start of the engine Starting operation, and controls the revolution speed of the motor/ generator 2. Then, the control System Starts the fuel injection at the step S36. The target driving force produced by the motor/generator 2 in place of the engine 1 is a driving force corresponding to the force of creep when the automatic transmission 3 is driven by the engine 1 through the torque converter 4. The output of the torque converter 4 is calculated from a torque ratio t determined in accordance with a speed ratio between input and output Speed, a torque capacity t, and an engine speed Ne, as txtxnef. The required driving force is a driving force at a drive wheel, So that it is converted to an output torque of the torque converter by using the wheel radius, the final gear ratio, and the Speed ratio of the transmission. Accordingly, the target input speed (the engine 30 speed) N of the torque converter 4 is given by; N=(TED0/ GRBYRT/RATIO/TRQRTO/TAU)'. In this equation, TED0 is the driving force, GRBYRT is the final gear ratio/the wheel radius, RATIO is the actual speed ratio, TRORTO is the torque ratio of the torque converter 4, and TAU is the capacity of the torque converter 4. Alternatively, it is possible to determine the target Speed by lookup from a map as shown in FIG. 3, as a function of the depression degree (accelerator opening) of the accelera torpedal and the time from a Start of the restarting operation (or the vehicle speed after the start of the restarting operation). As shown in FIG. 3, the target speed increases as the time from a start of the Starting operation increases, and the rate of increase of the target Speed increases as the accelerator opening increases. After the Start of the fuel Supply, the engine 1 produces a torque. Therefore, the target Speed used in this control is based on a Sum of the torque of the engine 1 and the torque of the motor/generator 2. If the engine Speed increases excessively by the torque of the engine 1, the motor/ generator 2 Serves as a load by functioning as an electric generator and thereby prevents the engine Speed from increasing beyond the target Speed. This control System restarts the engine 1 without changing the shift position of the automatic transmission 3. When the automatic transmission 3 is in the D range, this control System holds the automatic transmission 3 invariably in the Drange during the restart operation, and produces the force of creep corresponding to the idle Speed, from the beginning if the accelerator pedal is not depressed. If the automatic transmission 3 is in the N range, the control System controls the input Speed of the automatic transmission 3 equal to the idle Speed without providing the creep. In any case, this control System does not produce a shock due to a return to the D range from the N range as in a conventional System. When the select position of the automatic transmission 3 is in the R range, the controller 10 proceeds from the step S8 to a step S29 and examines, at the step S29, whether the engine 1 is in the Stop State. When the engine 1 is in the Stop state, the controller 10 proceeds to a step S30, and checks the flag FRFST reset at the step S9 to determine whether this is the first operation in the R range mode. In the case of the first operation in the R range mode, FRFST=0, and hence the controller 10 proceeds to a step S31. At the step S31, the controller 10 sets a delay time (2 seconds, for example) for engine stoppage, and sets the flag FRFST to one (FRFST=1). At the end of the delay time set at the step S31, the controller 10 proceeds from the step S32 to the step S22 and starts the engine restart operation of the steps S22-S28 and S33-S36. FIG. 4 illustrates operations of the control system accord ing to this embodiment. The feature of this automatic engine Stop and restart System according to this embodiment resides in the engine restart control. In the example of FIG. 4, the stop and restart system restarts the engine 1 in the Drange. When the driver releases the brake pedal in the automatic Stop State in which the engine is automatically stopped, the System terminates the idling Stop operation, and Starts the cranking operation of the engine 1 with the motor/generator 2. The motor/generator 2 forcibly turns the engine 1, and accordingly the torque converter 4 produce the creep force. Even when the engine 1 is in the Stop State in which the engine is Stationary, the external oil pump 14 Supplies the oil pressure, So that the line pressure in the automatic transmis sion 3 is held at the normal level. Therefore, in the D range, the CVT unit 6 is in the drive state with the variable pulley pressure held at a level maintaining the driving connection without slippage of the metal belt 6, and the forward clutch of the forward reverse mechanism 5 is held in the engaged State. This System prevents the oil pressure from becoming excessive and thereby minimizes the loss of driving the pump to protect the fuel economy. At the end of a predetermined short time (1.5 second, for example) after the start of the engine cranking operation, the System starts the fuel injection, So that the engine torque increases. The predetermined short time is a time required to develop an engine boost to a level of about -400 mmhg (s48 kpa). In this way, this system waits for a build up of engine boost, and then Starts the fuel injection, So that the combustion torque is relatively Small, and the torque is varied Smoothly from the torque of the motor/generator 2 to the torque of the engine 1. This System controls the Sum of the engine torque and the motor/generator torque So as to make the Sum equal to the target driving torque.
10 7 In the State in which the engine torque increases sharply, the input Speed of the automatic transmission 3 tends to increase beyond the target Speed in the manner of overshoot. In this case, the motor/generator 2 is operated as a generator, and absorbs an excess of the engine output So that the produced torque becomes equal to the target torque and the creep force is held at a desired value. After the engine 1 has reached the State of Self-Supporting revolution, the System returns the engine to the normal operating State when the actual engine Speed increases to the target engine Speed and the required motor torque becomes ZCO. During this engine restarting operation, the Select position of the automatic transmission 3 is held unchanged. When, for example, the Select position is in the Drange, the engine 1 is restarted in the D range, and the creep force is produced from the Start of the engine Starting operation, first by the motor/generator 2 and then by the engine 1. Therefore, this System can prevent unnatural feeling, and a shock which would be caused if the transmission is held in the neutral State and returned to the drive range. When the engine 1 is restarted in the N range, this system produces no creep force. In this case, however, the driver is aware that the Select position is in the N range, and antici pates a shock due to a shift from the N range to the D range as usual. When the engine 1 is restarted in the state in which the accelerator pedal is depressed by the driver, this System can increase the driving force rapidly as demanded by the driver. In this case, the control System Sets the target Speed in the restarting operation So that the target Speed increases as the accelerator opening increases, and the target Speed increases as the time from the Start of the engine Starting operation or the vehicle Speed increases. Since the engine Speed cannot increase immediately, the control System increases the torque of the motor/generator 2. Therefore, the motor/ generator 2 increases its Speed sharply while rotating the engine 1, and thereby produces the driving torque as requested by the driver. The control system reduces the output of the motor/generator 2 to Zero when the engine Speed reaches the target Speed. The motor/generator 2 pro duces electric energy by consuming the engine torque when the battery 13 is to be charged, or when a regenerative operation is required during deceleration. FIG. 5 shows a control process according to a Second embodiment of the present invention. The control process of FIG. 5 is different from FIG. 2 only in the addition of a step S50 between the step S24 and the step S25. At the step S50, the controller 10 checks the driving condition of the auto matic transmission 3. In this example, the controller 10 proceeds from the step S50 directly to the step S26 if the automatic transmission 3 is in the N or P range. Otherwise, the controller 10 proceeds from the step S50 to the next step S25. Therefore, in the example of FIG. 5, the target engine Speed is Set at the idle Speed in the case of the N or Prange, without regard to the accelerator opening degree. The System according to the Second embodiment can prevent the engine Speed from being increased even if the driver races the engine in the N or P range. This adds a contribution to the improvement of fuel economy and reduc tion of noises. On the other hand, the control System according to the first embodiment can provide a natural feeling as in an ordinary vehicle, by allowing the engine Speed to increase in response to depression of the accelerator pedal in the N or P range. This application is based on a Japanese Patent Application No The entire contents of this Japanese Patent Application with a filing date of Mar. 19, 1999 are hereby incorporated by reference. The present invention is not limited to the embodiments described above. Modifications and variations of the embodiments described above will occur to those skilled in the art in light of the above teachings. What is claimed is: 1. A vehicle comprising: an engine; a motor for Starting the engine; an automatic transmission connected with the engine and the motor, for receiving input rotation from the engine and the motor and providing output rotation to drive the vehicle; a Sensing device for Sensing a vehicle operating condition; and a controller for performing an automatic engine Stop operation for automatically stopping the engine and an automatic engine restart operation for automatically restarting the engine in accordance with the vehicle operating condition, for producing an engine restart request signal to request a restart of the engine during the automatic engine Stop operation, for determining a target engine Speed for the automatic engine restart operation, and for performing the automatic engine restart operation, in response to the engine restart request Signal, by driving the motor in accordance with the target Speed while holding a transmission State of the automatic transmission unchanged. 2. A vehicle according to claim 1 wherein the controller is configured to perform the automatic engine restart opera tion in response to the engine restart request Signal, and to hold the automatic transmission in a drive range during the automatic engine restart operation if the automatic transmis Sion is in the drive range at the Start of the engine restart operation. 3. A vehicle according to claim 1 wherein the controller produces a first condition Signal when an accelerator pedal of the vehicle is depressed, a Second condition Signal when a brake pedal of the vehicle is released, a third condition Signal when a vehicle Speed of the vehicle is increased from Zero, and a fourth condition signal when a time duration of the automatic engine Stop operation becomes equal to or greater than a predetermined time length, and the controller produces the restart request Signal when at least one of the first, Second, third and fourth condition Signals is produced. 4. A vehicle according to claim 3 wherein the Sensing device comprises an accelerator Sensor for Sensing a condi tion of the accelerator pedal of the vehicle, a brake Sensor for Sensing a condition of the brake pedal of the vehicle, and a vehicle Speed Sensor for Sensing the vehicle Speed of the vehicle, and the controller produces the first, Second and third condition signals, respectively, in accordance with Signals from the accelerator Sensor, the brake Sensor and the vehicle Speed Sensor. 5. A vehicle according to claim 1 wherein the controller determines the target engine Speed for the automatic engine restart operation in accordance with an accelerator opening degree. 6. A vehicle according to claim 5 wherein the controller Sets the target engine Speed equal to an idle Speed when the accelerator opening degree is equal to a minimum Setting. 7. A vehicle according to claim 5 wherein the controller increases the target engine Speed for the automatic engine restart operation in accordance with the accelerator opening degree.
11 9 8. A vehicle according to claim 5 wherein the controller increases the target engine Speed for the automatic engine restart operation in accordance with an operating parameter which is one of a time elapsed from a start of the automatic engine restart operation and a vehicle Speed of the vehicle. 9. A vehicle according to claim 8 wherein the controller increases a rate of increase of the target engine Speed with respect to the parameter as the accelerator opening degree increases. 10. A vehicle according to claim 1 wherein the controller Sets the target engine Speed for the automatic engine restart operation equal to an idle Speed when the transmission is in a non-driving State in which a driving torque is not trans mitted through the transmission. 11. A vehicle according to claim 1 wherein the Sensing device further comprises a transmission condition Sensor for Sensing a condition of the automatic transmission, and the controller checks the condition of the automatic transmis Sion in response to the restart request signal and determines the target engine Speed for the automatic engine restart operation in accordance with the condition of the automatic transmission. 12. A vehicle according to claim 1 wherein the controller controls a torque of the engine and a torque of the motor in the automatic engine restart operation So as to make an actual engine Speed equal to the target Speed. 13. A vehicle according to claim 12 wherein the Sensing device comprises an engine Speed Sensor for Sensing an actual engine Speed of the engine, and the controller controls the motor in the automatic engine restart operation So as to reduce a deviation of the actual engine Speed from the target engine Speed. 14. A vehicle according to claim 13 wherein the controller operates the motor in a power generating mode for gener ating electric power by absorbing energy of the engine when the actual engine Speed is higher than the target Speed. 15. A vehicle according to claim 1 wherein, in the automatic engine restart operation, the controller first cranks the engine with the motor without fuel injection for a predetermined time duration to increase an engine boost to a predetermined level, and Starts fuel Supply to the engine at the end of the predetermined time duration. 16. A vehicle according to claim 1 wherein the vehicle further comprises an oil pump for Supplying oil pressure to the automatic transmission even when the engine is at rest An automatic engine Stop and restart control apparatus for automatically stopping an engine for a vehicle and automatically restarting the engine with a starting motor, the automatic engine Stop and restart control apparatus com prising: means for automatically stopping the engine in a prede termined vehicle Situation; means for producing an automatic restart request Signal in accordance with a vehicle operating condition in the predetermined vehicle situation; means for monitoring a driving condition of an automatic transmission connected with the engine; means for determining a target engine Speed for an automatic engine restart operation in accordance with the driving condition of the automatic transmission; and means for restarting the engine in response to the auto matic engine restart request Signal, by controlling the Starting motor in accordance with the target engine Speed. 18. An automatic engine Stop and restart control process for automatically stopping an engine for a vehicle and automatically restarting the engine with a starting motor, the automatic engine Stop and restart control process compris ing: putting the engine in an automatic Stop State in a prede termined vehicle Situation; producing an automatic restart request Signal in accor dance with a vehicle operating condition in the prede termined vehicle Situation; detecting a driving condition of an automatic transmission connected with the engine; determining a target engine Speed for an automatic engine restart operation in accordance with the driving condi tion of the automatic transmission; and initiating the automatic engine restart operation for restarting the engine in response to the automatic engine restart request Signal, by controlling the Starting motor in accordance with the target engine Speed.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Tomita et al. USOO6619259B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2003 (54) ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED THROTTLE CONTROL SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Tsugio Tomita, Hitachi (JP);
(12) United States Patent Tomita et al. USOO6619259B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2003 (54) ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED THROTTLE CONTROL SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Tsugio Tomita, Hitachi (JP);
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8384329B2 (12) United States Patent Natsume (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) WIPER SYSTEMAND WIPER CONTROL METHOD Inventor: Takashi Natsume, Toyohashi (JP) Assignee: ASMO Co.,
USOO8384329B2 (12) United States Patent Natsume (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) WIPER SYSTEMAND WIPER CONTROL METHOD Inventor: Takashi Natsume, Toyohashi (JP) Assignee: ASMO Co.,
United States Patent (19) Kitami et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kitami et al. 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,846,768 Jul. 11, 1989 (54) VARIABLE-SPEED DRIVING DEVICE 75) Inventors: Yasuo Kitami; Hidenori Tezuka; 73 Assignee: Syuji
United States Patent (19) Kitami et al. 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,846,768 Jul. 11, 1989 (54) VARIABLE-SPEED DRIVING DEVICE 75) Inventors: Yasuo Kitami; Hidenori Tezuka; 73 Assignee: Syuji
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,730,000 B1
 USOO673OOOOB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Leising et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) INTERACTIVE PROCESS DURING ENGINE 6,556,910 B2 4/2003 Suzuki et al.... 701/54 IDLE STOP MODE
USOO673OOOOB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Leising et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) INTERACTIVE PROCESS DURING ENGINE 6,556,910 B2 4/2003 Suzuki et al.... 701/54 IDLE STOP MODE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7357465B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,357.465 B2 Young et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2008 (54) BRAKE PEDAL FEEL SIMULATOR 3,719,123 A 3/1973 Cripe 3,720,447 A * 3/1973 Harned
(12) United States Patent USOO7357465B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,357.465 B2 Young et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2008 (54) BRAKE PEDAL FEEL SIMULATOR 3,719,123 A 3/1973 Cripe 3,720,447 A * 3/1973 Harned
United States Patent (19) Muranishi
 United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,651,070 B2
 USOO8651070B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,651,070 B2 Lindner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 18, 2014 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS TO CONTROL USPC... 123/41.02, 41.08-41.1, 41.44, 198C
USOO8651070B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,651,070 B2 Lindner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 18, 2014 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS TO CONTROL USPC... 123/41.02, 41.08-41.1, 41.44, 198C
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1
 USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
III. United States Patent (19) Shirai et al. 5,669,351. Sep. 23, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: CONSTANTS PID CONTROL
 United States Patent (19) Shirai et al. 54) ENGINE THROTTLE CONTROL WITH WARYING CONTROL 75) Inventors: Kazunari Shirai, Chita-gun; Hidemasa Miyano, Kariya; Shigeru Kamio, Nagoya; Yoshimasa Nakaya, Nagoya,
United States Patent (19) Shirai et al. 54) ENGINE THROTTLE CONTROL WITH WARYING CONTROL 75) Inventors: Kazunari Shirai, Chita-gun; Hidemasa Miyano, Kariya; Shigeru Kamio, Nagoya; Yoshimasa Nakaya, Nagoya,
3 23S Sé. -Né 33% (12) United States Patent US 6,742,409 B2. Jun. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: 6B M 2 O. (51) Int. Cl...
 (12) United States Patent Blanchard USOO6742409B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 2004 (54) DEVICE FORTRANSMISSION BETWEEN A PRIMARY MOTOR SHAFT AND AN OUTPUT SHAFT AND LAWN MOWER PROVIDED
(12) United States Patent Blanchard USOO6742409B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 2004 (54) DEVICE FORTRANSMISSION BETWEEN A PRIMARY MOTOR SHAFT AND AN OUTPUT SHAFT AND LAWN MOWER PROVIDED
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,641,228 B2
 USOO6641228B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,641,228 B2 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) DETACHABLE FRONT WHEEL STRUCTURE (56) References Cited OF GOLF CART U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
USOO6641228B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,641,228 B2 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) DETACHABLE FRONT WHEEL STRUCTURE (56) References Cited OF GOLF CART U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,626,061 B2. Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003
 USOO6626061B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) ACCELERATOR PEDAL DEVICE 6,276,229 B1 * 8/2001 Gohring et al... 74/513 6,289,762 B1 9/2001
USOO6626061B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) ACCELERATOR PEDAL DEVICE 6,276,229 B1 * 8/2001 Gohring et al... 74/513 6,289,762 B1 9/2001
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Ogasawara et al. (54) 75 RDING LAWN MOWER Inventors: Hiroyuki Ogasawara; Nobuyuki Yamashita; Akira Minoura, all of Osaka, Japan Assignee: Kubota Corporation, Osaka, Japan Appl.
United States Patent (19) Ogasawara et al. (54) 75 RDING LAWN MOWER Inventors: Hiroyuki Ogasawara; Nobuyuki Yamashita; Akira Minoura, all of Osaka, Japan Assignee: Kubota Corporation, Osaka, Japan Appl.
USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999
 USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999 54 SERIALLY CONNECTED CHARGER Primary Examiner Edward H. Tso Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Rosenberger,
USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999 54 SERIALLY CONNECTED CHARGER Primary Examiner Edward H. Tso Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Rosenberger,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Itabashi et al. USOO6329777B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2001 (54) MOTOR DRIVE CONTROL APPARATUS AND METHOD HAVING MOTOR CURRENT LIMIT FUNCTION UPON MOTOR
(12) United States Patent Itabashi et al. USOO6329777B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2001 (54) MOTOR DRIVE CONTROL APPARATUS AND METHOD HAVING MOTOR CURRENT LIMIT FUNCTION UPON MOTOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0312869A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0312869 A1 WALTER (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016 (54) CVT DRIVE TRAIN Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2016.0312869A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0312869 A1 WALTER (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016 (54) CVT DRIVE TRAIN Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
United States Patent (19) Fuchita et al.
 United States Patent (19) Fuchita et al. USOO61622A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 19, 2000 54 CONTROLLER OF ENGINE AND WARIABLE CAPACITY PUMP 75 Inventors: Seiichi Fuchita, Katano; Fujitoshi
United States Patent (19) Fuchita et al. USOO61622A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 19, 2000 54 CONTROLLER OF ENGINE AND WARIABLE CAPACITY PUMP 75 Inventors: Seiichi Fuchita, Katano; Fujitoshi
Earl Sch yang y Lee, 5,457,342 10/1995 Herbst, II /712
 US005920264A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM PROTECTION 5,189,314 2/1993 Georgiou et al.... 307/271 DEVICE 5,287.292 2/1994
US005920264A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM PROTECTION 5,189,314 2/1993 Georgiou et al.... 307/271 DEVICE 5,287.292 2/1994
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,899,031 B2
 US008899.031B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,899,031 B2 Turnis et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2014 (54) COLD START VALVE (58) Field of Classification Search CPC... F15B 21/042: F15B
US008899.031B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,899,031 B2 Turnis et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2014 (54) COLD START VALVE (58) Field of Classification Search CPC... F15B 21/042: F15B
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150224968A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0224968 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) CONTROL METHOD FOR HILL START ASSIST CONTROL SYSTEM (71)
(19) United States US 20150224968A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0224968 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) CONTROL METHOD FOR HILL START ASSIST CONTROL SYSTEM (71)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0088848A1 Owen et al. US 20140O88848A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) SELECTIVE AUTOMATED VEHICLE BRAKE FORCE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0088848A1 Owen et al. US 20140O88848A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) SELECTIVE AUTOMATED VEHICLE BRAKE FORCE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1. Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002
 USOO6435993B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1 Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) HYDRAULIC CHAIN TENSIONER WITH 5,707.309 A 1/1998 Simpson... 474/110 VENT DEVICE AND
USOO6435993B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1 Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) HYDRAULIC CHAIN TENSIONER WITH 5,707.309 A 1/1998 Simpson... 474/110 VENT DEVICE AND
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,516 B1
 USOO6779516B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shureb () Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) CLOSED CRANKCASE VENTILATION 4.856,487 A * 8/1989 Furuya... 123/574 SYSTEM WITH FLOW METER FOR 5,003,943
USOO6779516B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shureb () Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) CLOSED CRANKCASE VENTILATION 4.856,487 A * 8/1989 Furuya... 123/574 SYSTEM WITH FLOW METER FOR 5,003,943
US 7, B2. Loughrin et al. Jan. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: and/or the driven component. (12) United States Patent (54) (75)
 USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2
 US0087.08325B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,708.325 B2 Hwang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2014 (54) PAPER CLAMPINGAPPARATUS FOR (56) References Cited OFFICE MACHINE (75) Inventors:
US0087.08325B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,708.325 B2 Hwang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2014 (54) PAPER CLAMPINGAPPARATUS FOR (56) References Cited OFFICE MACHINE (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 USO09597628B2 (12) United States Patent Kummerer et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) OPTIMIZATION OF A VAPOR RECOVERY UNIT Applicant:
USO09597628B2 (12) United States Patent Kummerer et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) OPTIMIZATION OF A VAPOR RECOVERY UNIT Applicant:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6989498B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,989,498 B1 Linder et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2006 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR LOCKING (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent USOO6989498B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,989,498 B1 Linder et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2006 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR LOCKING (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,469,466 B1
 USOO6469466B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,469,466 B1 Suzuki (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2002 (54) AUTOMATIC GUIDED VEHICLE JP 7-2S1768 10/1995 JP 8-1553 1/1996 (75) Inventor: Takayuki
USOO6469466B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,469,466 B1 Suzuki (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2002 (54) AUTOMATIC GUIDED VEHICLE JP 7-2S1768 10/1995 JP 8-1553 1/1996 (75) Inventor: Takayuki
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,047,956 B2. Masaoka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2006
 US007047956B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Masaoka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2006 (54) KICKBACK PREVENTING DEVICE FOR (56) References Cited ENGINE (75) Inventors: Akira Masaoka,
US007047956B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Masaoka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2006 (54) KICKBACK PREVENTING DEVICE FOR (56) References Cited ENGINE (75) Inventors: Akira Masaoka,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO64994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Matsumoto (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) STATIONARY BIKE (52) U.S. Cl.... 482/8 (76) Inventor: Masaaki Matsumoto,
(19) United States US 2005OO64994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Matsumoto (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) STATIONARY BIKE (52) U.S. Cl.... 482/8 (76) Inventor: Masaaki Matsumoto,
Phillips (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 10, (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search
 (12) United States Patent US008747274B2 () Patent No.: Phillips () Date of Patent: Jun., 2014 (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search TRANSMISSION USPC... 74/3, 331; 475/207
(12) United States Patent US008747274B2 () Patent No.: Phillips () Date of Patent: Jun., 2014 (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search TRANSMISSION USPC... 74/3, 331; 475/207
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
(19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,511,619 B2
 USOO851 1619B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,511,619 B2 Mann (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2013 (54) SLAT DEPLOYMENT MECHANISM (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Alan Mann, Bristol
USOO851 1619B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,511,619 B2 Mann (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2013 (54) SLAT DEPLOYMENT MECHANISM (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Alan Mann, Bristol
(12) United States Patent
 US008998577B2 (12) United States Patent Gustafson et al. (10) Patent No.: US 8,998,577 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 7, 2015 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) TURBINE LAST STAGE FLOW PATH Inventors:
US008998577B2 (12) United States Patent Gustafson et al. (10) Patent No.: US 8,998,577 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 7, 2015 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) TURBINE LAST STAGE FLOW PATH Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O181130A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0181130 A1 Fukunaga (43) Pub. Date: Jul.19, 2012 (54) TORQUE CONVERTER Publication Classification 51) Int.
(19) United States US 2012O181130A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0181130 A1 Fukunaga (43) Pub. Date: Jul.19, 2012 (54) TORQUE CONVERTER Publication Classification 51) Int.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,196,085 B1
 USOO6196085B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,196,085 B1 Chimonides et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) COUPLING AN ACCESSORY TO AN ENGINE 3,576,336 4/1971 Uhlig... 403/281 CRANKSHAFT
USOO6196085B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,196,085 B1 Chimonides et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) COUPLING AN ACCESSORY TO AN ENGINE 3,576,336 4/1971 Uhlig... 403/281 CRANKSHAFT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0157272 A1 Uhler et al. US 2009015.7272A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) FOUR-PASSAGE MULTIFUNCTION TOROUE CONVERTER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0157272 A1 Uhler et al. US 2009015.7272A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) FOUR-PASSAGE MULTIFUNCTION TOROUE CONVERTER
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,840,124 B2
 USOO884O124B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Serhan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2014 (54) ROLLATOR HAVING ASITTO-LOCK BRAKE (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Michael Serhan, Arcadia,
USOO884O124B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Serhan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2014 (54) ROLLATOR HAVING ASITTO-LOCK BRAKE (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Michael Serhan, Arcadia,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O168664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0168664 A1 Senda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 2, 2004 (54) ENGINE STARTER HAVING STARTER (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2004O168664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0168664 A1 Senda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 2, 2004 (54) ENGINE STARTER HAVING STARTER (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,590,360 B2
 USOO659036OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Hirata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2003 (54) CONTROL DEVICE FOR PERMANENT 4,879,502 A * 11/1989 Endo et al.... 318/808 MAGNET MOTOR SERVING
USOO659036OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Hirata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2003 (54) CONTROL DEVICE FOR PERMANENT 4,879,502 A * 11/1989 Endo et al.... 318/808 MAGNET MOTOR SERVING
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2. Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005
 United States Patent USOO6915721B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2 Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) CORDLESS RATCHET WRENCH 6,311,583 B1 11/2001 Izumisawa... 81/57.13 6,715,380
United States Patent USOO6915721B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2 Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) CORDLESS RATCHET WRENCH 6,311,583 B1 11/2001 Izumisawa... 81/57.13 6,715,380
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fujita 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,727,957 Mar. 1, 1988 (54) RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATOR FOR MUFFLER 75 Inventor: Akio Fujita, Fujisawa, Japan 73) Assignee: Bridgestone
United States Patent (19) Fujita 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,727,957 Mar. 1, 1988 (54) RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATOR FOR MUFFLER 75 Inventor: Akio Fujita, Fujisawa, Japan 73) Assignee: Bridgestone
United States Patent 19 Schechter
 United States Patent 19 Schechter (54) 75 73) 21) (22) (51) (52) 58 (56) SPOOL VALVE CONTROL OF AN ELECTROHYDRAULIC CAMILESS WALVETRAIN Inventor: Michael M. Schechter, Farmington Hills, Mich. Assignee:
United States Patent 19 Schechter (54) 75 73) 21) (22) (51) (52) 58 (56) SPOOL VALVE CONTROL OF AN ELECTROHYDRAULIC CAMILESS WALVETRAIN Inventor: Michael M. Schechter, Farmington Hills, Mich. Assignee:
Kikuiri et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, (54) CAPACITIVE PRESSURE SENSOR 5, A 12, 1996 Ko /53
 (12) United States Patent USOO7382599B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,382,599 B2 Kikuiri et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, 2008 (54) CAPACITIVE PRESSURE SENSOR 5,585.311 A 12, 1996 Ko... 438/53 5,656,781 A *
(12) United States Patent USOO7382599B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,382,599 B2 Kikuiri et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, 2008 (54) CAPACITIVE PRESSURE SENSOR 5,585.311 A 12, 1996 Ko... 438/53 5,656,781 A *
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2
 USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Hozumi et al. 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,889,164 Dec. 26, 1989 54). SOLENOID CONTROLLED WALVE (75 Inventors: Kazuhiro Hozumi; Masaru Arai, both of Chiba; Yoshitane
United States Patent (19) Hozumi et al. 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,889,164 Dec. 26, 1989 54). SOLENOID CONTROLLED WALVE (75 Inventors: Kazuhiro Hozumi; Masaru Arai, both of Chiba; Yoshitane
E. E. 2. Attorney, Agent, Or Firm-Finnegan, HenderSon, Farabow,
 USOO5906645A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,906,645 Kagawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: *May 25, 1999 54 AUTO-DRIVE CONTROL UNIT FOR 4,932,617 6/1990 Heddebaut et al.... 340/933 VEHICLES
USOO5906645A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,906,645 Kagawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: *May 25, 1999 54 AUTO-DRIVE CONTROL UNIT FOR 4,932,617 6/1990 Heddebaut et al.... 340/933 VEHICLES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US00906 1731B1 (10) Patent No.: US 9,061,731 B1 DO (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 23, 2015 (54) SELF-CHARGING ELECTRIC BICYCLE (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Hung Do, Las Vegas,
(12) United States Patent US00906 1731B1 (10) Patent No.: US 9,061,731 B1 DO (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 23, 2015 (54) SELF-CHARGING ELECTRIC BICYCLE (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Hung Do, Las Vegas,
IIIHIIII 5,509,863. United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. Apr. 23, Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent:
 United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. 54) TRANSMISSION DEVICE, ESPECIALLY FOR BOAT MOTORS 75 Inventors: Staffan Månsson, Hjalteby; Benny Hedlund, Hönö, both of Sweden 73 Assignee: AB Volvo Penta, Gothenburg,
United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. 54) TRANSMISSION DEVICE, ESPECIALLY FOR BOAT MOTORS 75 Inventors: Staffan Månsson, Hjalteby; Benny Hedlund, Hönö, both of Sweden 73 Assignee: AB Volvo Penta, Gothenburg,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,446,482 B1. Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002
 USOO64.46482B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002 (54) BATTERY OPERATED HYDRAULIC D408.242 S 4/1999 Yamamoto... D8/61 COMPRESSION TOOL WITH RAPID
USOO64.46482B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002 (54) BATTERY OPERATED HYDRAULIC D408.242 S 4/1999 Yamamoto... D8/61 COMPRESSION TOOL WITH RAPID
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1
 USOO648.4362B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1 Ku0 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) RETRACTABLE HANDLE ASSEMBLY WITH 5,692,266 A 12/1997 Tsai... 16/113.1 MULTIPLE ENGAGING
USOO648.4362B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1 Ku0 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) RETRACTABLE HANDLE ASSEMBLY WITH 5,692,266 A 12/1997 Tsai... 16/113.1 MULTIPLE ENGAGING
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9671 011B2 (12) United States Patent Kimijima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,671,011 B2 Jun. 6, 2017 (54) WORM BIASING STRUCTURE (71) Applicant: Showa Corporation, Gyoda-shi (JP)
USOO9671 011B2 (12) United States Patent Kimijima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,671,011 B2 Jun. 6, 2017 (54) WORM BIASING STRUCTURE (71) Applicant: Showa Corporation, Gyoda-shi (JP)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O152831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0152831 A1 Sakamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2002 (54) ACCELERATOR PEDAL DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazunori
(19) United States US 2002O152831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0152831 A1 Sakamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2002 (54) ACCELERATOR PEDAL DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazunori
United States Patent (19) Kim et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kim et al. 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR COATING AWAFER WITH A MINIMAL LAYER OF PHOTORESIST 75 Inventors: Moon-woo Kim, Kyungki-do; Byung-joo Youn, Seoul, both of Rep. of Korea
United States Patent (19) Kim et al. 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR COATING AWAFER WITH A MINIMAL LAYER OF PHOTORESIST 75 Inventors: Moon-woo Kim, Kyungki-do; Byung-joo Youn, Seoul, both of Rep. of Korea
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070247877A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0247877 A1 KWON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2007 54) ACTIVE-CLAMP CURRENTSOURCE 3O Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070247877A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0247877 A1 KWON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2007 54) ACTIVE-CLAMP CURRENTSOURCE 3O Foreign Application
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Minnerop 54) DEVICE FOR WATER COOLING OF ROLLED STEEL SECTIONS 75 Inventor: Michael Minnerop, Ratingen, Germany 73 Assignee: SMS Schloemann-Siemag Aktiengesellschaft, Dusseldorf,
United States Patent (19) Minnerop 54) DEVICE FOR WATER COOLING OF ROLLED STEEL SECTIONS 75 Inventor: Michael Minnerop, Ratingen, Germany 73 Assignee: SMS Schloemann-Siemag Aktiengesellschaft, Dusseldorf,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,408,626 B1
 USOO6408626B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,408,626 B1 Arnell (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 25, 2002 (54) ARRANGEMENT AND METHOD FOR 4,048.872 A * 9/1977 Webb... 464/24 POWER TRANSMISSION
USOO6408626B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,408,626 B1 Arnell (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 25, 2002 (54) ARRANGEMENT AND METHOD FOR 4,048.872 A * 9/1977 Webb... 464/24 POWER TRANSMISSION
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7246672B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,246,672 B2 Shirai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 24, 2007 (54) HYBRID-VEHICLE POWER TRAIN 6,007.443 A * 12/1999 Onimaru et al.... 475/5 6,344,008
(12) United States Patent USOO7246672B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,246,672 B2 Shirai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 24, 2007 (54) HYBRID-VEHICLE POWER TRAIN 6,007.443 A * 12/1999 Onimaru et al.... 475/5 6,344,008
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080056631A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0056631 A1 Beausoleil et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2008 (54) TUNGSTEN CARBIDE ENHANCED Publication Classification
US 20080056631A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0056631 A1 Beausoleil et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2008 (54) TUNGSTEN CARBIDE ENHANCED Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7242106B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,242,106 B2 Kelly (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 10, 2007 (54) METHOD OF OPERATION FOR A (56) References Cited SE NYAVE ENERGY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent USOO7242106B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,242,106 B2 Kelly (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 10, 2007 (54) METHOD OF OPERATION FOR A (56) References Cited SE NYAVE ENERGY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent
 US00704.4047B1 (12) United States Patent Bennett et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) CYLNDER MOUNTED STROKE CONTROL Inventors: Robert Edwin Bennett,
US00704.4047B1 (12) United States Patent Bennett et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) CYLNDER MOUNTED STROKE CONTROL Inventors: Robert Edwin Bennett,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO698.1746B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,981,746 B2 Chung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 2006 (54) ROTATING CAR SEAT MECHANISM 4,844,543 A 7/1989 Ochiai... 297/344.26 4,925,227
(12) United States Patent USOO698.1746B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,981,746 B2 Chung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 2006 (54) ROTATING CAR SEAT MECHANISM 4,844,543 A 7/1989 Ochiai... 297/344.26 4,925,227
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0159457 A1 Saint-Marc et al. US 2016015.9457A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) RUDDER BAR FOR AN AIRCRAFT (71) Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0159457 A1 Saint-Marc et al. US 2016015.9457A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) RUDDER BAR FOR AN AIRCRAFT (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent
 US007307230B2 (12) United States Patent Chen (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,307,230 B2 Dec. 11, 2007 (54) MECHANISM FOR CONTROLLING CIRCUITCLOSINGAOPENING OF POWER RATCHET WRENCH (75) Inventor:
US007307230B2 (12) United States Patent Chen (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,307,230 B2 Dec. 11, 2007 (54) MECHANISM FOR CONTROLLING CIRCUITCLOSINGAOPENING OF POWER RATCHET WRENCH (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,083,631 B2. Shiohara (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 27, 2011
 US008.083631 B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Shiohara (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 27, 2011 (54) PLANETARY GEARTYPE GEARBOX (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Masaki Shiohara, Komatsu (JP) U.S.
US008.083631 B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Shiohara (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 27, 2011 (54) PLANETARY GEARTYPE GEARBOX (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Masaki Shiohara, Komatsu (JP) U.S.
ENGINE. ean III. United States Patent (19) Pinkowski CONTROL. A method and system for controlling the illumination of a
 United States Patent (19) Pinkowski III USOO5606308A 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 1997 54 75) (73 21 22 51 (52) (58) 56) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONTROLLING THE LLUMINATION OFA VEHICULAR
United States Patent (19) Pinkowski III USOO5606308A 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 1997 54 75) (73 21 22 51 (52) (58) 56) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONTROLLING THE LLUMINATION OFA VEHICULAR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,278,955 B1. Hartman et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 21, 2001
 USOO6278955B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,278,955 B1 Hartman et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 21, 2001 (54) METHOD FOR AUTOMATICALLY 5,327,345 7/1994 Nielsen et al.... 172/4.5 POSITONING
USOO6278955B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,278,955 B1 Hartman et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 21, 2001 (54) METHOD FOR AUTOMATICALLY 5,327,345 7/1994 Nielsen et al.... 172/4.5 POSITONING
USOO58065OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,806,500 Fargo et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 15, 1998
 USOO58065OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,806,500 Fargo et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 15, 1998 54 FUEL VAPOR RECOVERY SYSTEM 5,456,238 10/1995 Horiuchi et al.. 5,460,136 10/1995 Yamazaki
USOO58065OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,806,500 Fargo et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 15, 1998 54 FUEL VAPOR RECOVERY SYSTEM 5,456,238 10/1995 Horiuchi et al.. 5,460,136 10/1995 Yamazaki
United States Patent (19) Koitabashi
 United States Patent (19) Koitabashi 54 75 (73) 1 (51) (5) (58 56) ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH WITH AN IMPROVED MAGNETC ROTATABLE MEMBER Inventor: Takatoshi Koitabashi, Annaka, Japan Assignee: Sanden Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Koitabashi 54 75 (73) 1 (51) (5) (58 56) ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH WITH AN IMPROVED MAGNETC ROTATABLE MEMBER Inventor: Takatoshi Koitabashi, Annaka, Japan Assignee: Sanden Corporation,
HHHHHH. United States Patent (19) Mizuta et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,086,858. (22) Filed: Dec. 3, 1990
 United States Patent (19) Mizuta et al. (54) AIR INTAKE SYSTEM FOR UTILITY VEHICLE 75 Inventors: Fumio Mizuta, Akashi; Takashi Arii, Kakogawa; Yoshiharu Matsuda, Akashi; itsuo Takegami, Kobe, all of (73)
United States Patent (19) Mizuta et al. (54) AIR INTAKE SYSTEM FOR UTILITY VEHICLE 75 Inventors: Fumio Mizuta, Akashi; Takashi Arii, Kakogawa; Yoshiharu Matsuda, Akashi; itsuo Takegami, Kobe, all of (73)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US B1
 USOO7628442B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Spencer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 2009 (54) QUICK RELEASE CLAMP FOR TONNEAU (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/100.04, COVER 296/100.07,
USOO7628442B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Spencer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 2009 (54) QUICK RELEASE CLAMP FOR TONNEAU (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/100.04, COVER 296/100.07,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,215,503 B2. Appel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 10, 2012
 US008215503B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,215,503 B2 Appel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 10, 2012 (54) CRANE WITH TELESCOPIC BOOM 3,921,819 A * 1 1/1975 Spain... 212,349 4,394,108
US008215503B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,215,503 B2 Appel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 10, 2012 (54) CRANE WITH TELESCOPIC BOOM 3,921,819 A * 1 1/1975 Spain... 212,349 4,394,108
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.408,189 B2
 USOO8408189B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 8.408,189 B2 Lutz et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2013 (54) PETROL ENGINE HAVING A LOW-PRESSURE EGR CIRCUIT (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT
USOO8408189B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 8.408,189 B2 Lutz et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2013 (54) PETROL ENGINE HAVING A LOW-PRESSURE EGR CIRCUIT (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT
E. E. E.O.E. comprises a diverter valve downstream of the turbine, an
 USOO63056B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lui (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 2001 (54) INTEGRATED BLEED AIR AND ENGINE 5,363,641 11/1994 Dixon et al.. STARTING SYSTEM 5,414,992 5/1995 Glickstein.
USOO63056B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lui (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 2001 (54) INTEGRATED BLEED AIR AND ENGINE 5,363,641 11/1994 Dixon et al.. STARTING SYSTEM 5,414,992 5/1995 Glickstein.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2
 US009 168973B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2 Offe (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2015 (54) MOTORCYCLE SUSPENSION SYSTEM (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Andrew Offe, Wilunga
US009 168973B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2 Offe (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2015 (54) MOTORCYCLE SUSPENSION SYSTEM (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Andrew Offe, Wilunga
United States Patent (19) Ochi et al.
 United States Patent (19) Ochi et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,945,272 Jul. 31, 1990 54 ALTERNATOR FORMOTOR VEHICLES 75 Inventors: Daisuke Ochi; Yasuhiro Yoshida; Yoshiyuki Iwaki, all of
United States Patent (19) Ochi et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,945,272 Jul. 31, 1990 54 ALTERNATOR FORMOTOR VEHICLES 75 Inventors: Daisuke Ochi; Yasuhiro Yoshida; Yoshiyuki Iwaki, all of
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0139355A1 Lee et al. US 2013 O1393.55A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) HINGEMECHANISMAND FOLDABLE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0139355A1 Lee et al. US 2013 O1393.55A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) HINGEMECHANISMAND FOLDABLE
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Belanger et al. 4 MECHANISM FOR GLUE GUN (76) Inventors: (21) 22 (1) 2) 8 (6) Richard W. Belanger, 2 Collins St., Amesbury, Mass. 01913; Peter S. Melendy, 11 Crestview Dr., Exeter,
United States Patent (19) Belanger et al. 4 MECHANISM FOR GLUE GUN (76) Inventors: (21) 22 (1) 2) 8 (6) Richard W. Belanger, 2 Collins St., Amesbury, Mass. 01913; Peter S. Melendy, 11 Crestview Dr., Exeter,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,205,840 B1
 USOO620584OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,205,840 B1 Thompson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) TIME CLOCK BREATHALYZER 4,749,553 * 6/1988 Lopez et al.... 73/23.3 X COMBINATION
USOO620584OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,205,840 B1 Thompson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) TIME CLOCK BREATHALYZER 4,749,553 * 6/1988 Lopez et al.... 73/23.3 X COMBINATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,055,613 B1. Bissen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2006
 US007055613B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,055,613 B1 Bissen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2006 (54) SELF LEVELING BOOM SYSTEM WITH (58) Field of Classification Search... 169/24,
US007055613B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,055,613 B1 Bissen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2006 (54) SELF LEVELING BOOM SYSTEM WITH (58) Field of Classification Search... 169/24,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,870,248 B2 Graute (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 2014
 USOO8870248B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,870,248 B2 Graute (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 2014 (54) VEHICLE DOOR LATCH (52) US. Cl. CPC..... E053 83/36 (2013.01); E053 77/28 (71) Applicant:
USOO8870248B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,870,248 B2 Graute (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 2014 (54) VEHICLE DOOR LATCH (52) US. Cl. CPC..... E053 83/36 (2013.01); E053 77/28 (71) Applicant:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Aoyama et al. 54 HYBRID VEHICLE EMPLOYING PARALLEL HYBRID SYSTEM, USING BOTH INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE AND ELECTRIC MOTOR FOR PROPULSION 75 Inventors: Shunichi Aoyama, Kanagawa;
United States Patent (19) Aoyama et al. 54 HYBRID VEHICLE EMPLOYING PARALLEL HYBRID SYSTEM, USING BOTH INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE AND ELECTRIC MOTOR FOR PROPULSION 75 Inventors: Shunichi Aoyama, Kanagawa;
United States Statutory Invention Registration (19)
 United States Statutory Invention Registration (19) P00rman 54 ELECTRO-HYDRAULIC STEERING SYSTEM FOR AN ARTICULATED VEHICLE 75 Inventor: Bryan G. Poorman, Princeton, Ill. 73 Assignee: Caterpillar Inc.,
United States Statutory Invention Registration (19) P00rman 54 ELECTRO-HYDRAULIC STEERING SYSTEM FOR AN ARTICULATED VEHICLE 75 Inventor: Bryan G. Poorman, Princeton, Ill. 73 Assignee: Caterpillar Inc.,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0130234A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0130234 A1 Phillips (43) Pub. Date: (54) THREE-MODE HYBRID POWERTRAIN (52) U.S. Cl.... 475/5: 903/911 WITH
(19) United States US 2011 0130234A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0130234 A1 Phillips (43) Pub. Date: (54) THREE-MODE HYBRID POWERTRAIN (52) U.S. Cl.... 475/5: 903/911 WITH
75 Inventors: William H. Robertson, Jr., Plantation; Primary Examiner-Peter S. Wong
 USOO592O178A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,920,178 Robertson, Jr. et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) BATTERY PACK HAVING INTEGRATED 56) References Cited CHARGING CIRCUIT AND CHARGING
USOO592O178A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,920,178 Robertson, Jr. et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) BATTERY PACK HAVING INTEGRATED 56) References Cited CHARGING CIRCUIT AND CHARGING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9, B2
 USOO9656556B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,656.556 B2 Syed et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2017 (54) CAPACITOR DISCHARGING DURING 2011/0221370 A1* 9, 2011 Fukuta... HO2M 1/32 DEACTIVATION
USOO9656556B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,656.556 B2 Syed et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2017 (54) CAPACITOR DISCHARGING DURING 2011/0221370 A1* 9, 2011 Fukuta... HO2M 1/32 DEACTIVATION
United States Patent (19) Mathis
 United States Patent (19) Mathis 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,884,545 Dec. 5, 1989 54 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM FOR AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (75) Inventor: Christian Mathis, Arbon, Switzerland
United States Patent (19) Mathis 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,884,545 Dec. 5, 1989 54 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM FOR AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (75) Inventor: Christian Mathis, Arbon, Switzerland
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.442,100 B2
 USOO74421 OOB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.442,100 B2 KOrhonen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS TO CONTROL A (58) Field of Classification Search...
USOO74421 OOB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.442,100 B2 KOrhonen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS TO CONTROL A (58) Field of Classification Search...
(12) United States Patent
 US009113558B2 (12) United States Patent Baik (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,113,558 B2 Aug. 18, 2015 (54) LED MOUNT BAR CAPABLE OF FREELY FORMING CURVED SURFACES THEREON (76) Inventor: Seong
US009113558B2 (12) United States Patent Baik (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,113,558 B2 Aug. 18, 2015 (54) LED MOUNT BAR CAPABLE OF FREELY FORMING CURVED SURFACES THEREON (76) Inventor: Seong
$s. I 2 ;" (12) United States Patent US 6,975,908 B1. Dec. 13, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Njdskov (54) HANDHELD PIEZOELECTRIC
 (12) United States Patent Njdskov USOO6975908B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 13, 2005 (54) HANDHELD PIEZOELECTRIC ACUPUNCTURE STIMULATOR (75) Inventor: Preben Nodskov, Rungsted Kyst (DK)
(12) United States Patent Njdskov USOO6975908B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 13, 2005 (54) HANDHELD PIEZOELECTRIC ACUPUNCTURE STIMULATOR (75) Inventor: Preben Nodskov, Rungsted Kyst (DK)
NSN. 2%h, WD. United States Patent (19) Vranken 4,829,401. May 9, Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 54) ROTATING TRANSFORMER WITH FOIL
 United States Patent (19) Vranken 54) ROTATING TRANSFORMER WITH FOIL WINDINGS (75) Inventor: Roger A. Vranken, Eindhoven, Netherlands (73) Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Vranken 54) ROTATING TRANSFORMER WITH FOIL WINDINGS (75) Inventor: Roger A. Vranken, Eindhoven, Netherlands (73) Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21 Appl. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0091943 A1 Manor et al. US 2012009 1943A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (86) (60) SOLAR CELL CHARGING CONTROL Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0091943 A1 Manor et al. US 2012009 1943A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (86) (60) SOLAR CELL CHARGING CONTROL Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 200800301 65A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0030165 A1 Lisac (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2008 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR SUPPLYING A CHARGE WITH ELECTRIC
(19) United States US 200800301 65A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0030165 A1 Lisac (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2008 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR SUPPLYING A CHARGE WITH ELECTRIC
United States Patent (19) Hormel et al.
 United States Patent (19) Hormel et al. 54 (75) (73) 21) 22) (51) 52) (58) 56) LAMP FAILURE INDICATING CIRCUIT Inventors: Ronald F. Hormel, Mt. Clemens; Frederick O. R. Miesterfeld, Troy, both of Mich.
United States Patent (19) Hormel et al. 54 (75) (73) 21) 22) (51) 52) (58) 56) LAMP FAILURE INDICATING CIRCUIT Inventors: Ronald F. Hormel, Mt. Clemens; Frederick O. R. Miesterfeld, Troy, both of Mich.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,758,066 B2
 USOO7758.066 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,758,066 B2 Sia, Jr. et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) REAR PILLAR GARNISH ASSEMBLY 7,040,649 B2 5/2006 Totani et al. 7,118,153
USOO7758.066 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,758,066 B2 Sia, Jr. et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) REAR PILLAR GARNISH ASSEMBLY 7,040,649 B2 5/2006 Totani et al. 7,118,153
(12) United States Patent Burkitt et a1.
 US008567174B2 (12) United States Patent Burkitt et a1. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,567,174 B2 Oct. 29, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) VALVE ASSEMBLY
US008567174B2 (12) United States Patent Burkitt et a1. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,567,174 B2 Oct. 29, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) VALVE ASSEMBLY
Aug. 19, 1996 JP Japan or the slide door open-close mechanism, a clutch (56) for
 US006134836A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: KawanObe et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2000 54) DEVICE FOR AUTOMATICALLY 5,396,158 3/1995 Long et al.... 3.18/282 CONTROLLING THE CLOSURE
US006134836A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: KawanObe et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2000 54) DEVICE FOR AUTOMATICALLY 5,396,158 3/1995 Long et al.... 3.18/282 CONTROLLING THE CLOSURE
