15 Claims, 6 Drawing Figs. U.S. Clk /187, 318/197,318/205. Int. Cli... H02.p 7/46. Field of Search /138,
|
|
|
- Lawrence McDaniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
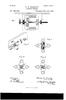
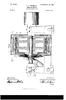
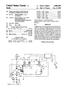
1 United States Patent (11) 3,611, Inventor 21 ) Appl. No. Filed Patented Assignee Norbert L. Schmitz Middleton, Wis. 884,934 Dec. 15, 1969 Oct. 5, 1971 Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation Madison, Wis. 3,418,550 12/1968 Kolatorowicz et al /38 3,421,062 l/1969 Dickey /187 3,448,363 6/1969 Pierro et al /197 Primary Examiner-Gene Z. Rubinson Attorney-Burmeister, Palmatier & Hamby (50) VARIABLE SPEED ELECTRIC MOTORSYSTEM HAVING STATOR ANDROTOR WINDINGS ENERGIZED IN OPPOSITE PHASE SEQUENCE WITH ALTERNATING CURRENT CORRESPONDENG IN ANGULARVELOCITY TO ONE-HALF THE ANGULARVELOCITY OF THE ROTOR 15 Claims, 6 Drawing Figs. U.S. Clk /187, 318/197,318/205 Int. Cli... H02.p 7/46 Field of Search /138, 187, 197,205 (56) References Cited UNITED STATES PATENTS 2,896, 143 7/1959 Bekey /187X ABSTRACT: The motor system utilizes a conventional wound rotor induction motor but achieves operating characteristics similar to those of a series field direct current motor. Both the stator coils and the rotor coils of the motor are supplied with alternating current power from a variable frequency power supply. However, the phase sequence of the rotor coils is reversed with respect to that of the stator coils. The voltage phase and the frequency of the power delivered to the motor are determined by a shaft position transducer coupled to the motor shaft. The adjustment of the transducer determines the torque angle between the alternating voltage phase and the position of the shaft. This torque angle is maintained constant at all speeds. The speed of the motor can be varied by varying the voltage of the alternating current supplied to the motor. A tachometer governor arrangement can be used to hold the speed constant. The shaft position transducer may utilize ro tary variable capacitors supplied with a carrier signal, or mag netodiodes positioned adjacent to a rotary magnet. f(2 Aeference -34 M Voltage Potentioneder : se-p(3: MotorSafé put Supply Woundezor , 2: SE 2 A1 eig? EW, 26 / Shaft Asition Transducer Position at () Carrier reguracy 30 Efs 5upply
2 PATENTEDOCT 597 SHEET 1 OF 3 *::: Olde PotentÉter 3.6ll,082 Pouyer Auer input Supply / Shaft Pasition Transducer f 12Position eatio for 2PbleMachines Carrier frequincy 5upply WVFW7 OR Norbert L.5chmziz, 4za'A414 Citys
3 PATENTEDOCT 597 SHEET 2 OF 3 3, 6 O82 a? PIAZ svºjfydding youo?pply^ o, ()
4 PATENTEDOCT 5197 SHEET 3 OF 3 3, 6l. O82 CUARAEWT (attp: ras) Fr. G. 6 (dotted) AEED rpm 7- f f200 kated 5 foo 4 AOO f 2OO
5 1. VARABLESPEED ELECTRCMOTORSYSTEM HAVING STATOR ANDROTORWINDINGSENERGZED IN OPPOSITEPHASE SEQUENCE WITH ALTERNATING CURRENT CORRESPONDING IN ANGULARVELOCITY TO ONE-HALF THE ANGULARVELOCITY OF THE ROTOR This invention relates to a variable speed electric motor system which utilizes an alternating current induction motor, but provides operating characteristics similar to those of a se ries field direct current motor. The motor system can be operated from either alternating current or direct current. One of the objects of the present invention is to provide a variable speed electric motor system which utilizes an alter nating current induction motor. The speed may be varied by changing either the supply voltage to the motor, or the trans ducer phase angle. A further object is to provide a motor system utilizing an al ternating current induction motor, yet providing high starting and overload torque capabilities, similar to those of a direct current series field motor. Another object is to provide an electric motor system in which both the stator windings and rotor windings of the in duction motor are supplied with power, whereby the motor is operated with improved efficiency, so that a high-power out put can be obtained in relation to the size of the motor. A further object is to provide an electric motor system utilizing an alternating current induction motor yet providing desirable speed-torque characteristics, corresponding to those of a direct current seriesfield motor. Another object is to provide a new and improved electric motor system utilizing a wound rotor alternating current machine, while avoiding the problems with pullout and hunt ing experienced with certain prior motor arrangements. Thus, the present invention preferably comprises a plural phase double armature induction motor having a wound rotor, as well as a wound stator. Both the rotor and stator are em ployed as armatures. Alternating current power is fed to both the stator and rotor coils by a variable frequency power supply. The stator and rotor coils may be connected either in series or in parallel. The phase sequence of the rotor coils is reversed with respect to the sequence of the stator coils. The variable frequency power supply is controlled by signals from a shaft position transducer, connected to the shaft of the mo tor. The phase of the signals from the transducer has either a fixed or an adjustable relationship to the position of the rotor. The alternating voltage supplied to the motor by the power supply has the same phase as the signals from the transducer. As the motor picks up speed, this relationship remains con stant for a constant transducer angle setting, while the frequency of the alternating current increases with the in creasing speed. Means may be provided to vary the operating speed by varying the alternating current voltage. A tachome ter governor arrangement may be employed to limit the operating speed and to hold it constant. Means may also be provided to control the speed-torque relationship by varying the phase at the alternating voltage relative to the shaft posi tion, either by rotating the stator of the transducer or interpos ing electrical phase shifting means between transducer and motor power supply. The power supply may be operated from either alternating or direct current. For use with an alternating current input, the power supply comprises a variable frequency cyclocon verter, controlled by the signals from the shaft position trans ducer. For use with direct current, the power supply com prises an inverter system controlled by the signals from the transducer. The shaft position transducer may utilize any device which provides output signals corresponding in phase to the position of the shaft. Thus, the transducer may comprise a rotary varia ble capacitor fed with a carrier signal. Alternatively, the trans ducer may comprise one or more magnetodiodes under the in fluence of a rotary magnet. The resistance of the mag netodiodes is thus varied in accordance with the position of the shaft. 3,611, Further objects, advantages and features of the present in vention will appear from the following description, taken with the accompanying drawings in which: FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram of an electric motor system to be described as an illustrative embodiment of the present inven tion. FIG. 2 is a more detailed circuit diagram of a slightly modified electric motor system. FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating the details of a two-phase motor for use in the system of FIG.2. FIG. 4 is a diagrammatic elevation of a shaft position trans ducer utilizing magnetodiodes. FIG. 5 is a circuit diagram of the shaft position transducer utilizing magnetodiodes. FIG. 6 is a set of graphs representing the operating charac teristics of the electric motor system. It will be seen that FIG. 1 illustrates an electric motor system 10 utilizing a double armature wound rotor induction motor 12. Thus, the motor 12 comprises a stator 14 having ar mature coils 14a, b and c. The motor 12 also has a wound rotor 16 with armature coils 16a, b and c. The illustrated motor 12 is of the three-phase type, but it will be understood that the invention is applicable to motors having any desired number of phases. In this case, the stator and rotor coils are connected in series in a Y connection. However, the stator and rotor coils may also be connected in parallel, and in either a Y or delta con nection. Both the stator and rotor coils are energized by a variable frequency alternating current power supply 18, illustrated as having three output lines or phases 18a, b and c. While both the stator and rotor coils are energized from the lines 18a, b and c, the phase sequence of the rotor coils is reversed with respect to the sequence of the stator coils. Thus, the stator and rotor coils 14a and 16a are connected in series between the line 18a and the central junction 20 of the Y connection. Because of the reversed sequence, the stator coil 14b and the rotor coil 16care connected in series between the line 18b and the junction 20. Likewise, the stator coil 14c and the rotor coil 16b are connected in series between the line 18c and the junc tion 20. The input power to the power supply 18 may be either alter nating current or direct current. As shown in FIG. 1, the power supply 18 receives its power from a power line 22. When a high-frequency ( cp.s.) power source is available. It is preferred to arrange the power supply 18 so that it may be energized from an alternating current power line, preferably with a plurality of phases, as will be described in greater detail in connection with FIG. 2. In that case, the power supply 18 acts as a frequency converter or cyclocon verter. When the power supply 18 is energized from direct current, the power supply is arranged to act as an inverter hav ing a variable frequency output. The stator coils 14a, b and c produce a magnetic field which rotates in one direction relative to the stator coils. Due to the reversed connection of the rotor coils 16a, b and c, they produce a magnetic field which rotates in the opposite direction relative to the rotor coils. During operation, there is a tendency for the rotating fields to become aligned, with the result that the rotor 16 tends to rotate at a synchronous speed which is twice the speed of the rotating magnetic field produced by the stator coils 14a, b and c. The phase and frequency of the alternating current output from the power supply 18 are determined by a shaft position transducer 24 having a mechanical connection to the rotor 16. The rotor 16 has an output shaft 26 which is coupled to the transducer 24. Thus, the phase and frequency of the output of the power supply 18 are determined by the instantaneous posi tion of the motor shaft 26. As shown in FIG. 1, a speed chang ing device 28 is interposed between the motor shaft 26 and the transducer 24. For a two-pole machine, the speed change device 28 has a speed ratio of 1 to 2, so that the rotatable ele ment of the transducer 24 is driven at one-half the speed of the shaft 26. This speed reduction is necessitated by the tendency
6 3 of the rotor to rotate at a synchronous speed which is twice the rotary speed of the stator magnetic field. For a four-pole machine direct drive at 1:1 to a two-pole transducer is possi ble. For an eight-pole machine direct drive at 1:1 to a four pole transducer is possible. Suitable speed relationships can be established for machines with any number of poles. Direct drive is possible when the number of poles is divisible by four. The transducer 24 produces a signal which varies cyclically in accordance with the instantaneous rotor position. It will be understood that the angular velocity of such signal cor responds to one-half the angular velocity of the rotor, and that this relationship can be achieved mechanically, as by the mechanical speed change in the transducer drive, or electri cally, as by the halving of the number of transducer poles, as explained above. This signal is delivered to the power supply 18 and is used to govern the phase and frequency of the alter nating current output. An adjustable phase shifter 29 may be provided between the transducer 24 and the power supply so that the phase can be adjusted. The shaft position transducer 24 may be of any suitable type. Thus, for example, it may be arranged to modulate a car rier signal in accordance with the shaft position. Accordingly, the transducer 24 of FIG. 1 is supplied with such a signal by a carrier frequency supply 30. This type of transducer will be described in greater detail in connection with FIG. 2. The transducer 24 may also utilize solid-state diodes which are magnetically responsive. A transducer of this type will be described in greater detail in connection with FIGS. 4 and 5. An electromagnetic transducer can also be employed. With the arrangement shown in FIG. 1, the operating speed of the motor 12 is determined by the input voltage, transducer angle setting and the mechanical load connected to the shaft of the motor. Thus, the speed can be varied by changing either the input voltage or the torque angle. As shown in FIG. 1, a voltage control device 32 is connected to the power supply 18. Such device may be of the electronic switching type or of any other known or suitable type. The voltage control device 32 may be arranged to regulate the output voltage of the power supply 18 in accordance with a variable reference voltage from an adjustable potentiometer 34, or any other suitable Source. Automatic speed regulation may be achieved by operating the voltage varying device 32 from a reference signal drive from a tachometer 36, connected to the rotor shaft 26. With this arrangement, the rotor speed can be stabilized to any desired operating value. FIG. 2 is a more detailed illustration of a somewhat modified electric motor system 40 utilizing an induction motor 42. For illustrative purposes, the motor 42 is shown as the two-phase type, but it will be understood that the inven tion is applicable to three-phase motors, and also to motors of any desired number of phases. The two-phase motor 42 is shown in detail in FIG. 3. It will be seen that the motor 42 has a stator 44 with two coils for each phase. Thus, the stator 44 comprises coils 44al, 44a2, 44b1 and 44b2. The motor 42 also comprises a rotor 46having two coils for each phase. Such coils are designated as 46a 1, 46a2, 46b and 46b2. As before, the phase sequence of the rotor coils is reversed with respect to the phase sequence of the stator coils. Thus, the coils 44al and 46b1 are connected in series. Likewise, the coils 44a2 and 44b2 are connected in series. Similarly, the coils 44b1 and 46al are connected in series, while the coil 44b2 is connected in series with the coil 46a2. The motor coils in FIG. 2 have the same designations as in FIG. 3. The motor system 40 of FIG. 2 utilizes a power supply 48 which operates from alternating current and thus is in the form of a frequency converter or cycloconverter. The alternating current power to energize the cycloconverter 48 is derived from alternating current powerlines 50a, b and c. While the power source is ill lustrated as having three phases, it will be understood that any suitable number of phases may be employed. A master switch 52 with three poles 52a, b and c is preferably connected in se ries with the supply lines 50a, b and c. 3,61 1, Each set of motor coils is supplied with power by three con trolled rectifiers, or other suitable control devices, connected between the three supply phases and the particular set of coils. Thus, silicon controlled rectifiers 54a, b and care connected from the powerlines 50a, b and c to the coils 44a and 46b1. Likewise, silicon control rectifiers 56a, b and care connected from the supply lines 50a, b and c to the coils 44a2 and 46b2. Similarly, silicon control rectifiers 58a, b and care connected from the lines 50a, b and c to the coils 44b1 and 46al. Finally, silicon control rectifiers 60a, b and care connected between the lines 50a, b and cand the coils 44b2 and 46a2. In the system of FIG. 2 all of the coils are returned to a com mon line 62. Diode rectifiers 64a, b and c are connected between the line 62 and the supply lines 50a, b and c. The polarization of the rectifiers 64a, b and c is opposite to that of the silicon control rectifiers 54a-60c. It will be understood that additional motor rectifiers may be employed if desired. Thus, for example, the motor 42 may be of the three-phase type, in which case additional motor coils and silicon control rectifiers will be utilized. The firing of the silicon control rectifiers 54a-60c is con trolled by a shaft position transducer 64 having a rotary ele ment 66 which is connected to the shaft 68 of the rotor 46. As before, a speed reducing device 70 is connected between the motor shaft 68 and the rotary element 66 of the transducer 64. For the illustrated two-pole machine, the speed reducing device 70 has a ratio of 1 to 2, so that the rotary element 66 of the transducer 64 operates at one-half the speed of the motor shaft 68. The shaft position transducer is of the type which modulates a carrier signal. Such signal may be supplied by a radiofrequency generator 72. To modulate the carrier signal, the transducer 64 preferably employs a plurality of rotary vari able capacitors, one for each motor phase. Thus, the illus trated transducer 64 comprises rotary capacitors 74a and b having rotor plates 76a and b. The rotary capacitor 74a has two sets of stator plates 78a and 80a. Likewise, capacitor 74b has two sets of stator plates 78b and 80b. The rotary variable capacitors 74a and b are connected to the associated silicon control rectifiers in the same manner. It will suffice, therefore, to describe the connections employed for the capacitor 74a. The rotor 76a of the capacitor 74a is grounded. Likewise, one side of the radiofrequency generator 72 is grounded, Transformers 82a and b are employed in connection with the stator plates 78a and b. Thus, the primary winding of the trans former 82a is connected between the stator plate 78a and a line 84 leading to the ungrounded side of the generator 72. Similarly, the primary winding of the transformer 82b is con nected between the stator plate 80a and the line 84. The secondary winding of the transformer 62a is connected through a full wave bridge rectifier 86a and resistances 88a to the control electrodes or gates of the silicon controlled rectifiers 54a, b and c. In like manner, the secondary winding of the transformer 82b is connected to the gates of the silicon control rectifiers 56a, b and c through a bridge rectifier 86b and resistances 88b. Thus, the silicon controlled rectifiers are rendered conduc tive when signals are received from the shaft position trans ducer. There is a phase difference of 90 between the rotors 76a and b of the variable capacitors 74a and b. As a result, there is a phase difference of 90 between the voltages sup plied to the two sets of armature coils of the motor. The first set comprises the coils 44al, 44a2, 46b1 and 46b2. The second set comprises the coils 44b1, 44b2, 46al and 46a2. The stator plates 78a, 78b, 80a and 80b are preferably con structed and arranged for angular adjustment, so that the phase angle of the power supply output voltage can be varied, to change the speed of the motor. It is understood that the invention may be applied to a three-phase induction motor. Such an application requires the provision of three rotary variable capacitors in the shaft posi tion transducer. In that case, there is a displacement of 120 between the successive rotors.
7 S FIGS. 4 and 5 illustrate a modified shaft position transducer 94 utilizing magnetodiodes. Such diodes are solid-state devices which are responsive to magnetic fields. The re sistance of such diodes is changed in response to changing magnetic fields. The transducer 94 of FG. 4 is intended for use with a three phase induction motor. Thus, the transducer utilizes three magnetodiodes 96a, b and c, located on a stator 97 adjacent a rotary magnet 98, preferably a permanent magnet. The mag net 98 is arranged to be rotated by the shaft of the motor, as in the case of the rotary elements of the transducer 64, shown in FIG. 2. The magnetodiodes 96a, b and c of FIG. 4 are spaced apart at equal angular intervals of 120, about the rotary axis of the magnet 98. FIG. 5 illustrates the circuit which may be employed in con nection with the magnetodiode 96a. Similar circuit connec tions are employed for the magnetodiodes 96b and c. Thus, it will suffice to describe the circuit of FIG.S. It will be seen that the magnetodiode 96a comprises two diode elements 96al and 2, connected in a bridge arrange ment with two resistors 98 and 100, and a balancing poten tiometer 102. The movable tap 104 of the potentiometer 102 is employed as one of the output terminals and is grounded in FIG. 5. The other output terminal 106 is connected to the junction between the diode elements 96a1 and 2. A battery 108 and a potentiometer 110 are employed to energize the bridge circuit, comprising the diode elements 96a and 2 and the resistors 98, 100 and 102. It will be un derstood that the battery 108 represents any suitable source of direct current. The rotation of the magnet 98 varies the strength and polarity of the magnetic field at each of the magnetodiodes 96a, b and c. The corresponding variations in the resistance of the diodes are reflected as voltage variations at the outputter minals 104 and 106. These variable voltages are coupled to the control electrodes of the silicon controlled rectifiers, in much the same manner as illustrated in FIG. 2. The angular position of the stator 97 can be varied to change the phase angle of the signals from the magnetodiodes. in this way, the speed of the motor can be varied. FIG. 6 comprises graphs or curves representing the charac teristics of the motor system of the present invention. The speed of the motor is plotted against the torque developed by the motor in the solid line curves, for different values of the torque angle. The dotted line curves represent the variation of the motor current with the developed torque. The various curves are for the following values of the torque angle: Curve Number Torque Angle-Degrees S Os s 79 It will be seen from the graphs of FIG. 6 that the charac teristics of the motor system are quite similar to those of a se ries field direct current motor. The motor system of the present invention is characterized by high starting torque and high overload torque. In particular, the overload torque is two or three times as great as can be obtained from the same motor connected as an ordinary induction motor. Inasmuch as the system utilizes both the stator and the rotor as armatures, high efficiency and power output are achieved. Thus, more power output is achieved for a given size of the motor. For a particular power output the size of the motor can be minimized. I claim: 1. An electrical drive system, 3,611,082 O comprising a plural-phase double armature induction motor having a stator with a wound stator armature and a rotor with a wound rotor armature, said stator armature having a set of plural-phase stator windings, said rotor armature having a set of plural-phase rotor windings, a variable frequency power supply, means for connecting said stator and rotor windings to said variable frequency power supply for energizing said stator windings with one phase sequence while energizing said rotor windings with the opposite sequence of phase rota tion, the energization of said stator windings thereby producing a stator magnetic field rotating in one direction relative to said stator, the energization of said rotor windings thereby producing a rotor magnetic field rotating in the opposite direction relative to said rotor, and a transducer having a rotatable element connected to said rotor, said transducer having means operable by said rotatable ele ment for producing a control signal at one-half the angu lar velocity of said rotor, said transducer having control means responsive to said control signal and connected to said power supply to cause said power supply to generate alternating current power corresponding in angular velocity and phase to one-half the angular velocity and phase position of said rotor. 2. A system according to claim 1, in which said transducer is constructed to provide an ad justable torque angle between the energizing power and the rotary position of said rotor. 3. A system according to claim 1, in which said control means of said transducer comprises a source of carrier signal, and a rotary capacitor operable by the rotor and connected between said source and said power supply. 4. A system according to claim 1, in which said control means of said transducer comprises a rotatable magnet connected to said rotor, and at least one magneto-responsive element adjacent said magnet and connected to said power supply. 5. A system according to claim 4, in which said magneto-responsive element comprises a mag netodiode. 6. A system according to claim 5, in which said magnetodiode has a resistance which is varia ble in response to a varying magnetic field. 7. A system according to claim 1, in which said power supply comprises a cycloconverter operable by alternating current power of a fixed frequen cy and capable of producing an alternating current output at a variable frequency. 8. A system according to claim 7, in which said cycloconverter comprises solid-state devices having control elements connected to said control means of said transducer. 9. A system according to claim 7, in which said cycloconverter comprises controlled rectifiers having control elements connected to said control means of said transducer. 10. A system according to claim 1, in which said power supply comprises an inverter operative to convert direct current power to variable frequency al ternating current power. 11. A system according to claim 1, including speed control means connected to said power supply for varying the voltage output of said power supply. 12. A system according to claim 11,
8 7 including a tachometer operable by said rotor and con nected to said speed control means to regulate the speed of said rotor. 13. A system according to claim 1, including means for varying the output phase angle of said transducer to change the phase angle of the output from said power supply. 14. A system according to claim 1, in which said transducer comprises a rotor and a stator, 3,61 1, said system comprising means for adjusting the angular position of said transducer stator so as to vary the output phase angle of said transducer. 15. A system according to claim 1, including a phase shifter for changing the phase angle of said signalso as to vary the phase angle of the output from said power supply
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 200800301 65A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0030165 A1 Lisac (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2008 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR SUPPLYING A CHARGE WITH ELECTRIC
(19) United States US 200800301 65A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0030165 A1 Lisac (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2008 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR SUPPLYING A CHARGE WITH ELECTRIC
NSN. 2%h, WD. United States Patent (19) Vranken 4,829,401. May 9, Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 54) ROTATING TRANSFORMER WITH FOIL
 United States Patent (19) Vranken 54) ROTATING TRANSFORMER WITH FOIL WINDINGS (75) Inventor: Roger A. Vranken, Eindhoven, Netherlands (73) Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Vranken 54) ROTATING TRANSFORMER WITH FOIL WINDINGS (75) Inventor: Roger A. Vranken, Eindhoven, Netherlands (73) Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21 Appl. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070247877A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0247877 A1 KWON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2007 54) ACTIVE-CLAMP CURRENTSOURCE 3O Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070247877A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0247877 A1 KWON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2007 54) ACTIVE-CLAMP CURRENTSOURCE 3O Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,590,360 B2
 USOO659036OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Hirata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2003 (54) CONTROL DEVICE FOR PERMANENT 4,879,502 A * 11/1989 Endo et al.... 318/808 MAGNET MOTOR SERVING
USOO659036OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Hirata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2003 (54) CONTROL DEVICE FOR PERMANENT 4,879,502 A * 11/1989 Endo et al.... 318/808 MAGNET MOTOR SERVING
United States Patent (19) Hormel et al.
 United States Patent (19) Hormel et al. 54 (75) (73) 21) 22) (51) 52) (58) 56) LAMP FAILURE INDICATING CIRCUIT Inventors: Ronald F. Hormel, Mt. Clemens; Frederick O. R. Miesterfeld, Troy, both of Mich.
United States Patent (19) Hormel et al. 54 (75) (73) 21) 22) (51) 52) (58) 56) LAMP FAILURE INDICATING CIRCUIT Inventors: Ronald F. Hormel, Mt. Clemens; Frederick O. R. Miesterfeld, Troy, both of Mich.
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O168664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0168664 A1 Senda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 2, 2004 (54) ENGINE STARTER HAVING STARTER (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2004O168664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0168664 A1 Senda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 2, 2004 (54) ENGINE STARTER HAVING STARTER (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Larsen et al. USOO6844656B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,844,656 B1 Jan. 18, 2005 (54) ELECTRIC MULTIPOLE MOTOR/ GENERATOR WITH AXIAL MAGNETIC FLUX (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent Larsen et al. USOO6844656B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,844,656 B1 Jan. 18, 2005 (54) ELECTRIC MULTIPOLE MOTOR/ GENERATOR WITH AXIAL MAGNETIC FLUX (75) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Miller
 United States Patent (19) Miller 54 LAMPHOLDER FITTING WITH THREE-WAY BRIGHTNESS SOLD-STATE FLUORESCENT LAMP BALLAST 76) Inventor: Jack V. Miller, 700 N. Auburn Ave., Sierra Madre, Calif. 91024 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Miller 54 LAMPHOLDER FITTING WITH THREE-WAY BRIGHTNESS SOLD-STATE FLUORESCENT LAMP BALLAST 76) Inventor: Jack V. Miller, 700 N. Auburn Ave., Sierra Madre, Calif. 91024 21 Appl.
USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999
 USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999 54 SERIALLY CONNECTED CHARGER Primary Examiner Edward H. Tso Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Rosenberger,
USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999 54 SERIALLY CONNECTED CHARGER Primary Examiner Edward H. Tso Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Rosenberger,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2
 US007592736 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2 Scott et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 2009 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ELECTRIC (56) References Cited GENERATOR WITH ROTOR CIRCUMIFERENTIALLY
US007592736 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2 Scott et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 2009 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ELECTRIC (56) References Cited GENERATOR WITH ROTOR CIRCUMIFERENTIALLY
310/227, 228 Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Head, Johnson & Kachigian
 US005742111A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Reed 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54 D.C. ELECTRIC MOTOR 4,930,210 6/1990 Wang... 29/597 5,001,375 3/1991 Jones... 310/68 75) Inventor: Troy
US005742111A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Reed 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54 D.C. ELECTRIC MOTOR 4,930,210 6/1990 Wang... 29/597 5,001,375 3/1991 Jones... 310/68 75) Inventor: Troy
United States Patent (19) Kitami et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kitami et al. 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,846,768 Jul. 11, 1989 (54) VARIABLE-SPEED DRIVING DEVICE 75) Inventors: Yasuo Kitami; Hidenori Tezuka; 73 Assignee: Syuji
United States Patent (19) Kitami et al. 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,846,768 Jul. 11, 1989 (54) VARIABLE-SPEED DRIVING DEVICE 75) Inventors: Yasuo Kitami; Hidenori Tezuka; 73 Assignee: Syuji
3 23S Sé. -Né 33% (12) United States Patent US 6,742,409 B2. Jun. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: 6B M 2 O. (51) Int. Cl...
 (12) United States Patent Blanchard USOO6742409B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 2004 (54) DEVICE FORTRANSMISSION BETWEEN A PRIMARY MOTOR SHAFT AND AN OUTPUT SHAFT AND LAWN MOWER PROVIDED
(12) United States Patent Blanchard USOO6742409B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 2004 (54) DEVICE FORTRANSMISSION BETWEEN A PRIMARY MOTOR SHAFT AND AN OUTPUT SHAFT AND LAWN MOWER PROVIDED
United States Patent (19) Miller, Sr.
 United States Patent (19) Miller, Sr. 11 Patent Number: 5,056,448 (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 1991 (54) (76. (21) (22) 51 (52) (58) PVC BOAT Inventor: Terry L. Miller, Sr., P.O. Box 162, Afton, Okla.
United States Patent (19) Miller, Sr. 11 Patent Number: 5,056,448 (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 1991 (54) (76. (21) (22) 51 (52) (58) PVC BOAT Inventor: Terry L. Miller, Sr., P.O. Box 162, Afton, Okla.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1
 USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6989498B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,989,498 B1 Linder et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2006 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR LOCKING (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent USOO6989498B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,989,498 B1 Linder et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2006 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR LOCKING (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US009277323B2 (10) Patent No.: L0cke et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2016 (54) COMPACT AUDIO SPEAKER (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA (US) U.S.
(12) United States Patent US009277323B2 (10) Patent No.: L0cke et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2016 (54) COMPACT AUDIO SPEAKER (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA (US) U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2
 US009 168973B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2 Offe (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2015 (54) MOTORCYCLE SUSPENSION SYSTEM (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Andrew Offe, Wilunga
US009 168973B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2 Offe (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2015 (54) MOTORCYCLE SUSPENSION SYSTEM (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Andrew Offe, Wilunga
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,687,950 B2. Kuckes (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 30, 2010
 USOO768795OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,687,950 B2 Kuckes (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 30, 2010 (54) DRILLSTRING ALTERNATOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Arthur F. Kuckes,
USOO768795OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,687,950 B2 Kuckes (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 30, 2010 (54) DRILLSTRING ALTERNATOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Arthur F. Kuckes,
W. Hope. 15 Claims, 5 Drawing Figs. (52) U.S. Cl , 5ll int. Cl... F16k 43100, F16k 5/14
 United States Patent (72 inventor Clyde H. Chronister 4 Kings Row, Rte. 14, Houston, Tex. 77040 (2) Appl. No. 823,103 (22 Filed May 8, 1969 45 Patented Jan. 26, 197i. 54) GATE WALVE 15 Claims, 5 Drawing
United States Patent (72 inventor Clyde H. Chronister 4 Kings Row, Rte. 14, Houston, Tex. 77040 (2) Appl. No. 823,103 (22 Filed May 8, 1969 45 Patented Jan. 26, 197i. 54) GATE WALVE 15 Claims, 5 Drawing
(12) United States Patent
 USOO861 8656B2 (12) United States Patent Oh et al. (54) FLEXIBLE SEMICONDUCTOR PACKAGE APPARATUS HAVING ARESPONSIVE BENDABLE CONDUCTIVE WIRE MEMBER AND A MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Tac Keun.
USOO861 8656B2 (12) United States Patent Oh et al. (54) FLEXIBLE SEMICONDUCTOR PACKAGE APPARATUS HAVING ARESPONSIVE BENDABLE CONDUCTIVE WIRE MEMBER AND A MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Tac Keun.
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,080,888 B2. Hach (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006
 United States Patent US007080888B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,080,888 B2 Hach (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006 (54) DUAL NOZZLE HYDRO-DEMOLITION 6,049,580 A * 4/2000 Bodin et al.... 376/.316 SYSTEM 6,224,162
United States Patent US007080888B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,080,888 B2 Hach (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006 (54) DUAL NOZZLE HYDRO-DEMOLITION 6,049,580 A * 4/2000 Bodin et al.... 376/.316 SYSTEM 6,224,162
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD20: Last updated: 26th September 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD20: Last updated: 26th September 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2
 US009035508B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2 Grosskopf et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 19, 2015 (54) ROTATING RESISTOR ASSEMBLY H02K II/042 (2013.01); H02K II/0057 (2013.01):
US009035508B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2 Grosskopf et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 19, 2015 (54) ROTATING RESISTOR ASSEMBLY H02K II/042 (2013.01); H02K II/0057 (2013.01):
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent A USOO6208061B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,061 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) NO-LOAD GENERATOR (75) Inventor: Jong-Sok An, Chunchen (KR) (73) Assignee: Kyung-Soo Kim,
(12) United States Patent A USOO6208061B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,061 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) NO-LOAD GENERATOR (75) Inventor: Jong-Sok An, Chunchen (KR) (73) Assignee: Kyung-Soo Kim,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0072365A1 DNULOVC et al. US 2016.0072365A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (86) (30) COMMUNICATION DEVICE Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0072365A1 DNULOVC et al. US 2016.0072365A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (86) (30) COMMUNICATION DEVICE Applicant:
United States Patent (19) Muranishi
 United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
--- HG) F CURRENT (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. f 60 HG) (19) United States MEASUREMENT
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169284 A1 Park US 20120169284A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) BATTERY CHARGING METHOD AND BATTERY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0169284 A1 Park US 20120169284A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) BATTERY CHARGING METHOD AND BATTERY
US 7, B2. Loughrin et al. Jan. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: and/or the driven component. (12) United States Patent (54) (75)
 USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,255,755 B1
 USOO6255755B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Fei (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 3, 2001 (54) SINGLE PHASE THREE SPEED MOTOR 3,619,730 11/1971 Broadway et al.... 318/224 R WITH SHARED WINDINGS 3,774,062
USOO6255755B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Fei (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 3, 2001 (54) SINGLE PHASE THREE SPEED MOTOR 3,619,730 11/1971 Broadway et al.... 318/224 R WITH SHARED WINDINGS 3,774,062
(12) United States Patent
 US00704.4047B1 (12) United States Patent Bennett et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) CYLNDER MOUNTED STROKE CONTROL Inventors: Robert Edwin Bennett,
US00704.4047B1 (12) United States Patent Bennett et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) CYLNDER MOUNTED STROKE CONTROL Inventors: Robert Edwin Bennett,
"(2.4% May 4, 1954 C. A. GUSTAFSON 2,677,202. Filed April 3, l95l AND EJECTOR OF EARTH-MOWING SCRAPERS 3. Sheets-Sheet CAR. A.
 May 4, 1954 C. A. GUSTAFSON 2,677,202 HYDRAULIC ACTUATOR FOR OPERATING THE APRON Filed April 3, l95l AND EJECTOR OF EARTH-MOWING SCRAPERS 3. Sheets-Sheet INVENTOR, CAR. A. G2/S7AASOM/ "(2.4%. 2.-- ATTORME,
May 4, 1954 C. A. GUSTAFSON 2,677,202 HYDRAULIC ACTUATOR FOR OPERATING THE APRON Filed April 3, l95l AND EJECTOR OF EARTH-MOWING SCRAPERS 3. Sheets-Sheet INVENTOR, CAR. A. G2/S7AASOM/ "(2.4%. 2.-- ATTORME,
HHRH. United States Patent (19) Lissaman et al. (11) Patent Number: 5,082,079 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 1992 (51) (54) (75) (73)
 United States Patent (19) Lissaman et al. HHRH US00082079A (11) Patent Number:,082,079 (4) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 1992 (4) (7) (73) 21) 22 (1) (2) (8) PASSIVELY STABLE HOVERNG SYSTEM Inventors: Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Lissaman et al. HHRH US00082079A (11) Patent Number:,082,079 (4) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 1992 (4) (7) (73) 21) 22 (1) (2) (8) PASSIVELY STABLE HOVERNG SYSTEM Inventors: Assignee:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040085703A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0085703 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) MULTI-PULSE HVDC SYSTEM USING AUXILARY CIRCUIT (76)
(19) United States US 20040085703A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0085703 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) MULTI-PULSE HVDC SYSTEM USING AUXILARY CIRCUIT (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 01 17420A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0117420 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) BUS BAR AND BATTERY MODULE INCLUDING THE SAME (52)
US 2011 01 17420A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0117420 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) BUS BAR AND BATTERY MODULE INCLUDING THE SAME (52)
C. S. BRADLEY. ELECTRIC MOTOR. No. 439,102, Patented Oct. 28, n AA es'- Q wiza. -%%-4ge
 (No Model,) C. S. BRADLEY. 3. Sheets-Sheet 1, No. 439,102, Patented Oct. 28, 1890. ly W st 2. n AA 772279 es'- Q62-6- 27 22. wiza. -%%-4ge (No Mode.) - C. S., BR, ADLEY, 3. Sheets-Sheet 2. No. 439,102,
(No Model,) C. S. BRADLEY. 3. Sheets-Sheet 1, No. 439,102, Patented Oct. 28, 1890. ly W st 2. n AA 772279 es'- Q62-6- 27 22. wiza. -%%-4ge (No Mode.) - C. S., BR, ADLEY, 3. Sheets-Sheet 2. No. 439,102,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Yenisey 54 FUSE OR CIRCUIT BREAKER STATUS INDICATOR 75) Inventor: 73) Assignee: Osman M. Yenisey, Manalapan, N.J. AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. (21) Appl. No.: 942,878
United States Patent (19) Yenisey 54 FUSE OR CIRCUIT BREAKER STATUS INDICATOR 75) Inventor: 73) Assignee: Osman M. Yenisey, Manalapan, N.J. AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. (21) Appl. No.: 942,878
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Ogasawara et al. (54) 75 RDING LAWN MOWER Inventors: Hiroyuki Ogasawara; Nobuyuki Yamashita; Akira Minoura, all of Osaka, Japan Assignee: Kubota Corporation, Osaka, Japan Appl.
United States Patent (19) Ogasawara et al. (54) 75 RDING LAWN MOWER Inventors: Hiroyuki Ogasawara; Nobuyuki Yamashita; Akira Minoura, all of Osaka, Japan Assignee: Kubota Corporation, Osaka, Japan Appl.
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8384329B2 (12) United States Patent Natsume (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) WIPER SYSTEMAND WIPER CONTROL METHOD Inventor: Takashi Natsume, Toyohashi (JP) Assignee: ASMO Co.,
USOO8384329B2 (12) United States Patent Natsume (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) WIPER SYSTEMAND WIPER CONTROL METHOD Inventor: Takashi Natsume, Toyohashi (JP) Assignee: ASMO Co.,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fujita 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,727,957 Mar. 1, 1988 (54) RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATOR FOR MUFFLER 75 Inventor: Akio Fujita, Fujisawa, Japan 73) Assignee: Bridgestone
United States Patent (19) Fujita 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,727,957 Mar. 1, 1988 (54) RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATOR FOR MUFFLER 75 Inventor: Akio Fujita, Fujisawa, Japan 73) Assignee: Bridgestone
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,791,205 B2
 USOO6791205B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Woodbridge (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2004 (54) RECIPROCATING GENERATOR WAVE 5,347,186 A 9/1994 Konotchick... 310/17 POWER BUOY 5,696,413 A 12/1997
USOO6791205B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Woodbridge (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2004 (54) RECIPROCATING GENERATOR WAVE 5,347,186 A 9/1994 Konotchick... 310/17 POWER BUOY 5,696,413 A 12/1997
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4924,123. Hamajima et al. 45 Date of Patent: May 8, 1990
 United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4924,123 Hamajima et al. 45 Date of Patent: May 8, 1990 54) LINEAR GENERATOR 4,454,426 6/1984 Benson... 290/1 R s 8 8 4,500,827 2/1985 Merritt et al.... 322/3
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4924,123 Hamajima et al. 45 Date of Patent: May 8, 1990 54) LINEAR GENERATOR 4,454,426 6/1984 Benson... 290/1 R s 8 8 4,500,827 2/1985 Merritt et al.... 322/3
J. Brosius. disclaimed. Appl. No.: 561,873 Filed: Dec. 15, 1983 Int. Cl'... B61G 9/00 U.S. C /50; 213/56, 213/62 R
 United States Patent (19) Altherr (54) (75) 73 (*) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) 56) RALWAY CAR DRAWBAR CONNECTION WITH GUIDED SLACK ADJUSTING WEDGES Inventor: Assignee: Notice: Russell G. Altherr, Munster, Ind.
United States Patent (19) Altherr (54) (75) 73 (*) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) 56) RALWAY CAR DRAWBAR CONNECTION WITH GUIDED SLACK ADJUSTING WEDGES Inventor: Assignee: Notice: Russell G. Altherr, Munster, Ind.
United States Patent Moulton
 United States Patent Moulton 54 THREE-WHEELEED ELECTRICALLY PROPELLIED CART 72) Inventor: H. Douglass Moulton, 234 Foxhurst Drive, Pittsburgh, Pa. 15238 22 Filed: June 8, 1970 21 Appl. No.: 44,185 52 U.S.C...
United States Patent Moulton 54 THREE-WHEELEED ELECTRICALLY PROPELLIED CART 72) Inventor: H. Douglass Moulton, 234 Foxhurst Drive, Pittsburgh, Pa. 15238 22 Filed: June 8, 1970 21 Appl. No.: 44,185 52 U.S.C...
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD22: Last updated: 11th December 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent application shows the details of a device which it is claimed, can produce electricity
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD22: Last updated: 11th December 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent application shows the details of a device which it is claimed, can produce electricity
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7357465B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,357.465 B2 Young et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2008 (54) BRAKE PEDAL FEEL SIMULATOR 3,719,123 A 3/1973 Cripe 3,720,447 A * 3/1973 Harned
(12) United States Patent USOO7357465B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,357.465 B2 Young et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2008 (54) BRAKE PEDAL FEEL SIMULATOR 3,719,123 A 3/1973 Cripe 3,720,447 A * 3/1973 Harned
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,603,232 B2. Van Dine et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003
 USOO6603232B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Van Dine et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET RETAINING 4,745,319 A * 5/1988 Tomite et al.... 310/154.26 ARRANGEMENT FOR
USOO6603232B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Van Dine et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET RETAINING 4,745,319 A * 5/1988 Tomite et al.... 310/154.26 ARRANGEMENT FOR
Jan. 14, ,421,236. Filed June 22, E, U, MOYER ATTORNEYS LINKAGE FOR AN EJECTOR TYPE BUCKET, LOADER
 Jan. 14, 1969 Filed June 22, E, U, MOYER LINKAGE FOR AN EJECTOR TYPE BUCKET, LOADER ATTORNEYS Jan. 14, 1969 E. U. MOYER LINKAGE FOR AN EJECTOR TYPE BUCKET, LOADER Filed June 22, 1967 Sheet a of 2. INVENTOR
Jan. 14, 1969 Filed June 22, E, U, MOYER LINKAGE FOR AN EJECTOR TYPE BUCKET, LOADER ATTORNEYS Jan. 14, 1969 E. U. MOYER LINKAGE FOR AN EJECTOR TYPE BUCKET, LOADER Filed June 22, 1967 Sheet a of 2. INVENTOR
April 24, 1951 LE ROY S. schell, JR 2,550,500
 April 24, 1951 LE ROY S. schell, JR LOW YOKE TRANSFORMER CORE Filed Sept. 24, l943 3. Sheets-Sheet Inventor: LeRouy S. Schell, v Jr., bu-all s 73Mass 29 His Attorneu. April 24, 1951 Filed Sept. 24, 1948
April 24, 1951 LE ROY S. schell, JR LOW YOKE TRANSFORMER CORE Filed Sept. 24, l943 3. Sheets-Sheet Inventor: LeRouy S. Schell, v Jr., bu-all s 73Mass 29 His Attorneu. April 24, 1951 Filed Sept. 24, 1948
Six R. Seizi. United States Patent 19 ZKK, 2.S. NSS NEG. Sayo et al. 11 4,150, Apr. 24, ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH NS3NS
 United States Patent 19 Sayo et al. 54 ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH 75 Inventors: Kosaku Sayo, Katsuta; Seijiro Tani, Naka; Atsushi Sugirauma, Hitachi, all of Japan 73) Assignee: Hitachi, Ltd., Japan 21 Appl.
United States Patent 19 Sayo et al. 54 ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH 75 Inventors: Kosaku Sayo, Katsuta; Seijiro Tani, Naka; Atsushi Sugirauma, Hitachi, all of Japan 73) Assignee: Hitachi, Ltd., Japan 21 Appl.
s: K K Isk is is ki. It
 US007859 125B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,859,125 B2 Nielsen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010 (54) METHOD OF CONTROLLING A WIND 6,924,565 B2 * 8/2005 Wilkins et al.... 29044
US007859 125B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,859,125 B2 Nielsen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010 (54) METHOD OF CONTROLLING A WIND 6,924,565 B2 * 8/2005 Wilkins et al.... 29044
United States Patent (19) Dasa
 United States Patent (19) Dasa 54 MULTIPLE CONFIGURATION MODEL AIRCRAFT 76) Inventor: Madhava Dasa, P.O. Box 461, Kula, Hi. 96790-0461 (21) Appl. No.: 103,954 22 Filed: Oct. 2, 1987 51) Int. Cl.... A63H
United States Patent (19) Dasa 54 MULTIPLE CONFIGURATION MODEL AIRCRAFT 76) Inventor: Madhava Dasa, P.O. Box 461, Kula, Hi. 96790-0461 (21) Appl. No.: 103,954 22 Filed: Oct. 2, 1987 51) Int. Cl.... A63H
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,092,999 Lilie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2000
 i & RS USOO6092999A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,092,999 Lilie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2000 54 RECIPROCATING COMPRESSOR WITH A 4,781,546 11/1988 Curwen... 417/417 LINEAR MOTOR
i & RS USOO6092999A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,092,999 Lilie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2000 54 RECIPROCATING COMPRESSOR WITH A 4,781,546 11/1988 Curwen... 417/417 LINEAR MOTOR
United States Patent (19) Maloof
 United States Patent (19) Maloof 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 1984 54 CART WITH SEAT AND STORAGE COMPARTMENT 76 Inventor: John J. Maloof, 20 Greenwood St., East Hartford, Conn. 06118
United States Patent (19) Maloof 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 1984 54 CART WITH SEAT AND STORAGE COMPARTMENT 76 Inventor: John J. Maloof, 20 Greenwood St., East Hartford, Conn. 06118
Phillips (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 10, (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search
 (12) United States Patent US008747274B2 () Patent No.: Phillips () Date of Patent: Jun., 2014 (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search TRANSMISSION USPC... 74/3, 331; 475/207
(12) United States Patent US008747274B2 () Patent No.: Phillips () Date of Patent: Jun., 2014 (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search TRANSMISSION USPC... 74/3, 331; 475/207
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD11: Last updated: 3rd February 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly Electrical power is frequently generated by spinning the shaft of a generator which has some
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD11: Last updated: 3rd February 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly Electrical power is frequently generated by spinning the shaft of a generator which has some
360 MECH, United States Patent. (15) 3,705,459 (45) Dec. 12, 1972
 United States Patent Biddison - (54) WAVE WINDING OF ARMATURES (72) Inventor: John M. Biddison, Dayton, Ohio 73) Assignee: The Globe Tool and Engineering Company, Dayton, Ohio 22 Filed: June 24, 1971 21
United States Patent Biddison - (54) WAVE WINDING OF ARMATURES (72) Inventor: John M. Biddison, Dayton, Ohio 73) Assignee: The Globe Tool and Engineering Company, Dayton, Ohio 22 Filed: June 24, 1971 21
April 2, 1968 A. L. NASVYTIs 3,375,739 CONICAL, PLANETARY FRICTION GEAR DRIVE Filed Feb. 17, Sheets-Sheet l N. N S
 April 2, 1968 A. L. NASVYTIs CONICAL, PLANETARY FRICTION GEAR DRIVE Filed Feb. 17, 1966 3 Sheets-Sheet l st SS N. N S A. N S INVENTOR. 167/raas Z. Maszy/7s -3% 1%-1. 72e-este, "4e 71-16tz,ORNEYS April
April 2, 1968 A. L. NASVYTIs CONICAL, PLANETARY FRICTION GEAR DRIVE Filed Feb. 17, 1966 3 Sheets-Sheet l st SS N. N S A. N S INVENTOR. 167/raas Z. Maszy/7s -3% 1%-1. 72e-este, "4e 71-16tz,ORNEYS April
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,939,978 B2
 US007939978B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Best et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 2011 (54) ELECTRIC MOTOR (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Dieter Best, Ingelfingen (DE); Michael Sturm,
US007939978B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Best et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 2011 (54) ELECTRIC MOTOR (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Dieter Best, Ingelfingen (DE); Michael Sturm,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2
 USOO8721495 B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 8,721.495 B2 Kitamura et al. () Date of Patent: May 13, 2014 (54) REAR DERAILLEUR AND GEARSHIFT 6,380,731 B1 4/2002 Nishimoto SYSTEM 7,015,598
USOO8721495 B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 8,721.495 B2 Kitamura et al. () Date of Patent: May 13, 2014 (54) REAR DERAILLEUR AND GEARSHIFT 6,380,731 B1 4/2002 Nishimoto SYSTEM 7,015,598
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,892,675 Yatsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999
 USOO5892675A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Yatsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999 54 ACCURRENT SOURCE CIRCUIT FOR 4,876,635 10/1989 Park et al.... 363/17 CONVERTING DC VOLTAGE INTO
USOO5892675A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Yatsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999 54 ACCURRENT SOURCE CIRCUIT FOR 4,876,635 10/1989 Park et al.... 363/17 CONVERTING DC VOLTAGE INTO
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9, B2
 USOO9482426B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,482.426 B2 Diotte (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 1, 2016 (54) ILLUMINABLE WALL SOCKET PLATES 24/78 (2013.01); F2IV 23/0442 (2013.01); AND SYSTEMIS
USOO9482426B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,482.426 B2 Diotte (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 1, 2016 (54) ILLUMINABLE WALL SOCKET PLATES 24/78 (2013.01); F2IV 23/0442 (2013.01); AND SYSTEMIS
United States Patent (19) Edahiro et al.
 United States Patent (19) Edahiro et al. 54 REAR SUSPENSION SYSTEM FOR FOUR-WHEEL-STEERED VEHICLE 75 Inventors: Takeshi Edahiro; Seita Kanai; Kouichi Ushio, all of Hiroshima, Japan 73 Assignee: Mazda Motor
United States Patent (19) Edahiro et al. 54 REAR SUSPENSION SYSTEM FOR FOUR-WHEEL-STEERED VEHICLE 75 Inventors: Takeshi Edahiro; Seita Kanai; Kouichi Ushio, all of Hiroshima, Japan 73 Assignee: Mazda Motor
3.s. isit. United States Patent (19) Momotet al. 2 Šg. 11 Patent Number: 4,709,634 (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 1, Zxx (54) (75) (73)
 United States Patent (19) Momotet al. (54) (75) (73) (1) () 51 5 (58) 56) PLATE CYLNDER REGISTER CONTROL Inventors: Stanley Momot, La Grange; William G. Hannon, Westchester, both of Ill. Assignee: Rockwell
United States Patent (19) Momotet al. (54) (75) (73) (1) () 51 5 (58) 56) PLATE CYLNDER REGISTER CONTROL Inventors: Stanley Momot, La Grange; William G. Hannon, Westchester, both of Ill. Assignee: Rockwell
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,007,548 B2
 USOO7007548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Jahn et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 7, 2006 (54) ROAD TEST SIMULATOR WITH PLURAL 3,520,180 A 7/1970 Ris et al.... 73/670 ROLLERS 4,385,518 A *
USOO7007548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Jahn et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 7, 2006 (54) ROAD TEST SIMULATOR WITH PLURAL 3,520,180 A 7/1970 Ris et al.... 73/670 ROLLERS 4,385,518 A *
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Hozumi et al. 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,889,164 Dec. 26, 1989 54). SOLENOID CONTROLLED WALVE (75 Inventors: Kazuhiro Hozumi; Masaru Arai, both of Chiba; Yoshitane
United States Patent (19) Hozumi et al. 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,889,164 Dec. 26, 1989 54). SOLENOID CONTROLLED WALVE (75 Inventors: Kazuhiro Hozumi; Masaru Arai, both of Chiba; Yoshitane
Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) J (12) Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 774 824 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: ition: (51) IntCI.6: H02K 3/52, H02K
(19) J (12) Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 774 824 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: ition: (51) IntCI.6: H02K 3/52, H02K
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0044499 A1 Dragan et al. US 20100.044499A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SIX ROTOR HELICOPTER Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0044499 A1 Dragan et al. US 20100.044499A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SIX ROTOR HELICOPTER Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Koitabashi
 United States Patent (19) Koitabashi 54 75 (73) 1 (51) (5) (58 56) ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH WITH AN IMPROVED MAGNETC ROTATABLE MEMBER Inventor: Takatoshi Koitabashi, Annaka, Japan Assignee: Sanden Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Koitabashi 54 75 (73) 1 (51) (5) (58 56) ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH WITH AN IMPROVED MAGNETC ROTATABLE MEMBER Inventor: Takatoshi Koitabashi, Annaka, Japan Assignee: Sanden Corporation,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0312869A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0312869 A1 WALTER (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016 (54) CVT DRIVE TRAIN Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2016.0312869A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0312869 A1 WALTER (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016 (54) CVT DRIVE TRAIN Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001 0023637A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0023637 A1 Klitmose et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2001 (54) FLEXIBLE PISTON ROD (76) Inventors: Lars Peter
(19) United States US 2001 0023637A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0023637 A1 Klitmose et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2001 (54) FLEXIBLE PISTON ROD (76) Inventors: Lars Peter
(12) United States Patent
 US007307230B2 (12) United States Patent Chen (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,307,230 B2 Dec. 11, 2007 (54) MECHANISM FOR CONTROLLING CIRCUITCLOSINGAOPENING OF POWER RATCHET WRENCH (75) Inventor:
US007307230B2 (12) United States Patent Chen (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,307,230 B2 Dec. 11, 2007 (54) MECHANISM FOR CONTROLLING CIRCUITCLOSINGAOPENING OF POWER RATCHET WRENCH (75) Inventor:
$s. I 2 ;" (12) United States Patent US 6,975,908 B1. Dec. 13, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Njdskov (54) HANDHELD PIEZOELECTRIC
 (12) United States Patent Njdskov USOO6975908B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 13, 2005 (54) HANDHELD PIEZOELECTRIC ACUPUNCTURE STIMULATOR (75) Inventor: Preben Nodskov, Rungsted Kyst (DK)
(12) United States Patent Njdskov USOO6975908B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 13, 2005 (54) HANDHELD PIEZOELECTRIC ACUPUNCTURE STIMULATOR (75) Inventor: Preben Nodskov, Rungsted Kyst (DK)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO64994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Matsumoto (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) STATIONARY BIKE (52) U.S. Cl.... 482/8 (76) Inventor: Masaaki Matsumoto,
(19) United States US 2005OO64994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Matsumoto (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) STATIONARY BIKE (52) U.S. Cl.... 482/8 (76) Inventor: Masaaki Matsumoto,
Earl Sch yang y Lee, 5,457,342 10/1995 Herbst, II /712
 US005920264A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM PROTECTION 5,189,314 2/1993 Georgiou et al.... 307/271 DEVICE 5,287.292 2/1994
US005920264A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM PROTECTION 5,189,314 2/1993 Georgiou et al.... 307/271 DEVICE 5,287.292 2/1994
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201201.07098A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0107098 A1 Tirone, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 3, 2012 (54) GASTURBINE ENGINE ROTOR TIE SHAFT (52) U.S.
(19) United States US 201201.07098A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0107098 A1 Tirone, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 3, 2012 (54) GASTURBINE ENGINE ROTOR TIE SHAFT (52) U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,178,395 B2
 US009 178395 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,178,395 B2 Qin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 3, 2015 (54) TRACTION MOTOR FOR ELECTRIC 5,783,891 A * 7/1998 Auinger et al.... 310,180 VEHICLES
US009 178395 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,178,395 B2 Qin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 3, 2015 (54) TRACTION MOTOR FOR ELECTRIC 5,783,891 A * 7/1998 Auinger et al.... 310,180 VEHICLES
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Hodgetts (54) (75) 73 (1) ) (51) (5) (58) (56) NTERNALLY MUNTED DRIVE MECHANISM FR A BELT-WINDING DRUM Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Graham L. Hodgetts, Mars, Pa. Rolflor
United States Patent (19) Hodgetts (54) (75) 73 (1) ) (51) (5) (58) (56) NTERNALLY MUNTED DRIVE MECHANISM FR A BELT-WINDING DRUM Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Graham L. Hodgetts, Mars, Pa. Rolflor
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) USOO5287906A 11 Patent Number: 5,287,906 Stech (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 22, 1994 54 AIR CONTROL SYSTEM FOR PNEUMATIC 3,100,6 8/1963 Work... 285/33 TRES ON A WEHICLE 4,387,931
United States Patent (19) USOO5287906A 11 Patent Number: 5,287,906 Stech (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 22, 1994 54 AIR CONTROL SYSTEM FOR PNEUMATIC 3,100,6 8/1963 Work... 285/33 TRES ON A WEHICLE 4,387,931
O E. (12) United States Patent US 7,187,087 B sa. Mar. 6, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.:
 US007 187087B2 (12) United States Patent Khalizadeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2007 (54) FLYWHEEL SYSTEM WITH SYNCHRONOUS RELUCTANCE AND PERMANIENT MAGNET GENERATORS (75) Inventor: Claude
US007 187087B2 (12) United States Patent Khalizadeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2007 (54) FLYWHEEL SYSTEM WITH SYNCHRONOUS RELUCTANCE AND PERMANIENT MAGNET GENERATORS (75) Inventor: Claude
(12) United States Patent
 US0088.33729B2 (12) United States Patent Bill et al. (10) Patent o.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,833,729 B2 Sep. 16, 2014 (54) PROPORTIOAL THROTTLE VALVE (75) Inventors: Markus Bill, Heusweiler (DE); Peter
US0088.33729B2 (12) United States Patent Bill et al. (10) Patent o.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,833,729 B2 Sep. 16, 2014 (54) PROPORTIOAL THROTTLE VALVE (75) Inventors: Markus Bill, Heusweiler (DE); Peter
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8905448B2 (12) United States Patent Vaz Coelho et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,905,448 B2 Dec. 9, 2014 (54) SIZE-ADJUSTABLE, PIVOTABLE TRIPLE CONNECTION DEVICE (75) Inventors: Joao
USOO8905448B2 (12) United States Patent Vaz Coelho et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,905,448 B2 Dec. 9, 2014 (54) SIZE-ADJUSTABLE, PIVOTABLE TRIPLE CONNECTION DEVICE (75) Inventors: Joao
United States Patent (19) Woodburn
 United States Patent (19) Woodburn 54 (76) 21) 22 (51) 52 58 56 MOTOR VEHICLE AND BOAT TRALER Inventor: Clarence A. Woodburn, 43884 Pioneer Ave., Hemet, Calif. 92344 Appl. No.: 329,163 Filed: Mar. 17,
United States Patent (19) Woodburn 54 (76) 21) 22 (51) 52 58 56 MOTOR VEHICLE AND BOAT TRALER Inventor: Clarence A. Woodburn, 43884 Pioneer Ave., Hemet, Calif. 92344 Appl. No.: 329,163 Filed: Mar. 17,
No. 714,412. Patented Nov. 25, C. P. SEN METZ. INDUCTION MOTOR. Application filed Mar. 22, 1900.) (No Mode.) 2 Sheets-Sheet. N.W. S.
 No. 714,412. Patented Nov., 1902. C. P. SEN METZ. INDUCTIN MTR. Application filed Mar. 22, 1900.) (No Mode.) 2 Sheets-Sheet. N.W. S. - S N N SS s N N 2 ES Ese V SS His S. NS i SS Sir still All 2 H2SHA
No. 714,412. Patented Nov., 1902. C. P. SEN METZ. INDUCTIN MTR. Application filed Mar. 22, 1900.) (No Mode.) 2 Sheets-Sheet. N.W. S. - S N N SS s N N 2 ES Ese V SS His S. NS i SS Sir still All 2 H2SHA
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,900,734 Munson (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 1999
 USOO5900734A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,900,734 Munson (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 1999 54) LOW BATTERY VOLTAGE DETECTION 5,444,378 8/1995 Rogers... 324/428 AND WARNING SYSTEM 5,610,525
USOO5900734A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,900,734 Munson (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 1999 54) LOW BATTERY VOLTAGE DETECTION 5,444,378 8/1995 Rogers... 324/428 AND WARNING SYSTEM 5,610,525
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Belanger et al. 4 MECHANISM FOR GLUE GUN (76) Inventors: (21) 22 (1) 2) 8 (6) Richard W. Belanger, 2 Collins St., Amesbury, Mass. 01913; Peter S. Melendy, 11 Crestview Dr., Exeter,
United States Patent (19) Belanger et al. 4 MECHANISM FOR GLUE GUN (76) Inventors: (21) 22 (1) 2) 8 (6) Richard W. Belanger, 2 Collins St., Amesbury, Mass. 01913; Peter S. Melendy, 11 Crestview Dr., Exeter,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0068960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0068960 A1 Kopecek (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2006 (54) DRIVE ASSEMBLIES Publication Classification (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2006.0068960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0068960 A1 Kopecek (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2006 (54) DRIVE ASSEMBLIES Publication Classification (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,899,031 B2
 US008899.031B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,899,031 B2 Turnis et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2014 (54) COLD START VALVE (58) Field of Classification Search CPC... F15B 21/042: F15B
US008899.031B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,899,031 B2 Turnis et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2014 (54) COLD START VALVE (58) Field of Classification Search CPC... F15B 21/042: F15B
United States Patent 19 [11] Patent Number: 4,877,983 Johnson (45) Date of Patent: Oct 31, 1989
![United States Patent 19 [11] Patent Number: 4,877,983 Johnson (45) Date of Patent: Oct 31, 1989 United States Patent 19 [11] Patent Number: 4,877,983 Johnson (45) Date of Patent: Oct 31, 1989](/thumbs/80/81257393.jpg) United States Patent 19 [11] Patent Number: 4,877,983 Johnson (45) Date of Patent: Oct 31, 1989 54 MAGNETICFORCE GENERATING 56 References Cited METHOD AND APPARATUS U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,074,153 2/1978
United States Patent 19 [11] Patent Number: 4,877,983 Johnson (45) Date of Patent: Oct 31, 1989 54 MAGNETICFORCE GENERATING 56 References Cited METHOD AND APPARATUS U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,074,153 2/1978
United States Patent (19) Kline et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kline et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 1990 54 BRAKING SYSTEMAND BREAK-AWAY BRAKNG SYSTEM 76 Inventors: Wayne K. Kline, R.D. 1, Box 340, Turbotville, Pa. 17772;
United States Patent (19) Kline et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 1990 54 BRAKING SYSTEMAND BREAK-AWAY BRAKNG SYSTEM 76 Inventors: Wayne K. Kline, R.D. 1, Box 340, Turbotville, Pa. 17772;
United States Patent (19) Priede
 United States Patent (19) Priede 11 Patent Number: Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 1988 54 CLOCKSPRING INTERCONNECTOR 75 Inventor: Lorenz H. Priede, Valparaiso, Ind. 73 Assignee: Method Electronics, Inc., Chicago,
United States Patent (19) Priede 11 Patent Number: Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 1988 54 CLOCKSPRING INTERCONNECTOR 75 Inventor: Lorenz H. Priede, Valparaiso, Ind. 73 Assignee: Method Electronics, Inc., Chicago,
June 25, 1968 ROTH 3,389,738 WINDOW SHADE APPARATUS FG. 2ASE. 4b. NVENTOR LEO ROTH. was 11- a-40, 2.11u1 2y 7. A2-2.1a-42a (arte?. ATTORNEYS.
 June 25, 1968 RTH 3,389,738 Filed Feb. 23, l967 FG. WINDW SHADE APPARATUS 2 Sheets-Sheet 2ASE 35 WF 9 4b. BY year NVENTR LE RTH 2.11u1 2y 7 was 11- a-40, A2-2.1a-42a (arte?. ATTRNEYS. June 25, 1968 RTH
June 25, 1968 RTH 3,389,738 Filed Feb. 23, l967 FG. WINDW SHADE APPARATUS 2 Sheets-Sheet 2ASE 35 WF 9 4b. BY year NVENTR LE RTH 2.11u1 2y 7 was 11- a-40, A2-2.1a-42a (arte?. ATTRNEYS. June 25, 1968 RTH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0159457 A1 Saint-Marc et al. US 2016015.9457A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) RUDDER BAR FOR AN AIRCRAFT (71) Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0159457 A1 Saint-Marc et al. US 2016015.9457A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) RUDDER BAR FOR AN AIRCRAFT (71) Applicant:
Avitan 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, MATERIAL HANDLING VEHICLE /1986 Holland /252 X
 United States Patent (19) 11 USOO528598A Patent Number: Avitan 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1992 54 MATERIAL HANDLING VEHICLE 4.573.548 3/1986 Holland... 180/252 X STEERING SYSTEM 4,683.973 8/1987 Honjo
United States Patent (19) 11 USOO528598A Patent Number: Avitan 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1992 54 MATERIAL HANDLING VEHICLE 4.573.548 3/1986 Holland... 180/252 X STEERING SYSTEM 4,683.973 8/1987 Honjo
United States Patent (19) Cox
 United States Patent (19) Cox 54 CAPACITOR TESTING APPARATUS 76) Inventor: Elbert W. Cox, P. O. Box 770, The Dalles, Oreg. 21 Appl. No.: 883,142 22 Filed: Mar. 3, 1978 51) Int. C.... G01R 27/26 52 U.S.
United States Patent (19) Cox 54 CAPACITOR TESTING APPARATUS 76) Inventor: Elbert W. Cox, P. O. Box 770, The Dalles, Oreg. 21 Appl. No.: 883,142 22 Filed: Mar. 3, 1978 51) Int. C.... G01R 27/26 52 U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O231027A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0231027 A1 SU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 16, 2010 (54) WHEEL WITH THERMOELECTRIC (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2010O231027A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0231027 A1 SU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 16, 2010 (54) WHEEL WITH THERMOELECTRIC (30) Foreign Application Priority
United States Patent (19) Mathis
 United States Patent (19) Mathis 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,884,545 Dec. 5, 1989 54 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM FOR AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (75) Inventor: Christian Mathis, Arbon, Switzerland
United States Patent (19) Mathis 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,884,545 Dec. 5, 1989 54 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM FOR AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (75) Inventor: Christian Mathis, Arbon, Switzerland
United States Patent (19) Yamauchi et al.
 United States Patent (19) Yamauchi et al. 54). GAS INSULATED SWITCHGEAR APPARATUS 75 Inventors: Takao Yamauchi; Masazumi Yamamoto; Kiyokazu Torimi; Hiroki Sanuki, all of Tokyo, Japan 73 Assignee: Mitsubishi
United States Patent (19) Yamauchi et al. 54). GAS INSULATED SWITCHGEAR APPARATUS 75 Inventors: Takao Yamauchi; Masazumi Yamamoto; Kiyokazu Torimi; Hiroki Sanuki, all of Tokyo, Japan 73 Assignee: Mitsubishi
