Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p References: Photovoltaic Systems, Chap. 7 National Electrical Code (NEC), Articles 110,
|
|
|
- Hilda Henderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Charge controllers are required in most PV systems using a battery to protect against battery overcharging and overdischarging. There are different types of charge controller design, and their specifications dictate their intended operating limits and applications. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p. 175 References: Photovoltaic Systems, Chap. 7 National Electrical Code (NEC), Articles 110,
2 A charge controller is equipment used to regulate the charging of a battery, by limiting the voltage and/or current from the charging source such as a PV array. Charge control is required for most PV systems that use batteries. Charge control may not be required for very small systems, where the PV array has been carefully matched to the voltage and current charging requirements of the battery, and the maximum charge current multiplied by one hour is less than 3 percent of the manufacturer s rated ampere-hour capacity. For example, a 200 ampere-hour battery charged by a PV array producing a maximum charging current of 6 amps or higher requires charge control. Charge controllers used in PV system vary widely in their size, functions and features. Suggested Exercise: Review charge controller manufacturer s specifications and installation instructions. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p References: NEC (A), Photovoltaic Systems, p
3 The primary function of charge controllers is to prevent battery overcharge. Many charge controllers also provide overdischarge protection for the battery by disconnecting DC loads at low voltage and low state-of-charge condition. Additional functions may also be performed by charge controllers, including controlling lighting loads or multiple energy sources. Special controllers are also available that regulate battery charge by diverting excess power to auxiliary loads. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p References: Photovoltaic Systems, p See video clip on CD-ROM
4 Charge controllers are also used to protect a battery from excessively deep discharges that can damage the battery and shorten its life. Typically, the controller disconnects DC loads at a predetermined battery voltage, corresponding to low state-of-charge conditions. High-current DC utilization equipment like inverters are usually connected directly to batteries rather than through charge controllers, and have integral low-voltage disconnect means. A charge controller may protect a battery from both overcharge and/or overdischarge with the same unit or separate equipment. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p Charge controllers are classified by the way they regulate the PV array current and battery charging process. The charging current from a PV array can be controlled by either short-circuiting (shunt) or by open-circuiting (series) the PV array. A charge controller algorithm is the method of charge regulation. Simple interrupting type controllers regulate the PV array current in an on-off manner, while more advanced algorithms use multi-stage methods. Solid-state switching devices can be used to regulate array current at high-frequencies or in a linear manner to gradually reduce current applied to the battery as it reaches full state-of-charge. Some charge controllers also provide array maximum power point tracking. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p
5 A shunt charge controller regulates battery charging by short-circuiting the PV array. Since PV arrays are current-limited, this does not harm the array. However, a blocking diode is required to prevent short-circuiting the battery. The shunt device can be a power transistor, Zener diode or a linear solid-state device that shortcircuits the PV array or decreases the shunt resistance as the battery reaches full charge. Shunt-type controllers are usually limited to 20 amps due to their heat dissipation requirements. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p A Zener diode can be used as the short-circuiting device for a shunt-type controller. The Zener diode (D1) conducts current in the reverse direction once the diode breakdown voltage is reached, regulating the array current while holding the battery at constant voltage. The value for the Resistor R1 is determined by voltage drop across R1 divided by the circuit current. Assuming the circuit current is 400 ma, and the voltage drop is 5 volts, then the value of R1 would be 5 V/0.4 A = 21.5 ohms, and the minimum power rating for the resistor should be 0.4 A x 5 V = 2 watts. The Zener diode should have a Zener (breakdown) voltage of approximately 14 volts for a nominal 12 V lead-acid battery, and be rated for at least 156% of the PV module short-circuit current. The minimum power rating for the Zener diode should be at least the Zener voltage times the circuit current, or 14 V x 0.4 A = 5.6 watts. Diode D2 may be an inexpensive silicon diode, with a current rating of at least 156% of the maximum PV module short circuit current, and a voltage rating 125% of the PV module open-circuit voltage. This diode prevents reverse current flow from the battery to the PV module at night and when the Zener diode is regulating. Suggested Exercise: Build and test a simple Zener diode shunt charge controller using small components
6 A series charge controller regulates battery charging by open-circuiting the PV array. The series element can be a power transistor or a linear solid-state device that open-circuits the PV array or increases the series resistance as the battery reaches full charge. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p Pulse-Width-Modulation (PWM) charge controllers regulate battery charge by modulating the charging current on a high-frequency carrier signal. When the battery is at lower state-of-charge, the width of the current pulses is wider, applying the full charge current to the battery for a longer interval. When the battery approaches full charge, the width of the current pulses narrows, limiting the current to the battery. PWM controllers can be either shunt or series types. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p
7 MPPT charge controllers operate PV arrays at maximum power under all operating conditions independent of battery voltage. Typically, the PV array is configured at higher voltages than the battery, and DC to DC power conversion circuits in the controller automatically provides a lower voltage and higher current output to the battery. MPPT controllers can improve array energy utilization and allow nonstandard and higher array operating voltages, requiring smaller conductors and fewer source circuits. A diversionary charge controller diverts excess PV array power to auxiliary loads when the primary battery system is fully charged, allowing a greater utilization of PV array energy. Whenever a diversionary charge controller is used, a second independent charge controller is required to prevent battery overcharge in the event the diversion loads are unavailable or the diversion charge controller fails. The additional charge controller uses a higher regulation voltage, and permits the diversionary charge controller to operate as the primary control. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p. 184 References: NEC (B)(1) Photovoltaic Systems, p See video clip on CD-ROM
8 Several requirements apply to PV systems using DC diversionary loads and DC diversion charge controllers. These requirements are intended to help prevent hazardous conditions and protect the battery if the diversion controller fails or the DC loads are unavailable. References: NEC (B)(2) Photovoltaic Systems, p Some interactive PV systems use battery-based inverters as a backup power source when the utility is de-energized. These systems must also have a second independent charge controller to prevent battery overcharge when the grid or loads are not available to divert excess power. Normally, these systems regulate the battery charge by diverting excess PV array DC power through the inverter to produce AC power to feed site loads or the grid. When the grid de-energizes, an automatic transfer switch disconnects loads from utility network and the system operates in stand-alone mode. If all loads have been met and the grid is not available, the battery can be overcharged. References: NEC (B)(3) Photovoltaic Systems, p
9 Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p Set points are the battery voltage levels at which a charge controller performs regulation or control functions. The regulation voltage (VR) is the maximum voltage set point the controller allows the battery to reach before the array current is disconnected or limited. For interrupting type controllers, the array reconnect voltage (ARV) is the voltage set point at which the array is again reconnected to charge the battery. The regulation voltage hysteresis (VRH) is difference or span between the VR and ARV set points. PWM and constant-voltage type controllers do not have a definable ARV. The proper VR and VRH set points are critical for optimal battery charging. The low-voltage disconnect (LVD) is the battery voltage set point at which the controller disconnects the system loads to prevent overdischarge. The LVD defines the maximum battery depth-of-discharge at the given discharge rate. The load reconnect voltage (LRV) set point is the voltage that load are permitted to be reconnected to the battery. The low-voltage disconnect hysteresis (LVDH) is the voltage difference between the LVD and LRV. A higher LRV and LVDH allow a battery to receive more charge before loads are reconnected to the battery
10 Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p Optimal charge regulation set points depend on the type of battery and control method used. Higher charge regulation voltages are required for all types of batteries using interrupting type controllers, compared to more effective constantvoltage, PWM or linear designs. References: Photovoltaic Systems, p Charge controller and battery manufacturer s specifications
11 References: Photovoltaic Systems, p Charge controller and battery manufacturer s specifications. Some charge controllers provide the capability for manual or automatic or equalization charging. The equalization charge settings may be programmable, or set with jumpers on the controller circuit board. Equalization charging is performed on flooded, open-vent batteries to help minimize differences and restore consistency between individual cells, and can help reduce sulfation and stratification. Flooded lead-acid batteries are normally equalized at approximately 2.6 volts per cell (VPC) at 25 C for 1-3 hour periods once or twice a month. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p
12 Charge controller set point adjustments may be fixed, programmable or manually adjusted by the installer. Because improper charge control settings may create a hazardous condition for batteries, any adjusting means for a charge controller must only be accessible to qualified persons. Suggested Exercise: Use a min/max recording voltmeter the measure and adjust the charge controller set points in a small stand-alone PV system. References: NEC (A) Photovoltaic Systems, p Temperature compensation is a feature of charge controllers that automatically adjusts the charge regulation voltage for battery temperature changes. Where battery temperatures vary seasonally more than 10 C, compensation of the charge regulation set point is normally used. Temperature compensation is also recommended for all types of sealed batteries, which are much more sensitive to overcharging than flooded types. Temperature compensation helps to fully charge a battery during colder conditions, and helps protect it from overcharge during warmer conditions. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p
13 Temperature compensation sensors are used to monitor battery temperature remotely from a charge controller. This is particularly important where the controller and battery are located in different enclosures or thermal environments. Sensors are typically resistive thermal devices (RTDs) that vary resistance with temperature. Some sensors are intended to be permanently affixed to the sides of the internal battery bank, while others are connected to the negative battery terminal. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p
14 These two charts illustrate the daily operating characteristics for a small stand-alone PV lighting system operating with a shunt-interrupting charge controller. Beginning at the left on the charts (midnight), the light is operating and discharging the battery at about 3 amps (Ibat), while the battery voltage decreases from about 12.1 volts to 11.9 volts. Just after 0400 hours, the load is disconnected by the charge controller load timing circuit, the battery current (Ibat) goes to zero, and the battery voltage (Vbat) rises to about 12.3 volts. At sunrise (0700 hours), the battery voltage increases as the PV array begins to recharge the battery. Until about noon time (1200 hours), the charging current (Ipv) and the battery voltage (Vbat) increase steadily with increasing solar irradiance as the battery is being recharged. Note that during this period, the battery charge controller is not regulating and the PV array current is approximately the same as the battery current. At about noon, the battery voltage reaches the charge controller regulation voltage (about 14.1 volts), and the controller begins to regulate the battery current in an on-off manner. Because the shunt controller short-circuits the PV array, the average PV array current follows the solar irradiance while the average PV array voltage reduces to about 5 volts, indicating regulation. With the onset of regulation, the minimum and maximum battery voltages are distinguished from the six-minute average voltage, and show the approximate charge controller set points. After regulation, the maximum battery voltage is between 14.3 and 14.5 volts and corresponds to the voltage regulation set point. The minimum battery voltage is about 13.7 volts, corresponding to the point at which the charge controller reconnects the array to the battery to resume charging. Towards the end of the sunlight hours ( hours), the PV array current output reduces to a low enough value, in this case about 2.5 amps, where regulation is not required to limit the battery voltage below the charge regulation set point, and the PV array remains connected to the battery for the remainder of the day. Once the sun sets (about 1800 hours), the battery voltage begins a gradual decrease to its steady-state voltage. Note how the battery voltage at this time is higher than in the morning before the battery was recharged. At about 2030 hours, the 3 amp lighting load is again connected and the battery voltage begins to steadily decrease. These two charts illustrate the daily operating characteristics for a small stand-alone PV lighting system operating with a series-interrupting charge controller. Beginning at the left on the charts (midnight), the light is operating and discharging the battery at about 3 amps (Ibat), while the battery voltage decreases from about 11.9 volts to 11.7 volts. Just after 0400 hours, the load is disconnected by the charge controller load timing circuit, the battery current (Ibat) goes to zero, and the battery voltage (Vbat) rises to about 12.1 volts. At sunrise (0700 hours), the battery voltage increases as the PV array begins to recharge the battery. Until about noon time (1200 hours), the charging current (Ipv) and the battery voltage (Vbat) increase steadily with increasing solar irradiance as the battery is being recharged. Note that during this period, the battery charge controller is not regulating and the PV array current is approximately the same as the battery current. At about noon, the battery voltage reaches the charge controller regulation voltage (about 14.1 volts), and the controller begins to regulate the battery current in an on-off manner. Because the series controller open-circuits the PV array, the average PV array current decreases while the average PV array voltage approaches the array open-circuit voltage. With the onset of regulation, the minimum and maximum battery voltages are distinguished from the six-minute average voltage, and show the approximate charge controller set points. After regulation, the maximum battery voltage is about 14.1 volts and corresponds to the voltage regulation set point. The minimum battery voltage is between 13.2 and 13.4 volts, corresponding to the point at which the charge controller reconnects the array to the battery to resume charging. Once the sun sets (about 1800 hours), the battery voltage begins a gradual decrease to its steadystate voltage. Note how the battery voltage at this time is higher than in the morning before the battery
15 was recharged. At about 2030 hours, the 3 amp lighting load is again connected and the battery voltage begins to steadily decrease. These two charts illustrate the daily operating characteristics for a small stand-alone PV lighting system operating with a series pulse-width-modulated charge controller. Beginning at the left of the two graphs (midnight), the load is operating and battery voltage decreases steadily from about 12.2 volts to 11.9 volts while being discharged at about 3 amps. At about 0430 hours, the load is disconnected, the battery current goes to zero, and there is a sharp rise in the battery voltage as it approaches steady-state of about 12.3 volts. At sunrise (about 0700 hours), the battery voltage begins to increase as the PV array current charges the battery. Before noon, the PV array current and battery voltage increase steadily with increasing solar irradiance as the battery is being recharged. At noon, the battery voltage reaches the regulation voltage set point for the charge controller (about 14.5 volts), and the controller begins to regulate the PV array current for the remainder of the day. The series switching characteristic can be seen by the fact that once regulation begins, the average PV array current also decreases, while the average PV array voltage approaches the open-circuit array voltage. The PWM controller regulates the array by decreasing current pulses to the battery, which are modulated on a high-frequency carrier signal. When the regulation voltage is reached, the current pulses are gradually reduced to hold the battery voltage at the regulation set point, as long as array current is available
16 Advanced charge controllers use a multi-stage charging process, and have multiple set points. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p. 156, 178 Multiple charge controllers may be used on individual subarrays for larger systems. One subarray may be directly connected to battery without charge control if the charge current multiplied by one hour is less than 3% of the battery capacity, and may improve battery finishing charge. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p
17 Voltage drop in the circuit from a charge controller to a battery can result in charge regulation occurring at lower battery voltages than the controller set points. Some battery charge controllers have separate connections to measure battery voltage independent of the conductors that carry the charging current. These additional sensing leads measure voltage directly at the battery terminals, and eliminate the affects of voltage drop on the charge regulation set points. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p Self-regulating PV systems are stand-alone PV systems using batteries that are designed to operate without charge control. Charge control may only be eliminated under special circumstances when the load is well-defined and the battery is oversized with respect to the charging source. The U.S. Coast Guard commonly uses self-regulating PV systems for navigational aids. Suggested Exercise: Discuss the design requirements for self-regulating standalone PV systems. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p
18 Special lower-voltage PV modules are used in self-regulating systems. Typically, 36 series-connected silicon solar cells are required to provide adequate charging voltage for nominal 12-volt batteries in PV systems using charge control. For selfregulating systems, PV modules with only 29 or 30 series-connected cells are commonly used. The intention in self-regulating systems is to operate the PV array to the right of the maximum power point on its IV curve, limiting the array current as the battery voltage increases to the regulation voltage. The temperature effects on PV arrays and batteries work in conjunction to make self-regulating system designs possible. As temperature decreases, both the optimal battery charge regulation voltage and the PV array maximum power voltage both increase. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p Charge controllers are rated for certain electrical parameters, that are used to properly select and size the controller for specific system applications. The nominal system voltage is the voltage at which the battery, charge controller and DC loads operate in a PV system. Most charge controllers are designed for operation at a specific voltage, while others may be configured for different standard voltages, such as 12, 24 or 48-volts. For larger systems, higher system (battery) voltages are generally used to lower the peak operating currents, reducing the size and ratings of conductors, overcurrent protection, disconnect means and charge controllers required. MPPT charge controllers will have different voltage ratings for their input and output circuits, and specify the range of array voltages at which it will track maximum power. Charge controllers are also rated for the maximum PV current they can handle. Charge controllers used in PV systems must be listed to UL 1741: Inverters, Converters, Controllers and Interconnection System Equipment for Use With Distributed Energy Resources. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p
19 Charge controllers, conductors and overcurrent protection devices must normally be sized for at least 125% of the maximum PV output circuit current. Since the maximum PV output circuit current is 125% of the short-circuit current, the combined factors equal 156%. Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p Some charge controllers may be listed for continuous operation at 100% of their maximum current, and are permitted to be utilized at 100% of their rating. This requires the controller to be sized for only 125% of the array short-circuit current. Reference: NEC
20 Reference: Photovoltaic Systems, p
PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM CONTROLLERS SUNSAVER MODELS INCLUDED IN THIS MANUAL SS-6 / SS-6L SS-10 / SS-10L SS-10-24V / SS-10L-24V SS-20L SS-20L-24V
 PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM CONTROLLERS OPERATOR S MANUAL SUNSAVER MODELS INCLUDED IN THIS MANUAL SS-6 / SS-6L SS-10 / SS-10L SS-10-24V / SS-10L-24V SS-20L SS-20L-24V 6A / 12V 10A / 12V 10A / 24V 20A / 12V 20A
PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM CONTROLLERS OPERATOR S MANUAL SUNSAVER MODELS INCLUDED IN THIS MANUAL SS-6 / SS-6L SS-10 / SS-10L SS-10-24V / SS-10L-24V SS-20L SS-20L-24V 6A / 12V 10A / 12V 10A / 24V 20A / 12V 20A
SOLAR LIGHTING CONTROLLER SUNLIGHT MODELS INCLUDED IN THIS MANUAL SL-10 SL-10-24V SL-20 SL-20-24V
 SOLAR LIGHTING CONTROLLER OPERATOR S MANUAL SUNLIGHT MODELS INCLUDED IN THIS MANUAL SL-10 SL-10-24V SL-20 SL-20-24V 10A / 12V 10A / 24V 20A / 12V 20A / 24V 1098 Washington Crossing Road Washington Crossing,
SOLAR LIGHTING CONTROLLER OPERATOR S MANUAL SUNLIGHT MODELS INCLUDED IN THIS MANUAL SL-10 SL-10-24V SL-20 SL-20-24V 10A / 12V 10A / 24V 20A / 12V 20A / 24V 1098 Washington Crossing Road Washington Crossing,
Components for your PV Solar Electric System
 Components for your PV Solar Electric System Here is a brief description of the major components of a Solar Electric System. The components vary depending on whether batteries will be used in your system.
Components for your PV Solar Electric System Here is a brief description of the major components of a Solar Electric System. The components vary depending on whether batteries will be used in your system.
SUPPLEMENTAL CORRECTION SHEET FOR SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS - ELECTRICAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL CORRECTION SHEET FOR SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS - ELECTRICAL This is intended to provide uniform application of the codes by the plan check staff and to help the public apply the codes correctly.
SUPPLEMENTAL CORRECTION SHEET FOR SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS - ELECTRICAL This is intended to provide uniform application of the codes by the plan check staff and to help the public apply the codes correctly.
The Traveler Series: Wanderer
 The Traveler Series: Wanderer RENOGY 30A Charge Controller Manual 2775 E. Philadelphia St., Ontario, CA 91761 1-800-330-8678 Version: 2.0 Important Safety Instructions Please save these instructions. This
The Traveler Series: Wanderer RENOGY 30A Charge Controller Manual 2775 E. Philadelphia St., Ontario, CA 91761 1-800-330-8678 Version: 2.0 Important Safety Instructions Please save these instructions. This
The Traveler Series: Wanderer
 The Traveler Series: Wanderer RENOGY 30A PWM Charge Controller Manual 2775 E. Philadelphia St., Ontario, CA 91761 1-800-330-8678 1 Version: 2.3 Important Safety Instructions Please save these instructions.
The Traveler Series: Wanderer RENOGY 30A PWM Charge Controller Manual 2775 E. Philadelphia St., Ontario, CA 91761 1-800-330-8678 1 Version: 2.3 Important Safety Instructions Please save these instructions.
This is intended to provide uniform application of the codes by the plan check staff and to help the public apply the codes correctly.
 SUPPLEMENTAL CORRECTION SHEET FOR SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS (ELEC) This is intended to provide uniform application of the codes by the plan check staff and to help the public apply the codes correctly.
SUPPLEMENTAL CORRECTION SHEET FOR SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS (ELEC) This is intended to provide uniform application of the codes by the plan check staff and to help the public apply the codes correctly.
Energy 142 NABCEP (North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners) Entry Level Test Review. System Components
 Energy 142 NABCEP (North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners) Entry Level Test Review System Components ESS 034 Advanced Photovoltaic Systems 1 Lesson Plan Safety Review Any Questions? NABCEP
Energy 142 NABCEP (North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners) Entry Level Test Review System Components ESS 034 Advanced Photovoltaic Systems 1 Lesson Plan Safety Review Any Questions? NABCEP
Glossary. * Credit for glossary starter: Florida Solar Energy Center. August 2015 PV Installer's Course: Glossary 1
 ALTERNATING CURRENT (AC): Electric current (flow of electrons) in which the direction of flow is reversed at constant intervals, such as 60 cycles per second. AMORPHOUS SILICON: silicon with no crystal
ALTERNATING CURRENT (AC): Electric current (flow of electrons) in which the direction of flow is reversed at constant intervals, such as 60 cycles per second. AMORPHOUS SILICON: silicon with no crystal
Diversion Manual (Section 6.0): 31 March 03
 Diversion Manual (Section 6.0): 31 March 03 The TriStar's third mode of operation is diversion load battery charge control. As the battery becomes fully charged, the TriStar will divert excess current
Diversion Manual (Section 6.0): 31 March 03 The TriStar's third mode of operation is diversion load battery charge control. As the battery becomes fully charged, the TriStar will divert excess current
Designing Stand Alone Systems. Overview, components and function, Elements in Design
 Designing Stand Alone Systems Overview, components and function, Elements in Design What Stand Alone System Does Loads that are Reasonable for a Stand Alone System to Power: Yes or No Dishwasher? Refrigerator
Designing Stand Alone Systems Overview, components and function, Elements in Design What Stand Alone System Does Loads that are Reasonable for a Stand Alone System to Power: Yes or No Dishwasher? Refrigerator
OFF GRID Solar system
 OFF GRID Solar system Off-Grid solar system Off-Grid solar system has 5 components as follows: Solar panel - Solar panel is used to collect the sunlight energy and to convert it into electricity Battery
OFF GRID Solar system Off-Grid solar system Off-Grid solar system has 5 components as follows: Solar panel - Solar panel is used to collect the sunlight energy and to convert it into electricity Battery
PV System Components. EE 495/695 Spring 2011
 PV System Components EE 495/695 Spring 2011 Main Components of Grid-Connected PV systems Battery storage is added to some grid-tied PV systems. Example of a grid-tied PV systems Main Components of Stand-Alone
PV System Components EE 495/695 Spring 2011 Main Components of Grid-Connected PV systems Battery storage is added to some grid-tied PV systems. Example of a grid-tied PV systems Main Components of Stand-Alone
Chapter 6. Batteries. Types and Characteristics Functions and Features Specifications and Ratings Jim Dunlop Solar
 Chapter 6 Batteries Types and Characteristics Functions and Features Specifications and Ratings 2012 Jim Dunlop Solar Overview Describing why batteries are used in PV systems. Identifying the basic components
Chapter 6 Batteries Types and Characteristics Functions and Features Specifications and Ratings 2012 Jim Dunlop Solar Overview Describing why batteries are used in PV systems. Identifying the basic components
672W Off Grid Residential Package
 672W Off Grid Residential Package List Price:$9,578.71 Our Price: $8,523.43 Save: $1,055.28 Our Code: KITOFFGRID-A This item is a package made up of the following components. Please call to speak to a
672W Off Grid Residential Package List Price:$9,578.71 Our Price: $8,523.43 Save: $1,055.28 Our Code: KITOFFGRID-A This item is a package made up of the following components. Please call to speak to a
Owner s Manual. Solar Controller GP-PWM-30
 Owner s Manual Solar Controller GP-PWM-30 1.0 Installation Overview 1.1 Introduction A Solar Controller (or Charge Controller / Regulator) is an essential component of your photovoltaic solar system. The
Owner s Manual Solar Controller GP-PWM-30 1.0 Installation Overview 1.1 Introduction A Solar Controller (or Charge Controller / Regulator) is an essential component of your photovoltaic solar system. The
The Traveler Series: Adventurer
 The Traveler Series: Adventurer RENOGY 30A Flush Mount Charge Controller Manual 2775 E. Philadelphia St., Ontario, CA 91761 1-800-330-8678 Version: 2.2 Important Safety Instructions Please save these instructions.
The Traveler Series: Adventurer RENOGY 30A Flush Mount Charge Controller Manual 2775 E. Philadelphia St., Ontario, CA 91761 1-800-330-8678 Version: 2.2 Important Safety Instructions Please save these instructions.
Photovoltaic Solar Plan Review
 PAIGE B. VAUGHAN, CBO Director of Building and Safety Phone (310) 605-5509 Fax Line (310) 605-5598 E-mail:lbutler@comptoncity.org Building & Safety Department Photovoltaic Solar Plan Review Plan Check
PAIGE B. VAUGHAN, CBO Director of Building and Safety Phone (310) 605-5509 Fax Line (310) 605-5598 E-mail:lbutler@comptoncity.org Building & Safety Department Photovoltaic Solar Plan Review Plan Check
The Traveler Series TM : Adventurer
 The Traveler Series TM : Adventurer 30A PWM Flush Mount Charge Controller w/ LCD Display 2775 E. Philadelphia St., Ontario, CA 91761 1-800-330-8678 Version: 3.4 Important Safety Instructions Please save
The Traveler Series TM : Adventurer 30A PWM Flush Mount Charge Controller w/ LCD Display 2775 E. Philadelphia St., Ontario, CA 91761 1-800-330-8678 Version: 3.4 Important Safety Instructions Please save
Manual Installation & Operation
 Manual Installation & Operation Model: NCxxLxx 12A or 30A Solid State Solar Charging Regulator and 12A Load Controller. 231 Patent #: 5,642,030 Applies Page 1 Warnings When Installing, connect grounds,
Manual Installation & Operation Model: NCxxLxx 12A or 30A Solid State Solar Charging Regulator and 12A Load Controller. 231 Patent #: 5,642,030 Applies Page 1 Warnings When Installing, connect grounds,
CHAPTER 10 ELECTRICAL. Notes:
 CHAPTER 10 ELECTRICAL 1001.0 General Requirements. Electrical wiring and equipment shall comply with the requirements of NFPA 70, National Electrical Code (NEC), or local ordinances. 1002.0 Solar Photovoltaic
CHAPTER 10 ELECTRICAL 1001.0 General Requirements. Electrical wiring and equipment shall comply with the requirements of NFPA 70, National Electrical Code (NEC), or local ordinances. 1002.0 Solar Photovoltaic
Off-grid Power for Wireless Networks. Training materials for wireless trainers
 Off-grid Power for Wireless Networks Training materials for wireless trainers Goals Provide a general view of the parts that comprise a solar photovoltaic system for telecommunication Understand the variables
Off-grid Power for Wireless Networks Training materials for wireless trainers Goals Provide a general view of the parts that comprise a solar photovoltaic system for telecommunication Understand the variables
Code Calculations. for an Off-Grid PV System
 Code Calculations for an Off-Grid PV System John Wiles Sponsored by the Photovoltaic Systems Assistance Center, Sandia National Laboratories Judy LaPointe s home is on its way to becoming a finished, off-grid
Code Calculations for an Off-Grid PV System John Wiles Sponsored by the Photovoltaic Systems Assistance Center, Sandia National Laboratories Judy LaPointe s home is on its way to becoming a finished, off-grid
2016 Photovoltaic Solar System Plan Review List
 Building Division 555 Santa Clara Street Vallejo CA 94590 707.648.4374 2016 Photovoltaic Solar System Plan Review List GENERAL PROJECT INFORMATION PLAN CHECK NO DATE JOB ADDRESS CITY ZIP REVIEWED BY PHONE
Building Division 555 Santa Clara Street Vallejo CA 94590 707.648.4374 2016 Photovoltaic Solar System Plan Review List GENERAL PROJECT INFORMATION PLAN CHECK NO DATE JOB ADDRESS CITY ZIP REVIEWED BY PHONE
Gay E. Canough. OFF-GRID Design. Dr. Gay E. Canough, Master trainer. Living Off the Grid
 OFF-GRID Design Dr. Gay E. Canough, Master trainer 1 Understand the Customer s load 2 Load sizing Gay E. Canough AC Appliance watts amps how many of these? number of hours it is used per day equals watt-hr/
OFF-GRID Design Dr. Gay E. Canough, Master trainer 1 Understand the Customer s load 2 Load sizing Gay E. Canough AC Appliance watts amps how many of these? number of hours it is used per day equals watt-hr/
Ningbo Star Solar Co.,Ltd Tel:(86) Fax:(86)
 Tracer MPPT Solar charge controller Tracer series 40A mppt solar controller adopts MPPT technology (Maximum Power Point Tracking). The advanced tracking algorithm make the solar panel operate at ideal
Tracer MPPT Solar charge controller Tracer series 40A mppt solar controller adopts MPPT technology (Maximum Power Point Tracking). The advanced tracking algorithm make the solar panel operate at ideal
Photovoltaic Systems Engineering
 Photovoltaic Systems Engineering Ali Karimpour Associate Professor Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Reza Bakhshi Ph.D. candidate Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Ali Karimpour & Reza Bakhshi Lecture 7 Off-grid
Photovoltaic Systems Engineering Ali Karimpour Associate Professor Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Reza Bakhshi Ph.D. candidate Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Ali Karimpour & Reza Bakhshi Lecture 7 Off-grid
MPPT75HV MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING SOLAR BATTERY CHARGE CONTROLLER
 MPPT75HV MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING SOLAR BATTERY CHARGE CONTROLLER The Intronics Power Inc. MPPT75HV Solar Charge Controller continually tracks the maximum power point of the solar panel array, adjusting
MPPT75HV MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING SOLAR BATTERY CHARGE CONTROLLER The Intronics Power Inc. MPPT75HV Solar Charge Controller continually tracks the maximum power point of the solar panel array, adjusting
Rover Series. Rover 20A 40A Maximum Power Point Tracking Solar Charge Controller
 Rover Series Rover 20A 40A Maximum Power Point Tracking Solar Charge Controller 0 2775 E. Philadelphia St., Ontario, CA 91761 1-800-330-8678 Version 1.5 Important Safety Instructions Please save these
Rover Series Rover 20A 40A Maximum Power Point Tracking Solar Charge Controller 0 2775 E. Philadelphia St., Ontario, CA 91761 1-800-330-8678 Version 1.5 Important Safety Instructions Please save these
Off Grid Cabin Special Pkg 1-170W PV
 Off Grid Cabin Special Pkg 1-170W PV List Price: $2,693.75 Our Price: $2,346.90 Save: $346.85 Model: Solar Cabin DC Package 1 Our Code: KITCABIN1 This item is a package made up of the following components.
Off Grid Cabin Special Pkg 1-170W PV List Price: $2,693.75 Our Price: $2,346.90 Save: $346.85 Model: Solar Cabin DC Package 1 Our Code: KITCABIN1 This item is a package made up of the following components.
Off Grid Residential Package 1.0KW
 Off Grid Residential Package 1.0KW List Price: $12,876.63 Our Price: $11,545.59 Save: $1,331.04 (10%) Model: Off-Grid Res Pkg 1kW Our Code: KITOFFGRID-B This item is a package made up of the following
Off Grid Residential Package 1.0KW List Price: $12,876.63 Our Price: $11,545.59 Save: $1,331.04 (10%) Model: Off-Grid Res Pkg 1kW Our Code: KITOFFGRID-B This item is a package made up of the following
12-Batteries and Inverters. ECEGR 452 Renewable Energy Systems
 12-Batteries and Inverters ECEGR 452 Renewable Energy Systems Overview Batteries Lead-Acid Batteries Battery Specifications Battery Charge Controllers Inverters Dr. Louie 2 Batteries Incorporation of a
12-Batteries and Inverters ECEGR 452 Renewable Energy Systems Overview Batteries Lead-Acid Batteries Battery Specifications Battery Charge Controllers Inverters Dr. Louie 2 Batteries Incorporation of a
Title Goes Here and Can Run Solar Photovoltaic up to 3 lines as shown here Systems as you see
 Title Goes Here and Can Run Solar Photovoltaic up to 3 lines as shown here Systems as you see CHAPTER 2 Outline the components of a solar photovoltaic system Describe the operation of a solar photovoltaic
Title Goes Here and Can Run Solar Photovoltaic up to 3 lines as shown here Systems as you see CHAPTER 2 Outline the components of a solar photovoltaic system Describe the operation of a solar photovoltaic
3400W Solar Battery Charger Maximum Power Point Tracker
 Page 1 of 8 A simple, compact low cost MPPT to efficiently charge lead acid and lithium iron batteries from a wide range of photovoltaic panels. The MPPT 60-2 is designed to charge lead acid and lithium
Page 1 of 8 A simple, compact low cost MPPT to efficiently charge lead acid and lithium iron batteries from a wide range of photovoltaic panels. The MPPT 60-2 is designed to charge lead acid and lithium
First Responder System Identification Quiz. Presented by the NY-SUN PV Trainers Network
 First Responder System Identification Quiz Presented by the NY-SUN PV Trainers Network SYSTEM 1 Questions: 1) Is there a solar electric system at the site? 2) What is your next step? SYSTEM 1 3) Given
First Responder System Identification Quiz Presented by the NY-SUN PV Trainers Network SYSTEM 1 Questions: 1) Is there a solar electric system at the site? 2) What is your next step? SYSTEM 1 3) Given
SMT. Installation and Operation Manual. Model:SMT WITH MPPT TECHNOLOGY
 SMT WITH MPPT TECHNOLOGY Installation and Operation Manual Model:SMT SMT Dimensions Specification Summary System Voltage 12 V/24V Rated Battery Current 12V, 5A 8A 10A 15A 20A 25A 24V, 5A 8A 10A 15A Rated
SMT WITH MPPT TECHNOLOGY Installation and Operation Manual Model:SMT SMT Dimensions Specification Summary System Voltage 12 V/24V Rated Battery Current 12V, 5A 8A 10A 15A 20A 25A 24V, 5A 8A 10A 15A Rated
Eclipse Solar Suitcase
 Eclipse Solar Suitcase Renogy 100W 200W 2775 E. Philadelphia St., Ontario, CA 91761 1-800-330-8678 Version 1.0 Important Safety Instructions Please save these instructions. This manual contains important
Eclipse Solar Suitcase Renogy 100W 200W 2775 E. Philadelphia St., Ontario, CA 91761 1-800-330-8678 Version 1.0 Important Safety Instructions Please save these instructions. This manual contains important
Owner s Manual. Contents GP-PWM-10-SQ
 Owner s Manual Contents 1.0 Installation Overview... 2 2.0 Warnings... 2 3.0 Choosing a Location... 3 4.0 Installation Instructions... 3 5.0 Operating Instructions... 4 6.0 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)...
Owner s Manual Contents 1.0 Installation Overview... 2 2.0 Warnings... 2 3.0 Choosing a Location... 3 4.0 Installation Instructions... 3 5.0 Operating Instructions... 4 6.0 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)...
How To Set Up SimpliPhi Batteries Using OutBack Chargers
 Introduction How To Set Up SimpliPhi Batteries Using OutBack Chargers The main focus of this application note will be on setting up OutBack charging sources for best operational performance for SimpliPhi
Introduction How To Set Up SimpliPhi Batteries Using OutBack Chargers The main focus of this application note will be on setting up OutBack charging sources for best operational performance for SimpliPhi
SOLAR BOOST 3024i 30AMP 12/24VDC MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING PHOTOVOLTAIC CHARGE CONTROLLER
 SOLAR BOOST 3024i 30AMP 12/24VDC MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING PHOTOVOLTAIC CHARGE CONTROLLER INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL THIS MANUAL INCLUDES IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS FOR MODELS SB3024i AND
SOLAR BOOST 3024i 30AMP 12/24VDC MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING PHOTOVOLTAIC CHARGE CONTROLLER INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL THIS MANUAL INCLUDES IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS FOR MODELS SB3024i AND
1700W Solar Battery Charger Maximum Power Point Tracker
 Page 1 of 8 A simple, compact low cost mppt to efficiently charge lead acid and lithium iron batteries from a wide range of photovoltaic panels. The is designed to charge lead acid and lithium batteries
Page 1 of 8 A simple, compact low cost mppt to efficiently charge lead acid and lithium iron batteries from a wide range of photovoltaic panels. The is designed to charge lead acid and lithium batteries
User Manual Solar Charge Controller 3KW
 User Manual Solar Charge Controller 3KW Version: 1.3 CONTENTS 1 ABOUT THIS MANUAL... 1 1.1 Purpose... 1 1.2 Scope... 1 1.3 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS... 1 2 INTRODUCTION... 2 2.1 Features... 2 2.2 Product Overview...
User Manual Solar Charge Controller 3KW Version: 1.3 CONTENTS 1 ABOUT THIS MANUAL... 1 1.1 Purpose... 1 1.2 Scope... 1 1.3 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS... 1 2 INTRODUCTION... 2 2.1 Features... 2 2.2 Product Overview...
Owner s Manual. Contents GP-PWM-30-SQ GP-PWM-30-SQ
 Owner s Manual Contents 1.0 Installation Overview... 2 2.0 Warnings... 2 3.0 Choosing a Location...3 4.0 Installation Instructions... 3 5.0 Operating Instructions...4 6.0 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)...6
Owner s Manual Contents 1.0 Installation Overview... 2 2.0 Warnings... 2 3.0 Choosing a Location...3 4.0 Installation Instructions... 3 5.0 Operating Instructions...4 6.0 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)...6
JEE4980 Sr Design Project. Residential Concept
 JEE4980 Sr Design Project Photovoltaic System (PV) Module through Main Service Panel Project Implementation Discussion Wilcox Chapter 2 Lab Time continued project design work Refer to your electronic handout
JEE4980 Sr Design Project Photovoltaic System (PV) Module through Main Service Panel Project Implementation Discussion Wilcox Chapter 2 Lab Time continued project design work Refer to your electronic handout
SimpliPhi Power PHI Battery
 Power. On Your Terms. SimpliPhi Power PHI Battery INTEGRATION GUIDE: VICTRON Optimized Energy Storage & Management for Residential & Commercial Applications Utilizing Efficient, Safe, Non-Toxic, Energy
Power. On Your Terms. SimpliPhi Power PHI Battery INTEGRATION GUIDE: VICTRON Optimized Energy Storage & Management for Residential & Commercial Applications Utilizing Efficient, Safe, Non-Toxic, Energy
PV Charge Controller SBC-7108 / 7112 / 7120
 PV Charge Controller SBC-7108 / 7112 / 7120 User's Manual NOTE: Please note that features like LCD read out of AH logging of 3 days (see Section 3.3) and 10 Night-light mode (see Section 4.3) are available
PV Charge Controller SBC-7108 / 7112 / 7120 User's Manual NOTE: Please note that features like LCD read out of AH logging of 3 days (see Section 3.3) and 10 Night-light mode (see Section 4.3) are available
SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS INSPECTOR CHECKLIST
 SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS INSPECTOR CHECKLIST The following checklist is an outline of the general requirements found in the 1999 National Electrical Code (NEC) Article 690 for Photovoltaic (PV) Power
SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS INSPECTOR CHECKLIST The following checklist is an outline of the general requirements found in the 1999 National Electrical Code (NEC) Article 690 for Photovoltaic (PV) Power
A Study of Lead-Acid Battery Efficiency Near Top-of-Charge and the Impact on PV System Design
 A Study of Lead-Acid Battery Efficiency Near Top-of-Charge and the Impact on PV System Design John W. Stevens and Garth P. Corey Sandia National Laboratories, Photovoltaic System Applications Department
A Study of Lead-Acid Battery Efficiency Near Top-of-Charge and the Impact on PV System Design John W. Stevens and Garth P. Corey Sandia National Laboratories, Photovoltaic System Applications Department
Green Building Technology
 Green Building Technology Renewable Energy Sources and Design/Specification Guidelines Presented by: Kurt Uhlir & Brian Kustwin Why Renewables? Reduction of SO 2 and NOX along with greenhouse gases such
Green Building Technology Renewable Energy Sources and Design/Specification Guidelines Presented by: Kurt Uhlir & Brian Kustwin Why Renewables? Reduction of SO 2 and NOX along with greenhouse gases such
User Manual. Solar Charge Controller 3KW
 User Manual Solar Charge Controller 3KW 1 CONTENTS 1 ABOUT THIS MANUAL... 3 1.1 Purpose... 3 1.2 Scope... 3 1.3 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS... 3 2 INTRODUCTION... 4 2.1 Features... 4 2.2 Product Overview... 5
User Manual Solar Charge Controller 3KW 1 CONTENTS 1 ABOUT THIS MANUAL... 3 1.1 Purpose... 3 1.2 Scope... 3 1.3 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS... 3 2 INTRODUCTION... 4 2.1 Features... 4 2.2 Product Overview... 5
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) System Components
 az1742 August 2017 Solar Photovoltaic (PV) System Components Dr. Ed Franklin Introduction Solar photovoltaic (PV) energy systems are made up of different components. Each component has a specific role.
az1742 August 2017 Solar Photovoltaic (PV) System Components Dr. Ed Franklin Introduction Solar photovoltaic (PV) energy systems are made up of different components. Each component has a specific role.
Duo Battery Charge Controller
 Duo Battery Charge Controller RENOGY 10A 20A Pulse Width Modulation Solar Charge Controller Manual 1 2775 E. Philadelphia St., Ontario CA 91761 1-800-330-8678 Version: 1.2 Important Safety Instructions
Duo Battery Charge Controller RENOGY 10A 20A Pulse Width Modulation Solar Charge Controller Manual 1 2775 E. Philadelphia St., Ontario CA 91761 1-800-330-8678 Version: 1.2 Important Safety Instructions
SCC-MPPT Solar Charge Controller
 Solar Charge Controller Quick Guide 200W 300W 400W 600W 850W V. 2.2 1. Introduction solar charge controller uses PWM-based DSP controller to keep the batteries regulated and prevent batteries from overcharging
Solar Charge Controller Quick Guide 200W 300W 400W 600W 850W V. 2.2 1. Introduction solar charge controller uses PWM-based DSP controller to keep the batteries regulated and prevent batteries from overcharging
GP-MPPT-40. User Manual Go Power!
 User Manual Contents 1.0 Installation Overview 3 1.1 Introduction 3 1.2 Specifications 4 2.0 Warnings 5 3.0 Tools and Materials Needed 5 4.0 Choosing a Location 6 5.0 Choosing an Array 6 6.0 Installation
User Manual Contents 1.0 Installation Overview 3 1.1 Introduction 3 1.2 Specifications 4 2.0 Warnings 5 3.0 Tools and Materials Needed 5 4.0 Choosing a Location 6 5.0 Choosing an Array 6 6.0 Installation
3500W Solar Battery Charger Maximum Power Point Tracker
 Page 1 of 8 This revolutionary maximum power point tracker solar charger was designed using the technology that won GSL Electronics the prestigious EDN Innovation Awards 08 and 09 and the Greentech Consensus
Page 1 of 8 This revolutionary maximum power point tracker solar charger was designed using the technology that won GSL Electronics the prestigious EDN Innovation Awards 08 and 09 and the Greentech Consensus
Duracell Battery Glossary
 Duracell Battery Glossary 1 Duracell Battery Glossary AB Absorption Alloy Ambient Humidity Ambient Temperature Ampere-Hour Capacity Anode Battery or Pack Bobbin C-Rate (also see Hourly Rate) Capacity Capacity
Duracell Battery Glossary 1 Duracell Battery Glossary AB Absorption Alloy Ambient Humidity Ambient Temperature Ampere-Hour Capacity Anode Battery or Pack Bobbin C-Rate (also see Hourly Rate) Capacity Capacity
Batteries and Charge Control in Stand-Alone Photovoltaic Systems
 Batteries and Charge Control in Stand-Alone Photovoltaic Systems Fundamentals and Application Author James P. Dunlop Publication Number FSEC-CR-1292-01 Copyright Copyright Florida Solar Energy Center/University
Batteries and Charge Control in Stand-Alone Photovoltaic Systems Fundamentals and Application Author James P. Dunlop Publication Number FSEC-CR-1292-01 Copyright Copyright Florida Solar Energy Center/University
Microinverters and AC PV modules are becoming. Microinverters and AC PV Modules. Different Beasts. Perspectives on PV.
 Perspectives on PV Microinverters and AC PV Modules Are Different Beasts by John Wiles Microinverters and AC PV modules are becoming very common in residential and small commercial PV systems. See photos
Perspectives on PV Microinverters and AC PV Modules Are Different Beasts by John Wiles Microinverters and AC PV modules are becoming very common in residential and small commercial PV systems. See photos
Model NCHC-xx Owners Manual
 Model NCHC-xx Owners Manual Ultra High Efficiency Industrial Grade, High Ampere, Alternative Energy Battery Charge Controller MODEL: NCHC-12, 24, 36, 48 For GEL, AGM, and Flooded Cell Lead Acid Batteries
Model NCHC-xx Owners Manual Ultra High Efficiency Industrial Grade, High Ampere, Alternative Energy Battery Charge Controller MODEL: NCHC-12, 24, 36, 48 For GEL, AGM, and Flooded Cell Lead Acid Batteries
GLOSSARY: TECHNICAL BATTERY TERMS
 GLOSSARY: TECHNICAL BATTERY TERMS AB5 Absorption Alloy Ambient Humidity Ambient Temperature Ampere-Hour Capacity Anode Battery or Pack Bobbin C-Rate (also see Hourly Rate) Capacity Capacity Retention (or
GLOSSARY: TECHNICAL BATTERY TERMS AB5 Absorption Alloy Ambient Humidity Ambient Temperature Ampere-Hour Capacity Anode Battery or Pack Bobbin C-Rate (also see Hourly Rate) Capacity Capacity Retention (or
Sizing a Grid-Tied PV System
 Sizing a Grid-Tied PV System...with Battery Backup by Flint Richter Courtesy Honey Electric Solar A professionally installed grid-tied PV system with battery backup using the Schneider (Xantrex) XW inverter
Sizing a Grid-Tied PV System...with Battery Backup by Flint Richter Courtesy Honey Electric Solar A professionally installed grid-tied PV system with battery backup using the Schneider (Xantrex) XW inverter
SCC-MPPT Solar Charge Controller
 Table 3: Charging voltage for 4 types of battery Battery Battery 12V battery system 24V battery system Type Type Code Bulk Floating Bulk Floating Vented 01 14.3 V 13.2 V 28.6 V 26.4 V Sealed 02 14.3 V
Table 3: Charging voltage for 4 types of battery Battery Battery 12V battery system 24V battery system Type Type Code Bulk Floating Bulk Floating Vented 01 14.3 V 13.2 V 28.6 V 26.4 V Sealed 02 14.3 V
3. Customer shall provide space for metering equipment and meter base as per Springville City Power requirements.
 A. General This Customer-Owned Generation Standards for Customer-Owned Grid Connected Electric Generating Systems sets forth the requirements and conditions for interconnected non-utility-owned electric
A. General This Customer-Owned Generation Standards for Customer-Owned Grid Connected Electric Generating Systems sets forth the requirements and conditions for interconnected non-utility-owned electric
FC/FCA 12, 24, 32 & 48 VOLT, 6 & 10 AMP BATTERY CHARGER OPERATION & MAINTENANCE GUIDE
 FC/FCA 12, 24, 32 & 48 VOLT, 6 & 10 AMP BATTERY CHARGER OPERATION & MAINTENANCE GUIDE SENS part number: 101037 Document revision: A Engineering change number: 105073 Date: 1/13/2006 1840 Industrial Circle
FC/FCA 12, 24, 32 & 48 VOLT, 6 & 10 AMP BATTERY CHARGER OPERATION & MAINTENANCE GUIDE SENS part number: 101037 Document revision: A Engineering change number: 105073 Date: 1/13/2006 1840 Industrial Circle
Renewable Hybrid / Off-grid Solutions
 Renewable Hybrid / Off-grid Solutions APPLICATION : BTS and micro-wave communications for remote telecommunications provider, hybrid systems are particularly well-suited for applications in remote areas,
Renewable Hybrid / Off-grid Solutions APPLICATION : BTS and micro-wave communications for remote telecommunications provider, hybrid systems are particularly well-suited for applications in remote areas,
MANUAL Model: PT 12/24-60 Solar Converters Inc. - Rev. F
 1.0 Specification MANUAL Model: PT 12/24-60 Solar Converters Inc. - Rev. F Note: This unit is a Multi - Voltage unit with adjustable input panel and output battery adjustment. Please review the section
1.0 Specification MANUAL Model: PT 12/24-60 Solar Converters Inc. - Rev. F Note: This unit is a Multi - Voltage unit with adjustable input panel and output battery adjustment. Please review the section
Installation and Operating Instructions. MPPT Solar System Controller ISC3040
 Installation and Operating Instructions MPPT Solar System Controller ISC3040 ABOUT THIS MANUAL These operating instructions come with the product and should be kept with it as a reference to all user s
Installation and Operating Instructions MPPT Solar System Controller ISC3040 ABOUT THIS MANUAL These operating instructions come with the product and should be kept with it as a reference to all user s
OPTI-Solar PWM SERIES
 OPTI-Solar PWM SERIES SOLAR CHARGE CONTROLLER SC-45/ SC-60 Installation and Operation Manual USER MANUAL Solar Battery Charging Load Control Diversion Charge Control CONTENTS Specifications...I Chapter
OPTI-Solar PWM SERIES SOLAR CHARGE CONTROLLER SC-45/ SC-60 Installation and Operation Manual USER MANUAL Solar Battery Charging Load Control Diversion Charge Control CONTENTS Specifications...I Chapter
LS0512 Solar Charge Controller
 LandStar LS0512 Solar Charge Controller Nominal system voltage Maximum PV input voltage Nominal charge / discharge current 12VDC 35V 5A Contents 1 Important Safety Information... 1 2 General Information...
LandStar LS0512 Solar Charge Controller Nominal system voltage Maximum PV input voltage Nominal charge / discharge current 12VDC 35V 5A Contents 1 Important Safety Information... 1 2 General Information...
Instruction Manual. Duo-battery Solar Panel Controller EPIP20-DB series For Both 10 and 20 amp. Controllers (for use with solar panels only) + -
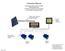 Instruction Manual Duo-battery Solar Panel Controller EPIP20-DB series For Both 10 and 20 amp. Controllers (for use with solar panels only) + - Optional - Switch to disconnect solar panel when engine alternator
Instruction Manual Duo-battery Solar Panel Controller EPIP20-DB series For Both 10 and 20 amp. Controllers (for use with solar panels only) + - Optional - Switch to disconnect solar panel when engine alternator
3400W Solar Battery Charger Maximum Power Point Tracker
 Page 1 of 8 This revolutionary maximum power point tracker solar charger was designed using the technology that won GSL Electronics the prestigious EDN Innovation Awards 08 and 09 and the Greentech Consensus
Page 1 of 8 This revolutionary maximum power point tracker solar charger was designed using the technology that won GSL Electronics the prestigious EDN Innovation Awards 08 and 09 and the Greentech Consensus
PV Charge Controller SBC-6108 / 6112 / 6120 / 6130
 PV Charge Controller SBC-6108 / 6112 / 6120 / 6130 User's Manual Table of Contents Precautions and Specifications 1 1. Introduction 2 2. Control and Indicator 2 3. Installation and Indication 3 3.1 Connection
PV Charge Controller SBC-6108 / 6112 / 6120 / 6130 User's Manual Table of Contents Precautions and Specifications 1 1. Introduction 2 2. Control and Indicator 2 3. Installation and Indication 3 3.1 Connection
the National PhotoVoltaic protection note 5 I rated Introduction points of interest When to Fuse, When Not to Fuse
 Sizing Fuses for Photovoltaic Systems per the National Electrical Code PhotoVoltaic protection note 5 By Robert Lyons, Jr. Product Manager Introduction Properly sizing fuses for photovoltaic (PV) systems
Sizing Fuses for Photovoltaic Systems per the National Electrical Code PhotoVoltaic protection note 5 By Robert Lyons, Jr. Product Manager Introduction Properly sizing fuses for photovoltaic (PV) systems
SOLAR POWER SYSTEMS MANUAL
 SOLAR POWER SYSTEMS MANUAL Gordon L.Gibby KX4Z Version 1.00 Friday June 22 2018 Two solar power systems have been constructed as follows: System Solar Panel & Connections 1 250 Watt 30-volt nominal solar
SOLAR POWER SYSTEMS MANUAL Gordon L.Gibby KX4Z Version 1.00 Friday June 22 2018 Two solar power systems have been constructed as follows: System Solar Panel & Connections 1 250 Watt 30-volt nominal solar
UniverSOL Charge Station
 UniverSOL Charge Station Group 17 Jonathan German Amy Parkinson John Curristan Brock Stoops Sponsored by Motivations Environmental Renewable Energy Carbon Emissions Power Demand Power Dependency Availability
UniverSOL Charge Station Group 17 Jonathan German Amy Parkinson John Curristan Brock Stoops Sponsored by Motivations Environmental Renewable Energy Carbon Emissions Power Demand Power Dependency Availability
INSTRUCTION MANUAL EPSOLAR. Tracer-3215RN. Maximum Power Point Tracking Solar Charge Controller
 EPSOLAR Utility model patent NO. 201120064092.1 Tracer-3215RN Maximum Power Point Tracking Solar Charge Controller INSTRUCTION MANUAL Thank you very much for selecting our product! This manual offers important
EPSOLAR Utility model patent NO. 201120064092.1 Tracer-3215RN Maximum Power Point Tracking Solar Charge Controller INSTRUCTION MANUAL Thank you very much for selecting our product! This manual offers important
Solar Charge Controller
 Table 3: Charging voltage for 4 types of battery Battery Type Battery Type Code SC-600W MPPT Bulk Voltage Floating Voltage Vented 01 28.6 V 26.4 V Sealed 02 28.6 V 26.8 V Gel 03 28.6 V 27.4 V NiCd 04 28.6
Table 3: Charging voltage for 4 types of battery Battery Type Battery Type Code SC-600W MPPT Bulk Voltage Floating Voltage Vented 01 28.6 V 26.4 V Sealed 02 28.6 V 26.8 V Gel 03 28.6 V 27.4 V NiCd 04 28.6
KIT-STCS60D KIT-STCS100D Solar Suitcase 60W and 100W Owner s Manual
 KIT-STCS60D KIT-STCS100D Solar Suitcase 60W and 100W Owner s Manual RNG Group Inc. (Renogy) 14288 Central Ave., Suite A Chino, CA 91710 1-800-330-8678 Product Description The Renogy Solar Suitcases combine
KIT-STCS60D KIT-STCS100D Solar Suitcase 60W and 100W Owner s Manual RNG Group Inc. (Renogy) 14288 Central Ave., Suite A Chino, CA 91710 1-800-330-8678 Product Description The Renogy Solar Suitcases combine
Montana State University: Solar Cells Lecture 9: PV Systems. Montana State University: Solar Cells Lecture 9: PV Systems
 EE580 Solar Cells Todd J. Kaiser Lecture 09 Photovoltaic Systems Several types of operating modes Centralized power plant Large PV system located in an optimum location, feeding into the grid Distributed
EE580 Solar Cells Todd J. Kaiser Lecture 09 Photovoltaic Systems Several types of operating modes Centralized power plant Large PV system located in an optimum location, feeding into the grid Distributed
Types of Solar Photovoltaic Systems
 Types of Solar Photovoltaic Systems Item Type text; Book Authors Franklin, Ed Publisher College of Agriculture, University of Arizona (Tucson, AZ) Download date 13/06/2018 20:07:28 Item License http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
Types of Solar Photovoltaic Systems Item Type text; Book Authors Franklin, Ed Publisher College of Agriculture, University of Arizona (Tucson, AZ) Download date 13/06/2018 20:07:28 Item License http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
RU BMS Power Supply and Battery Management System Owners Guide
 RU2-4012- BMS Power Supply and Battery Management System Owners Guide (These instructions are intended for use by a technician familiar with electronic products) RU2-4012- BMS is a continuous duty power
RU2-4012- BMS Power Supply and Battery Management System Owners Guide (These instructions are intended for use by a technician familiar with electronic products) RU2-4012- BMS is a continuous duty power
A Solar Power System for a Residential Application
 A Solar Power System for a Residential Application Osman N. Muneer ECET 490 Final Presentation Due: 12/18/08 Instructor: Paul I-Hai Lin, P.E. (EE) Faculty Advisor: Iskandar Hack, P.E. (EE) 1 Introduction
A Solar Power System for a Residential Application Osman N. Muneer ECET 490 Final Presentation Due: 12/18/08 Instructor: Paul I-Hai Lin, P.E. (EE) Faculty Advisor: Iskandar Hack, P.E. (EE) 1 Introduction
SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6576 Solar Panel Power Supply System
 2004 Specifications CSJ 1068-04-126, 0197-02-108 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6576 Solar Panel Power Supply System 1. Description. This work shall consist of furnishing and installing an integrated solar Panel
2004 Specifications CSJ 1068-04-126, 0197-02-108 SPECIAL SPECIFICATION 6576 Solar Panel Power Supply System 1. Description. This work shall consist of furnishing and installing an integrated solar Panel
Battery Capacity Versus Discharge Rate
 Exercise 2 Battery Capacity Versus Discharge Rate EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the effects of the discharge rate and battery temperature on the capacity
Exercise 2 Battery Capacity Versus Discharge Rate EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the effects of the discharge rate and battery temperature on the capacity
CHAPTER 10 ELECTRICAL
 1001.0 General Requirements. 1001.1 Electrical Wiring and Equipment. Electrical wiring and equipment shall comply with the requirements of NFPA 70, National Electrical Code (NEC), or local ordinances.
1001.0 General Requirements. 1001.1 Electrical Wiring and Equipment. Electrical wiring and equipment shall comply with the requirements of NFPA 70, National Electrical Code (NEC), or local ordinances.
BlueSolar charge controller MPPT 100/30
 Manual EN Handleiding NL Manuel FR Anleitung DE Manual ES Användarhandbok SE Appendix BlueSolar charge controller MPPT 100/30 1. General Description 1.1 Charge current up to 30 A and PV voltage up to 100
Manual EN Handleiding NL Manuel FR Anleitung DE Manual ES Användarhandbok SE Appendix BlueSolar charge controller MPPT 100/30 1. General Description 1.1 Charge current up to 30 A and PV voltage up to 100
LS0512R Solar Light Controller
 LandStar LS0512R Solar Light Controller Nominal system voltage Maximum PV input voltage Nominal charge / discharge current 12VDC 35V 5A Contents 1 Important Safety Information... 1 2 General Information...
LandStar LS0512R Solar Light Controller Nominal system voltage Maximum PV input voltage Nominal charge / discharge current 12VDC 35V 5A Contents 1 Important Safety Information... 1 2 General Information...
INSTRUCTION MANUAL EPSOLAR. Tracer-4215RN. Maximum Power Point Tracking Solar Charge Controller
 EPSOLAR Utility model patent NO. 201120064092.1 Tracer-4215RN Maximum Power Point Tracking Solar Charge Controller INSTRUCTION MANUAL Thank you very much for selecting our product! This manual offers important
EPSOLAR Utility model patent NO. 201120064092.1 Tracer-4215RN Maximum Power Point Tracking Solar Charge Controller INSTRUCTION MANUAL Thank you very much for selecting our product! This manual offers important
SCC-MPPT Solar Charge Controller
 Table 4: Alarm point for low battery voltage table Model Alarm point SCC-MPPT-300 10.5 V SCC-MPPT-600 21.0 V Table 5: Charging hour table for reference Battery Capacity To 90% capacity @ 25A charging current
Table 4: Alarm point for low battery voltage table Model Alarm point SCC-MPPT-300 10.5 V SCC-MPPT-600 21.0 V Table 5: Charging hour table for reference Battery Capacity To 90% capacity @ 25A charging current
Electricity and New Energy. Wind Power Systems. Course Sample
 Electricity and New Energy Wind Power Systems Course Sample 593991 Order no.: 593991 (Printed version) 594307 (CD-ROM) First Edition Revision level: 09/2018 By the staff of Festo Didactic Festo Didactic
Electricity and New Energy Wind Power Systems Course Sample 593991 Order no.: 593991 (Printed version) 594307 (CD-ROM) First Edition Revision level: 09/2018 By the staff of Festo Didactic Festo Didactic
Solar Controller GP-PWM-30. Owner s Manual Go Power! By Valterra Power
 Solar Controller GP-PWM-30 Owner s Manual 1 2 CONTENTS 1.0 Installation Overview 4 1.1 Introduction 4 1.2 Specifications 5 2.0 Warnings 6 3.0 Tools and Materials Needed 7 4.0 Choosing a Location 7 5.0
Solar Controller GP-PWM-30 Owner s Manual 1 2 CONTENTS 1.0 Installation Overview 4 1.1 Introduction 4 1.2 Specifications 5 2.0 Warnings 6 3.0 Tools and Materials Needed 7 4.0 Choosing a Location 7 5.0
NorthStar Battery (NSB) Telecom Application Manual
 NorthStar Battery (NSB) Telecom Application Manual Contents Silver Star Technology TM... 3 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 The Silver Star Technology TM and Semi-Stable Mains... 3 1.2 Discharge Rate... 3 2 Charge...
NorthStar Battery (NSB) Telecom Application Manual Contents Silver Star Technology TM... 3 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 The Silver Star Technology TM and Semi-Stable Mains... 3 1.2 Discharge Rate... 3 2 Charge...
2011/2008/2005 NATIONAL ELECTRICAL CODE SOLAR PV CODE COMPLIANCE REFERENCE
 2011/2008/2005 NATIONAL ELECTRICAL CODE SOLAR PV CODE COMPLIANCE REFERENCE PAGE 1 OF 5 This Reference provides a very comprehensive list of aspects of a solar PV installation that could be reviewed, clarifying
2011/2008/2005 NATIONAL ELECTRICAL CODE SOLAR PV CODE COMPLIANCE REFERENCE PAGE 1 OF 5 This Reference provides a very comprehensive list of aspects of a solar PV installation that could be reviewed, clarifying
Super PWRgate PG40S Spring City Drive Waukesha, WI
 Super PWRgate PG40S www.westmountainradio.com 1020 Spring City Drive Waukesha, WI 53186 262-522-6503 sales@westmountainradio.com 2015, All rights reserved. All trademarks are the property of their respective
Super PWRgate PG40S www.westmountainradio.com 1020 Spring City Drive Waukesha, WI 53186 262-522-6503 sales@westmountainradio.com 2015, All rights reserved. All trademarks are the property of their respective
Solar Controller GP-PWM-30. Owner s Manual
 Owner s Manual 1 2 CONTENTS 1.0 Installation Overview 4 1.1 Introduction 4 1.2 Specifications 5 2.0 Warnings 6 3.0 Tools and Materials Needed 7 4.0 Choosing a Location 7 5.0 Installation Instructions 8
Owner s Manual 1 2 CONTENTS 1.0 Installation Overview 4 1.1 Introduction 4 1.2 Specifications 5 2.0 Warnings 6 3.0 Tools and Materials Needed 7 4.0 Choosing a Location 7 5.0 Installation Instructions 8
PHOTOVOLTAIC ELECTRICAL POWER SYSTEMS INSPECTOR/INSTALLER CHECKLIST
 PHOTOVOLTAIC ELECTRICAL POWER SYSTEMS INSPECTOR/INSTALLER CHECKLIST The following checklist is an outline of the general requirements found in the 2005 National Electrical Code (NEC) Article 690 for Photovoltaic
PHOTOVOLTAIC ELECTRICAL POWER SYSTEMS INSPECTOR/INSTALLER CHECKLIST The following checklist is an outline of the general requirements found in the 2005 National Electrical Code (NEC) Article 690 for Photovoltaic
Using Inverter Input Modes for Smart Grid Management
 Using Inverter Input Modes for Smart Grid Management Some battery based grid connected inverters from OutBack Power have a unique collection of functions designed to optimize utility power usage for OutBack
Using Inverter Input Modes for Smart Grid Management Some battery based grid connected inverters from OutBack Power have a unique collection of functions designed to optimize utility power usage for OutBack
- SPECIFICATIONS - - GREEN
 - SPECIFICATIONS - - GREEN 1 - THE TRAFICAM SENSOR, SOLAR POWERED TrafiCam is a video sensor for Vehicle Presence Detection at and nearby signalised intersections. Due to its low power consumption TrafiCam
- SPECIFICATIONS - - GREEN 1 - THE TRAFICAM SENSOR, SOLAR POWERED TrafiCam is a video sensor for Vehicle Presence Detection at and nearby signalised intersections. Due to its low power consumption TrafiCam
M T E C o r p o r a t i o n MATRIX FILTER. SERIES B Volts, 50HZ USER MANUAL PART NO. INSTR REL MTE Corporation
 M T E C o r p o r a t i o n MATRIX FILTER SERIES B 380-415 Volts, 50HZ USER MANUAL PART NO. INSTR - 015 REL. 060628 2006 MTE Corporation IMPORTANT USER INFORMATION NOTICE The MTE Corporation Matrix Filter
M T E C o r p o r a t i o n MATRIX FILTER SERIES B 380-415 Volts, 50HZ USER MANUAL PART NO. INSTR - 015 REL. 060628 2006 MTE Corporation IMPORTANT USER INFORMATION NOTICE The MTE Corporation Matrix Filter
SMPPT. Solar Charge Controller with Maximum Power Point Tracking. Installation & Operation Manual
 SMPPT Solar Charge Controller with Maximum Power Point Tracking 10A/20A/30A 12V/24V Installation & Operation Manual 1 Dear Consumer: Thank you very much for using our product! We will offer you the permanent
SMPPT Solar Charge Controller with Maximum Power Point Tracking 10A/20A/30A 12V/24V Installation & Operation Manual 1 Dear Consumer: Thank you very much for using our product! We will offer you the permanent
