TEPZZ 596 8_B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
|
|
|
- Ernest McGee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) TEPZZ 96 8_B_T (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: Bulletin 17/13 (21) Application number: (22) Date of filing: (1) Int Cl.: F21S 4/00 (16.01) F21V 14/02 (06.01) F21S 9/03 (06.01) F21L 13/06 (06.01) F21V 3/00 (1.01) F21S 2/00 (16.01) F21Y 11/ (16.01) F21Y / (16.01) F21V 21/30 (06.01) F21Y 7/30 (16.01) (86) International application number: PCT/IB11/ (87) International publication number: WO 12/0963 ( Gazette 12/04) (4) LAMP WITH ORIENTABLE LIGHTING SOURCE LAMPE MIT AUSRICHTBARER BELEUCHTUNGSQUELLE LAMPE À SOURCE D ÉCLAIRAGE ORIENTABLE (84) Designated Contracting States: AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR (30) Priority: IN DE1723 (43) Date of publication of application: Bulletin 13/22 (73) Proprietor: Schneider Electric Industries SAS 9200 Rueil-Malmaison (FR) (72) Inventors: DHRUV, Bharadwaj Bangalore (IN) SAI KRISHNA, Kunchala Bangalore (IN) RUPAN, Sarkar Bangalore (IN) (74) Representative: Zerbi, Guido Maria Murgitroyd & Company Piazza Borromeo, Milano (IT) (6) References cited: US-A US-A US-A US-A US-A US-A US-A US-A EP B1 Note: Within nine months of the publication of the mention of the grant of the European patent in the European Patent Bulletin, any person may give notice to the European Patent Office of opposition to that patent, in accordance with the Implementing Regulations. Notice of opposition shall not be deemed to have been filed until the opposition fee has been paid. (Art. 99(1) European Patent Convention). Printed by Jouve, 7001 PARIS (FR)
2 1 EP B1 2 Description BACKGROUND OF INVENTION 1. Field of Invention [0001] The present invention is directed to illumination devices, and more specifically, to electrical lamps having reorientable lighting panels. 2. Discussion of Related Art [0002] In underdeveloped and/or developing countries and in rural areas, the availability of reliable electric grid power systems remains spotty at best and alternative electrical source systems can be expensive to install and operate and are not always compatible with available lighting systems. Further, alternate lighting systems often do not provide sufficient room level lighting. As an alternative to electrical lighting in these areas, kerosene lamps are often used, and while these can reliably provide continuous light, they can be dangerous to use, cause health problems, and contribute to increases in atmospheric CO 2. US09/13611A1 is an example of prior art portable lamp. SUMMARY OF INVENTION [0003] At least one embodiment discussed herein is directed to an efficient lighting system for use particularly in areas having unreliable and or prohibitively expensive electric grid systems. [0004] A first aspect of the invention is directed to a portable lamp. The portable lamp comprises a base having an upper surface, a substrate coupled to the base on the upper surface of the base, the substrate including at least one surface having a plurality of light emitting units disposed thereon, the substrate being movable relative to the base to direct light emitted from the light emitting units in a desired direction, and a light-transmitting cover surrounding the substrate. [000] In some embodiments, the substrate includes at least two panels rotatably mounted about a vertical axis perpendicular to the upper surface of the base, a first of the at least two panels being rotatable relative to a second of the at least two panels. [0006] In some embodiments, each of the plurality of light emitting units comprises a light emitting diode. [0007] In some embodiments, the at least two panels are configured to rotate into positions such that the at least two panels are substantially coplanar. [0008] In some embodiments, the at least two panels are configured to rotate into positions wherein the at least two panels substantially circumscribe a closed two dimensional polygon oriented perpendicular to the vertical axis. [0009] In some embodiments, each of the at least two panels is hingedly coupled to at least one other of the at least two panels. [00] In some embodiments, the base includes a compartment for at least one battery, and the at least two panels are configured to be powered by the at least one battery. [0011] In some embodiments, the base includes a dynamo configured to be manually operated to charge the at least one battery. [0012] In some embodiments, the portable lamp further comprises a solar cell configured to simultaneously provide power for illumination of the plurality of light emitting units as well as charge the at least one battery upon exposure of the solar cell to light.. [0013] In some embodiments, the portable lamp further comprises an AC power inlet. [0014] In some embodiments, the portable lamp further comprises a first circuit configured to simultaneously provide power for illumination of the plurality of light emitting units as well as charge a battery included in the portable lamp with power provided through the AC power inlet. [001] In some embodiments, the portable lamp further comprises a second circuit configured to detect the availability of power from the AC inlet and the solar cell, and when power is available from both the AC inlet and the solar cell, to operate the lamp using power from the solar cell only. [0016] In some embodiments, the portable lamp further comprises a third circuit configured to detect the unavailability of power from the AC inlet, the solar cell, and the dynamo, and in response, switch from a mode in which the substrate is operated utilizing power provided through the AC inlet, the solar cell, or the dynamo to a mode in which the substrate is operated utilizing power provided by the battery. [0017] Another aspect of the invention is directed to a method of operating a lamp including a plurality of configurable lighting panels. The method comprises electrically coupling a source of power to the plurality of configurable lighting panels, and orienting the plurality of configurable lighting panels in a desired position ranging from an open position in which the plurality of configurable lighting panels are positioned in a substantially planar configuration and a closed position in which the plurality of configurable lighting panels circumscribe a substantially closed two dimensional figure. [0018] In some embodiments, the method further comprises electrically coupling a source of power positioned external to the lamp to a source of power positioned internal to the lamp. [0019] In some embodiments, the method further comprises orienting the plurality of configurable lighting panels into an intermediate position in which the plurality of configurable lighting panels are positioned in a substantially non-planar configuration. [00] Another aspect of the invention is directed to a lamp. The lamp comprises base and a plurality of light panels, each configured to extend from the base in a first 2
3 3 EP B1 4 direction defined by a first axis, and each having a plurality of lighting elements configured to provide illumination along at least one of a plurality of axes that reside in a first plane which is perpendicular to the first axis, wherein each of the plurality of light panels are rotatably mounted to the base and rotatable about a rotation axis that is parallel to the first axis. [0021] In some embodiments, a first of the plurality of light panels is rotatable relative to a second of the plurality of light panels. [0022] In some embodiments, the first of the plurality of light panels and the second of the plurality of light panels are configured to rotate into positions such that the first of the plurality of light panels and the second of the plurality of light panels are substantially coplanar. [0023] In some embodiments, the first of the plurality of light panels and the second of the plurality of light panels are configured to rotate to a position wherein the plurality of light panels substantially circumscribe a closed two dimensional figure oriented perpendicular to the first axis. [0024] In some embodiments, each of the plurality of light panels is hingedly coupled to at least one other of the plurality of light panels. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS [002] The accompanying drawings are not intended to be drawn to scale. In the drawings, each identical or nearly identical component that is illustrated in various figures is represented by a like numeral. For purposes of clarity, not every component may be labeled in every drawing. In the drawings: FIG. 1 is an isometric view of a lamp in accordance with one embodiment including a set of light emitting panels in an open position; FIG. 2 is an isometric view of the lamp of FIG. 1 with the set of light emitting panels in a partially closed position; FIG. 3 is an isometric view of the lamp of FIG. 1 with the set of light emitting panels in a fully closed position; FIG. 4 is a plan view of the lamp of FIG. 1 from above, with the set of light emitting panels in an open position; FIG. is a plan view of the lamp of FIG. 1 from above, with the set of light emitting panels in a closed position; FIG. 6 illustrates a set of gears for reorienting the light emitting panels according to one embodiment, with the set of light emitting panels in an open position; FIG. 7 illustrates a set of gears for reorienting the light emitting panels according to the embodiment of FIG. 6, with the set of light emitting panels in a closed position; FIG. 8 shows an LED array used in the embodiment of FIGS. 1-; FIG. 9 shows a functional block diagram of a lamp in accordance with one embodiment; FIG. shows a functional block diagram of a lamp in accordance with another embodiment; and FIG. 11 shows a functional block diagram of a lamp in accordance with another embodiment. DETAILED DESCRIPTION [0026] The systems and methods described herein are not limited in their application to the details of construction and the arrangement of components set forth in the following description or illustrated in the drawings. The invention is capable of other embodiments and of being practiced or of being carried out in various ways. Also, the phraseology and terminology used herein is for the purpose of description and should not be regarded as limiting. The use of "including," "comprising," or "having," "containing," "involving," and variations thereof herein, is meant to encompass the items listed thereafter and equivalents thereof as well as additional items. [0027] At least some embodiments disclosed herein are directed to modular, portable, lighting systems and methods, including LED lamps, operable from DC power sources including battery power sources, solar power, and AC power sources including a utility electrical grid, generator, or other AC power source. At least some embodiments are directed to LED lamps having LEDs arranged to provide full room lighting from a compact, portable unit, and are configurable for dual power mode operation and in some embodiments, to provide for low power operation on battery power. [0028] At least some embodiments disclosed herein are directed toward lamps having one or more orientable light emitting panels or substrates. The terms "panels" and "substrates" are used interchangeably herein. In accordance with one embodiment, a lamp has a plurality of light emitting panels that may be oriented to provide light 360 degrees around the lamp. The light emitting panels are re-arrangeable or reorientable such that they can also provide light from the lamp substantially unidirectionally. In use, the lamp is configurable to provide light 360 degrees about the lamp when placed in the center of a room or a table, and configurable to provide a unidirectional light source when placed against a wall or in a corner of a room. Embodiments of the lamp may also provide illumination covering any desired angle between a single direction and 360 degrees. [0029] In a first embodiment, illustrated in FIGS. 1-, a portable lamp includes a plurality of light emitting panels 1. In FIGS. 1-, the lamp is illustrated as including three light emitting panels 1, however, in alternate embodiments, more or fewer light emitting panels may be provided. For example, in some embodiments, only a single panel may be present in the lamp. In some embodiments, this single panel may be fixed relative to the base of the lamp, and in other embodiments, the single panel may 3
4 EP B be rotatable relative to the base, using for example a crank or a shank coupled to the panel and extending outward from a body or a cover of the lamp. Each of the light emitting panels includes an array of light emitting elements (also referred to herein as light emitting units) 2. In the embodiment illustrated, these light emitting elements are LEDs. [0030] In one embodiment, the LED array 2 on each light emitting panel 1 is implemented using a 3 x 30 array of closely spaced LEDs as shown in FIG. 8. In one embodiment, the three rows are spaced 6.98 mm apart, with the LEDs of each row spaced at 8.6mm intervals, and with each LED having a five mm diameter. In one embodiment, the LEDs have a forward voltage of 3.0 to 3. volts, a peak forward current of ma, a reverse voltage of five volts, reverse current of ten microamps, a luminous intensity of milli Candela (mcd) and are white with a wavelength of 800K. In other embodiments, LEDs having different characteristics may be used. [0031] In one embodiment, additional indicator lights, including for example, a green LED, a red LED, and/or a yellow LED are also provided, and in this embodiment, illumination of the green LED indicates that the power from the grid supply, the solar panel, or an alternate source of power is available and is charging a battery internal to the lamp, illumination of the yellow LED indicates that the battery is fully charged, and illumination of the red LED indicates that the battery is drained and load is cut off from the battery. In other embodiments, different of these LEDs are illuminated to indicate different conditions. [0032] The light emitting panels 1 are mounted on a base 3 of the lamp 0, specifically on a top surface of the base. A light transmitting cover 7 surrounds the light emitting panels 1. In some embodiments the light transmitting cover 7 is transparent and in other embodiments, the light transmitting cover 7 is translucent. The base 3 further includes a crank 11 protruding from a side thereof that is used to adjust the position of the light emitting panels 1, as will be explained in further detail below. The lamp base 3 is in one embodiment made from plastic (for example, ABS Abstron IM 17A) while the cover 7 is made from transparent plastic (for example, PMMA 876G). In other embodiments, other plastic material(s) or metals can be used for the base 3 and the cover 7. [0033] In the arrangement illustrated in FIGS. 1 and 4, the three light emitting panels 1 have substantially planar surfaces and are arranged co-planar with one another. In this arrangement, light produced by the three light emitting sources is cast substantially unidirectionally. Each of the LEDs in the LED array on each light emitting panel casts light in a conical pattern, in some embodiments, in a cone having both a horizontal and vertical angular spread of about 1 degrees. Thus, the light emitted by the lamp with the light emitting panels aligned as in FIGS. 1 and 4 would not be cast completely unidirectionally, but would have a degree of horizontal and vertical spread. In other embodiments, different LEDs or other light emitting elements which have a greater or lesser degree of spread in light emitted are used, thus providing for different angular areas that would be illuminated by the lamp when the light emitting elements were arranged as in FIGS. 1 and 4. In some embodiments, the light emitting panel 1 may be positioned to be parallel to one another, but not necessarily in a co-planar arrangement. In further embodiments, one or more of the light emitting panels may have a non-planar surface. For example, in some embodiments, one or more of the light emitting panels may have a curved surface upon which light emitting elements are mounted. In some embodiments one or more of the light emitting panels may comprise multiple sections, with at least one section joined to at least one other section at an angle. [0034] In some embodiments, the light emitting panels 1 are attached to one another by hinges 113 (see FIGS. 4 and.) The hinges 113 provide for the light emitting panels to rotate relative to each other. In some embodiments, the light emitting panels are not attached directly to one another by the hinges 113. Rather, the hinges may be in the form of projections from either the top or bottom, or both of one or more of the light emitting panels which are inserted into holes or recesses in the top surface of the base, or in an internal surface of the cover 7, such as an internal surface proximate an upper portion of the cover 7. These projections may be in the form of rods. The hinges may thus, in some embodiments, both support the light emitting panels in place in the lamp and provide for rotation of the panels relative to one another. In some embodiments, the hinges 113 are omitted. [003] In the arrangement shown in FIG. 2, the end light emitting panels 1 are angled relative to the center light emitting panel 1 by an angle of about 10 degrees. This arrangement of the light emitting panels 1 provides for the emission of light covering a greater horizontal area than in the arrangement of light emitting panels illustrated in FIGS. 1 and 4. FIGS. 3 and illustrate the light emitting panels 1 angled relative to one another in a closed position such that the end light emitting panels 1 contact each other along an outer edge. The three light emitting panels 1 thus completely surround an area between them. In the arrangement in FIGS. 3 and, this area approximates a triangle in cross section in a plane perpendicular to a vertical axis of the lamp when viewed from above. In embodiments where a greater number of light emitting panels are used, when in a closed position, a different two-dimensional polygon would be circumscribed by the inner surfaces of the light emitting panels. For example, in embodiments including four light emitting panels, when the light emitting sources are in a closed position, they define an area with a square or rectangular cross section when viewed from above. In some embodiments, one or more of the light emitting panels may be non-planar. Thus, in some embodiments, when 4
5 7 EP B1 8 the light emitting panels are in a closed potion, the area surrounded by the light emitting panels may be a figure other than a polygon, for example, a circle, an ellipse, or a triangle or rectangle with curved sides. [0036] In some embodiments, the end light emitting panels 1 do not make physical contact with each other along their outer edges, but rather are configured to maintain a small spacing between their respective outer edges. Maintaining a small spacing between the outer edges of the end light emitting panels 1 prevents the end light emitting panels 1 from colliding with, and potentially damaging each other. In embodiments wherein a small spacing is maintained between the outer edges of the end light emitting panels 1, when the light emitting panels 1 are angled relative to one another in a closed position, the light emitting panels 1 will circumscribe a substantially closed two dimensional polygon oriented perpendicular to a vertical axis of the lamp. [0037] The light emitting panels 1 are rotated relative to each other by manual rotation of the crank 11. In one embodiment, the crank 11 is mechanically coupled to a series of gears, as is illustrated in FIGS. 6 and 7. Crank 11 is mechanically coupled through shaft 117 to gear 119. Teeth of gear 119 interlock with teeth of gear 121. Thus, a rotation of crank 11 about a horizontal axis relative to the base of the lamp causes a rotation of gear 119 about the horizontal axis and rotation of gear 121 about a vertical axis relative to the base of the lamp. [0038] Gear 121 is mechanically coupled to gear 123 and, through gear 123, to gear 12. End light emitting panels 1 are mechanically coupled to gears 123 and 12. The crank 11 may be used as a user interface to rotate one or more of the gears 121, 123, 12 and/or the light emitting panels 1. A rotation of crank 11 which results in a clockwise rotation of gear 121, as viewed from above, will cause a counterclockwise rotation of gear 123 and a clockwise rotation of gear 12. Starting from an open position of end light emitting panels 1, as illustrated in FIG. 6, a counterclockwise rotation of gear 123 and the clockwise rotation of gear 12 will cause end light emitting panels 1 to rotate coaxially with gears 123 and 12, transitioning from the open position to a closed position, as illustrated in FIG. 7. In some embodiments, the crank 11 is located on an underside of the base 3 of the lamp, and is connected directly to gear 119, or in other embodiments, through another gear which is coupled to gear 119. In some embodiments, a series of belts mounted about a group disks are utilized instead of gears to transmit motion from the crank to the light emitting panels. [0039] In some embodiments, stoppers 9 and 111 are provided on the surface of the base of the lamp. Stoppers 9 and 111 are protrusions from the upper surface of the base 3. These stoppers 9 and 111 prevent the rotation of the end light emitting panels 1 past defined positions. The utilization of stoppers 9 and 111 to constrain the range of rotation of end light emitting panels 1 prevents the light emitting panels from being rotated into positions where they would impact each other or overextend the hinges 113. The utilization of stoppers 9 and 111 to constrain the range off rotation of the end light emitting panels 1 thus reduces the potential for a user to inadvertently damage elements of the lamp 0. In some embodiments, the stoppers extend upward from the upper surface of the base 3 to a height above a lower edge of the light emitting panels 1. In some embodiments, the stoppers 9, 111, do not block light from any of the light emitting elements in the arrays of light emitting elements 2 on the light emitting panels 1. In some embodiments, the stoppers 9, 111 are shaped as rectangular protrusions, and in other embodiments are shaped as cylinders or pins protruding from the upper surface of the base 3. In some embodiments, some of the stoppers 9, 111 are shaped differently than others of the stoppers 9, 111. Embodiments of the lamp are not limited to any particular shape of stoppers 9, 111. [0040] In alternate embodiments, different arrangements of gears are used to rotate the light emitting panels 1. For example, additional gears may be used to reposition or rotate the light emitting panels when more than three light emitting panels 1 are used in the lamp 0. It would be apparent to one of skill in the art how to design various gearing systems to rotate/reposition of any number of light emitting panels. [0041] In further embodiments, rather that using a crank 11 to rotate/reposition the light emitting panels 1, an electric motor is used to rotate/reposition the light emitting panels 1. In some embodiments, a user would press a button (or, in some embodiments, reposition a switch) to move the light emitting panels from an open arrangement (for example, as illustrated in FIG. 1) through various positions including a closed position (for example, as illustrated in FIG. 3), and press another button (or in some embodiments, reposition the switch into another position) to move the light emitting panels 1 from a closed arrangement toward an open arrangement. In some embodiments, the electric motor would take the place of the crank 11 and drive gears such as gears 119, 121, 123, and 12 in a similar manner as rotation of the crank 11 would. In other embodiments, multiple electric motors are used to move one or more light emitting panels each. [0042] FIG. 9 is directed to a functional block diagram of the lamp 0 in accordance with one embodiment. The lamp 0 includes an array of LEDs 2, a dual power output control circuit 4, an LED driver circuit 6, a detection circuit 8, mode switches 1 and 112, a battery monitoring circuit 114, a charge control circuit 116, a DC-DC converter 118, a switch mode power supply (SMPS) 1, a battery 122, a solar power source 124, an AC power source 126, a dynamo 127 and associated regulator 129, and power supply mixer 131. In some embodiments, the lamp 0 may also include an electrical connection 316 for charging a cell phone. In different embodiments, functional circuits are grouped differently
6 9 EP B1 than shown in FIG. 9. As used below, references to the LED array 2 are meant to encompass the LED arrays 2 on each light emitting panel 1 of the lamp 0. [0043] The LED array 2 is coupled between the dual power output control circuit 4 and the LED driver 6. Mode switches 1 and 112 are coupled between the LED driver circuit 6 and the battery 122, and the mode switches are also coupled to an output of the charge controller 116. The DC-DC converter 118 is coupled between the solar power source 124 and the mixer 131 and the charge controller 116. The SMPS 1 is coupled between the AC power source and the mixer 131 and the charge controller 116. The regulator 129 is coupled between the dynamo 127 and the mixer 131 and the charge controller 116. The battery 122 is coupled to the charge controller 116, mode switch 112, and the battery monitoring circuit 114. The detection circuit 8 is coupled to the SMPS 1 output, DC -DC converter 118 output, the regulator 129 output, and the dual power output control circuit 4. [0044] In operation, light is provided by the LED array from power provided from one of the AC power source 126, the solar power source 124, the dynamo 127, and the battery 122. When operated from the AC power source, the SMPS receives the input AC power and converts the AC power to DC power. In one embodiment, the input AC voltage is 230 volts at 0 Hz, although in other embodiments, other input voltages at other frequencies may also be used. In one embodiment, the output of both the SMPS 1 and the regulator 129 is 9.3 volts, but other output voltages may also be used. [004] The charge controller 116 receives the voltage from the SMPS and provides an output voltage to the mode switches 1 and 112. The charge controller also provides a charging voltage for the battery 122 (if a battery is included in the system). In AC mode of operation (and in solar and dynamo modes of operation), mode switch 112 is open to isolate the battery, while mode switch 1 is configured to couple the output of the charge controller to the LED driver. The LED driver circuit receives the output voltage of the charge controller 116 and provides a constant current output for the LED array 2 to light the LEDs. [0046] The dual power output control circuit 4 is used to provide a low power mode of operation of the lamp 0 when operated from battery power. In the AC, dynamo, and solar modes of operation, the dual power output control circuit is controlled to operate in normal, high power mode of operation. [0047] Operation in solar mode is the same as in AC mode except that the charge controller 116 receives DC input power provided by the DC-DC converter 118. In one embodiment, the DC-DC converter is configured to receive DC power from an external solar power system having a voltage between 16 volts and 21 volts and to provide output DC power of 9.8 volts to the charge controller 116. In other embodiments, other voltages may be used to accommodate operation with other solar power systems. [0048] Operation in dynamo mode is the same as in AC mode except that the charge controller 116 receives DC input power provided by the regulator 129. In one embodiment, the regulator is configured to receive DC power from the dynamo 127 and to provide output DC power of 9.8 volts to the charge controller 116. In other embodiments, other voltages may be used to accommodate operation with other solar power systems. In some embodiments, the lamp is configured so that the dynamo 127 is utilized to provide power to the LEDs 2 directly, and also used to provide power to charge the battery 122. [0049] In battery mode of operation, DC power is provided from the battery 122 to the internal switch 112, and both mode switch 112 and mode switch 1 are configured to couple the output of the battery to the input of the LED driver. In one embodiment, the lighting system is configured to operate with a battery having an output voltage of 9 volts to. volts, but in other embodiments, other battery voltages may be used. In at least one embodiment, the lighting system is configured to operate with an external battery to accommodate larger, higher capacity batteries, however, in other embodiments, an internal battery may be used in addition to an external battery or in place of the external battery. [000] The detection circuit 8 detects the presence of AC, dynamo, and solar power, and in one embodiment, controls the charge controller 116 to select operation from the solar power source when both AC power and solar power is available to operate the lighting system 0 in a more economical manner. In some embodiments, whenever both AC and solar power is available, the charge controller 116 will preferentially utilize power derived from the solar power input to charge the battery. In some embodiments, whenever both dynamo and solar power is available, the charge controller 116 will preferentially utilize power derived from the dynamo power input to charge the battery. In some embodiments, whenever all of AC, dynamo, and solar power are available, the charge controller 116 will preferentially utilize power derived from the solar power input to charge the battery. The detection circuit 8 also provides a signal to the dual power output control circuit 4 to control the circuit for high power operation if one of AC power, dynamo power, or solar power is available. If none of AC power, dynamo power, nor solar power is available, then the detection circuit 8 controls the dual power output control circuit to operate in low power mode. Operation of the lighting system at low power in battery mode of operation allows the battery to operate for a longer period of time. In one embodiment, the dual power output control circuit 4 is implemented using parallel resistors in series with the LED array, and a switch (such as a transistor) is used to alter the value of the resistance in series with the LED array to limit the drive current to the LED array. In one embodiment, the total current through the LED array is 80mA in high power mode of operation and is reduced to 00mA in low power mode of operation. How- 6
7 11 EP B1 12 ever, depending on the number and type of LEDs used in the array, other values of drive current may be used in other embodiments. [001] As shown in FIG. 9, switch 1 is a manually operated switch that may be used by a user to power the lighting system 0 on and off. As shown in FIG. 9, in one embodiment, the switch 1 is connected between charge controller 116 output, internal switch 112, and LED driver 6. A dimmer 130 is also provided in some embodiments, which provides for a user to manually control the brightness of the lamp and the power consumed. In some embodiments, the dimmer may be located in a different position than is illustrated in FIG. 9. For example, in some embodiments, the dimmer 130 is located between the switch 1 and the LED driver 6. In some embodiments, the dimmer 130 comprises a potentiometer. The dimmer 130, in some embodiments, is manually operated by a knob or switch (not shown) extending from the body of the lamp. [002] In one embodiment, the internal switch 112 is a controllable switch, such as a diode. The switch may be controlled by forward biasing or reverse biasing the diode. The diode is reverse biased when power is available either from SMPS 1 and/or DC -DC converter 118 and/or regulator 129, thereby disconnecting the driver 6 from the battery 122. The diode is forward biased when power is not available either from SMPS 1 and/or DC -DC converter 118 and/or regulator 129 and the lamp 0 is powered from the battery 122. In one embodiment, switch 112 is controlled to be in the open position if solar, dynamo, or AC power is available, and if none of these is available, the switch 112 is closed to couple the battery 122 to the LED driver. In one embodiment, the battery monitoring circuit 114 is coupled to output of battery 122 and LED driver 6. This circuit monitors remaining charge of the battery and gives a signal to the driver 6 to cut off the power supply to LED array 2 when the battery drains to 0% of its full charge level. In other embodiments, the battery may be drained to 80% of its full charge level. The red indication LED is illuminated when the battery drains to 0% of its full charge capacity and the switch 1 is ON position. [003] As discussed in more detail below, in at least some embodiments, the lamp 0 is a modular, upgradeable assembly, having several versions, and the specific electronics contained in the lamp can be varied based on the particular version of the lamp. More specifically, the SMPS board, the dynamo board (comprising the dynamo 127 and regulator 129), and the solar board may be removed or upgraded to change the version of the lamp. To easily accommodate changing the SMPS board, the dynamo board, and the solar board, connection between the boards is accomplished, in one embodiment, using flexible cables between the boards with terminal block connectors coupling the cables to the boards. The LED driver board, the solar board, the dynamo board, and the SMPS board are, in one embodiment, all mounted within the base 3 of the lamp [004] The light emitting panels 1, in one embodiment, contain the LED array 2 mounted on a printed circuit board with the board electrically coupled to the LED driver board. [00] As briefly discussed above, in one embodiment, the lamp 0 can be modular and easily configured between multiple different versions. The modularity allows cost-efficient operation that effectively matches the lamp to a user based on power available to the user, allowing a user to purchase only the electronic circuitry needed to match the power sources available. In one embodiment, six different versions are provided. The six versions include: (1) LED lamp powered by battery only; (2) LED lamp powered by AC supply with a battery backup; (3) LED lamp powered by solar panel with a battery backup, (4) LED lamp powered by dynamo with a battery backup, () LED lamp powered by AC supply or solar panel with a battery backup; and (6) LED lamp powered by AC supply or solar panel or dynamo with a battery backup. Version 1 is considered the most basic version and with additional circuitry added, version 1 can be upgraded to any one of versions 2, 3, or 4. Each of versions 2, 3, and 4 is considered an intermediate version and each of these can be upgraded to versions or 6 which are considered advanced versions. The functional block diagram shown in FIG. 9 is representative of version 6, an advanced version, in accordance with one embodiment. [006] Functional block diagrams of the different versions of the lamp 0 are shown in FIGS. and 11, along with representations of the differences between the versions. FIGS and 11 illustrate versions 1, 2, 3, and. For clarity, the additional circuitry for versions 4 and 6 are not illustrated. Versions 4 and 6 would be similar to the versions illustrated in FIGS. and 11, but with the dynamo board substituted for or added in addition to the AC board 308 and/or solar board 3 shown. Reference numerals used for the functional circuit blocks in the functional block diagrams of FIGS. and 11 are the same as those used in FIG. 9. The basic version 300 includes the array of LEDs 2, the LED driver circuitry 6, the battery monitoring and control circuitry 114, the charge controller 116, and the battery 122. The battery 122 may be an internal battery or a larger external battery to provide additional capacity. In one embodiment, the basic version also includes the detection circuit 8 and the dual power circuit 4 of FIG. 9. [007] As illustrated in FIG., the basic version can be upgraded to either the intermediate version (2) 302 or the intermediate version (3) 304 by adding additional functional module 308 or 3, respectively. Functional module 308 includes the SMPS 1, and an AC supply 126. Functional module 3 includes the DC-DC converter 118 and the solar power source 124. In some embodiments of the invention, the AC source is not included on the body of the lamp, but rather a connection for an AC source is added, and similarly, solar panels and associated devices are not added to the body of the lamp, but rather a connection to a source of solar power is add- 7
8 13 EP B1 14 ed. In a similar manner, the basic version could be upgraded to an intermediate version including a dynamo by adding a dynamo and a corresponding circuit board (not shown), [008] As illustrated in FIG. 11, either of the intermediate versions may be upgraded to the advanced version by adding the functionality provided by either functional module 312 or functional module 314. Functional module 312 includes the DC-DC converter 118 and the solar power source 124. Functional module 314 includes the SMPS 1 and the AC supply 126. A dynamo and a functional module including circuitry such as the regulator 129 could also be added to an intermediate version to produce an advanced version of the lamp including a dynamo power source. [009] In the modular embodiment described above, the charge controller 116 is a part of the basic version, and accordingly, is not included in the modules added to the basic version to create the intermediate versions. In this embodiment, the lamp 0 can be configured in the basic version with the driver board included in the base 3, and both the SMPS board and the solar board removed from the base. The lamp 0 is upgraded to version (2) by adding the SMPS board in the base 3. The lamp can then be upgraded from version (2) to version () by adding the solar board inside the base. Version (3) is achieved by adding the solar board to version (1), and version (3) can be upgraded to version () with the addition of the SMPS board. In another embodiment, the charge controller 116 is not included in the basic version, but is included in both intermediate versions. [0060] The ability to upgrade the lamp 0 allows a user to purchase an affordable light assembly to meet current needs and to upgrade the lamp 0 as additional power sources become available. The modularity also simplifies manufacturing by allowing a single upgradeable assembly to be configured in six different versions, rather than providing six separate assemblies. [0061] Embodiments of the lamp described above use LEDs as a source of light. In other embodiments, fluorescent bulbs, compact fluorescent bulbs, incandescent bulbs, and/or other light sources may be used in place of the LEDs. [0062] In embodiments described above, four primary sources of power are discussed: AC grid, dynamo, battery, and solar. In other embodiments, lamps may be configured for operation with other power sources, including fuel cells and wind power in place of, or in addition to AC grid, dynamo, battery, and solar power. [0063] Any references above to front and back, left and right, top and bottom, or upper and lower and the like are intended for convenience of description, not to limit the present systems and methods or their components to any one positional or spatial orientation. [0064] Any references to embodiments or elements or acts of the systems and methods herein referred to in the singular may also embrace embodiments including a plurality of these elements, and any references in plural to any embodiment or element or act herein may also embrace embodiments including only a single element. References in the singular or plural form are not intended to limit the presently disclosed systems or methods, their components, acts, or elements to single or plural configurations. [006] Any embodiment disclosed herein may be combined with any other embodiment, and references to "an embodiment," "some embodiments," "an alternate embodiment," "various embodiments," "one embodiment" or the like are not necessarily mutually exclusive and are intended to indicate that a particular feature, structure, or characteristic described in connection with the embodiment may be included in at least one embodiment. Such terms as used herein are not necessarily all referring to the same embodiment. Any embodiment may be combined with any other embodiment in any manner consistent with the aspects and embodiments disclosed herein. [0066] References to "or" may be construed as inclusive so that any terms described using "or" may indicate any of a single, more than one, and all of the described terms. [0067] Where technical features in the drawings, detailed description or any claim are followed by references signs, the reference signs have been included for the sole purpose of increasing the intelligibility of the drawings, detailed description, and claims. Accordingly, neither the reference signs nor their absence have any limiting effect on the scope of any claim elements. [0068] Accordingly, the foregoing description and drawings are by way of example only. Claims 1. A portable lamp (0) comprising: a base (3) having an upper surface () ; a substrate coupled to the base on the upper surface of the base, the substrate including at least one surface having a plurality of light emitting units (2) disposed thereon, the substrate being movable relative to the base to direct light emitted from the light emitting units (2) in a desired direction; a light-transmitting cover (7) surrounding the substrate; and a battery (122), the lamp being modular and configurable between at least two versions, the versions including (1) a basic version in which the lamp is powered by battery only, (2) an intermediate version in which the lamp is powered by an alternating current (AC) supply with a battery backup, (3) an intermediate version in which the lamp is powered by a solar panel with a battery backup, (4) an intermediate version in which the lamp is powered by a dynamo with a battery backup, () an advanced version in which the 8
9 1 EP B1 16 lamp is powered by an AC supply or solar panel with a battery backup, and (6) an advanced version in which the lamp is powered by an AC supply or solar panel with a battery backup or dynamo with a battery backup, the basic version upgradeable to version (2) by addition of a switch mode power supply (SMPS) (1) and an AC supply (126) into the base, the basic version upgradeable to intermediate version (3) by addition of a DC-DC converter (118) and a solar power source (124) into the base, the basic version upgradeable to intermediate version (4) by adding a dynamo and a corresponding circuit board into the base, the intermediate versions upgradeable to the advanced versions by adding functionality provided by other functional modules (312, 314). 2. The portable lamp (0) of claim 1, wherein the substrate includes at least two panels (1) rotatably mounted about a vertical axis perpendicular to the upper surface of the base, a first of the at least two panels (1) being rotatable relative to a second of the at least two panels (1). 3. The portable lamp (0) of claim 2, wherein each of the plurality of light emitting units (2) comprises a light emitting diode The portable lamp (0) of claim 1, further comprising an AC power inlet. 11. The portable lamp (0) of claim, further comprising a first circuit configured to simultaneously provide power for illumination of the plurality of light emitting units (2) as well as charge a battery included in the portable lamp (0) with power provided through the AC power inlet. 12. The portable lamp (0) of claim 11, further comprising a second circuit configured to detect the availability of power from the AC inlet and the solar cell, and when power is available from both the AC inlet and the solar cell, to operate the lamp using power from the solar cell only. 13. The portable lamp (0) of claim 11, further comprising a third circuit configured to detect the unavailability of power from the AC inlet, the solar cell, and the dynamo, and in response, switch from a mode in which the substrate is operated utilizing power provided through the AC inlet, the solar cell, or the dynamo to a mode in which the substrate is operated utilizing power provided by the battery. 14. A method of operating a lamp including a plurality of configurable lighting panels, the method comprising: 4. The portable lamp (0) of claim 2, wherein the at least two panels (1) are configured to rotate into positions such that the at least two panels (1) are substantially coplanar.. The portable lamp (0) of claim 2, wherein the at least two panels (1) are configured to rotate into positions wherein the at least two panels (1) substantially circumscribe a closed two dimensional polygon oriented perpendicular to the vertical axis. 6. The portable lamp (0) of claim 2, wherein each of the at least two panels (1) is hingedly coupled to at least one other of the at least two panels(1). 7. The portable lamp (0) of claim 2, wherein the base includes a compartment for at least one battery, and the at least two panels (1) are configured to be powered by the at least one battery. 8. The portable lamp (0) of claim 7, wherein the base includes a dynamo configured to be manually operated to charge the at least one battery. 9. The portable lamp (0) of claim 7, further comprising a solar cell configured to simultaneously provide power for illumination of the plurality of light emitting units (2) as well as charge the at least one battery upon exposure of the solar cell to light supplying power to the lamp from a source of power mounted in a base of the lamp, the lamp being modular and configurable between at least two versions, the versions including (1) a basic version in which the lamp is powered by battery only, (2) an intermediate version in which the lamp is powered by an alternating current (AC) supply with a battery backup, (3) an intermediate version in which the lamp is powered by a solar panel with a battery backup, (4) an intermediate version in which the lamp is powered by a dynamo with a battery backup, () an advanced version in which the lamp is powered by an AC supply or solar panel with a battery backup, the basic version upgradeable to version (2) by addition of a switch mode power supply (SMPS) (1) and an AC supply (126) into the base, the basic version upgradeable to version (3) by addition of a DC-DC converter (118) and a solar power source (124) into the base; the basic version upgradeable to version (4) by adding a dynamo and a corresponding circuit board into the base, the intermediate versions upgradeable to the advanced versions by adding functionality provided by other functional modules; electrically coupling the source of power to the plurality of configurable lighting panels; and orienting the plurality of configurable lighting 9
10 17 EP B1 18 panels in a desired position ranging from an open position in which the plurality of configurable lighting panels are positioned in a substantially planar configuration and a closed position in which the plurality of configurable lighting panels circumscribe a substantially closed two dimensional figure. 1. The method of claim 14, further comprising electrically coupling a source of power positioned external to the lamp to a source of power positioned internal to the lamp. Patentansprüche 1. Eine tragbare Lampe (0), die das Folgende beinhaltet: ein Unterteil (3), das eine obere Oberfläche () aufweist; ein Trägermaterial, das auf der oberen Oberfläche des Unterteils an das Unterteil gekoppelt ist, wobei das Trägermaterial mindestens eine Oberfläche umfasst, die eine Vielzahl von lichtemittierenden Einheiten (2) darauf angeordnet aufweist, wobei das Trägermaterial relativ zum Unterteil beweglich ist, um von den lichtemittierenden Einheiten (2) emittiertes Licht in eine gewünschte Richtung zu lenken; eine lichtdurchlässige Abdeckung (7), die das Trägermaterial umgibt; und eine Batterie (122), wobei die Lampe modular ist und zwischen mindestens zwei Versionen konfigurierbar ist, wobei die Versionen (1) eine Basisversion, bei der die Lampe nur durch eine Batterie mit Strom versorgt wird, (2) eine Mittelversion, bei der die Lampe durch eine Wechselstromversorgung mit einer Batterienotstromversorgung mit Strom versorgt wird, (3) eine Mittelversion, bei der die Lampe durch ein Solarpanel mit einer Batterienotstromversorgung mit Strom versorgt wird, (4) eine Mittelversion, bei der die Lampe durch einen Dynamo mit einer Batterienotstromversorgung mit Strom versorgt wird, () eine erweiterte Version, bei der die Lampe durch eine Wechselstromversorgung oder ein Solarpanel mit einer Batterienotstromversorgung mit Strom versorgt wird, und (6) eine erweiterte Version, bei der die Lampe durch eine Wechselstromversorgung oder ein Solarpanel mit einer Batterienotstromversorgung oder einen Dynamo mit einer Batterienotstromversorgung mit Strom versorgt wird, umfassen, wobei die Basisversion zur Version (2) aufgerüstet werden kann, indem ein Schaltnetzteil (SNT) (1) und eine Wechselstromversorgung (126) im Unterteil hinzugefügt werden, die Basisversion zur Mittelversion (3) aufgerüstet werden kann, indem ein Gleichstromwandler (118) und eine Solarstromquelle (124) im Unterteil hinzugefügt werden, die Basisversion zur Mittelversion (4) aufgerüstet werden kann, indem ein Dynamo und eine entsprechende Leiterplatte im Unterteil hinzugefügt werden, die Mittelversionen zu den erweiterten Versionen aufgerüstet werden können, indem Funktionalität hinzugefügt wird, die durch andere funktionale Module (312, 314) bereitgestellt wird. 2. Tragbare Lampe (0) gemäß Anspruch 1, wobei das Trägermaterial mindestens zwei Platten (1) umfasst, die drehbar um eine Vertikalachse senkrecht zur oberen Oberfläche des Unterteils montiert sind, wobei eine erste der mindestens zwei Platten (1) relativ zu einer zweiten der mindestens zwei Platten (1) drehbar ist. 3. Tragbare Lampe (0) gemäß Anspruch 2, wobei jede der Vielzahl von lichtemittierenden Einheiten (2) eine lichtemittierende Diode beinhaltet. 4. Tragbare Lampe (0) gemäß Anspruch 2, wobei die mindestens zwei Platten (1) konfiguriert sind, um sich so in Positionen zu drehen, dass die mindestens zwei Platten (1) im Wesentlichen koplanar sind.. Tragbare Lampe (0) gemäß Anspruch 2, wobei die mindestens zwei Platten (1) konfiguriert sind, um sich in Positionen zu drehen, wobei die mindestens zwei Platten (1) im Wesentlichen ein geschlossenes zweidimensionales Vieleck umschreiben, das senkrecht zur Vertikalachse ausgerichtet ist. 6. Tragbare Lampe (0) gemäß Anspruch 2, wobei jede der mindestens zwei Platten (1) mit mindestens einer anderen der mindestens zwei Platten (1) klappbar gekoppelt ist. 7. Tragbare Lampe (0) gemäß Anspruch 2, wobei das Unterteil ein Fach für mindestens eine Batterie umfasst und die mindestens zwei Platten (1) konfiguriert sind, um durch die mindestens eine Batterie mit Strom versorgt zu werden. 8. Tragbare Lampe (0) gemäß Anspruch 7, wobei das Unterteil einen Dynamo umfasst, der konfiguriert ist, um manuell betrieben zu werden, um die mindestens eine Batterie zu laden. 9. Tragbare Lampe (0) gemäß Anspruch 7, die ferner eine Solarzelle beinhaltet, die konfiguriert ist, um Strom für die Beleuchtung der Vielzahl von lichtemittierenden Einheiten (2) bereitzustellen und,
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/42
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 512 002 A2 (43) Date of publication: 17.10.2012 Bulletin 2012/42 (51) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 (2006.01) H02J 7/35 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11250613.4
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 512 002 A2 (43) Date of publication: 17.10.2012 Bulletin 2012/42 (51) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 (2006.01) H02J 7/35 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11250613.4
TEPZZ Z Z 85A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ Z Z 8A_T (11) EP 3 0 38 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 18.0.16 Bulletin 16/ (21) Application number: 1482271.7 (22)
(19) TEPZZ Z Z 8A_T (11) EP 3 0 38 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 18.0.16 Bulletin 16/ (21) Application number: 1482271.7 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: B66C 13/14 ( ) B66C 3/00 ( ) A01G 23/08 ( ) E02F 9/22 ( ) E02F 3/36 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 8 4Z59A_T (11) EP 2 824 059 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.01.2015 Bulletin 2015/03 (21) Application number: 13181144.0 (51) Int Cl.: B66C 13/14 (2006.01) B66C
(19) TEPZZ 8 4Z59A_T (11) EP 2 824 059 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.01.2015 Bulletin 2015/03 (21) Application number: 13181144.0 (51) Int Cl.: B66C 13/14 (2006.01) B66C
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: F16H 47/04 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 6774A T (11) EP 2 67 74 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.10.2013 Bulletin 2013/44 (1) Int Cl.: F16H 47/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1316271.1 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 6774A T (11) EP 2 67 74 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.10.2013 Bulletin 2013/44 (1) Int Cl.: F16H 47/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1316271.1 (22) Date
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/41
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001585051A1* (11) EP 1 585 051 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 12.10.2005 Bulletin 2005/41
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001585051A1* (11) EP 1 585 051 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 12.10.2005 Bulletin 2005/41
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2008/04
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 880 821 A1 (43) Date of publication: 23.01.2008 Bulletin 2008/04 (51) Int Cl.: B29C 45/14 (2006.01) H04M 1/02 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 07008807.5
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 880 821 A1 (43) Date of publication: 23.01.2008 Bulletin 2008/04 (51) Int Cl.: B29C 45/14 (2006.01) H04M 1/02 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 07008807.5
TEPZZ Z6 Z79A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01L 19/14 ( ) G01L 19/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ Z6 Z79A_T (11) EP 3 062 079 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.08.2016 Bulletin 2016/3 (1) Int Cl.: G01L 19/14 (2006.01) G01L 19/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ Z6 Z79A_T (11) EP 3 062 079 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.08.2016 Bulletin 2016/3 (1) Int Cl.: G01L 19/14 (2006.01) G01L 19/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
TEPZZ 6Z7 _6A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2013/26
 (19) TEPZZ 6Z7 _6A_T (11) EP 2 607 216 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (51) Int Cl.: B62D 55/21 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13160462.1 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 6Z7 _6A_T (11) EP 2 607 216 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (51) Int Cl.: B62D 55/21 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13160462.1 (22)
TEPZZ 5 59 A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 5 59 A T (11) EP 2 535 922 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 19.12.2012 Bulletin 2012/51 (21) Application number: 12172230.0 (51) Int Cl.: H01J 61/26 (2006.01) H01J
(19) TEPZZ 5 59 A T (11) EP 2 535 922 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 19.12.2012 Bulletin 2012/51 (21) Application number: 12172230.0 (51) Int Cl.: H01J 61/26 (2006.01) H01J
TEPZZ 7_ Z6ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 ( ) H02K 7/18 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 7_ Z6ZA_T (11) EP 2 712 060 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.03.2014 Bulletin 2014/13 (51) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 (2006.01) H02K 7/18 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ 7_ Z6ZA_T (11) EP 2 712 060 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.03.2014 Bulletin 2014/13 (51) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 (2006.01) H02K 7/18 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(51) Int Cl.: B41F 31/30 ( ) B41F 31/34 ( ) B41F 31/36 ( ) B41F 13/20 ( ) B41F 7/04 ( ) B41F 7/12 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 7ZZ5Z4A T (11) EP 2 700 504 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.02.2014 Bulletin 2014/09 (21) Application number: 13179814.2 (51) Int Cl.: B41F 31/30 (2006.01) B41F
(19) TEPZZ 7ZZ5Z4A T (11) EP 2 700 504 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.02.2014 Bulletin 2014/09 (21) Application number: 13179814.2 (51) Int Cl.: B41F 31/30 (2006.01) B41F
(51) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 ( ) H02J 7/02 ( ) A61B 17/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_684 96B_T (11) EP 1 684 396 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 29.04. Bulletin /18 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 (06.01) H02J 7/02
(19) TEPZZ_684 96B_T (11) EP 1 684 396 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 29.04. Bulletin /18 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 (06.01) H02J 7/02
TEPZZ 6 6 8_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ 6 6 8_A_T (11) EP 2 626 281 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.2013 Bulletin 2013/33 (1) Int Cl.: B62D 3/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1214679.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 6 6 8_A_T (11) EP 2 626 281 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.2013 Bulletin 2013/33 (1) Int Cl.: B62D 3/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1214679.0 (22)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2009/04
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 017 118 A1 (43) Date of publication: 21.01.2009 Bulletin 2009/04 (51) Int Cl.: B60M 1/06 (2006.01) B60M 3/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 08159353.5
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 017 118 A1 (43) Date of publication: 21.01.2009 Bulletin 2009/04 (51) Int Cl.: B60M 1/06 (2006.01) B60M 3/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 08159353.5
TEPZZ 67_744A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B60K 6/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 67_744A_T (11) EP 2 671 744 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/50 (51) Int Cl.: B60K 6/10 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13169502.5 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 67_744A_T (11) EP 2 671 744 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/50 (51) Int Cl.: B60K 6/10 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13169502.5 (22)
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/09
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 159 888 A2 (43) Date of publication: 03.03.2010 Bulletin 2010/09 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 13/53 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09167901.9 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 159 888 A2 (43) Date of publication: 03.03.2010 Bulletin 2010/09 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 13/53 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09167901.9 (22) Date of filing:
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/20
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001531305A1* (11) EP 1 531 305 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.05.2005 Bulletin 2005/20
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001531305A1* (11) EP 1 531 305 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.05.2005 Bulletin 2005/20
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2001/43
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001147979A1* (11) EP 1 147 979 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.10.2001 Bulletin 2001/43
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001147979A1* (11) EP 1 147 979 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.10.2001 Bulletin 2001/43
TEPZZ ZZ9 78A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B65D 85/804 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ ZZ9 78A_T (11) EP 3 009 378 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.04.16 Bulletin 16/16 (1) Int Cl.: B6D 8/804 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1189391.4 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ ZZ9 78A_T (11) EP 3 009 378 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.04.16 Bulletin 16/16 (1) Int Cl.: B6D 8/804 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1189391.4 (22) Date of
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2006/42
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 712 388 A1 (43) Date of publication: 18.10.2006 Bulletin 2006/42 (51) Int Cl.:
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 712 388 A1 (43) Date of publication: 18.10.2006 Bulletin 2006/42 (51) Int Cl.:
(51) Int Cl.: B61F 5/38 ( ) (54) Two- axle bogie for railway vehicle with radially adjustable wheelsets with cross coupling
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 157 007 A1 (43) Date of publication: 24.02.2010 Bulletin 2010/08 (51) Int Cl.: B61F 5/38 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09475002.3 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 157 007 A1 (43) Date of publication: 24.02.2010 Bulletin 2010/08 (51) Int Cl.: B61F 5/38 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09475002.3 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ 7 Z4_ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2014/20
 (19) TEPZZ 7 Z4_ZA_T (11) EP 2 730 410 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.05.2014 Bulletin 2014/20 (21) Application number: 13191611.6 (22) Date of filing: 05.11.2013 (51)
(19) TEPZZ 7 Z4_ZA_T (11) EP 2 730 410 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.05.2014 Bulletin 2014/20 (21) Application number: 13191611.6 (22) Date of filing: 05.11.2013 (51)
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2007/47
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 88 077 A2 (43) Date of publication: 21.11.2007 Bulletin 2007/47 (1) Int Cl.: H01L 23/367 (2006.01) H01L 2/06 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 070731.2
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 88 077 A2 (43) Date of publication: 21.11.2007 Bulletin 2007/47 (1) Int Cl.: H01L 23/367 (2006.01) H01L 2/06 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 070731.2
TEPZZ 7 Z88A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 7 Z88A_T (11) EP 2 722 088 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 23.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/17 (21) Application number: 12799927.4
(19) TEPZZ 7 Z88A_T (11) EP 2 722 088 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 23.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/17 (21) Application number: 12799927.4
TEPZZ 7 8Z6ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 7 8Z6ZA_T (11) EP 2 738 060 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.06.2014 Bulletin 2014/23 (21) Application number: 12194849.1 (51) Int Cl.: B61D 41/04 (2006.01) B60N
(19) TEPZZ 7 8Z6ZA_T (11) EP 2 738 060 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.06.2014 Bulletin 2014/23 (21) Application number: 12194849.1 (51) Int Cl.: B61D 41/04 (2006.01) B60N
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2003/49
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001366948A1* (11) EP 1 366 948 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.12.2003 Bulletin 2003/49
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001366948A1* (11) EP 1 366 948 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.12.2003 Bulletin 2003/49
(54) LITHIUM SECONDARY BATTERY PACK HAVING ENBLOC CLIP FORM COMBINED TO COINCIDE WITH TWO OR FOUR BATTERY COMPARTMENTS OF ELECTRONIC DEVICE
 (19) TEPZZ Z79_8ZA_T (11) EP 3 079 180 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 12..16 Bulletin 16/41 (21) Application number: 14867926.9
(19) TEPZZ Z79_8ZA_T (11) EP 3 079 180 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 12..16 Bulletin 16/41 (21) Application number: 14867926.9
TEPZZ 557 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 557 A_T (11) EP 3 115 573 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/02 (21) Application number: 16176199.4 (51) Int Cl.: F02B 25/20 (2006.01) F02M
(19) TEPZZ 557 A_T (11) EP 3 115 573 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/02 (21) Application number: 16176199.4 (51) Int Cl.: F02B 25/20 (2006.01) F02M
TEPZZ 57847_B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 57847_B_T (11) EP 2 578 471 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 16.03.2016 Bulletin 2016/11 (21) Application number: 11789623.3
(19) TEPZZ 57847_B_T (11) EP 2 578 471 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 16.03.2016 Bulletin 2016/11 (21) Application number: 11789623.3
TEPZZ 55 B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ B_T (11) EP 2 3 332 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.03.16 Bulletin 16/12 (21) Application number: 117609.2 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ B_T (11) EP 2 3 332 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.03.16 Bulletin 16/12 (21) Application number: 117609.2 (22) Date
TEPZZ Z56 96A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2016/33
 (19) TEPZZ Z6 96A_T (11) EP 3 06 396 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 17.08.16 Bulletin 16/33 (21) Application number: 161074.4 (1) Int Cl.: B60T 8/17 (06.01) B60T 8/88 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ Z6 96A_T (11) EP 3 06 396 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 17.08.16 Bulletin 16/33 (21) Application number: 161074.4 (1) Int Cl.: B60T 8/17 (06.01) B60T 8/88 (06.01)
Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) J (12) Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 810 112 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) nt. CI.6: B60H 1/34 03.12.1997
(19) J (12) Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 810 112 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) nt. CI.6: B60H 1/34 03.12.1997
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2009/31
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 083 6 A2 (43) Date of publication: 29.07.09 Bulletin 09/31 (1) Int Cl.: H0K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 08172.9 (22) Date of filing: 0.02.08 (84)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 083 6 A2 (43) Date of publication: 29.07.09 Bulletin 09/31 (1) Int Cl.: H0K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 08172.9 (22) Date of filing: 0.02.08 (84)
TEPZZ _84894A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: F23N 5/12 ( ) F23N 5/24 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ _84894A_T (11) EP 3 184 894 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.06.17 Bulletin 17/26 (1) Int Cl.: F23N /12 (06.01) F23N /24 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1681.0
(19) TEPZZ _84894A_T (11) EP 3 184 894 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.06.17 Bulletin 17/26 (1) Int Cl.: F23N /12 (06.01) F23N /24 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1681.0
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,820,200 Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
TEPZZ 9 Z79A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 9 Z79A_T (11) EP 2 922 079 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.09.2015 Bulletin 2015/39 (21) Application number: 151573.2 (51) Int Cl.: H01H 31/12 (2006.01) H01H
(19) TEPZZ 9 Z79A_T (11) EP 2 922 079 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.09.2015 Bulletin 2015/39 (21) Application number: 151573.2 (51) Int Cl.: H01H 31/12 (2006.01) H01H
TEPZZ 4_8Z84B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 4_8Z84B_T (11) EP 2 418 084 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.09.13 Bulletin 13/36 (21) Application number: 0984.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 4_8Z84B_T (11) EP 2 418 084 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.09.13 Bulletin 13/36 (21) Application number: 0984.0 (22)
TEPZZ ZZ _A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: F28F 3/10 ( ) F28F 3/08 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ ZZ _A_T (11) EP 3 001 131 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.03.16 Bulletin 16/13 (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/ (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1418664.2
(19) TEPZZ ZZ _A_T (11) EP 3 001 131 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.03.16 Bulletin 16/13 (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/ (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1418664.2
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
(19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
TEPZZ Z874Z7B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ Z874Z7B_T (11) EP 2 087 407 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 17.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/29 (21) Application number: 07860559.9
(19) TEPZZ Z874Z7B_T (11) EP 2 087 407 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 17.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/29 (21) Application number: 07860559.9
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 9778 A_T (11) EP 2 977 82 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.01.16 Bulletin 16/04 (21) Application number: 1417804.4 (1) Int Cl.: F02B 19/ (06.01) F02B 19/12 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 9778 A_T (11) EP 2 977 82 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.01.16 Bulletin 16/04 (21) Application number: 1417804.4 (1) Int Cl.: F02B 19/ (06.01) F02B 19/12 (06.01)
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: A61F 5/01 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 86 47A_T (11) EP 2 862 47 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 22.04.201 Bulletin 201/17 (1) Int Cl.: A61F /01 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 14167197.4 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 86 47A_T (11) EP 2 862 47 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 22.04.201 Bulletin 201/17 (1) Int Cl.: A61F /01 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 14167197.4 (22) Date
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial Number 09/208.155 Filing Date 1 December 1998 Inventor Peter W. Machado Edward C. Baccei NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should
Serial Number 09/208.155 Filing Date 1 December 1998 Inventor Peter W. Machado Edward C. Baccei NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0226455A1 Al-Anizi et al. US 2011 0226455A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SLOTTED IMPINGEMENT PLATES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0226455A1 Al-Anizi et al. US 2011 0226455A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SLOTTED IMPINGEMENT PLATES
[0003] [0004] [0005] [0006] [0007]
![[0003] [0004] [0005] [0006] [0007] [0003] [0004] [0005] [0006] [0007]](/thumbs/87/95842819.jpg) MIXING VALVE [0003] The present invention relates to mixing valves. More particularly it relates to thermostatic mixing valves with improved access to check valves and filter screens, and improved settings
MIXING VALVE [0003] The present invention relates to mixing valves. More particularly it relates to thermostatic mixing valves with improved access to check valves and filter screens, and improved settings
TEPZZ Z85967A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ Z8967A_T (11) EP 3 08 967 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26..16 Bulletin 16/43 (21) Application number: 14871329.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ Z8967A_T (11) EP 3 08 967 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26..16 Bulletin 16/43 (21) Application number: 14871329.0 (22)
Your interest is appreciated and hope the next 37 pages offers great profit potential for your new business. Copyright 2017 Frank Seghezzi
 Description and comparison of the ultimate new power source, from small engines to power stations, which should be of interest to Governments the general public and private Investors Your interest is appreciated
Description and comparison of the ultimate new power source, from small engines to power stations, which should be of interest to Governments the general public and private Investors Your interest is appreciated
TEPZZ Z 44Z8A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B64D 33/02 ( ) B64D 41/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ Z 44Z8A_T (11) EP 3 034 8 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 22.06.16 Bulletin 16/2 (1) Int Cl.: B64D 33/02 (06.01) B64D 41/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1199431.6
(19) TEPZZ Z 44Z8A_T (11) EP 3 034 8 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 22.06.16 Bulletin 16/2 (1) Int Cl.: B64D 33/02 (06.01) B64D 41/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1199431.6
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD20: Last updated: 26th September 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD20: Last updated: 26th September 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
ADJUSTABLE PEDAL ASSEMBLY WITH ELECTRONIC THROTTLE CONTROL RELATED APPLICATION. filed Jan. 26, 1999, U.S. Pat. No. 6,109,241.
 ADJUSTABLE PEDAL ASSEMBLY WITH ELECTRONIC THROTTLE CONTROL RELATED APPLICATION [0001] This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 09/236,975, filed Jan. 26, 1999, U.S. Pat. No. 6,109,241.
ADJUSTABLE PEDAL ASSEMBLY WITH ELECTRONIC THROTTLE CONTROL RELATED APPLICATION [0001] This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 09/236,975, filed Jan. 26, 1999, U.S. Pat. No. 6,109,241.
TEPZZ 55_5Z6A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2013/05
 (19) TEPZZ _Z6A T (11) EP 2 1 06 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/0 (1) Int Cl.: F02K 1/72 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1217601.0 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ _Z6A T (11) EP 2 1 06 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/0 (1) Int Cl.: F02K 1/72 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1217601.0 (22) Date of
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,270 B2
 USOO654327OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,270 B2 Cmelik (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) AUTOBODY DENT REPAIR TOOL 4,461,192 A * 7/1984 Suligoy et al.... 81/177.7 4,502,317
USOO654327OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,270 B2 Cmelik (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) AUTOBODY DENT REPAIR TOOL 4,461,192 A * 7/1984 Suligoy et al.... 81/177.7 4,502,317
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Imai USOO6581225B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,581,225 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2003 (54) MATTRESS USED FOR PREVENTING BEDSORES OR THE LIKE (76) Inventor: KaZumichi Imai, 7-29-1222,
(12) United States Patent Imai USOO6581225B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,581,225 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2003 (54) MATTRESS USED FOR PREVENTING BEDSORES OR THE LIKE (76) Inventor: KaZumichi Imai, 7-29-1222,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070257638A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0257638A1 Amend et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2007 (54) TWIST LOCK BATTERY INTERFACE FOR (52) U.S. Cl....
US 20070257638A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0257638A1 Amend et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2007 (54) TWIST LOCK BATTERY INTERFACE FOR (52) U.S. Cl....
Europaisches Patentamt (19) J. European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) J Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 885 802 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) int. CI.6: B62M 23/02 23.12.1998 Bulletin
(19) J Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 885 802 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) int. CI.6: B62M 23/02 23.12.1998 Bulletin
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,205,840 B1
 USOO620584OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,205,840 B1 Thompson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) TIME CLOCK BREATHALYZER 4,749,553 * 6/1988 Lopez et al.... 73/23.3 X COMBINATION
USOO620584OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,205,840 B1 Thompson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) TIME CLOCK BREATHALYZER 4,749,553 * 6/1988 Lopez et al.... 73/23.3 X COMBINATION
(12) United States Patent
 (1) United States Patent US007 1158B1 (10) Patent No.: US 7,115,8 B1 Day et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 006 (54) INDIRECT ENTRY CABLE GLAND (56) References Cited ASSEMBLY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75)
(1) United States Patent US007 1158B1 (10) Patent No.: US 7,115,8 B1 Day et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 006 (54) INDIRECT ENTRY CABLE GLAND (56) References Cited ASSEMBLY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Muranishi
 United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
TEPZZ Z788 6A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: F02C 7/36 ( ) B22F 5/08 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ Z788 6A_T (11) EP 3 078 836 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 12..2016 Bulletin 2016/41 (51) Int Cl.: F02C 7/36 (2006.01) B22F 5/08 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ Z788 6A_T (11) EP 3 078 836 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 12..2016 Bulletin 2016/41 (51) Int Cl.: F02C 7/36 (2006.01) B22F 5/08 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
Continuously Variable Transmission
 Continuously Variable Transmission TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to a transmission, and more particularly, a continuously variable transmission capable of a continuous and constant variation
Continuously Variable Transmission TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to a transmission, and more particularly, a continuously variable transmission capable of a continuous and constant variation
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1
 USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
TEPZZ 9658 A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 968 A T (11) EP 2 96 833 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.01.16 Bulletin 16/02 (21) Application number: 1419648.8 (1) Int Cl.: B21J 1/02 (06.01) B21J 1/14 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 968 A T (11) EP 2 96 833 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.01.16 Bulletin 16/02 (21) Application number: 1419648.8 (1) Int Cl.: B21J 1/02 (06.01) B21J 1/14 (06.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0312869A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0312869 A1 WALTER (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016 (54) CVT DRIVE TRAIN Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2016.0312869A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0312869 A1 WALTER (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016 (54) CVT DRIVE TRAIN Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1
 USOO648.4362B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1 Ku0 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) RETRACTABLE HANDLE ASSEMBLY WITH 5,692,266 A 12/1997 Tsai... 16/113.1 MULTIPLE ENGAGING
USOO648.4362B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1 Ku0 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) RETRACTABLE HANDLE ASSEMBLY WITH 5,692,266 A 12/1997 Tsai... 16/113.1 MULTIPLE ENGAGING
TEPZZ 9 4 7A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 9 4 7A_T (11) EP 2 924 237 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 143822.3 (1) Int Cl.: F01D /08 (06.01) F01D 11/00 (06.01) F01D
(19) TEPZZ 9 4 7A_T (11) EP 2 924 237 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 143822.3 (1) Int Cl.: F01D /08 (06.01) F01D 11/00 (06.01) F01D
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,643,958 B1
 USOO6643958B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Krejci (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 11, 2003 (54) SNOW THROWING SHOVEL DEVICE 3,435,545. A 4/1969 Anderson... 37/223 3,512,279 A 5/1970 Benson... 37/244
USOO6643958B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Krejci (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 11, 2003 (54) SNOW THROWING SHOVEL DEVICE 3,435,545. A 4/1969 Anderson... 37/223 3,512,279 A 5/1970 Benson... 37/244
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD11: Last updated: 3rd February 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly Electrical power is frequently generated by spinning the shaft of a generator which has some
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD11: Last updated: 3rd February 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly Electrical power is frequently generated by spinning the shaft of a generator which has some
Europaisches Patentamt (1 9) Qjl) European Patent Office. Office eurodeen des brevets (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 Europaisches Patentamt (1 9) Qjl) European Patent Office Office eurodeen des brevets (11) EP 0 702 165 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) int. CI.6: F16F7/09, D06F 37/20
Europaisches Patentamt (1 9) Qjl) European Patent Office Office eurodeen des brevets (11) EP 0 702 165 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) int. CI.6: F16F7/09, D06F 37/20
TEPZZ Z4Z 75A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ Z4Z 7A_T (11) EP 3 0 27 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.07.16 Bulletin 16/27 (21) Application number: 1161787. (1) Int Cl.: B64D 13/06 (06.01) B64D 37/32 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ Z4Z 7A_T (11) EP 3 0 27 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.07.16 Bulletin 16/27 (21) Application number: 1161787. (1) Int Cl.: B64D 13/06 (06.01) B64D 37/32 (06.01)
(51) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 ( ) H02K 1/32 ( ) H02K 1/20 ( ) H02K 7/18 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 4ZZ6 4B_T (11) EP 2 400 634 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 02.10.2013 Bulletin 2013/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 (2006.01)
(19) TEPZZ 4ZZ6 4B_T (11) EP 2 400 634 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 02.10.2013 Bulletin 2013/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 (2006.01)
(51) Int Cl.: A47C 7/44 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 66_986B_T (11) EP 2 661 986 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (51) Int Cl.: A47C 7/44 (2006.01)
(19) TEPZZ 66_986B_T (11) EP 2 661 986 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (51) Int Cl.: A47C 7/44 (2006.01)
III III III. United States Patent 19 Justice. 11 Patent Number: position. The panels are under tension in their up position
 United States Patent 19 Justice (54) (76) (21) 22) (51) (52) 58 56) TRUCK BED LOAD ORGANIZER APPARATUS Inventor: 4,733,898 Kendall Justice, P.O. Box 20489, Wickenburg, Ariz. 85358 Appl. No.: 358,765 Filed:
United States Patent 19 Justice (54) (76) (21) 22) (51) (52) 58 56) TRUCK BED LOAD ORGANIZER APPARATUS Inventor: 4,733,898 Kendall Justice, P.O. Box 20489, Wickenburg, Ariz. 85358 Appl. No.: 358,765 Filed:
(SE) Box 236, S Hagfors (SE)
 Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Publication number: 0 1 6 8 6 1 8 Office europeen des brevets r^e- A? EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 85106975.7 int. a.*-. B 60 P 3/12, B
Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Publication number: 0 1 6 8 6 1 8 Office europeen des brevets r^e- A? EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 85106975.7 int. a.*-. B 60 P 3/12, B
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0290654 A1 GOVari et al. US 20070290654A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 20, 2007 (54) INDUCTIVE CHARGING OF TOOLS ON SURGICAL TRAY (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0290654 A1 GOVari et al. US 20070290654A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 20, 2007 (54) INDUCTIVE CHARGING OF TOOLS ON SURGICAL TRAY (76)
Exhibit AA - Socarras References 35 U.S.C. 103 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS WACO DIVISION
 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS WACO DIVISION RETROLED COMPONENTS, LLC, Plaintiff, v. PRINCIPAL LIGHTING GROUP, LLC Defendant. Civil Case No. 6:18-cv-55-ADA JURY TRIAL
IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS WACO DIVISION RETROLED COMPONENTS, LLC, Plaintiff, v. PRINCIPAL LIGHTING GROUP, LLC Defendant. Civil Case No. 6:18-cv-55-ADA JURY TRIAL
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial No.. Filing Date April Inventor Neil J. Dubois NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to: OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH
Serial No.. Filing Date April Inventor Neil J. Dubois NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to: OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
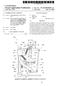 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0159457 A1 Saint-Marc et al. US 2016015.9457A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) RUDDER BAR FOR AN AIRCRAFT (71) Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0159457 A1 Saint-Marc et al. US 2016015.9457A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) RUDDER BAR FOR AN AIRCRAFT (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US B1
 USOO7628442B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Spencer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 2009 (54) QUICK RELEASE CLAMP FOR TONNEAU (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/100.04, COVER 296/100.07,
USOO7628442B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Spencer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 2009 (54) QUICK RELEASE CLAMP FOR TONNEAU (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/100.04, COVER 296/100.07,
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,531,492 Raskevicius (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 1996
 IIIHIIII US005531492A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,531,492 Raskevicius (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 1996 (54) RATCHETING LATCH MECHANISM FOR A 3,123,387 3/1964 Jackson et al.... 292/21
IIIHIIII US005531492A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,531,492 Raskevicius (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 1996 (54) RATCHETING LATCH MECHANISM FOR A 3,123,387 3/1964 Jackson et al.... 292/21
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B60T 8/17 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9445 6A_T (11) EP 2 944 526 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.11.2015 Bulletin 2015/47 (51) Int Cl.: B60T 8/17 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 15166035.4 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 9445 6A_T (11) EP 2 944 526 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.11.2015 Bulletin 2015/47 (51) Int Cl.: B60T 8/17 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 15166035.4 (22)
75 Inventors: William H. Robertson, Jr., Plantation; Primary Examiner-Peter S. Wong
 USOO592O178A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,920,178 Robertson, Jr. et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) BATTERY PACK HAVING INTEGRATED 56) References Cited CHARGING CIRCUIT AND CHARGING
USOO592O178A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,920,178 Robertson, Jr. et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) BATTERY PACK HAVING INTEGRATED 56) References Cited CHARGING CIRCUIT AND CHARGING
(51) Int Cl. 7 : B60B 33/04. (56) References cited:
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP000958150B1* (11) EP 0 958 150 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP000958150B1* (11) EP 0 958 150 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080056631A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0056631 A1 Beausoleil et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2008 (54) TUNGSTEN CARBIDE ENHANCED Publication Classification
US 20080056631A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0056631 A1 Beausoleil et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2008 (54) TUNGSTEN CARBIDE ENHANCED Publication Classification
IIIHIIII 5,509,863. United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. Apr. 23, Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent:
 United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. 54) TRANSMISSION DEVICE, ESPECIALLY FOR BOAT MOTORS 75 Inventors: Staffan Månsson, Hjalteby; Benny Hedlund, Hönö, both of Sweden 73 Assignee: AB Volvo Penta, Gothenburg,
United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. 54) TRANSMISSION DEVICE, ESPECIALLY FOR BOAT MOTORS 75 Inventors: Staffan Månsson, Hjalteby; Benny Hedlund, Hönö, both of Sweden 73 Assignee: AB Volvo Penta, Gothenburg,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 20110283931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0283931 A1 Moldovanu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2011 (54) SUBMARINE RENEWABLE ENERGY GENERATION SYSTEMUSING
US 20110283931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0283931 A1 Moldovanu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2011 (54) SUBMARINE RENEWABLE ENERGY GENERATION SYSTEMUSING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Swihla et al. USOO6287091B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,287,091 B1 Sep. 11, 2001 (54) TURBOCHARGER WITH NOZZLE RING COUPLNG (75) Inventors: Gary R Svihla, Clarendon
(12) United States Patent Swihla et al. USOO6287091B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,287,091 B1 Sep. 11, 2001 (54) TURBOCHARGER WITH NOZZLE RING COUPLNG (75) Inventors: Gary R Svihla, Clarendon
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. WOOdrow (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 20, 2005
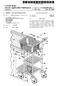 US 2005OO12286A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0012286 A1 WOOdrow (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 20, 2005 (54) SHOPPING CART AND METHOD OF USE Publication Classification
US 2005OO12286A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0012286 A1 WOOdrow (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 20, 2005 (54) SHOPPING CART AND METHOD OF USE Publication Classification
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial No.. Filing Date July Inventor Richard Bonin NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to: OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH
Serial No.. Filing Date July Inventor Richard Bonin NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to: OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH
(12) United States Patent
 US009113558B2 (12) United States Patent Baik (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,113,558 B2 Aug. 18, 2015 (54) LED MOUNT BAR CAPABLE OF FREELY FORMING CURVED SURFACES THEREON (76) Inventor: Seong
US009113558B2 (12) United States Patent Baik (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,113,558 B2 Aug. 18, 2015 (54) LED MOUNT BAR CAPABLE OF FREELY FORMING CURVED SURFACES THEREON (76) Inventor: Seong
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0041248A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0041248 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2011 (54) BEDSORE PREVENTION MATTRESS (76) Inventor: Ju Young KIM,
(19) United States US 2011 0041248A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0041248 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2011 (54) BEDSORE PREVENTION MATTRESS (76) Inventor: Ju Young KIM,
Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office. Publication number: Office europeen des brevets EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 Europaisches Patentamt J t European Patent Office Publication number: 0 265 682 Office europeen des brevets A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 87114152.9 Date of filing: 28.09.87 int. ci*
Europaisches Patentamt J t European Patent Office Publication number: 0 265 682 Office europeen des brevets A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 87114152.9 Date of filing: 28.09.87 int. ci*
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0119137 A1 Cirincione, II et al. US 201701 19137A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) IMPACT ABSORBNG
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0119137 A1 Cirincione, II et al. US 201701 19137A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) IMPACT ABSORBNG
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2
 USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2
 US007125133B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2 Bilotti et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2006 (54) LED LIGHTING SYSTEM FOR PATIO 4.425,602 A 1/1984 Lansing UMBRELLA 5,053,931
US007125133B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2 Bilotti et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2006 (54) LED LIGHTING SYSTEM FOR PATIO 4.425,602 A 1/1984 Lansing UMBRELLA 5,053,931
WWWWWWWWVA IWWA. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1 IWW IWWIWWI IWWWWWW IWW IWWIYIVIVIVINNINWWWWWWIV
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0169926 A1 Watanabe et al. US 2007 O169926A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 >(54) HEAT EXCHANGER (75) Inventors: Haruhiko Watanabe,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0169926 A1 Watanabe et al. US 2007 O169926A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 >(54) HEAT EXCHANGER (75) Inventors: Haruhiko Watanabe,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,220,819 B1
 USOO6220819B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,220,819 B1 Chien et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 24, 2001 (54) CENTRIFUGAL PUMP IMPELLER 3.368,744 2/1968 Jenn... 416/237 4,236,871 12/1980
USOO6220819B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,220,819 B1 Chien et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 24, 2001 (54) CENTRIFUGAL PUMP IMPELLER 3.368,744 2/1968 Jenn... 416/237 4,236,871 12/1980
~ mi mi ii mi ii imiii i ii ii i ii European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) J (12) ~ mi mi ii mi ii imiii i ii ii i ii European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 770 762 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) Int. CI.6: F01 L 1/14,
(19) J (12) ~ mi mi ii mi ii imiii i ii ii i ii European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 770 762 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) Int. CI.6: F01 L 1/14,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O00861 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0008610 A1 PetersOn (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2002 (54) KEY FOB WITH SLIDABLE COVER (75) Inventor: John Peterson,
(19) United States US 2002O00861 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0008610 A1 PetersOn (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2002 (54) KEY FOB WITH SLIDABLE COVER (75) Inventor: John Peterson,
