SERVICE MANUAL. Common Rail System for NISSAN YD1-K2 Type Engine. Operation. For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only
|
|
|
- Vincent Dean
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for NISSAN YD1-K2 Type Engine Operation June, E
2 Foreword To meet the high pressurization requirements for the engine to deliver cleaner exhaust gas emissions, lower fuel consumption and reduced noise, advanced electronic control technology is being adopted in the fuel injection system. This manual covers the electronic control model Common Rail system with HP3 pump for the NISSAN YD1-K2 type engine. Complex theories, special functions and components made by manufacturers other than DENSO are omitted from this manual. This manual will help the reader develop an understanding of the basic construction, operation and system configuration of the DENSO manufactured components and brief diagnostic information. TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Product Application Application System Components Parts Number Outline Features of System Outline of System Construction and Operation Description of Main Components Description of Control System Components Various Types of Controls DTC (Diagnosis Trouble Codes) Table About the Codes shown in the table DTC (Diagnosis Trouble Code) Table External Wiring Diagram ECU External Wiring Diagram ECU Connector Diagram
3 1. Product Application 1-1. Application Vehicle Name Vehicle Model Engine Model Exhaust Volume Reference PREMERA ED YD1-K2 2.2L Made in France ALMERA TINO HS HM 1-2. System Components Parts Number Part Name ED 100 Applicable Model HS HS HM HM 82 DENSO Part Number Car Manufacturer Part Number Reference Supply pump O O O O O AW401 Rail O O O O O AW400 Injector O O O AW kW Engine O O BN800 82kW Engine Engine ECU O AW402 Standard O AW407 w/vdc O AW410 w/ascd O AW415 w/ascd, VDC O BN811 Standard O BN kW Engine w/vdc O BN800 82kW Engine O BN805 82kW Engine w/vdc O BU712 Standard O BU kW Engine w/vdc O BU700 82kW Engine O BU705 82kW Engine w/vdc Crankshaft position sensor O O O O O AW400 Cylinder recognition sensor O O O O O AW410-1-
4 2. Outline 2-1. Features of System The common rail system was developed primarily to cope with exhaust gas regulations for diesel engines, and aimed for 1. further improved fuel economy; 2. noise reduction; and 3. high power output. A. System Characteristics The common rail system uses a type of accumulation chamber called a rail to store pressurized fuel, and injectors that contain electronically controlled solenoid valves to spray the pressurized fuel into the cylinders. Because the engine ECU controls the injection system (including the injection pressure, injection rate, and injection timing), the injection system is unaffected by the engine speed or load. This ensures a stable injection pressure at all times, particularly in the low engine speed range, and dramatically decreases the amount of black smoke ordinarily emitted by a diesel engine during startup and acceleration. As a result, exhaust gas emissions are cleaner and reduced, and higher power output is achieved. a. Injection Pressure Control Enables high-pressure injection even at low engine speeds. Optimizes control to minimize particulate matter and NOx emissions. b. Injection Timing Control Enables finely tuned optimized control in accordance with driving conditions. c. Injection Rate Control Pilot injection control sprays a small amount of fuel before the main injection. -2-
5 B. Comparison to the Conventional System -3-
6 2-2. Outline of System A. Main System Components -4-
7 B. Composition The common rail system consists primarily of a supply pump, rail, injectors, and ECU. C. Operation a. Supply Pump (HP3) The supply pump draws fuel from the fuel tank, and pumps the high pressure fuel to the rail. The quantity of fuel discharged from the supply pump controls the pressure in the rail. The SCV (Suction Control Valve) in the supply pump effects this control in accordance with the command received from the ECU. b. Rail The rail is mounted between the supply pump and the injector, and stores the high-pressure fuel. c. Injector This injector replaces the conventional injection nozzle, and achieves optimal injection by effecting control in accordance with signals from the ECU. Signals from the ECU determine the length of time and the timing in which current is applied to the injector. This in turn, determines the quantity, rate and timing of the fuel that is injected from the injector. d. Engine ECU The engine ECU calculates data received from the sensors to comprehensively control the injection quantity, timing and pressure, as well as the EGR (exhaust gas recirculation). -5-
8 D. Fuel System This system comprises the route through which diesel fuel flows from the fuel tank to the supply pump, via the rail, and is injected through the injector, as well as the route through which the fuel returns to the tank via the overflow pipe. E. Control System In this system, the engine ECU controls the fuel injection system in accordance with the signals received from various sensors. The components of this system can be broadly divided into the following three types: (a) Sensors; (b) ECU; and (c) Actuators. a. Sensors Detect the engine and driving conditions, and convert them into electrical signals. b. Engine ECU Performs calculations based on the electrical signals received from the sensors, and sends them to the actuators in order to achieve optimal conditions. c. Actuators Operate in accordance with electrical signals received from the ECU. Injection system control is undertaken by electronically controlling the actuators. The injection quantity and timing are determined by controlling the duration and the timing in which the current is applied to the TWV (Two-Way Valve) in the injector. The injection pressure is determined by controlling the SCV (Suction Control Valve) in the supply pump. -6-
9 3. Construction and Operation 3-1. Description of Main Components A. Supply Pump (HP3) a. Outline The supply pump consists primarily of the pump body (eccentric cam, ring cam, and plungers), SCV (Suction Control Valve), fuel temperature sensor, and feed pump. The two plungers are positioned vertically on the outer ring cam for compactness. The engine drives the supply pump at a ratio of 1:2. The supply pump has a built-in feed pump (trochoid type), and draws the fuel from the fuel tank, sending it to the plunger chamber. The internal camshaft drives the two plungers, and they pressurize the fuel sent to the plunger chamber and send it to the rail. The quantity of fuel supplied to the rail is controlled by the SCV, using signals from the engine ECU. The SCV is a normally opened type (the intake valve opens during de-energization). -7-
10 b. Supply Pump Exploded Diagram -8-
11 c. Supply Pump Internal Fuel Flow The fuel that is drawn from the fuel tank passes through the route in the supply pump as illustrated, and is fed into the rail. d. Construction of Supply Pump The eccentric cam is attached to the drive shaft. The eccentric cam is connected to the ring cam. As the drive shaft rotates, the eccentric cam rotates in the eccentric state, and the ring cam moves up and down while rotating. -9-
12 The plunger and the suction valve are attached to the ring cam. The feed pump is connected to the rear of the drive shaft. e. Operation of the Supply Pump As shown in the illustration below, the rotation of the eccentric cam causes the ring cam to push Plunger A upwards. Due to the spring force, Plunger B is pulled in the opposite direction to Plunger A. As a result, Plunger B draws in fuel, while Plunger A pumps it to the rail. -10-
13 B. Description of Supply Pump Components a. Feed Pump The trochoid type feed pump, which is integrated in the supply pump, draws fuel from the fuel tank and feeds it to the two plungers via the fuel filter and the SCV (Suction Control Valve). The feed pump is driven by the drive shaft. With the rotation of the inner rotor, the feed pump draws fuel from its suction port and pumps it out through the discharge port. This is done in accordance with the space that increases and decreases with the movement of the outer and inner rotors. b. SCV: Suction Control Valve A linear solenoid type valve has been adopted. The ECU controls the duty ratio (the length of time that the current is applied to the SCV), in order to control the quantity of fuel that is supplied to the high-pressure plunger. Because only the quantity of fuel that is required for achieving the target rail pressure is drawn in, the actuating load of the supply pump decreases. When current flows to the SCV, variable electromotive force is created in accordance with the duty ratio, moving the armature to the left side. The armature moves the cylinder to the left side, changing the opening of the fuel passage and thus regulating the fuel quantity. With the SCV OFF, the return spring contracts, completely opening the fuel passage and supplying fuel to the plungers. (Full quantity intake and full quantity discharge) When the SCV is ON, the force of the return spring moves the cylinder to the right, closing the fuel passage (normally opened). By turning the SCV ON/OFF, fuel is supplied in an amount corresponding to the actuation duty ratio, and fuel is discharged by the plungers. -11-
14 (1) In case of short duty ON Short duty ON => large valve opening => maximum intake quantity -12-
15 (2) In case of long duty ON Long duty ON => small valve opening => minimum intake quantity -13-
16 C. Rail a. Outline Stores pressurized fuel (0 to 180 MPa) that has been delivered from the supply pump and distributes the fuel to each cylinder injector. A rail pressure sensor and a pressure limiter are adopted in the rail. The rail pressure sensor (Pc sensor) detects the fuel pressure in the rail and sends a signal to the engine ECU, while the pressure limiter controls the fuel pressure in the rail. This ensures optimum combustion and reduces combustion noise. b. Rail Pressure (Pc) Sensor This sensor detects fuel pressure in the rail and sends a signal to the ECU. It is a semi-conductor type pressure sensor that utilizes the characteristic whereby electrical resistance changes when pressure is applied to silicon. c. Pressure Limiter (made by another manufacturer) The pressure limiter relieves pressure by opening the valve if abnormally high pressure is generated. The valve opens when pressure in the rail reaches approximately 200 MPa, and closes when pressure falls to approximately 50 MPa. Fuel leaked by the pressure limiter returns to the fuel tank. -14-
17 D. Injector a. Outline The injectors inject the high-pressure fuel from the rail into the combustion chambers at the optimum injection timing, rate, and spray condition, in accordance with commands received from the ECU. b. Characteristics A compact, energy-saving solenoid-control type TWV (Two-Way Valve) injector has been adopted. A hollow screw with a damper is fitted in the fuel leak pipe connection to improve the injection precision. c. Construction -15-
18 d. Operation The TWV solenoid valve opens and closes the outlet orifice to control the pressure in the control chamber, and the start and end of injection. (1) No injection When no current is supplied to the solenoid, the spring force is stronger than the hydraulic pressure in the control chamber. Thus, the solenoid valve is pushed downward, effectively closing the outlet orifice. For this reason, the hydraulic pressure that is applied to the command piston causes the nozzle spring to compress. This closes the nozzle needle, and as a result, fuel is not injected. (2) Injection When current is initially applied to the solenoid, the attraction of the solenoid pulls the TWV up, effectively opening the outlet orifice and allowing the fuel to flow out of the control chamber. After the fuel flows out, the pressure in the control chamber decreases, pulling the command piston up. This causes the nozzle needle to rise and injection to start. The fuel that flows past the outlet orifice flows to the leak pipe and below the command piston. The fuel that flows below the nozzle needle lifts the it upward, which helps to improve the nozzle's opening and closing response. When current continues to be applied to the solenoid, the nozzle reaches its maximum lift, where the injection rate is also at the maximum level. When current to the solenoid is turned OFF, the TWV falls, causing the nozzle needle to close immediately and the injection to stop. -16-
19 e. Harness Connector with Correction Resistor A correction resistor is provided in the harness connector (4-pin connector) of each injector to minimize the variances in the injection volume among the cylinders (adjusted in the production line). -17-
20 3-2. Description of Control System Components A. Engine Control System Diagram -18-
21 B. ECU (Electronic Control Unit) a. Outline This is the command center that controls the fuel injection system and engine operation in general. The EDU is contained inside the ECU. The EDU has been adapted to support the high-speed actuation of the injectors. The high-speed actuation of the injector solenoid valve is made possible through the use of a high-voltage generating device (DC/DC converter). b. EDU Operation The high-voltage generating device converts the battery voltage into a high voltage. The Engine ECU sends signals to terminals B through E of the EDU in accordance with the signals from the sensors. Upon receiving these signals, the EDU outputs signals to the injectors from terminals H through K. -19-
22 C. Description of Sensors a. Crankshaft Position Sensor (NE) An NE pulsar attached to the crankshaft timing gear outputs a signal for detecting the crankshaft angle and engine speed. b. Cylinder Recognition Sensor (G) A cylinder recognition sensor (G pulsar) is attached to the supply pump timing gear, and outputs a cylinder recognition signal so that the ECU can calculate fuel injection timing. -20-
23 c. Fuel Temperature Sensor (THF) The fuel temperature sensor is mounted on the supply pump, and detects the fuel temperature, sending a signal to the engine ECU. The detection component utilizes a thermistor. -21-
24 3-3. Various Types of Controls A. Outline This system effects fuel injection quantity and injection timing control more appropriately than the mechanical governor and timer used in the conventional injection pump. The engine ECU performs the necessary calculations in accordance with the sensors installed on the engine and the vehicle. It then controls the timing and duration of time in which current is applied to the injectors, in order to realize both optimal injection and injection timing. a. Fuel Injection Quantity Control Function The fuel injection quantity control function replaces the conventional governor function. It controls the fuel injection to an optimal injection quantity based on the engine speed and accelerator position signals. b. Fuel Injection Timing Control Function The fuel injection timing control function replaces the conventional timer function. It controls the injection to an optimal timing based on the engine speed and the injection quantity. c. Fuel Injection Rate Control Function Pilot injection control injects a small amount of fuel before the main injection. d. Fuel Injection Pressure Control Function (Rail Pressure Control Function) The fuel injection pressure control function (rail pressure control function) controls the discharge volume of the pump by measuring the fuel pressure at the rail pressure sensor and feeding it back to the ECU. It effects pressure feedback control so that the discharge volume matches the optimal (command) value set in accordance with the engine speed and the injection quantity. -22-
25 B. Fuel Injection Quantity Control a. Outline This control determines the fuel injection quantity by adding coolant temperature, fuel temperature, intake air temperature, and mass airflow corrections to the basic injection quantity that is calculated by the engine ECU, based on the engine operating conditions and driving conditions. b. Injection Quantity Calculation Method c. Basic Injection Quantity The basic injection quantity is determined by the engine speed (NE) and the accelerator position. The injection quantity is increased when the accelerator position signal is increased while the engine speed remains constant. -23-
26 d. Maximum Injection Quantity The maximum injection quantity is calculated by adding the mass airflow correction, intake air temperature correction, atmospheric pressure correction and the cold operation maximum injection quantity correction to the basic maximum injection quantity that is determined by the engine speed. e. Starting Injection Quantity When the starter switch is turned ON, the injection quantity is calculated in accordance with the starting base injection quantity and the starter ON time. The base injection quantity and the inclination of the quantity increase/decrease change in accordance with the coolant temperature and the engine speed. f. Idle Speed Control (ISC) System This system controls the idle speed by regulating the injection quantity in order to match the actual speed to the target speed that is calculated by the engine ECU. The target speed varies according to the type of transmission (manual or automatic), whether the air conditioner is ON or OFF, the shift position, and the coolant water temperature. g. Idle Vibration Reduction Control To reduce engine vibrations during idle, this function compares the angle speeds (times) of the cylinders and regulates the injection quantity for the individual cylinders if there is a large the difference, in order to achieve a smooth engine operation. -24-
27 C. Fuel Injection Timing Control a. Outline Fuel injection timing is controlled by varying the timing in which current is applied to the injectors. b. Main and Pilot Injection Timing Control (1) Main Injection Timing The engine ECU calculates the basic injection timing based on the engine speed the final injection quantity, and adds various types of corrections in order to determine the optimal main injection timing. (2) Pilot Injection Timing (Pilot Interval) Pilot injection timing is controlled by adding a pilot interval to the main injection timing. The pilot interval is calculated based on the final injection quantity, engine speed, coolant temperature (map correction). The pilot interval at the time the engine is started is calculated from the coolant temperature and speed. c. Injection Timing Calculation Method (1) Outline of Control Timing (2) Injection Timing Calculation Method -25-
28 D. Fuel Injection Rate Control While the injection rate increases with the adoption of high-pressure fuel injection, the ignition lag, which is the delay from the start of injection to the beginning of combustion, cannot be shortened to less than a certain value. As a result, the quantity of fuel that is injected until main ignition occurs increases, resulting in an explosive combustion at the time of main ignition. This increases both NOx and noise. For this reason, pilot injection is provided to minimize the initial injection rate, prevent the explosive first-stage combustion, and reduce noise and NOx. E. Fuel Injection Pressure Control A value that is determined by the final injection quantity, the water temperature and the engine speed is calculated. During the starting of the engine, the calculation is based on the water temperature and the atmospheric pressure F. Other Controls Limit maximum injection quantity Gradual acceleration injection quantity Gradual deceleration injection quantity Post-acceleration damping injection quantity Reference injection quantity Fuel cutoff EGR Turbo control Glow plug relay -26-
29 4 DTC (Diagnosis Trouble Codes) Table 4-1. About the Codes shown in the table The "SAE" under the DTC code indicates the codes that are output when the STT (DST-1) is used, and the "Light" indicates the codes that are output when the CHECK ENGINE warning light is used. (SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers, U.S.A.) If multiple DTCs are output, they are shown in order starting with the lowest number DTC (Diagnosis Trouble Code) Table *1: The area with *1 are purely vehicle side. Code No. Diagnostic Item Description of Diagnosis Inspection Area U1000 *1 CAN communication line ECM cannot communicate with other control units. ECM cannot communicate for more than the specified time. P0016 Crankshaft position-camshaft position The correlation between the crank- correlation shaft position sensor signal and camshaft position sensor signal is outside the normal range. P0088 Fuel rail pressure too high Fuel pressure is exessively higher than the specified value. P0089 Fuel pump performance Fuel pressure is too much higher than the target value. P0093 Fuel system leak "ECM detects a fuel system leak". (The relation between the output voltage to the fuel pump and the input voltage from the fuel rail pressure sensor is outside the normal range.) P0102 Mass airflow sensor circuit low input Excessively low voltage from the sensor to the ECM. P0103 Mass airflow sensor circuit high Excessively high voltage from the input sensor to the ECM. P0112 Intake air temperature sensor circuit Excessively low voltage from the low input sensor to the ECM. (CAN communication line is open or shorted) Timing chain Signal plate Fuel pump (The fuel pump circuit is open or Fuel pump Fuel pump Fuel rail Fuel pipe Fuel rail pressure relief valve (The sensor circuit is open or Mass airflow sensor (The sensor circuit is open or Mass airflow sensor (The sensor circuit is open or Intake air temperature sensor -27-
30 Code No. Diagnostic Item Description of Diagnosis Inspection Area P0113 Intake air temperature sensor circuit high input Excessively high voltage from the sensor to the ECM. P0117 Engine coolant temperature sensor Excessively low voltage from the circuit low input sensor to the ECM. P0118 Engine coolant temperature sensor Excessively high voltage from the circuit high input sensor to the ECM. P0122 Accelerator pedal position sensor 1 Excessively low voltage from the circuit low input APP sensor 1 to the ECM. P0123 Accelerator pedal position sensor 1 Excessively high voltage from the circuit high input APP sensor 1 to the ECM. P0182 Fuel pump temperature sensor circuit Excessively low voltage from the low input sensor to the ECM. P0183 Fuel pump temperature sensor circuit Excessively high voltage from the high input sensor to the ECM. P0192 Fuel rail pressure sensor circuit low Excessively low voltage from the input sensor to the ECM. P0193 Fuel rail pressure sensor circuit high Excessively high voltage from the input sensor to the ECM. P0200 Fuel injector power supply circuit ECM detects an excessively high/ low voltage from the fuel injection power source. (The sensor circuit is open or Intake air temperature sensor (The sensor circuit is open or Engine coolant temperature sensor (The sensor circuit is open or Engine coolant temperature sensor (The APP sensor 1 circuit is open or Accelerator pedal position sensor (Accelerator pedal position sensor 1) (The APP sensor 1 circuit is open or Accelerator pedal position sensor (Accelerator pedal position sensor 1) (The sensor circuit is open or Fuel pump temperature sensor (The sensor circuit is open or Fuel pump temperature sensor (The sensor circuit is open or Fuel rail pressure sensor (The sensor circuit is open or Fuel rail pressure sensor ECM -28-
31 Code No. Diagnostic Item Description of Diagnosis Inspection Area P0201 No. 1 cylinder fuel injector circuit open An improper voltage signal is sent to the ECM by the No. 1 cylinder fuel injector. P0202 No. 2 cylinder fuel injector circuit An improper voltage signal is sent to open the ECM by the No. 2 cylinder fuel injector. P0203 No. 3 cylinder fuel injector circuit An improper voltage signal is sent to open the ECM by the No. 3 cylinder fuel injector. P0204 No. 4 cylinder fuel injector circuit open An improper voltage signal is sent to the ECM by the No. 4 cylinder fuel injector. P0217 Engine overheating Cooling fan does not operate properly (overheating). Cooling fan system does not operate properly (overheating). Engine coolant was not added to the system using the proper filling method. P0222 Accelerator pedal position sensor 2 Excessively low voltage from the circuit low input APP sensor 2 to the ECM. P0223 Accelerator pedal position sensor 2 Excessively high voltage from the circuit high input APP sensor 2 to the ECM. P0234 Turbocharger overboost condition ECM detects excessively high turbocharger boost pressure. (The sensor circuit is open or Fuel injector #1 (The sensor circuit is open or Fuel injector #2 (The sensor circuit is open or Fuel injector #3 (The sensor circuit is open or Fuel injector #4 (The cooling fan circuit is open or Cooling fan Radiator hose Radiator Radiator cap Water pump Thermostat (The APP sensor 2 circuit is open or Accelerator pedal position sensor (Accelerator pedal position sensor 2) (The APP sensor 2 circuit is open or Accelerator pedal position sensor (Accelerator pedal position sensor 2) Turbocharger Vacuum hose (YD22DDTi engine models) Turbocharger boost control solenoid valve (YD22DDTi engine models) -29-
32 Code No. Diagnostic Item Description of Diagnosis Inspection Area P0237 Turbocharger boost sensor circuit low input Excessively low voltage from the sensor to the ECM. (The sensor circuit is open or Turbocharger boost sensor P0238 Turbocharger boost sensor circuit high input Excessively high voltage from the sensor to the ECM. (The sensor circuit is open or Turbocharger boost sensor P0335 Crankshaft position sensor circuit Crankshaft position sensor signal is not detected by the ECM when the engine is running. (The sensor circuit is open or Crankshaft position sensor P0336 Crankshaft position sensor circuit range/performance Crankshaft position sensor signal is not the normal pattern when the Crankshaft position sensor Signal plate engine is running. P0340 Camshaft position sensor circuit Camshaft position sensor signal is not detected by the ECM when the engine is running. (The sensor circuit is open or Camshaft position sensor P0341 Camshaft position sensor circuit range/performance Camshaft position sensor signal is not the normal pattern when the Camshaft position sensor Signal plate engine is running. P0563 Battery voltage high Excessively high voltage from the battery to the ECM. Battery Battery terminal Alternator P0605 Engine control module (ROM) ECM ROM is malfunctioning. ECM P0606 Engine control module (Processor) ECM calculation function is malfunctioning. ECM P0628 Fuel pump control circuit low input ECM detects a fuel pump control circuit is open or short to the ground. (The fuel pump circuit is open or Fuel pump P0629 Fuel pump control circuit high input ECM detects a fuel pump control circuit is short to power source. (The fuel pump circuit is open or Fuel pump P0642 Accelerator pedal position sensor 1 power supply circuit low ECM detects an excessively low APP sensor 1 power source. (The APP sensor 1 power supply circuit is open or Accelerator pedal position sensor (Accelerator pedal position sensor 1) -30-
33 Code No. Diagnostic Item Description of Diagnosis Inspection Area P0643 Accelerator pedal position sensor 1 power supply circuit high ECM detects an excessively high APP sensor 1 power source. P0652 Accelerator pedal position sensor 2 ECM detects an excessively low power supply circuit low APP sensor 2 power source. P0653 Accelerator pedal position sensor 2 ECM detects an excessively high power supply circuit high APP sensor 2 power source. P0686 ECM relay circuit ECM detects ECM relay is stuck closed even if the ignition switch OFF. P1211 TCS control unit ECM received malfunction information *1 from the ESP/TCS/ABS control unit. P1212 TCS communication line ECM cannot continuously receive *1 information from the ESP/TCS/ABS control unit. P1260 No. 1 cylinder fuel injector adjustment Excessively low voltage from the resistor low input No. 1 cylinder fuel injector adjust- ment resistor to the ECM. P1261 No. 1 cylinder fuel injector adjustment Excessively high voltage from the resistor high input No. 1 cylinder fuel injector adjust- ment resistor to the ECM. P1262 No. 3 cylinder fuel injector adjustment Excessively low voltage from the resistor low input No. 3 cylinder fuel injector adjust- ment resistor to the ECM. (The APP sensor 1 power supply circuit is open or Accelerator pedal position sensor (Accelerator pedal position sensor 1) (The APP sensor 2 power supply circuit is open or Accelerator pedal position sensor (Accelerator pedal position sensor 2) (The APP sensor 2 power supply circuit is open or Accelerator pedal position sensor (Accelerator pedal position sensor 2) (The ECM relay circuit is ECM relay ESP/TCS/ABS control unit TCS related parts (The CAN communication line is open or ESP/TCS/ABS control unit Dead (Weak) battery (The fuel injector adjustment resistor circuit is open or Fuel injector adjustment resistor #1 (The fuel injector adjustment resistor circuit is open or Fuel injector adjustment resistor #1 (The fuel injector adjustment resistor circuit is open or Fuel injector adjustment resistor #3-31-
34 Code No. Diagnostic Item Description of Diagnosis Inspection Area P1263 No. 3 cylinder fuel injector adjustment resistor high input Excessively high voltage from the No. 3 cylinder fuel injector adjustment resistor to the ECM. P1264 No. 4 cylinder fuel injector adjustment Excessively low voltage from the resistor low input No. 4 cylinder fuel injector adjust- ment resistor to the ECM. P1265 No. 4 cylinder fuel injector adjustment Excessively high voltage from the resistor high input No. 4 cylinder fuel injector adjust- ment resistor to the ECM. P1266 No. 2 cylinder fuel injector adjustment Excessively low voltage from the resistor low input No. 2 cylinder fuel injector adjust- ment resistor to the ECM. P1267 No. 2 cylinder fuel injector adjustment Excessively high voltage from the resistor high input No. 2 cylinder fuel injector adjust- ment resistor to the ECM. P1268 No. 1 cylinder fuel injector The valve built into No. 1 cylinder fuel injector does not close properly (stuck open) when the injector is not energized. P1269 No. 2 cylinder fuel injector The valve built into No. 2 cylinder fuel injector does not close properly (stuck open) when the injector is not energized. P1270 No. 3 cylinder fuel injector The valve built into No. 3 cylinder fuel injector does not close properly (stuck open) when the injector is not energized. P1271 No. 4 cylinder fuel injector The valve built into No. 4 cylinder fuel injector does not close properly (stuck open) when the injector is not energized. P1272 Fuel rail pressure relief valve open Fuel rail pressure relief valve is open. P1273 Fuel pump insufficient flow ECM detects an abnormal fuel pressure pulse. (The fuel injector adjustment resistor circuit is open or Fuel injector adjustment resistor #3 (The fuel injector adjustment resistor circuit is open or Fuel injector adjustment resistor #4 (The fuel injector adjustment resistor circuit is open or Fuel injector adjustment resistor #4 (The fuel injector adjustment resistor circuit is open or Fuel injector adjustment resistor #2 (The fuel injector adjustment resistor circuit is open or Fuel injector adjustment resistor #2 Fuel injector #1 Fuel injector #2 Fuel injector #3 Fuel injector #4 Fuel rail pressure relief valve Fuel pump -32-
35 Code No. Diagnostic Item Description of Diagnosis Inspection Area P1274 Fuel pump protection Fuel pressure much higher than the target value. (The fuel pump circuit is open or Fuel pump P1275 Fuel pump exchange Fuel pressure much higher than the target value. (The fuel pump circuit is open or Fuel pump P1610 Immobi. related -1612, P *1 P2135 "Accelerator pedal position sensor 1, 2 signal correlation" The correlation between the APP sensor 1 signal and APP sensor 2 signal is outside the normal range. (The APP sensor circuit is open or Accelerator pedal position sensor P2146 No. 1 and 4 cylinder fuel injector power supply circuit open Improper voltage signal sent to the ECM by the No. 1 and 4 cylinder fuel (The fuel injector circuit is open.) injectors. P2147 Fuel injector circuit low input ECM detects the fuel injector circuit is shorted to the ground. (Fuel injector circuit P2148 Fuel injector circuit high input ECM detects the fuel injector circuit is shorted to the power source. (Fuel injector circuit P2149 No. 2 and 3 cylinder fuel injector power supply circuit open Improper voltage signal is sent to the ECM by the No. 2 and 3 cylinder (The fuel injector circuit is open.) fuel injectors. P2228 Barometric pressure sensor circuit Excessively low voltage from the ECM low input barometric pressure sensor (builtinto ECM) to the ECM. P2229 Barometric pressure sensor circuit high input Excessively high voltage from the barometric pressure sensor (builtinto ECM) to the ECM. ECM -33-
36 -34-5 External Wiring Diagram 5-1. ECU External Wiring Diagram A. Diagram 1
37 -35- B. Diagram 2
38 5-2. ECU Connector Diagram A. ECU Connector Terminal Layout B. Terminal Connections No. Pin Symbol Connections No. Pin Symbol Connections 1 P-GND POWER GROUND 31 2 P-GND POWER GROUND 32 3 P-GND POWER GROUND 33 4 COMMON 1 INJECTION COMMON 34 5 COMMON 1 INJECTION COMMON 35 6 VNT EVRV FOR VNT SCV+ SUCTION CONTROL VALVE 40 TWV3 INJECTION DRIVE TWV3 INJECTION DRIVE TWV1 INJECTION DRIVE TWV1 INJECTION DRIVE A-VCC3 SENSOR (POWER SUPPLY) A-VCC4 SENSOR (POWER SUPPLY) NE+ CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR G+ CYLINDER RECOGNITION SENSOR PFUEL RAIL PRESSURE SENSOR PFUEL RAIL PRESSURE SENSOR THF FUEL TEMP 21 TWV4 INJECTION DRIVE 4 51 THW COOLANT TEMP 22 TWV4 INJECTION DRIVE 4 52 BOOST BOOST SENSOR 23 TWV2 INJECTION DRIVE TWV2 INJECTION DRIVE 2 54 AMF AMF SENSOR 25 EGR#1 STEP MOTOR A 55 EXT-A-TMP EXT-AIR-TEMP-SENSOR 26 EGR#2 STEP MOTOR B~ EGR#3 STEP MOTOR A~ EGR#4 STEP MOTOR B SCV- SUCTION CONTROL VALVE 59 RINJ1 INJECTOR CORRECTION RINJ2 INJECTOR CORRECTION 2-36-
39 No. Pin Symbol Connections No. Pin Symbol Connections 61 RINJ3 INJECTOR CORRECTION 3 92 APS2GND SENSOR GROUND 62 RINJ4 INJECTOR CORRECTION A-VCC5 SENSOR (POWER SUPPLY) A-VCC6 SENSOR (POWER SUPPLY) 95 CAN1-H CAN COMMUNICATION 65 NE- ENGINE SPEED SENSOR G- CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR S-GND SHIELD GROUND PFUELRTN SENSOR GROUND 99 STA-SW STARTER SW 69 THFRTN FUEL TEMP RTN 100 BRK1 BRAKE SW1 70 THWRTN COOLANT TEMP RTN BOOSTRTN BOOST SENSOR RTN EGRLIFTRTN EGR LIFT SENSOR RTN AMFRTN AMF RTN EXT-A-RTN EXT-AIR-TEMP-SENSOR RTN 105 M-REL MAIN RELAY IG-SW IGNITION SW IG-SW IGNITION SW 78 A-GND INJECTOR CORRECTION RTN AD5 ANALOG INPUT OPTION 110 N-SW NEUT SW 80 AD6 ANALOG INPUT OPTION 111 PS-SW POWER STRG SW 81 AD7 ANALOG INPUT OPTION A-VCC1 SENSOR (POWER SUPPLY) 113 M-REL MAIN RELAY 83 APS1 ACCEL PEDAL SENSOR 114 C-GND SIGNAL GROUND 84 APS1GND SENSOR GROUND S-GND SHIELD GROUND(APS) CAN1-L CAN COMMUNICATION BP BATTERY+ (MAIN RELAY) 89 K-LINE KWP2000 K-LINE 120 +BP BATTERY+ (MAIN RELAY) 90 A-VCC2 SENSOR (POWER SUPPLY) 121 BATT BATTERY+ 91 APS2 ACCEL PEDAL SENSOR -37-
40 Published: June 2003 Duplication prohibited without permission Edited and published by: Service Department, DENSO Corporation 1-1 Showa-cho, Kariya, Aichi Prefecture, Japan [DTP]
Diesel Injection Pump SERVICE MANUAL. FORD Puma Common Rail System Functional Parts OPERATION. February, E
 Diesel Injection Pump SERVICE MANUAL FORD Puma Common Rail System Functional Parts OPERATION February, 2006 00400090E 2006 DENSO CORPORATION All Rights Reserved. This book may not be reproduced or copied,
Diesel Injection Pump SERVICE MANUAL FORD Puma Common Rail System Functional Parts OPERATION February, 2006 00400090E 2006 DENSO CORPORATION All Rights Reserved. This book may not be reproduced or copied,
SERVICE MANUAL. for MITSUBISHI L200/TRITON 4D56/4M41Engine OPERATION. Diesel Injection Pump DENSO INTERNATIONAL THAILAND CO., LTD.
 Diesel Injection Pump SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System (HP3) for MITSUBISHI L200/TRITON 4D56/4M41Engine OPERATION June, 2005 DENSO INTERNATIONAL THAILAND CO., LTD. TG00400010E 2005 DENSO INTERNATIONAL
Diesel Injection Pump SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System (HP3) for MITSUBISHI L200/TRITON 4D56/4M41Engine OPERATION June, 2005 DENSO INTERNATIONAL THAILAND CO., LTD. TG00400010E 2005 DENSO INTERNATIONAL
SERVICE MANUAL. Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation. For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only
 For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS)
 MITSUBISHI 4N13, 4N14 ENGINES COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) Issued : November 2010 Applicable Vehicle : Vehicle Manufacturer MITSUBISHI Vehicle Name LANCER ASX OUTLANDER 50000023E 2010 DENSO CORPORATION All
MITSUBISHI 4N13, 4N14 ENGINES COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) Issued : November 2010 Applicable Vehicle : Vehicle Manufacturer MITSUBISHI Vehicle Name LANCER ASX OUTLANDER 50000023E 2010 DENSO CORPORATION All
SERVICE BULLETIN FUEL INJECTION PUMP NEW PRODUCTS
 SERVICE BULLETIN FUEL INJECTION PUMP NEW PRODUCTS DENSO AUTHORIZED ECD SERVICE DEALER ONLY 1 E-ECD 02-06 October, 2002 SUBJECT: New Common Rail System (ECD-U2P) for MAZDA 1. Application Model Name Model
SERVICE BULLETIN FUEL INJECTION PUMP NEW PRODUCTS DENSO AUTHORIZED ECD SERVICE DEALER ONLY 1 E-ECD 02-06 October, 2002 SUBJECT: New Common Rail System (ECD-U2P) for MAZDA 1. Application Model Name Model
COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS)
 TOYOTA 1KD/2KD ENGINE COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) Issued : September 2009 00400706E 2009 DENSO CORPORATION All rights reserved. This material may not be reproduced or copied, in whole or in part, without
TOYOTA 1KD/2KD ENGINE COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) Issued : September 2009 00400706E 2009 DENSO CORPORATION All rights reserved. This material may not be reproduced or copied, in whole or in part, without
COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) SERVICE MANUAL: Operation
 N04C-# Engine COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) SERVICE MANUAL: Operation Issued : March 2007 Revised : December 2009 Applicable Vehicle : Manufacturer TOYOTA HINO Vehicle Name DYNA COASTER DUTRO 00400058EB Revision
N04C-# Engine COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) SERVICE MANUAL: Operation Issued : March 2007 Revised : December 2009 Applicable Vehicle : Manufacturer TOYOTA HINO Vehicle Name DYNA COASTER DUTRO 00400058EB Revision
Diesel Injection Pump SERVICE MANUAL OPEL Z17DT TYPE ENGINE COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) OPERATION. January, E
 Diesel Injection Pump SERVICE MANUAL OPEL Z17DT TYPE ENGINE COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) OPERATION January, 2007 00400588E 2006 DENSO CORPORATION All Rights Reserved. This book may not be reproduced or copied,
Diesel Injection Pump SERVICE MANUAL OPEL Z17DT TYPE ENGINE COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) OPERATION January, 2007 00400588E 2006 DENSO CORPORATION All Rights Reserved. This book may not be reproduced or copied,
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
Diesel Injection Pump SERVICE MANUAL COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) FOR ISUZU 6DE1 ENGINE OPERATION. April, E
 Diesel Injection Pump SERVICE MANUAL COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) FOR ISUZU 6DE1 ENGINE OPERATION April, 2006 00400558E 2006 DENSO CORPORATION All Rights Reserved. This book may not be reproduced or copied,
Diesel Injection Pump SERVICE MANUAL COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) FOR ISUZU 6DE1 ENGINE OPERATION April, 2006 00400558E 2006 DENSO CORPORATION All Rights Reserved. This book may not be reproduced or copied,
3GR-FSE FUEL. Fuel Pump (High Pressure) Cold Start Fuel Injector *
 ENGINE EG 75 General This engine uses the D-4 (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine) system. A (low pressure) fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump located
ENGINE EG 75 General This engine uses the D-4 (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine) system. A (low pressure) fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump located
3. Engine Control System Diagram
 ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 59 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Pump Resister Circuit Opening Fuel Relay Filter Intake Temp. Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Fuel Pump
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 59 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Pump Resister Circuit Opening Fuel Relay Filter Intake Temp. Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Fuel Pump
P Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit P Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit Range/Performance P Fuel Volume Regulator Control
 P0001 - Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit P0002 - Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit Range/Performance P0003 - Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit Low P0004 - Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit
P0001 - Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit P0002 - Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit Range/Performance P0003 - Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit Low P0004 - Fuel Volume Regulator Control Circuit
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G9>
 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
(3) (4) (6) (5) (10) (9) (8) (7)
 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter. Fuel injection pressure is regulated to an optimum
3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter. Fuel injection pressure is regulated to an optimum
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM. 1. General ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE
 ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE 69 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 3VZ FE engine has the same basic construction and operation as for the 2VZ FE engine. However, the sequential
ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE 69 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 3VZ FE engine has the same basic construction and operation as for the 2VZ FE engine. However, the sequential
Oregon Fuel Injection
 2001 2006 Dodge Mercedes - Freightliner Sprinter Diagnostics In order to do proper diagnostics you will need a scan tool and some special tools available from Mopar Special Tools http://mopar.snapon.com.
2001 2006 Dodge Mercedes - Freightliner Sprinter Diagnostics In order to do proper diagnostics you will need a scan tool and some special tools available from Mopar Special Tools http://mopar.snapon.com.
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) <2.4L ENGINE>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L
 G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS
 09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
09-3 EGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. ENGINE ECU AND OTHER COMPONENTS ECU/Barometric Sensor Camshaft Position Sensor HFM Sensor / Intake Air Temperature Sensor Fuel Filter (Water Sensor) Preheating Relay Accelerator
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART (SAE Controlled)
 1MZFE ENGINE EG2404 (SAE Controlled) HINT: Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. DTC No. Detection Item Diagnostic Trouble
1MZFE ENGINE EG2404 (SAE Controlled) HINT: Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. DTC No. Detection Item Diagnostic Trouble
ENGINE GENERAL ENGINE GENERAL GENERAL OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. STRUCTURE...
 GENERAL 1. STRUCTURE... 3 OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. ENGINE CONTROLS COMPONENTS... 2. INTAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 3. EXHAUST SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 5. COOLING SYSTEM
GENERAL 1. STRUCTURE... 3 OVERVIEW AND OPERATION PROCESS 1. ENGINE CONTROLS COMPONENTS... 2. INTAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 3. EXHAUST SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 4. LUBRICATION SYSTEM COMPONENTS... 5. COOLING SYSTEM
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
 XJ EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 25-1 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS 2.5L DIESEL ENGINE... 1 EXHAUST EMISSION CONTROLS 2.5L DIESEL ENGINE... 6 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS 2.5L DIESEL
XJ EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 25-1 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS 2.5L DIESEL ENGINE... 1 EXHAUST EMISSION CONTROLS 2.5L DIESEL ENGINE... 6 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS 2.5L DIESEL
Diesel Injection Pump SERVICE MANUAL COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) FOR ISUZU 6DE1 ENGINE OPERATION. April, E
 Diesel Injection Pump SERVICE MANUAL COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) FOR ISUZU 6DE1 ENGINE OPERATION April, 2006 00400558E 2006 DENSO CORPORATION All Rights Reserved. This book may not be reproduced or copied,
Diesel Injection Pump SERVICE MANUAL COMMON RAIL SYSTEM (CRS) FOR ISUZU 6DE1 ENGINE OPERATION April, 2006 00400558E 2006 DENSO CORPORATION All Rights Reserved. This book may not be reproduced or copied,
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
 XJ EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 25-1 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM CONTENTS EXHAUST EMISSION CONTROLS 2.5L DIESEL ENGINE... 6 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS 2.5L DIESEL ENGINE... 1 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS 2.5L DIESEL ENGINE INDEX
XJ EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 25-1 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM CONTENTS EXHAUST EMISSION CONTROLS 2.5L DIESEL ENGINE... 6 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS 2.5L DIESEL ENGINE... 1 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS 2.5L DIESEL ENGINE INDEX
Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps
 Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
Page 1 of 16 S60 (-09), 2004, D5244T, M56, L.H.D, YV1RS799242356771, 356771 22/1/2014 PRINT Combustion process Emission cleaning Fuel distribution Glow plugs Injectors Low and high pressure pumps Fuel
EvoX EFI ECU Pinouts Last Updated Tuesday, 24 April :40
 HOW TO: Reset your Fuel trims... Open your bonnet, open the fuse box, pull out 7.5A number 2 fuse, this is battery backup for your main ECU, remove for 2 seconds, and replace. Your fuel trims and learned
HOW TO: Reset your Fuel trims... Open your bonnet, open the fuse box, pull out 7.5A number 2 fuse, this is battery backup for your main ECU, remove for 2 seconds, and replace. Your fuel trims and learned
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 DI158 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: ENGINE (2JZGTE) Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a malfunction code
DI158 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: ENGINE (2JZGTE) Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a malfunction code
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)
 13A-1 GROUP 13A CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION...13A-2 CONTROL UNIT...13A-7 SENSOR...13A-9 ACTUATOR...13A-26 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL...13A-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME...13A-36
13A-1 GROUP 13A CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION...13A-2 CONTROL UNIT...13A-7 SENSOR...13A-9 ACTUATOR...13A-26 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL...13A-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME...13A-36
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE. 1. Description 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES
 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
ProECU Subaru DIT. DTC List 2012-onward Model Year. v1.0
 ProECU Subaru DIT DTC List 2012-onward Model Year v1.0 Engine DTC List P000A A CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE (BANK 1) P000B B CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE (BANK 1) P000C A CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE
ProECU Subaru DIT DTC List 2012-onward Model Year v1.0 Engine DTC List P000A A CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE (BANK 1) P000B B CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE (BANK 1) P000C A CAMSHAFT POSITION SLOW RESPONSE
ProECU Subaru BRZ Toyota GT86 Scion FR-S
 ProECU Subaru BRZ Toyota GT86 Scion FR-S DTC List 2012-onward Model Year v1.0 Engine DTC List P000A Camshaft Position "A" - Timing Slow Response Bank 1 P000B Camshaft Position "B" - Timing Slow Response
ProECU Subaru BRZ Toyota GT86 Scion FR-S DTC List 2012-onward Model Year v1.0 Engine DTC List P000A Camshaft Position "A" - Timing Slow Response Bank 1 P000B Camshaft Position "B" - Timing Slow Response
Air Management System Components
 AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
AIR M anagement Sys tem Air Management System Components Air Management System Features Series Sequential The series sequential turbocharger is a low pressure/high pressure design working in series with
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION 35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE
 35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1UZ FE engine in the 95 LS400 is a V8, 4.0 liter, 32 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation are basically the same as those of the
35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1UZ FE engine in the 95 LS400 is a V8, 4.0 liter, 32 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation are basically the same as those of the
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT:
 DIAGNOSTICS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: SFI SYSTEM (1MZFE) 05241 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a
DIAGNOSTICS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: SFI SYSTEM (1MZFE) 05241 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a
2 OPERATION 2.1 DDEC BENEFITS FEATURES DDEC SYSTEM--HOW IT WORKS DDEC RELATED PUBLICATIONS...
 2 OPERATION Section Page 2.1 DDEC BENEFITS... 2-3 2.2 FEATURES... 2-4 2.3 DDEC SYSTEM--HOW IT WORKS... 2-5 2.4 DDEC RELATED PUBLICATIONS... 2-23 (Rev. 2/03) All information subject to change without notice.
2 OPERATION Section Page 2.1 DDEC BENEFITS... 2-3 2.2 FEATURES... 2-4 2.3 DDEC SYSTEM--HOW IT WORKS... 2-5 2.4 DDEC RELATED PUBLICATIONS... 2-23 (Rev. 2/03) All information subject to change without notice.
FUEL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM. Electronic Control of Fuel System
 07 5 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM Electronic Control of Fuel System IMV valve Low and high pressure pump Fuel temperature sensor High pressure pump Water separator Water detection sensor Fuel filter System composition
07 5 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM Electronic Control of Fuel System IMV valve Low and high pressure pump Fuel temperature sensor High pressure pump Water separator Water detection sensor Fuel filter System composition
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL 17-2 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-2 AUTO-CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-3 CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION 17-5 17-7 GENERAL INFORMATION
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL 17-2 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-2 AUTO-CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-3 CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION 17-5 17-7 GENERAL INFORMATION
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle
 Document ID# 850406 2002 Pontiac Firebird Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle DTC DTC 021 and/or 031 DTC 022 and/or 032 DTC 023 or 033 DTC 24/34 DTC 025 and/or 035 DTC 041 DTC 042 DTC 043 DTC
Document ID# 850406 2002 Pontiac Firebird Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle DTC DTC 021 and/or 031 DTC 022 and/or 032 DTC 023 or 033 DTC 24/34 DTC 025 and/or 035 DTC 041 DTC 042 DTC 043 DTC
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-27
 W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
OBD-II Diagnostic Powertrain (P) Trouble Codes
 OBD-II Diagnostic Powertrain (P) Trouble Codes Please use our new & improved search engine to find information on your trouble codes. Search Now! This list contains standard diagnostic trouble codes (DTC
OBD-II Diagnostic Powertrain (P) Trouble Codes Please use our new & improved search engine to find information on your trouble codes. Search Now! This list contains standard diagnostic trouble codes (DTC
4HK1-TC ENGINE -Engine Mechanical Features- -Engine Control System & Diagnosis-
 FOR SERVICE TRAINING 4HK1-TC ENGINE -Engine Mechanical Features- -Engine Control System & Diagnosis- Applicable Model Model Year Vehicle Model Main Market 2005 NPR & NQR General Export (Euro 3 Regulation)
FOR SERVICE TRAINING 4HK1-TC ENGINE -Engine Mechanical Features- -Engine Control System & Diagnosis- Applicable Model Model Year Vehicle Model Main Market 2005 NPR & NQR General Export (Euro 3 Regulation)
Engine Control (2KD FTV)
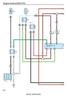 Engine Control (KD FTV) (T) (T) 80 O 5 EFI J E MIN elay 4 D J J 4 J 8 J J EDU elay D55 VV (E) 5 5 E TT E IE 0 (), (), D(C), D(D) Engine ECU + ME 8 C O elay 4 D D5 low lug 04 HICE (ED6E) 8 D + DUT E VF
Engine Control (KD FTV) (T) (T) 80 O 5 EFI J E MIN elay 4 D J J 4 J 8 J J EDU elay D55 VV (E) 5 5 E TT E IE 0 (), (), D(C), D(D) Engine ECU + ME 8 C O elay 4 D D5 low lug 04 HICE (ED6E) 8 D + DUT E VF
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) <3.8L ENGINE>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 13B-2....................... 13B-5 ACTUATOR.................... 13B-5 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL...... 13B-7
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 13B-2....................... 13B-5 ACTUATOR.................... 13B-5 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL...... 13B-7
U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
 CH-125 U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE DESCRIPTI The 02 Camry line-up uses the following types of automatic transaxles: 2AZ-FE U241E 1MZ-FE U140E These automatic transaxles are compact and high-capacity
CH-125 U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE DESCRIPTI The 02 Camry line-up uses the following types of automatic transaxles: 2AZ-FE U241E 1MZ-FE U140E These automatic transaxles are compact and high-capacity
CHASSIS AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE. Destination New Model Previous Model Change (from previous model)
 CHASSIS AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE CH-37 U341E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 1. General The compact and high-capacity 4-speed U341E automatic transaxle [Super ECT (Electronic Controlled Transaxle)] is used. The following
CHASSIS AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE CH-37 U341E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 1. General The compact and high-capacity 4-speed U341E automatic transaxle [Super ECT (Electronic Controlled Transaxle)] is used. The following
1 of :23
 1 of 8 2013.02.09 03:23 Published: 08-Jun-2012 Electronic Engine Controls - TDV8 3.6L Diesel - Electronic Engine Controls 3.6L (TdV8) Diesel Diagnosis and Testing Overview This section covers the components
1 of 8 2013.02.09 03:23 Published: 08-Jun-2012 Electronic Engine Controls - TDV8 3.6L Diesel - Electronic Engine Controls 3.6L (TdV8) Diesel Diagnosis and Testing Overview This section covers the components
14. Engine Control System
 48 4. Engine Control System General The engine control system of the 2GR-FE engine has the following features. The Engine ECU that controls this system is made by DENSO. System EFI (Electric Fuel Injection)
48 4. Engine Control System General The engine control system of the 2GR-FE engine has the following features. The Engine ECU that controls this system is made by DENSO. System EFI (Electric Fuel Injection)
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
 EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
Component Location. NOTE The figure shows LHD vehicle. For RHD vehicle, parts with (*) are installed at the opposite side. 12* 7 d.
 1A-12 Engine General Information and Diagnosis: Electronic Control System Components Location Component Location Edited by Foxit PDF Editor Copyright (c) by Foxit Software Company, 2004 NOTE The figure
1A-12 Engine General Information and Diagnosis: Electronic Control System Components Location Component Location Edited by Foxit PDF Editor Copyright (c) by Foxit Software Company, 2004 NOTE The figure
FUEL 13-1 CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)... 2 FUEL SUPPLY ON-VEHICLE SERVICE GENERAL SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 4 SEALANT...
 13-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)....... 2 GENERAL............................... 2 Outline of Change......................... 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS.............. 4 SEALANT...............................
13-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)....... 2 GENERAL............................... 2 Outline of Change......................... 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS.............. 4 SEALANT...............................
HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE
 16 07 HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE High Pressure Pump Description This pump generates high fuel pressure and is driven by timing chain (radial plunger principle). This pump pressurizes the fuel to approx. 1600
16 07 HIGH FUEL PRESSURE LINE High Pressure Pump Description This pump generates high fuel pressure and is driven by timing chain (radial plunger principle). This pump pressurizes the fuel to approx. 1600
Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting
 RENR1271-11 February 2006 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 3126B and 3126E Truck Engine BKD1-Up (Engine) G3E1-Up (Engine) DPF1-Up (Engine) 1AJ1-Up (Engine) 8YL1-Up (Engine) CKM1-Up (Engine) CRP1-Up
RENR1271-11 February 2006 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 3126B and 3126E Truck Engine BKD1-Up (Engine) G3E1-Up (Engine) DPF1-Up (Engine) 1AJ1-Up (Engine) 8YL1-Up (Engine) CKM1-Up (Engine) CRP1-Up
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G63-Turbo>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13B-2 SENSOR....................... 13B-8 THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CTROL.............. 13B-9 FUEL INJECTI
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13B-2 SENSOR....................... 13B-8 THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CTROL.............. 13B-9 FUEL INJECTI
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
ProECU Nissan GT-R & Juke
 ProECU Nissan GT-R & Juke DTC List 2008-onward Model Year v1.23 1.1. Engine DTC List U0101 Lost communication with TCM U0164 Lost communication with HVAC U1001 CAN Communication Line Error P0011 Intake
ProECU Nissan GT-R & Juke DTC List 2008-onward Model Year v1.23 1.1. Engine DTC List U0101 Lost communication with TCM U0164 Lost communication with HVAC U1001 CAN Communication Line Error P0011 Intake
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM. 1. General CH-16 CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
 CH-16 ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The electronic control system of the U340E automatic transaxle consists of the controls listed below. System Clutch Pressure Control (See page CH-20) Line Pressure
CH-16 ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The electronic control system of the U340E automatic transaxle consists of the controls listed below. System Clutch Pressure Control (See page CH-20) Line Pressure
CH-23 CHASSIS AA80E AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION. Function of Shift Solenoid Valves. Spool Valve. Hydraulic Pressure. Sleeve. Current. Shift Solenoid Valve
 CH-23 Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SL2 Current 036CH29TE Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SLU Current 036CH27TE Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SLT
CH-23 Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SL2 Current 036CH29TE Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SLU Current 036CH27TE Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SLT
GROUP 13Ab. 13Ab-2 CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-29 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS...
 13Ab-1 GROUP 13Ab CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. 13Ab-2 DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-29 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS..... 13Ab-2 FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION REFERENCE TABLE........................ 13Ab-20 DIAGNOSTIC
13Ab-1 GROUP 13Ab CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. 13Ab-2 DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-29 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS..... 13Ab-2 FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION REFERENCE TABLE........................ 13Ab-20 DIAGNOSTIC
Hyundai - Specific Trouble Codes
 Hyundai - Specific Trouble Codes P1100 Map Sensor - Malfunction P1101 Map Sensor - Abnormal P1102 Map Sensor - Low Input P1103 Map Sensor - High Input P1104 Air Flow P1105 Air Flow - Abnormal P1106 Air
Hyundai - Specific Trouble Codes P1100 Map Sensor - Malfunction P1101 Map Sensor - Abnormal P1102 Map Sensor - Low Input P1103 Map Sensor - High Input P1104 Air Flow P1105 Air Flow - Abnormal P1106 Air
TNV TIER3 INTRODUCTION
 TNV TIER3 INTRODUCTION ECO governor system operation Actuator Eco-Governor Fuel Pomp Rack position Speed Intake EGR-Valve Re-circulation Exhaust Inj.Nozzle Liner Piston Key Switch Switch Starting Aid CW
TNV TIER3 INTRODUCTION ECO governor system operation Actuator Eco-Governor Fuel Pomp Rack position Speed Intake EGR-Valve Re-circulation Exhaust Inj.Nozzle Liner Piston Key Switch Switch Starting Aid CW
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing
 Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
Electronic control system
 Electronic control system Date 28 March 2013 Vico de Bres Customer Service Department Yanmar Europe B.V. Content 1. Overview 2. ECU connections 3. Sensors Page1 Overview Page2 Engine sensors and actuators
Electronic control system Date 28 March 2013 Vico de Bres Customer Service Department Yanmar Europe B.V. Content 1. Overview 2. ECU connections 3. Sensors Page1 Overview Page2 Engine sensors and actuators
11. Diagnostics Chart with Trouble Code
 DTC No. Abbreviation (Subaru select monitor) ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS II SYSTEM 11. Diagnostics Chart with Trouble Code A: DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) LIST P0100 QA Mass air flow sensor circuit malfunction
DTC No. Abbreviation (Subaru select monitor) ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS II SYSTEM 11. Diagnostics Chart with Trouble Code A: DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) LIST P0100 QA Mass air flow sensor circuit malfunction
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP(SEBP ) - Document Structure. Media Number -RENR Publication Date -01/02/2008 Date Updated -07/02/2008
 Page 1 of 11 Shutdown SIS Previous Screen Product: TRUCK ENGINE Model: 3406E TRUCK ENGINE 5EK Configuration: 3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP Systems Operation 3406E Truck Engine Media Number -RENR1273-07
Page 1 of 11 Shutdown SIS Previous Screen Product: TRUCK ENGINE Model: 3406E TRUCK ENGINE 5EK Configuration: 3406E Truck Engine 5EK01821-UP Systems Operation 3406E Truck Engine Media Number -RENR1273-07
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) Maybach Engine M285
 512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
512 HO M285 Engine (FrechW) 08-06-03 Maybach Engine M285 These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check
2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components
 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Fuel Delivery and Air Induction > Description and Operation
2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Locations > Components 2012 Chevy Truck Equinox FWD L4-2.4L Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Fuel Delivery and Air Induction > Description and Operation
EG1 189 EFI SYSTEM 5S FE ENGINE DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
 5SFE ENGINE EG1189 DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The ECU contains a builtin selfdiagnosis system by which troubles with the engine signal network are detected and a CHECK engine warning light on the combination
5SFE ENGINE EG1189 DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The ECU contains a builtin selfdiagnosis system by which troubles with the engine signal network are detected and a CHECK engine warning light on the combination
13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) FUEL SUPPLY... 13B
 13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI)... 13A FUEL SUPPLY... 13B 13A-2 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 6 SEALANT... 6 SPECIAL TOOLS...
13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI)... 13A FUEL SUPPLY... 13B 13A-2 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 6 SEALANT... 6 SPECIAL TOOLS...
Service Bulletin. DTC Detection Item Associated Monitor
 Service Bulletin 03-010 Applies To: All OBD II equipped models except SLX March 29, 2003 OBD II DTCs and Their Associated Monitors This is a list of all DTCs for all OBD II models. No one model has all
Service Bulletin 03-010 Applies To: All OBD II equipped models except SLX March 29, 2003 OBD II DTCs and Their Associated Monitors This is a list of all DTCs for all OBD II models. No one model has all
1 of 9 9/18/2017, 10:09 AM
 1 of 9 9/18/2017, 10:09 AM DTC P0505 IDLE AIR CONTROL VALVE (IACV) - AUXILIARY AIR CONTROL (AAC) VALVE Description SYSTEM DESCRIPTION This system automatically controls engine idle speed to a specified
1 of 9 9/18/2017, 10:09 AM DTC P0505 IDLE AIR CONTROL VALVE (IACV) - AUXILIARY AIR CONTROL (AAC) VALVE Description SYSTEM DESCRIPTION This system automatically controls engine idle speed to a specified
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) <2.4L ENGINE>
 13A-1 GROUP 13A MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 13A-2 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL...... 13A-5 THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CONTROL..................... 13A-6
13A-1 GROUP 13A MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 13A-2 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL...... 13A-5 THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CONTROL..................... 13A-6
Common Rail System (CRS) Service Manual
 MAZDA SKYACTIV-D Engine (EURO 6) Common Rail System (CRS) Service Manual Issued : April 2012 Applicable Vehicle : Vehicle Name Release Date CX-5 March 2012 50000061E 2012 by DENSO CORPORATION All rights
MAZDA SKYACTIV-D Engine (EURO 6) Common Rail System (CRS) Service Manual Issued : April 2012 Applicable Vehicle : Vehicle Name Release Date CX-5 March 2012 50000061E 2012 by DENSO CORPORATION All rights
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART 05 35 HINT: As for the vehicle for MEXICO, refer to Repair Manual 2003 COROLLA MATRIX (Pub. No. RM940U). Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART 05 35 HINT: As for the vehicle for MEXICO, refer to Repair Manual 2003 COROLLA MATRIX (Pub. No. RM940U). Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your
1012-Electrical Diagrams
 Term Absolute Pressure 1012-Electrical Diagrams Definition Total or true pressure. Gauge pressure plus atmospheric pressure. Absolute that includes the atmospheric pressure in its reading. This sensor
Term Absolute Pressure 1012-Electrical Diagrams Definition Total or true pressure. Gauge pressure plus atmospheric pressure. Absolute that includes the atmospheric pressure in its reading. This sensor
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (continued) GM Specific Codes
 85 GM Specific Codes P11XX Fuel and Air Metering P1106 MAP Sensor Circuit Intermittent High Voltage P1107 MAP Sensor Circuit Intermittent Low Voltage P1108 BARO to MAP Signal Comparison Too High P1111
85 GM Specific Codes P11XX Fuel and Air Metering P1106 MAP Sensor Circuit Intermittent High Voltage P1107 MAP Sensor Circuit Intermittent Low Voltage P1108 BARO to MAP Signal Comparison Too High P1111
CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 ISX CM2250 Service Workshop Manual
 Instant Manual Download CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 ISX CM2250 Service Workshop Manual Download Here CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 Service Workshop Repair Shop Manual PLEASE NOTE: YOU NEED TO BE CONNECTED TO THE INTERNET
Instant Manual Download CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 ISX CM2250 Service Workshop Manual Download Here CUMMINS ENGINE ISX15 Service Workshop Repair Shop Manual PLEASE NOTE: YOU NEED TO BE CONNECTED TO THE INTERNET
SAS light Check Engine Malfunction Indicator Lamp
 SAS light Check Engine Malfunction Indicator Lamp Here's how to do it: In car ECM Diagnostics/ECM Reset procedure: 1) Sit in the driver's seat. 2) Turn the ignition key to the ON position and wait three
SAS light Check Engine Malfunction Indicator Lamp Here's how to do it: In car ECM Diagnostics/ECM Reset procedure: 1) Sit in the driver's seat. 2) Turn the ignition key to the ON position and wait three
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: DI231 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your readings due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a malfunction code is displayed
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: DI231 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your readings due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a malfunction code is displayed
OBD-Codes.com Your OBD-II Trouble Codes Repair Site
 Page 1 sur 11 OBD-Codes.com Your OBD-II Trouble Codes Repair Site URL of this page: Like 261 likes. Sign Up to see what your friends like. OBD-II (Check Engine Light) Trouble Codes Welcome to OBD-Codes.com,
Page 1 sur 11 OBD-Codes.com Your OBD-II Trouble Codes Repair Site URL of this page: Like 261 likes. Sign Up to see what your friends like. OBD-II (Check Engine Light) Trouble Codes Welcome to OBD-Codes.com,
A: ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL FOR MT VEHICLES. Signal (V) Ignition SW ON (Engine OFF) B B B
 5. Specified Data A: ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL FOR MT VEHICLES B2M2267A Crankshaft Camshaft Throttle Rear oxygen Front oxygen (A/F) heater Rear oxygen heater Engine coolant temperature Signal
5. Specified Data A: ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL FOR MT VEHICLES B2M2267A Crankshaft Camshaft Throttle Rear oxygen Front oxygen (A/F) heater Rear oxygen heater Engine coolant temperature Signal
3GR-FSE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
 ENGINE EG 13 Engine Control System Description This engine controls the following systems in a highly accurate manner: Sequential Fuel Injection (SFI), Electronic Spark Advance (ESA), Electronic Throttle
ENGINE EG 13 Engine Control System Description This engine controls the following systems in a highly accurate manner: Sequential Fuel Injection (SFI), Electronic Spark Advance (ESA), Electronic Throttle
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM. System Sensors
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM System Sensors Throttle position sensor - Used to relay throttle position information to the ECU. Throttle opening angle is used by the ECU to determine fuelling and ignition requirements
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM System Sensors Throttle position sensor - Used to relay throttle position information to the ECU. Throttle opening angle is used by the ECU to determine fuelling and ignition requirements
INJECTOR. Edge filter. Leak off nipple. C2I label. Nozzle holder body. Bobbin. Control valve. C2I value. Cap nut. Adaptor plate.
 52 07 INJECTOR The C21 labels including injector characteristics are attached in each injector. These C21 values should be input to ECU by using Scan-i when replacing the ECU or injectors. Special cautions:
52 07 INJECTOR The C21 labels including injector characteristics are attached in each injector. These C21 values should be input to ECU by using Scan-i when replacing the ECU or injectors. Special cautions:
Lotus Service Notes Section EMR
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMR Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMR.1 3 Component Function EMR.2 7 Component Location EMR.3 9 Diagnostic Guide EMR.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMR Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMR.1 3 Component Function EMR.2 7 Component Location EMR.3 9 Diagnostic Guide EMR.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition
 Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
H - TESTS W/O CODES Nissan 240SX INTRODUCTION TROUBLE SHOOTING SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS WILL NOT START
 H - TESTS W/O CODES 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Trouble Shooting - No Codes Nissan; 240SX, Axxess, Maxima, Pathfinder, Pickup, Pulsar, Sentra, Van, INTRODUCTION Before diagnosing symptoms
H - TESTS W/O CODES 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Trouble Shooting - No Codes Nissan; 240SX, Axxess, Maxima, Pathfinder, Pickup, Pulsar, Sentra, Van, INTRODUCTION Before diagnosing symptoms
ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION
 Table of Contents ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION Section 3B - Troubleshooting and Diagnostics TROUBLESHOOTING AND DIAGNOSTICS Specifications........................... 3B-1 Special Tools...........................
Table of Contents ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION Section 3B - Troubleshooting and Diagnostics TROUBLESHOOTING AND DIAGNOSTICS Specifications........................... 3B-1 Special Tools...........................
The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine
 Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
Service Training Self-study Programme 351 The common rail fuel injection system fitted in the 3.0l V6 TDI engine Design and Function The constant increase in requirements pertaining to low fuel consumption,
DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION EG2 170
 EG2170 DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The ECM contains a builtin self diagnosis system by which troubles with the engine signal network are detected and a malfunction indicator lamp on the combination meter
EG2170 DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The ECM contains a builtin self diagnosis system by which troubles with the engine signal network are detected and a malfunction indicator lamp on the combination meter
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS II SYSTEM. 5. Specified Data. Signal (V) Ignition SW ON (Engine OFF)
 1. ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL OBD0092A Crankshaft Camshaft Mass air flow Throttle Signal (+) 8 0 7 +7 Sensor output waveform Signal ( ) 29 0 0 Shield 54 0 0 Signal (+) 7 0 7 +7 Sensor output
1. ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL OBD0092A Crankshaft Camshaft Mass air flow Throttle Signal (+) 8 0 7 +7 Sensor output waveform Signal ( ) 29 0 0 Shield 54 0 0 Signal (+) 7 0 7 +7 Sensor output
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
 WJ EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 25-1 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM CONTENTS page ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS 3.1L DIESEL ENGINE... 1 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS 3.1L DIESEL ENGINE INDEX page GENERAL INFORMATION SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
WJ EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 25-1 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM CONTENTS page ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS 3.1L DIESEL ENGINE... 1 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS 3.1L DIESEL ENGINE INDEX page GENERAL INFORMATION SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
A rotary solenoid type ISC system is used, which controls the fast idle and idle speeds.
 44 ENGINE 5S FE ENGINE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General Basic functions of the engine control system of the new 5S FE engine for the new Camry are the same as those in the 5S FE engine for the 90 model
44 ENGINE 5S FE ENGINE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General Basic functions of the engine control system of the new 5S FE engine for the new Camry are the same as those in the 5S FE engine for the 90 model
3. Fuel System FUEL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-7
 W1860BE.book Page 7 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter.
W1860BE.book Page 7 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter.
3. At sea level, the atmosphere exerts psi of pressure on everything.
 41 Chapter Gasoline Injection Fundamentals Name Instructor Date Score Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to explain the construction, operation, and classifications of modern gasoline
41 Chapter Gasoline Injection Fundamentals Name Instructor Date Score Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to explain the construction, operation, and classifications of modern gasoline
