(51) Int Cl.: F02M 51/06 ( ) F02M 61/12 ( )
|
|
|
- Pearl Bryan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) TEPZZ ZZ968B_T (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: Bulletin 17/36 (1) Int Cl.: F02M 1/06 (06.01) F02M 61/12 (06.01) (21) Application number: (22) Date of filing: (4) Injector for injecting fluid Injektor zum Einspritzen von Flüssigkeit Injecteur pour injection de fluides (84) Designated Contracting States: AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR (43) Date of publication of application: Bulletin 16/16 (73) Proprietor: Continental Automotive GmbH 16 Hannover (DE) Falaschi, Filippo 6043 Luciana (IT) Izzo, Ivano 6127 Pisa (IT) (6) References cited: EP-A EP-A EP-A EP-A EP-A WO-A1-13/081 US-A US-A (72) Inventors: Marchi, Luigi 6123 Pisa (IT) EP B1 Note: Within nine months of the publication of the mention of the grant of the European patent in the European Patent Bulletin, any person may give notice to the European Patent Office of opposition to that patent, in accordance with the Implementing Regulations. Notice of opposition shall not be deemed to have been filed until the opposition fee has been paid. (Art. 99(1) European Patent Convention). Printed by Jouve, 7001 PARIS (FR)
2 1 EP B1 2 Description [0001] The invention relates to an injector for injecting fluid and relates particularly to an injector for injecting fuel into an internal combustion engine. [0002] Injection valves are in widespread use, in particular for internal combustion engines where they may be arranged in order to dose the fluid into an intake manifold of the internal combustion engine or directly into the combustion chamber of a cylinder of the internal combustion engine. [0003] Injection valves are manufactured in various forms in order to satisfy the various needs for the various combustion engines. Therefore, for example, their length, diameter as well as various elements of the injection valve which are responsible for the way the fluid is dosed may vary within a wide range. In addition to that, injection valves may accommodate an actuator for actuating a valve needle of an injection valve, which may, for example, be an electromagnetic actuator. [0004] In order to enhance the combustion process with regard to the reduction of unwanted emissions, the respective injection valve may be suited to dose fluids under very high pressure. The pressure may be, in the case of a gasoline engine, for example in the range of up to 00 bar, and in the case of diesel engines in the range of up to 0 bar. [000] EP A1 discloses an injection valve which comprises a housing with an injection opening. An internal pole is location fixed with respect to the housing. A solenoid acts magnetically on the internal pole. A magnetic armature is linearly movable relative to the housing. A valve needle is linearly movable relative to the housing and against the magnetic armature, which forms a valve seat together with the housing. A stop surface is location fixed relative to the housing and is formed on the internal pole. [0006] US 11/ A1 relates to a direct fuel injector which includes a body having a passage between inlet and outlet ends. A seat is at the outlet end and a closure member is associated with the seat. A needle member is associated with the closure member and is movable with respect to a pole piece between a first, closed position and a second, open position. A spring biases the needle member to the first position. An armature is free-floating with respect to the needle member. An intermediate pole structure is coupled with the needle member and is disposed between the pole piece and the armature and is decoupled there-from. An armature stop is coupled to the needle member and is spaced from the intermediate pole structure. An electromagnetic coil is associated with the pole piece, intermediate pole structure and armature. The injector reduces bounce of the needle assembly. [0007] EP A1 relates to a valve assembly for an injection valve, comprising a valve body including a central longitudinal axis, the valve body comprising a cavity with a fluid inlet portion and a fluid outlet portion, a valve needle axially movable in the cavity, the valve needle preventing a fluid flow through the fluid outlet portion in a closing position and releasing the fluid flow through the fluid outlet portion in further positions. The valve needle comprises a retainer element extending in radial direction. An electromagnetic actuator unit comprises an armature and a pole piece, the armature being axially movable in the cavity and being designed to actuate the valve needle via the retainer element, the pole piece being fixedly coupled to the valve body and comprising an inner recess, the retainer element being at least partially arranged in the inner recess. The pole piece comprises a stop element extending into the inner recess of the pole piece in radial direction. The stop element has a stop surface facing the fluid outlet portion and the retainer element. The stop surface of the stop element is designed to limit the axial movement of the retainer element. The invention relates to an injection valve with a valve assembly. [0008] In EP 2811 A1, which is prior art according to Art. 4(3) EPC, a fluid injection valve is disclosed. It comprises a valve body having a central longitudinal axis and defining a cavity. A valve needle is arranged in the cavity, being axially displaceable in a first axial direction away from its closing position. The fluid injection valve further comprises a pole piece and an armature, the latter being axially displaceable with respect to the pole piece and with respect to the valve needle. The valve needle comprises a retainer element, which is operable to interact with the armature to limit axial displacement of the armature with respect to the valve needle in the first axial direction and which is operable to contact the pole piece for limiting axial displacement of the valve needle in the first axial direction. [0009] One object of the invention is to create an injector for injecting fluid that contributes to a controllability of an amount of injected fluid and enables efficient operation of the injector. [00] The object is achieved by the features of the independent claim. Further embodiments of the invention are given in the dependent claims. [0011] According to one aspect of the invention, an injector for injecting fluid comprises a valve assembly with a valve body and a valve needle. The valve body has a longitudinal axis and comprises a cavity with a valve seat. [0012] Furthermore, the valve needle comprises an armature retainer that is coupled in a fixed way to the valve needle. Moreover, the armature retainer comprises an armature retainer constriction surface. [0013] The cavity is operable to take in the valve needle. The cavity and the valve needle are operable to prevent an injection of fluid from the cavity to external to the injector in a closing position of the valve needle, in which the valve needle is seated on the valve seat. Moreover, the cavity and the valve needle are operable to enable the injection of fluid when the valve needle is spaced apart from the closing position. [0014] The injector further comprises an electromag- 2
3 3 EP B1 4 netic actuator assembly, which is operable to exert a force for influencing a position of the valve needle. The electromagnetic actuator assembly comprises a pole piece and an armature. The pole piece is received in the cavity and positionally fix with the valve body. The pole piece comprises a pole piece constriction surface facing towards the armature. [001] The armature is received in the cavity and operable to be axially displaced relative to the pole piece. The armature is further operable to take along the armature retainer when being displaced towards the pole piece. [0016] A hydraulically effective restriction is formed between the armature retainer constriction surface and the pole piece constriction surface in at least a range of an axial displacement of the valve needle from a maximum displacement away from the closing position to a restriction displacement. The hydraulically effective restriction in particular effects a first damping force which is exerted on the valve needle. In this context, the "restriction displacement" is in particular an axial position of the valve needle between the closing position and that axial position which corresponds to the maximum displacement away from the closing position. [0017] In other words, the hydraulically effective restriction is a fluid channel which is defined by a surface of the armature retainer - which is referred to as the armature retainer constriction surface - and a surface of the pole piece - which is referred to as the pole piece constriction surface. The fluid channel can be also be referred to as a gap. A hydraulic diameter of said fluid channel is dependent on the axial displacement of the valve needle from the closing position. Specifically, the hydraulic diameter decreases with increasing displacement of the valve needle from the closing position. The hydraulic diameter of the fluid channel is at least twice as large - in on embodiment at least three times or four times as large - when the valve needle is in the closing position compared to the hydraulic diameter when the valve needle is at the maximum displacement away from the closing position. The reduction of the hydraulic diameter by the movement of the armature retainer against the hydraulic force of the fluid in the fluid channel may generate the first damping force. Fluid which enters the cavity at a fluid inlet end of the valve body and flows to a fluid outlet end of the valve body where the valve seat is positioned has to pass through said fluid channel. [0018] Advantageously, a velocity of the valve needle is decreased by the first damping force such that an amount of injected fluid is suitably influenced. In particular, the first damping force contributes to a controllability of the injector in a ballistic phase of an opening phase of the injector. Particularly, a variation of the amount of injected fluid within a given time window is kept low. In other words, it is contributed to a controllability of the amount of injected fluid. [0019] The restriction displacement of the valve needle away from the closing position is greater than zero; for example, it has a value of one third of the maximum displacement or more. Moreover, the range in which the hydraulically effective restriction is formed may be greater than zero; for example, it has a value of 1 % or more, in particular of % or more of the maximum displacement. In particular, the restriction displacement, respectively the range is dimensioned as to enable exertion of a desired damping force on the valve needle. Particularly, it is further dimensioned such that the velocity of the valve needle is substantially uninfluenced in a first portion of the opening phase of the injector, hence enabling efficient operation of the injector. [00] In one embodiment, the armature retainer constriction surface and the pole piece constriction surface comprise a smallest distance between the pole piece and the armature retainer at least when the valve needle is axially displaced in the range from the maximum displacement away from the closing position to the restriction displacement. Particularly, the armature retainer constriction surface and the pole piece constriction surface may comprise the smallest distance between the pole piece and the armature retainer when the valve needle is axially displaced to the maximum displacement and/or the restriction displacement. [0021] In particular, the maximum displacement of the valve needle away from the closing position may be reached when the valve needle is in an opening position, in which the armature abuts the pole piece. [0022] According to one embodiment, the armature retainer constriction surface has a first sloped shape. According to a further embodiment, the pole piece constriction surface has a second sloped shape. The first and/or second sloped shape may be a conical shape, for example, in particular a truncated conical shape. The second sloped shape may be equally sloped to the first sloped shape; in this case, the width of the fluid channel - i.e. the distance between the two constriction surfaces - is in particular independent from a position in the fluid channel along a flow direction of the fluid through the fluid channel. In particular, the armature retainer constriction surface with its first sloped shape and the pole piece constriction surface with its second sloped shape face each other in order to enable a suitable formation of the hydraulically effective restriction. [0023] According to a further embodiment, the armature retainer constriction surface has a first curvature. Advantageously, the first curvature contributes to a prevention of jamming of the armature retainer, particularly when the valve needle is tilted. Particularly, the armature retainer is constructed convex, at least at the armature retainer constriction surface. [0024] According to a further embodiment, the pole piece constriction surface has a second curvature. Advantageously, the second curvature contributes to a prevention of jamming of the armature retainer, particularly when the valve needle is tilted. Particularly, the pole piece is constructed concave, at least at the pole piece constriction surface. 3
4 EP B [002] According to a further embodiment, the second curvature is less than or equal to the first curvature. This enables the effective hydraulic restriction with merely a small section of the armature retainer, hence contributing to a reliable operation of the injector, particularly in the case when the valve needle is tilted. [0026] According to a further embodiment, the first damping force exerted on the valve needle is dependent on the position of the valve needle. Advantageously, this allows for reliably decreasing the velocity of the valve needle in order to achieve a suitably controllable amount of injected fluid, particularly within the range between the maximum displacement of the valve needle and the restriction displacement, while keeping it substantially uninfluenced in the first instant of the opening phase of the injector which contributes to an efficient operation of the injector. [0027] According to a further embodiment, the armature retainer comprises an armature retainer guiding surface. Moreover, the pole piece comprises a pole piece guiding surface. The armature retainer is operable for axially guiding the valve needle with the armature retainer guiding surface gliding along the pole piece guiding surface when the valve needle is axially displaced. In other words, the armature retainer has a side surface - referred to as the armature retainer guiding surface - and the pole piece has a side surface - referred to as the pole piece guiding surface - which are in sliding contact for axially guiding the valve needle. Advantageously, the axial guiding of the valve needle contributes to a prevention of tilting of the valve needle, thus enabling efficient operation of the injector. [0028] According to a further embodiment, the armature retainer guiding surface is convexly curved with respect to the valve needle. A convex curvature of the armature retainer guiding surface contributes to a prevention of jamming of the armature retainer, particularly when the valve needle is tilted. Thus an efficient operation of the injector is enabled. [0029] According to a further embodiment, the armature retainer guiding surface is substantially spherically shaped, i.e. it has the basic shape of a sphere. Advantageously, a spherical curvature of the armature retainer guiding surface contributes to a reliable prevention of jamming of the armature retainer, particularly when the valve needle is tilted, thus enabling an efficient operation of the injector. [00] According to a further embodiment, the armature retainer guiding surface comprises at least one axial channel for enabling a fluid flow axially through the cavity. This has the advantage that reliable guiding of the valve needle is enabled while also enabling efficient operation of the injector. [0031] According to a further embodiment, the armature is axially movable relative to the valve needle. Advantageously, particularly when the armature abuts the pole piece or when the valve needle comes in contact with the valve seat, an axial movement of the valve needle may be decoupled from an axial movement of the armature. This for example contributes to a prevention of a transmission of an undesired bouncing of the armature to the valve needle, hence enabling efficient operation of the injector. [0032] According to a further embodiment, the armature retainer comprises an armature retainer limiting surface for limiting an axial displacement of the armature relative to the valve needle. The armature retainer limiting surface is a surface of the armature retainer which faces towards the armature and laterally extends away from the valve needle. According to a further embodiment, the armature comprises an armature impact area facing towards the armature retainer limiting surface. The armature retainer limiting surface is operable to engage with the armature impact area. To put it differently, the armature retainer is in particular operable to limit the axial displacement of the armature relative to the valve needle by means of a form-fit engagement between a surface portion of the armature - referred to as the armature impact area - and and the armature retainer limiting surface. [0033] Particularly, the armature retainer limiting surface allows for a reliable force transmission of the armature to the valve needle. Particularly in the case that the armature is axially movable relative to the valve needle, the armature retainer limiting surface enables the valve needle to engage with the armature and to be taken along with the armature when the armature is axially displaced towards the pole piece. In the case that the injector further comprises a disc element, wherein the disc element is coupled in a fixed way to the valve needle for limiting an axial displacement of the armature relative to the valve needle away from the pole piece, the armature may be coupled to the valve needle by the disc element and the armature retainer limiting surface so that it has an axial play between the armature retainer limiting surface and the disc element. [0034] In one embodiment, a lateral extension of the armature retainer limiting surface away from the valve needle is constructed such that a relative movement between the armature and the armature retainer is damped. [003] Advantageously the armature retainer limiting surface contributes to a prevention of bouncing of the valve needle, particularly when the armature abuts the pole piece. This contributes to an efficient operation of the injector. [0036] For example, the armature impact area and the armature retainer limiting surface may be parallel. In particular, a lateral extension of the armature impact area away from the valve needle is constructed such that the relative movement between the armature and the armature retainer is damped. For this reason, the lateral extension of the armature impact area may be greater than or equal to the lateral extension of the armature retainer limiting surface. [0037] In one embodiment, the armature retainer limiting surface and the armature retainer constriction surface are comprised by a stopper portion of the armature 4
5 7 EP B1 8 retainer and on opposite axial sides of the stopper portion. The armature retainer limiting surface and the armature retainer constriction surface are preferably inclined or curved relative to one another in such fashion that the stopper portion tapers in radial outward direction. [0038] In one development, the armature retainer further has a guiding portion which comprises the armature retainer guiding surface as its outer surface or as a portion of its outer surface. The guiding portion may expediently be arranged on the axial side of the stopper portion which is remote from the armature and in particular merges with the stopper portion. Preferably, the armature retainer has a constriction in a region where the guiding portion and the stopper portion merge. [0039] In an advantageous development, the stopper portion - and therefore in particular the armature retainer limiting surface and the armature retainer constriction surface which both preferably extend radially to an outer contour of the stopper portion - projects radially beyond the guiding portion. Preferably, the maximum radial dimension of the stopper portion is at least twice as large as the maximum radial dimension of the guiding portion. Such dimensions are particularly advantageous for efficient damping of the relative movement between the armature and the armature retainer. [00] According to a further embodiment, the injector comprises a return spring, which is operable to bias the armature in axial direction away from the armature retainer. For example, the armature return spring is seated in precompressed fashion against the armature retainer and the armature. [0041] Advantageously, a large impulse transfer to the valve needle is enabled when the armature comes into contact with the armature retainer. This also enables an opening of the valve needle against a large hydraulic load with only limited actuator power. The return spring may particularly be seated on the armature retainer limiting surface. [0042] Exemplary embodiments of the invention are explained in the following with the aid of schematic drawings and reference numbers. Identical reference number designate elements or components with identical functions. It is shown: Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3a Figure 3b a first embodiment of an injector in a longitudinal section view, an enlarged longitudinal section view of the injector according to figure 1, a first graph of an amount of injected fluid over time of the injector according to figure 1, and a second graph and a third graph of a respective amount of injected fluid over time of a respective further injector [0043] Figure 1 shows a first embodiment of an injector 1 with a valve assembly 3 and an electromagnetic actuator assembly 19. The valve assembly 3 comprises a valve body and a valve needle 7. The valve body has a longitudinal axis 9 and comprises a cavity 11 with a valve seat 13. [0044] The valve needle 7 is received in the cavity 11 and is axially movable relative to the valve body. The valve needle 7 comprises an armature retainer 1 that is coupled in a fixed way to the valve needle 7. It may further comprise a disc element 41 being axially displaced to the armature retainer 1 and coupled in a fixed way to the valve needle 7. [004] The valve needle 7 is operable to prevent an injection of fluid in a closing position, in which the valve needle 7 is seated on the valve seat 13, from the cavity 11 external to the injector 1, for example into a combustion chamber. The valve needle 7 is further operable to enable the injection of fluid when it is apart from the closing position. The injector 1 may comprise a valve spring 43 for biasing the valve needle 7 towards the closing position, for example in order to contribute to a leak tightness of the injector 1. [0046] The electromagnetic actuator assembly 19 comprises a pole piece 21, an armature 23 and a magnetic coil 4, in particular solenoid, positioned in a housing which laterally surrounds at least a portion of the valve body. The magnetic coil 4, together with the armature 23 and the pole piece 21 forms a magnetic circuit of the electromagnetic actuator assembly 19 when the magnetic coil 4 is energized. In this context, the electromagnetic actuator assembly 19 may further comprise a yoke 47 for shaping the magnetic circuit of the electromagnetic actuator assembly 19. [0047] The electromagnetic actuator assembly 19 is thus operable to exert a force for influencing a position of the valve needle 7. Particularly, the valve needle 7 may be axially displaced by the electromagnetic actuator assembly 19 relative to the valve body, for example in reciprocating fashion. [0048] Figure 2 shows an enlarged longitudinal section view of the injector according to figure 1, particularly of the electromagnetic actuator assembly 19. The pole piece 21 is received in the cavity 11 and positionally fix with the valve body. In other embodiments, the pole piece 21 may be comprised by the valve body. The armature 23 is received in the cavity 11 and operable to be axially displaced relative to the pole piece 21. The armature 23 is further operable to take along the armature retainer 1 when being displaced towards the pole piece 21. [0049] In this embodiment, the armature 23 is axially movable relative to the valve needle 7, particularly between the armature retainer 1 and the disc element 41, which both limit an axial displacement of the armature 23 relative to the valve needle 7. The armature 23 may comprise a return spring 39 in this context in order to enable a large impulse transfer to the valve needle 7
6 9 EP B1 when the armature 23 comes into contact with the armature retainer 1. The return spring may further enable an opening of the valve needle 7 against large hydraulic loads with limited actuator power, for example bar. In other embodiments, the armature 23 may be arranged to be positionally fixed to the valve needle 7. The armature 23 may further comprise at least one bore in order to allow an axial fluid flow through the cavity 11. [000] In this embodiment, the pole piece 21 comprises a pole piece guiding surface 33. Furthermore, the armature retainer 1 may comprise an armature retainer guiding surface 31. In this context, the pole piece 21 may comprise a recess with the pole piece guiding surface 33 in order to receive the armature retainer 1 with its armature retainer guiding surface 31. An axial guiding of the valve needle 7 is thereby provided, with the armature retainer guiding surface 31 gliding along the pole piece guiding surface 33 when the valve needle 7 is axially displaced. [001] Particularly, the armature retainer guiding surface 31 is convexly curved with respect to the valve needle 7. In particular, it is for example substantially spherically shaped in order to avoid jamming of the armature retainer 1 when the valve needle 7 is tilted. [002] Particularly, the armature retainer guiding surface 31 comprises at least one channel for enabling a fluid flow axially through the cavity 11. The at least one channel may be an axial recess of the armature retainer 1. In the representation of Fig. 2, the channels are visible on the left and right sides of the armature retainer 1 so that the spherical basic shape is not visible in Fig. 2. [003] The armature retainer guiding surface 31 defines a guiding portion of the armature retainer 1. The guiding portion merges with a stopper portion of the armature retainer 1 at a downstream axial end of the guiding portion. In the interface region between the guiding portion and the stopper portion, the armature guide 1 has a circumferential constriction. In the present embodiment, the stopper portion is in the basic shape of a disc having a rounded outer contour. In another embodiment, it has a wedged shape in a longitudinal section view, i.e. it tapers in radial outward direction. [004] The stopper portion of the armature retainer 23 comprises an armature retainer limiting surface 3 of the armature retainer 1 for limiting the axial displacement of the armature 23 relative to the valve needle 7. The armature retainer limiting surface 3 enables, for example, an engagement with an armature impact area 37 of the armature 23 in order to allow the valve needle 7 to be taken along with the armature 23 when the armature 23 is axially displaced towards the pole piece 21. [00] In particular, the armature retainer limiting surface 3 laterally extends away from the valve needle 7, particularly projecting away from the armature retainer guiding surface 31. A lateral extension of the armature retainer limiting surface 3 is constructed such that a relative movement between the armature 23 and the armature retainer 1 is hydraulically damped. In the present embodiment this is achieved by the radial extension of the armature retainer limiting surface 3 - which is also the radial extension of the stopper portion of the armature retainer 1 - being at least twice as large as the radial extension of the guiding portion of the armature retainer 1. [006] The pole piece 21 further comprises a pole piece constriction surface 2 that is facing towards the armature 23. Moreover, the armature retainer 1 comprises an armature retainer constriction surface 17, towards which the pole piece constriction surface 2 is facing. The armature retainer constriction surface 17 is arranged at an axial side of the stopper portion opposite of that axial side on which the armature retainer limiting surface 3 is arranged. [007] Particularly, at least when the valve needle 7 is axially displaced in a range from a maximum displacement away from the closing position to a restriction displacement, the armature retainer constriction surface 17 and the pole piece constriction surface 2 comprise a smallest distance between the pole piece 21 and the armature retainer 23 in the axial region of the stopper portion, forming a hydraulically effective restriction between the armature retainer constriction surface 17 and the pole piece constriction surface 2. [008] In other words, a gap between the pole piece 21 and the armature retainer 1, through which fluid may flow, changes depending on the axial displacement of the armature retainer 1. In particular, an axial distance between the pole piece constriction surface 2 and the armature retainer constriction surface 17 decreases when the armature retainer 1 is axially displaced towards the pole piece 21. A hydraulic diameter of the hydraulically effective restriction is dependent on the axial displacement of the valve needle 7 from the closing position and is at least twice at large when the valve needle 7 is in the closing position compared to the hydraulic diameter when the valve needle 7 is at the maximum displacement away from the closing position. [009] In particular, the maximum displacement of the valve needle 7 away from the closing position may be reached when the valve needle 7 is in an opening position, in which, for example, the armature 23 abuts the pole piece 21. [0060] Moreover, the restriction displacement of the valve needle 7 away from the closing position may particularly be greater than zero. In particular, the restriction displacement, respectively the range is dimensioned as to allow a formation of the hydraulically effective restriction between the armature retainer constriction surface 17 and the pole piece constriction surface 2, while still enabling fluid to flow through the cavity 11 such that a pressure difference in axial direction is small enough to allow for a reliable and efficient injection of the injector 1. [0061] Due to the hydraulically effective restriction between the armature retainer constriction surface 17 and the pole piece constriction surface 2, a first damping force is exerted on the valve needle 7 when the armature 6
7 11 EP B1 12 retainer 1 is axially displaced towards the pole piece 21. Advantageously a velocity of the valve needle 7 is thereby decreased such that a controllability of the injection, particularly in a ballistic phase 63 (see figure 3a) of an opening phase of the injector is contributed to. Particularly, a variation of an amount of injected fluid within a given time window 61 (see figure 3a) is kept low. [0062] Particularly, the restriction displacement, respectively the range is dimensioned as to enable an exertion of a desired damping force on the valve needle 7. Particularly, it is further dimensioned such that the velocity of the valve needle is substantially uninfluenced in a first instant of the opening phase of the injector. [0063] In one embodiment, the armature retainer constriction surface 17 has a first sloped shape. Particularly, the pole piece constriction surface 2 may have a second sloped shape. This enables the effective hydraulic restriction to be formed by merely a small section of the armature retainer 1, allowing the first damping force to be reliably provided, particularly in the case when the valve needle 7 is tilted. The second sloped shape may be equally sloped to the first sloped shape. [0064] In one embodiment, the armature retainer constriction surface 17 has a first curvature. Particularly, the pole piece constriction surface 2 has a second curvature. The second curvature may be less than or equal to the first curvature. This enables the effective hydraulic restriction to be formed by merely a small section of the armature retainer 1, allowing the first damping force to be reliably provided, particularly in the case when the valve needle 7 is tilted. Moreover, this contributes to a prevention of jamming of the valve needle 7. [006] Figure 3a shows a first graph 49 of an amount of injected fluid per activation over time of the injector 1 according to figure 1. Compared to a second graph 1 (figure 3b) of a fast opening injector and a third graph 3 of a slow opening injector, wherein no hydraulically effective restriction is formed between a respective armature retainer and a respective pole piece, it can be seen that a respective variability, 7, 9 of the amount of injected fluid within the given time window 61 of the first graph 49 is minimized, similar to the slow opening injector depicted in graph 3. Thus, it is contributed to the controllability of the injection, particularly in the ballistic phase 63. The given time window 61 is particularly given by an electrical pulse width. Moreover, the velocity of the valve needle 7 in the first instant of the opening phase is maintained, similar to the fast opening injector depicted in graph 1, thus contributing to a spray stability of the injector having a longitudinal axis (9) and comprising a cavity (11) with a valve seat (13), the valve needle (7) comprising an armature retainer (1), being coupled in a fixed way to the valve needle (7) and comprising an armature retainer constriction surface (17), the cavity (11) being operable to take in the valve needle (7), the cavity (11) and the valve needle (7) being operable to prevent in a closing position of the valve needle (7), in which the valve needle (7) is seated on the valve seat (13), an injection of fluid from the cavity (11) to external to the injector (1), and to enable the injection of fluid when the valve needle (7) is apart from the closing position, - an electromagnetic actuator assembly (19), which is operable to exert a force for influencing a position of the valve needle (7), comprising a pole piece (21) and an armature (23), the pole piece (21) being received in the cavity (11), being positionally fix with the valve body () and comprising a pole piece constriction surface (2) facing towards the armature (23), the armature (23) being received in the cavity (11), operable to be axially displaced relative to the pole piece (21) and to take along the armature retainer (1) when being displaced towards the pole piece (21), characterized in that - a fluid channel through which fluid which enters the cavity (11) at a fluid inlet end of the valve body () and flows to a fluid outlet end of the valve body () where the valve seat (13) is positioned has to pass is defined by the armature retainer constriction surface (17) and the pole piece constriction surface (2) and - a first damping force is exerted on the valve needle (7) by means of a hydraulic diameter of said fluid channel being at least twice as large when the valve needle (7) is in the closing position compared to the hydraulic diameter when the valve needle (7) is at a maximum displacement away from the closing position. 2. Injector (1) according to claim 1, wherein the armature retainer constriction surface (17) has a first sloped shape. 3. Injector (1) according to any of claims 1 or 2, wherein the pole piece constriction surface (2) has a second sloped shape. Claims 1. Injector (1) for injecting fluid with - a valve assembly (3) comprising a valve body () and a valve needle (7), the valve body () 4. Injector (1) according to any of claims 1 to 3, wherein the armature retainer constriction surface (17) has a first curvature.. Injector (1) according to any of claims 1 to 4, wherein the pole piece constriction surface (2) has a second curvature. 7
8 13 EP B Injector (1) according to claims 4 and, wherein the second curvature is less than or equal to the first curvature. Patentansprüche 1. Injektor (1) zum Einspritzen von Flüssigkeit mit 7. Injector (1) according to any of claims 1 to 6, wherein the first damping force exerted on the valve needle (7) is dependent on the position of the valve needle (7). 8. Injector (1) according to any of claims 1 to 7, with the armature retainer (1) comprising an armature retainer guiding surface (31) and the pole piece (21) comprising a pole piece guiding surface (33), wherein the armature retainer (1) is operable for axially guiding the valve needle (7) with the armature retainer guiding surface (31) gliding along the pole piece guiding surface (33) when the valve needle (7) is axially displaced. 9. Injector (1) according to claim 8, wherein the armature retainer guiding surface (31) is convexly curved with respect to the valve needle (7).. Injector (1) according to any of claims 8 or 9, wherein the armature retainer guiding surface (31) is substantially spherically shaped. 11. Injector (1) according to any of claims 8 to, wherein the armature retainer guiding surface (31) comprises at least one channel for enabling a fluid flow axially through the cavity (11). 12. Injector (1) according to any of claims 1 to 11, wherein the armature (23) is axially movable relative to the valve needle (7). 13. Injector (1) according to any of claims 1 to 12, with the armature retainer (1) comprising an armature retainer limiting surface (3) for limiting an axial displacement of the armature (23) relative to the valve needle (7), facing towards the armature (23) and laterally extending away from the valve needle (7). 14. Injector (1) according to claim 13, with the armature (23) comprising an armature impact area (37) facing towards the armature retainer limiting surface (3), the armature retainer limiting surface (3) being operable to engage with the armature impact area (37), wherein a lateral extension of the armature retainer limiting surface (3) away from the valve needle (7) is constructed such that a relative movement between the armature (23) and the armature retainer (1) is damped. 1. Injector (1) according to any of claims 1 to 14, wherein the armature (23) comprises a return spring (39), which is operable to bias the armature (23) in axial direction away from the armature retainer (1) einer Ventilanordnung (3), die einen Ventilkörper () und eine Ventilnadel (7) aufweist, wobei der Ventilkörper () einen Längsachse (9) aufweist und einen Hohlraum (11) mit einem Ventilsitz (13) aufweist, wobei die Ventilnadel (7) eine Ankerhalterung (1) aufweist, die auf feste Weise an die Ventilnadel (7) gekoppelt ist und eine Ankerhalterungsverengungsfläche (17) aufweist, wobei der Hohlraum (11) in der Lage ist, die Ventilnadel (7) aufzunehmen, wobei der Hohlraum (11) und die Ventilnadel (7) in der Lage sind, in einer Schließstellung der Ventilnadel (7), in der die Ventilnadel (7) auf dem Ventilsitz (13) sitzt, eine Einspritzung von Flüssigkeit aus dem Hohlraum (11) auf die Außenseite des Injektors (1) zu verhindern und die Einspritzung von Flüssigkeit zu ermöglichen, wenn die Ventilnadel (7) von der Schließstellung getrennt ist, - einer elektromagnetischen Betätigungsanordnung (19), die in der Lage ist, eine Kraft zum Beeinflussen einer Stellung der Ventilnadel (7) auszuüben, und die ein Polstück (21) und einen Anker (23) aufweist, wobei das Polstück (21) in dem Hohlraum (11) aufgenommen ist, sich in einer festen Position mit dem Ventilkörper () befindet und eine Polstückverengungsfläche (2) aufweist, die dem Anker (23) zugewandt ist, wobei der Anker (23) in dem Hohlraum (11) aufgenommen und in der Lage ist, relativ zum dem Polstück (21) axial verlagert zu werden und die Ankerhalterung (1) mitzunehmen, wenn er in Richtung zu dem Polstück (21) verlagert wird, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass - ein Flüssigkeitskanal, durch den Flüssigkeit, die in den Hohlraum (11) an einem Flüssigkeitseinlassende des Ventilkörpers () eintritt und zu einem Flüssigkeitsauslassende des Ventilkörpers (), an dem der Ventilsitz (13) positioniert ist, strömt, fließen muss, durch die Ankerhalterungsverengungsfläche (17) und die Polstückverengungsfläche (2) festgelegt ist und - eine erste Dämpfungskraft dadurch auf die Ventilnadel (7) ausgeübt wird, dass, wenn sich die Ventilnadel (7) in der Schließstellung befindet, ein hydraulischer Durchmesser des Flüssigkeitskanals wenigstens zwei Mal so groß wie der hydraulische Durchmesser ist, wenn sich die Ventilnadel (7) in einer maximalen Verlagerung weg von der Schließstellung befindet. 2. Injektor (1) nach Anspruch 1, wobei die Ankerhalterungsverengungsfläche (17) eine erste schräge Form aufweist. 8
9 1 EP B Injektor (1) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 oder 2, wobei die Polstückverengungsfläche (2) eine zweite schräge Form aufweist. 4. Injektor (1) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, wobei die Ankerhalterungsverengungsfläche (17) eine erste Krümmung aufweist.. Injektor (1) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 4, wobei die Polstückverengungsfläche (2) eine zweite Krümmung aufweist. 6. Injektor (1) nach Anspruch 4 und, wobei die zweite Krümmung kleiner oder gleich der ersten Krümmung ist. 7. Injektor (1) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 6, wobei die erste auf die Ventilnadel (7) ausgeübte Dämpfungskraft von der Stellung der Ventilnadel (7) abhängig ist. 8. Injektor (1) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 7, wobei die Ankerhalterung (1) eine Ankerhalterungsführungsfläche (31) aufweist und das Polstück (21) eine Polstückführungsfläche (33) aufweist, wobei die Ankerhalterung (1) in der Lage ist, die Ventilnadel (7) axial zu führen, wobei die Ankerhalterungsführungsfläche (31) entlang der Polstückführungsfläche (33) gleitet, wenn die Ventilnadel (7) axial verlagert wird. 9. Injektor (1) nach Anspruch 8, wobei die Ankerhalterungsführungsfläche (31) in Bezug auf die Ventilnadel (7) konvex gekrümmt ist.. Injektor (1) nach einem der Ansprüche 8 oder 9, wobei die Ankerhalterungsführungsfläche (31) im Wesentlichen kugelförmig ist. 11. Injektor (1) nach einem der Ansprüche 8 bis, wobei die Ankerhalterungsführungsfläche (31) wenigstens einen Kanal aufweist, um einen axialen Flüssigkeitsstrom durch den Hohlraum (11) zu ermöglichen. 12. Injektor (1) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 11, wobei der Anker (23) relativ zu der Ventilnadel (7) axial bewegbar ist. 13. Injektor (1) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 12, wobei die Ankerhalterung (1) eine Ankerhalterungsbegrenzungsfläche (3) zur Begrenzung einer axialen Verlagerung des Ankers (23) relativ zu der Ventilnadel (7) aufweist, die dem Anker (23) zugewandt ist und sich seitlich weg von der Ventilnadel (7) erstreckt Injektor (1) nach Anspruch 13, wobei der Anker (23) einen Ankerstoßbereich (37) aufweist, der der Ankerhalterungsbegrenzungsfläche (3) zugewandt ist, wobei die Ankerhalterungsbegrenzungsfläche (3) in der Lage ist, in den Ankerstoßbereich (37) einzugreifen, wobei eine seitliche Erstreckung der Ankerhalterungsbegrenzungsfläche (3) weg von der Ventilnadel (7) so ausgeführt ist, dass eine relative Bewegung zwischen dem Anker (23) und der Ankerhalterung (1) gedämpft wird. 1. Injektor (1) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 14, wobei der Anker (23) eine Rückholfeder (39) aufweist, die in der Lage ist, den Anker (23) in axialer Richtung weg von der Ankerhalterung (1) vorzuspannen. Revendications 1. Injecteur (1), pour injecter un fluide avec - un ensemble soupape (3) comprenant un corps de soupape () et un pointeau de soupape (7), le corps de soupape () possédant un axe longitudinal (9) et comprenant une cavité (11) avec un siège de soupape (13), le pointeau de soupape (7) comprenant un dispositif de retenue d induit (1), accouplé de manière fixe au pointeau de soupape (7) et comprenant une surface de constriction de dispositif de retenue d induit (17), la cavité (11) étant utilisable pour recevoir le pointeau de soupape (7), la cavité (11) et le pointeau de soupape (7) étant utilisables pour empêcher, dans une position de fermeture du pointeau de soupape (7), dans laquelle le pointeau de soupape (7) est assis sur le siège de soupape (13), une injection de fluide de la cavité (11) à l extérieur de l injecteur (1), et pour permettre l injection de fluide lorsque le pointeau de soupape (7) est séparé de la position de fermeture, - un ensemble actionneur électromagnétique (19), qui est utilisable pour exercer une force pour influencer une position du pointeau de soupape (7), comprenant une pièce polaire (21) et un induit (23), la pièce polaire (21) étant reçue dans la cavité (11), étant fixe de façon positionnelle avec le corps de soupape () et comprenant une surface de constriction de pièce polaire (2) tournée vers l induit (23), l induit (23) étant reçu dans la cavité (11), utilisable pour être axialement déplacé par rapport à la pièce polaire (21) et emmener le dispositif de retenue d induit (1) lorsqu il est déplacé vers la pièce polaire (21), caractérisé en ce que - un canal de fluide, à travers lequel un fluide, qui entre dans la cavité (11) à une extrémité d entrée de fluide du corps de soupape () et s écoule vers une extrémité de sortie de fluide 9
10 17 EP B1 18 du corps de soupape () où le siège de soupape (13) est positionné, doit passer, est défini par la surface de constriction de dispositif de retenue d induit (17) et la surface de constriction de pièce polaire (2), et - une première force d amortissement est exercée sur le pointeau de soupape (7) au moyen d un diamètre hydraulique dudit canal de fluide au moins deux fois plus grand lorsque le pointeau de soupape (7) est dans la position de fermeture par rapport au diamètre hydraulique lorsque le pointeau de soupape (7) est éloigné, d un déplacement maximum, de la position de fermeture. 2. Injecteur (1) selon la revendication 1, dans lequel la surface de constriction de dispositif de retenue d induit (17) présente une première forme inclinée. 3. Injecteur (1) selon l une quelconque des revendications 1 ou 2, dans lequel la surface de constriction de pièce polaire (2) présente une seconde forme inclinée. 4. Injecteur (1) selon l une quelconque des revendications 1 à 3, dans lequel la surface de constriction de dispositif de retenue d induit (17) présente une première courbure.. Injecteur (1) selon l une quelconque des revendications 1 à 4, dans lequel la surface de constriction de pièce polaire (2) présente une seconde courbure. 6. Injecteur (1) selon les revendications 4 et, dans lequel la seconde courbure est inférieure ou égale à la première courbure. 7. Injecteur (1) selon l une quelconque des revendications 1 à 6, dans lequel la première force d amortissement exercée sur le pointeau de soupape (7) dépend de la position du pointeau de soupape (7) Injecteur (1) selon l une quelconque des revendications 8 ou 9, dans lequel la surface de guidage de dispositif de retenue d induit (31) est de forme sensiblement sphérique. 11. Injecteur (1) selon l une quelconque des revendications 8 à, dans lequel la surface de guidage de dispositif de retenue d induit (31) comprend au moins un canal pour permettre un écoulement fluide axialement à travers la cavité (11). 12. Injecteur (1) selon l une quelconque des revendications 1 à 11, dans lequel l induit (23) est axialement mobile par rapport au pointeau de soupape (7). 13. Injecteur (1) selon l une quelconque des revendications 1 à 12, avec le dispositif de retenue d induit (1) comprenant une surface de limitation de dispositif de retenue d induit (3) pour limiter un déplacement axial de l induit (23) par rapport au pointeau de soupape (7), tournée vers l induit (23) et s éloignant, par extension latérale, du pointeau de soupape (7). 14. Injecteur (1) selon la revendication 13, avec l induit (23) comprenant une zone d impact d induit (37) tournée vers la surface de limitation de dispositif de retenue d induit (3), la surface de limitation de dispositif de retenue d induit (3) étant utilisable pour entrer en prise avec la zone d impact d induit (37), dans lequel une extension latérale de la surface de limitation de dispositif de retenue d induit (3), s éloignant du pointeau de soupape (7), est construite de telle sorte qu un mouvement relatif entre l induit (23) et le dispositif de retenue d induit (1) soit amorti. 1. Injecteur (1) selon l une quelconque des revendications 1 à 14, dans lequel l induit (23) comprend un ressort de rappel (39), qui est utilisable pour solliciter l induit (23) dans une direction axiale s éloignant du dispositif de retenue d induit (1). 8. Injecteur (1) selon l une quelconque des revendications 1 à 7, avec le dispositif de retenue d induit (1) comprenant une surface de guidage de dispositif de retenue d induit (31) et la pièce polaire (21) comprenant une surface de guidage de pièce polaire (33), dans lequel le dispositif de retenue d induit (1) est utilisable pour axialement guider le pointeau de soupape (7) avec la surface de guidage de dispositif de retenue d induit (31) glissant le long de la surface de guidage de pièce polaire (33) lorsque le pointeau de soupape (7) est axialement déplacé Injecteur (1) selon la revendication 8, dans lequel la surface de guidage de dispositif de retenue d induit (31) est incurvée de façon convexe par rapport au pointeau de soupape (7).
(51) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 ( ) H02K 1/32 ( ) H02K 1/20 ( ) H02K 7/18 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 4ZZ6 4B_T (11) EP 2 400 634 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 02.10.2013 Bulletin 2013/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 (2006.01)
(19) TEPZZ 4ZZ6 4B_T (11) EP 2 400 634 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 02.10.2013 Bulletin 2013/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 (2006.01)
(51) Int Cl.: A47C 7/44 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 66_986B_T (11) EP 2 661 986 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (51) Int Cl.: A47C 7/44 (2006.01)
(19) TEPZZ 66_986B_T (11) EP 2 661 986 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (51) Int Cl.: A47C 7/44 (2006.01)
TEPZZ 6Z7 _6A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2013/26
 (19) TEPZZ 6Z7 _6A_T (11) EP 2 607 216 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (51) Int Cl.: B62D 55/21 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13160462.1 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 6Z7 _6A_T (11) EP 2 607 216 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (51) Int Cl.: B62D 55/21 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13160462.1 (22)
TEPZZ Z Z 85A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ Z Z 8A_T (11) EP 3 0 38 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 18.0.16 Bulletin 16/ (21) Application number: 1482271.7 (22)
(19) TEPZZ Z Z 8A_T (11) EP 3 0 38 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 18.0.16 Bulletin 16/ (21) Application number: 1482271.7 (22)
TEPZZ 5 59 A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 5 59 A T (11) EP 2 535 922 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 19.12.2012 Bulletin 2012/51 (21) Application number: 12172230.0 (51) Int Cl.: H01J 61/26 (2006.01) H01J
(19) TEPZZ 5 59 A T (11) EP 2 535 922 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 19.12.2012 Bulletin 2012/51 (21) Application number: 12172230.0 (51) Int Cl.: H01J 61/26 (2006.01) H01J
TEPZZ 6 6 8_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ 6 6 8_A_T (11) EP 2 626 281 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.2013 Bulletin 2013/33 (1) Int Cl.: B62D 3/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1214679.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 6 6 8_A_T (11) EP 2 626 281 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.2013 Bulletin 2013/33 (1) Int Cl.: B62D 3/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1214679.0 (22)
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: F16H 47/04 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 6774A T (11) EP 2 67 74 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.10.2013 Bulletin 2013/44 (1) Int Cl.: F16H 47/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1316271.1 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 6774A T (11) EP 2 67 74 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.10.2013 Bulletin 2013/44 (1) Int Cl.: F16H 47/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1316271.1 (22) Date
TEPZZ ZZ9 78A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B65D 85/804 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ ZZ9 78A_T (11) EP 3 009 378 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.04.16 Bulletin 16/16 (1) Int Cl.: B6D 8/804 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1189391.4 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ ZZ9 78A_T (11) EP 3 009 378 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.04.16 Bulletin 16/16 (1) Int Cl.: B6D 8/804 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1189391.4 (22) Date of
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/41
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001585051A1* (11) EP 1 585 051 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 12.10.2005 Bulletin 2005/41
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001585051A1* (11) EP 1 585 051 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 12.10.2005 Bulletin 2005/41
(51) Int Cl. 7 : B60B 33/04. (56) References cited:
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP000958150B1* (11) EP 0 958 150 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP000958150B1* (11) EP 0 958 150 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant
(51) Int Cl.: H05F 3/02 ( ) F16K 1/22 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 1 637 016 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 13.02.08 Bulletin 08/07 (21) Application number: 047769.3 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (11) EP 1 637 016 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 13.02.08 Bulletin 08/07 (21) Application number: 047769.3 (22) Date of filing:
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/42
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 512 002 A2 (43) Date of publication: 17.10.2012 Bulletin 2012/42 (51) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 (2006.01) H02J 7/35 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11250613.4
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 512 002 A2 (43) Date of publication: 17.10.2012 Bulletin 2012/42 (51) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 (2006.01) H02J 7/35 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11250613.4
(51) Int Cl.: B66C 13/14 ( ) B66C 3/00 ( ) A01G 23/08 ( ) E02F 9/22 ( ) E02F 3/36 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 8 4Z59A_T (11) EP 2 824 059 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.01.2015 Bulletin 2015/03 (21) Application number: 13181144.0 (51) Int Cl.: B66C 13/14 (2006.01) B66C
(19) TEPZZ 8 4Z59A_T (11) EP 2 824 059 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.01.2015 Bulletin 2015/03 (21) Application number: 13181144.0 (51) Int Cl.: B66C 13/14 (2006.01) B66C
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2009/04
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 017 118 A1 (43) Date of publication: 21.01.2009 Bulletin 2009/04 (51) Int Cl.: B60M 1/06 (2006.01) B60M 3/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 08159353.5
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 017 118 A1 (43) Date of publication: 21.01.2009 Bulletin 2009/04 (51) Int Cl.: B60M 1/06 (2006.01) B60M 3/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 08159353.5
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/09
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 159 888 A2 (43) Date of publication: 03.03.2010 Bulletin 2010/09 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 13/53 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09167901.9 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 159 888 A2 (43) Date of publication: 03.03.2010 Bulletin 2010/09 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 13/53 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09167901.9 (22) Date of filing:
(51) Int Cl.: B41F 31/30 ( ) B41F 31/34 ( ) B41F 31/36 ( ) B41F 13/20 ( ) B41F 7/04 ( ) B41F 7/12 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 7ZZ5Z4A T (11) EP 2 700 504 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.02.2014 Bulletin 2014/09 (21) Application number: 13179814.2 (51) Int Cl.: B41F 31/30 (2006.01) B41F
(19) TEPZZ 7ZZ5Z4A T (11) EP 2 700 504 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.02.2014 Bulletin 2014/09 (21) Application number: 13179814.2 (51) Int Cl.: B41F 31/30 (2006.01) B41F
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2008/04
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 880 821 A1 (43) Date of publication: 23.01.2008 Bulletin 2008/04 (51) Int Cl.: B29C 45/14 (2006.01) H04M 1/02 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 07008807.5
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 880 821 A1 (43) Date of publication: 23.01.2008 Bulletin 2008/04 (51) Int Cl.: B29C 45/14 (2006.01) H04M 1/02 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 07008807.5
TEPZZ 7 Z4_ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2014/20
 (19) TEPZZ 7 Z4_ZA_T (11) EP 2 730 410 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.05.2014 Bulletin 2014/20 (21) Application number: 13191611.6 (22) Date of filing: 05.11.2013 (51)
(19) TEPZZ 7 Z4_ZA_T (11) EP 2 730 410 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.05.2014 Bulletin 2014/20 (21) Application number: 13191611.6 (22) Date of filing: 05.11.2013 (51)
TEPZZ 7_ Z6ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 ( ) H02K 7/18 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 7_ Z6ZA_T (11) EP 2 712 060 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.03.2014 Bulletin 2014/13 (51) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 (2006.01) H02K 7/18 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ 7_ Z6ZA_T (11) EP 2 712 060 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.03.2014 Bulletin 2014/13 (51) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 (2006.01) H02K 7/18 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(51) Int Cl.: F16C 17/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 47 749B_T (11) EP 2 473 749 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.12.2015 Bulletin 2015/52 (21) Application number: 09848790.3
(19) TEPZZ 47 749B_T (11) EP 2 473 749 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.12.2015 Bulletin 2015/52 (21) Application number: 09848790.3
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2001/43
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001147979A1* (11) EP 1 147 979 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.10.2001 Bulletin 2001/43
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001147979A1* (11) EP 1 147 979 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.10.2001 Bulletin 2001/43
TEPZZ 9 4 7A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 9 4 7A_T (11) EP 2 924 237 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 143822.3 (1) Int Cl.: F01D /08 (06.01) F01D 11/00 (06.01) F01D
(19) TEPZZ 9 4 7A_T (11) EP 2 924 237 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 143822.3 (1) Int Cl.: F01D /08 (06.01) F01D 11/00 (06.01) F01D
TEPZZ 557 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 557 A_T (11) EP 3 115 573 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/02 (21) Application number: 16176199.4 (51) Int Cl.: F02B 25/20 (2006.01) F02M
(19) TEPZZ 557 A_T (11) EP 3 115 573 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/02 (21) Application number: 16176199.4 (51) Int Cl.: F02B 25/20 (2006.01) F02M
TEPZZ 67_744A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B60K 6/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 67_744A_T (11) EP 2 671 744 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/50 (51) Int Cl.: B60K 6/10 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13169502.5 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 67_744A_T (11) EP 2 671 744 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/50 (51) Int Cl.: B60K 6/10 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13169502.5 (22)
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 9778 A_T (11) EP 2 977 82 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.01.16 Bulletin 16/04 (21) Application number: 1417804.4 (1) Int Cl.: F02B 19/ (06.01) F02B 19/12 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 9778 A_T (11) EP 2 977 82 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.01.16 Bulletin 16/04 (21) Application number: 1417804.4 (1) Int Cl.: F02B 19/ (06.01) F02B 19/12 (06.01)
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/20
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001531305A1* (11) EP 1 531 305 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.05.2005 Bulletin 2005/20
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001531305A1* (11) EP 1 531 305 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.05.2005 Bulletin 2005/20
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2006/42
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 712 388 A1 (43) Date of publication: 18.10.2006 Bulletin 2006/42 (51) Int Cl.:
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 712 388 A1 (43) Date of publication: 18.10.2006 Bulletin 2006/42 (51) Int Cl.:
TEPZZ 57847_B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 57847_B_T (11) EP 2 578 471 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 16.03.2016 Bulletin 2016/11 (21) Application number: 11789623.3
(19) TEPZZ 57847_B_T (11) EP 2 578 471 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 16.03.2016 Bulletin 2016/11 (21) Application number: 11789623.3
TEPZZ 7 8Z6ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 7 8Z6ZA_T (11) EP 2 738 060 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.06.2014 Bulletin 2014/23 (21) Application number: 12194849.1 (51) Int Cl.: B61D 41/04 (2006.01) B60N
(19) TEPZZ 7 8Z6ZA_T (11) EP 2 738 060 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.06.2014 Bulletin 2014/23 (21) Application number: 12194849.1 (51) Int Cl.: B61D 41/04 (2006.01) B60N
(51) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 ( ) H02J 7/02 ( ) A61B 17/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_684 96B_T (11) EP 1 684 396 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 29.04. Bulletin /18 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 (06.01) H02J 7/02
(19) TEPZZ_684 96B_T (11) EP 1 684 396 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 29.04. Bulletin /18 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 (06.01) H02J 7/02
TEPZZ 4_8Z84B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 4_8Z84B_T (11) EP 2 418 084 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.09.13 Bulletin 13/36 (21) Application number: 0984.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 4_8Z84B_T (11) EP 2 418 084 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.09.13 Bulletin 13/36 (21) Application number: 0984.0 (22)
TEPZZ 55_5Z6A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2013/05
 (19) TEPZZ _Z6A T (11) EP 2 1 06 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/0 (1) Int Cl.: F02K 1/72 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1217601.0 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ _Z6A T (11) EP 2 1 06 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/0 (1) Int Cl.: F02K 1/72 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1217601.0 (22) Date of
(51) Int Cl.: B61F 5/38 ( ) (54) Two- axle bogie for railway vehicle with radially adjustable wheelsets with cross coupling
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 157 007 A1 (43) Date of publication: 24.02.2010 Bulletin 2010/08 (51) Int Cl.: B61F 5/38 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09475002.3 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 157 007 A1 (43) Date of publication: 24.02.2010 Bulletin 2010/08 (51) Int Cl.: B61F 5/38 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09475002.3 (22) Date of filing:
(51) Int Cl.: B66F 9/08 ( ) B66F 17/00 ( ) B66F 9/20 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _ 96B_T (11) EP 2 123 96 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 17..12 Bulletin 12/42 (1) Int Cl.: B66F 9/08 (06.01) B66F 17/00
(19) TEPZZ _ 96B_T (11) EP 2 123 96 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 17..12 Bulletin 12/42 (1) Int Cl.: B66F 9/08 (06.01) B66F 17/00
TEPZZ 7 Z88A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 7 Z88A_T (11) EP 2 722 088 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 23.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/17 (21) Application number: 12799927.4
(19) TEPZZ 7 Z88A_T (11) EP 2 722 088 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 23.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/17 (21) Application number: 12799927.4
(51) Int Cl.: F16H 63/06 ( ) F16H 9/18 ( ) F16H 55/56 ( ) (56) References cited:
 (19) TEPZZ 784 8B_T (11) EP 2 784 38 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.01.2016 Bulletin 2016/01 (1) Int Cl.: F16H 63/06 (2006.01)
(19) TEPZZ 784 8B_T (11) EP 2 784 38 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.01.2016 Bulletin 2016/01 (1) Int Cl.: F16H 63/06 (2006.01)
TEPZZ _84894A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: F23N 5/12 ( ) F23N 5/24 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ _84894A_T (11) EP 3 184 894 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.06.17 Bulletin 17/26 (1) Int Cl.: F23N /12 (06.01) F23N /24 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1681.0
(19) TEPZZ _84894A_T (11) EP 3 184 894 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.06.17 Bulletin 17/26 (1) Int Cl.: F23N /12 (06.01) F23N /24 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1681.0
(51) Int Cl.: H02J 7/35 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 2 0 12 B1 (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.02.12 Bulletin 12/0 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 7/3 (06.01) (21) Application number: 08172418.9
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 2 0 12 B1 (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.02.12 Bulletin 12/0 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 7/3 (06.01) (21) Application number: 08172418.9
(51) Int Cl.: B62J 17/00 ( ) B62J 17/02 ( ) B62J 23/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 6_ 8Z6B_T (11) EP 2 612 806 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 05.11.2014 Bulletin 2014/45 (51) Int Cl.: B62J 17/00 (2006.01)
(19) TEPZZ 6_ 8Z6B_T (11) EP 2 612 806 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 05.11.2014 Bulletin 2014/45 (51) Int Cl.: B62J 17/00 (2006.01)
(51) Int Cl.: F01D 5/08 ( ) F01D 5/30 ( ) F01D 11/00 ( ) F01D 25/12 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _46ZB_T (11) EP 2 146 0 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28.11.2012 Bulletin 2012/48 (1) Int Cl.: F01D /08 (2006.01) F01D
(19) TEPZZ _46ZB_T (11) EP 2 146 0 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28.11.2012 Bulletin 2012/48 (1) Int Cl.: F01D /08 (2006.01) F01D
(51) Int Cl.: F16L 3/205 ( ) F16F 7/14 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9 8 6B_T (11) EP 2 392 836 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.03.2013 Bulletin 2013/ (51) Int Cl.: F16L 3/205 (2006.01)
(19) TEPZZ 9 8 6B_T (11) EP 2 392 836 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.03.2013 Bulletin 2013/ (51) Int Cl.: F16L 3/205 (2006.01)
(51) Int Cl.: F03D 11/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9 66B_T (11) EP 2 92 266 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 2.06.2014 Bulletin 2014/26 (1) Int Cl.: F03D 11/02 (2006.01) (21)
(19) TEPZZ 9 66B_T (11) EP 2 92 266 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 2.06.2014 Bulletin 2014/26 (1) Int Cl.: F03D 11/02 (2006.01) (21)
TEPZZ Z6 Z79A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01L 19/14 ( ) G01L 19/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ Z6 Z79A_T (11) EP 3 062 079 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.08.2016 Bulletin 2016/3 (1) Int Cl.: G01L 19/14 (2006.01) G01L 19/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ Z6 Z79A_T (11) EP 3 062 079 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.08.2016 Bulletin 2016/3 (1) Int Cl.: G01L 19/14 (2006.01) G01L 19/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
TEPZZ ZZ _A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: F28F 3/10 ( ) F28F 3/08 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ ZZ _A_T (11) EP 3 001 131 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.03.16 Bulletin 16/13 (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/ (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1418664.2
(19) TEPZZ ZZ _A_T (11) EP 3 001 131 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.03.16 Bulletin 16/13 (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/ (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1418664.2
(51) Int Cl.: H02K 51/00 ( ) H02K 49/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z8_59B_T (11) EP 2 308 159 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.09.2017 Bulletin 2017/39 (21) Application number: 09776927.7
(19) TEPZZ Z8_59B_T (11) EP 2 308 159 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.09.2017 Bulletin 2017/39 (21) Application number: 09776927.7
(51) Int Cl.: B04B 11/02 ( ) B04B 13/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 6 7797B_T (11) EP 2 637 797 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.04.2016 Bulletin 2016/14 (21) Application number: 11784932.3
(19) TEPZZ 6 7797B_T (11) EP 2 637 797 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.04.2016 Bulletin 2016/14 (21) Application number: 11784932.3
(51) Int Cl.: F23D 1/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z_ZZB_T (11) EP 2 01 00 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.06.2017 Bulletin 2017/24 (1) Int Cl.: F23D 1/02 (2006.01) (21)
(19) TEPZZ Z_ZZB_T (11) EP 2 01 00 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.06.2017 Bulletin 2017/24 (1) Int Cl.: F23D 1/02 (2006.01) (21)
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2003/49
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001366948A1* (11) EP 1 366 948 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.12.2003 Bulletin 2003/49
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001366948A1* (11) EP 1 366 948 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.12.2003 Bulletin 2003/49
(51) Int Cl.: B60R 19/00 ( ) E01F 15/14 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 725 435 B1 (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 18.07.2007 Bulletin 2007/29 (21) Application number: 05711175.9 (22) Date of
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 725 435 B1 (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 18.07.2007 Bulletin 2007/29 (21) Application number: 05711175.9 (22) Date of
(51) Int Cl.: F16K 17/04 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 786Z B_T (11) EP 2 786 02 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 24.02.16 Bulletin 16/08 (21) Application number: 12799019.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 786Z B_T (11) EP 2 786 02 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 24.02.16 Bulletin 16/08 (21) Application number: 12799019.0 (22)
TEPZZ 9 Z79A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 9 Z79A_T (11) EP 2 922 079 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.09.2015 Bulletin 2015/39 (21) Application number: 151573.2 (51) Int Cl.: H01H 31/12 (2006.01) H01H
(19) TEPZZ 9 Z79A_T (11) EP 2 922 079 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.09.2015 Bulletin 2015/39 (21) Application number: 151573.2 (51) Int Cl.: H01H 31/12 (2006.01) H01H
(51) Int Cl.: E05F 3/22 ( ) E05F 3/10 ( ) E05F 3/20 ( ) E05D 7/04 ( ) E05D 5/02 ( ) E05D 7/081 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 68 55 B_T (11) EP 2 682 553 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 22.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/12 (21) Application number: 12180603.8
(19) TEPZZ 68 55 B_T (11) EP 2 682 553 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 22.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/12 (21) Application number: 12180603.8
(51) Int Cl.: B60K 11/08 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 8 7_7B_T (11) EP 2 837 17 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.01.2016 Bulletin 2016/01 (1) Int Cl.: B60K 11/08 (2006.01)
(19) TEPZZ 8 7_7B_T (11) EP 2 837 17 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.01.2016 Bulletin 2016/01 (1) Int Cl.: B60K 11/08 (2006.01)
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2007/47
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 88 077 A2 (43) Date of publication: 21.11.2007 Bulletin 2007/47 (1) Int Cl.: H01L 23/367 (2006.01) H01L 2/06 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 070731.2
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 88 077 A2 (43) Date of publication: 21.11.2007 Bulletin 2007/47 (1) Int Cl.: H01L 23/367 (2006.01) H01L 2/06 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 070731.2
TEPZZ Z874Z7B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ Z874Z7B_T (11) EP 2 087 407 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 17.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/29 (21) Application number: 07860559.9
(19) TEPZZ Z874Z7B_T (11) EP 2 087 407 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 17.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/29 (21) Application number: 07860559.9
(51) Int Cl.: B62K 19/30 ( ) B62K 11/00 ( ) B62M 6/90 ( ) B62K 19/40 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _ 49 B_T (11) EP 2 134 92 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.02.2013 Bulletin 2013/09 (21) Application number: 08717.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ _ 49 B_T (11) EP 2 134 92 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.02.2013 Bulletin 2013/09 (21) Application number: 08717.0 (22)
TEPZZ Z85967A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ Z8967A_T (11) EP 3 08 967 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26..16 Bulletin 16/43 (21) Application number: 14871329.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ Z8967A_T (11) EP 3 08 967 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26..16 Bulletin 16/43 (21) Application number: 14871329.0 (22)
TEPZZ ZZ7987B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.: F04B 43/073 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ ZZ7987B_T (11) EP 2 007 987 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28.11.12 Bulletin 12/48 (21) Application number: 07760277.9
(19) TEPZZ ZZ7987B_T (11) EP 2 007 987 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28.11.12 Bulletin 12/48 (21) Application number: 07760277.9
TEPZZ 55 B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ B_T (11) EP 2 3 332 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.03.16 Bulletin 16/12 (21) Application number: 117609.2 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ B_T (11) EP 2 3 332 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.03.16 Bulletin 16/12 (21) Application number: 117609.2 (22) Date
(51) Int Cl.: F02M 25/07 ( ) F01N 3/04 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 1 03 070 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.06.07 Bulletin 07/2 (1) Int Cl.: F02M 2/07 (06.01) F01N 3/04 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) (11) EP 1 03 070 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.06.07 Bulletin 07/2 (1) Int Cl.: F02M 2/07 (06.01) F01N 3/04 (06.01) (21) Application
(51) Int Cl.: B62D 35/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 6 6 8_B_T (11) EP 2 626 281 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 08.06.16 Bulletin 16/23 (1) Int Cl.: B62D 3/00 (06.01) (21)
(19) TEPZZ 6 6 8_B_T (11) EP 2 626 281 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 08.06.16 Bulletin 16/23 (1) Int Cl.: B62D 3/00 (06.01) (21)
TEPZZ 8998 ZB_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8998 ZB_T (11) EP 2 899 8 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.08.17 Bulletin 17/3 (21) Application number: 11018.7 (1) Int Cl.:
(19) TEPZZ 8998 ZB_T (11) EP 2 899 8 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.08.17 Bulletin 17/3 (21) Application number: 11018.7 (1) Int Cl.:
(51) Int Cl.: A61M 5/24 ( ) A61M 5/32 ( ) A61M 5/20 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 6548 8B_T (11) EP 2 654 838 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.08.2017 Bulletin 2017/34 (21) Application number: 11802724.2
(19) TEPZZ 6548 8B_T (11) EP 2 654 838 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.08.2017 Bulletin 2017/34 (21) Application number: 11802724.2
(51) Int Cl.: H02K 1/14 ( ) H02K 1/24 ( ) H02K 15/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 994977B_T (11) EP 2 994 977 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.12.16 Bulletin 16/0 (21) Application number: 14721769.9 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 994977B_T (11) EP 2 994 977 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.12.16 Bulletin 16/0 (21) Application number: 14721769.9 (22)
TEPZZ Z 44Z8A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B64D 33/02 ( ) B64D 41/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ Z 44Z8A_T (11) EP 3 034 8 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 22.06.16 Bulletin 16/2 (1) Int Cl.: B64D 33/02 (06.01) B64D 41/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1199431.6
(19) TEPZZ Z 44Z8A_T (11) EP 3 034 8 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 22.06.16 Bulletin 16/2 (1) Int Cl.: B64D 33/02 (06.01) B64D 41/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1199431.6
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2009/31
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 083 6 A2 (43) Date of publication: 29.07.09 Bulletin 09/31 (1) Int Cl.: H0K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 08172.9 (22) Date of filing: 0.02.08 (84)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 083 6 A2 (43) Date of publication: 29.07.09 Bulletin 09/31 (1) Int Cl.: H0K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 08172.9 (22) Date of filing: 0.02.08 (84)
TEPZZ_99 5 ZB_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ_99 ZB_T (11) EP 1 992 20 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 31.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/31 (1) Int Cl.: B60N 2/60 (2006.01) B60N
(19) TEPZZ_99 ZB_T (11) EP 1 992 20 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 31.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/31 (1) Int Cl.: B60N 2/60 (2006.01) B60N
(51) Int Cl.: B62K 19/32 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 1 16 807 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 13.06.07 Bulletin 07/24 (1) Int Cl.: B62K 19/32 (06.01) (21) Application number:
(19) (11) EP 1 16 807 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 13.06.07 Bulletin 07/24 (1) Int Cl.: B62K 19/32 (06.01) (21) Application number:
(51) Int Cl.: H01J 61/34 ( ) F21V 17/04 ( ) H01J 61/70 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 683 184 B1 (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.12.2007 Bulletin 2007/0 (21) Application number: 0477493.2 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 683 184 B1 (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.12.2007 Bulletin 2007/0 (21) Application number: 0477493.2 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: A61F 5/01 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 86 47A_T (11) EP 2 862 47 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 22.04.201 Bulletin 201/17 (1) Int Cl.: A61F /01 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 14167197.4 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 86 47A_T (11) EP 2 862 47 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 22.04.201 Bulletin 201/17 (1) Int Cl.: A61F /01 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 14167197.4 (22) Date
TEPZZ 68 A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2014/02
 (19) TEPZZ 68 A T (11) EP 2 682 333 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.01.2014 Bulletin 2014/02 (21) Application number: 13174817.0 (51) Int Cl.: B62K 25/08 (2006.01) F16F
(19) TEPZZ 68 A T (11) EP 2 682 333 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.01.2014 Bulletin 2014/02 (21) Application number: 13174817.0 (51) Int Cl.: B62K 25/08 (2006.01) F16F
TEPZZ_9459 8B T EP B2 (19) (11) EP B2. (12) NEW EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION After opposition procedure
 (19) TEPZZ_949 8B T (11) EP 1 94 928 B2 (12) NEW EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION After opposition procedure (4) Date of publication and mention of the opposition decision: 2.11.1 Bulletin 1/48 (4) Mention
(19) TEPZZ_949 8B T (11) EP 1 94 928 B2 (12) NEW EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION After opposition procedure (4) Date of publication and mention of the opposition decision: 2.11.1 Bulletin 1/48 (4) Mention
TEPZZ 9_8945A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: F24J 3/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9_894A_T (11) EP 2 918 94 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.09.1 Bulletin 1/38 (1) Int Cl.: F24J 3/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1416093.1 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ 9_894A_T (11) EP 2 918 94 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.09.1 Bulletin 1/38 (1) Int Cl.: F24J 3/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1416093.1 (22) Date of filing:
(51) Int Cl.: A01D 34/74 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 877_ZB_T (11) EP 2 87 7 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 19..2016 Bulletin 2016/42 (1) Int Cl.: A01D 34/74 (2006.01) (21)
(19) TEPZZ 877_ZB_T (11) EP 2 87 7 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 19..2016 Bulletin 2016/42 (1) Int Cl.: A01D 34/74 (2006.01) (21)
(51) Int Cl.: F16L 33/04 ( ) F16L 21/00 ( ) F16L 21/06 ( ) F16L 55/172 ( ) F01N 13/18 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_7_4Z6B_T (11) EP 1 714 06 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 17.12.14 Bulletin 14/1 (21) Application number: 0713378.7 (22)
(19) TEPZZ_7_4Z6B_T (11) EP 1 714 06 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 17.12.14 Bulletin 14/1 (21) Application number: 0713378.7 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: B62K 21/00 ( ) B62K 25/16 ( ) B62K 25/28 ( ) B62J 15/00 ( ) B62K 21/20 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 1 910 159 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.01.2010 Bulletin 2010/04 (21) Application number: 05764546.7 (22) Date of
(19) (11) EP 1 910 159 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.01.2010 Bulletin 2010/04 (21) Application number: 05764546.7 (22) Date of
(51) Int Cl.: E21B 25/00 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 1 212 12 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 16.01.08 Bulletin 08/03 (21) Application number: 0097211.6 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (11) EP 1 212 12 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 16.01.08 Bulletin 08/03 (21) Application number: 0097211.6 (22) Date of filing:
Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) J (12) Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 810 112 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) nt. CI.6: B60H 1/34 03.12.1997
(19) J (12) Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 810 112 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) nt. CI.6: B60H 1/34 03.12.1997
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1
 USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
US 7, B2. Loughrin et al. Jan. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: and/or the driven component. (12) United States Patent (54) (75)
 USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
(54) LITHIUM SECONDARY BATTERY PACK HAVING ENBLOC CLIP FORM COMBINED TO COINCIDE WITH TWO OR FOUR BATTERY COMPARTMENTS OF ELECTRONIC DEVICE
 (19) TEPZZ Z79_8ZA_T (11) EP 3 079 180 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 12..16 Bulletin 16/41 (21) Application number: 14867926.9
(19) TEPZZ Z79_8ZA_T (11) EP 3 079 180 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 12..16 Bulletin 16/41 (21) Application number: 14867926.9
(51) Int Cl. 7 : F16H 48/08
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001287274B1* (11) EP 1 287 274 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001287274B1* (11) EP 1 287 274 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD20: Last updated: 26th September 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD20: Last updated: 26th September 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
3 23S Sé. -Né 33% (12) United States Patent US 6,742,409 B2. Jun. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: 6B M 2 O. (51) Int. Cl...
 (12) United States Patent Blanchard USOO6742409B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 2004 (54) DEVICE FORTRANSMISSION BETWEEN A PRIMARY MOTOR SHAFT AND AN OUTPUT SHAFT AND LAWN MOWER PROVIDED
(12) United States Patent Blanchard USOO6742409B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 2004 (54) DEVICE FORTRANSMISSION BETWEEN A PRIMARY MOTOR SHAFT AND AN OUTPUT SHAFT AND LAWN MOWER PROVIDED
(51) Int Cl.: C10L 1/02 ( ) F02B 77/04 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _8_66 A_T (11) EP 3 181 663 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.06.17 Bulletin 17/2 (1) Int Cl.: CL 1/02 (06.01) F02B 77/04 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1382628.4
(19) TEPZZ _8_66 A_T (11) EP 3 181 663 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.06.17 Bulletin 17/2 (1) Int Cl.: CL 1/02 (06.01) F02B 77/04 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1382628.4
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1. Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002
 USOO6435993B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1 Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) HYDRAULIC CHAIN TENSIONER WITH 5,707.309 A 1/1998 Simpson... 474/110 VENT DEVICE AND
USOO6435993B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1 Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) HYDRAULIC CHAIN TENSIONER WITH 5,707.309 A 1/1998 Simpson... 474/110 VENT DEVICE AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020052578A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0052578A1 Moller (43) Pub. Date: May 2, 2002 (54) INJECTION DEVICE (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20020052578A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0052578A1 Moller (43) Pub. Date: May 2, 2002 (54) INJECTION DEVICE (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
TEPZZ Z4Z 75A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ Z4Z 7A_T (11) EP 3 0 27 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.07.16 Bulletin 16/27 (21) Application number: 1161787. (1) Int Cl.: B64D 13/06 (06.01) B64D 37/32 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ Z4Z 7A_T (11) EP 3 0 27 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.07.16 Bulletin 16/27 (21) Application number: 1161787. (1) Int Cl.: B64D 13/06 (06.01) B64D 37/32 (06.01)
IIIHIIII 5,509,863. United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. Apr. 23, Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent:
 United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. 54) TRANSMISSION DEVICE, ESPECIALLY FOR BOAT MOTORS 75 Inventors: Staffan Månsson, Hjalteby; Benny Hedlund, Hönö, both of Sweden 73 Assignee: AB Volvo Penta, Gothenburg,
United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. 54) TRANSMISSION DEVICE, ESPECIALLY FOR BOAT MOTORS 75 Inventors: Staffan Månsson, Hjalteby; Benny Hedlund, Hönö, both of Sweden 73 Assignee: AB Volvo Penta, Gothenburg,
(51) Int Cl.: F03D 3/06 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z47_4 B_T (11) EP 3 047 142 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21.06.2017 Bulletin 2017/25 (21) Application number: 14786540.6
(19) TEPZZ Z47_4 B_T (11) EP 3 047 142 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21.06.2017 Bulletin 2017/25 (21) Application number: 14786540.6
Y-Né Š I/? S - - (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States 2S) (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 20, 2003 (54) (75)
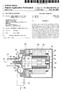 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0035740 A1 Knoll et al. US 2003.0035740A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 20, 2003 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) WET TYPE ROTOR PUMP Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0035740 A1 Knoll et al. US 2003.0035740A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 20, 2003 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) WET TYPE ROTOR PUMP Inventors:
(86) International application number: PCT/GB97/ (56) References cited:
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP000951611B1* (11) EP 0 951 611 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP000951611B1* (11) EP 0 951 611 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant
~ mi mi ii mi ii imiii i ii ii i ii European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) J (12) ~ mi mi ii mi ii imiii i ii ii i ii European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 770 762 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) Int. CI.6: F01 L 1/14,
(19) J (12) ~ mi mi ii mi ii imiii i ii ii i ii European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 770 762 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) Int. CI.6: F01 L 1/14,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080056631A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0056631 A1 Beausoleil et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2008 (54) TUNGSTEN CARBIDE ENHANCED Publication Classification
US 20080056631A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0056631 A1 Beausoleil et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2008 (54) TUNGSTEN CARBIDE ENHANCED Publication Classification
(51) Int Cl.: G01B 5/255 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_787Z84B_T (11) EP 1 787 084 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.04.2013 Bulletin 2013/1 (21) Application number: 0787008.1 (22)
(19) TEPZZ_787Z84B_T (11) EP 1 787 084 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.04.2013 Bulletin 2013/1 (21) Application number: 0787008.1 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: F01N 1/02 ( ) F01N 13/02 ( ) F01N 1/00 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 1 789 660 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.05.2010 Bulletin 2010/19 (21) Application number: 05815839.5 (22) Date of
(19) (11) EP 1 789 660 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.05.2010 Bulletin 2010/19 (21) Application number: 05815839.5 (22) Date of
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Swihla et al. USOO6287091B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,287,091 B1 Sep. 11, 2001 (54) TURBOCHARGER WITH NOZZLE RING COUPLNG (75) Inventors: Gary R Svihla, Clarendon
(12) United States Patent Swihla et al. USOO6287091B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,287,091 B1 Sep. 11, 2001 (54) TURBOCHARGER WITH NOZZLE RING COUPLNG (75) Inventors: Gary R Svihla, Clarendon
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0312869A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0312869 A1 WALTER (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016 (54) CVT DRIVE TRAIN Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2016.0312869A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0312869 A1 WALTER (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016 (54) CVT DRIVE TRAIN Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(SE) Box 236, S Hagfors (SE)
 Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Publication number: 0 1 6 8 6 1 8 Office europeen des brevets r^e- A? EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 85106975.7 int. a.*-. B 60 P 3/12, B
Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Publication number: 0 1 6 8 6 1 8 Office europeen des brevets r^e- A? EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 85106975.7 int. a.*-. B 60 P 3/12, B
Europaisches Patentamt (1 9) Qjl) European Patent Office. Office eurodeen des brevets (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 Europaisches Patentamt (1 9) Qjl) European Patent Office Office eurodeen des brevets (11) EP 0 702 165 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) int. CI.6: F16F7/09, D06F 37/20
Europaisches Patentamt (1 9) Qjl) European Patent Office Office eurodeen des brevets (11) EP 0 702 165 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) int. CI.6: F16F7/09, D06F 37/20
