0 INTRODUCTION TO FLUID FILM BEARINGS AND SEALS
|
|
|
- Patricia Murphy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Notes 0 INTRODUCTION TO FLUID FILM BEARINGS AND SEALS A turbomachinery is a rotating structure where the load and/or the driver handle a process fluid from which power is extracted or delivered to. Examples of turbomachines include pumps and compressors, gas and steam turbines, turbo generators and turbo expanders, turbochargers, APU (auxiliary power units), etc. Most turbomachinery is supported on oil lubricated fluid film bearings, although modern advances and environmental restrictions are pushing towards the implementation of process fluid bearings and even gas bearing applications. Fluid film bearings are used due to their adequate load support, good damping characteristics and absence of wear if properly designed and operated. Turbomachines also include a number of other mechanical elements which provide stiffness and damping characteristics and affect the dynamics of the rotor-bearing system. Impeller seals, floating ring seals, thrust collars and balance pistons are a few of these elements. The adequate operation of a turbomachine is defined by its ability to tolerate normal (and even abnormal) vibrations levels without affecting significantly its overall performance (reliability and efficiency). The rotordynamics of turbomachinery encompasses the structural analysis of rotors (shafts and disks) and the design of fluid film bearings and seals that determine the best dynamic performance given the required operating conditions. This best performance is denoted by well-characterized natural frequencies (and critical speeds) with amplitudes of synchronous dynamic response within required standards and demonstrated absence of subsynchronous vibration instabilities. A rotordynamic analysis considers the interaction between the elastic and inertia properties of the rotor and the mechanical impedances from the fluid film bearing supports, oil seal rings, seals, etc. The most commonly recurring problems in rotordynamics are 1. Excessive steady state synchronous vibration levels. 2. Subharmonic rotor instabilities. Steady state vibration levels may be reduced by: a) Improving balancing. b) Modifying rotor-bearing systems: tune system critical speeds out of RPM operating range. c) Introducing damping to limit peak amplitudes at critical speeds that must be traversed. Subharmonic rotor instabilities may be avoided by: a) Raising the natural frequency of rotor system as much as possible. b) Eliminating the instability mechanism, i.e. change bearing design if oil whip is present. c) Introducing damping to raise onset speed above the operating speed range. Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
2 Rotordynamic instabilities have become more and more common as the speed and horsepower of turbomachinery have increased. These instabilities can sometimes be erratic, seemingly increasing vibration amplitudes for no apparent reason. A common denominator among many stability problems is that they tend to grow with time as the affected component(s) begins to wear or fatigue. For example, two typical destabilizing forces well documented in the technical literature are due to the aerodynamic effects of labyrinth seals and the hydrodynamic effects of cylindrical bearings and floating oil ring seals in centrifugal compressors. Load, gas molecular weight, and oil pressure and temperature appear to be among the factors bringing severe problems in problematic turbomachinery. The detailed study of rotordynamics demands accurate knowledge of the specific mechanical elements that support the rotor, i.e. fluid film bearings and seals. Fluid film bearings Fluid film bearings are machine elements designed to produce smooth (low friction) motion between solid surfaces in relative motion and to generate a load support for mechanical components. The lubricant or fluid between the surfaces may be a liquid, a gas or even a solid. Fluid film bearings, when well designed and operated, are able to support static and dynamic loads, and consequently, their effects on the performance of rotating machinery are of great importance. Our study will concentrate on the analysis of bearings with a full film separating the mechanical surfaces. The word film implies that the fluid thickness (gap or clearance) separating the surfaces is several orders of magnitude smaller than the other dimensions of the bearing, i.e. width and length. The basic operational principles of fluid film bearings are hydrodynamic, hydrostatic or hybrid (a combination of the former two). Hydrodynamic fluid film bearings or self-acting bearings In these bearings, see Figure 1, there is relative motion between two mechanical surfaces with a particular wedge shape. The fluid is dragged into the film and hydrodynamic pressures are generated and able to support an externally applied load. Hydrostatic fluid film bearings or externally-presurized bearings In these bearings, see Figure 2, an external source of pressurized fluid forces the lubricant or fluid between the surfaces, thus providing their separation and the ability to support a load without surface contact. Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
3 Hydrodynamic or self-acting fluid film bearings Advantages Do not require external source of pressure. Fluid flow is dragged into the convergent gap in the direction of the surface relative motion. Support heavy loads. The load support is a function of the lubricant viscosity, surface speed, surface area, film thickness and geometry of the bearing. Long life (infinite in theory) without wear of surfaces. Provide stiffness and damping coefficients of large magnitude. Disadvantages Thermal effects affect performance if film thickness is too small or available flow rate is too low. Require of surface relative motion to generate load support. Induce large drag torque (power losses) and potential surface damage at start-up (before lift-off) and touch down. Potential to induce hydrodynamic instability, i.e. loss of effective damping for operation well above critical speed of rotorbearing system. Pressure journal rotation Relative motion fluid Slider bearing Hydrodynamic wedge pressure Plain journal bearing Figure 1. Examples of hydrodynamic (self-acting) fluid film bearings Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
4 Hydrostatic or externally pressurized fluid film bearings Advantages Support very large loads. The load support is a function of the pressure drop across the bearing and the area of fluid pressure action. Load does not depend on film thickness nor lubricant viscosity. Long life (infinite in theory) without wear of surfaces Provide stiffness and damping coefficients of very large magnitude. Excellent for exact positioning and control. Disadvantages Require ancillary equipment. Larger installation and maintenance costs. Need of fluid filtration equipment. Loss of performance with fluid contamination. High power consumption because of pumping losses. Potential to induce hydrodynamic instability in hybrid mode operation. Potential to show pneumatic hammer instability for highly compressible fluids, i.e. loss of damping at low and high frequencies of operation due to compliance and time lag of trapped fluid volumes. recess Pressure Ps Pr fluid restrictor Fluid at Ps journal recess film Flow supply at Ps orifice Figure 2. Examples of hydrostatic (externally pressurized) fluid film bearings Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
5 PLAIN JOURNAL BEARING PARTIAL ARC JOURNAL BEARING FLOATING RING JOURNAL BEARING Tilting pad bearings Figure 3. Typical configurations of cylindrical journal bearings Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
6 Squeeze film dampers Oscillatory or periodic motions can also generate hydrodynamic pressures in the thin film separating two surfaces. This squeeze film action mechanism works effectively only for compressive loads, i.e. those forcing the approach of one surface to the other. Squeeze film dampers are routinely implemented to reduce vibration amplitudes and isolate structural components in gas jet engines, high performance compressors, and occasionally in water pumps. A squeeze film damper consists of an inner non rotating journal and a stationary outer bearing, both of nearly identical diameters. Figure 4 shows an idealized schematic of this type of fluid film bearing. A journal is mounted on the external race of a rolling element bearing and prevented from spinning with loose pins or a squirrel cage that provides a centering elastic mechanism. The annular thin film, typically less than mm, between the journal and housing is filled with a lubricant provided as a splash from the rolling bearing elements lubrication system or by a dedicated pressurized delivery. In operation, as the journal moves due to dynamic forces acting on the system, the fluid is displaced to accommodate these motions. As a result, hydrodynamic squeeze film pressures exert reaction forces on the journal and provide for a mechanism to attenuate transmitted forces and to reduce the rotor amplitude of motion. journal anti-rotation pin shaft ω ball bearing lubricant film housing Figure 4. Typical squeeze film damper configuration Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
7 Radial seals (annular, labyrinth or honeycomb) separate regions of high pressure and low pressure in rotating machinery and their function is to minimize the leakage and improve the overall efficiency of a rotating machine extracting or delivering power to a fluid. Typical applications include neck ring seals on impeller eyes and interstage seals as well as balance pistons in pump and compressor applications. See Figure 5 for a depiction of these mechanical elements in a typical pump. Seals have larger clearances than load carrying fluid film bearings. Yet their impact on the rotordynamics of turbomachinery is of importance since seals are located at rotor locations where large vibrations (rotor elastic deflections) occur, as shown in Figure 6. Interstage Seal Impeller Eye Seal Balance Piston Seal Flow of process fluid Stator High Pressur Rotor Low Pressur e LABYRINTH SEAL on ROTOR OD Figure 5. Seals in a Multistage Centrifugal Pump or Compressor Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
8 Figure 6. Straight-through and back-to-back bompressor configurations and their fundamental elastic mode shapes Extensive testing has shown that seals with macroscopic roughness; i.e. textured stator surfaces, offer major improvements in reducing leakage as well as cross-coupled stiffness coefficients. Figure 7 depicts two textured seals and a conventional labyrinth seal (teeth on stator). A textured surface like a round-hole pattern or a honeycomb increases the friction thus reducing leakage, and aids to retard the development of the circumferential flow velocity -the physical condition generating the cross-coupled stiffness coefficients. Since the late 1990s, compressor and pump manufacturers, as well as end users, implement or use textured seals with noticeable improvements in pump or compressor efficiency and ensured rotordynamic stability. Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
9 Hole-Pattern Seal Unwrap Honeycomb Seal Unwrap Labyrinth Seal Round hole-pattern seal Figure 7. Hole-pattern, honeycomb and labyrinth seal configurations Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
10 Example of a rotordynamic analysis Figure 8. Cut-away view of a centrifugal compressor The following brief description shows the major elements of a rotordynamic analysis performed on a seven-stage compressor handling a light hydrocarbon mixture. The objectives of a rotordynamic analysis are: a) To model the rotor (shaft and disks) and to determine its freefree natural frequencies. b) To model the fluid film bearing and seal elements and to calculate the mechanical impedances (stiffness, damping and inertia force coefficients) connecting the rotor to its casing. c) To perform an eigenvalue analysis, i.e. to predict the natural frequencies and damping ratios for the different modes (rigid and elastic) of vibration of the rotor as the rotor speed increases to magnitudes well above the design operating conditions. Positive damping ratios evidence the absence of rotordynamic instability. d) To perform a synchronous response analysis to calibrated imbalances in order to predict the maximum amplitudes of vibration, the safe passage through critical speeds and to estimate the loads transmitted through the bearing supports. The results of studies (c) and (d) must satisfy stringent conditions as requested by API norms (API 610, for example). Note that the typical rotordynamic analysis is linear, i.e. it relies on the representation of the bearings and seals as linear mechanical elements. That is, the second order differential equations describing the motion about an equilibrium position are linear. Of course a nonlinear analysis could also be performed but its efficiency and (improved) accuracy are, to this date, questionable. Furthermore, a linear analysis is mandatory to determine the operability of the turbomachine. It is important to stress that the tasks (objective) described above need of extensive experimental and field support verification. Analysis without adequate measurements is usually not very useful in rotordynamics. The example intends to show the complexity of a typical analysis. Figure 9 depicts the structural model with the rotor partitioned into 36 stations (each with inertia and inertia properties). The circles denote added inertias such as those from the impellers and thrust Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
11 collars. The spring-like connections to ground denote the bearing and seal elements supporting the rotor. Tables 1 to 3 show the physical properties of the rotor, the compressor operating conditions (current and desired), and a brief description of the bearings and seals in place. Shaft Radius, inches Rotor dynamic analysis Compressor C-2100, supported on original bearings, laby seals and locked oil seals Bearing Floating Impeller seals Balance Floating Bearing Ring piston ring Free end Axial Location, inches 80 Figure 9. Structural rotordynamic model of a multiple-stage centrifugal compressor Table 1. Geometry of rotor for compressor Compresor C-2100 Physical units Number of impellers 7 Shaft length 85.6 (2.17 m) Rotor weight incluydes thrust collar 1,024 lb (4,550 N) Center of mass from coupling side station 34 Mass moment of inertia (transversal0 302,815 lbm-in 2 Mass moment of inertia (polar) 16,749 lbm-in 2 Static load on bearing (coupling side) 469 lb (2,085 N) Static load on bearing (free end) 554 lb (2,465 N) Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
12 Table 2. Operating conditions (actual and desired) for compresor Hydrocarbon mixture (molecular weight 8.72) 5,700 RPM 9,850 RPM Stage Pressure Temperature (K) Pressure Temperature (K) (bar) (bar) Table 3 shows the location of the mechanical impedances to ground. The rotor is supported on two multiple lobe cylindrical bearings operating with ISO VG 32 oil. Furthermore, pressurized floating oil seal rings isolate the process gas from the environment. There are also seven eye impeller seals and six interstage seals of the labyrinth type. At the free end of the compressor there is a long balance piston. Note to reader: f you have a genuine interest in the example, ask the lecturer for a more detailed description of the bearings and seals, i.e. dimensions and operating conditions. Table 3. Bearing and seal locations in compressor Station Mechanical element Description 8 Hydrodynamic bearing Three lobe bearing (coupling end) 56 Hydrodynamic bearing Three lobe bearing (free end) 15 Floating ring seal Pressurized, lubricant 50 Floating ring seal Pressurized, lubricant 46 Balance piston Process Gas, 27 teeth 20, 24, 28 Impeller seals neck ring (eye) Labyrinth type, process gas 32, 36, 40 and interstage 4 teeth 44 Eye Impulsor # 7 seal Labyrinth type, process gas The structural analysis predicts the free-free mode natural frequencies of the rotor, as given in Table 4. q free-free mode is an elastic natural mode of the rotor without any connection to ground, i.e., without bearings and seals. The good correlation with the field measurement is encouraging. The field test usually consists of hanging the rotor from long cables; then raping the shaft with a heavy object; and, recording the natural frequency (and mode shape) of motion. Table 4. Free-free mode natural frequency of rotor (no thrust collar) calculated Field measurement Fundamental 14,431 (RPM) 14,400 (RPM) frequency (240 Hz) 2nd frequency 27,081 Not recorded 3rd frequency 40,927 The rotordynamic analysis predicts the eigenvalues (damped natural frequency map, see Figure 10, and damping ratios, see Figure 11) of the rotor operating on its bearings Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
13 and seals for speeds to 20,000 rpm, twice the design value. The predictions show a lightly damped critical speed at 4,000 rpm. Most importantly, the analysis reveals a rotordynamic instability at 8,163 rpm. This speed is known as the threshold speed of instability. The instability is due to the loss of effective damping (needed to dissipate mechanical energy of vibrations) and excitation of the system (lowest) natural frequency with dangerously high amplitude vibrations. The field measurements evidence of the subsynchronous vibration at a lower speed, i.e rpm! Table 5. Threshold speed of instability: predicted and measured Threshold Whirl Whirl Mode speed frequency ratio Predicted 8,163 rpm 4,000 rpm 0.49 Elastic Field data 7,850 rpm 3,532 rpm 0.44 Natural Frequency, cpm Critical speed Rotor Speed, rpm Figure 10. Natural frequency versus rotor speed for multiple-stage compressor Damping Ratio Natural Frequency, cpm Figure 11. Damping ratio versus natural frequency for multiple-stage compressor Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
14 Figure 12 shows the amplitude of synchronous rotor motion versus rotor speed for a specified mass imbalance distribution. The predictions are shown for the rotor at one of the bearing locations. Figure 13 depicts the mode shape of vibration at a rotor speed of 8,750 rpm. Note that the predicted results are not valid for rotor speeds above the threshold speed of instability since the rotor (would) vibrate with a subsynchronous whirl frequency component of much larger amplitude than the one synchronous with rotor speed. Response, mils p-p Rotordynam ic Response Plot Rotor dynamic analysis Compressor C2100 w ith dry-seal inertias and MODIFIED BEARINGS Sta. No. 8: drive end bearing Rotor Spe e d, r pm Major Amp Horz Amp Vert Amp Figure 12. Predicted rotor imbalance response at drive end bearing Rotor dynamic analysis Compressor C2100 w ith dry-seal inertias and MODIFIED BEARINGS forward backward f=4041. cpm d= zeta N=8750 rpm Figure 13. Deflected rotor mode shape at 8,750 rpm The mode shape shows that at the bearing locations the rotor motion is quite small, while the vibration amplitude at the seal locations (rotor midspan) is much larger. Hence, the instability is certainly associated with a poor design of the support multiple-lobe bearings and the unfortunate lockup of the oil seal rings. Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
15 Finally, Figure 14 presents the field recorded vibration spectra. The rotor speed is 7,860 rpm and the dangerously high amplitude subsynchronous vibration develops at 3,532 rpm. The rotordynamic predictions are overly conservative! B - C-103 FCC GAS COMP C-103-8V COMP OUTBOARD BRG - VERT Route Spectrum 01-DEC-97 15:40 * P-P Displacement in Mils OVRALL= 3.69 D-DG P-P = 3.67 LOAD = RPM = RPS = Frequency in CPM Freq: Ordr: Spec: Figure 14. Field vibration spectrum showing rotordynamic instability for compressor example. The example evidences the importance of fluid film bearings and seals on the dynamics of rotating machinery. Note that the example referred brought an unexpected stop in the operation of the unit with an enormous cost to the owner, several hundred thousand of dollars per day over an undisclosed amount of time. Fortunately, current monitoring techniques enabled the engineers to prevent a catastrophic failure with a potentially enormous financial impact and even human lives cost. Closure The following lectures provide the fundamentals of fluid film lubrication and rotordynamics that will enable the interested reader to begin analyzing fluid film bearings and seals for applications in turbomachinery. The study initiates with a detailed analysis of the fundamentals of lubrication theory and its applications to oil-lubricated bearings and ring seals. Next, seals and squeeze film dampers are thoroughly covered. The importance of fluid inertia and flow turbulence on modern and envisioned bearing and seal applications is also covered. Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
16 Performance Objectives for the Modern Lubrication Course 1. To learn about the physical concepts and mathematical models for the analysis and design of fluid film bearings and seals. 2. To acquire knowledge based on the detailed review of the literature on fluid film lubrication and rotordynamics. 3. To identify the mechanical effects of importance on the static and dynamic forced performance of fluid film bearings. 4. To learn about the effects of fluid film bearings on the rotordynamics of turbomachinery. 5. To identify the future trends in applications of bearing and seal technologies and the needs for further research. 6. To provide the basics of efficient computational skills for the prediction of the static and dynamic forced performance of fluid film bearings. Notes 0. Introduction to bearings and seals. Dr. Luis San Andrés
Introduction to rotordynamics and lubricated elements
 August 2016 Introduction to rotordynamics and lubricated elements Dr. Luis San Andres Mast-Childs Chair Professor Turbomachinery Laboratory Texas A&M University Lsanandres@tamu.edu 1 Turbomachinery A turbomachinery
August 2016 Introduction to rotordynamics and lubricated elements Dr. Luis San Andres Mast-Childs Chair Professor Turbomachinery Laboratory Texas A&M University Lsanandres@tamu.edu 1 Turbomachinery A turbomachinery
Introduction to triblogy, rotordynamics & lubricated elements
 August 2018 Introduction to triblogy, rotordynamics & lubricated elements Dr. Luis San Andres Mast-Childs Chair Professor Turbomachinery Laboratory Texas A&M University Lsanandres@tamu.edu 1 Tribology?
August 2018 Introduction to triblogy, rotordynamics & lubricated elements Dr. Luis San Andres Mast-Childs Chair Professor Turbomachinery Laboratory Texas A&M University Lsanandres@tamu.edu 1 Tribology?
CHAPTER 1. Introduction and Literature Review
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction and Literature Review 1.1 Introduction The Active Magnetic Bearing (AMB) is a device that uses electromagnetic forces to support a rotor without mechanical contact. The AMB offers
CHAPTER 1 Introduction and Literature Review 1.1 Introduction The Active Magnetic Bearing (AMB) is a device that uses electromagnetic forces to support a rotor without mechanical contact. The AMB offers
ROTATING MACHINERY DYNAMICS
 Pepperdam Industrial Park Phone 800-343-0803 7261 Investment Drive Fax 843-552-4790 N. Charleston, SC 29418 www.wheeler-ind.com ROTATING MACHINERY DYNAMICS SOFTWARE MODULE LIST Fluid Film Bearings Featuring
Pepperdam Industrial Park Phone 800-343-0803 7261 Investment Drive Fax 843-552-4790 N. Charleston, SC 29418 www.wheeler-ind.com ROTATING MACHINERY DYNAMICS SOFTWARE MODULE LIST Fluid Film Bearings Featuring
CONTENTS. 5 BALANCING OF MACHINERY Scope Introduction Balancing Machines Balancing Procedures
 CONTENTS 1 OVERVIEW.....................................................................1-1 1.1 Introduction.................................................................1-1 1.2 Organization.................................................................1-1
CONTENTS 1 OVERVIEW.....................................................................1-1 1.1 Introduction.................................................................1-1 1.2 Organization.................................................................1-1
Notes 11. High Pressure Floating Ring Oil Seals
 Notes 11. High Pressure Floating Ring Oil Seals Outer seal P a Outer seal land Oil supply (P S +P) Shaft Inner seal land Anti-rotation pin Seal loading spring Inner seal Process Gas (P S ) Fig. 1 Typical
Notes 11. High Pressure Floating Ring Oil Seals Outer seal P a Outer seal land Oil supply (P S +P) Shaft Inner seal land Anti-rotation pin Seal loading spring Inner seal Process Gas (P S ) Fig. 1 Typical
Failure of a Test Rig Operating with Pressurized Gas Bearings: a Lesson on Humility
 Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2015: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, June 15-19, 2015, Montreal, Canada GT2015-42556 Failure of a Test Rig Operating with Pressurized Gas Bearings: a Lesson
Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2015: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, June 15-19, 2015, Montreal, Canada GT2015-42556 Failure of a Test Rig Operating with Pressurized Gas Bearings: a Lesson
APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE
 Colloquium DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 2012 Prague, February 7 8, 2011 CzechNC APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE Jiří Šimek Abstract: New type of aerodynamic
Colloquium DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 2012 Prague, February 7 8, 2011 CzechNC APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE Jiří Šimek Abstract: New type of aerodynamic
Magnetic Bearings for Supercritical CO2 Turbomachinery
 The 6 th International Supercritical CO 2 Power Cycles Symposium March 27-29, 2018, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Magnetic Bearings for Supercritical CO2 Turbomachinery Richard Shultz Chief Engineer Waukesha
The 6 th International Supercritical CO 2 Power Cycles Symposium March 27-29, 2018, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Magnetic Bearings for Supercritical CO2 Turbomachinery Richard Shultz Chief Engineer Waukesha
XLTRC 2 TURBOMACHINERY RESEARCH CONSORTIUM ROTORDYNAMICS SOFTWARE SUITE
 XLTRC 2 TURBOMACHINERY RESEARCH CONSORTIUM ROTORDYNAMICS SOFTWARE SUITE WHAT IS XLTRC2? XLTRC2 is a suite of very fast, accurate and experimentally verified, and user- friendly codes for executing a complete
XLTRC 2 TURBOMACHINERY RESEARCH CONSORTIUM ROTORDYNAMICS SOFTWARE SUITE WHAT IS XLTRC2? XLTRC2 is a suite of very fast, accurate and experimentally verified, and user- friendly codes for executing a complete
Dynamic Coefficients in Hydrodynamic Bearing Analysis Steven Pasternak C.O. Engineering Sleeve and Sleevoil Bearings 8/10/18 WP0281
 Dynamic Coefficients in Hydrodynamic Bearing Analysis Steven Pasternak C.O. Engineering Sleeve and Sleevoil Bearings 8/10/18 WP0281 Hydrodynamic Bearing Basics Hydrodynamic journal bearings operate by
Dynamic Coefficients in Hydrodynamic Bearing Analysis Steven Pasternak C.O. Engineering Sleeve and Sleevoil Bearings 8/10/18 WP0281 Hydrodynamic Bearing Basics Hydrodynamic journal bearings operate by
PNEUMATIC HIGH SPEED SPINDLE WITH AIR BEARINGS
 PNEUMATIC HIGH SPEED SPINDLE WITH AIR BEARINGS Terenziano RAPARELLI, Federico COLOMBO and Rodrigo VILLAVICENCIO Department of Mechanics, Politecnico di Torino Corso Duca degli Abruzzi 24, Torino, 10129
PNEUMATIC HIGH SPEED SPINDLE WITH AIR BEARINGS Terenziano RAPARELLI, Federico COLOMBO and Rodrigo VILLAVICENCIO Department of Mechanics, Politecnico di Torino Corso Duca degli Abruzzi 24, Torino, 10129
Balancing and over-speed testing of flexible rotors
 Balancing and over-speed testing of flexible rotors Installations for low- and high-speed balancing and for over-speed testing HS 16 - HS 34 Application Balancing of flexible rotors from turbo-machinery
Balancing and over-speed testing of flexible rotors Installations for low- and high-speed balancing and for over-speed testing HS 16 - HS 34 Application Balancing of flexible rotors from turbo-machinery
Gallery of Charts Created by XLRotor
 Gallery of Charts Created by XLRotor What follows are samples of the charts created automatically by XLRotor. The formats for each chart are copied from templates in a file named XLRGRPH.XLS located in
Gallery of Charts Created by XLRotor What follows are samples of the charts created automatically by XLRotor. The formats for each chart are copied from templates in a file named XLRGRPH.XLS located in
CRITICAL SPEED ANALYSIS FOR DUAL ROTOR SYSTEM USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 CRITICAL SPEED ANALYSIS FOR DUAL ROTOR SYSTEM USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Kai Sun, Zhao Wan, Huiying Song, Shaohui Wang AVIC Commercial Aircraft Engine Co. Ltd, 3998 South Lianhua Road, 201108 Shanghai,
CRITICAL SPEED ANALYSIS FOR DUAL ROTOR SYSTEM USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Kai Sun, Zhao Wan, Huiying Song, Shaohui Wang AVIC Commercial Aircraft Engine Co. Ltd, 3998 South Lianhua Road, 201108 Shanghai,
NOVEL CARBON-GRAPHITE GAS BEARINGS FOR TURBOMACHINERY
 May 2018 NOVEL CARBON-GRAPHITE GAS BEARINGS FOR TURBOMACHINERY Luis San Andrés Mast-Childs Chair Professor Porous Type Gas Bearings Porous type gas bushing pads Porous type gas bearings (PTGB) have sub-micron
May 2018 NOVEL CARBON-GRAPHITE GAS BEARINGS FOR TURBOMACHINERY Luis San Andrés Mast-Childs Chair Professor Porous Type Gas Bearings Porous type gas bushing pads Porous type gas bearings (PTGB) have sub-micron
Externally Pressurized Bearings and Machinery Diagnostics
 D23 Externally Pressurized MD.qxd 9/1/22 11:17 AM Page 499 499 Chapter 23 Externally Pressurized Bearings and Machinery Diagnostics IN PREVIOUS SECTIONS OF THIS BOOK, we have discussed machinery diagnostics
D23 Externally Pressurized MD.qxd 9/1/22 11:17 AM Page 499 499 Chapter 23 Externally Pressurized Bearings and Machinery Diagnostics IN PREVIOUS SECTIONS OF THIS BOOK, we have discussed machinery diagnostics
TRANSLATION (OR LINEAR)
 5) Load Bearing Mechanisms Load bearing mechanisms are the structural backbone of any linear / rotary motion system, and are a critical consideration. This section will introduce most of the more common
5) Load Bearing Mechanisms Load bearing mechanisms are the structural backbone of any linear / rotary motion system, and are a critical consideration. This section will introduce most of the more common
Investigations of Oil Free Support Systems to Improve the Reliability of ORC Hermetic High Speed Turbomachinery
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 15, No. 3 (2011) 355 365 c Technical University of Lodz Investigations of Oil Free Support Systems to Improve the Reliability of ORC Hermetic High Speed Turbomachinery
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 15, No. 3 (2011) 355 365 c Technical University of Lodz Investigations of Oil Free Support Systems to Improve the Reliability of ORC Hermetic High Speed Turbomachinery
Structural and Rotordynamic Force Coefficients of a Shimmed Bump Foil Bearing: an Assessment of a Simple Engineering Practice
 Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2015: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, June 15-19, 2015, Montreal, Canada Paper GT2015-43734 Structural and Rotordynamic Force Coefficients of a Shimmed Bump
Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2015: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, June 15-19, 2015, Montreal, Canada Paper GT2015-43734 Structural and Rotordynamic Force Coefficients of a Shimmed Bump
EFFECT OFSHIMMING ON THE ROTORDYNAMIC FORCE COEFFICIENTS OF A BUMP TYPE FOIL BEARING TRC-B&C
 TRC Project 32513/1519F3 EFFECT OFSHIMMING ON THE ROTORDYNAMIC FORCE COEFFICIENTS OF A BUMP TYPE FOIL BEARING TRC-B&C-01-2014 A Shimmed Bump Foil Bearing: Measurements of Drag Torque, Lift Off Speed, and
TRC Project 32513/1519F3 EFFECT OFSHIMMING ON THE ROTORDYNAMIC FORCE COEFFICIENTS OF A BUMP TYPE FOIL BEARING TRC-B&C-01-2014 A Shimmed Bump Foil Bearing: Measurements of Drag Torque, Lift Off Speed, and
White Paper: The Physics of Braking Systems
 White Paper: The Physics of Braking Systems The Conservation of Energy The braking system exists to convert the energy of a vehicle in motion into thermal energy, more commonly referred to as heat. From
White Paper: The Physics of Braking Systems The Conservation of Energy The braking system exists to convert the energy of a vehicle in motion into thermal energy, more commonly referred to as heat. From
Identification of Structural Stiffness and Material Loss Factor in a Shimmed (Generation One) Bump Type Foil Bearing
 Texas A&M University Mechanical Engineering Department Turbomachinery Laboratory Tribology Group Identification of Structural Stiffness and Material Loss Factor in a Shimmed (Generation One) Bump Type
Texas A&M University Mechanical Engineering Department Turbomachinery Laboratory Tribology Group Identification of Structural Stiffness and Material Loss Factor in a Shimmed (Generation One) Bump Type
SOME INTERESTING ESTING FEATURES OF TURBOCHARGER ROTOR DYNAMICS
 Colloquium DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 2013 Prague, February 5 6, 2013 CzechNC 1. I SOME INTERESTING ESTING FEATURES OF TURBOCHARGER ROTOR DYNAMICS Jiří Šimek Abstract: Turbochargers for combustion engines are
Colloquium DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 2013 Prague, February 5 6, 2013 CzechNC 1. I SOME INTERESTING ESTING FEATURES OF TURBOCHARGER ROTOR DYNAMICS Jiří Šimek Abstract: Turbochargers for combustion engines are
Bearings. Rolling-contact Bearings
 Bearings A bearing is a mechanical element that limits relative motion to only the desired motion and at the same time it reduces the frictional resistance to the desired motion. Depending on the design
Bearings A bearing is a mechanical element that limits relative motion to only the desired motion and at the same time it reduces the frictional resistance to the desired motion. Depending on the design
EFFECT OF LUBRICANT SUPPLY PRESSURE ON SFD PERFORMANCE: ENDS SEALED WITH O-RINGS & PISTON RINGS
 May 2017 Year V EFFECT OF LUBRICANT SUPPLY PRESSURE ON SFD PERFORMANCE: ENDS SEALED WITH O-RINGS & PISTON RINGS TRC-SFD-01-17 Bonjin Koo Leping Yu Graduate Research Assistants Luis San Andrés Mast-Childs
May 2017 Year V EFFECT OF LUBRICANT SUPPLY PRESSURE ON SFD PERFORMANCE: ENDS SEALED WITH O-RINGS & PISTON RINGS TRC-SFD-01-17 Bonjin Koo Leping Yu Graduate Research Assistants Luis San Andrés Mast-Childs
HYDROGEN COMPRESSOR SEAL CASE STUDY UTILIZING HALO (NON-CONTACTING, COMPLIANT) INTER-STAGE, IMPELLER EYE, BUFFER AND FAIL- SAFE SEALS
 HYDROGEN COMPRESSOR SEAL CASE STUDY UTILIZING HALO (NON-CONTACTING, COMPLIANT) INTER-STAGE, IMPELLER EYE, BUFFER AND FAIL- SAFE SEALS Author Information John Justak, President/CEO of ATGI Over 28 years
HYDROGEN COMPRESSOR SEAL CASE STUDY UTILIZING HALO (NON-CONTACTING, COMPLIANT) INTER-STAGE, IMPELLER EYE, BUFFER AND FAIL- SAFE SEALS Author Information John Justak, President/CEO of ATGI Over 28 years
Experimental research on dynamic characteristics of gas bearing-rotor with different radial clearances
 Experimental research on dynamic characteristics of gas bearing-rotor with different radial clearances Long Hao 1, Jinfu Yang 2, Dongjiang Han 3, Changliang Tang 4 Institute of Engineering Thermophysics,
Experimental research on dynamic characteristics of gas bearing-rotor with different radial clearances Long Hao 1, Jinfu Yang 2, Dongjiang Han 3, Changliang Tang 4 Institute of Engineering Thermophysics,
Experimental Response of a Rotor Supported on Flexure Pivot Hydrostatic Pad Gas Bearings
 Texas A&M University Mechanical Engineering Department Turbomachinery Laboratory Experimental Response of a Rotor Supported on Flexure Pivot Hydrostatic Pad Gas Bearings Research Progress Report to the
Texas A&M University Mechanical Engineering Department Turbomachinery Laboratory Experimental Response of a Rotor Supported on Flexure Pivot Hydrostatic Pad Gas Bearings Research Progress Report to the
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A TURBOCHARGER IN FLOATING BUSHING BEARINGS
 Dyrobes Rotoynamics Software https://dyrobes.com ISCORMA-3, Cleveland, Ohio, 19-23 September 2005 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A TURBOCHARGER IN FLOATING BUSHING BEARINGS Edgar J. Gunter RODYN VIBRATION ANALYSIS,
Dyrobes Rotoynamics Software https://dyrobes.com ISCORMA-3, Cleveland, Ohio, 19-23 September 2005 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A TURBOCHARGER IN FLOATING BUSHING BEARINGS Edgar J. Gunter RODYN VIBRATION ANALYSIS,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012
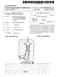 US 2012O163742A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0163742 A1 Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) AXIAL GAS THRUST BEARING FOR (30) Foreign
US 2012O163742A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0163742 A1 Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) AXIAL GAS THRUST BEARING FOR (30) Foreign
FSI and Modal Analysis of Elastic Ring Squeeze Film Damper for Small Gas Turbine Engines
 FSI and Modal Analysis of Elastic Ring Squeeze Film Damper for Small Gas Turbine Engines Thennavarajan Subramanian 1*, Jeyaraj P 2, Manikandan L P 3, S S Kulkarni 4, Soumendu Jana 5 Technical Officer,
FSI and Modal Analysis of Elastic Ring Squeeze Film Damper for Small Gas Turbine Engines Thennavarajan Subramanian 1*, Jeyaraj P 2, Manikandan L P 3, S S Kulkarni 4, Soumendu Jana 5 Technical Officer,
Year I. TRC-SEAL Luis San Andrés. Weilian Shan Graduate Research Assistant. May rd Turbomachinery Research Consortium Meeting
 33 rd Turbomachinery Research Consortium Meeting Predictions vs. Test Results for Leakage and Force Coefficients of a Fully Partitioned Pocket Damper Seal and a Labyrinth Seal Limitations of the Current
33 rd Turbomachinery Research Consortium Meeting Predictions vs. Test Results for Leakage and Force Coefficients of a Fully Partitioned Pocket Damper Seal and a Labyrinth Seal Limitations of the Current
Test Results for Load-On-Pad and Load-Between- Pad Hybrid Flexure Pivot Tilting Pad Gas Bearings
 Texas A&M University Mechanical Engineering Department Turbomachinery Laboratory Test Results for Load-On-Pad and Load-Between- Pad Hybrid Flexure Pivot Tilting Pad Gas Bearings Research Progress Report
Texas A&M University Mechanical Engineering Department Turbomachinery Laboratory Test Results for Load-On-Pad and Load-Between- Pad Hybrid Flexure Pivot Tilting Pad Gas Bearings Research Progress Report
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rolling Contact Bearings Over Sliding Contact Bearings
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Rolling Contact Bearings Over Sliding Contact Bearings Advantages 1. Low starting and running friction except at very high speeds. 2. Ability to withstand momentary shock
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rolling Contact Bearings Over Sliding Contact Bearings Advantages 1. Low starting and running friction except at very high speeds. 2. Ability to withstand momentary shock
Evaluating and Correcting Subsynchronous Vibration in Vertical Pumps
 Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software https://dyrobes.com Evaluating and Correcting Subsynchronous Vibration in Vertical Pumps Abstract By Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Co. Kelly J. Conner
Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software https://dyrobes.com Evaluating and Correcting Subsynchronous Vibration in Vertical Pumps Abstract By Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Co. Kelly J. Conner
CASE STUDY ON RESOLVING OIL WHIRL ISSUES ON GAS COMPRESSOR
 CASE STUDY ON RESOLVING OIL WHIRL ISSUES ON GAS COMPRESSOR John J. Yu, Ph.D. Nicolas Péton Sergey Drygin, Ph.D. GE Oil & Gas 1 / Abstract This case is a site vibration issue on a Gas compressor module.
CASE STUDY ON RESOLVING OIL WHIRL ISSUES ON GAS COMPRESSOR John J. Yu, Ph.D. Nicolas Péton Sergey Drygin, Ph.D. GE Oil & Gas 1 / Abstract This case is a site vibration issue on a Gas compressor module.
MEASUREMENTS OF ROTORDYNAMIC RESPONSE IN A HIGH TEMPERATURE ROTOR SUPPORTED ON TWO METAL MESH FOIL BEARINGS
 Texas A&M University Mechanical Engineering Department Turbomachinery Laboratory Tribology Group MEASUREMENTS OF ROTORDYNAMIC RESPONSE IN A HIGH TEMPERATURE ROTOR SUPPORTED ON TWO METAL MESH FOIL BEARINGS
Texas A&M University Mechanical Engineering Department Turbomachinery Laboratory Tribology Group MEASUREMENTS OF ROTORDYNAMIC RESPONSE IN A HIGH TEMPERATURE ROTOR SUPPORTED ON TWO METAL MESH FOIL BEARINGS
Experimental Response of a Rotor Supported on Rayleigh Step Gas Bearings
 Texas A&M University Mechanical Engineering Department Turbomachinery Laboratory Experimental Response of a Rotor Supported on Rayleigh Step Gas Bearings Research Progress Report to the Turbomachinery
Texas A&M University Mechanical Engineering Department Turbomachinery Laboratory Experimental Response of a Rotor Supported on Rayleigh Step Gas Bearings Research Progress Report to the Turbomachinery
A Test Rig for Evaluation of Thrust Bearings and Face Seals
 TRC-B&C-02-2015 TRC Project 32513/1519F2 May 2015 Year II A Test Rig for Evaluation of Thrust Bearings and Face Seals Luis San Andrés, Michael Rohmer, Scott Wilkinson Justification Compressors, turbochargers,
TRC-B&C-02-2015 TRC Project 32513/1519F2 May 2015 Year II A Test Rig for Evaluation of Thrust Bearings and Face Seals Luis San Andrés, Michael Rohmer, Scott Wilkinson Justification Compressors, turbochargers,
Silencers. Transmission and Insertion Loss
 Silencers Practical silencers are complex devices, which operate reducing pressure oscillations before they reach the atmosphere, producing the minimum possible loss of engine performance. However they
Silencers Practical silencers are complex devices, which operate reducing pressure oscillations before they reach the atmosphere, producing the minimum possible loss of engine performance. However they
LESSON Transmission of Power Introduction
 LESSON 3 3.0 Transmission of Power 3.0.1 Introduction Earlier in our previous course units in Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering, we introduced ourselves to the concept of support and process systems
LESSON 3 3.0 Transmission of Power 3.0.1 Introduction Earlier in our previous course units in Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering, we introduced ourselves to the concept of support and process systems
Research on vibration reduction of multiple parallel gear shafts with ISFD
 Research on vibration reduction of multiple parallel gear shafts with ISFD Kaihua Lu 1, Lidong He 2, Wei Yan 3 Beijing Key Laboratory of Health Monitoring and Self-Recovery for High-End Mechanical Equipment,
Research on vibration reduction of multiple parallel gear shafts with ISFD Kaihua Lu 1, Lidong He 2, Wei Yan 3 Beijing Key Laboratory of Health Monitoring and Self-Recovery for High-End Mechanical Equipment,
Development of TPL and TPS Series Marine Turbocharger
 Development of TPL and TPS Series Marine Turbocharger IWAKI Fuminori : MITSUBORI Ken : General Machinery Engineering Department, Rotating Machinery Division, Industrial Machinery Chief Engineer, General
Development of TPL and TPS Series Marine Turbocharger IWAKI Fuminori : MITSUBORI Ken : General Machinery Engineering Department, Rotating Machinery Division, Industrial Machinery Chief Engineer, General
May 2015 IDENTIFICATION OF STRUCTURAL STIFFNESS AND MATERIAL LOSS FACTOR IN A LARGE DIAMETER METAL MESH FOIL BEARING. Luis San Andrés and Travis Cable
 TRC Project 32513/1519N1 May 2015 IDENTIFICATION OF STRUCTURAL STIFFNESS AND MATERIAL LOSS FACTOR IN A LARGE DIAMETER METAL MESH FOIL BEARING Luis San Andrés and Travis Cable Justification Foil bearings
TRC Project 32513/1519N1 May 2015 IDENTIFICATION OF STRUCTURAL STIFFNESS AND MATERIAL LOSS FACTOR IN A LARGE DIAMETER METAL MESH FOIL BEARING Luis San Andrés and Travis Cable Justification Foil bearings
Compressor Noise Control
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1972 Compressor Noise Control G. M. Diehl Ingersoll-Rand Research Follow this and additional
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1972 Compressor Noise Control G. M. Diehl Ingersoll-Rand Research Follow this and additional
High pressure washpipe assembly with integral reservoir. Revision 1 October 10, 2017
 Kalsi Seals Handbook Chapter E6 High pressure washpipe assembly with integral reservoir Revision 1 October 10, 2017 Individual chapters of the Kalsi Seals Handbook are periodically updated. To determine
Kalsi Seals Handbook Chapter E6 High pressure washpipe assembly with integral reservoir Revision 1 October 10, 2017 Individual chapters of the Kalsi Seals Handbook are periodically updated. To determine
FEASIBILITY STYDY OF CHAIN DRIVE IN WATER HYDRAULIC ROTARY JOINT
 FEASIBILITY STYDY OF CHAIN DRIVE IN WATER HYDRAULIC ROTARY JOINT Antti MAKELA, Jouni MATTILA, Mikko SIUKO, Matti VILENIUS Institute of Hydraulics and Automation, Tampere University of Technology P.O.Box
FEASIBILITY STYDY OF CHAIN DRIVE IN WATER HYDRAULIC ROTARY JOINT Antti MAKELA, Jouni MATTILA, Mikko SIUKO, Matti VILENIUS Institute of Hydraulics and Automation, Tampere University of Technology P.O.Box
ENHANCED ROTORDYNAMICS FOR HIGH POWER CRYOGENIC TURBINE GENERATORS
 The 9th International Symposium on Transport Phenomena and Dynamics of Rotating Machinery Honolulu, Hawaii, February -1, ENHANCED ROTORDYNAMICS FOR HIGH POWER CRYOGENIC TURBINE GENERATORS Joel V. Madison
The 9th International Symposium on Transport Phenomena and Dynamics of Rotating Machinery Honolulu, Hawaii, February -1, ENHANCED ROTORDYNAMICS FOR HIGH POWER CRYOGENIC TURBINE GENERATORS Joel V. Madison
Lecture 6. Systems review exercise To be posted this weekend Due next Friday (3/6)
 150 Systems review exercise To be posted this weekend Due next Friday (3/6) Lecture 6 Coming week: Lab 13: Hydraulic Power Steering Lab 14: Integrated Lab (Hydraulic test bench) Topics today: Pumps and
150 Systems review exercise To be posted this weekend Due next Friday (3/6) Lecture 6 Coming week: Lab 13: Hydraulic Power Steering Lab 14: Integrated Lab (Hydraulic test bench) Topics today: Pumps and
ME 343: Mechanical Design-3
 What are bearings? ME 343: Mechanical Design-3 Bearings Dr. Aly Mousaad Aly Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty of Engineering, Alexandria University Machines with moving parts must have some
What are bearings? ME 343: Mechanical Design-3 Bearings Dr. Aly Mousaad Aly Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty of Engineering, Alexandria University Machines with moving parts must have some
APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE
 Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 19, 2012, No. 5, p. 359 368 359 APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE Jiří Šimek* New type of aerodynamic tilting pad journal
Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 19, 2012, No. 5, p. 359 368 359 APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE Jiří Šimek* New type of aerodynamic tilting pad journal
III B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, May/June
 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, May/June - 2015 1 a) Derive the expression for Gyroscopic Couple? b) A disc with radius of gyration of 60mm and a mass of 4kg is mounted centrally
Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, May/June - 2015 1 a) Derive the expression for Gyroscopic Couple? b) A disc with radius of gyration of 60mm and a mass of 4kg is mounted centrally
REVAMPING AND PRELIMINARY OPERATION OF A THRUST BEARING TEST RIG
 Texas A&M University Mechanical Engineering Department Turbomachinery Laboratory Tribology Group REVAMPING AND PRELIMINARY OPERATION OF A THRUST BEARING TEST RIG Research Progress Report to TAMU Turbomachinery
Texas A&M University Mechanical Engineering Department Turbomachinery Laboratory Tribology Group REVAMPING AND PRELIMINARY OPERATION OF A THRUST BEARING TEST RIG Research Progress Report to TAMU Turbomachinery
ME 343: Mechanical Design-3. Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty of Engineering, Alexandria University
 ME 343: Mechanical Design-3 Bearings Dr Aly Mousaad Aly Dr. Aly Mousaad Aly Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty of Engineering, Alexandria University What are bearings? Machines with moving parts
ME 343: Mechanical Design-3 Bearings Dr Aly Mousaad Aly Dr. Aly Mousaad Aly Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty of Engineering, Alexandria University What are bearings? Machines with moving parts
Module 2 : Dynamics of Rotating Bodies; Unbalance Effects and Balancing of Inertia Forces
 Module 2 : Dynamics of Rotating Bodies; Unbalance Effects and Balancing of Inertia Forces Lecture 3 : Concept of unbalance; effect of unbalance Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Unbalance
Module 2 : Dynamics of Rotating Bodies; Unbalance Effects and Balancing of Inertia Forces Lecture 3 : Concept of unbalance; effect of unbalance Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Unbalance
DETERMINING THE ROOT CAUSES OF SUBSYNCHRONOUS INSTABILITY PROBLEMS IN TWO CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS
 DETERMINING THE ROOT CAUSES OF SUBSYNCHRONOUS INSTABILITY PROBLEMS IN TWO CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS by Ed Wilcox CVO Rotating Equipment Team Lead Lyondell/Equistar Channelview, Texas and David P. O Brien
DETERMINING THE ROOT CAUSES OF SUBSYNCHRONOUS INSTABILITY PROBLEMS IN TWO CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS by Ed Wilcox CVO Rotating Equipment Team Lead Lyondell/Equistar Channelview, Texas and David P. O Brien
High Speed Gears - New Developments
 High Speed Gears - New Developments by T. Oeeg Contents: 1. Introduction 2. Back to Back Test Bed 3. Radial Tilting Pad Bearings 3.1 Design 3.2 Test Results 3.3 Deformation Analysis 4. Axial Tilting Pad
High Speed Gears - New Developments by T. Oeeg Contents: 1. Introduction 2. Back to Back Test Bed 3. Radial Tilting Pad Bearings 3.1 Design 3.2 Test Results 3.3 Deformation Analysis 4. Axial Tilting Pad
Case Study - Fluidic Instability
 Case Study - Fluidic Instability Date : October 6, 2014 Fluidic Instability - Its Detection, Causes and Rectification Fluidic instability is one such malfunction in rotary machines which is uncommon and
Case Study - Fluidic Instability Date : October 6, 2014 Fluidic Instability - Its Detection, Causes and Rectification Fluidic instability is one such malfunction in rotary machines which is uncommon and
By William A Glaeser (Member, STLE), Richard C Erickson (Member, STLE), Keith F Dufrane (Member, STLE) and Jerrold W Kannel Battelle Columbus, Ohio
 TRIBOLOGY: THE SCIENCE OF COMBATTING WEAR By William A Glaeser (Member, STLE), Richard C Erickson (Member, STLE), Keith F Dufrane (Member, STLE) and Jerrold W Kannel Battelle Columbus, Ohio Reprinted with
TRIBOLOGY: THE SCIENCE OF COMBATTING WEAR By William A Glaeser (Member, STLE), Richard C Erickson (Member, STLE), Keith F Dufrane (Member, STLE) and Jerrold W Kannel Battelle Columbus, Ohio Reprinted with
THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERS = r 345 E 47 St., New York, N.Y credit should be given to ASIVIE to cs P i n and the autnor(sl
 80-GT-151 u `^, `rery.,,,,teg 3 THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERS = r 345 E 47 St., New York, N.Y. 10017 `.. ' The Society shall not be responsible for,t.item nts or opinions advanced in papers
80-GT-151 u `^, `rery.,,,,teg 3 THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERS = r 345 E 47 St., New York, N.Y. 10017 `.. ' The Society shall not be responsible for,t.item nts or opinions advanced in papers
Improvements for Ver November 23, 2017
 Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software dyrobes.com Improvements for Ver 20.00 November 23, 2017 Add new features in BePerf for fixed-lobe and tilting pad journal bearing design: 1) Parametric study 2) Design Comparison.
Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software dyrobes.com Improvements for Ver 20.00 November 23, 2017 Add new features in BePerf for fixed-lobe and tilting pad journal bearing design: 1) Parametric study 2) Design Comparison.
Basic Static Load Rating of Rolling Contact Bearings
 Basic Static Load Rating of Rolling Contact Bearings The load carried by a non-rotating bearing is called a static load. The basic static load rating is defined as the static radial load (in case of radial
Basic Static Load Rating of Rolling Contact Bearings The load carried by a non-rotating bearing is called a static load. The basic static load rating is defined as the static radial load (in case of radial
AGN 076 Alternator Bearings
 Application Guidance Notes: Technical Information from Cummins Generator Technologies AGN 076 Alternator Bearings BEARING TYPES In the design of STAMFORD and AvK alternators, the expected types of rotor
Application Guidance Notes: Technical Information from Cummins Generator Technologies AGN 076 Alternator Bearings BEARING TYPES In the design of STAMFORD and AvK alternators, the expected types of rotor
Design and Test of Transonic Compressor Rotor with Tandem Cascade
 Proceedings of the International Gas Turbine Congress 2003 Tokyo November 2-7, 2003 IGTC2003Tokyo TS-108 Design and Test of Transonic Compressor Rotor with Tandem Cascade Yusuke SAKAI, Akinori MATSUOKA,
Proceedings of the International Gas Turbine Congress 2003 Tokyo November 2-7, 2003 IGTC2003Tokyo TS-108 Design and Test of Transonic Compressor Rotor with Tandem Cascade Yusuke SAKAI, Akinori MATSUOKA,
Advanced Rotordynamic Bearing Technology And Case Histories in the Rotating Machinery Industry
 Location: Florence, Italy Rotor Bearing Solutions International (RBSI) General Electric Oil and Gas Lecturers: 1. Paul Allaire, Chief Technical Officer, Rotor Bearing Solutions International (RBSI), Also,
Location: Florence, Italy Rotor Bearing Solutions International (RBSI) General Electric Oil and Gas Lecturers: 1. Paul Allaire, Chief Technical Officer, Rotor Bearing Solutions International (RBSI), Also,
November 8, 2018 GAS TURBINE ENGINE SECONDARY FLOW SYSTEMS
 November 8, 2018 GAS TURBINE ENGINE SECONDARY FLOW SYSTEMS Agenda 1 What is Secondary Flow? Purpose for the Secondary Flow Systems Chargeable Vs Nonchargeable Flows Seals Selection and Leakage Effects
November 8, 2018 GAS TURBINE ENGINE SECONDARY FLOW SYSTEMS Agenda 1 What is Secondary Flow? Purpose for the Secondary Flow Systems Chargeable Vs Nonchargeable Flows Seals Selection and Leakage Effects
TURBOLINK BEARINGS L U I D I L M E A R I N G S. Manufcturing Engineering Consulting Service & Retrofit
 TURBOLINK BEARINGS Manufcturing Engineering Consulting Service & Retrofit L U I D I L M E A R I N G S 제작 : 2012. 10 #111 5th Standard Factory, 41-3 Paryongdong, Changwon, 641-847 Korea Tel : +82-55-267-3715
TURBOLINK BEARINGS Manufcturing Engineering Consulting Service & Retrofit L U I D I L M E A R I N G S 제작 : 2012. 10 #111 5th Standard Factory, 41-3 Paryongdong, Changwon, 641-847 Korea Tel : +82-55-267-3715
Further Imbalance Response Measurements of Rotor Supported on Bump-Type Gas Foil Bearings: Operation to 50 krpm
 Texas A&M University Mechanical Engineering Department Turbomachinery Laboratory Tribology Group Further Imbalance Response Measurements of Rotor Supported on Bump-Type Gas Foil Bearings: Operation to
Texas A&M University Mechanical Engineering Department Turbomachinery Laboratory Tribology Group Further Imbalance Response Measurements of Rotor Supported on Bump-Type Gas Foil Bearings: Operation to
Eddy Current Displacement Transducer Specifications
 March 213 CSI 65 Machinery Health TM Monitor Eddy Current Displacement Transducer Specifications The PR 6422 is a non-contact eddy current transducer with a rugged construction and designed for extremely
March 213 CSI 65 Machinery Health TM Monitor Eddy Current Displacement Transducer Specifications The PR 6422 is a non-contact eddy current transducer with a rugged construction and designed for extremely
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR ROTATING UNIONS SEALING TECHNOLOGIES
 DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR ROTATING UNIONS SEALING TECHNOLOGIES Rotating unions convey fluid from a stationary supply line to equipment or a rotating tool. They are critical elements in a variety of applications
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR ROTATING UNIONS SEALING TECHNOLOGIES Rotating unions convey fluid from a stationary supply line to equipment or a rotating tool. They are critical elements in a variety of applications
Chapter 11 Rolling Contact Bearings
 Chapter 11 Rolling Contact Bearings 1 2 Chapter Outline Bearing Types Bearing Life Bearing Load Life at Rated Reliability Bearing Survival: Reliability versus Life Relating Load, Life, and Reliability
Chapter 11 Rolling Contact Bearings 1 2 Chapter Outline Bearing Types Bearing Life Bearing Load Life at Rated Reliability Bearing Survival: Reliability versus Life Relating Load, Life, and Reliability
ACTIVE AXIAL ELECTROMAGNETIC DAMPER
 ACTIVE AXIAL ELECTROMAGNETIC DAMPER Alexei V. Filatov, Larry A. Hawkins Calnetix Inc., Cerritos, CA, 973, USA afilatov@calnetix.com Venky Krishnan, Bryan Lam Direct Drive Systems Inc., Cerritos, CA, 973,
ACTIVE AXIAL ELECTROMAGNETIC DAMPER Alexei V. Filatov, Larry A. Hawkins Calnetix Inc., Cerritos, CA, 973, USA afilatov@calnetix.com Venky Krishnan, Bryan Lam Direct Drive Systems Inc., Cerritos, CA, 973,
COMPULSATOR ROTORDYNAMICS AND SUSPENSION DESIGN
 COMPULSATOR ROTORDYNAMICS AND SUSPENSION DESIGN B. T. Murphy, S. M. Manifold and J. R. Kitzmiller Center For Electromechanics, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, Texas ABSTRACT High speed compulsator
COMPULSATOR ROTORDYNAMICS AND SUSPENSION DESIGN B. T. Murphy, S. M. Manifold and J. R. Kitzmiller Center For Electromechanics, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, Texas ABSTRACT High speed compulsator
Liberec,
 POWER GYROSCOPES OF STABILIZING SYSTEM Šimek, J. 1 - Šklíba, J. 2 - Sivčák, M. 2 Škoda, J. 2 Abstract: The paper deals with problems concerning power gyroscopes for stabilization of vibro-izolation system.
POWER GYROSCOPES OF STABILIZING SYSTEM Šimek, J. 1 - Šklíba, J. 2 - Sivčák, M. 2 Škoda, J. 2 Abstract: The paper deals with problems concerning power gyroscopes for stabilization of vibro-izolation system.
Lecture 19. Magnetic Bearings
 Lecture 19 Magnetic Bearings 19-1 Magnetic Bearings It was first proven mathematically in the late 1800s by Earnshaw that using only a magnet to try and support an object represented an unstable equilibrium;
Lecture 19 Magnetic Bearings 19-1 Magnetic Bearings It was first proven mathematically in the late 1800s by Earnshaw that using only a magnet to try and support an object represented an unstable equilibrium;
Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers
 Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers U. Bin-Nun FLIR Systems Inc. Boston, MA 01862 ABSTRACT Cryocooler self induced vibration is a major consideration in the design of IR
Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers U. Bin-Nun FLIR Systems Inc. Boston, MA 01862 ABSTRACT Cryocooler self induced vibration is a major consideration in the design of IR
VALMONT MITIGATOR TR1
 VALMONT MITIGATOR TR1 Research Verification of the Valmont TR1 Damper Performance MITIGATOR TR1 VIBRATION DAMPER The Valmont TR1 damper has been specifically designed using vibration theory and innovative
VALMONT MITIGATOR TR1 Research Verification of the Valmont TR1 Damper Performance MITIGATOR TR1 VIBRATION DAMPER The Valmont TR1 damper has been specifically designed using vibration theory and innovative
ROTORDYNAMICS OF SEMI-RIGID AND OVERHUNG TURBOMACHINERY
 ROTORDYNAMICS OF SEMI-RIGID AND OVERHUNG TURBOMACHINERY Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Co. P.O. BOX 157 Dickinson, TX 77539 MLeader@RotorBearingDynamics.COM Abstract: This paper continues
ROTORDYNAMICS OF SEMI-RIGID AND OVERHUNG TURBOMACHINERY Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Co. P.O. BOX 157 Dickinson, TX 77539 MLeader@RotorBearingDynamics.COM Abstract: This paper continues
Analysis of journal bearing regarding number and position of lobes
 2015; 1(2): 82-86 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 3.4 IJAR 2015; 1(2): 82-86 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 15-12-2014 Accepted: 08-01-2015 M.N.V.M. Mallikarjuna Rao M.
2015; 1(2): 82-86 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 3.4 IJAR 2015; 1(2): 82-86 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 15-12-2014 Accepted: 08-01-2015 M.N.V.M. Mallikarjuna Rao M.
IJTC STABILITY ANALYSIS OF A HIGH SPEED AUTOMOTIVE TURBOCHARGER. Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software
 Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software http://dyrobes.com Proceedings of IJTC26 STLE/ASME international Joint Tribology Conference October 22-25, 26, San Antonio, TX, USA STABILITY ANALYSIS OF A HIGH SPEED AUTOMOTIVE
Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software http://dyrobes.com Proceedings of IJTC26 STLE/ASME international Joint Tribology Conference October 22-25, 26, San Antonio, TX, USA STABILITY ANALYSIS OF A HIGH SPEED AUTOMOTIVE
R10 Set No: 1 ''' ' '' '' '' Code No: R31033
 R10 Set No: 1 III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 2013 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks:
R10 Set No: 1 III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 2013 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks:
TECHNICAL INFORMATION
 General Nomenclature Spherical Roller Bearings The spherical roller bearing is a combination radial and thrust bearing designed for taking misalignment under load When loads are heavy, alignment of housings
General Nomenclature Spherical Roller Bearings The spherical roller bearing is a combination radial and thrust bearing designed for taking misalignment under load When loads are heavy, alignment of housings
Introduction to Vibration & Pulsation in Reciprocating Compressors
 Introduction to Vibration & Pulsation in Reciprocating Compressors Shelley D. Greenfield, P.Eng. Vice President, Design Services sgreenfield@betamachinery.com Luis de la Roche Operations Manager ldelaroche@betamachinery.com
Introduction to Vibration & Pulsation in Reciprocating Compressors Shelley D. Greenfield, P.Eng. Vice President, Design Services sgreenfield@betamachinery.com Luis de la Roche Operations Manager ldelaroche@betamachinery.com
Low-torque Deep-groove Ball Bearings for Transmissions
 New Product Low-torque Deep-groove Ball Bearings for Transmissions Katsuaki SASAKI To achieve low fuel consumption in response to environmental concerns, we have focused on reducing the friction of tapered
New Product Low-torque Deep-groove Ball Bearings for Transmissions Katsuaki SASAKI To achieve low fuel consumption in response to environmental concerns, we have focused on reducing the friction of tapered
LECTURE-23: Basic concept of Hydro-Static Transmission (HST) Systems
 MODULE-6 : HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS LECTURE-23: Basic concept of Hydro-Static Transmission (HST) Systems 1. INTRODUCTION The need for large power transmissions in tight space and their control
MODULE-6 : HYDROSTATIC TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS LECTURE-23: Basic concept of Hydro-Static Transmission (HST) Systems 1. INTRODUCTION The need for large power transmissions in tight space and their control
Training Courses Information
 Training Courses Information Health & Condition Monitoring Center Sustainable Manufacturing Systems Laboratory Iran University of Science & Technology Condition Monitoring, Maintenance & Reliability (Overview)
Training Courses Information Health & Condition Monitoring Center Sustainable Manufacturing Systems Laboratory Iran University of Science & Technology Condition Monitoring, Maintenance & Reliability (Overview)
Design 3. Bearings(1/2) Bearings. Bearings. Provides support for rotating machine elements. Contents. Hamidreza G.Darabkhani. Course Leader: A.
 Design 3 Bearings Hamidreza G.Darabkhani Course Leader: A. Starr Contents Bearings Bearings Classification Loads on Bearings Rolling elements bearings Ball bearings Roller bearings Needle bearings Linear
Design 3 Bearings Hamidreza G.Darabkhani Course Leader: A. Starr Contents Bearings Bearings Classification Loads on Bearings Rolling elements bearings Ball bearings Roller bearings Needle bearings Linear
Stability Analysis of a Turbocharger for Marine Diesel Engine Service. Master of Science in Mechanical Engineering
 Stability Analysis of a Turbocharger for Marine Diesel Engine Service by Michael S. Adams Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
Stability Analysis of a Turbocharger for Marine Diesel Engine Service by Michael S. Adams Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
FUNCTION OF A BEARING
 Bearing FUNCTION OF A BEARING The main function of a rotating shaft is to transmit power from one end of the line to the other. It needs a good support to ensure stability and frictionless rotation. The
Bearing FUNCTION OF A BEARING The main function of a rotating shaft is to transmit power from one end of the line to the other. It needs a good support to ensure stability and frictionless rotation. The
Metal Mesh Foil Gas Bearings for Oil-Free Turbomachinery
 12 th National Conference on Gas Lubrication, Dry Gas Seal and Micro Gravity in China May 218 Metal Mesh Foil Gas Bearings for Oil-Free Turbomachinery An introduction to Oil-Free MTM requirements and metal
12 th National Conference on Gas Lubrication, Dry Gas Seal and Micro Gravity in China May 218 Metal Mesh Foil Gas Bearings for Oil-Free Turbomachinery An introduction to Oil-Free MTM requirements and metal
Chapter 7. Shafts and Shaft Components
 Chapter 7 Shafts and Shaft Components 2 Chapter Outline Introduction Shaft Materials Shaft Layout Shaft Design for Stress Deflection Considerations Critical Speeds for Shafts Miscellaneous Shaft Components
Chapter 7 Shafts and Shaft Components 2 Chapter Outline Introduction Shaft Materials Shaft Layout Shaft Design for Stress Deflection Considerations Critical Speeds for Shafts Miscellaneous Shaft Components
719. Diagnostic research of rotor systems with variable inertia moment
 719. Diagnostic research of rotor systems with variable inertia moment Valentinas Kartašovas 1, Vytautas Barzdaitis 2, Pranas Mažeika 3, Marius Vasylius 4 1, 2 Kaunas University of Technology, Mickevičiaus
719. Diagnostic research of rotor systems with variable inertia moment Valentinas Kartašovas 1, Vytautas Barzdaitis 2, Pranas Mažeika 3, Marius Vasylius 4 1, 2 Kaunas University of Technology, Mickevičiaus
DEVELOPMENT AND IMPLEMENTATION OF VFD ACTIVE DAMPING TO SMOOTH TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS ON A GEARED TRAIN
 DEVELOPMENT AND IMPLEMENTATION OF VFD ACTIVE DAMPING TO SMOOTH TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS ON A GEARED TRAIN L. Naldi GE Oil&Gas P. Rotondo GE Oil&Gas J. Kocur ExxonMobil 37 th Turbomachinery Symposium Talk Overview
DEVELOPMENT AND IMPLEMENTATION OF VFD ACTIVE DAMPING TO SMOOTH TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS ON A GEARED TRAIN L. Naldi GE Oil&Gas P. Rotondo GE Oil&Gas J. Kocur ExxonMobil 37 th Turbomachinery Symposium Talk Overview
Effect Of Bearing Faults On Dynamic Behavior And Electric Power Consumption Of Pumps
 Effect Of Bearing Faults On Dynamic Behavior And Electric Power Consumption Of Pumps Abstract Samir M. Abdel-Rahman Dalia M. Al-Gazar M. A. Helal Associate Professor Engineer Professor Mechanical & Electrical
Effect Of Bearing Faults On Dynamic Behavior And Electric Power Consumption Of Pumps Abstract Samir M. Abdel-Rahman Dalia M. Al-Gazar M. A. Helal Associate Professor Engineer Professor Mechanical & Electrical
MAIN SHAFT SUPPORT FOR WIND TURBINE WITH A FIXED AND FLOATING BEARING CONFIGURATION
 Technical Paper MAIN SHAFT SUPPORT FOR WIND TURBINE WITH A FIXED AND FLOATING BEARING CONFIGURATION Tapered Double Inner Row Bearing Vs. Spherical Roller Bearing On The Fixed Position Laurentiu Ionescu,
Technical Paper MAIN SHAFT SUPPORT FOR WIND TURBINE WITH A FIXED AND FLOATING BEARING CONFIGURATION Tapered Double Inner Row Bearing Vs. Spherical Roller Bearing On The Fixed Position Laurentiu Ionescu,
AN END-USER S GUIDE TO CENTRIFUGAL PUMP ROTORDYNAMICS
 AN END-USER S GUIDE TO CENTRIFUGAL PUMP ROTORDYNAMICS William D. Marscher President & Technical Director Mechanical Solutions, Inc. Whippany, NJ, USA Bill Marscher, P.E. founded Mechanical Solutions, Inc.
AN END-USER S GUIDE TO CENTRIFUGAL PUMP ROTORDYNAMICS William D. Marscher President & Technical Director Mechanical Solutions, Inc. Whippany, NJ, USA Bill Marscher, P.E. founded Mechanical Solutions, Inc.
Hydrostatic Pivoted Pad Bearing for Oil-Free Turbomachinery
 Hydrostatic Pivoted Pad Bearing for Oil-Free Turbomachinery Lyn M. Greenhill Valerie J. Lease DynaTech Engineering, Inc. Roseville, CA, 95661 USA ABSTRACT To replace traditional rolling element bearings
Hydrostatic Pivoted Pad Bearing for Oil-Free Turbomachinery Lyn M. Greenhill Valerie J. Lease DynaTech Engineering, Inc. Roseville, CA, 95661 USA ABSTRACT To replace traditional rolling element bearings
The Death of Whirl AND Whip
 REEARCH & DEVELOPMENT The Death of Whirl AND Whip Use of Externally Pressurized Bearings and eals for Control of Whirl and Whip Instability Editor s Note: In the First Quarter 2001 issue of ORBIT, we featured
REEARCH & DEVELOPMENT The Death of Whirl AND Whip Use of Externally Pressurized Bearings and eals for Control of Whirl and Whip Instability Editor s Note: In the First Quarter 2001 issue of ORBIT, we featured
Balancing with the presence of a rub
 Balancing with the presence of a rub Nicolas Péton 1 1 GE Measurement & Control, 14 rue de la Haltinière, CS 10356, 44303 Nantes, Cedex 3, France Abstract During commissioning of a cogeneration plant the
Balancing with the presence of a rub Nicolas Péton 1 1 GE Measurement & Control, 14 rue de la Haltinière, CS 10356, 44303 Nantes, Cedex 3, France Abstract During commissioning of a cogeneration plant the
