Series and Parallel Circuits Virtual Lab
|
|
|
- Patience Roberta McLaughlin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Series and Parallel Circuits Virtual Lab Learning Goals: Students will be able to Discuss basic electricity relationships Discuss basic electricity relationships in series and parallel circuits Build series, parallel and combination circuits from schematic drawings Use an ammeter and voltmeter to take readings in circuits. Provide reasoning to explain the measurements and relationships in circuits. For your lab report, you may copy this into a word processor. But be sure to enter your answers in a different colored font. I. Observing voltage relationships Go to the PHeT web site and use the Circuit Construction Kit simulation (CCK): Drag out three batteries. Measure the voltage of each using the voltmeter and record the voltage in a table like the one shown. Then move the batteries end to end as below to measure combined voltage. Battery + ++ Voltage (V) a. Describe the relationship between the number of batteries and the voltage and explain what you think might be happening. b. What could you vary to test your description about the relationship? (Right click on the batteries to change characteristics ) Run several tests recording your data in an organized table. c. Talk to another group about their description, tests and results. Rewrite your description to include the more broad tests. II. Using voltage Use the Circuit Construction Kit simulation to build a circuit with a battery and a light bulb in the Lifelike visual mode. a. Draw what your circuit looks like (you may cut and past your circuit into your lab report if you wish). b. How does the voltage of the battery compare to the light bulb voltage? Explain what you think is happening. c. Vary the voltage of the battery and write observations about how the brightness is affected by voltage. d. d. Think about a real light bulb and battery; explain what you think is happening that causes the changes in brightness.
2 III. Using voltage in series circuits Use CCK to build the circuits below with a battery at about volts and light bulbs. Turn on the voltmeter and ammeter to measure voltage of the battery and current into it. Record bulb brightness with descriptive language. # of Bulbs Battery Voltage (V) Current Out of Battery (A) Brightness of Bulbs a. Summarize the relationships you observed and explain what you think is happening. b. Test to see if changing the battery voltage causes you to modify any of your conclusions. Explain what you measured and any conclusions you draw from your tests. c. What happens when you take a wire out of a circuit? Explain what you think is happening. d. Test using the voltmeter or ammeter in different ways. For example: Does it matter if you take the reading on the left or right of the battery? Switch the meter ends? Describe your tests and results.
3 IV. Using voltage in parallel circuits Use CCK to build the circuits below with a battery at about volts and light bulbs. Turn on the voltmeter and ammeter to measure voltage of the battery and current into it. Record bulb brightness with descriptive language. # of Bulbs Battery Voltage (V) Current Out of Battery (A) Brightness of Bulbs a. Summarize the relationships you observed and explain what you think is happening. b. Test to see if changing the battery voltage causes you to modify any of your conclusions. Explain what you measured and any conclusions you draw from your tests. c. What happens when you take a wire out of a circuit? Explain what you think is happening. d. Test using the voltmeter or ammeter in different ways. For example: Does it matter if you take the reading on the left or right of the battery? Switch the meter ends? Describe your tests and results.
4 V. Observing voltage and current relationships with resistors Use CCK to build the circuit below. Vary the voltage of the battery to at least 5 different values. Record the battery voltage and the current in the circuit in a table. a. Explain what might be happening to cause the change in current. b. How are current and battery voltage related? What is the shape of the graph? c. Describe how you could use the simulation to verify the relationship. Test your ideas and make modifications to your original answers if necessary. Be sure to explain your reasoning.
5 VI. Series Circuit Construct the circuit below using The Circuit Construction Kit (CCK) simulation. Make the resistors have different value and record the value of each resistor. Use the ammeter moving it to take readings in the different places seen in figure. Then use the voltmeter to take voltage readings. Calculate R using Ohm s Law (V=IR) for the total resistance in last column. Resistor Voltage (V) Current (A) Resistance ( ) Total V T reading= A T reading= * Calculate R T =V T /I T * A T is the ammeter that is measuring I T. a. How is the total resistance related to the individual resistances? Total current to the individual currents? Total voltage to the individual voltages? b. Write a paragraph explaining what you think is happening in series circuits to cause the above relationships to occur. (You made a similar circuit with light bulbs using CCK. You may want to experiment with the sim again, keeping in mind that light bulbs are just resistors that glow.).
6 VII. Parallel Circuit Construct the circuit below using The Circuit Construction Kit (CCK) simulation. Make the resistors have different value and record the value of each resistor. Use the ammeter moving it to take readings in the different places seen in figure. Then use the voltmeter to take voltage readings. Calculate R using Ohm s Law (V=IR) for the total resistance in last column. Resistor Voltage (V) Current (A) Resistance ( ) Total V T reading= A T reading= * Calculate R T =V T /I T * A T is the ammeter that is measuring I T. a. How is the total resistance related to the individual resistances? Explain what you think is happening. b. Look up the mathematical relationship for finding total resistance in a parallel circuit. Show that your data fits the equation. c. Summarize the similarities and differences between the series and parallel circuits. Include your reasoning about what you think is happening.
7 VIII. Combination Circuit. Put three resistors on the work area. Right click on each to make the resistances different from one another. Make a data table like the one given and record the individual resistances.. Build the circuit shown below. Make a table like the one below and complete it by measuring the voltage across each resistor and the power supply and measuring the current through each resistor and the total current coming out the power supply.. Resistor Total Resistance ( ) Theoretical Value: Current (A) Voltage (V) Equivalent Resistance ( ). Provide evidence that your table information is reasonable. Write down your reasoning and show your calculations. Before you take apart your experiment, show your results to your instructor to see if they are acceptable. Credit is given only if the results are correct and your reasoning is sound.
8 IX. Another Combination Circuit. Put three resistors on the work area. Right click on each to make the resistances different from one another. Make a data table like the one given and record the individual resistances.. Build the circuit shown below. Make a table like the one below and complete it by measuring the voltage across each resistor and the power supply and measuring the current through each resistor and the total current coming out the power supply. Resistor Total Resistance ( ) Theoretical Value: Current (A) Voltage (V) Equivalent Resistance ( ) 5. Provide evidence that your table information is reasonable. Write down your reasoning and show your calculations. Before you take apart your experiment, show your results to your instructor to see if they are acceptable. Credit is given only if the results are correct and your reasoning is sound.
PROPERTIES OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
 Name: PROPERTIES OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Date: Go to www.linville.ca and click on the page Computer Simulations or go to http://phet.colorado.edu/simulations open the Circuit Construction: DC and then click
Name: PROPERTIES OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Date: Go to www.linville.ca and click on the page Computer Simulations or go to http://phet.colorado.edu/simulations open the Circuit Construction: DC and then click
Lab 4. DC Circuits II
 Physics 2020, Spring 2005 Lab 4 page 1 of 7 Lab 4. DC Circuits II INTRODUCTION: This week we will continue with DC circuits, but now with an emphasis on current rather than voltage. Of course, in order
Physics 2020, Spring 2005 Lab 4 page 1 of 7 Lab 4. DC Circuits II INTRODUCTION: This week we will continue with DC circuits, but now with an emphasis on current rather than voltage. Of course, in order
Mandatory Experiment: Electric conduction
 Name: Class: Mandatory Experiment: Electric conduction In this experiment, you will investigate how different materials affect the brightness of a bulb in a simple electric circuit. 1. Take a battery holder,
Name: Class: Mandatory Experiment: Electric conduction In this experiment, you will investigate how different materials affect the brightness of a bulb in a simple electric circuit. 1. Take a battery holder,
Student Exploration: Advanced Circuits
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Advanced Circuits [Note to teachers and students: This Gizmo was designed as a follow-up to the Circuits Gizmo. We recommend doing that activity before trying this one.]
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Advanced Circuits [Note to teachers and students: This Gizmo was designed as a follow-up to the Circuits Gizmo. We recommend doing that activity before trying this one.]
Batteries n Bulbs: Voltage, Current and Resistance (8/6/15) (approx. 2h)
 Batteries n Bulbs: Voltage, Current and Resistance (8/6/15) (approx. 2h) Introduction A simple electric circuit can be made from a voltage source (batteries), wires through which current flows and a resistance,
Batteries n Bulbs: Voltage, Current and Resistance (8/6/15) (approx. 2h) Introduction A simple electric circuit can be made from a voltage source (batteries), wires through which current flows and a resistance,
34.5 Electric Current: Ohm s Law OHM, OHM ON THE RANGE. Purpose. Required Equipment and Supplies. Discussion. Procedure
 Name Period Date CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS Experiment 34.5 Electric : Ohm s Law OHM, OHM ON THE RANGE Thanx to Dean Baird Purpose In this experiment, you will arrange a simple circuit involving a power source
Name Period Date CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS Experiment 34.5 Electric : Ohm s Law OHM, OHM ON THE RANGE Thanx to Dean Baird Purpose In this experiment, you will arrange a simple circuit involving a power source
Lab 4. DC Circuits II
 Physics 2020, Spring 2005 Lab 4 page 1 of 7 Lab 4. DC Circuits II INTRODUCTION: This week we will continue with DC circuits, but now with an emphasis on current rather than voltage. Of course, in order
Physics 2020, Spring 2005 Lab 4 page 1 of 7 Lab 4. DC Circuits II INTRODUCTION: This week we will continue with DC circuits, but now with an emphasis on current rather than voltage. Of course, in order
POWER and ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
 POWER and ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Name For many of us, our most familiar experience with the word POWER (units of measure: WATTS) is when we think about electricity. Most of us know that when we change a light
POWER and ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Name For many of us, our most familiar experience with the word POWER (units of measure: WATTS) is when we think about electricity. Most of us know that when we change a light
INVESTIGATION ONE: WHAT DOES A VOLTMETER DO? How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured?
 How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow rate
How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow rate
Electric Circuits Lab
 Electric Circuits Lab Purpose: To construct series and parallel circuits To compare the current, voltage, and resistance in series and parallel circuits To draw schematic (circuit) diagrams of various
Electric Circuits Lab Purpose: To construct series and parallel circuits To compare the current, voltage, and resistance in series and parallel circuits To draw schematic (circuit) diagrams of various
SC10F Circuits Lab Name:
 SC10F Circuits Lab Name: Purpose: In this lab you will be making, both, series and parallel circuits. You will then be using a millimeter to take readings at various points in these circuits. Using these
SC10F Circuits Lab Name: Purpose: In this lab you will be making, both, series and parallel circuits. You will then be using a millimeter to take readings at various points in these circuits. Using these
Searching for Patterns in Series and Parallel Circuits
 Searching for Patterns in Series and Parallel Circuits Use the Circuit Construction Kit on phet.colorado.edu (DC Circuits only) to build the following circuits. fter building each circuit, use the ammeter
Searching for Patterns in Series and Parallel Circuits Use the Circuit Construction Kit on phet.colorado.edu (DC Circuits only) to build the following circuits. fter building each circuit, use the ammeter
EXPERIMENT - 1 OHM S LAW
 NOTE: While you copy the practical record see that you are following the note. Write Aim, theory, materials required, procedure, results, discussion and precautions on the right side of your record. While
NOTE: While you copy the practical record see that you are following the note. Write Aim, theory, materials required, procedure, results, discussion and precautions on the right side of your record. While
7. How long must a 100-watt light bulb be used in order to dissipate 1,000 joules of electrical energy? 1) 10 s 3) 1,000 s 2) 100 s 4) 100,000 s
 1. Which quantity must be the same for each component in any series circuit? 1) power 3) current 2) resistance 4) voltage 2. A student needs a 4-ohm resistor to complete a circuit. Only a large quantity
1. Which quantity must be the same for each component in any series circuit? 1) power 3) current 2) resistance 4) voltage 2. A student needs a 4-ohm resistor to complete a circuit. Only a large quantity
1103 Period 16: Electrical Resistance and Joule Heating
 Name Section 1103 Period 16: Electrical Resistance and Joule Heating Activity 16.1: What Does the Electrical Resistance of a Wire Depend Upon? 1) Measuring resistance a) Resistor length, L Use a multimeter
Name Section 1103 Period 16: Electrical Resistance and Joule Heating Activity 16.1: What Does the Electrical Resistance of a Wire Depend Upon? 1) Measuring resistance a) Resistor length, L Use a multimeter
Unit 9. (Filled In) Draw schematic circuit diagrams for resistors in series and in parallel
 Name: Date: Period: Unit 9 Series & Parallel Circuits (Filled In) Essential Questions: Does adding resistors to a circuit always reduce current? Does adding more light bulbs to a circuit always make them
Name: Date: Period: Unit 9 Series & Parallel Circuits (Filled In) Essential Questions: Does adding resistors to a circuit always reduce current? Does adding more light bulbs to a circuit always make them
Circuits-Circuit Analysis
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the information and diagram below. 4. A 9-volt battery is connected to a 4-ohm resistor and a 5-ohm resistor as shown in the diagram below. A 3.0-ohm resistor,
Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the information and diagram below. 4. A 9-volt battery is connected to a 4-ohm resistor and a 5-ohm resistor as shown in the diagram below. A 3.0-ohm resistor,
Phys 202A. Lab 7 Batteries, Bulbs and Current
 Phys 202A Lab 7 Batteries, Bulbs and Current Name Objectives: To understand how a voltage (potential difference) results in a current flow through a conductor. To learn to design and wire simple circuits
Phys 202A Lab 7 Batteries, Bulbs and Current Name Objectives: To understand how a voltage (potential difference) results in a current flow through a conductor. To learn to design and wire simple circuits
Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 2 Basic Electrical Meters and Ohm s Law
 Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 2 Basic Electrical Meters and Ohm s Law Administration: o Prayer o Bible Verse o Turn in quiz Meters: o Terms and Definitions: Analog vs. Digital Displays: Analog
Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 2 Basic Electrical Meters and Ohm s Law Administration: o Prayer o Bible Verse o Turn in quiz Meters: o Terms and Definitions: Analog vs. Digital Displays: Analog
Physics Experiment 9 Ohm s Law
 Fig. 9-1 Simple Series Circuit Equipment: Universal Circuit Board Power Supply 2 DMM's (Digital Multi-Meters) with Leads 150- Resistor 330- Resistor 560- Resistor Unknown Resistor Miniature Light Bulb
Fig. 9-1 Simple Series Circuit Equipment: Universal Circuit Board Power Supply 2 DMM's (Digital Multi-Meters) with Leads 150- Resistor 330- Resistor 560- Resistor Unknown Resistor Miniature Light Bulb
PHYSICS 111 LABORATORY Experiment #3 Current, Voltage and Resistance in Series and Parallel Circuits
 PHYSCS 111 LABORATORY Experiment #3 Current, Voltage and Resistance in Series and Parallel Circuits This experiment is designed to investigate the relationship between current and potential in simple series
PHYSCS 111 LABORATORY Experiment #3 Current, Voltage and Resistance in Series and Parallel Circuits This experiment is designed to investigate the relationship between current and potential in simple series
Investigation Electrical Circuits
 ACTIVITY #1 Task: To design and construct a circuit where 2 light bulbs can turn on and off at the same time Materials: - 1 power supply - 2 light bulbs - Connecting wires ( ) - Switch(s) - Multi-meter
ACTIVITY #1 Task: To design and construct a circuit where 2 light bulbs can turn on and off at the same time Materials: - 1 power supply - 2 light bulbs - Connecting wires ( ) - Switch(s) - Multi-meter
Academic Year
 EXCELLENCE INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL First Term, Work sheet (1) Grade (9) Academic Year 2014-2015 Subject: quantities Topics:- Static electricity - Eelectrical NAME: DATE: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: 1 - A circuit
EXCELLENCE INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL First Term, Work sheet (1) Grade (9) Academic Year 2014-2015 Subject: quantities Topics:- Static electricity - Eelectrical NAME: DATE: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: 1 - A circuit
Name: Base your answer to the question on the information below and on your knowledge of physics.
 Name: Figure 1 Base your answer to the question on the information below and on your knowledge of physics. A student constructed a series circuit consisting of a 12.0-volt battery, a 10.0-ohm lamp, and
Name: Figure 1 Base your answer to the question on the information below and on your knowledge of physics. A student constructed a series circuit consisting of a 12.0-volt battery, a 10.0-ohm lamp, and
Equivalent Meter Resistance
 Equivalent Meter Resistance This installation of N.E.R.D discusses meter resistance. The equipment referenced here is found in the Undergraduate Electronics Lab at the University of Houston. Topics covered
Equivalent Meter Resistance This installation of N.E.R.D discusses meter resistance. The equipment referenced here is found in the Undergraduate Electronics Lab at the University of Houston. Topics covered
LAB 7. SERIES AND PARALLEL RESISTORS
 Name: LAB 7. SERIES AND PARALLEL RESISTORS Problem How do you measure resistance, voltage, and current in a resistor? How are these quantities related? What is the difference between a series circuit and
Name: LAB 7. SERIES AND PARALLEL RESISTORS Problem How do you measure resistance, voltage, and current in a resistor? How are these quantities related? What is the difference between a series circuit and
UNIT 3: GENErAL ELECTriCAL SySTEM DiAGNOSiS
 Electrical/Electronic Systems UNIT 3: GENErAL ELECTriCAL SySTEM DiAGNOSiS LESSON 3: TEST electrical circuits I. Types of electrical circuit tests and electrical faults A. Different types of electrical
Electrical/Electronic Systems UNIT 3: GENErAL ELECTriCAL SySTEM DiAGNOSiS LESSON 3: TEST electrical circuits I. Types of electrical circuit tests and electrical faults A. Different types of electrical
Electric current, resistance and voltage in simple circuits
 Lab 6: Electric current, resistance and voltage in simple circuits Name: Group Members: Date: T s Name: pparatus: ulb board with batteries, connecting wires, two identical bulbs and a different bulb, a
Lab 6: Electric current, resistance and voltage in simple circuits Name: Group Members: Date: T s Name: pparatus: ulb board with batteries, connecting wires, two identical bulbs and a different bulb, a
Essential Electricity Homework Exercise 1
 Homework Exercise 1 1. For each of the following electrical symbols, copy the symbol into you jotter and label it using the words below. Word bank resistor, voltmeter, battery, ammeter, bulb V A 2. State
Homework Exercise 1 1. For each of the following electrical symbols, copy the symbol into you jotter and label it using the words below. Word bank resistor, voltmeter, battery, ammeter, bulb V A 2. State
Chapter 26 DC Circuits
 Chapter 26 DC Circuits Electric circuit needs battery or generator to produce current these are called sources of emf. Battery is a nearly constant voltage source, but does have a small internal resistance,
Chapter 26 DC Circuits Electric circuit needs battery or generator to produce current these are called sources of emf. Battery is a nearly constant voltage source, but does have a small internal resistance,
Chapter 26 DC Circuits. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 26 DC Circuits 26-1 EMF and Terminal Voltage Electric circuit needs battery or generator to produce current these are called sources of emf. Battery is a nearly constant voltage source, but does
Chapter 26 DC Circuits 26-1 EMF and Terminal Voltage Electric circuit needs battery or generator to produce current these are called sources of emf. Battery is a nearly constant voltage source, but does
Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above?
 Name: ( ) Class: Date: Electricity Exercises 1. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above? (1) Electrons flow from right to left through the bulb A. (2) Charges will be used
Name: ( ) Class: Date: Electricity Exercises 1. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above? (1) Electrons flow from right to left through the bulb A. (2) Charges will be used
Cabrillo College Physics 10L. LAB 7 Circuits. Read Hewitt Chapter 23
 Cabrillo College Physics 10L Name LAB 7 Circuits Read Hewitt Chapter 23 What to learn and explore Every electrical circuit must have at least one source (which supplies electrical energy to the circuit)
Cabrillo College Physics 10L Name LAB 7 Circuits Read Hewitt Chapter 23 What to learn and explore Every electrical circuit must have at least one source (which supplies electrical energy to the circuit)
16.3 Ohm s Law / Energy and Power / Electric Meters
 16.3 Ohm s Law / Energy and Power / Electric Meters Voltage Within a battery, a chemical reaction occurs that transfers electrons from one terminal to another terminal. This potential difference across
16.3 Ohm s Law / Energy and Power / Electric Meters Voltage Within a battery, a chemical reaction occurs that transfers electrons from one terminal to another terminal. This potential difference across
Physics Work with your neighbor. Ask me for help if you re stuck. Don t hesistate to compare notes with nearby groups.
 Physics 9 2016-04-13 Work with your neighbor. Ask me for help if you re stuck. Don t hesistate to compare notes with nearby groups. Today we ll build on what we did Monday with batteries and light bulbs.
Physics 9 2016-04-13 Work with your neighbor. Ask me for help if you re stuck. Don t hesistate to compare notes with nearby groups. Today we ll build on what we did Monday with batteries and light bulbs.
Electric Circuits Exam
 Electric Circuits Exam 1. The diagram below represents a lamp, a 10-volt battery, and a length of nichrome wire connected in series. 4. Which circuit has the smallest equivalent resistance? A) B) As the
Electric Circuits Exam 1. The diagram below represents a lamp, a 10-volt battery, and a length of nichrome wire connected in series. 4. Which circuit has the smallest equivalent resistance? A) B) As the
Series and Parallel Networks
 Series and Parallel Networks Department of Physics & Astronomy Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, TX January 17, 2014 1 Introduction In this experiment you will examine the brightness of light bulbs
Series and Parallel Networks Department of Physics & Astronomy Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, TX January 17, 2014 1 Introduction In this experiment you will examine the brightness of light bulbs
7.9.2 Potential Difference
 7.9.2 Potential Difference 62 minutes 69 marks Page 1 of 20 Q1. A set of Christmas tree lights is made from twenty identical lamps connected in series. (a) Each lamp is designed to take a current of 0.25
7.9.2 Potential Difference 62 minutes 69 marks Page 1 of 20 Q1. A set of Christmas tree lights is made from twenty identical lamps connected in series. (a) Each lamp is designed to take a current of 0.25
Review for formula, circuit and resistance test
 Review for formula, circuit and resistance test 1. Fill in the table giving the symbol and unit(s) for each. Current intensity Potential difference Voltage Resistance Power Energy Time 2. Give the formula
Review for formula, circuit and resistance test 1. Fill in the table giving the symbol and unit(s) for each. Current intensity Potential difference Voltage Resistance Power Energy Time 2. Give the formula
PHYSICS MCQ (TERM-1) BOARD PAPERS
 GRADE: 10 PHYSICS MCQ (TERM-1) BOARD PAPERS 1 The number of division in ammeter of range 2A is 10 and voltmeter of range 5 V is 20. When the switch of the circuit given below is closed, ammeter reading
GRADE: 10 PHYSICS MCQ (TERM-1) BOARD PAPERS 1 The number of division in ammeter of range 2A is 10 and voltmeter of range 5 V is 20. When the switch of the circuit given below is closed, ammeter reading
Sharjah Indian School Sharjah Boys Wing
 Read the instructions given below carefully before writing the fair record book. The following details are to be written on the LEFT HAND SIDE of the book. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM CALCULATIONS The remaining details
Read the instructions given below carefully before writing the fair record book. The following details are to be written on the LEFT HAND SIDE of the book. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM CALCULATIONS The remaining details
Section 6 HOW ARE VALUES OF CIRCUIT VARIABLES MEASURED?
 Section 6 HOW RE VUES OF CIRCUIT VRIBES MESURED? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow
Section 6 HOW RE VUES OF CIRCUIT VRIBES MESURED? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow
Laboratory 5: Electric Circuits Prelab
 Phys 132L Fall 2018 Laboratory 5: Electric Circuits Prelab 1 Current and moving charges Atypical currentinanelectronic devicemightbe5.0 10 3 A.Determinethenumber of electrons that pass through the device
Phys 132L Fall 2018 Laboratory 5: Electric Circuits Prelab 1 Current and moving charges Atypical currentinanelectronic devicemightbe5.0 10 3 A.Determinethenumber of electrons that pass through the device
A device that measures the current in a circuit. It is always connected in SERIES to the device through which it is measuring current.
 Goals of this second circuit lab packet: 1 to learn to use voltmeters an ammeters, the basic devices for analyzing a circuit. 2 to learn to use two devices which make circuit building far more simple:
Goals of this second circuit lab packet: 1 to learn to use voltmeters an ammeters, the basic devices for analyzing a circuit. 2 to learn to use two devices which make circuit building far more simple:
Circuit Analysis Questions A level standard
 1. (a) set of decorative lights consists of a string of lamps. Each lamp is rated at 5.0 V, 0.40 W and is connected in series to a 230 V supply. Calculate the number of lamps in the set, so that each lamp
1. (a) set of decorative lights consists of a string of lamps. Each lamp is rated at 5.0 V, 0.40 W and is connected in series to a 230 V supply. Calculate the number of lamps in the set, so that each lamp
Experiment 3: Ohm s Law; Electric Power. Don t take circuits apart until the instructor says you don't need to double-check anything.
 Experiment 3: Ohm s Law; Electric Power. How to use the digital meters: You have already used these for DC volts; turn the dial to "DCA" instead to get DC amps. If the meter has more than two connectors,
Experiment 3: Ohm s Law; Electric Power. How to use the digital meters: You have already used these for DC volts; turn the dial to "DCA" instead to get DC amps. If the meter has more than two connectors,
PHY222 Lab 4 Ohm s Law and Electric Circuits Ohm s Law; Series Resistors; Circuits Inside Three- and Four-Terminal Black Boxes
 PHY222 Lab 4 Ohm s Law and Electric Circuits Ohm s Law; Series Resistors; Circuits Inside Three- and Four-Terminal Black Boxes Print Your Name Print Your Partners' Names Instructions February 8, 2017 Before
PHY222 Lab 4 Ohm s Law and Electric Circuits Ohm s Law; Series Resistors; Circuits Inside Three- and Four-Terminal Black Boxes Print Your Name Print Your Partners' Names Instructions February 8, 2017 Before
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4)
 ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4) 1. Which two electrical quantities are measured in volts? A current and e.m.f. B current and resistance C e.m.f. and potential difference D potential
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4) 1. Which two electrical quantities are measured in volts? A current and e.m.f. B current and resistance C e.m.f. and potential difference D potential
Technical Workshop: Electrical December 3, 2016
 Technical Workshop: Electrical December 3, 2016 ELECTRICAL: CIRCUITS Key terms we will be using today: Voltage (V): The difference in electrical potential at one point in a circuit in relation to another.
Technical Workshop: Electrical December 3, 2016 ELECTRICAL: CIRCUITS Key terms we will be using today: Voltage (V): The difference in electrical potential at one point in a circuit in relation to another.
13.10 How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ
 13.10 How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ In Activity 13.2, you observed that when the two lamps were connected in series, the brightness of the lamps was less than when the lamps were connected in
13.10 How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ In Activity 13.2, you observed that when the two lamps were connected in series, the brightness of the lamps was less than when the lamps were connected in
11.1 CURRENT ELECTRICITY. Electrochemical Cells (the energy source) pg Wet Cell. Dry Cell. Positive. Terminal. Negative.
 Date: SNC1D: Electricity 11.1 CURRENT ELECTRICITY Define: CIRCUIT: path that electrons follow. CURRENT ELECTRICITY: continuous flow of electrons in a circuit LOAD: device that converts electrical energy
Date: SNC1D: Electricity 11.1 CURRENT ELECTRICITY Define: CIRCUIT: path that electrons follow. CURRENT ELECTRICITY: continuous flow of electrons in a circuit LOAD: device that converts electrical energy
Electrical Circuits. Vanderbilt Student Volunteers for Science. Training Presentation VINSE/VSVS Rural
 Electrical Circuits Vanderbilt Student Volunteers for Science Training Presentation 2018-2019 VINSE/VSVS Rural Important! Please use this resource to reinforce your understanding of the lesson! Make sure
Electrical Circuits Vanderbilt Student Volunteers for Science Training Presentation 2018-2019 VINSE/VSVS Rural Important! Please use this resource to reinforce your understanding of the lesson! Make sure
COMPOUND CIRCUITS LOGGING ON
 OMPOUN IUITS LOGGING ON HTTPS://PHET.OLOO.EU/EN/SIMULTION/IUIT-ONSTUTION-KIT- GETTING STTE To build a simple circuit with a single bulb and battery, use the cursor to drag a battery, two wires, and a bulb.
OMPOUN IUITS LOGGING ON HTTPS://PHET.OLOO.EU/EN/SIMULTION/IUIT-ONSTUTION-KIT- GETTING STTE To build a simple circuit with a single bulb and battery, use the cursor to drag a battery, two wires, and a bulb.
Voltage and Current in Simple Circuits (Voltage Sensor, Current Sensor)
 68 Voltage and Current in Simple Circuits (Voltage Sensor, Current Sensor) E&M: Voltage and current Equipment List DataStudio file: 68 Simple Circuits.ds Qty Items Part Numbers 1 PASCO interface (for two
68 Voltage and Current in Simple Circuits (Voltage Sensor, Current Sensor) E&M: Voltage and current Equipment List DataStudio file: 68 Simple Circuits.ds Qty Items Part Numbers 1 PASCO interface (for two
Physics - Chapters Task List
 Name Hour Physics - Chapters 34-35 Task List Task In Class? (Yes/No) Date Due Grade Lab 33.1 - Wet Cell Battery Yes */15 * Vodcast #1 Electric Circuits & Ohm s Law /21 Worksheet Concept Review #1-12, Ch
Name Hour Physics - Chapters 34-35 Task List Task In Class? (Yes/No) Date Due Grade Lab 33.1 - Wet Cell Battery Yes */15 * Vodcast #1 Electric Circuits & Ohm s Law /21 Worksheet Concept Review #1-12, Ch
Exam-style questions: electricity
 Exam-style questions: electricity Q. The diagram shows an electrical circuit. (a) Complete the two labels on the diagram. P and Q are meters. What is meter P measuring?... () What is meter Q measuring?...
Exam-style questions: electricity Q. The diagram shows an electrical circuit. (a) Complete the two labels on the diagram. P and Q are meters. What is meter P measuring?... () What is meter Q measuring?...
Science 10-Electricity & Magnetism Activity 4 (2007) Activity 3E Investigating Electric Current
 Science 10-Electricity & Magnetism ctivity 4 (2007) ctivity 3E Investigating Electric Current Name Due Date Show Me Hand In Purpose: To use an ammeter to measure electric current in circuits with lamps
Science 10-Electricity & Magnetism ctivity 4 (2007) ctivity 3E Investigating Electric Current Name Due Date Show Me Hand In Purpose: To use an ammeter to measure electric current in circuits with lamps
45 Current Electricity. February 09, Current Electricity. What we will learn, Arc Attack. Electric Man. 1
 Current Electricity What we will learn, Arc Attack Electric Man www.mrcjcs.com 1 Conductors and Insulators An electric current is a flow of electric charge. Set up a simple electrical circuit and insert
Current Electricity What we will learn, Arc Attack Electric Man www.mrcjcs.com 1 Conductors and Insulators An electric current is a flow of electric charge. Set up a simple electrical circuit and insert
Goals. Introduction (4.1) R = V I
 Lab 4. Ohm s Law Goals To understand Ohm s law, used to describe behavior of electrical conduction in many materials and circuits. To calculate electrical power dissipated as heat. To understand and use
Lab 4. Ohm s Law Goals To understand Ohm s law, used to describe behavior of electrical conduction in many materials and circuits. To calculate electrical power dissipated as heat. To understand and use
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 Q1. A battery of emf 9.0 V and internal resistance, r, is connected in the circuit shown in the figure below. (a) The current in the battery is 1.0 A. (i) Calculate the pd between points A and B in the
Q1. A battery of emf 9.0 V and internal resistance, r, is connected in the circuit shown in the figure below. (a) The current in the battery is 1.0 A. (i) Calculate the pd between points A and B in the
VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE Electrical Circuits VINSE/VSVS Rural
 VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE http://studentorgs.vanderbilt.edu/vsvs/ Electrical Circuits 2018-2019 VINSE/VSVS Rural Series and Parallel Circuits (Adapted from Student Guide for Electric Snap
VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE http://studentorgs.vanderbilt.edu/vsvs/ Electrical Circuits 2018-2019 VINSE/VSVS Rural Series and Parallel Circuits (Adapted from Student Guide for Electric Snap
Lab # 4 Parallel Circuits
 Lab # 4 Parallel Circuits Name(s) Obtain an Electro-Trainer and wire it exactly as shown (Be sure to use the 100 ohm resistor) 1) Record the volt drop and current flow for the Switch, the Resistor and
Lab # 4 Parallel Circuits Name(s) Obtain an Electro-Trainer and wire it exactly as shown (Be sure to use the 100 ohm resistor) 1) Record the volt drop and current flow for the Switch, the Resistor and
Science Olympiad Shock Value ~ Basic Circuits and Schematics
 Science Olympiad Shock Value ~ Basic Circuits and Schematics Use a single D battery, a single bare wire and a light bulb. Find four different ways to light the light bulb using only a battery, one wire
Science Olympiad Shock Value ~ Basic Circuits and Schematics Use a single D battery, a single bare wire and a light bulb. Find four different ways to light the light bulb using only a battery, one wire
Chapter Assessment Use with Chapter 22.
 Date Period 22 Use with Chapter 22. Current Electricity Understanding Concepts Part A Use each of the following terms once to complete the statements below. ampere electric current potential difference
Date Period 22 Use with Chapter 22. Current Electricity Understanding Concepts Part A Use each of the following terms once to complete the statements below. ampere electric current potential difference
Lab 08: Circuits. This lab is due at the end of the laboratory period
 Name: Partner(s): 1114 section: Desk # Date: Purpose Lab 08: Circuits This lab is due at the end of the laboratory period The purpose of this lab is to gain experience with setting up electric circuits
Name: Partner(s): 1114 section: Desk # Date: Purpose Lab 08: Circuits This lab is due at the end of the laboratory period The purpose of this lab is to gain experience with setting up electric circuits
ACTIVITY 1: Electric Circuit Interactions
 CYCLE 5 Developing Ideas ACTIVITY 1: Electric Circuit Interactions Purpose Many practical devices work because of electricity. In this first activity of the Cycle you will first focus your attention on
CYCLE 5 Developing Ideas ACTIVITY 1: Electric Circuit Interactions Purpose Many practical devices work because of electricity. In this first activity of the Cycle you will first focus your attention on
Current, resistance and potential difference
 Multiple choice questions 1. Three conductors join as shown in the diagram. The direction of the current in each conductor is shown by the arrow. Y Z X The current in the conductor Z is 10 A. The current
Multiple choice questions 1. Three conductors join as shown in the diagram. The direction of the current in each conductor is shown by the arrow. Y Z X The current in the conductor Z is 10 A. The current
PHY152H1S Practical 3: Introduction to Circuits
 PHY152H1S Practical 3: Introduction to Circuits Don t forget: List the NAMES of all participants on the first page of each day s write-up. Note if any participants arrived late or left early. Put the DATE
PHY152H1S Practical 3: Introduction to Circuits Don t forget: List the NAMES of all participants on the first page of each day s write-up. Note if any participants arrived late or left early. Put the DATE
Electricity Unit Review
 Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
EPSE Project 1: Sample Diagnostic Questions - Set 3
 EPSE Project 1: Sample Diagnostic Questions - Set 3 Circuit behaviour These questions probe pupils understanding of the behaviour of simple electric circuits. Most are about series circuits, and check
EPSE Project 1: Sample Diagnostic Questions - Set 3 Circuit behaviour These questions probe pupils understanding of the behaviour of simple electric circuits. Most are about series circuits, and check
Data Sheet for Series and Parallel Circuits Name: Partner s Name: Date: Period/Block:
 Data Sheet for Series and Parallel Circuits Name: Partner s Name: Date: _ Period/Block: _ Build the two circuits below using two AAA or AA cells. Measure and record Voltage (Volts), Current (A), and Resistance
Data Sheet for Series and Parallel Circuits Name: Partner s Name: Date: _ Period/Block: _ Build the two circuits below using two AAA or AA cells. Measure and record Voltage (Volts), Current (A), and Resistance
Electric Circuits. Lab. FCJJ 16 - Solar Hydrogen Science Kit. Next Generation Science Standards. Initial Prep Time. Lesson Time. Assembly Requirements
 Next Generation Science Standards NGSS Science and Engineering Practices: Asking questions and defining problems Developing and using models Planning and carrying out investigations Analyzing and interpreting
Next Generation Science Standards NGSS Science and Engineering Practices: Asking questions and defining problems Developing and using models Planning and carrying out investigations Analyzing and interpreting
2. A student sets up the circuit shown. The switch is open (off). Which lamps are on and which lamps are off?
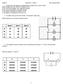 1. A polythene rod repels an inflated balloon hanging from a nylon thread. What charges must the rod and the balloon carry? A The rod and the balloon carry opposite charges. B The rod and the balloon carry
1. A polythene rod repels an inflated balloon hanging from a nylon thread. What charges must the rod and the balloon carry? A The rod and the balloon carry opposite charges. B The rod and the balloon carry
Resistance. Resistance is a property of matter that slows movement.
 Resistance Resistance Resistance is a property of matter that slows movement. The friction of a car s tires against the road is an example of resistance. The flow of water through a pipe is also an example
Resistance Resistance Resistance is a property of matter that slows movement. The friction of a car s tires against the road is an example of resistance. The flow of water through a pipe is also an example
Circuit Notes. Def: 1. Power supply:
 Circuit Notes Def: Parts of a circuit 1. Power supply: Types: 1- photovoltaic cell: generates current when exposed to light. ex: solar calculator or watch. 2- Batteries and generators. 2. Wires: 3. Switch
Circuit Notes Def: Parts of a circuit 1. Power supply: Types: 1- photovoltaic cell: generates current when exposed to light. ex: solar calculator or watch. 2- Batteries and generators. 2. Wires: 3. Switch
EXPERIMENT 4 OHM S LAW, RESISTORS IN SERIES AND PARALLEL
 220 4- I. THEOY EXPEIMENT 4 OHM S LAW, ESISTOS IN SEIES AND PAALLEL The purposes of this experiment are to test Ohm's Law, to study resistors in series and parallel, and to learn the correct use of ammeters
220 4- I. THEOY EXPEIMENT 4 OHM S LAW, ESISTOS IN SEIES AND PAALLEL The purposes of this experiment are to test Ohm's Law, to study resistors in series and parallel, and to learn the correct use of ammeters
AP Physics B Ch 18 and 19 Ohm's Law and Circuits
 Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B Ch 18 and 19 Ohm's Law and Circuits MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A device that produces electricity
Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B Ch 18 and 19 Ohm's Law and Circuits MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A device that produces electricity
Lab #1: Electrical Measurements I Resistance
 Lab #: Electrical Measurements I esistance Goal: Learn to measure basic electrical quantities; study the effect of measurement apparatus on the quantities being measured by investigating the internal resistances
Lab #: Electrical Measurements I esistance Goal: Learn to measure basic electrical quantities; study the effect of measurement apparatus on the quantities being measured by investigating the internal resistances
Laboratory 2 Electronics Engineering 1270
 Laboratory 2 Electronics Engineering 1270 DC Test Equipment Purpose: This lab will introduce many of the fundamental test equipment and procedures used for verifying the operations of electrical circuits.
Laboratory 2 Electronics Engineering 1270 DC Test Equipment Purpose: This lab will introduce many of the fundamental test equipment and procedures used for verifying the operations of electrical circuits.
Unit P.2, P2.3. Currents in electric circuits E ½. F Fuel gauge indicator. Fuel tank. Ammeter. Float. Battery. Sliding contact. Pivot 12V.
 Currents in electric circuits 1. The diagram shows the fuel gauge assembly in a car. The sliding contact touches a coil of wire and moves over it. The sliding contact and the coil form a variable resistor.
Currents in electric circuits 1. The diagram shows the fuel gauge assembly in a car. The sliding contact touches a coil of wire and moves over it. The sliding contact and the coil form a variable resistor.
LABORATORY 2 MEASUREMENTS IN RESISTIVE NETWORKS AND CIRCUIT LAWS
 LABORATORY 2 MEASUREMENTS IN RESISTIVE NETWORKS AND CIRCUIT LAWS The objective of this experiment is to provide working knowledge of the ammeter, voltmeter, and ohmmeter as well as their limitations in
LABORATORY 2 MEASUREMENTS IN RESISTIVE NETWORKS AND CIRCUIT LAWS The objective of this experiment is to provide working knowledge of the ammeter, voltmeter, and ohmmeter as well as their limitations in
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Series and Parallel Circuits 1 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Series and Parallel Circuits 2 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are series and parallel circuits? 3 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Circuit components can
Series and Parallel Circuits 1 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Series and Parallel Circuits 2 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are series and parallel circuits? 3 of 23 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Circuit components can
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 Ohm s Law and Resistivity. Your name Lab section
 Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 Ohm s Law and Resistivity Your name Lab section 1. What do you investigate in this lab? 2. When 1.0-A electric current flows through a piece of cylindrical copper wire, the voltage
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 Ohm s Law and Resistivity Your name Lab section 1. What do you investigate in this lab? 2. When 1.0-A electric current flows through a piece of cylindrical copper wire, the voltage
Electric Circuits. Lab. FCJJ 16 - Solar Hydrogen Science Kit. Goals. Background
 Goals Build a complete circuit with a solar panel Power a motor and electrolyzer with a solar panel Measure voltage and amperage in different circuits Background Electricity has fundamentally changed the
Goals Build a complete circuit with a solar panel Power a motor and electrolyzer with a solar panel Measure voltage and amperage in different circuits Background Electricity has fundamentally changed the
Two Stroke Engines Snowmobile Engines Disassembly
 Name: Two Stroke Engines Snowmobile Engines Disassembly Objectives: The Student Will Be Able To: 1. Appreciate teaching methods and safety practices used in the small engine disassembly/assembly; 2. Properly
Name: Two Stroke Engines Snowmobile Engines Disassembly Objectives: The Student Will Be Able To: 1. Appreciate teaching methods and safety practices used in the small engine disassembly/assembly; 2. Properly
Write the term that correctly completes the statement. Use each term once. ampere. electric current. resistor battery.
 Date Period Name CHAPTER 22 Study Guide Current Electricity Vocabulary Review Write the term that correctly completes the statement. Use each term once. ampere electric current resistor battery kilowatt-hour
Date Period Name CHAPTER 22 Study Guide Current Electricity Vocabulary Review Write the term that correctly completes the statement. Use each term once. ampere electric current resistor battery kilowatt-hour
Electricity. Electric Charge. Before You Read. Read to Learn. Positive and Negative Charges. Picture This. section.
 chapter 6 Electricity 1 section Electric Charge What You ll Learn how electric charges exert forces about conductors and insulators how things become electrically charged Before You Read Think about some
chapter 6 Electricity 1 section Electric Charge What You ll Learn how electric charges exert forces about conductors and insulators how things become electrically charged Before You Read Think about some
12.7 Power in Electric Circuits
 1.7 1.7 Power in Electric Circuits To predict the amount of energy used by an electrical device, such as a radio, stove, lights, or television, we first need to know the amount of time the device will
1.7 1.7 Power in Electric Circuits To predict the amount of energy used by an electrical device, such as a radio, stove, lights, or television, we first need to know the amount of time the device will
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS HRA101 ELECTRICITY FOR HVAC. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: William Kaune. Revised Date: March 17, 2014
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS HRA101 ELECTRICITY FOR HVAC 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: William Kaune Revised Date: March 17, 2014 Dena McCaffrey, Ed.D., Dean, Career & Technical Education HRA101 Electricity
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS HRA101 ELECTRICITY FOR HVAC 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: William Kaune Revised Date: March 17, 2014 Dena McCaffrey, Ed.D., Dean, Career & Technical Education HRA101 Electricity
Engaging Inquiry-Based Activities Grades 3-6
 ELECTRICITY AND CIRCUITS Engaging Inquiry-Based Activities Grades 3-6 Janette Smith 2016 Janette Smith 2016 1 What s Inside Activity 1: Light it Up!: Students investigate different ways to light a light
ELECTRICITY AND CIRCUITS Engaging Inquiry-Based Activities Grades 3-6 Janette Smith 2016 Janette Smith 2016 1 What s Inside Activity 1: Light it Up!: Students investigate different ways to light a light
Level 3 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of electrical systems Batteries and Kirchoff s Laws - Answers
 Level 3 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of electrical systems Batteries and Kirchoff s Laws - Answers In 03, AS 956 replaced AS 9053. The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. In AS 9053 there was
Level 3 Physics: Demonstrate understanding of electrical systems Batteries and Kirchoff s Laws - Answers In 03, AS 956 replaced AS 9053. The Mess that is NCEA Assessment Schedules. In AS 9053 there was
Basic voltmeter use. Resources and methods for learning about these subjects (list a few here, in preparation for your research):
 Basic voltmeter use This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Basic voltmeter use This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Current Score: 0/20. Due: Mon Feb :15 PM EST. Question Points. 0/40/100/40/10/1 Total 0/20. Description
 1 of 5 2/4/2010 3:35 PM Current Score: 0/20 Due: Mon Feb 15 2010 10:15 PM EST Question Points 1 2 3 4 5 0/40/100/40/10/1 Total 0/20 Description This assignment is worth 20 points. Each part is worth 1
1 of 5 2/4/2010 3:35 PM Current Score: 0/20 Due: Mon Feb 15 2010 10:15 PM EST Question Points 1 2 3 4 5 0/40/100/40/10/1 Total 0/20 Description This assignment is worth 20 points. Each part is worth 1
Electricity 2 Questions NAT 5
 Electricity 2 Questions NAT 5 1) a) A 25W lamp is designed to be used with the mains voltage. Calculate the resistance of the lamp. b) Four of the lamps are connected in parallel. Calculate the total resistance
Electricity 2 Questions NAT 5 1) a) A 25W lamp is designed to be used with the mains voltage. Calculate the resistance of the lamp. b) Four of the lamps are connected in parallel. Calculate the total resistance
ECSE-2100 Fields and Waves I Spring Project 1 Beakman s Motor
 Names _ and _ Project 1 Beakman s Motor For this project, students should work in groups of two. It is permitted for groups to collaborate, but each group of two must submit a report and build the motor
Names _ and _ Project 1 Beakman s Motor For this project, students should work in groups of two. It is permitted for groups to collaborate, but each group of two must submit a report and build the motor
PHA3/W PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 3 Current Electricity and Elastic Properties of Solids
 Surname Centre Number Other Names Candidate Number Leave blank Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2005 Advanced Subsidiary Examination PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) PHA3/W Unit 3 Current
Surname Centre Number Other Names Candidate Number Leave blank Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2005 Advanced Subsidiary Examination PHYSICS (SPECIFICATION A) PHA3/W Unit 3 Current
Figure 1. Figure
 Q1.Figure 1 shows a circuit including a thermistor T in series with a variable resistor R. The battery has negligible internal resistance. Figure 1 The resistance temperature (R θ) characteristic for T
Q1.Figure 1 shows a circuit including a thermistor T in series with a variable resistor R. The battery has negligible internal resistance. Figure 1 The resistance temperature (R θ) characteristic for T
Period 11 Activity Sheet Solutions: Electric Current
 Period 11 Activity Sheet Solutions: Electric Current Activity 11.1: How Can Electric Charge Do Work? Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what
Period 11 Activity Sheet Solutions: Electric Current Activity 11.1: How Can Electric Charge Do Work? Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what
Overcurrent protection
 Overcurrent protection This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Overcurrent protection This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Lab 12: Faraday s Effect and LC Circuits
 Part 1) Faraday s Law OBJECTIVES In this part of the lab you will Use Faraday s law to predict the emf produced in a coil from a time-varying magnetic field Measure the emf produced in a coil for a time-varying
Part 1) Faraday s Law OBJECTIVES In this part of the lab you will Use Faraday s law to predict the emf produced in a coil from a time-varying magnetic field Measure the emf produced in a coil for a time-varying
