ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General
|
|
|
- Hilary Nash
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EG-37 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General System Comparison List System Outline SC430 LS430 EFI (Electronic Fuel Injection) (For details, see page EG-46) ESA Electronic Spark Advance (For details, see page EG-48) VVT-i Variable Valve Timing-intelligent (For details, see page EG-49) ETCS-i Electronic Throttle Control System-intelligent An L-type EFI system directly detects the intake air mass with a hot wire type air flow meter. The fuel injection system is a sequential multiport fuel injection system. Ignition timing is determined by the engine ECU based on signals from various sensors. Corrects ignition timing in response to engine knocking. 2 knock sensors are used to improve knock detection. The torque control correction during gear shifting has been used to minimize the shift shock. Controls the intake camshaft to an optimal valve timing in accordance with the engine condition. Optimally controls the throttle valve opening in accordance with the amount of accelerator pedal effort and the condition of the engine and the vehicle. (For details, see page EG-54) Torque activated power train control has been adopted. ACIS Acoustic Control Induction System (For details, see page EG-57) Cooling Fan Control (For details, see page EG-60) Fuel Pump Control (For details, see page EG-61) Oxygen Sensor Heater Control Air Conditioner Cut-Off Control Evaporative Emission Control Engine Immobiliser (For details, see page BE-107) Function to communicate with multiplex communication system (For details, see page BE-2) Diagnosis s (For details, see page EG-62) Fail-Safe (For details, see page EG-65) The intake air passage are switched according to the engine speed and throttle valve angle to increase performance in all speed ranges. An electric cooling fan system has been adopted. The engine ECU steplessly controls the speed of the fans in accordance with the engine coolant temperature, vehicle speed, engine speed, and air conditioner operating conditions. As a result, the cooling performance has been improved. The fuel pump speed is controlled by the fuel pump relay and the fuel pump resistor. A fuel cut control is adopted to stop the fuel pump when the airbag is deployed at the front or side collision. Maintains the temperature of the oxygen sensor at an appropriate level to increase accuracy of detection of the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. By controlling the air conditioner compressor ON or OFF in accordance with the engine condition, drivability is maintained. The engine ECU controls the purge flow of evaporative emissions (HC) in the charcoal canister in accordance with engine conditions. Prohibits fuel delivery and ignition if an attempt is made to start the engine with an invalid ignition key. Communicates with the meter ECU, A/ C ECU, etc., on the body side, to input/ output necessary signals. When the engine ECU detects a malfunction, the engine ECU makes a diagnosis and memorizes the failed section. To increase the speed for processing the signals, the 32-bit CPU of the engine ECU has been adopted. When the engine ECU detects a malfunction, the engine ECU stops or controls the engine according to the data already stored in the memory.
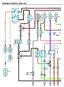
2 EG-38 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE 2. Construction The configuration of the engine control system in the 3UZ-FE engine of the SC430 is as shown in the following chart. SENSORS ACTUATORS AIR FLOW METER VG EFI CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR VVT SENSOR (Bank 1, Bank 2) Camshaft Position Signal THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR WATER TEMP. SENSOR INTAKE AIR TEMP. SENSOR NE G2 VVL VVR VTA VTA2 VPA VPA2 THW THA #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 #7 #8 IGT1, 4, 6, 7 IF1R, IF1L IGT2, 3, 5, 8 IF2R, IF2L No. 1 INJECTOR No. 2 INJECTOR No. 3 INJECTOR No. 4 INJECTOR No. 5 INJECTOR No. 6 INJECTOR No. 7 INJECTOR No. 8 INJECTOR ESA IGNITION COIL with IGNITER No. 1, 4, 6 and 7 IGNITION COIL with IGNITER No. 2, 3, 5 and 8 HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (Bank 1, Sensor 1) OXL1 Engine ECU SPARK PLUGS SPARK PLUGS No. 2, 3, 5 and 8 No. 1, 4, 6 and 7 HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (Bank 2, Sensor 1) OXR1 M ETCS-i THROTTLE CONTROL MOTOR HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (Bank 1, Sensor 2) OXL2 VVT-i HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (Bank 2, Sensor 2) KNOCK SENSORS OXR2 KNKL KNKR OCV OCR CAMSHAFT TIMING OIL CONTROL VALVE (Bank 1) CAMSHAFT TIMING OIL CONTROL VALVE (Bank 2) VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR (for Transmission) SP2 ACIS ACIS VSV IGNITION SWITCH Starting Signal (ST Terminal) Ignition Signal (IG Terminal) STA IGSW FPR FUEL PUMP CONTROL FUEL PUMP RELAY FUEL PUMP NEUTRAL START SWITCH Neutral Start Signal Shift Lever Position Signal P, N R, D, 3, 2 FC CIRCUIT OPENING RELAY AIR CONDITIONER CONTROL SHIFT LOCK ECU Shift Lever Position Signal 4, L ACMG AIR CONDITIONER MAGNET CLUTCH (Continued)
3 EG-39 PASSENGER SIDE J/B ECU MPX1 OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER CONTROL SNOW SNOW SWITCH PWR PATTERN SELECT SWITCH HTL HTR HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER (Bank 1, Sensor 1) HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER (Bank 2, Sensor 1) AIR CONDITIONER ECU MPX2 HTL2 HTR2 HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER (Bank 1, Sensor 2) HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER (Bank 2, Sensor 2) STOP LIGHT SWITCH SKID CONTROL ECU STP TRC ENG Engine ECU PRG EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL VSV (for EVAP) TRANSPONDER KEY ECU IMI IMO RFC COOLING FAN CONTROL COOLING FAN ECU CRUISE CONTROL SWITCH CCS MREL EFI MAIN RELAY DATA LINK CONNECTOR 3 SIL TC W ENGINE CHECK WARNING LIGHT EFI MAIN RELAY +B BATT BATTERY
4 EG-40 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Fuel Pump Resistor Circuit Opening Relay Fuel Pump Intake Air Relay Temp. Sensor Throttle Position Sensor Fuel Pump Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Charcoal Canister VSV (for EVAP) Air Flow Meter Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve VVT Sensor * 3 * 2 Throttle Control Motor Injector * 1 VSV (for ACIS) Injector Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve Camshaft Position Sensor VVT Sensor * 3 * 2 * 2 Knock Sensor Knock Sensor Crankshaft Position Sensor * 2 Engine ECU Battery Check Engine Warning Light DLC3 Air Conditioner Starter Vehicle Speed Sensor (for Transmission) Neutral Start Switch * 1 : Water Temp. Sensor * 2 : Heated Oxygen Sensor * 3 : Ignition Coil (with Igniter) Electronic Controlled Transmission Solenoid Valves 202EG04
5 EG Layout of Main Component Neutral Start Switch Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Air Flow Meter DLC3 Fuel Pump Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 2, Sensor 1) Throttle Position Sensor Throttle Control Motor Knock Sensor (Bank 2) VVT Sensor (Bank 2) Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 1, Sensor 2) Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 2, Sensor 2) Heated Oxygen Sensor (Bank 1, Sensor 1) VSV (for EVAP) Injector Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve (Bank 2) Knock Sensor (Bank 1) VVT Sensor (Bank 1) Ignition Coil (with Ignition) Water Temp. Sensor VSV (for ACIS) Crankshaft Position Sensor Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve (Bank 1) Camshaft Position Sensor 202EG05
6 EG-42 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE 5. Main Components of Engine Control System General The following table compares the main components. : Changed Engine Type 3UZ-FE 1UZ-FE Component Outline Quantity Outline Quantity Engine ECU 32-bit CPU 1 16-bit CPU 1 Air Flow Meter Hot-wire Type 1 Crankshaft Position Sensor (Rotor Teeth) Pick-up Coil Type (36-2) 1 Camshaft Position Sensor (Rotor Teeth) Pick-up Coil Type (1) 1 VVT Sensor (Rotor Teeth) Pick-up Coil Type (3) 2 Throttle Position Sensor Linear Type 1* Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Linear Type 1* Knock Sensor Built-in Piezoelectric Type 2 Oxygen Sensor (Bank 1, Sensor 1) (Bank 1, Sensor 2) with Heater Type 4 (Bank 2, Sensor 1) (Bank 2, Sensor 2) Injector 4-hole Type (with Air Assist) 8 *: 2 Output Type Engine ECU Changes The 32-bit CPU of the engine ECU has been changed from the 16-bit CPU to increase the speed for processing the signals. Service Tip The length of time to clear the DTC via the battery terminal has been changed from the previous 10 seconds to 1 minute. The engine ECU is installed in the engine ECU box in the engine compartment. As a result, the wiring harness has been shortened, thus realizing weight reduction. Utilizing the vacuum that is generated by the cooling fan, air flow is introduced through the engine ECU box to restrain the increase in the temperature in the engine ECU box. Front Front Engine ECU Box Radiator Intake Duct Exhaust Duct Air Flow Cooling Fan Exhaust Duct Engine ECU Intake Duct Engine ECU Side Member Engine ECU Box 199EG50
7 EG-43 Air Flow Meter This air flow meter, which is a plug-in type, allows a portion of the intake air to flow through the detection area. By directly measuring the mass and the flow rate of the intake air, the detection precision has been improved and the intake air resistance has been reduced. This air flow meter has a built-in intake air temperature sensor. Changes It has been made more compact and lightweight than on the previous air flow meter. Intake Air Temp. Sensor Intake Air Temp. Sensor Platinum Hot-Wire Air Flow 199EG35 Crankshaft Position Sensor The timing rotor of the crankshaft consists of 34 teeth, with 2 teeth missing. The crankshaft position sensor outputs the crankshaft rotation signals every 10, and the missing teeth are used to determine the top-deadcenter. Timing Rotor Ne Signal Plate (720CA) Crankshaft Position Sensor 2 Teeth Missing 10CA 2 Teeth Missing 199EG36
8 EG-44 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE Camshaft Position Sensor The camshaft position sensor is mounted on the left bank cylinder head. To detect the camshaft position, a protrusion that is provided on the timing pulley is used to generate 1 pulse for every 2 revolution of the crankshaft. Timing Rotor G Signal Plate (720CA) Camshaft Position Sensor 199EG37 VVT Sensor A VVT sensor is mounted on the intake side of each cylinder head. To detect the camshaft position, a timing rotor that is provided on the intake camshaft is used to generate 3 pulses for every 2 revolutions of the crankshaft. Timing Rotor VVT Sensor VVT Signal Plate (720CA) 270CA 270CA 180CA 199EG38
9 EG-45 Throttle Position Sensor This sensor converts the throttle valve opening angles into electronic signals with two differing characteristics and outputs them to the engine ECU. One is the VTA signal that linearly outputs the voltage along the entire range of the throttle valve opening angle. The other is the VTA2 signal that outputs an offset voltage. Close Open Open Close E2 VTA2 VTA VC V 5.0 VTA2 Throttle Position Sensor Output Voltage VTA 0 Close Open 199EG39 Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor This sensor converts the accelerator pedal depressed angles into electric signals with two differing characteristics and outputs them to the engine ECU. One is the VPA signal that linearly outputs the voltage along the entire range of the accelerator pedal depressed angle. The other is the VPA2 signal that outputs on offset voltage. Changes (from 1UZ-FE Engine) The accelerator pedal position sensor is attached to the accelerator pedal. Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Open Close Close Open EP2 VPA2 VCP2 EP1 VPA VCP1 5 Output Voltage VPA2 VPA Close Open Accelerator Pedal Depressed Angle 199EG40
10 EG-46 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE 6. EFI (Electronic Fuel Injection) System General An L-type EFI system directly detects the intake air mass with a hot wire type air flow meter. An independent injection system (in which fuel is injected once into each cylinder for each two revolutions of the crankshaft) has been adopted. There are two types of fuel injection: One is synchronous injection in which corrections based on the signals from the sensors are added to the basic injection time so that injection occurs always at the same position. The other is non-synchronous injection in which injection is effected by detecting the requests from the signals of the sensors regardless of the crankshaft angle. Furthermore, to protect the engine and improve fuel economy, the system effects fuel cutoff in which the injection of fuel is stopped temporarily in accordance with the driving conditions. Synchronous Injection #1 #8 #4 #3 #6 #5 #7 #2 Intake Combustion Independent Injection (Fuel injected into each cylinder) Ignition Non-Synchronous Injection 199EG41 System Operation 1) Synchronous Injection The synchronous injection time can be expressed by the formula given below. During the starting of the engine, the injection time is determined in accordance with the engine speed, battery voltage, and the engine coolant temperature. To prevent excessive amounts of fuel from being injected during starting, the injection volume is regulated in accordance with the cranking time. Synchronous Injection = A. Basic Injection Time + B. Correction Injection Time + C. Ineffective Injection Coefficient
11 EG-47 A. Basic Injection Time B. Correction Injection Time Intake Temperature Correction Post-Warm-Up Enrichment Correction Post-Start Enrichment Correction Transient Air-Fuel Ratio Correction Wall Adhesion Correction High-Load Enrichment Correction Constant Fuel Pressure Control Air-Fuel Ratio Feedback Control C. Ineffective Injection Coefficient It is the basic injection time that is determined by the intake air volume and the engine speed. It is a coefficient that is used to achieve the air-fuel mixture that is appropriate for the engine condition at that time, in accordance with the signals from the sensors. Enriches the mixture when the intake air temperature is low because the air density is high. Enriches the mixture when the engine coolant temperature is low to ensure drivability during cold operation. Enriches the mixture after the engine is started in accordance with the engine coolant temperature and the engine speed in order to ensure a stable engine operation after starting. The enrichment is at the highest ratio immediately after the engine is started, and decreases gradually thereafter. Enriches or leans the mixture in accordance with the acceleration or deceleration conditions determined by the changes in the intake air volume. Correction is made by calculating the adhesion of fuel to the wall surface based on the engine coolant temperature, engine speed, and throttle valve opening. Prevents the exhaust temperature from rising by detecting the high-load driving conditions in accordance with the signals from the sensors and enriching the mixture. Corrects the deviation of the fuel injection volume that results from the changes in the intake manifold pressure to achieve a constant pressure. Controls the air-fuel ratio to a narrow range near the stoichiometric ratio (in which the cleaning performance of the three-way catalyst is at the highest level) by making corrections based on the signals from the heated oxygen sensor. Corrects the operation lag of the injectors 2) Non-Synchronous Injection Apart from the normal (synchronous) fuel injection, this function simultaneously injects a prescribed volume of fuel to all the cylinders only immediately after the signals from the sensors are input, in order to ensure the proper startability and acceleration response. During synchronous injection, the injection time is extended for the amount of non-synchronous injection. The following are the three types of non-synchronous injection: Starting Non-Synchronous Injection Acceleration Non-Synchronous Injection Engine Speed Drop Non-Synchronous Injection Effects non-synchronous injection once immediately after the starter signal is input, thus improving startability. Effects non-synchronous injection when the increased amount of the throttle valve opening is greater than the preset value, to improve response during acceleration. Effects non-synchronous injection when the engine speed drops suddenly during a fuel cutoff or when resuming from a fuel cutoff, thus ensuring the proper drivability.
12 EG-48 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE 3) Fuel Cutoff The following are the three types of fuel cutoff: Deceleration Fuel Cutoff Engine Speed Fuel Cutoff N D Shift Fuel Cutoff Stops the injection of fuel when the engine speed is higher than the specified value (1400 rpm) during deceleration (throttle OFF detected by engine ECU). This prevents the TWC (Three-Way Catalyst) from overheating due to misfiring and improves fuel economy. The fuel cutoff and resumption speeds are higher when the coolant temperature is low. Stops the injection of fuel when the engine speed is higher than the specified value (6450 rpm) to prevent over-revolution. Stops the injection of fuel for a prescribed length of time when shifting from N to D, if the engine speed is higher than the specified value to reduce shift shock. 7. ESA (Electronic Spark Advance) System This system selects the optimal ignition timing in accordance with the signals received from the sensors and sends the (IGt) ignition signal to the igniter. The ignition timing can be expressed by the formula given below. The default ignition timing is set to 5 BTDC. Ignition Timing = A. Default Ignition Timing or B. Basic Timing Advance + C. Correction Timing Advance A. Fixed Timing Advance Characteristic B. Basic Timing Advance Characteristic C. Correction Timing Advance Characteristic Warm-Up Timing Advance Characteristic Idle Stabilization Timing Advance Characteristic Fuel Cutoff Resumption Timing Retard Acceleration Timing Retard Knock Correction Timing Retard During the starting of the engine, the timing is fixed to 5 BTDC. If the throttle valve is turned OFF by shorting the service terminals, the timing becomes fixed to 10 BTDC. The optimal ignition timing is selected from the map based on the signals received from the sensors. Appropriately advances or retards the timing in accordance with the conditions of the engine based on the signals received from the sensors. Advances the ignition timing in accordance with the driving conditions when the engine coolant temperature is low, in order to improve drivability. Advances the ignition timing when the idle speed decreases, in order to stabilize the idle speed. Conversely, retards the timing if the idle speed increases. Retards the ignition timing when the fuel injection is resumed from a fuel cutoff, in order to lessen the shock. Temporarily retards the ignition timing during acceleration in order to improve drivability. Corrects the ignition timing in accordance with the signals received from the knock sensor when knocking occurs. Depending on the extent of the knocking that is detected, this function retards the timing by a prescribed angle at a time until there is no more knocking. After no more knocking occurs, this function advances the timing by a prescribed angle at a time. If knocking occurs again while advancing the timing, it retards the timing again. Maximum Timing Advance: 48 BTDC Minimum Timing Advance: 10 ATDC
13 EG VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing intelligent) System General The VVT-i system is designed to control the intake camshaft within a wide range of 45 (of crankshaft angle) to provide a valve timing that is optimally suited to the engine condition, thus realizing improved torque in all the speed ranges and fuel economy, and reduce exhaust emissions. Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve Engine ECU Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Sensor VVT-i Controllers VVT Sensor VVT Sensor Water Temp. Sensor Crankshaft Position Sensor Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve Oil Pump 199EG42 In proportion to the engine speed, intake air volume, throttle position and engine coolant temperature, the engine ECU calculates an optimal valve timing under each driving condition and control the camshaft timing oil control valve. In addition, engine ECU uses signal from the VVT sensors and the crankshaft position sensor to detect the actual valve timing, thus performing feedback control to achieve the target valve timing. Engine ECU Crankshaft Position Sensor Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Sensor Water Temp. Sensor VVT Sensors Target Valve Timing Feedback Correction Actual Valve Timing Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valves Duty Control 157EG23 Changes (from 1UZ-FE Engine) Due to the engine characteristics, the operation range of the VVT-i system has been changed from 50 (of crankshaft angle) to 45. This is determined by the helical spline angle of the VVT-i controller.
14 EG-50 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE Construction 1) VVT-i Controller The VVT-i controller comprises the outer gear that is driven by the timing belt, the inner gear that is affixed to the camshaft and a movable piston that is placed between the outer gear and inner gear. Having helical splines (twisted, vertical grooves) on its inner and outer periphery, the piston moves in the axial direction to shift the phase of the outer gear and inner gear, thus causing the valve timing to change continuously. The VVT tube drives the exhaust camshaft via the scissors gear that is installed on the back. Timing Pulley VVT Tube Piston Intake Camshaft Inner Gear Outer Gear Exhaust Camshaft Scissors Gear 151EG29 2) Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve The camshaft timing oil control valve controls the spool valve position in accordance with the duty control from the engine ECU. When the engine is stopped, the camshaft timing oil control valve is in the most retarded state. To VVT-i Controller (Advance Side) To VVT-i Controller (Retard Side) Coil Drain Drain Spring Oil Pressure Spool Valve Plunger 165EG34
15 EG-51 Operation The camshaft timing oil control valve selects the path to the VVT-i controller according to the advance, retard or hold signal from the engine ECU. The VVT-i controller rotates the intake camshaft in the timing advance or retard position or holds it according to the position where the oil pressure is applied. Operation Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve Drive Signal Description Advance Piston Timing Pulley Intake Camshaft Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve Drain Oil Pressure 188EG48 Advance Signal Duty Ratio 157EG35 When the camshaft timing oil control valve is positioned as illustrated in accordance with the advance signal from the engine ECU, the oil pressure is applied to the chamber at the advance side. Then, the twist of the helical spline causes the camshaft to rotate in the direction of timing advance. Retard Drain Oil Pressure 188EG49 Retard Signal Duty Ratio 157EG36 When the camshaft timing oil control valve is positioned as illustrated in accordance with the retard signal from the engine ECU, the oil pressure is applied to the chamber at the retard side. Then, the twist of the helical spline causes the camshaft to rotate in the direction of timing retard. Hold 188EG50 Hold Signal Duty Ratio 157EG37 The engine ECU calculates the target timing angle according to the traveling state to perform control as described above. After setting at the target timing, the valve timing is held by keeping the camshaft timing oil control valve in the neutral position unless the traveling state changes. This adjusts the valve timing at the desired target position and prevents the engine oil from running out when it is unnecessary.
16 EG-52 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE Operation During Various Driving Condition (Conceptual Diagram) Full Load Performance Range 4 Range 5 Engine Load Range 3 Range 1, 2 Engine Speed 150EG34 Operation State Range Valve Timing Objective Effect During Idling 1 EX TDC Latest Timing IN Eliminating overlap to reduce blow back to the intake side Stabilized idling rpm Better fuel economy BDC 188EG51 To Retard Side At Light Load 2 EX IN Decreasing overlap to eliminate blow back to the intake side Ensured engine stability 188EG64 To Advance Side At Medium load 3 EX IN Increasing overlap to increase internal EGR for pumping loss elimination Better fuel economy Improved emission control 188EG65
17 EG-53 Operation State Range Valve Timing Objective Effect TDC In Low to Medium Speed Range with Heavy Load 4 EX BDC IN To Advance Side 188EG66 Advancing the intake valve close timing for volumetric efficiency improvement Improved torque in low to medium speed range In High Speed Range with Heavy Load 5 EX IN Retarding the intake valve close timing for volumetric efficiency improvement Improved output To Retard Side 188EG67 Latest Timing At Low Temperatures EX IN Eliminating overlap to prevent blow back to the intake side leads to the lean burning condition, and stabilizes the idling speed at fast idling. Stabilized fast idle rpm Better fuel economy 188EG52 Latest Timing Upon Starting/ Stopping the Engine EX IN Eliminating overlap to minimize blow back to the intake side Improved startability 188EG53
18 EG-54 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE 9. ETCS-i (Electronic Throttle Control System-intelligent) General In the conventional throttle body, the throttle valve opening is determined invariably by the amount of the accelerator pedal effort. In contrast, the ETCS-i uses the engine ECU to calculate the optimal throttle valve opening that is appropriate for the respective driving condition and uses a throttle control motor to control the opening. Changes (from 1UZ-FE Engine) The torque-activated power train control has been newly adopted. This control enables the engine to generate the necessary torque as desired by the driver, as well as to realize a smooth engine output characteristic. The accelerator cable and link have been discontinued, and an a accelerator position sensor has been provided on the accelerator pedal. Accordingly the limp-mode control during the fail-safe mode has been changed. System Diagram Throttle Valve Throttle Position Sensor Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Throttle Control Motor Skid Control ECU Air Flow Meter Engine ECU Passenger Side J/B ECU Pattern Select Switch SNOW Switch BEAN (Instrument Panel Bus) Ignition Coil Fuel Injector 202EG09
19 EG-55 Operation 1) General The engine ECU drives the throttle control motor by determining the target throttle valve opening in accordance with the respective operation condition. Torque Activated Power Train Control Normal-mode Control, Power mode Control, and SNOW-mode Control Idle Speed Control Shift Shock Reduction Control TRC Throttle Control VSC Coordination Control Cruise Control 2) Torque Activated Power Train Control Controls the throttle to an optimal throttle valve opening that is appropriate for the driving condition such as the amount of the accelerator pedal effort and the engine operating condition. As a result, excellent throttle control and comfort in all operating ranges, as well as smooth startoff acceleration and elastic acceleration have been achieved. Vehicle s Longitudinal G with Control without Control 0 Time Throttle Valve Opening Angle Accelerator Pedal Depressed Angle 0 0 Constant Opening 188EG58
20 EG-56 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE 3) Normal-mode, Power-mode, SNOW-mode Controls a. Normal-mode Control Controls the throttle to an optimal throttle valve opening that is appropriate for the driving condition such as the amount of the accelerator pedal effort and the engine operating condition in order to realize excellent throttle control and comfort in all operating ranges. b. Power-mode Control If turning ON the POWER switch of the pattern select switch and selecting the power-mode, the throttle valve opening angle is controlled to react more directly to operation of the accelerator pedal than the normal mode. With this, sporty driving is realized. c. SNOW-mode Control In situations in which low- surface conditions can be anticipated, such as when driving in the snow, the throttle valve can be controlled to help vehicle stability while driving over the slippery surface. This is accomplished by turning on the SNOW switch of the pattern select switch, which, in response to the amount of the accelerator pedal effort that is applied, reduces the engine output from that of the normal driving level. Power-mode Throttle Valve Opening Angle Normal-mode SNOW-mode Accelerator Pedal Opening Angle Conceptual Diagram 189EG38 4) Idle Speed Control Controls the engine ECU and the throttle valve in order to constantly effect ideal idle speed control. 5) Shift Shock Reduction Control The throttle control is synchronized to the ECT (Electronically Controlled Transmission) control during the shifting of the transmission in order to reduce the shift shock. 6) TRC Throttle Control As part of the TRC system, the throttle valve is closed by a demand signal from the skid control ECU if an excessive amount of slippage is created at a driving wheel, thus facilitating the vehicle in ensuring stability and driving force. 7) VSC Coordination Control In order to bring the effectiveness of the VSC system control into full play, the throttle valve opening angle is controlled by effecting a coordination control with the skid control ECU. 8) Cruise Control An engine ECU with an integrated cruise control ECU directly actuates the throttle valve to effect the operation of the cruise control.
21 EG ACIS (Acoustic Control Induction System) General The ACIS (Acoustic Control Induction System) is realized by using a bulkhead to divide the intake manifold into 2 stages, with an intake air control valve in the bulkhead being opened and closed to vary the effective length of the intake manifold in accordance with the engine speed and throttle valve opening angle. This increases the power output in all ranges from low to high speed. Changes (from 1UZ-FE Engine) Due to the engine characteristics, the operation range of the ACIS has been changed. System Diagram Throttle Position Sensor Actuator Intake Air Control Valve VSV Vacuum Tank Engine ECU Crankshaft Position Sensor 151EG13
22 EG-58 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE Construction 1) Intake Air Control Valve The intake air control valve, which is provided in the middle of the intake manifold in the intake air chamber, opens and closes to change the effective length of the intake manifold in two stages. Intake Air Control Valve Front 2) VSV (Vacuum Switching Valve) Controls the vacuum that is applied to the actuator by way of the signal (ACIS) that is output by the engine ECU. Actuator 188EG35 From Vacuum Tank To Actuator Atmosphere è 151EG42 3) Vacuum Tank Equipped with an internal check valve, the vacuum tank stores the vacuum that is applied to the actuator in order to maintain the intake air control valve fully closed even during low-vacuum conditions.
23 EG-59 Operation 1) When the Intake Control Valve Closes (VSV ON) The engine ECU activates the VSV to match the longer pulsation cycle so that the negative pressure acts on the diaphragm chamber of the actuator. This closes the control valve. As a result, the effective length of the intake manifold is lengthened and the intake efficiency in the low-to-medium speed range is improved due to the dynamic effect of the intake air, thereby increasing the power output. : Effective Intake Manifold Length VSV ON Throttle Valve Opening Angle EG14 2) When the Intake Control Valve Open (VSV OFF) Engine Speed 4700 (rpm) 189EG22 The engine ECU deactivates the VSV to match the shorter pulsation cycle so that atmospheric air is led into the diaphragm chamber of the actuator and opens the control valve. When the control valve is open, the effective length of the intake air chamber is shortened and peak intake efficiency is shifted to the high engine speed range, thus providing greater output at high engine speeds. : Effective Intake Manifold Length VSV OFF 151EG15 Throttle Valve Opening Angle 60 Engine Speed 4700 (rpm) 189EG23
24 EG-60 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE 11. Cooling Fan System General To achieve an optimal fan speed in accordance with the engine coolant temperature, vehicle speed, engine speed, and air conditioning operating conditions, the engine ECU calculates the proper fan speed and sends the signals to the cooling fan ECU. Upon receiving the signals from the engine ECU, the cooling fan ECU actuates the fan motors. Also, the fan speed is controlled by engine ECU using the stepless control. Wiring Diagram Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor Crankshaft Position Sensor Engine ECU Vehicle Speed Signal (for Transmission) BEAN (Instrument Panel Bus) A/C ECU A/C Switch A/C Pressure Sensor From Battery Fan Main Relay From Ignition Relay Cooling Fan ECU Fan Motor No. 1 (Main) Fan Motor No. 2 (Sub) Operation As illustrated below, the engine ECU determines the required fan speed by selecting the fastest fan speed from among the following: (A) The fan speed required by the engine coolant temperature. (B) The fan speed required by the air condition refrigerant pressure. (C) The fan speed required by the engine speed. (D) The fan speed required by the vehicle speed. The cooling fan ECU controls fan motors No. 1 and No. 2 in accordance with the signals received from the engine ECU. (A) (B) 199EG44 Fan Speed Fan Speed Engine Coolant Temperature 189EG13 Refrigerant Pressure 189EG14 (C) Fan Speed (D) Fan Speed Engine Speed 189EG15 Vehicle Speed 189EG16
25 EG Fuel Pump Control This control system increases the fuel pump output by switching the fuel pump speed to high if a large amount of fuel is required by the engine ECU. In normal operations where the engine speeds are low, the fuel pump rotates at low speed to reduce unnecessary consumption of electric power and to manitain fuel pump durability. A fuel cut control is adopted to stop the fuel pump when the airbag is deployed at the front or side collision. In this system, the airbag deployment signal from the airbag sensor assembly is detected by the engine ECU, which turns OFF the circuit opening relay. After the fuel cut control has been activated, turning the ignition switch from OFF to ON cancels the fuel cut control, thus engine can be restarted. Front Airbag Sensor Assembly Side Airbag Sensor Assembly Airbag Sensor Assembly BEAN Engine ECU Fuel Pump Relay Circuit Opening Relay Fuel Pump Resistor Fuel Pump Motor 199EG52
26 EG-62 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE 13. Diagnosis When the engine ECU detects a malfunction, the engine ECU makes a diagnosis and memorizes the failed section. Furthermore, the check engine warning light in the combination meter illuminates or blinks to inform the driver. The engine ECU will also store the DTCs of the malfunctions. The DTCs can be accessed the use of the hand-held tester or SST ( ). For details, see the LEXUS SC430 Repair Manual (Pub. No. RM858E). Changes (from 1UZ-FE Engine) The diagnosis system of the Europe model has adopted the EURO-OBD (Europe On-Board Diagnosis) that complies with European regulations. The diagnosis system of the Australia model has adopted the M-OBD (Multiplex On-Board Diagnosis). Item EURO-OBD, M-OBD DLC3 TC TAC Data Link Connector CG 165EG39 SIL Diagnostic Trouble Code Check Method CG: Chassis Ground SIL: Provides communication between the engine ECU and the hand-held tester. TAC: Outputs the engine speed signal. TC: Provides the same function as the previous TE1 and Tc terminals. The diagnostic trouble codes can be displayed by connecting a hand-held tester to the DLC3. After terminals TC and CG of the DLC3 are connected, the codes are displayed on the check engine warning light in the combination meter.
27 EG-63 Furthermore, the functions listed below can be utilized by connecting the hand-held tester to the DLC3. The diagnosis system of the EURO-OBD system and M-OBD system are compared below. Function Diagnostic Trouble Code Continuous Test Results Freeze-Frame Data Output Engine ECU Data Active Test Trouble Code Clear Check Engine Warning Light Clear Details The system can output 5-digit diagnostic trouble codes to the tester, which are more detailed than the previous 2-digit diagnostic trouble codes, thus making if easier to identify the location of the problem. Example: Code 28 (Oxygen Sensor) P0130 (Oxygen Sensor) P0135 (Oxygen Sensor Heater) However, in the EURO-OBD system, the diagnostic trouble codes that are not output by the M-OBD, such as misfires, are also output. Refer to the LEXUS SC430 Repair Manual (Pub. No. RM858E). A diagnostic trouble code may require a condition to be present for several drive cycles, while the equivalent continuous test code may be set with the first occurrence of the condition. The system can output freeze-frame data to the tester. This data (while depicts the condition of the engine control system and the vehicle) is stored in the engine ECU at the very moment when the engine ECU has detected its last data of malfunction. The engine ECU s control data can be output. Output Data Speed: 9.6 kbps Through the use of the tester, the actuators (VSV, fuel pump, VVT-i system, etc.) cane activated to a desired state. Through the use of the tester, trouble codes that are stored in the engine ECU can be cleared. If the engine ECU detects the malfunction of the vehicle, it makes the check engine warning light come on. Later, if that malfunction will not occur again, it automatically turns off the check engine warning light. If the engine ECU detects the malfunction of the vehicle, it makes the check engine warning light come on. Later, if the same malfunction will not occur again during 3 trips continuously, it automatically turns off the check engine warning light. EURO -OBD M-OBD For details on the diagnostic trouble codes, active test, etc. described above, refer to the LEXUS SC430 Repair Manual (Pub., No. RM858E). For details of the hand-held tester, refer to the Hand-Held Tester Operator s Manual.
28 EG-64 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE The DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes) listed below have been added or discontinued. EURO-OBD Added DTCs DTC No. Detection Item DTC No. Detection Item P0116/22 P0125/91 P0133/21 P0153/28 P0172/26 Engine Coolant Temp. Circuit P0307/94 Cylinder 7 Misfire Detected Range/Performance Problem P0308/94 Cylinder 8 Misfire Detected Insufficient Coolant Temp. for Closed Loop Fuel Control Oxygen Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1, Sensor 1) P0420/94 P0430/94 Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2) Oxygen Sensor Circuit Slow Evaporative Emission Control Response (Bank 2, Sensor 1) P0443/94 System Purge Control Vent System too Rich Control Malfunction (A/F Rich Malfunction, Bank 1) P0505/33 Idle Control System Malfunction P0175/26 System too Rich VVT Sensor/Camshaft Position (A/F Rich Malfunction, Bank 2) P1346/18 Sensor Circuit Range/Performance P0300/93 Random/Multiple Cylinder Problem (Bank 1) Misfire Detected VVT Sensor/Camshaft Position P0301/94 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected P1351/18 Sensor Circuit Range/Performance P0302/94 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected Problem (Bank 2) P0303/94 Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected P0304/94 Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected P1520/95 Stop Light Switch Signal Malfunction P0305/94 Cylinder 5 Misfire Detected P1600/96 Engine ECU BATT Malfunction P0306/94 Cylinder 6 Misfire Detected P1651/96 VSV for ACIS Circuit Malfunction M-OBD Added DTCs EURO-OBD and OBD Discontinued DTC DTC No. Detection Item VVT Sensor/Camshaft Position P1346/18 Sensor Circuit Range/ Performance Problem (Bank 1) VVT Sensor/Camshaft Position P1351/18 Sensor Circuit Range/ Performance Problem (Bank 2) P1520/95 Stop Light Switch Signal Malfunction DTC No. P1126/89 Detection Item Magnetic Clutch Circuit Malfunction
29 EG Fail-Safe General When the engine ECU detects a malfunction, the engine ECU stops or controls the engine according to the data already stored in the memory. Fail-Safe Control List : Changes Location of Malfunction Air Flow Meter Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (For details, see page EG-67) Throttle Position Sensor (For details, see page EG-67) Water Temp. Sensor and Intake Air Temp. Sensor Knock Sensor Ignition Coil (with Igniter) Camshaft Position Sensor and VVT Sensor Description of Control In case of a signal malfunction, the engine could operate poorly or the catalyst could overheat if the engine continues to be controlled with the signals from the sensors. Therefore, the engine ECU effects control by using the values in the engine ECU or stops the engine. In case of a signal malfunction, the engine ECU calculates the accelerator pedal opening angle that is limited by the dual system sensor value and continues effecting throttle valve control. If both systems malfunction, the engine ECU considers that the accelerator pedal is fully closed. In case of a signal malfunction, the engine ECU cuts off the current to the throttle control motor. The throttle valve returns to the prescribed opening by the force of the return spring. The engine ECU then adjusts the engine output by controlling the fuel injection and ignition timing in accordance with the accelerator pedal opening angle to enable the vehicle to continue driving. In case of a signal malfunction, the use of the values from the sensors will make the air-fuel ratio become too rich or too lean, which could cause the engine to stall or to run poorly during cold operation. Therefore, the engine ECU fixes the air-fuel ratio to the stoichiometric ratio and uses the constant values of 80C engine coolant temperature and 20C intake air temperature to perform the calculation. In case of a malfunction in the knock sensor or in the knocking signal system (open or short circuit), the engine could become damaged if the timing is advanced despite the presence of knocking. Therefore, if a malfunction is detected in the knock sensor system, the engine ECU turns the timing retard correction of the knock sensor into the maximum retard value. In case of a malfunction in the ignition system, such as an open circuit in the ignition coil, the catalyst could become overheated due to engine misfire. Therefore, if the (IGf) ignition signal is not input twice or more in a row, the engine ECU determines that a malfunction occurred in the ignition system and stops only the injection of fuel into the cylinder with the malfunction. In case of a signal malfunction (open or short circuit) or a mechanical malfunction, the engine ECU stops the VVT-i control.
30 EG-66 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE Fail-Safe of Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor The accelerator pedal position sensor comprises two (main, sub) sensor circuits. If a malfunction occurs in either one of the sensor circuits, the engine ECU detects the abnormal signal voltage difference between these two sensor circuits and switches to the limp mode. In the limp mode, the remaining circuit is used to calculate the accelerator pedal opening, in order to operate the vehicle under limp mode control. Engine ECU Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Open Main Sub Main Sub Throttle Position Sensor Throttle Valve Return Spring Throttle Control Motor Accelerator Pedal Throttle Body 199EG45 If both systems malfunction, the engine ECU detects the abnormal signal voltage between these two sensor circuits and regards that the opening angle of the accelerator pedal is fully opened and then continues the throttle control. At this time, the vehicle can be driven within its idling range. Engine ECU Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Close Main Sub Main Sub Throttle Position Sensor Throttle Valve Return Spring Throttle Control Motor Accelerator Pedal Throttle Body 199EG46
31 EG-67 Fail-Safe of Throttle Position Sensor The throttle position sensor comprises two (main, sub) sensor circuits. If a malfunction occurs in either one of the sensor circuits, the engine ECU detects the abnormal signal voltage difference between these two sensor circuits, cuts off the current to the throttle control motor, and switches to the limp mode. Then, the force of the return spring causes the throttle valve to return and stay at the prescribed opening. At this time, the vehicle can be driven in the limp mode while the engine output is regulated through the control of the fuel injection and ignition timing in accordance with the accelerator opening. The same control as above is effected if the engine ECU detects a malfunction in the throttle control motor system. Injectors Engine ECU Ignition Coils Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Open Main Sub Main Sub Throttle Position Sensor Throttle Valve Return Spring Throttle Control Motor Accelerator Pedal Throttle Body 199EG47
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM. 1. General ENGINE 1G-FE ENGINE 53. The engine control system for the 1G-FE engine has following system.
 ENGINE 1G-FE ENGINE 53 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 1G-FE engine has following system. System EFI Electronic Fuel Injection ESA Electronic Spark Advance VVT-i Variable
ENGINE 1G-FE ENGINE 53 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 1G-FE engine has following system. System EFI Electronic Fuel Injection ESA Electronic Spark Advance VVT-i Variable
ENGINE 1UZ-FE ENGINE 45. System Outline GS LS400 SFI
 ENGINE 1UZ-FE ENGINE 45 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system of the new 1UZ-FE engine is basically same in construction and operation as that of the 1UZ-FE engine for the 98 LS400.
ENGINE 1UZ-FE ENGINE 45 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system of the new 1UZ-FE engine is basically same in construction and operation as that of the 1UZ-FE engine for the 98 LS400.
14. Engine Control System
 48 4. Engine Control System General The engine control system of the 2GR-FE engine has the following features. The Engine ECU that controls this system is made by DENSO. System EFI (Electric Fuel Injection)
48 4. Engine Control System General The engine control system of the 2GR-FE engine has the following features. The Engine ECU that controls this system is made by DENSO. System EFI (Electric Fuel Injection)
3. Engine Control System Diagram
 ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 59 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Pump Resister Circuit Opening Fuel Relay Filter Intake Temp. Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Fuel Pump
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 59 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Pump Resister Circuit Opening Fuel Relay Filter Intake Temp. Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Fuel Pump
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM. 1. General ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE
 ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE 69 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 3VZ FE engine has the same basic construction and operation as for the 2VZ FE engine. However, the sequential
ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE 69 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 3VZ FE engine has the same basic construction and operation as for the 2VZ FE engine. However, the sequential
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM. 1. General EG-26 ENGINE 2UZ-FE ENGINE. The engine control system for the 2UZ-FE engine has following system.
 EG-26 ENGINE 2UZ-FE ENGINE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 2UZ-FE engine has following system. System SFI (Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection) ESA (Electronic Spark
EG-26 ENGINE 2UZ-FE ENGINE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 2UZ-FE engine has following system. System SFI (Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection) ESA (Electronic Spark
2UZ-FE ENGINE. Engine Control System TOYOTA TUNDRA - NEW FEATURES
 2UZ-FE ENGINE Engine Control System General The engine control system of the 2UZ-FE engine on the 06 has following systems. System SFI Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection ESA Electronic Spark Advance ETCS-i
2UZ-FE ENGINE Engine Control System General The engine control system of the 2UZ-FE engine on the 06 has following systems. System SFI Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection ESA Electronic Spark Advance ETCS-i
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM. 1. General EG-28 ENGINE 2ZR-FE ENGINE. The engine control system for the 2ZR-FE engine has following systems.
 EG-28 ENGINE 2ZR-FE ENGINE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 2ZR-FE engine has following systems. System SFI (Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection) ETCS-i (Electronic Throttle
EG-28 ENGINE 2ZR-FE ENGINE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 2ZR-FE engine has following systems. System SFI (Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection) ETCS-i (Electronic Throttle
ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION 35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE
 35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1UZ FE engine in the 95 LS400 is a V8, 4.0 liter, 32 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation are basically the same as those of the
35 ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE ENGINE 1UZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1UZ FE engine in the 95 LS400 is a V8, 4.0 liter, 32 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation are basically the same as those of the
PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
 3MZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 29 SFI SYSTEM PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE Symptom Suspected area See page 1. Starter ST-8 Engine does not crank (Does not start) 2. ST relay ST-2 3. Park/neutral position
3MZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 29 SFI SYSTEM PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE Symptom Suspected area See page 1. Starter ST-8 Engine does not crank (Does not start) 2. ST relay ST-2 3. Park/neutral position
1FZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION MAJOR DIFFERENCES NEW FEATURES INTERIOR DESIGN & 1FZ FE ENGINE
 NEW FEATURES INTERIOR DESIGN & 1FZ FE ENGINE 77 1FZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1FZ FE engine in the 95 Land Cruiser is an in line 6 cylinder, 4.5 liter, 24 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation
NEW FEATURES INTERIOR DESIGN & 1FZ FE ENGINE 77 1FZ FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1FZ FE engine in the 95 Land Cruiser is an in line 6 cylinder, 4.5 liter, 24 valve DOHC engine. Its construction and operation
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT:
 DIAGNOSTICS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: SFI SYSTEM (1MZFE) 05241 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a
DIAGNOSTICS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: SFI SYSTEM (1MZFE) 05241 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a
NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE. 1. Description 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES
 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
7. ETCS-i (Electronic Throttle Control System-intelligent)
 5 7. ETCS-i (Electronic System-intelligent) General The ETCS-i is used, providing excellent throttle control in all the operating ranges. In the new 1GR-FE engine, the accelerator cable has been discontinued,
5 7. ETCS-i (Electronic System-intelligent) General The ETCS-i is used, providing excellent throttle control in all the operating ranges. In the new 1GR-FE engine, the accelerator cable has been discontinued,
CHASSIS AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE. Destination New Model Previous Model Change (from previous model)
 CHASSIS AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE CH-37 U341E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 1. General The compact and high-capacity 4-speed U341E automatic transaxle [Super ECT (Electronic Controlled Transaxle)] is used. The following
CHASSIS AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE CH-37 U341E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 1. General The compact and high-capacity 4-speed U341E automatic transaxle [Super ECT (Electronic Controlled Transaxle)] is used. The following
SC300/400 NEW FEATURES. 1UZ FE Engine Item No. of Cyls. & Arrangement 8 Cylinder, V Type
 51 1UZ FE ENGINE 1. Description Various improvement have been made to the 1UZ FE engine in order to realize weight reduction and low friction performance. As a result, the engine provides both high power
51 1UZ FE ENGINE 1. Description Various improvement have been made to the 1UZ FE engine in order to realize weight reduction and low friction performance. As a result, the engine provides both high power
3GR-FSE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
 ENGINE EG 13 Engine Control System Description This engine controls the following systems in a highly accurate manner: Sequential Fuel Injection (SFI), Electronic Spark Advance (ESA), Electronic Throttle
ENGINE EG 13 Engine Control System Description This engine controls the following systems in a highly accurate manner: Sequential Fuel Injection (SFI), Electronic Spark Advance (ESA), Electronic Throttle
CH-23 CHASSIS AA80E AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION. Function of Shift Solenoid Valves. Spool Valve. Hydraulic Pressure. Sleeve. Current. Shift Solenoid Valve
 CH-23 Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SL2 Current 036CH29TE Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SLU Current 036CH27TE Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SLT
CH-23 Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SL2 Current 036CH29TE Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SLU Current 036CH27TE Spool Valve Hydraulic Sleeve Shift Solenoid Valve SLT
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L
 G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART (SAE Controlled)
 1MZFE ENGINE EG2404 (SAE Controlled) HINT: Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. DTC No. Detection Item Diagnostic Trouble
1MZFE ENGINE EG2404 (SAE Controlled) HINT: Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. DTC No. Detection Item Diagnostic Trouble
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART 05 35 HINT: As for the vehicle for MEXICO, refer to Repair Manual 2003 COROLLA MATRIX (Pub. No. RM940U). Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART 05 35 HINT: As for the vehicle for MEXICO, refer to Repair Manual 2003 COROLLA MATRIX (Pub. No. RM940U). Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your
A rotary solenoid type ISC system is used, which controls the fast idle and idle speeds.
 44 ENGINE 5S FE ENGINE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General Basic functions of the engine control system of the new 5S FE engine for the new Camry are the same as those in the 5S FE engine for the 90 model
44 ENGINE 5S FE ENGINE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General Basic functions of the engine control system of the new 5S FE engine for the new Camry are the same as those in the 5S FE engine for the 90 model
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: DI231 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your readings due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a malfunction code is displayed
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: DI231 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your readings due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a malfunction code is displayed
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE ENGINE
 36 ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE ENGINE 2UZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The engine on the Sequoia is the 2UZ-FE engine that supports the U-LEV (Ultra-Low Emission Vehicle) requirements. It is based on the 2UZ-FE engine,
36 ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE ENGINE 2UZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The engine on the Sequoia is the 2UZ-FE engine that supports the U-LEV (Ultra-Low Emission Vehicle) requirements. It is based on the 2UZ-FE engine,
U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES
 ASSIS U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES -41 U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES DESCRIPTION The new model uses 2 types (U340E, U441E) of automatic transaxle. A U340E automatic transaxle is provided
ASSIS U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES -41 U340E AND U441E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLES DESCRIPTION The new model uses 2 types (U340E, U441E) of automatic transaxle. A U340E automatic transaxle is provided
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM. 1. General CH-16 CHASSIS - U340E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
 CH-16 ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The electronic control system of the U340E automatic transaxle consists of the controls listed below. System Clutch Pressure Control (See page CH-20) Line Pressure
CH-16 ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The electronic control system of the U340E automatic transaxle consists of the controls listed below. System Clutch Pressure Control (See page CH-20) Line Pressure
ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE
 ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION On 01 LS430, base on the 1UZ-FE engine adopted on 00 LS400, 3UZ-FE engine of V8, 4.3-liter, 32-valve DOHC with the enlarged bore has been adopted. This engine has adopted
ENGINE 3UZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION On 01 LS430, base on the 1UZ-FE engine adopted on 00 LS400, 3UZ-FE engine of V8, 4.3-liter, 32-valve DOHC with the enlarged bore has been adopted. This engine has adopted
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
 2 2UZ-FE SFI SYSTEM PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE Symptom Suspected Area See page 1. Cranking holding function circuit -46 Engine does not crank (does not start) 2. Starter ST-12 3. Starter relay ST-1 4. VC output
2 2UZ-FE SFI SYSTEM PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE Symptom Suspected Area See page 1. Cranking holding function circuit -46 Engine does not crank (does not start) 2. Starter ST-12 3. Starter relay ST-1 4. VC output
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 DI158 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: ENGINE (2JZGTE) Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a malfunction code
DI158 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: ENGINE (2JZGTE) Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a malfunction code
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-27
 W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE. Self-Diagnostics - RAV4. Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs).
 2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Self-Diagnostics - RAV4 INTRODUCTION NOTE: Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). To properly diagnosis and repair this
2002 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Self-Diagnostics - RAV4 INTRODUCTION NOTE: Before performing testing procedures, check for any related Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). To properly diagnosis and repair this
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) <2.4L ENGINE>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
 CH-125 U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE DESCRIPTI The 02 Camry line-up uses the following types of automatic transaxles: 2AZ-FE U241E 1MZ-FE U140E These automatic transaxles are compact and high-capacity
CH-125 U140E AND U241E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE DESCRIPTI The 02 Camry line-up uses the following types of automatic transaxles: 2AZ-FE U241E 1MZ-FE U140E These automatic transaxles are compact and high-capacity
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
TOYOTA TUNDRA NEW FEATURES. The main components of the 2UZ-FE engine control system are as follows:
 60 TOYOTA TUNDRA NEW FEATURES Main Components of Engine Control System ) General The main components of the 2UZ-FE engine control system are as follows: 05 Toyota Tundra 04 4Runner Component Outline Quantity
60 TOYOTA TUNDRA NEW FEATURES Main Components of Engine Control System ) General The main components of the 2UZ-FE engine control system are as follows: 05 Toyota Tundra 04 4Runner Component Outline Quantity
DI 3 ENGINE DIAGNOSTICS DI PRE CHECK
 FI0534 PRECHECK DI3 DI09603 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Description When troubleshooting OBD II vehicles, the only difference from the usual troubleshooting procedure is that you connect to the vehicle the
FI0534 PRECHECK DI3 DI09603 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Description When troubleshooting OBD II vehicles, the only difference from the usual troubleshooting procedure is that you connect to the vehicle the
SERVICE MANUAL. Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation. For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only
 For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0 L 2002.25 Model Year Refer to page 2 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries. Jaguar X-TYPE 2.0
ENGINE CONTROL (5VZ-FE)
 ENGINE CONTROL (VZ-FE) SYSTEM OUTLINE The engine control system utilizes a microcomputer and maintains overall control of the engine transmission etc. An outline of engine control is given here.. INPUT
ENGINE CONTROL (VZ-FE) SYSTEM OUTLINE The engine control system utilizes a microcomputer and maintains overall control of the engine transmission etc. An outline of engine control is given here.. INPUT
DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION CHECK ENGINE WARNING LIGHT CHECK
 FI146 EFI SYSTEM (3VZE) DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The engine (engine and ECT) ECU contains a builtin, selfdiagnosis system which detects troubles within the engine signal network and flashes the warning
FI146 EFI SYSTEM (3VZE) DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The engine (engine and ECT) ECU contains a builtin, selfdiagnosis system which detects troubles within the engine signal network and flashes the warning
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type o instrumen or other actors. I a malunction code is displayed during the DTC
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type o instrumen or other actors. I a malunction code is displayed during the DTC
2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM TERMINALS OF ECM. Terminal No. (Symbols) Wiring Color Terminal Description Condition Specified Condition
 2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 29 TERMINALS OF ECM E8 E7 E5 E4 A066714E10 The standard normal voltage between each pair of the ECM terminals is shown in the table below. The appropriate conditions
2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 29 TERMINALS OF ECM E8 E7 E5 E4 A066714E10 The standard normal voltage between each pair of the ECM terminals is shown in the table below. The appropriate conditions
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM TERMINALS OF ECM 1. SFI SYSTEM
 40 2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM TERMINALS OF 1. SFI SYSTEM C55 A55 A107881E29 The standard normal voltage between each pair of the terminals is shown in the table below. The appropriate conditions
40 2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM TERMINALS OF 1. SFI SYSTEM C55 A55 A107881E29 The standard normal voltage between each pair of the terminals is shown in the table below. The appropriate conditions
ENGINE CONTROL (2RZ FE)
 ENGINE CONTROL (RZ FE) IF (A/T) AM IG 6 FROM POER SOURCE SYSTEM (SEE PAGE 44) AM ACC IG ST IF. A STA F FUSE O. A IGN A EFI 0A OD A STOP I4 IGNITION S (A/T) (A/T) F 0 (M/T) Y Y V (A/T) IK3 (A/T) (M/T) 3
ENGINE CONTROL (RZ FE) IF (A/T) AM IG 6 FROM POER SOURCE SYSTEM (SEE PAGE 44) AM ACC IG ST IF. A STA F FUSE O. A IGN A EFI 0A OD A STOP I4 IGNITION S (A/T) (A/T) F 0 (M/T) Y Y V (A/T) IK3 (A/T) (M/T) 3
2UZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM
 160 2UZ-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM DTC P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1) DTC P0172 System Too Rich (Bank 1) DTC P0174 System Too Lean (Bank 2) DTC P0175 System Too Rich (Bank 2) DCRIPTION The fuel
160 2UZ-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM DTC P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1) DTC P0172 System Too Rich (Bank 1) DTC P0174 System Too Lean (Bank 2) DTC P0175 System Too Rich (Bank 2) DCRIPTION The fuel
EG1 189 EFI SYSTEM 5S FE ENGINE DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
 5SFE ENGINE EG1189 DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The ECU contains a builtin selfdiagnosis system by which troubles with the engine signal network are detected and a CHECK engine warning light on the combination
5SFE ENGINE EG1189 DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The ECU contains a builtin selfdiagnosis system by which troubles with the engine signal network are detected and a CHECK engine warning light on the combination
DI 3 ENGINE DIAGNOSTICS DI00H 22 PRE CHECK
 PRECHECK DI3 DI00H22 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Description When troubleshooting OBD II vehicles, the only difference from the usual troubleshooting procedure is that you connect to the vehicle the OBD II
PRECHECK DI3 DI00H22 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Description When troubleshooting OBD II vehicles, the only difference from the usual troubleshooting procedure is that you connect to the vehicle the OBD II
TROUBLESHOOTING FOR EFI ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT WITH VOLT/OHMMETER
 FI118 TROUBLESHOOTING FOR EFI ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT WITH VOLT/OHMMETER HINT: Because the following troubleshooting procedures are designed for inspection of each separate system, the actual troubleshooting
FI118 TROUBLESHOOTING FOR EFI ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT WITH VOLT/OHMMETER HINT: Because the following troubleshooting procedures are designed for inspection of each separate system, the actual troubleshooting
Lotus Service Notes Section EMR
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMR Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMR.1 3 Component Function EMR.2 7 Component Location EMR.3 9 Diagnostic Guide EMR.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMR Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMR.1 3 Component Function EMR.2 7 Component Location EMR.3 9 Diagnostic Guide EMR.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2001.5 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2001.5 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
Powertrain DTC Summaries EOBD
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar S-TYPE V6, V8 N/A and V8 SC 2002.5 Model Year Refer to pages 2 9 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries.
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar S-TYPE V6, V8 N/A and V8 SC 2002.5 Model Year Refer to pages 2 9 for important information regarding the use of Powertrain DTC Summaries.
ENGINE 1MZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION ENGINE 1MZ-FE ENGINE
 EG CH BO BE 22 ENGINE 1MZ-FE ENGINE ENGINE 1MZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1MZ-FE engine has adopted the VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-intelligent) system and 3-stage ACIS (Acoustic Control Induction System)
EG CH BO BE 22 ENGINE 1MZ-FE ENGINE ENGINE 1MZ-FE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The 1MZ-FE engine has adopted the VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-intelligent) system and 3-stage ACIS (Acoustic Control Induction System)
Appendix B. Data Parameters. Current and Past TMC Engines Covered in this Section. Fig. B-1. TL874fB01. Engine Control Systems II - Course 874 B-1
 Data Parameters Current and Past TMC Engines Covered in this Section Fig. B-1 TL874fB01 Engine Control Systems II - Course 874 B-1 OBD Data Parameters Signal Category Display Item Parameter Description
Data Parameters Current and Past TMC Engines Covered in this Section Fig. B-1 TL874fB01 Engine Control Systems II - Course 874 B-1 OBD Data Parameters Signal Category Display Item Parameter Description
DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION EG2 170
 EG2170 DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The ECM contains a builtin self diagnosis system by which troubles with the engine signal network are detected and a malfunction indicator lamp on the combination meter
EG2170 DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The ECM contains a builtin self diagnosis system by which troubles with the engine signal network are detected and a malfunction indicator lamp on the combination meter
5. Main Components of Engine Control System
 EG-38 5. Main Components of Engine Control System General The following table compares the main components. Components 3MZ-FE 1MZ-FE Outline Quantity Outline Quantity ECM 3-bit CPU 1 16-bit CPU 1 ir Fuel
EG-38 5. Main Components of Engine Control System General The following table compares the main components. Components 3MZ-FE 1MZ-FE Outline Quantity Outline Quantity ECM 3-bit CPU 1 16-bit CPU 1 ir Fuel
Powertrain DTC Summaries OBD II
 Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2002 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
Powertrain DTC Summaries Quick Reference Diagnostic Guide Jaguar X-TYPE 2.5L and 3.0L 2002 Model Year Revised January, 2002: P0706, P0731, P0732, P0733, P0734, P0735, P0740, P1780 POSSIBLE CAUSES Revised
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G9>
 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
9. Subaru Select Monitor
 9. A: OPERATION 1. HOW TO USE SUBARU SELECT MONI- TOR 1) Prepare the kit. CAUTION: Do not connect the scan tools except for Subaru Select
9. A: OPERATION 1. HOW TO USE SUBARU SELECT MONI- TOR 1) Prepare the kit. CAUTION: Do not connect the scan tools except for Subaru Select
DATA LIST / ACTIVE TEST
 2UZFE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 43 DATA LIST / ACTIVE TT 1. DATA LIST HINT: Using the intelligent tester's DATA LIST allows switch, sensor, actuator and other item values to be read without removing
2UZFE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 43 DATA LIST / ACTIVE TT 1. DATA LIST HINT: Using the intelligent tester's DATA LIST allows switch, sensor, actuator and other item values to be read without removing
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle
 Document ID# 850406 2002 Pontiac Firebird Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle DTC DTC 021 and/or 031 DTC 022 and/or 032 DTC 023 or 033 DTC 24/34 DTC 025 and/or 035 DTC 041 DTC 042 DTC 043 DTC
Document ID# 850406 2002 Pontiac Firebird Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle DTC DTC 021 and/or 031 DTC 022 and/or 032 DTC 023 or 033 DTC 24/34 DTC 025 and/or 035 DTC 041 DTC 042 DTC 043 DTC
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS
 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS DTC Description P0010 Variable Valve Timing Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1) P0020 Variable Valve Timing Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2)
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DEFINITIONS DTC Description P0010 Variable Valve Timing Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1) P0020 Variable Valve Timing Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2)
NEW FEATURES 1GR-FE ENGINE. 1. General FJ CRUISER NEW FEATURES
 FJ CRUISER NEW FEATURES 5 NEW FEATURES 1GR-FE ENGINE 1. General The 1GR-FE engine is a 4.0-liter, 24-valve DOHC V6 engine. In this engine, a Dual Variable Valve Timing-intelligent (Dual VVT-i) system,
FJ CRUISER NEW FEATURES 5 NEW FEATURES 1GR-FE ENGINE 1. General The 1GR-FE engine is a 4.0-liter, 24-valve DOHC V6 engine. In this engine, a Dual Variable Valve Timing-intelligent (Dual VVT-i) system,
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL 17-2 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-2 AUTO-CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-3 CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION 17-5 17-7 GENERAL INFORMATION
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL 17-2 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-2 AUTO-CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-3 CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION 17-5 17-7 GENERAL INFORMATION
1996 Tacoma (L4 VIN:M)
 1996 Tacoma (L4 VIN:M) SYSTEM OUTLINE THE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM UTILIZES A MICROCOMPUTER AND MAINTAINS OVERALL CONTROL OF THE ENGINE, TRANSMISSION, ETC. AN OUTLINE OF ENGINE CONTROL IS GIVEN HERE. Report
1996 Tacoma (L4 VIN:M) SYSTEM OUTLINE THE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM UTILIZES A MICROCOMPUTER AND MAINTAINS OVERALL CONTROL OF THE ENGINE, TRANSMISSION, ETC. AN OUTLINE OF ENGINE CONTROL IS GIVEN HERE. Report
ENGINE 3S GTE ENGINE DESCRIPTION ENGINE 3S GTE ENGINE
 39 ENGINE 3S GTE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The new MR2 has the 2.0 liter, 16 valve, DOHC 3S GTE engine with turbocharger which is used in the Celica All Trac/4WD models and has been well received. The 3S GTE
39 ENGINE 3S GTE ENGINE DESCRIPTION The new MR2 has the 2.0 liter, 16 valve, DOHC 3S GTE engine with turbocharger which is used in the Celica All Trac/4WD models and has been well received. The 3S GTE
CHECK MODE PROCEDURE ES 41
 1GRFE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 41 CHECK MODE PROCEDURE DLC3 CAN VIM Intelligent Tester Intelligent tester only: Compared to normal mode, check mode is more sensitive to malfunctions. Therefore,
1GRFE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 41 CHECK MODE PROCEDURE DLC3 CAN VIM Intelligent Tester Intelligent tester only: Compared to normal mode, check mode is more sensitive to malfunctions. Therefore,
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EvoX EFI ECU Pinouts Last Updated Tuesday, 24 April :40
 HOW TO: Reset your Fuel trims... Open your bonnet, open the fuse box, pull out 7.5A number 2 fuse, this is battery backup for your main ECU, remove for 2 seconds, and replace. Your fuel trims and learned
HOW TO: Reset your Fuel trims... Open your bonnet, open the fuse box, pull out 7.5A number 2 fuse, this is battery backup for your main ECU, remove for 2 seconds, and replace. Your fuel trims and learned
2TR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM SYSTEM DIAGRAM 1. SYSTEM DIAGRAM ECM BATT #10 STA #20 NSW IGSW. #40 Injector Stop Light Switch ST1- STP AIRP
 6 2TR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM SYSTEM DIGRM 1. SYSTEM DIGRM ECM C/OPN Relay TT + FC M Fuel Pump Ignition Switch MREL EFI Relay Starter #10 Injector Starter Relay ST #20 Injector Ignition Switch
6 2TR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM SYSTEM DIGRM 1. SYSTEM DIGRM ECM C/OPN Relay TT + FC M Fuel Pump Ignition Switch MREL EFI Relay Starter #10 Injector Starter Relay ST #20 Injector Ignition Switch
Lotus Service Notes Section EMD
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMD Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMD.1 3 Component Function EMD.2 8 Component Location EMD.3 10 Diagnostic Guide EMD.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMD Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMD.1 3 Component Function EMD.2 8 Component Location EMD.3 10 Diagnostic Guide EMD.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
DATA LIST / ACTIVE TEST
 1GRFE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 49 DATA LIST / ACTIVE TT 1. DATA LIST HINT: By reading the DATA LIST displayed on an intelligent tester, you can check values, including those of the switches, sensors,
1GRFE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 49 DATA LIST / ACTIVE TT 1. DATA LIST HINT: By reading the DATA LIST displayed on an intelligent tester, you can check values, including those of the switches, sensors,
1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE TOYOTA SYSTEM & COMPONENT TESTING
 1 of 65 12/5/2014 1:13 PM 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE TOYOTA SYSTEM & COMPONENT TESTING INTRODUCTION Before testing separate components or systems, perform procedures in articles listed below: BASIC TESTING
1 of 65 12/5/2014 1:13 PM 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE TOYOTA SYSTEM & COMPONENT TESTING INTRODUCTION Before testing separate components or systems, perform procedures in articles listed below: BASIC TESTING
GROUP 13Ab. 13Ab-2 CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-29 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS...
 13Ab-1 GROUP 13Ab CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. 13Ab-2 DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-29 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS..... 13Ab-2 FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION REFERENCE TABLE........................ 13Ab-20 DIAGNOSTIC
13Ab-1 GROUP 13Ab CONTENTS TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY.. 13Ab-2 DATA LIST REFERENCE TABLE... 13Ab-29 TROUBLE CODE DIAGNOSIS..... 13Ab-2 FAIL-SAFE FUNCTION REFERENCE TABLE........................ 13Ab-20 DIAGNOSTIC
Lotus Service Notes Section EMQ
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
1GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM
 134 1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM DTC P0136 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (ank 1 Sensor ) DTC P0137 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (ank 1 Sensor ) DTC P0138 Oxygen Sensor Circuit High Voltage
134 1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM DTC P0136 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (ank 1 Sensor ) DTC P0137 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (ank 1 Sensor ) DTC P0138 Oxygen Sensor Circuit High Voltage
ProECU Subaru BRZ Toyota GT86 Scion FR-S
 ProECU Subaru BRZ Toyota GT86 Scion FR-S DTC List 2012-onward Model Year v1.0 Engine DTC List P000A Camshaft Position "A" - Timing Slow Response Bank 1 P000B Camshaft Position "B" - Timing Slow Response
ProECU Subaru BRZ Toyota GT86 Scion FR-S DTC List 2012-onward Model Year v1.0 Engine DTC List P000A Camshaft Position "A" - Timing Slow Response Bank 1 P000B Camshaft Position "B" - Timing Slow Response
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Continuously Variable Transaxle Specification. Forward/Reverse Switching Mechanism Double Pinion Type Planetary Gear
 CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41B Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1nr-fe engine models. 2. The K41B CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41B Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1nr-fe engine models. 2. The K41B CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G63-Turbo>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13B-2 SENSOR....................... 13B-8 THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CTROL.............. 13B-9 FUEL INJECTI
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13B-2 SENSOR....................... 13B-8 THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CTROL.............. 13B-9 FUEL INJECTI
DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected. DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected. DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected
 1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 171 DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected DTC P030 Cylinder Misfire Detected DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected
1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 171 DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected DTC P030 Cylinder Misfire Detected DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected
DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected. DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected. DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected
 1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 169 DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire
1GR-FE EINE CONTROL SYSTEM SFI SYSTEM 169 DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)
 13A-1 GROUP 13A CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION...13A-2 CONTROL UNIT...13A-7 SENSOR...13A-9 ACTUATOR...13A-26 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL...13A-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME...13A-36
13A-1 GROUP 13A CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION...13A-2 CONTROL UNIT...13A-7 SENSOR...13A-9 ACTUATOR...13A-26 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL...13A-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME...13A-36
Continuously Variable Transaxle Specification. Forward/Reverse Switching Mechanism Double Pinion Type Planetary Gear
 CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41A Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1kr-fe engine models. 2. The K41A CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41A Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1kr-fe engine models. 2. The K41A CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
DTC Summaries. NipponDenso V12 Engine Management
 DTC Summaries NipponDenso V12 Engine Management OBD II MONITORING CONDITIONS: When testing for DTC reoccurrence, it can be determined if the Service Drive Cycle was of sufficient length by performing a
DTC Summaries NipponDenso V12 Engine Management OBD II MONITORING CONDITIONS: When testing for DTC reoccurrence, it can be determined if the Service Drive Cycle was of sufficient length by performing a
DATA LIST/ACTIVE TEST
 05-406 DATA LIST/ACTIVE TEST 1. DATA LIST HINT: DIAGNOSTICS - SFI SYSTEM (3MZ-FE)(From August, 2004) Using the hand-held tester DATA LIST allows switch, sensor, actuator and other item values to be read
05-406 DATA LIST/ACTIVE TEST 1. DATA LIST HINT: DIAGNOSTICS - SFI SYSTEM (3MZ-FE)(From August, 2004) Using the hand-held tester DATA LIST allows switch, sensor, actuator and other item values to be read
DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2)
 05498 DIAGNOSTICS DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) 05EXR06 DTC P0172 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2) DTC P0175 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 2) CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION The fuel trim is
05498 DIAGNOSTICS DTC P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1) 05EXR06 DTC P0172 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 1) DTC P0174 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 2) DTC P0175 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 2) CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION The fuel trim is
Lexus IS300 ECU Harness. Connector E
 Lexus IS300 ECU Harness Connector A Connector B Connector C Connector D Connector E Connector/Pin # Signal Full name/destination Wire Color Notes A1 EOM Chassis Ground White/Black A2 EC Chassis Ground
Lexus IS300 ECU Harness Connector A Connector B Connector C Connector D Connector E Connector/Pin # Signal Full name/destination Wire Color Notes A1 EOM Chassis Ground White/Black A2 EC Chassis Ground
CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM
 CRUISE CONTROL CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM PRECAUTION 1 1. HANDLING PRECAUTION FOR CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM (a) Turn the cruise control main switch OFF when not using the cruise control system.
CRUISE CONTROL CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM PRECAUTION 1 1. HANDLING PRECAUTION FOR CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM (a) Turn the cruise control main switch OFF when not using the cruise control system.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing
 Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
Page 1 of 49 01-12 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) memory, checking and erasing Check DTC Memory (function 02) - Connect VAS5051 tester Page 01-7 and select vehicle system "01 - Engine electronics". Engine
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
 Last Modified: 4-26-2007 Service Category: Engine/Hybrid System 1.6 G Section: Engine Mechanical Model Year: 2007 Model: 4Runner Doc ID: RM0000017L8004X Title: 1GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL: ENGINE: ON-VEHICLE
Last Modified: 4-26-2007 Service Category: Engine/Hybrid System 1.6 G Section: Engine Mechanical Model Year: 2007 Model: 4Runner Doc ID: RM0000017L8004X Title: 1GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL: ENGINE: ON-VEHICLE
Engine Control Systems
 Engine Control Systems verview Atkinson Cycle The 1NZ FXE engine is optimized for its role as one of two sources of motive power in the Prius. The system controls the distribution of the engine and motor
Engine Control Systems verview Atkinson Cycle The 1NZ FXE engine is optimized for its role as one of two sources of motive power in the Prius. The system controls the distribution of the engine and motor
3GR-FSE FUEL. Fuel Pump (High Pressure) Cold Start Fuel Injector *
 ENGINE EG 75 General This engine uses the D-4 (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine) system. A (low pressure) fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump located
ENGINE EG 75 General This engine uses the D-4 (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine) system. A (low pressure) fuel pump located inside the fuel tank pumps fuel to the high-pressure fuel pump located
Lotus Service Notes Section EMQ
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Cylinder Numbering 2 Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Cylinder Numbering 2 Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11
Engine Control (1MZ-FE)
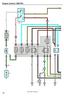 Engine Control (MZ-FE) - M CC IG ST - 7 M IG 6 ST - I5 Ignition S IF - - 5 M 3 IF6 C E - G - - - 0 IG - - E 4 9 3 4 C 0 T 30 M 5 /F 0 EFI 5 3 EFI elay C/OPN elay 5 3 /F HT elay 5 3 5 C 6 K 4 D 6 C 7 C
Engine Control (MZ-FE) - M CC IG ST - 7 M IG 6 ST - I5 Ignition S IF - - 5 M 3 IF6 C E - G - - - 0 IG - - E 4 9 3 4 C 0 T 30 M 5 /F 0 EFI 5 3 EFI elay C/OPN elay 5 3 /F HT elay 5 3 5 C 6 K 4 D 6 C 7 C
Description P1083 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1084 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1085 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank
 Code Description P1083 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1084 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1085 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 2 Sensor 1) P1086 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank
Code Description P1083 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1084 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) P1085 Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 2 Sensor 1) P1086 Fuel Control Mixture Rich (Bank
1 of 13 10/17/2016 1:36 PM
 1 of 13 10/17/2016 1:36 PM DTC P2195 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2196 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2197 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck
1 of 13 10/17/2016 1:36 PM DTC P2195 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2196 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) DTC P2197 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck
Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (-40 )
 149000 153 1. ENGINE DATA LIST Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (40 ) Intake air temperature 40~130 (varies according to ambient air temperature or engine mode) Idle speed rpm
149000 153 1. ENGINE DATA LIST Data Unit Value Coolant temperature 0.436V (130 ) ~4.896V (40 ) Intake air temperature 40~130 (varies according to ambient air temperature or engine mode) Idle speed rpm
5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal
 5. A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION B134 B135 B136 B137 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 35 34 33 32 31
5. A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION B134 B135 B136 B137 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 35 34 33 32 31
