(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,474,324 B1
|
|
|
- Pierce Cannon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 USOO B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Despart et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 5, 2002 (54) ARCHERY BOWS, ARCHERY BOW CAM 5,505,185 A 4/1996 Miller /25.6 ASSEMBLIES, AND ARCHERY BOW 5, A * 4/1997 Kudlacek /25.6 ANCHORS 5,687,703 A * 11/1997 Vyprachticky /25.6 5,697,355 A * 12/1997 Schaffer /25.6 5,782,229 A 7/1998 Evans et al /25.6 (75) Inventors: ly tryout." 5,791,322 A 8/1998 McPherson /25.6 s y G. s 5,803,069 A * 9/1998 Schreiber /86 Walla, WA (US) 5,890,480 A 4/1999 McPherson /25.6 5,947,099 A * 9/1999 Derus /25.6 (73) ASSignee: Main Archery, Inc., Walla Walla, WA 5.975,067 A 11/1999 Strother /25.6 * cited by examiner (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 Primary Examiner John A. Ricci U.S.C. 154(b) by 33 days. (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm Wells St. John P.S. 57 ABSTRACT (21) Appl. No.: 09/716,027 (57) (22) Filed: Nov. 17, 2000 In one aspect, the invention includes an archery bow having e -- is a first limb and a second limb, and a handle between the (51) Int. Cl... F41B 5/10 limbs. A rotating member includes at least two cams rotat (52) U.S. Cl /256 ably joined to the first limb with a first of the at least two (58) Field of Search /23.1, 25.6, cams having an eccentric profile to provide a first camming 124/86,900 Surface and a Second of the at least two cams having an eccentric profile to provide a Second camming Surface. The (56) References Cited eccentric profile of the first cam is Substantially Symmetrical relative to the eccentric profile of the Second cam. A String extends between the rotating member and Second limb. U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 5, /1992 Martin et al /25.6 5,368,006 A 11/1994 McPherson / Claims, 14 Drawing Sheets 10b
2 U.S. Patent Nov. 5, 2002 Sheet 1 of 14
3 U.S. Patent Nov. 5, 2002 Sheet 2 of 14
4 U.S. Patent Nov. 5, 2002 Sheet 3 of 14 QC) N s 2.
5 U.S. Patent Nov. 5, =N [[TOEF N Sheet 4 of 14 [] 24 LO & D ZZZ LO Q 23 FIE
6 U.S. Patent Nov. 5, 2002 She et 5 of Zz z7 Az7 (C) Qò SNS= LO OO 46
7 U.S. Patent Nov. 5, 2002 Sheet 6 of 14
8 U.S. Patent Nov. 5, 2002 Sheet 7 of 14 N s S
9 U.S. Patent Nov. 5, Sheet 8 of 14 3O b 24 7O A z z7 / a A z z7 - Z 7
10 U.S. Patent Nov. 5, 2002 Sheet 9 of 14 al s s s DE
11 U.S. Patent Nov. 5, 2002 Sheet 10 of 14
12 U.S. Patent Nov. 5, 2002 Sheet 11 of ======~? ^`?
13 U.S. Patent Nov. 5, 2002 Sheet 12 of 14
14 U.S. Patent Nov. 5, 2002 Sheet 13 of 14
15 U.S. Patent Nov. 5, 2002 Sheet 14 of 14
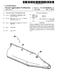
16 1 ARCHERY BOWS, ARCHERY BOW CAM ASSEMBLIES, AND ARCHERY BOW ANCHORS TECHNICAL FIELD The invention pertains to archery bows, archery bow cam assemblies, and archery bow anchors. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION Various types of archery bows have been developed, including traditional bows (i.e., long bows and recurved bows) and compound bows. All archery bows include a pair of opposed limbs extending from a handle of the bow. AS an archer draws the bow by pulling on a drawstring, the limbs flex and Store energy. This energy is transferred to the arrow as the archer releases the drawstring. A compound bow is a popular design for archery bows and comprises incorporating one or more cams (for example, eccentric wheels or pulleys) into the bow. These bows use a cable System which extends over at least one cam rotatably mounted at a distal end of a bow limb to provide a mechani cal advantage during the drawback of the drawstring. Such cams enable a peak draw force (i.e., a peak pull force on a drawstring of a bow to maintain a draw) to be reached in the middle of a draw such that the draw force drops at full draw. With this arrangement, when the drawstring is in the full draw position, maximum potential energy is Stored in the bow while the force required to maintain the drawstring in the full draw position is less than the maximum draw force of the bow. In short, as the drawstring is being drawn, the draw force applied to the bow increases to a maximum force and reduces to a lower draw force at the full draw position. Accordingly, maximum energy is Stored in the limbs without requiring maximum force to be applied to the drawstring to hold the bow at the full draw position. This permits the archer to maintain aim on his target prior to release for a longer period of time for a better shot. A general goal of archery bow designs is to increase the Speed in which an arrow is projected by a bow. Arrows which fly faster can maintain a flatter trajectory over a greater distance than slower traveling arrows. This can enable faster flying arrows to be fired more accurately than slower traveling arrows. Methods to increase arrow Speed include maximizing energy transferred to the arrow from the bow. Accordingly, one general goal of archery bow design is to alleviate twisting of bow limbs that occurs during a draw. The twisting of bow limbs uses energy that cannot be transferred to the arrow, and therefore, the energy is lost for increasing arrow speed. Another goal of archery bow designs is to decrease frictional forces between moving components within a bow, Such as, for example, bearings and axles. The more frictional forces associated with moving components, the more energy not available for increasing arrow Speed. A general goal of compound bow designs is to provide a cable System that allows for fletching and Sighting clear ances. A fletching clearance is the area of clearance needed for the cross-sectional area of a bow Shaft and radially extending feathers to pass unimpeded. A sighting clearance is a region for aiming at a target unimpeded by the cable System. The conventional method for establishing fletching and Sighting clearances is to provide cable guards. However, the cable guards create unbalanced forces in the limbs which twist the limbs detrimentally as discussed previously In light of the above discussed goals, it would be desirable to develop an archery bow to minimize the above-mentioned design inefficiencies and difficulties. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION In one aspect, the invention includes an archery bow having a first limb and a Second limb, and a handle between the limbs. A rotating member comprises at least two cams rotatably joined to the first limb with a first of the at least two cams having an eccentric profile to provide a first camming Surface and a Second of the at least two cams having an eccentric profile to provide a Second camming Surface. The eccentric profile of the first cam is Substantially Symmetrical relative to the eccentric profile of the Second cam. A String extends between the rotating member and Second limb. In another aspect, the invention includes an archery bow having a pair of flexible resilient bow limbs forming first and Second Outer bow limb ends and forming first and Second inner bow limb ends. A handle connects the first and Second inner bow limb ends and a string extends between the first and second outer bow limb ends. At least four cables extend between the first and second outer bow limb ends. In yet another aspect, the invention includes an archery bow cam assembly having a first cam with an eccentric profile to provide a first camming Surface. A Second cam has an eccentric profile to provide a Second camming Surface and the eccentric profile of the first cam is Substantially Symmetrical relative to the eccentric profile of the Second cam. The archery bow cam assembly includes a primary cam between the first and Second cams. In Still another aspect, the invention includes an archery bow anchor having an outward Surface with a plurality of peripheral discrete grooves. Each groove is laterally dis placed from an adjacent groove. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS Preferred embodiments of the invention are described below with reference to the following accompanying draw ings. FIG. 1 is a diagrammatic side view of a first embodiment archery bow of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a perspective view of an archery bow cam in accordance with a first embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 3 is a fragmentary view of the archery bow of FIG. 1 emphasizing a side view of the archery bow cam of FIG. 2 shown at a rest position relative a full draw. FIG. 4 is an exploded view of the archery bow cam of FIG. 3. FIG. 5 is an enlarged fragmentary partial Sectional view of an archery bow in accordance with a first embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 6 is an enlarged fragmentary partial Sectional view of an archery bow in accordance with a Second embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 7 is a side view of a cable anchor in accordance with a first embodiment of the present invention, and shown in cooperation with a archery bow limb (illustrated in phantom). FIG. 8 is a perspective view of the cable anchor in FIG. 7. FIG. 9 is a perspective view of a cable anchor in accor dance with another embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 10 is a fragmentary view of an archery bow from the perspective of an archer using the bow and shown in a rest position relative a full draw.
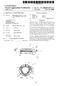
17 3 FIG. 11 is a fragmentary view of the FIG. 10 archery bow shown in a full draw position. FIG. 12 is a front view of the FIG. 2 archery bow cam. FIG. 13 is a front view of an archery bow cam in accordance with another embodiment of the present inven tion. FIG. 14 is a view of the FIG. 1 archery bow from the perspective of an archer using the present invention, this embodiment including additional components than shown in the FIG. 1 bow. FIG. 15 is an enlarged fragmentary view of the FIG. 14 archery bow. FIG. 16 is a diagrammatic side view of an archery bow in accordance with another embodiment of the present inven tion. FIG. 17 is a perspective view of an archery bow cam in accordance with another embodiment of the present inven tion. FIG. 18 is a fragmentary view of the archery bow of FIG. 16 emphasizing a side view of the archery bow cam of FIG. 17 shown at a rest position relative a full draw. FIG. 19 is a fragmentary view of the FIG.16 archery bow emphasizing an idler wheel in accordance with one embodi ment of the present invention. FIG. 20 is a partial sectional view of a yoke assembly in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention used with the FIG. 16 archery bow. FIG. 21 is a fragmentary view of the FIG.16 archery bow from the perspective of an archer using the bow. FIG.22 is a fragmentary view of an archery bow empha sizing an idler wheel in accordance with another embodi ment of the present invention, and shown at a rest position relative a full draw. FIG. 23 is a view of the FIG.22 archery bow shown at a full draw position. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS This disclosure of the invention is Submitted in further ance of the constitutional purposes of the U.S. Patent Laws to promote the progress of Science and useful arts (Article 1, Section 8). FIG. 1 shows a first embodiment archery bow 10 of the present invention. Archery bow 10 comprises a handle 12, and a pair of limbs 14 and 16 attached to handle 12. Exemplary bow 10 further comprises a first rotating member 18 rotatably attached to limb 14 and a second rotating member 20 rotatably attached to limb 16. A cable, for example a String or drawstring 22, extends between first and second limbs 14 and 16. In one embodiment, string 22 extends between first and second rotating members 18 and 20. A plurality of cables 21 and 23, for example power cables, extend between first and second limbs 14 and 16. This exemplary bow embodiment illustrates the first rotating member 18 having the same configuration as the Second rotating member 20. Accordingly, any Subsequent descrip tion regarding first rotating member 18 applies equally to rotating member 20. It should be understood, however, that rotating member 20 could be different than member 18, and could, for example, be an idler wheel. It should also be understood Second limb 16 may not have a rotating member, and that cables could be directly attached to limb 16. A first embodiment of rotating member 18 is illustrated in FIG. 2 and comprises a plurality of cams, for example, a primary cam 24 between at least two cams. In the shown embodiment, primary cam 24 is between a first cam 25 and a Second cam 26. First cam 25 comprises an eccentric profile to provide a first camming Surface 30 and Second cam 26 comprises an eccentric profile to provide a Second camming Surface 31. In this exemplary embodiment of rotating mem ber 18, the eccentric profile of first cam 25 is substantially Symmetrical relative to the eccentric profile of Second cam 26. In this document, Substantially Symmetrical and Sub Stantially Symmetrically aligned mean Symmetry and align ment within tolerances of fabrication techniques. Additionally, the eccentric profiles are aligned wherein the eccentric profile of first cam 25 forms substantially a mirror image of the eccentric profile of Second cam 26 relative primary cam 24. In this document, mirror image means alignment within fabrication tolerances. Primary cam 24 comprises an eccentric profile to provide another camming Surface 28, and the eccentric profile of primary cam 24 is not Substantially Symmetrical relative the eccentric profiles of first and second cams 25 and 26. Camming surfaces 28, 30 and 31 form grooves to receive cables. Exemplary first and Second cams 25 and 26 are parallel and equidistant relative primary cam 24. An anchor 32, for example a cable anchor, laterally extends from first rotating member 18 and com prises grooves 34 and 36 to receive, or anchor, cables. An opening 38 in rotating member 18 receives an axle (FIG.3). The substantially symmetrical design of rotating member 18 allows for the forces created in rotating member 18 by cables riding over the camming Surfaces to be balanced, and therefore, alleviates unbalanced forces exist to be distributed unevenly within limb 14 causing twisting of limb 14. Referring to FIG.3, rotating member 18 is illustrated with String 22 at a rest position relative a full draw position, i.e., no pull force is applied to String 22. Rotating member 18 receives an axle 46 in opening 38 to rotatably join rotating member 18 to first limb 14. Cable 21 is received over first cam 25 and secured to cable anchor 32 in groove 34. String 22 is received over primary cam 24 and Secured to cable anchor 32 in groove 36. Referring to FIG.4, an exemplary embodiment of rotating member 18 includes primary cam 24 and second cam 26 formed as a one piece member 40, and first cam 25 formed as a discrete member secured to the one piece member 40 by threaded members 42. A stabilizer member 43 is received in aligned openings 45 and 47 of first cam 25 and one piece member 40, respectively, for added support between first cam 25 and one piece member 40. Limb 14 includes a distal end that comprises forked members 44 in which rotating member 18 is rotatable secured on axle 46. Axle 46 is secured to forked members 44 by clips 48, and exemplary clips comprise c-clips. In one embodiment, the axle 46 extends outwardly from each forked member 44 to receive an anchor, for example an axle anchor 50, having a periph eral groove 51 to receive cables. Threaded member 52 secures cable anchor 32 to one piece member 40. Various washers 54 may be used to relieve friction and distribute pressure between the anchors 50, axle 46 and forked mem bers 44. It should be understood that rotating member 18 could be manufactured as one piece comprising primary cam 24 and first and second cams 25 and 26. Furthermore, it should be understood that rotating member 18 could be manufactured as three discrete pieces comprising primary cam 24, first cam 25 and Second cam 26, and Subsequently assembled and Secured together by, for example, threaded members. Referring to FIG. 5, a first embodiment of a rotating member 18 cooperating between forked members 44 is
18 S illustrated wherein the entire width of rotating member 18 rotatably rests on axle 46 for rotatable support. It should be understood that opening 38 could have enlarged diametric dimensions partially along the width of rotating member 18, for example, for the entire width of primary cam 24, Such that the entire width of rotating member 18 structure does not contact axle 46 thereby reducing friction between the components. It should be understood that rotating member 18 may only contact axle 46 in a central portion of primary cam 24. Furthermore, it should be understood that rotating member 18 could make intermittent contact with axle 46 along its entire width for rotatable Support. Lessening con tact between axle 46 and rotating member 18 reduces friction to provide a more efficient archery bow 10, allowing more energy to transfer from the bow 10 to an arrow. A Second embodiment of a rotating member 18 cooper ating between fork members 44 is illustrated in FIG. 6. Bearings 60 rotatably support rotating member 18 by Sup porting first and second cams 25 and 26 on axle 46 with primary cam 24 defining an opening 62 having a greater diameter than the diameter of axle 46, and therefore, primary cam 24 does not contact axle 46. It should be understood that a third bearing could occupy opening 62 to Support primary cam 24 on axle 46, either in combination with bearings 60, or without bearings 60. It should be understood one con tinuous bearing could Support rotating member 18 along its entire width. Additionally, it should be understood that intermittently spaced plurality of discreet bearings could be Spaced along the width of rotating member 18. In referring to Subsequent figures, Similar numbering to that utilized in describing the first embodiments of FIGS. 1-6 will be used, with differences indicated by the suffix a,"b, c, or by different numerals. Referring to FIG. 7, an embodiment of an anchor 50a, for example a cable anchor or axle anchor, is shown laterally extending from forked member 44 (shown in phantom) of a bow limb and supported on axle 46 by washer 54 and clip 48. Anchor 50a comprises generally a cylindrical shape having a plurality of discrete circumferential grooves 64 and each groove 64 is laterally displaced from an adjacent groove 64. Each groove 64 is capable of receiving a cable to provide lateral adjust ment of a cable relative the bow 10 or string 22. Accordingly, cable guards routinely used to spread cables from a drawstring are not needed. Exemplary plurality of grooves of the shown embodiment comprise three grooves 64 incrementally spaced laterally from adjacent grooves 64. Referring to FIG. 8, one embodiment of an anchor 50b comprises one or more grooves 64 with a cylindrical open ing 38b to receive axle 46 (FIG. 7). Referring to FIG. 9, another embodiment of an anchor 50c comprises one or more grooves 64 with an opening 38c. Opening 38c is contoured to receive axle 46 for adjusting movement of anchor 50c on axle 46. In one embodiment, opening 38c defines two intersecting oblong openings to allow anchor 50c to move generally perpendicularly relative a longitudinal axis of axle 46. An anchor 50c capable of Such movement relative the axle 46 allows for adjustment of tension in cables which are mounted to anchor 50c. It should be understood that anchor embodiments 50a, 50b and 50c could be positioned on axle 46 between forked members 44 and rotating member 18. Additionally, it should be under stood that the opening or openings within an anchor to receive an axle can be designed as any shape limited only by the imagination of the designer. FIGS. 10 and 11 illustrate rotating member 18 in a rest position and a draw position, respectively. Referring to FIG , archery bow 10 is illustrated at a rest position, i.e., no pull force is applied to String 22, and therefore, rotating member 18 is in a rest position without rotation on the axle 46. An X-axis is oriented along axle 46 and an y-axis perpendicular to the X-axis is oriented along String 22 for illustration purposes. Referring to FIG. 11, archery bow 10 is illustrated at a full draw position, i.e., the String 22 has been pulled from bow 10 and is in a static position. The rotating member 18 has rotated on axle 46. AS illustrated, the X- and y-axes are oriented the same as in FIG. 10 demonstrating no twisting of forked members 44 or first limb 14. Whether the rotating member 18 is in the rest position, or rotated somewhere between the rest position up to the full draw position, the X and y-axes are oriented the same. Since the tensile forces in the cables are balanced on the rotating member 18 relative the centrally located primary cam 24, no unbalanced forces exist to be transferred into forked member 44 and limb 14. The limbs of a conventional bow have unbalanced forces in the limbs because the rotating members are not Substantially Symmetrically designed to evenly distribute the tensile forces in the cables. Accordingly, a plane established by the X- and y-axes (i.e., the plane of the page) would be rotated around an imaginary Z-axis extending perpendicularly from the page. Additionally, for a conventional bow, the X-axis would be rotated around the y-axis. This twisting of the limbs depletes the energy that can be used to drive the arrow. Referring to FIG. 12, an exemplary rotating member 18 is shown. Axis 70 marks the centerline of grooves 30 and 31 for first and second cams 25 and 26, respectively. In this embodiment, cables 21 and 56 ride in grooves 30 and 31, respectively, angled from axis 70. Referring to FIG. 13, another embodiment of rotating member 18b is illustrated. First and second cams 25 and 26 are angled from primary cam 24 while Still maintaining a mirror image relationship. Accordingly, cables 21 and 56 are aligned with axis 70 of grooves 30 and 31. Centering the cables within the cams can increase the longevity of use fulness of the cables. Referring to FIG. 14, an embodiment of archery bow 10 is shown from the perspective an archer using bow 10. Limb 14 rotatably supports rotating member 18 and limb 16 rotatably supports rotating member 20. Bow 10 includes a Sighting apparatus 74 and an arrow rest 80 to receive an arrow 82. This perspective illustrates the configuration of string 22 and four cables 21, 23, 56, and 58 on archery bow 10. For sake of discussion, consider a plane defined by the String 22 extending out of the page and centrally through bow 10. Accordingly, two sides of bow 10 are defined, a right Side and a left Side relative the plane. Each side of the plane includes two cables extending between the limbs 14 and 16. For example, cables 21 and 23 extend between limbs 14 and 16 on the left side of the plane and cables 56 and 58 extend between limbs 14 and 16 on the right side of the plane. Each cable is a discrete cable and comprises two terminal ends. One terminal end is Secured to an axle anchor of one limb and the other terminal end is secured to the rotating member on the other limb on the same side of bow 10. For example, one end of cable 23 extends from axle anchor 50 of limb 14 on the left side of bow 10 to ride over cam 27 on the left side of rotating member 20 of limb 16 and anchors to rotating member 20. One end of cable 21 is anchored to rotating member 18 of limb 14 on the left side of bow 10 and rides over cam 26 on the left side to extend to limb 16 and anchors to axle anchor 50 on the left side of bow 10. This cable configuration of cables 21 and 23 is a mirror image of cable configuration of cables 56 and 58 on
19 7 the right side of the bow 10 relative the plane. Due to this Symmetry between the cables on either side of String 22, the tensile forces in the cables on the left side are balanced with the tensile forces in the cables on the right Side. Referring to FIG. 15, an enlarged portion of bow 10 from FIG. 14 is shown, particularly emphasizing the area around handle 12. The Sighting apparatus 74 defines a region termed a sighting clearance 78 (shown in phantom) for an archer to aim arrow 82 at a target. Arrow 82 is supported on bow 10 by an arrow rest 80. The arrow 82 comprises a plurality of vanes or feathers 86, for example three, and a nock 84 that Secures the arrow 82 to String 22. The cross-sectional area of the arrow and radially extending feathers 86 define a region termed a fletching clearance 90 (shown in phantom). The sighting clearance 78 and fletching clearance 90 are unim peded by cables 21, 23, 56 and 58 traversing the clearance regions 78 and 90. Two reasons account for the clearances 78 and 90 being unimpeded. First, since the symmetry of the cable configuration has each cable extending between the limbs on the Same side of the bow, no cable crosses into the clearance regions 78 and 90. Secondly, the use of axle anchors described previously regarding FIGS. 7-9 allows for adjustment of the cables away from the clearance regions as needed. Conventional bows routinely use less than four cables and a String. Increasing the number of cables Secured between limbs of the archery bow allows for decreasing the diameter dimensions of at least one cable. For example, one or more of cables 21, 23, 56, and 58 may include diameter dimen Sions greater than 0 inch and less than /s inch, for example, from about 3/32 inch to less than /s inch. An exemplary diametric range comprises from about 3/32 inch to less than /s inch. The String may include diameter dimensions ranging from about 1/16 inch to less than %16 inch. Smaller dimen Sioned cables and String can increase the efficiency of a bow. Referring to FIG. 16, another embodiment of bow 10b is illustrated comprising another embodiment of a rotating member 100. Rotating member 100 is rotatably joined to limb 16 and an idler wheel 102 is rotatably secured to limb 14. A yoke 110 secures drawstring 22 to a cable assembly, for example to cable 106, more thoroughly described and illustrated in FIG. 21. It should be understood that rotating member 100 could be rotatably joined to limb 14, and idler wheel 102 rotatable secured to limb 16. Another embodi ment includes no rotating member on limb 14 with String 22 extending between limb 14 and rotating member 100. Referring to FIG. 17, rotating member 100 is illustrated and comprises a first cam 122 having an eccentric profile to provide a first camming surface 127. First cam 122 has a first outwardly facing Surface 134. A Second cam 123 has an eccentric profile to provide a Second camming Surface 129. Second cam 123 has a second outwardly facing surface 136 (shown in FIG. 21). A primary cam 120 is oriented between the first and second cams 122 and 123. The eccentric profile of the first cam 122 is substantially symmetrically oriented as a mirror image of the eccentric profile of the Second cam 123 relative primary cam 120. A fourth cam 124 extends outwardly from the first outwardly facing surface 134 of the first cam 122 and the fourth cam 124 has an eccentric profile to provide a fourth camming surface 131. A fifth cam 125 (shown in FIG. 21) extends outwardly from the second outwardly facing surface 136 (shown in FIG. 21) of second cam 123. The fifth cam 125 has an eccentric profile to provide a fifth camming surface 132 (shown in FIG.21). The eccentric profile of the fourth cam 124 is substantially Symmetrically oriented as a mirror image of the eccentric profile of the fifth cam 125 relative the primary cam First and Second cams 122 and 123 are equidistant and parallel relative primary cam 120 and fourth and fifth cams 124 and 125 are equidistant and parallel relative primary cam 120. Accordingly, the cam design on either Side of primary cam 120 is Substantially Symmetrical to balance forces in rotating member 100 associated with the tensile forces from the cables and String. The Symmetry minimizes the twisting of limbs. It should be understood that an embodiment of bow 10b could include a rotating member 100 rotatably joined to limb 14 and a rotating member 100 rotatably joined to limb 16. Referring to FIG. 19, an embodiment of bow 10b com prises an idler wheel 102 rotatably joined to limb 14. Idler wheel 102 includes a concentric profile defining a single centrally positioned groove 103 to receive String 22. Referring to FIG. 20, an exemplary yoke 110 has string 22 terminating in yoke 110 and cable 106 slidingly held within yoke 110. It should be understood that various arrangements of string 22 and cable 106 could be designed. For example, String 22 could slidingly cooperate around or through yoke 110. Another example includes cable 106 with two ends terminating within yoke 110. Another embodiment includes string 22 branching off into two strings 106 without the use of the yoke 110. Yoke 110 comprises any material capable of handling the tensile Stresses common in bow cables, for example, metal. Referring to FIG. 21, archery bow 10b is illustrated from the perspective of an archer using the bow 10b. Cable 106 is received by cams 124 and 125 and extends through yoke 110. Cable 104 is received by cam 122 and terminates at anchor 50 of limb 14 (only forked member 44 is shown) on the right side of bow 10b. Cable 108 is received by cam 123 and terminates at anchor 50 of limb 14 (only forked member 44 is shown) on the left side of bow 10b. The cable configuration on one side of bow 10b is a mirror image of the cable configuration on the other Side once again estab lishing Symmetry. Referring to FIGS. 22 and 23, another embodiment of idler wheel 102a is illustrated. In FIG. 22, idler wheel is shown in the rest position and comprises a central portion 112 and opposed helical grooves 114 and 116 substantially Symmetrically oriented on either Side of the central portion 112. The grooves receive String 22 wherein the String 22 splits into two cables 22a and 22b before riding on idler wheel 102a. Strings 22a and 22b are received on opposite Sides of the central portion 112 in grooves most adjacent the central portion 112. Cable 22a rides in grooves 116 and cable 22b rides in grooves 114. Referring to FIG. 23, idler wheel 102a is shown in a draw position. Idler wheel 102a rotates to move the two cables 22a and 22b in opposite directions by the opposed helical grooves 114 and 116. While this embodiment does not use yoke 110, the cables are still substantially symmetrically received over the idler wheel 102a to balance the tensile forces of the cables transferred into the bow. Again referring to FIG. 22, cables 22a and 22b are illustrated beginning at the front of idler wheel 102a, riding over idler wheel 102a in grooves 116 and 114, respectively, and exiting the grooves 116 and 114 at the back of idler wheel 102a for a 180 wrap around idler wheel 102a. However, it should be understood that cables 22a and 22b could wrap an additional 360 (or any multiple thereof) around idler wheel 102a for a total of 540. Furthermore, it should be understood that if cables 22a and 22b are to wrap around idler wheel 102a an additional number of times, for example, Such as wrapping cables 22a and 22b around idler
20 wheel 102a twice for a total of additional 720, cables 22a and 22b may need to be longer than illustrated to accom modate the increased wraps, and idler wheel 102a may need to include more grooves 114 and 116 to accommodate the longer cables 22a and 22b. In compliance with the Statute, the invention has been described in language more or less Specific as to structural and methodical features. It is to be understood, however, that the invention is not limited to the Specific features shown and described, Since the means herein disclosed comprise preferred forms of putting the invention into effect. The invention is, therefore, claimed in any of its forms or modifications within the proper Scope of the appended claims appropriately interpreted in accordance with the doctrine of equivalents. What is claimed is: 1. An archery bow comprising: a first limb and a second limb; a handle between the limbs; a rotating member comprising at least two cams rotatably joined to the first limb, a first of the two cams com prising an eccentric profile to provide a first camming Surface and a Second of the two cams comprising an eccentric profile to provide a Second camming Surface, the eccentric profile of the first cam is Substantially Symmetrical relative to the eccentric profile of the Second cam; and a String extending between the rotating member and Second limb. 2. The archery bow of claim 1 wherein the eccentric profile of the first cam is parallel to the eccentric profile of the Second cam. 3. The archery bow of claim 1 wherein the eccentric profile of the first cam is Substantially Symmetrically aligned to the eccentric profile of the Second cam. 4. The archery bow of claim 1 wherein the eccentric profile of the first cam is Substantially Symmetrically aligned and angled relative to the eccentric profile of the Second C. 5. The archery bow of claim 1 wherein the rotating member further comprises a primary cam in rotational cooperation with the first and Second cams. 6. The archery bow of claim 1 wherein the rotating member further comprises a primary cam between the first and Second cams. 7. The archery bow of claim 1 wherein the rotating member further comprises a primary cam between the first and Second cams, the primary cam comprising an eccentric profile not Substantially Symmetrical relative the eccentric profiles of the first and Second cams. 8. The archery bow of claim 1 wherein the rotating member further comprises a primary cam between the first and Second cams, the primary cam comprises an eccentric profile parallel to the eccentric profiles of the first and Second cams. 9. The archery bow of claim 1 wherein the rotating member further comprises a primary cam between the first and Second cams, and wherein the first and Second cams are equidistant from the primary cam. 10. The archery bow of claim 1 wherein the rotating member further comprises a primary cam between the first and Second cams, and wherein the eccentric profile of the first cam is Substantially Symmetrically aligned relative to the eccentric profile of the Second cam. 11. The archery bow of claim 1 wherein the rotating member further comprises a primary cam between the first and Second cams, the primary cam comprises an eccentric profile, the eccentric profiles of the first and Second cams are angled relative the eccentric profile of the primary cam, and the eccentric profile of the first cam forms Substantially a mirror image of the eccentric profile of the Second cam relative to the eccentric profile of the primary cam. 12. The archery bow of claim 1 wherein the rotating member is further comprises a primary cam between the first and Second cams, and wherein the first and Second cams are integrally formed with the primary cam to form a single integral Structure for the rotating member. 13. The archery bow of claim 1 wherein the rotating member further comprises a primary cam between the first and Second cams, and the first and Second cams are discrete Structures removably attached to the primary cam. 14. The archery bow of claim 1 wherein the rotating member further comprises a primary cam between the first and Second cams, and at least one of the first and Second cams is a discrete Structure removably attached to the primary cam. 15. The archery bow of claim 1 further comprising a member rotatably joined to the second limb. 16. The archery bow of claim 1 further comprising at least one generally cylindrical anchor removably attached to a limb and comprising a plurality of discrete circumferential grooves with each groove laterally Spaced from the limb. 17. The archery bow of claim 1 further comprising a rotating component rotatably joined to the Second limb, the String extending between the rotating member and rotating component. 18. The archery bow of claim 1 wherein the rotating member further comprises a primary cam between the first and Second cams, the first cam comprises a first outwardly facing Surface and the Second cam comprises a Second outwardly facing Surface, a fourth cam extends outwardly from the first outwardly facing Surface, a fifth cam extends outwardly from the Second outwardly facing Surface. 19. The archery bow of claim 18 wherein the fourth cam comprises an eccentric profile to provide a fourth camming Surface and the fifth cam comprises an eccentric profile to provide a fifth camming Surface, the eccentric profile of the fourth cam is Substantially Symmetrical relative to the eccen tric profile of the fifth cam. 20. The archery bow of claim 18 wherein the fourth cam is aligned in Substantially a mirror image relationship with the fifth cam. 21. An archery bow comprising: a pair of flexible resilient bow limbs forming first and Second outer bow limb ends and forming first and Second inner bow limb ends; a handle connecting the first and Second inner bow limb ends, a String extending between the first and Second Outer bow limb ends; and at least four cables extending between the first and Second outer bow limb ends. 22. The archery bow of claim 21 wherein the four cables are discrete cables relative to one another. 23. The archery bow of claim 21 further comprising at least one cable anchor laterally extending from an outer bow limb end, the cable anchor comprising generally a cylindri cal Surface having a plurality of discrete circumferential grooves, each groove laterally displaced from an adjacent groove. 24. The archery bow of claim 21 wherein each outer bow limb end comprises two laterally outwardly facing Sides, and the archery bow further comprises at least one cable anchor
21 11 laterally extending outwardly from each laterally outwardly facing Side, the cable anchors comprising a plurality of discrete grooves, each groove laterally displaced from an adjacent groove. 25. The archery bow of claim 24 wherein the four cables are discrete cables relative to one another, and each cable comprises two terminal ends, one terminal end Secured to one cable anchor of one outer bow limb end and the other terminal end secured to the other outer bow limb end, the two terminal ends of each cable Secured to the same Side of the first and second outer bow limb ends. 26. The archery bow of claim 21 wherein the archery bow comprises opposed Sides, two of the four cables extend between first and second outer bow limb ends on one side of the bow, and the other two cables extend between first and Second outer bow limb ends on the other side of the bow. 27. An archery bow comprising: a handle, a first flexible bow limb and a second flexible bow limb, the first and Second bow limbs being mounted on and projecting oppositely from the handle and terminating in first and Second bow limb tips, respectively; a String extending between the first and Second bow limb tips, and at least one cable anchor laterally extending from one flexible bow limb, the cable anchor comprising an outward Surface having a plurality of peripheral dis crete grooves, each groove laterally displaced from an adjacent groove. 28. The archery bow of claim 27 wherein each bow limb tip defines a slot having inside Surfaces, the cable anchor laterally extending inwardly from the inside Surfaces. 29. The archery bow of claim 27 wherein each bow limb tip comprises outwardly facing opposed Surfaces, the cable anchor laterally extending outwardly from one outwardly facing Surface. 30. The archery bow of claim 27 further comprises an axle secured within each bow limb tip and the cable anchor laterally extends from one bow limb tip removably secured on the axle. 31. The archery bow of claim 27 further comprises an axle secured within each bow limb tip and the cable anchor comprises an opening contoured to Securely receive the axle. 32. The archery bow of claim 27 further comprises an axle secured within each bow limb tip and the cable anchor comprises an opening contoured to receive the axle and allow adjusting movement of the axle within the cable anchor. 33. The archery bow of claim 27 further comprises an axle secured within each bow limb tip and each bow limb tip comprises two sides with each Side facing laterally out Wardly opposite the other side, a cable anchor laterally extends outward from each side of each bow limb tip removably Secured on the axle. 34. An archery bow comprising: a first limb and a second limb; a handle between the limbs; and at least one cable extending between the first and Second limbs, the cable having a diameter dimension greater than 0 inches and ranging from about 3/32 inch to less than /s inch. 35. The archery bow of claim 34 wherein the at least one cable comprises a diameter dimension ranging from about 3/32 inch to less than /s inch. 36. The archery bow of claim 34 further comprising a String having diameter dimensions ranging from about /16 inch to less than %16 inch The archery bow of claim 34 wherein each limb comprises two laterally outwardly facing Sides, and the archery bow further comprises at least one cable anchor laterally extending outwardly from each laterally outwardly facing Side, the cable anchors comprising generally a cylin drical shape having a plurality of discrete circumferential grooves, each groove laterally displaced from an adjacent groove and capable of receiving the cable, the cable capable of being positioned laterally outward from the archery bow by positioning the cable in a more outward groove relative the archery bow. 38. The archery bow of claim 34 further comprising a plurality of cables with at least two of the cables having diameter dimensions ranging from about 3/32 inch to less than /s inch. 39. The archery bow of claim 34 further comprising four cables and a String, the String having diameter dimensions ranging from about /16 inch to less than %16 inch. 40. The archery bow of claim 34 further comprising four cables and a String, the cables having diameter dimensions ranging from about 3/32 inch to less than % inch and the String having diameter dimensions ranging from about /16 inch to less than %16 inch. 41. An archery bow comprising: a handle having opposing ends, a first flexible limb and a second flexible limb, each limb extending outwardly from the handle opposing ends, and each limb having a distal end; an axle secured within the distal end of the first flexible limb; a rotating member Secured on the axle, a String extending between the rotating member and a region proximate the distal end of the Second flexible limb; at least two discrete bearings rotatably mounted on the axle to rotatably Support the rotating member; and wherein the rotating member comprises a primary cam between two Secondary cams. 42. The archery bow of claim 41 further comprising one discrete bearing contacting one Secondary cam and the other discrete bearing contacting the other Secondary cam. 43. The archery bow of claim 41 further comprising a plurality of discrete bearings Spaced from each other for evenly distributing and balancing the Support weight of the rotating member on each bearing. 44. The archery bow of claim 41 further comprising at least one cable and at least one cable anchor laterally extending from one limb, the cable anchor comprising generally a cylindrical shape having a plurality of discrete circumferential grooves, each groove laterally displaced from an adjacent groove and capable of receiving the cable. 45. The archery bow of claim 41 wherein the primary cam has two outward Sides, the primary cam between a plurality of Secondary cams, a plurality of Secondary cams on each Side of the primary cam, one discrete bearing Supporting the rotating member on one side of the primary cam and the other discrete bearing Supporting the rotating member on the other Side of the primary cam, the discrete bearings equi distant from the primary cam. 46. The archery bow of claim 41 wherein the primary cam has two outward Sides, the primary cam between a plurality of Secondary cams, a plurality of Secondary cams on each Side of the primary cam, a plurality of discrete bearings Spaced from each other for evenly distributing and balancing the Support weight of the rotating member on each bearing.
22 An archery bow comprising: a first limb and a second limb; a handle between the limbs; a first rotating member comprising at least two cams rotatably joined to the first limb, a first of the at least two cams comprising an eccentric profile to provide a first camming Surface and a Second of the at least two cams comprising an eccentric profile to provide a Second camming Surface, the eccentric profile of the first cam is Substantially Symmetrical relative to the eccentric profile of the Second cam; a Second rotating member comprising at least two cams rotatably joined to the second limb, a third of the at least two cams comprising an eccentric profile to provide a third camming Surface and a fourth of the at least two cams comprising an eccentric profile to provide a fourth camming Surface, the eccentric profile of the third cam is substantially symmetrical relative to the eccentric profile of the fourth cam; and a String extending between the first and Second rotating members. 48. The archery bow of claim 47 wherein the first rotating member comprises a primary cam between the first and Second cams and the Second rotating member comprises a primary cam between the third and fourth cams. 49. The archery bow of claim 47 wherein the first rotating member comprises a first primary cam between the first and Second cams and the Second rotating member comprises a Second primary cam between the third and fourth cams, the first and Second cams are parallel and equidistant relative the first primary cam and the third and fourth cams are parallel and equidistant relative the Second primary cam. 50. The archery bow of claim 49 wherein the string has two ends and extends between the first and Second primary cams with one end Secured to the first rotating member and the other end Secured to the Second rotating member, the String and primary cams establish a centrally vertical plane through the archery bow to define a right side of the bow and a left side of the bow opposite the right side relative the plane. 51. The archery bow of claim 50 further comprising four cables, two cables positioned between the limbs on the right Side of the plane and two cables positioned between the limbs on the left side of the plane, the two cables on one side are Secured to the bow in the Same fashion as the two cables on the other side. 52. The archery bow of claim 51 wherein each cable comprises two ends, the two cables on the right Side com prise one cable having one end Secured to the first limb and the other end secured over the fourth cam to the second rotating member of the second limb and the other cable on the right Side having one end Secured to the Second limb and the other end Secured over the Second cam to the first rotating member of the first limb, and the two cables on the left Side of the plane configured the Same as the right side cables. 53. The archery bow of claim 52 wherein the ends of the cables secured to the limbs are secured to the limbs by cable anchors, the cable anchors having a plurality of discrete peripheral grooves to receive the cable ends, the grooves generally parallel to the plane established by the String and primary cams and each groove laterally spaced from the adjacent groove. 54. An archery bow comprising: a central handle having opposing ends, a first flexible power limb extending outwardly from one handle end and a Second flexible power limb extending outwardly from the other handle end, each of the limbs having an inner end connected with the handle and an Outer free end; a rotating member rotatably joined to the outer free end of the first flexible power limb, the rotating member comprising: a first cam comprising an eccentric profile to provide a first camming Surface, the first cam having a first outwardly facing Surface; a Second cam comprising an eccentric profile to provide a Second camming Surface, the Second cam having a Second outwardly facing Surface; a primary cam between the first and Second cams, and wherein the eccentric profile of the first cam is sub Stantially Symmetrically oriented as a mirror image of the eccentric profile of the Second cam relative the primary cam; a fourth cam extending outwardly from the first outwardly facing Surface of the first cam, the fourth cam com prising an eccentric profile to provide a fourth camming Surface; and a fifth cam extending outwardly from the Second out Wardly facing Surface of the Second cam, the fifth cam comprising an eccentric profile to provide a fifth cam ming Surface, and wherein the eccentric profile of the fourth cam is Substantially Symmetrically oriented as a mirror image of the eccentric profile of the fifth cam relative the primary cam; and a String extending between the rotating member and the outer free end of the second flexible power limb. 55. The archery bow of claim 54 wherein the outer free end of the second flexible power limb rotatably supports an idler wheel comprising opposed helical grooves to receive the String. 56. The archery bow of claim 54 wherein the outer free end of the second flexible power limb rotatably supports an idler wheel comprising a central portion with opposed helical grooves Substantially Symmetrically oriented on either Side of the central portion, the grooves receive the String. 57. The archery bow of claim 54 wherein the outer free end of the second flexible power limb rotatably supports an idler wheel comprising a central portion with opposed helical grooves Substantially Symmetrically oriented on either Side of the central portion, the grooves receive the String, and wherein the String splits into two cables before received in the grooves. 58. The archery bow of claim 54 wherein the outer free end of the second flexible power limb rotatably supports an idler wheel comprising a central portion with opposed helical grooves Substantially Symmetrically oriented on either Side of the central portion, the grooves receive the String, and wherein the String splits into two cables before received in the grooves, the two cables are received in the grooves most adjacent the central portion wherein rotation of the idler wheel moves the two cables in the opposed helical grooves to Space apart the two cables. 59. An archery bow anchor comprising: an outward Surface having a plurality of peripheral dis crete grooves, each groove laterally displaced from an adjacent groove, and an opening extending axially through the anchor and dimensioned to receive a bow axle. 60. The archery bow anchor of claim 59 wherein the opening is dimensioned to allow adjusting movement of the axle.
23 The archery bow anchor of claim 59 wherein the outward Surface defines generally a cylindrical shape. 62. An archery bow cam assembly comprising: a first cam comprising an eccentric profile to provide a first camming Surface, a Second cam comprising an eccentric profile to provide a Second camming Surface, the eccentric profile of the first cam is Substantially Symmetrical relative to the eccentric profile of the Second cam; and a primary cam between the first and Second cams. 63. The archery bow cam assembly of claim 62 wherein the eccentric profile of the first cam is Substantially Sym metrically aligned to the eccentric profile of the Second cam. 64. The archery bow cam assembly of claim 62 wherein the eccentric profile of the first cam forms Substantially a mirror image of the eccentric profile of the Second cam relative the primary cam, and the first and Second cams are angled relative the primary cam. 65. The archery bow cam assembly of claim 62 wherein the primary cam comprises an eccentric profile not Substan tially symmetrical relative the eccentric profiles of the first and Second cams The archery bow cam assembly of claim 62 wherein at least one of the first and Second cams is a discrete Structure removably attached to the primary cam. 67. The archery bow cam assembly of claim 62 wherein the first cam comprises a first outwardly facing Surface and the Second cam comprises a Second outwardly facing Surface, a fourth cam extends outwardly from the first outwardly facing Surface of the first cam, a fifth cam extends outwardly from the Second outwardly facing Surface of the Second cam. 68. The archery bow cam assembly of claim 67 wherein the fourth cam comprises an eccentric profile to provide a fourth camming Surface and the fifth cam comprises an eccentric profile to provide a fifth camming Surface, the eccentric profile of the fourth cam is Substantially Symmetri cal relative to the eccentric profile of the fifth cam. 69. The archery bow cam assembly of claim 67 wherein the fourth cam is aligned in Substantially a mirror image relationship with the fifth cam. k k k k k
United States Patent (19) Smith
 United States Patent (19) Smith 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,546,754 Oct. 15, 1985 (54) YOKE ANCHOR FOR COMPOUND BOWS (75) Inventor: Max D. Smith, Evansville, Ind. 73 Assignee: Indian Industries,
United States Patent (19) Smith 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,546,754 Oct. 15, 1985 (54) YOKE ANCHOR FOR COMPOUND BOWS (75) Inventor: Max D. Smith, Evansville, Ind. 73 Assignee: Indian Industries,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,305,979 B1
 USOO7305979B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,305,979 B1 Yehe (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2007 (54) DUAL-CAMARCHERY BOW WITH 6,082,347 A * 7/2000 Darlington... 124/25.6 SMULTANEOUS POWER
USOO7305979B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,305,979 B1 Yehe (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2007 (54) DUAL-CAMARCHERY BOW WITH 6,082,347 A * 7/2000 Darlington... 124/25.6 SMULTANEOUS POWER
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Swihla et al. USOO6287091B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,287,091 B1 Sep. 11, 2001 (54) TURBOCHARGER WITH NOZZLE RING COUPLNG (75) Inventors: Gary R Svihla, Clarendon
(12) United States Patent Swihla et al. USOO6287091B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,287,091 B1 Sep. 11, 2001 (54) TURBOCHARGER WITH NOZZLE RING COUPLNG (75) Inventors: Gary R Svihla, Clarendon
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070257638A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0257638A1 Amend et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2007 (54) TWIST LOCK BATTERY INTERFACE FOR (52) U.S. Cl....
US 20070257638A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0257638A1 Amend et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2007 (54) TWIST LOCK BATTERY INTERFACE FOR (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8042596B2 (12) United States Patent Llagostera Forns (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) ARTICULATION DEVICE FOR AN AWNING ELBOW JOINT Inventor: Sep. 27, 2006 Joan Llagostera
USOO8042596B2 (12) United States Patent Llagostera Forns (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) ARTICULATION DEVICE FOR AN AWNING ELBOW JOINT Inventor: Sep. 27, 2006 Joan Llagostera
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
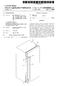 (19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
(19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060066075A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0066075A1 Zlotkowski (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2006 (54) TOWING TRAILER FOR TWO OR THREE Publication Classification
US 20060066075A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0066075A1 Zlotkowski (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2006 (54) TOWING TRAILER FOR TWO OR THREE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2
 US007592736 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2 Scott et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 2009 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ELECTRIC (56) References Cited GENERATOR WITH ROTOR CIRCUMIFERENTIALLY
US007592736 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2 Scott et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 2009 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ELECTRIC (56) References Cited GENERATOR WITH ROTOR CIRCUMIFERENTIALLY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1
 USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US B1
 USOO7628442B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Spencer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 2009 (54) QUICK RELEASE CLAMP FOR TONNEAU (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/100.04, COVER 296/100.07,
USOO7628442B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Spencer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 2009 (54) QUICK RELEASE CLAMP FOR TONNEAU (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/100.04, COVER 296/100.07,
od f 11 (12) United States Patent US 7,080,599 B2 Taylor Jul. 25, 2006 (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.:
 US007080599B2 (12) United States Patent Taylor (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006 (54) RAILROAD HOPPER CAR TRANSVERSE DOOR ACTUATING MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Fred J. Taylor, 6485 Rogers
US007080599B2 (12) United States Patent Taylor (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006 (54) RAILROAD HOPPER CAR TRANSVERSE DOOR ACTUATING MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Fred J. Taylor, 6485 Rogers
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,641,228 B2
 USOO6641228B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,641,228 B2 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) DETACHABLE FRONT WHEEL STRUCTURE (56) References Cited OF GOLF CART U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
USOO6641228B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,641,228 B2 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) DETACHABLE FRONT WHEEL STRUCTURE (56) References Cited OF GOLF CART U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,237,582 B1
 USOO6237582B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,237,582 B1 McPhersOn 45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 9 (54) ARCHERY BOW WITH BOW STRING 5,174,268 12/1992 Martin et al.... 124/25.6 COPLANAR
USOO6237582B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,237,582 B1 McPhersOn 45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2001 9 (54) ARCHERY BOW WITH BOW STRING 5,174,268 12/1992 Martin et al.... 124/25.6 COPLANAR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1
 USOO648.4362B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1 Ku0 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) RETRACTABLE HANDLE ASSEMBLY WITH 5,692,266 A 12/1997 Tsai... 16/113.1 MULTIPLE ENGAGING
USOO648.4362B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1 Ku0 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) RETRACTABLE HANDLE ASSEMBLY WITH 5,692,266 A 12/1997 Tsai... 16/113.1 MULTIPLE ENGAGING
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7654162B2 (12) United States Patent Braaten (54) DEVICE FOR INSTALLATION OF A PROBE AND PROBEACCOMMODATING ARRANGEMENT (75) Inventor: Nils A. Braaten, Trondheim (NO) (73) Assignee: Roxar ASA, Stavanger
USOO7654162B2 (12) United States Patent Braaten (54) DEVICE FOR INSTALLATION OF A PROBE AND PROBEACCOMMODATING ARRANGEMENT (75) Inventor: Nils A. Braaten, Trondheim (NO) (73) Assignee: Roxar ASA, Stavanger
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
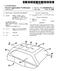 (19) United States US 20090045655A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0045655A1 Willard et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 19, 2009 (54) MULTI-PANEL PANORAMIC ROOF MODULE (75) Inventors:
(19) United States US 20090045655A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0045655A1 Willard et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 19, 2009 (54) MULTI-PANEL PANORAMIC ROOF MODULE (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 US0072553.52B2 (12) United States Patent Adis et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 14, 2007 (54) PRESSURE BALANCED BRUSH SEAL (75) Inventors: William Edward Adis, Scotia, NY (US); Bernard
US0072553.52B2 (12) United States Patent Adis et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 14, 2007 (54) PRESSURE BALANCED BRUSH SEAL (75) Inventors: William Edward Adis, Scotia, NY (US); Bernard
3 23S Sé. -Né 33% (12) United States Patent US 6,742,409 B2. Jun. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: 6B M 2 O. (51) Int. Cl...
 (12) United States Patent Blanchard USOO6742409B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 2004 (54) DEVICE FORTRANSMISSION BETWEEN A PRIMARY MOTOR SHAFT AND AN OUTPUT SHAFT AND LAWN MOWER PROVIDED
(12) United States Patent Blanchard USOO6742409B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 2004 (54) DEVICE FORTRANSMISSION BETWEEN A PRIMARY MOTOR SHAFT AND AN OUTPUT SHAFT AND LAWN MOWER PROVIDED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0226455A1 Al-Anizi et al. US 2011 0226455A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SLOTTED IMPINGEMENT PLATES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0226455A1 Al-Anizi et al. US 2011 0226455A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SLOTTED IMPINGEMENT PLATES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O190837A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0190837 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2003 (54) BATTERY HOLDER HAVING MEANS FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 439/500 SECURELY
US 2003O190837A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0190837 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2003 (54) BATTERY HOLDER HAVING MEANS FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 439/500 SECURELY
III III III. United States Patent 19 Justice. 11 Patent Number: position. The panels are under tension in their up position
 United States Patent 19 Justice (54) (76) (21) 22) (51) (52) 58 56) TRUCK BED LOAD ORGANIZER APPARATUS Inventor: 4,733,898 Kendall Justice, P.O. Box 20489, Wickenburg, Ariz. 85358 Appl. No.: 358,765 Filed:
United States Patent 19 Justice (54) (76) (21) 22) (51) (52) 58 56) TRUCK BED LOAD ORGANIZER APPARATUS Inventor: 4,733,898 Kendall Justice, P.O. Box 20489, Wickenburg, Ariz. 85358 Appl. No.: 358,765 Filed:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,270 B2
 USOO654327OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,270 B2 Cmelik (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) AUTOBODY DENT REPAIR TOOL 4,461,192 A * 7/1984 Suligoy et al.... 81/177.7 4,502,317
USOO654327OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,270 B2 Cmelik (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) AUTOBODY DENT REPAIR TOOL 4,461,192 A * 7/1984 Suligoy et al.... 81/177.7 4,502,317
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,695,581 B2
 USOO6695581B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,695,581 B2 Wass0n et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 2004 (54) COMBINATION FAN-FLYWHEEL-PULLEY JP 59-81.835 2/1984 ASSEMBLY AND METHOD OF
USOO6695581B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,695,581 B2 Wass0n et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 2004 (54) COMBINATION FAN-FLYWHEEL-PULLEY JP 59-81.835 2/1984 ASSEMBLY AND METHOD OF
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2
 US009 168973B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2 Offe (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2015 (54) MOTORCYCLE SUSPENSION SYSTEM (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Andrew Offe, Wilunga
US009 168973B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2 Offe (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2015 (54) MOTORCYCLE SUSPENSION SYSTEM (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Andrew Offe, Wilunga
United States Patent (19) Koitabashi
 United States Patent (19) Koitabashi 54 75 (73) 1 (51) (5) (58 56) ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH WITH AN IMPROVED MAGNETC ROTATABLE MEMBER Inventor: Takatoshi Koitabashi, Annaka, Japan Assignee: Sanden Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Koitabashi 54 75 (73) 1 (51) (5) (58 56) ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH WITH AN IMPROVED MAGNETC ROTATABLE MEMBER Inventor: Takatoshi Koitabashi, Annaka, Japan Assignee: Sanden Corporation,
ADJUSTABLE PEDAL ASSEMBLY WITH ELECTRONIC THROTTLE CONTROL RELATED APPLICATION. filed Jan. 26, 1999, U.S. Pat. No. 6,109,241.
 ADJUSTABLE PEDAL ASSEMBLY WITH ELECTRONIC THROTTLE CONTROL RELATED APPLICATION [0001] This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 09/236,975, filed Jan. 26, 1999, U.S. Pat. No. 6,109,241.
ADJUSTABLE PEDAL ASSEMBLY WITH ELECTRONIC THROTTLE CONTROL RELATED APPLICATION [0001] This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 09/236,975, filed Jan. 26, 1999, U.S. Pat. No. 6,109,241.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,643,958 B1
 USOO6643958B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Krejci (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 11, 2003 (54) SNOW THROWING SHOVEL DEVICE 3,435,545. A 4/1969 Anderson... 37/223 3,512,279 A 5/1970 Benson... 37/244
USOO6643958B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Krejci (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 11, 2003 (54) SNOW THROWING SHOVEL DEVICE 3,435,545. A 4/1969 Anderson... 37/223 3,512,279 A 5/1970 Benson... 37/244
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
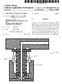 US 2004.00431 O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0043102 A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2004 (54) ALIGNMENT COLLAR FOR A NOZZLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 425/567
US 2004.00431 O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0043102 A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2004 (54) ALIGNMENT COLLAR FOR A NOZZLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 425/567
US 7, B2. Loughrin et al. Jan. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: and/or the driven component. (12) United States Patent (54) (75)
 USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,805,593 B2
 USOO6805593B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,805,593 B2 Spaulding et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 2004 (54) QUICK CONNECT BATTERY TERMINAL 3,764,961. A 10/1973 Poltras... 439/759
USOO6805593B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,805,593 B2 Spaulding et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 2004 (54) QUICK CONNECT BATTERY TERMINAL 3,764,961. A 10/1973 Poltras... 439/759
(10) Patent No.: US 8,181,638 B1
 US008181638B1 (12) United States Patent Yehe (54) (76) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) ECCENTRC POWER CABLE LET OUT MECHANISMFORA COMPOUND ARCHERY BOW Inventor: Notice: Craig T. Yehle, Junction City,
US008181638B1 (12) United States Patent Yehe (54) (76) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) ECCENTRC POWER CABLE LET OUT MECHANISMFORA COMPOUND ARCHERY BOW Inventor: Notice: Craig T. Yehle, Junction City,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Minnerop 54) DEVICE FOR WATER COOLING OF ROLLED STEEL SECTIONS 75 Inventor: Michael Minnerop, Ratingen, Germany 73 Assignee: SMS Schloemann-Siemag Aktiengesellschaft, Dusseldorf,
United States Patent (19) Minnerop 54) DEVICE FOR WATER COOLING OF ROLLED STEEL SECTIONS 75 Inventor: Michael Minnerop, Ratingen, Germany 73 Assignee: SMS Schloemann-Siemag Aktiengesellschaft, Dusseldorf,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.:
 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: USOO96371 64B2 Shavrnoch et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2017 (54) NYLON RESIN DRIVEN PULLEY (58) Field of Classification Search CPC... B62D 5700; B62D 5/04;
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: USOO96371 64B2 Shavrnoch et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2017 (54) NYLON RESIN DRIVEN PULLEY (58) Field of Classification Search CPC... B62D 5700; B62D 5/04;
United States Patent (19) Maloof
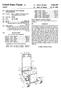 United States Patent (19) Maloof 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 1984 54 CART WITH SEAT AND STORAGE COMPARTMENT 76 Inventor: John J. Maloof, 20 Greenwood St., East Hartford, Conn. 06118
United States Patent (19) Maloof 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 1984 54 CART WITH SEAT AND STORAGE COMPARTMENT 76 Inventor: John J. Maloof, 20 Greenwood St., East Hartford, Conn. 06118
United States Patent (19) Miller, Sr.
 United States Patent (19) Miller, Sr. 11 Patent Number: 5,056,448 (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 1991 (54) (76. (21) (22) 51 (52) (58) PVC BOAT Inventor: Terry L. Miller, Sr., P.O. Box 162, Afton, Okla.
United States Patent (19) Miller, Sr. 11 Patent Number: 5,056,448 (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 1991 (54) (76. (21) (22) 51 (52) (58) PVC BOAT Inventor: Terry L. Miller, Sr., P.O. Box 162, Afton, Okla.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,446,482 B1. Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002
 USOO64.46482B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002 (54) BATTERY OPERATED HYDRAULIC D408.242 S 4/1999 Yamamoto... D8/61 COMPRESSION TOOL WITH RAPID
USOO64.46482B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002 (54) BATTERY OPERATED HYDRAULIC D408.242 S 4/1999 Yamamoto... D8/61 COMPRESSION TOOL WITH RAPID
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2
 US007125133B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2 Bilotti et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2006 (54) LED LIGHTING SYSTEM FOR PATIO 4.425,602 A 1/1984 Lansing UMBRELLA 5,053,931
US007125133B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2 Bilotti et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2006 (54) LED LIGHTING SYSTEM FOR PATIO 4.425,602 A 1/1984 Lansing UMBRELLA 5,053,931
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9281614B1 (10) Patent No.: US 9.281,614 B1 Bonucci et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) CONNECTOR ASSEMBLY HAVING (56) References Cited LOCKING MEMBERS U.S. PATENT
(12) United States Patent USOO9281614B1 (10) Patent No.: US 9.281,614 B1 Bonucci et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) CONNECTOR ASSEMBLY HAVING (56) References Cited LOCKING MEMBERS U.S. PATENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0290354 A1 Marty et al. US 20140290354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) AIR DATA PROBE SENSE PORT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0290354 A1 Marty et al. US 20140290354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) AIR DATA PROBE SENSE PORT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,603,232 B2. Van Dine et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003
 USOO6603232B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Van Dine et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET RETAINING 4,745,319 A * 5/1988 Tomite et al.... 310/154.26 ARRANGEMENT FOR
USOO6603232B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Van Dine et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET RETAINING 4,745,319 A * 5/1988 Tomite et al.... 310/154.26 ARRANGEMENT FOR
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1. Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002
 USOO6435993B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1 Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) HYDRAULIC CHAIN TENSIONER WITH 5,707.309 A 1/1998 Simpson... 474/110 VENT DEVICE AND
USOO6435993B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1 Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) HYDRAULIC CHAIN TENSIONER WITH 5,707.309 A 1/1998 Simpson... 474/110 VENT DEVICE AND
21 Appl. No.: 934,807 Abattery dispenser system with detachable dispensing units
 USOO5855422A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Naef (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 1999 54 BATTERY DISPENSER SYSTEM WITH Primary Examiner Peter M. Cuomo DETACHABLE DISPENSING UNITS ASSistant Examiner-James
USOO5855422A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Naef (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 1999 54 BATTERY DISPENSER SYSTEM WITH Primary Examiner Peter M. Cuomo DETACHABLE DISPENSING UNITS ASSistant Examiner-James
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,469,466 B1
 USOO6469466B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,469,466 B1 Suzuki (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2002 (54) AUTOMATIC GUIDED VEHICLE JP 7-2S1768 10/1995 JP 8-1553 1/1996 (75) Inventor: Takayuki
USOO6469466B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,469,466 B1 Suzuki (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2002 (54) AUTOMATIC GUIDED VEHICLE JP 7-2S1768 10/1995 JP 8-1553 1/1996 (75) Inventor: Takayuki
(12) United States Patent
 USOO861 8656B2 (12) United States Patent Oh et al. (54) FLEXIBLE SEMICONDUCTOR PACKAGE APPARATUS HAVING ARESPONSIVE BENDABLE CONDUCTIVE WIRE MEMBER AND A MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Tac Keun.
USOO861 8656B2 (12) United States Patent Oh et al. (54) FLEXIBLE SEMICONDUCTOR PACKAGE APPARATUS HAVING ARESPONSIVE BENDABLE CONDUCTIVE WIRE MEMBER AND A MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Tac Keun.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080264.753A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0264753 A1 Rollion et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2008 (54) FRICTIONAL CLUTCH WITH O-RING Publication Classification
US 20080264.753A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0264753 A1 Rollion et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2008 (54) FRICTIONAL CLUTCH WITH O-RING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0121100A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0121100 A1 Feenstra (43) Pub. Date: May 26, 2011 (54) COVER FOR PROTECTINGA FUSIBLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2011 0121100A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0121100 A1 Feenstra (43) Pub. Date: May 26, 2011 (54) COVER FOR PROTECTINGA FUSIBLE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007026 1863A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0261863 A1 MACLEOD et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2007 (54) SEALING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 166/387: 166/202
(19) United States US 2007026 1863A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0261863 A1 MACLEOD et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2007 (54) SEALING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 166/387: 166/202
IIII. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,775,234 Solomon et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998
 IIII USOO5775234A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,775,234 Solomon et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998 54) HEIGHT ADJUSTABLE OVERBED TABLE FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS AND LOCKING DEVICE THEREFOR
IIII USOO5775234A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,775,234 Solomon et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998 54) HEIGHT ADJUSTABLE OVERBED TABLE FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS AND LOCKING DEVICE THEREFOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O00861 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0008610 A1 PetersOn (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2002 (54) KEY FOB WITH SLIDABLE COVER (75) Inventor: John Peterson,
(19) United States US 2002O00861 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0008610 A1 PetersOn (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2002 (54) KEY FOB WITH SLIDABLE COVER (75) Inventor: John Peterson,
and Crew LLP Mar. 4, 1999 (DE) Int. Cl."... GO2N 11/06
 (1) United States Patent Raffer USOO64O77OB1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 5, 001 (54) ROTARY VISCOSIMETER (75) Inventor: Gerhard Raffer, Graz (AT) (73) Assignee: Anton Paar GmbH, Graz (AT)
(1) United States Patent Raffer USOO64O77OB1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 5, 001 (54) ROTARY VISCOSIMETER (75) Inventor: Gerhard Raffer, Graz (AT) (73) Assignee: Anton Paar GmbH, Graz (AT)
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,820,200 Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080056631A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0056631 A1 Beausoleil et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2008 (54) TUNGSTEN CARBIDE ENHANCED Publication Classification
US 20080056631A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0056631 A1 Beausoleil et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2008 (54) TUNGSTEN CARBIDE ENHANCED Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 US00704.4047B1 (12) United States Patent Bennett et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) CYLNDER MOUNTED STROKE CONTROL Inventors: Robert Edwin Bennett,
US00704.4047B1 (12) United States Patent Bennett et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) CYLNDER MOUNTED STROKE CONTROL Inventors: Robert Edwin Bennett,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,220,819 B1
 USOO6220819B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,220,819 B1 Chien et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 24, 2001 (54) CENTRIFUGAL PUMP IMPELLER 3.368,744 2/1968 Jenn... 416/237 4,236,871 12/1980
USOO6220819B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,220,819 B1 Chien et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 24, 2001 (54) CENTRIFUGAL PUMP IMPELLER 3.368,744 2/1968 Jenn... 416/237 4,236,871 12/1980
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Ogasawara et al. (54) 75 RDING LAWN MOWER Inventors: Hiroyuki Ogasawara; Nobuyuki Yamashita; Akira Minoura, all of Osaka, Japan Assignee: Kubota Corporation, Osaka, Japan Appl.
United States Patent (19) Ogasawara et al. (54) 75 RDING LAWN MOWER Inventors: Hiroyuki Ogasawara; Nobuyuki Yamashita; Akira Minoura, all of Osaka, Japan Assignee: Kubota Corporation, Osaka, Japan Appl.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2
 USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO698.1746B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,981,746 B2 Chung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 2006 (54) ROTATING CAR SEAT MECHANISM 4,844,543 A 7/1989 Ochiai... 297/344.26 4,925,227
(12) United States Patent USOO698.1746B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,981,746 B2 Chung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 2006 (54) ROTATING CAR SEAT MECHANISM 4,844,543 A 7/1989 Ochiai... 297/344.26 4,925,227
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150292.498A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0292498A1 Williams (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 15, 2015 (54) OIL PUMPINGAPPARATUS INCLUDING A (52) U.S. Cl. CYCLOIDAL
US 20150292.498A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0292498A1 Williams (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 15, 2015 (54) OIL PUMPINGAPPARATUS INCLUDING A (52) U.S. Cl. CYCLOIDAL
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,080,888 B2. Hach (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006
 United States Patent US007080888B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,080,888 B2 Hach (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006 (54) DUAL NOZZLE HYDRO-DEMOLITION 6,049,580 A * 4/2000 Bodin et al.... 376/.316 SYSTEM 6,224,162
United States Patent US007080888B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,080,888 B2 Hach (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006 (54) DUAL NOZZLE HYDRO-DEMOLITION 6,049,580 A * 4/2000 Bodin et al.... 376/.316 SYSTEM 6,224,162
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,028,376 B2. filed on Jul. 2, 2012, now Pat No. 8,814,763, and a Assistant Examiner Nyca TNguyen
 USOO9028376B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: *May 12, 2015 (54) ABDOMEN EXERCISE MACHINE (2013.01); A63B 23/0216 (2013.01); A63B 23/03525 (2013.01); A63B 23/03533
USOO9028376B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: *May 12, 2015 (54) ABDOMEN EXERCISE MACHINE (2013.01); A63B 23/0216 (2013.01); A63B 23/03525 (2013.01); A63B 23/03533
US 9, B2. Stamps et al. Jul. 11, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (12) United States Patent (54)
 US0097.02402B2 (12) United States Patent Stamps et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,702.402 B2 Jul. 11, 2017 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) INCREASED CAPACITY SPHERICAL
US0097.02402B2 (12) United States Patent Stamps et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,702.402 B2 Jul. 11, 2017 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) INCREASED CAPACITY SPHERICAL
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9671 011B2 (12) United States Patent Kimijima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,671,011 B2 Jun. 6, 2017 (54) WORM BIASING STRUCTURE (71) Applicant: Showa Corporation, Gyoda-shi (JP)
USOO9671 011B2 (12) United States Patent Kimijima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,671,011 B2 Jun. 6, 2017 (54) WORM BIASING STRUCTURE (71) Applicant: Showa Corporation, Gyoda-shi (JP)
Your interest is appreciated and hope the next 37 pages offers great profit potential for your new business. Copyright 2017 Frank Seghezzi
 Description and comparison of the ultimate new power source, from small engines to power stations, which should be of interest to Governments the general public and private Investors Your interest is appreciated
Description and comparison of the ultimate new power source, from small engines to power stations, which should be of interest to Governments the general public and private Investors Your interest is appreciated
USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999
 USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999 54 SERIALLY CONNECTED CHARGER Primary Examiner Edward H. Tso Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Rosenberger,
USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999 54 SERIALLY CONNECTED CHARGER Primary Examiner Edward H. Tso Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Rosenberger,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2
 US0087.08325B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,708.325 B2 Hwang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2014 (54) PAPER CLAMPINGAPPARATUS FOR (56) References Cited OFFICE MACHINE (75) Inventors:
US0087.08325B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,708.325 B2 Hwang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2014 (54) PAPER CLAMPINGAPPARATUS FOR (56) References Cited OFFICE MACHINE (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9457897B2 (12) United States Patent Sutton et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.457,897 B2 Oct. 4, 2016 (54) (71) ROTOR SYSTEM SHEAR BEARING Applicant: Bell Helicopter Textron Inc., Fort
USOO9457897B2 (12) United States Patent Sutton et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.457,897 B2 Oct. 4, 2016 (54) (71) ROTOR SYSTEM SHEAR BEARING Applicant: Bell Helicopter Textron Inc., Fort
Phillips (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 10, (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search
 (12) United States Patent US008747274B2 () Patent No.: Phillips () Date of Patent: Jun., 2014 (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search TRANSMISSION USPC... 74/3, 331; 475/207
(12) United States Patent US008747274B2 () Patent No.: Phillips () Date of Patent: Jun., 2014 (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search TRANSMISSION USPC... 74/3, 331; 475/207
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,342,062 B1
 USOO6342062B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Suon et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 29, 2002 (54) RETRIEVAL DEVICES FOR VENA CAVA 5,344,427 A 9/1994 Cottenceau et al.... 606/200 FILTER 5,370,657
USOO6342062B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Suon et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 29, 2002 (54) RETRIEVAL DEVICES FOR VENA CAVA 5,344,427 A 9/1994 Cottenceau et al.... 606/200 FILTER 5,370,657
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial Number 09/652.305 Filing Date 20 August 2000 Inventor Antoniko M. Amaral Stanley J. Olson NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should
Serial Number 09/652.305 Filing Date 20 August 2000 Inventor Antoniko M. Amaral Stanley J. Olson NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,358,076 B1
 USOO68076B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,8,076 B1 Haag (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 19, 2002 (54) TWIST-LOCK CONNECTOR FOR 5,240,426. A 8/1993 Barla... 439/136 ELECTRICAL PLUG AND WALL
USOO68076B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,8,076 B1 Haag (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 19, 2002 (54) TWIST-LOCK CONNECTOR FOR 5,240,426. A 8/1993 Barla... 439/136 ELECTRICAL PLUG AND WALL
United States Patent (19) Dasa
 United States Patent (19) Dasa 54 MULTIPLE CONFIGURATION MODEL AIRCRAFT 76) Inventor: Madhava Dasa, P.O. Box 461, Kula, Hi. 96790-0461 (21) Appl. No.: 103,954 22 Filed: Oct. 2, 1987 51) Int. Cl.... A63H
United States Patent (19) Dasa 54 MULTIPLE CONFIGURATION MODEL AIRCRAFT 76) Inventor: Madhava Dasa, P.O. Box 461, Kula, Hi. 96790-0461 (21) Appl. No.: 103,954 22 Filed: Oct. 2, 1987 51) Int. Cl.... A63H
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Imai USOO6581225B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,581,225 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2003 (54) MATTRESS USED FOR PREVENTING BEDSORES OR THE LIKE (76) Inventor: KaZumichi Imai, 7-29-1222,
(12) United States Patent Imai USOO6581225B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,581,225 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2003 (54) MATTRESS USED FOR PREVENTING BEDSORES OR THE LIKE (76) Inventor: KaZumichi Imai, 7-29-1222,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
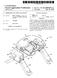 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0018979 A1 McCoy et al. US 201200 18979A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) FIFTH WHEEL HITCH ISOLATION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0018979 A1 McCoy et al. US 201200 18979A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) FIFTH WHEEL HITCH ISOLATION
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Scegiel et al. 54 (75) (73) (21) 22 (51) (52) 58 (56) BEEHVE LIFTING DEVICE Inventors: Mark J. Scegiel, Crown Point; John R. Hicks, Larwill, both of Ind. Assignee: Stow-A-Crane
United States Patent (19) Scegiel et al. 54 (75) (73) (21) 22 (51) (52) 58 (56) BEEHVE LIFTING DEVICE Inventors: Mark J. Scegiel, Crown Point; John R. Hicks, Larwill, both of Ind. Assignee: Stow-A-Crane
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8919333B2 (12) United States Patent Miller (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 30, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52) (58) BALANCED PULLEYASSEMBLY FOR COMPOUND ARCHERY
USOO8919333B2 (12) United States Patent Miller (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 30, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52) (58) BALANCED PULLEYASSEMBLY FOR COMPOUND ARCHERY
United States Patent (19) Cronk et al.
 United States Patent (19) Cronk et al. (S4) LANDING GEAR FOR ULTRALIGHT AIRCRAFT 76) Inventors: David Cronk, 1069 Eucalyptus Ave., Vista, Calif. 92025; Lyle M. Byrum, 1471 Calle Redonda, Escondido, Calif.
United States Patent (19) Cronk et al. (S4) LANDING GEAR FOR ULTRALIGHT AIRCRAFT 76) Inventors: David Cronk, 1069 Eucalyptus Ave., Vista, Calif. 92025; Lyle M. Byrum, 1471 Calle Redonda, Escondido, Calif.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6989498B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,989,498 B1 Linder et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2006 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR LOCKING (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent USOO6989498B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,989,498 B1 Linder et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2006 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR LOCKING (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.448,812 B2
 USOO8448812B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.448,812 B2 Gruber et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 28, 2013 (54) WASTE CONTAINER WITH BASE MEMBER 3,394,832 A * 7/1968 McAllister et. al....
USOO8448812B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.448,812 B2 Gruber et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 28, 2013 (54) WASTE CONTAINER WITH BASE MEMBER 3,394,832 A * 7/1968 McAllister et. al....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120072180A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0072180 A1 Stuckey et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 22, 2012 (54) TIRE MOLD DESIGN METHOD TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 703/1
(19) United States US 20120072180A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0072180 A1 Stuckey et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 22, 2012 (54) TIRE MOLD DESIGN METHOD TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 703/1
US A United States Patent Patent Number: 6, Lewis 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2000
 US006024.459A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 6,024.459 9 9 Lewis 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2000 9 54 EXTENDABLE REARVIEW MIRROR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS 76 Inventor: Jimmie L. Lewis, 523 Indian
US006024.459A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 6,024.459 9 9 Lewis 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2000 9 54 EXTENDABLE REARVIEW MIRROR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS 76 Inventor: Jimmie L. Lewis, 523 Indian
United States Patent (19) Muranishi
 United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
-10 III. United States Patent to. 39a. 39b. 21 Claims, 3 Drawing Sheets. Appl. No.: 643,492 Fied: May 6, 1996 Int. Cla.m.
 United States Patent to Lutzker III US005683166A 11 Patent Number: 5,683,166 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997 54 (76 21 22) 51 52 (58) ELECTROLUMNESCENT WALLPLATE Inventor: Robert S. Lutzker, Woodstone
United States Patent to Lutzker III US005683166A 11 Patent Number: 5,683,166 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997 54 (76 21 22) 51 52 (58) ELECTROLUMNESCENT WALLPLATE Inventor: Robert S. Lutzker, Woodstone
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O115854A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0115854 A1 Clever et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2016 (54) ENGINE BLOCKASSEMBLY (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... F0IP3/02
(19) United States US 2016O115854A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0115854 A1 Clever et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 28, 2016 (54) ENGINE BLOCKASSEMBLY (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... F0IP3/02
Continuously Variable Transmission
 Continuously Variable Transmission TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to a transmission, and more particularly, a continuously variable transmission capable of a continuous and constant variation
Continuously Variable Transmission TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to a transmission, and more particularly, a continuously variable transmission capable of a continuous and constant variation
United States Patent (19) Belter
 United States Patent (19) Belter 11) 45) Patent Number: Date of Patent: 4,746,023 May 24, 1988 (54) PUNCTURABLE OIL SEAL 75) Inventor: Jerome G. Belter, Mt. Prospect, Ill. 73) Assignee: Dana Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Belter 11) 45) Patent Number: Date of Patent: 4,746,023 May 24, 1988 (54) PUNCTURABLE OIL SEAL 75) Inventor: Jerome G. Belter, Mt. Prospect, Ill. 73) Assignee: Dana Corporation,
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2. Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005
 United States Patent USOO6915721B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2 Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) CORDLESS RATCHET WRENCH 6,311,583 B1 11/2001 Izumisawa... 81/57.13 6,715,380
United States Patent USOO6915721B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2 Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) CORDLESS RATCHET WRENCH 6,311,583 B1 11/2001 Izumisawa... 81/57.13 6,715,380
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,588,825 B1
 USOO6588825B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,588,825 B1 Wheatley (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2003 (54) RAIN DIVERTING DEVICE FOR A 6,024.402 A * 2/2000 Wheatley... 296/100.18 TONNEAU
USOO6588825B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,588,825 B1 Wheatley (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2003 (54) RAIN DIVERTING DEVICE FOR A 6,024.402 A * 2/2000 Wheatley... 296/100.18 TONNEAU
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,511,619 B2
 USOO851 1619B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,511,619 B2 Mann (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2013 (54) SLAT DEPLOYMENT MECHANISM (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Alan Mann, Bristol
USOO851 1619B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,511,619 B2 Mann (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2013 (54) SLAT DEPLOYMENT MECHANISM (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Alan Mann, Bristol
J. Brosius. disclaimed. Appl. No.: 561,873 Filed: Dec. 15, 1983 Int. Cl'... B61G 9/00 U.S. C /50; 213/56, 213/62 R
 United States Patent (19) Altherr (54) (75) 73 (*) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) 56) RALWAY CAR DRAWBAR CONNECTION WITH GUIDED SLACK ADJUSTING WEDGES Inventor: Assignee: Notice: Russell G. Altherr, Munster, Ind.
United States Patent (19) Altherr (54) (75) 73 (*) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) 56) RALWAY CAR DRAWBAR CONNECTION WITH GUIDED SLACK ADJUSTING WEDGES Inventor: Assignee: Notice: Russell G. Altherr, Munster, Ind.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO923.3816B1 (10) Patent No.: US 9.233,816 B1 Mendez (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 12, 2016 (54) BLIND FLANGE LIFTING DEVICE 1/66; B25J 15/009; C03E335/20: H01L 21/68707 (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent USOO923.3816B1 (10) Patent No.: US 9.233,816 B1 Mendez (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 12, 2016 (54) BLIND FLANGE LIFTING DEVICE 1/66; B25J 15/009; C03E335/20: H01L 21/68707 (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,626,061 B2. Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003
 USOO6626061B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) ACCELERATOR PEDAL DEVICE 6,276,229 B1 * 8/2001 Gohring et al... 74/513 6,289,762 B1 9/2001
USOO6626061B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) ACCELERATOR PEDAL DEVICE 6,276,229 B1 * 8/2001 Gohring et al... 74/513 6,289,762 B1 9/2001
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,295,304
 O H USOO5295304A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,295,304 Ashley, Jr. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 22, 1994 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCING A FULL FACE Primary Examiner-P. W. Echols FABRICATED WHEEL
O H USOO5295304A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,295,304 Ashley, Jr. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 22, 1994 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCING A FULL FACE Primary Examiner-P. W. Echols FABRICATED WHEEL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,603,073 B2
 USOO6603073B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,603,073 B2 Ferris (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003 (54) SNAP TOGETHER CABLE TROUGH FR 2 365 902 4/1978 SYSTEM GB 549840 12/1942 GB 612162
USOO6603073B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,603,073 B2 Ferris (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003 (54) SNAP TOGETHER CABLE TROUGH FR 2 365 902 4/1978 SYSTEM GB 549840 12/1942 GB 612162
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2
 US009035508B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2 Grosskopf et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 19, 2015 (54) ROTATING RESISTOR ASSEMBLY H02K II/042 (2013.01); H02K II/0057 (2013.01):
US009035508B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2 Grosskopf et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 19, 2015 (54) ROTATING RESISTOR ASSEMBLY H02K II/042 (2013.01); H02K II/0057 (2013.01):
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0119137 A1 Cirincione, II et al. US 201701 19137A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) IMPACT ABSORBNG
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0119137 A1 Cirincione, II et al. US 201701 19137A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) IMPACT ABSORBNG
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Siltanen USOO6533006B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 18, 2003 (54) WINTER TIRE FOR VEHICLE, PARTICULARLY ATRACTION WINTER TIRE FOR HEAVY TRUCKS (75) Inventor: Teppo
(12) United States Patent Siltanen USOO6533006B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 18, 2003 (54) WINTER TIRE FOR VEHICLE, PARTICULARLY ATRACTION WINTER TIRE FOR HEAVY TRUCKS (75) Inventor: Teppo
United States Patent (19) Yamauchi et al.
 United States Patent (19) Yamauchi et al. 54). GAS INSULATED SWITCHGEAR APPARATUS 75 Inventors: Takao Yamauchi; Masazumi Yamamoto; Kiyokazu Torimi; Hiroki Sanuki, all of Tokyo, Japan 73 Assignee: Mitsubishi
United States Patent (19) Yamauchi et al. 54). GAS INSULATED SWITCHGEAR APPARATUS 75 Inventors: Takao Yamauchi; Masazumi Yamamoto; Kiyokazu Torimi; Hiroki Sanuki, all of Tokyo, Japan 73 Assignee: Mitsubishi
