Lisa T-MND CONTROLLER h-1000 RPM SENSOR. United States Patent (19) Obayashi et al.
|
|
|
- Nigel Willis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 United States Patent (19) Obayashi et al. 54) DRIVE CONTROL APPARATUS FOR ELECTRIC SYNCHRONOUS MACHINE HAVING FIELD WINDING 75 Inventors: Kazuyoshi Obayashi, Chita-gun; Hiroya Tsuji, Yokkaichi, Tsuneyuki Egami, Gamagori, all of Japan 73 Assignee: Denso Corporation, Kariya, Japan 21 Appl. No.: 09/290, Filed: Apr. 12, Foreign Application Priority Data Apr. 28, 1998 JP Japan (51) Int. Cl."... HO2P1/46 52 U.S. Cl /712; 318/705; 318/714; 318/716; 318/ Field of Search /712, 705, 318/714, 716, ) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,366,420 12/1982 Ackermann et al /139 USOO A 11 Patent Number: 6,118,247 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, ,157,228 10/1992 Ackermann et al /806 5,955,807 9/1999 Kajiura. FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS /1997 Japan /1998 Japan. Primary Examiner Karen Masih Attorney, Agent, or Firm- Pillsbury Madison & Sutro LLP 57 ABSTRACT A drive control apparatus for an electric Synchronous machine is composed of armature current control means and transient operation detection means. When the Synchronous machine is intended to increase power in a transient operation, the current control means Supplies the armature winding with compensation current to cancel counter electromotive force formed when field current is supplied to the field winding through a mutual inductance of the field winding and the armature winding. 6 Claims, 7 Drawing Sheets 400 if 1115 : SEACH COL FIELD. H. 2 CIRCUIT r 5OO 1OO 123O T-MND CONTROLLER h-1000 Lisa 1110 RPM SENSOR
2 U.S. Patent Sep. 12, 2000 Sheet 1 of 7 6,118, !--- OWZºº NNS?HOSNES VNd}} -i 096 OOG C1NWOO- 100
3 U.S. Patent Sep. 12, 2000 Sheet 2 of 7 6,118,247 GOE V O? EO3 r O b- - - b. ---
4 U.S. Patent Sep. 12, 2000 Sheet 3 of 7 6,118,247 FIG i k N SS HILIII; TNN 1932 i. XNLILIII K to a I X 2: i-4310 (g ZNIN X X M NIH 1. &L 2 DX N SaaS
5 U.S. Patent Sep. 12, 2000 Sheet 4 of 7 6,118,247
6 U.S. Patent Sep. 12, 2000 Sheet 5 of 7 6,118,247 FIG. 5 TORQUE CONTROL READ T', Nm S1 O1 S1O2 NO RANSENT OPERATION? S1O3 YES S1O4 do - S105 S1O6 idh S1O7 id= ido+idh READ iu, W READ 6 S1 O8 S1O9 S11 O
7 U.S. Patent Sep. 12, 2000 Sheet 6 of 7 6,118,247 FIG.6 O idiq -S111 Sigis S112 S113 S114 Vf PWM RESISTER S115 S116 RETURN
8 U.S. Patent Sep. 12, 2000 Sheet 7 of 7 6,118,247 FIG 7 ef F M S ()f (00 Vf Vd FIG.S 0.08 FIELD 0.06 MAG. FLUX 0.04 Wb] 0.02 TIME ms)
9 1 DRIVE CONTROLAPPARATUS FOR ELECTRIC SYNCHRONOUS MACHINE HAVING FIELD WINDING CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATION The present application is based on and claims priority from Japanese Patent Application Hei filed on Apr. 28, 1998, the contents of which are incorporated herein by reference. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates to a drive control apparatus of an electric Synchronous machine having a field winding. 2. Description of the Related Art An electric Synchronous machine is composed of a three phase armature winding and a field winding. The armature winding has three phase-windings which are Supplied respectively with driving phase-currentiu, iv and iw. Voltage Vf is applied across the field winding to Supply field current if, thereby generating field magnetic flux. The field current may be controlled in a vector control process using d-q rectangular coordinate axes with the magnetic field component Set on one of the axes. A synchronous electric machine disclosed in JP-A is mounted in a parallel hybrid vehicle together with an engine and an infinite variable-speed transmission. The Synchronous machine is not used when the vehicle is driven at a constant Speed but is used only when the vehicle is in a transient operation Such accelerated or decelerated. Preferably, the field current should be supplied only when the vehicle is accelerated or decelerated to improve the power efficiency of the hybrid vehicle. However, in the conventional drive control apparatus can not increase the field current immediately when driving power or battery charging energy of the Synchronous machine is needed during the transient operation. If field voltage Vf is applied to the field winding, counter-electromotive force ef is gen erated as expressed in the following expression. ef=lf (diffdt), where Lf is an inductance of the field winding. The counter electromotive force ef impedes increase in the field current if and, in turn, increase in magnetic flux (pf. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The invention is made in view of the above problems, and a main object of the invention is to provide an improved drive control apparatus which can improve rise-up of the field magnetic flux. In order to attain the above object, a drive control appa ratus according to a main feature of the invention is com posed of detection means for detecting a torque command Signal commanding output power of the Synchronous machine, judge means for judging transient operation of the Synchronous motor according to the torque command Signal, field control means for Supplying field current to the field winding when the transient operation is detected, armature control means for controlling basic armature current accord ing to the torque command Signal to provide commanded output power; and compensation means for adding an amount of compensation current component to the basic 6,118,247 E armature current to generate electromotive force in the field winding through a mutual inductance between the field winding and the armature winding to cancel counter electromotive force generated when the field current is Supplied. Accordingly, the rise-up time of the field magnetic flux is improved and torque response is improved. The principle of the vector control according to the invention is described with reference to FIG. 7. In a graph of d-q rectangular axes, the magnetic field of field winding F is put on d-axis, and component id of the armature current of armature winding S is put on d-axis. A counter electro motive force efis generated in the field winding as expressed in the following expression E2. Here, Lf is an inductance of the field winding, and Mfd is a mutual inductance between the field winding and the armature winding. Because the electromotive force Mfd (did/dt) acts to cancel the counter-electromotive force ef, the rise up Speed of the field magnetic flux can be increased. Practically, in the drive control apparatus according to the invention, the armature control means calculates a target amount of magnetic flux necessary to provide the com manded output power, an amount of a component of the basic armature current generating the commanded output power. The armature control means also calculates the amount of compensation current component from a differ ence between the target magnetic flux and actual magnetic flux. According to another feature of the invention, the com pensation amount can be calculated from a difference between a target field current and an actual field current. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS Other objects, features and characteristics of the present invention as well as the functions of related parts of the present invention will become clear from a study of the following detailed description, the appended claims and the drawings. In the drawings: FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a structure of a drive control apparatus of an electric vehicle according to a preferred embodiment; FIG. 2 is a circuit diagram of an inverter circuit of the drive control apparatus according to the preferred embodi ment, FIG. 3 is a longitudinally cross-sectional view of a motor mounted in an electric vehicle to be controlled by the drive control apparatus according to the embodiment; FIG. 4A is a cross-sectional view of the motor shown in FIG. 3 cut along line 4A-4A, and FIG. 4B is a cross sectional view of the motor shown in FIG. 3 cut along line 4B-4B; FIG. 5 is a flow diagram of a part of a main program for a controller of the drive control apparatus according to the embodiment; FIG. 6 is a flow diagram of another part of the main program, FIG. 7 illustrates a principle of the invention; and FIG. 8 is a graph showing changes in magnetic flux with time. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS A drive control apparatus according to a preferred embodiment of the invention is described with reference to the appended drawings.
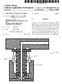
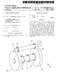
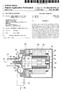
10 3 In FIG. 1, the control apparatus is connected to Synchro nous motor 1000 which has three-phase armature winding 1110 and a field winding Motor 100 is mounted as a driving Source in an electric Vehicle. The control apparatus is composed of controller 100, inverter 200, battery unit 300 and field control circuit 400. Controller 100 has a microcomputer, which receives a torque command Signal, which is provided by torque com mand circuit 500 when an accelerator or a brake pedal is operated. Controller 100 controls motor 1000 in response to the torque command Signal according to programs Stored in a ROM. Controller 100 has a signal process section which detects the position of rotor 1200 according to a signal from rotor position sensor Inverter 200 is connected to controller 100, battery unit 300 and three input terminals of armature winding As shown in FIG. 2, inverter 200 has main input terminals 201, 202 connected to plus and minus terminals of battery unit 300, output terminals 203, 204, 205 connected respec tively to U, V, W-phase windings of motor 1000, and input terminals 206, 207, 208, 209, 210, 211 connected to gate drive circuits (not shown) of controller 100. Inverter also has IGBT modules 212, 213, 214, current sensors 215, 216 and output terminals 217, 218 thereof. Each of IGBT modules 212, 213, 214 has two sets of an IGBT element (insulation gate type bi-polar transistors) and a o flywheel diode, which are well-known. IGBT module 212 has terminal C1 connected to main input terminal 201, terminal E2 connected to main terminal 202, and terminals E1 and C2 jointly connected to output terminal 203, thereby forming a drive circuit for the U-phase winding of motor IGBT modules 213, 214 have also substantially the same components as IGBT module 212 forming drive cir cuits for the V-phase and W-phase windings. Current sensors 215, 216 are fixed to lead wires respec tively connected to terminals 203, 205, and connected to controller 100 through terminals 217, 218. Each of current sensors 215, 216 is composed of a Hall element and is a clamp-and-non-contact type Sensor. current Sensors 215, 216 respectively detect output current of terminal 203, 205 and provide Voltage Signals. That is, current Sensor 215 detects current iu of U-phase winding, and current Sensor 216 detects current iw of W-phase winding. Field control circuit 400 is connected to controller 100 and to field winding 1230 to control field current if supplied thereto. Inverter 200 and field control circuit 400 are con trolled by controller 100. As shown in FIGS. 3, 4A and 4B, motor 1000 is composed of front frame 1910, end frame 1911, stator 1100 housed in frames 1910, 1911, a pair of bearings 1920, 1921, rotor 1200 respectively and rotatably supported by frames 1910, 1911 via the pair of bearings 1920, 1921, and rotor position sensor Rotor 1200 rotates at an air gap radially inner side of Stator Rotor position sensor 1930 is composed of a known set of resolver rotor 1931 and resolver stator 1932 which is con nected to controller 100. Controller 100 calculates rotor position a according to the Signal from rotor position Sensor Stator 1100 is composed of three-phase winding 1110 and stator core 1120 which is a lamination of a plurality of electric steel sheets. Stator core 1120 has a plurality of slots 1121, teeth 1122 and core back portion 1123 to accommo date three-phase armature winding Rotor 1200 is composed of rotor yoke 1210 which is a cylindrical lamination of a plurality of electric Steel sheets, 6,118, a pair of wheel-like rotor yokes 1220 which is a lamination of a plurality of electric Steel sheet disposed opposite ends of rotor yoke 1210, and field winding 1230 disposed inside rotor yoke Cylindrical rotor yokes 1210, the pair of wheel-like rotor yokes 1220 and field winding 1230 form magnetic circuit Section A pair of nonmagnetic plates 1260 is disposed on the opposite ends of magnetic circuit Section In magnetic circuit Section 1250, cylindrical iron core 1231 is press-fitted to shaft 1240 at a serrated portion thereof and resinous bobbin 1232 is fixed on the outer periphery of iron core Field winding 1230 is wound on bobbin 1232 in one way direction. A spline 1241 is formed on a left portion of shaft 1240 in FIG.3. Shaft 1240 is the output shaft of motor 1000 to be connected to vehicle wheels (not shown). Field winding 1230 is supplied with field current by field control circuit 400 through brush holders 1310, brushes 1320, slip rings 1330 and lead wires Lead wires 1350 are integrated with shaft 1240 by resinous insulating mold As shown in FIG. 4A, rotor yoke 1210 has twelve magnet holes 1211 on a circumference at equal intervals. Twelve permanent magnets are inserted in magnetic holes 1211 respectively. Rotor yoke 1210 also has twelve round holes 1212 formed between magnet holes As shown in FIG. 4B, rotor yoke 1220 has annular portion 1221, hub portion 1222 and six spokes 1223 connecting annular portion 1221 and hub portion In other words, spokes 1223 are spaced apart from one another at 720/12 (12 is the number of poles) or 60 degree in angle. Annular portion 1221 has twelve magnet holes 1224, as in rotor yoke 1210, on a circumference at equal intervals and round holes 1225 formed at circumferentially central portions between magnet holes 1224 adjacent to each other. Magnet holes 1211 of rotor yoke 1210 are the same in shape and size as magnet holes 1224 of rotor yoke 1220, and round holes 1212 are also the Same in Shape and size as round holes Accordingly, the magnet circuit Section has 24 through holes extending from one axial end thereof to the other. In FIG. 3, a pair of right and left rotor yokes 1220 is assembled so that spokes 1223 of one can not circumferentially overlap with spokes 1223 of the other. Permanent magnets 1280 are inserted respectively into magnet holes 1211, 1224 in the direction perpendicular to the figure So that one circumferential Side of one of perma nent magnets has the same polarity as the other circumfer ential Side of another permanent magnet adjacent thereto. Soft iron pins 1281 are also press-fitted to respective round holes 1212, 1225 to join rotor yokes 1210, 1220 together. Permanent magnets 1280 are magnetized in the circum ferential direction to provide N and Spoles alternately on the outer periphery of rotor The magnetic flux bypasses from the N pole of permanent magnets 1280 to the S pole thereof through N-pole-side soft iron pin 1281, N-pole-side spoke 1223, iron core 1231, S-pole-side spoke 1223, and S-pole-side soft iron pin Thus, bypassing circuits of the magnetic flux of the permanent magnets 1280 are provided. Accordingly, reluctance of the bypassing circuit can be controlled, and the effective magnetic flux that is Supplied to the Stator through the air gap can be controlled whether field winding 1230 is energized or not. Motor 1000 is controlled in a vector control mode accord ing to torque command Signal T, rotor position 0, amounts of currents of the U-phase and W-phase windings detected by current sensors 215, 216.
11 S The main program is started when a vehicle ignition key Switch is turned on. As shown in FIGS. 5 and 6, controller 100 reads torque command signal T and motor rotation speed Nm at step S101. Torque command signal T is generated when the accelerator pedal or brake pedal is operated. Motor rotation speed Nm is calculated from the signal of rotor position sensor At step S102, controller 100 calculates basic amount id0 of the d-axis component of the armature current necessary to generate required output power of the motor 1000 at normal operation, target amountiq of the q-axis component of the armature current (herein after referred to as q-axis current), and target amount if of the field current (hereinafter referred to target field current) from current torque com mand signal T and current motor rotation speed Nm with reference to a map stored in a ROM. At step S103, controller 100 examine whether the vehicle is in the transient operation or not. If a level of torque command Signal T is a certain value higher or lower than the last level thereof, it is determined that the vehicle is accelerated, decelerated, or in a transient operation. Otherwise, NO is provided at step S103, and controller 100 sets compensation amount idh of the d-axis component of the armature current (hereinafter referred to as d-axis compensation current) to 0. That is, no compensation is made on the armature current. Then step S108 follows. On the other hand, if the vehicle is in the transient operation, YES is provided at step S103, and controller 100 calculates d-axis compensation current idh in step S Target total amount p0 of the magnetic flux (hereinafter referred to as target total flux) in the air gap is calculated at step S105. Target total flux (p0 is calculated from the following expression E3). The above expression includes target field magnetic flux (pfo Supplied from field winding 1230, target amount cpd0 of the armature magnetic flux (hereinafter referred to target armature flux) generated by amount id0 of the d-axis com ponent of basic armature current (hereinafter referred to as d-axis basic current), permanent magnet flux pm Supplied from permanent magnets 1280, self inductance Lf of field winding 1230, a mutual inductance between field winding 1230 and a d-axis component of armature winding 1110, the number of turns Nf of field winding 1230, the number of turns Nd of the d-axis component of armature winding 1110, target field current if, and target amount id of d-axis component of the armature current. Here, the basic armature current is Supplied to generate a commanded output power (driving torque or battery charging energy) of the Synchro nous machine in the normal operation. Target total flux (p0 can be Selected from a map. At step S106, controller 100 calculates an actual total amount (p1 of magnetic flux (hereinafter referred to as actual total flux) in the air gap, which is given by the following expression E4. Here, (pf1 is an actual amount of the field magnetic flux (hereinafter referred to as actual field flux) supplied by field winding 1230, (pd1 is an actual amount of the armature magnetic flux in the air gap generated by an amount id1 of the d-axis component of the armature current (hereinafter referred to as d-axis actual current). (p1=pf1+(pd1+(pn=(lf/nf) if1+(mfd/nd)-id1+(pm In E4, actual field current if1 and d-axis actual current, id1 are respectively calculated from amounts of U-phase 6,118,247 E currentiu and W-phase current iw. However, actual total flux (p1 can be detected by a sensor 1115 Such as a search coil disposed between stator 1100 and rotor At step S107, controller 100 calculates d-axis compensa tion current idh to reduce a difference between target total flux (p0 and actual total flux (p1. This can be carried out by a well-known feedback System, feed forward System or a combination thereof. At step S108, controller 100 adds d-axis basic current id0 and d-axis compensation current idh to obtain d-axis target current id. If the field current is Sufficiently large, d-axis target current id is controlled to induce a negative counter electromotive force. On the other hand, if the field current is not large, the d-axis target current id is controlled to induce a positive counter-electromotive force. Thereafter, controller 100 reads amounts iu, iw of U-phase and W-phase armature current by current Sensors 215,216 at step S109 and reads rotor position 0 at step S110. At step S111, controller 100 calculates amounts id, iq of d-axis component and q-axis component of the armature current of the d-q rectangular coordinate axes from the detected amounts iu and iw. At step S112, controller 100 provides current differences ed and eq, where, ed=idf-id, eq=iq*-iq. At Step 113, d-axis component target Voltage Vd and q-axis-component target Voltage Vd are calculated from ed, eq and electric constants of motor At step S114, controller 100 calculates target phase-voltages Vui, Vv, and Vw from d-axis-component target Voltage Vd and q-axis-component target Voltage Vd. Then, controller 100 calculates target field-voltage Vf from target field current if and the resistance of field winding 1230 at step S115. At step S116, target phase voltages Vu, Vv*, and VW and the target field voltage Vf are modulated respectively to pulse width modulation (PWM) signals at frequency of 10 khz, for example, and written into a PWM resistor to supply the calculated arma ture current and the field current. Thus, field winding 1230 is prevented from impeding rise-up of the field magnetic flux. In FIG. 8, a solid line represents the magnetic flux in the air gap according to the embodiment of the invention, and dotted line represents the magnetic flux in the air gap of a conventional apparatus. It is clear that the magnetic flux of the embodiment of the invention rises up much faster than that of the conventional apparatus. Step S103 corresponds to the means for detecting tran sient operation, steps S correspond to armature current control means, and steps S correspond to the compensation means. The calculation for the compensation can be replaced by a map based on changes in the magnetic flux and in the field Current. The present invention is applicable other than the control to System of a electric vehicle. For example, it can be applied to the control system of a hybrid vehicle or synchronous motors for use in devices other than vehicles. In the foregoing description of the present invention, the invention has been disclosed with reference to specific embodiments thereof. It will, however, be evident that various modifications and changes may be made to the Specific embodiments of the present invention without departing from the broader Spirit and Scope of the invention as Set forth in the appended claims. Accordingly, the descrip tion of the present invention in this document is to be regarded in an illustrative, rather than restrictive, Sense.
12 7 What is claimed is: 1. A drive control apparatus for controlling an electric Synchronous machine having a field winding and a multi phase armature winding comprising: detection means for detecting a torque command Signal commanding output power of Said Synchronous machine; judge means for judging transient operation of Said Syn chronous motor according to Said torque command Signal; field control means for Supplying field current to Said field winding, and armature control means for controlling basic armature current according to Said torque command Signal to provide commanded output power; wherein Said armature control means adds an amount of compen sation current component to Said basic armature current to generate electromotive force in Said field winding through a mutual inductance between Said field wind ing and Said armature winding to cancel counter electromotive force generated when Said judge means judges Said transient operation. 2. The drive control apparatus as claimed in claim 1, wherein Said detection means further detects actual armature cur rent and total magnetic flux, and Said armature control means calculates a target amount of magnetic flux necessary to provide Said commanded output power, an amount of a component of Said basic armature current generating Said commanded Output power and calculates Said amount of compensation current component from a difference between Said target magnetic flux and Said actual magnetic flux. 3. The drive control apparatus as claimed in claim 1, wherein Said detection means further detects actual armature cur rent and actual field current, and Said armature control means calculates a target amount of field current necessary to provide Said commanded output power, an amount of a component of Said basic armature current generating Said commanded output power, and calculates Said compensation current com ponent from a difference between Said target amount of field current and Said actual field current. 6,118,247 1O The drive control apparatus as claimed in claim 1, wherein Said armature control means controls said compensation current component to induce a negative counter electromotive force when said field current is large enough to generate Said commanded output power and a positive counter-electromotive force when Said field current is not large enough to generate Said commanded output power. 5. A method of controlling an electric Synchronous machine having a field winding, a multi-phase armature winding comprising the Steps of detecting a torque command Signal commanding output power of Said Synchronous machine and rotation Speed of Said machine; calculating a target amount of armature current necessary to generate commanded output power and a target amount of field current necessary to generate Said commanded output power from Said torque command Signal and Said rotation Speed; determining whether Said Synchronous machine is in transient operation or not according to Said torque command Signal; calculating a target amount of total magnetic flux neces Sary to generate Said commanded output power accord ing to Said torque command Signal and Said rotation Speed; detecting an actual amount of total magnetic flux; calculating an amount of compensation current compo nent of Said armature current according to a difference between said target amount of Said total magnetic flux and Said actual amount of Said total magnetic flux, and Supplying Said target amount of field current to Said field winding and Supplying Said amount of compensation current component to Said armature winding in addition to Said basic amount of armature current when Said Synchronous machine is determined to be in transient operation. 6. The method as claimed in claim 5, wherein Said armature winding is composed of three phase windings, and Said three phase windings are Supplied with respective amounts of phase current calculated from Said target amount of armature current.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O168664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0168664 A1 Senda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 2, 2004 (54) ENGINE STARTER HAVING STARTER (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2004O168664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0168664 A1 Senda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 2, 2004 (54) ENGINE STARTER HAVING STARTER (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2
 US007592736 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2 Scott et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 2009 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ELECTRIC (56) References Cited GENERATOR WITH ROTOR CIRCUMIFERENTIALLY
US007592736 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2 Scott et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 2009 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ELECTRIC (56) References Cited GENERATOR WITH ROTOR CIRCUMIFERENTIALLY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,178,395 B2
 US009 178395 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,178,395 B2 Qin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 3, 2015 (54) TRACTION MOTOR FOR ELECTRIC 5,783,891 A * 7/1998 Auinger et al.... 310,180 VEHICLES
US009 178395 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,178,395 B2 Qin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 3, 2015 (54) TRACTION MOTOR FOR ELECTRIC 5,783,891 A * 7/1998 Auinger et al.... 310,180 VEHICLES
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,590,360 B2
 USOO659036OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Hirata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2003 (54) CONTROL DEVICE FOR PERMANENT 4,879,502 A * 11/1989 Endo et al.... 318/808 MAGNET MOTOR SERVING
USOO659036OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Hirata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2003 (54) CONTROL DEVICE FOR PERMANENT 4,879,502 A * 11/1989 Endo et al.... 318/808 MAGNET MOTOR SERVING
310/227, 228 Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Head, Johnson & Kachigian
 US005742111A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Reed 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54 D.C. ELECTRIC MOTOR 4,930,210 6/1990 Wang... 29/597 5,001,375 3/1991 Jones... 310/68 75) Inventor: Troy
US005742111A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Reed 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54 D.C. ELECTRIC MOTOR 4,930,210 6/1990 Wang... 29/597 5,001,375 3/1991 Jones... 310/68 75) Inventor: Troy
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006
 US 2006005 1222A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0051222 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) MINIATURE PUMP FOR LIQUID COOLING Publication Classification
US 2006005 1222A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0051222 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) MINIATURE PUMP FOR LIQUID COOLING Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,598,045 Ohtake et al. 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 28, 1997
 US005598045A United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,598,045 Ohtake et al. 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 28, 1997 54 MINIATURE MOTOR 5,281,876 1/1994 Sato... 310/40 MM 5,294,852 3/1994 Straker... 310/68
US005598045A United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,598,045 Ohtake et al. 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 28, 1997 54 MINIATURE MOTOR 5,281,876 1/1994 Sato... 310/40 MM 5,294,852 3/1994 Straker... 310/68
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1
 USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
United States Patent (19) Koitabashi
 United States Patent (19) Koitabashi 54 75 (73) 1 (51) (5) (58 56) ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH WITH AN IMPROVED MAGNETC ROTATABLE MEMBER Inventor: Takatoshi Koitabashi, Annaka, Japan Assignee: Sanden Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Koitabashi 54 75 (73) 1 (51) (5) (58 56) ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH WITH AN IMPROVED MAGNETC ROTATABLE MEMBER Inventor: Takatoshi Koitabashi, Annaka, Japan Assignee: Sanden Corporation,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,603,232 B2. Van Dine et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003
 USOO6603232B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Van Dine et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET RETAINING 4,745,319 A * 5/1988 Tomite et al.... 310/154.26 ARRANGEMENT FOR
USOO6603232B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Van Dine et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET RETAINING 4,745,319 A * 5/1988 Tomite et al.... 310/154.26 ARRANGEMENT FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160049835A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0049835 A1 FUKUMOTO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2016 (54) SYNCHRONOUS RELUCTANCE MOTOR (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20160049835A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0049835 A1 FUKUMOTO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2016 (54) SYNCHRONOUS RELUCTANCE MOTOR (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
(19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,900,569 B2
 USOO6900569B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stevenson et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2005 (54) INCREASED TORQUE IN RETARDER 5,054,587 A * 10/1991 Matsui et al... 188/267 BRAKE SYSTEM
USOO6900569B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stevenson et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2005 (54) INCREASED TORQUE IN RETARDER 5,054,587 A * 10/1991 Matsui et al... 188/267 BRAKE SYSTEM
Patent Application Publication Nov. 27, 2014 Sheet 1 of 7 US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0346290 A1 YOSHIDA et al. US 20140346290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) SLIDING TYPE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0346290 A1 YOSHIDA et al. US 20140346290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) SLIDING TYPE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO64994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Matsumoto (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) STATIONARY BIKE (52) U.S. Cl.... 482/8 (76) Inventor: Masaaki Matsumoto,
(19) United States US 2005OO64994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Matsumoto (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) STATIONARY BIKE (52) U.S. Cl.... 482/8 (76) Inventor: Masaaki Matsumoto,
III. United States Patent (19) Shirai et al. 5,669,351. Sep. 23, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: CONSTANTS PID CONTROL
 United States Patent (19) Shirai et al. 54) ENGINE THROTTLE CONTROL WITH WARYING CONTROL 75) Inventors: Kazunari Shirai, Chita-gun; Hidemasa Miyano, Kariya; Shigeru Kamio, Nagoya; Yoshimasa Nakaya, Nagoya,
United States Patent (19) Shirai et al. 54) ENGINE THROTTLE CONTROL WITH WARYING CONTROL 75) Inventors: Kazunari Shirai, Chita-gun; Hidemasa Miyano, Kariya; Shigeru Kamio, Nagoya; Yoshimasa Nakaya, Nagoya,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,791,205 B2
 USOO6791205B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Woodbridge (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2004 (54) RECIPROCATING GENERATOR WAVE 5,347,186 A 9/1994 Konotchick... 310/17 POWER BUOY 5,696,413 A 12/1997
USOO6791205B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Woodbridge (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2004 (54) RECIPROCATING GENERATOR WAVE 5,347,186 A 9/1994 Konotchick... 310/17 POWER BUOY 5,696,413 A 12/1997
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,089,190 B2
 USO08089190B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,089,190 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 2012 (54) ROTOR FOR AN INTERIOR PERMANENT (52) U.S. Cl.... 31 O/156.53 MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS
USO08089190B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,089,190 B2 Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 2012 (54) ROTOR FOR AN INTERIOR PERMANENT (52) U.S. Cl.... 31 O/156.53 MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,455,976 B1. Nakano (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 24, 2002
 USOO6455976B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,455,976 B1 Nakano (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 24, 2002 (54) MOTOR/GENERATOR WITH SEPARATED 4,695,795 A * 9/1987 Nakamizo et al.... 324/208 CORES
USOO6455976B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,455,976 B1 Nakano (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 24, 2002 (54) MOTOR/GENERATOR WITH SEPARATED 4,695,795 A * 9/1987 Nakamizo et al.... 324/208 CORES
United States Patent (19) Muranishi
 United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,687,950 B2. Kuckes (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 30, 2010
 USOO768795OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,687,950 B2 Kuckes (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 30, 2010 (54) DRILLSTRING ALTERNATOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Arthur F. Kuckes,
USOO768795OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,687,950 B2 Kuckes (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 30, 2010 (54) DRILLSTRING ALTERNATOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor: Arthur F. Kuckes,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O225192A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0225192 A1 Jeung (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 9, 2010 (54) PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD AND METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2010O225192A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0225192 A1 Jeung (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 9, 2010 (54) PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD AND METHOD Publication Classification
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Minnerop 54) DEVICE FOR WATER COOLING OF ROLLED STEEL SECTIONS 75 Inventor: Michael Minnerop, Ratingen, Germany 73 Assignee: SMS Schloemann-Siemag Aktiengesellschaft, Dusseldorf,
United States Patent (19) Minnerop 54) DEVICE FOR WATER COOLING OF ROLLED STEEL SECTIONS 75 Inventor: Michael Minnerop, Ratingen, Germany 73 Assignee: SMS Schloemann-Siemag Aktiengesellschaft, Dusseldorf,
Six R. Seizi. United States Patent 19 ZKK, 2.S. NSS NEG. Sayo et al. 11 4,150, Apr. 24, ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH NS3NS
 United States Patent 19 Sayo et al. 54 ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH 75 Inventors: Kosaku Sayo, Katsuta; Seijiro Tani, Naka; Atsushi Sugirauma, Hitachi, all of Japan 73) Assignee: Hitachi, Ltd., Japan 21 Appl.
United States Patent 19 Sayo et al. 54 ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH 75 Inventors: Kosaku Sayo, Katsuta; Seijiro Tani, Naka; Atsushi Sugirauma, Hitachi, all of Japan 73) Assignee: Hitachi, Ltd., Japan 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Hozumi et al. 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,889,164 Dec. 26, 1989 54). SOLENOID CONTROLLED WALVE (75 Inventors: Kazuhiro Hozumi; Masaru Arai, both of Chiba; Yoshitane
United States Patent (19) Hozumi et al. 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,889,164 Dec. 26, 1989 54). SOLENOID CONTROLLED WALVE (75 Inventors: Kazuhiro Hozumi; Masaru Arai, both of Chiba; Yoshitane
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,892,675 Yatsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999
 USOO5892675A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Yatsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999 54 ACCURRENT SOURCE CIRCUIT FOR 4,876,635 10/1989 Park et al.... 363/17 CONVERTING DC VOLTAGE INTO
USOO5892675A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Yatsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999 54 ACCURRENT SOURCE CIRCUIT FOR 4,876,635 10/1989 Park et al.... 363/17 CONVERTING DC VOLTAGE INTO
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,626,061 B2. Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003
 USOO6626061B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) ACCELERATOR PEDAL DEVICE 6,276,229 B1 * 8/2001 Gohring et al... 74/513 6,289,762 B1 9/2001
USOO6626061B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) ACCELERATOR PEDAL DEVICE 6,276,229 B1 * 8/2001 Gohring et al... 74/513 6,289,762 B1 9/2001
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120072180A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0072180 A1 Stuckey et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 22, 2012 (54) TIRE MOLD DESIGN METHOD TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 703/1
(19) United States US 20120072180A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0072180 A1 Stuckey et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 22, 2012 (54) TIRE MOLD DESIGN METHOD TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 703/1
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007884512B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,884,512 B2 Horng et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 8, 2011 (54) FIXING STRUCTURE FOR PRINTED (56) References Cited CIRCUIT BOARD OF MICRO MOTOR
(12) United States Patent US007884512B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,884,512 B2 Horng et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 8, 2011 (54) FIXING STRUCTURE FOR PRINTED (56) References Cited CIRCUIT BOARD OF MICRO MOTOR
United States Patent (19) Kitami et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kitami et al. 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,846,768 Jul. 11, 1989 (54) VARIABLE-SPEED DRIVING DEVICE 75) Inventors: Yasuo Kitami; Hidenori Tezuka; 73 Assignee: Syuji
United States Patent (19) Kitami et al. 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,846,768 Jul. 11, 1989 (54) VARIABLE-SPEED DRIVING DEVICE 75) Inventors: Yasuo Kitami; Hidenori Tezuka; 73 Assignee: Syuji
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Ogasawara et al. (54) 75 RDING LAWN MOWER Inventors: Hiroyuki Ogasawara; Nobuyuki Yamashita; Akira Minoura, all of Osaka, Japan Assignee: Kubota Corporation, Osaka, Japan Appl.
United States Patent (19) Ogasawara et al. (54) 75 RDING LAWN MOWER Inventors: Hiroyuki Ogasawara; Nobuyuki Yamashita; Akira Minoura, all of Osaka, Japan Assignee: Kubota Corporation, Osaka, Japan Appl.
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9671 011B2 (12) United States Patent Kimijima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,671,011 B2 Jun. 6, 2017 (54) WORM BIASING STRUCTURE (71) Applicant: Showa Corporation, Gyoda-shi (JP)
USOO9671 011B2 (12) United States Patent Kimijima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,671,011 B2 Jun. 6, 2017 (54) WORM BIASING STRUCTURE (71) Applicant: Showa Corporation, Gyoda-shi (JP)
Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) J (12) Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 774 824 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: ition: (51) IntCI.6: H02K 3/52, H02K
(19) J (12) Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 774 824 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: ition: (51) IntCI.6: H02K 3/52, H02K
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. YAMAGISH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 7, 2012
 US 2012O139382A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0139382 A1 YAMAGISH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 7, 2012 (54) END PLATE, AND ROTOR FOR ROTARY Publication Classification
US 2012O139382A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0139382 A1 YAMAGISH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 7, 2012 (54) END PLATE, AND ROTOR FOR ROTARY Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8384329B2 (12) United States Patent Natsume (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) WIPER SYSTEMAND WIPER CONTROL METHOD Inventor: Takashi Natsume, Toyohashi (JP) Assignee: ASMO Co.,
USOO8384329B2 (12) United States Patent Natsume (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) WIPER SYSTEMAND WIPER CONTROL METHOD Inventor: Takashi Natsume, Toyohashi (JP) Assignee: ASMO Co.,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004.00431 O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0043102 A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2004 (54) ALIGNMENT COLLAR FOR A NOZZLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 425/567
US 2004.00431 O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0043102 A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2004 (54) ALIGNMENT COLLAR FOR A NOZZLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 425/567
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,695,581 B2
 USOO6695581B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,695,581 B2 Wass0n et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 2004 (54) COMBINATION FAN-FLYWHEEL-PULLEY JP 59-81.835 2/1984 ASSEMBLY AND METHOD OF
USOO6695581B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,695,581 B2 Wass0n et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 2004 (54) COMBINATION FAN-FLYWHEEL-PULLEY JP 59-81.835 2/1984 ASSEMBLY AND METHOD OF
Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,969,453. Aoshima [45] Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 1999
![Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,969,453. Aoshima [45] Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 1999 Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,969,453. Aoshima [45] Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 1999](/thumbs/96/128288181.jpg) US005969453A Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,969,453 Aoshima [45] Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 1999 [54] MOTOR US. Patent Application No. 09/027,244, Feb. 1998. [75] Inventor: Chikara Aoshima,
US005969453A Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 5,969,453 Aoshima [45] Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 1999 [54] MOTOR US. Patent Application No. 09/027,244, Feb. 1998. [75] Inventor: Chikara Aoshima,
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4924,123. Hamajima et al. 45 Date of Patent: May 8, 1990
 United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4924,123 Hamajima et al. 45 Date of Patent: May 8, 1990 54) LINEAR GENERATOR 4,454,426 6/1984 Benson... 290/1 R s 8 8 4,500,827 2/1985 Merritt et al.... 322/3
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4924,123 Hamajima et al. 45 Date of Patent: May 8, 1990 54) LINEAR GENERATOR 4,454,426 6/1984 Benson... 290/1 R s 8 8 4,500,827 2/1985 Merritt et al.... 322/3
(12) United States Patent
 US007350605B2 (12) United States Patent Mizutani et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 2008 (54) IN-WHEEL MOTOR CAPABLE OF 5,087.229 A * 2/1992 Hewko et al.... 475,149 EFFICIENTLY COOLING
US007350605B2 (12) United States Patent Mizutani et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 2008 (54) IN-WHEEL MOTOR CAPABLE OF 5,087.229 A * 2/1992 Hewko et al.... 475,149 EFFICIENTLY COOLING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Swihla et al. USOO6287091B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,287,091 B1 Sep. 11, 2001 (54) TURBOCHARGER WITH NOZZLE RING COUPLNG (75) Inventors: Gary R Svihla, Clarendon
(12) United States Patent Swihla et al. USOO6287091B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,287,091 B1 Sep. 11, 2001 (54) TURBOCHARGER WITH NOZZLE RING COUPLNG (75) Inventors: Gary R Svihla, Clarendon
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Larsen et al. USOO6844656B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,844,656 B1 Jan. 18, 2005 (54) ELECTRIC MULTIPOLE MOTOR/ GENERATOR WITH AXIAL MAGNETIC FLUX (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent Larsen et al. USOO6844656B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,844,656 B1 Jan. 18, 2005 (54) ELECTRIC MULTIPOLE MOTOR/ GENERATOR WITH AXIAL MAGNETIC FLUX (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1. Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002
 USOO6435993B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1 Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) HYDRAULIC CHAIN TENSIONER WITH 5,707.309 A 1/1998 Simpson... 474/110 VENT DEVICE AND
USOO6435993B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1 Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) HYDRAULIC CHAIN TENSIONER WITH 5,707.309 A 1/1998 Simpson... 474/110 VENT DEVICE AND
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial No.. Filing Date July Inventor Richard Bonin NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to: OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH
Serial No.. Filing Date July Inventor Richard Bonin NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to: OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH
United States Patent (19) Hormel et al.
 United States Patent (19) Hormel et al. 54 (75) (73) 21) 22) (51) 52) (58) 56) LAMP FAILURE INDICATING CIRCUIT Inventors: Ronald F. Hormel, Mt. Clemens; Frederick O. R. Miesterfeld, Troy, both of Mich.
United States Patent (19) Hormel et al. 54 (75) (73) 21) 22) (51) 52) (58) 56) LAMP FAILURE INDICATING CIRCUIT Inventors: Ronald F. Hormel, Mt. Clemens; Frederick O. R. Miesterfeld, Troy, both of Mich.
N NE WTS 7. / N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States 17 N-M72.
 (19) United States US 2003OO12672A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0012672 A1 Sowa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2003 (54) COMPRESSOR, METHOD AND JIG FOR BALANCING THE SAME
(19) United States US 2003OO12672A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0012672 A1 Sowa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2003 (54) COMPRESSOR, METHOD AND JIG FOR BALANCING THE SAME
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD11: Last updated: 3rd February 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly Electrical power is frequently generated by spinning the shaft of a generator which has some
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD11: Last updated: 3rd February 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly Electrical power is frequently generated by spinning the shaft of a generator which has some
NSN. 2%h, WD. United States Patent (19) Vranken 4,829,401. May 9, Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 54) ROTATING TRANSFORMER WITH FOIL
 United States Patent (19) Vranken 54) ROTATING TRANSFORMER WITH FOIL WINDINGS (75) Inventor: Roger A. Vranken, Eindhoven, Netherlands (73) Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Vranken 54) ROTATING TRANSFORMER WITH FOIL WINDINGS (75) Inventor: Roger A. Vranken, Eindhoven, Netherlands (73) Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Kim et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kim et al. 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR COATING AWAFER WITH A MINIMAL LAYER OF PHOTORESIST 75 Inventors: Moon-woo Kim, Kyungki-do; Byung-joo Youn, Seoul, both of Rep. of Korea
United States Patent (19) Kim et al. 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR COATING AWAFER WITH A MINIMAL LAYER OF PHOTORESIST 75 Inventors: Moon-woo Kim, Kyungki-do; Byung-joo Youn, Seoul, both of Rep. of Korea
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,469,466 B1
 USOO6469466B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,469,466 B1 Suzuki (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2002 (54) AUTOMATIC GUIDED VEHICLE JP 7-2S1768 10/1995 JP 8-1553 1/1996 (75) Inventor: Takayuki
USOO6469466B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,469,466 B1 Suzuki (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2002 (54) AUTOMATIC GUIDED VEHICLE JP 7-2S1768 10/1995 JP 8-1553 1/1996 (75) Inventor: Takayuki
USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999
 USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999 54 SERIALLY CONNECTED CHARGER Primary Examiner Edward H. Tso Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Rosenberger,
USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999 54 SERIALLY CONNECTED CHARGER Primary Examiner Edward H. Tso Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Rosenberger,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Siltanen USOO6533006B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 18, 2003 (54) WINTER TIRE FOR VEHICLE, PARTICULARLY ATRACTION WINTER TIRE FOR HEAVY TRUCKS (75) Inventor: Teppo
(12) United States Patent Siltanen USOO6533006B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 18, 2003 (54) WINTER TIRE FOR VEHICLE, PARTICULARLY ATRACTION WINTER TIRE FOR HEAVY TRUCKS (75) Inventor: Teppo
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
22 Š. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1 SSSNS. (19) United States Z SN a. (43) Pub.
 (19) United States US 200801 05234A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0105234 A1 Yoshizumi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FUEL INJECTION PUMP EQUIPPED WITH ROTARY DEFLECTOR (76)
(19) United States US 200801 05234A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0105234 A1 Yoshizumi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FUEL INJECTION PUMP EQUIPPED WITH ROTARY DEFLECTOR (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O181130A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0181130 A1 Fukunaga (43) Pub. Date: Jul.19, 2012 (54) TORQUE CONVERTER Publication Classification 51) Int.
(19) United States US 2012O181130A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0181130 A1 Fukunaga (43) Pub. Date: Jul.19, 2012 (54) TORQUE CONVERTER Publication Classification 51) Int.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2
 US009035508B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2 Grosskopf et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 19, 2015 (54) ROTATING RESISTOR ASSEMBLY H02K II/042 (2013.01); H02K II/0057 (2013.01):
US009035508B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2 Grosskopf et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 19, 2015 (54) ROTATING RESISTOR ASSEMBLY H02K II/042 (2013.01); H02K II/0057 (2013.01):
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,255,755 B1
 USOO6255755B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Fei (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 3, 2001 (54) SINGLE PHASE THREE SPEED MOTOR 3,619,730 11/1971 Broadway et al.... 318/224 R WITH SHARED WINDINGS 3,774,062
USOO6255755B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Fei (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 3, 2001 (54) SINGLE PHASE THREE SPEED MOTOR 3,619,730 11/1971 Broadway et al.... 318/224 R WITH SHARED WINDINGS 3,774,062
(12) United States Patent
 US007191669B2 (12) United States Patent Nakane et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Nov. 14, 2002 (JP)...
US007191669B2 (12) United States Patent Nakane et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Nov. 14, 2002 (JP)...
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Itabashi et al. USOO6329777B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2001 (54) MOTOR DRIVE CONTROL APPARATUS AND METHOD HAVING MOTOR CURRENT LIMIT FUNCTION UPON MOTOR
(12) United States Patent Itabashi et al. USOO6329777B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2001 (54) MOTOR DRIVE CONTROL APPARATUS AND METHOD HAVING MOTOR CURRENT LIMIT FUNCTION UPON MOTOR
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent A USOO6208061B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,061 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) NO-LOAD GENERATOR (75) Inventor: Jong-Sok An, Chunchen (KR) (73) Assignee: Kyung-Soo Kim,
(12) United States Patent A USOO6208061B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,061 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) NO-LOAD GENERATOR (75) Inventor: Jong-Sok An, Chunchen (KR) (73) Assignee: Kyung-Soo Kim,
US 7, B2. Loughrin et al. Jan. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: and/or the driven component. (12) United States Patent (54) (75)
 USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O194855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0194855A1 HaSebe et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2005 (54) AXIAL GAP ROTATING ELECTRICAL MACHINE (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O194855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0194855A1 HaSebe et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2005 (54) AXIAL GAP ROTATING ELECTRICAL MACHINE (76) Inventors:
Earl Sch yang y Lee, 5,457,342 10/1995 Herbst, II /712
 US005920264A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM PROTECTION 5,189,314 2/1993 Georgiou et al.... 307/271 DEVICE 5,287.292 2/1994
US005920264A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM PROTECTION 5,189,314 2/1993 Georgiou et al.... 307/271 DEVICE 5,287.292 2/1994
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2
 USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
United States Patent (19) Lee
 United States Patent (19) Lee 54 METHOD FORESTIMATING RESISTANCE VALUES OF STATOR AND ROTOR OF INDUCTION MOTOR 75 Inventor: Sang-hoon Lee, Sungnam, Rep. of Korea 73 Assignee: Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.,
United States Patent (19) Lee 54 METHOD FORESTIMATING RESISTANCE VALUES OF STATOR AND ROTOR OF INDUCTION MOTOR 75 Inventor: Sang-hoon Lee, Sungnam, Rep. of Korea 73 Assignee: Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.,
(12) United States Patent
 US0072553.52B2 (12) United States Patent Adis et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 14, 2007 (54) PRESSURE BALANCED BRUSH SEAL (75) Inventors: William Edward Adis, Scotia, NY (US); Bernard
US0072553.52B2 (12) United States Patent Adis et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 14, 2007 (54) PRESSURE BALANCED BRUSH SEAL (75) Inventors: William Edward Adis, Scotia, NY (US); Bernard
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2
 US007125133B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2 Bilotti et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2006 (54) LED LIGHTING SYSTEM FOR PATIO 4.425,602 A 1/1984 Lansing UMBRELLA 5,053,931
US007125133B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2 Bilotti et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2006 (54) LED LIGHTING SYSTEM FOR PATIO 4.425,602 A 1/1984 Lansing UMBRELLA 5,053,931
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O190837A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0190837 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2003 (54) BATTERY HOLDER HAVING MEANS FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 439/500 SECURELY
US 2003O190837A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0190837 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2003 (54) BATTERY HOLDER HAVING MEANS FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 439/500 SECURELY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060066075A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0066075A1 Zlotkowski (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2006 (54) TOWING TRAILER FOR TWO OR THREE Publication Classification
US 20060066075A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0066075A1 Zlotkowski (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2006 (54) TOWING TRAILER FOR TWO OR THREE Publication Classification
III. United States Patent (19) Hsu et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,330, Date of Patent: Jul. 19, electric power in addition to human force.
 United States Patent (19) Hsu et al. (54 REMOTE-CONTROLLED ELECTRIC SKATE-BOARD 76 Inventors: Chi-Hsueh Hsu, 4F, No. 144, Chu-Lin Rd., Yung-Ho Shih, Taipei Hsien; Shih-Hsin Chen, 4F, No. 35-1, Hsin-Ching,
United States Patent (19) Hsu et al. (54 REMOTE-CONTROLLED ELECTRIC SKATE-BOARD 76 Inventors: Chi-Hsueh Hsu, 4F, No. 144, Chu-Lin Rd., Yung-Ho Shih, Taipei Hsien; Shih-Hsin Chen, 4F, No. 35-1, Hsin-Ching,
United States Patent (19) 11) 4,324,219
 United States Patent (19) 11) 4,324,219 Hayashi 45) Apr. 13, 1982 54). SPARK INTENSIFIER IN GASOLINE 56) References Cited ENGINE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS s 703,759 7/1902 Brown... 123/169 PH 75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) 11) 4,324,219 Hayashi 45) Apr. 13, 1982 54). SPARK INTENSIFIER IN GASOLINE 56) References Cited ENGINE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS s 703,759 7/1902 Brown... 123/169 PH 75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070247877A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0247877 A1 KWON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2007 54) ACTIVE-CLAMP CURRENTSOURCE 3O Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070247877A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0247877 A1 KWON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2007 54) ACTIVE-CLAMP CURRENTSOURCE 3O Foreign Application
III III III. United States Patent 19 Justice. 11 Patent Number: position. The panels are under tension in their up position
 United States Patent 19 Justice (54) (76) (21) 22) (51) (52) 58 56) TRUCK BED LOAD ORGANIZER APPARATUS Inventor: 4,733,898 Kendall Justice, P.O. Box 20489, Wickenburg, Ariz. 85358 Appl. No.: 358,765 Filed:
United States Patent 19 Justice (54) (76) (21) 22) (51) (52) 58 56) TRUCK BED LOAD ORGANIZER APPARATUS Inventor: 4,733,898 Kendall Justice, P.O. Box 20489, Wickenburg, Ariz. 85358 Appl. No.: 358,765 Filed:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,196,085 B1
 USOO6196085B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,196,085 B1 Chimonides et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) COUPLING AN ACCESSORY TO AN ENGINE 3,576,336 4/1971 Uhlig... 403/281 CRANKSHAFT
USOO6196085B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,196,085 B1 Chimonides et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) COUPLING AN ACCESSORY TO AN ENGINE 3,576,336 4/1971 Uhlig... 403/281 CRANKSHAFT
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,820,200 Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9, B2
 US0093.97535B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,397.535 B2 Yamaguchi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul.19, 2016 (54) BRUSHLESS MOTOR AND (56) References Cited ELECTRIC-POWERED TOOL (71) Applicant:
US0093.97535B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,397.535 B2 Yamaguchi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul.19, 2016 (54) BRUSHLESS MOTOR AND (56) References Cited ELECTRIC-POWERED TOOL (71) Applicant:
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,092,999 Lilie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2000
 i & RS USOO6092999A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,092,999 Lilie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2000 54 RECIPROCATING COMPRESSOR WITH A 4,781,546 11/1988 Curwen... 417/417 LINEAR MOTOR
i & RS USOO6092999A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,092,999 Lilie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2000 54 RECIPROCATING COMPRESSOR WITH A 4,781,546 11/1988 Curwen... 417/417 LINEAR MOTOR
(12) United States Patent
 US007307230B2 (12) United States Patent Chen (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,307,230 B2 Dec. 11, 2007 (54) MECHANISM FOR CONTROLLING CIRCUITCLOSINGAOPENING OF POWER RATCHET WRENCH (75) Inventor:
US007307230B2 (12) United States Patent Chen (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,307,230 B2 Dec. 11, 2007 (54) MECHANISM FOR CONTROLLING CIRCUITCLOSINGAOPENING OF POWER RATCHET WRENCH (75) Inventor:
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD20: Last updated: 26th September 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD20: Last updated: 26th September 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
United States Patent (19) Ochi et al.
 United States Patent (19) Ochi et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,945,272 Jul. 31, 1990 54 ALTERNATOR FORMOTOR VEHICLES 75 Inventors: Daisuke Ochi; Yasuhiro Yoshida; Yoshiyuki Iwaki, all of
United States Patent (19) Ochi et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,945,272 Jul. 31, 1990 54 ALTERNATOR FORMOTOR VEHICLES 75 Inventors: Daisuke Ochi; Yasuhiro Yoshida; Yoshiyuki Iwaki, all of
(12) United States Patent
 USOO861 8656B2 (12) United States Patent Oh et al. (54) FLEXIBLE SEMICONDUCTOR PACKAGE APPARATUS HAVING ARESPONSIVE BENDABLE CONDUCTIVE WIRE MEMBER AND A MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Tac Keun.
USOO861 8656B2 (12) United States Patent Oh et al. (54) FLEXIBLE SEMICONDUCTOR PACKAGE APPARATUS HAVING ARESPONSIVE BENDABLE CONDUCTIVE WIRE MEMBER AND A MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Tac Keun.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O1521.35A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0152135 A1 Jang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2014 (54) MOTOR WITH VARIABLE MAGNET FLUX (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2014O1521.35A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0152135 A1 Jang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2014 (54) MOTOR WITH VARIABLE MAGNET FLUX (30) Foreign Application
United States Patent (19) Yamauchi et al.
 United States Patent (19) Yamauchi et al. 54). GAS INSULATED SWITCHGEAR APPARATUS 75 Inventors: Takao Yamauchi; Masazumi Yamamoto; Kiyokazu Torimi; Hiroki Sanuki, all of Tokyo, Japan 73 Assignee: Mitsubishi
United States Patent (19) Yamauchi et al. 54). GAS INSULATED SWITCHGEAR APPARATUS 75 Inventors: Takao Yamauchi; Masazumi Yamamoto; Kiyokazu Torimi; Hiroki Sanuki, all of Tokyo, Japan 73 Assignee: Mitsubishi
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,095,324 B2
 USOO8095324B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Dooley (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 10, 2012 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ROTOR CRACK 5,648,721. A 7/1997 Wincheski et al. DETECTION 5,952,836 A 9, 1999 Haake
USOO8095324B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Dooley (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 10, 2012 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ROTOR CRACK 5,648,721. A 7/1997 Wincheski et al. DETECTION 5,952,836 A 9, 1999 Haake
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070257638A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0257638A1 Amend et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2007 (54) TWIST LOCK BATTERY INTERFACE FOR (52) U.S. Cl....
US 20070257638A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0257638A1 Amend et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2007 (54) TWIST LOCK BATTERY INTERFACE FOR (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0139355A1 Lee et al. US 2013 O1393.55A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) HINGEMECHANISMAND FOLDABLE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0139355A1 Lee et al. US 2013 O1393.55A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) HINGEMECHANISMAND FOLDABLE
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2. Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005
 United States Patent USOO6915721B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2 Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) CORDLESS RATCHET WRENCH 6,311,583 B1 11/2001 Izumisawa... 81/57.13 6,715,380
United States Patent USOO6915721B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2 Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) CORDLESS RATCHET WRENCH 6,311,583 B1 11/2001 Izumisawa... 81/57.13 6,715,380
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080209237A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0209237 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: (54) COMPUTER APPARATUS AND POWER SUPPLY METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Dae-hyeon
(19) United States US 20080209237A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0209237 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: (54) COMPUTER APPARATUS AND POWER SUPPLY METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Dae-hyeon
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,047,956 B2. Masaoka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2006
 US007047956B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Masaoka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2006 (54) KICKBACK PREVENTING DEVICE FOR (56) References Cited ENGINE (75) Inventors: Akira Masaoka,
US007047956B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Masaoka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2006 (54) KICKBACK PREVENTING DEVICE FOR (56) References Cited ENGINE (75) Inventors: Akira Masaoka,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,083,631 B2. Shiohara (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 27, 2011
 US008.083631 B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Shiohara (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 27, 2011 (54) PLANETARY GEARTYPE GEARBOX (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Masaki Shiohara, Komatsu (JP) U.S.
US008.083631 B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Shiohara (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 27, 2011 (54) PLANETARY GEARTYPE GEARBOX (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Masaki Shiohara, Komatsu (JP) U.S.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO698.1746B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,981,746 B2 Chung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 2006 (54) ROTATING CAR SEAT MECHANISM 4,844,543 A 7/1989 Ochiai... 297/344.26 4,925,227
(12) United States Patent USOO698.1746B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,981,746 B2 Chung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 2006 (54) ROTATING CAR SEAT MECHANISM 4,844,543 A 7/1989 Ochiai... 297/344.26 4,925,227
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,446,482 B1. Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002
 USOO64.46482B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002 (54) BATTERY OPERATED HYDRAULIC D408.242 S 4/1999 Yamamoto... D8/61 COMPRESSION TOOL WITH RAPID
USOO64.46482B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002 (54) BATTERY OPERATED HYDRAULIC D408.242 S 4/1999 Yamamoto... D8/61 COMPRESSION TOOL WITH RAPID
WWWWWWWWVA IWWA. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1 IWW IWWIWWI IWWWWWW IWW IWWIYIVIVIVINNINWWWWWWIV
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0169926 A1 Watanabe et al. US 2007 O169926A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 >(54) HEAT EXCHANGER (75) Inventors: Haruhiko Watanabe,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0169926 A1 Watanabe et al. US 2007 O169926A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 >(54) HEAT EXCHANGER (75) Inventors: Haruhiko Watanabe,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007.0099.746A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0099746A1 Hahlbeck (43) Pub. Date: MaV 3, 2007 9 (54) SELF ALIGNING GEAR SET Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2007.0099.746A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0099746A1 Hahlbeck (43) Pub. Date: MaV 3, 2007 9 (54) SELF ALIGNING GEAR SET Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0119926 A1 LIN US 2013 0119926A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 16, 2013 (54) WIRELESS CHARGING SYSTEMAND METHOD (71) Applicant: ACER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0119926 A1 LIN US 2013 0119926A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 16, 2013 (54) WIRELESS CHARGING SYSTEMAND METHOD (71) Applicant: ACER
ADJUSTABLE PEDAL ASSEMBLY WITH ELECTRONIC THROTTLE CONTROL RELATED APPLICATION. filed Jan. 26, 1999, U.S. Pat. No. 6,109,241.
 ADJUSTABLE PEDAL ASSEMBLY WITH ELECTRONIC THROTTLE CONTROL RELATED APPLICATION [0001] This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 09/236,975, filed Jan. 26, 1999, U.S. Pat. No. 6,109,241.
ADJUSTABLE PEDAL ASSEMBLY WITH ELECTRONIC THROTTLE CONTROL RELATED APPLICATION [0001] This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 09/236,975, filed Jan. 26, 1999, U.S. Pat. No. 6,109,241.
Y-Né Š I/? S - - (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States 2S) (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 20, 2003 (54) (75)
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0035740 A1 Knoll et al. US 2003.0035740A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 20, 2003 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) WET TYPE ROTOR PUMP Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0035740 A1 Knoll et al. US 2003.0035740A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 20, 2003 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) WET TYPE ROTOR PUMP Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,156,856 B2. Abe (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2012
 USOO8156856B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Abe (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2012 (54) HYDRAULIC CYLINDER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS JP 9-411 7/1997 (75) Inventor: Yoshiyuki Abe, Nihonmatsu
USOO8156856B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Abe (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2012 (54) HYDRAULIC CYLINDER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS JP 9-411 7/1997 (75) Inventor: Yoshiyuki Abe, Nihonmatsu
