World Urbanization Prospects The 2007 Revision
|
|
|
- Julius Martin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 World Urbanization Prospects The 2007 Revision E c o n o m i c & S o c i a l A f f a i r s Highlights United Nations New York
2
3 ESA/P/WP/205 February 2008 English only Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division World Urbanization Prospects The 2007 Revision Highlights United Nations New York, 2008
4 DESA The Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat is a vital interface between global policies in the economic, social and environmental spheres and national action. The Department works in three main interlinked areas: (i) it compiles, generates and analyses a wide range of economic, social and environmental data and information on which States Members of the United Nations draw to review common problems and take stock of policy options; (ii) it facilitates the negotiations of Member States in many intergovernmental bodies on joint courses of action to address ongoing or emerging global challenges; and (iii) it advises interested Governments on the ways and means of translating policy frameworks developed in United Nations conferences and summits into programmes at the country level and, through technical assistance, helps build national capacities. Note The designations employed in this report and the material presented in it do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Secretariat of the United Nations concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Symbols of United Nations documents are composed of capital letters combined with figures. This publication has been issued without formal editing.
5 PREFACE The Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs at the United Nations Secretariat is responsible for providing the international community with up-to-date and scientifically objective information on population and development. The Population Division provides guidance to the United Nations General Assembly, Economic and Social Council, and the Commission on Population and Development on population and development issues and undertakes regular studies on population levels and trends, population estimates and projections, population policies, and population and development inter-relationships. The Population Division s work encompasses the following substantive areas: the study of mortality, fertility, international and internal migration, including their levels and trends as well as their causes and consequences; estimates and projections of the distribution of the population between urban and rural areas and in cities; estimates and projections of population size, age and sex structure, and demographic indicators for all countries of the world; the documentation and analysis of population and development policies at the national and international levels; and the study of the relationship between socio-economic development and population change. This report presents the highlights of the 2007 Revision of World Urbanization Prospects including the official United Nations estimates and projections of urban and rural populations for major areas, regions and countries of the world and of all urban agglomerations with 750,000 inhabitants or more in The data in this Revision are consistent with the total populations estimated and projected according to the medium variant of the 2006 Revision of the United Nations global population estimates and projections, published in World Population Prospects: The 2006 Revision 1. This Revision updates and supersedes previous estimates and projections published by the United Nations. Wall charts entitled Urban Agglomerations 2007 and Urban and Rural Areas 2007 will also be issued in A CD-ROM containing major results of the 2007 Revision can be purchased from the Population Division. A description of the databases and an order form are given on pages of this publication and are also posted on the Population Division s web site at All basic data and a complete list of data sources can be retrieved from an on-line database at the same web site. This publication may also be accessed on the website of the Population Division at For further information about the 2007 Revision, please contact the office of Ms. Hania Zlotnik, Director, Population Division, DESA, United Nations, New York, NY 10017, USA; tel.: (1 212) , fax: (1 212) World Population Prospects: The 2006 Revision, vol. I, Comprehensive Tables (United Nations publication, Sales No. E.07.XIII.2). iii
6
7 CONTENTS Page PREFACE... EXPLANATORY NOTES... iii vii HIGHLIGHTS... 1 SOURCES OF DATA DATA IN DIGITAL FORM ORDER FORM No. TABLES 1. Total, urban and rural populations by development group, selected periods, Percentage urban by development group, selected periods, Total, urban and rural populations by major area, selected periods, Percentage urban by major area, selected periods, Population distribution of the world and development groups, by area of residence and size class of urban settlement, 1975, 2007 and Population of urban agglomerations with 10 million inhabitants or more, 1950, 1975, 2007 and Population of urban agglomerations with 10 million inhabitants or more in 2007 and their average annual rates of change, selected periods, Government views on the spatial distribution of the population, FIGURES 1. Urban and rural population of the world, Urban and rural populations, by development group, Percentage of the population in urban areas, 2007, 2025 and Distribution of the world urban population by major area, 1950, 2007 and ANNEX TABLES A.1. Population of urban and rural areas at mid-year and percentage urban, A.2. Percentage of population at mid-year residing in urban areas by major area, region and country, A.3. Urban population at mid-year by major area, region and country, A.4. Rural population at mid-year by major area, region and country, A.5. Total population at mid-year by major area, region and country, v
8 No. Page A.6. A.7. A.8. A.9. A.10. Average annual rate of change of the urban population by major area, region and country, Average annual rate of change of the rural population by major area, region and country, Average annual rate of change of the total population by major area, region and country, Average annual rate of change of the percentage urban by major area, region and country, Average annual rate of change of the percentage rural by major area, region and country, A.11. The 30 largest urban agglomerations ranked by population size, A.12. Population of urban agglomerations with 750,000 inhabitants or more in 2007, by country, A.13. Population of capital cities in A.14. A.15. A.16. A.17. Average annual rate of change of urban agglomerations with 750,000 inhabitants or more in 2007, by country, Percentage of the urban population residing in each urban agglomeration with 750,000 inhabitants or more in 2007, by country, Percentage of the total population residing in each urban agglomeration with 750,000 inhabitants or more in 2007, by country, Urban population, number of cities and percentage of urban population, by size class of settlement, major area and region, vi
9 EXPLANATORY NOTES The following symbols have been used in the tables throughout this report: Two dots (..) indicate that the item is not applicable. Three dots (...) indicate that data are not available or are not separately reported. An em dash ( ) indicates that the value is zero (magnitude zero). 0 or 0.0 indicates that the magnitude is not zero, but less than half of the unit employed. A minus sign (-) before a figure indicates a decrease. A full stop (.) is used to indicate decimals. Years given start on 1 July. Use of a hyphen (-) between years, for example, , signifies the full period involved, from 1 July of the beginning year to 30 June of the end year. Details and percentages in tables do not necessarily add to totals because of rounding. References to countries, territories, areas and urban locations The designations employed and the material in this publication do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Secretariat of the United Nations concerning the legal status of any country, territory or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. The designations more developed and less developed regions are intended for statistical convenience and do not necessarily express a judgment about the stage reached by a particular country or area in the development process. The term country, as used in this publication, also refers, as appropriate, to territories or areas. More developed regions comprise all regions of Europe plus Northern America, Australia/New Zealand and Japan. The term developed countries is used to designate countries in the more developed regions. Less developed regions comprise all regions of Africa, Asia (excluding Japan) and Latin America and the Caribbean, as well as Melanesia, Micronesia and Polynesia. The term developing countries is used to designate countries in the less developed regions. The group of least developed countries, as defined by the United Nations General Assembly in 2003, comprises 50 countries, of which 34 are in Africa, 10 in Asia, 1 in Latin America and the Caribbean, and 5 in Oceania. Country names and the composition of geographical areas follow those of Standard country or area codes for statistical use (ST/ESA/STAT/SER.M/49/Rev.3), available at: Names of cities or urban agglomerations are presented in their original language, following the names used by National Statistical Offices or the United Nations Demographic Yearbook. For cities with names in more than one language, different names are separated by a hyphen. If the country uses script with non-latin characters, a transliteration of the original spelling into Latin script is used. If cities have established alternative names or English names, these names are added in brackets. The administrative subdivision to which a city belongs is appended, if needed, to the city name to identify the city unambiguously. For convenience, the term growth rate is used in this report instead of the more precise term rate of change which reflects that populations can grow or decline. The following abbreviations have been used: DESA SAR HDI Department of Economic and Social Affairs Special Administrative Region Human Development Index vii
10 For analytical purposes, the following country groupings have been used: CLASSIFICATION OF COUNTRIES BY MAJOR AREA AND REGION OF THE WORLD Africa Eastern Africa Middle Africa Northern Africa Western Africa Burundi Angola Algeria Benin Comoros 2 Cameroon Egypt Burkina Faso Djibouti Central African Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Cape Verde Eritrea Chad Morocco Côte d Ivoire Ethiopia Congo Sudan Gambia Kenya Democratic Republic of the Tunisia Ghana Madagascar Congo Western Sahara Guinea Malawi Equatorial Guinea Guinea-Bissau Mauritius 3 Gabon Southern Africa Liberia Mozambique São Tomé and Príncipe Mali Réunion Botswana Mauritania Rwanda Lesotho Niger Seychelles Namibia Nigeria Somalia South Africa Saint Helena 4 Uganda Swaziland Senegal United Republic of Tanzania Sierra Leone Zambia Togo Zimbabwe Eastern Asia South-central Asia 5 South-eastern Asia Western Asia China Afghanistan Brunei Darussalam Armenia China, Hong Kong SAR Bangladesh Cambodia Azerbaijan China, Macao SAR Bhutan Indonesia Bahrain Democratic People s India Lao People s Democratic Cyprus Republic of Korea Iran (Islamic Republic of) Republic Georgia Japan Kazakhstan Malaysia Iraq Mongolia Kyrgyzstan Myanmar Israel Republic of Korea Maldives Philippines Jordan Nepal Singapore Kuwait Pakistan Thailand Lebanon Sri Lanka Timor-Leste Occupied Palestinian Tajikistan Viet Nam Territory Turkmenistan Uzbekistan Asia Oman Qatar Saudi Arabia Syrian Arab Republic Turkey United Arab Emirates Yemen 2 Including the island of Mayotte. 3 Including the islands of Agalega, Rodrigues, and Saint Brandon. 4 Including the islands of Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. 5 The regions Southern Asia and Central Asia are combined into South-Central Asia. viii
11 CLASSIFICATION OF COUNTRIES (continued) Europe Eastern Europe Northern Europe Southern Europe Western Europe Belarus Channel Islands 6 Albania Austria Bulgaria Denmark Andorra Belgium Czech Republic Estonia Bosnia and Herzegovina France Hungary Faeroe Islands Croatia Germany Moldova Finland 7 Gibraltar Liechtenstein Poland Iceland Greece Luxembourg Romania Ireland Holy See Monaco Russian Federation Isle of Man Italy Netherlands Slovakia Latvia Malta Switzerland Ukraine Lithuania Montenegro Norway 8 Portugal Sweden San Marino United Kingdom of Great Serbia Britain and Northern Slovenia Ireland 9 Spain The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia 10 Latin America and the Caribbean Caribbean Central America South America Anguilla Belize Argentina Antigua and Barbuda Costa Rica Bolivia Aruba El Salvador Brazil Bahamas Guatemala Chile Barbados Honduras Colombia British Virgin Islands Mexico Ecuador Cayman Islands Nicaragua Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Cuba Panama French Guiana Dominica Guyana Dominican Republic Paraguay Grenada Peru Guadeloupe Suriname Haiti Uruguay Jamaica Venezuela (Bolivarian Martinique Republic of) Montserrat Netherlands Antilles Puerto Rico Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Trinidad and Tobago Turks and Caicos Islands United States Virgin Islands 6 Including the islands of Guernsey and Jersey. 7 Including Åland Islands. 8 Including Svalbard and Jan Mayen Islands. 9 Also referred to as United Kingdom. 10 Also referred to as TFYR Macedonia. ix
12 CLASSIFICATION OF COUNTRIES (continued) Northern America Bermuda Canada Greenland Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon United States of America Oceania Australia/New Zealand Melanesia Micronesia Polynesia Australia 11 Fiji Guam American Samoa New Zealand New Caledonia Kiribati Cook Islands Papua New Guinea Marshall Islands French Polynesia Solomon Islands Micronesia Niue Vanuatu (Federated States of) Pitcairn Nauru Samoa Northern Mariana Islands Palau Tokelau Tonga Tuvalu Wallis and Futuna Islands Sub-Saharan Africa Angola Côte d'ivoire Kenya Nigeria Swaziland Benin Democratic Republic Lesotho Réunion Togo Botswana of the Congo Liberia Rwanda Uganda Burkina Faso Djibouti Madagascar Saint Helena United Republic Burundi Equatorial Guinea Malawi São Tomé and Príncipe of Tanzania Cameroon Eritrea Mali Senegal Zambia Cape Verde Ethiopia Mauritania Seychelles Zimbabwe Central African Repub- Gabon Mauritius Sierra Leone Chad Gambia Mozambique Somalia Comoros Ghana Namibia South Africa Congo Guinea Niger Sudan Guinea-Bissau 11 Including Christmas Island, Cocos (Keeling) Islands, and Norfolk Island. x
13 CLASSIFICATION OF COUNTRIES (continued) Least developed countries Afghanistan Gambia Rwanda Angola Guinea Samoa Bangladesh Guinea-Bissau São Tomé and Príncipe Benin Haiti Senegal Bhutan Kiribati Sierra Leone Burkina Faso Lao People s Democratic Republic Solomon Islands Burundi Lesotho Somalia Cambodia Liberia Sudan Cape Verde Madagascar Timor-Leste Central African Republic Malawi Togo Chad Maldives Tuvalu Comoros Mali Uganda Democratic Republic of the Congo Mauritania United Republic of Tanzania Djibouti Mozambique Vanuatu Equatorial Guinea Myanmar Yemen Eritrea Nepal Zambia Ethiopia Niger xi
14
15 HIGHLIGHTS Since 1988 the Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations has been issuing every two years revised and updated estimates and projections of the urban and rural populations of all countries in the world and of their major urban agglomerations. This note presents the main findings of the 2007 Revision of World Urbanization Prospects which are consistent with the size of the total population of each country as estimated or projected in the 2006 Revision of World Population Prospects (United Nations, 2008). The 2007 Revision presents estimates and projections of the total, urban and rural populations of the world for the period The results are shown for development groups, six major areas (i.e., Africa, Asia, Europe, Latin America and the Caribbean, Northern America and Oceania) and 21 regions. Data are further disaggregated for the 229 countries or areas of the world. The 2007 Revision also provides estimates and projections of the population of urban agglomerations with 750,000 inhabitants or more in 2007 for the period Estimates of the proportion of the population living in urban areas and the population of cities are derived on the basis of national statistics. The most common source of data on the proportion urban and the population of cities and urban agglomerations is the population census. For some countries, the basic data are obtained from population registers or administrative statistics. The 2007 Revision corroborates that the world population will reach a landmark in 2008: for the first time in history the urban population will equal the rural population of the world and, from then on, the world population will be urban in its majority. This event is a consequence of rapid urbanization in the last decades, especially in the less developed regions. Nevertheless, major parts of the world remain largely rural. In Africa and Asia, still six out of every ten persons live in rural areas. Between 2007 and 2050, the world population is expected to increase by 2.5 billion, passing from 6.7 billion to 9.2 billion (United Nations, 2008). At the same time, the population living in urban areas is projected to gain 3.1 billion, passing from 3.3 billion in 2007 to 6.4 billion Thus, the urban areas of the world are expected to absorb all the population growth expected over the next four decades while at the same time drawing in some of the rural population. As a result, the world rural population is projected to start decreasing in about a decade and 0.6 billion fewer rural inhabitants are expected in 2050 than today. Furthermore, most of the population growth expected in urban areas will be concentrated in the cities and towns of the less developed regions. Asia, in particular, is projected to see its urban population increase by 1.8 billion, Africa by 0.9 billion, and Latin America and the Caribbean by 0.2 billion. Population growth is therefore becoming largely an urban phenomenon concentrated in the developing world. Realization of these projections is contingent on the continuation of fertility reductions in the developing world. If fertility were to remain constant at current levels and the pace of urbanization remained that projected in the 2007 Revision, the world urban population would increase to 8.1 billion by 2050 instead of the 6.4 billion expected when fertility is assumed to continue declining in all developing regions. In many countries, natural increase (the difference of births minus deaths) accounts for 60 per cent or more of urban population growth. Consequently, policies that facilitate the reduction of fertility by allowing couples to have the number of children they desire can contribute to moderate increases in the number of urban dwellers, thereby making it easier for developing countries to adjust to the transformations associated with growing urbanization. There is significant diversity in the urbanization levels reached by different regions. The transformative power of urbanization was felt earlier in today s more developed regions and they have reached high levels of urbanization. Thus, 74 per cent of the inhabitants of more developed regions lived in urban areas in 2007, 1
16 whereas just 44 per cent of those in the less developed regions did so. Urbanization is expected to continue rising in both the more developed and the less developed regions so that, by 2050, urban dwellers will likely account for 86 per cent of the population in the more developed regions and for 67 per cent of that in the less developed regions. Overall, the world population is expected to be 70 per cent urban in Today s 3.4 billion urban dwellers are distributed unevenly among urban settlements of different size. In discussing urbanization, the focus often is on large cities, cities whose populations are larger than those of many countries. In 2007, 19 urban agglomerations qualified as megacities because they had at least 10 million inhabitants. Despite their visibility and dynamism, megacities account for a small though increasing proportion of the world urban population: nearly 9 per cent in 2007 and nearly 10 per cent in At the same time, over half of the urban population lives and will continue to live in small urban centres with fewer than half a million inhabitants. These and other key findings of the 2007 Revision are summarized below. Key Findings of the 2007 Revision 1. During 2008, for the first time in history, the proportion of the population living in urban areas will reach 50 per cent (figure I.1). While in the more developed regions, the proportion urban was already nearly 53 per cent in 1950, in the less developed regions the 50 per cent level will likely be reached around 2019 (figure I.2). Figure I.1. Urban and rural populations of the world, Population (millions) Urban population Year Rural population 2
17 2. The world urban population is expected nearly to double by 2050, increasing from 3.3 billion in 2007 to 6.4 billion in By mid-century the world urban population will likely be the same size as the world s total population in Virtually all of the world s population growth will be absorbed by the urban areas of the less developed regions, whose population is projected to increase from 2.4 billion in 2007 to 5.3 billion in The urban population of the more developed regions is projected to increase modestly, from 0.9 billion in 2007 to 1.1 billion in 2050 (table I.1) Figure I.2. Urban and rural populations, by development group, Population (millions) More developed regions, urban population More developed regions, rural population Year Less developed regions, urban population Less developed regions, rural population TABLE I.1. TOTAL, URBAN AND RURAL POPULATIONS BY DEVELOPMENT GROUP, SELECTED PERIODS, Population (billion) Average annual rate of change (percentage) Development group Total population World More developed regions Less developed regions Urban population World More developed regions Less developed regions Rural population World More developed regions Less developed regions
18 TABLE I.2. PERCENTAGE URBAN BY DEVELOPMENT GROUP, SELECTED PERIODS, Rate of urbanization Percentage urban (percentage) Development group World More developed regions Less developed regions The world rural population is expected to reach a maximum of 3.5 billion in 2018 or 2019 and to decline slowly thereafter, to reach 2.8 billion in 2050 (figure I.1). These global trends are driven mostly by the dynamics of rural population growth in the less developed regions, which house today 90 per cent of the world rural population. Whereas the rural population of the more developed regions has been declining steadily during the second half of the twentieth century and will continue to do so for the foreseeable future, the rural population of the less developed regions more than doubled since 1950 and will likely continue to grow until 2021 before a long-term decline sets in. 4. The rate of growth of the world urban population is slowing down (table I.1). Between 1950 and 2007, the world urban population grew at an average rate of 2.6 per cent per year and more than quadrupled over the period, passing from 0.7 billion to 3.3 billion. During , the world urban population is projected to grow at an average annual rate of 1.8 per cent, which, if maintained, would lead to a doubling of the urban population in 38 years. During , the urban growth rate is expected to decline further to 1.3 per cent per year, implying a doubling time of 52 years. 5. The sustained increase of the urban population combined with the pronounced deceleration of rural population growth will result in continued urbanization, that is, in increasing proportions of the population living in urban areas. Globally, the level of urbanization is expected to rise from 50 per cent in 2008 to 70 per cent in 2050 (table I.2). More developed regions are expected to see their level of urbanization rise from 74 per cent to 86 per cent over the same period. In the less developed regions, the proportion urban will likely increase from 44 per cent in 2007 to 67 per cent in 2050 (table I.2). 6. Historically, the process of rapid urbanization started first in today s more developed regions. In 1920, just under 30 per cent of their population was urban and by 1950, more than half of their population was living in urban areas. In 2007, high levels of urbanization, surpassing 80 per cent, characterized Australia, New Zealand and Northern America. Europe, with 72 per cent of its population living in urban areas, was the least urbanized major area in the developed world. By 2050, Australia, New Zealand and Northern America are all expected to be over 90 per cent urban while Europe s level of urbanization is projected to be lower, at 84 per cent (table I.4). 7. Among the less developed regions, Latin America and the Caribbean has an exceptionally high level of urbanization (78 per cent), higher than that of Europe. Africa and Asia, in contrast, remain mostly rural, with 38 per cent and 41 per cent, respectively, of their populations living in urban areas. Over the coming decades, the level of urbanization is expected to increase in all major areas of the developing world, with Africa and Asia urbanizing more rapidly than the rest (table I.4). Nevertheless, by mid-century, Africa and Asia are expected still to have lower levels of urbanization than the more developed regions or Latin America and the Caribbean (figure I.3). 4
19 TABLE I.3. TOTAL, URBAN AND RURAL POPULATIONS BY MAJOR AREA, SELECTED PERIODS, Population (millions) Major area Average annual rate of change (percentage) Total population Africa Asia Europe Latin America and the Caribbean Northern America Oceania Urban population Africa Asia Europe Latin America and the Caribbean Northern America Oceania Rural population Africa Asia Europe Latin America and the Caribbean Northern America Oceania TABLE I.4. PERCENTAGE URBAN BY MAJOR AREA, SELECTED PERIODS, Percentage urban Major area Rate of urbanization (percentage) Africa Asia Europe Latin America and the Caribbean Northern America Oceania
20 Figure I.3. Percentage of the population in urban areas, 2007, 2025 and Source: United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division: World Population Prospects DEMOBASE extract NOTE: The boundaries shown on the present map do not imply official endorsement or acceptance by the United Nations. 6
21 Figure I.4. Distribution of the world urban population by major area, 1950, 2007, % 50% 50% 54% 40% 38% 32% 30% 20% 10% 0% 4% 11% 19% 16% 9% 9% 14% 11% Africa Asia Europe Latin America and the Caribbean 15% 8% 6% Northern America 1% 1% 1% Oceania Despite its low level of urbanization, in 2007 Asia was home to about half of the urban population in the world. Europe had the second highest share, at 16 per cent (figure I.4). Over the next four decades, Africa and Asia will experience a marked increase in their urban populations. In Africa the urban population is likely to treble and in Asia it will more than double (table I.3). By mid-century, most of the urban population of the world will be concentrated in Asia (54 per cent) and Africa (19 per cent) (figure I.4) 9. With the exception of Africa and Oceania, all major areas are expected to have smaller rural populations in 2050 than today (table I.3). Africa s rural population may start to decline before the mid-century. Today, the majority of rural dwellers live in Asia (71 per cent) and Africa (18 per cent) and the concentration of the world rural population in these two major areas combined is expected to increase so that, by 2050, 64 per cent of all rural inhabitants are projected to live in Asia and 27 per cent in Africa. 10. The world urban population is highly concentrated in a few countries. In 2007, three quarters of the 3.3 billion urban dwellers on Earth lived in 25 countries, whose urban populations ranged from 29 million in South Africa to 561 million in China. China, India and the United States of America accounted for 35 per cent of the world urban population. Most of the 25 countries with the largest urban populations are highly urbanized, but seven have levels of urbanization ranging from 27 per cent to just over 50 per cent and they include some of the most populous countries in the world: Bangladesh, China, India, Indonesia, Nigeria and Pakistan. 11. Most countries have small urban populations. In 2007, two thirds of the 229 countries or areas considered had fewer than 5 million urban dwellers and they accounted for 5.8 per cent of the world urban population. Among them, 60 per cent had urban populations below one million and accounted for 0.6 per cent of all urban dwellers on Earth. By 2050, just half of all countries or areas are expected to have fewer than 5 million urban dwellers and to account for barely 2 per cent of the world urban population. 7
22 12. Similarly, the increases in the world urban population are concentrated in a few countries, with China and India projected to account together for about a third of the increase in the urban population in the coming decades. Between 2007 and 2025, the urban areas of the world are expected to gain 1.3 billion people, including 261 million in China and 197 million in India, which account together for 35 per cent of the total increase. Nine additional countries are projected to contribute 29 per cent of the urban increment, with increases ranging from 20 million to 62 million. The countries involved are: Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of Congo in Africa; Bangladesh, Indonesia, Pakistan and the Philippines in Asia; Brazil and Mexico in Latin America, and the United States of America. Among them, those in Africa and Asia will experience high rates of urban population growth, surpassing 2 per cent or even 3 per cent per year. 13. A further urban increment of 1.8 billion people is expected globally during , with India being the major contributor (377 million) and China following (205 million). Together, the two most populous countries on Earth are expected to account for 32 per cent of urban growth during In 2050, China will still have the largest urban population (1 billion), followed by India (0.9 billion). 14. In a few developed countries, the urban population will decrease. Despite the projected increases in the level of urbanization, overall population decline in several countries will lead to a reduction in the number of urban dwellers. Between 2007 and 2025, the urban population of the Russian Federation and that of Ukraine are projected to decline by 8 million and 3 million, respectively. Between 2025 and 2050, more countries will experience reductions in the urban population. Those with the largest drops include Japan (a reduction of 4 million), the Republic of Korea (4 million), the Russian Federation (7 million) and Ukraine (4 million). 15. The rural population is even more highly concentrated in a few countries than the urban population. In 2007, 18 countries accounted for 75 per cent of the rural population and all but three (Japan, the Russian Federation and the United States) are located in Africa or Asia. India has the largest rural population (828 million), followed by China (767 million). Together, they account for 47 per cent of the world rural population. Bangladesh, Indonesia and Pakistan follow, each with over 100 million rural inhabitants. In Africa, the largest rural populations are located in Nigeria (78 million), Ethiopia (69 million), Egypt (43 million), the Democratic Republic of Congo (42 million), the United Republic of Tanzania (30 million) and Kenya (30 million). During , the rural populations of most of those African countries are projected to increase at rates equal to or higher than 1 per cent per year, the only exception being Nigeria. Among populous countries in Asia, Pakistan will have the highest rural growth rate during (0.8 per cent per year). In contrast, in eight of the 18 countries with large rural populations the rural population is declining, with China, Indonesia, Japan, the Russian Federation and the United States having the fastest rates of decline. 16. As in the case of the urban population, most countries have small rural populations. In 2007, 69 per cent of the 229 countries or areas considered had at most 5 million rural inhabitants and accounted for 4.8 per cent of the world rural population. In three quarters of them, the rural population is projected to decrease during The 3.3 billion urban dwellers in 2007 were distributed unevenly among urban settlements of different size. Over half of the world urban population (52 per cent) lived in cities or towns with fewer than half a million inhabitants. In the more developed regions, 54 per cent of the urban population lived in small urban centres and 51 per cent did so in the less developed regions. Between 2007 and 2025, small urban centres are expected to absorb nearly half of the expected increase in the urban population. 18. Cities in the next size class, whose population ranges from 500,000 to one million inhabitants, are numerous (460 in 2007 rising to 551 in 2025), but they account for just 10 per cent of the overall urban population. Medium-sized cities, with more than a million inhabitants but fewer than 5 million, are also numerous (382 in 2007 increasing to 524 in 2025) and they account for 23 per cent of the urban population (table I.5). 8
23 19. Large cities, whose populations range from 5 million to just under 10 million, numbered 30 in 2007 and are expected to number 48 in 2025, but accounted for just 7 per cent of the urban population. Three quarters of these megacities in waiting are located in developing countries. TABLE I.5. POPULATION DISTRIBUTION OF THE WORLD AND DEVELOPMENT GROUPS, BY AREA OF RESIDENCE AND SIZE CLASS OF URBAN SETTLEMENT, 1975, 2007 AND 2025 Development group World More developed regions Less developed regions Area of residence and size class of urban settlement (number of Population (millions) Percentage distribution inhabitants) Urban area million or more million to 10 million million to 5 million ,000 to 1 million Fewer than 500, Urban area million or more million to 10 million million to 5 million ,000 to 1 million Fewer than 500, Urban area million or more million to 10 million million to 5 million ,000 to 1 million Fewer than 500,
24 TABLE I.6. POPULATION OF URBAN AGGLOMERATIONS WITH 10 MILLION INHABITANTS OR MORE, 1950, 1975, 2007 AND 2025 (MILLIONS) Rank Urban agglomeration Population Rank Urban agglomeration Population 1 New York-Newark, USA Tokyo, Japan Tokyo, Japan New York-Newark, USA Ciudad de México (Mexico City), Mexico Rank Urban agglomeration Population Rank Urban agglomeration Population 1 Tokyo, Japan Tokyo, Japan New York-Newark, USA Mumbai (Bombay), India Ciudad de México (Mexico City), Mexico Delhi, India Mumbai (Bombay), India Dhaka, Bangladesh São Paulo, Brazil São Paulo, Brazil Delhi, India Ciudad de México (Mexico City), Mexico Shanghai, China New York-Newark, USA Kolkata (Calcutta), India Kolkata (Calcutta), India Dhaka, Bangladesh Shanghai, China Buenos Aires, Argentina Karachi, Pakistan Los Angeles-Long Beach-Santa Ana, USA Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo Karachi, Pakistan Lagos, Nigeria Al-Qahirah (Cairo), Egypt Al-Qahirah (Cairo), Egypt Rio de Janeiro, Brazil Manila, Philippines Osaka-Kobe, Japan Beijing, China Beijing, China Buenos Aires, Argentina Manila, Philippines Los Angeles-Long Beach-Santa Ana, USA Moskva (Moscow), Russian Federation Rio de Janeiro, Brazil Istanbul, Turkey Jakarta, Indonesia Istanbul, Turkey Guangzhou, Guangdong, China Osaka-Kobe, Japan Moskva (Moscow), Russian Federation Lahore, Pakistan Shenzhen, China Chennai (Madras), India Paris, France Megacities are urban agglomerations with at least 10 million inhabitants. There are today 19 megacities on Earth and their number is expected to increase to 27 in The proportion of people living in megacities is small. In 2007, 9 per cent of the world urban population resided in megacities and by 2025 their share is expected to raise to almost 10 per cent. In relation to the whole world population, megacities account today for 4 per cent of the population, meaning that just one in twenty-five people on Earth live in megacities. 21. Asia has eleven megacities; Latin America has four; Northern America, two; and Africa and Europe have one each. Eleven of these megacities are capitals of their countries. By 2025, when the number of megacities rises to 27, Asia would have increased its number by five; Africa by two, and Europe by one. 10
25 22. The distribution of the urban population by city size class varies among the major areas. In Latin America and the Caribbean, for instance, urban dwellers are more concentrated in the megacities than in the world as a whole: 14 per cent live in megacities. Relatively high concentrations of urban dwellers in megacities are also found in Northern America (11 per cent) and Asia (10 per cent). In contrast, 58 per cent of urban dwellers in Africa live in small urban centres with fewer than half a million inhabitants and 68 per cent of those in Europe do the same. 23. With nearly 36 million inhabitants in 2007, Tokyo is by far the most populous urban agglomeration in the world, but it encompasses all contiguous densely inhabited districts in Tokyo-to (ku-bu) plus those in 87 surrounding cities and towns, including Yokohama, Kawasaki and Chiba, important cities in their own rights. Other megacities, while named after the major city at their core, also encompass a large area and a number of urban settlements within it, constituting therefore complex urban agglomerations. Following Tokyo, the next largest urban agglomerations are New York-Newark, Ciudad de México, Mumbai and São Paulo, each with about 19 million inhabitants. In 2025, Tokyo is still expected to be the world s most populous urban agglomeration with 36 million inhabitants, followed by Mumbai (with 26 million), Delhi (23 million), Dhaka (22 million) and São Paulo (21 million) (table I.6). TABLE I.7. POPULATION OF URBAN AGGLOMERATIONS WITH 10 MILLION INHABITANTS OR MORE IN 2007 AND THEIR AVERAGE ANNUAL RATES OF CHANGE, SELECTED PERIODS, Population (millions) Average annual rate of change (percentage) Urban agglomeration Tokyo, Japan New York-Newark, USA Ciudad de México (Mexico City), Mexico Mumbai (Bombay), India São Paulo, Brazil Delhi, India Shanghai, China Kolkata (Calcutta), India Dhaka, Bangladesh Buenos Aires, Argentina Los Angeles-Long Beach-Santa Ana, USA Karachi, Pakistan Al-Qahirah (Cairo), Egypt Rio de Janeiro, Brazil Osaka-Kobe, Japan Beijing, China Manila, Philippines Moskva (Moscow), Russian Federation Istanbul, Turkey NOTE: Urban agglomerations are ordered according to their population size in Large urban agglomerations are not necessarily experiencing fast population growth. Among the 19 megacities in 2007, one-third experienced annual population growth below 1.5 per cent between 1975 and 2007 and just five grew at rates above 3 per cent per year (table I.7): Dhaka in Bangladesh (5.6 per cent per year); Delhi (4.0 per cent) and Mumbai (3.1 per cent) in India; Karachi in Pakistan (3.5 per cent), and Istanbul in Turkey (3.2 per cent). Between 2007 and 2025, two-thirds of the megacities are projected to experience 11
26 annual population growth below 1.5 per cent and only two (Dhaka and Karachi) will maintain population growth rates above 2 per cent. 25. Faced with the numerous opportunities and challenges associated with urbanization, many Governments have consistently considered their population s spatial distribution as a concern. In 2007, 85 per cent of Governments expressed concern about their pattern of population distribution, a percentage comparable to that recorded in the 1970s (table I.8). Among developing countries, 56 per cent wished to make a major change in the spatial distribution of their populations, whereas 32 per cent desired a minor change. Among developed countries, 37 per cent desired a major change and 39 per cent a minor change. Dissatisfaction regarding patterns of population distribution was highest in Africa (74 per cent of its countries desired a major change) and Asia (51 per cent desired a major change). In Latin America and the Caribbean, Oceania and Europe, about 40 per cent of Governments considered that major changes in spatial distribution were desirable (United Nations, 2007). 26. A common policy to modify population distribution includes various types of measures to reduce migrant flows to large cities. The percentage of developing countries having implemented such policies rose from 44 per cent to 74 per cent between 1976 and Among developed countries, the proportion with policies to reduce flows to large cities declined from 55 per cent in 1975 to 26 per cent in 1996 and then rebounded to reach 39 per cent in In Oceania, 83 per cent of countries have such policies, in Africa 78 per cent, in Asia 71 per cent and in Latin America and the Caribbean 68 per cent. TABLE I.8. GOVERNMENT VIEWS ON THE SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE POPULATION, 2007 Major change desired Minor change desired Satisfactory Total Major change desired Minor change desired Satisfactory Total Number of countries Percentage World More developed regions Less developed regions Source: World Population Policies 2007 (United Nations publication, Sales No. E.08.XIII.8). 12
27 SOURCES OF DATA This chapter contains information on the sources of data used in estimating and projecting the population of urban areas and urban agglomerations. Section A presents the sources of data and the definitions underlying the data on urban populations. The definitions presented are generally those used by national statistical offices in carrying out the latest available census. When the definition used in the latest census was not the same as in previous censuses, the data were adjusted whenever possible so as to maintain consistency. In cases where adjustments were made in such a way as to ensure consistency with the definition used in previous censuses, that information is included in the sources listed below. United Nations estimates and projections are based, to the extent possible, on actual enumerations. In some cases, however, it was desirable to incorporate official or other estimates of urban population size as part of the input for the estimation of trends. The sources below indicate when that was done. Section B presents sources of data and the statistical concepts underlying the data used in estimating and projecting the populations of urban agglomerations and capital cities. The term Urban agglomeration refers to the population contained within the contours of a contiguous territory inhabited at urban density levels without regard to administrative boundaries. It usually incorporates the population in a city or town plus that in the suburban areas lying outside the city proper but being adjacent to the city boundaries. Whenever possible, data classified according to the concept of urban agglomeration are used. However, some countries do not produce data according to that concept but use instead that of metropolitan area or City proper. If possible, such data are adjusted to conform to the concept of urban agglomeration. When sufficient information is not available to permit such an adjustment, data based on the concept of City proper or metropolitan area are used. The sources listed in section B indicate whether data were adjusted to conform to the concept of urban agglomeration or whether a different concept was used. A. SOURCES OF DATA ON THE URBAN POPULATION Afghanistan Sources of data: Census of 1979; estimates for 1950, 1966, 1971 and Definition: Sixty-six localities and provincial centers. Albania Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1960, 1969, 1979, 1989, 2001 and 2007; estimates for 1991 and Definition: Towns and other industrial centres with more than 400 inhabitants. Algeria Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1960, 1966, 1977, 1987 and Definition: All communes having as chef-lieu a city, a rural town or an urban agglomeration. American Samoa Sources of data: Census of 2000; UN estimates for 1970, 1980 and Definition: Urban areas, according to the 2000 census, are densely settled territory that meets minimum population density requirements and encompasses a population of at least 2,500. The proportion urban for earlier years was adjusted for consistency with this definition. Andorra Sources of data: Estimates for 1985, 1990, 2000 and 2004; UN estimates for 1950 and Definition: Parishes of Andorra la Vella, Escaldes-Engordany, Saint Julia, Encamp and La Massana. 13
28 Angola Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960 and 1970; estimate for 1994; UN estimate for Definition: Localities with at least 2,000 inhabitants. Anguilla Sources of data: UN Estimates for 1960, 1974, 1984, 1992 and Definition: In the absence of more detailed information, the entire population is considered urban. Antigua and Barbuda Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1991 and Definition: St. John s (capital). Argentina Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and Definition: Population centres with 2,000 inhabitants or more. Armenia Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2001; estimate for Definition: Cities and urban-type localities, officially designated as such, usually according to the criteria of number of inhabitants and predominance of agricultural or non-agricultural workers and their families. Aruba Sources of data: Censuses of 1991 and 2000; estimate for 1965; UN estimate for Definition: Oranjestad (capital) and Sant Nicolas. Australia Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1961, 1971, 1976, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996 and Definition: All urban centres with 1,000 inhabitants or more. Starting in 1991, the definition of urban has changed in the census counts. Austria Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and 2001; estimates for 2005 and Definition: Based on the concept of a functional and structural urban area (Stadtregion) consisting of an urban core area (Kernzone) and surrounding urban areas. (Außenzone). The surrounding urban areas is defined as an area in which at least 30 per cent of working adults commute daily into the corresponding core area. Azerbaijan Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 1999; estimates for 1974, 1984 and Definition: Cities and urban-type localities, officially designated as such, usually according to the criteria of number of inhabitants and predominance of agricultural or non-agricultural workers and their families. Bahamas Sources of data: Censuses of 1963, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Definition: For the 1980, 1990 and 2000 census counts, sum of the cities. Bahrain Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1965, 1991 and 2001; UN estimate for Definition: Communes or villages with 2,500 inhabitants or more. For consistency purposes, the 1971 and 1981 census estimates were excluded. Bangladesh Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1974, 1981, 1991 and Definition: Places having a municipality (pourashava), a town (shahar) committee or a cantonment board. In general, urban areas have at least 5,000 inhabitants in a contiguous set of houses with a well developed sense of community and access to public utilities, such as roads, street lighting, water supply, sanitary arrangements, etc. Urban places are generally centres of trade and commerce where the labour force is mostly non-agricultural and literacy levels are high. An area that has urban characteristics but has fewer than 5,000 inhabitants may, in special cases, be considered urban. 14
29 Barbados Sources of data: Censuses of 1970, 1980, 1990 and Definition: Bridgetown (capital). Belarus Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 1999; estimates for 1964, 1974, 1984 and Definition: Cities and urban-type localities officially designated as such (cities and towns, semiurban centers, industrial communities and health resort communities). Belgium Sources of data: Census of 1981; estimate for 1976; UN estimates for 1961, 2000 and Definition: Cities, urban agglomerations and urban communes following the 1977 administrative reclassification. For 2000 and 2006, UN estimates are based on communes with 5,000 inhabitants or more. Belize Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and 2000; estimate for Definition: Not available. Benin Sources of data: Censuses of 1992 and 2002; estimate for 1979; Sample Survey of Definition: Localities with 10,000 inhabitants or more. Bermuda Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and Definition: Entire population. Bhutan Sources of data: Census of 2005; estimate for Definition: The urban definition used in the 2005 census follows the classification of the Department of Urban Development and Engineering Services (DUDES). As of 2005, there are 28 declared urban centres and 26 satellite towns. Bolivia Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1976, 1992 and 2001; estimate for Definition: Localities with 2,000 inhabitants or more. Bosnia and Herzegovina Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981 and Definition: Not available. Botswana Sources of data: Censuses of 1964, 1971, 1981, 1991 and 2001; UN estimate for Definition: Agglomerations of 5,000 inhabitants or more where 75 per cent of the economic activity is non-agricultural. Brazil Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991, 1996 and Definition: Urban and suburban zones of administrative centres of municipios and districts. British Virgin Islands Sources of data: UN Estimates for 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and Definition: Road Town. Brunei Darussalam Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Definition: Municipalities and areas having urban socio-economic characteristics. Bulgaria Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1965, 1975, 1985, 1992 and 2001; estimates for 1960, 1970, 1980 and Definition: Towns, that is, localities legally established as urban. Burkina Faso Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1975, 1985 and Definition: Localities with 10,000 inhabitants or more and with sufficient socio-economic and administrative infrastructures. 15
30 Burundi Sources of data: Censuses of 1965, 1970, 1979 and 1990; estimate for Definition: Commune of Bujumbura. Cambodia Sources of data: Censuses of 1962, 1980 and 1998; estimates for 1950, 1966, 1990, 1993 and 2002; Sample Survey of 1996; UN estimates for 1970, 1975, 1975 and Definition: Municipalities of Phnom Penh, Bokor and Kep plus 13 additional urban centres. Cameroon Sources of data: Censuses of 1976 and 1987; estimates for 1959, 1970, 1997 and Definition: Administrative centres of territorial units (district, sub-division, division or province) or any locality with more than 5,000 inhabitants and sufficient socio-economic and administrative infrastructures. Canada Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1956, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996, 2001 and Definition: Areas with at least 1,000 inhabitants and a population density of at least 400 persons per square kilometer (as of 1981; the definition of urban has changed slightly between 1951 and 1981). Cape Verde Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimates for 1985 and 2003; UN estimate for Definition: As of 1990, municipalities of Praia, Mindelo, Sao Filipe and Espargos/Sal. Cayman Islands Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1979, 1989 and Definition: Entire population. Central African Republic Sources of data: Censuses of 1975, 1988 and 2003; estimates for 1960, 1963, 1967 and Definition: Twenty principal centres with a population of over 3,000 inhabitants each. Chad Sources of data: Census of 1993; estimates for 1972 and 1978; Sample Survey of 1964; UN estimate for Definition: Administrative centres of prefectures, sous-prefectures and administrative posts. Channel Islands Sources of data: Censuses of 1971, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996 and Definition: Civil Parish of St. Peter Port, Guernsey; Civil Parish of St. Helier, Jersey. Chile Sources of data: Censuses of 1952, 1960, 1970, 1982, 1992 and 2002; estimates for 1997 and Definition: Populated centres with definite urban characteristics, such as certain public and municipal services. China Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1982, 1990 and 2000; estimates for 1964, 1970, 1975 and 1996; UN estimate for Definition: Up to 1982 the urban population included all the population of cities and towns. Cities were localities with at least 100,000 inhabitants or those that had special administrative, strategic or economic importance. Towns were either settlements with more than 3,000 inhabitants, at least 70 per cent of whom were registered as nonagricultural, or settlements with a population ranging between 2,500 and 3,000 inhabitants, at least 85 per cent of whom were registered as nonagricultural. According to the 1990 census, the urban population included: (1) all residents of urban districts in provincial and prefectural-level cities; (2) all the resident population of streets (jiedao) in county-level cities; (3) the population of all residents' committees in towns. According to the 2000 census, the urban population of mainland China includes the population in City Districts with an average population density of at least 1,500 persons per square kilometer; the population in sub-district units and township-level units meeting criteria such as contiguous built-up area, being the location of local government, being a street or having a resident committee. 16
31 China, Hong Kong SAR Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996 and 2001; UN estimate for Definition: Hong Kong Island, New Kowloon and new towns in New Territories. China, Macao SAR Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970 and 2001; UN estimates for 1981, 1995 and Definition: Prior to 2001, the city of Macao comprised of the population of the country, except for the population of Coloane, Taipa, Co-Thai and the maritime population. After 2001, the entire population of Macao was considered urban. Colombia Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1964, 1973, 1985, 1993 and Definition: Population living in a nucleus with 2,000 inhabitants or more. Comoros Sources of data: Censuses of 1966, 1980, 1991 and 2003; UN estimate for Definition: Administrative centres of prefectures and localities with 5,000 inhabitants or more. Congo Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1974, 1984 and 1996; estimate for Definition: As of 1984, six communes (Brazzaville, Pointe-Noire, Dolisie/Loubomo, Nkayi, Ouesso and Mossendjo). Cook Islands Sources of data: Censuses of 1966, 1971, 1976, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996 and Definition: Island of Rarotonga. Costa Rica Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1963, 1973, 1984 and 2000; estimate for Definition: Administrative centres of cantons, including adjacent areas with clear urban characteristics such as streets, urban services and electricity. Côte d'ivoire Sources of data: Censuses of 1958, 1975, 1988 and 1998; estimate for 2006; Sample Survey of 1965 and Definition: Urban agglomerations with more than 10,000 inhabitants; agglomerations with populations ranging from 4,000 to 10,000 persons and with more than 50 per cent of the households engaged in non-agricultural activities; and the administrative centres of Grand Lahoun and Dabakala. The urban population excludes the milieu urbain of Bouna, which has a population of 11,000 persons. Croatia Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Definition: Not available. Cuba Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1970, 1981 and 2002; estimates for 1990, 1996, 2000, 2003, 2004 and Definition: Places with 2,000 inhabitants or more, and places with fewer inhabitants but with paved streets, street lighting, piped water, sewage, a medical centre and educational facilities. Cyprus Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1960, 1973, 1982, 1992 and Definition: Six district towns and the suburbs of Nicosia and Larnaka. Czech Republic Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1961, 1970, 1980, 1991 and Definition: Municipalities with 2,000 inhabitants or more. Dem. People s Republic of Korea Sources of data: Census of 1993; estimates for 1950, 1960, 1967, 1970, 1975 and Definition: Not available. 17
32 Democratic Republic of the Congo Sources of data: Census of 1984; estimates for 1950, 1960 and Definition: Places with 2,000 inhabitants or more where the predominant economic activity is nonagricultural; and places with fewer inhabitants considered urban because of their type of economic activity (predominantly non-agricultural). Denmark Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1960, 1965 and 1970; estimates for 1990, 2000, 2001, 2003 and 2004; Registers of 1976, 1981 and Definition: Localities with 200 inhabitants or more. Djibouti Sources of data: Censuses of 1960 and 1983; estimates for 1956, 1989 and 1998; Sample Survey of Definition: For 1956 and 1960: Djibouti (capital). For 1983: the urban population of the districts of Djibouti, Ali-Sabieh, Dikhil, Tadjourah and Obock. For 1991: the following 9 towns: Djibouti (capital), Dikhil, Ali-Sabieh, Tadjourah, Obock, Arta, Damerjog, Yoboki and Randa. Nomads are included in the rural population. For 1998: localities of 1,500 inhabitants or more. Dominica Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1981 and Definition: Cities and villages with 500 inhabitants or more (as of 1970). Dominican Republic Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1981, 1993 and Definition: Administrative centres of comunas and municipal districts. Ecuador Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1962, 1974, 1982, 1990 and 2001; estimate for Definition: Capitals of provinces and cantons. Egypt Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1966, 1976, 1986, 1996 and Definition: Governorates of Al-Qahirah (Cairo), Al-Iskandariyah (Alexandria), Bur Sa'id (Port Said), Al-Isma'iliyah (Ismailia) and As-Suways (Suez); frontier governorates; and capitals of other governorates as well as district capitals (markaz). El Salvador Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1961, 1971 and 1992; estimates for 1998, 2000, 2003 and Definition: Administrative centres of municipios. Equatorial Guinea Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1983, 1994 and Definition: District centres and localities with at least 300 dwellings or at least 1,500 inhabitants. Eritrea Sources of data: Census of 1984; estimate for 1990; UN estimates for 1950 and Definition: Localities with 2,000 inhabitants or more. Estonia Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2000; estimates for 1994 and Definition: Population of officially designated urban settlements including cities, cities without municipal status and towns. Ethiopia Sources of data: Censuses of 1984 and 1994; estimates for 1950, 1967, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002 and Definition: Localities with 2,000 inhabitants or more. Faeroe Islands Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1960, 1966, 1970 and 1977; estimates for 1989, 1990, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999 and 2002; UN estimate for Definition: Torshavn (capital). 18
33 Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Sources of data: Censuses of 1972, 1980, 1986, 1991, 1996 and 2001; estimates for 1953 and Definition: Stanley (capital) and the civil population of Mount Pleasant (as of 1996). Fiji Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1976, 1986 and 1996; UN estimate for Definition: Places with 1,000 inhabitants or more. Finland Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Definition: Urban communes. France Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1962, 1968, 1975, 1982, 1990 and Definition: Communes with 2,000 inhabitants or more living in houses separated by at most 200 meters; or communes in which the majority of the population is part of a multi-communal agglomeration. French Guiana Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1961, 1967, 1982, 1990 and Definition: Not available. French Polynesia Sources of data: Censuses of 1962, 1971, 1983, 1988, 1996 and 2002; estimate for 1977; UN estimate for Definition: Places with 1,000 inhabitants or more. Gabon Sources of data: Censuses of 1961 and 1993; estimates for 1950, 1970, 1981 and Definition: As of 1993 census, towns with 3,000 inhabitants or more. Gambia Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1963, 1973, 1983 and Definition: No official definition. In this report, settlements with 5,000 inhabitants or more. Georgia Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2002; estimate for Definition: Cities and urban-type localities, officially designated as such, usually according to criteria regarding the number of inhabitants and the predominance of non-agricultural workers and their families. Germany Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1961 and 1987; estimates for 1970, 1980, 1981, 1982, 1983, 1984, 1985, 1986, 1987, 1988, 1989, 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004 and Definition: Communes (kreisfreie Staedte and Kreise) with a population density of at least 150 inhabitants per square kilometer. Ghana Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1984 and Definition: Localities with at least 5,000 inhabitants. Gibraltar Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1970, 1981, 1991 and Definition: Entire population. Greece Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and 2001 Definition: Municipalities and communes in population centres with at least 10,000 inhabitants, plus 18 urban agglomerations as defined in the 1991 census: Greater Athens (Athínai), Thessaloniki, Pátrai, Iraklion, Vólos, Chania, Irannina, Chalkida, Agrino, Kalamata, Katerini, Kerkyra, Salamina, Chios, Egio, Rethymno, Ermoúpolis and Spárti. Greenland Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1965, 1970 and 1976; estimates for 1992, 1993, 1996 and 2000; Register of 2005; UN estimate for Definition: Localities with 200 inhabitants or more. 19
34 Grenada Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1981, 1991 and Definition: Parishes of St. George s Town (capital) and St. George. Guadeloupe Sources of data: UN Estimates for 1954, 1961, 1967, 1974, 1982, 1990 and Definition: Localities with 2,000 inhabitants or more. Guam Sources of data: Census of 2000; estimate for 2004; UN estimates for 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980 and Definition: Urban areas, defined in the 2000 census as densely settled territory that meets minimum population density requirements and encompasses a population of at least 2,500 persons. The proportion urban for earlier years was adjusted for consistency with the new definition. Guatemala Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1964, 1973, 1981 and Definition: The municipio of Guatemala Department and the officially recognized administrative centres of other departments and municipalities. The urban population for 1981 is officially adjusted to include the urbanized suburbs bordering the municipio of Guatemala in a way consistent with the previous census. Guinea Sources of data: Censuses of 1955, 1983 and Definition: As of 1983, administrative centres of prefectures. Guinea-Bissau Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1979 and 1991; estimate for Definition: As of 1991, capitals of regions or sectors and localities with 1,500 inhabitants or more. Guyana Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980 and Definition: City of Georgetown (capital), and three other towns. Haiti Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1971, 1982 and 2003; estimates for 1992, 1996, 1999 and Definition: Administrative centres of communes. Holy See Sources of data: Estimates for 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and 2000; UN estimates for 1965, 1975, 1985 and Definition: The entire population is considered urban. Honduras Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1974, 1988 and Definition: Populated centres with 2,000 inhabitants or more with the following services: piped water; communication by land (road or train) or regular air or maritime service; complete primary school (6 grades); postal service or telegraph; and at least one of the following: electrical light, sewer system, or a health centre. Hungary Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and 2001; estimate for Definition: Budapest and all legally designated towns. Iceland Sources of data: Census of 1950; estimates for 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990, 1998 and Definition: Localities with 200 inhabitants or more. 20
35 India Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and 2001; estimates for 1996 and Definition: Urban areas include towns (places with municipal corporation, municipal area committee, town committee, notified area committee or cantonment board) and all places having 5,000 inhabitants or more, a density of less than 1,000 persons per square mile or 390 per square kilometer, pronounced urban characteristics and at least threefourths of adult males not employed in agriculture. Indonesia Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimates for 1950 and 1997; Sample Survey of Definition: Municipalities (kotamadya), regency capitals (kabupaten) and other places with urban characteristics. Iran (Islamic Republic of) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1976, 1986, 1991 and 1996; estimates for 2000 and Definition: Every district with a municipality. In censuses prior to 1986, all county centres (shahrestan), regardless of size, and all localities with a population of 5,000 persons and more. Iraq Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1965, 1977, 1987 and 1997; estimates for 2003 and Definition: Area within the boundaries of municipality councils (Al-Majlis Al-Baldei). Ireland Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1956, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996, 2002 and Definition: Population clusters with at least 1,500 inhabitants (aggregate town areas, including suburbs). Isle of Man Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976, 1996, 2001 and 2006; UN estimates for 1981, 1986 and Definition: Towns of Castletown, Douglas, Peel and Ramsey. Israel Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1972, 1983 and 1995; estimates for 1953, 1955, 2001 and Definition: All settlements with more than 2,000 inhabitants, except those where at least one third of the households participating in the civilian labour force earn their living from agriculture. Italy Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Definition: Communes with 10,000 inhabitants or more. Jamaica Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1982, 1991 and 2001; estimate for 2004 Definition: Kingston metropolitan area and selected main towns. Japan Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1965, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000 and Definition: Densely inhabited districts (DID), defined as groups of contiguous basic unit blocks, each of which has a population density of 4,000 inhabitants or more per square kilometer or has public, industrial, educational and recreational facilities and whose total population is 5,000 persons or more within a shi, ku, machi or mura. Jordan Sources of data: Censuses of 1952, 1961, 1979, 1994 and 2004; estimates for 1967 and 1989; UN estimate for Definition: Localities with 5,000 inhabitants or more as well as the district and sub-district centres of each governorate, irrespective of population size. Kazakhstan Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 1999; estimates for 1964, 1974, 1984, 1994, 2004, 2005 and Definition: Cities and urban-type localities, officially designated as such, usually according to criteria based on the number of inhabitants and the predominance of non-agricultural workers and their families. 21
36 Kenya Sources of data: Censuses of 1962, 1969, 1979, 1989 and Definition: Municipalities, town councils, and other urban centres with 2,000 inhabitants or more. Because of substantial changes in the delineations of urban areas in the 1999 census, only the population in the urban core is considered as urban to ensure consistency with the definition used in previous censuses. Kiribati Sources of data: Censuses of 1968, 1973, 1978, 1985, 1990, 1995 and 2000; estimate for 2005; UN estimate for Definition: The island of South Tarawa. Kuwait Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1965, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985 and 1995; UN estimate for Definition: For 1970 and 1975: Capital Governorate and localities of 10,000 inhabitants or more. For data relative to 1980 through 1995: the urban agglomeration of Al-Kuwayt and localities of 10,000 inhabitants or more. Kyrgyzstan Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 1999; estimate for Definition: Cities and urban-type localities, officially designated as such, usually according to criteria based on the number of inhabitants and predominance of non-agricultural workers and their families. Lao People s Democratic Republic Sources of data: Censuses of 1958, 1966, 1973, 1985, 1995 and Definition: Urban villages are defined in the 2005 census as areas within municipal vicinity of the centre of a municipality having more than 600 residents or more than 100 households. Such areas should have certain urban characteristics (roads, electricity, market function, tap water supply). Latvia Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2000; estimates for 1981, 1986, 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005 and Definition: Cities and urban-type localities, officially designated as such, usually according to criteria based on the number of inhabitants and predominance of non-agricultural workers and their families. Lebanon Sources of data: Estimate for 1988; Sample Survey of 1970; UN estimates for 1950, 1958, 1998 and Definition: Localities with 5,000 inhabitants or more. Lesotho Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1976, 1986, 1996 and 2006; estimate for 1972; UN estimate for Definition: District headquarters and other settlements with rapid population growth and with facilities that tend to encourage people to engage in non-agricultural economic activities. Liberia Sources of data: Censuses of 1962, 1974 and Definition: Localities with 2,000 inhabitants or more. Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1973, 1984 and 1995; estimate for Definition: Municipalities of Tarabulus and Bangazi and urban parts of other municipalities. Liechtenstein Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1960, 1970, 1980 and 1990; estimates for 1995, 2000 and Definition: No official definition. In this report, Vaduz municipality. 22
37 Lithuania Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2001; estimates for 1950, 2005 and Definition: Cities and urban-type localities, officially designated as such, according to criteria based on the number of inhabitants and the predominance of non-agricultural workers and their families. Luxembourg Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1981 and 1991; estimates for 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000 and Definition: Communes with 2,000 inhabitants or more. Madagascar Sources of data: Censuses of 1975 and 1993; estimates for 1950, 1970 and 2004; Sample Survey of Definition: Centres with 5,000 inhabitants or more. Malawi Sources of data: Censuses of 1966, 1977, 1987 and 1998; estimate for Definition: All townships, town planning areas and district centres. Malaysia Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1991 and 2000; estimates for 1970 and Definition: Gazetted areas with their adjoining built-up areas and with a combined population of 10,000 persons or more. Built-up areas are areas contiguous to a gazetted area with at least 60 per cent of their population aged 10 years and over engaged in non-agricultural activities. These areas should also have modern toilet facilities in their housing units. Maldives Sources of data: Censuses of 1965, 1967, 1970, 1977, 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000 and Definition: The capital of Male and other small settlements. Mali Sources of data: Censuses of 1976, 1987 and 1998; estimate for Definition: Localities with 5,000 inhabitants or more and district centres. Malta Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1967, 1985, 1995 and Definition: No official definition available. In this publication, localities with at least 2,500 inhabitants. Marshall Islands Sources of data: Censuses of 1973, 1980, 1988 and 1999; UN estimates for 1958 and Definition: The entire population of Majuro Atoll and the town of Ebeye Island on Kwajalein Atoll. Martinique Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1961, 1982, 1990 and 1999; estimate for Definition: For the census in 1990 and 1999, total population of the Commune of Fort-de-France plus the agglomerations of other communes with 2,000 inhabitants or more. Mauritania Sources of data: Censuses of 1964, 1977, 1988 and Definition: Localities with 5,000 inhabitants or more. Mauritius Sources of data: Censuses of 1952, 1962, 1972, 1983, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Definition: Towns with proclaimed legal limits. Mexico Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990, 1995, 2000 and Definition: Localities with at least 2,500 inhabitants. 23
38 Micronesia (Fed. States of) Sources of data: Censuses of 1973, 1980, 1994 and 2000; UN estimates for 1950 and Definition: Localities with at least 1,000 inhabitants. Moldova Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979 and 1989; estimate for 1996; UN estimate for Definition: Cities and urban-type localities, officially designated as such, usually according to criteria based on the number of inhabitants and the predominance of non-agricultural workers and their families. Monaco Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1962, 1968, 1975, 1982, 1990 and Definition: Monaco (capital). Mongolia Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1963, 1969, 1979, 1989 and 2000; UN estimate for Definition: Capital city and district centres. Montenegro Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1991 and 2003; estimate for Definition: Not available. Montserrat Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980 and 1991; UN estimates for 1950, 1955, 1997, 1997, 2001 and Definition: Brades Estate/Plymouth (capital). Due to volcanic activity, Plymouth was abandoned in The government premises have been established at Brades Estate, in the Carr's Bay/Little Bay vicinity at the northwest end of Montserrat. Morocco Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1971, 1982, 1994 and 2004; estimate for Definition: Respectively 250 and 370 localities in the 1982 and 1994 censuses. Mozambique Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980 and 1997; UN estimate for Definition: From 1950 to 1970: Conselho of Maputo and Beira; in the 1980 census: 12 cities (Maputo, nine provincial capitals and the cities of Nacala-Porto and Chokwe); in the 1997 census: 23 cities and 68 towns (vilas). Myanmar Sources of data: Censuses of 1973 and 1983; estimate for 1953; Sample Survey of Definition: Not available. Namibia Sources of data: Censuses of 1991 and 2001; UN estimates for 1951, 1960, 1970 and Definition: The district headquarters and other settlements of rapid population growth with facilities that encourage people to engage in nonagricultural activities. Nauru Sources of data: Censuses of 1977, 1983, 1992 and Definition: Entire population. Nepal Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and 2001; UN estimate for Definition: According to the 1961 census, localities with 5,000 inhabitants or more (panchayats); According to later censuses, localities with at least 9,000 inhabitants. The criteria used to identify urban localities in terms of population size, density, contiguity and occupational structure have changed over time and a set of complex rules that vary according to ecological zone and are based on annual revenue, population size and infrastructure has been used since Netherlands Sources of data: UN Estimates for 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and Definition: Due to several changes in the definition of urban areas, in this report urban includes all municipalities with 20,000 inhabitants or more. 24
39 Netherlands Antilles Sources of data: Censuses of 1992 and 2001; UN estimates for 1950 and Definition: Population of the urban agglomerations of Willemstad, Philipsburg and Kralendjik. New Caledonia Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1969, 1976, 1983, 1989, 1996 and Definition: Nouméa and communes of Dumbéa, Mont-Doré and Païta (as of 1969). New Zealand Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1956, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996 and 2001; estimates for 2002 and 2003; UN estimate for Definition: All cities plus boroughs, town districts, townships and country towns with a population of 1,000 inhabitants or more. Nicaragua Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1963, 1971, 1995 and Definition: Localities with more than 1000 inhabitants and with some urban characteristics, such as electricity, industrial and commercial centres. Niger Sources of data: Censuses of 1977, 1988 and 2001; estimates for 1956, 1962, 1966 and Definition: Urban centres, defined as localities serving as administrative headquarters for departments and arrondissements as well as all administrative centres with 2,500 inhabitants or more. Nigeria Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1963 and Definition: Towns with at least 20,000 inhabitants, engaged mostly in non-agricultural work. Niue Sources of data: Censuses of 1966, 1971, 1986, 1991, 1997 and 2001; UN estimate for Definition: Alofi (capital). Northern Mariana Islands Sources of data: Census of 2000; UN estimates for 1950, 1958, 1967, 1973, 1980, 1990 and Definition: Urban areas, defined in the 2000 census as densely settled territory that meets minimum population density requirements and encompasses a population of at least 2,500 persons. The estimated proportion urban for 1980 and 1990 was calculated by assuming that the entire population of Saipan Island was urban and the rest of the country was rural. For previous years, parts of Saipan Island were assumed to be rural. Norway Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980 and 1990; estimates for 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2002, 2003 and 2004; Register of Definition: Localities with 2000 inhabitants or more. Occupied Palestinian Territory Sources of data: Census of 1997; estimates for 1950, 1961, 1975, 1997, 2001 and Definition: Any locality with at least 10,000 inhabitants; all governorate and district centres regardless of size; and localities whose populations vary from 4,000 to 9,999 persons provided they have at least four of the following services: public electricity network, public water network, post office, health centre with a full-time physician and a school offering a general secondary education certificate. Oman Sources of data: Censuses of 1993 and 2003; UN estimates for 1950 and Definition: Not available. Pakistan Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1972, 1981 and Definition: Places with a municipal corporation, town committee or cantonment. 25
40 Palau Sources of data: Censuses of 1973, 1980, 1986, 1990, 1995, 2000 and Definition: Koror Island. Panama Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and Definition: Localities with 1,500 inhabitants or more, having the following urban services: electricity, water-supply and sewerage systems, paved roads, access to commercial establishments, secondary schools, and social and recreational centres. Papua New Guinea Sources of data: Censuses of 1966, 1971, 1980, 1990 and 2000; UN estimate for Definition: Centres with 500 inhabitants or more, excluding separately located schools, hospitals, missions, plantations, rural settlements and rural villages, regardless of population size. Paraguay Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1962, 1972, 1982, 1992 and Definition: Administrative centres of the official districts of the Republic. Peru Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1972, 1981, 1993 and Definition: Populated centres with 100 dwellings or more grouped contiguously and administrative centres of districts. Philippines Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1975, 1980 and 1990; estimates for 1995 and Definition: All cities and municipalities with a density of at least 1,000 persons per square kilometer; administrative centres, barrios with at least 2,000 inhabitants, and barrios with at least 1,000 inhabitants which are contiguous to the administrative centre; all cities and municipalities with a density of at least 500 persons per square kilometer; and all other administrative centres with at least 2,500 inhabitants. Pitcairn Sources of data: Censuses of 1986, 1991, 1993 and 1999; estimates for 2002, 2005 and Definition: No urban population. Adamstown (capital) defined according to administrative boundaries. Poland Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1978, 1988 and 2002; estimate for Definition: Towns and settlements of urban nature (for example, workers settlements, fishermen s settlements and health resorts). Portugal Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1981, 1991 and Definition: Agglomerations of 2,000 inhabitants or more. Puerto Rico Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and Definition: Urban areas are densely settled territory that meets minimum population density requirements and encompasses a population of at least 2,500 inhabitants. A change of definition in the 2000 census, from place-based to density-based, affects comparability before and after that date. Qatar Sources of data: Censuses of 1986, 1997 and 2004; UN estimates for 1956, 1963, 1971 and Definition: Localities with 5,000 inhabitants or more. Republic of Korea Sources of data: Censuses of 1955, 1960, 1966, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995 and Definition: Places with at least 50,000 inhabitants are usually considered urban. However, the reported proportion urban from the census refers to the total population of administrative units named dong, an administrative division of urban areas, rather than to places. 26
41 Réunion Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1967, 1974, 1982, 1990 and Definition: Communes with 2,000 inhabitants or more living in houses separated by at most 200 meters or communes in which the majority of the population is part of a multi-communal agglomeration. Romania Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1977 and 1992; estimates for 2002 and Definition: Municipalities and towns with certain urban socio-economic characteristics. Russian Federation Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2002; estimates for 1964, 1974, 1984, 2005 and Definition: Cities and urban-type localities, officially designated as such, usually according to criteria based on the number of inhabitants and the predominance of non-agricultural workers and their families. Rwanda Sources of data: Censuses of 1970, 1978, 1991 and 2002; estimates for 1960 and Definition: Kigali; administrative centres of préfectures and important agglomerations and their surroundings. Saint Helena Sources of data: Censuses of 1956 and Definition: Jamestown (capital) and Half Tree Hollow. Saint Kitts and Nevis Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and Definition: Basseterre (capital) and Charlestown. Saint Lucia Sources of data: Census of 1991; estimates for 1996 and 2001; UN estimate for Definition: Not available. Saint Pierre and Miquelon Sources of data: Censuses of 1962, 1982, 1990 and 1999; estimate for Definition: Saint-Pierre (capital). Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970 and 1980; estimates for 1991 and Definition: Not available. Samoa Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1956, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976, 1981, 1991 and Definition: Urban area of Apia (capital), comprising the districts of Vaimauga West and Faleata East. San Marino Sources of data: Census of 1976; estimates for 1987 and 1992; UN estimates for 1950, 1960, 1970, 2001 and Definition: Municipalities with 1,000 inhabitants or more. São Tomé and Príncipe Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1981, 1991 and Definition: The district of Água Grande (São Tomé and Pantufo) and six other small settlements (as of 1991). Saudi Arabia Sources of data: Censuses of 1974 and 2004; estimates for 1962 and 1986; UN estimates for 1950 and Definition: Cities with 5,000 inhabitants or more. Senegal Sources of data: Censuses of 1976, 1988 and 2002; estimates for 1960 and Definition: Agglomerations of 10,000 inhabitants or more. 27
42 Serbia Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981 and 1991; estimate for Definition: Not available. Seychelles Sources of data: UN Estimates for 1960, 1971, 1977 and Definition: No official definition. In the present publication, prior to 1971, Victoria City proper (capital). From 1971, greater Victoria agglomeration plus districts with population density greater than 1,500 persons per inhabited square kilometer in 2002 (Cascades, Pointe Larue, Anse aux Pins). Sierra Leone Sources of data: Censuses of 1963, 1974, 1985 and Definition: Towns with 2,000 inhabitants or more. Singapore Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1970, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Definition: City of Singapore, including residents and non-residents. Slovakia Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1961, 1970, 1980, 1991 and Definition: Cities with 5,000 inhabitants or more. Slovenia Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and 2002; estimate for Definition: Settlements with over 3,000 inhabitants; settlements with 2,000-3,000 inhabitants and a surplus of workplaces; settlements that are seats of municipalities and have at least 1,400 inhabitants and a surplus of workplaces; suburban settlements that have fewer inhabitants but are spatially and functionally integrated with the city. Solomon Islands Sources of data: Censuses of 1970, 1976, 1986 and 1999; UN estimates for 1950 and Definition: Places with 1,000 inhabitants or more. Somalia Sources of data: Census of 1975; estimates for 1953 and 1963; Sample Survey of 2002; UN estimate for Definition: All district capitals and any other town or village with at least 1,500 inhabitants. South Africa Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1960, 1970, 1996 and 2001; UN estimates for 1980, 1985 and Definition: Localities are classified according to dominant settlement type and land use. Cities, towns, townships, suburbs, etc., are typical urban settlements. Enumeration areas comprising informal settlements, hostels, institutions, industrial and recreational areas, and smallholdings within or adjacent to any formal urban settlement are classified as urban. The 1996 estimate was adjusted to match the 2001 census definition. Estimates for 1980, 1985 and 1991 obtained taking into account the populations of Transkei, Bophuthatswana, Venda and Ciskei. Spain Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1981, 1991 and Definition: Municipalities (municipios) with 10,000 inhabitants or more. Sri Lanka Sources of data: Censuses of 1953 and 2001; UN estimates for 1963, 1971 and Definition: Municipalities and urban councils only. Urban data for the censuses of 1963, 1971 and 1981 also include town councils, adjusted so as to match the revised definition used in
43 Sudan Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1973, 1983 and Definition: Localities of administrative and/or commercial importance or with a population of 5,000 inhabitants or more. Suriname Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1964, 1971 and 1980; estimates for 1987 and Definition: Great Paramaribo. Swaziland Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1976, 1986 and 1997; UN estimate for Definition: Localities defined as urban. Sweden Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1965, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985 and 1990; estimates for 1995 and 2000; Register of Definition: Built-up areas with at least 200 inhabitants and where dwellings are separated by at most 200 meters from each other (according to the administrative divisions of 2003). Switzerland Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimates for 2003, 2004 and Definition: Communes with at least 10,000 inhabitants, including suburbs, and urban agglomerations with contiguous built-up area and at least 20,000 inhabitants. Syrian Arab Republic Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1981 and 1994; estimate for Definition: Cities, Mohafaza centres and Mantika centres, and communities with 20,000 inhabitants or more. Tajikistan Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2000; estimates for 2003 and 2005; UN estimate for Definition: Cities and urban-type localities, officially designated as such, usually according to criteria based on the number of inhabitants and the predominance of non-agricultural workers and their families. TFYR Macedonia Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Definition: Population whose official place of residence is in urban settlements and settlements which, as urban units, have been integrated into urban settlements and, taken together, represent one unit. Thailand Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and Definition: Municipalities. In 1999, 981 sanitary districts were reclassified as Tambon municipalities and estimates of the proportion urban were adjusted retrospectively. Timor-Leste Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960 and 2004; UN estimate for Definition: Dili (capital) and other small settlements (sucos) defined as urban. For 2004, the functional definition of urban given by the National Statistics Directorate of Timor-Leste was used. Togo Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970 and 1981; estimates for 1988 and Definition: Up to 1970: seven urban communes. Since the 1981 census: 21 administrative centres of prefectures. 29
44 Tokelau Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1986, 1991, 1996, 2001 and Definition: Not available. Tonga Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1976, 1986 and 1996; estimate for Definition: Population of Nuku'alofa. Trinidad and Tobago Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and Definition: Port-of-Spain (capital), Arima borough and San Fernando town. Tunisia Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1975, 1984, 1994 and Definition: Population living in communes. Turkey Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1965, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990 and 2000; estimates for 1960, 2002 and Definition: Population of localities within the municipal limits of administrative centres of provinces and districts. Turkmenistan Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979 and 1989; estimates for 1992, 2001, 2002, 2003 and Definition: Cities and urban-type localities, officially designated as such, usually according to criteria based on the number of inhabitants and the predominance of non-agricultural workers and their families. Turks and Caicos Islands Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and 2001; estimate for 2006; UN estimate for Definition: Refers to the islands of Grand Turk and Providenciales. Tuvalu Sources of data: Censuses of 1979, 1985, 1991 and Definition: Island of Funafuti. Uganda Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1969, 1980, 1991 and Definition: For 1991 and earlier: cities, municipalities, towns, town boards and all trading centres with more than 1,000 inhabitants. For 2002: gazetted cities, municipalities and towns with more than 2,000 inhabitants. Ukraine Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2001; estimates for 1950, 1964, 1974, 1984, 2004, 2005 and Definition: Cities and urban-type localities, officially designated as such, usually according to criteria based on the number of inhabitants and predominance of non-agricultural workers and their families. United Arab Emirates Sources of data: Censuses of 1975, 1980, 1985 and 1995; UN estimates for 1950 and Definition: Nine cities or towns (as of 1975). 30
45 United Kingdom Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961 and 1971; estimates for 1981, 1991 and Definition: For England and Wales, urban areas encompass continuously built-up urban land, the largest urban areas forming agglomerations in which urban subdivisions are recognized. In Scotland, urban localities are identified as in England and Wales except that they do not extend across local government district boundaries. In Northern Ireland, urban areas are formed of continuously built-up land, forming an agglomeration in which urban subdivisions are recognized. Prior to 1974 (England and Wales) and 1975 (Scotland) the definition of urban and rural was based on administrative boundaries. The census cover the de facto population. In order to use a consistent definition of urban areas over time, for the 2001 census urban areas were defined as localities with at last 1,500 people in England and Wales, at least 1,000 inhabitants in Northern Ireland, and all settlements and localities in Scotland. United Republic of Tanzania Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1967, 1978, 1988 and Definition: For the 1957 and 1967 censuses: 16 gazetted townships. Since the 1978 census, urban areas are defined using several criteria and include all regional and district headquarters, and all wards with urban characteristics (i.e., exceeding certain minimal level of population size or population density or have few inhabitants in agricultural occupations). Size and density limits are not available. Wards are urban based on a decision of the District or Regional Census Committees. United States of America Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and Definition: Urban areas are defined as densely settled territory that meets minimum population density requirements and encompasses a population of at least 2,500 inhabitants. As of the 2000 census, the urban definition was changed from a placebased one to one based on density. However, this change has only a small effect on the comparability of estimates before and after United States Virgin Islands Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960 and Definition: In the 2000 census urban areas are defined as densely settled territory that meets minimum population density requirements and encompasses a population of at least 2,500 inhabitants. The proportion urban for earlier years was adjusted for consistency with this definition. Uruguay Sources of data: Censuses of 1963, 1975, 1985, 1996 and Definition: Cities as officially defined. Uzbekistan Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979 and 1989; estimates for 1994, 1997 and Definition: Cities and urban-type localities, officially designated as such, usually according to criteria based on number of inhabitants and the predominance of non-agricultural workers and their families. Vanuatu Sources of data: Censuses of 1967, 1979, 1989 and Definition: Port-Vila and Luganville. Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1990 and 2001; estimate for Definition: Places with 2,500 inhabitants or more. Viet Nam Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1979, 1989 and 1999; estimates for 1970 and 2002; UN estimates for 1992 and Definition: Places with 4,000 inhabitants or more. Wallis and Futuna Islands Sources of data: Censuses of 1969, 1976, 1983, 1990, 1996 and Definition: No urban population. Mata-Utu (capital) defined according to administrative boundaries. 31
46 Western Sahara Sources of data: Censuses of 1970, 1982, 1994 and 2004; UN estimates for 1950, 1960 and Definition: Not available. Yemen Sources of data: Censuses of 1986, 1994 and 2004; estimates for 1950, 1960 and Definition: Capitals of 17 governorates and other towns. Zambia Sources of data: Censuses of 1963, 1969, 1980, 1990 and 2000; UN estimates for 1950 and Definition: Localities of at least 5,000 inhabitants and a majority of the labour force in nonagricultural activities. Zimbabwe Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1962, 1969, 1982, 1992 and 2002; estimate for Definition: Designated urban areas and places with at least 2,500 inhabitants whose population resides in a compact settlement and where more than half of the employed population is engaged in non-agricultural activities. B. SOURCES OF DATA FOR ESTIMATES OF URBAN AGGLOMERATION AND CAPITAL CITIES Afghanistan Kabul (capital) Sources of data: Census of 1979; estimates for 1966, 1971, 1986 and 2004; Sample Survey of 1999; UN estimate for Albania Tiranë (Tirana) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1960, 1969, 1979, 1989 and Algeria El Djazaïr (Algiers) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1960, 1977 and 1987; Sample Survey of Note: Data refer to the Governorate of Grand Algiers. Wahran (Oran) Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1966, 1977, 1987 and American Samoa Pago Pago (capital) Sources of data: Census of 2000; UN estimates for 1970, 1980 and Note: Data refer to the urban cluster, that is, contiguous territory in and around the city that meets minimum population density requirements. Prior to 2000, only City proper data were published. For other years, it was assumed that the ratio of the population of the Pago Pago agglomeration to the total urban population was the same as in Andorra Andorra la Vella (capital) Sources of data: Estimates for 1950, 1959, 1965, 1980, 1981, 1982, 1983, 1984, 1985, 1986, 1987, 1988, 1989, 1990, 1999 and Angola Huambo Sources of data: Censuses of 1960 and 1970; estimates for 1950, 1983, 1993, 2000 and
47 Luanda (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960 and 1970; estimates for 1983, 1991, 1993, 1996 and Anguilla The Valley (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1992 and 2001; UN estimates for 1960, 1974 and Antigua and Barbuda St. John s (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1991 and Argentina Buenos Aires (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and Note: Data for Buenos Aires refer to Gran Buenos Aires. Córdoba Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and Note: Data for Córdoba refer to Gran Córdoba. Mendoza Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and Note: Data for Mendoza refer to Gran Mendoza. Rosario Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and San Miguel de Tucumán Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and Note: Data for San Miguel de Tucumán refer to Gran San Miguel de Tucumán. Armenia Yerevan (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2001; estimate for Aruba Oranjestad (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1991 and 2000; estimate for Note: Oranjestad includes Oranjestad West and Oranjestad East. Australia Adelaide, Brisbane, Melbourne, Perth, Sydney Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976 and 1981; estimates for 1950, 1986, 1991, 1996, 2001 and Canberra (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976 and 1981; estimates for 1986, 1991, 1996, 2001 and Note: Refers to Canberra and Queanbeyan. Austria Wien (Vienna) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1981, 1991 and 2001; estimate for Note: Based on the concept of a functional and structural urban area (Stadtregion) consisting of an urban core area (Kernzone) and surrounding urban areas (Außenzone). The surrounding urban area is defined as an area in which at least 30 per cent of working adults commute daily into the corresponding core area. Azerbaijan Baku (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 1999; estimate for Note: The data include communities under the authority of the Town Council. The 1989 census produced data referring only to the city proper; the population of the urban agglomeration for that date 33
48 was estimated by assuming that the ratio of the population of the urban agglomeration to that of the city proper was the same as in Bahamas Nassau (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1963, 1970, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Bahrain Al-Manamah (Manama) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1959, 1965, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Note: Data refer to the municipality of Al- Manamah. Bangladesh Chittagong, Khulna, Rajshahi Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1974, 1981, 1991 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Dhaka (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1974, 1981, 1991 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Mega city Barbados Bridgetown (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1970, 1980, 1990 and Note: Refers to the Parish of St. Michael. Belarus Minsk (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 1999; estimates for 1950, 1955 and Note: The data include communities under the authority of the Town Council. The 1989 census produced data referring to the city proper only; the population of the urban agglomeration for that date was estimated by assuming that the ratio of the population of the urban agglomeration to that of the city proper was the same as in Belgium Antwerpen Sources of data: Censuses of 1970 and 1981; estimates for 1988, 1991 and 1995; UN estimate for Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Bruxelles-Brussel (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1970 and 1981; estimates for 1988, 1991 and 1995; UN estimate for Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: The data refer to the population of the arrondissement of Brussels. Belize Belmopan (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1980, 1991 and 2000; estimate for Benin Cotonou Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1956, 1979, 1992 and 2002; estimates for 1953, 1955 and 1965; Sample Survey, Porto-Novo (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1979, 1992 and 2002; estimate for 1965; Sample Survey, Bermuda Hamilton (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and Bhutan Thimphu (capital) Sources of data: Census of 2005; estimates for 1950, 1960, 1970, 1977, 1990 and Bolivia La Paz (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1976, 1992 and 2001; estimate for Note: Which includes El Alto. 34
49 Santa Cruz Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1976, 1992 and 2001; estimate for Sucre (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1976, 1992 and 2001; estimate for Bosnia and Herzegovina Sarajevo (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981 and 1991; estimate for Botswana Gaborone (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1964, 1971, 1981, 1991 and 2001; UN estimate for Brazil Baixada Santista, Campinas, Goiânia, Grande São Luís, Grande Vitória, Maceió, Manaus Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and 2000; estimate for Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Belém Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980 and 2000; estimate for 2005; UN estimate for Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Belo Horizonte Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980 and 2000; UN estimate for Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Brasília (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: The regiõe metropolitana refers to the Regiõe Integrada de Desenvolvimento do Distrito Federal e Entorno. Campo Grande Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and 2000; estimate for Cuiabá, João Pessoa, Teresina Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and 2000; estimate for Curitiba, Fortaleza, Natal, Norte/Nordeste Catarinense, Pôrto Alegre, Recife, Rio de Janeiro, Salvador, São Paulo Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Florianópolis Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970 and 2000; estimate for 2005; UN estimates for 1980 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. British Virgin Islands Road Town (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1980 and 1991; estimate for 1970; UN estimate for Brunei Darussalam Bandar Seri Begawan (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Bulgaria Sofia (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1965, 1985 and 1992; estimates for 2001, 2002, 2003 and Burkina Faso Ouagadougou (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1960, 1975, 1985 and 1996; Sample Survey of
50 Burundi Bujumbura (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1979 and 1990; estimates for 1970 and 2003; Register of 1950; Sample Survey of Cambodia Phnum Pénh (Phnom Penh) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1962, 1980 and 1998; estimates for 1950, 1966, 1970, 1975, 1975, 1979, 1985, 1990, 1993 and Note: Data refer to the municipality of Phnon Penh including suburban areas. Cameroon Douala Sources of data: Censuses of 1955, 1976 and 1987; estimate for 2001; Sample Survey of Yaoundé (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1976 and 1987; estimates for 1969 and 2001; Sample Survey of 1962 and Canada Calgary, Montréal, Ottawa-Gatineau (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996, 2001 and 2006; estimate for Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Refers to the Census Metropolitan Area. Edmonton Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996, 2001 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Data refer to the Census Metropolitan Area Toronto, Vancouver Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996, 2001 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Data refer to the Census Metropolitan Area. Cape Verde Praia (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and Cayman Islands George Town (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1979, 1989 and Central African Republic Bangui (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1955, 1964, 1975, 1988 and 2003; estimate for 1966; Sample Survey of Chad N Djaména (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1962 and 1993; estimates for 1972 and 1978; Sample Survey of Channel Islands St. Helier (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1971, 1976, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996 and Statistical concept: Others. Note: Data refer to the parish. St. Helier is the capital of the Bailiwick of Jersey. St. Peter Port Sources of data: Censuses of 1971, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996 and Statistical concept: Others. Note: Data refer to the parish. St. Peter Port is the capital of the Bailiwick of Guernsey. Chile Santiago (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1952, 1960, 1970, 1982, 1992 and Note: Data refer to Gran Santiago, which includes the Province of Santiago plus cities within the Provinces of Puente Alto and San Bernardo. 36
51 Valparaíso Sources of data: Censuses of 1952, 1960, 1970, 1982, 1992 and Note: Data refer to the Greater Valparaíso. China Anshan (Liaoning), Benxi, Changchun, Dalian, Fushun (Liaoning), Jinan (Shandong), Jinzhou, Nanchang, Tangshan (Hebei) Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1982, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Anshun, Jining (Shandong) Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimate for Anyang, Bengbu, Jixi (Heilongjiang) Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1982, 1990 and Baoding, Chengdu, Guangzhou (Guangdong), Jilin, Lanzhou, Liuzhou, Nanning, Qingdao, Shijiazhuang, Wuhan, Xi an (Shaanxi) Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimate for Baotou, Luoyang Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Beijing (capital), Shanghai Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1990 and 2000; UN estimate for Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Changde, Dandong, Hengyang, Heze, Huaibei, Huainan, Huzhou, Jiamusi, Jiaozuo, Jiaxing, Kaifeng Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and Changsha (Hunan), Fuzhou (Fujian), Haerbin, Hangzhou Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1982, 1990 and 2000; estimate for 1964; UN estimate for Changzhou (Jiangsu), Daqing, Guilin, Hefei Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimate for Chifeng, Tongliao, Weifang Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Chongqing Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1982, 1990 and 2000; estimate for 1964; UN estimate for Datong (Shanxi), Guiyang, Hohhot Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; estimate for 1964; UN estimate for Dongguan (Guangdong), Foshan Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimates for 1950 and Fuxin Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimate for Fuyang Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimate for Handan Sources of data: Censuses of 1982 and 2000; estimate for 1964; UN estimate for Huai an Sources of data: Censuses of 1990 and Jinxi (Liaoning) Sources of data: Censuses of 1982 and 1990; estimate for 1953; UN estimate for
52 Kaohsiung, Taipei Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1964, 1982 and 1990; estimates for 1970, 1975 and Kunming, Nanjing (Jiangsu), Shenyang, Suzhou (Jiangsu) Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1982, 1990 and 2000; estimate for 1964; UN estimate for Langfang, Linfen, Pingdingshan (Henan) Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimate for Leshan, Lianyungang, Liaoyang, Linyi (Shandong), Mianyang (Sichuan), Shantou, Suining (Sichuan), Taian (Shandong) Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and Liuan Sources of data: Censuses of 1982 and Liupanshui Sources of data: Census of 2000; UN estimates for 1950 and Luzhou, Mudanjiang, Nantong, Nanyang (Henan), Ningbo, Qinhuangdao, Quanzhou, Shangqiu, Suzhou (Anhui) Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimate for Nanchong, Shenzhen Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimates for 1953 and Neijiang Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimate for Pingxiang (Jiangxi) Sources of data: Census of 2000; UN estimate for Qiqihaer Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Shaoxing Sources of data: Censuses of 1990 and 2000; UN estimates for 1950 and Taichung Sources of data: Censuses of 1982 and 1990; estimates for 1970, 1975 and Tainan Sources of data: Censuses of 1982 and 1990; estimates for 1970, 1975 and Taiyuan (Shanxi) Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1982, 1990, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Tianjin Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1964, 1990 and 2000; UN estimate for Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Tianmen, Xiantao, Xingyi (Guizhou), Xinyu, Yongzhou Sources of data: Censuses of 1990 and Tianshui, Wuhu (Anhui), Xianyang (Shaanxi) Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and Ürümqi (Wulumqi) Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; estimate for 1964; UN estimate for Wenzhou, Xiamen, Xining, Xinyang, Yichang, Yinchuan, Zhenjiang (Jiangsu), Zunyi Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimate for
53 Wuxi (Jiangsu), Xuzhou, Zhengzhou Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1982, 1990 and 2000; estimate for 1964; UN estimate for Xiangfan (Hubei) Sources of data: Censuses of 1982 and 2000; UN estimates for 1950 and Xinxiang, Yichun (Heilongjiang), Yingkou, Yiyang (Hunan), Yueyang, Zaozhuang, Zhangjiakou, Zhanjiang, Zibo, Zigong Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and Xuanzhou Sources of data: Censuses of 1982 and Yancheng (Jiangsu), Yulin (Guangxi) Sources of data: Census of 2000; UN estimate for Yantai Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimates for 1953 and Yibin Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimate for Yichun (Jiangxi) Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Yuci Sources of data: Censuses of 1982 and 1990; UN estimates for 1950 and Zhaotong Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimate for Zhuhai, Zhuzhou Sources of data: Censuses of 1982, 1990 and 2000; UN estimates for 1950 and China, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Hong Kong (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996, 2001 and 2006; estimate for Note: Data for Hong Kong consist of the population of Hong Kong Island, New Kowloon, the new towns in New Territories and the marine areas. China, Macao Special Administrative Region Macao (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1981, 1991, 2001 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Prior to 2001, the city of Macao included all the population in the country except for that of Coloane, Taipa, Co-Thai and the maritime population. After 2001, the entire population of Macao is considered urban. Colombia Barranquilla Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1964, 1973, 1985, 1993 and Note: Refers to the nuclei of Barranquilla, Soledad, Malambo and Puerto Colombia. Bogotá (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1964, 1973, 1985, 1993 and Note: Refers to the nuclei of Santa Fe de Bogotá, Soacha, Chia and Funza. Bucaramanga Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1964, 1973, 1985, 1993 and Note: Refers to the nuclei of Bucaramanga, Floridablanca, Girón and Piedecuesta. 39
54 Cali Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1964, 1973, 1985, 1993 and Note: Refers to the nuclei of Cali and Yumbo. Cartagena Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1964, 1973, 1985, 1993 and Medellín Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1964, 1973, 1985, 1993 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Refers to the nuclei of Medellín, Barbosa, Bello, Caldas, Copacabana, Envigado, Girardota, Itagui, La Estrella and Sabaneta. Comoros Moroni (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1966, 1980, 1991 and 2003; estimates for 1950 and Congo Brazzaville (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1955, 1961, 1974, 1984 and 1996; estimates for 1950, 2004 and Cook Islands Rarotonga (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1981, 1986, 1991 and 1996; estimates for 1966, 1971 and 1976; UN estimate for Note: Data refer to the island of Rarotonga. The capital Avarua is located on Rarotonga. Population estimates for Avarua proper are not available. Costa Rica San José (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1963, 1973, 1984 and 2000; estimate for Note: Urban population at the canton level. Côte d'ivoire Abidjan (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1975, 1988 and 1998; estimate for 2006; Sample Survey of 1963 and Yamoussoukro Sources of data: Censuses of 1975, 1988 and 1998; estimate for Croatia Zagreb (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Cuba La Habana (Havana) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1970, 1981 and 2002; estimates for 1990, 1996, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Cyprus Lefkosia (Nicosia) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1960, 1973, 1982, 1992 and 2001; estimate for Czech Republic Praha (Prague) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1961, 1970, 1980, 1991 and 2001; estimate for Democratic People's Republic of Korea Hamhung Sources of data: Census of 1993; estimates for 1960, 1967, 1980 and N ampo Sources of data: Census of 1993; estimates for 1960 and
55 P yongyang (capital) Sources of data: Census of 1993; estimates for 1950, 1960, 1967, 1980 and Democratic Republic of the Congo Kananga Sources of data: Censuses of 1956 and 1984; estimates for 1950, 1960, 1969 and Kinshasa (capital) Sources of data: Census of 1984; estimate for 2004; Register of 1950 and 1958; Sample Survey of Lubumbashi Sources of data: Censuses of 1956 and 1984; estimates for 1950, 1960, 1969, 1970 and Mbuji-Mayi Sources of data: Census of 1984; estimates for 1960, 1969 and Denmark København (Copenhagen) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1960, 1965 and 1970; estimates for 1976, 1981, 1986, 1989, 1990, 1992, 1994, 1996, 1997 and 1998; Register of 2002 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Data refer to the Greater Copenhagen Region which, from 1999 onward, consists of 16 municipalities, in whole or in part. Data prior to 1976 are based on the previous definition, where 28 municipalities were included in whole or in part. Djibouti Djibouti (capital) Sources of data: Census of 1960; estimates for 1957, 1970 and 1995; Sample Survey of 1991; UN estimates for 1998 and Note: Data refer to the population of the cercle. Dominica Roseau (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1981, 1991 and 2001; UN estimate for Dominican Republic Santo Domingo (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1981, 1993 and Ecuador Guayaquil Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1962, 1974, 1982, 1990 and Note: Data include the population of the locality of Eloy Alfaro. Quito (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1962, 1974, 1982, 1990 and 2001; estimate for Egypt Al-Iskandariyah (Alexandria) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1966, 1976, 1986, 1996 and Al-Qahirah (Cairo) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1966, 1976, 1986, 1996 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Data refer to the Governorate of Al- Qahirah (Cairo) and the cities of Al-Jizah (Giza) and Shubra al-khaymah (Shubra-El-Khema). El Salvador San Salvador (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1961, 1971 and 1992; UN estimate for Note: Data refer to the urban parts of the municipios of San Salvador, Mejicanos, Soyapango, Delgado, Ilopango, Cuscatancingo, Ayutuxtepeque and San Marcos. 41
56 Equatorial Guinea Malabo (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1983 and Eritrea Asmara (capital) Sources of data: Census of 1984; estimates for 1950, 1967, 1989, 1990, 2002 and Estonia Tallinn (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2000; estimates for 1996, 2001, 2002 and Ethiopia Addis Ababa (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1984 and 1994; estimates for 1950, 1967, 1999 and Faeroe Islands Tórshavn (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1960, 1966, 1970 and 1977; estimates for 1987, 1989, 1990, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000 and Note: Data refer to the municipality. Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Stanley (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1962, 1972, 1980, 1986, 1991, 1996, 2001 and Federated States of Micronesia Palikir (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1980, 1989, 1994 and Fiji Greater Suva (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1976, 1986 and Note: Data include Lami. Finland Helsinki (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1985, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Note: Data includes Espoo and Vantaa. France Bordeaux, Lyon, Marseille-Aix-en-Provence, Nice-Cannes, Paris (capital), Toulouse Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1962, 1968, 1975, 1982, 1990 and Lille Sources of data: Censuses of 1962, 1968, 1975, 1982, 1990 and 1999; UN estimate for French Guiana Cayenne (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1961, 1967, 1982, 1990 and Note: Data refer to the commune. French Polynesia Papeete (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1962, 1977, 1983, 1988, 1996 and 2002; UN estimates for 1956 and Gabon Libreville (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1958, 1959, 1961, 1969 and 1993; estimates for 1960, 1961, 1965, 1967, 1968, 1970, 1971, 1972, 1973, 1974, 1975, 1976, 1977, 1980 and 1981; Register of 1951 and 1957; Sample Survey of
57 Gambia Banjul (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1963, 1973, 1983, 1993 and 2003; estimate for Note: Data refer to the local government areas of Banjul and Kanifing. Georgia Tbilisi (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2002; estimate for Germany Berlin, Hamburg, Köln (Cologne) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1961, 1970 and 1987; estimates for 1980, 1981, 1982, 1983, 1984, 1985, 1986, 1987, 1988, 1989, 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004 and München (Munich) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1961 and 1970; estimates for 1980, 1981, 1982, 1983, 1984, 1985, 1986, 1987, 1988, 1989, 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004 and Ghana Accra (capital), Kumasi Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1984 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Gibraltar Gibraltar (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1970, 1981, 1991 and Greece Athínai (Athens) (capital), Thessaloniki Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Note: The agglomeration of Athínai includes the localities of Calithèa, Peristérion and Piraeus, among others. Greenland Nuuk (Godthåb) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1965, 1970 and 1976; estimates for 1992, 1993, 1995, 1996, 2000 and Grenada St.George s (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1981, 1991 and Note: Data include the parishes of St. George's Town and St. George. Guadeloupe Basse-Terre Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1961, 1967, 1982, 1990 and Guam Hagåtña (capital) Sources of data: Census of 2000; UN estimates for 1960, 1970, 1980 and Note: Data refer to the urbanized area, that is, the contiguous territory in and around the city that meets minimum population density requirements. Prior to 2000, only data relative to the city proper were published. To obtain comparable estimates for those years, it was assumed that the ratio of the population of the capital agglomeration to the total urban population was the same as in
58 Guatemala Ciudad de Guatemala (Guatemala City) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1964, 1973, 1981, 1994 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Data refer to the municipio of Ciudad de Guatemala. Guinea Conakry (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1960, 1983 and 1996; estimate for Guinea-Bissau Bissau (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1979 and 1991; estimates for 2001, 2002, 2003 and Guyana Georgetown (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1991 and Haiti Port-au-Prince (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1971 and 1982; estimates for 1992 and 1996; UN estimate for Note: Data for 1971 and later refer to the urban agglomeration. Data for 1950 refer to the city proper. The 1999 estimate refers to the urban agglomeration that includes Port-au-Prince, Delmas and Carrefour. Holy See Vatican City (capital) Sources of data: Estimates for 1950, 1964, 1970, 1978, 1980, 1990, 2000 and 2004; UN estimates for 1955, 1965, 1975, 1985 and Note: Data refer solely to the population of the Vatican City State. Honduras Tegucigalpa (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1961, 1974, 1988 and 2001; estimate for Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Hungary Budapest (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and 2001; estimates for 2002, 2003, 2004 and Iceland Reykjavík (capital) Sources of data: Estimates for 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990, 1993, 1996, 1999, 2001 and 2003; Register of Note: Data refer to the urban area in the region of the capital. India Agra, Ahmadabad, Allahabad, Amritsar, Asansol, Aurangabad, Bangalore, Bareilly, Bhopal, Chennai (Madras), Coimbatore, Delhi (capital), Dhanbad, Durg-Bhilainagar, Faridabad, Ghaziabad, Gwalior, Hyderabad, Indore, Jabalpur, Jaipur, Jalandhar, Jamshedpur, Kanpur, Kochi (Cochin), Kolkata (Calcutta), Lucknow, Ludhiana, Madurai, Meerut, Moradabad, Mumbai (Bombay), Nagpur, Nashik, Patna, Pune (Poona), Raipur, Ranchi, Salem, Srinagar, Surat, Tiruchirappalli, Vadodara, Varanasi (Benares), Vijayawada, Visakhapatnam Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Aligarh, Bhiwandi, Bhubaneswar, Hubli- Dharwad, Jodhpur, Kota, Kozhikode (Calicut), Mysore, Rajkot, Solapur, Thiruvananthapuram Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and
59 Chandigarh Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Guwahati (Gauhati) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1971, 1991 and Jammu Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1971, 1981 and Indonesia Bandar Lampung Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Note: Data refer to the municipality. Bandung Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimates for 1950 and Note: Data refer to the municipality. Bogor Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Note: Data refer to the municipality. Jakarta (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimates for 1950 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Data refer to the functional urban area, that is, contiguous areas that are consistently urban in character given their population density, economic functions and facilities. Jakarta covers five municipalities (kotamadya): Jakarta Selatan, Jakarta Timur, Jakarta Pusat, Jakarta Barat, and Jakarta Utara. For 1990 the data available did not refer to the functional urban area. An estimate for 1990 was derived by assuming that the ratio of the population in the functional urban area to the population in the relevant municipalities remained the same as in Malang Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Note: Data refer to the municipality. Medan, Surabaya Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimates for 1950 and Note: Data refer to the municipality. Padang, Pekan Baru Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Note: Data refer to the municipality. Palembang Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Note: Data refer to the municipality. Semarang Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimates for 1950 and Note: The data for 1990 were adjusted to represent the population in the functional urban area as described in the case of Jakarta. Ujung Pandang Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1980 and Note: Data refer to the municipality. Iran (Islamic Republic of) Ahvaz, Esfahan, Karaj, Kermanshah, Mashhad, Qom, Shiraz, Tabriz, Tehran (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1976, 1986, 1991, 1996 and Iraq Al-Basrah (Basra) Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1965, 1987 and 1997; estimate for
60 Al-Mawsil (Mosul) Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1965, 1987 and 1997; estimate for Note: Data for earlier years refer to city proper. Baghdad (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1965, 1977, 1987 and 1997; estimate for 2003; UN estimates for 2007 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Irbil (Erbil) Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1965 and 1987; estimate for 1997; UN estimate for Ireland Dublin (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1956, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996, 2002 and Note: Estimates for 1991 were obtained by using the ratio of the population in the urban agglomeration to that in the city proper as recorded in the 1986 census. Isle of Man Douglas (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976, 1981, 1986, 1991, 1996, 2001 and Israel Hefa (Haifa) Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1972 and 1983; estimates for 1955, 1995, 1998, 2002 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Data prior to 1995 refer to the urban agglomeration. Jerusalem (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1972 and 1983; estimates for 1950, 1955, 1991, 1995, 1998, 2000, 2002 and Tel Aviv-Yafo (Tel Aviv-Jaffa) Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1972 and 1983; estimates for 1955, 1995, 1998, 2000, 2002 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Data prior to 1995 refer to the urban agglomeration. Italy Milano (Milan), Napoli (Naples), Palermo, Roma (Rome) (capital), Torino (Turin) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: The metropolitan area was defined on the basis of the local labour market system (Sistemi locali del lavoro) as captured by the 2001 census. The estimates presented in the 2007 Revision are based on a historically consistent series spanning the period and referring to municipalities linked by strong flows of daily commuters for work. Jamaica Kingston (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1982, 1991 and Note: Data include St. Andrew. Japan Fukuoka-Kitakyushu, Kyoto, Osaka-Kobe Sources of data: Censuses of 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000 and 2005; estimates for 1950, 1955 and Note: The Statistics Bureau of Japan has provided the list of cities, towns and villages included in the urban agglomerations associated with the cities of Fukuoka-Kitakyushu, Kyoto, Nagoya and Osaka-Kobe for each census year from 1960 to The number of cities, towns and villages included in these agglomerations has been rising as the agglomerations have expanded territorially. In 1990, the urban agglomeration of Fukuoka- Kitakyushu consisted of the contiguous densely inhabited districts (DIDs) of Fukuoka, nine cities surrounding Fukuoka, Kitakyushu and two cities surrounding Kitakyushu. The urban agglomeration of Kyoto consisted of the DIDs of Kyoto and six cities surrounding Kyoto. The agglomeration of Nagoya 46
61 consisted of the DIDs of Nagoya and 19 cities surrounding Nagoya. The agglomeration of Osaka consisted of the DIDs of Osaka, 35 cities surrounding Osaka, the city of Kobe and six cities surrounding Kobe. The estimates for 1995, 2000 and 2005 were calculated on the basis of the same definitions, including adjustments made to the DIDs after Hiroshima, Sendai Sources of data: Censuses of 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Following the current definition of the metropolitan area used by the Statistics Bureau of Japan, estimates prior to 1970 are higher than official estimates for the city proper. Nagoya Sources of data: Censuses of 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000 and 2005; estimates for 1950, 1955 and Note: The Statistics Bureau of Japan has provided the list of cities, towns and villages included in the urban agglomeration associated with the city of Nagoya for each census year from 1960 to The number of cities, towns and villages included in this agglomeration has been rising as the agglomeration has expanded territorially. In 1990, the urban agglomeration of Nagoya consisted of the DIDs of Nagoya and 19 cities surrounding Nagoya. The estimates for 1995, 2000 and 2005 were calculated on the basis of that definition, including adjustments made to the DIDs after Sapporo Sources of data: Censuses of 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Following the current definition of the metropolitan area used by the Statistics Bureau of Japan, estimates prior to 1970 are higher than official estimates for the city proper. Tokyo (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1965, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: As defined by the Statistics Bureau of Japan, census figures from 1990 to 2000 are based on the Keihinyo major metropolitan area (M.M.A.) and figures from 1960 to 1985 are based on the Keihin M.M.A. The population of Tokyo-to was estimated at 12.1 million persons in 2000 and that of the Kuarea of Tokyo, at 8.1 million persons. Jordan Amman (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1952, 1961, 1979, 1994 and 2004; estimate for Kazakhstan Almaty Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 1999; estimate for Astana (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 1999; estimates for 2004 and Kenya Mombasa, Nairobi (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1962, 1969, 1979, 1989 and Kiribati Tarawa (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1968, 1973, 1978, 1985, 1990, 1995 and 2000; estimate for Note: Data refer to the island of South Tarawa, including the towns of Bairiki and Bikenibeu. The capital is Bairiki, but population estimates for Bairiki are not available. 47
62 Kuwait Al Kuwayt (Kuwait City) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1965, 1970, 1975, 1980 and 1985; UN estimates for 1991, 1995 and Note: Data for 1985 and 1995 refer to the Governorates of Capital, Hawalli and Farwaniya. The number and names of the governorates constituting the city have changed over time together with the limits of the urban agglomeration. Kyrgyzstan Bishkek (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 1999; estimate for Lao People's Democratic Republic Vientiane (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1973, 1985, 1995 and 2005; estimates for 1958 and Latvia Riga (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2000; estimates for 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004 and Lebanon Bayrut (Beirut) (capital) Sources of data: Estimates for 1958, 1964, 1975, 1982, 1988, 1997, 1998, 2001, 2002 and 2005; Sample Survey of 1970; UN estimate for Lesotho Maseru (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1976, 1986, 1996 and Liberia Monrovia (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1962, 1974 and 1984; estimates for 1991, 1995, 1996, 1999, 2004 and 2006; UN estimates for 2007 and Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Banghazi Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1964, 1973 and 1984; estimate for 1995; UN estimate for Tarabulus (Tripoli) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1964, 1973 and 1984; estimates for 1990 and Note: Data prior to 1984 refer to city proper. Liechtenstein Vaduz (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980 and 1990; estimates for 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1999 and Lithuania Vilnius (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2001; estimates for 2006 and Luxembourg Luxembourg-Ville (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1981 and 1991; estimates for 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006 and Madagascar Antananarivo (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1975 and 1993; estimates for 1952, 1955, 1956, 1957, 1958, 1959, 1971 and 2001; Sample Survey of
63 Malawi Lilongwe (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1966, 1977, 1987 and Malaysia Johore Bharu, Klang Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1991 and 2000; estimates for 1970 and 1980; UN estimate for Kuala Lumpur (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1991 and 2000; estimates for 1970 and Maldives Male (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1965, 1967, 1970, 1974, 1977, 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000 and Mali Bamako (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1965, 1976, 1987 and 1998; estimates for 1960 and Malta Valletta (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1967, 1985, 1995 and Note: Data include all the localities of the Northern and Southern Harbour regions. Marshall Islands Majuro (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1973, 1980, 1988 and 1999; UN estimates for 1958 and Martinique Fort-de-France (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1961, 1967, 1982, 1990 and Note: Data refer to the commune. Mauritania Nouakchott (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1964, 1977, 1988 and 2000; estimate for Mauritius Port Louis (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1952, 1962, 1972, 1983, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Mexico Aguascalientes, Ciudad Juárez, Culiacán Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990, 2000 and 2005; Sample Survey Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Chihuahua, Saltillo Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990, 2000 and 2005; Sample Survey Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Ciudad de México (Mexico City) (capital), Guadalajara, Mexicali, Monterrey, Puebla, Querétaro, San Luis Potosí, Tijuana, Torreón Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990, 2000 and 2005; Sample Survey Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. León de los Aldamas, Mérida, Toluca de Lerdo Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990, 2000 and 2005; Sample Survey Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Data refer to conurbations, each of which includes several localities. Moldova Chisinau (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and Monaco Monaco (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1956, 1962, 1968, 1975, 1982, 1990 and
64 Mongolia Ulaanbaatar (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1963, 1969, 1979, 1989 and 2000; estimate for Montenegro Podgorica (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Montserrat Brades Estate (capital) Sources of data: UN Estimates for 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991, 1997, 1997, 2001 and Plymouth (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970 and 1980; estimate for 1991; UN estimates for 1950, 1955, 1993, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1997 and Note: Due to volcanic activity, the former capital, Plymouth, was abandoned in The government premises were established at Brades Estate, in the Carr's Bay/Little Bay vicinity at the northwest end of Montserrat. Morocco Dar-el-Beida (Casablanca) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1971, 1982, 1994 and 2004; estimate for Note: Casablanca includes Mohammedia. Fès Sources of data: Censuses of 1971, 1982, 1994 and 2004; estimates for 1952 and Marrakech Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1971, 1982, 1994 and 2004; estimate for Rabat (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1952, 1960, 1971, 1982, 1994 and Note: Rabat includes Salé and Temara. Mozambique Maputo (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980 and Myanmar Mandalay Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1973 and Nay Pyi Taw (capital) Sources of data: Estimate for 2007; UN estimates for 2005 and Yangon Sources of data: Censuses of 1973 and 1983; UN estimate for Namibia Windhoek (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1960, 1970, 1981, 1991 and Nauru Nauru (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1977, 1983, 1992 and Note: The island of Nauru is considered a single urban agglomeration; the Government s offices are located in Yaren District. Nepal Kathmandu (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Note: Data refer to the municipality. 50
65 Netherlands Amsterdam (capital) Sources of data: Register of 1960, 1965, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000 and Note: Data refer to the municipalities of Amstelveen, Amsterdam, Diemen, Landsmeer, Oostzaan, Wormerland, Zaanstad Rotterdam Sources of data: Register of 1960, 1965, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000 and Note: Data refer to the municipalities of Barendrecht, Capelle a/d Ijssel, Krimpen a/d Ijssel, Maasland, Maassluis, Rotterdam, Rozenburg, Schiedam, Spijkenisse, Vlaardingen s-gravenhage (The Hague) Sources of data: Register of 1960, 1965, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000 and Note: Data refer to the municipalities of s-gravenhage, Leidschendam, Leidschendam- Voorburg, Rijswijk, Voorburg, Wassenaar, Wateringen Netherlands Antilles Willemstad (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1981, 1992 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: The 1981 census provided data only for the city proper. The population of the urban agglomeration for that date was estimated using the ratio of the population in the urban agglomeration to that in the city proper derived from the 1960 census. New Caledonia Nouméa (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1963, 1969, 1976, 1983, 1989, 1996 and Note: Greater Nouméa includes the communes of Dumbéa, Mont-Doré and Païta (as of 1983). New Zealand Auckland, Wellington (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1956, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976, 1986, 1991, 1996, 2001 and Note: Population estimates for are based on the 2001 boundaries of urban areas, whereas estimates from 2001 onwards are based on 2006 boundaries of urban areas. Nicaragua Managua (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1963, 1971, 1995 and Niger Niamey (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1977, 1988 and 2001; estimates for 1962 and Nigeria Abuja (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1991 and 2006; UN estimates for 1953 and Benin City, Ibadan Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1963, 1991 and Note: Data for 1953 and 1963 refer to city proper. Data for 1991 and 2006 refer to urban agglomeration. Ilorin Sources of data: Censuses of 1963 and 1991; UN estimate for
66 Kaduna, Kano, Maiduguri, Zaria Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1963 and 1991; UN estimate for Note: The 1983 data for the city proper were adjusted by assuming that the ratio of the population of the urban agglomeration to that of the city proper was the same as in Data for 1953, 1963 and 1971 refer to city proper. Lagos Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1963, 1991 and 2006; estimate for Note: Data refer to Lagos State. Ogbomosho Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1963 and Port Harcourt Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1963 and 1991; UN estimate for Niue Alofi (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1966, 1971, 1986, 1991, 1997 and Northern Mariana Islands Saipan (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1980, 1990, 1995 and 2000; UN estimates for 1950, 1958, 1967 and Note: From 1980 to 2000, data refer to the island of Saipan (municipality of Saipan in the year 2000). The capital is Garapan, located on the island of Saipan, whose population was estimated at 3,588 persons in Government offices are located in Capitol Hill. Norway Oslo (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980 and 1990; estimates for 1999 and 2002; Register of Occupied Palestinian Territory Ramallah (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1961 and 1997; estimates for 2004 and Note: Data include Al Bira. Oman Masqat (capital) Sources of data: Census of 1993; estimates for 1950, 1960, 1999, 2000, 2001 and Note: The 1993 census and all estimates since 1999 also include As Seeb, Bawshar and Mutrah. Pakistan Faisalabad, Gujranwala, Hyderabad, Karachi, Lahore, Multan, Peshawar, Quetta, Rawalpindi Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1972, 1981 and Islamabad (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1972, 1981 and Palau Melekeok Sources of data: Censuses of 1980, 1986, 1990, 1995, 2000 and
67 Panama Ciudad de Panamá (Panama City) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and Note: Data refer to the urban agglomeration of Panama City, including the urban districts of Balboa (Ancón), Arrajian, La Chorrera and San Miguelito. Papua New Guinea Port Moresby (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1966, 1971, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Paraguay Asunción (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1962, 1972, 1982, 1992 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Peru Arequipa Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1972, 1981, 1993 and Note: Data include the numerous urban districts of Arequipa, Miraflores, Yanahuara, Paucarpata, Cayma, Sabandia, Socabaya and Sachaca. Lima (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1972, 1981, 1993 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Gran Lima includes the capitals of the departments of Lima and Callao as well as surrounding populated centres. Philippines Cebu, Davao, Zamboanga Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1990, 1995 and Manila (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1990, 1995 and 2000; estimate for Note: Data refer to the National Capital Region. Pitcairn Adamstown (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1986 and 1991; estimates for 1995, 2000 and Statistical concept: Others. Poland Kraków (Cracow), Lódz, Warszawa (Warsaw) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1978 and 2002; estimates for 1992 and Note: The 2007 Revision is based on a time series of consistent city population data available for the period Portugal Lisboa (Lisbon) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1981, 1991 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: Data refer to municipalities included in Grande Lisboa and the Peninsula of Setúbal, as well as that of Azambuja). Porto Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1981, 1991 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Puerto Rico San Juan (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and Note: Data refer to the urbanized area, that is, the contiguous territory in and around the city that meets minimum population density requirements. The implementation of a revised definition of the urbanized area in the 2000 census led to changes in the boundaries of the San Juan Urbanized Area. In the 2007 Revision, the time series for the San Juan Urbanized Area has been adjusted to maintain consistency with the 2000 census. The San Juan Urbanized Area now includes the former urbanized areas of Caguas, Cayay, Humacao, and Vega Baja- Manati. 53
68 Qatar Ad-Dawhah (Doha) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1986, 1997 and 2004; estimates for 1962, 1967 and 2006; UN estimates for 1956 and Republic of Korea Bucheon Sources of data: Censuses of 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000 and 2005; UN estimate for Busan, Daegu, Daejon, Gwangju, Incheon, Seoul (capital), Suweon Sources of data: Censuses of 1955, 1960, 1966, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000 and Note: The data refer to the metropolitan city in each case. Goyang Sources of data: Censuses of 1980, 1990, 1995, 2000 and Note: The data refer to the metropolitan city in each case. Seongnam Sources of data: Censuses of 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000 and Note: The data refer to the metropolitan city in each case. Ulsan Sources of data: Censuses of 1966, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000 and Note: The data refer to the metropolitan city in each case. Réunion Saint-Denis (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1954, 1961, 1967, 1974, 1982, 1990 and 1999; estimate for Romania Bucuresti (Bucharest) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1977, 1992 and 2002; estimate for Russian Federation Chelyabinsk, Kazan Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2002; estimates for 1999, 2004 and Krasnoyarsk, Nizhniy Novgorod, Novosibirsk, Omsk, Perm, Rostov-na-Donu (Rostov-on-Don), Saratov, Volgograd, Voronezh, Yekaterinburg Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2002; estimates for 2004 and Moskva (Moscow) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2002; estimates for 1992, 1994, 1996, 1998, 2000, 2002, 2003, 2005 and Note: The data include communities under the authority of the Town Council. The 1989 census produced data referring only to the city proper; the population of the urban agglomeration for that date was estimated by assuming that the ratio of the population of the urban agglomeration to that of the city proper was the same as in Samara Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2002; estimate for Sankt Peterburg (Saint Petersburg) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2002; estimates for 1992, 1994, 1996, 1998, 2000, 2002, 2004, 2005 and Note: The data include communities under the authority of the Town Council. The 1989 census produced data referring only to the city proper; the population of the urban agglomeration for that date was estimated by assuming that the ratio of the population of the urban agglomeration to that of the city proper was the same as in The same adjustment was made in regard to the 2002 census. 54
69 Ufa Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2002; estimates for 2004, 2004 and Rwanda Kigali (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1970, 1978, 1991 and 2002; estimate for 1960; Sample Survey of Saint Helena Jamestown (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1976, 1987 and 1998; estimate for 1950; UN estimate for Saint Kitts and Nevis Basseterre (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1991 and 2001; estimate for Saint Lucia Castries (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1970, 1980 and 1991; estimates for 1996, 1998 and Note: The data include Castries Town and Castries Sub-Urban. Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint-Pierre (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1962, 1982, 1990 and 1999; estimate for Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Kingstown (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970 and 1980; estimates for 1991 and Samoa Apia (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1956, 1961, 1966, 1971, 1976, 1981, 1991 and San Marino San Marino (capital) Sources of data: Estimates for 1962, 1973, 1982, 1986, 1989, 1991, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2005 and Sao Tome and Principe São Tomé (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1981, 1991 and 2001; estimate for Note: Data refers to district of Água-Grande. Saudi Arabia Ad-Dammam Sources of data: Censuses of 1974, 1992 and 2004; estimate for 1962; UN estimate for Al-Madinah (Medina) Sources of data: Censuses of 1974, 1992 and 2004; estimates for 1950 and Ar-Riyadh (Riyadh) (capital), Jiddah, Makkah (Mecca) Sources of data: Censuses of 1962, 1974, 1992 and 2004; estimate for Senegal Dakar (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1955, 1976, 1988 and 2002; estimate for 1969; Sample Survey of Serbia Beograd (Belgrade) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Note: The data include ten municipalities of the City of Belgrade. 55
70 Seychelles Victoria (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1977, 1987, 1994, 1997 and 2002; UN estimate for Note: The data refer to city proper before 1971 and to the urban agglomeration since 1971, which contains the following districts: English River, Mont Buxton, St Louis, Bel Air, Mont Fleuri, Plaisance, Roche Caiman, Les Mamelles. Sierra Leone Freetown (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1963, 1974, 1985 and Singapore Singapore (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1970, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimates for 2004 and Note: The data include the resident and nonresident population. Slovakia Bratislava (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1961, 1970, 1980, 1991 and 2001; estimate for Slovenia Ljubljana (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and 2002; estimate for Solomon Islands Honiara (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1976, 1986 and 1999; UN estimate for Somalia Muqdisho (Mogadishu) (capital) Sources of data: Census of 1975; estimates for 1955, 1956, 1957, 1958, 1959, 1963, 1972, 1982, 1984 and 2001; UN estimates for 1991 and Note: Data for 1972 refer to urban agglomeration. South Africa Bloemfontein (capital), Cape Town (capital), Port Elizabeth, Pretoria (capital), Vereeniging Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1960, 1970, 1985, 1991, 1996 and Durban Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1960, 1970, 1991, 1996 and Ekurhuleni (East Rand) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1960, 1970, 1985, 1996 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Johannesburg Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1960, 1970, 1991, 1996 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Spain Barcelona, Madrid (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1981 and 1991; Register of Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Valencia Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1981 and 1991; Register of
71 Sri Lanka Colombo (capital), Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte Sources of data: Censuses of 1953, 1963, 1971, 1981 and Sudan Al-Khartum (Khartoum) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1973, 1983 and 1993; UN estimates for 1996, 2001 and Suriname Paramaribo (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1964, 1971, 1980 and 2004; estimate for Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: The data refer to the district of Paramaribo. Swaziland Mbabane (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1976, 1986 and Sweden Stockholm (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960 and 1965; estimates for 1970, 1980, 1990, 1995 and 2000; Register of Note: The data refers to tätort, according to the administrative divisions of Switzerland Bern (capital), Zürich (Zurich) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and 2000; estimate for Note: The data refer to the population contained within the contours of contiguous territory inhabited by at least 20,000 inhabitants consisting of a core area and surrounding area. The core and the surrounding areas have certain urban characteristics in terms of population density and economic functions. Syrian Arab Republic Dimashq (Damascus) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970 and 1981; UN estimate for Halab (Aleppo), Hims (Homs) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1981 and Tajikistan Dushanbe (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and Thailand Krung Thep (Bangkok) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia Skopje (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and 1994; estimate for Timor-Leste Dili (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1990 and Note: The data refer to city proper prior to 1990 and to the urban agglomeration after Togo Lomé (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1970 and 1981; estimates for 1988 and 2005; Sample Survey of
72 Tokelau No capital. Non-self-governing territory of New Zealand. Each atoll (Atafu, Fakaofo and Nukunonu) has its own administrative center. Tonga Nuku alofa (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1976, 1986 and 1996; estimates for 1950 and Trinidad and Tobago Port of Spain (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and Tunisia Tunis (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1956, 1966, 1975, 1984, 1994 and 2004; estimate for Turkey Adana Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1960, 1965, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990 and Note: Adana includes Seyhan and Yuregir. Ankara (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1960, 1965, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1997 and Note: Ankara includes Altindag, Cankaya, Etimesgut, Golbasi, Keçioren, Mamak, Sincan and Yenimahalle. Antalya Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1965, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990 and Bursa Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1960, 1965, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1997 and Note: Bursa includes Nilufer, Osmangazi and Yildirim. Gaziantep Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1960, 1965, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990 and Note: The data for Gaziantep include the population of Sahinbey and Sehitkami. Istanbul Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1960, 1965, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1997 and Note: Istanbul includes Adalar, Avcilar, Bagicilar, Bahçelievler, Bakirkoy, Bayrampasa, Besiktas, Beykoz, Beyoglu, Eminonu, Esenler, Eyup, Fatih, Gaziosmanpasa, Gungoren, Kadikoy, Kagithane, Kartal, Kuçukçekmece, Maltepe, Pendik, Sariyer, Sisli, Tuzla, Umraniye, Uskudar and Zeytinburnu Izmir Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1960, 1965, 1970, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990, 1997 and Note: Izmir includes Balcova, Bornova, Buca, Cigli, Gaziemir, Guzelbahce Karsiyaka, Konak and Narlidere. The 1950 and 1955 data for Izmir refer to the city proper. Konya Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1955, 1960, 1965, 1975, 1980, 1985, 1990 and Note: Konya includes Karatay, Meram and Selçuklu. 58
73 Turkmenistan Ashgabat (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 1995; estimate for Turks and Caicos Islands Grand Turk (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1975, 1980 and 1990; estimate for Tuvalu Funafuti (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1979, 1985, 1991 and Note: Data refer to the island of Funafuti. Uganda Kampala (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1969, 1980, 1991 and Ukraine Dnipropetrovs k, Donets k, Kharkiv, Kyiv (Kiev) (capital), Odesa, Zaporizhzhya Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979, 1989 and 2001; estimate for United Arab Emirates Abu Zaby (Abu Dhabi) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1975, 1980, 1985 and 1995; estimates for 1960, 1968, 2002 and Dubayy (Dubai) Sources of data: Censuses of 1975, 1980, 1985 and 1995; estimates for 1950, 1960, 1968, 2002 and United Kingdom Birmingham, Liverpool, London (capital), Manchester, Newcastle upon Tyne, West Yorkshire Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and Note: The urban agglomeration of Birmingham (also known as the West Midlands urban area) consists of 10 urban divisions, including Birmingham, Dudley, Oldbury/Smethwick, Solihull, Sutton Coldfield, Walsall, West Bromwich, and Wolverhampton. Glasgow Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1961, 1971, 1991 and United Republic of Tanzania Dar es Salaam Sources of data: Censuses of 1952, 1957, 1967, 1978, 1988 and Dodoma (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1957, 1967, 1978, 1988 and United States of America Atlanta, Austin, Baltimore, Boston, Bridgeport- Stamford, Buffalo, Charlotte, Chicago, Cincinnati, Cleveland, Columbus (Ohio), Dallas-Fort Worth, Dayton, Denver-Aurora, Detroit, Hartford, Honolulu, Houston, Indianapolis, Jacksonville (Florida), Kansas City, Las Vegas, Los Angeles-Long Beach-Santa Ana, Louisville, Memphis, Miami, Milwaukee, Minneapolis-St. Paul, Nashville-Davidson, New Orleans, New York- Newark, Oklahoma City, Orlando, Philadelphia, Phoenix-Mesa, Pittsburgh, Portland, Providence, Richmond, Riverside-San Bernardino, Sacramento, Salt Lake City, San Antonio, San Diego, San Francisco-Oakland, San Jose, Seattle, St. Louis, Tampa-St. Petersburg, Tucson, Virginia Beach, Washington (D.C.) (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and Note: The data refer to the urbanized area (UA), that is, contiguous territory that meets minimum population density requirements. Each UA is named after the most populous place or places contained within it. The implementation of a revised definition of UA for the 2000 census led to changes in the boundaries of several UAs. In the 2007 Revision, the time series for each affected UA has been adjusted where possible for consistency with the
74 census. Specifically, the UA of Baltimore is now defined to include the former Annapolis UA but no longer includes the separate Aberdeen-Havre de Grace-Bel Air UA; that of Boston now includes the former Brockton, Lawrence-Haverhill, Lowell, and Taunton UAs; that of Bridgeport-Stamford now includes the former Bridgeport-Milford, Stamford, and Norwalk UAs; that of Chicago now includes the former Aurora, Crystal Lake, Elgin, and Joliet UAs; that of Cincinnati now includes the former Hamilton UA; that of Hartford now includes the former Bristol and New Britain UAs; that of Kansas City no longer includes the Lee's Summit UA; that of Los Angeles-Long Beach-Santa Ana no longer includes the Mission Viejo and Santa Clarita UAs; that of Miami now includes the former Fort Lauderdale- Hollywood-Pompano Beach and West Palm Beach- Boca Raton-Delray Beach UAs; that of Oklahoma City no longer includes the Norman UA; that of Philadelphia now includes the former Wilmington UA and that portion of the Trenton UA that was in the state of Pennsylvania; that of Providence now includes the former Fall River and Newport UAs; that of Richmond now includes the former Petersburg UA; that of San Francisco-Oakland no longer includes the Concord, Livermore, and Vallejo UAs; that of San Jose no longer includes the Gilroy- Morgan Hill UA; that of Seattle now includes the former Tacoma UA but no longer includes the Marysville UA; and the Virginia Beach UA, which was formerly called Norfolk-Virginia Beach- Newport News, no longer includes the Suffolk urban cluster. El Paso, Rochester Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990 and United States Virgin Islands Charlotte Amalie (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1960 and 2000; UN estimates for 1970, 1980 and Note: Data refer to the urban cluster, that is, contiguous territory that meets minimum population density requirements. Prior to 2000, only data for the city proper were published. To estimate the population for the urban agglomeration in 1970, 1980 and 1990, it was assumed that the ratio of the population of the capital agglomeration to the total urban population was the same as in Data for 1950 and 1960 refer to city proper. Uruguay Montevideo (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1963, 1975, 1985, 1996 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Note: The metropolitan area of Montevideo includes the urban population of surrounding localities. Uzbekistan Tashkent (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1959, 1970, 1979 and 1989; estimates for 1991, 1997, 2000 and Vanuatu Port Vila (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1979, 1989 and 1999; estimate for Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of) Barquisimeto Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1990 and Caracas (capital), Maracaibo, Maracay Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1990 and Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Valencia Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1990 and 2001; estimate for Statistical concept: Metropolitan area. Viet Nam Hà Noi (capital), Thành Pho Ho Chí Minh (Ho Chi Minh City) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1979 and 1989; estimate for
75 Hai Phòng Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1979, 1989 and 1999; estimate for Wallis and Futuna Islands Matu-Utu (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1976, 1983, 1990, 1996 and Statistical concept: Other. Western Sahara El Aaiún (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1960, 1970, 1982, 1994 and 2004; UN estimates for 1950 and Yemen Al-Hudaydah, Ta izz Sources of data: Censuses of 1975, 1986 and Sana a (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1975, 1986, 1994 and 2004; estimates for 1950 and Statistical concept: Data for 1950, 1960 and 1975 refer to city proper and data for 1986, 1994 and 2004 refer to urban agglomeration. Zambia Lusaka (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1950, 1963, 1969, 1980, 1990 and Zimbabwe Harare (capital) Sources of data: Censuses of 1951, 1956, 1969, 1982, 1992 and 2002; estimates for 1972 and
76
77 UNITED NATIONS NATIONS UNIES Department of Economic and Social Affairs POPULATION DIVISION DATA IN DIGITAL FORM The 2007 Revision of the World Urbanization Prospects, prepared by the United Nations Population Division, provides a comprehensive and consistent set of urban and rural population estimates and projections for the all countries and areas of the world, as well as for urban agglomerations with more than 750,000 inhabitants in The data referring to urban and rural areas cover the period and those referring to urban agglomerations cover the period Detailed results from the 2007 Revision are available for purchase in two sets of files, distributed on a single CD-ROM. The files are prepared in Excel 2003, which is compatible with all versions since Excel 5.0/95. The CD- ROM version launches a navigation interface upon insertion. The interface provides direct access to the files. In the data sets, figures for are estimates and those for years beyond 2007 are projections. With the exception of a selected set of annual indicators, estimates and projections are presented for years that are multiples of five. The urban, rural and city data presented are consistent with the medium variant of the 2006 Revision of World Population Prospects, the official United Nations population estimates and projections at the national level. A short description of each set of files is presented below; the list of file names and their contents are presented in detail in tables A and B on the following pages. (1) Urban and rural areas: Ten files present estimates and projections of the population in urban and rural areas as well as associated indicators. The data are presented for 229 countries and areas individually and for 33 country aggregates, including the world as a whole, the more developed regions and the less developed regions, the major world areas and the world regions. The projected values cover the period The files present information on: (1) the urban and rural population and the percentage urban in 2007; (2) the percentage of the population residing in urban areas; (3) the urban population by country; (4) the rural population by country; (5) the total population by country; (6) the average annual rate of change of the urban population; (7) the average annual rate of change of the rural population; (8) the average annual rate of change of the total population; (9) the urbanization rate or average annual rate of change of the percentage urban, and (10) the average annual rate of change of the percentage rural. All these data are presented for five-year periods. Annual time series are provided for the following five indicators: (10) the total population by country; (11) the urban population by country; (12) the rural population by country; (13) the percentage of the population residing in urban areas. (2) Urban agglomerations: Eleven files present estimates and projections of the population in urban agglomerations with 750,000 inhabitants or more in They cover the following indicators: (1) the total population of each urban agglomeration (also included as annual time series); (2) the average annual rate of change of the population of each urban agglomeration; (3) the percentage of the urban population residing in each urban agglomeration; (4) the percentage of the total population residing in each urban agglomeration. Three more files provide data for specific sets of urban agglomerations. The first one presents the 30 largest urban agglomerations ranked by population size over the period The second presents a time series for the period of the population of the 30 largest urban agglomerations in The third presents the population of the capital cities of each country for the year Lastly, four files (one per indicator) provide summary statistics for major areas, regions and countries with a population of at least 100,000 in 2007 on the number of cities, the percentage of the urban population and the urban population by size class of urban settlement. The following citation should be used to indicate the source of any data derived from the data sets described above: United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2008). World Urbanization Prospects: The 2007 Revision. CD-ROM Edition, data in digital form (POP/DB/WUP/Rev.2007). 63
78 Table A: Schematic Contents of Dataset on Urban and Rural Areas, POP/DB/WUP/Rev.2007/1 All rights reserved. File number File name Indicator presented Units Geographical coverage Number of countries or areas Type of indicator Reference date Time period covered Table in World Urbanization Prospects File 1 WUP2007-F01- Total_Urban_Rural.xls Total, urban and rural population and percentage urban Thousands and Per cent All countries and areas 229 Stock indicator 01-Jul 2007 A.1 File 2 File 3 WUP2007-F02- Proportion_Urban.xls WUP2007-F03- Urban_Population.xls Percentage of the population residing in urban areas Total population residing in urban areas Per cent Thousands All countries and areas All countries and areas Stock indicator Stock indicator 01-Jul 01-Jul 1950, 1955, 1960, 2045, , 1955, 1960, 2045, 2050 A.2 A.3 File 4 WUP2007-F04- Rural_Population.xls Total population residing in rural areas Thousands All countries and areas 229 Stock indicator 01-Jul 1950, 1955, 1960, 2045, 2050 A.4 File 5 WUP2007-F05- Total_Population.xls Total population Thousands All countries and areas 229 Stock indicator 01-Jul 1950, 1955, 1960, 2045, 2050 A.5 64 File 6 File 7 File 8 File 9 File 10 File 18 WUP2007-F06- Urban_Growth_Rate.xls WUP2007-F07- Rural_Growth_Rate.xls WUP2007-F08- Total_Growth_Rate.xls WUP2007-F09- Urbanization_Rate.xls WUP2007-F10- Rate_Proportion_Rural.xls WUP2007-F18- Total_Population_Annual.xls Average annual rate of change of the urban population Average annual rate of change of the rural population Average annual rate of change of the total population Average annual rate of change of the percentage urban Average annual rate of change of the percentage rural Total population Per cent Per cent Per cent Per cent Per cent Thousands All countries and areas All countries and areas All countries and areas All countries and areas All countries and areas All countries and areas Period indicator Period indicator Period indicator Period indicator Period indicator Stock indicator Average per year Average per year Average per year Average per year Average per year 01-Jul , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , 1951, 1952, 2049, 2050 A.6 A.7 A.8 A.9 A.10 File 19 WUP2007-F19- Urban_Population_Annual.xls Total population residing in urban areas Thousands All countries and areas 229 Stock indicator 01-Jul 1950, 1951, 1952, 2049, 2050 File 20 File 21 WUP2007-F20- Rural_Population_Annual.xls WUP2007-F21- Proportion_Urban_Annual.xls Total population residing in rural areas Percentage of the population residing in urban areas Thousands Per cent All countries and areas All countries and areas Stock indicator Stock indicator 01-Jul 01-Jul 1950, 1951, 1952, 2049, , 1951, 1952, 2049, 2050
79 Table B: Schematic Contents of Dataset on Urban Agglomerations, POP/DB/WUP/Rev.2007/2 All rights reserved. File number File 11a File 11b File 12 Geographical coverage WUP2007-F11a- 30_Largest_Cities.xls File name Indicator presented Units WUP2007-F11b- 30_Largest_Cities_in_2007_by_tim e.xls WUP2007-F12- Cities_Over_750K.xls Population of the 30 largest urban agglomerations ranked by population size at each point in time Time series of the population of the 30 largest urban agglomerations in 2007 Population of each urban agglomeration Millions Millions Thousands The 30 most populous cities at each point in time The 30 most populous cities in 2007 All cities with 750,000 inhabitants or more in 2007 Number of countries or areas 229 Type of indicator Stock indicator Stock indicator Stock indicator Reference date 01-Jul 01-Jul 01-Jul Time period covered 1950, 1955,., 2020, , 1955,., 2020, , 1955,., 2020, 2025 Table in World Urbanization Prospects A.11 A.11 A.12 File 14 WUP2007-F14- Growth_Rate_Cities.xls Average annual rate of change of the population of each urban agglomeration Per cent All cities with 750,000 inhabitants or more in Stock indicator Average per year , , , A File 15 File 16 File 17a File 17b File 17c File 17d File 13 File 22 WUP2007-F15- Percentage_Urban_in_Cities.xls WUP2007-F16- Percentage_Total_in_Cities.xls WUP2007-F17a- City_Size_Class.xls WUP2007-F17b-City_Size_Class- Number.xls WUP2007-F17c-City_Size_Class- Percentage.xls WUP2007-F17d-City_Size_Class- Population.xls WUP2007-F13-Capital_Cities.xls WUP2007-F22- Cities_Over_750K_Annual.xls Percentage of the urban population residing in each urban agglomeration Percentage of the total population residing in each urban agglomeration Urban population, number of cities and percentage of urban population by size class of urban settlement Number of cities classified by size class of urban settlement Percentage of urban population in cities classified by size class of urban settlement Population in cities classified by size class of urban settlement Population of capital cities in 2007 Population of each urban agglomeration Per cent Per cent Various Number of cities Per cent Thousands All cities with 750,000 inhabitants or more in 2007 All cities with 750,000 inhabitants or more in 2007 All countries and areas All countries and areas All countries and areas All countries and areas Thousands Capital cities 229 Thousands All cities with 750,000 inhabitants or more in Stock indicator Stock indicator Stock indicator Stock indicator Stock indicator Stock indicator Stock indicator Stock indicator 01-Jul 01-Jul 01-Jul 01-Jul 01-Jul 01-Jul 1950, 1955,., 2020, , 1955,., 2020, , 1955,., 2020, , 1955,., 2020, , 1955,., 2020, , 1955,., 2020, 2025 A.15 A.16 A.17 A.17 A.17 A Jul 2007 A Jul 1950, 1951, 1952, 2024, 2025 A.17
80 UNITED NATIONS NATIONS UNIES Department of Economic and Social Affairs POPULATION DIVISION Data in Digital Form Copyright United Nations 2008 All rights reserved Order Form Date: Data set requested (please mark appropriate box with an x ) Price in US$ CD-ROM:. CD-ROM Edition Data in digital form (POP/DB/WUP/Rev.2007)...$200.- SHIP TO: Name:... Institution:... Address:... Telephone:...Fax No:... address: For overnight or express mail delivery, please provide a billing account number:... Notes 1. Data contained in the above data sets are copyrighted by the United Nations. No portion of the data files contained on the CD-ROM can be reproduced, distributed or used to prepare derivative works or for any other purpose without the express permission of the United Nations, to be obtained from the Secretary of the United Nations Publications Board. For further information, please contact the Director, Population Division/DESA, United Nations (Room DC2-1950), New York, NY 10017, U.S.A. Telephone No. (1 212) ; Fax No. (1 212) The order form should be accompanied by a cheque or an international money order in US dollars drawn on a United States Bank for the correct amount, payable to the UNITED NATIONS POPULATION DIVISION and mailed to: The Director, Population Division/DESA, United Nations, DC2-1950, New York, NY 10017, U.S.A. Credit cards are not accepted.
Country Risk Scores Table Results
 s Table - 2014 Results Afghanistan 73 73 53 71 70 49 48 50 59 54 63 75 54 89 4.7 Albania 60 67 59 73 50 32 39 26 35 47 32 43 46 32 8.8 Algeria 79 82 88 67 63 30 39 24 79 81 74 49 51 38 10.0 Andorra 47
s Table - 2014 Results Afghanistan 73 73 53 71 70 49 48 50 59 54 63 75 54 89 4.7 Albania 60 67 59 73 50 32 39 26 35 47 32 43 46 32 8.8 Algeria 79 82 88 67 63 30 39 24 79 81 74 49 51 38 10.0 Andorra 47
Green: 348. Yellow/Orange: Yellow/Orange: Green: 348. Yellow/Orange: Green: 348. Yellow/Orange:137 Bronze: 145
 Afghanistan 348 Albania 186 Algeria 348 Andorra 286 348 137 Bronze: 145 Angola 137 Antigua and Barbuda 314 137 Argentina 279 137 Armenia 286 165 186 Australia 2768 Austria Azerbaijan Warm red 485 282 348
Afghanistan 348 Albania 186 Algeria 348 Andorra 286 348 137 Bronze: 145 Angola 137 Antigua and Barbuda 314 137 Argentina 279 137 Armenia 286 165 186 Australia 2768 Austria Azerbaijan Warm red 485 282 348
Table 19 Production, trade and supply of other kerosene Thousand metric tons and kilograms per capita
 Table Notes Production includes output from refineries and plants. For China, data include kerosene-type jet fuel. Please refer to the Definitions Section on pages ix to xv for the appropriate product
Table Notes Production includes output from refineries and plants. For China, data include kerosene-type jet fuel. Please refer to the Definitions Section on pages ix to xv for the appropriate product
Total fleet. Oil tankers
 184 as at 1 January 2011 (in thousands of dwt) DEVELOPING ECONOMIES OF AFRICA Algeria 809 30 204 66 0 509 Angola 58 10 0 14 0 34 Benin 0 0 0 0 0 0 Cameroon 10 0 0 4 0 6 Cape Verde 22 5 0 12 0 6 Comoros
184 as at 1 January 2011 (in thousands of dwt) DEVELOPING ECONOMIES OF AFRICA Algeria 809 30 204 66 0 509 Angola 58 10 0 14 0 34 Benin 0 0 0 0 0 0 Cameroon 10 0 0 4 0 6 Cape Verde 22 5 0 12 0 6 Comoros
Table 19 Production, trade and supply of other kerosene Thousand metric tons and kilograms per capita
 Table 19 Production, trade and supply of other kerosene Table Notes Production includes output from refineries and plants. For China, data up to 2013 include kerosenetype jet fuel. Please refer to the
Table 19 Production, trade and supply of other kerosene Table Notes Production includes output from refineries and plants. For China, data up to 2013 include kerosenetype jet fuel. Please refer to the
TABLE 1 WHO ASSESSED CONTRIBUTIONS: MEMBERS WITH NO CHANGE IN CONTRIBUTION
 :25/'+($/7+25*$1,=$7,21 (;(&87,9(%2$5' WK6HVVLRQ 3URYLVLRQDODJHQGDLWHP (%,1)'2& 'HFHPEUH $VVHVVPHQWVIRU 1. Document EB109/21 includes as an Annex a table indicating for each Member and Associate Member
:25/'+($/7+25*$1,=$7,21 (;(&87,9(%2$5' WK6HVVLRQ 3URYLVLRQDODJHQGDLWHP (%,1)'2& 'HFHPEUH $VVHVVPHQWVIRU 1. Document EB109/21 includes as an Annex a table indicating for each Member and Associate Member
Summary of debt securities outstanding
 Summary of debt securities outstanding All countries........................ 22,695 15,852 6,665 3,427 1,762 Developed countries........................ 16,504 13,087 5,869 2,716 701 Austria 510 173 44
Summary of debt securities outstanding All countries........................ 22,695 15,852 6,665 3,427 1,762 Developed countries........................ 16,504 13,087 5,869 2,716 701 Austria 510 173 44
LPI ranking and scores, 2014
 ing and scores, 2014 Germany 1 4.12 100.0 Netherlands 2 4.05 97.6 Belgium 3 4.04 97.5 United Kingdom 4 4.01 96.6 Singapore 5 4.00 96.2 Sweden 6 3.96 94.9 Norway 7 3.96 94.8 Luxembourg 8 3.95 94.4 United
ing and scores, 2014 Germany 1 4.12 100.0 Netherlands 2 4.05 97.6 Belgium 3 4.04 97.5 United Kingdom 4 4.01 96.6 Singapore 5 4.00 96.2 Sweden 6 3.96 94.9 Norway 7 3.96 94.8 Luxembourg 8 3.95 94.4 United
STATES ELIGIBLE FOR ELECTION
 ANNEX STATES ELIGIBLE FOR ELECTION List No. 1 States Eligible for Election as Members of the Executive Committee of the Paris Union (that is, States members of the Assembly of the Paris Union) (175) 1
ANNEX STATES ELIGIBLE FOR ELECTION List No. 1 States Eligible for Election as Members of the Executive Committee of the Paris Union (that is, States members of the Assembly of the Paris Union) (175) 1
Global and Regional Tables
 Global and Regional Tables Freedom of the Press 2006 1 Finland 9 F Iceland 9 F 3 Denmark 10 F Norway 10 F Sweden 10 F 6 Belgium 11 F Luxembourg 11 F Netherlands 11 F Switzerland 11 F 10 Liechtenstein 13
Global and Regional Tables Freedom of the Press 2006 1 Finland 9 F Iceland 9 F 3 Denmark 10 F Norway 10 F Sweden 10 F 6 Belgium 11 F Luxembourg 11 F Netherlands 11 F Switzerland 11 F 10 Liechtenstein 13
Lower bound. Upper bound. Lower bound. Afghanistan
 EMBARGOED UNTIL 00:01 GMT 18 September 2018 Under-five () with 90 per cent uncertainty interval () (per cent) under-five with 90 per cent uncertainty interval Afghanistan 175 160 192 68 52 85 3.5 2.6 4.5
EMBARGOED UNTIL 00:01 GMT 18 September 2018 Under-five () with 90 per cent uncertainty interval () (per cent) under-five with 90 per cent uncertainty interval Afghanistan 175 160 192 68 52 85 3.5 2.6 4.5
FCCC/SBI/2016/INF.15. United Nations. Revised indicative contributions for the biennium
 United Nations FCCC/SBI//INF.15 Distr.: General 20 September English only Subsidiary Body for Implementation Forty fifth session Marrakech, 7 14 November Item 17(a) of the provisional agenda Administrative,
United Nations FCCC/SBI//INF.15 Distr.: General 20 September English only Subsidiary Body for Implementation Forty fifth session Marrakech, 7 14 November Item 17(a) of the provisional agenda Administrative,
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 1 of 6 14/09/2011 22:38 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia This is a list of countries by natural gas exports mostly based on The World Factbook [1] (https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2183rank.html).
1 of 6 14/09/2011 22:38 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia This is a list of countries by natural gas exports mostly based on The World Factbook [1] (https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2183rank.html).
5.01 Secondary education enrollment rate
 5.01 Secondary education enrollment rate Gross secondary education enrollment rate 2011 or most recent year available RANK COUNTRY/ECONOMY Value 1 Australia 8...131.3 2 Spain...128.5 3 Seychelles...123.9
5.01 Secondary education enrollment rate Gross secondary education enrollment rate 2011 or most recent year available RANK COUNTRY/ECONOMY Value 1 Australia 8...131.3 2 Spain...128.5 3 Seychelles...123.9
THEIR RANKING BY SIZE, 1999 AND Population (thousands) Country or area
 TABLE 5. POPULATION OF THE COUNTRIES OF THE WORLD AND THEIR RANKING BY SIZE, 1999 AND 2050 World 5 978 401 8 909 095 Afghanistan 21 923 61 004 45 25 Albania 3 113 4 322 129 132 Algeria 30 774 57 731 34
TABLE 5. POPULATION OF THE COUNTRIES OF THE WORLD AND THEIR RANKING BY SIZE, 1999 AND 2050 World 5 978 401 8 909 095 Afghanistan 21 923 61 004 45 25 Albania 3 113 4 322 129 132 Algeria 30 774 57 731 34
9.01 ICT use for business-to-business transactions
 9.01 ICT use for business-to-business transactions To what extent do businesses in your country use ICTs for communicating and carrying out transactions with other businesses? [1 = not at all; 7 = extensively]
9.01 ICT use for business-to-business transactions To what extent do businesses in your country use ICTs for communicating and carrying out transactions with other businesses? [1 = not at all; 7 = extensively]
Hotel Price Indicatice max. as from 22 Nov International per diem TOWNS/ DESTINATION COUNTRY
 Appendix 1: VLIR-UOS hotel allowances and international amounts valid from 22 Nov, 2017, onwards COUNTRY Afghanistan all destinations 180 72 Albania all destinations 175 96 Algeria all destinations 219
Appendix 1: VLIR-UOS hotel allowances and international amounts valid from 22 Nov, 2017, onwards COUNTRY Afghanistan all destinations 180 72 Albania all destinations 175 96 Algeria all destinations 219
Table 33 Electricity supply and consumption Gigawatt-hours and kilowatt-hours per capita
 Table 33 Electricity supply and consumption Table Notes is calculated as production plus imports minus exports. EIOU and losses refers to energy industries own use of electricity, including for pumped
Table 33 Electricity supply and consumption Table Notes is calculated as production plus imports minus exports. EIOU and losses refers to energy industries own use of electricity, including for pumped
Part III STATISTICAL ANNEX
 Part III STATISTICAL ANNEX STATISTICAL ANNEX 125 TABLE A1 Production of livestock products, 1995 2007 Meat Milk Eggs (Thousand tonnes) (Annual % (Thousand tonnes) (Annual % (Thousand tonnes) (Annual %
Part III STATISTICAL ANNEX STATISTICAL ANNEX 125 TABLE A1 Production of livestock products, 1995 2007 Meat Milk Eggs (Thousand tonnes) (Annual % (Thousand tonnes) (Annual % (Thousand tonnes) (Annual %
Table 20 Production, trade and supply of jet fuels Thousand metric tons and kilograms per capita
 Table 20 Production, trade and supply of jet fuels Table Notes Data refer to aviation gasoline, gasoline-type jet fuel and kerosene-type jet fuel. Production includes output from refineries and plants.
Table 20 Production, trade and supply of jet fuels Table Notes Data refer to aviation gasoline, gasoline-type jet fuel and kerosene-type jet fuel. Production includes output from refineries and plants.
Figure Geographic distribution Change in country participation in international nongovernmental organizations (NGOs): 1992 and 2002
 Figure 2.2.3. Geographic distribution Change in country participation in international nongovernmental s (NGOs): 1992 and 2002 This table gives the and (international NGOs of types A to F) for a given
Figure 2.2.3. Geographic distribution Change in country participation in international nongovernmental s (NGOs): 1992 and 2002 This table gives the and (international NGOs of types A to F) for a given
Summary of Contributions to UN Peacekeeping by Country and Post.
 Summary of Contributions to UN Peacekeeping by Country and Post. Police,UN Military, s and Troops 31/07/2018 1 Country Name POST MALE FEMALE TOTAL Algeria 2 3 4 5 6 7 Argentina Armenia Australia Austria
Summary of Contributions to UN Peacekeeping by Country and Post. Police,UN Military, s and Troops 31/07/2018 1 Country Name POST MALE FEMALE TOTAL Algeria 2 3 4 5 6 7 Argentina Armenia Australia Austria
Global Competitiveness Index Rankings
 APPENDIX B Global Competitiveness Index 2017 2018 Rankings The following pages report the GCI 2017 2018 rankings for the three subindexes (Table 1) and their corresponding pillars (Tables 2 4). Detailed
APPENDIX B Global Competitiveness Index 2017 2018 Rankings The following pages report the GCI 2017 2018 rankings for the three subindexes (Table 1) and their corresponding pillars (Tables 2 4). Detailed
International Sugar Organization WORLD SUGAR BALANCES 2002/ /16
 International Sugar Organization WORLD SUGAR BALANCES 2002/2003-2015/16 FEBRUARY 2016 WORLD SUGAR BALANCES (October/September) in thousand tonnes, tel quel Production 166,833 171,180 171,386 172,029 164,629
International Sugar Organization WORLD SUGAR BALANCES 2002/2003-2015/16 FEBRUARY 2016 WORLD SUGAR BALANCES (October/September) in thousand tonnes, tel quel Production 166,833 171,180 171,386 172,029 164,629
UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION EXECUTIVE BOARD. Hundred and sixty-fourth Session
 164 EX/INF.7 PARIS, 14 May 2002 English & French only UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION EXECUTIVE BOARD Hundred and sixty-fourth Session Item 3.1.1 of the provisional agenda
164 EX/INF.7 PARIS, 14 May 2002 English & French only UNITED NATIONS EDUCATIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND CULTURAL ORGANIZATION EXECUTIVE BOARD Hundred and sixty-fourth Session Item 3.1.1 of the provisional agenda
Price (CZK) with V.A.T.
 Price category 100 100 101* 101* 102 102 103 103 Weight (kg) Price (CZK) 0,5 kg 229,74 278,00 229,74 278,00 599,97 726,00 699,96 847,00 1 kg 260,32 315,00 319,82 387,00 649,55 786,00 749,54 907,00 2 kg
Price category 100 100 101* 101* 102 102 103 103 Weight (kg) Price (CZK) 0,5 kg 229,74 278,00 229,74 278,00 599,97 726,00 699,96 847,00 1 kg 260,32 315,00 319,82 387,00 649,55 786,00 749,54 907,00 2 kg
Section III Macroeconomic environment
 Data Tables Section III Macroeconomic environment 2.2: Data Tables Section III: Macroeconomic environment 422 3.01 Government budget balance General government budget balance as a percentage of GDP 2010
Data Tables Section III Macroeconomic environment 2.2: Data Tables Section III: Macroeconomic environment 422 3.01 Government budget balance General government budget balance as a percentage of GDP 2010
Country Rate Country Rate Country Rate
 Afghanistan $1.080 Alaska $0.099 Albania $0.259 Algeria $0.269 American Samoa $0.139 American Samoa (Mobile) $0.209 Andorra $0.089 Andorra (Mobile) $0.319 Angola $0.349 Angola (Mobile) $0.569 Anguilla
Afghanistan $1.080 Alaska $0.099 Albania $0.259 Algeria $0.269 American Samoa $0.139 American Samoa (Mobile) $0.209 Andorra $0.089 Andorra (Mobile) $0.319 Angola $0.349 Angola (Mobile) $0.569 Anguilla
Table 6A: External positions of reporting banks vis-à-vis all sectors
 Table 6A: External positions of reporting banks vis-à-vis all sectors Vis-à-vis individual countries in millions of US dollars All countries 29,841,389 29,212,683 28,267,608 28,518,559 75,538 1,110,929
Table 6A: External positions of reporting banks vis-à-vis all sectors Vis-à-vis individual countries in millions of US dollars All countries 29,841,389 29,212,683 28,267,608 28,518,559 75,538 1,110,929
Table 6A: External positions of reporting banks vis-à-vis all sectors
 Table 6A: External positions of reporting banks vis-à-vis all sectors Vis-à-vis individual countries in millions of US dollars All countries 29,227,490 29,015,072 28,531,726 28,040,625 1,147,749 1,456,989
Table 6A: External positions of reporting banks vis-à-vis all sectors Vis-à-vis individual countries in millions of US dollars All countries 29,227,490 29,015,072 28,531,726 28,040,625 1,147,749 1,456,989
2.01 Availability of latest technologies
 2.01 Availability of latest technologies To what extent are the latest technologies available in your country? [1 = not available; 7 = widely available] 2010 2011 weighted average RANK COUNTRY/ECONOMY
2.01 Availability of latest technologies To what extent are the latest technologies available in your country? [1 = not available; 7 = widely available] 2010 2011 weighted average RANK COUNTRY/ECONOMY
PwC Belgium Daily lump-sum allowances list for traveling abroad please visit for more information
 allowances list for traveling abroad Allowances given by an employer to his employee to cover foreign business travel expenses are costs proper to the employer. These allowances are tax exempt for the
allowances list for traveling abroad Allowances given by an employer to his employee to cover foreign business travel expenses are costs proper to the employer. These allowances are tax exempt for the
Table 7B: External loans and deposits of reporting banks vis-à-vis the non-bank sector
 Table 7B: External loans and deposits of reporting banks vis-à-vis the non-bank sector Vis-à-vis individual countries in millions of US dollars All countries 6,618,147 6,859,916 6,854,545 6,829,602 92,045
Table 7B: External loans and deposits of reporting banks vis-à-vis the non-bank sector Vis-à-vis individual countries in millions of US dollars All countries 6,618,147 6,859,916 6,854,545 6,829,602 92,045
Table 7B: External loans and deposits of reporting banks vis-à-vis the non-bank sector
 Table 7B: External loans and deposits of reporting banks vis-à-vis the non-bank sector Vis-à-vis individual countries in millions of US dollars All countries 6,871,257 7,040,175 6,972,597 6,946,298 71,425
Table 7B: External loans and deposits of reporting banks vis-à-vis the non-bank sector Vis-à-vis individual countries in millions of US dollars All countries 6,871,257 7,040,175 6,972,597 6,946,298 71,425
Effective October 1, 2006, Sprint Global Savings will no longer be available to new customers.
 Sprint Global Savings International Calling Plan Dial-1 ute International for Calls Made from 1 Effective October 1, 2006, Sprint Global Savings will no longer be available to new customers. Some calls
Sprint Global Savings International Calling Plan Dial-1 ute International for Calls Made from 1 Effective October 1, 2006, Sprint Global Savings will no longer be available to new customers. Some calls
A. Assessment of Member States under General Assembly resolution 71/268
 United Nations Secretariat Distr.: General 9 January 2017 Original: English Assessment of Member States contributions for the financing of the International Tribunal for the Prosecution of Persons Responsible
United Nations Secretariat Distr.: General 9 January 2017 Original: English Assessment of Member States contributions for the financing of the International Tribunal for the Prosecution of Persons Responsible
Enterprise Voice Trunking: Domestic, International and inbound Toll Free Rates
 Overage Domestic Long Distance toll $0.03 On net* Inbound Toll Free $0.029 International Long Distance toll See table below Customers subscribing to MOU packages of 100,000 minutes and larger will receive
Overage Domestic Long Distance toll $0.03 On net* Inbound Toll Free $0.029 International Long Distance toll See table below Customers subscribing to MOU packages of 100,000 minutes and larger will receive
Fiche 1 Quelques données de la Banque Mondiale
 Fiche 1 Quelques données de la Banque Mondiale 274 WORLD DEVELOPMENT REPORT 2000 2001 Table 1. Size of the economy Surface Population area density Gross national product (GNP) GNP per capita GNP measured
Fiche 1 Quelques données de la Banque Mondiale 274 WORLD DEVELOPMENT REPORT 2000 2001 Table 1. Size of the economy Surface Population area density Gross national product (GNP) GNP per capita GNP measured
Table 21 Production, trade and supply of gas oil/diesel oil Thousand metric tons and kilograms per capita
 Table Notes Production includes output from refineries and plants, together with quantities from other sources which include any blended biodiesel. Please refer to the Definitions Section on pages ix to
Table Notes Production includes output from refineries and plants, together with quantities from other sources which include any blended biodiesel. Please refer to the Definitions Section on pages ix to
Demographic and Socioeconomic Statistics
 Demographic and Socioeconomic Statistics Country WHO region number Population a annual growth rate in urban areas Total fertility rate a Adolescent fertility proportion b (000) 1995 (per woman) Year 1
Demographic and Socioeconomic Statistics Country WHO region number Population a annual growth rate in urban areas Total fertility rate a Adolescent fertility proportion b (000) 1995 (per woman) Year 1
Net Migration Rate per 1,000 Population. Rate of Natural Increase (%)
 mid-2009 Births per POPULATION, HEALTH, AND ENVIRONMENT DATA AND ESTIMATES Deaths per Rate of Natural Increase Net Migration Rate per 2025 2050 Change 2009 2050 Infant Mortality Rate a Percent of Total
mid-2009 Births per POPULATION, HEALTH, AND ENVIRONMENT DATA AND ESTIMATES Deaths per Rate of Natural Increase Net Migration Rate per 2025 2050 Change 2009 2050 Infant Mortality Rate a Percent of Total
JURISDICTIONS PARTICIPATING IN THE CONVENTION ON MUTUAL ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANCE IN TAX MATTERS
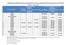 JURISDICTIONS PARTICIPATING IN THE CONVENTION ON MUTUAL ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANCE IN TAX MATTERS STATUS 27 JULY 2018 ORIGINAL CONVENTION 27-05-2010) OR OR 1. ALBANIA 01-03-2013 (AC) 08-08-2013 01-12-2013
JURISDICTIONS PARTICIPATING IN THE CONVENTION ON MUTUAL ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANCE IN TAX MATTERS STATUS 27 JULY 2018 ORIGINAL CONVENTION 27-05-2010) OR OR 1. ALBANIA 01-03-2013 (AC) 08-08-2013 01-12-2013
Table 33 Electricity supply and consumption Gigawatt-hours and kilowatt-hours per capita
 Terawatt-hours Table 33 Table Notes is calculated as Production plus Imports minus Exports. EIOU and losses refers to energy industries own use of electricity, including for pumped storage, and losses.
Terawatt-hours Table 33 Table Notes is calculated as Production plus Imports minus Exports. EIOU and losses refers to energy industries own use of electricity, including for pumped storage, and losses.
Calls made to a mobile phone may be charged a per minute International Mobile Termination Surcharge, see Sprint Wireline Fees and Surcharges Matrix.
 A discounted rate will apply to the country a customer calls the most (based on total dollars). If the customer has equal Dial-1 voice usage to two or more countries, the tie breakers will be the number
A discounted rate will apply to the country a customer calls the most (based on total dollars). If the customer has equal Dial-1 voice usage to two or more countries, the tie breakers will be the number
Percentage and total number of foreign national prisoners worldwide
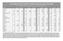 Percentage and total number of foreign national prisoners worldwide Source: World Prison Brief (International Centre for Prison Studies www.prisonstudies.org) 1 Country % Total 2003 FNP 2003 % Total 2005
Percentage and total number of foreign national prisoners worldwide Source: World Prison Brief (International Centre for Prison Studies www.prisonstudies.org) 1 Country % Total 2003 FNP 2003 % Total 2005
Table 13 Production, trade and supply of conventional crude oil Thousand metric tons; kilograms per capita; reserves production ratio (R/P) in years
 , trade and supply of conventional crude oil Thousand metric tons; kilograms per capita; reserves production ratio (R/P) in years Table Notes The Reserves / ratio refers to crude oil and natural gas liquids.
, trade and supply of conventional crude oil Thousand metric tons; kilograms per capita; reserves production ratio (R/P) in years Table Notes The Reserves / ratio refers to crude oil and natural gas liquids.
Table 33 Electricity supply and consumption Gigawatt-hours and kilowatt-hours per capita
 Table Notes is calculated as Production plus Imports minus Exports. EIOU and losses refers to energy industries own use of electricity, including for pumped storage, and losses. Total Final (TFC) refers
Table Notes is calculated as Production plus Imports minus Exports. EIOU and losses refers to energy industries own use of electricity, including for pumped storage, and losses. Total Final (TFC) refers
International Investment Position: World and Regional Tables
 BOPCOM/08/18 Twenty-First Meeting of the IMF Committee on Balance of Payments Statistics Washington, D.C., November 4 7, 2008 International Investment Position: World and Regional Tables Prepared by the
BOPCOM/08/18 Twenty-First Meeting of the IMF Committee on Balance of Payments Statistics Washington, D.C., November 4 7, 2008 International Investment Position: World and Regional Tables Prepared by the
Table 9A: Consolidated claims of reporting banks - immediate borrower basis
 Table 9A: Consolidated claims of reporting banks - immediate borrower basis On individual countries by maturity and sector / Amounts outstanding In millions of US dollars Total Consolidated cross-border
Table 9A: Consolidated claims of reporting banks - immediate borrower basis On individual countries by maturity and sector / Amounts outstanding In millions of US dollars Total Consolidated cross-border
Table 13 Production, trade and supply of conventional crude oil Thousand metric tons; kilograms per capita; reserves production ratio (R/P) in years
 Million metric tons Million metric tons Table 13, trade and supply of conventional crude oil Thousand metric tons; kilograms per capita; reserves production ratio (R/P) in years Table Notes The Reserves
Million metric tons Million metric tons Table 13, trade and supply of conventional crude oil Thousand metric tons; kilograms per capita; reserves production ratio (R/P) in years Table Notes The Reserves
Table 5 Production, trade and supply of hard coal Thousand metric tons and kilograms per capita
 Table Notes Production includes production from other sources as defined in the previous table. Data for China include brown coal. Please refer to the Definitions Section on pages ix to xv for the appropriate
Table Notes Production includes production from other sources as defined in the previous table. Data for China include brown coal. Please refer to the Definitions Section on pages ix to xv for the appropriate
SAVER PLAN Standard Rate Table Service Description Rate AUD$ (per minute) Flagfall Other Charges
 SAVER PLAN Standard Rate Table Service Description Voicemail Retrieval (121, 1211, 1212, 1213, 1218, 1219) Call Forward Hello Mobile Customer Care via 126 999 Hello Mobile Customer Care via 1300 126 999
SAVER PLAN Standard Rate Table Service Description Voicemail Retrieval (121, 1211, 1212, 1213, 1218, 1219) Call Forward Hello Mobile Customer Care via 126 999 Hello Mobile Customer Care via 1300 126 999
Table III Immigrant Visas Issued (by Foreign State of Chargeability or Place of Birth) Fiscal Year 2018
 Africa Algeria 437 2 198 18 1,343 1,998 Angola 26 0 14 1 17 58 Benin 138 0 60 1 237 436 Botswana 10 0 4 0 0 14 Burkina Faso 121 2 35 3 107 268 Burundi 74 0 13 0 97 184 Cabo Verde 395 1 980 6 1 1,383 Cameroon
Africa Algeria 437 2 198 18 1,343 1,998 Angola 26 0 14 1 17 58 Benin 138 0 60 1 237 436 Botswana 10 0 4 0 0 14 Burkina Faso 121 2 35 3 107 268 Burundi 74 0 13 0 97 184 Cabo Verde 395 1 980 6 1 1,383 Cameroon
Annex. Courtesy EcoPort (www.ecoport.org) : P. Oudhia
 Courtesy EcoPort (www.ecoport.org) : P. Oudhia TABLE 1 Basic data on countries and areas Country/area Land area a Population 2004 GDP 2004 Total (1 000 ha) (1 000) Density (Population/ km 2 ) Annual growth
Courtesy EcoPort (www.ecoport.org) : P. Oudhia TABLE 1 Basic data on countries and areas Country/area Land area a Population 2004 GDP 2004 Total (1 000 ha) (1 000) Density (Population/ km 2 ) Annual growth
Lincolnshire Business Call Charges
 Lincolnshire Business Call Charges Geographic Calls Call Charge (Pence Per Minute, At All Times) Voice Tariff KCOM 2 KCOM calling (K)* Local (A1) National (A2 & B) Ex VAT Inc. VAT Ex VAT Inc. VAT Ex VAT
Lincolnshire Business Call Charges Geographic Calls Call Charge (Pence Per Minute, At All Times) Voice Tariff KCOM 2 KCOM calling (K)* Local (A1) National (A2 & B) Ex VAT Inc. VAT Ex VAT Inc. VAT Ex VAT
Table 13 Production, trade and supply of conventional crude oil Thousand metric tons; kilograms per capita; reserves production ratio (R/P) in years
 Table 13, trade and supply of conventional crude oil Thousand metric tons; kilograms per capita; reserves production ratio (R/P) in years Table Notes The Reserves / ratio refers to crude oil and natural
Table 13, trade and supply of conventional crude oil Thousand metric tons; kilograms per capita; reserves production ratio (R/P) in years Table Notes The Reserves / ratio refers to crude oil and natural
Table 2 Components of total energy supply Petajoules and Gigajoules per capita
 Table 2 Components of total energy supply Table Notes Production Included in the production of primary energy for Solids are hard coal, lignite, peat, oil shale, primary solid biofuels and wastes; Liquids
Table 2 Components of total energy supply Table Notes Production Included in the production of primary energy for Solids are hard coal, lignite, peat, oil shale, primary solid biofuels and wastes; Liquids
Table 5 Production, trade and supply of hard coal Thousand metric tons and kilograms per capita
 Table Notes Production includes production from other sources as defined in the previous table. Data for China include brown coal. Please refer to the Definitions Section on pages ix to xv for the appropriate
Table Notes Production includes production from other sources as defined in the previous table. Data for China include brown coal. Please refer to the Definitions Section on pages ix to xv for the appropriate
2014/ /2015 Ghana / /2015 Syrian Arab Republic / /2015
 Exhibit C: international cotton trade data Source: International Cotton Advisory Committee, ICAC World Cotton Database, available at www.icac.org, last checked 1 April 2016. International Cotton Advisory
Exhibit C: international cotton trade data Source: International Cotton Advisory Committee, ICAC World Cotton Database, available at www.icac.org, last checked 1 April 2016. International Cotton Advisory
GLOBAL ECONOMIC PROSPECTS January Statistical Annex
 1 TABLE A.1 GDP Growth (Constant 2010 U.S. Dollars) Annual estimates and forecasts a Quarterly growth b 2013 2014 00-10 c 2011 2012 2013 2014e 2015f 2016f 2017f Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 World 2.8 3.1 2.4 2.5
1 TABLE A.1 GDP Growth (Constant 2010 U.S. Dollars) Annual estimates and forecasts a Quarterly growth b 2013 2014 00-10 c 2011 2012 2013 2014e 2015f 2016f 2017f Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 World 2.8 3.1 2.4 2.5
Percentage living alone (9)
 Number (thousands) POPULATION AGED 60 YEARS OR OLDER Percentage Percentage 80 years or currently older married 1 Percentage of total population Percentage living alone Percentage in labour force 2 Sex
Number (thousands) POPULATION AGED 60 YEARS OR OLDER Percentage Percentage 80 years or currently older married 1 Percentage of total population Percentage living alone Percentage in labour force 2 Sex
Table 16 Refinery distillation capacity, throughput and output Thousand metric tons
 Million metric tons Table 16 Refinery distillation capacity, throughput and output Table Notes Output is equal to the sum of production from refineries for aviation gasoline, bitumen, gas/diesel oil, ethane,
Million metric tons Table 16 Refinery distillation capacity, throughput and output Table Notes Output is equal to the sum of production from refineries for aviation gasoline, bitumen, gas/diesel oil, ethane,
Governance Indicators World Map: Voice & Accountability
 Governance Indicators: Voice & Accountability (VA), Political Stability (PS), Government Effectiveness (GE), Regulatory Quality (RQ), Rule of Law (RL), Control of Corruption (CC) Percentile Ranks, 2004
Governance Indicators: Voice & Accountability (VA), Political Stability (PS), Government Effectiveness (GE), Regulatory Quality (RQ), Rule of Law (RL), Control of Corruption (CC) Percentile Ranks, 2004
Global Performance (Data in US Dollars)
 Global Performance (Data in US Dollars) April 2007 vs April Year to Date - April 2007 vs April 2007 2007 2007 Occ. ADR RevPAR 2007 2007 2007 Occ. ADR RevPAR Asia Pacific 69.3 70.9 139.42 125.23 96.62 88.77-2.2
Global Performance (Data in US Dollars) April 2007 vs April Year to Date - April 2007 vs April 2007 2007 2007 Occ. ADR RevPAR 2007 2007 2007 Occ. ADR RevPAR Asia Pacific 69.3 70.9 139.42 125.23 96.62 88.77-2.2
up to and including 31 December 2002
 The ISO Survey of ISO 9000 and ISO 14001 Certificates Twelfth cycle : up to and including 31 December T a b l e o f c o n t e n t s The ISO Survey : twelfth cycle () highlights......................................................................
The ISO Survey of ISO 9000 and ISO 14001 Certificates Twelfth cycle : up to and including 31 December T a b l e o f c o n t e n t s The ISO Survey : twelfth cycle () highlights......................................................................
Global Performance (Data in US Dollars)
 Global Performance (Data in US Dollars) September 2008 vs September Year to Date - September 2008 vs September September YTD 2008 2008 2008 Occ. ADR RevPAR 2008 2008 2008 Occ. ADR RevPAR Asia Pacific 61.3
Global Performance (Data in US Dollars) September 2008 vs September Year to Date - September 2008 vs September September YTD 2008 2008 2008 Occ. ADR RevPAR 2008 2008 2008 Occ. ADR RevPAR Asia Pacific 61.3
In all tables, the regional breakdown reflects geographical rather than economic or political groupings.
 nnex 5 Annex Notes on the annex tables In all tables, the regional breakdown reflects geographical rather than economic or political groupings. = not available 0 = either a true zero or an insignificant
nnex 5 Annex Notes on the annex tables In all tables, the regional breakdown reflects geographical rather than economic or political groupings. = not available 0 = either a true zero or an insignificant
Table 23 Production of minor oil products from refineries - by type Thousand metric tons
 Table 23 Production of minor oil from refineries - by type Table Notes Data refer to production from refineries of refinery, ethane, naphtha, lubricants, bitumen, paraffin, petroleum, white spirit, and
Table 23 Production of minor oil from refineries - by type Table Notes Data refer to production from refineries of refinery, ethane, naphtha, lubricants, bitumen, paraffin, petroleum, white spirit, and
Delinquent Payments Voluntary Assessed Contributions to the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control
 Delinquent Payments Voluntary Assessed Contributions to the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control The operations of the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) are principally financed through
Delinquent Payments Voluntary Assessed Contributions to the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control The operations of the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) are principally financed through
SOFTWARE REGIOGRAPH ANALYSIS PLANNING STRATEGY
 SOFTWARE REGIOGRAPH RegioGraph allows you to quickly and easily display your company data on digital maps. In combination with purchasing power data, this reveals trends and relationships that would not
SOFTWARE REGIOGRAPH RegioGraph allows you to quickly and easily display your company data on digital maps. In combination with purchasing power data, this reveals trends and relationships that would not
C H AP TE R 1 G LO BAL EC O NO MIC P ROS P EC TS J U NE 2017
 4 C H AP TE R 1 G LO BAL EC O NO MIC P ROS P EC TS J U NE 2017 TABLE 1.1 Real GDP 1 (percent change from previous year) 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2016 2017 2018 2019 Percentage point differences Estimates
4 C H AP TE R 1 G LO BAL EC O NO MIC P ROS P EC TS J U NE 2017 TABLE 1.1 Real GDP 1 (percent change from previous year) 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2016 2017 2018 2019 Percentage point differences Estimates
Microsoft Social Engagement Translation Guide Last Updated: October 2017
 Microsoft Social Engagement Translation Guide Last Updated: October 2017 Microsoft Social Engagement is translated and supported by Microsoft and made generally available in the countries/regions and languages
Microsoft Social Engagement Translation Guide Last Updated: October 2017 Microsoft Social Engagement is translated and supported by Microsoft and made generally available in the countries/regions and languages
Table 3A Early childhood care and education (ECCE): care
 7 238 / ANNEX 2 Early childhood care and education (ECCE): care Education for All Global Monitoring Report Arab States Algeria Bahrain Djibouti Egypt Iraq Jordan Kuwait Lebanon Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Mauritania
7 238 / ANNEX 2 Early childhood care and education (ECCE): care Education for All Global Monitoring Report Arab States Algeria Bahrain Djibouti Egypt Iraq Jordan Kuwait Lebanon Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Mauritania
JURISDICTIONS PARTICIPATING IN THE CONVENTION ON MUTUAL ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANCE IN TAX MATTERS
 JURISDICTIONS PARTICIPATING IN THE CONVENTION ON MUTUAL ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANCE IN TAX MATTERS COUNTRY/JURISDICTION * STATUS 15 DECEMBER 2017 1. ALBANIA 01-03-2013 (AC) 08-08-2013 01-12-2013 2. ANDORRA
JURISDICTIONS PARTICIPATING IN THE CONVENTION ON MUTUAL ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANCE IN TAX MATTERS COUNTRY/JURISDICTION * STATUS 15 DECEMBER 2017 1. ALBANIA 01-03-2013 (AC) 08-08-2013 01-12-2013 2. ANDORRA
International Tariff Guide for Residential Customers
 International Tariff Guide for Residential Customers Prices from 1 st December 2014 Notes 15.97p call set-up fee applies to Standard BT international rate calls made with Unlimited Calls, Unlimited Evening
International Tariff Guide for Residential Customers Prices from 1 st December 2014 Notes 15.97p call set-up fee applies to Standard BT international rate calls made with Unlimited Calls, Unlimited Evening
Table 16 Refinery distillation capacity, throughput and output Thousand metric tons
 Table 16 Refinery distillation capacity, throughput and output Table Notes Output is equal to the sum of production from refineries for aviation gasoline, bitumen, gas/diesel oil, ethane, feedstocks, gasoline-type
Table 16 Refinery distillation capacity, throughput and output Table Notes Output is equal to the sum of production from refineries for aviation gasoline, bitumen, gas/diesel oil, ethane, feedstocks, gasoline-type
Frontier Simply International Rate Plans
 Frontier Simply International Rate Plans Residential - Optional International Rate Plans Asia Canada Europe Mexico Block-Of-Time (minutes included per option) 125 150 150 50 Monthly Recurring Charge $4.99
Frontier Simply International Rate Plans Residential - Optional International Rate Plans Asia Canada Europe Mexico Block-Of-Time (minutes included per option) 125 150 150 50 Monthly Recurring Charge $4.99
JURISDICTIONS PARTICIPATING IN THE CONVENTION ON MUTUAL ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANCE IN TAX MATTERS
 JURISDICTIONS PARTICIPATING IN THE CONVENTION ON MUTUAL ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANCE IN TAX MATTERS COUNTRY/JURISDICTION * STATUS 10 NOVEMBER 2017 1. ALBANIA 01-03-2013 (AC) 08-08-2013 01-12-2013 2. ANDORRA
JURISDICTIONS PARTICIPATING IN THE CONVENTION ON MUTUAL ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANCE IN TAX MATTERS COUNTRY/JURISDICTION * STATUS 10 NOVEMBER 2017 1. ALBANIA 01-03-2013 (AC) 08-08-2013 01-12-2013 2. ANDORRA
SOFTWARE REGIOGRAPH ANALYSIS PLANNING STRATEGY
 SOFTWARE REGIOGRAPH RegioGraph allows you to quickly and easily display your company data on digital maps. In combination with purchasing power data, this reveals trends and relationships that would not
SOFTWARE REGIOGRAPH RegioGraph allows you to quickly and easily display your company data on digital maps. In combination with purchasing power data, this reveals trends and relationships that would not
International Direct Dial (IDD)
 International Direct Dial (IDD) Flagfall (retail) Cost/min (retail) International Calls (per 60 secs) ex. GST inc. GST ex. GST inc. GST Zone Afghanistan $2.570000 $2.827000 IDD Zone1 Albania $2.290000
International Direct Dial (IDD) Flagfall (retail) Cost/min (retail) International Calls (per 60 secs) ex. GST inc. GST ex. GST inc. GST Zone Afghanistan $2.570000 $2.827000 IDD Zone1 Albania $2.290000
Table 2 Components of total energy supply Petajoules and Gigajoules per capita
 Table 2 Components of total energy supply Table Notes Included in the Primary energy production for Solids are hard coal, lignite, peat, oil shale, primary solid biofuels and wastes; Liquids are comprised
Table 2 Components of total energy supply Table Notes Included in the Primary energy production for Solids are hard coal, lignite, peat, oil shale, primary solid biofuels and wastes; Liquids are comprised
Table 1. Demographics and Standards of Living Across Countries Total Population Annual Annual # Under 5 GNP % under 5 s Net primary Total Maternal
 Table 1. Demographics and Standards of Living Across Countries Total Population Annual Annual # Under 5 GNP % under 5 s Net primary Total Maternal Population under 18 # of births < age 5 deaths mortality
Table 1. Demographics and Standards of Living Across Countries Total Population Annual Annual # Under 5 GNP % under 5 s Net primary Total Maternal Population under 18 # of births < age 5 deaths mortality
REGIOGRAPH SOFTWARE AVAILABLE VERSIONS UPDATE AND UPGRADE PRICE ONGOING SAVINGS OF 50%! PRICE LIST
 PRICE LIST REGIOGRAPH SOFTWARE RegioGraph allows you to visualize and evaluate your company data directly on digital maps. This provides insight into data trends and relationships and lends objectivity
PRICE LIST REGIOGRAPH SOFTWARE RegioGraph allows you to visualize and evaluate your company data directly on digital maps. This provides insight into data trends and relationships and lends objectivity
Production of minor oil products from refineries - by type Thousand metric tons
 Production of minor oil from refineries - by type Table 23 Table Notes Data refer to production from refineries of refinery, ethane, naphtha, lubricants, bitumen, paraffin, petroleum, white spirit, and
Production of minor oil from refineries - by type Table 23 Table Notes Data refer to production from refineries of refinery, ethane, naphtha, lubricants, bitumen, paraffin, petroleum, white spirit, and
Call rates are charged on a pay-as-you-go (PAYG) basis, billed per minute. International rates are subject to change without notice.
 Updated: 23 January 2018 International call rates apply to all Pennytel customers who have chosen to enable the international calling feature on their service. Call rates are charged on a pay-as-you-go
Updated: 23 January 2018 International call rates apply to all Pennytel customers who have chosen to enable the international calling feature on their service. Call rates are charged on a pay-as-you-go
Updated: 13 June 2018
 Updated: 13 June 2018 PENNYTEL AUSTRALIA PTY LTD 4/580 George Street Sydney NSW 2000 ABN: 12 166 566 63 PennyTel mobile supports international calling. For security, this service is switched off by default.
Updated: 13 June 2018 PENNYTEL AUSTRALIA PTY LTD 4/580 George Street Sydney NSW 2000 ABN: 12 166 566 63 PennyTel mobile supports international calling. For security, this service is switched off by default.
APPENDIX B KEY ASPECTS OF LONG-TERM FINANCE
 GLOBAL FINANCIAL DEVELOPMENT REPORT 2015/2016 APPENDIX B 165 APPENDIX B KEY ASPECTS OF LONG-TERM FINANCE Economies and Their Maturity Structure of Finance, 2013 GDP at Afghanistan 8.9 8.2 0.7 0.00 Albania
GLOBAL FINANCIAL DEVELOPMENT REPORT 2015/2016 APPENDIX B 165 APPENDIX B KEY ASPECTS OF LONG-TERM FINANCE Economies and Their Maturity Structure of Finance, 2013 GDP at Afghanistan 8.9 8.2 0.7 0.00 Albania
Euromoney Country Risk Q RESULTS
 1 Euromoney Country Risk Q3 218 RESULTS 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction (Scoring) 2. Q/Q update 3. Y/Y update 4. Contacts 3 SCORING Euromoney Country Risk is a platform designed to capture and aggregate
1 Euromoney Country Risk Q3 218 RESULTS 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction (Scoring) 2. Q/Q update 3. Y/Y update 4. Contacts 3 SCORING Euromoney Country Risk is a platform designed to capture and aggregate
Doing business in a more transparent world
 2012 Doing business in a more transparent world COMPARING REGULATION FOR DOMESTIC FIRMS IN 183 ECONOMIES ii DOING BUSINESS 2012 THE DOING BUSINESS WEBSITE Current features News on the Doing Business project
2012 Doing business in a more transparent world COMPARING REGULATION FOR DOMESTIC FIRMS IN 183 ECONOMIES ii DOING BUSINESS 2012 THE DOING BUSINESS WEBSITE Current features News on the Doing Business project
Foreign Country per diem and accommodation costs (valid as of January 1, 2016)
 Foreign Country per diem and accommodation costs (valid as of January 1, 2016) Country Town per diem in Accommodation costs up to... with proof*) Afghanistan 25 95 Albania 24 90 Algeria 32 190 Andorra
Foreign Country per diem and accommodation costs (valid as of January 1, 2016) Country Town per diem in Accommodation costs up to... with proof*) Afghanistan 25 95 Albania 24 90 Algeria 32 190 Andorra
Level 3 Certificate Quantitative Problem Solving (MEI) H867/02 Statistical Problem Solving. Wednesday 24 May 2017 Morning Time allowed: 2 hours
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Level 3 Certificate Quantitative Problem Solving (MEI) H867/02 Statistical Problem Solving Insert *6835425514* Wednesday 24 May 2017 Morning Time allowed: 2 hours INFORMATION FOR
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Level 3 Certificate Quantitative Problem Solving (MEI) H867/02 Statistical Problem Solving Insert *6835425514* Wednesday 24 May 2017 Morning Time allowed: 2 hours INFORMATION FOR
Retail prices (street price), US$/gram
 3.4 Prices 3.4.1 Opiates: Wholesale, street prices and purity levels Retail prices (street price), US$/gram EUROPE 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Austria
3.4 Prices 3.4.1 Opiates: Wholesale, street prices and purity levels Retail prices (street price), US$/gram EUROPE 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Austria
The Great Transition: Shifting from Fossil Fuels to Solar and Wind Energy Supporting Data - Hydropower
 The Great Transition: Shifting from Fossil Fuels to Solar and Wind Energy Supporting Data - Hydropower World Installed Hydroelectric Generating Capacity, 1980-2013 GRAPH: World Installed Hydroelectric
The Great Transition: Shifting from Fossil Fuels to Solar and Wind Energy Supporting Data - Hydropower World Installed Hydroelectric Generating Capacity, 1980-2013 GRAPH: World Installed Hydroelectric
RATES BROCHURE. Our locations: Ave NE, Calgary AB T2A 6C Parsons Road, Edmonton AB T6N 1B4 102 Central Ave, Sweet Grass MT 59484
 RATES BROCHURE Ship as if you were from the United States Use DYK Post s USA address to ship Save up to 70% on U.S. Bound or International Shipping Get the reverse logistics services for your return parcels
RATES BROCHURE Ship as if you were from the United States Use DYK Post s USA address to ship Save up to 70% on U.S. Bound or International Shipping Get the reverse logistics services for your return parcels
Table 6a: Red List Category summary country totals (Animals)
 IUCN Red List version 2017-2: Table 6a Last Updated: 14 September 2017 Table 6a: Red List Category summary country totals (Animals) IUCN Red List Categories: EX - Extinct, EW - Extinct in the Wild, CR
IUCN Red List version 2017-2: Table 6a Last Updated: 14 September 2017 Table 6a: Red List Category summary country totals (Animals) IUCN Red List Categories: EX - Extinct, EW - Extinct in the Wild, CR
Table 6a: Red List Category summary country totals (Animals)
 IUCN Red List version 2017-3: Table 6a Last Updated: 05 December 2017 Table 6a: Red List Category summary country totals (Animals) IUCN Red List Categories: EX - Extinct, EW - Extinct in the Wild, CR -
IUCN Red List version 2017-3: Table 6a Last Updated: 05 December 2017 Table 6a: Red List Category summary country totals (Animals) IUCN Red List Categories: EX - Extinct, EW - Extinct in the Wild, CR -
Table 6a: Red List Category summary country totals (Animals)
 IUCN Red List version 2016-3: Table 6a Last Updated: 13 December 2016 Table 6a: Red List Category summary country totals (Animals) IUCN Red List Categories: EX - Extinct, EW - Extinct in the Wild, CR -
IUCN Red List version 2016-3: Table 6a Last Updated: 13 December 2016 Table 6a: Red List Category summary country totals (Animals) IUCN Red List Categories: EX - Extinct, EW - Extinct in the Wild, CR -
International Passenger Traffic to and from Reporting Airports (in Thousands) by Country Table 11
 International Passenger Traffic to and from Reporting Airports (in Thousands) by Country 2005-2015 Table 11 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 AUSTRIA 1 796 1 788 1 877 1 826 1 746
International Passenger Traffic to and from Reporting Airports (in Thousands) by Country 2005-2015 Table 11 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 AUSTRIA 1 796 1 788 1 877 1 826 1 746
Technical Cooperation Report for 2015
 Technical Cooperation Report for 2015 Report by the Director General Supplement GC(60)/INF/4/SUPPLEMENT TECHNICAL COOPERATION REPORT FOR 2015 REPORT BY THE DIRECTOR GENERAL Printed by the International
Technical Cooperation Report for 2015 Report by the Director General Supplement GC(60)/INF/4/SUPPLEMENT TECHNICAL COOPERATION REPORT FOR 2015 REPORT BY THE DIRECTOR GENERAL Printed by the International
Imports of seed for sowing by country Calendar year 2011 Source: ISF compilation based on official statistics and international seed trade reports
 USA 157,432 15,562 464 173,458 523 318 67 908 Germany 195,159 5,913 520 201,592 595 97 22 714 France 125,701 4,389 277 130,367 522 150 11 683 Netherlands 140,899 12,253 796 153,948 250 330 48 628 Italy
USA 157,432 15,562 464 173,458 523 318 67 908 Germany 195,159 5,913 520 201,592 595 97 22 714 France 125,701 4,389 277 130,367 522 150 11 683 Netherlands 140,899 12,253 796 153,948 250 330 48 628 Italy
