Who are ROLLVIS? medical electrical cylinders m easuring machines and laser machines robotics, chemicals, a nd all other fi elds of high technology
|
|
|
- Randolph Alexander
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Who are ROLLVIS? After its founding in 1970, ROLLVIS SA soon began to focus on the manufacture and marketing of satellite roller screws under the trademark «Rollvis swiss». Now a benchmark in this highly specialised fi eld, ROLLVIS SA has invested in the most powerful machines for the production of screws with low tolerance margins designed to individual specifi cations. A fast-growing company with a young and highly qualifi ed workforce, ROLLVIS SA recently moved into new ultra-modern premises near to Geneva. It is structured to preserve its human scale and its capacity to listen and adapt perfectly to its customers requirements. Four decades and more of skills and experience combined with the latest high-end techniques ensure its products comply with the most stringent and demanding standards, notably in the following applications: aeronautics, space defence, car industry moulding, injection (plastics and metal) optics, graphics special machine tools medical electrical cylinders m easuring machines and laser machines robotics, chemicals, a nd all other fi elds of high technology To ensure its satellite roller screws always gain by the latest progress in technology to make them ever more reliable, ROLLVIS SA has set up its own «Research and Development» department where its highly qualifi ed engineers and technicians use the most recent and most powerful design software available in their unceasing quest for the control of avant-garde technologies. New processes are constantly reviewed to optimise the product, production system, quality control, tests and trials for individual requirements. Even the most exacting customers swear by the outstanding reliability and quality of ROLLVIS products. Present on all the continents, over time ROLLVIS SA has built up an excellent sales network, so that wherever you are in the world, there are experts to give you answers and advice.
3 contents Introduction Satellite roller screws compared to ball screws Types of roller screws 3 and 4 Identifi cation system 5 Accuracy / Effi ciency 6 Geometry 7 Preloading 8 Preloading examples 9 2 Mean speed and axial load 10 Nominal lifespan 11 Rigidity 12 Rotation speed 13 Driving torque 14 and 15 Calculation example 16 and 17 Lubrication 18 and 19 Handling advice 20 Preference program Type RV diameters of 3.5 to Type RV diameters of 15 to Type RV diameters of 25 to Type RV diameters of 39 to Type RV diameters of 51 to Type RV diameters of 80 to Type BRV diameters of 8 to Type RVR diameters of 8 to Applications 30 à 32 No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions. i We reserve the right to make changes in the interest of technical progress
4 Introduction ROLLVIS satellite roller screws are used to transform rotary movements into linear movements and vice versa. The bearing elements are threaded rollers between the screw and the nut. The high number of points of contact enables satellite roller screws to support very heavy loads. The ROLLVIS manufacturing programme comprises satellite roller screws without roller recycling (types RV and BRV) and with roller recycling (type RVR), in a range of accuracy classes. The ROLLVIS range also includes other types such as the reverse roller screw (type RVI) and the differential screw (type RVD). Satellite roller screws compared to ball screws The satellite roller screw is similar to the ball screw with the difference that the load transfer elements are threaded rollers. The main advantage of satellite roller screws is that they have a high number of points of contact to support the load. Load capacity and lifespan The main advantage of roller screws compared to ball screws is that their admissible static and dynamic load capacities are higher. The bearing function is ensured by threaded rollers instead of balls and the load is spread over a higher number of points of contact. Satellite roller screws like ball screws use Hertz s law. The admissible Hertz pressure is the same for satellite roller screws and ball screws. Satellite roller screws thus have a static load 3 times greater than that of ball screws and their lifespan is 15 times longer. Speed & acceleration Satellite roller screws can rotate much faster and support much greater acceleration. RV and BRV satellite roller screws are designed so that the rollers are not recycled. This means the mechanism can support twice the rotation speed of a ball screw. Acceleration can reach up to 3g. Lead & pitch Planetary roller screw can be achieved with smaller leads compared to ball screws. As the lead is a function of the pitch of the planetary roller screw, the lead can be very small (0.5mm and even less). Planetary roller screws can be achieved with entire or real numbers (i.e. lead of 3.32mm per revolution), which avoid reduction gears. This is an advantage compared to ball screws. The lead can be chosen and realised without any geometrical changes of both the screw shaft and the nut body, which allows updates with minor changes. In a ball screw the lead is limited by the dimension (OD) of the bearing ball, which is a standard feature. Rigidity & strength The many points of contact give a satellite roller screw greater rigidity and shock tolerance than a ball screw
5 Types of roller screws RV and BRV screws The main elements of RV and BRV satellite roller screws are the screw, the nut and satellite rollers. The screw has a multiple-start thread. The angle between the fl anks is 90 and the profi le is triangular. The nut has an internal thread identical to that of the screw. The rollers have a single-start thread with an angle the same as that of the nut. This ensures there is no axial movement between the nut and the rollers. The rollers do not therefore need to be recycled. The fl anks of the roller thread are convex. At each end of the rollers there is a cylindrical pivot and gear teeth. The pivots are mounted in the holes of the end rings, thus ensuring the rollers are equidistant. The end rings are fl oated in the nut body and axially secured with circlips. The gear teeth engage in gear wheels fi xed in the nut. This guides the rollers parallel to the axis to ensure perfect functioning. RV et BRV RVR screws RVR satellite roller screws have very fi ne threads and are used when very great positioning accuracy is required along with high rigidity and load-carrying capacity. The main elements of RVR satellite roller screws are the screw, the nut and the rollers which are guided and maintained at the correct distance in a cage. The screw has a single- or two-start thread with a triangular profi le. The angle between the fl anks is 90. The nut has the same internal thread as the screw. The rollers are not threaded but have grooves perpendicular to the screw axis. The distance between the grooves matches the exposed thread of the screw and nut. The fl anks are convex and the angle between them is 90. When the screw or nut rotates, the rollers are axially displaced in the nut. After a complete revolution, each roller is returned to its initial position by two cams at the end of each nut. They can be recycled this way because there is a groove the length of the nut. RVR The cage pockets are slightly longer than the rollers to enable them to move axially within the nut
6 Types of roller screws ( ctd.) RVI screws RVI satellite roller screws work on the same principle as RV and BRV screws except that their nut system is reversed. This means the rollers themselves rotate around the screw (instead of the nut in RV and BRV screws) and move axially within the nut. Apart from the screw threading where the rollers orbit, the journal is smooth and can have a special shape (e.g.: antirotation). The nut is threaded along its entire length and is much longer than on RV and BRV screws. It governs the overall travel of the complete screw and therefore limits it if needed. RVI RVD screws The RVD differential screw is actually a variant of the RV and BRV screws. Its components, expertly calculated and adjusted, are used to produce extremely fi ne threads (less than 0.02 mm). The movement of the rollers in this somewhat complex mechanism does however prevent a wide range of travel. The nuts are larger than on the RV and BRV types
7 Identifi cation system ExampleRV2 1 0 /30.5.R Design RV = ground thread, non-recycling rollers BRV = rolled thread, non-recycling rollers RVR = ground thread, recycling rollers RVI = ground thread reverse system RVD = ground thread differential screw Nut types 1 = single nut 2 = split nut 3 = double nut Nut design 1 = cylindrical nut 6 = nut with fl ange at one end 7 = nut with central fl ange 8 = special nut design Seal 0 = without wipers 1 = with wipers Screw diameter d 0 in mm Nominal lead P in mm Thread direction R = right B = right/left L = left Thread accuracyg1 = 6 µm/300 mm G3 = 12 µm/300 mm G5 = 23 µm/300 mm G9 = 200 µm/1000 mm (BRV only) 6-digit number to identify customer s specification - 5 -
8 Accuracy Satellite roller screws are divided into tolerance classes based on DIN 69051, part 3 (ball screws). The determining factor is the lead error V 300p referred to a thread length of 300 mm. The table opposite shows the tolerance classes: Tolerance Cl V 300p G1 6 µm/300 mm G3 12 µm/300 mm G5 23 µm/300 mm G9 200 µm/1000 mm Positioning satellite roller screws are supplied in tolerance classes G1, G3 and G5 and transport satellite roller screws (type BRV) in tolerance class G9. Lead accuracy symbols according to DIN 69051/3 P e 0 V 300p e p V up V 2πp L u nominal lead difference between required lead and nominal lead difference between actual and nominal lead over 300 mm difference between actual and nominal lead over a length L u travel variation over a length L u travel variation over one revolution effective travel Lead error The lead error e p relative to effective travel L u is calculated for the transport satellite roller screw by the following formula: Lead errors e p for positioning satellite roller screws are shown in the table opposite. For tolerance classes G1 and G3, the lead and torque diagrams are supplied with the screws. Lead is checked by a 3D measuring machine or on a measuring bench equipped with a laser interferometer. L E p in microns u for tolerance class up to morethan G1 G3 G5 315 mm mm 400 mm mm 500 mm mm 630 mm mm 800 mm mm 1000 mm mm 1250 mm mm 1600 mm mm 2000 mm mm 2500 mm mm 3150 mm 93 Effi ciency η 1 η2 Satellite roller screw Rollvis satellite roller screws achieve high rates of mechanical effi ciency. The figure opposite shows effi ciency rates η 1 for the ascent and η 2 for the descent, according to the helix angle. The effi ciency of a trapezoidal thread screw is shown for comparison. Satellite roller screws, unlike friction screws, are not self-locking. 60 Efficiency in % Trapezoidal thread screw Advantages High axial load capacity Long lifespan High effi ciency No backlash Extremely high rigidity Accuracy greater than 6 µm/300 mm High rotation speed (RV and BRV systems) Small leads (from 0.25 mm) with wide diameters (system RVR) Fast acceleration and deceleration Helix angle ϕ in deg. Applications Rollvis satellite roller screws have proved their superior worth in many fi elds of applications such as: Machine tools Measuring machines Specifi c machines (benders) Robotics Aeronautics (aeroplanes and helicopters) Space (rockets and satellites) Defence (tanks, cannons, missiles, etc.) Oil industry Nuclear industry Medical Chemical industry Optical Telescopes Graphics Laser machines Injection moulding machines Car industry - 6 -
9 Geometry Nut geometry and shape Standard satellite roller screws are available with 3 nut designs: single nut (ES) split nut (EF) double nut (ED) Single nuts have low axial backlash of 0.01 to 0.03 mm. The split cylindrical nut is preloaded by clamping the two halves of the nut in a housing. A precision spacer ring is mounted between the two halves to maintain the required level of preloading. Split nuts with a fl ange at one end have a spacer ring designed to hold the halves apart. The halves are aligned by a parallel key. Double nuts are preloaded in the same way as split nuts. SINGLE NUTS: Nuts in one piece with axial backlash Wipers (if requested by the customer) SPLIT NUTS: Nuts in two pieces, preloaded, without backlash Same dimensions as single nuts Reduced load capacities Wipers (if requested by the customer) DOUBLE NUTS: Two single nuts, preloaded, without backlash Same load capacities as single nuts About twice as long as single nuts Wipers (if requested by the customer) FLANGE SHAPES Shape A Shape B
10 Preloading F V F 1 F 2 Preloaded nuts are used to eliminate backlash and increase rigidity. Preloading should be carefully calculated to achieve the highest rate of effi ciency and the longest possible lifespan (see figure above). For preloaded nuts, in addition to the individual loads F 1 F n, preload F v must also be taken into account to determine the mean load F m. This yields new individual loads F 1v F nv. If for example an absence of backlash is required for all operational loads, preload F v must be selected according to the maximum load F max. Resulting load depending on preload F v An axial load on a preloaded nut system increases the load of one of the halves and relieves the other from the preloading force. The resulting load can be estimated by the following equations: Loaded half of nut: F nv(1) = F v + 0,65. F n [N] if F n < 2,83. F v [N] F nv(1) = F n [N] if F n 2,83. F v [N] Relieved half of nut: F nv(2) = F v - 0,35. F n [N] if F n < 2,83. F v [N] F nv(2) = 0 [N] if F n 2,83. F v [N] If a satellite roller screw only needs to be backlash-free for a specifi c load, preload F v should be selected according to the corresponding load F n. Unless the customer otherwise requests, split and double nuts are preloaded in the standard version to a maximum of 5% of the dynamic load capacity. F 1 F n [N] : individual loads F v [N] : preloading force F nv [N] : load resulting from the individual load and preloading F ma [N] : mean load taking into account preloading - 8 -
11 Preloading examples Preloading with rigid spacer (thickness calibrated by Rollvis SA) Flange nut Cylindrical nut Preloading with elastic washers Elastic washers Flange nut Cylindrical nut - 9 -
12 Mean speed and axial load For variable speed and load, lifespan should be calculated with mean values n m et F m. For a variable load at constant speed, the mean load F m is used (figure below). For variable speed and constant load with speed n, the mean speed n m is used (figure below). For a variable load at variable speed, the mean load F m is used. For a variable linear load at constant speed, the mean load F m is used (figure below). n m [min -1 ] : mean speed n 1 n n [min -1 ] : individual speeds q 1 q n [%] : time percentage F m [N] : mean load F ; F 1 F n ; F min ; F max [N] : actual forces
13 Nominal lifespan The nominal lifespan L 10 or L h of a satellite roller screw is attained with a probability of 90%. If greater reliability is required, the nominal lifespan L 10 or L h must be multiplied by the reliability factor f r (table opposite). Durée modifi ée L n = L 10. f r [ revolutions] respectivement L hn = L h. f r [h] Reliability % f r Nominal lifespan of single nuts (with backlash) The nominal lifespan of single nuts is calculated by the following formula: or If the lifespan is predetermined, the dynamic load capacity is calculated as follows: The lifespan in actual hours L hn is calculated by the following formula: The utilisation factor f N is calculated as follows: Nominal lifespan of preloaded nuts For preloaded nuts, it is fi rst necessary to calculate the lifespan of each half of the nut with the corresponding dynamic load capacity C and the mean axial load F ma (including preload). The total lifespan L 10 of the preloaded nut is obtained with the two lifespan values L 10(1) and L 10(2) (in revolutions). L n [revolutions] : modifi ed lifespan (revolutions) L hn [h] : modifi ed lifespan (hours) L 10 [revolutions] : nominal lifespan (revolutions) L h [h] : nominal lifespan (hours) L hn [h] : lifetime in actual hours f r [-] : reliability factor C [N] : dynamic load capacity F m [N] : mean load (single nut with backlash) F ma [N] : mean load (preloaded nut) n m [min-1] : mean speed f N [-] : utilisation factor
14 Rigidity Case 1 : f kn = 0.25 Case 3 : f kn = 2.0 Case 2 : f kn = 1.0 Case 4 : f kn = 4.0 Satellite roller screw rigidity The overall rigidity C ges of a satellite roller screw is made up of the following individual rigidity values: Screw rigidity C S Screw rigidity C S can be determined by the following simplifi ed formula: C me nut rigidity C Sp screw rigidity C L C u bearing rigidity r igidity of the surrounding construction Nut rigidity C me The rigidity C me of a complete satellite roller screw nut can be approximated with the following formula: C me = f m. f K. F 1/3 n [N/µm] f m for single nut ES = 0.75 f m for split nut EF = 1 f m for double nut ED = 1.5 Permissible buckling force F knzul at rotation speed n = 0 Permissible buckling force can be calculated by the following formula: The following condition is set for F n for the C me values shown in the table for standard preloading: F n = F V [N] Fv [N] : preloading force F n [N] : axial load C me [N/µm] : nut rigidity C s [N/µm] : screw rigidity f k [N 2/3 /µm] : rigidity factor f m [-] : correction factor L : free screw length d 0 : nominal diameter of screw F knzul [N] : permissible buckling force f kn [-] : correction factor for bearing type
15 Rotation speed L L Case 1 : f kr = 0.32 Case 3 : f kr = 1.55 L L Case 2 : f kr = 1.0 Case 4 : f kr = 2.24 Permissible rotation speed and axial load Satellite roller screws are restricted by the internal confi guration of the nut, the bearings at the end of the screw and the critical number of revolutions n kr due to fl exural vibration. The value of the permissible speed applied can be: RV : d 0. n RVR : d 0. n Critical speed n kr with axial load Fn = 0 Critical speed is infl uenced by the axial load. It can be calculated on request for every satellite roller screw confi guration. When the correct screw end bearings are chosen, their maximum speed will have no effect on the desired speed. All that needs to be determined is the critical speed n kr for fl exural vibration. The critical speed n kr for fl exural vibration can be calculated by the formula below. The correction factor f kr depends on the type of bearing and the clamping conditions (figure above). The calculation is based on the assumption that satellite roller screw nuts provide no guidance and the bearings at the screw end are considered rigid in the radial direction. The permissible critical speed can be calculated by taking the bearing type into account: n [min -1 ] : rotation speed n kr [min -1 ] : critical rotation speed n krzul [min -1 ] : permissible critical rotation speed L : free screw length d 0 : nominal diameter of screw f kr [-] : correction factor for bearing type 0,8 [-] : safety factor
16 Driving torque F Screw lead P J 2 v i = D 1 D 2 M M J 1 J M n M Driving torque All the values for motor rating can be calculated by the formulas below. Note that the load-free torque M v must be taken into account for preloaded nuts (based on preloading F v ). For single nuts with backlash, the formula is: M v = 0 [Nm] Motor driving torque M M at constant speed Load-free torque «Ascent» load torque «Descent» load torque The frictional forces of the guide slideway must be taken into account in feed force F. Motor driving torque If, as is possible in «Descent» mode, the motor driving torque is negative, the motor must have a brake. Motor driving power d : external diameter of screw d 2 : core diameter of screw P : screw lead L : length of satellite roller screw m T [kg] : mass to move D 1 : diameter of driving wheel D 2 : diameter of driven wheel i [-] : reduction ratio F [N] : feed force F v [N] : preloading force F a [N] : acceleration force M v [Nm] : load-free torque M L1 [Nm] : «ascent» load torque at constant speed M L2 [Nm] : «descent» load torque at constant speed M M [Nm] : motor driving torque M La [Nm] : load torque on acceleration M B [Nm] : acceleration torque M Ma [Nm] : motor driving torque on acceleration M R [Nm] : frictional torque of screw bearings J M [kgm 2 ] : moment of inertia of motor
17 Motor driving torque M Ma with acceleration The rotary moment of inertia of screw J R is a rough estimate. We shall be happy to calculate the exact value on request. Load torque Translatory moment of inertia Rotary moment of inertia (screw) Sum of reduced moments of inertia Motor speed Acceleration torque M B = f (n M ) Acceleration torque M B = f (s B ) Acceleration time t B = f (n M ) Acceleration time t B = f (s B ) Rotation speed reached after acceleration Path travelled during acceleration Motor driving torque Motor driving power J R [kgm 2 ] : rotary moment of inertia of screw J T [kgm 2 ] : translatory moment of inertia of screw J [kgm 2 ] : moment of inertia J 1 [kgm 2 ] : moment of inertia of driving wheel J 2 [kgm 2 ] : moment of inertia of driven wheel P M [W] : driving power of motor at constant speed P Ma [W] : driving power of motor on acceleration s B : acceleration path t B [s] : acceleration time v [m/s] : speed rate n M [min -1 ] : rotation speed of motor η [-] : mechanical effi ciency of gearing η 1 [-] : mechanical effi ciency of satellite roller screw for «ascent» η 1 = 0,71 0,89 η 2 [-] : mechanical effi ciency of satellite roller screw for «descent» η 2 = 0,61 0,85 c [-] : coeffi cient of friction referred to preloading c = 0,1 0,5 ( for effi ciencies η 1 + η 2 see page 6)
18 Calculation example Satellite roller screws RV 20 x 5 Nominal diameter : d 0 = 20 mm Lead : P = 5 mm Nut : split nut (EF), preloaded Mounting position : horizontal Load direction : both sides Rapid mode : one side, opposite to working load N Operating mode Time percentage q [%] Rotation speed n [min -1 ] Axial load F n [N] 1 Peak load q 1 = 5 n 1 = 15 F 1 = Roughing feed q 2 = 40 n 2 = 110 F 2 = Finishing feed q 3 = 50 n 3 = 70 F 3 = Rapid q 4 = 5 n 4 = 1700 F 4 = 1150 Mean speed Preloading Preloading is defi ned for the «fi nishing feed» operating mode (F 3 = 4200 N). Load on nut half 1 Nut half 1 is loaded in operating modes 1, 2 and 3. As F1, F2 eand F F v : Load on nut half 2 Nut half 1 is only partly loaded in operating mode 4. As F4 = 1150 N < 2.83 F v : Half nut 2 is loaded in operating mode 4. Half nut 2 is not loaded in operating modes 1, 2 and 3. As F 4 < F v, on a : Charge Mean load Nut 1 Nut 2 Lifespan Dynamic load capacity of a nut C = N Half nut 1 Half nut
19 Total lifespan Lifespan in hours (with utilisation factor f N = 0.6) Nut rigidity Satellite roller screw rigidity Free length between fi xed bearing and nut Nominal diameter of screw 1 = 1000 mm d 1 = 20 mm Bearing rigidity Total rigidity of satellite roller screw system Driving torque Driving torque MM is calculated for the peak load of F 1 = 8300 N. The screw is directly driven by the motor (i = 1) : Load-free torque: Load torque: Frictional torque of bearings: Peak driving torque of motor at constant speed: Motor driving power reaches its peak in rapid mode with F 4 = 1150 N. Moment en Load torque: : Peak driving power of motor at constant speed:
20 Lubrication As a general rule, the same lubricants are used for satellite roller screws as for roller bearings, i.e. either oil or grease. The type of lubricant used mostly depends on operating and maintenance conditions. Unless the customer explicitly instructs otherwise, standard Rollvis grease is applied at the factory. Oil lubrication Circulating mineral oils with EP additives to enhance resistance to aging and corrosion in compliance with CL based on DIN 51517, part 2, are especially suitable for the lubrication of satellite roller screws. Speed, ambient temperature and operating temperature are determining factors in the choice of viscosity. The amount of oil required depends on the screw diameter, the number of supporting rollers and the amount of heat to dissipate. 1 cm 3 /h (for small screw diameters) to 30 cm 3 /h (for large screw diameters) can be used as reference values. The shortest possible lubrication intervals ( 5 minutes) are recommended for high loads and longer intervals (5 minutes to 1 hr) for low loads. Automatic lubrication is recommended for high loads and speeds. For immersion lubrication, the oil level should be such that the bottommost roller is completely submerged in the oil. The amount of oil and the oil-change intervals depend on the loading and installation. The viscosity of the oil should be chosen to enable an adequate fi lm of lubricant to form on the contact surfaces. Figure a shows the operating viscosity ν κ to achieve for the mean speed of the satellite roller screw and screw diameter. Viscosity ν κ ensures a state of lubrication to fulfi l the nominal lifespan provided the lubrication system is free of foreign bodies. Nominal viscosity can be calculated on the basis of viscosity ν κ with the viscosity-temperature diagram (diagram ν-t, figure b) and the operating temperature. Nominal viscosity is the viscosity of oil at 40 C. Viscosity classes ISO VG (DIN 51519) are plotted in diagram ν-t. Figure a shows the nominal diameters of RV satellite roller screws. The diameters of RVR satellite roller screws are slightly different. The requisite operating viscosity values can be obtained by interpolation. Intermediate values can be obtained from the steps. These must be rounded up to the nearest viscosity value. The operating temperature must be known or estimated to calculate nominal viscosity. The operating temperature must be measured on the nut after stabilisation. A suitable oil can be found in oil suppliers lists with the nominal viscosity at 40 C. In general, an operating temperature of 30 C can be taken as a basis for selecting a lubricant. Example: Satellite roller screw RV 39 x 10 Mean operating speed: n m = 1400 min -1 Operating temperature (estimated): t = 25 C In figure a, for a number of revolutions nm = 1400 min -1 and a nominal diameter of 39mm, the nominal viscosity is ν κ = 33 mm 2 /s. In diagram ν-t (figure b), the 25 C temperature and 34 mm 2 /s viscosity lines intersect between ISO VG 15 and ISO VG 22. The oil to choose will be in viscosity class VG 22. A suitable CLP (DIN 51517) or HLP (DIN 51525) oil can be selected from this class. Grease lubrication The best grease lubricants to use are KP (DIN 51825, part 3) with a consistency factor of 2. Lubrication intervals depend on the screw arrangement, size and operating conditions. Rollvis can provide recommendations for any type of application
21 mm [ 2 s ] ν κ operating viscosity Mean screw rotation speed n m [min -1 ] Nominal diameter d Figure a Figure b Operating temperature t [ C] ν mm [ 2 κ operating viscosity s ]
22 Handling advice Assembly If possible, the nut and screw should not be dismantled. However, should this be necessary, an assembly sleeve must be used. External diameter d 3 of assembly sleeve: 0 d 3 = d 2-0,05 (d 2 = screw core diameter) Screw assembly Montage de la vis The following points must be followed when assembling the screw: 1 Align the screw and slide guideways axially parallel. 2 Fix the nut in housing. 3 Run the nut along the entire length of the thread and check the screw for ease of movement CAUTION RV screws always have a multiple-start thread. If the friction torque is different after the nut is reassembled, the nut must be taken off again and refitted on the next thread start until friction torque is correct! Handling Please read the following handling instructions carefully. To ensure optimal operation and a long lifespan for satellite roller screws, the following points must be scrupulously complied with. If in doubt, please contact Rollvis. Lubrication Satellite roller screws are greased prior to shipment (unless oil lubrication is requested). Do not remove this grease. Only use this type of grease for relubrication. Transport Handle screws with care: do not drop them or damage the thread. Installation Do not unscrew the nut (or only with an assembly sleeve). Carefully align satellite roller screws parallel to the guideways. Alignment errors will damage satellite roller screws. Storage Only remove satellite roller screws from their original packing just before installation. Bending Avoid applying radial forces to the nut
23 program Preference Type RV diameters of 3.5 to Type RV diameters of 15 to Type RV diameters of 25 to Type RV diameters of 39 to Type RV diameters of 51 to Type RV diameters of 80 to Type BRV diameters of 8 to Type RVR diameters of 8 to
24 Type RV - Ground screws Flange shapes and Drilling s drawings Shape A Shape B Drilling s drawing 1 Single nut, with backlash and double nut Split nut, preloaded, without backlash Split nuts, preloaded, preloading torque Without wipers With wipers Efficiency [N 2/3 /µm] Type D x P N d0 d1 d2 C Co F K C Co F K F V M V D1 D2 D5 D7 L1 L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 RV 3.5 x RV 5 x RV 5 x RV 5 x RV 7 x RV 7 x RV 7 x RV 7 x RV 7 x RV 8 x RV 8 x RV 8 x RV 8 x RV 8 x RV 8 x RV 10 x RV 10 x RV 10 x RV 10 x RV 10 x RV 12 x RV 12 x RV 12 x RV 12 x RV 12 x RV 12 x Maximum backlash of single nuts: 0.03mm (can be less on request). If possible, provide a lubrication hole in the nut (contact Rollvis for feasibility and position). [N 2/3 /µm] [N] [Ncm] Terms used in tables P Lead d1 External diameter F k Rigidity factor D Reference diameter d2 Thread bottom diameter F v Preloading force N Number of starts C Dynamic load capacity M v Load-free torque due to preloading d0 Nominal diameter Co Static load capacity
25 Type RV - Ground screws Drilling s drawing 2 Drilling s drawing 3 Drilling s drawing 4 Single nut, with backlash and double nut Split nut, preloaded, without backlash Split nuts, preloaded, preloading torque Without wipers With wipers Efficiency [N 2/3 /µm] Type D x P N d0 d1 d2 C Co F K C Co F K F V M V D1 D2 D5 D7 L1 L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 RV 15 x RV 15 x RV 15 x RV 15 x RV 15 x RV 15 x RV 20 x RV 20 x RV 20 x RV 20 x RV 20 x RV 20 x RV 20 x RV 21 x RV 21 x RV 21 x RV 21 x RV 21 x RV 21 x RV 21 x RV 23 x RV 23 x RV 23 x RV 23 x RV 23 x RV 23 x RV 23 x Maximum backlash of single nuts: 0.03mm (can be less on request). If possible, provide a lubrication hole in the nut (contact Rollvis for feasibility and position). [N 2/3 /µm] [N] [Ncm] Terms used in tables P Lead d1 External diameter F k Rigidity factor D Reference diameter d2 Thread bottom diameter F v Preloading force N Number of starts C Dynamic load capacity M v Load-free torque due to preloading d0 Nominal diameter Co Static load capacity
26 Type RV - Ground screws Flange shapes and Drilling s drawings Shape A Shape B Drilling s drawing 1 Single nut, with backlash and double nut Split nut, preloaded, without backlash Split nuts, preloaded, preloading torque Without wipers With wipers Efficiency [N 2/3 /µm] Type D x P N d0 d1 d2 C Co F K C Co F K F V M V D1 D2 D5 D7 L1 L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 RV 25 x RV 25 x RV 25 x RV 25 x RV 25 x RV 25 x RV 27 x RV 27 x RV 27 x RV 27 x RV 27 x RV 27 x RV 30 x RV 30 x RV 30 x RV 30 x RV 30 x RV 30 x RV 30 x RV 30 x RV 30 x RV 36 x RV 36 x RV 36 x RV 36 x RV 36 x RV 36 x RV 36 x RV 36 x Maximum backlash of single nuts: 0.03mm (can be less on request). If possible, provide a lubrication hole in the nut (contact Rollvis for feasibility and position). [N 2/3 /µm] [N] [Ncm] Terms used in tables P Lead d1 External diameter F k Rigidity factor D Reference diameter d2 Thread bottom diameter F v Preloading force N Number of starts C Dynamic load capacity M v Load-free torque due to preloading d0 Nominal diameter Co Static load capacity
27 Type RV - Ground screws Drilling s drawing 2 Drilling s drawing 3 Drilling s drawing 4 Single nut, with backlash and double nut Split nut, preloaded, without backlash Split nuts, preloaded, preloading torque Without wipers With wipers Efficiency [N 2/3 /µm] Type D x P N d0 d1 d2 C Co F K C Co F K F V M V D1 D2 D5 D7 L1 L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 RV 39 x RV 39 x RV 39 x RV 39 x RV 39 x RV 39 x RV 39 x RV 39 x RV 39 x RV 44 x RV 44 x RV 44 x RV 44 x RV 44 x RV 48 x RV 48 x RV 48 x RV 48 x RV 48 x RV 48 x RV 48 x RV 48 x RV 48 x RV 48 x RV 48 x RV 48 x RV 48 x RV 48 x RV 48 x Maximum backlash of single nuts: 0.03mm (can be less on request). If possible, provide a lubrication hole in the nut (contact Rollvis for feasibility and position). [N 2/3 /µm] [N] [Ncm] Terms used in tables P Lead d1 External diameter F k Rigidity factor D Reference diameter d2 Thread bottom diameter F v Preloading force N Number of starts C Dynamic load capacity M v Load-free torque due to preloading d0 Nominal diameter Co Static load capacity
28 Type RV - Ground screws Flange shapes and Drilling s drawings Shape A Shape B Drilling s drawing 1 Efficiency Single nut, with backlash and double nut [N 2/3 /µm] Split nut, preloaded, without backlash Split nuts, preloaded, preloading torque Without wipers With wipers Type D x P N d0 d1 d2 C Co F K C Co F K F V M V D1 D2 D5 D7 L1 L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 RV 51 x RV 51 x RV 51 x RV 51 x RV 51 x RV 60 x RV 60 x RV 60 x RV 60 x RV 60 x RV 60 x RV 60 x RV 60 x RV 60 x RV 60 x RV 60 x RV 64 x RV 64 x RV 64 x RV 64 x RV 64 x RV 64 x RV 70 x RV 70 x RV 70 x RV 70 x RV 75 x RV 75 x RV 75 x RV 75 x RV 75 x RV 75 x RV 75 x RV 75 x Maximum backlash of single nuts: 0.03mm (can be less on request). If possible, provide a lubrication hole in the nut (contact Rollvis for feasibility and position). [N 2/3 /µm] [N] [Ncm] Terms used in tables P Lead d1 External diameter F k Rigidity factor D Reference diameter d2 Thread bottom diameter F v Preloading force N Number of starts C Dynamic load capacity M v Load-free torque due to preloading d0 Nominal diameter Co Static load capacity High capacity defi nition
29 Type RV - Ground screws Drilling s drawing 2 Drilling s drawing 3 Drilling s drawing 4 Efficiency Single nut, with backlash and double nut [N 2/3 /µm] Split nut, preloaded, without backlash Split nuts, preloaded, preloading torque Without wipers With wipers Type D x P N d0 d1 d2 C Co F K C Co F K F V M V D1 D2 D5 D7 L1 L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 RV 80 x RV 80 x RV 80 x RV 80 x RV 80 x RV 80 x RV 80 x RV 80 x RV 80 x RV 92 x RV 92 x RV 92 x RV 100 x RV 100 x RV 100 x RV 100 x RV 100 x RV 100 x RV 100 x RV 100 x RV 100 x RV 120 x RV 120 x RV 120 x RV 120 x RV 120 x RV 120 x RV 120 x RV 120 x RV 120 x RV 120 x RV 135 x RV 135 x RV 135 x RV 135 x RV 150 x RV 150 x RV 150 x RV 150 x Maximum backlash of single nuts: 0.03mm (can be less on request). If possible, provide a lubrication hole in the nut (contact Rollvis for feasibility and position). Terms used in tables P Lead d1 External diameter F k Rigidity factor D Reference diameter d2 Thread bottom diameter F v Preloading force N Number of starts C Dynamic load capacity M v Load-free torque due to preloading d0 Nominal diameter Co Static load capacity High capacity defi nition [N 2/3 /µm] [N] [Ncm]
30 Type BRV - Rolled screws Flange shapes and Drilling s drawings Shape A Shape B Drilling s drawing 1 Single nut, with backlash and double nut Split nut, preloaded, without backlash Split nuts, preloaded, preloading torque Without wipers With wipers Efficiency [N 2/3 /µm] Type D x P N d0 d1 d2 C Co F K C Co F K F V M V D1 D2 D5 D7 L1 L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 BRV 8 x BRV 12 x BRV 12 x BRV 15 x BRV 15 x BRV 20 x BRV 20 x BRV 23 x BRV 23 x BRV 23 x BRV 27 x BRV 27 x BRV 30 x BRV 39 x BRV 39 x BRV 44 x Maximum backlash of single nuts: 0.03mm (can be less on request). If possible, provide a lubrication hole in the nut (contact Rollvis for feasibility and position). [N 2/3 /µm] [N] [Ncm] Terms used in tables P Lead d1 External diameter F k Rigidity factor D Reference diameter d2 Thread bottom diameter F v Preloading force N Number of starts C Dynamic load capacity M v Load-free torque due to preloading d0 Nominal diameter Co Static load capacity
31 Type RVR - Ground screws - System with rollers recycling Drilling s drawing 2 Drilling s drawing 3 Drilling s drawing 4 Efficiency Single nut, with backlash and double nut [N 2/3 /µm] Split nut, preloaded, without backlash [N 2/3 /µm] Split nuts, preloaded, preloading torque [N] [Ncm] Without wipers With wipers Type D x P N d0 d1 d2 C Co F K C Co F K F V M V D1 D2 D5 D7 L1 L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 RVR 8 x RVR 8 X RVR 8 X RVR 10 x RVR 10 X RVR 10 X RVR 12 x RVR 12 X RVR 12 X RVR 16 x RVR 16 X RVR 16 X RVR 20 X RVR 20 X RVR 20 X RVR 25 X RVR 25 X RVR 32 X RVR 32 X RVR 40 X RVR 40 X RVR 50 X RVR 50 X RVR 50 X RVR 50 X RVR 63 X RVR 63 X RVR 63 X RVR 80 X RVR 80 X RVR 80 X RVR 100 X RVR 100 X RVR 100 X RVR 125 x Maximum backlash of single nuts: 0.03mm (can be less on request). If possible, provide a lubrication hole in the nut (contact Rollvis for feasibility and position). Terms used in tables P Lead d1 External diameter F k Rigidity factor D Reference diameter d2 Thread bottom diameter F v Preloading force N Number of starts C Dynamic load capacity M v Load-free torque due to preloading d0 Nominal diameter Co Static load capacity
32 Applications The great flexibility of Rollvis SA means it can make all types of screws and nuts as shown in the examples below: RV 4 x 1 RV 8 x 2 RV 12 x 8 RV 30 x 30 RV 48 x 10 RVR 100 x
33 RV 20 x 3 RV 36 x 3 RV 39 x 5 RVR 12 x 1 RV 8 x 5 RV 25 x
34 Applications ( ctd.) RV 12 x 8 RV 15 x 5 RV 39 x 10 RV 12 x 7 RV 100 x 10 RV 30 x
3 rue JC Milleret, Immeuble Horizon, SAINT ETIENNE FRANCE /
 3 rue JC Milleret, Immeuble Horizon, 42000 AINT ETIENNE FRANCE +33 4 77 24 43 07 www.reckondrives.com / contact@reckondrives.com HIGH PERFORMANCE ELECTRO-MECHANICAL ACTUATOR Reckon high performance electromechanical
3 rue JC Milleret, Immeuble Horizon, 42000 AINT ETIENNE FRANCE +33 4 77 24 43 07 www.reckondrives.com / contact@reckondrives.com HIGH PERFORMANCE ELECTRO-MECHANICAL ACTUATOR Reckon high performance electromechanical
Slotted nut NMG. Housing nut GWR. Bosch Rexroth AG. for economical constructions. a min. 0,3. M A = tightening torque of slotted nut.
 R310EN 3301 (2009.08) Precision Ball Screw Assemblies Bosch Rexroth AG 113 Slotted nut NMG for economical constructions B D d d1 b M A = tightening torque of slotted nut a min. 0,3 Polyamide insert Designation
R310EN 3301 (2009.08) Precision Ball Screw Assemblies Bosch Rexroth AG 113 Slotted nut NMG for economical constructions B D d d1 b M A = tightening torque of slotted nut a min. 0,3 Polyamide insert Designation
Precision Modules PSK. The Drive & Control Company
 Precision Modules PSK The Drive & Control Company 2 Bosch Rexroth Coporation Precision Modules PSK R310A 2414 (2008.07) Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear
Precision Modules PSK The Drive & Control Company 2 Bosch Rexroth Coporation Precision Modules PSK R310A 2414 (2008.07) Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear
...components in motion. Miniature Linear Guideways
 ...components in motion Miniature Linear Introduction Miniature linear guideway systems are widely used throughout industry for precise, compact applications. Precise and Stainless The gothic arch shape
...components in motion Miniature Linear Introduction Miniature linear guideway systems are widely used throughout industry for precise, compact applications. Precise and Stainless The gothic arch shape
Creative Motion Control Planetary Roller Screws
 Creative Motion Control Planetary Roller Screws DELIVERING INNOVATIVE LINEAR MOTION SOLUTIONS PRODUCT CATALOG Table of Contents 1. Technical Information........................... 4 2. The CMC Difference............................7
Creative Motion Control Planetary Roller Screws DELIVERING INNOVATIVE LINEAR MOTION SOLUTIONS PRODUCT CATALOG Table of Contents 1. Technical Information........................... 4 2. The CMC Difference............................7
Inner block. Grease nipple. Fig.1 Structure of LM Guide Actuator Model KR
 LM Guide ctuator Model LM Guide + all Screw = Integral-structure ctuator Stopper Housing all screw Inner block Grease nipple Outer rail earing (supported side) Housing Stopper Double-row ball circuit earing
LM Guide ctuator Model LM Guide + all Screw = Integral-structure ctuator Stopper Housing all screw Inner block Grease nipple Outer rail earing (supported side) Housing Stopper Double-row ball circuit earing
Acme Screw Jacks. Catalogue
 Acme Screw Jacks Catalogue SERVOMECH Screw Jacks MA Series Screw Jacks - high efficiency Max. duty cycle: travelling screw: 40 % over 10 min (30 % over 1 hour) travelling nut: 30 % over 10 min (20 % over
Acme Screw Jacks Catalogue SERVOMECH Screw Jacks MA Series Screw Jacks - high efficiency Max. duty cycle: travelling screw: 40 % over 10 min (30 % over 1 hour) travelling nut: 30 % over 10 min (20 % over
Ball. Ball cage. Fig.1 Structure of Caged Ball LM Guide Actuator Model SKR
 Caged all LM Guide Actuator Model Inner block all screw shaft Grease nipple Outer rail all cage all Structure and Features Fig.1 Structure of Caged all LM Guide Actuator Model Caged all LM Guide Actuator
Caged all LM Guide Actuator Model Inner block all screw shaft Grease nipple Outer rail all cage all Structure and Features Fig.1 Structure of Caged all LM Guide Actuator Model Caged all LM Guide Actuator
Linear Guideways ov -linear -guidew ays-divider - U pdated
 Linear Guideways ov-linear-guideways-divider - Updated - 11-01-2017 163 Linear Guideways Linear Guideways Introduction L1016 Linear guideways Linear guideways are widely used throughout industry for heavy-duty
Linear Guideways ov-linear-guideways-divider - Updated - 11-01-2017 163 Linear Guideways Linear Guideways Introduction L1016 Linear guideways Linear guideways are widely used throughout industry for heavy-duty
Industry. SNR Linear Motion : Ball screws
 Industry SNR Linear Motion : Ball screws SNR A global manufacturer of bearings. For almost a century, SNR has designed, developed and manufactured bearings to meet the most demanding of applications. In
Industry SNR Linear Motion : Ball screws SNR A global manufacturer of bearings. For almost a century, SNR has designed, developed and manufactured bearings to meet the most demanding of applications. In
Precision Modules PSK
 Precision Modules PSK 2 Bosch Rexroth AG Precision Modules PSK R999000500 (2015-12) Identification system for short product names Short product name Example:: P S K - 050 - N N - 1 System = Precision Module
Precision Modules PSK 2 Bosch Rexroth AG Precision Modules PSK R999000500 (2015-12) Identification system for short product names Short product name Example:: P S K - 050 - N N - 1 System = Precision Module
506E. LM Guide Actuator General Catalog
 LM Guide Actuator General Catalog A LM Guide Actuator General Catalog A Product Descriptions 506E Caged Ball LM Guide Actuator Model SKR.. A2-4 Structure and Features... A2-4 Caged Ball Technology... A2-6
LM Guide Actuator General Catalog A LM Guide Actuator General Catalog A Product Descriptions 506E Caged Ball LM Guide Actuator Model SKR.. A2-4 Structure and Features... A2-4 Caged Ball Technology... A2-6
SRG. Caged Roller LM Guide Ultra-high Rigidity Type Model SRG. Point of Selection. Point of Design. Options. Model No. Precautions on Use
 Caged Roller LM Guide Ultra-high Rigidity Type Model LM block LM rail End seal Endplate 45 45 Caged roller Roller 45 Cross section 45 * or the caged roller, see. Point of Selection A Point of Design Options
Caged Roller LM Guide Ultra-high Rigidity Type Model LM block LM rail End seal Endplate 45 45 Caged roller Roller 45 Cross section 45 * or the caged roller, see. Point of Selection A Point of Design Options
Ball screw drives KGT General technical data
 KGT General technical data Manufacturing process The thread profile is produced by cold rolling in the thread rolling method. Both screw and nut have a gothic thread profile. The load angle is 45. Linear
KGT General technical data Manufacturing process The thread profile is produced by cold rolling in the thread rolling method. Both screw and nut have a gothic thread profile. The load angle is 45. Linear
Easy Slide Rails ov -easy_slide_divider - U pdated
 Easy Slide Rails ov-easy_slide_divider - Updated - 18-09-2017 163 Easy Slide Rails Easy Slide Rails Introduction The Easy Slide family of linear rails have a compact cross-section and low-friction movement.
Easy Slide Rails ov-easy_slide_divider - Updated - 18-09-2017 163 Easy Slide Rails Easy Slide Rails Introduction The Easy Slide family of linear rails have a compact cross-section and low-friction movement.
Cross Roller Guide/Ball Guide General Catalog
 General Catalog A Product Descriptions Features and Types... A7-2 Features of the.. A7-2 Structure and Features... A7-2 Types of the.. A7-3 Types and Features... A7-3 Point of Selection... A7-4 Rated Load
General Catalog A Product Descriptions Features and Types... A7-2 Features of the.. A7-2 Structure and Features... A7-2 Types of the.. A7-3 Types and Features... A7-3 Point of Selection... A7-4 Rated Load
Contents. Page. 1. Product description. 2. The AXC line of linear axes. 3. AXLT line of linear tables. AXC and AXS product overview...
 SNR Industry Contents Page 3 1. Product description AXC and AXS product overview... 6-8 Dynamic load ratings of the linear motion systems... 9 Compact modules... 10-11 Linear tables... 12 Telescopic axes...
SNR Industry Contents Page 3 1. Product description AXC and AXS product overview... 6-8 Dynamic load ratings of the linear motion systems... 9 Compact modules... 10-11 Linear tables... 12 Telescopic axes...
Ball Rail Systems RE / The Drive & Control Company
 Ball Rail Systems RE 82 202/2002-12 The Drive & Control Company Rexroth Linear Motion Technology Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Standard Ball Rail Systems Super Ball Rail Systems Ball Rail Systems
Ball Rail Systems RE 82 202/2002-12 The Drive & Control Company Rexroth Linear Motion Technology Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Standard Ball Rail Systems Super Ball Rail Systems Ball Rail Systems
MINIRAIL Profiled miniature guideway
 MINIRAIL Profiled miniature guideway Table of Contents 1 Product overview and technical informations MINIRAIL a range of high-precision products.... 2 MINIRAIL overview accuracy classes:.... 3 MINIRAIL
MINIRAIL Profiled miniature guideway Table of Contents 1 Product overview and technical informations MINIRAIL a range of high-precision products.... 2 MINIRAIL overview accuracy classes:.... 3 MINIRAIL
Axial-radial cylindrical roller bearings
 Axial-radial cylindrical roller bearings Designs and variants.............. 320 Bearing data..................... 321 (Boundary dimensions, tolerances) Product table 5.1 Axial-radial cylindrical roller
Axial-radial cylindrical roller bearings Designs and variants.............. 320 Bearing data..................... 321 (Boundary dimensions, tolerances) Product table 5.1 Axial-radial cylindrical roller
NSR-TBC. LM Guide Self-aligning Type Model NSR-TBC. Point of Selection. Point of Design. Options. Model No. Precautions on Use
 LM Guide Self-aligning Type Model LM casing Spline nut End seal LM rail Grease nipple Side plate Clearance adjustment bolt 90 Side seal (Optional) Ball Retainer Cross section 30 Point of Selection A Point
LM Guide Self-aligning Type Model LM casing Spline nut End seal LM rail Grease nipple Side plate Clearance adjustment bolt 90 Side seal (Optional) Ball Retainer Cross section 30 Point of Selection A Point
Bevel gearboxes. Catalogue
 Bevel gearboxes Catalogue INDEX Bevel gearbox description... page 2 Manufacturing features... page 2 Materials and components... page 4 Bevel gearbox selection... page 5 Thermal power limit... page 7
Bevel gearboxes Catalogue INDEX Bevel gearbox description... page 2 Manufacturing features... page 2 Materials and components... page 4 Bevel gearbox selection... page 5 Thermal power limit... page 7
Miniature Ball Rail Systems
 R310EN 2210 (2004.06) The Drive & Control Company 2 Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Miniature-BRS R310EN 2210 (2004.06) Linear Motion Systems Ball Rail System Standard Ball Rail
R310EN 2210 (2004.06) The Drive & Control Company 2 Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Miniature-BRS R310EN 2210 (2004.06) Linear Motion Systems Ball Rail System Standard Ball Rail
SHS. Caged Ball LM Guide Global Standard Size Model SHS. Point of Selection. Point of Design. Options. Model No. Precautions on Use
 Caged Ball LM Guide Global Standard Size Model LM block LM rail Endplate End seal 45 Ball Ball cage Cross section 45 * For the Ball Cage, see. Point of Selection Point of Design Options Model No. Precautions
Caged Ball LM Guide Global Standard Size Model LM block LM rail Endplate End seal 45 Ball Ball cage Cross section 45 * For the Ball Cage, see. Point of Selection Point of Design Options Model No. Precautions
Linear Drive with Toothed Belt and Integrated Guide with Recirculating Ball Bearing Guide with Roller Guide Series OSP-E..BHD
 Linear Drive with and Integrated Guide with Recirculating Ball Bearing Guide with Roller Guide Contents Description Page Overview 11-14 Version with Recirculating Ball Bearing Guide Technical Data 15-17
Linear Drive with and Integrated Guide with Recirculating Ball Bearing Guide with Roller Guide Contents Description Page Overview 11-14 Version with Recirculating Ball Bearing Guide Technical Data 15-17
Product overview. 10 Bosch Rexroth Corporation Compact Modules R310A 2602 ( ) Compact Modules CKK. Compact Modules with ball screw drive (CKK)
 10 Bosch Rexroth Corporation R310A 2602 (2008.09) CKK with ball screw drive (CKK) Product overview are precision, ready-to-install linear motion systems characterized by their high performance and compact
10 Bosch Rexroth Corporation R310A 2602 (2008.09) CKK with ball screw drive (CKK) Product overview are precision, ready-to-install linear motion systems characterized by their high performance and compact
Courtesy of CMA/Flodyne/Hydradyne Motion Control Hydraulic Pneumatic Electrical Mechanical (800)
 01_1 Miniature st Headline_36 Ball Rail pt/14.4 Systems mm second line 2 Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Miniature Ball Rail Systems Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear Bushings and Shafts
01_1 Miniature st Headline_36 Ball Rail pt/14.4 Systems mm second line 2 Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Miniature Ball Rail Systems Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear Bushings and Shafts
...components in motion. Easy Rail
 ...components in motion Easy Rail Easy Rail Introduction The Easy Rail family have a compact cross-section and low-friction movement. Robust and Long Service Life Easy Rail s range of cross-sectional rail
...components in motion Easy Rail Easy Rail Introduction The Easy Rail family have a compact cross-section and low-friction movement. Robust and Long Service Life Easy Rail s range of cross-sectional rail
HSR. LM Guide Global Standard Size Model HSR. Point of Selection. Point of Design. Options. Model No. Precautions on Use
 LM Guide Global Standard Size Model Retainer plate Endplate End seal Grease nipple Ball Retainer plate Inner seal (Optional) Side seal LM rail Cross section 45 45 Point of Selection A Point of Design Options
LM Guide Global Standard Size Model Retainer plate Endplate End seal Grease nipple Ball Retainer plate Inner seal (Optional) Side seal LM rail Cross section 45 45 Point of Selection A Point of Design Options
PRS Series Planetary Roller Screws. A Superior Alternative to Hydraulic or Pneumatic Motion Providing 15 times the Life of a Ballscrew
 PRS Series Planetary Roller Screws A Superior Alternative to Hydraulic or Pneumatic Motion Providing 15 times the Life of a Ballscrew Exlar Roller Screw Advantage Roller Screw Overview A roller screw is
PRS Series Planetary Roller Screws A Superior Alternative to Hydraulic or Pneumatic Motion Providing 15 times the Life of a Ballscrew Exlar Roller Screw Advantage Roller Screw Overview A roller screw is
Axial Piston Variable Pump A10VO
 Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics inear Motion and Assembly Technologies Pneumatics ervice Axial Piston Variable Pump A10VO RA 92703/11.07 1/44 Replaces: 06.07 Data sheet eries 52/53 ize 10...85
Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics inear Motion and Assembly Technologies Pneumatics ervice Axial Piston Variable Pump A10VO RA 92703/11.07 1/44 Replaces: 06.07 Data sheet eries 52/53 ize 10...85
Precision ball screws
 Recirculating ball screws Precision ball screws Thomson Linear Motion. Optimized. Linear Motion. Optimized. The ideal solution often is not found in the fastest, most robust, most precise or even the most
Recirculating ball screws Precision ball screws Thomson Linear Motion. Optimized. Linear Motion. Optimized. The ideal solution often is not found in the fastest, most robust, most precise or even the most
10 Thrust ball bearings
 10 Thrust ball bearings Designs and variants.............. 1010 Single direction thrust ball bearings... 1010 Double direction thrust ball bearings.. 1010 Cages............................ 1010 Bearings
10 Thrust ball bearings Designs and variants.............. 1010 Single direction thrust ball bearings... 1010 Double direction thrust ball bearings.. 1010 Cages............................ 1010 Bearings
EMC-HD. C 01_2 Subheadline_15pt/7.2mm
 C Electromechanical 01_1 Headline_36pt/14.4mm Cylinder EMC-HD C 01_2 Subheadline_15pt/7.2mm 2 Elektromechanischer Zylinder EMC-HD Short product name Example: EMC 085 HD 1 System = ElectroMechanical Cylinder
C Electromechanical 01_1 Headline_36pt/14.4mm Cylinder EMC-HD C 01_2 Subheadline_15pt/7.2mm 2 Elektromechanischer Zylinder EMC-HD Short product name Example: EMC 085 HD 1 System = ElectroMechanical Cylinder
A superior alternative to hydraulic or pneumatic motion providing 15 times the life of a ball screw. Planetary Roller Screws
 A superior alternative to hydraulic or pneumatic motion providing 15 times the life of a ball screw Planetary Roller Screws Exlar Your Linear Motion Experts Exlar Corporation is committed to providing
A superior alternative to hydraulic or pneumatic motion providing 15 times the life of a ball screw Planetary Roller Screws Exlar Your Linear Motion Experts Exlar Corporation is committed to providing
Precision, Caged Ball Screw
 Models SBN, SBK, SDA, HBN and SBKH Pipe presser Screw shaft Return pipe Ball screw nut Ball Ball cage Fig.1 Structure of High-Speed Ball Screw with Ball Cage Model SBN Point of Selection Options Model
Models SBN, SBK, SDA, HBN and SBKH Pipe presser Screw shaft Return pipe Ball screw nut Ball Ball cage Fig.1 Structure of High-Speed Ball Screw with Ball Cage Model SBN Point of Selection Options Model
Precision Modules PSK
 Precision Modules PSK The Drive & Control Company Rexroth Linear Motion Technology Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Standard Ball Rail Systems Super Ball Rail Systems Ball Rail Systems with Aluminum
Precision Modules PSK The Drive & Control Company Rexroth Linear Motion Technology Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Standard Ball Rail Systems Super Ball Rail Systems Ball Rail Systems with Aluminum
Profi le rail guides LLR
 Profi le rail guides LLR Content The SKF brand now stands for more than ever before, and means more to you as a valued customer. While SKF maintains its leadership as the hallmark of quality bearings throughout
Profi le rail guides LLR Content The SKF brand now stands for more than ever before, and means more to you as a valued customer. While SKF maintains its leadership as the hallmark of quality bearings throughout
Home at last. The new FNL fl anged bearing housing
 Home at last The new FNL fl anged bearing housing Approved by the family Previously it was blue-green. Yet was seen as the black sheep of the family. Now it s the other way around. FNL offers everything
Home at last The new FNL fl anged bearing housing Approved by the family Previously it was blue-green. Yet was seen as the black sheep of the family. Now it s the other way around. FNL offers everything
Caged Ball LM Guide Actuator SKR
 Caged Ball LM Guide Actuator SKR For details, visit THK at www.thk.com Product information is updated regularly on the THK website. CATALOG No.309-11E Integrated LM Guide and Ball Screw High-rigidity /
Caged Ball LM Guide Actuator SKR For details, visit THK at www.thk.com Product information is updated regularly on the THK website. CATALOG No.309-11E Integrated LM Guide and Ball Screw High-rigidity /
Components for parallel kinematics
 Components for parallel kinematics Series GLK, GLK 2, GLK 3 and GLAE Parallel kinematic components consist of a number of parallel, longitudinally adjustable mechanical struts that are arranged between
Components for parallel kinematics Series GLK, GLK 2, GLK 3 and GLAE Parallel kinematic components consist of a number of parallel, longitudinally adjustable mechanical struts that are arranged between
Screw jacks MA Series
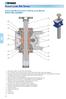 Screw jacks MA Series Screw jacks MA Series with travelling screw (Mod.A) STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS 1 10 11 8 7 6 1 3 13 4 9 14 8 11 10 5 6 7 1 - acme screw in steel C 43 (UNI 7847), whirled thread - worm shaft
Screw jacks MA Series Screw jacks MA Series with travelling screw (Mod.A) STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS 1 10 11 8 7 6 1 3 13 4 9 14 8 11 10 5 6 7 1 - acme screw in steel C 43 (UNI 7847), whirled thread - worm shaft
V SWISS MADE LINEAR TECHNOLOGY
 Compact units Excerpt from main catalogue SWISS MADE LINEAR TECHNOLOGY V 11-15 Line Tech compact units Table of contents Product overview 106 107 Design fundamentals / Lubrication / Maintenance 108 Profile
Compact units Excerpt from main catalogue SWISS MADE LINEAR TECHNOLOGY V 11-15 Line Tech compact units Table of contents Product overview 106 107 Design fundamentals / Lubrication / Maintenance 108 Profile
R310EN 2302 ( ) The Drive & Control Company
 R31EN 232 (26.4) The Drive & Control Company Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Linear Bushings and Shafts Ball Screw Drives Linear Motion Systems Basic Mechanical
R31EN 232 (26.4) The Drive & Control Company Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Linear Bushings and Shafts Ball Screw Drives Linear Motion Systems Basic Mechanical
Linear Guideways HG Series
 18 G99TE1-67 Linear Guideways 2-1 - Heavy Load Ball Type Linear Guideway HG series linear guideways are designed with load capacity and rigidity higher than other similar products with circular-arc groove
18 G99TE1-67 Linear Guideways 2-1 - Heavy Load Ball Type Linear Guideway HG series linear guideways are designed with load capacity and rigidity higher than other similar products with circular-arc groove
Miniature profi le rail guides
 Miniature profi le rail guides Contents The SKF brand now stands for more than ever before, and means more to you as a valued customer. While SKF maintains its leadership as the hallmark of quality bearings
Miniature profi le rail guides Contents The SKF brand now stands for more than ever before, and means more to you as a valued customer. While SKF maintains its leadership as the hallmark of quality bearings
511E. Ball Screw General Catalog
 Ball Screw General Catalog A Ball Screw General Catalog A Product Descriptions Types of Ball Screws... A15-6 Point of Selection... A15-8 Flowchart for Selecting a Ball Screw... A15-8 Accuracy of the Ball
Ball Screw General Catalog A Ball Screw General Catalog A Product Descriptions Types of Ball Screws... A15-6 Point of Selection... A15-8 Flowchart for Selecting a Ball Screw... A15-8 Accuracy of the Ball
Main Catalogue. EichenbergerGewinde. 100 % Swiss made
 EichenbergerGewinde 100 % Swiss made Main Catalogue Carry ball screws Carry Speed-line high-helix ball screws Speedy high-helix lead screws Rondo round thread lead screws The choice is yours Thread rolling
EichenbergerGewinde 100 % Swiss made Main Catalogue Carry ball screws Carry Speed-line high-helix ball screws Speedy high-helix lead screws Rondo round thread lead screws The choice is yours Thread rolling
2. Motion relationships and torques
 2. Motion relationships and torques 2.1 Rotation angle of a single joint as a function of defl ection angle ß 1 Input rotation angle 2 Output rotation angle If a single joint is deflected by angle ß and
2. Motion relationships and torques 2.1 Rotation angle of a single joint as a function of defl ection angle ß 1 Input rotation angle 2 Output rotation angle If a single joint is deflected by angle ß and
Features of the Ball Screw
 Features of the Driving Torque One Third of the Sliding Screw With the, balls roll between the screw shaft and the nut to achieve high effi ciency. Its required driving torque is only one third of the
Features of the Driving Torque One Third of the Sliding Screw With the, balls roll between the screw shaft and the nut to achieve high effi ciency. Its required driving torque is only one third of the
Features of the LM Guide
 Features of the Functions Required for Linear Guide Surface Large permissible load Highly rigid in all directions High positioning repeatability Running accuracy can be obtained easily High accuracy can
Features of the Functions Required for Linear Guide Surface Large permissible load Highly rigid in all directions High positioning repeatability Running accuracy can be obtained easily High accuracy can
Single direction thrust ball bearings Double direction thrust ball bearings
 Thrust ball bearings Single direction thrust ball bearings... 838 Double direction thrust ball bearings... 839 Bearing data general... 840 Dimensions... 840 Tolerances... 840 Misalignment... 840 Cages...
Thrust ball bearings Single direction thrust ball bearings... 838 Double direction thrust ball bearings... 839 Bearing data general... 840 Dimensions... 840 Tolerances... 840 Misalignment... 840 Cages...
...our linkages, your solution. Rod Ends
 ...our linkages, your solution Technical Information Introduction All of our rod ends incorporate either a plain spherical bearing, ball bearing, or roller bearing. Below is an overview of each type. Plain
...our linkages, your solution Technical Information Introduction All of our rod ends incorporate either a plain spherical bearing, ball bearing, or roller bearing. Below is an overview of each type. Plain
Medical equipment. Press brakes EDM. Woodworking
 Ball screws Medical equipment Press brakes EDM Woodworking General Contents d Ø Load C o Rolling element Recommendations for selection Overview: ball screw nuts ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ball screws Medical equipment Press brakes EDM Woodworking General Contents d Ø Load C o Rolling element Recommendations for selection Overview: ball screw nuts ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Axial piston variable pump (A)A4VSO
 Axial piston variable pump (A)A4VSO RA 92050-A/06.09 1/64 Replaces: 09.97 Data sheet Series 10, 11 and 30 Size 40...1000 Nominal pressure 5100 psi (350 bar) Peak pressure 5800 psi (400 bar) Open circuit
Axial piston variable pump (A)A4VSO RA 92050-A/06.09 1/64 Replaces: 09.97 Data sheet Series 10, 11 and 30 Size 40...1000 Nominal pressure 5100 psi (350 bar) Peak pressure 5800 psi (400 bar) Open circuit
LM Guide Radial Type Model SR
 LM Guide Radial Type Model Endplate LM block Grease nipple End seal LM rail 90 Ball Retainer plate Side seal (Optional) Cross section 30 Point of Selection A Point of Design Options Model No. Precautions
LM Guide Radial Type Model Endplate LM block Grease nipple End seal LM rail 90 Ball Retainer plate Side seal (Optional) Cross section 30 Point of Selection A Point of Design Options Model No. Precautions
Variable Displacement Plug-In Motor A6VE
 Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics Linear Motion and Assembly echnologies Pneumatics Service Variable Displacement Plug-In Motor A6VE RE 91 606/06.05 1/16 Replaces: 05.99 echnical data sheet Series
Electric Drives and Controls Hydraulics Linear Motion and Assembly echnologies Pneumatics Service Variable Displacement Plug-In Motor A6VE RE 91 606/06.05 1/16 Replaces: 05.99 echnical data sheet Series
High Precision Bearings for Combined Loads
 High Precision Bearings for Combined Loads Axial/radial bearings Axial angular contact ball bearings Axial/radial bearings with angular measuring system added competence for your success With their forward-looking
High Precision Bearings for Combined Loads Axial/radial bearings Axial angular contact ball bearings Axial/radial bearings with angular measuring system added competence for your success With their forward-looking
R310EN 2211 ( ) The Drive & Control Company
 eline Ball Rail Systems R310EN 2211 (2006.04) The Drive & Control Company Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear Bushings and Shafts Ball
eline Ball Rail Systems R310EN 2211 (2006.04) The Drive & Control Company Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear Bushings and Shafts Ball
Axial piston variable pump A7VO
 Axial piston variable pump A7VO RE 92203/06.09 1/52 Replaces: 05.99 Data sheet Series 63 Sizes NG250 to 500 Nominal pressure 350 bar Peak pressure 400 bar Open circuit Contents Type code for Standard program
Axial piston variable pump A7VO RE 92203/06.09 1/52 Replaces: 05.99 Data sheet Series 63 Sizes NG250 to 500 Nominal pressure 350 bar Peak pressure 400 bar Open circuit Contents Type code for Standard program
Axial Piston Fixed Motor A2FM
 Axial Piston Fixed Motor A2FM RE 91001/06.2012 1/46 Replaces: 09.07 Data sheet Series 6 Size Nominal pressure/maximum pressure 5 315/350 bar 10 to 200 400/450 bar 250 to 1000 350/400 bar Open and closed
Axial Piston Fixed Motor A2FM RE 91001/06.2012 1/46 Replaces: 09.07 Data sheet Series 6 Size Nominal pressure/maximum pressure 5 315/350 bar 10 to 200 400/450 bar 250 to 1000 350/400 bar Open and closed
Linear Drive with Ball Screw Drive Series OSP-E..SB
 Linear Drive with Ball Screw Drive Series OSP-E..SB Contents Description Data Sheet No. Page Overview 1.30.001E 47-50 Technical Data 1.30.002E-1 to 5 51-55 Dimensions 1.30.002E-6, -7 56-57 Order instructions
Linear Drive with Ball Screw Drive Series OSP-E..SB Contents Description Data Sheet No. Page Overview 1.30.001E 47-50 Technical Data 1.30.002E-1 to 5 51-55 Dimensions 1.30.002E-6, -7 56-57 Order instructions
Welcome to where precision is. Miniature Ball Screws Diameter 3 16 mm
 Welcome to where precision is. Miniature Ball Screws Diameter 3 16 mm 54 Welcome to where precision is. Welcome to Steinmeyer! 3 Welcome to where precision is. HISTORY 1927 1942 1943 The Steinmeyer company
Welcome to where precision is. Miniature Ball Screws Diameter 3 16 mm 54 Welcome to where precision is. Welcome to Steinmeyer! 3 Welcome to where precision is. HISTORY 1927 1942 1943 The Steinmeyer company
Compact Modules. with ball screw drive and toothed belt drive R310EN 2602 ( ) The Drive & Control Company
 with ball screw drive and toothed belt drive R310EN 2602 (2007.02) The Drive & Control Company Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear Bushings
with ball screw drive and toothed belt drive R310EN 2602 (2007.02) The Drive & Control Company Bosch Rexroth AG Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Linear Bushings
V SWISS MADE LINEAR TECHNOLOGY
 Excerpt from main catalogue inear modules V 11-15 SWISS MDE INER TECHNOOGY ine Tech inear modules Table of contents Product overview 6 7 Design fundamentals / ubrication / Maintenance 8 Profile cross-sections
Excerpt from main catalogue inear modules V 11-15 SWISS MDE INER TECHNOOGY ine Tech inear modules Table of contents Product overview 6 7 Design fundamentals / ubrication / Maintenance 8 Profile cross-sections
2-9 RG Series High Rigidity Roller Type Linear Guideway
 G99TE17-136 2-9 High Rigidity Roller Type Linear Guideway 2-9-1 Advantages and features The new RG series from Hiwin features a roller as the rolling element instead of steel balls. The roller series offers
G99TE17-136 2-9 High Rigidity Roller Type Linear Guideway 2-9-1 Advantages and features The new RG series from Hiwin features a roller as the rolling element instead of steel balls. The roller series offers
12.1 SINGLE ROW BALL BEARINGS
 12.1 SINGLE ROW BALL BEARINGS Due to the versatility of applications, single row ball bearings are among the most frequently used types of rolling bearings. They are made as non-separable without a filling
12.1 SINGLE ROW BALL BEARINGS Due to the versatility of applications, single row ball bearings are among the most frequently used types of rolling bearings. They are made as non-separable without a filling
HSR-M1. LM Guide High Temperature Type Model HSR-M1. Point of Selection. Point of Design. Options. Model No. Precautions on Use
 LM Guide High Temperature Type Model Endplate SUS304 End seal (High temperature rubber material) LM THK-EX50 Ball SUS440C Side seal (High temperature rubber material) LM rail THK-EX50 Cross section 45
LM Guide High Temperature Type Model Endplate SUS304 End seal (High temperature rubber material) LM THK-EX50 Ball SUS440C Side seal (High temperature rubber material) LM rail THK-EX50 Cross section 45
RSR. LM Guide Miniature Types Model RSR. Point of Selection. Point of Design. Options. Model No. Precautions on Use
 LM Guide Miniature Types Model Endplate LM block End seal LM rail Ball Grease nipple Cross section Point of Selection A Point of Design Options Model No. Precautions on Use Accessories for Lubrication
LM Guide Miniature Types Model Endplate LM block End seal LM rail Ball Grease nipple Cross section Point of Selection A Point of Design Options Model No. Precautions on Use Accessories for Lubrication
LINEAR ACTUATORS. Courtesy of Steven Engineering, Inc. - (800)
 LINEAR ACTUATORS Pre-assembled, all-in-one linear actuators save design and installation time. Choose from NSK's two product lines: MonocarrierTM and ToughcarrierTM. Courtesy of Steven Engineering, Inc.
LINEAR ACTUATORS Pre-assembled, all-in-one linear actuators save design and installation time. Choose from NSK's two product lines: MonocarrierTM and ToughcarrierTM. Courtesy of Steven Engineering, Inc.
SSR. Caged Ball LM Guide Radial Type Model SSR. Point of Selection. Point of Design. Options. Model No. Precautions on Use
 Caged Ball LM Guide Radial Type Model Endplate LM block End seal LM 90 30 Ball Ball cage Cross section * For the Ball Cage, see A. Point of Selection A Point of Design Options Precautions on Use Accessories
Caged Ball LM Guide Radial Type Model Endplate LM block End seal LM 90 30 Ball Ball cage Cross section * For the Ball Cage, see A. Point of Selection A Point of Design Options Precautions on Use Accessories
Modification Method of Back-up Roll Bearing by Replacing Oil Film Bearing with Rolling Bearing
 TECHNICAL REPORT Modification Method of Back-up Roll Bearing by Replacing Oil Film Bearing with Rolling Bearing J. KUBO N. SUZUKI As back-up roll s in rolling mills must support several thousand tons of
TECHNICAL REPORT Modification Method of Back-up Roll Bearing by Replacing Oil Film Bearing with Rolling Bearing J. KUBO N. SUZUKI As back-up roll s in rolling mills must support several thousand tons of
INDEX EASY RAIL: THE SOLUTION IS EASY...D4 EXAMPLES OF LOAD CAPACITIES...D5 ORDER CODES...D6 MOUNTING EXAMPLES...D7 TECHNICAL DATA...
 INDEX EASY RAIL: THE SOLUTION IS EASY...D4 EXAMPLES OF LOAD CAPACITIES...D5 ORDER CODES...D6 MOUNTING EXAMPLES...D7 TECHNICAL DATA...D8 STANDARD CONFIGURATIONS...D10 VERIFICATION UNDER STATIC LOAD...D12
INDEX EASY RAIL: THE SOLUTION IS EASY...D4 EXAMPLES OF LOAD CAPACITIES...D5 ORDER CODES...D6 MOUNTING EXAMPLES...D7 TECHNICAL DATA...D8 STANDARD CONFIGURATIONS...D10 VERIFICATION UNDER STATIC LOAD...D12
3. BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN
 3. BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN 3.1 GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ROLLING BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN Rotating shaft or another component arranged in rolling bearings is guided by them in radial as well as in axial
3. BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN 3.1 GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ROLLING BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN Rotating shaft or another component arranged in rolling bearings is guided by them in radial as well as in axial
Ball Screw Assemblies eline. The Drive & Control Company
 Ball Screw Assemblies eline The Drive & Control Company 2 Bosch Rexroth Corp. Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies eline BSA R310A 3314 (2005.04) Linear Motion Technology Ball Rail Systems Standard
Ball Screw Assemblies eline The Drive & Control Company 2 Bosch Rexroth Corp. Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies eline BSA R310A 3314 (2005.04) Linear Motion Technology Ball Rail Systems Standard
alpha Value Line - NPS Sizing and Technical Data Efficient Flexible Reliable
 alpha Value Line - NPS Sizing and Technical Data Efficient Flexible Reliable alpha Value Line NP NPS NPL NPT NPR Ratios 3-100 Torsional backlash [arcmin] 8 Output type Smooth output shaft Grooved output
alpha Value Line - NPS Sizing and Technical Data Efficient Flexible Reliable alpha Value Line NP NPS NPL NPT NPR Ratios 3-100 Torsional backlash [arcmin] 8 Output type Smooth output shaft Grooved output
1.1 UNITS AND DEFINITIONS 12
 PRODUCT TECHNOLOGY 11 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.1 UNITS AND DEFINITIONS 12 1.2 PRECISION AND TOLERANCES 13 1.2.1 Qualities 13 1.2.2 Profile tolerances 13 1.2.3 Lengths, hole distances 13 1.2.4 Matching 14 1.2.5
PRODUCT TECHNOLOGY 11 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.1 UNITS AND DEFINITIONS 12 1.2 PRECISION AND TOLERANCES 13 1.2.1 Qualities 13 1.2.2 Profile tolerances 13 1.2.3 Lengths, hole distances 13 1.2.4 Matching 14 1.2.5
NEW LM Actuator. US Only. Optimal for high speed and long stroke Long term maintenance-free operation is actualized Lightweight, compact structure
 NEW LM Actuator Optimal for high speed and long stroke Long term maintenance-free operation is actualized Lightweight, compact structure TY US Only CATALOG No.352E Structure of Model TY This belt drive
NEW LM Actuator Optimal for high speed and long stroke Long term maintenance-free operation is actualized Lightweight, compact structure TY US Only CATALOG No.352E Structure of Model TY This belt drive
carriages to carry the load (taking into account any moment loads). Unlike the N series sliders these CS sliders do not have protective side seals.
 Light Duty Sliders, size 18 no side seal, front fixing Long Linear s L1918.CS Material Zinc plated steel body. Steel rollers (100Cr6) with metal (2Z) or rubber (2RS) seals. Technical notes To be used with
Light Duty Sliders, size 18 no side seal, front fixing Long Linear s L1918.CS Material Zinc plated steel body. Steel rollers (100Cr6) with metal (2Z) or rubber (2RS) seals. Technical notes To be used with
LM Guide Actuator KR. For details, visit THK at CATALOG No E. Product information is updated regularly on the THK website.
 LM Guide Actuator KR For details, visit THK at www.thk.com Product information is updated regularly on the THK website. CATALOG No.209-10E Integrated LM Guide and all Screw High-rigidity / High-precision
LM Guide Actuator KR For details, visit THK at www.thk.com Product information is updated regularly on the THK website. CATALOG No.209-10E Integrated LM Guide and all Screw High-rigidity / High-precision
In-house development Own manufacturing Sole distributor in Germany Working with distributors worldwide
 In-house development Own manufacturing Sole distributor in Germany Working with distributors worldwide External Clamping devices Overview 3073 Mini-Range For very low torque transmission Very small profile
In-house development Own manufacturing Sole distributor in Germany Working with distributors worldwide External Clamping devices Overview 3073 Mini-Range For very low torque transmission Very small profile
Planetary. Roller Screw. We invite you to explore and challenges for the future of Kim
 Planetary Roller Screw We invite you to explore and challenges for the future of Kim ontents 05 08 18 24 25 Kim o., td. Design Guidelines Product Information Service Range Application onfiguartion Worksheet
Planetary Roller Screw We invite you to explore and challenges for the future of Kim ontents 05 08 18 24 25 Kim o., td. Design Guidelines Product Information Service Range Application onfiguartion Worksheet
Shaft Couplings Flange-Couplings Rigid Shaft Couplings Flexible Couplings
 Shaft Couplings Flange-Couplings Rigid Shaft Couplings Flexible Couplings 44 Edition 2013/2014 RINGSPANN Registered Trademark of RINGSPANN GmbH, Bad Homburg 2 Table of Contents Flange-Couplings Page Flange-Couplings
Shaft Couplings Flange-Couplings Rigid Shaft Couplings Flexible Couplings 44 Edition 2013/2014 RINGSPANN Registered Trademark of RINGSPANN GmbH, Bad Homburg 2 Table of Contents Flange-Couplings Page Flange-Couplings
SNR, YOUR GUIDE TO LINEAR MODULES
 SNR, YOUR GUIDE TO LINEAR MODULES A bearing manufacturer known across the world For almost a century NTN-SNR has been focusing on the development, design and manufacture of bearings. Today NTN-SNR has
SNR, YOUR GUIDE TO LINEAR MODULES A bearing manufacturer known across the world For almost a century NTN-SNR has been focusing on the development, design and manufacture of bearings. Today NTN-SNR has
alpha Value Line - NP Sizing and Technical Data Effi cient Flexible Reliable
 alpha Value Line - P Sizing and Technical Data Effi cient lexible Reliable alpha Value Line P PS PL PT PR Ratios 3-100 Torsional backlash [arcmin] 8 Output type Smooth output shaft Grooved output shaft
alpha Value Line - P Sizing and Technical Data Effi cient lexible Reliable alpha Value Line P PS PL PT PR Ratios 3-100 Torsional backlash [arcmin] 8 Output type Smooth output shaft Grooved output shaft
CLASSIFICATION OF ROLLING-ELEMENT BEARINGS
 CLASSIFICATION OF ROLLING-ELEMENT BEARINGS Ball bearings can operate at higher speed in comparison to roller bearings because they have lower friction. In particular, the balls have less viscous resistance
CLASSIFICATION OF ROLLING-ELEMENT BEARINGS Ball bearings can operate at higher speed in comparison to roller bearings because they have lower friction. In particular, the balls have less viscous resistance
Heavy-Duty Rod Ends - Male with integral spherical plain bearing
 Heavy-Duty Rod Ends - Male with integral spherical plain bearing 65700 Order No. Thread (hand) d 1 l 1 d 2 d 3 d 4 l 2 l 3 X g H7 65700.W0005 Right 5 33 M 5 11,11 18 20 9 14 65700.W0006 Right 6 36 M 6
Heavy-Duty Rod Ends - Male with integral spherical plain bearing 65700 Order No. Thread (hand) d 1 l 1 d 2 d 3 d 4 l 2 l 3 X g H7 65700.W0005 Right 5 33 M 5 11,11 18 20 9 14 65700.W0006 Right 6 36 M 6
GSM. Modular Design. Versions of the series. Type GSM. Gripper type P Z W R. Size. {} AS IS without O.D. clamping I.D. clamping
 GSM Pneumatic Gripper-Swivel System Modular Design Versions of the series Type GSM Gripper type P Z W R Size 32 40 50 64 30 38 45 16 20 25 32 40 16 20 25 32 40 Gripping force safety device {} AS IS without
GSM Pneumatic Gripper-Swivel System Modular Design Versions of the series Type GSM Gripper type P Z W R Size 32 40 50 64 30 38 45 16 20 25 32 40 16 20 25 32 40 Gripping force safety device {} AS IS without
Servomechkaramoottorit
 Solutions for power transmission Servomechkaramoottorit www.konaflex.fi INDEX 1 Servomech 1. THE PRODUCT 1.1 SERVOMECH Linear Actuators......................... Page 2 1.2 SERVOMECH Linear Actuators range............................
Solutions for power transmission Servomechkaramoottorit www.konaflex.fi INDEX 1 Servomech 1. THE PRODUCT 1.1 SERVOMECH Linear Actuators......................... Page 2 1.2 SERVOMECH Linear Actuators range............................
 www.motiontech.com.au Copyright SERVOMECH This catalogue contents are under publisher copyright and may not be reproduced unless permission is agreed. Every care has been taken to ensure the accuracy of
www.motiontech.com.au Copyright SERVOMECH This catalogue contents are under publisher copyright and may not be reproduced unless permission is agreed. Every care has been taken to ensure the accuracy of
RV1P /118 ED VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT VANE PUMPS SERIES 10 OPERATING PRINCIPLE TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS HYDRAULIC SYMBOL
 14 201/118 ED RV1P VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT VANE PUMPS OPERATING PRINCIPLE TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS (measured with mineral oil with viscosity of 46 cst at 40 C) RV1P are variable displacement vane pumps with
14 201/118 ED RV1P VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT VANE PUMPS OPERATING PRINCIPLE TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS (measured with mineral oil with viscosity of 46 cst at 40 C) RV1P are variable displacement vane pumps with
ROTARY TABLES SERIE TC TECHNOLOGY THAT INSPIRES
 ROTARY TABLES SERIE TC TECHNOLOGY THAT INSPIRES TC FIXED-STATION ROTARY INDEXING TABLES TC ROTARY INDEXING TABLE TC ROTARY INDEXING TABLE: RELIABILITY FOR A LIFETIME EXTENDED WARRANTY Using our rotary
ROTARY TABLES SERIE TC TECHNOLOGY THAT INSPIRES TC FIXED-STATION ROTARY INDEXING TABLES TC ROTARY INDEXING TABLE TC ROTARY INDEXING TABLE: RELIABILITY FOR A LIFETIME EXTENDED WARRANTY Using our rotary
The Classification Chart of PMI Linear Guideways
 1 The Characteristics of MI s The Classification Chart of MI s 2 (1) igh positioning accuracy, high repeatability The MI linear guideway is a design of rolling motion with a low friction coefficient, and
1 The Characteristics of MI s The Classification Chart of MI s 2 (1) igh positioning accuracy, high repeatability The MI linear guideway is a design of rolling motion with a low friction coefficient, and
Components for parallel kinematics
 Components for parallel kinematics Series GLK, GLAE Joints and struts form the core components of machines with parallel kinematics (PKM). Irrespective of the control technology possibilities, good mechanical
Components for parallel kinematics Series GLK, GLAE Joints and struts form the core components of machines with parallel kinematics (PKM). Irrespective of the control technology possibilities, good mechanical
Main Catalogue. EichenbergerGewinde. 100 % Swiss made
 EichenbergerGewinde 100 % Swiss made Main Catalogue Carry ball screws Carry Speed-line high-helix ball screws Speedy high-helix lead screws Rondo round thread lead screws The choice is yours Thread rolling
EichenbergerGewinde 100 % Swiss made Main Catalogue Carry ball screws Carry Speed-line high-helix ball screws Speedy high-helix lead screws Rondo round thread lead screws The choice is yours Thread rolling
Precision Reduction Gear RV TM. E Series / C Series / Original Series
 Precision Reduction Gear RV TM E Series C Series Original Series Nabtesco's technologies o es supporting port society Contributing to society with our Moving it. Stopping it. technologies Nabtesco manufactures
Precision Reduction Gear RV TM E Series C Series Original Series Nabtesco's technologies o es supporting port society Contributing to society with our Moving it. Stopping it. technologies Nabtesco manufactures
Studying the Positioning Accuracy
 Ball Screw Studying the Positioning Accuracy Causes of Error in the Positioning Accuracy Point of Selection Studying the Positioning Accuracy The causes of error in the positioning accuracy include the
Ball Screw Studying the Positioning Accuracy Causes of Error in the Positioning Accuracy Point of Selection Studying the Positioning Accuracy The causes of error in the positioning accuracy include the
Bearing preload. Preload considerations
 Bearing preload There may be some applications where the bearing arrangement needs to be preloaded i.e. requires a negative operating clearance. In applications such as machine tool spindles, automotive
Bearing preload There may be some applications where the bearing arrangement needs to be preloaded i.e. requires a negative operating clearance. In applications such as machine tool spindles, automotive
Features of the LM Guide
 Features of the Functions Required for Linear Guide Surface Large permissible load Highly rigid in all directions High positioning repeatability Running accuracy can be obtained easily High accuracy can
Features of the Functions Required for Linear Guide Surface Large permissible load Highly rigid in all directions High positioning repeatability Running accuracy can be obtained easily High accuracy can
Slides. Dynamic and precise
 Slides Dynamic and precise Product catalog 2017 Latest version of the catalogs You can always find the latest version of our catalogs in the Download area of our website. Disclaimer This publication has
Slides Dynamic and precise Product catalog 2017 Latest version of the catalogs You can always find the latest version of our catalogs in the Download area of our website. Disclaimer This publication has
