SOME TRIBOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF DISC BRAKE PADS
|
|
|
- Samuel Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOME TRIBOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF DISC BRAKE PADS ANDRZEJ GAJEK 1, WOJCIECH SZCZYPIŃSKI-SALA 2 Cracow University of Technology Summary The article presents results of experiments carried out to investigate the impact of modelled conditions of the vehicle operation and its environment on the coefficient of friction in the disc brake friction pair. The influence of these factors on the scatter of values of the coefficient of friction was analysed. The tests were carried out in laboratory conditions on a test stand provided with appropriate instruments and equipment. The friction pair was modelled by a set-up of materials as used in passenger car brakes, consisting of a cast-iron brake disc and composite brake pads. Time histories of the coefficient of friction in the friction pair were tested at various operating conditions (rotational speed of the brake disc, number of braking cycles) and environmental factors (presence of water or brake fluid in the friction area). Changes in the surface roughness of the cast-iron brake disc resulting from the application of various brake pad materials and from different operating conditions and parameters set on the test stand were examined as well. The histories and values of the parameters measured as recorded during the tests were used as input material for analyses. The results of the research work and the conclusions drawn that are applicable to the analysis of criteria of the acceptable differences between the braking forces measured on diagnostic roller test stands have been presented here in a synthetic form. Keywords: disc brakes, friction linings, coefficient of friction, humidity of linings. 1. Introduction The braking system is one of the critical systems of a vehicle, extremely important for active safety. Its effective, efficient, and reliable functioning is a prerequisite condition of safe driving. The length of the braking distance is determined by inter alia the braking torque applied to vehicle wheels by the wheel brake mechanism. With certain simplification, we may state that the braking torque applied to one wheel is a product of the friction force developed between the brake pad and disc or between the brake lining and drum and the friction force arm equal to the inner radius of the brake drum or the arithmetic mean 1 Cracow University of Technology, Institute of Motor Vehicles and Internal Combustion Engines, 37 Al. Jana Pawła II, Cracow, gajeka@mech.pk.edu.pl, ph.: Cracow University of Technology, Institute of Motor Vehicles and Internal Combustion Engines, 37 Al. Jana Pawła II, Cracow, ws@.mech.pk.edu.pl, ph.: SKLAD PIMOT 57_165x234mm+3mm.indd :30:03
2 34 Andrzej Gajek, Wojciech Szczypiński-Sala between the maximum and minimum radii of the area of contact between the brake pad and the brake disc for drum and disc brakes, respectively. In brake mechanisms, the braking torque is directly influenced by the force with which the brake pad or lining is pressed against the brake disc or drum and by the value of the coefficient of friction between the elements rubbing against each other. The functions to be fulfilled by the braking system and the conditions in which the braking system is to operate dictate certain requirements that must be met by the materials used for the friction pairs taken as a whole, i.e. the brake pad and brake disc or the brake lining and brake drum. The requirements arise not only from the necessity that the brake mechanism must fulfil its basic function, i.e. it must control the vehicle speed, but also from the fact that the braking system must not adversely affect the ride comfort. The mass production of motor vehicles and the price competition enforce reductions in the vehicle production and operation costs. The demands that the harmful environmental impact of the products of wear of the friction pair materials should be reduced to minimum constitute another group of expectations formulated in relation to braking system components. In spite of ongoing introduction of new groups of materials to the construction of braking friction pairs, grey cast iron and asbestos-free polymer-organic friction elements still remain the basic materials used for this purpose. According to literature, if the brake assembly components are appropriately designed in respect of reducing their thermal loading then the brakes with cast-iron brake discs and polymer-organic brake pads constitute a very effective solution from the point of view of optimising the braking performance and rationalising the vehicle manufacturing and operation costs. Such brakes are still a subject matter of development work [1, 2, 4, 5]. 2. Purpose of object of the research work The work was undertaken to investigate the impact of various vehicle operation conditions on changes in the coefficient of friction in the disc brake friction pair. The tests were carried out in laboratory conditions on a test stand provided with appropriate instruments and equipment. The object tested was a friction pair defined as a wheel brake mechanism of a passenger car, consisting of a cast-iron disc brake and composite brake pads. 3. Properties of the materials making the brake disc and brake pad friction pair At present, grey cast iron is most commonly used as a material for the production of brake discs of motor vehicles. In spite of numerous drawbacks of this material such as high specific gravity or poor corrosion resistance, the list of its good points predominates. The grey cast iron is characterised by favourable tribological properties and low price. In the case of parts made from this material, the production process methods have already been well mastered and no problems are encountered, either, with the disposal SKLAD PIMOT 57_165x234mm+3mm.indd :30:03
3 Some tribological characteristics of disc brake pads 35 of worn-out products. In most cases, brake discs are made from grey cast iron, where graphite precipitates have the form of flakes, although spheroidal graphite iron is also used. The adding of appropriate alloying agents makes it possible to improve the corrosion resistance, but such a solution is not too frequently applied because of the resulting increase in production costs. Various technical innovations such as material changes or lightening holes introduced in the brake disc design to reduce the total vehicle mass produce some favourable effect but the necessity to maintain adequate mechanical strength of this vehicle component makes this benefit not as conspicuous as it is when other materials, e.g. composites based on light metal alloys, are used [1, 3, 5, 7]. Cast-iron brake discs are shaped in the production process by the machining of castings. The cast brake disc blanks should have no casting defects because the cyclic nature of disc loads would quickly result in damage to such parts during operation. The discs are machined by turning and then their friction surfaces are ground for the required surface roughness parameters to be achieved. The relieving of internal process stresses in the discs makes it possible to reduce the risk of disc deformations during use; therefore, appropriate thermal treatment or seasoning of blanks is applied before the discs are put into service. It should be emphasised here that one of the most important features of cast-iron brake discs from the disc operation point of view is the condition of the working (friction) surface of the disc because this surface is not homogenous, being divided into areas of pearlitic and ferritic structure and other areas where graphite precipitates predominate. Thanks to such an overall structure of the friction surface, high-frequency vibrations are damped. The features considered most important may be indicated not only for brake discs but also for friction materials. In the latter case, vibration-damping capacity may be mentioned as an example; as a rule, the friction materials are heat insulators and their thermal conduction characteristics differ from those of cast iron; when rubbed, such materials emit wear process products to the environment. The friction material components may be classified in four basic groups. The structural components cause the material to have appropriate strength characteristics. In most cases, they have the form of fibres and their surface having been chemically activated should ensure good adhesion to the binder. Thanks to higher thermal conductivity, metallic fibres perform an additional function, i.e. they carry away heat from the friction material. Appropriate fibre orientation and structure makes it possible to obtain desired heat conduction characteristics. Binding agents bind together individual components of the friction material. As the binding agents, phenol resins or synthetic rubber are usually used. The other two groups may be defined as filling agents (fillers) and friction modifiers. The latter group includes the components the role of which is to keep the friction coefficient values stable during the operation of brakes over a wide range of the brake operation conditions. They include metal sulphides, graphite, coke, aluminium oxide, barite, chalk, or zircon sand [1, 2, 4, 6]. SKLAD PIMOT 57_165x234mm+3mm.indd :30:03
4 36 Andrzej Gajek, Wojciech Szczypiński-Sala At present, the stuff collectively defined as asbestos-free organic friction materials finds the widest application in motor vehicle brakes, with fibres of various kinds, such as metallic, glass, aramid, and mineral fibres, being used as the basic structural component of such materials [8,9]. The mechanical strength of friction materials chiefly depends on the types of the structural components and binders used. The thermal resistance is determined by characteristics of the organic components, which are the first to undergo degradation under the impact of raised temperatures. A typical organic friction material consists of over twenty components. A characteristic feature of such materials is low thermal conduction. For the operation of the friction pair, this has the meaning that most of the friction heat generated goes to the brake disc. To meet the increasingly stringent requirements concerning the thermal loads of brakes, materials with increased metallic contents have been introduced. Metallic components may fulfil structural functions, i.e. constitute the matrix of the brake pad, as well as play the role of filler. In the former application, they have the form of fibres, while metallic powders are used in the latter case. Metallic components have a decisive impact on thermal characteristics of the friction material. Higher concentration of metallic components results in better thermal conduction. A favourable effect of better thermal conduction is the fact that heat is faster carried away from the friction area. This, however, is connected with the necessity to insulate the brake pad from the hydraulic piston in the brake calliper in order to prevent the transfer of excessive heat amounts to brake fluid [5, 6, 7]. The brake pad production process includes thermal treatment by holding the pads at a raised temperature to improve performance characteristics of the pads that have to operate in high temperature conditions when the brakes must be repeatedly applied with high intensity. When the pads are held at a raised temperature, degassing takes place in the compacted mouldings of the friction material. This process prevents a loss of friction ability of the brake friction pair in result of the forming of a gaseous phase between the friction surfaces when the brakes are intensively used in extreme vehicle operation conditions. 4. Results of testing the coefficient of friction of the brake friction pair The investigation of the impact of the actual condition of a disc brake friction pair on the coefficient of friction in this pair and the subsequent evaluation of variations in the values of this coefficient is of significant importance for the analysis of the braking process. The objective of this part of the research work was to determine the impact of the type of a brake pad in its nominal condition on the value and scatter of the coefficient of friction in the friction pair involved. Results of this work should be taken into account at defining the acceptable differences between the braking forces measured during diagnostic examination of vehicle brakes on roller test stands [9]. SKLAD PIMOT 57_165x234mm+3mm.indd :30:03
5 Some tribological characteristics of disc brake pads 37 The following conditions were adopted for the tests carried out on the test stand: The rotational speed of the brake disc could vary within a range from 26.2 to 87.2 rad/s, which corresponded to the vehicle linear speed ranging from 30 to 100 km/h; The average length of the friction force arm was m; The unit pressure between the working surfaces of the friction pair ranged from 320 to 530 N/cm 2, which corresponded to a fluid pressure in the braking system of the model passenger car ranging from 6 to 10 MPa, i.e. the brake fluid pressure occurring at hard braking; The friction pairs under tests were tribological systems consisting of brake pads and cast-iron brake discs; the friction material of the brake pads was made to four different process methods and the friction surfaces of the brake discs were ground to obtain a surface roughness of R a = 0.25 µm. The friction coefficient values obtained in result of experiments carried out for friction pairs consisting of cast-iron brake discs with surface roughness as specified above and brake pads manufactured to different process methods (by different manufacturers) have been presented in Table 1. Table 1. Average values of the coefficient of friction in the friction pairs under tests Process method (manufacturer) Average value of the coefficient of friction av Standard deviation S( ) S( )/ av [%] I II III IV Significant scatter in the friction coefficient values was observed, as the values ranged from 0.39 to 0.54 (see Table 1). Visual examination of the condition of the friction surfaces, confirmed by spectrographic examinations, revealed distinct differences to exist between the brake pads made by different manufacturers, regarding the granulation and distribution of individual material components, the degree of compacting and tightness of material structure, as well as the quantity and distribution of the filler and metal particles carrying away heat from the friction surface. The factors as indicated above have a significant impact on the coefficient of friction and the characteristics of interaction between elements of the brake friction pair. The coefficient of friction measured for friction pairs with materials made by different manufacturers changed, i.e. rose by 5 to 40%, during a single braking process (Figs. 1 4). Individual braking tests were carried out in conditions corresponding to those occurring at long-lasting normal braking on a road. The least changes in the friction coefficient values were recorded for the brake pads made by manufacturer IV. SKLAD PIMOT 57_165x234mm+3mm.indd :30:03
6 38 Andrzej Gajek, Wojciech Szczypiński-Sala Fig. 1. Changes in the coefficient of friction of brake pads during a single braking process. Manufacturer I; test conditions: p = 530 N/cm 2, n = 500 rpm = 52.3 rad/s Fig. 2. Changes in the coefficient of friction of brake pads during a single braking process. Manufacturer II; test conditions: p = 530 N/cm 2, n = 500 rpm = 52.3 rad/s The tests carried out showed the changes in the friction coefficient values to be caused by the friction heat generated during the braking. This finding was confirmed by measurements of temperature of the brake disc, because the temperature of the friction surface continuously rose during the 20 s time of duration of the braking process. The SKLAD PIMOT 57_165x234mm+3mm.indd :30:03
7 Some tribological characteristics of disc brake pads 39 Fig. 3. Changes in the coefficient of friction of brake pads during a single braking process. Manufacturer III; test conditions: p = 530 N/cm 2, n = 500 rpm = 52.3 rad/s Fig. 4. Changes in the coefficient of friction of brake pads during a single braking process. Manufacturer IV; test conditions: p = 530 N/cm 2, n = 500 rpm = 52.3 rad/s dependence of the coefficient of friction on temperature has been shown in Fig. 5. This dependence was determined for a relatively narrow range of changes in the brake disc temperature, corresponding to the changes that take place during vehicle braking in urban traffic conditions. SKLAD PIMOT 57_165x234mm+3mm.indd :30:03
8 40 Andrzej Gajek, Wojciech Szczypiński-Sala Fig. 5. The impact of changes in the temperature of the friction pair on the coefficient of friction. Test conditions: p = 425 N/cm 2, n = 500 rpm Fig. 6. Changes in the coefficient of friction in the disc brake friction pair during the running-in period. Manufacturer I; test conditions: p = 425 N/cm 2, n = 500 rpm The period of running-in of new brake pads to the brake disc was also tested. During multiple repeated braking, the coefficient of friction considerably increased. At the beginning of the running-in period, the friction coefficient value made about 66% of that measured at the final stage of this process (Fig. 6). The increase took place during the first several dozen applications of brakes. During this process, the surface roughness of the brake disc considerably changed (Fig. 7). Originally, the surface roughness of the brand new cast-iron SKLAD PIMOT 57_165x234mm+3mm.indd :30:03
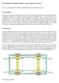
9 Some tribological characteristics of disc brake pads 41 Fig. 7. Profilograms of the brake disc friction surface, taken along the direction of motion: a) new disc (ground); b) disc after 10 braking cycles; c) disc after 200 braking cycles SKLAD PIMOT 57_165x234mm+3mm.indd :30:04
10 42 Andrzej Gajek, Wojciech Szczypiński-Sala disc was R a = 0.26 µm. After 10 braking cycles, the surface roughness parameter dropped to a value of R a = 0.11 µm and the friction coefficient value increased by about 30%. After 200 braking cycles, the disc surface roughness was R a = 0.04 µm. 5. Research on the impact of water on the coefficient of friction of brake pads It is an inherent design feature of disc brake mechanisms that they are exposed to the impact of external factors. It is normal in the conditions of operation of braking systems that brake pads get damp, brake discs are temporarily or permanently wet, and all these parts become contaminated. This is due to the easy access of contaminants of any kind to the area of interaction between friction elements. One of the objectives of the research work carried out was to assess the impact of external (atmospheric) factors, e.g. water, and internal (vehicle-related) factors, e.g. brake fluid, on the functioning and performance of the disc brake friction pair. The impact of dampness of the friction surfaces in the brake mechanism on braking performance was assessed on the grounds of rig test results, with analysing the history of the coefficient of friction in the friction pair exposed to water attack during the process of braking. The tests were carried out for two values of the rotational speed, i.e. 530 rpm and 250 rpm, which corresponded to vehicle drive speeds of 64 km/h and 30 km/h, respectively, and Fig. 8. Time histories of the coefficient of friction, with the condition of the brake friction pair being changed from dry to wet, for 10 braking tests. Test conditions: p = 425 N/cm 2, n = 500 rpm SKLAD PIMOT 57_165x234mm+3mm.indd :30:04
11 Some tribological characteristics of disc brake pads 43 for two brake disc wetting modes, i.e. temporary and continuous wetting. The test results have been presented in Figs. 8, 9, and 10. When the braking test was started from a speed of 64 km/h with the brake disc being dry and then the disc was wetted during the test, the wetting resulted in a sudden drop in the coefficient of friction by about 40%. After about 1.5 to 3 s from the wetting, the coefficient of friction gradually increased to a level of about 80% of that recorded for the friction pair with dry brake disc. After the test, the temperature of the brake disc was about 40 C. The increase in the coefficient of friction resulted from the fact that water was automatically removed from the disc. At the tests carried out with a lower initial speed, corresponding to a vehicle speed of 30 km/h, the single wetting of the brake disc caused the coefficient of friction to drop by about 30% and this coefficient remained low for several seconds (Fig. 9), much longer than it was at the initial speed of 530 rpm (cf. Fig. 8). This may be probably explained by lower values of the centrifugal forces acting on water droplets and, in consequence, slower rate of the self-cleaning process. Fig. 9. Time histories of the coefficient of friction, with the condition of the brake friction pair being changed from dry to wet, for 10 braking tests. Test conditions: p = 425 N/cm 2, n = 250 rpm At the braking test carried out with continuous wetting of the brake disc, the coefficient of friction permanently remained on a low level of below 0.3 (Fig. 10) as against the values of 0.4 to 0.45 recorded when the friction pair was dry. Such an effect occurs at vehicle speeds ranging from 30 to 40 km/h, i.e. in urban traffic conditions, when the automatic removal of water from the brake disc is rather poor. SKLAD PIMOT 57_165x234mm+3mm.indd :30:04
12 44 Andrzej Gajek, Wojciech Szczypiński-Sala Fig. 10. Time histories of the coefficient of friction, with the brake friction pair being continuously wetted, for 10 braking tests. Test conditions: p = 425 N/cm 2, n = 250 rpm 6. Research on the impact of brake fluid on the coefficient of friction Results of evaluation how the presence of brake fluid in the friction pair affects the braking performance have been presented in graphs in Fig. 11. They depict time histories of changes in the coefficient of friction during multiple braking. The first braking cycle was started with the brake disc and pad being dry and then the brake disc was moistened with brake fluid during the braking. The next braking cycles were carried out with the same brake disc, without cleaning it, and the moistening of the disc with brake fluid was repeated during the braking. The time histories of the coefficient of friction determined for the friction pairs with brake pads made by various manufacturers did not considerably differ from each other. The appearance of even a small quantity of brake fluid on the friction surface of the brake disc resulted in a radical drop in the coefficient of friction in comparison with the value observed when the disc was dry. The first braking cycle presented in Fig. 11 depicts the interaction between the brake pad with the dry disc. The introduction of brake fluid into the contact area within the friction pair caused a very significant drop, by about 70%, in the coefficient of friction. At the next braking cycles, the friction coefficient value did not exceed a level of 0.1 and did not show any rising trend. This means that the brake fluid once absorbed by the contacting surfaces of the friction elements remains present there and significantly reduces the coefficient of friction. It was also observed that the next moistening of the rubbing surfaces with brake fluid caused the coefficient of friction to SKLAD PIMOT 57_165x234mm+3mm.indd :30:05
13 Some tribological characteristics of disc brake pads 45 drop by another 50% (Fig. 11), but this was a short-lived effect followed by an increase in this coefficient. This tendency to rise, resembling a regeneration ability of the friction material, probably depends on the material structure. In the case of the brake pad specimens made by manufacturer I, the re-application of brake liquid caused a temporary drop in the coefficient of friction to a value of about 0.05 followed by a phase of slow-rate rising trend in this coefficient; for the pads made by manufacturer II, the regeneration effect, i.e. the recovery of the coefficient of friction to its value preceding the re-application of brake fluid, came within a much shorter time. In both cases, however, the coefficient of friction did not recover to its value as measured for the friction pair being dry (about 0.35 to 0.39) and remained on a level close to that recorded when the disc was moistened with brake fluid for the first time (about 0.1). Fig. 11. Changes in the coefficient of friction in the disc brake friction pair contaminated with brake fluid. The tests were carried out for two different brake pad materials Test conditions: p = 425 N/cm 2, n = 250 rpm 7. Conclusions 1. The tribological experiments have revealed that differences of the order of 4% may occur in the coefficient of friction between friction pairs with brake pads made by the same manufacturer. The friction surface temperature has also been observed to have a significant impact on the friction coefficient value. 2. In consideration of the revealed differences in friction coefficient values and the accuracy of diagnostic roller test stands of the order of 5% of the measured braking force value, a statement should be made that for brand new braking system components SKLAD PIMOT 57_165x234mm+3mm.indd :30:05
14 46 Andrzej Gajek, Wojciech Szczypiński-Sala in full running order, the results of testing the braking forces on the right and left wheels on diagnostic test stands are likely to differ from each other by about 10%. Such a difference should not be considered a functional defect of the braking system because it may result from normal scatter in the characteristics of friction materials and from the properties of measuring stands. 3. If the brake of one of vehicle wheels is suddenly wetted with water and the brake on the other side operates in normal conditions then an instantaneous difference of even up to 40% in the coefficient of friction between the dry and wet brake may develop, which would then decline during the braking process to about 20%. At the next braking cycle, the coefficient of friction recovers to a value as that of the dry friction pair. At long-lasting wetting, the coefficient of friction in the friction pair drops by about 25% in comparison with that of the same friction pair when dry. 4. Damage to the brake assembly resulting in contamination of the brake disc surface with brake fluid causes the coefficient of friction in the brake friction pair to drop by even 70% and thus significantly reduces the braking torque; in consequence, the vehicle braking performance is dangerously lowered. Such a failure should be immediately detected and indicated to the driver by the on-board diagnostic system. References [1] FLEURY E., LEE S. M., KIM J. S., KIM D. H., KIM W. T., AHN H. S.: Tribological properties of Al-Ni-Co-Si quasicrystalline coatings against Cr-coated cast iron disc. Wear, 253, [2] KENNEDY F. E., BALBAHADUR A. C., LASHMORE D. S.: The friction and wear of Cu-based silicon carbide particulate metal matrix composites for brake applications. Wear, , [3] SHERRINGTON I., HAYHURST P.: Simultaneous observation of the evolution of debris density and friction coefficient in dry sliding steel contacts. Wear, 249, [4] BERNS H.: Comparison of wear resistant MMC and white cast iron. Wear, 254, [5] ERIKSSON M., JACOBSON S.: Tribological surfaces of organic brake pads. Tribology International, 33, [6] JAWORSKI J.: Okładziny cierne do hamulców i sprzęgieł pojazdów mechanicznych (Friction linings for brakes and clutches of motor vehicles). WKiŁ, Warszawa, [7] FOMAR company publications, [8] STADLER Z., KRNEL K., KOSMAC T. Friction and wear of sintered metallic brake linings on a C/C-SiC composite brake disc. Wear 265, [9] SEONG J. K., MIN H. C., KEUN H. C., HO J., Complementary effects of solid lubricants in the automotive brake lining. Tribology International 40, The research work was carried out within the research and development project of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education No. NM Development of diagnostic monitors for an on-board passenger car brakes diagnostic system. SKLAD PIMOT 57_165x234mm+3mm.indd :30:05
Examining the braking energy recovery in a vehicle with a hybrid drive system
 Examining the braking energy recovery in a vehicle with a hybrid drive system ANDRZEJ GAJEK 1, PIOTR STRZĘPEK 2 Cracow University of Technology Summary Results of examining the braking energy recovery
Examining the braking energy recovery in a vehicle with a hybrid drive system ANDRZEJ GAJEK 1, PIOTR STRZĘPEK 2 Cracow University of Technology Summary Results of examining the braking energy recovery
PREPARATION, TESTING AND COMPARISON OF FRICTION COMPOSITES. Nanotechnology Centre, VŠB-Technical University of Ostrava, Czech Republic
 PREPARATION, TESTING AND COMPARISON OF FRICTION COMPOSITES Marek Krygel 1, Miroslav Vaculik 1,2, Jana Kukutschova 1,2, Peter Filip 1 1 Nanotechnology Centre, VŠB-Technical University of Ostrava, Czech
PREPARATION, TESTING AND COMPARISON OF FRICTION COMPOSITES Marek Krygel 1, Miroslav Vaculik 1,2, Jana Kukutschova 1,2, Peter Filip 1 1 Nanotechnology Centre, VŠB-Technical University of Ostrava, Czech
COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES
 COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES No. Course Learning Outcome 1. 2. Compare working principle and identify advantages/disadvantages between the disc and drum brake systems used in passenger vehicles Analyze deceleration
COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES No. Course Learning Outcome 1. 2. Compare working principle and identify advantages/disadvantages between the disc and drum brake systems used in passenger vehicles Analyze deceleration
Design of Piston Ring Surface Treatment for Reducing Lubricating Oil Consumption
 The 3rd International Conference on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES 2014 Pilsen, Czech Republic, August 31 September 3, 2014 Design of Piston Ring Surface Treatment for Reducing Lubricating Consumption
The 3rd International Conference on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES 2014 Pilsen, Czech Republic, August 31 September 3, 2014 Design of Piston Ring Surface Treatment for Reducing Lubricating Consumption
MULTI-PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION OF BRAKE OF PISTON
 3 2 1 MULTI-PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION OF BRAKE OF PISTON Á. Horváth 1, I. Oldal 2, G. Kalácska 1, M. Andó 3 Institute for Mechanical Engineering Technology, Szent István University, 2100 Gödöllő, Páter Károly
3 2 1 MULTI-PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION OF BRAKE OF PISTON Á. Horváth 1, I. Oldal 2, G. Kalácska 1, M. Andó 3 Institute for Mechanical Engineering Technology, Szent István University, 2100 Gödöllő, Páter Károly
Performance Testing of Composite Bearing Materials for Large Hydraulic Cylinders
 TECHNICAL Performance Testing of Composite Bearing Materials for Large Hydraulic Cylinders Leo Dupuis, Bosch-Rexroth Sr. Development Engineer Introduction Large hydraulic cylinders (LHCs) are integral
TECHNICAL Performance Testing of Composite Bearing Materials for Large Hydraulic Cylinders Leo Dupuis, Bosch-Rexroth Sr. Development Engineer Introduction Large hydraulic cylinders (LHCs) are integral
Extremely High Load Capacity Tapered Roller Bearings
 New Product Extremely High Load Capacity Tapered Roller Bearings Takashi UENO Tomoki MATSUSHITA Standard tapered roller bearing Extreme high load capacity bearing NTN developed a tapered roller bearing
New Product Extremely High Load Capacity Tapered Roller Bearings Takashi UENO Tomoki MATSUSHITA Standard tapered roller bearing Extreme high load capacity bearing NTN developed a tapered roller bearing
Application Note #1013 Measuring the Behavior of Brake Materials More Efficiently: Correlation Between Benchtop and Dynamometer Tests
 Deceleration Test Brake Material Screening Tester UMT TriboLab Application Note #1013 Measuring the Behavior of Brake Materials More Efficiently: Correlation Between Benchtop and Dynamometer Tests Testing
Deceleration Test Brake Material Screening Tester UMT TriboLab Application Note #1013 Measuring the Behavior of Brake Materials More Efficiently: Correlation Between Benchtop and Dynamometer Tests Testing
Article: The Formation & Testing of Sludge in Bunker Fuels By Dr Sunil Kumar Laboratory Manager VPS Fujairah 15th January 2018
 Article: The Formation & Testing of Sludge in Bunker Fuels By Dr Sunil Kumar Laboratory Manager VPS Fujairah 15th January 2018 Introduction Sludge formation in bunker fuel is the source of major operational
Article: The Formation & Testing of Sludge in Bunker Fuels By Dr Sunil Kumar Laboratory Manager VPS Fujairah 15th January 2018 Introduction Sludge formation in bunker fuel is the source of major operational
Simulating Rotary Draw Bending and Tube Hydroforming
 Abstract: Simulating Rotary Draw Bending and Tube Hydroforming Dilip K Mahanty, Narendran M. Balan Engineering Services Group, Tata Consultancy Services Tube hydroforming is currently an active area of
Abstract: Simulating Rotary Draw Bending and Tube Hydroforming Dilip K Mahanty, Narendran M. Balan Engineering Services Group, Tata Consultancy Services Tube hydroforming is currently an active area of
CHAPTER 5 PARAMETRIC STUDIES AND SQUEAL REDUCTION METHODS
 17 CHAPTER 5 PARAMETRIC STUDIES AND SQUEAL REDUCTION METHODS 5.1 INTRODUCTION Generally, there are a number of methods that have been used in order to reduce squeal for the improvement of passengers comfort.
17 CHAPTER 5 PARAMETRIC STUDIES AND SQUEAL REDUCTION METHODS 5.1 INTRODUCTION Generally, there are a number of methods that have been used in order to reduce squeal for the improvement of passengers comfort.
DISC BRAKES. Section 4. Components and Operation of Disc Brakes. Disc Brake Assembly
 DISC BRAKES Components and Operation of Disc Brakes A disc brake assembly consists of a: cast iron disc (disc rotor) that rotates with the wheel. caliper assembly attached to the steering knuckle. friction
DISC BRAKES Components and Operation of Disc Brakes A disc brake assembly consists of a: cast iron disc (disc rotor) that rotates with the wheel. caliper assembly attached to the steering knuckle. friction
TWO-PIECE BRAKE DISCS IN A VEHICLE
 TWO-PIECE BRAKE DISCS IN A VEHICLE www.hella-pagid.com TWO-PIECE BRAKE DISCS IN A VEHICLE Ever since the disc brake system was introduced into cars, the brake disc has been a significant structural component
TWO-PIECE BRAKE DISCS IN A VEHICLE www.hella-pagid.com TWO-PIECE BRAKE DISCS IN A VEHICLE Ever since the disc brake system was introduced into cars, the brake disc has been a significant structural component
Kolbenschmidt Pierburg Group
 Kolbenschmidt Pierburg Group KS Aluminum Pistons for Truck Applications Requirements The development of on- and off-highway diesel engines for a wide spectrum of applications is affected by global emission
Kolbenschmidt Pierburg Group KS Aluminum Pistons for Truck Applications Requirements The development of on- and off-highway diesel engines for a wide spectrum of applications is affected by global emission
STUDY OF THE INFLUENCE OF THE TYPE OF FUEL USED IN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES OVER THE RHEOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF LUBRICANTS
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 9 (58) No. 2 - Special Issue 2016 Series I: Engineering Sciences STUDY OF THE INFLUENCE OF THE TYPE OF FUEL USED IN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES OVER
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 9 (58) No. 2 - Special Issue 2016 Series I: Engineering Sciences STUDY OF THE INFLUENCE OF THE TYPE OF FUEL USED IN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES OVER
C. Brake pads Replaceable friction surfaces that are forced against the rotor by the caliper piston.
 BRAKES UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION TO BRAKE SYSTEMS LESSON 1: FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES OF BRAKE SYSTEMS I. Terms and definitions A. Brake fading Loss of brakes, usually due to heat. B. Brake lining Material mounted
BRAKES UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION TO BRAKE SYSTEMS LESSON 1: FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES OF BRAKE SYSTEMS I. Terms and definitions A. Brake fading Loss of brakes, usually due to heat. B. Brake lining Material mounted
MULTIPOINT SPARK IGNITION ENGINE OPERATING ON LEAN MIXTURE
 MULTIPOINT SPARK IGNITION ENGINE OPERATING ON LEAN MIXTURE Karol Cupiał, Arkadiusz Kociszewski, Arkadiusz Jamrozik Technical University of Częstochowa, Poland INTRODUCTION Experiment on multipoint spark
MULTIPOINT SPARK IGNITION ENGINE OPERATING ON LEAN MIXTURE Karol Cupiał, Arkadiusz Kociszewski, Arkadiusz Jamrozik Technical University of Częstochowa, Poland INTRODUCTION Experiment on multipoint spark
RENEP CGLP. High-performance slideway oils for machine tools, with excellent demulsification properties. Description. Advantages
 Description The quality of machined components depends heavily on the accurate feed and accurate positioning provided by machine tool slideways with slideway oils playing an important role. Slideway oils
Description The quality of machined components depends heavily on the accurate feed and accurate positioning provided by machine tool slideways with slideway oils playing an important role. Slideway oils
FEATURE ARTICLE Opacimeter MEXA-130S
 FEATURE ARTICLE Opacimeter MEXA-13S Technical Reports Nobutaka Kihara System configuration diagram Detector Unit Fan Sample gas inlet Detector gas Light Mirror Heater source Half-mirror Lens Principle
FEATURE ARTICLE Opacimeter MEXA-13S Technical Reports Nobutaka Kihara System configuration diagram Detector Unit Fan Sample gas inlet Detector gas Light Mirror Heater source Half-mirror Lens Principle
PRODUCT INFORMATION SHEET
 Page 1 of 18 31592 WYNN S DPF Cleaner & Regenerator WYNN S Diesel Particulate Filter Cleaner & Regenerator Product Number: 31592 12 x 325ml New technologies to reduce emissions with diesel engines The
Page 1 of 18 31592 WYNN S DPF Cleaner & Regenerator WYNN S Diesel Particulate Filter Cleaner & Regenerator Product Number: 31592 12 x 325ml New technologies to reduce emissions with diesel engines The
AIR CLASSIFIERS FOR INDUSTRIAL MINERALS CTM SERIES
 AIR CLASSIFIERS FOR INDUSTRIAL MINERALS CTM SERIES w w w. c e m t e c. a t CEMTEC your partner for success. CEMTEC operates on the basis of individual responsibility. Each member of our team is authorised
AIR CLASSIFIERS FOR INDUSTRIAL MINERALS CTM SERIES w w w. c e m t e c. a t CEMTEC your partner for success. CEMTEC operates on the basis of individual responsibility. Each member of our team is authorised
2016 International Conference on Engineering Tribology and Applied Technology
 Tribological Performance Evaluation of Biodiesel Distilled Residues Blended with Fossil Diesel Yang-Ching Lin 1,a, Hung-Shiau Chen 1,b, Chun-Ching Hsu 1,c, YONG-YUAN KU 2,d, KE-WEI LIN 2,e 1 Department
Tribological Performance Evaluation of Biodiesel Distilled Residues Blended with Fossil Diesel Yang-Ching Lin 1,a, Hung-Shiau Chen 1,b, Chun-Ching Hsu 1,c, YONG-YUAN KU 2,d, KE-WEI LIN 2,e 1 Department
Modelling and Assembly of Single Plate Clutch
 Modelling and Assembly of Single Plate Clutch V. Nikesh M.Tech (CAD\CAM) Tudi Ram Reddy Institute of Technology and Science. ABSTACT A Clutch is a machine member used to connect the driving shaft to a
Modelling and Assembly of Single Plate Clutch V. Nikesh M.Tech (CAD\CAM) Tudi Ram Reddy Institute of Technology and Science. ABSTACT A Clutch is a machine member used to connect the driving shaft to a
M-11 MARINE DIESEL ENGINE FUEL INJECTOR
 Guideline No.M-11(201510) M-11 MARINE DIESEL ENGINE FUEL INJECTOR Issued date: 20 October 2015 China Classification Society Foreword This Guideline constitutes the CCS rules, and establishes the applicable
Guideline No.M-11(201510) M-11 MARINE DIESEL ENGINE FUEL INJECTOR Issued date: 20 October 2015 China Classification Society Foreword This Guideline constitutes the CCS rules, and establishes the applicable
Noise Reduction in Railway Traffic Noise Abatement at Source
 Noise Reduction in Railway Traffic Noise Abatement at Source Dipl.-Ing. Harald Willrich, FUCHS LUBRITECH GmbH, D-67685 Weilerbach 1 The Problem Many railway companies throughout the world are increasingly
Noise Reduction in Railway Traffic Noise Abatement at Source Dipl.-Ing. Harald Willrich, FUCHS LUBRITECH GmbH, D-67685 Weilerbach 1 The Problem Many railway companies throughout the world are increasingly
Influence of Fuel Injector Position of Port-fuel Injection Retrofit-kit to the Performances of Small Gasoline Engine
 Influence of Fuel Injector Position of Port-fuel Injection Retrofit-kit to the Performances of Small Gasoline Engine M. F. Hushim a,*, A. J. Alimin a, L. A. Rashid a and M. F. Chamari a a Automotive Research
Influence of Fuel Injector Position of Port-fuel Injection Retrofit-kit to the Performances of Small Gasoline Engine M. F. Hushim a,*, A. J. Alimin a, L. A. Rashid a and M. F. Chamari a a Automotive Research
Effect of plus sizing on driving comfort and safety of users
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effect of plus sizing on driving comfort and safety of users To cite this article: I. Hetmaczyk 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effect of plus sizing on driving comfort and safety of users To cite this article: I. Hetmaczyk 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
ANALYSIS OF THE ENGINE FUELS IMPACT ON CARBON DIOXIDE EMISSIONS
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 18, No. 4 2011 ANALYSIS OF THE ENGINE FUELS IMPACT ON CARBON DIOXIDE EMISSIONS Barbara Worsztynowicz AGH University of Science and Technology Faculty of
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 18, No. 4 2011 ANALYSIS OF THE ENGINE FUELS IMPACT ON CARBON DIOXIDE EMISSIONS Barbara Worsztynowicz AGH University of Science and Technology Faculty of
The Testing and Data Analyzing of Automobile Braking Performance. Peijiang Chen
 International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering (ICCSE 2015) The Testing and Data Analyzing of Automobile Braking Performance Peijiang Chen School of Automobile, Linyi University, Shandong,
International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering (ICCSE 2015) The Testing and Data Analyzing of Automobile Braking Performance Peijiang Chen School of Automobile, Linyi University, Shandong,
THE EFFECT OF AUTOMOTIVE VEHICLE BRAKING SYSTEM FAILURE ON DRIVING SAFETY
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 20, No. 1 2013 THE EFFECT OF AUTOMOTIVE VEHICLE BRAKING SYSTEM FAILURE ON DRIVING SAFETY Mariusz Kowalski The First Airlift Base wirki i Wigury Street 1c,
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 20, No. 1 2013 THE EFFECT OF AUTOMOTIVE VEHICLE BRAKING SYSTEM FAILURE ON DRIVING SAFETY Mariusz Kowalski The First Airlift Base wirki i Wigury Street 1c,
Proven to be better. Development trends in industrial rolling bearings
 Proven to be better Development trends in industrial rolling bearings Contents 1. General trends in power transmission and in machine construction and plant engineering Page 3 2. General trends in rolling
Proven to be better Development trends in industrial rolling bearings Contents 1. General trends in power transmission and in machine construction and plant engineering Page 3 2. General trends in rolling
Continuous Stribeck Curve Measurement Using Pin-on-Disk Tribometer
 Continuous Stribeck Curve Measurement Using Pin-on-Disk Tribometer Prepared by Duanjie Li, PhD 6 Morgan, Ste156, Irvine CA 92618 P: 949.461.9292 F: 949.461.9232 nanovea.com Today's standard for tomorrow's
Continuous Stribeck Curve Measurement Using Pin-on-Disk Tribometer Prepared by Duanjie Li, PhD 6 Morgan, Ste156, Irvine CA 92618 P: 949.461.9292 F: 949.461.9232 nanovea.com Today's standard for tomorrow's
BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES
 BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES AUTOMOTIVE BRAKING SYSTEMS How brakes manufacturing industry is different then rest of the automotive
BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES AUTOMOTIVE BRAKING SYSTEMS How brakes manufacturing industry is different then rest of the automotive
I. INTRODUCTION. Sehsah, E.M. Associate Prof., Agric. Eng. Dept Fac, of Agriculture, Kafr El Sheikh Univ.33516, Egypt
 Manuscript Processing Details (dd/mm/yyyy) : Received : 14/09/2013 Accepted on : 23/09/2013 Published : 13/10/2013 Study on the Nozzles Wear in Agricultural Hydraulic Sprayer Sehsah, E.M. Associate Prof.,
Manuscript Processing Details (dd/mm/yyyy) : Received : 14/09/2013 Accepted on : 23/09/2013 Published : 13/10/2013 Study on the Nozzles Wear in Agricultural Hydraulic Sprayer Sehsah, E.M. Associate Prof.,
Electromagnetic Field Analysis for Permanent Magnet Retarder by Finite Element Method
 017 Asia-Pacific Engineering and Technology Conference (APETC 017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-443-1 Electromagnetic Field Analysis for Permanent Magnet Retarder by Finite Element Method Chengye Liu, Xinhua Zhang
017 Asia-Pacific Engineering and Technology Conference (APETC 017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-443-1 Electromagnetic Field Analysis for Permanent Magnet Retarder by Finite Element Method Chengye Liu, Xinhua Zhang
Rolling resistance as a part of total resistance plays a
 Rolling resistance plays a critical role in fuel consumption of mining haul trucks A. Soofastaei, L. Adair, S.M. Aminossadati, M.S. Kizil and P. Knights Mining3, The University of Queensland Australia.
Rolling resistance plays a critical role in fuel consumption of mining haul trucks A. Soofastaei, L. Adair, S.M. Aminossadati, M.S. Kizil and P. Knights Mining3, The University of Queensland Australia.
Design and Analysis of Electromagnetic Tubular Linear Actuator for Higher Performance of Active Accelerate Pedal
 Journal of Magnetics 14(4), 175-18 (9) DOI: 1.483/JMAG.9.14.4.175 Design and Analysis of Electromagnetic Tubular Linear Actuator for Higher Performance of Active Accelerate Pedal Jae-Yong Lee, Jin-Ho Kim-,
Journal of Magnetics 14(4), 175-18 (9) DOI: 1.483/JMAG.9.14.4.175 Design and Analysis of Electromagnetic Tubular Linear Actuator for Higher Performance of Active Accelerate Pedal Jae-Yong Lee, Jin-Ho Kim-,
WEAR PROFILE OF THE CYLINDER LINER IN A MOTOR TRUCK DIESEL ENGINE
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol.14, No. 4 27 WEAR PROFILE OF THE CYLINDER LINER IN A MOTOR TRUCK DIESEL ENGINE Grzegorz Kosza ka, Andrzej Niewczas Lublin University of Technology Dept. of
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol.14, No. 4 27 WEAR PROFILE OF THE CYLINDER LINER IN A MOTOR TRUCK DIESEL ENGINE Grzegorz Kosza ka, Andrzej Niewczas Lublin University of Technology Dept. of
The influence of fuel injection pump malfunctions of a marine 4-stroke Diesel engine on composition of exhaust gases
 Article citation info: LEWIŃSKA, J. The influence of fuel injection pump malfunctions of a marine 4-stroke Diesel engine on composition of exhaust gases. Combustion Engines. 2016, 167(4), 53-57. doi:10.19206/ce-2016-405
Article citation info: LEWIŃSKA, J. The influence of fuel injection pump malfunctions of a marine 4-stroke Diesel engine on composition of exhaust gases. Combustion Engines. 2016, 167(4), 53-57. doi:10.19206/ce-2016-405
INVESTIGATION OF FRICTION COEFFICIENTS OF ADDITIVATED ENGINE LUBRICANTS IN FALEX TESTER
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 7 (56) No. 2-2014 Series I: Engineering Sciences INVESTIGATION OF FRICTION COEFFICIENTS OF ADDITIVATED ENGINE LUBRICANTS IN FALEX TESTER L. GERGELY
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 7 (56) No. 2-2014 Series I: Engineering Sciences INVESTIGATION OF FRICTION COEFFICIENTS OF ADDITIVATED ENGINE LUBRICANTS IN FALEX TESTER L. GERGELY
Experimental Investigation of Effects of Shock Absorber Mounting Angle on Damping Characterstics
 Experimental Investigation of Effects of Shock Absorber Mounting Angle on Damping Characterstics Tanmay P. Dobhada Tushar S. Dhaspatil Prof. S S Hirmukhe Mauli P. Khapale Abstract: A shock absorber is
Experimental Investigation of Effects of Shock Absorber Mounting Angle on Damping Characterstics Tanmay P. Dobhada Tushar S. Dhaspatil Prof. S S Hirmukhe Mauli P. Khapale Abstract: A shock absorber is
Normal vs Abnormal Combustion in SI engine. SI Combustion. Turbulent Combustion
 Turbulent Combustion The motion of the charge in the engine cylinder is always turbulent, when it is reached by the flame front. The charge motion is usually composed by large vortexes, whose length scales
Turbulent Combustion The motion of the charge in the engine cylinder is always turbulent, when it is reached by the flame front. The charge motion is usually composed by large vortexes, whose length scales
Is Low Friction Efficient?
 Is Low Friction Efficient? Assessment of Bearing Concepts During the Design Phase Dipl.-Wirtsch.-Ing. Mark Dudziak; Schaeffler Trading (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China Dipl.-Ing. (TH) Andreas Krome,
Is Low Friction Efficient? Assessment of Bearing Concepts During the Design Phase Dipl.-Wirtsch.-Ing. Mark Dudziak; Schaeffler Trading (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China Dipl.-Ing. (TH) Andreas Krome,
Improving Methods of Wear Resistance in Heavy Loaded Sliding Friction Pairs
 Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Okayama University, Vol.39, pp.1-6, January, 2005 Improving Methods of Wear Resistance in Heavy Loaded Sliding Friction Pairs Vladimir I. KLOCHIKHIN Russian Academy
Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Okayama University, Vol.39, pp.1-6, January, 2005 Improving Methods of Wear Resistance in Heavy Loaded Sliding Friction Pairs Vladimir I. KLOCHIKHIN Russian Academy
Tests of the acoustic emission of the power steering column equipped with a modified composite worm gear housing
 Tests of the acoustic emission of the power steering column equipped with a modified composite worm gear housing Marek Płaczek 1, Andrzej Wróbel 2, Mateusz Czechowski 3, Andrzej Baier 4 Silesian University
Tests of the acoustic emission of the power steering column equipped with a modified composite worm gear housing Marek Płaczek 1, Andrzej Wróbel 2, Mateusz Czechowski 3, Andrzej Baier 4 Silesian University
Merkel PRW 1 Double Wiper with Integrated Pressure Relieve. Product Information Merkel Hydraulics
 Merkel PRW 1 Double Wiper with Integrated Pressure Relieve Product Information Merkel Hydraulics Simrit, Your Global Technology Specialist for Seals and Vibration Control Simrit, Your Global Technology
Merkel PRW 1 Double Wiper with Integrated Pressure Relieve Product Information Merkel Hydraulics Simrit, Your Global Technology Specialist for Seals and Vibration Control Simrit, Your Global Technology
Featured Articles Utilization of AI in the Railway Sector Case Study of Energy Efficiency in Railway Operations
 128 Hitachi Review Vol. 65 (2016), No. 6 Featured Articles Utilization of AI in the Railway Sector Case Study of Energy Efficiency in Railway Operations Ryo Furutani Fumiya Kudo Norihiko Moriwaki, Ph.D.
128 Hitachi Review Vol. 65 (2016), No. 6 Featured Articles Utilization of AI in the Railway Sector Case Study of Energy Efficiency in Railway Operations Ryo Furutani Fumiya Kudo Norihiko Moriwaki, Ph.D.
3. BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN
 3. BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN 3.1 GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ROLLING BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN Rotating shaft or another component arranged in rolling bearings is guided by them in radial as well as in axial
3. BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN 3.1 GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ROLLING BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN Rotating shaft or another component arranged in rolling bearings is guided by them in radial as well as in axial
Design and experiment of hydraulic impact loading system for mine cable bolt
 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 1 (2009) 1337 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia The 6 th International Conference on Mining Science & Technology Design and experiment
Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 1 (2009) 1337 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia The 6 th International Conference on Mining Science & Technology Design and experiment
COATING YOUR WAY TO LOWER EMISSIONS
 COATING YOUR WAY TO LOWER EMISSIONS With vehicle production growing annually and manufacturers under pressure to reduce exhaust emissions, new and innovative methods will have to be found to increase engine
COATING YOUR WAY TO LOWER EMISSIONS With vehicle production growing annually and manufacturers under pressure to reduce exhaust emissions, new and innovative methods will have to be found to increase engine
Temperature Field in Torque Converter Clutch
 3rd International Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Intelligent Systems (ICMEIS 2015) Temperature Field in Torque Converter Clutch Zhenjie Liu 1, a, Chao Yi 1,b and Ye Wang 1,c 1 The State Key Laboratory
3rd International Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Intelligent Systems (ICMEIS 2015) Temperature Field in Torque Converter Clutch Zhenjie Liu 1, a, Chao Yi 1,b and Ye Wang 1,c 1 The State Key Laboratory
ARMOURED VEHICLES BRAKES TESTS
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 18, No. 3 2011 ARMOURED VEHICLES BRAKES TESTS Zbigniew Skorupka, Rafa Kajka, Wojciech Kowalski Institute of Aviation, Landing Gear Department Aleja Krakowska
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 18, No. 3 2011 ARMOURED VEHICLES BRAKES TESTS Zbigniew Skorupka, Rafa Kajka, Wojciech Kowalski Institute of Aviation, Landing Gear Department Aleja Krakowska
Triple offset butterfly valve meets the stringent requirements of TA-Luft and ISO Advanced environmental protection the ZETRIX way!
 Triple offset butterfly valve meets the stringent requirements of TA-Luft and ISO 15848 Author: Michael Vullhorst (Laboratory Manager ARI-Armaturen) Introduction Both TA-Luft [1] and DIN EN ISO 15848-1
Triple offset butterfly valve meets the stringent requirements of TA-Luft and ISO 15848 Author: Michael Vullhorst (Laboratory Manager ARI-Armaturen) Introduction Both TA-Luft [1] and DIN EN ISO 15848-1
ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES
 ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN: 1995-0772 Published BYAENSI Publication EISSN: 1998-1090 http://www.aensiweb.com/anas 2017 April 11(4): pages 544-550 Open Access Journal Analysis Of Sliding
ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN: 1995-0772 Published BYAENSI Publication EISSN: 1998-1090 http://www.aensiweb.com/anas 2017 April 11(4): pages 544-550 Open Access Journal Analysis Of Sliding
Fatigue properties of railway axles: new results of full-scale specimens
 Fatigue properties of railway axles: new results of full-scale specimens Steven Cervello Lucchini RS, Italy TC24 Meeting Advances in: Axle Durability Analysis and Maintenance Politecnico di Milano 1-2
Fatigue properties of railway axles: new results of full-scale specimens Steven Cervello Lucchini RS, Italy TC24 Meeting Advances in: Axle Durability Analysis and Maintenance Politecnico di Milano 1-2
COMPRESSIBLE FLOW ANALYSIS IN A CLUTCH PISTON CHAMBER
 COMPRESSIBLE FLOW ANALYSIS IN A CLUTCH PISTON CHAMBER Masaru SHIMADA*, Hideharu YAMAMOTO* * Hardware System Development Department, R&D Division JATCO Ltd 7-1, Imaizumi, Fuji City, Shizuoka, 417-8585 Japan
COMPRESSIBLE FLOW ANALYSIS IN A CLUTCH PISTON CHAMBER Masaru SHIMADA*, Hideharu YAMAMOTO* * Hardware System Development Department, R&D Division JATCO Ltd 7-1, Imaizumi, Fuji City, Shizuoka, 417-8585 Japan
Gauge Face Wear Caused with Vehicle/Track Interaction
 Gauge Face Wear Caused with Vehicle/Track Interaction Makoto ISHIDA*, Mitsunobu TAKIKAWA, Ying JIN Railway Technical Research Institute 2-8-38 Hikari-cho, Kokubunji-shi, Tokyo 185-8540, Japan Tel: +81-42-573-7291,
Gauge Face Wear Caused with Vehicle/Track Interaction Makoto ISHIDA*, Mitsunobu TAKIKAWA, Ying JIN Railway Technical Research Institute 2-8-38 Hikari-cho, Kokubunji-shi, Tokyo 185-8540, Japan Tel: +81-42-573-7291,
GMD 13 New gravimetric measuring system with evaluation on location
 Dr. Födisch Umweltmesstechnik AG Zwenkauer Strasse 159 04420 Markranstädt Germany Phone: +49 34205 755-0 Fax: +49 34205 755-40 E-mail: sales@foedisch.de Internet: www.foedisch.de GMD 13 New gravimetric
Dr. Födisch Umweltmesstechnik AG Zwenkauer Strasse 159 04420 Markranstädt Germany Phone: +49 34205 755-0 Fax: +49 34205 755-40 E-mail: sales@foedisch.de Internet: www.foedisch.de GMD 13 New gravimetric
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 11, November -2015 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 DESIGN
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 11, November -2015 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 DESIGN
INTEROPERABILITY UNIT FRICTION ELEMENTS FOR WHEEL TREAD BRAKES FOR FREIGHT WAGONS
 INTEROPERABILITY UNIT TECHNICAL DOCUMENT FRICTION ELEMENTS FOR WHEEL TREAD BRAKES FOR FREIGHT WAGONS REFERENCE: ERA/TD/2013-02/INT DOCUMENT TYPE: TECHNICAL DOCUMENT VERSION: 3.0 DATE: 27/11/2015 ERA/TD/2013-02/INT
INTEROPERABILITY UNIT TECHNICAL DOCUMENT FRICTION ELEMENTS FOR WHEEL TREAD BRAKES FOR FREIGHT WAGONS REFERENCE: ERA/TD/2013-02/INT DOCUMENT TYPE: TECHNICAL DOCUMENT VERSION: 3.0 DATE: 27/11/2015 ERA/TD/2013-02/INT
OT PEENING PROCESS AND ITS APPLICATIONS
 lmerwtvmal Conference on Shot Peening and Blast Cleaning OT PEENING PROCESS AND ITS APPLICATIONS P. S. PURANIK Department of Mechanical Engineering, V. V. P Engineering College, Virda - Vajdi, Kalawad
lmerwtvmal Conference on Shot Peening and Blast Cleaning OT PEENING PROCESS AND ITS APPLICATIONS P. S. PURANIK Department of Mechanical Engineering, V. V. P Engineering College, Virda - Vajdi, Kalawad
Development of High-performance Phenolic Resin Idler Pulley
 TECHNICAL PAPER Development of High-performance Phenolic Resin Idler Pulley H. ARAI K. MORI Resins idler pulleys in automotive engines are increasingly used for improving fuel efficiency through weight
TECHNICAL PAPER Development of High-performance Phenolic Resin Idler Pulley H. ARAI K. MORI Resins idler pulleys in automotive engines are increasingly used for improving fuel efficiency through weight
The analysis of the accuracy of the wheel alignment inspection method on the side-slip plate stand
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The analysis of the accuracy of the wheel alignment inspection method on the side-slip plate stand To cite this article: A Gajek
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The analysis of the accuracy of the wheel alignment inspection method on the side-slip plate stand To cite this article: A Gajek
Safety factor and fatigue life effective design measures
 Safety factor and fatigue life effective design measures Many catastrophic failures have resulted from underestimation of design safety and/or fatigue of structures. Failure examples of engineered structures
Safety factor and fatigue life effective design measures Many catastrophic failures have resulted from underestimation of design safety and/or fatigue of structures. Failure examples of engineered structures
Plastic Ball Bearing Design Improvement Using Finite Element Method
 2017 Published in 5th International Symposium on Innovative Technologies in Engineering and Science 29-30 September 2017 (ISITES2017 Baku - Azerbaijan) Plastic Ball Bearing Design Improvement Using Finite
2017 Published in 5th International Symposium on Innovative Technologies in Engineering and Science 29-30 September 2017 (ISITES2017 Baku - Azerbaijan) Plastic Ball Bearing Design Improvement Using Finite
RANDO HDZ. Rando HDZ, our premium, zinc additized, anti-wear hydraulic oil that helps provide you with:
 HYDRAULIC OILS RANDO HDZ The demands on your equipment, time and bottom line multiply daily. Rando HDZ helps keep your equipment operating longer, faster and harder, allowing you to extend the time between
HYDRAULIC OILS RANDO HDZ The demands on your equipment, time and bottom line multiply daily. Rando HDZ helps keep your equipment operating longer, faster and harder, allowing you to extend the time between
Application Note Original Instructions Development of Gas Fuel Control Systems for Dry Low NOx (DLN) Aero-Derivative Gas Turbines
 Application Note 83404 Original Instructions Development of Gas Fuel Control Systems for Dry Low NOx (DLN) Aero-Derivative Gas Turbines Woodward reserves the right to update any portion of this publication
Application Note 83404 Original Instructions Development of Gas Fuel Control Systems for Dry Low NOx (DLN) Aero-Derivative Gas Turbines Woodward reserves the right to update any portion of this publication
E/ECE/324/Rev.1/Add.89/Rev.3/Amend.3 E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.1/Add.89/Rev.3/Amend.3
 22 February 2017 Agreement Concerning the Adoption of Uniform Technical Prescriptions for Wheeled Vehicles, Equipment and Parts which can be Fitted and/or be Used on Wheeled Vehicles and the Conditions
22 February 2017 Agreement Concerning the Adoption of Uniform Technical Prescriptions for Wheeled Vehicles, Equipment and Parts which can be Fitted and/or be Used on Wheeled Vehicles and the Conditions
The Effect of Spring Pressure on Carbon Brush Wear Rate
 The Effect of Spring Pressure on Carbon Brush Wear Rate By Jeff D. Koenitzer, P.E. Milwaukee, Wisconsin, USA Preface 2008 For decades there was extensive testing of countless different carbon brush contact
The Effect of Spring Pressure on Carbon Brush Wear Rate By Jeff D. Koenitzer, P.E. Milwaukee, Wisconsin, USA Preface 2008 For decades there was extensive testing of countless different carbon brush contact
TESTING OF AUTOMOBILE VW GOLF OPERATING ON THREE DIFFERENT FUELS
 TESTING OF AUTOMOBILE VW GOLF OPERATING ON THREE DIFFERENT FUELS Ilmars Dukulis, Vilnis Pirs, Zanis Jesko, Aivars Birkavs, Gints Birzietis Latvia University of Agriculture Ilmars.Dukulis@llu.lv, Vilnis.Pirs@llu.lv,
TESTING OF AUTOMOBILE VW GOLF OPERATING ON THREE DIFFERENT FUELS Ilmars Dukulis, Vilnis Pirs, Zanis Jesko, Aivars Birkavs, Gints Birzietis Latvia University of Agriculture Ilmars.Dukulis@llu.lv, Vilnis.Pirs@llu.lv,
THE USE OF DIGITAL HYDRAULIC TO THE POSITION CONTROL OF HYDRAULIC CYLINDER
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 23, No. 3 2016 THE USE OF DIGITAL HYDRAULIC TO THE POSITION CONTROL OF HYDRAULIC CYLINDER Piotr Kucybała, Andrzej Sobczyk ISSN: 1231-4005 e-issn: 2354-0133
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 23, No. 3 2016 THE USE OF DIGITAL HYDRAULIC TO THE POSITION CONTROL OF HYDRAULIC CYLINDER Piotr Kucybała, Andrzej Sobczyk ISSN: 1231-4005 e-issn: 2354-0133
Module7:Advanced Combustion Systems and Alternative Powerplants Lecture 32:Stratified Charge Engines
 ADVANCED COMBUSTION SYSTEMS AND ALTERNATIVE POWERPLANTS The Lecture Contains: DIRECT INJECTION STRATIFIED CHARGE (DISC) ENGINES Historical Overview Potential Advantages of DISC Engines DISC Engine Combustion
ADVANCED COMBUSTION SYSTEMS AND ALTERNATIVE POWERPLANTS The Lecture Contains: DIRECT INJECTION STRATIFIED CHARGE (DISC) ENGINES Historical Overview Potential Advantages of DISC Engines DISC Engine Combustion
The influence of thermal regime on gasoline direct injection engine performance and emissions
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The influence of thermal regime on gasoline direct injection engine performance and emissions To cite this article: C I Leahu
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The influence of thermal regime on gasoline direct injection engine performance and emissions To cite this article: C I Leahu
OVERALL INSPECTION AND INTEGRITY ASSESSMENT OF OIL AND OIL PRODUCTS STORAGE TANKS R.S.
 OVERALL INSPECTION AND INTEGRITY ASSESSMENT OF OIL AND OIL PRODUCTS STORAGE TANKS R.S. Gaspariants., G.A. Giller (JSC VNIIST, RUSSIA) L.Y. Mogilner., Y.Y. Semin (CJSC VNIIST-Diagnostika, RUSSIA) Steel
OVERALL INSPECTION AND INTEGRITY ASSESSMENT OF OIL AND OIL PRODUCTS STORAGE TANKS R.S. Gaspariants., G.A. Giller (JSC VNIIST, RUSSIA) L.Y. Mogilner., Y.Y. Semin (CJSC VNIIST-Diagnostika, RUSSIA) Steel
DaimlerChrysler Alternative Particulate Measurement page 1/8
 DaimlerChrysler Alternative Particulate Measurement page 1/8 Investigation of Alternative Methods to Determine Particulate Mass Emissions Dr. Oliver Mörsch Petra Sorsche DaimlerChrysler AG Background and
DaimlerChrysler Alternative Particulate Measurement page 1/8 Investigation of Alternative Methods to Determine Particulate Mass Emissions Dr. Oliver Mörsch Petra Sorsche DaimlerChrysler AG Background and
INTERPRETATION OF USED COOLANT ANALYSIS
 RECO-COOL TECHNICAL BULLETIN 0006/12 INTERPRETATION OF USED COOLANT ANALYSIS Testing of coolants in use (whilst still within service) can give a vital indication on the health of the cooling system of
RECO-COOL TECHNICAL BULLETIN 0006/12 INTERPRETATION OF USED COOLANT ANALYSIS Testing of coolants in use (whilst still within service) can give a vital indication on the health of the cooling system of
SKF Explorer spherical roller bearings Optimized for superior field performance
 SKF Explorer spherical roller bearings Optimized for superior field performance Continuous improvement to optimize The timeline below illustrates SKF milestones in the development of self-aligning bearings.
SKF Explorer spherical roller bearings Optimized for superior field performance Continuous improvement to optimize The timeline below illustrates SKF milestones in the development of self-aligning bearings.
The Experimental Study of the Plateau Performance of the F6L913 Diesel Engine
 Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com The Experimental Study of the Plateau Performance of the F6L913 Diesel Engine 1 Weiming Zhang, 2 Jiang Li 1, 2 Dept. of Petroleum Supply
Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com The Experimental Study of the Plateau Performance of the F6L913 Diesel Engine 1 Weiming Zhang, 2 Jiang Li 1, 2 Dept. of Petroleum Supply
INVESTIGATION OF ICING EFFECTS ON AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF AIRCRAFT AT TSAGI
 INVESTIGATION OF ICING EFFECTS ON AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF AIRCRAFT AT TSAGI Andreev G.T., Bogatyrev V.V. Central AeroHydrodynamic Institute (TsAGI) Abstract Investigation of icing effects on aerodynamic
INVESTIGATION OF ICING EFFECTS ON AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF AIRCRAFT AT TSAGI Andreev G.T., Bogatyrev V.V. Central AeroHydrodynamic Institute (TsAGI) Abstract Investigation of icing effects on aerodynamic
White paper: Pneumatics or electrics important criteria when choosing technology
 White paper: Pneumatics or electrics important criteria when choosing technology The requirements for modern production plants are becoming increasingly complex. It is therefore essential that the drive
White paper: Pneumatics or electrics important criteria when choosing technology The requirements for modern production plants are becoming increasingly complex. It is therefore essential that the drive
A manufacturer s view of bushing reliability, testing and analysis. Lars Jonsson Håkan Rudegard
 A manufacturer s view of bushing reliability, testing and analysis By Lars Jonsson Håkan Rudegard 1 A manufacturer s view of bushing reliability, testing and analysis Lars Jonsson Håkan Rudegard ABB Sweden
A manufacturer s view of bushing reliability, testing and analysis By Lars Jonsson Håkan Rudegard 1 A manufacturer s view of bushing reliability, testing and analysis Lars Jonsson Håkan Rudegard ABB Sweden
LEVER OPTIMIZATION FOR TORQUE STANDARD MACHINES
 LEVER OPTIMIZATION FOR TORQUE STANDARD MACHINES D. Röske, K. Adolf and D. Peschel Torque laboratory Division for Mechanics and Acoustics Phys.-Techn. Bundesanstalt, D-38116 Braunschweig, Germany Abstract:
LEVER OPTIMIZATION FOR TORQUE STANDARD MACHINES D. Röske, K. Adolf and D. Peschel Torque laboratory Division for Mechanics and Acoustics Phys.-Techn. Bundesanstalt, D-38116 Braunschweig, Germany Abstract:
Using cloud to develop and deploy advanced fault management strategies
 Using cloud to develop and deploy advanced fault management strategies next generation vehicle telemetry V 1.0 05/08/18 Abstract Vantage Power designs and manufactures technologies that can connect and
Using cloud to develop and deploy advanced fault management strategies next generation vehicle telemetry V 1.0 05/08/18 Abstract Vantage Power designs and manufactures technologies that can connect and
Development of Motor-Assisted Hybrid Traction System
 Development of -Assisted Hybrid Traction System 1 H. IHARA, H. KAKINUMA, I. SATO, T. INABA, K. ANADA, 2 M. MORIMOTO, Tetsuya ODA, S. KOBAYASHI, T. ONO, R. KARASAWA Hokkaido Railway Company, Sapporo, Japan
Development of -Assisted Hybrid Traction System 1 H. IHARA, H. KAKINUMA, I. SATO, T. INABA, K. ANADA, 2 M. MORIMOTO, Tetsuya ODA, S. KOBAYASHI, T. ONO, R. KARASAWA Hokkaido Railway Company, Sapporo, Japan
Performance Testing of Single Plate Automatic Clutch
 Performance Testing of Single Plate Automatic Clutch Nilkanth Badhe 1, S.V.Patil 2 P.G. Student, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, RMD Sinhgad School of Engineering, Pune, Maharashtra, India 1 Associate
Performance Testing of Single Plate Automatic Clutch Nilkanth Badhe 1, S.V.Patil 2 P.G. Student, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, RMD Sinhgad School of Engineering, Pune, Maharashtra, India 1 Associate
Variable Valve Drive From the Concept to Series Approval
 Variable Valve Drive From the Concept to Series Approval New vehicles are subject to ever more stringent limits in consumption cycles and emissions. At the same time, requirements in terms of engine performance,
Variable Valve Drive From the Concept to Series Approval New vehicles are subject to ever more stringent limits in consumption cycles and emissions. At the same time, requirements in terms of engine performance,
Illustrations of the need for precision and repeatability in tribology testing
 Illustrations of the need for precision and repeatability in tribology testing Falex Tribology nv dr. ir. Dirk Drees Tribology is the science and technology related to friction, wear and lubrication Introduction
Illustrations of the need for precision and repeatability in tribology testing Falex Tribology nv dr. ir. Dirk Drees Tribology is the science and technology related to friction, wear and lubrication Introduction
CFD ANALYSIS ON LOUVERED FIN
 CFD ANALYSIS ON LOUVERED FIN P.Prasad 1, L.S.V Prasad 2 1Student, M. Tech Thermal Engineering, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam, India 2Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam,
CFD ANALYSIS ON LOUVERED FIN P.Prasad 1, L.S.V Prasad 2 1Student, M. Tech Thermal Engineering, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam, India 2Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam,
White Paper Bearing Lubrication
 White Paper Bearing Lubrication Lubrication of Rolling Bearings One of the most important requirements for effective function of bearing arrangements is proper lubrication. The lubricant forms the layer
White Paper Bearing Lubrication Lubrication of Rolling Bearings One of the most important requirements for effective function of bearing arrangements is proper lubrication. The lubricant forms the layer
EXAMINATION OF THE AMMONIA DOSE INFLUENCE ON NITRIC OXIDES TRANSFORMATIONS INTO COMBINED OXIDE-PLATINUM SCR CATALYST
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 19, No. 4 2012 EXAMINATION OF THE AMMONIA DOSE INFLUENCE ON NITRIC OXIDES TRANSFORMATIONS INTO COMBINED OXIDE-PLATINUM SCR CATALYST Wojciech Kamela, Stanis
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 19, No. 4 2012 EXAMINATION OF THE AMMONIA DOSE INFLUENCE ON NITRIC OXIDES TRANSFORMATIONS INTO COMBINED OXIDE-PLATINUM SCR CATALYST Wojciech Kamela, Stanis
USING ENGINE OIL TO IMPROVE FUEL ECONOMY
 USING ENGINE OIL TO IMPROVE FUEL ECONOMY Everything you need to know about HTHS viscosity Brian Humphrey, OEM Technical Liaison - HD Driveline, Petro-Canada Lubricants 1 CONTENT OUTLINE 1. What is HTHS
USING ENGINE OIL TO IMPROVE FUEL ECONOMY Everything you need to know about HTHS viscosity Brian Humphrey, OEM Technical Liaison - HD Driveline, Petro-Canada Lubricants 1 CONTENT OUTLINE 1. What is HTHS
A Fundamental Study Concerning the Proper Performance of Lift Buffers in Revised JIS A 4306
 A Fundamental Study Concerning the Proper Performance of Lift Buffers in Revised JIS A 4306 Osamu Furuya 1, Naoki Fujiwara 2 and Satoshi Fujita 3 1 Associate Professor, Division of Electronics and Mechanical
A Fundamental Study Concerning the Proper Performance of Lift Buffers in Revised JIS A 4306 Osamu Furuya 1, Naoki Fujiwara 2 and Satoshi Fujita 3 1 Associate Professor, Division of Electronics and Mechanical
Modal Analysis of Automobile Brake Drum Based on ANSYS Workbench Dan Yang1, 2,Zhen Yu1, 2, Leilei Zhang1, a * and Wentao Cheng2
 7th International Conference on Mechatronics, Computer and Education Informationization (MCEI 2017) Modal Analysis of Automobile Brake Drum Based on ANSYS Workbench Dan Yang1, 2,Zhen Yu1, 2, Leilei Zhang1,
7th International Conference on Mechatronics, Computer and Education Informationization (MCEI 2017) Modal Analysis of Automobile Brake Drum Based on ANSYS Workbench Dan Yang1, 2,Zhen Yu1, 2, Leilei Zhang1,
YOUR PARTNER FOR THE MACHINING OF CRANKSHAFTS AND CAMSHAFTS. A Company of the SWAROVSKI Group
 YOUR PARTNER FOR THE MACHINING OF CRANKSHAFTS AND CAMSHAFTS A Company of the SWAROVSKI Group www.tyrolit.com TYROLIT TECHNOLOGICAL LEADER AND PARTNER ON EQUAL FOOTING TYROLIT has been developing innovative
YOUR PARTNER FOR THE MACHINING OF CRANKSHAFTS AND CAMSHAFTS A Company of the SWAROVSKI Group www.tyrolit.com TYROLIT TECHNOLOGICAL LEADER AND PARTNER ON EQUAL FOOTING TYROLIT has been developing innovative
Design Analysis and Optimization of Disc Brake
 Design Analysis and Optimization of Disc Brake Assembly of A 4- Wheeler Race C ar Avijit Singh Gangwar B.E. Automobile Engineer Manipal Institute Of Technology Abstract-A disc brake is a wheel brake which
Design Analysis and Optimization of Disc Brake Assembly of A 4- Wheeler Race C ar Avijit Singh Gangwar B.E. Automobile Engineer Manipal Institute Of Technology Abstract-A disc brake is a wheel brake which
To study the constructional features of ammeter, voltmeter, wattmeter and energymeter.
 Experiment o. 1 AME OF THE EXPERIMET To study the constructional features of ammeter, voltmeter, wattmeter and energymeter. OBJECTIVE 1. To be conversant with the constructional detail and working of common
Experiment o. 1 AME OF THE EXPERIMET To study the constructional features of ammeter, voltmeter, wattmeter and energymeter. OBJECTIVE 1. To be conversant with the constructional detail and working of common
High-performance slideway oils for machine tools, with excellent demulsification properties
 CGLP SLIDEWAY OILS High-performance slideway oils for machine tools, with excellent demulsification properties Description The quality of machined components depends heavily on the accurate feed and accurate
CGLP SLIDEWAY OILS High-performance slideway oils for machine tools, with excellent demulsification properties Description The quality of machined components depends heavily on the accurate feed and accurate
Burn Characteristics of Visco Fuse
 Originally appeared in Pyrotechnics Guild International Bulletin, No. 75 (1991). Burn Characteristics of Visco Fuse by K.L. and B.J. Kosanke From time to time there is speculation regarding the performance
Originally appeared in Pyrotechnics Guild International Bulletin, No. 75 (1991). Burn Characteristics of Visco Fuse by K.L. and B.J. Kosanke From time to time there is speculation regarding the performance
Mining, mineral processing and cement industries Solutions for mills and crushers
 Mining, mineral processing and cement industries Solutions for mills and crushers THE POWER OF KNOWLEDGE ENGINEERING Mining and cement plant operators face a major challenge: keeping up a high-quality
Mining, mineral processing and cement industries Solutions for mills and crushers THE POWER OF KNOWLEDGE ENGINEERING Mining and cement plant operators face a major challenge: keeping up a high-quality
White Paper: The Physics of Braking Systems
 White Paper: The Physics of Braking Systems The Conservation of Energy The braking system exists to convert the energy of a vehicle in motion into thermal energy, more commonly referred to as heat. From
White Paper: The Physics of Braking Systems The Conservation of Energy The braking system exists to convert the energy of a vehicle in motion into thermal energy, more commonly referred to as heat. From
