Full-scale measurements on the Erasmus bridge after rain/wind induced cable vibrations
|
|
|
- Meryl Dorsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Full-scale measurements on the Erasmus bridge after rain/wind induced cable vibrations A.J. Persoon and K. Noorlander
2 Full-scale measurements on the Erasmus bridge after rain/wind induced cable vibrations A.J. Persoon and K. Noorlander* * Public Works Rotterdam This report is based on a presentation held at the 10 th International Conference on Wind Engineering, Copenhagen, Denmark, June 21-24, The report will also be published as an article in the Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics. The contents of this report may be cited on condition that full credit is given to NLR and the authors. Division: Fluid Dynamics Issued: March 1999 Classification of title: unclassified
3 -2- Abstract In November 1996, the Erasmus bridge showed the phenomenon rain/wind induced vibrations. Under rain and windy weather the stay-cables started to vibrate. During this incident the bridge was closed for all traffic while the stay-cables were immediately connected to the bridge deck by poly-ethyleen ropes, whereafter the vibrations quickly died out. A full-scale test campaign was initiated by the Public Works of Rotterdam to avoid cable vibrations in future, resulting in newly installed hydraulic dampers between cables and bridge deck. A preliminary monitoring system was installed to verify whether the dampers did not introduce negative effects on the vibrational behaviour of the bridge deck itself and to verify the vibrational amplitudes due to vortex excitation as predicted by wind tunnel tests. Up till now, no vibrations of any importance have been reported.
4 -3- Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Preventing cable vibrations 5 3 Design of the dampers 6 4 Full-scale tests 8 5 Bridge deck monitoring 11 6 Concluding remarks 15 7 References 16 (16 pages in total)
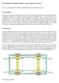
5 -4-1 Introduction In the morning of November 4 th, 1996, the stay-cables of the Erasmus bridge located in Rotterdam (the Netherlands) started to vibrate under rain and windy weather. Cable vibrations were observed with amplitudes of around 2 to 3 times the diameter (0.2 m) being 0.5 to 0.7 m mostly in the second mode shape. The bridge deck showed minor vibrations with amplitudes of around 25 mm. Precautions were taken by mounting poly-ethyleen ropes between the cables and bridge deck whereafter the vibrations quickly died out. After intensive discussions, also with experts from abroad, it became clear that the Erasmus bridge, like many other bridges worldwide, was subjected to the phenomenom wind/rain induced vibrations. Although the main span of the bridge is of a medium size (285 m), the longest cables have a length of nearly 300 m, because the bridge has only one pylon (Fig. 1). Obviously the cables, having a smooth poly-ethyleen casing, became vulnerable to the specific excitation mechanism by which water rivulets, as observed on the cables, play an important role (Matsumoto 1992 and Hikami 1988). As the original installed dampers, mainly designed to supress vortex excitation, were not capable of preventing unstable behaviour of the cables, a full-scale test campaign was initiated by the Public Works of Rotterdam in order to find a solution to prevent cable vibrations in the future. This resulted, within one year, in the installation of new hydraulic dampers between cables and bridge deck. Simultaneously, equipment was installed to monitor the behaviour of the bridge deck on the long term. This paper summarizes the design of the dampers, presents some significant results from full-scale testing and deals with the general idea that monitoring becomes more and more important to understand the behaviour of civil structures on the long term. poly-ethyleen ropes stay-cable m Fig. 1 The Erasmus Bridge
6 -5-2 Preventing cable vibrations In the open literature, a number of measures are described to prevent cable vibrations under rain and windy conditions (Fig. 2). Aerodynamic means such as surface roughness or protuberances on the casing as a precaution were not selected by the Public Works of Rotterdam, as the effectiveness of such means is still under discussion (Flamand 1994 and Matsumoto 1990) e.g. under circumstances like for example the occurrence of ice accretion. Furthermore taking such measures on existing cables will result in high costs, or it may even to be impossible to modify the outer shape from a practical point of view. From discussions by the Public Works with Japanese specialists, it was concluded that increasing of the structural damping by hydraulic dampers was the most promising counter-measure to control cable vibrations. For that reason, a test-campaign was initiated to verify the design of prototype dampers which have to increase the structural damping of the cables to at least 0.8% c/cr (percentage of critical damping) within a frequency range up to 3 Hz. Above this frequency (being the sixth or seventh vibration mode) no cable vibrations are reported in literature. This is due to the fact that the required high wind speeds will blow water rivulets away from the cable casing and consequently eliminate the excitation mechanism. hydraulic damper (proposed by Public Works) aerodynamic Fig. 2 Aerodynamic counter-measures to prevent cable vibrations
7 -6-3 Design of the dampers The original dampers were chosen in accordance with the recommendations of the Eurocode to suppress vibrations by vortex shedding. Chosen were automobile type shock absorbers. Through a mechanical linkage formed by the anti-vandalism tube, the point of application of the damping force was about 6.5 m from the end point of the stays. As already mentioned the amount of damping of this system, although sufficient to suppress resonance due to vortex shedding, was too low to suppress vibrations by the rain/wind phenomena. Extensive Finite Element calculations showed that the dampers should have a damping coefficient of 30 to 40 knms -1 in order to reach the intended level of damping. The new damping system should not only fulfil damping requirements; quite important were reliability, maintenance and aesthetical viewpoints. The position of the dampers with respect to the distance of the fixed end point of the stay was governed by the consideration that the dampers should be effective up to 3 Hz. For the longest stay this would mean up to seven eigen frequencies and a maximum distance of the damper of about 20 m. From an aesthetic viewpoint the damper should be as near to the fixed end point as possible. Further, the design should give the impression that the dampers were a logical part of the stay system and not an addition. For structural reasons there should be two dampers on each stay. A consequence of the placement of the dampers near the end point is that high damping rates influence not only the amplitudes but the vibration modes as well. From the design curve (Fig. 3) it can be inferred that only at low damping rates the damper is effective for the full 100%. In our case the damper characteristics are located on the top of the design curve. The effect of the dampers was confirmed by a finite element simulation with the DIANA programme. It was clearly demonstrated that a vibrating stay could be damped sufficiently. Fig. 3 Calculated and measured ( ) damping values
8 -7- Several types of dampers were studied, in particular visco-elastic and hydraulic systems. Structural requirements dictated dampers with a reasonably large displacement. On account of the traffic loads on the bridge the sag of the longest stays is diminishing from about 2.5 m in the dead load situation to 1.2 m under full load. This means that the observed displacements during the vibration are about half of the displacements under live load. Higher stressing of the stays is physically impossible because the force in the stay is directly related to the mass of the bridge section it is supporting. From this viewpoint hydraulic dampers were the best solution. Further, these dampers are highly reliable, as is indicated by their use in railway stock. Physical requirements were that the dampers should be as linear in behaviour as possible and should also be working at very low amplitudes (less than 1 mm). Because the design of this type of dampers is a very specialised job requiring a lot of experience, two manufacturers were invited to design and deliver prototypes for testing on the bridge. The selected firms were LISEGA (Germany) and KONI (the Netherlands). LISEGA had experience in the production of prototype dampers for the supression of earthquake effects on bridges, and KONI is specialised in all types of dampers ranging from passenger cars to railway cars and even heavier ones. Both firms produced dampers which were remarkable linear in behaviour in factory tests. Internally this was achieved by a combination of orifices and spring loaded valves. During testing on the bridge some effects appeared which were not observed during factory testing. At high amplitudes the dampers showed not to be as effective as was expected. Analysis of the test results indicated that play in the connection between damper and stay had a reducing effect. By incorporating a tension spring in the system which pre-stressed the connection of the damper to the stay this problem was solved. In the final design the spring forms an integral part of the damper. Reducing the play in the connection by using a clamp without play was not considered practical because the high contact pressure involved would surely damage the protective coating of the strands from which the stay is constructed. A special problem was observed at low amplitudes. Cable damping was then reduced. It was concluded that this was caused by the internal friction on seals inside the damper. By modifying this part this problem was solved too. For the final selection of the manufacturer technical reasons did not play a role. Both designs functioned equally well. Decisions were mainly governed by the practical point that the dampers should be placed before the 4 th of November 1997, one year after the problems started. KONI could fulfil this requirement (Fig. 4). Fig. 4 Actual damper system
9 -8-4 Full-scale tests Full-scale testing of the cables was performed by means of a small hydraulic actuator owned by TNO Building and Construction Research (the Netherlands). The actuator was fitted to the cable of concern by a relatively soft helical spring (Fig. 5). Instrumentation consisted of a force transducer, several displacement transducers (for the lowest frequency) and one piëzo-resistive accelerometer on the cable itself (for the higher frequencies). accelerometer cable 16 displacement meters chain soft spring cable 15 prototype damper actuator load-cel anti-vandalism tube bridge deck original damper displacement meter Fig. 5 Hydraulic Actuator System Excitation of the cable was of a sinusoïdal type by which the well-known 90 degrees phase criterion was applied to set the cable purely in one of its natural frequencies. When a steady amplitude was obtained, the excitation was switched off resulting in a decay from which the damping (logaritmic decrement) was estimated by a quick-look method (NLR) and a curve-fit procedure (TNO). Upon agreement about the damping factor, the excitation was started again and the next natural frequency was adjusted. The test programme looked simple: first some representative cables (nr 13 and 16, western side) without any damping devices should be subjected to sine excitation whereafter prototype dampers were installed and the sequence of excitation and decaying should be repeated. However, a number of practical inconveniences were encountered during the tests, mostly caused by traffic.
10 Practical considerations As adjustment of the 90 degrees phase crititerion and reaching steady amplitude of the cable took some time (around five minutes), traffic was continuously a source of inconvenience. Passage of especially heavy vehicles did move the bridge deck, changed the cable tension to a certain amount and with that the cable s natural frequency. In such circumstances the phase criterion could hardly be maintained especially for the lowest frequency of the cables without damper devices. This resulted mostly in conflicting decays as shown in Fig. 6. Two attemps with cable 13 are shown at a natural frenquency of f = Hz. Neither the first nor the the second attempt gave a satisfactory estimation of the damping factor. Another inconvenience was the excitation at higher frequencies (f > 1.2 Hz) of the cables without damping devices. As the modal mass, as well as the damping, is substantially lower at higher mode shapes, a small sinusoïdal excitation resulted in large amplitudes fully out of control, so it was decided to cancel the tests at higher frequencies. Fig. 6 Conflicting decay s of cable 13 without damping devices The same test procedures were applied once the prototype damper was installed; first at cable 13, later on at cable 16. In first instance the dampers failed as they did not fulfil the expectation of 0.8% damping. The reason was a certain amount of play between cable strings and the poly-ethyleen casing to which the damper was connected. This shortcoming was quickly solved by mounting a helical spring between cable casing and bridge deck. A pre-tension of around 6500N was sufficient to eliminate the play and resulted in a satisfactory damping behaviour as function of the cable frequencies (next section). 4.2 Results of damping measurements on cables 13 and Without damping devices As already mentioned the frequency range in which the cables could be excited was very limited. From the decay s it was observed that the structural damping of the cables itself is very low (around 0.1% to 0.2% c/cr). At the lowest cable frequency of 0.4 Hz however, the damping tends to be higher. This can be explained by interaction with the bridge deck having a first bending frequency of f = 0.44 Hz with a damping of at least 0.6% c/cr. The latter value was obtained from monitoring of the bridge deck (section 5).
11 With new hydraulic dampers Once the dampers were installed with pre-tension on the cables, decays such as shown in Fig. 7a and 7b were obtained. Besides a quick-look analysis on the bridge, a more detailed analysis was applied afterwards by means of a curve-fit procedure (LnDec) performed at NLR. Damping factors as a function of the natural frequency of the cables are presented in Fig. 8 from which it can be observed that the longest cable (Fig. 8a) does not fulfill the requirement of 0.8% damping for all frequencies. At some of the frequencies still play was detected which means that the pre-tension on that cable was probably too low. It is the expectation that increasing the pre-tension may result in higher damping values over the entire frequency range like those valid for stay cable 13 (Fig. 8b). a) Cable 16 (f = 0,76 Hz) b) Cable 13 (f = 1,03 Hz) Fig. 7 Decay of cable with prototype dampers and the curve-fit procedure (LnDec) b (%) 1.2 b (%) 1.2 required required f (Hz) 0 f (Hz) a) Cable 16 (west) with dampers ( = average) b) Cable 13 (west) with dampers ( = average) Fig. 8 Damping obtained with prototype dampers
12 -11-5 Bridge deck monitoring A preliminary monitoring system was in operation from July 1997 till November 1998, with the aim to verify wind tunnel predictions once vortex excitation occurs. This monitoring system was based on two accelerometers which were placed at a specific position (at a node of the mode shape of the second bending) in both main girders to eliminate vibrations other than those from the first bending and first torsion. After narrow-band filtering ( Hz), the accelerations were summed and subtracted. By applying appropriate weighing factors, the signals were representative for bending and torsional amplitudes with reference to the position of the hand railings. By a level detector, the crossings of pre-selected accelerations were counted. The data was converted to amplitudes and stored in the memory of the level detector. A diagram of the monitoring equipment is presented in Fig Z EAST 0.86V/g SUNSTRAND (QA 1200).. Z WEST 0.86V/g COND. UNIT GAIN : 10 X COND. UNIT GAIN : 10 X 8.6V/g 8.6V/g FILTER Hz dB/OCT FILTER Hz Σ AND Σ Σ Σ 3-4 SPECTRA POT LEVEL DETECTOR DATA TAPE 48dB/OCT B A PHILIPS SCOPE SONY DAT REC PC 208 STRUC. DYN. ANAL. HP 3562A OPTIONAL Fig. 9 Diagram of monitoring equipment 5.1 Results from monitoring Results expressed as peak-to-peak amplitudes at the railing s position were obtained during the period July 1997 till November An example is shown in Fig. 10. Most of the time, the bridge deck behaves moderately, also at high wind speeds (up to 30 ms -1 ). Only in the beginning of March 1998 some vortex excitation appeared to be present (after analysing the countings in more detail) resulting in a peak-to-peak amplitude of around 5 cm of the lowest bending mode. This amplitude is nearly half the value predicted from wind tunnel testing in a smooth flow. As turbulence will be present in practice, which counteracts vortex shedding, it is not the expectation that this bridge will respond with much higher amplitudes than already measured. The character of the bridge deck response is illustrated by Fig. 11. The time signals show that the response remains low, though there are time segments where the amplitude starts to rise but dies rapidly.
13 -12- Fig. 10 Results of monitoring (amplitudes peak to peak) at the position of railing a) During 10 minutes b) During 100 seconds ( s) Fig. 11 Example of time signals of accelerometers (east and west)
14 Additional data reduction At the end of 1997, the monitoring system was extended with a digital/analog recorder and a dual-channel dynamic signal analyser because of the large variety in wind conditions expected at that time. Frequency spectra of the bridge deck accelerations were obtained after sampling the time signals up to 190 hours continuously. An interesting result for the torsional behaviour of the bridge deck is presented in Fig. 12. A measurement of 72 hours continuously during which no wind was present showed two closely spaced frequency peaks of f = 0.65 Hz and f = 0.67 Hz. Both peaks are torsional modes as the real part of the cross-spectrum is negative at those frequencies. The cause of such a behaviour is not fully understood as computations only showed one torsional frequency of f = 0.69 Hz. A reason could be the characteristics of passing vehicles possibly working as a tuned damper. With wind and traffic only one torsional frequency is coming up (f = 0.66 Hz) just between the two peaks mentioned before. a) Excitation by traffic (no wind) b) Excitation by traffic and wind ( 12 ms -1 ) Fig. 12 Cross spectra between signals of east/west accelerometer
15 -14- Finally two examples of spectra (after a measurement of 120 hours) from which the damping factors are derived, are presented in Fig. 13. A curve-fit procedure was applied from which a damping factor of around 0.9 to 1.0% (c/cr) was obtained for both the lowest bending and torsion mode of the bridge. At that time excitation took place by traffic and wind of ms -1 from the south, more or less perpendicular to the bridge. first bending cable freq s a) First bending first torsion b) First torsion Fig. 13 Determination of damping (c/cr) by a curve-fit after 120 hrs sampling (excitation: traffic and wind)
16 -15-6 Concluding remarks From full-scale tests on the Erasmus bridge it is concluded that a bridge already in use should be closed for all traffic while one is carrying out damping measurements on the stay-cables. Although the length of this bridge is of a medium size, monitoring of such a structure remains important according to the results from a spectral analysis. Further the monitoring showed that this bridge deck is not vulnerable for vortex excitation. In general vibrational amplitudes are moderate, and lower than predicted from wind tunnel testing. Turbulence at the site might be a reason as it counteracts vortex excitation. Also at high wind speeds up to some 30 ms -1, perpendicular to the bridge, no vibrations of any importance were reported up till now.
17 -16-7 References Matsumoto, M.E.A., Rain-wind induced vibration of cables of cable-stayed bridges, Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, (1992), Elsevier, Amsterdam. Hikami, Y., Shiraishi, N., Rain-wind induced vibrations of cables in cable-stayed bridges, Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 29 (1988), Elsevier, Amsterdam. Flamand, O., Rain-wind induced vibrations of cables, CSTB, NANTES; Cable-stayed and suspension bridges, Proc. Vol. II, Deauville Oct Matsumoto, M.E.A., Aerodynamic behaviour of induced circular cylinders/cable aerodynamics, Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 33 (1990), Elsevier, Amsterdam.
w o r k o G E x - p e S i n c e r t Elegance and Strength BBR HiAm CONA Strand Stay Cable Damping Systems
 o b a l N e t w o r k l o G f A E x - p e S i n c e 1 9 4 4 - s r t Elegance and Strength BBR HiAm CONA Strand Stay Cable Damping Systems 1 Cable vibration and damping Despite the wide use of cable-stayed
o b a l N e t w o r k l o G f A E x - p e S i n c e 1 9 4 4 - s r t Elegance and Strength BBR HiAm CONA Strand Stay Cable Damping Systems 1 Cable vibration and damping Despite the wide use of cable-stayed
inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering August 2000, Nice, FRANCE
 Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 7.6 ROLLING NOISE FROM
Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 7.6 ROLLING NOISE FROM
CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL SHOCK TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY
 135 CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL SHOCK TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY 6.1 INTRODUCTION Shock is often defined as a rapid transfer of energy to a mechanical system, which results in a significant increase in the stress,
135 CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL SHOCK TESTS ON DIP-PCB ASSEMBLY 6.1 INTRODUCTION Shock is often defined as a rapid transfer of energy to a mechanical system, which results in a significant increase in the stress,
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF A 2-DIMENSIONAL VIBRATION ABSORBER ON A PRE-HEATER TOWER AT A CEMENT FACTORY
 Page number: 1 DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF A 2-DIMENSIONAL VIBRATION ABSORBER ON A PRE-HEATER TOWER AT A CEMENT FACTORY Kenan Y. Sanliturk 1 and H. Temel Belek 2 Istanbul Technical University, Faculty
Page number: 1 DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF A 2-DIMENSIONAL VIBRATION ABSORBER ON A PRE-HEATER TOWER AT A CEMENT FACTORY Kenan Y. Sanliturk 1 and H. Temel Belek 2 Istanbul Technical University, Faculty
A STUDY OF THE CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR DISCHARGE PIPELINE CONSTRAINED OSCILLATION. KIRILL SOLODYANKIN*, JIŘÍ BĚHAL ČKD KOMPRESORY, a.s.
 A STUDY OF THE CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR DISCHARGE PIPELINE CONSTRAINED OSCILLATION KIRILL SOLODYANKIN*, JIŘÍ BĚHAL ČKD KOMPRESORY, a.s. Abstract: The paper presents a solution of a pipeline constrained oscillation
A STUDY OF THE CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR DISCHARGE PIPELINE CONSTRAINED OSCILLATION KIRILL SOLODYANKIN*, JIŘÍ BĚHAL ČKD KOMPRESORY, a.s. Abstract: The paper presents a solution of a pipeline constrained oscillation
Oscillator Experiment of Simple Girder Bridge coupled with Vehicle
 The 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM 12) Seoul, Korea, August 26-30, 2012 Oscillator Experiment of Simple Girder Bridge coupled with Vehicle Mitsuo
The 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research (ACEM 12) Seoul, Korea, August 26-30, 2012 Oscillator Experiment of Simple Girder Bridge coupled with Vehicle Mitsuo
Chapter 4. Vehicle Testing
 Chapter 4 Vehicle Testing The purpose of this chapter is to describe the field testing of the controllable dampers on a Volvo VN heavy truck. The first part of this chapter describes the test vehicle used
Chapter 4 Vehicle Testing The purpose of this chapter is to describe the field testing of the controllable dampers on a Volvo VN heavy truck. The first part of this chapter describes the test vehicle used
Feasibility of Ultra Long-Span Suspension Bridges Made of All Plastics
 IASE SYMPOSIUM MELOURNE 1 Feasibility of Ultra Long-Span Suspension ridges Made of All Plastics Ken-ichi MAEDA Professor Dr. Eng. Tokyo Metropolitan Univ. Tokyo, Japan Torahiko IKEDA ridge Engineer M.
IASE SYMPOSIUM MELOURNE 1 Feasibility of Ultra Long-Span Suspension ridges Made of All Plastics Ken-ichi MAEDA Professor Dr. Eng. Tokyo Metropolitan Univ. Tokyo, Japan Torahiko IKEDA ridge Engineer M.
Fig.1 Sky-hook damper
 1. Introduction To improve the ride comfort of the Maglev train, control techniques are important. Three control techniques were introduced into the Yamanashi Maglev Test Line vehicle. One method uses
1. Introduction To improve the ride comfort of the Maglev train, control techniques are important. Three control techniques were introduced into the Yamanashi Maglev Test Line vehicle. One method uses
Experimental Study on Flutter Performance of a 1700m Long Truss Girder Suspension Bridge
 Experimental Study on Flutter Performance of a 1700m Long Truss Girder Suspension Bridge *Yanguo Sun 1), Haili Liao 2) and Mingshui Li 3) 1), 2), 3) Research Centre for Wind Eng., Southwest Jiaotong University,
Experimental Study on Flutter Performance of a 1700m Long Truss Girder Suspension Bridge *Yanguo Sun 1), Haili Liao 2) and Mingshui Li 3) 1), 2), 3) Research Centre for Wind Eng., Southwest Jiaotong University,
Special edition paper
 Efforts for Greater Ride Comfort Koji Asano* Yasushi Kajitani* Aiming to improve of ride comfort, we have worked to overcome issues increasing Shinkansen speed including control of vertical and lateral
Efforts for Greater Ride Comfort Koji Asano* Yasushi Kajitani* Aiming to improve of ride comfort, we have worked to overcome issues increasing Shinkansen speed including control of vertical and lateral
Development of an actively controlled, acoustically optimised single arm pantograph
 Development of an actively controlled, acoustically optimised single arm pantograph Authors Dr. Wilhelm Baldauf 1), Rene Blaschko 2), Dr. Wolfgang Behr 1), Dr. Christoph Heine 1), Michael Kolbe 1) 1) Deutsche
Development of an actively controlled, acoustically optimised single arm pantograph Authors Dr. Wilhelm Baldauf 1), Rene Blaschko 2), Dr. Wolfgang Behr 1), Dr. Christoph Heine 1), Michael Kolbe 1) 1) Deutsche
Special edition paper
 Development of a Brake System for Shinkansen Speed Increase Hiroshi Arai* Satoru Kanno* Kenji Fujino* Hiroyuki Kato* Koji Asano* In efforts to increase Shinkansen speeds toward a 360 km/h operating speed,
Development of a Brake System for Shinkansen Speed Increase Hiroshi Arai* Satoru Kanno* Kenji Fujino* Hiroyuki Kato* Koji Asano* In efforts to increase Shinkansen speeds toward a 360 km/h operating speed,
inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering August 2000, Nice, FRANCE
 Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 0.0 EFFECTS OF TRANSVERSE
Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 0.0 EFFECTS OF TRANSVERSE
Improvements of Existing Overhead Lines for 180km/h operation of the Tilting Train
 Improvements of Existing Overhead Lines for 180km/h operation of the Tilting Train K. Lee, Y.H. Cho, Y. Park, S. Kwon Korea Railroad Research Institute, Uiwang-City, Korea Abstract The purpose of this
Improvements of Existing Overhead Lines for 180km/h operation of the Tilting Train K. Lee, Y.H. Cho, Y. Park, S. Kwon Korea Railroad Research Institute, Uiwang-City, Korea Abstract The purpose of this
Experimental Investigation of Effects of Shock Absorber Mounting Angle on Damping Characterstics
 Experimental Investigation of Effects of Shock Absorber Mounting Angle on Damping Characterstics Tanmay P. Dobhada Tushar S. Dhaspatil Prof. S S Hirmukhe Mauli P. Khapale Abstract: A shock absorber is
Experimental Investigation of Effects of Shock Absorber Mounting Angle on Damping Characterstics Tanmay P. Dobhada Tushar S. Dhaspatil Prof. S S Hirmukhe Mauli P. Khapale Abstract: A shock absorber is
Aerodynamic Investigation of Cable-stayed Bridge with 2-edge Girder
 Takuya Murakami*, Katsuaki Takeda**, Michiaki Takao*** and Rokusui Yui**** * Senior Research Engineer, Civil & Building Research Dept. Applied Technology Research Center ** Chief, Civil & Building Research
Takuya Murakami*, Katsuaki Takeda**, Michiaki Takao*** and Rokusui Yui**** * Senior Research Engineer, Civil & Building Research Dept. Applied Technology Research Center ** Chief, Civil & Building Research
Abstract In this paper, we developed a lateral damper to improve the running safety of railway vehicles
 Improvement of Running Safety of Railway Vehicles against an Earthquake Kohei Iida, Mitsugi Suzuki, Takefumi Miyamoto, Yukio Nishiyama, Daichi Nakajima Railway Technical Research Institute, Tokyo, JAPAN
Improvement of Running Safety of Railway Vehicles against an Earthquake Kohei Iida, Mitsugi Suzuki, Takefumi Miyamoto, Yukio Nishiyama, Daichi Nakajima Railway Technical Research Institute, Tokyo, JAPAN
Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train
 Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train A.R.Mokate 1, R.R.Navthar 2 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, PDVVP COE, A. Nagar, Maharashtra, India 1 Assistance Professor,
Vibration Measurement and Noise Control in Planetary Gear Train A.R.Mokate 1, R.R.Navthar 2 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, PDVVP COE, A. Nagar, Maharashtra, India 1 Assistance Professor,
Sulastic Rubber Springs
 Sulastic Rubber Springs 2007 Toyota Tundra Sulastic Isolator Evaluation October 13, 2007 SPECTRUM Technologies, Inc. 12245 Wormer, Redford, MI 48239 Phone: 313-387-3000, Fax: 313-387-3095 Engineering Report
Sulastic Rubber Springs 2007 Toyota Tundra Sulastic Isolator Evaluation October 13, 2007 SPECTRUM Technologies, Inc. 12245 Wormer, Redford, MI 48239 Phone: 313-387-3000, Fax: 313-387-3095 Engineering Report
Damping Ratio Estimation of an Existing 8-story Building Considering Soil-Structure Interaction Using Strong Motion Observation Data.
 Damping Ratio Estimation of an Existing -story Building Considering Soil-Structure Interaction Using Strong Motion Observation Data by Koichi Morita ABSTRACT In this study, damping ratio of an exiting
Damping Ratio Estimation of an Existing -story Building Considering Soil-Structure Interaction Using Strong Motion Observation Data by Koichi Morita ABSTRACT In this study, damping ratio of an exiting
2. Write the expression for estimation of the natural frequency of free torsional vibration of a shaft. (N/D 15)
 ME 6505 DYNAMICS OF MACHINES Fifth Semester Mechanical Engineering (Regulations 2013) Unit III PART A 1. Write the mathematical expression for a free vibration system with viscous damping. (N/D 15) Viscous
ME 6505 DYNAMICS OF MACHINES Fifth Semester Mechanical Engineering (Regulations 2013) Unit III PART A 1. Write the mathematical expression for a free vibration system with viscous damping. (N/D 15) Viscous
inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering August 2000, Nice, FRANCE
 Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 1.3 CURVE SQUEAL OF
Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 1.3 CURVE SQUEAL OF
Railway Engineering: Track and Train Interaction COURSE SYLLABUS
 COURSE SYLLABUS Week 1: Vehicle-Track Interaction When a railway vehicle passes over a track, the interaction between the two yields forces on both vehicle and track. What is the nature of these forces,
COURSE SYLLABUS Week 1: Vehicle-Track Interaction When a railway vehicle passes over a track, the interaction between the two yields forces on both vehicle and track. What is the nature of these forces,
test with confidence HV Series TM Test Systems Hydraulic Vibration
 test with confidence HV Series TM Test Systems Hydraulic Vibration Experience. Technology. Value. The Difference. HV Series TM. The Difference. Our philosophy is simple. Provide a system designed for optimum
test with confidence HV Series TM Test Systems Hydraulic Vibration Experience. Technology. Value. The Difference. HV Series TM. The Difference. Our philosophy is simple. Provide a system designed for optimum
DYNAMIC TESTS ON A CONCRETE SLAB WITH A TUNED MASS DAMPER
 MATEC Web of Conferences, 6 ( 15) DOI: 1.151/ matecconf/ 15 6 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 15 DYNAMIC TESTS ON A CONCRETE SLAB WITH A TUNED MASS DAMPER Jorge Eliécer Campuzano Carmona
MATEC Web of Conferences, 6 ( 15) DOI: 1.151/ matecconf/ 15 6 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 15 DYNAMIC TESTS ON A CONCRETE SLAB WITH A TUNED MASS DAMPER Jorge Eliécer Campuzano Carmona
MECHANICAL EQUIPMENT. Engineering. Theory & Practice. Vibration & Rubber Engineering Solutions
 MECHANICAL EQUIPMENT Engineering Theory & Practice Vibration & Rubber Engineering Solutions The characteristic of an anti-vibration mounting that mainly determines its efficiency as a device for storing
MECHANICAL EQUIPMENT Engineering Theory & Practice Vibration & Rubber Engineering Solutions The characteristic of an anti-vibration mounting that mainly determines its efficiency as a device for storing
Suppression of chatter vibration of boring tools using impact dampers
 International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture 40 (2000) 1141 1156 Suppression of chatter vibration of boring tools using impact dampers Satoshi Ema a,*, Etsuo Marui b a Faculty of Education, Gifu
International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture 40 (2000) 1141 1156 Suppression of chatter vibration of boring tools using impact dampers Satoshi Ema a,*, Etsuo Marui b a Faculty of Education, Gifu
Dynamic characteristics of railway concrete sleepers using impact excitation techniques and model analysis
 Dynamic characteristics of railway concrete sleepers using impact excitation techniques and model analysis Akira Aikawa *, Fumihiro Urakawa *, Kazuhisa Abe **, Akira Namura * * Railway Technical Research
Dynamic characteristics of railway concrete sleepers using impact excitation techniques and model analysis Akira Aikawa *, Fumihiro Urakawa *, Kazuhisa Abe **, Akira Namura * * Railway Technical Research
PROGRESS IN QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF CONVEYOR IDLERS
 PROGRESS IN QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF CONVEYOR IDLERS W. Bartelmus and W. Sawicki Wroc³aw University of Technology Faculty of Mining Machinery Systems Division Wroc³aw Poland Abstract: The paper deals with
PROGRESS IN QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF CONVEYOR IDLERS W. Bartelmus and W. Sawicki Wroc³aw University of Technology Faculty of Mining Machinery Systems Division Wroc³aw Poland Abstract: The paper deals with
Passive Vibration Reduction with Silicone Springs and Dynamic Absorber
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 19 (2011 ) 431 435 International Conference on Optics in Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology 2011 Passive Vibration Reduction with Silicone
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 19 (2011 ) 431 435 International Conference on Optics in Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology 2011 Passive Vibration Reduction with Silicone
AXLE HOUSING AND UNITIZE BEARING PACK SET MODAL CHARACTERISATION
 F2004F461 AXLE HOUSING AND UNITIZE BEARING PACK SET MODAL CHARACTERISATION 1 Badiola, Virginia*, 2 Pintor, Jesús María, 3 Gainza, Gorka 1 Dana Equipamientos S.A., España, 2 Universidad Pública de Navarra,
F2004F461 AXLE HOUSING AND UNITIZE BEARING PACK SET MODAL CHARACTERISATION 1 Badiola, Virginia*, 2 Pintor, Jesús María, 3 Gainza, Gorka 1 Dana Equipamientos S.A., España, 2 Universidad Pública de Navarra,
MAURER Cable damper systems
 Head Office Frankfurter Ring 193, 80807 München/Germany Telephone +49 89 323 94-0 Telefax +49 89 323 94-329 Branch Office Zum Holzplatz 2, 44536 Lünen/Germany Telephone +49 231 434 01-0 Telefax +49 231
Head Office Frankfurter Ring 193, 80807 München/Germany Telephone +49 89 323 94-0 Telefax +49 89 323 94-329 Branch Office Zum Holzplatz 2, 44536 Lünen/Germany Telephone +49 231 434 01-0 Telefax +49 231
VALMONT MITIGATOR TR1
 VALMONT MITIGATOR TR1 Research Verification of the Valmont TR1 Damper Performance MITIGATOR TR1 VIBRATION DAMPER The Valmont TR1 damper has been specifically designed using vibration theory and innovative
VALMONT MITIGATOR TR1 Research Verification of the Valmont TR1 Damper Performance MITIGATOR TR1 VIBRATION DAMPER The Valmont TR1 damper has been specifically designed using vibration theory and innovative
Seismic-upgrading of Existing Stacks of Nuclear Power Station using Structural Control Oil Dampers
 October 12-17, 28, Beijing, China ABSTRACT : Seismic-upgrading of Existing Stacks of Nuclear Power Station using Structural Control Oil Dampers Ryu Shimamoto 1, Fukashi Mori 2, Tomonori Kitaori 2, Satoru
October 12-17, 28, Beijing, China ABSTRACT : Seismic-upgrading of Existing Stacks of Nuclear Power Station using Structural Control Oil Dampers Ryu Shimamoto 1, Fukashi Mori 2, Tomonori Kitaori 2, Satoru
Technical Report Lotus Elan Rear Suspension The Effect of Halfshaft Rubber Couplings. T. L. Duell. Prepared for The Elan Factory.
 Technical Report - 9 Lotus Elan Rear Suspension The Effect of Halfshaft Rubber Couplings by T. L. Duell Prepared for The Elan Factory May 24 Terry Duell consulting 19 Rylandes Drive, Gladstone Park Victoria
Technical Report - 9 Lotus Elan Rear Suspension The Effect of Halfshaft Rubber Couplings by T. L. Duell Prepared for The Elan Factory May 24 Terry Duell consulting 19 Rylandes Drive, Gladstone Park Victoria
STRUCTURAL BEHAVIOUR OF 5000 kn DAMPER
 STRUCTURAL BEHAVIOUR OF 5000 kn DAMPER I.H. Mualla Dr. Eng. CTO of DAMPTECH A/S E.D. Jakupsson Dept. of Civil Engineering, Technical University of Denmark L.O. Nielsen Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering,
STRUCTURAL BEHAVIOUR OF 5000 kn DAMPER I.H. Mualla Dr. Eng. CTO of DAMPTECH A/S E.D. Jakupsson Dept. of Civil Engineering, Technical University of Denmark L.O. Nielsen Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering,
RELIABILITY IMPROVEMENT OF ACCESSORY GEARBOX BEVEL DRIVES Kozharinov Egor* *CIAM
 RELIABILITY IMPROVEMENT OF ACCESSORY GEARBOX BEVEL DRIVES Kozharinov Egor* *CIAM egor@ciam.ru Keywords: Bevel gears, accessory drives, resonance oscillations, Coulomb friction damping Abstract Bevel gear
RELIABILITY IMPROVEMENT OF ACCESSORY GEARBOX BEVEL DRIVES Kozharinov Egor* *CIAM egor@ciam.ru Keywords: Bevel gears, accessory drives, resonance oscillations, Coulomb friction damping Abstract Bevel gear
A CASE STUDY OF A FLOW-INDUCED TORSIONAL RESONANCE
 A CASE STUDY OF A FLOW-INDUCED TORSIONAL RESONANCE William F. Eckert, P.Eng., Ph.D. Field Services Manager Brian C. Howes, M.Sc., P.Eng. Chief Engineer Beta Machinery Analysis Ltd., Calgary, AB, Canada,
A CASE STUDY OF A FLOW-INDUCED TORSIONAL RESONANCE William F. Eckert, P.Eng., Ph.D. Field Services Manager Brian C. Howes, M.Sc., P.Eng. Chief Engineer Beta Machinery Analysis Ltd., Calgary, AB, Canada,
SUSPENSION OF A MOUNTAIN BIKE SVOČ FST Bc. Vít Prošek University of West Bohemia Univerzitni 8, Pilsen Czech Republic
 SUSPENSION OF A MOUNTAIN BIKE SVOČ FST 211 Bc. Vít Prošek University of West Bohemia Univerzitni 8, 36 14 Pilsen Czech Republic ABSTRACT This work is concerned about suspended mountain bikes, especially
SUSPENSION OF A MOUNTAIN BIKE SVOČ FST 211 Bc. Vít Prošek University of West Bohemia Univerzitni 8, 36 14 Pilsen Czech Republic ABSTRACT This work is concerned about suspended mountain bikes, especially
Semi-Active Suspension for an Automobile
 Semi-Active Suspension for an Automobile Pavan Kumar.G 1 Mechanical Engineering PESIT Bangalore, India M. Sambasiva Rao 2 Mechanical Engineering PESIT Bangalore, India Abstract Handling characteristics
Semi-Active Suspension for an Automobile Pavan Kumar.G 1 Mechanical Engineering PESIT Bangalore, India M. Sambasiva Rao 2 Mechanical Engineering PESIT Bangalore, India Abstract Handling characteristics
Experimental investigations of pressure pulsations damping in screw compressor system
 Experimental investigations of pressure pulsations damping in screw compressor system MSc eng. Przemysław Młynarczyk Supervisor: Prof. dr hab. inż. Piotr Cyklis Abstract Pressure pulsations are one of
Experimental investigations of pressure pulsations damping in screw compressor system MSc eng. Przemysław Młynarczyk Supervisor: Prof. dr hab. inż. Piotr Cyklis Abstract Pressure pulsations are one of
Full Scale Experimental Evaluation for Cable Dampers
 Full Scale Experimental Evaluation for Cable Dampers Liang Dong, Tian Jingxian, Du Chuang, Ma Jinlong Abstract One of the key techniques for building long span cable-stayed bridge is the mitigation of
Full Scale Experimental Evaluation for Cable Dampers Liang Dong, Tian Jingxian, Du Chuang, Ma Jinlong Abstract One of the key techniques for building long span cable-stayed bridge is the mitigation of
Seismic Capacity Test of Overhead Crane under Horizontal and Vertical Excitation - Element Model Test Results on Nonlinear Response Behavior-
 2th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 2) Espoo, Finland, August 9-14, 29 SMiRT 2-Division, Paper Seismic Capacity Test of Overhead Crane under Horizontal and
2th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 2) Espoo, Finland, August 9-14, 29 SMiRT 2-Division, Paper Seismic Capacity Test of Overhead Crane under Horizontal and
Gauge Face Wear Caused with Vehicle/Track Interaction
 Gauge Face Wear Caused with Vehicle/Track Interaction Makoto ISHIDA*, Mitsunobu TAKIKAWA, Ying JIN Railway Technical Research Institute 2-8-38 Hikari-cho, Kokubunji-shi, Tokyo 185-8540, Japan Tel: +81-42-573-7291,
Gauge Face Wear Caused with Vehicle/Track Interaction Makoto ISHIDA*, Mitsunobu TAKIKAWA, Ying JIN Railway Technical Research Institute 2-8-38 Hikari-cho, Kokubunji-shi, Tokyo 185-8540, Japan Tel: +81-42-573-7291,
Researches regarding a pressure pulse generator as a segment of model for a weighing in motion system
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Researches regarding a pressure pulse generator as a segment of model for a weighing in motion system To cite this article: I
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Researches regarding a pressure pulse generator as a segment of model for a weighing in motion system To cite this article: I
Is Low Friction Efficient?
 Is Low Friction Efficient? Assessment of Bearing Concepts During the Design Phase Dipl.-Wirtsch.-Ing. Mark Dudziak; Schaeffler Trading (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China Dipl.-Ing. (TH) Andreas Krome,
Is Low Friction Efficient? Assessment of Bearing Concepts During the Design Phase Dipl.-Wirtsch.-Ing. Mark Dudziak; Schaeffler Trading (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China Dipl.-Ing. (TH) Andreas Krome,
Rolling Element Bearing Acceptance and Life Testing (BAT) (UK Patent # GB )
 Rolling Element Bearing Acceptance and Life Testing (BAT) (UK Patent # GB 219584.) Prof. Dr. Ahmed Elkhatib Prof. of Machine Dynamics and Diagnostics Faculty of Engineering, Alexandria University, EGYPT
Rolling Element Bearing Acceptance and Life Testing (BAT) (UK Patent # GB 219584.) Prof. Dr. Ahmed Elkhatib Prof. of Machine Dynamics and Diagnostics Faculty of Engineering, Alexandria University, EGYPT
CHAPTER 4: EXPERIMENTAL WORK 4-1
 CHAPTER 4: EXPERIMENTAL WORK 4-1 EXPERIMENTAL WORK 4.1 Preamble 4-2 4.2 Test setup 4-2 4.2.1 Experimental setup 4-2 4.2.2 Instrumentation, control and data acquisition 4-4 4.3 Hydro-pneumatic spring characterisation
CHAPTER 4: EXPERIMENTAL WORK 4-1 EXPERIMENTAL WORK 4.1 Preamble 4-2 4.2 Test setup 4-2 4.2.1 Experimental setup 4-2 4.2.2 Instrumentation, control and data acquisition 4-4 4.3 Hydro-pneumatic spring characterisation
AERODYNAMIC STABILITY OF A SUPER LONG-SPAN BRIDGE WITH SLOTTED BOX GIRDER
 AERODYNAMIC STABILITY OF A SUPER LONG-SPAN BRIDGE WITH SLOTTED BOX GIRDER by Hiroshi SATO ), Nobuyuki HIRAHARA 2), Koichiro FUMOTO 3), Shigeru HIRANO 4) and Shigeki KUSUHARA 5) ABSTRACT Aerodynamic stability
AERODYNAMIC STABILITY OF A SUPER LONG-SPAN BRIDGE WITH SLOTTED BOX GIRDER by Hiroshi SATO ), Nobuyuki HIRAHARA 2), Koichiro FUMOTO 3), Shigeru HIRANO 4) and Shigeki KUSUHARA 5) ABSTRACT Aerodynamic stability
Noise Reduction in Railway Traffic Noise Abatement at Source
 Noise Reduction in Railway Traffic Noise Abatement at Source Dipl.-Ing. Harald Willrich, FUCHS LUBRITECH GmbH, D-67685 Weilerbach 1 The Problem Many railway companies throughout the world are increasingly
Noise Reduction in Railway Traffic Noise Abatement at Source Dipl.-Ing. Harald Willrich, FUCHS LUBRITECH GmbH, D-67685 Weilerbach 1 The Problem Many railway companies throughout the world are increasingly
Special edition paper
 Countermeasures of Noise Reduction for Shinkansen Electric-Current Collecting System and Lower Parts of Cars Kaoru Murata*, Toshikazu Sato* and Koichi Sasaki* Shinkansen noise can be broadly classified
Countermeasures of Noise Reduction for Shinkansen Electric-Current Collecting System and Lower Parts of Cars Kaoru Murata*, Toshikazu Sato* and Koichi Sasaki* Shinkansen noise can be broadly classified
Improvements for reduction of the brake squeal noise at Seoul metro rolling stock on tracks
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 23 (2009) 2206~2214 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738494x DOI 10.1007/s122060090518x Improvements for reduction
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 23 (2009) 2206~2214 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738494x DOI 10.1007/s122060090518x Improvements for reduction
Mechanism and Countermeasures for Abnormal Noise Produced by Idler Pulley Bearings under Low Temperature Conditions
 Mechanism and Countermeasures for Abnormal Noise Produced by Idler Pulley Bearings under Low Temperature Conditions M. UEDA Idler bearings are used for automobile engine accessories. This bearing sometimes
Mechanism and Countermeasures for Abnormal Noise Produced by Idler Pulley Bearings under Low Temperature Conditions M. UEDA Idler bearings are used for automobile engine accessories. This bearing sometimes
KINEMATICAL SUSPENSION OPTIMIZATION USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENT METHOD
 Jurnal Mekanikal June 2014, No 37, 16-25 KINEMATICAL SUSPENSION OPTIMIZATION USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENT METHOD Mohd Awaluddin A Rahman and Afandi Dzakaria Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti
Jurnal Mekanikal June 2014, No 37, 16-25 KINEMATICAL SUSPENSION OPTIMIZATION USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENT METHOD Mohd Awaluddin A Rahman and Afandi Dzakaria Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti
Multi-axial fatigue life assessment of high speed car body based on PDMR method
 MATEC Web of Conferences 165, 17006 (018) FATIGUE 018 https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/01816517006 Multi-axial fatigue life assessment of high speed car body based on PDMR method Chaotao Liu 1,*, Pingbo
MATEC Web of Conferences 165, 17006 (018) FATIGUE 018 https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/01816517006 Multi-axial fatigue life assessment of high speed car body based on PDMR method Chaotao Liu 1,*, Pingbo
EFFECTIVENESS OF THE ACTIVE PNEUMATIC SUSPENSION OF THE OPERATOR S SEAT OF THE MOBILE MACHINE IN DEPEND OF THE VIBRATION REDUCTION STRATEGIES
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 25, No. 3 2018 EFFECTIVENESS OF THE ACTIVE PNEUMATIC SUSPENSION OF THE OPERATOR S SEAT OF THE MOBILE MACHINE IN DEPEND OF THE VIBRATION REDUCTION STRATEGIES
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 25, No. 3 2018 EFFECTIVENESS OF THE ACTIVE PNEUMATIC SUSPENSION OF THE OPERATOR S SEAT OF THE MOBILE MACHINE IN DEPEND OF THE VIBRATION REDUCTION STRATEGIES
The Role & Interpretation of Damping in the Prediction of Human Induced Floor Vibration Response Levels
 The Role & Interpretation of Damping in the Prediction of Human Induced Floor Vibration Response Levels Jack Carson, Scott Hilliard Research Scholars, FSET, Swinburne University of Technology **Prof Nicholas
The Role & Interpretation of Damping in the Prediction of Human Induced Floor Vibration Response Levels Jack Carson, Scott Hilliard Research Scholars, FSET, Swinburne University of Technology **Prof Nicholas
Pulsation dampers for combustion engines
 ICLASS 2012, 12 th Triennial International Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Heidelberg, Germany, September 2-6, 2012 Pulsation dampers for combustion engines F.Durst, V. Madila, A.Handtmann,
ICLASS 2012, 12 th Triennial International Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Heidelberg, Germany, September 2-6, 2012 Pulsation dampers for combustion engines F.Durst, V. Madila, A.Handtmann,
Shimmy Identification Caused by Self-Excitation Components at Vehicle High Speed
 Shimmy Identification Caused by Self-Excitation Components at Vehicle High Speed Fujiang Min, Wei Wen, Lifeng Zhao, Xiongying Yu and Jiang Xu Abstract The chapter introduces the shimmy mechanism caused
Shimmy Identification Caused by Self-Excitation Components at Vehicle High Speed Fujiang Min, Wei Wen, Lifeng Zhao, Xiongying Yu and Jiang Xu Abstract The chapter introduces the shimmy mechanism caused
Examining the load peaks in high-speed railway transport
 Examining the load peaks in high-speed railway transport Yigit Fidansoy, M.Sc. Technische Universität Darmstadt, Germany fidansoy@verkehr.tu-darmstadt.de Paper prepared for DEMAND Centre Conference, Lancaster,
Examining the load peaks in high-speed railway transport Yigit Fidansoy, M.Sc. Technische Universität Darmstadt, Germany fidansoy@verkehr.tu-darmstadt.de Paper prepared for DEMAND Centre Conference, Lancaster,
Determination and improvement of bevel gear efficiency by means of loaded TCA
 Determination and improvement of bevel gear efficiency by means of loaded TCA Dr. J. Thomas, Dr. C. Wirth, ZG GmbH, Germany Abstract Bevel and hypoid gears are widely used in automotive and industrial
Determination and improvement of bevel gear efficiency by means of loaded TCA Dr. J. Thomas, Dr. C. Wirth, ZG GmbH, Germany Abstract Bevel and hypoid gears are widely used in automotive and industrial
The Application of Simulink for Vibration Simulation of Suspension Dual-mass System
 Sensors & Transducers 204 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com The Application of Simulink for Vibration Simulation of Suspension Dual-mass System Gao Fei, 2 Qu Xiao Fei, 2 Zheng Pei
Sensors & Transducers 204 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com The Application of Simulink for Vibration Simulation of Suspension Dual-mass System Gao Fei, 2 Qu Xiao Fei, 2 Zheng Pei
INTERIOR NOISE OF A KOREAN HIGH-SPEED TRAIN IN TUNNELS
 INTERIOR NOISE OF A KOREAN HIGH-SPEED TRAIN IN TUNNELS Sunghoon Choi, Chan-Woo Lee, Jae-Chul Kim, and Joon-Ho Cho Noise and Vibration Research Group, Korea Railroad Research Institute, Woulam-dong, Uiwang-city,
INTERIOR NOISE OF A KOREAN HIGH-SPEED TRAIN IN TUNNELS Sunghoon Choi, Chan-Woo Lee, Jae-Chul Kim, and Joon-Ho Cho Noise and Vibration Research Group, Korea Railroad Research Institute, Woulam-dong, Uiwang-city,
APMP TCAUV Workshop The application of acoustics, vibration and ultrasound metrology in transportation industry
 APMP TCAUV Workshop The application of acoustics, vibration and ultrasound metrology in transportation industry The Analysis of Pole and Viaduct Structural Vibration Induced by High Speed Train Speaker
APMP TCAUV Workshop The application of acoustics, vibration and ultrasound metrology in transportation industry The Analysis of Pole and Viaduct Structural Vibration Induced by High Speed Train Speaker
Load Analysis and Multi Body Dynamics Analysis of Connecting Rod in Single Cylinder 4 Stroke Engine
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 08, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Load Analysis and Multi Body Dynamics Analysis of Connecting Rod in Single Cylinder 4
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 08, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Load Analysis and Multi Body Dynamics Analysis of Connecting Rod in Single Cylinder 4
Geislinger Damper. The smallest possible damper for each engine
 The Geislinger damper is capable of adjusting the natural frequency of a system and of reducing torsional vibration. Thus it reliably protects the crankshafts, camshafts, intermediate and propeller shafts
The Geislinger damper is capable of adjusting the natural frequency of a system and of reducing torsional vibration. Thus it reliably protects the crankshafts, camshafts, intermediate and propeller shafts
Enhance the Performance of Heat Exchanger with Twisted Tape Insert: A Review
 Enhance the Performance of Heat Exchanger with Twisted Tape Insert: A Review M.J.Patel 1, K.S.Parmar 2, Umang R. Soni 3 1,2. M.E. Student, department of mechanical engineering, SPIT,Basna, Gujarat, India,
Enhance the Performance of Heat Exchanger with Twisted Tape Insert: A Review M.J.Patel 1, K.S.Parmar 2, Umang R. Soni 3 1,2. M.E. Student, department of mechanical engineering, SPIT,Basna, Gujarat, India,
STIFFNESS CHARACTERISTICS OF MAIN BEARINGS FOUNDATION OF MARINE ENGINE
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 23, No. 1 2016 STIFFNESS CHARACTERISTICS OF MAIN BEARINGS FOUNDATION OF MARINE ENGINE Lech Murawski Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 23, No. 1 2016 STIFFNESS CHARACTERISTICS OF MAIN BEARINGS FOUNDATION OF MARINE ENGINE Lech Murawski Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
THE LONGITUDINAL VIBRATION OF COMPOSITE DRIVE SHAFT
 THE LONGITUDINAL VIBRATION OF COMPOSITE DRIVE SHAFT Tongtong Zhang, Yongsheng Li, Weibo Wang National Key Laboratory on Ship Vibration and Noise, China Ship Scientific Research Centre, Wuxi, China email:
THE LONGITUDINAL VIBRATION OF COMPOSITE DRIVE SHAFT Tongtong Zhang, Yongsheng Li, Weibo Wang National Key Laboratory on Ship Vibration and Noise, China Ship Scientific Research Centre, Wuxi, China email:
Development of Rattle Noise Analysis Technology for Column Type Electric Power Steering Systems
 TECHNICAL REPORT Development of Rattle Noise Analysis Technology for Column Type Electric Power Steering Systems S. NISHIMURA S. ABE The backlash adjustment mechanism for reduction gears adopted in electric
TECHNICAL REPORT Development of Rattle Noise Analysis Technology for Column Type Electric Power Steering Systems S. NISHIMURA S. ABE The backlash adjustment mechanism for reduction gears adopted in electric
Modeling tire vibrations in ABS-braking
 Modeling tire vibrations in ABS-braking Ari Tuononen Aalto University Lassi Hartikainen, Frank Petry, Stephan Westermann Goodyear S.A. Tag des Fahrwerks 8. Oktober 2012 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Review
Modeling tire vibrations in ABS-braking Ari Tuononen Aalto University Lassi Hartikainen, Frank Petry, Stephan Westermann Goodyear S.A. Tag des Fahrwerks 8. Oktober 2012 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Review
Damping Assessment for Crankshaft Design to Reduce the High Vibrations
 International Journal for Ignited Minds (IJIMIINDS) Damping Assessment for Crankshaft Design to Reduce the High Vibrations Darshak T R a, Shivappa H A b & Preethi K c a PG Student, Dept of Mechanical Engineering,
International Journal for Ignited Minds (IJIMIINDS) Damping Assessment for Crankshaft Design to Reduce the High Vibrations Darshak T R a, Shivappa H A b & Preethi K c a PG Student, Dept of Mechanical Engineering,
ACOCAR active suspension
 ACOCAR active suspension Bert Vandersmissen Vehicle Dynamics Expo Stuttgart, 07/05/2008 Contents Introduction Active suspension hardware Quarter car test rig Skyhook quarter car control Experimental skyhook
ACOCAR active suspension Bert Vandersmissen Vehicle Dynamics Expo Stuttgart, 07/05/2008 Contents Introduction Active suspension hardware Quarter car test rig Skyhook quarter car control Experimental skyhook
Icing Wind Tunnel tests in the framework of a Wing Ice Protection system certification process
 Icing Wind Tunnel tests in the framework of a Wing Ice Protection system certification process AirTN-NextGen Workshop on Virtual testing, towards virtual certification Amsterdam (NL), May 25, 2016 Use
Icing Wind Tunnel tests in the framework of a Wing Ice Protection system certification process AirTN-NextGen Workshop on Virtual testing, towards virtual certification Amsterdam (NL), May 25, 2016 Use
Skid against Curb simulation using Abaqus/Explicit
 Visit the SIMULIA Resource Center for more customer examples. Skid against Curb simulation using Abaqus/Explicit Dipl.-Ing. A. Lepold (FORD), Dipl.-Ing. T. Kroschwald (TECOSIM) Abstract: Skid a full vehicle
Visit the SIMULIA Resource Center for more customer examples. Skid against Curb simulation using Abaqus/Explicit Dipl.-Ing. A. Lepold (FORD), Dipl.-Ing. T. Kroschwald (TECOSIM) Abstract: Skid a full vehicle
Procedia Engineering 00 (2009) Mountain bike wheel endurance testing and modeling. Robin C. Redfield a,*, Cory Sutela b
 Procedia Engineering (29) Procedia Engineering www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Mountain bike wheel endurance testing and modeling
Procedia Engineering (29) Procedia Engineering www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 9 th Conference of the International Sports Engineering Association (ISEA) Mountain bike wheel endurance testing and modeling
Vehicle Turn Simulation Using FE Tire model
 3. LS-DYNA Anwenderforum, Bamberg 2004 Automotive / Crash Vehicle Turn Simulation Using FE Tire model T. Fukushima, H. Shimonishi Nissan Motor Co., LTD, Natushima-cho 1, Yokosuka, Japan M. Shiraishi SRI
3. LS-DYNA Anwenderforum, Bamberg 2004 Automotive / Crash Vehicle Turn Simulation Using FE Tire model T. Fukushima, H. Shimonishi Nissan Motor Co., LTD, Natushima-cho 1, Yokosuka, Japan M. Shiraishi SRI
METHOD FOR TESTING STEERABILITY AND STABILITY OF MILITARY VEHICLES MOTION USING SR60E STEERING ROBOT
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 18, No. 1 11 METHOD FOR TESTING STEERABILITY AND STABILITY OF MILITARY VEHICLES MOTION USING SR6E STEERING ROBOT Wodzimierz Kupicz, Stanisaw Niziski Military
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 18, No. 1 11 METHOD FOR TESTING STEERABILITY AND STABILITY OF MILITARY VEHICLES MOTION USING SR6E STEERING ROBOT Wodzimierz Kupicz, Stanisaw Niziski Military
Balancing of aeroderivative turbine
 Balancing of aeroderivative turbine Guillaume Christin 1, Nicolas Péton 2 1 GE Measurement and Control, 68 chemin des Ormeaux, 69760 Limonest, France 2 GE Measurement and Control, 14 rue de la Haltinière,
Balancing of aeroderivative turbine Guillaume Christin 1, Nicolas Péton 2 1 GE Measurement and Control, 68 chemin des Ormeaux, 69760 Limonest, France 2 GE Measurement and Control, 14 rue de la Haltinière,
EXTERNAL DAMPING OF STAY CABLES USING ADAPTIVE AND SEMI-ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL
 EXTERNAL DAMPING OF STAY CABLES USING ADAPTIVE AND SEMI-ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL Andreas Andersson, Alan O Connor 2, Raid Karoumi 3 Researcher, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH, Stockholm, Sweden 2 Associate
EXTERNAL DAMPING OF STAY CABLES USING ADAPTIVE AND SEMI-ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL Andreas Andersson, Alan O Connor 2, Raid Karoumi 3 Researcher, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH, Stockholm, Sweden 2 Associate
Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers
 Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers U. Bin-Nun FLIR Systems Inc. Boston, MA 01862 ABSTRACT Cryocooler self induced vibration is a major consideration in the design of IR
Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers U. Bin-Nun FLIR Systems Inc. Boston, MA 01862 ABSTRACT Cryocooler self induced vibration is a major consideration in the design of IR
ROTATING MACHINERY DYNAMICS
 Pepperdam Industrial Park Phone 800-343-0803 7261 Investment Drive Fax 843-552-4790 N. Charleston, SC 29418 www.wheeler-ind.com ROTATING MACHINERY DYNAMICS SOFTWARE MODULE LIST Fluid Film Bearings Featuring
Pepperdam Industrial Park Phone 800-343-0803 7261 Investment Drive Fax 843-552-4790 N. Charleston, SC 29418 www.wheeler-ind.com ROTATING MACHINERY DYNAMICS SOFTWARE MODULE LIST Fluid Film Bearings Featuring
Poul Greibe 1 CHEVRON MARKINGS ON FREEWAYS: EFFECT ON SPEED, GAP AND SAFETY
 Poul Greibe 1 CHEVRON MARKINGS ON FREEWAYS: EFFECT ON SPEED, GAP AND SAFETY Submission: 13 October 2009 Revised: 2 Marts 2010 Word count: 3130 + 8 tables/figures = 5130 words. Author: Mr. Poul Greibe M.Sc.,
Poul Greibe 1 CHEVRON MARKINGS ON FREEWAYS: EFFECT ON SPEED, GAP AND SAFETY Submission: 13 October 2009 Revised: 2 Marts 2010 Word count: 3130 + 8 tables/figures = 5130 words. Author: Mr. Poul Greibe M.Sc.,
APS 420 ELECTRO-SEIS Long Stroke Shaker with Linear Ball Bearings Page 1 of 5
 Long Stroke Shaker with Linear Ball Bearings Page 1 of 5 The APS 420 ELECTRO-SEIS shaker is a long stroke, electrodynamic force generator specifically designed to be used alone or in arrays for studying
Long Stroke Shaker with Linear Ball Bearings Page 1 of 5 The APS 420 ELECTRO-SEIS shaker is a long stroke, electrodynamic force generator specifically designed to be used alone or in arrays for studying
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE LEAF SPRING
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 7, Issue 5, September October 2016, pp.177 183, Article ID: IJMET_07_05_019 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=7&itype=5
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 7, Issue 5, September October 2016, pp.177 183, Article ID: IJMET_07_05_019 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=7&itype=5
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF LOAD DISTRIBUTION IN RAILWAY TRACK UNDER WHEELSET
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol., No. 3 13 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF LOAD DISTRIBUTION IN RAILWAY TRACK UNDER WHEELSET Piotr Szurgott, Krzysztof Berny Military University of Technology Department
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol., No. 3 13 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF LOAD DISTRIBUTION IN RAILWAY TRACK UNDER WHEELSET Piotr Szurgott, Krzysztof Berny Military University of Technology Department
Technology Development of Dual Power Supply System for Mild Hybrid System and Micro Hybrid System
 DENSO TEN Technical Review Vol.1 Technology Development of Dual Power Supply System for Mild Hybrid System and Micro Hybrid System Yasuki MIO Masato HISANAGA Yoshinori SHIBACHI Keiichi YONEZAKI Yoshikazu
DENSO TEN Technical Review Vol.1 Technology Development of Dual Power Supply System for Mild Hybrid System and Micro Hybrid System Yasuki MIO Masato HISANAGA Yoshinori SHIBACHI Keiichi YONEZAKI Yoshikazu
MULTIBODY ANALYSIS OF THE M-346 PILOTS INCEPTORS MECHANICAL CIRCUITS INTRODUCTION
 MULTIBODY ANALYSIS OF THE M-346 PILOTS INCEPTORS MECHANICAL CIRCUITS Emanuele LEONI AERMACCHI Italy SAMCEF environment has been used to model and analyse the Pilots Inceptors (Stick/Pedals) mechanical
MULTIBODY ANALYSIS OF THE M-346 PILOTS INCEPTORS MECHANICAL CIRCUITS Emanuele LEONI AERMACCHI Italy SAMCEF environment has been used to model and analyse the Pilots Inceptors (Stick/Pedals) mechanical
Study Of Static And Frequency Responsible Analysis Of Hangers With Exhaust System
 International Journal of Advances in Scientific Research and Engineering (ijasre) ISSN: 2454-8006 [Vol. 03, Issue 5, June -2017] Study Of Static And Frequency Responsible Analysis Of Hangers With Exhaust
International Journal of Advances in Scientific Research and Engineering (ijasre) ISSN: 2454-8006 [Vol. 03, Issue 5, June -2017] Study Of Static And Frequency Responsible Analysis Of Hangers With Exhaust
Interim report on noise in F2C, October 2010 Rob Metkemeijer
 1 Interim report on noise in F2C, October 2010 Rob Metkemeijer 1. Introduction. At the 2010 CIAM plenary it was decided that in 2010 a strategy for noise control in F2C team race will be prepared, aiming
1 Interim report on noise in F2C, October 2010 Rob Metkemeijer 1. Introduction. At the 2010 CIAM plenary it was decided that in 2010 a strategy for noise control in F2C team race will be prepared, aiming
Development and validation of a vibration model for a complete vehicle
 Development and validation of a vibration for a complete vehicle J.W.L.H. Maas DCT 27.131 External Traineeship (MW Group) Supervisors: M.Sc. O. Handrick (MW Group) Dipl.-Ing. H. Schneeweiss (MW Group)
Development and validation of a vibration for a complete vehicle J.W.L.H. Maas DCT 27.131 External Traineeship (MW Group) Supervisors: M.Sc. O. Handrick (MW Group) Dipl.-Ing. H. Schneeweiss (MW Group)
Comparing FEM Transfer Matrix Simulated Compressor Plenum Pressure Pulsations to Measured Pressure Pulsations and to CFD Results
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 Comparing FEM Transfer Matrix Simulated Compressor Plenum Pressure Pulsations to Measured
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 Comparing FEM Transfer Matrix Simulated Compressor Plenum Pressure Pulsations to Measured
INFLUENCE OF CROSS FORCES AND BENDING MOMENTS ON REFERENCE TORQUE SENSORS FOR TORQUE WRENCH CALIBRATION
 XIX IMEKO World Congress Fundamental and Applied Metrology September 6 11, 2009, Lisbon, Portugal INFLUENCE OF CROSS FORCES AND BENDING MOMENTS ON REFERENCE TORQUE SENSORS FOR TORQUE WRENCH CALIBRATION
XIX IMEKO World Congress Fundamental and Applied Metrology September 6 11, 2009, Lisbon, Portugal INFLUENCE OF CROSS FORCES AND BENDING MOMENTS ON REFERENCE TORQUE SENSORS FOR TORQUE WRENCH CALIBRATION
Silencers. Transmission and Insertion Loss
 Silencers Practical silencers are complex devices, which operate reducing pressure oscillations before they reach the atmosphere, producing the minimum possible loss of engine performance. However they
Silencers Practical silencers are complex devices, which operate reducing pressure oscillations before they reach the atmosphere, producing the minimum possible loss of engine performance. However they
What is model validation? Overview about DynoTRAIN WP5. O. Polach Final Meeting Frankfurt am Main, September 27, 2013
 What is model validation? Overview about DynoTRAIN WP5 O. Polach Final Meeting Frankfurt am Main, September 27, 2013 Contents Introduction State-of-the-art on the railway dynamic modelling Suspension modelling
What is model validation? Overview about DynoTRAIN WP5 O. Polach Final Meeting Frankfurt am Main, September 27, 2013 Contents Introduction State-of-the-art on the railway dynamic modelling Suspension modelling
Analysis and control of vehicle steering wheel angular vibrations
 Analysis and control of vehicle steering wheel angular vibrations T. LANDREAU - V. GILLET Auto Chassis International Chassis Engineering Department Summary : The steering wheel vibration is analyzed through
Analysis and control of vehicle steering wheel angular vibrations T. LANDREAU - V. GILLET Auto Chassis International Chassis Engineering Department Summary : The steering wheel vibration is analyzed through
DYNAMIC LOAD IN OPERATION OF HIGH-SPEED TRACKED VEHICLES
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 16, No. 4 29 DYNAMIC LOAD IN OPERATION OF HIGH-SPEED TRACKED VEHICLES Wac aw Borkowski, Piotr Rybak Military University of Technology S. Kaliskiego Street
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 16, No. 4 29 DYNAMIC LOAD IN OPERATION OF HIGH-SPEED TRACKED VEHICLES Wac aw Borkowski, Piotr Rybak Military University of Technology S. Kaliskiego Street
EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH ON HELICOPTER TAIL SHAKE PHENOMENON
 EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH ON HELICOPTER TAIL SHAKE PHENOMENON Iskandar Shah Ishak, Shuhaimi Mansor, Tholudin Mat Lazim Department of Aeronautical Engineering, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti
EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH ON HELICOPTER TAIL SHAKE PHENOMENON Iskandar Shah Ishak, Shuhaimi Mansor, Tholudin Mat Lazim Department of Aeronautical Engineering, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Wind tunnel investigation of waste air re-entry with wall ventilation P. Broas Technical Research Centre of Finland, Ship Laboratory, Tekniikantie 12, SF-02150, Espoo, Finland ABSTRACT A wind tunnel investigation
Wind tunnel investigation of waste air re-entry with wall ventilation P. Broas Technical Research Centre of Finland, Ship Laboratory, Tekniikantie 12, SF-02150, Espoo, Finland ABSTRACT A wind tunnel investigation
