HVACR Electrical Systems
|
|
|
- Melinda Webb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HVACR Electrical Systems to The following HVAC Excellence competencies (rev. 2007) are covered in this publication. Only the covered compentencies are listed. The first column identifies the competency by name. The second colum identifies the exact location in this MAVCC publication where that competency is covered. Electrical Core Exam Electrical Theory Describe and identify conductors. Describe and identify insulators. Describe and identify semi-conductors. Describe Ohm s Law. Solve problems applying Ohm s Law. Demonstrate proficiency is calculating the total resistance in multiple resistors in a series circuit. Unit 1, Objective 7 Insulators, semiconductors, and conductors Unit 2, Objective 3 Electrical wiring Unit 1, Objective 7 Insulators, semiconductors, and conductors Unit 1, Objective 7 Insulators, semiconductors, and conductors Unit 1, Objective 18 The three equations for using Ohm s Law Unit 1, Objective 19 Using Ohm s Law to find unknown values Unit 1, Objective 20 Using Ohm s Law to determine values in a series circuit Unit 1, Objective 21 Using Ohm s Law to determine values in a parallel circuit Unit 1, Objective 22 Using Ohm s Law to determine values in series-parallel Unit 1, Assignment Sheet 2 Use Ohm s Law to determine unknown values in resistive Unit 1, Assignment Sheet 2 Use Ohm s Law to determine unknown values in resistive Demonstrate proficiency is calculating the total Unit 1, Assignment Sheet 2 Use Ohm s Law resistance in multiple resistors in a parallel circuit. to determine unknown values in resistive Describe and demonstrate the effects of voltage drop in a series circuit. Calculate and measure the voltage output of a transformer using the number of turns on the primary vs. the secondary sides. Unit 1, Assignment Sheet 2 Use Ohm s Law to determine unknown values in resistive Unit 6, Objective 2 How a transformer works Unit 6, Objective 3 Control transformer specifications xxv
2 Interpreting Electrical Diagrams Describe the differences between a Pictorial, a Ladder Diagram, and a Schematic. Identify standard electrical symbols used in schematics. Identify inoperative/defective component using schematic wiring diagrams. Identify voltage between two points using schematic wiring diagrams. Unit 4, Objective 5 Sources of wiring diagrams Unit 4, Objective 6 Pictorial wiring diagrams Unit 4, Objective 7 Schematic wiring diagrams Unit 4, Objective 8 Electronic wiring diagrams Unit 4, Objective 9 Draw a pictorial diagram Unit 4, Objective 10 Building a ladder schematic diagram Unit 4, Objective 11 Using symbols Located throughout this publication Unit 15, Assignment Sheet 1 Identify components on HVACR system electrical diagrams Unit 15, Assignment Sheet 2 Identify component operations from HVACR system electrical diagrams Unit 15, Assignment Sheet 3 Select test instruments or procedures for specific HVACR system troubleshooting Unit 15, Assignment Sheet 4 Solve HVACR electrical troubleshooting problems Unit 15, Job Sheet 1 Troubleshoot series electrical on selected HVACR Unit 15, Job Sheet 2 Troubleshoot parallel electrical on selected HVACR Unit 15, Job Sheet 3 Troubleshoot seriesparallel electrical on selected HVACR Unit 3, Assignment Sheet 1 Use Watt s Law to determine power Unit 4, Job Sheet 1 Draw pictorials, fabricate for basic series and parallel Unit 4, Job Sheet 2 Draw pictorials, fabricate for series-parallel Unit 4, Job Sheet 3 Draw pictorials, fabricate for with varied loads and switching xxvi
3 Determine sequence of operation using schematic wiring diagrams. Unit 5, Job Sheet 1 Draw pictorials, fabricate for shunt with one SPST switch Unit 5, Job Sheet 2 Draw pictorials, fabricate for with 3-way switches Unit 5, Job Sheet 3 Draw pictorials, fabricate for with 3-way and 4-way switches Unit 5, Job Sheet 4 Draw pictorials, fabricate for with safety switches Unit 5, Job Sheet 5 Draw pictorials, fabricate for a basic small refrigeration unit circuit Unit 6, Job Sheet 1 Check current relays with an ohmmeter Unit 6, Job Sheet 2 Check potential relays with an ohmmeter Unit 6, Job Sheet 3 Check current relays with an ammeter and a voltmeter Unit 6, Job Sheet 4 Check a potential relay with an ammeter and a voltmeter Unit 6, Job Sheet 5 Install a solid-state, time-delay relay Unit 6, Job Sheet 6 Draw pictorials, fabricate for with basic relays Unit 6, Job Sheet 7 Draw pictorials, fabricate for with dual relays Unit 6, Job Sheet 8 Draw pictorials, fabricate for with special applications Unit 6, Job Sheet 9 Draw pictorials, fabricate for with multiple relays Unit 15, Assignment Sheet 4 Solve HVACR electrical troubleshooting problems Unit 15, Assignment Sheet 1 Identify components on HVACR system electrical diagrams Unit 15, Assignment Sheet 2 Identify component operations from HVACR system electrical diagrams Unit 15, Assignment Sheet 3 Select test instruments or procedures for specific HVACR system troubleshooting Unit 15, Assignment Sheet 4 Solve HVACR electrical troubleshooting problems xxvii
4 Knowledge of Electrical Components Identify the types and describe the proper application and use of Circuit Protectors. Identify, describe, and explain the function and application of thermostats. Identify, describe, and explain the function and application of transformers. Unit 15, Job Sheet 1 Troubleshoot series electrical on selected HVACR Unit 15, Job Sheet 2 Troubleshoot parallel electrical on selected HVACR Unit 15, Job Sheet 3 Troubleshoot seriesparallel electrical on selected HVACR Unit 5, Objective 10 Protection devices Unit 5, Objective 11 Overcurrent protection devices Unit 7, Objective 2 Thermostat types and their applications Unit 7, Objective 3 Temperature sensors Unit 7, Objective 4 Electrical contacts Unit 7, Objective 5 Major components of a heating/cooling thermostat Unit 7, Objective 6 Heating thermostat anticipation Unit 7, Objective 7 Cooling thermostat anticipation Unit 7, Objective 8 Installing heating/cooling thermostats Unit 7, Objective 9 Multistage thermostats Unit 7, Objective 10 Subbase applications Unit 7, Objective 11 Basic internal thermostat switching Unit 7, Objective 12 Programmable thermostat applications Unit 7, Objective 13 Electronic thermostat Unit 7, Objective 14 Additional benefits of solid-state thermostats Unit 7, Objective 15 Special applications of line voltage thermostats Unit 3, Objective 3 Transformers Unit 3, Objective 5 Types of power supplies Unit 6, Objective 2 How a transformer works Unit 6, Objective 3 Control transformer specifications Unit 6, Objective 4 Providing DC power xxviii
5 Identify, describe, and explain the function and applications of relays. Identify, describe, and explain the function and application of switches. Evaluate and replace thermostats. Evaluate and replace relays. Unit 6, Objective 5 Relay components and uses Unit 6, Objective 6 Using relay symbols in electrical drawings Unit 6, Objective 7 Control relays and contactors Unit 6, Objective 8 Control relay and contactor switching arrangements Unit 6, Objective 9 Types of motor starting relays and their uses Unit 6, Objective 10 Motor starting current relay operations Unit 6, Objective 11 Motor starting current relay specifications Unit 6, Objective 12 Motor starting voltage relay operations Unit 6, Objective 13 Potential relay specifications Unit 6, Objective 14 Time delay relays Unit 5, Objective 2 Controls and their applications Unit 5, Objective 3 Types of controls Unit 5, Objective 4 Control systems Unit 5, Objective 5 Switch configurations and symbols Unit 5, Objective 6 Identifying switch symbols Unit 5, Objective 7 Three- and four-way switches and their applications Unit 7, Job Sheet 1 Install a wall thermostat and determine heat anticipation Unit 7, Job Sheet 2 Replace a standard thermostat with an electronic programmable thermostat Unit 7, Job Sheet 3 Program a programmable thermostat Unit 6, Job Sheet 1 Check current relays with an ohmmeter Unit 6, Job Sheet 2 Check potential relays with an ohmmeter Unit 6, Job Sheet 3 Check current relays with an ammeter and a voltmeter Unit 6, Job Sheet 4 Check a potential relay with an ammeter and a voltmeter Unit 6, Job Sheet 5 Install a solid-state, time-delay relay xxix
6 Evaluate and replace switches. Fundamentals of Motors/Capacitors Describe how capacitors are rated and tested. Describe the function of the parts of an induction motor. Disassemble and assemble an induction motor. Unit 6, Job Sheet 6 Draw pictorials, fabricate for with basic relays Unit 6, Job Sheet 7 Draw pictorials, fabricate for with dual relays Unit 6, Job Sheet 8 Draw pictorials, fabricate for with special applications Unit 6, Job Sheet 9 Draw pictorials, fabricate for with multiple relays Unit 5, Job Sheet 1 Draw pictorials, fabricate for shunt with one SPST switch Unit 5, Job Sheet 2 Draw pictorials, fabricate for with 3-way switches Unit 5, Job Sheet 3 Draw pictorials, fabricate for with safety switches Unit 5, Job Sheet 4 Draw pictorials, fabricate for a basic refrigeration circuit Unit 11, Objective 6 Guidelines for capacitor replacement Unit 11, Objective 7 Grouping capacitors Unit 8, Objective 5 Basic AC motor operation Unit 8, Objective 6 Single-phase AC motor starting Unit 8, Objective 7 Basic AC electric motor parts and their functions Unit 8, Objective 8 Types of motor construction Unit 8, Objective 9 Types of motor mounts and typical applications Unit 9, Job Sheet 2 Disassemble, inspect, clean, reassemble, and check operation of a shaded-pole motor Unit 10, Job Sheet 4 Disassemble, inspect, clean, reassemble, and check operation of a split-phase motor xxx
7 Measure locked rotor amps, and full load amps. Describe how overload protectors function. Describe the function, application, and wiring of a start capacitor. Evaluate and replace a start capacitor. Describe the function, application, and wiring of a run capacitor. Unit 2, Job Sheet 7 Use digital and analog ammeters to read start and run amperage of a motor Unit 9, Job Sheet 2 Disassemble, inspect, clean, reassemble, and check operation of a shaded-pole motor Unit 10, Job Sheet 4 Disassemble, inspect, clean, reassemble, and check operation of a split-phase motor Unit 12, Job Sheet 4 Disassemble, inspect, clean, reassemble, and check operation of a PSC fan motor Unit 5, Objective 10 Protection devices Unit 5, Objective 11 Overcurrent protection devices Unit 5, Objective 12 Pressure-actuated protection devices Unit 5, Objective 13 Motor protection devices Unit 5, Objective 14 Bimetal protection devices Unit 5, Objective 15 Protecting electronic Unit 8, Objective 7 Basic AC electric motor parts and their functions Unit 11, Objective 5 Types of capacitors Unit 12, Objective 3 CS motor Unit 12, Objective 4 PSC motor Unit 12, Objective 6 Troubleshooting capacitor motors Unit 11, Objective 6 Guidelines for capacitor replacement Unit 11, Job Sheet 1 Check capacitors with an analog ohmmeter Unit 11, Job Sheet 2 Check capacitors with a capacitor analyzer Unit 12, Job Sheet 6 Install a hard start kit Unit 12, Job Sheet 7 Troubleshoot a CSR compressor with an ammeter Unit 11, Objective 5 Types of capacitors Unit 11, Objective 6 Guidelines for capacitor replacement Unit 12, Objective 3 CS motor xxxi
8 Evaluate and replace a run capacitor. Describe and explain motor speed. Explain and change the direction of rotation in a single phase motor Describe the method used in change rotation direction in a three-phase motor. Demonstrate the method used in change rotation direction in a three-phase motor. Describe a three-phase motor. Explain the difference between a Wye and Delta three-phase motor. Describe a dual voltage three-phase motor. Demonstrate the wiring configurations of a dual voltage three-phase motor. Describe a permanent split capacitor motor. Unit 12, Objective 5 CSR motor Unit 12, Objective 6 Troubleshooting capacitor motors Unit 11, Job Sheet 1 Check capacitors with an analog ohmmeter Unit 11, Job Sheet 2 Check capacitors with a capacitor analyzer Unit 12, Job Sheet 7 Troubleshoot a CSR compressor with an ammeter Unit 8, Objective 12 Pulley selection Unit 9, Objective 3 Shaded-pole motor construction Unit 9, Objective 4 Controlling shaded-pole speed Unit 9, Objective 5 Shaded-pole motor rotation Unit 10, Objective 5 Wiring connections for split-phase motors Unit 14, Objective 4 Wiring connections for three-phase motors Unit 14, Job Sheet 1 Wire a dual-voltage, three-phase motor, reverse rotation, and check operation Unit 14, Objective 2 Characteristics and applications of three-phase motors Unit 14, Objective 3 Three-phase motor construction Unit 14, Objective 4 Wiring connections for three-phase motors Unit 14, Objective 3 Three-phase motor construction Unit 14, Objective 4 Wiring connections for three-phase motors Unit 14, Job Sheet 1 Wire a dual-voltage, three-phase motor, reverse rotation, and check operation Unit 12, Objective 2 Applications of capacitors to motors Unit 12, Objective 3 CS motor Unit 12, Objective 4 PSC motor xxxii
9 Describe a capacitor start induction run motor. Describe a multi-speed motor. Electrical Troubleshooting and Problem Solving Troubleshooting and problem solving questions involve diagnostic procedures requiring the use of test instruments, data plate information, and wiring diagrams. Unit 12, Objective 3 CS motor Unit 9, Objective 4 Controlling shaded-pole motor speed Unit 12, Objective 4 PSC motor Unit 15, Objective 1 Terms and definitions Unit 15, Objective 2 Guidelines for troubleshooting HVACR system electrical Unit 15, Objective 3 Identifying circuit components and their operations Unit 15, Objective 4 Guidelines for test meter selection Unit 15, Objective 5 Using a voltmeter Unit 15, Objective 6 Applying the hopscotch method for troubleshooting Unit 15, Objective 7 Using an ammeter Unit 15, Objective 8 Using an ohmmeter Unit 15, Objective 9 Check for shorts and grounds Unit 15, Objective 10 Using jumpers to troubleshoot Unit 15, Objective 11 Troubleshooting techniques Unit 15, Assignment Sheet 1 Identify components on HVACR system electrical diagrams Unit 15, Assignment Sheet 2 Identify component operation from HVACR system electrical diagrams Unit 15, Assignment Sheet 3 Select test instruments or procedures for specific HVACR system troubleshooting Unit 15, Assignment Sheet 4 Solve HVACR electrical troubleshooting problems Unit 15, Job Sheet 1 Troubleshoot series electrical on selected HVACR Unit 15, Job Sheet 2 Troubleshoot parallel electrical on selected HVACR Unit 15, Job Sheet 3 Troubleshoot seriesparallel electrical on selected HVACR xxxiii
10 Knowledge of the following test instruments Ohmmeter Ammeter Voltmeter Multimeter Electric Heat Thermostat Identify the proper location for and install a conventional thermostat. Explain the detailed wiring and operation of a set back programmable thermostat. Unit 2, Objective 7 Test instrument Unit 2, Objective 8 Reading test instruments Unit 2, Objective 10 Using ohmmeters Unit 2, Objective 11 Using an ohmmeter to check motors Unit 2, Objective 12 Checking a hermetic compressor motor with an ohmmeter Unit 2, Objective 7 Test instrument Unit 2, Objective 8 Reading test instruments Unit 2, Objective 13 Using ammeters Unit 2, Objective 7 Test instrument Unit 2, Objective 8 Reading test instruments Unit 2, Student Supplement 2 Multimeters Unit 2, Objective 7 Test instrument Unit 2, Objective 8 Reading test instruments Unit 2, Student Supplement 2 Multimeters Unit 7, Objective 8 Installing heating/cooling thermostats Unit 7, Job Sheet 1 Install a wall thermostat and determine heat anticipation Unit 7, Objective 12 Programmable thermostat applications Unit 7, Objective 13 Electronic thermostat Unit 7, Objective 14 Additional benefits of solid-state thermostats Unit 7, Job Sheet 2 Replace a standard thermostat with an electronic programmable thermostat Unit 7, Job Sheet 3 Program a programmable thermostat xxxiv
Electrical Controls. Syllabus
 Instructor: Jeremie Hedges (757)651-1007 Contact Hours: 72 hours Prerequisites: None Electrical Controls Syllabus Course Description: This course is designed to present a blend of electrical theory and
Instructor: Jeremie Hedges (757)651-1007 Contact Hours: 72 hours Prerequisites: None Electrical Controls Syllabus Course Description: This course is designed to present a blend of electrical theory and
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 15 Troubleshooting Basic Controls
 SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 15 Troubleshooting Basic Controls UNIT OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, the reader should be able to Describe and identify power- and non-power-consuming Describe
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 15 Troubleshooting Basic Controls UNIT OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, the reader should be able to Describe and identify power- and non-power-consuming Describe
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS HRA101 ELECTRICITY FOR HVAC. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: William Kaune. Revised Date: March 17, 2014
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS HRA101 ELECTRICITY FOR HVAC 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: William Kaune Revised Date: March 17, 2014 Dena McCaffrey, Ed.D., Dean, Career & Technical Education HRA101 Electricity
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS HRA101 ELECTRICITY FOR HVAC 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: William Kaune Revised Date: March 17, 2014 Dena McCaffrey, Ed.D., Dean, Career & Technical Education HRA101 Electricity
Electricity Course. Part B Course Outline
 Electricity Course Rev. Date: 10/01/2002 By: R. Crompton Part B Course Outline Subject Area 0 Orientation 2.6 0.0 0.1 To the School 1.0 0.2 To the Course 1.0 0.3 To the 0.3 0.3 0.4 To Possible Emergencies
Electricity Course Rev. Date: 10/01/2002 By: R. Crompton Part B Course Outline Subject Area 0 Orientation 2.6 0.0 0.1 To the School 1.0 0.2 To the Course 1.0 0.3 To the 0.3 0.3 0.4 To Possible Emergencies
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY 3 March 2008
 I. Course Description ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY 3 March 2008 The purpose for this course is to instruct potential electricians in the skills necessary for entry into the job market. During this course, the
I. Course Description ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY 3 March 2008 The purpose for this course is to instruct potential electricians in the skills necessary for entry into the job market. During this course, the
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapter 8 Pages Electricity & Electronics 37 Points. Automotive Service
 Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapter 8 Pages 97 110 Electricity & Electronics 37 Points Automotive Service 1. is the movement of electrons ( ) from atom to atom. Every vehicle system uses some type of
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapter 8 Pages 97 110 Electricity & Electronics 37 Points Automotive Service 1. is the movement of electrons ( ) from atom to atom. Every vehicle system uses some type of
Diesel Technology: Electrical and Electronic Systems
 Diesel Technology: Electrical and Electronic Systems Instructional/Task Analysis 2. Composition of atoms Unit 1: Introduction to Diesel Electrical and Electronic Systems 3. Electrical charges in atoms
Diesel Technology: Electrical and Electronic Systems Instructional/Task Analysis 2. Composition of atoms Unit 1: Introduction to Diesel Electrical and Electronic Systems 3. Electrical charges in atoms
SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 17: TYPES OF ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT OBJECTIVES UNIT OBJECTIVES 3/21/2012
 SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 17: TYPES OF ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, the reader should be able to Describe the different types of open single-phase motors used to drive
SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 17: TYPES OF ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, the reader should be able to Describe the different types of open single-phase motors used to drive
Basics of Control Components
 Basics of Control Components Table of Contents Introduction...2 Electrical Symbols...6 Line Diagrams...16 Overload Protection...22 Overload Relays...26 Manual Control...35 Magnetic Contactors and Starters...41
Basics of Control Components Table of Contents Introduction...2 Electrical Symbols...6 Line Diagrams...16 Overload Protection...22 Overload Relays...26 Manual Control...35 Magnetic Contactors and Starters...41
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE AERM 1314 BASIC ELECTRICITY-G Semester Hours Credit: 3 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS:
 I. INTRODUCTION CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE AERM 1314 BASIC ELECTRICITY-G Semester Hours Credit: 3 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS: A. Electricity is a vital part of modern aviation technology. This course lays the
I. INTRODUCTION CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE AERM 1314 BASIC ELECTRICITY-G Semester Hours Credit: 3 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS: A. Electricity is a vital part of modern aviation technology. This course lays the
Course Outcome Summary
 Course Information Division: ASET Contact Hours: 90 Theory: 30 Lab Hours: 60 Total Credits 4 Prerequisites ELEC 125 (Fundamentals of Electricity) Course Description This course is designed to provide students
Course Information Division: ASET Contact Hours: 90 Theory: 30 Lab Hours: 60 Total Credits 4 Prerequisites ELEC 125 (Fundamentals of Electricity) Course Description This course is designed to provide students
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE AERM 1445 AIRCRAFT ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS-A. Semester Hours Credit: 4 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS:
 A. INTRODUCTION CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE AERM 1445 AIRCRAFT ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS-A Semester Hours Credit: 4 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS: A. An aviation maintenance technician must understand the basic electrical
A. INTRODUCTION CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE AERM 1445 AIRCRAFT ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS-A Semester Hours Credit: 4 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS: A. An aviation maintenance technician must understand the basic electrical
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Motor Types
 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Motor Types Compressor Starting Matrix Motor Type Starting Device Capacitors Overload Protector Current Voltage PTC Start Run Relays Relays Split phase Induction Motor
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Motor Types Compressor Starting Matrix Motor Type Starting Device Capacitors Overload Protector Current Voltage PTC Start Run Relays Relays Split phase Induction Motor
Full file at
 CHAPTER 2 FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRICITY Job Assignment for This Chapter: You are on a service call and a customer does not understand the basic theory of electricity and thinks you are trying to sell parts
CHAPTER 2 FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRICITY Job Assignment for This Chapter: You are on a service call and a customer does not understand the basic theory of electricity and thinks you are trying to sell parts
Auto Service Technician
 Auto Service Technician Organization Washburn Institute of Technology Program Number 47.0604 Instructional Level Certificate Target Population Grades 11 & 12 Post-secondary Description The Auto Service
Auto Service Technician Organization Washburn Institute of Technology Program Number 47.0604 Instructional Level Certificate Target Population Grades 11 & 12 Post-secondary Description The Auto Service
Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 2 Basic Electrical Meters and Ohm s Law
 Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 2 Basic Electrical Meters and Ohm s Law Administration: o Prayer o Bible Verse o Turn in quiz Meters: o Terms and Definitions: Analog vs. Digital Displays: Analog
Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 2 Basic Electrical Meters and Ohm s Law Administration: o Prayer o Bible Verse o Turn in quiz Meters: o Terms and Definitions: Analog vs. Digital Displays: Analog
Unit 10 Measuring Instruments
 Objectives: Unit 10 Discuss the operation of a d Arsonval meter movement. Connect a voltmeter to a circuit. Read an analog multimeter. Connect an ammeter. Measure resistance using an ohmmeter. Analog meters
Objectives: Unit 10 Discuss the operation of a d Arsonval meter movement. Connect a voltmeter to a circuit. Read an analog multimeter. Connect an ammeter. Measure resistance using an ohmmeter. Analog meters
AG. 225 AGRICULTURAL SYSTEMS/ELECTRICITY AND HYDRAULICS
 AG. 225 AGRICULTURAL SYSTEMS/ELECTRICITY AND HYDRAULICS COURSE DESCRIPTION: A course designed to develop skills in operation of tools and equipment, wiring, controls, electric motors, and hydraulics. UNITS
AG. 225 AGRICULTURAL SYSTEMS/ELECTRICITY AND HYDRAULICS COURSE DESCRIPTION: A course designed to develop skills in operation of tools and equipment, wiring, controls, electric motors, and hydraulics. UNITS
Electrical Equipment and Safety: Operation, Control, Maintenance and Troubleshooting
 Electrical Equipment and Safety: Operation, Control, Maintenance and Troubleshooting Page 1 of 6 Why Attend This course covers the theoretical and practical operation of common electrical equipment and
Electrical Equipment and Safety: Operation, Control, Maintenance and Troubleshooting Page 1 of 6 Why Attend This course covers the theoretical and practical operation of common electrical equipment and
Building Operator Certification Level I
 Building Operator Certification Level I A Partnership of the CUNY Institute for Urban Systems Building Performance Lab, the CUNY School of Professional Studies, and the New York State Energy Research &
Building Operator Certification Level I A Partnership of the CUNY Institute for Urban Systems Building Performance Lab, the CUNY School of Professional Studies, and the New York State Energy Research &
Student Exploration: Advanced Circuits
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Advanced Circuits [Note to teachers and students: This Gizmo was designed as a follow-up to the Circuits Gizmo. We recommend doing that activity before trying this one.]
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Advanced Circuits [Note to teachers and students: This Gizmo was designed as a follow-up to the Circuits Gizmo. We recommend doing that activity before trying this one.]
Single Phase Induction Motor. Dr. Sanjay Jain Department Of EE/EX
 Single Phase Induction Motor Dr. Sanjay Jain Department Of EE/EX Application :- The single-phase induction machine is the most frequently used motor for refrigerators, washing machines, clocks, drills,
Single Phase Induction Motor Dr. Sanjay Jain Department Of EE/EX Application :- The single-phase induction machine is the most frequently used motor for refrigerators, washing machines, clocks, drills,
Electrical Maintenance
 Electrical Maintenance You Will Learn: The installation, operation, maintenance and management of boiler plants The steam and combustion processes Safe boiler operation techniques About pollutants and
Electrical Maintenance You Will Learn: The installation, operation, maintenance and management of boiler plants The steam and combustion processes Safe boiler operation techniques About pollutants and
PREVIEW ONLY - FULL COPY AVAILABLE TO CONSORTIUM MEMBERS. Escalator Specific Electrical Systems. Course 209 PARTICIPANT GUIDE
 Escalator Specific Electrical Systems Course 209 PARTICIPANT GUIDE Transit Elevator/Escalator Training Consortium Escalator: Electrical Systems Participant Guide Transit Elevator/Escalator Maintenance
Escalator Specific Electrical Systems Course 209 PARTICIPANT GUIDE Transit Elevator/Escalator Training Consortium Escalator: Electrical Systems Participant Guide Transit Elevator/Escalator Maintenance
IAE-101: Electrical Fundamentals for Non-Electrical Personnel
 IAE-101: Electrical Fundamentals for Non-Electrical Personnel Abstract Today s world of rapidly evolving technology poses a wealth of challenges just to remain competitive in the marketplace. Everyone
IAE-101: Electrical Fundamentals for Non-Electrical Personnel Abstract Today s world of rapidly evolving technology poses a wealth of challenges just to remain competitive in the marketplace. Everyone
Ohm s Law. 1-Introduction: General Physics Laboratory (PHY119) Basic Electrical Concepts:
 Ohm s Law General Physics Laboratory (PHY119) 1-Introduction: Basic Electrical Concepts: 1- Current (I): Is the flow of electrons through a conductor or semiconductor. For current to flow, it requires
Ohm s Law General Physics Laboratory (PHY119) 1-Introduction: Basic Electrical Concepts: 1- Current (I): Is the flow of electrons through a conductor or semiconductor. For current to flow, it requires
1012-Electrical Diagrams
 Term Absolute Pressure 1012-Electrical Diagrams Definition Total or true pressure. Gauge pressure plus atmospheric pressure. Absolute that includes the atmospheric pressure in its reading. This sensor
Term Absolute Pressure 1012-Electrical Diagrams Definition Total or true pressure. Gauge pressure plus atmospheric pressure. Absolute that includes the atmospheric pressure in its reading. This sensor
UNIT 1 ELECTRICIAN S MATH AND BASIC ELECTRICAL FORMULAS...1 Introduction...1. UNIT 2 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS...49 Introduction...49
 UNIT 1 ELECTRICIAN S MATH AND BASIC ELECTRICAL FORMULAS...1 Introduction...1 PART A ELECTRICIAN S MATH...1 Introduction...1 1.1 Whole Numbers...1 1.2 Decimal...1 1.3 Fractions...1 1.4 Percentages...2 1.5
UNIT 1 ELECTRICIAN S MATH AND BASIC ELECTRICAL FORMULAS...1 Introduction...1 PART A ELECTRICIAN S MATH...1 Introduction...1 1.1 Whole Numbers...1 1.2 Decimal...1 1.3 Fractions...1 1.4 Percentages...2 1.5
Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) Level 3
 Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) Level 3 Rev. September 2005 Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) Unit: G5 Prime Movers I Diesel 1 Level: Duration: Three 60 hours Theory: 20 hours Practical: 40 hours Overview:
Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) Level 3 Rev. September 2005 Industrial Mechanic (Millwright) Unit: G5 Prime Movers I Diesel 1 Level: Duration: Three 60 hours Theory: 20 hours Practical: 40 hours Overview:
Physics Experiment 9 Ohm s Law
 Fig. 9-1 Simple Series Circuit Equipment: Universal Circuit Board Power Supply 2 DMM's (Digital Multi-Meters) with Leads 150- Resistor 330- Resistor 560- Resistor Unknown Resistor Miniature Light Bulb
Fig. 9-1 Simple Series Circuit Equipment: Universal Circuit Board Power Supply 2 DMM's (Digital Multi-Meters) with Leads 150- Resistor 330- Resistor 560- Resistor Unknown Resistor Miniature Light Bulb
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT Name : Electrical and Electronics Engineering Code : A40203 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT Name : Electrical and Electronics Engineering Code : A40203 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch :
Circuits-Circuit Analysis
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the information and diagram below. 4. A 9-volt battery is connected to a 4-ohm resistor and a 5-ohm resistor as shown in the diagram below. A 3.0-ohm resistor,
Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the information and diagram below. 4. A 9-volt battery is connected to a 4-ohm resistor and a 5-ohm resistor as shown in the diagram below. A 3.0-ohm resistor,
Electrical and Power Transmission Installers, Other CIP Task Grid. Secondary Competency Task List. Level 1 Level 2 Level 3
 1 100 BASIC SAFETY 101 Demonstrate proper use of personal protective equipment. 5 102 Identify causes of job site accidents. 5 103 Identify job site hazards. 5 104 Working safely with job hazards. 5 105
1 100 BASIC SAFETY 101 Demonstrate proper use of personal protective equipment. 5 102 Identify causes of job site accidents. 5 103 Identify job site hazards. 5 104 Working safely with job hazards. 5 105
Power Factor Correction
 AE9-1249 R10 August 2008 Power Factor Correction Index Page 1. Introduction... 1 2. Electrical Fundamentals... 1 3. Electrical Formulas... 2 4. Apparent Power and Actual Power... 2 5. Effects of Poor Power
AE9-1249 R10 August 2008 Power Factor Correction Index Page 1. Introduction... 1 2. Electrical Fundamentals... 1 3. Electrical Formulas... 2 4. Apparent Power and Actual Power... 2 5. Effects of Poor Power
Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace
 Assessment Requirements Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace Content: Basic electrical principles a. Explain the direction of current flow
Assessment Requirements Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace Content: Basic electrical principles a. Explain the direction of current flow
Diesel Technology: Engines
 Diesel Technology: Engines NATEF Crosswalk The following NATEF Diesel Engines tasks (rev. 2004) are covered in this publication. The chart shows where each task is located within the publication. The first
Diesel Technology: Engines NATEF Crosswalk The following NATEF Diesel Engines tasks (rev. 2004) are covered in this publication. The chart shows where each task is located within the publication. The first
CHAPTER 19 DC Circuits Units
 CHAPTER 19 DC Circuits Units EMF and Terminal Voltage Resistors in Series and in Parallel Kirchhoff s Rules EMFs in Series and in Parallel; Charging a Battery Circuits Containing Capacitors in Series and
CHAPTER 19 DC Circuits Units EMF and Terminal Voltage Resistors in Series and in Parallel Kirchhoff s Rules EMFs in Series and in Parallel; Charging a Battery Circuits Containing Capacitors in Series and
16.3 Ohm s Law / Energy and Power / Electric Meters
 16.3 Ohm s Law / Energy and Power / Electric Meters Voltage Within a battery, a chemical reaction occurs that transfers electrons from one terminal to another terminal. This potential difference across
16.3 Ohm s Law / Energy and Power / Electric Meters Voltage Within a battery, a chemical reaction occurs that transfers electrons from one terminal to another terminal. This potential difference across
Marine and Outdoor Power Equipment Technician Level 2
 Level 2 Unit: B2 Trade Mathematics II Level: Two Duration: 16 hours Theory: Practical: 16 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit is designed to provide the apprentice with the knowledge and ability to apply
Level 2 Unit: B2 Trade Mathematics II Level: Two Duration: 16 hours Theory: Practical: 16 hours 0 hours Overview: This unit is designed to provide the apprentice with the knowledge and ability to apply
JARD by MARS JARD by MARS
 Table of Contents Description Page No. Capacitors Motor Run....................................................................................... J-3 J-5 Motor Start...........................................................................................J-6
Table of Contents Description Page No. Capacitors Motor Run....................................................................................... J-3 J-5 Motor Start...........................................................................................J-6
MILLWRIGHT. Learner Program Content:
 MILLWRIGHT Course Duration On average 45 Months - 18 Months institutional training - 24 Months on-the-job - 03 Months trade test preparation and Trade test Learner Program Content: BASIC PHASE ADVANCED
MILLWRIGHT Course Duration On average 45 Months - 18 Months institutional training - 24 Months on-the-job - 03 Months trade test preparation and Trade test Learner Program Content: BASIC PHASE ADVANCED
Electricity Unit Review
 Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
Automotive. Automotive Body and Repair
 Automotive Body and Repair This program is designed to prepare the student for employment as a body repair and paint apprentice in privately owned repair shops or automotive dealerships. A student could
Automotive Body and Repair This program is designed to prepare the student for employment as a body repair and paint apprentice in privately owned repair shops or automotive dealerships. A student could
ELECTRICAL. CDTA Technical Training Center
 ELECTRICAL ATOMIC STRUCTURE Protons positive charge Electron negative charge Neutron - neutral Electricity is the movement of electrons from atom to atom ELECTRON FLOW CONDUCTOR - Materials which have
ELECTRICAL ATOMIC STRUCTURE Protons positive charge Electron negative charge Neutron - neutral Electricity is the movement of electrons from atom to atom ELECTRON FLOW CONDUCTOR - Materials which have
Focus Area Level Report Including Knowledge and Skills, and Performance Indicators
 Including Knowledge and Skills, and PST 01. Use physical science principles and engineering applications with power, structural and technical systems to solve problems and improve performance. PST 01.01.
Including Knowledge and Skills, and PST 01. Use physical science principles and engineering applications with power, structural and technical systems to solve problems and improve performance. PST 01.01.
Training & Didactic Systems. Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering
 Training & Didactic Systems Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering Catalog WA1E/01 Table of Contents Page Our Service, Our Customers and fields of technology 2 Introduction 4 Instruction modules measuring
Training & Didactic Systems Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering Catalog WA1E/01 Table of Contents Page Our Service, Our Customers and fields of technology 2 Introduction 4 Instruction modules measuring
Contents. Review of Electric Circuitd. Preface ;
 Preface ; Chapter 1 Review of Electric Circuitd 1.1 Introduction, 1 1.2 Direct Circuit Current, 1 1.2.1 Voltage, 3 1.2.2 Power, 3 1.2.3 Ohm's Law, 5 1.2.4 KirchhofTs Laws, 5 1.2.4.1 Kirchhoff s Current
Preface ; Chapter 1 Review of Electric Circuitd 1.1 Introduction, 1 1.2 Direct Circuit Current, 1 1.2.1 Voltage, 3 1.2.2 Power, 3 1.2.3 Ohm's Law, 5 1.2.4 KirchhofTs Laws, 5 1.2.4.1 Kirchhoff s Current
34.5 Electric Current: Ohm s Law OHM, OHM ON THE RANGE. Purpose. Required Equipment and Supplies. Discussion. Procedure
 Name Period Date CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS Experiment 34.5 Electric : Ohm s Law OHM, OHM ON THE RANGE Thanx to Dean Baird Purpose In this experiment, you will arrange a simple circuit involving a power source
Name Period Date CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS Experiment 34.5 Electric : Ohm s Law OHM, OHM ON THE RANGE Thanx to Dean Baird Purpose In this experiment, you will arrange a simple circuit involving a power source
I Ish. Figure 2 Ammeter made from galvanometer and shunt resistor.
 Page 1/6 Revision 2 1-Jun-10 OBJECTIVES Understand the galvanometer and its limitations. Use circuit laws to build a suitable ammeter and voltmeter from the galvanometer. Understand the loading effect
Page 1/6 Revision 2 1-Jun-10 OBJECTIVES Understand the galvanometer and its limitations. Use circuit laws to build a suitable ammeter and voltmeter from the galvanometer. Understand the loading effect
Chapter 9 Basic meters
 Chapter 9 Basic meters Core Competency Units UEENEEE003B Solve problems in extra-low voltage single path circuits UEENEEE004B Solve problems in multiple path DC Circuits Essential Knowledge and Associated
Chapter 9 Basic meters Core Competency Units UEENEEE003B Solve problems in extra-low voltage single path circuits UEENEEE004B Solve problems in multiple path DC Circuits Essential Knowledge and Associated
Demonstrate knowledge of electrical theory for Electrical Service Technician B
 Demonstrate knowledge of electrical theory for Electrical Service Technician B 10937 version 4 Page 1 of 5 Level 3 Credits 3 Purpose 'Electrical Service Technician B' (EST B) refers to a class of electrical
Demonstrate knowledge of electrical theory for Electrical Service Technician B 10937 version 4 Page 1 of 5 Level 3 Credits 3 Purpose 'Electrical Service Technician B' (EST B) refers to a class of electrical
INVESTIGATION ONE: WHAT DOES A VOLTMETER DO? How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured?
 How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow rate
How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow rate
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 19 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 19 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 19 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Electric current, resistance and voltage in simple circuits
 Lab 6: Electric current, resistance and voltage in simple circuits Name: Group Members: Date: T s Name: pparatus: ulb board with batteries, connecting wires, two identical bulbs and a different bulb, a
Lab 6: Electric current, resistance and voltage in simple circuits Name: Group Members: Date: T s Name: pparatus: ulb board with batteries, connecting wires, two identical bulbs and a different bulb, a
Low Profile Unit Cooler
 Low Profile Unit Cooler Publication No. 100.13 January, 2004 MEA Air Defrost - 3,900 to 39,000 BTUH Electric Defrost - 3,600 to 28,000 BTUH Hot Gas Defrost - 3,600 to 28,000 BTUH Small to Medium Walk -
Low Profile Unit Cooler Publication No. 100.13 January, 2004 MEA Air Defrost - 3,900 to 39,000 BTUH Electric Defrost - 3,600 to 28,000 BTUH Hot Gas Defrost - 3,600 to 28,000 BTUH Small to Medium Walk -
LAB 7. SERIES AND PARALLEL RESISTORS
 Name: LAB 7. SERIES AND PARALLEL RESISTORS Problem How do you measure resistance, voltage, and current in a resistor? How are these quantities related? What is the difference between a series circuit and
Name: LAB 7. SERIES AND PARALLEL RESISTORS Problem How do you measure resistance, voltage, and current in a resistor? How are these quantities related? What is the difference between a series circuit and
2.1 Warnings & Agency Approvals Electrical Connections - Specifications Standard Wiring Configurations...2 4
 CHAPTER ELECTRICAL 2 INSTALLATION Contents of this Chapter... 2.1 Warnings & Agency Approvals..................2 2 2.1.1 Isolation..............................................2 2 2.1.2 Electrical Power
CHAPTER ELECTRICAL 2 INSTALLATION Contents of this Chapter... 2.1 Warnings & Agency Approvals..................2 2 2.1.1 Isolation..............................................2 2 2.1.2 Electrical Power
Question Set(2017) Switch Gear & protection(5 th SEm) 9. Explain the construction and operating principle with proper diagram:
 Question Set(2017) Switch Gear & protection(5 th SEm) 1. What is fault in power system? Classify the fault. What are the bad effects of fault? 2. Define with example: Symmetrical fault and unsymmetrical
Question Set(2017) Switch Gear & protection(5 th SEm) 1. What is fault in power system? Classify the fault. What are the bad effects of fault? 2. Define with example: Symmetrical fault and unsymmetrical
AUTO 121 Auto Electrical I Fall Section J01 3 credits
 UAS Automotive Technology Course Syllabus AUTO 121 Auto Electrical I Fall 2012 - Section J01 3 credits Instructor: Tony Martin Phone: 796-6126 (office) or 796-2034 (home) Email: tony.martin@uas.alaska.edu
UAS Automotive Technology Course Syllabus AUTO 121 Auto Electrical I Fall 2012 - Section J01 3 credits Instructor: Tony Martin Phone: 796-6126 (office) or 796-2034 (home) Email: tony.martin@uas.alaska.edu
SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 20 TROUBLESHOOTING ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT OBJECTIVES 3/21/2012
 SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 20 TROUBLESHOOTING ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, the reader should be able to Describe different types of electric motor problems. List common
SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 20 TROUBLESHOOTING ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, the reader should be able to Describe different types of electric motor problems. List common
SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 20 TROUBLESHOOTING ELECTRIC MOTORS
 SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 20 TROUBLESHOOTING ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, the reader should be able to Describe different types of electric motor problems. List common
SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 20 TROUBLESHOOTING ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, the reader should be able to Describe different types of electric motor problems. List common
CSDA Best Practice. Hi-Cycle Concrete Cutting Equipment. Effective Date: Oct 1, 2010 Revised Date:
 CSDA Best Practice Title: Hi-Cycle Concrete Cutting Equipment Issue No: CSDA-BP-010 : Oct 1, 2010 Revised : Introduction Hi-cycle/high frequency concrete cutting equipment has become more prevalent in
CSDA Best Practice Title: Hi-Cycle Concrete Cutting Equipment Issue No: CSDA-BP-010 : Oct 1, 2010 Revised : Introduction Hi-cycle/high frequency concrete cutting equipment has become more prevalent in
Electrical Motor Controls Chapter 4 (Fourth Edition) Chapter 2 (Fifth Edition)
 Electrical Motor Controls Chapter 4 (Fourth Edition) Chapter 2 (Fifth Edition) 1. Which drawing type shows physical details as seen by the eye? 2. Which drawing is similar to a pictorial drawing but has
Electrical Motor Controls Chapter 4 (Fourth Edition) Chapter 2 (Fifth Edition) 1. Which drawing type shows physical details as seen by the eye? 2. Which drawing is similar to a pictorial drawing but has
2014 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY (Com. to ECE, EIE, BME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY (Com. to ECE, EIE, BME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
2. A student sets up the circuit shown. The switch is open (off). Which lamps are on and which lamps are off?
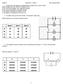 1. A polythene rod repels an inflated balloon hanging from a nylon thread. What charges must the rod and the balloon carry? A The rod and the balloon carry opposite charges. B The rod and the balloon carry
1. A polythene rod repels an inflated balloon hanging from a nylon thread. What charges must the rod and the balloon carry? A The rod and the balloon carry opposite charges. B The rod and the balloon carry
2010 Prince Edward Island Department of Education and Early Childhood Development P.O. Box 2000, Charlottetown Prince Edward Island Canada, C1A 7N8
 2010 Prince Edward Island Department of Education and Early Childhood Development P.O. Box 2000, Charlottetown Prince Edward Island Canada, C1A 7N8 Tel. (902) 368-4600 Fax. (902) 368-4622 http://www.gov.pe.ca/eecd/
2010 Prince Edward Island Department of Education and Early Childhood Development P.O. Box 2000, Charlottetown Prince Edward Island Canada, C1A 7N8 Tel. (902) 368-4600 Fax. (902) 368-4622 http://www.gov.pe.ca/eecd/
The ECM Textbook.
 Table of Contents - Overview of ECM Technology - Indoor Blower Motors o Variable Speed ECM o Constant Torque ECM The ECM Textbook www.thedealertoolbox.com About the Company When Regal Beloit acquired General
Table of Contents - Overview of ECM Technology - Indoor Blower Motors o Variable Speed ECM o Constant Torque ECM The ECM Textbook www.thedealertoolbox.com About the Company When Regal Beloit acquired General
NZQA registered unit standard version 3 Page 1 of 5. Demonstrate and apply knowledge of electrical machines
 Page 1 of 5 Title Demonstrate and apply knowledge of electrical machines Level 5 Credits 15 Purpose This unit standard covers knowledge and the application of d.c. and a.c. electrical machines for engineers.
Page 1 of 5 Title Demonstrate and apply knowledge of electrical machines Level 5 Credits 15 Purpose This unit standard covers knowledge and the application of d.c. and a.c. electrical machines for engineers.
Pretest Module 21 Units 1-3 AC Generators & Three-Phase Motors
 Pretest Module 21 Units 1-3 AC Generators & Three-Phase Motors 1. What are the two main parts of a three-phase 2. Which part of a three-phase squirrel-cage induction motor is a hollow core? 3. What are
Pretest Module 21 Units 1-3 AC Generators & Three-Phase Motors 1. What are the two main parts of a three-phase 2. Which part of a three-phase squirrel-cage induction motor is a hollow core? 3. What are
Course name: ELECTRICAL SKILLS 1. Short name:
 ELECTRICAL SKILLS 1 ES1 240 hrs Prerequisites: Working skills in four-function math including whole numbers, signed numbers, decimals and knowledge of Algebra and right angle Trigonometry. (Remediation
ELECTRICAL SKILLS 1 ES1 240 hrs Prerequisites: Working skills in four-function math including whole numbers, signed numbers, decimals and knowledge of Algebra and right angle Trigonometry. (Remediation
ECET 211 Electric Machines & Controls Lecture 2-2 (Part 2 of 3) Symbols and Drawing for Electric Motor Control Systems
 ECET 211 Electric Machines & Controls Lecture 2-2 (Part 2 of 3) Symbols and Drawing for Electric Motor Control Systems Text Book: Chapter 2. Understanding Electrical Drawings, Electric Motors and Control
ECET 211 Electric Machines & Controls Lecture 2-2 (Part 2 of 3) Symbols and Drawing for Electric Motor Control Systems Text Book: Chapter 2. Understanding Electrical Drawings, Electric Motors and Control
Chapter 19: DC Circuits
 Chapter 19: DC Circuits EMF and Terminal Voltage Resistors in Series and in Parallel Kirchhoff s Rules EMFs in Series and in Parallel; Charging a Battery Capacitors in Series and in Parallel RC Circuits
Chapter 19: DC Circuits EMF and Terminal Voltage Resistors in Series and in Parallel Kirchhoff s Rules EMFs in Series and in Parallel; Charging a Battery Capacitors in Series and in Parallel RC Circuits
Section 5 AIR - COOLED CONDENSING UNITS MODEL PC 05Z TO PC NOMINAL COOLING CAPACITY RANGE 56.6 TO 772 MBH
 AIR - COOLED CONDENSING UNITS MODEL PC 05Z TO PC 80-01 NOMINAL COOLING CAPACITY RANGE 56.6 TO 772 MBH 14 FEATURES MODEL PC 05Z TO PC 30-02 CABINET: Cabinets are constructed of heavily zinc coated galvanized
AIR - COOLED CONDENSING UNITS MODEL PC 05Z TO PC 80-01 NOMINAL COOLING CAPACITY RANGE 56.6 TO 772 MBH 14 FEATURES MODEL PC 05Z TO PC 30-02 CABINET: Cabinets are constructed of heavily zinc coated galvanized
Electricity and Magnetism. Introduction/Review
 Electricity and Magnetism Introduction/Review Overall Expectations By the end of this unit, students will: 1. Analyse the social, economic, and environmental impact of electrical energy production and
Electricity and Magnetism Introduction/Review Overall Expectations By the end of this unit, students will: 1. Analyse the social, economic, and environmental impact of electrical energy production and
Electricity and Electronics
 Advanced Automotive Electricity and Electronics James D. Halderman PEARSON Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco Upper Saddle River Amsterdam Cape Town Dubai London Madrid Milan Munich Paris
Advanced Automotive Electricity and Electronics James D. Halderman PEARSON Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco Upper Saddle River Amsterdam Cape Town Dubai London Madrid Milan Munich Paris
HSC Physics. Module 9.3. Motors and. Generators
 HSC Physics Module 9.3 Motors and Generators 9.3 Motors and Generators (30 indicative hours) Contextual Outline Electricity is a convenient and flexible form of energy. It can be generated and distributed
HSC Physics Module 9.3 Motors and Generators 9.3 Motors and Generators (30 indicative hours) Contextual Outline Electricity is a convenient and flexible form of energy. It can be generated and distributed
The Wound-Rotor Induction Motor Part I
 Experiment 1 The Wound-Rotor Induction Motor Part I OBJECTIVE To examine the construction of the three-phase wound-rotor induction motor. To understand exciting current, synchronous speed and slip in a
Experiment 1 The Wound-Rotor Induction Motor Part I OBJECTIVE To examine the construction of the three-phase wound-rotor induction motor. To understand exciting current, synchronous speed and slip in a
AC motor control circuits
 AC motor control circuits This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
AC motor control circuits This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Course Information Course Number: AMT 1003 Course Name: Automotive Foundations
 Course Information Course Number: AMT 1003 Course Name: Automotive Foundations Credit-By-Assessment (CBA) Competency List Written Assessment Competency List Electrical Describe the effects of temperature,
Course Information Course Number: AMT 1003 Course Name: Automotive Foundations Credit-By-Assessment (CBA) Competency List Written Assessment Competency List Electrical Describe the effects of temperature,
Application Engineering
 Application Engineering February, 2009 Copeland Digital Compressor Controller Introduction The Digital Compressor Controller is the electronics interface between the Copeland Scroll Digital Compressor
Application Engineering February, 2009 Copeland Digital Compressor Controller Introduction The Digital Compressor Controller is the electronics interface between the Copeland Scroll Digital Compressor
Direct-Current Circuits
 Chapter 26 Direct-Current Circuits PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 26 Looking forward at
Chapter 26 Direct-Current Circuits PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 26 Looking forward at
AP Physics B Ch 18 and 19 Ohm's Law and Circuits
 Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B Ch 18 and 19 Ohm's Law and Circuits MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A device that produces electricity
Name: Period: Date: AP Physics B Ch 18 and 19 Ohm's Law and Circuits MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A device that produces electricity
Job Ready Assessment Blueprint
 Blueprint Test Code: 4127 / Version: 01 Diesel Technology Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: Safety Demonstrate understanding of fire safety Demonstrate understanding of personal,
Blueprint Test Code: 4127 / Version: 01 Diesel Technology Specific Competencies and Skills Tested in this Assessment: Safety Demonstrate understanding of fire safety Demonstrate understanding of personal,
DISCUSSION OF FUNDAMENTALS. A hydraulic system can be controlled either manually or automatically:
 Unit 1 Introduction to Electrical Control of Hydraulic Systems UNIT OBJECTIVE When you have completed this unit, you will be able to identify the components used for electrical control of the Hydraulics
Unit 1 Introduction to Electrical Control of Hydraulic Systems UNIT OBJECTIVE When you have completed this unit, you will be able to identify the components used for electrical control of the Hydraulics
Unit 9. (Filled In) Draw schematic circuit diagrams for resistors in series and in parallel
 Name: Date: Period: Unit 9 Series & Parallel Circuits (Filled In) Essential Questions: Does adding resistors to a circuit always reduce current? Does adding more light bulbs to a circuit always make them
Name: Date: Period: Unit 9 Series & Parallel Circuits (Filled In) Essential Questions: Does adding resistors to a circuit always reduce current? Does adding more light bulbs to a circuit always make them
Electrical Measuring Instruments
 UNIT 12 Electrical Measuring Instruments Learning Objectives After studying this unit, the student will be able Understand different measuring instruments used in electricity Understand the working of
UNIT 12 Electrical Measuring Instruments Learning Objectives After studying this unit, the student will be able Understand different measuring instruments used in electricity Understand the working of
Teacher Assessment Blueprint. Diesel Technology. Test Code: 5270 / Version: 01. Copyright 2014 NOCTI. All Rights Reserved.
 Teacher Assessment Blueprint Diesel Technology Test Code: 5270 / Version: 01 Copyright 2014 NOCTI. All Rights Reserved. General Assessment Information Blueprint Contents General Assessment Information
Teacher Assessment Blueprint Diesel Technology Test Code: 5270 / Version: 01 Copyright 2014 NOCTI. All Rights Reserved. General Assessment Information Blueprint Contents General Assessment Information
SERVICE MANUAL (INTERNATIONAL)
 SERVICE MANUAL (INTERNATIONAL) IMPINGER CONVEYOR OVENS MODEL 1421-000-E, 1454, 1455 WITH PUSH BUTTON CONTROLS Lincoln Foodservice Products, LLC 1111 North Hadley Road Fort Wayne, Indiana 46804 United States
SERVICE MANUAL (INTERNATIONAL) IMPINGER CONVEYOR OVENS MODEL 1421-000-E, 1454, 1455 WITH PUSH BUTTON CONTROLS Lincoln Foodservice Products, LLC 1111 North Hadley Road Fort Wayne, Indiana 46804 United States
SERVICE MANUAL (DOMESTIC & INTERNATIONAL)
 SERVICE MANUAL (DOMESTIC & INTERNATIONAL) DUAL TECHNOLOGY FINISHER MODEL 1960 & 1980 SERIES Lincoln Foodservice Products, LLC 1111 North Hadley Road Fort Wayne, Indiana 46804 United States of America Telephone:
SERVICE MANUAL (DOMESTIC & INTERNATIONAL) DUAL TECHNOLOGY FINISHER MODEL 1960 & 1980 SERIES Lincoln Foodservice Products, LLC 1111 North Hadley Road Fort Wayne, Indiana 46804 United States of America Telephone:
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE FOR HEAT PUMP BOOSTERS MODELS: HPB11, HPB15, & HPB22
 V3 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE FOR HEAT PUMP BOOSTERS MODELS: HPB11, HPB15, & HPB22 PREFACE This guide contains instructions for troubleshooting the Steffes Corporation room heating units: Models HPB 11, HPB
V3 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE FOR HEAT PUMP BOOSTERS MODELS: HPB11, HPB15, & HPB22 PREFACE This guide contains instructions for troubleshooting the Steffes Corporation room heating units: Models HPB 11, HPB
Starting of Induction Motors
 1- Star Delta Starter The method achieved low starting current by first connecting the stator winding in star configuration, and then after the motor reaches a certain speed, throw switch changes the winding
1- Star Delta Starter The method achieved low starting current by first connecting the stator winding in star configuration, and then after the motor reaches a certain speed, throw switch changes the winding
Basic voltmeter use. Resources and methods for learning about these subjects (list a few here, in preparation for your research):
 Basic voltmeter use This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Basic voltmeter use This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
UNIT 3: GENErAL ELECTriCAL SySTEM DiAGNOSiS
 Electrical/Electronic Systems UNIT 3: GENErAL ELECTriCAL SySTEM DiAGNOSiS LESSON 3: TEST electrical circuits I. Types of electrical circuit tests and electrical faults A. Different types of electrical
Electrical/Electronic Systems UNIT 3: GENErAL ELECTriCAL SySTEM DiAGNOSiS LESSON 3: TEST electrical circuits I. Types of electrical circuit tests and electrical faults A. Different types of electrical
STATEWIDE CAREER/TECHNICAL EDUCATION COURSE ARTICULATION REVIEW MINUTES
 STATEWIDE CAREER/TECHNICAL EDUCATION COURSE ARTICULATION REVIEW MINUTES Articulation Agreement Identifier: ELT 110 2005-1 Identifier is the postsecondary course prefix followed by Plan-of-Instruction version
STATEWIDE CAREER/TECHNICAL EDUCATION COURSE ARTICULATION REVIEW MINUTES Articulation Agreement Identifier: ELT 110 2005-1 Identifier is the postsecondary course prefix followed by Plan-of-Instruction version
Diesel Technology: Steering and Suspension
 Diesel Technology: Steering and Suspension National Skills Crosswalk The following NATEF Suspension and Steering tasks (rev. 2004) are covered in this publication. The chart shows where each task is located
Diesel Technology: Steering and Suspension National Skills Crosswalk The following NATEF Suspension and Steering tasks (rev. 2004) are covered in this publication. The chart shows where each task is located
Chapter 26 DC Circuits
 Chapter 26 DC Circuits Electric circuit needs battery or generator to produce current these are called sources of emf. Battery is a nearly constant voltage source, but does have a small internal resistance,
Chapter 26 DC Circuits Electric circuit needs battery or generator to produce current these are called sources of emf. Battery is a nearly constant voltage source, but does have a small internal resistance,
Chapter 26 DC Circuits. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 26 DC Circuits 26-1 EMF and Terminal Voltage Electric circuit needs battery or generator to produce current these are called sources of emf. Battery is a nearly constant voltage source, but does
Chapter 26 DC Circuits 26-1 EMF and Terminal Voltage Electric circuit needs battery or generator to produce current these are called sources of emf. Battery is a nearly constant voltage source, but does
Electricity 2 Questions NAT 5
 Electricity 2 Questions NAT 5 1) a) A 25W lamp is designed to be used with the mains voltage. Calculate the resistance of the lamp. b) Four of the lamps are connected in parallel. Calculate the total resistance
Electricity 2 Questions NAT 5 1) a) A 25W lamp is designed to be used with the mains voltage. Calculate the resistance of the lamp. b) Four of the lamps are connected in parallel. Calculate the total resistance
OD0010 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM COMPONENT REPAIR
 SUBCOURSE OD0010 EDITION 5 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM COMPONENT REPAIR ELECTRICAL SYSTEM COMPONENT REPAIR OD0010 EDITION 5 23 CREDIT HOURS REVIEWED: 1988 United States Army Combined Arms Support Command Fort Lee,
SUBCOURSE OD0010 EDITION 5 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM COMPONENT REPAIR ELECTRICAL SYSTEM COMPONENT REPAIR OD0010 EDITION 5 23 CREDIT HOURS REVIEWED: 1988 United States Army Combined Arms Support Command Fort Lee,
Industrial Maintenance Technology Student Learning Outcomes
 Industrial Maintenance Technology Student Learning Outcomes February, 2017 ~ f ) FDTC Curriculum Map Program: Industrial Maintenance Technology Course# Course Title Credits Hours Lecture Lab Program Outcomes
Industrial Maintenance Technology Student Learning Outcomes February, 2017 ~ f ) FDTC Curriculum Map Program: Industrial Maintenance Technology Course# Course Title Credits Hours Lecture Lab Program Outcomes
