(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
|
|
|
- Eric Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
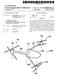
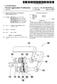
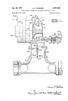
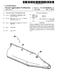
1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1 POSt US 2003OOO5851A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) INDUCTRACK CONFIGURATION (75) Inventor: Richard Freeman Post, Walnut Creek, CA (US) Correspondence Address: Alan H. Thompson Assistant Laboratory Counsel Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory P.O. Box 808, L-703 Livermore, CA (US) (73) Assignee: The Regents of the University of Cali (21) Appl. No.: (22) Filed: fornia 09/896,579 Jun. 29, 2001 Publication Classification (51) Int. CI B60L 13/04 (52) U.S. Cl /281 (57) ABSTRACT A simple permanent-magnet-excited maglev geometry pro vides levitation forces and is stable against Vertical displace ments from equilibrium but is unstable against horizontal displacements. An Inductrack System is then used in con junction with this System to effect Stabilization against horizontal displacements and to provide centering forces to overcome centrifugal forces when the vehicle is traversing curved Sections of a track or when any other transient horizontal force is present In Some proposed embodiments, the Inductrack track elements are also employed as the Stator of a linear induction-motor drive and braking System. Car body l 6 (3) Halbach array 3. Perrmanent nag. material 2O (i) Linear pole assem. o lo (4) inductrack track circuits (2) Linear track schematic drawing of modified inductrack configuration
2 Patent Application Publication Sheet 1 of 3 US 2003/ A1 Car body Permanent mag. 6 material (1) Linear pole assem. O (4) inductrack track circuits ld (2) Linear track Schematic drawing of modified inductrack configuration Figure 1.
3
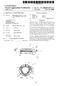
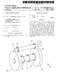
4 Patent Application Publication Sheet 3 of 3 US 2003/ A1 iron-plate guideway Levitating Halbach array t-2 "Flat track inductrack Figure 1: Schematic Drawing of Altenative inductrack Configuration F. G. 3
5 INDUCTRACK CONFIGURATION The United States Government has rights in this invention pursuant to Contract No. W-7405-ENG-48 between the United States Department of Energy and the University of California for the operation of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. BACKGROUND OF TITLE INVENTION 0002) 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates generally to magnetic levitation Systems for moving objects, and more specifically, to an improved magnetic levitation train System Description of Related Art 0005 Halbach arrays, invented by Klaus Halbach in the 1980s for use in particle accelerators, represent a maximally efficient way to arrange permanent-magnet material when it is desired to produce a Strong periodic magnetic field adjacent to the array. The beauty of the concept is that the effect of the cross-magnetized magnet bars in the array is to enhance the periodic magnetic field at the front face of the array, while canceling it back face of the array. Not only is the field enhanced, but analysis shows that in a long array the horizontal and Vertical components are nearly purely sinu Soidal in their Spatial variation, with negligible higher spatial harmonics. If the Halbach array is then fabricated from high-field permanent-magnet material, Such as NdFeB, peak fields near the front face of the array of order 1.0 Tesla are possible Particularly for lower-speed applications of mag netic levitation, Such as for urban train Systems, it is desir able to employ Systems that are simple in construction and operation and that have low drag at urban speeds. Conven tional maglev Systems, that is, ones employing Supercon ducting coils, or ones requiring Servo-controlled electromag nets for levitation, appear to fall Short on one or more of these counts Since it was first proposed the magnetic levitation of trains has been perceived to offer many potential advan tages over conventional train technology. Besides the ability of maglev trains to operate a higher speeds than are deemed possible with wheel-and-rail trains, maglev trains should require less maintenance and be much Smoother-riding and quieter than conventional rail Systems. These perceived advantages have Stimulated major development programs, particularly in Germany and Japan, to Solve the technical and economic challenges of this new technology. These decades-long efforts have resulted in impressive demonstra tion Systems, but as yet have not led to commercially operating rail Systems in these countries. Factors that have slowed the deployment of high-speed maglev trains based on these technologies include technical complexity and high capital cost In an attempt to address these issues by taking advantage of new concepts and new materials, a different approach, called the Inductrack, was proposed. The first proposed Inductrack disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 5,722,326, titled Magnetic Levitation System For Moving Objects, referred to herein as Inductrack I, employs Special arrays of permanent magnets ("Halbach arrays ), on the moving train car to produce the levitating magnetic fields. These fields interact with a close-packed ladder-like array of Shorted circuits in the track' to levitate the train car. In this first form of the Inductrack, Single arrays moving above the track produced the levitation. Whereas the Japanese maglev sys tem employs Superconducting coils and the German System requires Servo-controlled electromagnets for levitation, the Inductrack is based on the use of high-field permanent magnet material, arranged in a Special configuration called a Halbach array In the Inductrack maglev system Halbach arrays are used, located below the train car. When in motion the magnetic field of these arrays then induces currents in a Special track made up of close-packed shorted circuits. Analysis has shown that the combination of the three elements, Halbach arrays, NdFeB magnet material, and close-packed circuits in the track result in the possibility of achieving levitation forces in excess of 40 metric tons per Square meter of levitating magnets, corresponding to magnet weights of only a few percent of the levitated weight The use of Halbach arrays, high-field magnet material and close packed circuits as employed in the Inductrack thus over comes previous concerns, e.g., inadequate levitation forces, that led to questioning the practicality of using permanent magnets for maglev trains The theoretical analysis of the Inductrack leads to the evaluation of Such quantities as the Lift-to-Drag ratio and the levitation power requirements as a function of train Speed and of the magnet and track parameters. For the first-proposed, Single-Halbach-array, form of the Inductrack, the L/D ratio is given by a simple relationship, given in Equation 1 below. Lif L (1) = y 0011 Here k=2l/2, where (m.) is the wavelength of the Halbach array. Note that the Lift/Drag ratio increases lin early with the train Velocity and that its slope is determined by the inductance (Self plus mutual) and the resistance of the track circuits. For a ladder-like track, that is one composed of transverse bars terminated at both ends with shorting buses, typical values for Land R give Lift/Drag ratios of the order of 300 at speeds of 500 km/hr typical of high-speed maglev trains. This ratio is high enough to make the levi tation losses Small (less than 10 percent) of the aerodynamic losses at Such Speeds. Also, for the Inductrack the transition speed, the speed at which the lift has risen to half its final value (and also the speed where the lift and drag forces are equal) is low, of order a few meters/second (walking speeds). Thus the first-proposed form of the Inductrack would seem well Suited for high-speed maglev train appli cations However, an examination of the first-proposed form of the Inductrack for its possible use in an urban Setting, where the typical Speeds are of order one-tenth of that of a high-speed maglev System, shows that the older System leaves Something to be desired. Now, unless induc tive loading of the track circuits is employed, the Lift/Drag ratio will have dropped to 30 or less. For an urban train car weighing, Say, 20,000 kilograms, a Lift/Drag ratio of 30 at 50 km/hr corresponds to a drag force of about 6500 Newtons at a drag power in excess of 90 kilowatts.
6 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION It is an object of the present invention to provide a Simple permanent-magnet-excited maglev geometry that provides levitation forces and is stable against Vertical displacements from equilibrium but is unstable against hori Zontal displacements It is another object to provide an Inductrack system used in conjunction with the permanent-magnet-excited maglev geometry to effect Stabilization against horizontal displacements and to provide centering forces to overcome centrifugal forces when the vehicle is traversing curved Sections of a track or when any other transient horizontal force is present Another object of the present invention is to employ Inductrack track elements as the Stator of a linear induction-motor drive and braking System Still another object of the present invention is to provide an alternate design of a linear pole System that has improved levitating force capabilities and lessened lateral Stabilizer force requirements Another object of the invention is to provide a track for use with a linear pole array, where the track has improved properties for shielding the moving levitator poles from the effects of weather and from debris that might be deposited on the track Another object of the invention is to provide the levitating action by using a Halbach array attached to the moving object where the array is attracted upward to an iron-plate guideway and to further provide Stabilizing means using additional Halbach arrays comprised of an upper Halbach array and a lower Halbach array, with an Inductrack track located between them These and other objects will be apparent to those skilled in the art based on the disclosure herein One embodiment of the present invention is a Simple permanent-magnet-excited maglev geometry that provides levitation forces and is stable against Vertical displacements from equilibrium but is unstable against hori Zontal displacements. An Inductrack System is then used in conjunction with this System to effect Stabilization against horizontal displacements and to provide centering forces to overcome centrifugal forces when the vehicle is traversing curved Sections of the track or when any other transient horizontal force is present. In Some proposed embodiments, the Inductrack track elements are also employed as the Stator of a linear induction-motor drive and braking System This new configuration eliminates the need for centering wheels, except possibly when the car is at rest in the station or upon failure of the drive while in transit In such cases, below a low critical Speed, the wheels would restrain the system from lateral motion beyond a limit set by a predetermined spacing of the wheels from their guide rails One embodiment of the new configuration includes linear pole assemblies with iron poles, excited by perma nent-magnet material. These elements are mounted on the moving car. They interact magnetically with the pole faces of a linear track, also fabricated from magnetic material, Such as iron or Steel. AS shown, the poles exert a levitation force when they are displaced downward from the matching (attracting) poles on the track. The Sideways attractive force exerted by each pole is balanced, when in the centered position, by the attractive force from the mating pole. This System is unstable against transverse displacements from the centered position. In this embodiment, lateral Stabilization is provided by Inductrack Halbach arrays and the associated track circuits. AS long as the car is moving So that the various elements are in the centered State, no currents will be induced in the Inductrack track, So that losses will be minimal. Only when there is a deviation from the centered position will currents be induced. Thus the energy losses from the system should be substantially less than those of a conventional Inductrack System, where currents must flow to provide the necessary levitation forces. In addition, the car will always be magnetically levitated, whether at rest or in motion, Something that is not the case in the conventional Inductrack System Damping of vertical oscillations is provided by covering the face of the track magnet poles with a thin aluminum sheet. The planar Inductrack circuits may also function as the Stator of a linear induction motor System using powered electromagnets on the moving car An alternate design of the linear pole system is provided that has improved levitating force capabilities and lessened lateral Stabilizer force requirements. The track portion of this linear pole array has improved properties for Shielding the moving levitator poles from the effects of weather and from debris that might be deposited on the track In an alternate embodiment of the invention, the levitating action is provided by a Halbach array attached to the moving object The array is attracted upward to an iron-plate guideway. Stabilizing means are provided by additional Halbach arrays comprised of an upper Halbach array and a lower Halbach array, with an Inductrack track located between them. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0026 FIG. 1 shows a modified Inductrack configuration of the present invention FIG.2 shows an alternate Inductrack configuration of the present invention FIG. 3 shows a rail structure for an Inductrack System of the present invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION The present invention is an improved Inductrack configuration and represents a combination of the Inductrack principle of operation with another magnetic levitation con figuration. The new combination represents an improvement in certain properties that is not achievable by either of the two configurations taken alone. The general Inductrack principle employed in Some embodiments of this new idea is covered in U.S. Pat. No. 5,722,326, Magnetic Levitation System for Moving Objects, R. F. Post, incorporated herein by reference Other embodiments of the present invention employ the Inductrack II magnet configuration described in a copending U.S. patent application titled, "Improved Induc
7 track Magnet Configuration' filed on the same day as the present application and incorporated herein by reference. The magnet configuration of the above incorporated patent application is referred to Sometimes herein as Inductrack II', wherein dual arrays are used, one on each Side of track circuits The general concept involved in this new idea is as follows: A Simple permanent-magnet-excited maglev geom etry that is stable against vertical displacements from equi librium but is unstable against horizontal displacements is employed to provide levitation forces. An Inductrack II System is then used in conjunction with this System to effect Stabilization against horizontal displacements and to provide centering forces to overcome centrifugal forces when the vehicle is traversing curved Sections of the track or when any other transient horizontal force is present In Some proposed embodiments the Inductrack track elements are also employed as the Stator of a linear induction-motor drive and braking System Horizontal stabilization has required the use of a System of wheels that run on the track and thereby Supply the necessary centering forces. The use of Such wheels limits the Speed of the maglev system and introduces issues of fric tional losses, and mechanical failure from wear with asso ciated maintenance costs This new configuration eliminates the need for centering wheels, except possibly when the car is at rest in the station or upon failure of the drive while in transit. In Such cases, below a low critical Speed, the wheels would restrain the system from lateral motion beyond a limit set by a predetermined spacing of the wheels from their guide rails One embodiment of the new configuration is shown schematically in FIG. 1. This embodiment includes linear pole assemblies 10 with iron poles, excited by per manent-magnet material 12. These elements are mounted on the moving car 14. They interact magnetically with the pole faces of a linear track 16, also fabricated from magnetic material, Such as iron or Steel. AS shown the poles exert a levitation force when they are displaced downward from the mating (attracting) poles on the track. At the same time, the Sideways attractive force exerted by each pole is balanced, when in the centered position, by the attractive force from the mating pole. However, as dictated by Earnshaw's theo rem, this System is unstable against transverse displacements from the centered position. In this embodiment, lateral stabilization is provided by the Inductrack II Halbach arrays 18 and the associated track circuits 20. In the figure, a pair of Halbach arrays (mounted on the car) are shown, with a Stationary vertical Inductrack II element located between them in the configuration as described in the copending patent application. AS long as the car is moving So that the various elements are in the centered State, no currents will be induced in the track 20, so that losses will be minimal. Only when there is a deviation from the centered position will currents be induced. Thus the energy losses from the System should be substantially less than those of a conventional Inductrack System, where currents must flow to provide the necessary levitation forces. In addition, the car will always be magnetically levitated, whether at rest or in motion, Something that is not the case in the conventional Inductrack System Damping of vertical oscillations could be provided by covering the face of the track 16 magnet poles with, e.g., a thin aluminum sheet Other materials may be used as well, e.g., copper or thicker Stainless Steel. Eddy currents induced in this sheet by vertical displacements would provide the damping forces. 0036) As noted above, the planar Inductrack circuits shown could also do dual Service as the Stator of a linear induction motor System using powered electromagnets on the moving car Thus, an embodiment of the present invention consists of a combination of a permanent-magnet-excited linear pole levitation System and a vertically oriented Induc track II System, used here as a lateral Stabilizer for the levitation System. An alternate improved design of the linear pole System is now provided, one with both improved levitating force capabilities and lessened lateral Stabilizer force requirements. In addition, the Stationary track' por tion of this linear pole array has improved properties for Shielding the moving levitator poles from the effects of weather and from debris that might be deposited on the track. It also offers a simple means of Switching from one track System to another with minimal displacement of the track elements The improved linear-pole levitation magnetic geometry is shown schematically in FIG. 2. The rail, to be fabricated of magnetically Soft iron or Steel, is "C-shaped, with its open gap on the lower side. Within this structure the levitating element, cantilevered from the moving car, is shown as an assembly (not to Scale), consisting of perma nent-magnet material 32 laminated with thin magnetically Soft material 34. This magnetic configuration has the prop erty of minimizing the leakage flux from the magnet pole So as to maximize the lifting force on that pole caused by the proximity of the Stationary pole elements In this new structure, the levitating force exerted on the moving pole is increased due to the reduction in leakage flux that the new pole structure affords AS can be seen, the new rail' is configured so as to protect the moving pole assembly from Snow and ice and from debris that might be deposited on the rail. Another desirable property of this levitating configuration is that the levitating force is, to lowest order, independent of lateral displacement of the levitated pole, Since the decrease in levitating force of, Say, the left-side pole, caused by lateral motion (from a centered position) to the right, is compen Sated by a corresponding increase in the levitating force from the right-side pole. Also, in the centered position the lateral forces from the left-side and right-side poles balance out, and the Spatial derivative of the force is reduced Finally, the proposed rail pole structure should lend itself to Switching of the moving car to another track through the Simple expedient of moving down the end of an appropriately long Section of the rail (Supported fixedly at its other end) by a few inches, So as to mate with a lower rail that would lead to a Siding or to another line. The associated Inductrack stabilizer track would need only to be made Sufficiently high in the Switched Section of track to accom modate to this extra Vertical motion FIG. 3 shows an alternate embodiment of the present invention. The levitating action is provided by Halbach array 40 attached to the moving object 42. Array 40 is attracted upward to an iron-plate guideway 44. Here the
8 levitating Halbach arrays are oriented 90 degrees to the usual orientation used in the Inductrack, i.e., the direction of their periodicity is transverse to the direction of motion. In this orientation the magnetic field will be constant (except at the sides and ends of the Halbach array bars) in the direction of motion of the car, thus reducing the parasitic eddy currents induced in the iron guideway. Note that the con gruence of the edges of the Halbach array and the iron guideway will provide Strong centering forces for transverse displacements. Orienting the Halbach arrays 90 degrees to the usual orientation has the advantage of reducing eddy currents but the Halbach arrays could operate equally effec tively in other orientations Such as in the same direction as the Inductrack Halbach arrays Since the levitating configuration is unstable against vertical displacements (as dictated by Earnshaw's theorem), stabilizing means are provided by the additional Halbach arrays, shown in the figure. These are of the form described in the incorporated copending patent application, comprised of an upper Halbach array 46 and a lower Halbach array 48, with a flat-track' Inductrack track 50 located between them. However, by design, the main levi tating force is provided by the former set of Halbach arrays, So that the Second Set is called only to provide Stabilization, i.e., to provide an up or down force as needed to keep the System at the desired levitation Separation. 0044) It would be a simple matter to incorporate an adjustment means on the levitating Halbach arrays. So that they are trimmed to nearly the right force level to levitate a given load. This addition would further reduce the stabi lilzing force needed Note also that the Halbach stabilizer shown in FIG. 3 could be replaced by the combined stabilizer/drive-coil configuration described in the incorporated copending patent application. In this way the functions of levitation, Stabilization, and powered-guideway drive could be com bined in one compact assembly. AS discussed above, the levitating action is provided by Halbach array 40 attached to the moving object 42. Array 40 is attracted upward to an iron-plate guideway ) The propulsion mechanism used in the present invention may be a linear induction motor. Such a motor generally comprises a coil Structure or winding assembly carried by the vehicle and juxtaposed with a rail of ferro magnetic material mounted upon and fastened to the track So that a magnetic path is closed through this rail and, with appropriate energization of the winding assembly, develops a magnetic force component in the direction of vehicle propulsion The linear motors are, in effect, a linearly-unrolled version of the rotary motors. Among currently-known examples of the linear motors are a linear d.c. motor (monopolar or multipolar), linear Synchronous motor, linear induction motor and linear pulse motor. Thrust of the linear motors, corresponding to torque of the rotary motors, gen erally depends on the Structure of the motors. Other propul Sion mechanisms are usable in the present invention and will be apparent to those skilled in the art based on the disclosure herein The foregoing description of the invention has been presented for purposes of illustration and description and is not intended to be exhaustive or to limit the invention to the precise form disclosed. Many modifications and variations are possible in light of the above teaching. The embodiments were chosen and described to best explain the principles of the invention and its practical application to thereby enable others skilled in the art to best use the invention in various embodiments and with various modifications Suited to the particular use contemplated. The Scope of the invention is to be defined by the following claims. I claim: 1. A magnetic levitation System, comprising: a vehicle body; a permanent-magnet-excited geometry operatively attached to said vehicle body for providing levitation forces upon said vehicle body, wherein Said geometry is stable against displacements from equilibrium in a first plane but is unstable against displacements in a Second plane; and means for providing Stabilization against displacements in Said Second plane. 2. The magnetic levitation System of claim 1, wherein Said means for providing Stabilization comprises an Inductrack II System attached to Said vehicle body for providing Stabili Zation against displacements in Said Second plane and for providing centering forces. 3. The magnetic levitation System of claim 1, wherein Said first plane is Substantially a vertical plane, wherein Said Second plane is Substantially a horizontal plane. 4. The magnetic levitation System of claim 2, wherein said Inductrack II System is configured to overcome centrifugal forces when Said vehicle body encounters a transient hori Zontal force. 5. The magnetic levitation System of claim 2, wherein Said Inductrack II System is configured as the Stator of a linear induction-motor drive and braking System. 6. The magnetic levitation System of claim 1, wherein Said permanent-magnet-excited geometry comprises first pole assemblies with iron poles excited by permanent-magnet material, wherein Said linear pole assemblies are attached to said vehicle body. 7. The magnetic levitation System of claim 6, wherein Said permanent-magnet-excited geometry further comprises Sec ond pole assemblies attached to a Stationary Support, wherein Said Second pole assemblies comprise permanent magnet material, wherein Said first pole assemblies and Said Second pole assemblies are configured to magnetically attract each other. 8. The magnetic levitation System of claim 1, wherein Said Inductrack II System comprises: a first Halbach array having a first magnetic field and a Second Halbach array having a Second magnetic field, wherein said first Halbach array and said second Hal bach array are magnetically and Structurally connected together to form a first pair of Halbach arrays, wherein Said first Halbach array comprises magnet configura tions positioned with respect Said Second Halbach array and Said Second Halbach array comprises magnet con figurations positioned with respect Said first Halbach array Such that a first component of Said first magnetic field and a first component of Said Second magnetic field Substantially cancel at a first plane between Said first Halbach array and Said Second Halbach array, and
9 a Second component of Said first magnetic field and a Second component of Said Second magnetic field Sub Stantially add at Said first plane; a track of windings between said first pair of Halbach arrays, and a propulsion mechanism for moving Said first pair of Halbach arrays along Said track, wherein when Said first pair of Halbach arrays move along Said track and Said track is not located at Said first plane, a current is induced in Said windings and a restoring force is exerted on Said first pair of Halbach arrays. 9. The magnetic levitation system of claim 7, further comprising means for damping vertical oscillations in Said Second pole assemblies. 10. The magnetic levitation system of claim 9, wherein Said means for damping vertical oscillations comprises a sheet of material covering Said Second pole assemblies, wherein Said sheet of material is Selected from the group consisting of a thin aluminum sheet, copper and StainleSS Steel. 11. The magnetic levitation system of claim 1, further comprising at least one electromagnet attached to Said car, wherein Said track of windings is configured to operate as a linear induction motor assembly. 12. The magnetic levitation System of claim 1, wherein Said permanent-magnet-excited geometry comprises a Sta tionary rail comprising magnetically Soft material and hav ing an open gap on its lower Side, Said permanent-magnet excited geometry further comprising a levitating element attached to said vehicle, wherein said levitating element comprises permanent-magnet material laminated with mag netically Soft material, wherein Said rail and Said levitating element exert attracting magnetic force upon each other. 13. The magnetic levitation System of claim, wherein Said Stationary rail is C-shaped. 14. The magnetic levitation System of claim, wherein Said a permanent-magnet-excited geometry comprises a Halbach array connected to Said vehicle, Said geometry further com prising a Stationary iron plate guideway above Said Halbach array to which Said Halbach array is attracted. 15. The magnetic levitation system of claim 14, wherein Said first plane is a Substantially horizontal plane, wherein Said Second plane is a Substantially vertical plane, wherein the edges of Said Halbach array and Said iron guideway are congruent to provide centering forces for transverse dis placements. 16. The magnetic levitation System of claim 14, wherein Said Inductrack II System comprises two Substantially hori Zontally disposed Halbach arrays fixedly attached to Said vehicle, Said Inductrack I System further comprising a Sta tionery track between Said two Substantially horizontally disposed Halbach arrays 17. The magnetic levitation system of claim 14, wherein Said Halbach array comprises a Size relative to Said iron plate guideway that is adjusted to provide a desired levitating force. 18. The magnetic levitation system of claim 16, wherein Said track of windings and Said two horizontally disposed Halbach arrays are configured to operate as a linear induc tion motor assembly. 19. A magnetic levitation System, comprising: a vehicle body; a permanent-magnet-excited geometry operatively attached to said vehicle body for providing levitation forces upon said vehicle body, wherein Said geometry is stable against Substantially vertical displacements from equilibrium but is unstable against Substantially horizontal displacements, and means for providing Stabilization against Said Substan tially horizontal displacements and for providing cen tering forces. 20. The magnetic levitation system of claim 19, wherein Said means for providing Stabilization comprises an Induc track II system attached to said vehicle body. 21. A method for operating magnetic levitation System, comprising: providing a vehicle body; providing levitation forces upon said vehicle body using a permanent-magnet-excited geometry operatively attached to Said vehicle body, wherein Said geometry is Stable against displacements from equilibrium in a first plane but is unstable against displacements in a Second plane; and providing Stabilization against displacements in Said Sec ond plane and providing centering forces. 22. The method of claim 21, wherein the step of providing Stabilization is carried out with an Inductrack II System attached to said vehicle body. 23. The method of claim 21, wherein said first plane is Substantially a vertical plane, wherein Said Second plane is Substantially a horizontal plane. 24. The method of claim 22, wherein said Inductrack II System is configured to Substantially overcome centrifugal forces when Said vehicle body encounters a transient hori Zontal force. 25. The method claim 22, wherein said Inductrack II System is configured as the Stator of a linear induction-motor drive and braking System. 26. The magnetic levitation System of claim 1, wherein Said permanent-magnet-excited geometry comprises first pole assemblies with iron poles excited by permanent magnet material, wherein Said linear pole assemblies are attached to said vehicle body.
58 Field of Search ,281,282, respect to the other, a current is induced in the circuit. This
 USOO5722326A United States Patent (19 11 Patent Number: 5,722,326 Post 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 3, 1998 54). MAGNETICLEVITATION SYSTEM FOR 5,222,436 6/1993 Coffey... 104/281 MOVING OBJECTS 5222,437 6/1993
USOO5722326A United States Patent (19 11 Patent Number: 5,722,326 Post 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 3, 1998 54). MAGNETICLEVITATION SYSTEM FOR 5,222,436 6/1993 Coffey... 104/281 MOVING OBJECTS 5222,437 6/1993
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O225192A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0225192 A1 Jeung (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 9, 2010 (54) PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD AND METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2010O225192A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0225192 A1 Jeung (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 9, 2010 (54) PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD AND METHOD Publication Classification
DOUBLE ROW LOOP-COILCONFIGURATION FOR HIGH-SPEED ELECTRODYNAMIC MAGLEV SUSPENSION, GUIDANCE, PROPULSION AND GUIDEWAY DIRECTIONAL SWITCHING
 DOUBLE ROW LOOP-COILCONFIGURATION FOR HIGH-SPEED ELECTRODYNAMIC MAGLEV SUSPENSION, GUIDANCE, PROPULSION AND GUIDEWAY DIRECTIONAL SWITCHING Jianliang He and Donald M Rote DISCLAIMER 0 OD cv This report
DOUBLE ROW LOOP-COILCONFIGURATION FOR HIGH-SPEED ELECTRODYNAMIC MAGLEV SUSPENSION, GUIDANCE, PROPULSION AND GUIDEWAY DIRECTIONAL SWITCHING Jianliang He and Donald M Rote DISCLAIMER 0 OD cv This report
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0223666 A1 Cuthbert US 20080223666A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2008 (54) (76) (21) (22) (86) (30) TRACTION ARRANGEMENTS Inventor:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0223666 A1 Cuthbert US 20080223666A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2008 (54) (76) (21) (22) (86) (30) TRACTION ARRANGEMENTS Inventor:
310/227, 228 Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Head, Johnson & Kachigian
 US005742111A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Reed 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54 D.C. ELECTRIC MOTOR 4,930,210 6/1990 Wang... 29/597 5,001,375 3/1991 Jones... 310/68 75) Inventor: Troy
US005742111A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Reed 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 21, 1998 54 D.C. ELECTRIC MOTOR 4,930,210 6/1990 Wang... 29/597 5,001,375 3/1991 Jones... 310/68 75) Inventor: Troy
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O190837A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0190837 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2003 (54) BATTERY HOLDER HAVING MEANS FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 439/500 SECURELY
US 2003O190837A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0190837 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2003 (54) BATTERY HOLDER HAVING MEANS FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 439/500 SECURELY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2
 US007592736 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2 Scott et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 2009 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ELECTRIC (56) References Cited GENERATOR WITH ROTOR CIRCUMIFERENTIALLY
US007592736 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2 Scott et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 2009 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ELECTRIC (56) References Cited GENERATOR WITH ROTOR CIRCUMIFERENTIALLY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0088848A1 Owen et al. US 20140O88848A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) SELECTIVE AUTOMATED VEHICLE BRAKE FORCE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0088848A1 Owen et al. US 20140O88848A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) SELECTIVE AUTOMATED VEHICLE BRAKE FORCE
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD20: Last updated: 26th September 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD20: Last updated: 26th September 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0044499 A1 Dragan et al. US 20100.044499A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SIX ROTOR HELICOPTER Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0044499 A1 Dragan et al. US 20100.044499A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SIX ROTOR HELICOPTER Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O00861 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0008610 A1 PetersOn (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2002 (54) KEY FOB WITH SLIDABLE COVER (75) Inventor: John Peterson,
(19) United States US 2002O00861 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0008610 A1 PetersOn (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2002 (54) KEY FOB WITH SLIDABLE COVER (75) Inventor: John Peterson,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0226455A1 Al-Anizi et al. US 2011 0226455A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SLOTTED IMPINGEMENT PLATES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0226455A1 Al-Anizi et al. US 2011 0226455A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SLOTTED IMPINGEMENT PLATES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. YAMAGISH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 7, 2012
 US 2012O139382A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0139382 A1 YAMAGISH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 7, 2012 (54) END PLATE, AND ROTOR FOR ROTARY Publication Classification
US 2012O139382A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0139382 A1 YAMAGISH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 7, 2012 (54) END PLATE, AND ROTOR FOR ROTARY Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0121100A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0121100 A1 Feenstra (43) Pub. Date: May 26, 2011 (54) COVER FOR PROTECTINGA FUSIBLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2011 0121100A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0121100 A1 Feenstra (43) Pub. Date: May 26, 2011 (54) COVER FOR PROTECTINGA FUSIBLE Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4924,123. Hamajima et al. 45 Date of Patent: May 8, 1990
 United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4924,123 Hamajima et al. 45 Date of Patent: May 8, 1990 54) LINEAR GENERATOR 4,454,426 6/1984 Benson... 290/1 R s 8 8 4,500,827 2/1985 Merritt et al.... 322/3
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4924,123 Hamajima et al. 45 Date of Patent: May 8, 1990 54) LINEAR GENERATOR 4,454,426 6/1984 Benson... 290/1 R s 8 8 4,500,827 2/1985 Merritt et al.... 322/3
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US009277323B2 (10) Patent No.: L0cke et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2016 (54) COMPACT AUDIO SPEAKER (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA (US) U.S.
(12) United States Patent US009277323B2 (10) Patent No.: L0cke et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2016 (54) COMPACT AUDIO SPEAKER (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA (US) U.S.
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,820,200 Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
United States Patent 19 [11] Patent Number: 4,877,983 Johnson (45) Date of Patent: Oct 31, 1989
![United States Patent 19 [11] Patent Number: 4,877,983 Johnson (45) Date of Patent: Oct 31, 1989 United States Patent 19 [11] Patent Number: 4,877,983 Johnson (45) Date of Patent: Oct 31, 1989](/thumbs/80/81257393.jpg) United States Patent 19 [11] Patent Number: 4,877,983 Johnson (45) Date of Patent: Oct 31, 1989 54 MAGNETICFORCE GENERATING 56 References Cited METHOD AND APPARATUS U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,074,153 2/1978
United States Patent 19 [11] Patent Number: 4,877,983 Johnson (45) Date of Patent: Oct 31, 1989 54 MAGNETICFORCE GENERATING 56 References Cited METHOD AND APPARATUS U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,074,153 2/1978
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0119926 A1 LIN US 2013 0119926A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 16, 2013 (54) WIRELESS CHARGING SYSTEMAND METHOD (71) Applicant: ACER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0119926 A1 LIN US 2013 0119926A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 16, 2013 (54) WIRELESS CHARGING SYSTEMAND METHOD (71) Applicant: ACER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0251883 A1 WANG US 2016O251883A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2016 (54) LOCKING AND UNLOCKING MECHANISM FOR ADOOR LOCK (71) Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0251883 A1 WANG US 2016O251883A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2016 (54) LOCKING AND UNLOCKING MECHANISM FOR ADOOR LOCK (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 20110283931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0283931 A1 Moldovanu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2011 (54) SUBMARINE RENEWABLE ENERGY GENERATION SYSTEMUSING
US 20110283931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0283931 A1 Moldovanu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2011 (54) SUBMARINE RENEWABLE ENERGY GENERATION SYSTEMUSING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,557,473 B2
 US007557473B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,557,473 B2 Butler (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 2009 (54) ELECTROMAGNETIC RECIPROCATING 5,457,349 A * 10/1995 Gifford... 310,24 ENGINE 6,552.450
US007557473B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,557,473 B2 Butler (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 2009 (54) ELECTROMAGNETIC RECIPROCATING 5,457,349 A * 10/1995 Gifford... 310,24 ENGINE 6,552.450
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,791,205 B2
 USOO6791205B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Woodbridge (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2004 (54) RECIPROCATING GENERATOR WAVE 5,347,186 A 9/1994 Konotchick... 310/17 POWER BUOY 5,696,413 A 12/1997
USOO6791205B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Woodbridge (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2004 (54) RECIPROCATING GENERATOR WAVE 5,347,186 A 9/1994 Konotchick... 310/17 POWER BUOY 5,696,413 A 12/1997
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012
 US 2012O163742A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0163742 A1 Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) AXIAL GAS THRUST BEARING FOR (30) Foreign
US 2012O163742A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0163742 A1 Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) AXIAL GAS THRUST BEARING FOR (30) Foreign
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126110 A1 SHAHOSSEN et al. US 201701.2611 OA1 (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) ELECTROMAGNETC
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126110 A1 SHAHOSSEN et al. US 201701.2611 OA1 (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) ELECTROMAGNETC
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO64994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Matsumoto (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) STATIONARY BIKE (52) U.S. Cl.... 482/8 (76) Inventor: Masaaki Matsumoto,
(19) United States US 2005OO64994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Matsumoto (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) STATIONARY BIKE (52) U.S. Cl.... 482/8 (76) Inventor: Masaaki Matsumoto,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006
 US 2006005 1222A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0051222 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) MINIATURE PUMP FOR LIQUID COOLING Publication Classification
US 2006005 1222A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0051222 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) MINIATURE PUMP FOR LIQUID COOLING Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,643,958 B1
 USOO6643958B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Krejci (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 11, 2003 (54) SNOW THROWING SHOVEL DEVICE 3,435,545. A 4/1969 Anderson... 37/223 3,512,279 A 5/1970 Benson... 37/244
USOO6643958B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Krejci (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 11, 2003 (54) SNOW THROWING SHOVEL DEVICE 3,435,545. A 4/1969 Anderson... 37/223 3,512,279 A 5/1970 Benson... 37/244
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
(19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD11: Last updated: 3rd February 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly Electrical power is frequently generated by spinning the shaft of a generator which has some
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD11: Last updated: 3rd February 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly Electrical power is frequently generated by spinning the shaft of a generator which has some
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Cervantes et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 7, 2007
 US 20070 126577A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0126577 A1 Cervantes et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 7, 2007 (54) DOOR LATCH POSITION SENSOR Publication Classification
US 20070 126577A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0126577 A1 Cervantes et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 7, 2007 (54) DOOR LATCH POSITION SENSOR Publication Classification
United States Patent 19 Schechter
 United States Patent 19 Schechter (54) 75 73) 21) (22) (51) (52) 58 (56) SPOOL VALVE CONTROL OF AN ELECTROHYDRAULIC CAMILESS WALVETRAIN Inventor: Michael M. Schechter, Farmington Hills, Mich. Assignee:
United States Patent 19 Schechter (54) 75 73) 21) (22) (51) (52) 58 (56) SPOOL VALVE CONTROL OF AN ELECTROHYDRAULIC CAMILESS WALVETRAIN Inventor: Michael M. Schechter, Farmington Hills, Mich. Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Koitabashi
 United States Patent (19) Koitabashi 54 75 (73) 1 (51) (5) (58 56) ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH WITH AN IMPROVED MAGNETC ROTATABLE MEMBER Inventor: Takatoshi Koitabashi, Annaka, Japan Assignee: Sanden Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Koitabashi 54 75 (73) 1 (51) (5) (58 56) ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH WITH AN IMPROVED MAGNETC ROTATABLE MEMBER Inventor: Takatoshi Koitabashi, Annaka, Japan Assignee: Sanden Corporation,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060066075A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0066075A1 Zlotkowski (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2006 (54) TOWING TRAILER FOR TWO OR THREE Publication Classification
US 20060066075A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0066075A1 Zlotkowski (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2006 (54) TOWING TRAILER FOR TWO OR THREE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201201.07098A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0107098 A1 Tirone, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 3, 2012 (54) GASTURBINE ENGINE ROTOR TIE SHAFT (52) U.S.
(19) United States US 201201.07098A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0107098 A1 Tirone, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 3, 2012 (54) GASTURBINE ENGINE ROTOR TIE SHAFT (52) U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0018979 A1 McCoy et al. US 201200 18979A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) FIFTH WHEEL HITCH ISOLATION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0018979 A1 McCoy et al. US 201200 18979A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) FIFTH WHEEL HITCH ISOLATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Poulsen (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2012
 US 20120268067A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0268067 A1 Poulsen (43) Pub. Date: (54) CHARGING STATION FOR ELECTRIC (52) U.S. Cl.... 320/109; 29/401.1 VEHICLES
US 20120268067A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0268067 A1 Poulsen (43) Pub. Date: (54) CHARGING STATION FOR ELECTRIC (52) U.S. Cl.... 320/109; 29/401.1 VEHICLES
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US00893 1520B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,931,520 B2 Fernald (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 2015 (54) PIPE WITH INTEGRATED PROCESS USPC... 138/104 MONITORING (58) Field of Classification
(12) United States Patent US00893 1520B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,931,520 B2 Fernald (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 2015 (54) PIPE WITH INTEGRATED PROCESS USPC... 138/104 MONITORING (58) Field of Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,603,232 B2. Van Dine et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003
 USOO6603232B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Van Dine et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET RETAINING 4,745,319 A * 5/1988 Tomite et al.... 310/154.26 ARRANGEMENT FOR
USOO6603232B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Van Dine et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET RETAINING 4,745,319 A * 5/1988 Tomite et al.... 310/154.26 ARRANGEMENT FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004.00431 O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0043102 A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2004 (54) ALIGNMENT COLLAR FOR A NOZZLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 425/567
US 2004.00431 O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0043102 A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2004 (54) ALIGNMENT COLLAR FOR A NOZZLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 425/567
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0139355A1 Lee et al. US 2013 O1393.55A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) HINGEMECHANISMAND FOLDABLE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0139355A1 Lee et al. US 2013 O1393.55A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) HINGEMECHANISMAND FOLDABLE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1
 USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0091943 A1 Manor et al. US 2012009 1943A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (86) (60) SOLAR CELL CHARGING CONTROL Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0091943 A1 Manor et al. US 2012009 1943A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (86) (60) SOLAR CELL CHARGING CONTROL Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 20090314114A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0314114A1 Grosberg (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 24, 2009 (54) BACKLASH ELIMINATION MECHANISM (22) Filed: Jun. 15,
US 20090314114A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0314114A1 Grosberg (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 24, 2009 (54) BACKLASH ELIMINATION MECHANISM (22) Filed: Jun. 15,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US B1
 USOO7628442B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Spencer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 2009 (54) QUICK RELEASE CLAMP FOR TONNEAU (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/100.04, COVER 296/100.07,
USOO7628442B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Spencer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 2009 (54) QUICK RELEASE CLAMP FOR TONNEAU (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/100.04, COVER 296/100.07,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7357465B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,357.465 B2 Young et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2008 (54) BRAKE PEDAL FEEL SIMULATOR 3,719,123 A 3/1973 Cripe 3,720,447 A * 3/1973 Harned
(12) United States Patent USOO7357465B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,357.465 B2 Young et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2008 (54) BRAKE PEDAL FEEL SIMULATOR 3,719,123 A 3/1973 Cripe 3,720,447 A * 3/1973 Harned
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080264.753A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0264753 A1 Rollion et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2008 (54) FRICTIONAL CLUTCH WITH O-RING Publication Classification
US 20080264.753A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0264753 A1 Rollion et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2008 (54) FRICTIONAL CLUTCH WITH O-RING Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) Maloof
 United States Patent (19) Maloof 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 1984 54 CART WITH SEAT AND STORAGE COMPARTMENT 76 Inventor: John J. Maloof, 20 Greenwood St., East Hartford, Conn. 06118
United States Patent (19) Maloof 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 1984 54 CART WITH SEAT AND STORAGE COMPARTMENT 76 Inventor: John J. Maloof, 20 Greenwood St., East Hartford, Conn. 06118
United States Patent (19) Dasa
 United States Patent (19) Dasa 54 MULTIPLE CONFIGURATION MODEL AIRCRAFT 76) Inventor: Madhava Dasa, P.O. Box 461, Kula, Hi. 96790-0461 (21) Appl. No.: 103,954 22 Filed: Oct. 2, 1987 51) Int. Cl.... A63H
United States Patent (19) Dasa 54 MULTIPLE CONFIGURATION MODEL AIRCRAFT 76) Inventor: Madhava Dasa, P.O. Box 461, Kula, Hi. 96790-0461 (21) Appl. No.: 103,954 22 Filed: Oct. 2, 1987 51) Int. Cl.... A63H
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2
 USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
Redesign of Rotary Inductrack for Magnetic Train Levitation
 Redesign of Rotary Inductrack for Magnetic Train Levitation Bradley University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Senior Capstone Project Advisor: Dr. Anakwa Student: Glenn Zomchek Overview
Redesign of Rotary Inductrack for Magnetic Train Levitation Bradley University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Senior Capstone Project Advisor: Dr. Anakwa Student: Glenn Zomchek Overview
26, 5.3% gence Scott,
 April 25, 1967 R. J. RADUS ETAL 3,316,514 FAIL SAFE ELECTRO-MAGNETIC LIFTING DEVICE WITH SAFETY-STOP MEANS Filed March 29, 1965 WITNESSES: F.G. 3. FG. 4. F.G. 5. NVENTORS 26, 5.3% gence Scott, 3-2%y Raymond
April 25, 1967 R. J. RADUS ETAL 3,316,514 FAIL SAFE ELECTRO-MAGNETIC LIFTING DEVICE WITH SAFETY-STOP MEANS Filed March 29, 1965 WITNESSES: F.G. 3. FG. 4. F.G. 5. NVENTORS 26, 5.3% gence Scott, 3-2%y Raymond
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0119137 A1 Cirincione, II et al. US 201701 19137A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) IMPACT ABSORBNG
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0119137 A1 Cirincione, II et al. US 201701 19137A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) IMPACT ABSORBNG
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070011840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0011840 A1 Gilli (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 18, 2007 (54) WINDSCREEN WIPER ARM (75) Inventor: Marco Gilli, Chieri
(19) United States US 20070011840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0011840 A1 Gilli (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 18, 2007 (54) WINDSCREEN WIPER ARM (75) Inventor: Marco Gilli, Chieri
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,305,979 B1
 USOO7305979B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,305,979 B1 Yehe (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2007 (54) DUAL-CAMARCHERY BOW WITH 6,082,347 A * 7/2000 Darlington... 124/25.6 SMULTANEOUS POWER
USOO7305979B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,305,979 B1 Yehe (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2007 (54) DUAL-CAMARCHERY BOW WITH 6,082,347 A * 7/2000 Darlington... 124/25.6 SMULTANEOUS POWER
Patent Application Publication Nov. 27, 2014 Sheet 1 of 7 US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0346290 A1 YOSHIDA et al. US 20140346290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) SLIDING TYPE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0346290 A1 YOSHIDA et al. US 20140346290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) SLIDING TYPE
United States Patent (19) Reid
 United States Patent (19) Reid 54 76) 21 22 (51) 52) 58 56) CONVENIENT DUAL FUELTANK SYSTEM Inventor: Richard M. Reid, 25474 State St., Loma Linda, Calif. 92354 Appl. No.: 638,377 Filed: Aug. 7, 1984 Int.
United States Patent (19) Reid 54 76) 21 22 (51) 52) 58 56) CONVENIENT DUAL FUELTANK SYSTEM Inventor: Richard M. Reid, 25474 State St., Loma Linda, Calif. 92354 Appl. No.: 638,377 Filed: Aug. 7, 1984 Int.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0025.005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0025005 A1 HOWe (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 3, 2011 (54) BEACH BUGGY (76) Inventor: Tracy Howell, Venice, FL (US)
(19) United States US 2011 0025.005A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0025005 A1 HOWe (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 3, 2011 (54) BEACH BUGGY (76) Inventor: Tracy Howell, Venice, FL (US)
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial No.. Filing Date July Inventor Richard Bonin NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to: OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH
Serial No.. Filing Date July Inventor Richard Bonin NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to: OFFICE OF NAVAL RESEARCH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O231027A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0231027 A1 SU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 16, 2010 (54) WHEEL WITH THERMOELECTRIC (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2010O231027A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0231027 A1 SU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 16, 2010 (54) WHEEL WITH THERMOELECTRIC (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0041841 A1 Huazhao et al. US 20140041841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (62) (30) MICRO-CHANNEL HEAT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0041841 A1 Huazhao et al. US 20140041841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (62) (30) MICRO-CHANNEL HEAT
United States Patent (19) Muranishi
 United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
22-y 2 24, 7. -l- az. Z é - Jan. 26, 1971 D. F. webster 3,557,549 TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM FOR INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE. is is a ST.
 Jan. 26, 1971 D. F. webster 3,557,549 23 9 -a- 3. Sheets-Sheet El -l- Area Arena S is is a ST BY DONALD F. WEBSTER Y az. Z 224 724.0 2é - 22-y 2 24, 7 Jan. 26, 1971 D. F. WEBSTER 3,557,549 3 Sheets-Sheet
Jan. 26, 1971 D. F. webster 3,557,549 23 9 -a- 3. Sheets-Sheet El -l- Area Arena S is is a ST BY DONALD F. WEBSTER Y az. Z 224 724.0 2é - 22-y 2 24, 7 Jan. 26, 1971 D. F. WEBSTER 3,557,549 3 Sheets-Sheet
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0290654 A1 GOVari et al. US 20070290654A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 20, 2007 (54) INDUCTIVE CHARGING OF TOOLS ON SURGICAL TRAY (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0290654 A1 GOVari et al. US 20070290654A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 20, 2007 (54) INDUCTIVE CHARGING OF TOOLS ON SURGICAL TRAY (76)
Phillips (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 10, (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search
 (12) United States Patent US008747274B2 () Patent No.: Phillips () Date of Patent: Jun., 2014 (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search TRANSMISSION USPC... 74/3, 331; 475/207
(12) United States Patent US008747274B2 () Patent No.: Phillips () Date of Patent: Jun., 2014 (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search TRANSMISSION USPC... 74/3, 331; 475/207
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070247877A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0247877 A1 KWON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2007 54) ACTIVE-CLAMP CURRENTSOURCE 3O Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070247877A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0247877 A1 KWON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2007 54) ACTIVE-CLAMP CURRENTSOURCE 3O Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O104636A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0104636A1 Ortt et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) STATOR ASSEMBLY WITH AN (52) U.S. Cl.... 310/154.08; 310/89; 310/154.12;
(19) United States US 2004O104636A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0104636A1 Ortt et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) STATOR ASSEMBLY WITH AN (52) U.S. Cl.... 310/154.08; 310/89; 310/154.12;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Nelson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005
 US 2005O189800A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0189800 A1 Nelson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) ENERGY ABSORBING SEAT AND SEAT Publication Classification
US 2005O189800A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0189800 A1 Nelson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) ENERGY ABSORBING SEAT AND SEAT Publication Classification
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fujita 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,727,957 Mar. 1, 1988 (54) RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATOR FOR MUFFLER 75 Inventor: Akio Fujita, Fujisawa, Japan 73) Assignee: Bridgestone
United States Patent (19) Fujita 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,727,957 Mar. 1, 1988 (54) RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATOR FOR MUFFLER 75 Inventor: Akio Fujita, Fujisawa, Japan 73) Assignee: Bridgestone
United States Patent (19) Smith
 United States Patent (19) Smith 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,546,754 Oct. 15, 1985 (54) YOKE ANCHOR FOR COMPOUND BOWS (75) Inventor: Max D. Smith, Evansville, Ind. 73 Assignee: Indian Industries,
United States Patent (19) Smith 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,546,754 Oct. 15, 1985 (54) YOKE ANCHOR FOR COMPOUND BOWS (75) Inventor: Max D. Smith, Evansville, Ind. 73 Assignee: Indian Industries,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,205,840 B1
 USOO620584OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,205,840 B1 Thompson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) TIME CLOCK BREATHALYZER 4,749,553 * 6/1988 Lopez et al.... 73/23.3 X COMBINATION
USOO620584OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,205,840 B1 Thompson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) TIME CLOCK BREATHALYZER 4,749,553 * 6/1988 Lopez et al.... 73/23.3 X COMBINATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080056631A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0056631 A1 Beausoleil et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2008 (54) TUNGSTEN CARBIDE ENHANCED Publication Classification
US 20080056631A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0056631 A1 Beausoleil et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2008 (54) TUNGSTEN CARBIDE ENHANCED Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015 0084494A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084494 A1 Tonthat et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 (54) SLIDING RACK-MOUNTABLE RAILS FOR H05K 5/02 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 2015 0084494A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084494 A1 Tonthat et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 (54) SLIDING RACK-MOUNTABLE RAILS FOR H05K 5/02 (2006.01)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Minnerop 54) DEVICE FOR WATER COOLING OF ROLLED STEEL SECTIONS 75 Inventor: Michael Minnerop, Ratingen, Germany 73 Assignee: SMS Schloemann-Siemag Aktiengesellschaft, Dusseldorf,
United States Patent (19) Minnerop 54) DEVICE FOR WATER COOLING OF ROLLED STEEL SECTIONS 75 Inventor: Michael Minnerop, Ratingen, Germany 73 Assignee: SMS Schloemann-Siemag Aktiengesellschaft, Dusseldorf,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2
 US009035508B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2 Grosskopf et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 19, 2015 (54) ROTATING RESISTOR ASSEMBLY H02K II/042 (2013.01); H02K II/0057 (2013.01):
US009035508B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2 Grosskopf et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 19, 2015 (54) ROTATING RESISTOR ASSEMBLY H02K II/042 (2013.01); H02K II/0057 (2013.01):
NSN. 2%h, WD. United States Patent (19) Vranken 4,829,401. May 9, Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 54) ROTATING TRANSFORMER WITH FOIL
 United States Patent (19) Vranken 54) ROTATING TRANSFORMER WITH FOIL WINDINGS (75) Inventor: Roger A. Vranken, Eindhoven, Netherlands (73) Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Vranken 54) ROTATING TRANSFORMER WITH FOIL WINDINGS (75) Inventor: Roger A. Vranken, Eindhoven, Netherlands (73) Assignee: U.S. Philips Corporation, New York, N.Y. (21 Appl. No.:
Crowley (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, (54) HIGH-POWER ION SPUTTERING 4,356,073. A 10/1982 McKelvey. MAGNETRON 4,422,916 A 12/1983 McKelvey
 (12) United States Patent USOO6841051B2 (10) Patent No.: Crowley () Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) HIGH-POWER ION SPUTTERING 4,6,073. A 10/1982 McKelvey MAGNETRON 4,422,916 A 12/1983 McKelvey (75)
(12) United States Patent USOO6841051B2 (10) Patent No.: Crowley () Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) HIGH-POWER ION SPUTTERING 4,6,073. A 10/1982 McKelvey MAGNETRON 4,422,916 A 12/1983 McKelvey (75)
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9284.05OB2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.284,050 B2 Bagai (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2016 (54) AIRFOIL FOR ROTOR BLADE WITH (56) References Cited REDUCED PITCHING MOMENT U.S. PATENT
(12) United States Patent USOO9284.05OB2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.284,050 B2 Bagai (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2016 (54) AIRFOIL FOR ROTOR BLADE WITH (56) References Cited REDUCED PITCHING MOMENT U.S. PATENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 2015.0312679A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0312679 A1 LTTLE (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) LOUDSPEAKER WITH TWO MOTORS AND Publication Classification
US 2015.0312679A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0312679 A1 LTTLE (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) LOUDSPEAKER WITH TWO MOTORS AND Publication Classification
ia 451s, 10-y (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1 (19) United States Johnson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb.
 (19) United States US 2003OO29160A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0029160 A1 Johnson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2003 (54) COMBINED CYCLE PULSE DETONATION TURBINE ENGINE
(19) United States US 2003OO29160A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0029160 A1 Johnson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2003 (54) COMBINED CYCLE PULSE DETONATION TURBINE ENGINE
(51) Int. Cl... B62D 25/00 flush with the end of the bed and the other edge overlapping
 USOO5904391A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,904.391 9 9 Lilienauest et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 18, 9 1999 54). TAILGATE GAP COVER 5,664,822 9/1997 Rosenfeld... 296/39.2 76 Inventors:
USOO5904391A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,904.391 9 9 Lilienauest et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 18, 9 1999 54). TAILGATE GAP COVER 5,664,822 9/1997 Rosenfeld... 296/39.2 76 Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 01 17420A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0117420 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) BUS BAR AND BATTERY MODULE INCLUDING THE SAME (52)
US 2011 01 17420A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0117420 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) BUS BAR AND BATTERY MODULE INCLUDING THE SAME (52)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 20050132699A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0132699 A1 Newman (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) CONVERTNG PRESSURE ENERGY FROM Publication Classification
US 20050132699A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0132699 A1 Newman (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) CONVERTNG PRESSURE ENERGY FROM Publication Classification
Navy Case No Date: 10 October 2008
 DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFAE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: 401 832-3653 NEWPORT FAX: 401 832-4432 DSN: 432-3653 Navy Case No. 96674 Date: 10 October 2008 The below identified
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY NAVAL UNDERSEA WARFAE CENTER DIVISION NEWPORT OFFICE OF COUNSEL PHONE: 401 832-3653 NEWPORT FAX: 401 832-4432 DSN: 432-3653 Navy Case No. 96674 Date: 10 October 2008 The below identified
MAGNETIC LEVITATION TRAIN TECHNOLOGY II
 MAGNETIC LEVITATION TRAIN TECHNOLOGY II SENIOR PROJECT PROPOSAL Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Bradley University December 10, 2003 Students: Tony Pederson and Toby Miller Advisor: Winfred
MAGNETIC LEVITATION TRAIN TECHNOLOGY II SENIOR PROJECT PROPOSAL Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Bradley University December 10, 2003 Students: Tony Pederson and Toby Miller Advisor: Winfred
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0290354 A1 Marty et al. US 20140290354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) AIR DATA PROBE SENSE PORT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0290354 A1 Marty et al. US 20140290354A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) AIR DATA PROBE SENSE PORT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150224968A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0224968 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) CONTROL METHOD FOR HILL START ASSIST CONTROL SYSTEM (71)
(19) United States US 20150224968A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0224968 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) CONTROL METHOD FOR HILL START ASSIST CONTROL SYSTEM (71)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0109141 A1 Fritzinger US 2012O109141A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 3, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) ONE-WAY BEARING CABLE TENSIONING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0109141 A1 Fritzinger US 2012O109141A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 3, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) ONE-WAY BEARING CABLE TENSIONING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007.0099.746A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0099746A1 Hahlbeck (43) Pub. Date: MaV 3, 2007 9 (54) SELF ALIGNING GEAR SET Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2007.0099.746A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0099746A1 Hahlbeck (43) Pub. Date: MaV 3, 2007 9 (54) SELF ALIGNING GEAR SET Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,255,755 B1
 USOO6255755B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Fei (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 3, 2001 (54) SINGLE PHASE THREE SPEED MOTOR 3,619,730 11/1971 Broadway et al.... 318/224 R WITH SHARED WINDINGS 3,774,062
USOO6255755B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Fei (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 3, 2001 (54) SINGLE PHASE THREE SPEED MOTOR 3,619,730 11/1971 Broadway et al.... 318/224 R WITH SHARED WINDINGS 3,774,062
(12) United States Patent
 US007777377B2 (12) United States Patent Tkadlec (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,377 B2 *Aug. 17, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) MAGNETIC PROPULSION
US007777377B2 (12) United States Patent Tkadlec (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,377 B2 *Aug. 17, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) MAGNETIC PROPULSION
(12) United States Patent
 US00704.4047B1 (12) United States Patent Bennett et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) CYLNDER MOUNTED STROKE CONTROL Inventors: Robert Edwin Bennett,
US00704.4047B1 (12) United States Patent Bennett et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) CYLNDER MOUNTED STROKE CONTROL Inventors: Robert Edwin Bennett,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0090635 A1 May US 20140090635A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) PROPANETANKFUEL GAUGE FOR BARBECUE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0090635 A1 May US 20140090635A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) PROPANETANKFUEL GAUGE FOR BARBECUE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O131873A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Klingbail et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 22, 2006 (54) HIGH PRESSURE SWIVEL JOINT Publication Classification (76) Inventors:
US 2006O131873A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Klingbail et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 22, 2006 (54) HIGH PRESSURE SWIVEL JOINT Publication Classification (76) Inventors:
III IIII. United States Patent (19) Spencer et al. DISPLAY. Appl. No.: 493,622. Primary Examiner-Richard Chilcot
 United States Patent (19) Spencer et al. (54) (75) (73) 21) 22 (51) 52 (58) 56 ELECTROMAGNETC FLOW METER Inventors: Jordan L. Spencer; David C. Rodgers, both of Tenafly, N.J. Assignee: The Trustees of
United States Patent (19) Spencer et al. (54) (75) (73) 21) 22 (51) 52 (58) 56 ELECTROMAGNETC FLOW METER Inventors: Jordan L. Spencer; David C. Rodgers, both of Tenafly, N.J. Assignee: The Trustees of
United States Patent (19) Miller
 United States Patent (19) Miller 54 LAMPHOLDER FITTING WITH THREE-WAY BRIGHTNESS SOLD-STATE FLUORESCENT LAMP BALLAST 76) Inventor: Jack V. Miller, 700 N. Auburn Ave., Sierra Madre, Calif. 91024 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Miller 54 LAMPHOLDER FITTING WITH THREE-WAY BRIGHTNESS SOLD-STATE FLUORESCENT LAMP BALLAST 76) Inventor: Jack V. Miller, 700 N. Auburn Ave., Sierra Madre, Calif. 91024 21 Appl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150214458A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0214458 A1 Nandigama et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 30, 2015 (54) THERMOELECTRIC GENERATORSYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 20150214458A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0214458 A1 Nandigama et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 30, 2015 (54) THERMOELECTRIC GENERATORSYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.
