Voltage and batteries
|
|
|
- Marsha Manning
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Voltage and batteries Objectives Define voltage source. Distinguish between parallel and series arrangements of batteries. Construct electric circuits with batteries connected in series and in parallel. Calculate the combined voltage of batteries connected in series and in parallel. 1. Which statement below provides a correct practical definition of a voltage source? A voltage source... A. creates an electric potential difference between two points in a circuit, such as the two ends of a battery. 2. Identify which circuit has batteries connected in series and which has batteries in parallel. B. provides the electrical potential energy needed for a circuit to operate. C. is analogous to the pump in a system of circulating water. D. all of the above. 3. Calculate the voltage across the batteries for each circuit. 4. What does the 1.5 V label on the battery mean? A. The voltage of the positive terminal is 1.5 V. B. The voltage of the negative terminal is 0 V. C. The voltage between the positive and negative terminals is 1.5 V. D. All of the above 5. Did you successfully construct an arrangement of batteries in parallel and in series? Did you measure the voltage across them? 1
2 Physics terms voltage volt (V) battery voltmeter A reliable source of current Prior to 1800, no one knew how to create a steady supply of electric current. Alessandro Volta was the first to succeed. He discovered that placing two different metals in an acid or salt solution produced an electric current between the terminals. He connected multiple voltaic piles together to create a battery of them. Adolphe Ganot, Elementary Treatise on Physics, 1893 What is a battery? A battery is a device that converts stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Batteries come in many different kinds even lemons! Reading a battery Batteries come in many sizes and voltages: 1.5, 6, 9, 12 V, for example. Voltage is the electric potential difference between the two terminals of a battery. Voltage is measured in volts (V), named after Volta, the inventor of the battery. How is voltage measured? Voltage is measured using a voltmeter or a digital multimeter. To measure voltage, the two leads of the multimeter must touch the opposite ends of the battery or other circuit element. Volts and amps Current and voltage are the two most important physical quantities for understanding electric circuits. Current measures the flow of charge through a wire. Voltage measures the change in electrical potential energy per unit of charge. 2
3 A useful analogy A useful analogy Charges in a wire are analogous to water in a pipe. Charges in a wire are analogous to water in a pipe: Electric current is analogous to the flow of the water. The battery is analogous to the water pump. Voltage is analogous to the change in gravitational E p. Analogy: water and electricity Water flows because there is an energy difference, measured in height. Current flows because there is an energy difference, measured in volts. What if you have more than one battery? In 17B you will connect batteries together in series and in parallel, and measure the resulting voltage. The investigation is found on page 476 of your text. View this short video on page 475 of your e-book. What is a series connection? In a series connection, the batteries are connected one after the other. What is a parallel connection? In a parallel connection, the same ends of both batteries are connected together. The positive terminal of one battery is connected to the negative terminal of the next battery. 3
4 Part 1: Connecting batteries in parallel 1. Using voltage probes (such as on a digital multimeter), separately measure the voltage across each of the two batteries. Part 1: Connecting batteries in parallel 3. Use voltage probes to measure the voltage across the two batteries connected in parallel.. 2. Connect the two batteries in parallel: connect their positive terminals to each other, and connect their negative terminals to each other. Questions a. Read the voltage rating on the side of each battery. How does that voltage compare with what you measured? Why? b. How does the voltage of the two batteries connected in parallel compare with the voltage of either battery measured separately? Why? Part 2: Connecting batteries in series 1. Connect the two batteries in series: connect the negative terminal of one battery to the positive terminal of the other battery. 2. Using voltage probes, measure the voltage across the two batteries connected in series. Draw a conclusion How do you connect batteries together to create a larger voltage than either battery alone? Explain why this is the case by referring to the circuit diagrams. Summarizing the results To calculate the voltage across batteries connected in series or in parallel: When batteries are connected in series, the voltages add together. When identical batteries are connected in parallel, the total voltage remains the same. Explain why this is the case by using an analogy to water. 4
5 Why does it work this way? When these batteries are connected in series, the voltages add together. Electric charge (1 coulomb) passing through a 1.5 volt battery gains 1.5 joules of E p. Passing through a second 1.5 volt battery gains another 1.5 joules of E p. It s like climbing a stairway to the second floor, then another stairway to the third floor. Why does it work that way? When these batteries are connected in parallel, the total voltage remains the same. Electric charge passes through one battery OR the other. It ONLY gains 1.5 joules of E p because each charge ONLY passes through one battery. It s like climbing either of two stairways from the first to second floor. Going beyond the investigation How do you think the batteries in a flashlight are connected? In series or in parallel? Open up a flashlight, trace the connections, and see if you are right! How do you dispose of used batteries? Did you only use as many batteries as needed for your investigation? Batteries last for a long time, but what do you do when they are used up? Alkaline batteries: These batteries used to contain mercury, and so would have to be disposed with hazardous waste. Today, most alkaline batteries have no mercury and can be disposed in the trash. Do not pile many batteries together, however, because they can connect with each other and become hot! Rechargeable batteries: (nickel cadmium, lithium, car batteries, etc.) These must be recycled directly at a waste management center or through an auto dealer or home hardware store. 1. Which statement below provides a correct practical definition of a voltage source? A voltage source... A. creates an electric potential difference between two points in a circuit, such as the two ends of a battery. B. provides the electrical potential energy needed for a circuit to operate. C. is analogous to the pump in a system of circulating water. D. all of the above. 1. Which statement below provides a correct practical definition of a voltage source? A voltage source... A. creates an electric potential difference between two points in a circuit, such as the two ends of a battery. B. provides the electrical potential energy needed for a circuit to operate. C. is analogous to the pump in a system of circulating water. D. all of the above. 5
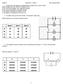
6 2. Identify which circuit has batteries connected in series and which has batteries in parallel. 2. Identify which circuit has batteries connected in series and which has batteries in parallel. 3. Calculate the voltage across the batteries for each circuit. 3. Calculate the voltage across the batteries for each circuit. 4.5 V 1.5 V 4. What does the 1.5 V label on the battery mean? A. The voltage of the positive terminal is 1.5 V. B. The voltage of the negative terminal is 0 V. C. The voltage between the positive and negative terminals is 1.5 V. D. All of the above 4. What does the 1.5 V label on the battery mean? A. The voltage of the positive terminal is 1.5 V. B. The voltage of the negative terminal is 0 V. C. The voltage between the positive and negative terminals is 1.5 V. Voltage is a potential difference that is always measured between two points in a circuit. D. All of the above 6
7 Going further: What s inside a battery 5. Did you successfully construct an arrangement of batteries in parallel and in series? Did you measure the voltage across them? 7
A Brief Look at Batteries
 A Brief Look at Batteries At some point during 501/502 you will need to use one or more batteries in order to provide power to a system that needs to be deployed away from line power. It s a good idea
A Brief Look at Batteries At some point during 501/502 you will need to use one or more batteries in order to provide power to a system that needs to be deployed away from line power. It s a good idea
Electricity Unit Review
 Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
Science 9 Electricity Unit Review Name: General Definitions: Neutral Object Charge Separation Electrical Discharge Electric Current Amperes (amps) Voltage (volts) Voltmeter Ammeters Galvanometer Multimeter
Cabrillo College Physics 10L. LAB 7 Circuits. Read Hewitt Chapter 23
 Cabrillo College Physics 10L Name LAB 7 Circuits Read Hewitt Chapter 23 What to learn and explore Every electrical circuit must have at least one source (which supplies electrical energy to the circuit)
Cabrillo College Physics 10L Name LAB 7 Circuits Read Hewitt Chapter 23 What to learn and explore Every electrical circuit must have at least one source (which supplies electrical energy to the circuit)
CELLS AND BATTERIES Understand the general features of cells and batteries Describe the relationship between cells and batteries. Describe the basic
 Cell & Batteries CELLS AND BATTERIES Understand the general features of cells and batteries Describe the relationship between cells and batteries. Describe the basic operation of a battery. Compare between
Cell & Batteries CELLS AND BATTERIES Understand the general features of cells and batteries Describe the relationship between cells and batteries. Describe the basic operation of a battery. Compare between
Lemon Battery. Creating. acidic solution.
 Lemon Battery From http://hilaroad.com/camp/projects/lemon/lemon_battery.html More science and technology projects from Hila Sciencee (geodesic domes, sundials, kites, trebuchets...) Follow these links
Lemon Battery From http://hilaroad.com/camp/projects/lemon/lemon_battery.html More science and technology projects from Hila Sciencee (geodesic domes, sundials, kites, trebuchets...) Follow these links
INVESTIGATION ONE: WHAT DOES A VOLTMETER DO? How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured?
 How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow rate
How Are Values of Circuit Variables Measured? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow rate
Batteries n Bulbs: Voltage, Current and Resistance (8/6/15) (approx. 2h)
 Batteries n Bulbs: Voltage, Current and Resistance (8/6/15) (approx. 2h) Introduction A simple electric circuit can be made from a voltage source (batteries), wires through which current flows and a resistance,
Batteries n Bulbs: Voltage, Current and Resistance (8/6/15) (approx. 2h) Introduction A simple electric circuit can be made from a voltage source (batteries), wires through which current flows and a resistance,
B How much voltage does a standard automobile battery usually supply?
 Chapter 2 B-003-16-01 How much voltage does a standard automobile battery usually supply? 1. About 240 volts 2. About 120 volts 3. About 12 volts 4. About 9 volts B-003-16-02 Which component has a positive
Chapter 2 B-003-16-01 How much voltage does a standard automobile battery usually supply? 1. About 240 volts 2. About 120 volts 3. About 12 volts 4. About 9 volts B-003-16-02 Which component has a positive
Unit 13 Batteries and Other Electrical Sources
 Batteries and Other Electrical Sources Objectives: Discuss the differences between primary and secondary cells. List voltages for different types of cells. Discuss different types of primary cells. Construct
Batteries and Other Electrical Sources Objectives: Discuss the differences between primary and secondary cells. List voltages for different types of cells. Discuss different types of primary cells. Construct
Redox Potentials and the Lead Acid Cell Minneapolis Community and Tech. College v I. Introduction. Part I
 Redox Potentials and the Lead Acid Cell Minneapolis Community and Tech. College v.11.12 I. Introduction Part I In these experiments you will first determine the reduction potentials of a series of five
Redox Potentials and the Lead Acid Cell Minneapolis Community and Tech. College v.11.12 I. Introduction Part I In these experiments you will first determine the reduction potentials of a series of five
Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 2 Basic Electrical Meters and Ohm s Law
 Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 2 Basic Electrical Meters and Ohm s Law Administration: o Prayer o Bible Verse o Turn in quiz Meters: o Terms and Definitions: Analog vs. Digital Displays: Analog
Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 2 Basic Electrical Meters and Ohm s Law Administration: o Prayer o Bible Verse o Turn in quiz Meters: o Terms and Definitions: Analog vs. Digital Displays: Analog
PHY132 Practicals Week 5 Student Guide
 PHY132 Practicals Week 5 Student Guide Concepts of this Module Introducing current and voltage Simple circuits Circuit diagrams Background When water flows through a garden hose, we can characterize the
PHY132 Practicals Week 5 Student Guide Concepts of this Module Introducing current and voltage Simple circuits Circuit diagrams Background When water flows through a garden hose, we can characterize the
Unit 13 Batteries and Other Electrical Sources
 Battery History Luigi Galvani in 1791 first noticed indications of electricity while experimenting with frog legs. Alessandro Volta in 1800 created the first practical battery. Batteries are composed of
Battery History Luigi Galvani in 1791 first noticed indications of electricity while experimenting with frog legs. Alessandro Volta in 1800 created the first practical battery. Batteries are composed of
Frog's leg Batteries. Current flow of electric charge. L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [3] Batteries use chemical energy to produce electricity
![Frog's leg Batteries. Current flow of electric charge. L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [3] Batteries use chemical energy to produce electricity Frog's leg Batteries. Current flow of electric charge. L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [3] Batteries use chemical energy to produce electricity](/thumbs/87/96343656.jpg) L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [3] Electric circuits what conducts electricity what doesn t conduct electricity Current voltage and resistance Ohm s Law Heat in a resistor power loss Making simple circuit
L 26 Electricity and Magnetism [3] Electric circuits what conducts electricity what doesn t conduct electricity Current voltage and resistance Ohm s Law Heat in a resistor power loss Making simple circuit
Batteries: Stored Energy Discussion Questions:
 Batteries: Stored Energy Discussion Questions: 1) How is energy stored in a battery? 2) How many different types of batteries are there? 3) What kinds of tools and machinery can run on batteries? 4) Can
Batteries: Stored Energy Discussion Questions: 1) How is energy stored in a battery? 2) How many different types of batteries are there? 3) What kinds of tools and machinery can run on batteries? 4) Can
PHY152H1S Practical 3: Introduction to Circuits
 PHY152H1S Practical 3: Introduction to Circuits Don t forget: List the NAMES of all participants on the first page of each day s write-up. Note if any participants arrived late or left early. Put the DATE
PHY152H1S Practical 3: Introduction to Circuits Don t forget: List the NAMES of all participants on the first page of each day s write-up. Note if any participants arrived late or left early. Put the DATE
Redox Potentials and the Lead Acid Cell Minneapolis Community and Tech. College v I. Introduction. Part I
 Redox Potentials and the Lead Acid Cell Minneapolis Community and Tech. College v.11.10 I. Introduction Part I In these experiments you will first determine the reduction potentials of a series of five
Redox Potentials and the Lead Acid Cell Minneapolis Community and Tech. College v.11.10 I. Introduction Part I In these experiments you will first determine the reduction potentials of a series of five
7. How long must a 100-watt light bulb be used in order to dissipate 1,000 joules of electrical energy? 1) 10 s 3) 1,000 s 2) 100 s 4) 100,000 s
 1. Which quantity must be the same for each component in any series circuit? 1) power 3) current 2) resistance 4) voltage 2. A student needs a 4-ohm resistor to complete a circuit. Only a large quantity
1. Which quantity must be the same for each component in any series circuit? 1) power 3) current 2) resistance 4) voltage 2. A student needs a 4-ohm resistor to complete a circuit. Only a large quantity
Period 11 Activity Sheet Solutions: Electric Current
 Period 11 Activity Sheet Solutions: Electric Current Activity 11.1: How Can Electric Charge Do Work? Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what
Period 11 Activity Sheet Solutions: Electric Current Activity 11.1: How Can Electric Charge Do Work? Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what
Investigation Electrical Circuits
 ACTIVITY #1 Task: To design and construct a circuit where 2 light bulbs can turn on and off at the same time Materials: - 1 power supply - 2 light bulbs - Connecting wires ( ) - Switch(s) - Multi-meter
ACTIVITY #1 Task: To design and construct a circuit where 2 light bulbs can turn on and off at the same time Materials: - 1 power supply - 2 light bulbs - Connecting wires ( ) - Switch(s) - Multi-meter
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4)
 ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4) 1. Which two electrical quantities are measured in volts? A current and e.m.f. B current and resistance C e.m.f. and potential difference D potential
ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM - EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (4) 1. Which two electrical quantities are measured in volts? A current and e.m.f. B current and resistance C e.m.f. and potential difference D potential
Chapter 2. Voltage and Current. Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Pearson [imprint]
![Chapter 2. Voltage and Current. Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Pearson [imprint] Chapter 2. Voltage and Current. Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Pearson [imprint]](/thumbs/78/76801413.jpg) Chapter 2 Voltage and Current OBJECTIVES Become aware of the basic atomic structure of conductors such as copper and aluminum and understand why they are used so extensively in the field. Understand how
Chapter 2 Voltage and Current OBJECTIVES Become aware of the basic atomic structure of conductors such as copper and aluminum and understand why they are used so extensively in the field. Understand how
Current, resistance and potential difference
 Multiple choice questions 1. Three conductors join as shown in the diagram. The direction of the current in each conductor is shown by the arrow. Y Z X The current in the conductor Z is 10 A. The current
Multiple choice questions 1. Three conductors join as shown in the diagram. The direction of the current in each conductor is shown by the arrow. Y Z X The current in the conductor Z is 10 A. The current
2. A student sets up the circuit shown. The switch is open (off). Which lamps are on and which lamps are off?
 1. A polythene rod repels an inflated balloon hanging from a nylon thread. What charges must the rod and the balloon carry? A The rod and the balloon carry opposite charges. B The rod and the balloon carry
1. A polythene rod repels an inflated balloon hanging from a nylon thread. What charges must the rod and the balloon carry? A The rod and the balloon carry opposite charges. B The rod and the balloon carry
11.1 CURRENT ELECTRICITY. Electrochemical Cells (the energy source) pg Wet Cell. Dry Cell. Positive. Terminal. Negative.
 Date: SNC1D: Electricity 11.1 CURRENT ELECTRICITY Define: CIRCUIT: path that electrons follow. CURRENT ELECTRICITY: continuous flow of electrons in a circuit LOAD: device that converts electrical energy
Date: SNC1D: Electricity 11.1 CURRENT ELECTRICITY Define: CIRCUIT: path that electrons follow. CURRENT ELECTRICITY: continuous flow of electrons in a circuit LOAD: device that converts electrical energy
Electric current, resistance and voltage in simple circuits
 Lab 6: Electric current, resistance and voltage in simple circuits Name: Group Members: Date: T s Name: pparatus: ulb board with batteries, connecting wires, two identical bulbs and a different bulb, a
Lab 6: Electric current, resistance and voltage in simple circuits Name: Group Members: Date: T s Name: pparatus: ulb board with batteries, connecting wires, two identical bulbs and a different bulb, a
SC10F Circuits Lab Name:
 SC10F Circuits Lab Name: Purpose: In this lab you will be making, both, series and parallel circuits. You will then be using a millimeter to take readings at various points in these circuits. Using these
SC10F Circuits Lab Name: Purpose: In this lab you will be making, both, series and parallel circuits. You will then be using a millimeter to take readings at various points in these circuits. Using these
Batteries Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 11
 Batteries Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 11 Administration: o Prayer o Early arrivals: Measure the current going through the power indicator LED on your breadboard. Introduction:
Batteries Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics I Week 11 Administration: o Prayer o Early arrivals: Measure the current going through the power indicator LED on your breadboard. Introduction:
Congratulations, Dorothy!
 Congratulations, Dorothy! Battery Overview Steve Garland Kyle Jamieson Outline Why is this important? Brief history of batteries Basic chemistry Battery types and characteristics Case study: ThinkPad battery
Congratulations, Dorothy! Battery Overview Steve Garland Kyle Jamieson Outline Why is this important? Brief history of batteries Basic chemistry Battery types and characteristics Case study: ThinkPad battery
34.5 Electric Current: Ohm s Law OHM, OHM ON THE RANGE. Purpose. Required Equipment and Supplies. Discussion. Procedure
 Name Period Date CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS Experiment 34.5 Electric : Ohm s Law OHM, OHM ON THE RANGE Thanx to Dean Baird Purpose In this experiment, you will arrange a simple circuit involving a power source
Name Period Date CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS Experiment 34.5 Electric : Ohm s Law OHM, OHM ON THE RANGE Thanx to Dean Baird Purpose In this experiment, you will arrange a simple circuit involving a power source
Electricity and Magnetism
 Electricity and Magnetism Electric Current and Electric Circuits What do you think? Read the statement below and decide whether you agree or disagree with it. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
Electricity and Magnetism Electric Current and Electric Circuits What do you think? Read the statement below and decide whether you agree or disagree with it. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
7.9.2 Potential Difference
 7.9.2 Potential Difference 62 minutes 69 marks Page 1 of 20 Q1. A set of Christmas tree lights is made from twenty identical lamps connected in series. (a) Each lamp is designed to take a current of 0.25
7.9.2 Potential Difference 62 minutes 69 marks Page 1 of 20 Q1. A set of Christmas tree lights is made from twenty identical lamps connected in series. (a) Each lamp is designed to take a current of 0.25
POWER and ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
 POWER and ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Name For many of us, our most familiar experience with the word POWER (units of measure: WATTS) is when we think about electricity. Most of us know that when we change a light
POWER and ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Name For many of us, our most familiar experience with the word POWER (units of measure: WATTS) is when we think about electricity. Most of us know that when we change a light
8.1. Electric Potential Energy and Voltage. Before You Read. What is a battery? How does a battery provide energy?
 Electric Potential Energy and Voltage Textbook pages 270 279 Section 8.1 Summary Before You Read Static electricity involves charges that build up and stay in the same place on an object. How could you
Electric Potential Energy and Voltage Textbook pages 270 279 Section 8.1 Summary Before You Read Static electricity involves charges that build up and stay in the same place on an object. How could you
A device that measures the current in a circuit. It is always connected in SERIES to the device through which it is measuring current.
 Goals of this second circuit lab packet: 1 to learn to use voltmeters an ammeters, the basic devices for analyzing a circuit. 2 to learn to use two devices which make circuit building far more simple:
Goals of this second circuit lab packet: 1 to learn to use voltmeters an ammeters, the basic devices for analyzing a circuit. 2 to learn to use two devices which make circuit building far more simple:
Electric Potential Energy and Voltage
 Electric Potential Energy and Voltage Textbook pages 270 279 Section 8.1 Summary Before You Read Static electricity involves charges that build up and stay in the same place on an object. How could you
Electric Potential Energy and Voltage Textbook pages 270 279 Section 8.1 Summary Before You Read Static electricity involves charges that build up and stay in the same place on an object. How could you
7J Electrical circuits Multiple-choice main test
 For each question, circle the correct answer. Question 1 A switch turns off a torch by... A) breaking the circuit B) making the circuit C) shorting the circuit D) turning a series circuit into a parallel
For each question, circle the correct answer. Question 1 A switch turns off a torch by... A) breaking the circuit B) making the circuit C) shorting the circuit D) turning a series circuit into a parallel
Two small batteries can be put into a CD player to bring you the thundering
 Two small batteries can be put into a CD player to bring you the thundering bass and screaming guitar of your favourite band. Batteries can also provide power for digital cameras, wristwatches, and flashlights.
Two small batteries can be put into a CD player to bring you the thundering bass and screaming guitar of your favourite band. Batteries can also provide power for digital cameras, wristwatches, and flashlights.
Every Friday, Bart and Lisa meet their friends at an after-school club. They spend the afternoon playing Power Up, a game about batteries.
 Battery Lab NAME Every Friday, Bart and Lisa meet their friends at an after-school club. They spend the afternoon playing Power Up, a game about batteries. The object of the game is to arrange battery
Battery Lab NAME Every Friday, Bart and Lisa meet their friends at an after-school club. They spend the afternoon playing Power Up, a game about batteries. The object of the game is to arrange battery
1. Spare Change Flashlight
 . Spare Change Flashlight.. Battery introduction (Adapted from reference 0) Today, batteries are all around us. They power computers, phones, smoke detectors, etc. Batteries are critical not only for current
. Spare Change Flashlight.. Battery introduction (Adapted from reference 0) Today, batteries are all around us. They power computers, phones, smoke detectors, etc. Batteries are critical not only for current
Chapter 19: DC Circuits
 Chapter 19: DC Circuits EMF and Terminal Voltage Resistors in Series and in Parallel Kirchhoff s Rules EMFs in Series and in Parallel; Charging a Battery Capacitors in Series and in Parallel RC Circuits
Chapter 19: DC Circuits EMF and Terminal Voltage Resistors in Series and in Parallel Kirchhoff s Rules EMFs in Series and in Parallel; Charging a Battery Capacitors in Series and in Parallel RC Circuits
Electricity and Magnetism Module 2 Student Guide
 Concepts of this Module Introducing current and voltage Simple circuits Circuit diagrams Background Electricity and Magnetism Module 2 Student Guide When water flows through a garden hose, we can characterize
Concepts of this Module Introducing current and voltage Simple circuits Circuit diagrams Background Electricity and Magnetism Module 2 Student Guide When water flows through a garden hose, we can characterize
ELECTRICAL FUNDAMENTALS
 ELECTRICAL FUNDAMENTALS PLUG OCTOBER 27, 2016 ARINDERPAL MATHARU IDEAWORKS MOHAWK COLLEGE Introduction Goal: To provide you with the Electrical Fundamentals Early 1800s Timeline 21 ST Century Current Current
ELECTRICAL FUNDAMENTALS PLUG OCTOBER 27, 2016 ARINDERPAL MATHARU IDEAWORKS MOHAWK COLLEGE Introduction Goal: To provide you with the Electrical Fundamentals Early 1800s Timeline 21 ST Century Current Current
Using Electricity. Summary Notes. 1. From the Wall Socket Household appliances. Earth wire and safety.
 Using Electricity Summary Notes Section Content 1. From the Wall Socket Household appliances. Earth wire and safety. 2. Alternating and Direct Battery and transformer. Current Circuit diagrams. Current
Using Electricity Summary Notes Section Content 1. From the Wall Socket Household appliances. Earth wire and safety. 2. Alternating and Direct Battery and transformer. Current Circuit diagrams. Current
Unit P.2, P2.3. Currents in electric circuits E ½. F Fuel gauge indicator. Fuel tank. Ammeter. Float. Battery. Sliding contact. Pivot 12V.
 Currents in electric circuits 1. The diagram shows the fuel gauge assembly in a car. The sliding contact touches a coil of wire and moves over it. The sliding contact and the coil form a variable resistor.
Currents in electric circuits 1. The diagram shows the fuel gauge assembly in a car. The sliding contact touches a coil of wire and moves over it. The sliding contact and the coil form a variable resistor.
Two Cell Battery. 6. Masking tape 7. Wire cutters 8. Vinegar 9. Salt 10. Lemon Juice DC ammeter
 Your Activity Build a two-cell Wet battery Materials 1. 2 150 ml beakers 2. 2 pieces aluminum foil (8 X 12 inch) 3. 2 small paper cups, cut ¾ from bottom 4. 3 31.5 inch of non-insulated copper wire gauge
Your Activity Build a two-cell Wet battery Materials 1. 2 150 ml beakers 2. 2 pieces aluminum foil (8 X 12 inch) 3. 2 small paper cups, cut ¾ from bottom 4. 3 31.5 inch of non-insulated copper wire gauge
Energy Storage. Electrochemical Cells & Batteries
 Energy Storage These notes cover the different methods that can be employed to store energy in various forms. These notes cover the storage of Electrical Energy, Kinetic Energy, and Pneumatic Energy. There
Energy Storage These notes cover the different methods that can be employed to store energy in various forms. These notes cover the storage of Electrical Energy, Kinetic Energy, and Pneumatic Energy. There
Science Olympiad Shock Value ~ Basic Circuits and Schematics
 Science Olympiad Shock Value ~ Basic Circuits and Schematics Use a single D battery, a single bare wire and a light bulb. Find four different ways to light the light bulb using only a battery, one wire
Science Olympiad Shock Value ~ Basic Circuits and Schematics Use a single D battery, a single bare wire and a light bulb. Find four different ways to light the light bulb using only a battery, one wire
SECTION #1 - The experimental design
 Six Lemons in a Series/Parallel Charging a 4.4 Farad Capacitor, NO Load Resistor SECTION #1 - The experimental design 1a. The goal of this experiment is to see what voltage I can obtain with the lemon
Six Lemons in a Series/Parallel Charging a 4.4 Farad Capacitor, NO Load Resistor SECTION #1 - The experimental design 1a. The goal of this experiment is to see what voltage I can obtain with the lemon
Activity 3 Solutions: Electricity
 Activity 3 Solutions: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Activity 3 Solutions: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Measuring Voltage and Current
 Lab 5: Battery Lab Clean Up Report Due June 4, 28, in class At the end of the lab you must clean up your own mess failure to do this will result in the loss of points on your lab.. Throw away your lemons,
Lab 5: Battery Lab Clean Up Report Due June 4, 28, in class At the end of the lab you must clean up your own mess failure to do this will result in the loss of points on your lab.. Throw away your lemons,
SNC1D PHYSICS 4/6/2013. THE CHARACTERISTICS OF ELECTRICITY L Electrical Resistance (P ) Electrical Resistance. Electrical Resistance
 SNC1D PHYSICS THE CHARACTERISTICS OF ELECTRICITY L Electrical Resistance (P.441-443) Electrical Resistance Have you ever noticed that when you recharge your cellphone, MP3 player, or laptop computer, the
SNC1D PHYSICS THE CHARACTERISTICS OF ELECTRICITY L Electrical Resistance (P.441-443) Electrical Resistance Have you ever noticed that when you recharge your cellphone, MP3 player, or laptop computer, the
FORT RUCKER Environmental Document
 Approved by: Melissa Lowlavar/Misty Howell 1.0 PURPOSE This procedure defines the requirements for management of used batteries on Fort Rucker. Control of environmental procedures is addressed in procedure
Approved by: Melissa Lowlavar/Misty Howell 1.0 PURPOSE This procedure defines the requirements for management of used batteries on Fort Rucker. Control of environmental procedures is addressed in procedure
IE1206 Embedded Electronics
 IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le1 Le3 Le4 Le2 Ex1 Ex2 PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors KC1 LAB1 I, U, R, P, serial and parallell Pulsesensors, Menuprogram Start of programing task Kirchoffs
IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le1 Le3 Le4 Le2 Ex1 Ex2 PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors KC1 LAB1 I, U, R, P, serial and parallell Pulsesensors, Menuprogram Start of programing task Kirchoffs
Voltage and Current in Simple Circuits (Voltage Sensor, Current Sensor)
 68 Voltage and Current in Simple Circuits (Voltage Sensor, Current Sensor) E&M: Voltage and current Equipment List DataStudio file: 68 Simple Circuits.ds Qty Items Part Numbers 1 PASCO interface (for two
68 Voltage and Current in Simple Circuits (Voltage Sensor, Current Sensor) E&M: Voltage and current Equipment List DataStudio file: 68 Simple Circuits.ds Qty Items Part Numbers 1 PASCO interface (for two
PHYSICS MCQ (TERM-1) BOARD PAPERS
 GRADE: 10 PHYSICS MCQ (TERM-1) BOARD PAPERS 1 The number of division in ammeter of range 2A is 10 and voltmeter of range 5 V is 20. When the switch of the circuit given below is closed, ammeter reading
GRADE: 10 PHYSICS MCQ (TERM-1) BOARD PAPERS 1 The number of division in ammeter of range 2A is 10 and voltmeter of range 5 V is 20. When the switch of the circuit given below is closed, ammeter reading
Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above?
 Name: ( ) Class: Date: Electricity Exercises 1. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above? (1) Electrons flow from right to left through the bulb A. (2) Charges will be used
Name: ( ) Class: Date: Electricity Exercises 1. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the circuit above? (1) Electrons flow from right to left through the bulb A. (2) Charges will be used
ACTIVITY 1: Electric Circuit Interactions
 CYCLE 5 Developing Ideas ACTIVITY 1: Electric Circuit Interactions Purpose Many practical devices work because of electricity. In this first activity of the Cycle you will first focus your attention on
CYCLE 5 Developing Ideas ACTIVITY 1: Electric Circuit Interactions Purpose Many practical devices work because of electricity. In this first activity of the Cycle you will first focus your attention on
Academic Year
 EXCELLENCE INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL First Term, Work sheet (1) Grade (9) Academic Year 2014-2015 Subject: quantities Topics:- Static electricity - Eelectrical NAME: DATE: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: 1 - A circuit
EXCELLENCE INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL First Term, Work sheet (1) Grade (9) Academic Year 2014-2015 Subject: quantities Topics:- Static electricity - Eelectrical NAME: DATE: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS: 1 - A circuit
9.2. The Power of Electricity. Did You Know? Words to Know
 9.2 The Power of Electricity Electrical power is the rate at which electric potential energy is being transformed. One joule (J) of electric potential energy transformed in one second is one watt (W) of
9.2 The Power of Electricity Electrical power is the rate at which electric potential energy is being transformed. One joule (J) of electric potential energy transformed in one second is one watt (W) of
A Practical Exercise Name: Section:
 Introduction to s Updated 7 AUG 06 A Practical Exercise Name: Section: I. Purpose.. Introduce the Hampden DC machine. Introduce the Hampden laboratory bench electrical power supplies 3. Introduce basic
Introduction to s Updated 7 AUG 06 A Practical Exercise Name: Section: I. Purpose.. Introduce the Hampden DC machine. Introduce the Hampden laboratory bench electrical power supplies 3. Introduce basic
Technical Workshop: Electrical December 3, 2016
 Technical Workshop: Electrical December 3, 2016 ELECTRICAL: CIRCUITS Key terms we will be using today: Voltage (V): The difference in electrical potential at one point in a circuit in relation to another.
Technical Workshop: Electrical December 3, 2016 ELECTRICAL: CIRCUITS Key terms we will be using today: Voltage (V): The difference in electrical potential at one point in a circuit in relation to another.
Phase 1 Workshop Home Study Guide
 Phase 1 Workshop Home Study Guide Vehicle Electrical-Electronics Troubleshooting Training Written and Developed by Vince Fischelli Director of Training Veejer Enterprises Inc. / Garland, Texas U.S.A. Phone:
Phase 1 Workshop Home Study Guide Vehicle Electrical-Electronics Troubleshooting Training Written and Developed by Vince Fischelli Director of Training Veejer Enterprises Inc. / Garland, Texas U.S.A. Phone:
All Worn Out! Measure the voltage of batteries as they discharge. Predict how different size batteries will behave when being discharged.
 All Worn Out! Computer 43 Have you ever wondered why some flashlights use small batteries and some use big ones? What difference does it make? Do larger batteries make the light brighter? Will the size
All Worn Out! Computer 43 Have you ever wondered why some flashlights use small batteries and some use big ones? What difference does it make? Do larger batteries make the light brighter? Will the size
ENVIRONMENTAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE CONTRIBUTIONS BATTERIES Portable - Industrial - Automotive
 ENVIRONMENTAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE CONTRIBUTIONS BATTERIES Portable - Industrial - Automotive valid from 1/1/2019 Button cells Button cells - 0,063 /unit Lead Lead Lithium rechargeable Lithium rechargeable
ENVIRONMENTAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE CONTRIBUTIONS BATTERIES Portable - Industrial - Automotive valid from 1/1/2019 Button cells Button cells - 0,063 /unit Lead Lead Lithium rechargeable Lithium rechargeable
Basic Circuits Notes- THEORY. An electrical circuit is a closed loop conducting path in which electrical current flows
 Basic Circuits Notes- THEORY NAME: An electrical circuit is a closed loop conducting path in which electrical current flows Now how does a circuit work? In order to get the water flowing, you d need a
Basic Circuits Notes- THEORY NAME: An electrical circuit is a closed loop conducting path in which electrical current flows Now how does a circuit work? In order to get the water flowing, you d need a
Batteries may be hazardous to human health and the environment if not properly handled.
 Environmental Standard Operating Procedure (Approved by Jonathan Aunger) Document Owner: Environmental Division File Name: BM-ESOP 02H003v3 Effective Date: 9 December 2010 Revised: 13 April 2015 Title:
Environmental Standard Operating Procedure (Approved by Jonathan Aunger) Document Owner: Environmental Division File Name: BM-ESOP 02H003v3 Effective Date: 9 December 2010 Revised: 13 April 2015 Title:
ELECTRIC CURRENT. Name(s)
 Name(s) ELECTRIC CURRT The primary purpose of this activity is to decide upon a model for electric current. As is the case for all scientific models, your electricity model should be able to explain observed
Name(s) ELECTRIC CURRT The primary purpose of this activity is to decide upon a model for electric current. As is the case for all scientific models, your electricity model should be able to explain observed
Flashlights. Flashlights 2. Flashlights 4. Flashlights 3. Flashlights 5. Flashlights 6
 Flashlights 1 Flashlights 2 Observations about Flashlights Flashlights You turn them on and off with switches Brighter flashlights usually have more batteries Flashlights grow dimmer as their batteries
Flashlights 1 Flashlights 2 Observations about Flashlights Flashlights You turn them on and off with switches Brighter flashlights usually have more batteries Flashlights grow dimmer as their batteries
Understanding the Battery
 Understanding the Battery Materials Needed For this lesson, you will need the following materials: Student Manual Dummy Battery Visuals Understanding a Battery training video Battery Application Guide
Understanding the Battery Materials Needed For this lesson, you will need the following materials: Student Manual Dummy Battery Visuals Understanding a Battery training video Battery Application Guide
Energy Conversions Questions CfE
 Energy Conversions Questions CfE 1) A 0.02kg mass is held at a height of 0.8m above the ground. a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in the mass before it is dropped. b) i) State the
Energy Conversions Questions CfE 1) A 0.02kg mass is held at a height of 0.8m above the ground. a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy stored in the mass before it is dropped. b) i) State the
1103 Period 16: Electrical Resistance and Joule Heating
 Name Section 1103 Period 16: Electrical Resistance and Joule Heating Activity 16.1: What Does the Electrical Resistance of a Wire Depend Upon? 1) Measuring resistance a) Resistor length, L Use a multimeter
Name Section 1103 Period 16: Electrical Resistance and Joule Heating Activity 16.1: What Does the Electrical Resistance of a Wire Depend Upon? 1) Measuring resistance a) Resistor length, L Use a multimeter
Lab # 4 Parallel Circuits
 Lab # 4 Parallel Circuits Name(s) Obtain an Electro-Trainer and wire it exactly as shown (Be sure to use the 100 ohm resistor) 1) Record the volt drop and current flow for the Switch, the Resistor and
Lab # 4 Parallel Circuits Name(s) Obtain an Electro-Trainer and wire it exactly as shown (Be sure to use the 100 ohm resistor) 1) Record the volt drop and current flow for the Switch, the Resistor and
Activity 3: Electricity
 Name Section Activity 3: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Name Section Activity 3: Electricity 3.1 Electric Charge, Voltage and Energy 1) Electric charge Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates electric charge. a) Describe what happens
Lipo Battery Charging & Safety Guide
 Lipo Battery Charging & Safety Guide Lithium Polymer or LiPo batteries are a great new way of storing energy for portable devices from cell phones to RC helicopters. They re great because they can store
Lipo Battery Charging & Safety Guide Lithium Polymer or LiPo batteries are a great new way of storing energy for portable devices from cell phones to RC helicopters. They re great because they can store
CHAPTER 19 DC Circuits Units
 CHAPTER 19 DC Circuits Units EMF and Terminal Voltage Resistors in Series and in Parallel Kirchhoff s Rules EMFs in Series and in Parallel; Charging a Battery Circuits Containing Capacitors in Series and
CHAPTER 19 DC Circuits Units EMF and Terminal Voltage Resistors in Series and in Parallel Kirchhoff s Rules EMFs in Series and in Parallel; Charging a Battery Circuits Containing Capacitors in Series and
Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card.
 THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
THE MOTOR EFFECT Q1. Figure 1 shows a straight wire passing through a piece of card. A current (I) is passing down through the wire. Figure 1 (a) Describe how you could show that a magnetic field has been
Incandescent Lightbulb. Electricity passes through a tungsten (W) filament, which in turn glows white hot (4500F).
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Incandescent Lightbulb Electricity passes through a tungsten (W) filament, which in turn glows white hot (4500F). Very inefficient: 90% of the electrical energy is lost
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Incandescent Lightbulb Electricity passes through a tungsten (W) filament, which in turn glows white hot (4500F). Very inefficient: 90% of the electrical energy is lost
Yaskawa Electric America Unit Troubleshooting Manual Section One: Introduction & Checks Without Power GPD 506/P5 and GPD 515/G5 (0.
 Yaskawa Electric America Unit Troubleshooting Manual Section One: Introduction & Checks Without Power GPD 506/P5 and GPD 515/G5 (0.4 ~ 160kW) Page 1 Introduction This manual is divided into three sections:
Yaskawa Electric America Unit Troubleshooting Manual Section One: Introduction & Checks Without Power GPD 506/P5 and GPD 515/G5 (0.4 ~ 160kW) Page 1 Introduction This manual is divided into three sections:
Figure 1: Graphs Showing the Energy and Power Consumed by Two Systems on an ROV during a Mission
 Power Systems 3 Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics III Notes primarily from Underwater Robotics Science Design and Fabrication, an excellent book for the design, fabrication, and operation
Power Systems 3 Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics III Notes primarily from Underwater Robotics Science Design and Fabrication, an excellent book for the design, fabrication, and operation
Inspecting and Cleaning the Battery Cables and Connections
 JOB SHEET 42 Inspecting and Cleaning the Battery Cables and Connections Name: -------------------------- Station: --------------------- Date: NATEF Correlation This Job Sheet addresses the following NATEF
JOB SHEET 42 Inspecting and Cleaning the Battery Cables and Connections Name: -------------------------- Station: --------------------- Date: NATEF Correlation This Job Sheet addresses the following NATEF
Section 6 HOW ARE VALUES OF CIRCUIT VARIABLES MEASURED?
 Section 6 HOW RE VUES OF CIRCUIT VRIBES MESURED? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow
Section 6 HOW RE VUES OF CIRCUIT VRIBES MESURED? INTRODUCTION People who use electric circuits for practical purposes often need to measure quantitative values of electric pressure difference and flow
Name Period. (c) Now replace the round bulb(s) with long bulb(s). How does the brightness change?
 Name Period P Phys 1 Discovery Lesson Electric Circuits 2.1 Experiment: Charge Flow Strength & Resistors circuit is an unbroken loop of conductors. Charge (q) can flow continuously in a circuit. If an
Name Period P Phys 1 Discovery Lesson Electric Circuits 2.1 Experiment: Charge Flow Strength & Resistors circuit is an unbroken loop of conductors. Charge (q) can flow continuously in a circuit. If an
Electric Circuits. Lab. FCJJ 16 - Solar Hydrogen Science Kit. Goals. Background
 Goals Build a complete circuit with a solar panel Power a motor and electrolyzer with a solar panel Measure voltage and amperage in different circuits Background Electricity has fundamentally changed the
Goals Build a complete circuit with a solar panel Power a motor and electrolyzer with a solar panel Measure voltage and amperage in different circuits Background Electricity has fundamentally changed the
Electricity MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 Electricity MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Electric charges Atoms and molecules can have electrical charges. These are caused by electrons and protons. Electrons are negatively charged. Protons are positively
Electricity MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Electric charges Atoms and molecules can have electrical charges. These are caused by electrons and protons. Electrons are negatively charged. Protons are positively
Laboratory 2 Electronics Engineering 1270
 Laboratory 2 Electronics Engineering 1270 DC Test Equipment Purpose: This lab will introduce many of the fundamental test equipment and procedures used for verifying the operations of electrical circuits.
Laboratory 2 Electronics Engineering 1270 DC Test Equipment Purpose: This lab will introduce many of the fundamental test equipment and procedures used for verifying the operations of electrical circuits.
8.2 Electric Circuits and Electrical Power
 8.2 Electric Circuits and Electrical Power Every electrical device uses current to carry energy and voltage to push the current. How are electrical devices designed? What types of parts are used in an
8.2 Electric Circuits and Electrical Power Every electrical device uses current to carry energy and voltage to push the current. How are electrical devices designed? What types of parts are used in an
Name Date Period. MATERIALS: Light bulb Battery Wires (2) Light socket Switch Penny
 Name Date Period Lab: Electricity and Circuits CHAPTER 34: CURRENT ELECTRICITY BACKGROUND: Just as water is the flow of H 2 O molecules, electric current is the flow of charged particles. In circuits of
Name Date Period Lab: Electricity and Circuits CHAPTER 34: CURRENT ELECTRICITY BACKGROUND: Just as water is the flow of H 2 O molecules, electric current is the flow of charged particles. In circuits of
PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I)
 PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I) 1 A student walks across a thick carpet and becomes positively charged as his shoes rub on the carpet. When he touches the metal handle of a door, negative
PURE PHYSICS ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM (PART I) 1 A student walks across a thick carpet and becomes positively charged as his shoes rub on the carpet. When he touches the metal handle of a door, negative
Laboratory 5: Electric Circuits Prelab
 Phys 132L Fall 2018 Laboratory 5: Electric Circuits Prelab 1 Current and moving charges Atypical currentinanelectronic devicemightbe5.0 10 3 A.Determinethenumber of electrons that pass through the device
Phys 132L Fall 2018 Laboratory 5: Electric Circuits Prelab 1 Current and moving charges Atypical currentinanelectronic devicemightbe5.0 10 3 A.Determinethenumber of electrons that pass through the device
Batteries. Eric Harris, Colin Hepton, Steven Hodgson, Martin Holland, Michael Hudson and Jonathan Ridyard. 14/11/2005
 Batteries Eric Harris, Colin Hepton, Steven Hodgson, Martin Holland, Michael Hudson and Jonathan Ridyard. 14/11/2005 A Brief History Alessandro Volta. Voltaic Pile. 1800s. Silver and Zinc Plates separated
Batteries Eric Harris, Colin Hepton, Steven Hodgson, Martin Holland, Michael Hudson and Jonathan Ridyard. 14/11/2005 A Brief History Alessandro Volta. Voltaic Pile. 1800s. Silver and Zinc Plates separated
Introduction to Electricity & Electrical Current
 Introduction to Electricity & Electrical Current Physical Science Georgia Performance Standards: SPS10a. Investigate static electricity in terms of friction, induction, and conduction. SPS10b. Explain
Introduction to Electricity & Electrical Current Physical Science Georgia Performance Standards: SPS10a. Investigate static electricity in terms of friction, induction, and conduction. SPS10b. Explain
JSUNIL TUTORIAL PUNJABI COLONY GALI 01
 10 th Electricity Numerical 1. The current passing through a room heater has been halved. What will happen to the heat produced by it? 2. An electric iron of resistance 20 ohm draws a current of 5 amperes.
10 th Electricity Numerical 1. The current passing through a room heater has been halved. What will happen to the heat produced by it? 2. An electric iron of resistance 20 ohm draws a current of 5 amperes.
2. Explore your model. Locate and identify the gears. Watch the gear mechanism in operation as you turn the crank.
 Experiment #1 79318 Using a Spur Gear System in a Crank Fan Objectives: Understand and describe the transfer of motion through a spur gear system and investigate the relationship between gear size, speed
Experiment #1 79318 Using a Spur Gear System in a Crank Fan Objectives: Understand and describe the transfer of motion through a spur gear system and investigate the relationship between gear size, speed
Searching for Patterns in Series and Parallel Circuits
 Searching for Patterns in Series and Parallel Circuits Use the Circuit Construction Kit on phet.colorado.edu (DC Circuits only) to build the following circuits. fter building each circuit, use the ammeter
Searching for Patterns in Series and Parallel Circuits Use the Circuit Construction Kit on phet.colorado.edu (DC Circuits only) to build the following circuits. fter building each circuit, use the ammeter
7.9.1 Circuits. 123 minutes. 170 marks. Page 1 of 56
 7.9.1 Circuits 123 minutes 170 marks Page 1 of 56 ## The diagram shows a motor, connected to a 240 V supply, driving a water pump. The ammeter reads 5.0 A. (a) How much charge flows through the motor in
7.9.1 Circuits 123 minutes 170 marks Page 1 of 56 ## The diagram shows a motor, connected to a 240 V supply, driving a water pump. The ammeter reads 5.0 A. (a) How much charge flows through the motor in
Based on results from TIMSS Key. bulb. bulb. switch. wir. battery. wir. switch. Lesson plan on investigative science. wire.
 bulb Based on results from TIMSS 2015 Key battery Key ba bu tte switch sw h itc bulb e wir battery switch wire bat sw Lesson plan on investigative science Electricity wir Electricity Pupils performed less
bulb Based on results from TIMSS 2015 Key battery Key ba bu tte switch sw h itc bulb e wir battery switch wire bat sw Lesson plan on investigative science Electricity wir Electricity Pupils performed less
Air Washington Electronics Direct Current
 11 Batteries This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/. Air Washington is an equal
11 Batteries This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/. Air Washington is an equal
Chapter Assessment Use with Chapter 22.
 Date Period 22 Use with Chapter 22. Current Electricity Understanding Concepts Part A Use each of the following terms once to complete the statements below. ampere electric current potential difference
Date Period 22 Use with Chapter 22. Current Electricity Understanding Concepts Part A Use each of the following terms once to complete the statements below. ampere electric current potential difference
Electric Current. Electric current: is the movement of electrons from a negative terminal back to the positive terminal of a battery.
 Electric Current Electric current: is the movement of electrons from a negative terminal back to the positive terminal of a battery. Electric Current Electrons flow from regions of high Potential Energy
Electric Current Electric current: is the movement of electrons from a negative terminal back to the positive terminal of a battery. Electric Current Electrons flow from regions of high Potential Energy
