Preface...x Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals
|
|
|
- Kristopher Tyler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Preface...x Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals Unit 1 Matter...3 Introduction Matter Atomic Theory Law of Electrical Charges Law of Atomic Charges...5 Negative Atomic Charge...5 Positive Atomic Charge Charged Material (Static Charge)...5 Static Voltage...6 Reducing Static Charge Neutralizing a Charge Lightning Lightning Protection...7 Unit 1 Summary...9 Unit 1 Conclusion...10 Unit 1 Practice Questions...11 Unit 2 Electron Theory...15 Introduction Electron Orbits Valence Electrons Freeing Electrons from an Atom Conductors Insulators Semiconductors Atomic Bonding Compounds...17 Unit 2 Summary...19 Unit 2 Conclusion...20 Unit 2 Practice Questions...21 Unit 3 Magnetism...23 Introduction The Natural Magnet Magnetic Polarities Magnetic Compass Magnetic Molecule Magnetic Properties How to Magnetize Iron Permanent and Temporary Magnets Demagnetizing Magnets Magnetic Lines of Force Magnetic Materials Law of Attraction and Repulsion Retentivity Permeability...26 Unit 3 Summary...27 Unit 3 Conclusion...28 Unit 3 Practice Questions...29 Unit 4 Electricity...33 Introduction Electrical Current Flow (Electricity) Electricity...34 Chemical Activity (Electrochemistry)...34 Magnetism (Magnetoelectricity)...34 Light (Photoelectricity)...35 Thermo Energy (Thermoelectricity)...36 Pressure (Piezoelectricity) Useful Purposes of Electricity...37 Electrochemistry...37 Electromagnetism...37 Heat (Resistance)...38 Illumination (Lighting) Danger of Electricity...39 Understanding Electrical Shock Hazard...39 What Determines the Severity of Electrical Shock?...39 Clearing a Ground Fault...40 Fire...41 Electrical Arc Blast National Electrical Code...42 Unit 4 Summary...43 Unit 4 Conclusion...45 Unit 4 Practice Questions...46 Unit 5 Electromagnetism...49 Introduction Electromagnetism in a Wire Field Intensity Field Interaction Field Interaction of Loops...50 iv iv
2 5.5 Electromagnetism in a Coil Magnetic Core Ampere and Turns...51 Unit 5 Summary...52 Unit 5 Conclusion...53 Unit 5 Practice Questions...54 Unit 6 Uses of Electromagnetism...57 Introduction Basic Electric Meters...57 Voltmeter...58 DC Voltmeter...58 DC Ammeter...58 Clamp-on AC Ammeter...59 Ohmmeters...60 Wheatstone Bridge...60 Megohmmeter Electric Motor...60 Motor Components...60 Understanding Motor Motion Electrical Generator...62 DC Generator...62 AC Generator Electromagnetic Relay...63 Contacts...63 Holding Relay...64 Unit 6 Summary...65 Unit 6 Conclusion...67 Unit 6 Practice Questions...68 Chapter 1 Final Exam...70 Chapter 2 Basic Electricity Unit 7 The Electrical Circuit...77 Introduction The Electrical Circuit Electron Current Flow Theory Conventional Current Flow Theory Voltage (Pressure) Resistance...79 Conductor Resistance Electric Current Power Electrical Formulas...80 Unit 7 Summary...81 Unit 7 Conclusion...82 Unit 7 Practice Questions...83 Unit 8 Math...85 Introduction Whole Numbers Decimal Fractions Percentages Multiplier Percent Increase Reciprocals Squaring a Number Square Root Volume Kilo Rounding Off Parentheses Testing Your Answer for Reasonableness...91 Unit 8 Summary...92 Unit 8 Conclusion...93 Unit 8 Practice Questions...94 Unit 9 Electrical Formulas...99 Introduction Electrical Circuit Power Source Direct Current Alternating Current Conductance Circuit Resistance Ohm s Law Ohm s Law and Alternating Current Direct Current Alternating Current Ohm s Law Formula Circle PIE Formula Circle Formula Wheel Using the Formula Wheel Power Losses of Conductors Cost of Power Power Changes with the Square of the Voltage Power Example at 230V Power Example at 208V Power Example at 240V Unit 9 Summary Unit 9 Conclusion Unit 9 Practice Questions Chapter 2 Final Exam v v
3 Chapter 3 Basic Electrical Circuits Unit 10 Series Circuits Introduction Practical Uses of the Series Circuit Lighting Control Circuit Signaling Circuit Internal Equipment Wiring Understanding Series Calculations Resistance Voltage Kirchoff s Voltage Law Kirchoff s Current Law Power Series Circuit Calculations Power Calculations Variations Series Circuit Notes Series-Connected Power Supplies Unit 10 Summary Unit 10 Conclusion Unit 10 Practice Questions Unit 11 Parallel Circuits Introduction Practical Uses of the Parallel Circuit Receptacle Lighting Other Uses Understanding Parallel Calculations Voltage Kirchoff s Current Law Power Circuit Resistance Equal Resistance Method Product-Over-Sum Method Reciprocal Method Parallel Circuit Notes Parallel-Connected Power Supplies Unit 11 Summary Unit 11 Conclusion Unit 11 Practice Questions Unit 12 Series-Parallel Circuits Introduction Review of Series and Parallel Circuits Series Circuit Review Parallel Circuit Review Working Series-Parallel Circuits Voltage Unit 12 Summary Unit 12 Conclusion Unit 12 Practice Questions Unit 13 Multiwire Circuits Introduction Neutral Conductor Grounded Conductor Current Flow on the Grounded (Neutral) Conductor Wire Circuit Wire, 120/240V, Single-Phase Circuit Balanced Systems Unbalanced Current Wire, 120/240V, Single-Phase Circuit Wire Circuit from a 4-wire, Three-Phase System Wire, Three-Phase Circuit Multiwire Branch Circuit Wire Circuit Voltage Drop Multiwire Circuit Voltage Drop Dangers of Multiwire Circuits Fire Hazard Destruction of Equipment as Well as Fire Hazard NEC Requirements Unit 13 Summary Unit 13 Conclusion Unit 13 Practice Questions Chapter 3 Final Exam Chapter 4 Electrical Systems and Protection Unit 14 The Electrical System Introduction Current Flow Utility Neutral Current Path Multipoint Neutral Ground Utility Ground-Fault Current Path Premises Neutral Current Path Single Point Neutral Bond Premises Ground-Fault Current Path Earth as Ground Fault Path for Systems 600V or Less vi vi
4 14.6 Utility High-Voltage Transmission Lines Conductor Voltage Drop Conductor Power Loss Current Reducing Voltage Drop and Power Loss kv Transmission Line Generating Plants Step-Up Substation at Generating Plant Transmission Line Step-Down Substation Primary Distribution Feeders Distribution Transformer Secondary Distribution Line Unit 14 Summary Unit 14 Conclusion Unit 14 Practice Questions Unit 15 Protection Devices Introduction Part A Overcurrent Protection Devices Overcurrent Protection Overload Ground Fault Short Circuit Clearing Faults Time Current Curves Remove Dangerous Touch Voltage Overcurrent Protection Device Types Fuse Construction Overload Protection Short-Circuit and Ground-Fault Protection Circuit Breaker Trip Elements Thermal Trip Element Magnetic Trip Element Circuit Breaker Types Inverse-Time Adjustable-Trip Instantaneous-Trip Available Short-Circuit Current Interrupting Rating Short-Circuit Current Rating Current-Limiting Protection Part B Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupters How a GFCI Works Neutral-to-Case Detection Line-to-Neutral Shock Hazard GFCI Fails Circuit Remains Energized GFCI Test Button Part C Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupter Arcing Definition Series Versus Parallel Arc Series Arc Parallel Arc AFCI and the NEC AFCI How They Operate Part D Ground-Fault Protection of Equipment Ground-Fault Protection of Equipment Definition Unit 15 Summary Unit 15 Conclusion Unit 15 Practice Questions Chapter 4 Final Exam Chapter 5 Alternating Current Unit 16 Alternating Current Introduction Current Flow Why Alternating Current is Used How Alternating Current is Produced AC Generator Waveform Direct-Current Waveform Alternating-Current Waveform Sine Wave Sinusoidal Waveform Nonsinusoidal Waveform Nonsymmetrical Waveform Frequency Phase Degrees Lead or Lag Leading Lagging Values of Alternating Current Instantaneous Value Peak Value Effective Value RMS Value Unit 16 Summary Unit 16 Conclusion Unit 16 Practice Questions vii vii
5 Unit 17 Capacitance Introduction Capacitor Current Flow Charged Capacitor Electrical Field Discharging a Capacitor Determining Capacitance Plate Distance Surface Area Dielectric Strength Uses of Capacitors Electronic Power Supplies Phase Relationship Unit 17 Summary Unit 17 Conclusion Unit 17 Practice Questions Unit 18 Induction Introduction Self-Induction Induced Voltage and Applied Current Opposes Current Flow Aids the Current Flow Conductor AC Resistance Eddy Currents Skin Effect Impedance Conductor Shape Current Winding Frequency Magnetic Cores Core Material Core Length Core Area Self-Induced and Applied Voltage Current Flow Inductive Reactance Phase Relationship Uses of Induction Unit 18 Summary Unit 18 Conclusion Unit 18 Practice Questions Unit 19 Power Factor and Efficiency Introduction Inductors and Capacitors Part A Power Factor Apparent Power (Volt-Ampere) True Power (Watts) Direct Current Alternating Current Power Factor Unity Power Factor Power Factor Formulas Cost of True Power Effects of Power Factor Part B Efficiency Efficiency Efficiency Formulas Unit 19 Summary Unit 19 Conclusion Unit 19 Practice Questions Chapter 5 Final Exam Chapter 6 Motors, Generators, and Transformers Unit 20 Motors Introduction Part A Motor Basics Motor Principles Stator Rotor Dual-Voltage AC Motors Motor Horsepower Rating Motor Current Ratings Motor Full-Load Ampere (FLA) Rating Actual Motor Current Motor Full-Load Current (FLC) Rating Calculating Motor FLA Single-Phase Three-Phase Motor-Starting Current Motor-Running Current Motor Locked-Rotor Current (LRC) Motor Overload Protection NEC Requirement Part B Direct-Current Motors Direct-Current Motor Principles Direct-Current Motor Types Shunt-Wound DC Motor Series-Wound DC Motor viii viii
6 20.12 Reversing the Rotation of a DC Motor Part C Alternating-Current Motors AC Induction Motor Alternating-Current Motor Types Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor Synchronous Motor Wound-Rotor Motor Universal Motor Reversing the Rotation of an AC Motor Unit 20 Summary Unit 20 Conclusion Unit 20 Practice Questions Unit 21 Generators Introduction Direct-Current Generator Excitation Current Alternating-Current Generator Three-Phase Generators Unit 21 Summary Unit 21 Conclusion Unit 21 Practice Questions Unit 22 Transformers Introduction Transformer Basics Primary Versus Secondary Mutual Induction Secondary Induced Voltage Autotransformers Step-Down Transformers Step-Up Transformers Power Losses Conductor Resistance Loss Flux Leakage Loss Eddy Currents Hysteresis Losses Harmonic Current Efficiency Transformer Turns Ratio Transformer kva Rating Current Flow Current Rating Unit 22 Summary Unit 22 Conclusion Unit 22 - Practice Questions Chapter 6 Final Exam Basic Electrical Theory Final Exam Basic Electrical Theory Final Conclusion Annex A Grounding and Bonding Introduction Understanding the Basics of Electrical Systems Understanding Electrical Shock Hazard What Determines the Severity of Electrical Shock Clearing a Ground Fault Why Grounding is Often Difficult to Understand Scope Definitions Other Code Sections General Requirements for Grounding and Bonding (A) Summary Objectionable (Neutral) Current Index ix ix
7 Article 90 Introduction Purpose of the NEC Scope of the NEC Code Arrangement Enforcement Mandatory Requirements and Explanatory Material Formal Interpretations Examination of Equipment for Product Safety Units of Measurement...7 Article 90 Questions...8 Chapter 1 General...9 Article 100 Definitions...11 Article 110 Requirements for Electrical Installations...31 Part I. General Requirements Scope Approval of Equipment Examination, Identification, Installation, and Use of Equipment Voltages Copper Conductors Conductor Sizes Conductor Insulation Suitable Wiring Methods Interrupting Protection Rating Short-Circuit Current Rating Deteriorating Agents Mechanical Execution of Work Mounting and Cooling of Equipment Conductor Termination High-Leg Conductor Identification Flash Protection Warning Manufacturer s Markings Identification of Disconnecting Means...43 Part II. 600V, Nominal or Less Spaces About Electrical Equipment Guarding...48 Article 110 Questions...49 Chapter 2 Wiring and Protection...51 Article 200 Use and Identification of Grounded Neutral Conductor Scope Identification of the Grounded Neutral Conductor Use of White or Gray Color Terminal Identification Identification of Terminals Polarity...57 Article 200 Questions...58 Article 210 Branch Circuits...59 Part I. General Provisions Scope Other Articles Branch-Circuit Rating Multiwire Branch Circuits Identification for Branch Circuits Branch-Circuit Voltage Limitation Branch-Circuit Receptacle Requirements GFCI-Protected Receptacles Branch-Circuits Required Arc-Fault Circuit-Interrupter (AFCI) Protection Guest Rooms and Guest Suites...71 Part II. Branch-Circuit Ratings Conductor Sizing Overcurrent Protection Outlet Device Rating Permissible Loads Common Area Branch Circuits...75 vi
8 Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume 1 Part III. Required Outlets General Dwelling Unit Receptacle Outlet Requirements Receptacles in Guest Rooms or Guest Suites for Hotels and Motels Heating, Air-Conditioning, and Refrigeration Equipment (HACR) Lighting Outlet Requirements...82 Article 210 Questions...85 Article 215 Feeders Scope Minimum Rating Overcurrent Protection High-Leg Conductor Identification Ground-Fault Protection of Equipment Identification for Feeders...89 Article 215 Questions...91 Article 220 Branch-Circuit, Feeder, and Service Calculations...93 Part I. General Scope Application of Other Articles Calculations...94 Part II. Branch-Circuit Load Calculations General Lighting Other Loads All Occupancies Maximum Load on a Branch Circuit...99 Part III. Feeder and Service Calculations General General Lighting Demand Factors Commercial Show Window and Track Lighting Load Commercial Receptacle Load Motor Load Fixed Electric Space-Heating Load Dwelling Unit Small-Appliance and Laundry Load Dwelling Unit Appliance Load Dwelling Unit Electric Clothes Dryer Load Dwelling Unit Electric Ranges and Cooking Appliances Commercial Kitchen Equipment Load Noncoincident Loads Feeder/Service Neutral Unbalanced Load Part IV. Optional Calculations for Computing Feeder and Service Loads Dwelling Unit Optional Load Calculation Table of Contents Multifamily Optional Load Calculation Optional Calculation Two Dwelling Units Article 220 Questions Article 225 Outside Wiring Part I General Requirements Scope Other Articles Minimum Size Conductors Luminaires Installed Outdoors Supports Over Buildings Attachment Masts as Support Clearances Clearances from Buildings Raceways on Exterior Surfaces of Buildings or Other Structures Trees for Conductor Support Part II. More Than One Building or Structure Number of Supplies Disconnecting Means Disconnect Location Maximum Number of Disconnects Grouping of Disconnects Access to Occupants Identified as Suitable for Service Equipment Identification of Multiple Supplies Disconnect Construction Rating of Disconnecting Means Article 225 Questions Article 230 Services Part I. General Scope Number of Services Pass Through a Building or Structure Conductors Considered Outside a Building Service Conductors Separate from Other Conductors Raceway Seals Clearance from Building Openings Vegetation as Support Part II. Overhead Service-Drop Conductors Size and Rating Clearances Point of Attachment Means of Attachment Service Masts Used as Supports vii
9 Table of Contents Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume 1 Part III. Underground Service-Lateral Conductors Size and Rating Protection Against Damage Part IV. Service Entrance Conductors Number of Service-Entrance Conductor Sets Size and Rating Wiring Methods Cable Trays Spliced Conductors Protection Against Physical Damage Aboveground Service Cable Supports Connections at Weatherheads High-Leg Identification Part V. Service Equipment General Identified as Suitable for Service Equipment Part VI. Service Equipment Disconnecting Means General Number of Disconnects Grouping of Disconnects Manual or Power Operated Rating of Disconnect Equipment Connected to the Supply Side of the Service Disconnect Part VII. Service Equipment Overcurrent Protection Overload Protection Required Ground-Fault Protection of Equipment Article 230 Questions Article 240 Overcurrent Protection Part I. General Scope Definitions Protection of Equipment Protection of Conductors Protection of Flexible Cords and Fixture Wires Standard Ampere Ratings Supplementary Overcurrent Protection Ground-Fault Protection of Equipment Part II. Location Ungrounded Conductors Overcurrent Protection Location in Circuit Location of Overcurrent Protection Devices Part III. Enclosures Damp or Wet Locations Vertical Position Part V. Plug Fuses, Fuseholders, and Adapters Edison-Base Fuse Type S Fuses Type S Fuses, Adapters, and Fuseholders Part VI. Cartridge Fuses and Fuseholders General Classification Part VII. Circuit Breakers Method of Operation Indicating Markings Applications Article 240 Questions Article 250 Grounding and Bonding Part I. General Scope Definitions General Requirements for Grounding and Bonding Objectionable Current Termination of Grounding and Bonding Conductors Protection of Fittings Clean Surface Part II. System Grounding and Bonding Systems Required to be Grounded and Bonded Grounding and Bonding at Service Equipment Main Bonding Jumper and System Bonding Jumper Grounding and Bonding of Separately Derived AC Systems Buildings or Structures Supplied by a Feeder or Branch Circuit Generators Portable and Vehicle-Mounted High-Impedance Grounded Neutral Systems Part III. Grounding Electrode System and Grounding Electrode Conductor Grounding Electrode System Grounding (Earthing) Electrodes Installation of Grounding Electrode System Supplementary Electrodes Resistance of Ground Rod Electrode Common Grounding (Earthing) Electrode Lightning Protection System Grounding (Earthing) Electrode Grounding Electrode Conductor Material Grounding Electrode Conductor Installation viii
10 Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume 1 Table of Contents Grounding Electrode Conductor Size Grounding Electrode Conductor Termination Grounding Electrode Conductor Termination Fitting Part IV. Grounding (Bonding) of Enclosure, Raceway, and Service Cable Service Enclosures Other Enclosures Part V. Bonding Service Bonding Grounding (Bonding) of Communications Systems Bonding Other Enclosures Bonding 277V/480V Bonding Hazardous (Classified) Locations Bonding Jumper Bonding of Piping Systems and Exposed Structural Metal Lightning Protection System Part VI. Equipment Grounding (Bonding) and Equipment Grounding (Bonding) Conductors Fixed Equipment Connected by Permanent Wiring Methods General Fixed Equipment Connected by Permanent Wiring Methods Specific Equipment Connected by Cord and Plug Types of Equipment Grounding (Bonding) Conductors Identification of Equipment Grounding (Bonding) Conductor Sizing Equipment Grounding (Bonding) Conductor Identification of Wiring Device Terminals Part VII. Methods of Equipment Grounding (Bonding) Equipment Grounding (Bonding) Conductor Connections Grounding (Bonding) Fixed Equipment Grounding (Bonding) Cord-and-Plug Connected Equipment Grounding (Bonding) Ranges, Ovens, and Clothes Dryers Use of Grounded Neutral Conductor for Equipment Grounding (Bonding) Connecting Receptacle Grounding Terminal to Box Continuity and Attachment of Equipment Grounding (Bonding) Conductors to Boxes Article 250 Questions Article 280 Surge Arresters Part I. General Scope Definition Number Required Surge Arrester Selection Part II. Installation Location Routing of Conductors Part III. Connecting Surge Arresters Installed at Services of Less Than 1,000V Installed on the Load Side of Services of Less Than 1,000V Article 280 Questions Article 285 Transient Voltage Surge Suppressors (TVSSs) Part I. General Scope Definition Uses Not Permitted Number Required Listing Short-Circuit Current Rating Part II. Installation Location Routing of Conductors Part III. Connecting Transient Voltage Surge Suppressors Connection Article 285 Questions Chapter 3 Wiring Methods and Materials Article 300 Wiring Methods Part I. General Requirements Scope Conductors Protection Against Physical Damage Underground Installations Protection Against Corrosion and Deterioration Raceways Exposed to Different Temperatures Not Permitted in Raceways Electrical Continuity Securing and Supporting ix
11 Table of Contents Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume Mechanical Continuity Splices and Pigtails Length of Free Conductors Boxes or Conduit Bodies Raceway Sizing Inserting Conductors in Raceways Supporting Conductors in Vertical Raceways Induced Currents in Metal Parts Spread of Fire or Products of Combustion Ducts, Plenums, and Air-Handling Spaces Panels Designed to Allow Access Article 300 Questions Article 310 Conductors For General Wiring Scope Conductors Stranded Conductors Conductors in Parallel Minimum Size Conductors Location Corrosive Conditions Insulation Temperature Limitation Conductor Identification Conductor Construction Conductor Ampacity Article 310 Questions Article 312 Cabinets, Cutout Boxes, and Meter Socket Enclosures Scope Part I. Installation Damp, Wet, or Hazardous (Classified) Locations Installed in Walls Repairing Gaps Around Plaster, Drywall, or Plasterboard Edges Enclosures Used for Raceway and Splices Article 312 Questions Article 314 Outlet, Device, Pull and Junction Boxes, Conduit Bodies, and Handhole Enclosures Part I. Scope and General Scope Nonmetallic Boxes Metal Boxes Short-Radius Conduit Bodies Part II. Installation Damp, Wet, or Hazardous (Classified) Locations Number of 6 AWG and Smaller Conductors in Boxes and Conduit Bodies Conductors That Enter Boxes or Conduit Bodies Boxes Recessed in Walls or Ceilings Repairing Gaps Around Boxes Surface Extensions Support of Boxes and Conduit Bodies Covers and Canopies Outlet Box Boxes and Conduit Bodies for Conductors 4 AWG and Larger Wiring to be Accessible Handhole Enclosures Article 314 Questions Article 320 Armored Cable (Type AC) Part I. General Scope Definition Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Exposed Work Through or Parallel to Framing Members In Accessible Attics or Roof Spaces Bends Secured and Supported Boxes and Fittings Conductor Ampacities Part III. Construction Specifications Construction Equipment Grounding (Bonding) Article 320 Questions Article 330 Metal-Clad Cable (Type MC) Part I. General Scope Definition Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Through or Parallel to Framing Members In Accessible Attics or Roof Spaces Bends Part II. Installation Secured and Supported x
12 Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume 1 Table of Contents Fittings Conductor Ampacities Part III. Construction Specifications Equipment Grounding (Bonding) Article 330 Questions Article 334 Nonmetallic-Sheathed Cable (Types NM and NMC) Part I. General Scope Definition Listed Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Exposed Through or Parallel to Framing Members Attics and Roof Spaces Bends Secured or Supported Conductor Ampacity Part III. Construction Specifications Construction Conductors Equipment Grounding Insulation Article 334 Questions Article 336 Power and Control Tray Cable (Type TC) Part I. General Scope Definition Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Article 336 Questions Article 338 Service-Entrance Cables (Types SE and USE) Part I. General Scope Definition Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Bends Article 338 Questions Article 340 Underground Feeder and Branch-Circuit Cable (Type UF) Part I. General Scope Definition Listing Requirements Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Bends Ampacity Insulation Article 340 Questions Article 342 Intermediate Metal Conduit (Type IMC) Part I. General Scope Definition Listing Requirements Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Dissimilar Metals Trade Size Number of Conductors Bends Number of Bends (360 ) Reaming Secured and Supported Couplings and Connectors Bushings Article 342 Questions Article 344 Rigid Metal Conduit (Type RMC) Part I. General Scope Definition Listing Requirements Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Dissimilar Metals Trade Size Number of Conductors Bends Number of Bends (360 ) Reaming Secured and Supported Couplings and Connectors xi
13 Table of Contents Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume Bushings Article 344 Questions Article 348 Flexible Metal Conduit (Type FMC) Part I. General Scope Definition Listing Requirements Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Trade Size Number of Conductors Bends Number of Bends (360 ) Trimming Secured and Supported Fittings Bonding Article 348 Questions Article 350 Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit (Type LFMC) Part I. General Scope Definition Listing Requirement Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Trade Size Number of Conductors Bends Number of Bends (360 ) Secured and Supported Fittings Bonding Article 350 Questions Article 352 Rigid Nonmetallic Conduit (Type RNC) Part I. General Scope Definition Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Trade Size Number of Conductors Bends Number of Bends (360 ) Trimming Secured and Supported Expansion Fittings Bushings Joints Grounding (Bonding) Article 352 Questions Article 353 High-Density Polyethylene Conduit (Type HDPE) Part I. General Scope Definition Listing Requirements Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Trade Size Number of Conductors Bends How Made Bends Number in One Run Trimming Bushings Joints Splices and Taps Grounding (Bonding) Article 353 Questions Article 354 Nonmetallic Underground Conduit with Conductors (Type NUCC) Part I. General Scope Definition Listing Requirement Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Trade Size Bends Number of Bends (360º) Trimming Bushings Joints Conductor Terminations Article 354 Questions xii
14 Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume 1 Article 356 Liquidtight Flexible Nonmetallic Conduit (Type LFNC) Part I. General Scope Definition Listing Requirement Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Trade Size Number of Conductors Bends Number of Bends (360 ) Secured and Supported Fittings Grounding (Bonding) Article 356 Questions Article 358 Electrical Metallic Tubing (Type EMT) Part I. General Scope Definition Listing Requirement Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Trade Size Number of Conductors Bends Number of Bends (360 ) Reaming and Threading Secured and Supported Coupling and Connectors Article 358 Questions Article 362 Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (Type ENT) Part I. General Scope Definition Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Trade Sizes Number of Conductors Bends Number of Bends (360 ) Table of Contents Trimming Secured and Supported Bushings Joints Grounding (Bonding) Article 362 Questions Article 376 Metal Wireways Part I. General Scope Definition Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Conductor Maximum Size Number of Conductors Wireway Sizing Supports Splices and Taps Article 376 Questions Article 378 Nonmetallic Wireways Part I. General Scope Definition Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Conductor Maximum Size Number of Conductors Wireway Sizing Supports Expansion Fittings Splices and Taps Grounding (Bonding) Article 378 Questions Article 380 Multioutlet Assembly Scope Uses Through Partitions Article 380 Questions Article 384 Strut-Type Channel Raceways Part I. General Scope Definition xiii
15 Table of Contents Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume 1 Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Conductor Maximum Size Number of Conductors Securing and Supporting Splices and Taps Grounding (Bonding) Article 384 Questions Article 386 Surface Metal Raceways Part I. General Scope Definition Listing Requirements Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Size of Conductors Number of Conductors Securing and Supporting Splices and Taps Grounding (Bonding) Separate Compartments Article 386 Questions Article 388 Surface Nonmetallic Raceways Part I. General Scope Definition Listing Requirements Part II. Installation Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Size of Conductors Number of Conductors Splices and Taps Grounding (Bonding) Separate Compartments Article 388 Questions Article 392 Cable Trays Scope Definition Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Installation Grounding (Bonding) Cable Installation Article 392 Questions Chapter 4 Equipment for General Use Article 400 Flexible Cords and Flexible Cables Scope Suitability Types of Flexible Cords and Flexible Cables Ampacity of Flexible Cords and Flexible Cables Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Pull at Joints and Terminals Overcurrent Protection Protection from Damage Article 400 Questions Article 402 Fixture Wires Scope Types Allowable Ampacity of Fixture Wires Minimum Size Raceway Size Grounded Neutral Conductor Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Overcurrent Protection Article 402 Questions Article 404 Switches Scope Switch Connections Switch Enclosures Wet Locations Position of Knife Switches Indicating Accessibility and Grouping Switch Cover Plates (Faceplate) Mounting Snap Switches Circuit Breakers Used as Switches Grounding (Bonding) Metal Enclosures Rating and Use of Snap Switches Switch Marking Article 404 Questions Article 406 Receptacles, Cord Connectors, and Attachment Plugs Caps Scope xiv
16 Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume Receptacle Rating and Type General Installation Requirements Receptacle Mounting Receptacle Faceplates Attachment Plugs, Cord Connectors, and Flanged Surface Devices Receptacles in Damp or Wet Locations Connecting Receptacle Grounding Terminal to Box Article 406 Questions Article 408 Switchboards and Panelboards Part I. General Scope Arrangement of Busbars and Conductors Circuit Directory or Circuit Identification Clearance for Conductor Entering Bus Enclosures Unused Openings Part III. Panelboards Classification of Panelboards Number of Overcurrent Protection Devices Overcurrent Protection of Panelboard Panelboards in Damp or Wet Locations Grounding (Bonding) of Panelboards Grounded Neutral Conductor Terminations Article 408 Questions Article 410 Luminaires, Lampholders, and Lamps Part I. General Scope Part II. Luminaire Locations Luminaires in Specific Locations Clothes Closets Part III. Luminaire Outlet Boxes and Covers Outlet Boxes to be Covered Connection of Electric-Discharge Luminaires Part IV. Luminaire Supports Supports Means of Support Part V. Grounding (Bonding) Exposed Luminaire Parts Part VI. Wiring of Luminaires Polarization of Luminaires Cord-Connected Luminaires Luminaires Used as a Raceway Table of Contents Wiring Luminaires Connected Together Branch-Circuit Conductors and Ballast Part VIII. Lampholders Screw-Shell Lampholder Part XI. Recessed Luminaires Thermally Protected Recessed Luminaire Clearances Wiring Part XIII. Electric-Discharge Lighting General Luminaire Mounting Part XV. Track Lighting Definition Installation Fastening Part XVI. Decorative Lighting and Similar Accessories Listing of Decorative Lighting Article 410 Questions Article 411 Lighting Systems Operating at 30V or Less Scope Definition Listing Required Locations Not Permitted Secondary Circuits Article 411 Questions Article 422 Appliances Part I. General Scope Other Articles Part II. Branch-Circuit Requirements Branch-Circuit Rating Overcurrent Protection Fossil Fuel Heating Equipment (Furnaces) Storage Water Heaters Central Vacuum Flexible Cords Support of Ceiling-Suspended (Paddle) Fans Part III. Disconnect Permanently Connected Appliance Disconnect Cord-and-Plug Connected Appliance Disconnect Unit Switch as Disconnect Cord-and-Plug Connected Vending Machines Article 422 Questions xv
17 Table of Contents Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume 1 Article 424 Fixed Electric Space-Heating Equipment Part I. General Scope Branch Circuits Permanently Installed Electric Baseboard Heaters with Receptacles Part III. Electric Space-Heating Equipment Disconnecting Means Part V. Electric Space-Heating Cables Installation of Cables in Concrete or Poured Masonry Floors Part VI. Duct Heaters Disconnect for Electric Duct Heater Controller Article 424 Questions Article 430 Motors, Motor Circuits, and Controllers Part I. General Scope Definitions Table FLC Versus Motor Nameplate Current Rating Marking on Controllers Motor Controller Terminal Requirements Location of Motors The Highest-Rated Motors Part II. Conductor Size Single Motor Conductor Size Several Motors Conductor Size Motor Feeder Taps Part III. Overload Protection Overload Overload Sizing Continuous-Duty Motors Use of Fuses for Overload Protection Number of Overload Devices Part IV. Branch-Circuit Short-Circuit and Ground-Fault Protection General Branch-Circuit Short-Circuit and Ground-Fault Protection Single Overcurrent Protective Device Part V. Feeder Short-Circuit and Ground-Fault Protection Feeder Protection Part VI. Motor Control Circuits Overcurrent Protection for Control Circuits Disconnect for Control Circuit Part VII. Motor Controllers Controller Rating Need Not Open All Conductors of the Circuit Controller for Each Motor Motor Controller Enclosure Types Part IX. Disconnecting Means Disconnect Requirement Disconnect Opens All Conductors Marking and Mounting Readily Accessible Disconnecting Means Rating Combination Controller-Disconnect Part X. Adjustable-Speed Drive Systems General Conductors Minimum Size and Ampacity Overload Protection Disconnecting Means Part XIV. Tables Table Full-Load Current, Single-Phase Motors Table Full-Load Current, Three-Phase Motors Table Locked-Rotor Currents Article 430 Questions Article 440 Air-Conditioning and Refrigeration Equipment Part I. General Scope Definitions Other Articles Marking on Hermetic Refrigerant Motor-Compressors and Equipment Ampacity and Rating Part II. Disconnecting Means Location Part III. Circuit Protection General Short-Circuit and Ground-Fault Protection Device Size Part IV. Conductor Sizing Conductor Size One Motor-Compressor Conductor Size Several Motor-Compressors Part VII. Room Air Conditioners Branch-Circuit Requirements xvi
18 Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume 1 Table of Contents Disconnecting Means Supply Cord Leakage Current Detection and Interruption, and Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupter Article 440 Questions Article 445 Generators Scope Marking Overcurrent Protection Ampacity of Conductors Disconnecting Means Article 445 Questions Article 450 Transformers and Transformer Vaults Part I. General Scope Overcurrent Protection Ventilation Marking Transformer Accessibility Part III. Transformer Vaults Location Walls, Roofs, and Floors Doorways Ventilation Openings Water Pipes and Accessories Storage in Vaults Article 450 Questions Article 460 Capacitors Scope Enclosing and Guarding Part I. 600V, Nominal, and Under Conductors Rating or Setting of Motor Overload Device Article 460 Questions xvii
19 Article 90 Introduction Purpose of the NEC Scope of the NEC Code Arrangement Enforcement Mandatory Requirements and Explanatory Material Formal Interpretations Examination of Equipment for Product Safety Units of Measurement...7 Article 90 Questions...8 Chapter 1 General...9 Article 100 Definitions...11 Article 100 Questions...29 Article 110 Requirements for Electrical Installations...31 Part I. General Requirements Scope Approval of Equipment Examination, Identification, Installation, and Use of Equipment Voltages Copper Conductors Conductor Sizes Conductor Insulation Suitable Wiring Methods Interrupting Protection Rating Short-Circuit Current Rating Deteriorating Agents Mechanical Execution of Work Mounting and Cooling of Equipment Conductor Termination High-Leg Conductor Identification Flash Protection Warning Manufacturer s Markings Identification of Disconnecting Means...43 Part II. 600V, Nominal or Less Spaces About Electrical Equipment Guarding...48 Article 110 Questions...49 Chapter 5 Special Occupancies Article 500 Hazardous (Classified) Locations Scope Articles 500 Through Definitions Other Articles General Classifications of Locations Material Groups Protection Techniques Equipment Specific Occupancies Article 500 Questions Article 501 Class I Hazardous (Classified) Locations Part I. General Scope General Part II. Wiring Wiring Methods Conduit and Cable Seals Conductor Insulation Bonding Surge Protection Multiwire Branch Circuits Part III. Equipment Transformers and Capacitors Meters, Instruments, and Relays Enclosures Control Transformers and Relays Motors and Generators Luminaires vi
20 Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume 2 Table of Contents Flexible Cords Receptacles and Attachment Plugs Low-Voltage, Limited-Energy, and Communications Systems Article 501 Questions Article 502 Class II Hazardous (Classified) Locations Part I. General Scope General Part II. Wiring Wiring Methods Seals Bonding Surge Protection Multiwire Branch Circuits Part III. Equipment Switches, Circuit Breakers, Motor Controllers, and Fuses Control Transformers Motors and Generators Luminaires Flexible Cords Receptacles and Attachment Plugs Low-Voltage, Limited-Energy, and Communications Systems Article 502 Questions Article 503 Class III Hazardous (Classified) Locations Part I. General Scope General Part II. Wiring Wiring Methods Bonding Part III. Equipment Switches, Circuit Breakers, Motor Controllers, and Fuses Control Transformers Motors and Generators Luminaires Flexible Cords Receptacles and Attachment Plugs Signaling, Alarm, Remote-Control, and Loudspeaker Systems Article 503 Questions Article 504 Intrinsically Safe Systems Scope Definitions Application of Other Articles Equipment Approval Equipment Installation Wiring Methods Separation of Intrinsically Safe Circuits Grounding (Earthing) Bonding Sealing Identification Article 504 Questions Article 511 Commercial Garages, Repair, and Storage Scope Classification of Hazardous Areas Wiring and Equipment in Hazardous (Classified) Locations Wiring and Equipment Above Hazardous (Classified) Locations Seals Special Equipment GFCI-Protected Receptacles Article 511 Questions Article 513 Aircraft Hangars Scope Classification of Locations Wiring and Equipment in Class I Locations Wiring Not Within Class I Locations Wiring in or Under Hangar Floor Sealing GFCI-Protected Receptacles Bonding Article 513 Questions Article 514 Motor Fuel Dispensing Facilities Scope Definition Classification of Locations Wiring and Equipment Within Class I Locations Wiring and Equipment Above Class I Locations Underground Wiring Raceway Seal Emergency Dispenser Disconnects Maintenance and Service of Dispensing Equipment vii
21 Table of Contents Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume Grounding (Bonding) Article 514 Questions Article 517 Health Care Facilities Part I. General Scope Definitions Part II. Wiring and Protection Applicability Wiring Methods Grounding (Bonding) Equipment in Patient Care Areas Isolated Ground Receptacles General Care Areas Essential Electrical Systems for Hospitals Article 517 Questions Article 518 Assembly Occupancies Scope General Classifications Other Articles Wiring Methods Article 518 Questions Article 525 Carnivals, Circuses, Fairs, and Similar Events Part I. General Requirements Scope Other Articles Overhead Conductor Clearances Protection of Electrical Equipment Part II. Power Sources Services Multiple Sources of Supply Wiring Methods Rides, Tents, and Concessions Outdoor Portable Distribution or Termination Boxes GFCI-Protected Receptacles and Equipment Part IV. Grounding and Bonding Equipment Bonding Equipment Grounding (Bonding) Grounding (Bonding) Conductor Continuity Assurance Article 525 Questions Article 547 Agricultural Buildings Scope Definitions Wiring Methods Equipotential Planes and Bonding of Equipotential Planes Article 547 Questions Article 550 Mobile Homes, Manufactured Homes, and Mobile Home Parks Part I. General Scope Definitions General Requirements Receptacle Outlets Arc-Fault Circuit-Interrupter (AFCI) Protection Part III. Services and Feeders Distribution Systems Allowable Demand Factors Disconnect Feeder Article 550 Questions Article 551 Recreational Vehicles and Recreational Vehicle Parks Part I. General Scope Definitions Other Articles Part VI. Recreational Vehicle Parks Type of Receptacles Required Calculated Load Clearance for Overhead Conductors Article 551 Questions Article 555 Marinas and Boatyards Scope Definitions Transformers Electrical Connections Load Calculations for Service and Feeder Conductors Boat Receptacle Disconnecting Means Receptacles Motor Fuel Dispensing Stations Repair Facilities Article 555 Questions viii
22 Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume 2 Table of Contents Article 590 Temporary Installations Scope All Installations Time Constraints General Ground-Fault Protection for Personnel Article 590 Questions Chapter 6 Special Equipment Article 600 Electric Signs and Outline Lighting Part I. General Scope Definitions Listing Markings Branch Circuits Disconnects Location Portable or Mobile Signs Ballasts, Transformers, and Electronic Power Supplies Article 600 Questions Article 604 Manufactured Wiring Systems Scope Definition Other Articles Uses Permitted Uses Not Permitted Construction Article 604 Questions Article 605 Office Furnishings (Wired Partitions) Scope General Partition Interconnections Fixed-Type Partitions Freestanding-Type Partitions Article 605 Questions Article 620 Elevators, Escalators, and Moving Walks Part I. General Scope Part III. Wiring Branch Circuit for Machine Room/Machinery Space Branch Circuit for Hoistway Pit Part IV. Installation of Conductors Wiring in Elevator Hoistways and Machine Rooms Part VI. Disconnecting Means and Control Disconnecting Means Part VIII. Machine Rooms, Control Rooms, Machinery Spaces, and Control Spaces GFCI-Protected Receptacles Article 620 Questions Article 625 Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Part I. General Scope Definitions Part IV. Control and Protection Personnel Protection System Loss of Primary Source Interactive Systems Article 625 Questions Article 630 Electric Welders Part I. General Scope Part II. Arc Welders Ampacity of Supply Conductors Overcurrent Protection Disconnecting Means Part III. Resistance Welders Ampacity of Supply Conductors Overcurrent Protection Disconnecting Means Article 630 Questions Article 640 Audio Signal Processing, Amplification, and Reproduction Equipment Part I. General Scope Definitions Locations and Other Articles Protection of Electrical Equipment Access to Electrical Equipment Mechanical Execution of Work Grounding (Earthing) and Bonding Wiring Methods ix
23 Table of Contents Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume Audio Systems Near Bodies of Water Part II. Permanent Audio System Installations Use of Flexible Cords and Flexible Cables Wiring of Equipment Racks Raceway Fill Loudspeakers in Fire-Resistance Rated Partitions, Walls, and Ceilings Article 640 Questions Article 645 Information Technology Equipment Scope Information Technology Equipment Room Supply Circuits and Interconnecting Cables Cables Not in Information Technology Equipment Room Penetrations Disconnecting Means Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) Grounding (Bonding) Article 645 Questions Article 647 Sensitive Electronic Equipment Scope General Wiring Methods Grounding (Bonding) Receptacles Article 647 Questions Article 680 Swimming Pools, Spas, Hot Tubs, Fountains, and Similar Installations Part I. General Requirements for Permanently Installed Pools, Storable Pools, Outdoor Spas, Outdoor Hot Tubs, or Fountains Scope Definitions Other Articles Cord-and-Plug Connected Equipment Overhead Conductor Clearance Electric Water Heater Underground Wiring Location Equipment Rooms and Pits Maintenance Disconnecting Means Part II. Permanently Installed Pools, Outdoor Spas, and Outdoor Hot Tubs Motors Area Lighting, Receptacles, and Equipment Underwater Luminaires Junction Boxes Feeders Equipotential Bonding Specialized Equipment Part III. Storable Swimming Pool General GFCI-Protected Receptacles Receptacle Locations Part IV. Spas and Hot Tubs General Emergency Switch for Spas and Hot Tubs Outdoor Installations Indoor Installations GFCI Protection Part V. Fountains General Luminaires, Submersible Pumps, and Other Submersible Equipment Bonding Methods of Grounding (Bonding) Cord-and-Plug Connected Equipment Signs in or Adjacent to Fountains GFCI-Protected Receptacles Part VII. Hydromassage Bathtubs Protection Other Electric Equipment Other Electrical Equipment Accessibility Bonding Article 680 Questions Article 690 Solar Photovoltaic Systems Part I. General Scope Article 692 Fuel Cell Systems Scope Definitions Listing Requirement Article 692 Questions Article 695 Fire Pumps Scope Power Sources Continuity of Power Transformers Power Wiring x
24 Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume Voltage Drop Control Wiring Article 695 Questions Table of Contents Accessibility Ground-Fault Protection of Equipment Coordination Article 701 Questions Chapter 7 Special Conditions Article 700 Emergency Power Systems Part I. General Scope Application of Other Articles Equipment Approval Tests and Maintenance Capacity Transfer Equipment Signs Part II. Circuit Wiring Wiring Part III. Sources of Power General Requirements Part IV. Emergency System Circuits for Lighting and Power Loads on Emergency Branch Circuits Emergency Illumination Part VI. Overcurrent Protection Accessibility Ground-Fault Protection of Equipment Coordination Article 700 Questions Article 701 Legally Required Standby Power Systems Part I. General Scope Definitions Application of Other Articles Equipment Approval Tests and Maintenance Capacity and Rating Transfer Equipment Signs Part II. Circuit Wiring Wiring Part III. Sources of Power Legally Required Standby Systems Part IV. Overcurrent Protection Article 702 Optional Standby Power Systems Part I. General Scope Definition Application of Other Articles Equipment Approval Capacity and Rating Transfer Equipment Signs Part II. Circuit Wiring Wiring Part III. Grounding and Bonding Portable Generator Grounding and Bonding Part IV. Sources of Power Outdoor Generator Sets Article 702 Questions Article 720 Circuits and Equipment Operating at Less than 50 Volts Article 720 Question Article 725 Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3 Remote- Control, Signaling, and Power-Limited Circuits Part I. General Scope Definitions Other Articles Access to Electrical Equipment Behind Panels Designed to Allow Access Mechanical Execution of Work Safety-Control Equipment Circuit Requirements Part II. Class 1 Circuit Requirements Class 1 Circuit Classifications and Power Source Requirements Class 1 Circuit Overcurrent Protection Class 1 Circuit Wiring Methods Conductors of Different Circuits in Same Cable, Enclosure, or Raceway Class 1 Circuit Conductors Number of Conductors in a Raceway xi
25 Table of Contents Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume 2 Part III. Class 2 and Class 3 Circuit Requirements Power Sources for Class 2 and Class 3 Circuits Equipment Marking Wiring Methods on Supply Side of the Class 2 or Class 3 Power Source Wiring Methods on Load Side of the Class 2 or Class 3 Power Source Separation from Other Systems Conductors of Different Circuits in Same Cable, Enclosure, or Raceway Class 2 or Class 3 Cables Exposed to Lightning Support Applications of Class 2 and Class 3 Cables Part VI. Listing Requirements Listing and Marking of Class 2 and Class 3 Cables Article 725 Questions Article 760 Fire Alarm Systems Part I. General Scope Definitions Other Articles Access to Electrical Equipment Behind Panels Designed to Allow Access Mechanical Execution of Work Fire Alarm Circuit and Equipment Grounding (Bonding) Fire Alarm Circuit Identification Fire Alarm Circuit Cables Exposed to Lightning Fire Alarm Circuit Requirements Part II. Nonpower-Limited Fire Alarm (NPLFA) Circuits GFCI and AFCI Protection NPLFA Circuit Overcurrent Protection NPLFA Circuit Wiring Methods Conductors of Different Circuits in Same Cable, Enclosure, or Raceway NPLFA Circuit Conductors Number of Conductors in a Raceway Part III. Power-Limited Fire Alarm (PLFA) Circuits Power Sources for PLFA Circuits Equipment Marking Wiring Methods and Materials on Load Side of the PLFA Power Source Separation from Other Circuit Conductors PLFA Circuits, Class 2, Class 3, and Communications Circuits Support Applications of Listed PLFA Cables Part IV. Listing Requirements Listing and Marking of NPLFA Cables Listing and Marking of PLFA Cables Article 760 Questions Article 770 Optical Fiber Cables and Raceways Part I. General Scope Definitions Locations and Other Articles Optical Fiber Cables Types Raceways for Optical Fiber Cables Access to Electrical Equipment Behind Panels Designed to Allow Access Mechanical Execution of Work Part III. Cables Within Buildings Listing of Optical Fiber Cables Installation of Optical Fibers and Electrical Conductors Applications of Listed Optical Fiber Cables and Raceways Part IV. Listing Requirements Listing Requirements for Optical Fiber Cables Listing Requirements for Optical Fiber Raceways Article 770 Questions Chapter 8 Communications Systems Article 800 Communications Circuits Part I. General Scope Definitions Other Articles Installation of Equipment Access to Electrical Equipment Behind Panels Designed to Allow Access Mechanical Execution of Work Overhead Communications Wires and Cables Part II. Conductors Outside and Entering Buildings Underground Circuits Entering Buildings Lightning Conductors Part III. Protection xii
26 Understanding the National Electrical Code, Volume 2 Table of Contents Primary Protection Cable Grounding Part IV. Grounding Methods Cable and Primary Protector Grounding Part V. Communications Wires and Cables Within Buildings Raceways for Communications Circuits Listing of Communications Wires and Cables Installation of Communications Circuits and Equipment Applications of Listed Communications Wires, Cables, and Raceways Part VI. Listing Requirements Communications Wires and Cables Communications Raceways Article 800 Questions Article 810 Radio and Television Equipment Part I. General Scope Other Articles Community Television Antenna Part II. Receiving Equipment Antenna Systems Support of Lead-In Cables Avoid Contact with Conductors of Other Systems Grounding Clearances Antenna Discharge Unit Grounding Conductors Article 810 Questions Article 820 Community Antenna Television (CATV) and Radio Distribution Systems Part I. General Scope Definitions Locations and Other Articles Energy Limitations Access to Electrical Equipment Behind Panels Designed to Allow Access Mechanical Execution of Work Part II. Cables Outside and Entering Buildings Overhead Cables Underground Circuits Entering Buildings Part III. Protection Grounding Cable Part IV. Grounding Methods Cable Grounding Part V. Cables Within Buildings Raceways for Coaxial Cables Listing and Markings Installation of Cables and Equipment Applications of Listed CATV Cables and Raceways Part VI. Listing Requirements Additional Listing Requirements CATV Raceways Article 820 Questions Article 830 Network-Powered Broadband Communications Systems Part I. General Scope Definitions Article 830 Questions Chapter 9 Tables Table 1 Conductor Fill Table 4 Raceway Dimensions Table 5 Conductor Cross-Sectional Area Table 8 Conductor Properties Table 9 AC Impedance for Conductors in Conduit Tubing Annex C Raceway Fill Tables Table C.1 Maximum Number of THNN/THWN Conductors in EMT Table C.10 Maximum Number of THNN/THWN Conductors in RNC xiii
27 UNIT 1 ELECTRICIAN S MATH AND BASIC ELECTRICAL FORMULAS...1 Introduction...1 PART A ELECTRICIAN S MATH...1 Introduction Whole Numbers Decimal Fractions Percentages Multiplier Percent Increase Reciprocals Squaring a Number Square Root Volume Kilo Rounding Off Parentheses Testing Your Answer for Reasonableness...6 PART B BASIC ELECTRICAL FORMULAS...7 Introduction Electrical Circuit Power Source Conductance Circuit Resistance Ohm s Law Ohm s Law and Alternating Current Ohm s Law Formula Circle PIE Formula Circle Formula Wheel Using the Formula Wheel Power Losses of Conductors Cost of Power Power Changes with the Square of the Voltage...14 PART C BASIC ELECTRIC METERS...16 Introduction Voltmeter DC Voltmeter DC Ammeter Clamp-on AC Ammeter Ohmmeters Wheatstone Bridge Megohmmeter...18 Conclusion...19 UNIT 2 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS...49 Introduction...49 PART A SERIES CIRCUITS...49 Introduction Practical Uses of the Series Circuit Understanding Series Calculations Series Circuit Calculations Power Calculations Variations Series Circuit Notes Series-Connected Power Supplies...54 PART B PARALLEL CIRCUITS...54 Introduction Practical Uses of the Parallel Circuit Understanding Parallel Calculations Circuit Resistance Parallel Circuit Notes Parallel-Connected Power Supplies...59 PART C SERIES-PARALLEL CIRCUITS...59 Introduction Review of Series and Parallel Circuits Working Series-Parallel Circuits Voltage...61 PART D MULTIWIRE BRANCH CIRCUITS...62 Introduction Neutral Conductor Grounded Conductor...62 vi
28 Electrical NEC Exam Preparation Table of Contents 2.18 Current Flow on the Grounded Neutral Conductor Balanced Systems Unbalanced Current Multiwire Branch Circuit Dangers of Multiwire Circuits NEC Requirements...67 Conclusion...68 UNIT 3 UNDERSTANDING ALTERNATING CURRENT...97 Introduction...97 PART A UNDERSTANDING ALTERNATING CURRENT...97 Introduction Current Flow Why Alternating Current is Used How Alternating Current is Produced AC Generator Waveform Sine Wave Nonsymmetrical Waveform Frequency Phase Degrees Lead or Lag Values of Alternating Current PART B CAPACITANCE Introduction Charged Capacitor Electrical Field Discharging a Capacitor Determining Capacitance Uses of Capacitors Phase Relationship PART C INDUCTION Introduction Self-Induction Induced Voltage and Applied Current Conductor AC Resistance Impedance Conductor Shape Magnetic Cores Self-Induced and Applied Voltage Current Flow Phase Relationship Uses of Induction PART D POWER FACTOR Introduction Apparent Power (Volt-Amperes) True Power (Watts) Power Factor Unity Power Factor Power Factor Formulas Cost of True Power Effects of Power Factor PART E EFFICIENCY Introduction Efficiency Formulas Conclusion UNIT 4 MOTORS AND TRANSFORMERS Introduction PART A MOTORS Introduction Motor Principles Dual-Voltage AC Motors Motor Horsepower Rating Motor Current Ratings Calculating Motor FLA Motor-Starting Current Motor-Running Current Motor Locked-Rotor Current (LRC) Motor Overload Protection Direct-Current Motor Principles Direct-Current Motor Types Reversing the Rotation of a DC Motor AC Induction Motor Alternating-Current Motor Types Reversing the Rotation of an AC Motor PART B TRANSFORMERS Introduction Transformer Basics Secondary Induced Voltage Autotransformers Power Losses Harmonic Current Efficiency Transformer Turns Ratio Transformer kva Rating Current Flow Current Rating Conclusion vii
29 Table of Contents UNIT 5 RACEWAY AND BOX CALCULATIONS Introduction PART A RACEWAY FILL Understanding the NEC, Chapter 9 Tables Raceway and Nipple Calculations Existing Raceway Calculations Tips for Raceway Calculations PART B OUTLET BOX FILL CALCULATIONS [314.16] Sizing Box Conductors All the Same Size [Table (A)] Conductor Equivalents [314.16(B)] Sizing Box Different Size Conductors [314.16(B)] PART C PULL BOXES, JUNCTION BOXES, AND CONDUIT BODIES Pull and Junction Box Size Calculations Depth of Box and Conduit Body Sizing [314.28(A)(2) Ex] Junction and Pull Box Sizing Tips Pull Box Examples Conclusion Electrical NEC Exam Preparation 6.13 Conductor Bundling Ampacity Adjustment Factor [Table (B)(2)(a)] Ambient Temperature Correction and Conductor Bundling Adjustment Factors Current-Carrying Conductors Conductor Sizing Summary Conclusion UNIT 7 MOTOR CALCULATIONS Introduction Single Motor Conductors [430.22(A)] Motor Overcurrent Protection Overload Protection [430.6(2) and (A)] Branch-Circuit Short-Circuit Ground-Fault Protection [430.51] Feeder Conductor Size [430.24] Feeder Protection [430.61] Highest-Rated Motor [430.17] Motor Calculations Steps Motor Calculation Review Motor VA Calculations Conclusion UNIT 6 CONDUCTOR SIZING AND PROTECTION CALCULATIONS Introduction PART A GENERAL CONDUCTOR REQUIREMENTS Conductor Insulation Property [Table ] Allowable Conductor Ampacity [310.15] Conductor Sizing [110.6] Terminal Ratings [110.14(C)] Conductors in Parallel [310.4] Conductor Size Voltage Drop [210.19(A)(1) FPN No. 4 and 215.2(A) FPN No. 2] Overcurrent Protection [Article 240] Overcurrent Protection of Conductors General Requirements [240.4] Overcurrent Protection of Conductors Specific Requirements Equipment Conductor Size and Protection Examples PART B CONDUCTOR AMPACITY CALCULATIONS Conductor Ampacity [310.10] Ambient Temperature Ampacity Correction Factor [Table ] UNIT 8 VOLTAGE-DROP CALCULATIONS Introduction PART A CONDUCTOR RESISTANCE CALCULATIONS Conductor Resistance Conductor Resistance Direct-Current Circuits [Chapter 9, Table 8] Conductor Impedance Alternating-Current Circuits Alternating-Current Impedance as Compared to Direct-Current Resistance Impedance [Chapter 9, Table 9] PART B VOLTAGE-DROP CALCULATIONS Voltage-Drop Considerations NEC Voltage-Drop Recommendations Determining Circuit Conductors Voltage Drop Sizing Conductors to Prevent Excessive Voltage Drop Limiting Conductor Length to Minimize Voltage Drop Limiting Current to Limit Voltage Drop Extending Circuits Conclusion viii
30 Electrical NEC Exam Preparation Table of Contents UNIT 9 DWELLING UNIT CALCULATIONS Introduction PART A GENERAL REQUIREMENTS General Requirements Voltages [220.5(A)] Fraction of an Ampere [220.5(B)] Small-Appliance Circuits [210.11(C)(1)] Cooking Equipment Branch Circuit [Table , Note 4] Laundry Receptacle(s) Circuit [210.11(C)(2)] Lighting and Receptacles PART B STANDARD METHOD FEEDER/SERVICE LOAD CALCULATIONS Dwelling Unit Feeder/Service Load Calculations (Article 220, Part III) Dwelling Unit Feeder/Service Calculations Examples PART C OPTIONAL METHOD FEEDER/SERVICE LOAD CALCULATIONS Dwelling Unit Optional Feeder/Service Calculations [220.82] Dwelling Unit Optional Calculation Examples Neutral Calculations General [220.61] Conclusion UNIT 10 MULTIFAMILY DWELLING CALCULATIONS Introduction Multifamily Dwelling Unit Calculations General PART A STANDARD METHOD FEEDER/SERVICE LOAD CALCULATIONS Multifamily Dwelling Unit Calculation Examples Standard Method Multifamily Dwelling Unit Calculations Standard Method PART B OPTIONAL METHOD FEEDER/SERVICE LOAD CALCULATIONS Multifamily Dwelling Unit Calculations [220.84] Optional Method Multifamily Optional Method Example 1 [220.84] Multifamily Optional Method Example 2 [220.84] Conclusion UNIT 11 COMMERCIAL CALCULATIONS Introduction PART A GENERAL General Requirements Conductor Ampacity [Article 100] Conductor Overcurrent Protection [240.4] Voltages [220.5(A)] Rounding an Ampere [220.5(B)] Air-Conditioning Branch Circuit Dryers Electric Heat Kitchen Equipment Laundry Equipment Lighting Demand Factors [Tables and ] Lighting Without Demand Factors [215.2(A)(1), (A)(1), and Table ] Lighting-Miscellaneous Multioutlet Receptacle Assembly [220.14(H)] Receptacle VA Load Banks and Offices General Lighting and Receptacles [220.14(K)] Signs [220.14(F) and 600.5] PART B STANDARD METHOD FEEDER/SERVICE LOAD CALCULATIONS Feeder/Service Load Calculation Neutral Calculations [220.61] PART C EXAMPLES Bank (120/240V, single-phase) Marina [555.12] Mobile/Manufactured Home Park [550.31] Office Building (277/480V, Three-phase) Recreational Vehicle Park [551.73] Restaurant Standard Load Calculation (120/208V, Three-phase) PART D OPTIONAL METHOD FEEDER/SERVICE LOAD CALCULATIONS New Restaurant Optional Method [220.88] School Optional Method [220.86] PART E ELECTRIC WELDERS Arc Welders Resistance Welders Light Industrial Calculation Conclusion ix
31 Table of Contents UNIT 12 DELTA/DELTA AND DELTA/WYE TRANSFORMERS Introduction Definitions Current Flow PART A DELTA/DELTA TRANSFORMERS Delta Transformer Voltage Delta High-Leg Delta Line Currents Delta Phase Currents Delta Phase versus Line Current Delta Current Triangle Delta Transformer Balancing Delta Transformer Sizing Delta Panel Balancing Delta Panelboard and Conductor Sizing Delta Neutral Current Delta Maximum Unbalanced Load Delta/Delta Example Electrical NEC Exam Preparation PART B DELTA/WYE TRANSFORMERS Wye Transformer Voltage Wye Voltage Triangle Wye Transformers Current Wye Line Current Wye Phase Current Wye Phase versus Line Current Wye Transformer Balancing Wye Transformer Sizing Wye Panel Balancing Wye Panelboard and Conductor Sizing Wye Neutral Current Wye Maximum Unbalanced Load Delta/Wye Example Delta versus Wye Conclusion INDEX x
32 Introduction...vii Passing the Exam...viii The National Electrical Code...xi About the Author...xvi Unit 1 Review Quiz Articles 90 through Practice Quiz Articles 80 through Challenge Quiz Articles 90 through Annex C...21 Unit 2 Review Quiz Articles 200 through Practice Quiz Articles 200 through Challenge Quiz Articles 90 through Annex C...48 Unit 3 Review Quiz Articles 230 through Practice Quiz Articles 230 through Challenge Quiz Articles 90 through Annex C...75 Unit 4 Review Quiz Articles 250 through Practice Quiz Articles 250 through Challenge Quiz Articles 90 through Annex C Unit 5 Review Quiz Articles 310 through Practice Quiz Articles 310 through Challenge Quiz Articles 90 through Annex C Unit 6 Review Quiz Articles 342 through Practice Quiz Articles 344 through Challenge Quiz Articles 90 through Annex C Unit 7 Review Quiz Articles 386 through Practice Quiz Articles 386 through Challenge Quiz Articles 90 through Annex C Unit 8 Review Quiz Articles 410 through Practice Quiz Articles 410 through Challenge Quiz Articles 90 through Annex C Unit 9 Review Quiz Articles 500 through Practice Quiz Articles 500 through Challenge Quiz Articles 90 through Annex C Unit 10 Review Quiz Articles 517 through Practice Quiz Articles 517 through Challenge Quiz Articles 90 through Annex C Unit 11 Review Quiz Articles 645 through Practice Quiz Articles 645 through Challenge Quiz Articles 90 through Annex C Unit 12 Review Quiz Articles 702 through Annex C Practice Quiz Articles 702 through Chapter Challenge Quiz Articles 90 through Annex C vi
Chapter 2 Wiring and Protection Article 200 Use and Identification of Grounded Neutral Conductor Chapter 1 General...9
 Article 90 Introduction...1 90.1 Purpose of the NEC...1 90.2 Scope of the NEC...2 90.3 Code Arrangement...4 90.4 Enforcement...5 90.5 Mandatory Requirements and Explanatory Material...6 90.6 Formal Interpretations...6
Article 90 Introduction...1 90.1 Purpose of the NEC...1 90.2 Scope of the NEC...2 90.3 Code Arrangement...4 90.4 Enforcement...5 90.5 Mandatory Requirements and Explanatory Material...6 90.6 Formal Interpretations...6
Table of Contents. Unit 3 Magnetism Unit 1 Matter Unit 4 Electricity Unit 2 Electron Theory Unit 5 Electromagnetism...
 Introduction...x How to Use This Textbook...xi About the Author...xii About the Graphic Illustrator...xiii Mike Holt Enterprises Team...xiv Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals... 1 Unit 1 Matter... 3 Introduction...
Introduction...x How to Use This Textbook...xi About the Author...xii About the Graphic Illustrator...xiii Mike Holt Enterprises Team...xiv Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals... 1 Unit 1 Matter... 3 Introduction...
UNIT 1 ELECTRICIAN S MATH AND BASIC ELECTRICAL FORMULAS...1 Introduction...1. UNIT 2 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS...49 Introduction...49
 UNIT 1 ELECTRICIAN S MATH AND BASIC ELECTRICAL FORMULAS...1 Introduction...1 PART A ELECTRICIAN S MATH...1 Introduction...1 1.1 Whole Numbers...1 1.2 Decimal...1 1.3 Fractions...1 1.4 Percentages...2 1.5
UNIT 1 ELECTRICIAN S MATH AND BASIC ELECTRICAL FORMULAS...1 Introduction...1 PART A ELECTRICIAN S MATH...1 Introduction...1 1.1 Whole Numbers...1 1.2 Decimal...1 1.3 Fractions...1 1.4 Percentages...2 1.5
TABLE OF CONTENTS. About the Mike Holt Enterprises Team... xviii CHAPTER 1 ELECTRICAL THEORY... 1
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...xv About the Mike Holt Enterprises Team... xviii CHAPTER 1 ELECTRICAL THEORY... 1 Unit 1 Electrician s Math and Basic Electrical Formulas... 1 Part A Electrician s Math...
TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...xv About the Mike Holt Enterprises Team... xviii CHAPTER 1 ELECTRICAL THEORY... 1 Unit 1 Electrician s Math and Basic Electrical Formulas... 1 Part A Electrician s Math...
TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 ELECTRICAL THEORY About This Textbook...xi. Passing Your Exam...xiv. How to Use the National Electrical Code...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS About This Textbook...xi Passing Your Exam...xiv How to Use the National Electrical Code... 1 CHAPTER 1 ELECTRICAL THEORY... 7 Unit 1 Electrician s Math and Basic Electrical Formulas...
TABLE OF CONTENTS About This Textbook...xi Passing Your Exam...xiv How to Use the National Electrical Code... 1 CHAPTER 1 ELECTRICAL THEORY... 7 Unit 1 Electrician s Math and Basic Electrical Formulas...
Table of Contents. CHAPTER 1 ElECTRiCAl THEoRY Mike Holt enterprises, inc neC.Code ( )
 CHAPTER 1 ElECTRiCAl THEoRY... 1 UniT 1 electrician s MaTH and BasiC electrical formulas... 3 Introduction to Unit 1... 3 Part A Electrician s Math... 3 Introduction... 3 1.1 Whole Numbers... 3 1.2 Decimals...
CHAPTER 1 ElECTRiCAl THEoRY... 1 UniT 1 electrician s MaTH and BasiC electrical formulas... 3 Introduction to Unit 1... 3 Part A Electrician s Math... 3 Introduction... 3 1.1 Whole Numbers... 3 1.2 Decimals...
Table of Contents. CHAPTER 1 BASIC ELECTRICAL THEORY (Essential for Journeyman and Master s Licensing Exams)... 1
 Introduction... x About This Textbook...xi Passing Your Exam...xiv How to Use the National Electrical Code... xviii About the Author...xxi About the Graphic Illustrator...xxii Mike Holt Enterprises Team...
Introduction... x About This Textbook...xi Passing Your Exam...xiv How to Use the National Electrical Code... xviii About the Author...xxi About the Graphic Illustrator...xxii Mike Holt Enterprises Team...
Chapter 1 Electrical Theory...1
 Electrical Formulas with Sample Calculations Table of Contents Chapter 1 Electrical Theory...1 Unit 1 Electrician s Math and Basic Electrical Formulas...3 Part A Electrician s Math...3 1 1 Fractions...3
Electrical Formulas with Sample Calculations Table of Contents Chapter 1 Electrical Theory...1 Unit 1 Electrician s Math and Basic Electrical Formulas...3 Part A Electrician s Math...3 1 1 Fractions...3
Spring Test 10 due 05/11/2013
 Spring Test 10 due 05/11/2013 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When installed in an agricultural building that houses livestock
Spring Test 10 due 05/11/2013 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When installed in an agricultural building that houses livestock
Spring Test 7 due 05/03/2013
 Spring Test 7 due 05/03/2013 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A raceway contains two 3-phase, 3-wire circuits that supply 38 ampere continuous
Spring Test 7 due 05/03/2013 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A raceway contains two 3-phase, 3-wire circuits that supply 38 ampere continuous
CHAPTER V RESIDENTIAL WIRING
 CHAPTER V RESIDENTIAL WIRING 5.1. THE SERVICE ENTRANCE Buildings and other structures receive the electrical energy through the service entrance. In residential wiring, the electric company supply this
CHAPTER V RESIDENTIAL WIRING 5.1. THE SERVICE ENTRANCE Buildings and other structures receive the electrical energy through the service entrance. In residential wiring, the electric company supply this
Volume 2 Charts, Formulas, and Other Useful Information
 Volume 2 Charts, Formulas, and Other Useful Information Aluminum Conductor Conductor Terminations 61 Compact Aluminum (Conduit Fill Tables) 68-79 Ampacity Dwelling Services 48 1-phase Loads on a 3-phase
Volume 2 Charts, Formulas, and Other Useful Information Aluminum Conductor Conductor Terminations 61 Compact Aluminum (Conduit Fill Tables) 68-79 Ampacity Dwelling Services 48 1-phase Loads on a 3-phase
2011 NEC Code Updates Part 3
 www.garyklinka.com Page 1 of 22 Instructions: Fee $35 1. Print these pages. 2. Circle the correct answers and transfer them to the answer sheet. 3. Page down to the last page for the verification forms
www.garyklinka.com Page 1 of 22 Instructions: Fee $35 1. Print these pages. 2. Circle the correct answers and transfer them to the answer sheet. 3. Page down to the last page for the verification forms
See Part 3 for the Introduction for Article 314
 See Part 3 for the Introduction for Article 314 76 314.25 Covers and Canopies When the installation is complete, each outlet box must be provided with a cover or faceplate, unless covered by a fixture
See Part 3 for the Introduction for Article 314 76 314.25 Covers and Canopies When the installation is complete, each outlet box must be provided with a cover or faceplate, unless covered by a fixture
Electrical Tech Note 111 Biosystems & Agricultural Engineering Department Michigan State University
 Electrical Tech Note 111 Biosystems & Agricultural Engineering Department Michigan State University Electrical Code Changes in Michigan 1 (Based on Part 8, P.A. 230, the 2005 NEC and the 2003 MRC) This
Electrical Tech Note 111 Biosystems & Agricultural Engineering Department Michigan State University Electrical Code Changes in Michigan 1 (Based on Part 8, P.A. 230, the 2005 NEC and the 2003 MRC) This
The following are specific provisions of 1910(a)(2) that could be seen in the LBM sector
 Know the Rules on Temporary Wiring OSHA Standard 1910.305, Wiring methods, components, and equipment for general use, addresses wiring methods, components, and equipment for general use as one of several
Know the Rules on Temporary Wiring OSHA Standard 1910.305, Wiring methods, components, and equipment for general use, addresses wiring methods, components, and equipment for general use as one of several
ECET Circuit Design Motor Loads. Branch Circuits. Article 210
 ECET 4520 Industrial Distribution Systems, Illumination, and the NEC Circuit Design Motor Loads Branch Circuits Article 210 210.1 Scope This article covers branch circuits except for those that supply
ECET 4520 Industrial Distribution Systems, Illumination, and the NEC Circuit Design Motor Loads Branch Circuits Article 210 210.1 Scope This article covers branch circuits except for those that supply
ARKANSAS ELECTRICIANS
 CONTINUING EDUCATION FOR ARKANSAS ELECTRICIANS 2014 NEC Code Change 8 Hours AMERICAN ELECTRICAL INSTITUTE N16 W23217 Stone Ridge Drive, Suite 290 Waukesha, WI 53188 855-780-5046 www.aeitraining.com DISCLAIMER
CONTINUING EDUCATION FOR ARKANSAS ELECTRICIANS 2014 NEC Code Change 8 Hours AMERICAN ELECTRICAL INSTITUTE N16 W23217 Stone Ridge Drive, Suite 290 Waukesha, WI 53188 855-780-5046 www.aeitraining.com DISCLAIMER
Electrical Tech Note 106
 Electrical Tech Note 106 Biosystems & Agricultural Engineering Department Michigan State University Master Exam Study Guide and Sample Questions 1 Based on the 2014 NEC, Part 8 of PA 230, PA 407, and the
Electrical Tech Note 106 Biosystems & Agricultural Engineering Department Michigan State University Master Exam Study Guide and Sample Questions 1 Based on the 2014 NEC, Part 8 of PA 230, PA 407, and the
Continued from Part 2 Rules
 Continued from Part 2 Rules 26 50. 51 250.94 Grounding (Bonding) of Communications Systems An accessible bonding point must be provided at service equipment or the disconnecting means of separate buildings
Continued from Part 2 Rules 26 50. 51 250.94 Grounding (Bonding) of Communications Systems An accessible bonding point must be provided at service equipment or the disconnecting means of separate buildings
CHAPTER 10 ELECTRICAL. Notes:
 CHAPTER 10 ELECTRICAL 1001.0 General Requirements. Electrical wiring and equipment shall comply with the requirements of NFPA 70, National Electrical Code (NEC), or local ordinances. 1002.0 Solar Photovoltaic
CHAPTER 10 ELECTRICAL 1001.0 General Requirements. Electrical wiring and equipment shall comply with the requirements of NFPA 70, National Electrical Code (NEC), or local ordinances. 1002.0 Solar Photovoltaic
NEC 2011 Code Changes
 NEC 2011 Code Changes Articles 280.21-300.50 CHANGES FROM 2008 TO 2011 CODE ARE IN RED Chapter 2 - Wiring and Protection ARTICLE 280 Surge Arresters, Over 1kV III. Connecting Surge Arresters 280.21 Connection
NEC 2011 Code Changes Articles 280.21-300.50 CHANGES FROM 2008 TO 2011 CODE ARE IN RED Chapter 2 - Wiring and Protection ARTICLE 280 Surge Arresters, Over 1kV III. Connecting Surge Arresters 280.21 Connection
MECKLENBURG COUNTY. Land Use and Environmental Service Agency Code Enforcement 2/8/12 ELECTRICAL CONSISTENCY MEETING. Code Consistency Questions
 MECKLENBURG COUNTY Land Use and Environmental Service Agency Code Enforcement 2/8/12 ELECTRICAL CONSISTENCY MEETING Code Consistency Questions 1. I am inspecting a building addition. They have a 480V to
MECKLENBURG COUNTY Land Use and Environmental Service Agency Code Enforcement 2/8/12 ELECTRICAL CONSISTENCY MEETING Code Consistency Questions 1. I am inspecting a building addition. They have a 480V to
Electrical Tech Note 105 Agricultural Engineering Department Michigan State University
 Electrical Tech Note 105 Agricultural Engineering Department Michigan State University Journey Exam Study Guide and Sample Questions 1 Based on the 2002 NEC, Part 8 of PA 230, and the 2003 MRC The Journey
Electrical Tech Note 105 Agricultural Engineering Department Michigan State University Journey Exam Study Guide and Sample Questions 1 Based on the 2002 NEC, Part 8 of PA 230, and the 2003 MRC The Journey
90.2 Scope. The installation of electrical conductors, equipment and raceways for:
 NEC Generator Primer Rules on the installation of generators and transfer switches 1 90.2 Scope The installation of electrical conductors, equipment and raceways for: public and private premises Conductors
NEC Generator Primer Rules on the installation of generators and transfer switches 1 90.2 Scope The installation of electrical conductors, equipment and raceways for: public and private premises Conductors
CHAPTER 10 ELECTRICAL
 1001.0 General Requirements. 1001.1 Electrical Wiring and Equipment. Electrical wiring and equipment shall comply with the requirements of NFPA 70, National Electrical Code (NEC), or local ordinances.
1001.0 General Requirements. 1001.1 Electrical Wiring and Equipment. Electrical wiring and equipment shall comply with the requirements of NFPA 70, National Electrical Code (NEC), or local ordinances.
TEMPORARY ELECTRIC WIRING FOR CARNIVALS, CONVENTIONS, EXHIBITIONS, FAIRS AND SIMILAR USES
 INFORMATION BULLETIN / PUBLIC - ELECTRICAL CODE REFERENCE NO.: LAMC 93.0230 Effective: 3-24-69 DOCUMENT NO. P/EC 2002-006 Revised: 11-17-00 Previously Issued As: RGA #7-69 TEMPORARY ELECTRIC WIRING FOR
INFORMATION BULLETIN / PUBLIC - ELECTRICAL CODE REFERENCE NO.: LAMC 93.0230 Effective: 3-24-69 DOCUMENT NO. P/EC 2002-006 Revised: 11-17-00 Previously Issued As: RGA #7-69 TEMPORARY ELECTRIC WIRING FOR
Fee $20 Course: NEC Changes 1 This course is valid for these credentials: Credential Description Cred Code Credit Hours
 www.garyklinka.com Page 1 of 18 Instructions: Fee $20 1. Print these pages. 2. Circle the correct answers and transfer them to the answer sheet. 3. Page down to the last page for the verification forms
www.garyklinka.com Page 1 of 18 Instructions: Fee $20 1. Print these pages. 2. Circle the correct answers and transfer them to the answer sheet. 3. Page down to the last page for the verification forms
WISCONSIN ELECTRICIANS
 Wisconsin Contractors Institute 2017 PART 2 3 CONTINUING EDUCATION FOR WISCONSIN ELECTRICIANS 2017 NEC Code Change Part 2 8 Hours WISCONSIN CONTRACTORS INSTITUTE N16 W23217 Stone Ridge Drive, Suite 290
Wisconsin Contractors Institute 2017 PART 2 3 CONTINUING EDUCATION FOR WISCONSIN ELECTRICIANS 2017 NEC Code Change Part 2 8 Hours WISCONSIN CONTRACTORS INSTITUTE N16 W23217 Stone Ridge Drive, Suite 290
Chapter 8 Interior Wiring and Lighting
 Chapter 8 Interior Wiring and Lighting Review Questions 1. What tool if any, is used to remove a fuse that is to be replaced? 1. Pliers 2. Screwdriver 3. Fuse puller 4. None 2. OSHA has established specific
Chapter 8 Interior Wiring and Lighting Review Questions 1. What tool if any, is used to remove a fuse that is to be replaced? 1. Pliers 2. Screwdriver 3. Fuse puller 4. None 2. OSHA has established specific
9/16/2010. Chapter , The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS. 2010, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 3 TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS 1 Transmitting large amounts of electric energy over long distances is accomplished most efficiently by using high-voltages. Without transformers the widespread distribution
Chapter 3 TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS 1 Transmitting large amounts of electric energy over long distances is accomplished most efficiently by using high-voltages. Without transformers the widespread distribution
CONTINUING EDUCATION FOR OREGON ELECTRICIANS NEC Code Change Part 2 Course # Hours
 AMERICAN ELECTRICAL INSTITUTE 2017 PART 2 3 CONTINUING EDUCATION FOR OREGON ELECTRICIANS 2017 NEC Code Change Part 2 Course #90817 8 Hours AMERICAN ELECTRICAL INSTITUTE N16 W23217 Stone Ridge Drive, Suite
AMERICAN ELECTRICAL INSTITUTE 2017 PART 2 3 CONTINUING EDUCATION FOR OREGON ELECTRICIANS 2017 NEC Code Change Part 2 Course #90817 8 Hours AMERICAN ELECTRICAL INSTITUTE N16 W23217 Stone Ridge Drive, Suite
WIRING DESIGN & PROTECTION REQUIREMENTS CHECKLIST
 WIRING DESIGN & PROTECTION REQUIREMENTS CHECKLIST Use & Identification of Grounded and Grounding Conductors YES NO N/A Grounded conductors are identifiable and distinguishable from all other conductors.
WIRING DESIGN & PROTECTION REQUIREMENTS CHECKLIST Use & Identification of Grounded and Grounding Conductors YES NO N/A Grounded conductors are identifiable and distinguishable from all other conductors.
SUPPLEMENTAL CORRECTION SHEET FOR SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS - ELECTRICAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL CORRECTION SHEET FOR SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS - ELECTRICAL This is intended to provide uniform application of the codes by the plan check staff and to help the public apply the codes correctly.
SUPPLEMENTAL CORRECTION SHEET FOR SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS - ELECTRICAL This is intended to provide uniform application of the codes by the plan check staff and to help the public apply the codes correctly.
FACT SHEET Standard: Electrical Safety
 What is a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter? FACT SHEET The ground-fault circuit interrupter, or GFCI, is a fast-acting circuit breaker designed to shut off electric power in the event of a ground-fault
What is a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter? FACT SHEET The ground-fault circuit interrupter, or GFCI, is a fast-acting circuit breaker designed to shut off electric power in the event of a ground-fault
Contents. Review of Electric Circuitd. Preface ;
 Preface ; Chapter 1 Review of Electric Circuitd 1.1 Introduction, 1 1.2 Direct Circuit Current, 1 1.2.1 Voltage, 3 1.2.2 Power, 3 1.2.3 Ohm's Law, 5 1.2.4 KirchhofTs Laws, 5 1.2.4.1 Kirchhoff s Current
Preface ; Chapter 1 Review of Electric Circuitd 1.1 Introduction, 1 1.2 Direct Circuit Current, 1 1.2.1 Voltage, 3 1.2.2 Power, 3 1.2.3 Ohm's Law, 5 1.2.4 KirchhofTs Laws, 5 1.2.4.1 Kirchhoff s Current
Overcurrent Protection (2014 NEC) (Homestudy)
 Overcurrent Protection (2014 NEC) (Homestudy) Oregon Electrical License The key sections of Article 240 will be discussed. Overcurrent protection for panelboards, appliances, motors, motor compressors,
Overcurrent Protection (2014 NEC) (Homestudy) Oregon Electrical License The key sections of Article 240 will be discussed. Overcurrent protection for panelboards, appliances, motors, motor compressors,
Have You Been Grounded Lately
 Have You Been Grounded Lately Thurs, Oct. 26, 2017 9:15-10:15 Phil Simmons Author, Electrical Grounding and Bonding Author Cengage Learning Phil Simmons Have You Been Grounded Lately 2017 NEC Changes Relative
Have You Been Grounded Lately Thurs, Oct. 26, 2017 9:15-10:15 Phil Simmons Author, Electrical Grounding and Bonding Author Cengage Learning Phil Simmons Have You Been Grounded Lately 2017 NEC Changes Relative
SINGLE PHASE WIRING SPECIFICATIONS
 SINGLE PHASE WIRING SPECIFICATIONS 1-866-MEC-ELEC (1-866-632-3532) Office Locations: Hondo Office 237 Hwy 173 N Hondo, TX 78661-0370 Fax 830.426.3335 Dilley Office 1718 W. FM 117 Dilley, TX 78017 Fax 830.965.1425
SINGLE PHASE WIRING SPECIFICATIONS 1-866-MEC-ELEC (1-866-632-3532) Office Locations: Hondo Office 237 Hwy 173 N Hondo, TX 78661-0370 Fax 830.426.3335 Dilley Office 1718 W. FM 117 Dilley, TX 78017 Fax 830.965.1425
9/7/2010. Objectives. Article 90. Introduction NEC Significant Changes. Review significant revisions in the 2011 NEC
 2011 NEC Significant Changes Courtesy of NJATC Courtesy of NFPA Presented By: Michael J. Johnston Executive Director of Standards and Safety, NECA Objectives Review significant revisions in the 2011 NEC
2011 NEC Significant Changes Courtesy of NJATC Courtesy of NFPA Presented By: Michael J. Johnston Executive Director of Standards and Safety, NECA Objectives Review significant revisions in the 2011 NEC
THREE PHASE WIRING SPECIFICATIONS
 THREE PHASE WIRING SPECIFICATIONS 1-866-MEC-ELEC (1-866-632-3532) Office Locations: Hondo Office 237 Hwy 173 N Hondo, TX 78661-0370 Fax 830.426.3335 Dilley Office 1718 W. FM 117 Dilley, TX 78017 Fax 830.965.1425
THREE PHASE WIRING SPECIFICATIONS 1-866-MEC-ELEC (1-866-632-3532) Office Locations: Hondo Office 237 Hwy 173 N Hondo, TX 78661-0370 Fax 830.426.3335 Dilley Office 1718 W. FM 117 Dilley, TX 78017 Fax 830.965.1425
2016 Photovoltaic Solar System Plan Review List
 Building Division 555 Santa Clara Street Vallejo CA 94590 707.648.4374 2016 Photovoltaic Solar System Plan Review List GENERAL PROJECT INFORMATION PLAN CHECK NO DATE JOB ADDRESS CITY ZIP REVIEWED BY PHONE
Building Division 555 Santa Clara Street Vallejo CA 94590 707.648.4374 2016 Photovoltaic Solar System Plan Review List GENERAL PROJECT INFORMATION PLAN CHECK NO DATE JOB ADDRESS CITY ZIP REVIEWED BY PHONE
Western Section 101 st Annual Meeting Hot Springs, Arkansas September 21, 2005 Charlie Trout Code Breakfast
 Western Section 101 st Annual Meeting Hot Springs, Arkansas September 21, 2005 Charlie Trout Code Breakfast 1.Question: An add on unit for a hydromassage bathtub consists of a small 1-gallon water heater
Western Section 101 st Annual Meeting Hot Springs, Arkansas September 21, 2005 Charlie Trout Code Breakfast 1.Question: An add on unit for a hydromassage bathtub consists of a small 1-gallon water heater
NEC 2014 Code Changes
 NEC 2014 Code Changes Articles 310 310.120 CHANGES FROM 2011 TO 2014 CODE ARE IN RED ARTICLE 310 Conductors for General Wiring I. General 310.2 Definitions Electrical Ducts Electrical conduits, or other
NEC 2014 Code Changes Articles 310 310.120 CHANGES FROM 2011 TO 2014 CODE ARE IN RED ARTICLE 310 Conductors for General Wiring I. General 310.2 Definitions Electrical Ducts Electrical conduits, or other
2014 NEC Changes Part 4
 www.garyklinka.com Page 1 of 14 Instructions: Fee $25 1. Print these pages. 2. Circle the correct answers and transfer them to the answer sheet. 3. Page down to the last page for the verification forms
www.garyklinka.com Page 1 of 14 Instructions: Fee $25 1. Print these pages. 2. Circle the correct answers and transfer them to the answer sheet. 3. Page down to the last page for the verification forms
Definitions of and have been revised. a. automatic b. nonautomatic c. none of the above d. both a and b
 www.garyklinka.com Page 1 of 12 Instructions: Fee $25 1. Print these pages. 2. Circle the correct answers and transfer them to the answer sheet. 3. Page down to the last page for the verification forms
www.garyklinka.com Page 1 of 12 Instructions: Fee $25 1. Print these pages. 2. Circle the correct answers and transfer them to the answer sheet. 3. Page down to the last page for the verification forms
Overcurrent Protection According to the 2011 NEC
 Overcurrent Protection According to the 2011 NEC Utah Electrical License This course will cover overcurrent protection according to the 2011 NEC. The key sections of Article 240 will be discussed. Overcurrent
Overcurrent Protection According to the 2011 NEC Utah Electrical License This course will cover overcurrent protection according to the 2011 NEC. The key sections of Article 240 will be discussed. Overcurrent
Generator Fire Safety: Generator assemblies should be located outside the building.
 SECTION 33 70 00 - ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION PACKAGED GENERATOR ASSEMBLIES Generator Fire Safety: Generator assemblies should be located outside the building. All fuel piping from the outside of the building
SECTION 33 70 00 - ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION PACKAGED GENERATOR ASSEMBLIES Generator Fire Safety: Generator assemblies should be located outside the building. All fuel piping from the outside of the building
2011 NEC Changes Part 2 (Homestudy) (Homestudy)
 2011 NEC Changes Part 2 (Homestudy) (Homestudy) North Carolina Electrical License This course will review the second half of the most important National Electrical Code changes from the 2011 NEC. Changes
2011 NEC Changes Part 2 (Homestudy) (Homestudy) North Carolina Electrical License This course will review the second half of the most important National Electrical Code changes from the 2011 NEC. Changes
(The actual state exam will be closer to 50 questions in 4 hours time) Master Electrician Practice Test
 (The actual state exam will be closer to 50 questions in 4 hours time) Master Electrician Practice Test 1. Accessible as applied to wiring methods means capable of being removed or exposed without damaging
(The actual state exam will be closer to 50 questions in 4 hours time) Master Electrician Practice Test 1. Accessible as applied to wiring methods means capable of being removed or exposed without damaging
2014 NEC Changes (Homestudy)
 2014 NEC Changes (Homestudy) Idaho Electrical License This course will review the most important National Electrical Code changes from the 2014 NEC. Changes in Articles 100 - Chapter 9 will be covered.
2014 NEC Changes (Homestudy) Idaho Electrical License This course will review the most important National Electrical Code changes from the 2014 NEC. Changes in Articles 100 - Chapter 9 will be covered.
Photovoltaic Solar Plan Review
 PAIGE B. VAUGHAN, CBO Director of Building and Safety Phone (310) 605-5509 Fax Line (310) 605-5598 E-mail:lbutler@comptoncity.org Building & Safety Department Photovoltaic Solar Plan Review Plan Check
PAIGE B. VAUGHAN, CBO Director of Building and Safety Phone (310) 605-5509 Fax Line (310) 605-5598 E-mail:lbutler@comptoncity.org Building & Safety Department Photovoltaic Solar Plan Review Plan Check
ADVANCED CALCULATIONS
 ADVANCED CALCULATIONS 101. Why is it permissible in some cases to fuse a #14 AWG motor conductor with a 60 amp breaker when normally a #14 AWG should only be fused at 15 amps? a) the motor can't start
ADVANCED CALCULATIONS 101. Why is it permissible in some cases to fuse a #14 AWG motor conductor with a 60 amp breaker when normally a #14 AWG should only be fused at 15 amps? a) the motor can't start
Pretest Module 29 High Voltage Unit 1
 Pretest Module 29 High Voltage Unit 1 1. Is a person qualified to work on high-voltage installations when this module is completed? 2. What is the code definition of high-voltage? 3. What is the IEEE definition
Pretest Module 29 High Voltage Unit 1 1. Is a person qualified to work on high-voltage installations when this module is completed? 2. What is the code definition of high-voltage? 3. What is the IEEE definition
This is intended to provide uniform application of the codes by the plan check staff and to help the public apply the codes correctly.
 SUPPLEMENTAL CORRECTION SHEET FOR SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS (ELEC) This is intended to provide uniform application of the codes by the plan check staff and to help the public apply the codes correctly.
SUPPLEMENTAL CORRECTION SHEET FOR SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS (ELEC) This is intended to provide uniform application of the codes by the plan check staff and to help the public apply the codes correctly.
TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS
 TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS Transmitting large amounts of electric energy over long distances is accomplished most efficiently by using high-voltages. Without transformers the widespread distribution of electric
TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS Transmitting large amounts of electric energy over long distances is accomplished most efficiently by using high-voltages. Without transformers the widespread distribution of electric
2011 NEC Significant Changes Part 1 The following course will summarize many of the important changes to the NEC code.
 2 PART 1 American Electrical Institute 2013 2011 NEC Significant Changes Part 1 The following course will summarize many of the important changes to the NEC code. The 2011 Code has added 3 new articles:
2 PART 1 American Electrical Institute 2013 2011 NEC Significant Changes Part 1 The following course will summarize many of the important changes to the NEC code. The 2011 Code has added 3 new articles:
SECTION 1: Field Inspection Guide for Rooftop Photovoltaic (PV) Systems
 COUNTY OF SANTA CRUZ PLANNING DEPARTMENT 701 OCEAN STREET, 4 th FLOOR, SANTA CRUZ, CA 95060 (831) 454-2580 FAX: (831) 454-2131 TDD: (831) 454-2123 KATHLEEN MOLLOY PREVISICH, PLANNING DIRECTOR Photovoltaic
COUNTY OF SANTA CRUZ PLANNING DEPARTMENT 701 OCEAN STREET, 4 th FLOOR, SANTA CRUZ, CA 95060 (831) 454-2580 FAX: (831) 454-2131 TDD: (831) 454-2123 KATHLEEN MOLLOY PREVISICH, PLANNING DIRECTOR Photovoltaic
ELECTRICAL POWER and POWER ELECTRONICS
 Introduction to ELECTRICAL POWER and POWER ELECTRONICS MUKUND R PATEL (cj* CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup, an informa
Introduction to ELECTRICAL POWER and POWER ELECTRONICS MUKUND R PATEL (cj* CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup, an informa
Pretest Module 24 Three-phase Service Entrance
 Pretest Module 24 Three-phase Service Entrance 1. What is the most widely used three-phase service entrance system? 2. What are the three most common voltage combinations for three-phase, four-wire systems?
Pretest Module 24 Three-phase Service Entrance 1. What is the most widely used three-phase service entrance system? 2. What are the three most common voltage combinations for three-phase, four-wire systems?
ECET 211 Electric Machines & Controls Lecture 8 Motor Control Circuits (1 of 2) Lecture 8 Motor Control Circuits
 ECET 211 Electric Machines & Controls Lecture 8 Motor Control Circuits (1 of 2) Text Book: Electric Motors and Control Systems, by Frank D. Petruzella, published by McGraw Hill, 2015. Paul I-Hai Lin, Professor
ECET 211 Electric Machines & Controls Lecture 8 Motor Control Circuits (1 of 2) Text Book: Electric Motors and Control Systems, by Frank D. Petruzella, published by McGraw Hill, 2015. Paul I-Hai Lin, Professor
9. Non-Residential Services (Commercial, Industrial, and Agricultural)
 Section 9 2016 Electric Service Requirements, 3rd Edition Section 9 Non-Residential Services Directory Page 9.1 General Requirements 68 9.2 Direct-Connect Metering, Single Installations 69 9.3 Direct-Connect
Section 9 2016 Electric Service Requirements, 3rd Edition Section 9 Non-Residential Services Directory Page 9.1 General Requirements 68 9.2 Direct-Connect Metering, Single Installations 69 9.3 Direct-Connect
A. Submit manufacturer's literature and technical data before starting work.
 SECTION 16425 SWITCHBOARD PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SUMMARY A. Related Section: 1. 16450 - Grounding. 1.02 SUBMITTALS A. Submit manufacturer's literature and technical data before starting work. B. Submit Shop
SECTION 16425 SWITCHBOARD PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SUMMARY A. Related Section: 1. 16450 - Grounding. 1.02 SUBMITTALS A. Submit manufacturer's literature and technical data before starting work. B. Submit Shop
2014 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY (Com. to ECE, EIE, BME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY (Com. to ECE, EIE, BME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Transmission & Distribution Glossary of Electrical Terms
 Transmission & Distribution Glossary of Electrical s Breaker Panel Bushing Circuit Circuit Breaker Conductor Conduit Consumption Current Distribution Electricity (Static vs. Current) Electron Feeder The
Transmission & Distribution Glossary of Electrical s Breaker Panel Bushing Circuit Circuit Breaker Conductor Conduit Consumption Current Distribution Electricity (Static vs. Current) Electron Feeder The
Corrections most seen on plan review October 18, 2017 David Rankin Seattle Department of Construction and Inspections
 Corrections most seen on plan review October 18, 2017 David Rankin Seattle Department of Construction and Inspections One-Line / Riser Diagrams Drawings are not reviewed prior to submission. Because of
Corrections most seen on plan review October 18, 2017 David Rankin Seattle Department of Construction and Inspections One-Line / Riser Diagrams Drawings are not reviewed prior to submission. Because of
ROCKY MOUNTAIN CHAPTER IAEI MARCH 15-16, 2012
 ROCKY MOUNTAIN CHAPTER IAEI MARCH 15-16, 2012 1) Can a switched outlet be on a small appliance branch circuit for dining room lighting? No, a switched outlet on a general purpose branch circuit may be
ROCKY MOUNTAIN CHAPTER IAEI MARCH 15-16, 2012 1) Can a switched outlet be on a small appliance branch circuit for dining room lighting? No, a switched outlet on a general purpose branch circuit may be
Mecklenburg County Common Code Defects
 Electrical Code Defects Improper Over Current Protection Code Description 310.15 Ampacities for s Rated 0 2000 Volts. (A) General. (1) Tables or Engineering Supervision. Ampacities for conductors shall
Electrical Code Defects Improper Over Current Protection Code Description 310.15 Ampacities for s Rated 0 2000 Volts. (A) General. (1) Tables or Engineering Supervision. Ampacities for conductors shall
Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI) FACT SHEET
 Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI) FACT SHEET THE AFCI The AFCI is an arc fault circuit interrupter. AFCIs are newly-developed electrical devices designed to protect against fires caused by arcing faults
Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI) FACT SHEET THE AFCI The AFCI is an arc fault circuit interrupter. AFCIs are newly-developed electrical devices designed to protect against fires caused by arcing faults
Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace
 Assessment Requirements Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace Content: Basic electrical principles a. Explain the direction of current flow
Assessment Requirements Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace Content: Basic electrical principles a. Explain the direction of current flow
Chapter 5. Imagine That Engineering Inc. Assured Equipment Grounding Conductor Program (AEGCP) Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)
 Chapter 5 Imagine That Engineering Inc. Assured Equipment Grounding Conductor Program (AEGCP) Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Imagine That Engineering Inc. has adopted this program for equipment
Chapter 5 Imagine That Engineering Inc. Assured Equipment Grounding Conductor Program (AEGCP) Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Imagine That Engineering Inc. has adopted this program for equipment
 APGENCO/APTRANSCO Assistant Engineer Electrical Previous Question Papers Q.1 The two windings of a transformer is conductively linked. inductively linked. not linked at all. electrically linked. Q.2 A
APGENCO/APTRANSCO Assistant Engineer Electrical Previous Question Papers Q.1 The two windings of a transformer is conductively linked. inductively linked. not linked at all. electrically linked. Q.2 A
Electrical Hazards in Construction
 Electrical Hazards in Construction WELCOME Tim Dawson Presentation developed by Dawson Safety Services - 2013 Dangers of Electrical Shock Currents above 10 ma* can paralyze or freeze muscles. Currents
Electrical Hazards in Construction WELCOME Tim Dawson Presentation developed by Dawson Safety Services - 2013 Dangers of Electrical Shock Currents above 10 ma* can paralyze or freeze muscles. Currents
4 Electric Circuits. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify Below each switch, label the circuit as a closed circuit or an open circuit.
 CHAPTER 17 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
CHAPTER 17 4 Electric Circuits SECTION Introduction to Electricity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the three main parts of a circuit?
TRI-SERVICE ELECTRICAL WORKING GROUP (TSEWG) 03/05/09 TSEWG TP-11: UFC N BEST PRACTICES
 TSEWG TP-11: UFC 3-500-10N BEST PRACTICES UFC 3-500-10N was developed by NAVFAC and was used as the starting point for the tri-services development of UFC 3-500-10, Design: Electrical Engineering. UFC
TSEWG TP-11: UFC 3-500-10N BEST PRACTICES UFC 3-500-10N was developed by NAVFAC and was used as the starting point for the tri-services development of UFC 3-500-10, Design: Electrical Engineering. UFC
DC CIRCUITS ELECTROMAGNETISM
 DC CIRCUITS 1. State and Explain Ohm s Law. Write in brief about the limitations of Ohm s Law. 2. State and explain Kirchhoff s laws. 3. Write in brief about disadvantages of series circuit and advantages
DC CIRCUITS 1. State and Explain Ohm s Law. Write in brief about the limitations of Ohm s Law. 2. State and explain Kirchhoff s laws. 3. Write in brief about disadvantages of series circuit and advantages
An average of one worker is electrocuted on the job every day There are four main types of electrical injuries:
 Electrical Safety Introduction An average of one worker is electrocuted on the job every day There are four main types of electrical injuries: Electrocution (death due to electrical shock) Electrical shock
Electrical Safety Introduction An average of one worker is electrocuted on the job every day There are four main types of electrical injuries: Electrocution (death due to electrical shock) Electrical shock
Western Section IAEI Code Panel Questions
 Western Section IAEI 2013 Code Panel Questions 1. Do the factory wings that many fluorescent troffers have designed to fold out over the grid meet the requirements for securely fastened to the framing?
Western Section IAEI 2013 Code Panel Questions 1. Do the factory wings that many fluorescent troffers have designed to fold out over the grid meet the requirements for securely fastened to the framing?
SECTION 300 OVERHEAD SERVICE
 SECTION 300 OVERHEAD SERVICE 300.01 General Company provides, installs, and maintains service drop to point of delivery approved by Company. Customer provides point of attachment which is acceptable to
SECTION 300 OVERHEAD SERVICE 300.01 General Company provides, installs, and maintains service drop to point of delivery approved by Company. Customer provides point of attachment which is acceptable to
CONTINUING EDUCATION FOR OREGON ELECTRICIANS NEC Code Change Part 1 8 Hours
 AMERICAN ELECTRICAL INSTITUTE 2017 PART 1 3 CONTINUING EDUCATION FOR OREGON ELECTRICIANS 2017 NEC Code Change Part 1 8 Hours AMERICAN ELECTRICAL INSTITUTE PO Box 31131 Spokane, WA 99223 855-780-5046 www.aeitraining.com
AMERICAN ELECTRICAL INSTITUTE 2017 PART 1 3 CONTINUING EDUCATION FOR OREGON ELECTRICIANS 2017 NEC Code Change Part 1 8 Hours AMERICAN ELECTRICAL INSTITUTE PO Box 31131 Spokane, WA 99223 855-780-5046 www.aeitraining.com
2014 NEC Changes Part 1 (Homestudy)
 2014 NEC Changes Part 1 (Homestudy) Wisconsin Electrical License This course will review the first half of the most important National Electrical Code changes from the 2014 NEC. Changes in Articles 100-404.2
2014 NEC Changes Part 1 (Homestudy) Wisconsin Electrical License This course will review the first half of the most important National Electrical Code changes from the 2014 NEC. Changes in Articles 100-404.2
Question Set(2017) Switch Gear & protection(5 th SEm) 9. Explain the construction and operating principle with proper diagram:
 Question Set(2017) Switch Gear & protection(5 th SEm) 1. What is fault in power system? Classify the fault. What are the bad effects of fault? 2. Define with example: Symmetrical fault and unsymmetrical
Question Set(2017) Switch Gear & protection(5 th SEm) 1. What is fault in power system? Classify the fault. What are the bad effects of fault? 2. Define with example: Symmetrical fault and unsymmetrical
MECKLENBURG COUNTY. Land Use and Environmental Service Agency Code Enforcement 9/14/11 ELECTRICAL CONSISTENCY MEETING. Code Consistency Questions
 MECKLENBURG COUNTY Land Use and Environmental Service Agency Code Enforcement 9/14/11 ELECTRICAL CONSISTENCY MEETING Code Consistency Questions 1. I recently installed a 45-KVA transformer, 480-volt primary
MECKLENBURG COUNTY Land Use and Environmental Service Agency Code Enforcement 9/14/11 ELECTRICAL CONSISTENCY MEETING Code Consistency Questions 1. I recently installed a 45-KVA transformer, 480-volt primary
Installing a Downstream Distribution Panelboard
 Job Sheet 5 Installing a Downstream Distribution Panelboard OBJECTIVE To install a downstream distribution panelboard (DDP) on the Mobile Workstation. To mechanically and electrically connect the DDP to
Job Sheet 5 Installing a Downstream Distribution Panelboard OBJECTIVE To install a downstream distribution panelboard (DDP) on the Mobile Workstation. To mechanically and electrically connect the DDP to
SECTION ENCLOSED SWITCHES AND CIRCUIT BREAKERS
 SECTION 26 28 16 ENCLOSED SWITCHES AND PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 SUMMARY A. Section includes the following individually mounted, enclosed switches and circuit breakers rated 600V AC and less: 1. Fusible switches.
SECTION 26 28 16 ENCLOSED SWITCHES AND PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 SUMMARY A. Section includes the following individually mounted, enclosed switches and circuit breakers rated 600V AC and less: 1. Fusible switches.
SERVICE ATTACHMENT ON A BUILDING WITH BUS DUCT SERVICE ENTRANCE AND INDOOR METERING
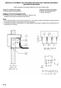 SERVICE ATTACHMENT ON A BUILDING WITH BUS DUCT SERVICE ENTRANCE AND INDOOR METERING Obtain acceptance and specific details from the local Company office. 1. Service entrance duct (see Note 1). Company
SERVICE ATTACHMENT ON A BUILDING WITH BUS DUCT SERVICE ENTRANCE AND INDOOR METERING Obtain acceptance and specific details from the local Company office. 1. Service entrance duct (see Note 1). Company
A system fault contribution of 750 mva shall be used when determining the required interrupting rating for unit substation equipment.
 General Unit substations shall be 500 kva minimum, 1500 kva maximum unless approved otherwise by the University. For the required configuration of University substations see Standard Electrical Detail
General Unit substations shall be 500 kva minimum, 1500 kva maximum unless approved otherwise by the University. For the required configuration of University substations see Standard Electrical Detail
SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 17: TYPES OF ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT OBJECTIVES UNIT OBJECTIVES 3/21/2012
 SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 17: TYPES OF ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, the reader should be able to Describe the different types of open single-phase motors used to drive
SECTION 4 ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT 17: TYPES OF ELECTRIC MOTORS UNIT OBJECTIVES After studying this unit, the reader should be able to Describe the different types of open single-phase motors used to drive
Metering and Service Installation:
 Table of Contents 1. Metering Installation Requirements, General... 1 2. Type of Service... 2 3. Definitions... 2 4. Who Provides Metering Equipment?... 2 5. Establishment of Service... 2 6. Meter Access...
Table of Contents 1. Metering Installation Requirements, General... 1 2. Type of Service... 2 3. Definitions... 2 4. Who Provides Metering Equipment?... 2 5. Establishment of Service... 2 6. Meter Access...
ELECTRICAL. 60 Minutes
 ELECTRICAL 60 Minutes AGENDA Electrical definitions Electrical shocks, burns and secondary injuries Electrical hazards in the workplace Safety devices and prevention steps Do s and Don ts INTRODUCTORY
ELECTRICAL 60 Minutes AGENDA Electrical definitions Electrical shocks, burns and secondary injuries Electrical hazards in the workplace Safety devices and prevention steps Do s and Don ts INTRODUCTORY
SECTION PANELBOARDS
 SECTION 16470 PANELBOARDS PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. The general provisions of the contract including General and Special Conditions and General Requirements shall apply to all work under
SECTION 16470 PANELBOARDS PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. The general provisions of the contract including General and Special Conditions and General Requirements shall apply to all work under
DEWALT Electrical Licensing Exam Guide CONTENTS
 DEWALT Electrical Licensing Exam Guide v ONTENTS How to Prepare for the Exam................................................ 2 How to Study.............................................................
DEWALT Electrical Licensing Exam Guide v ONTENTS How to Prepare for the Exam................................................ 2 How to Study.............................................................
Michigan State University Construction Standards SECONDARY UNIT SUBSTATIONS PAGE
 PAGE 261116-1 SECTION 261116 PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. Drawings and general provisions of the Contract, including General and Supplementary Conditions and Division 01 Specification Sections,
PAGE 261116-1 SECTION 261116 PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. Drawings and general provisions of the Contract, including General and Supplementary Conditions and Division 01 Specification Sections,
Electrical Design/Build Guide
 2017 Electrical Design/Build Guide Based on the 2017 National Electrical Code Copyright Durand & Associates 1986-2016 60 C Copper Ampacity 4 - Wire Fill - (Non-Current Carrying Neutral) 4 or 5 - Parallel
2017 Electrical Design/Build Guide Based on the 2017 National Electrical Code Copyright Durand & Associates 1986-2016 60 C Copper Ampacity 4 - Wire Fill - (Non-Current Carrying Neutral) 4 or 5 - Parallel
ELECTRICAL - GENERAL REQUIREMENTS SELF INSPECTION CHECKLIST
 Name of School: OPTIONAL INFORMATION Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: ELECTRICAL - GENERAL REQUIREMENTS SELF INSPECTION CHECKLIST Guidelines: This checklist covers
Name of School: OPTIONAL INFORMATION Date of Inspection: Vocational Program/Course/Room: Signature of Inspector: ELECTRICAL - GENERAL REQUIREMENTS SELF INSPECTION CHECKLIST Guidelines: This checklist covers
A Look at the 2017 NEC Significant Changes
 A Look at the 2017 NEC Significant Changes A Look at the 2017 NEC Significant Changes Michael J. Johnston NECA James T. Dollard Local 98 Philadelphia Electrical JATC This session is eligible for 1 Continuing
A Look at the 2017 NEC Significant Changes A Look at the 2017 NEC Significant Changes Michael J. Johnston NECA James T. Dollard Local 98 Philadelphia Electrical JATC This session is eligible for 1 Continuing
A. This Section includes Low Voltage Switchgear Work, as indicated on the drawings, and as specified herein.
 16425 SWITCHBOARD ************************************************************************************************************* SPECIFIER: CSI MasterFormat 2004 number: 26 24 13 An optional keynote to
16425 SWITCHBOARD ************************************************************************************************************* SPECIFIER: CSI MasterFormat 2004 number: 26 24 13 An optional keynote to
SECTION LOW VOLTAGE DISTRIBUTION EQUIPMENT
 SECTION 16400 LOW VOLTAGE DISTRIBUTION EQUIPMENT A. General 1. The University does not accept Series-Rated equipment for power distribution switchboards, distribution panels and branch circuit panelboards.
SECTION 16400 LOW VOLTAGE DISTRIBUTION EQUIPMENT A. General 1. The University does not accept Series-Rated equipment for power distribution switchboards, distribution panels and branch circuit panelboards.
Electricity Course. Part B Course Outline
 Electricity Course Rev. Date: 10/01/2002 By: R. Crompton Part B Course Outline Subject Area 0 Orientation 2.6 0.0 0.1 To the School 1.0 0.2 To the Course 1.0 0.3 To the 0.3 0.3 0.4 To Possible Emergencies
Electricity Course Rev. Date: 10/01/2002 By: R. Crompton Part B Course Outline Subject Area 0 Orientation 2.6 0.0 0.1 To the School 1.0 0.2 To the Course 1.0 0.3 To the 0.3 0.3 0.4 To Possible Emergencies
Data Bulletin. Ground-Censor Ground-Fault Protection System Type GC Class 931
 Data Bulletin 0931DB0101 July 2001 Cedar Rapids, IA, USA Ground-Censor Ground-Fault Protection System Type GC Class 931 09313063 GT Sensor Shunt Trip of Circuit Interrupter Window Area for Conductors GC
Data Bulletin 0931DB0101 July 2001 Cedar Rapids, IA, USA Ground-Censor Ground-Fault Protection System Type GC Class 931 09313063 GT Sensor Shunt Trip of Circuit Interrupter Window Area for Conductors GC
