THE NEW MULTI-BILLION DOLLAR ENGINE: WHY THE EXPERTS
|
|
|
- Eustacia Mason
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE NEW MULTI-BILLION DOLLAR ENGINE: WHY THE EXPERTS ARE SO EXCITED! The Counterpoise Bi-Radial Engine Will Cause A Revolution In Engine Building. An explanation from the Chief Science Officer. ebook
2 The New Multi-Billion Dollar Engine: Why the experts are so excited. THE COUNTERPOISE BI-RADIAL ENGINE Authored by Del Wolverton Chief Science Officer/Founder WolvertonBailey, Inc. SUMMARY This is the year, 2017, that we celebrate 140 years since Dr. Nikolas Otto patented the four-stroke internal combustion engine in His gasoline engine serves as the origin of the Otto Cycle which is used as the basis for seven internal combustion engine variants today. For purposes of this white paper, the four-cylinder Otto engine will be used as the reference engine. Since Dr. Otto s engine was built around the origin of the four-stroke-cycle of the pistons, this allows us to have a piston per cycle. Many changes have taken place during the past century in the size and shape of the engine as designed for various uses, however, this original four-stroke cycle is still used even in the latest internal combustion engine, the Counterpoise Bi-Radial Engine. This discussion will first describe the basis Otto Cycle, providing a simple, math-free description of each of the four strokes in the cycle. Then, in order to help understand the operation, power, and weight advantages gained in the evolution, the author will take you through the existing variants, all the way to the latest internal combustion engine complete with the final patented design, the WBI Counterpoise Bi-Radial Engine. CONTENTS Single-Piston of the Otto Cycle... 2 The Four Strokes... 2 Intake... 2 Compression... 3 Power... 4 Exhaust... 5 Four-Cylinder Engine... 6 Four-Cylinder Boxer Engine... 7 Six-Cylinder Straight-Six Engine... 8 Eight-Cylinder Engine (V8)... 9 Radial Engine Rotary Engine Bi-Radial Engine Counterpoise Bi-Radial Engine (The Final Modification) Conclusion... 14
3 SINGLE-PISTON OF THE OTTO CYCLE If we analyze how a single piston develops power, we can use it as a standard throughout our descriptions. Further, that piston can be used as a building block to explain all of the following engine types. THE FOUR STROKES INTAKE In the following series of pictures, a crankshaft is shown moving a piston downward inside a shaded block called a bore assembly. The red arrows show the motion of the piston from the beginning of the cycle and the red arc indicates the motion of the crankshaft. Further discussions will use the term cylinder to refer to both the pistons and the bore assembly as a unit. Intake (First Down-Stroke) Intake Stroke Breathing in a mixture of air and fuel Without considering the intake valves, the exhaust valves, and other common engine parts, it can be said that the first half-rotation of the crankshaft moves the piston down a chamber, creating a void which, when compared to atmospheric pressure, causes an inrush of air and fuel to fill the void. When the piston reaches the bottom of the stroke, the chamber is closed, and the next stroke is ready to begin. 2 of 14
4 COMPRESSION The end of the first stroke leaves the piston at the bottom of the void with a volatile mixture ready to ignite. However, this would not accomplish anything useful, as burning the fuel at this point would create a great deal of heat and expanding gases with nowhere to go. Compression (First Up-Stroke) Compression Stroke Squeeze the mixture while it is cool As the crankshaft continues for another half-rotation as shown above, the piston is forced back up the chamber and compresses the mixture of air and fuel into a very small portion of the void. How much it is compressed is called the Compression Ratio and is determined by the length of the void as compared to the motion of the piston. Three things are accomplished by the compression of the mixture: the first being that the piston will be at the top of the void ready to move back down in the next stroke. The second is that the mixture of air and fuel will become very hot as it is compressed due to the nature of pressure and temperature with regard to gasses. The third thing to happen is that the pressure inside the void will be multiplied by the Compression Ratio (in pounds per square inch, for example.) For ease of explanation, we can now see that in one revolution of the crankshaft we have prepared the void to ignite a volatile, compressed mixture, such that there is room for the piston to move if we increase the pressure inside the void. The Otto Cycle is now halfway through and the engine design takes into consideration that there now needs to be a quick ignition of the mixture. Many things determine exactly when this will happen in a modern engine, but for this discussion, the time to ignite is NOW! 3 of 14
5 POWER The end of the second stroke leaves the piston back at the top of the void with a volatile mixture ready to ignite, hot and under great pressure. All that is needed is a small spark to cause this mixture to burn very quickly. This would create a great deal of heat, and expanding gases begin to push with great force on all surfaces equally. Power (Second Down-Stroke) Power Stroke A nearly EXPLOSIVE increase in Temperature and Pressure A spark, properly timed by the engine components, ignites the pressurized mixture and an enormous increase in temperature from the burning fuel causes the pressure to increase many times over what it was per square inch. This pressure, like in a balloon, presses in every direction equally. However, there is only one surface that can move to reduce the pressure the top of the piston, which moves down, pushing the piston, the piston rod, and the crankshaft another half-rotation as shown above. During this POWER stroke, enough energy is released to force the rotating crankshaft and other masses to continue to rotate through all four cycles. There is more than enough pressure to make this a useful source of power for other devices. In fact, the power released by this one cylinder during the POWER stroke, if harnessed by a large flywheel, is actually a one cylinder engine. It should be understood, that if the single cylinder was not a source of positive rotational energy, then it would not matter how many of them you tried to harness together. The efficiency of the engine in its entirety is equal to the efficiency of a single cylinder. The piston then reaches the bottom of the chamber that started as a void, and is now filled with burned hot gas and pollutants. These are no longer useful to the engine, as pushing the piston down has decreased the compressed gasses while they expanded and cooled somewhat. 4 of 14
6 EXHAUST The end of the third stroke leaves the piston at the bottom of the chamber and has generated a lot of rotational energy into the crankshaft. This force causes the crankshaft to continue to rotate and finish the cycle shown below. Exhaust Stroke Cleaning house to start over Exhaust (Second Up-Stroke) As the momentum of the rotating mass and external components of the engine continue, the crankshaft causes the piston to move back up the chamber. An exhaust valve opening at the beginning of this stroke allows all of the gases and unburned fuel to be pushed out by the piston. At the end of this EXHAUST stroke, the piston is at the top of the chamber, which is again void of almost all air, fuel, and pollutants. This ends the Otto Cycle. The graph of power looks somewhat like this: The best thing about the Otto Cycle is that a variety of engines have been designed to service many different needs. The next logical step is to combine pistons in such a way that more powerful engines may be built that would take advantage of the Otto Cycle with different types of fuel and with shapes that are conducive to particular environments. 5 of 14
7 THE FOUR-CYLINDER OTTO ENGINE (this will be our reference engine ) Starting with an engine that has only one piston currently in each of the four cycles, it is clear that we would need four pistons so that a power stroke was always taking place. Four-Cylinder Otto Engine (Multiple Piston Otto Cycle) The most common configuration of the Otto Cycle engine is the simple four banger because of the minimum number of parts for the required cycles to be most productive. Four identical cylinders are aligned on a common crankshaft and if each cylinder starts the Otto Cycle a half stroke behind the previous cylinder, there will always be a POWER stroke taking place during each of the four cycles. This engine is the reference engine for all of our further discussions, as it provides a power stroke for each of the four cycles. In fact, because there are four cycles and four pistons, each cycle is always taking place. There is a constant vacuum on the intake and a constant output at the exhaust. There is also a constant drag on the engine from the compression taking place two power strokes per revolution of the crankshaft! Only the POWER stroke is shown above as it overpowers the losses of the other strokes. Engines can be designed for a variety of fuels, including some fuels that ignite at lower temperatures. In 1864, Nikolaus Otto patented the first Atmospheric Gas Engine. Rudolf Diesel patented the Diesel Engine, as a higher efficiency version of this engine in of 14
8 THE FOUR-CYLINDER BOXER ENGINE A very popular configuration of the Otto Cycle engine is the Boxer because of the minimum size and easy layout of parts for the required cycles to be completely productive. Four-Cylinder Boxer Engine Here, we see that if you reposition two cylinders to the left along the crankshaft and two cylinders to the right, the new configuration should have exactly the same power as the reference engine. Power in an Otto Cycle engine is primarily determined by the size of the VOID, or displacement of the piston. Just like the reference engine, if each cylinder starts the Otto Cycle a half-stroke behind the previous cylinder, the combined output will always have a POWER stroke taking place as shown: Everything we discovered about the reference engine is true for the Boxer as well. Again, since the POWER stroke is so powerful, it is overpowering the losses of the other strokes. A reduction in the depth of the engine is possible because there are two pistons on each side of the center crankshaft. This will have the effect of reducing weight, while maintaining the same power. This, coupled with other advantages, makes the Boxer a very popular small automobile engine. Like the reference engine, this engine has two power strokes per revolution of the crankshaft. In 1896, Karl Benz invented the first engine with horizontally opposed pistons called the Boxer. 7 of 14
9 THE SIX-CYLINDER STRAIGHT SIX ENGINE A popular truck configuration of the Otto Cycle engine is the Straight Six (or sometimes called the In- Line Six) because of the smoother pulse power generated at 120 degrees versus 180 degrees. Operation is similar to the reference engine otherwise. Six-Cylinder Otto Engine (Straight Six) The second-most common configuration of the Otto Cycle engine is the Straight Six. Six identical cylinders are aligned on a common crankshaft, allowing two extra power strokes during the Otto Cycle. Because each cylinder starts the Otto Cycle 120-degrees behind the previous cylinder, there will be three POWER strokes for each rotation of the crankshaft. This engine is designed to have higher torque than the four-cylinder engine because of the 120-degrees per cylinder power stroke and it possesses primary and secondary mechanical engine balance, resulting in much less vibration than engines with fewer cylinders. This engine provides 50% more power than the reference engine because there are 50% more cylinders. By firing at 120-degree increments, there are more pulses available to create higher torque, which is often required by trucks, busses, and power generators. The Ford F-150 is a fleet vehicle used by many towns across the country for city maintenance and in many businesses as a utility vehicle. Using the six-cylinder Straight Six engine for its power plant contributes to making the Ford F-150 the most common pick-up truck in the United States. Spyker, a Dutch automobile company, built the first 6-cyclinder straight-line engine in of 14
10 THE 8-CYLINDER V8 OTTO ENGINE A very powerful configuration of the Otto Cycle engine is the V8 because of the extra set of four pistons to increase the number of power strokes per revolution of the crankshaft. It is a bit more efficient on a power-to-weight ratio. 8-Cylinder V8 Otto Engine Here, we see that if you reposition four cylinders angled to the left, and add four angled cylinders to the right, the new configuration should have exactly twice the power of the reference engine. Notice that the V8 looks like two four bangers connected with a 90-degree offset. However, unlike the reference engine, each cylinder starts the Otto Cycle a quarter-stroke behind the previous cylinder. The combined output will always have TWO POWER strokes taking place per cycle, as shown: Because there are twice as many cylinders, there are twice as many pulses of power per rotation of the crankshaft. This increases the output power by a factor of two-to-one, as well as smoothing out the torque on the crankshaft. During light loads, the V8 requires less energy from each piston, but is not as efficient as the reference engine. Unlike the reference engine, this engine has four power strokes per revolution of the crankshaft. Leon Levasseur patented the first V8 engine in 1902, originally named the Antoinette. 9 of 14
11 THE RADIAL ENGINE An interesting configuration of the Otto Cycle engine is the Radial Engine, designed for minimum depth and airflow cooling. This engine was originally designed as a powerplant for aircraft. Radial Engine (Rotating Crankshaft) Here, the drawing shows that if you position one cylinder to the left, one cylinder to the right, and one cylinder at the top and the bottom in an array around the crankshaft from the reference engine, the new engine configuration should have exactly the same power as the reference engine. Everything we discovered about the reference engine is true for the Radial Engine, as well. Again, since the POWER stroke is so powerful, it is overpowering the losses of the other strokes. A reduction in the depth of the engine is possible because there are four pistons on each side of the center crankshaft. This will have the effect of reducing the weight, while maintaining the same power. Like the reference engine, this engine has two power strokes per revolution of the crankshaft. However, the depth of the engine is only one cylinder, as they all share the same crankshaft offset. The crankshaft rotates and forces the pistons to do exactly what was done in the reference engine. Like the reference engine, this engine has two power strokes per revolution of the crankshaft. 10 of 14
12 THE ROTARY ENGINE Similar to the Radial Engine, the Rotary Engine has four cylinders around a single crankshaft, but with the bore assembly rotating around the stationary crankshaft. Rotary Engine (Rotating Crankcase) Here, just like the Radial Engine, there are four cylinders, each positioned 90-degrees apart from one another; but in this configuration, instead of rotating the crankshaft, the crankshaft is stationary and we rotate the entire crankcase (bore assembly) around it. The new configuration should also have exactly the same power as the reference engine. Most of what we discovered about the Radial Engine is also true for the Rotary Engine. In fact, Rotary and Radial engines look strikingly similar when they are not running and can easily be confused, since both have cylinders arranged radially around a central crankshaft. However, unlike any engine so far, the pistons do not move up and down. Instead, they follow a circular path within the rotating bore assembly, causing them to appear to function the same. Also, the rapid change in direction has been cut in half, reducing the energy required by the piston motion and provides a slight increase in efficiency. Felix Millet patented the 5-cylinder version of the rotary engine using the Otto Cycle in Paris in 1888; it was put into production in London in of 14
13 THE BI-RADIAL ENGINE Unlike the reference engine, this engine has four power strokes per revolution of the bore assemblies in the crankcase. Combining the Radial Engine and the Rotary Engine, the Bi-Radial Engine has four cylinders around a single crankshaft. In this case, the crankshaft rotates, as well as the bore assemblies, but in opposite directions from one another. It is like superimposing the two engines on each other, providing double the power strokes. Bi-Radial Engine (Rotating Crankshaft and Crankcase) Here, the drawing shows that if you have a radial engine superimposed on a rotary engine, the new configuration should have twice the power as the reference engine, if measured for a full 720 degrees, because there will be two power strokes per cylinder. Unlike any engine so far, the pistons follow an elliptical path (see the bottom of final page for illustration) within the rotating bore assembly causing them to appear to have twice the function of the reference engine. This is because of the ellipse having 2 TDC s, thus providing power at every rotation. Therefore, it can be seen that a four-cylinder engine acts like an eight-cylinder engine for the same 720- degrees of crankshaft rotation. Siemens-Halske developed an 11-cylinder Bi-Radial Engine toward the end of WWII. 12 of 14
14 THE COUNTERPOISE BI-RADIAL ENGINE (The Final Modification) Counterpoise Bi-Radial Engine (Rotating Crankshaft and Crankcase) Similar to the Siemens-Halske Bi-Radial Engine, the Counterpoise Bi-Radial Engine has four cylinders around a single crankshaft and the crankshaft rotates as well as the bore assembly. Additional power is derived from the bore angle Here, a brand-new configuration draws on the benefits of the Bi-Radial Engine, with a reduction of piston flap, an elliptical path, (see the bottom of next page for illustration) and a power stroke per revolution. It will have at least twice the power as the reference engine, but wait there s more. Unlike any engine so far, the bore assemblies are positioned with a specific angle integrated into each bore, such that the pressure on the ceiling of the bore is pushing the bore in the desired direction to aid the output torque of the engine. This has never been accomplished before. Since the pressure on the piston and the ceiling of the bore are the same, the available torque is captured twice. Unlike the reference engine, this engine has four power strokes per revolution and unlike any other engine, manages to capture the energy on the ceiling of the bore. Del Wolverton and Derek Bailey of WBI patented the Counterpoise Engine in It is the only engine in existence that fits this category. 13 of 14
15 CONCLUSION The design path from the first Otto engine through the various rotaries and radials has shown that the Counterpoise Bi-Radial Engine is the last and final evolution of squeezing the most energy out of a tank of gasoline. There are also a few additional specifics that were overcome in the transitions. Both the Radial Engine and the Rotary Engine were found to function smoothly, only when there were an odd number of cylinders. It takes just a quick look at the diagrams on pages 9 and 10 to realize that a piston is going to have a power stroke every other rotation of the crankshaft, thus the series would have to be: Fire 1 Skip 2 Fire 3 Skip 4 and repeat. It would also follow that you need to Fire 1 again (next) except that cylinder 1 fired last rotation and needs to do an exhaust stroke this time. The solution is to add a 5th cylinder, such that you then have a firing order of: Fire 1 Fire 3 Fire 5 Fire 2 Fire 4 and repeat. In addition to the firing order dilemma, the engines are also very unbalanced because all of the pistons are traversing the crankshaft, which is moving in a circle about the center of the engine. This is an unbalanced mass with vibration issues and was not overcome in the prior radial-type engines. In the Counterpoise Bi-Radial Engine, the sets of two pistons are balanced against each other, moving in opposite directions from each other, because of the unique design of the crankshaft. The elliptical path1 of the cylinders and the sequence of firing the charged mixture permits the Counterpoise Bi-Radial Engine to fire at the top of the engine, each and every time it reaches the top. Every cylinder, in order, fires at the top and then has the three additional cycles before it reaches the top again. Thus, the Counterpoise Bi-Radial Engine is the first of this type of engine that can maintain dynamic balance with an even number of cylinders. 1 Illustration of elliptical path of piston rotation With all of the above, it is shown that this engine is the lightest, highest torque engine ever designed. The size can be modified for torque, weight, or fuel efficiency. To reiterate, the conclusion regarding the Counterpoise Bi-Radial Engine would be a higher efficiency engine with more torque, less weight, and lower emissions than any other engine ever designed! Contact: Pamela L. Summers, Public Relations Director, WolvertonBailey Inc., Santa Rosa, CA, psummers@wolvertonbailey.com WolvertonBailey Inc All rights reserved. Counterpoise Bi-Radial Engine, US Patent # US 9,074,527, B2 on July 7, of 14
ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION
 ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION Because the most widely used piston engine is the four-stroke cycle type, it will be used as the example for this section, Engine Operation and as the basis for comparison in the
ENGINES ENGINE OPERATION Because the most widely used piston engine is the four-stroke cycle type, it will be used as the example for this section, Engine Operation and as the basis for comparison in the
OBJECTIVE: GENERAL ASPECTS ABOUT ENGINES MECHANISM:
 LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE 3 COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Course code: MCE 211 Course title: Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Credit
LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE 3 COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Course code: MCE 211 Course title: Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Credit
Practical Exercise for Instruction Pack 2. Ed Abdo
 Practical Exercise for Instruction Pack 2 By Ed Abdo About the Author Edward Abdo has been actively involved in the motorcycle and ATV industry for over 25 years. He received factory training from Honda,
Practical Exercise for Instruction Pack 2 By Ed Abdo About the Author Edward Abdo has been actively involved in the motorcycle and ATV industry for over 25 years. He received factory training from Honda,
Internal Combustion Engine
 Internal Combustion Engine The development of the internal combustion engine was made possible by the earlier development of the STEAM ENGINE. Both types of engines burn fuel, releasing energy from it
Internal Combustion Engine The development of the internal combustion engine was made possible by the earlier development of the STEAM ENGINE. Both types of engines burn fuel, releasing energy from it
Unit C: Agricultural Power Systems. Lesson 1: Understanding Principles of Operation of Internal Combustion Engines
 Unit C: Agricultural Power Systems Lesson 1: Understanding Principles of Operation of Internal Combustion Engines 1 Terms Compression Compression stroke Connecting rod Crankshaft Cycle Cylinder Diesel
Unit C: Agricultural Power Systems Lesson 1: Understanding Principles of Operation of Internal Combustion Engines 1 Terms Compression Compression stroke Connecting rod Crankshaft Cycle Cylinder Diesel
Inside a typical car engine. Almost all cars today use a reciprocating internal combustion engine because this engine is:
 Tech Torque HOW PETROL ENGINES WORK The Basics The purpose of a gasoline car engine is to convert gasoline into motion so that your car can move. Currently the easiest way to create motion from gasoline
Tech Torque HOW PETROL ENGINES WORK The Basics The purpose of a gasoline car engine is to convert gasoline into motion so that your car can move. Currently the easiest way to create motion from gasoline
CHAPTER 3 ENGINE TYPES
 CHAPTER 3 CHAPTER 3 ENGINE TYPES CONTENTS PAGE Multi-Cylinders 02 Firing orders 06 2 Stroke Cycle 08 Diesel Cycle 10 Wankel Engine 12 Radial/Rotary 14 Engine Types Multi Cylinders Below are illustrated
CHAPTER 3 CHAPTER 3 ENGINE TYPES CONTENTS PAGE Multi-Cylinders 02 Firing orders 06 2 Stroke Cycle 08 Diesel Cycle 10 Wankel Engine 12 Radial/Rotary 14 Engine Types Multi Cylinders Below are illustrated
INTRODUCTION OF FOUR STROKE ENGINE
 INTRODUCTION OF FOUR STROKE ENGINE Engine: An engine is motor which converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Fuel/petrol engine: A petrol engine (known as a gasoline engine in North America) is
INTRODUCTION OF FOUR STROKE ENGINE Engine: An engine is motor which converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Fuel/petrol engine: A petrol engine (known as a gasoline engine in North America) is
Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1. Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje
 Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1 Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje 1 An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine where the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion
Introduction to I.C Engines CH. 1 Prepared by: Dr. Assim Adaraje 1 An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine where the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion
The Four Stroke Cycle
 1 Induction As the piston travels down the cylinder it draws filtered air at atmospheric pressure and ambient temperature through an air filter and inlet valves into the cylinder. 2 Compression When the
1 Induction As the piston travels down the cylinder it draws filtered air at atmospheric pressure and ambient temperature through an air filter and inlet valves into the cylinder. 2 Compression When the
Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1-3 ENGINE CLASSIFICATIONS Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition 1 (a) Spark Ignition (SI). An SI engine starts the combustion
Chapter 1 Introduction 1-3 ENGINE CLASSIFICATIONS Internal combustion engines can be classified in a number of different ways: 1. Types of Ignition 1 (a) Spark Ignition (SI). An SI engine starts the combustion
FUNDAMENTAL OF AUTOMOBILE SYSTEMS
 Prof. Kunalsinh Mechanical Engineering Dept. FUNDAMENTAL OF AUTOMOBILE SYSTEMS Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] UNIT-2 [ENGINES] PART-1 Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] Internal combustion
Prof. Kunalsinh Mechanical Engineering Dept. FUNDAMENTAL OF AUTOMOBILE SYSTEMS Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] UNIT-2 [ENGINES] PART-1 Prof. Kunalsinh kathia [MECHANICAL DEPT.] Internal combustion
Bronze Level Training
 Bronze Level Training Engine Principles of Operation While not everyone at the dealership needs to be a top rated service technician, it is good for all the employees to have a basic understanding of engine
Bronze Level Training Engine Principles of Operation While not everyone at the dealership needs to be a top rated service technician, it is good for all the employees to have a basic understanding of engine
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS 2.1 INTRODUCTION 2.2 CLASSIFICATION OF IC ENGINES. Objectives. Structure. 2.1 Introduction
 UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
UNIT 2 POWER PLANTS Power Plants Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Classification of IC Engines 2.3 Four Stroke Engines versus Two Stroke Engines 2.4 Working of Four Stroke Petrol Engine 2.5 Working
Fundamentals of Small Gas Engines
 Fundamentals of Small Gas Engines Objectives: Describe the four-stroke cycle engine operation and explain the purpose of each stroke Explain the concept of valve timing Describe two-stroke engine operation
Fundamentals of Small Gas Engines Objectives: Describe the four-stroke cycle engine operation and explain the purpose of each stroke Explain the concept of valve timing Describe two-stroke engine operation
Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine.
 Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine. Aim: To study the construction and working of 4- stroke petrol / diesel engine. Theory: A machine or device which derives heat from the combustion
Comparative Study Of Four Stroke Diesel And Petrol Engine. Aim: To study the construction and working of 4- stroke petrol / diesel engine. Theory: A machine or device which derives heat from the combustion
Engine Design Classifications
 Chapter 12 Engine Design Classifications Name: Date: Instructor: Score: Textbook pages 158-175 Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to describe and explain basic automotive engine designs
Chapter 12 Engine Design Classifications Name: Date: Instructor: Score: Textbook pages 158-175 Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to describe and explain basic automotive engine designs
ROYAL CANADIAN AIR CADETS PROFICIENCY LEVEL TWO INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SECTION 3 EO M EXPLAIN THE CYCLES OF A FOUR-STROKE PISTON-POWERED ENGINE
 ROYAL CANADIAN AIR CADETS PROFICIENCY LEVEL TWO INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SECTION 3 EO M232.03 EXPLAIN THE CYCLES OF A FOUR-STROKE PISTON-POWERED ENGINE Total Time: 60 min PREPARATION PRE-LESSON INSTRUCTIONS
ROYAL CANADIAN AIR CADETS PROFICIENCY LEVEL TWO INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SECTION 3 EO M232.03 EXPLAIN THE CYCLES OF A FOUR-STROKE PISTON-POWERED ENGINE Total Time: 60 min PREPARATION PRE-LESSON INSTRUCTIONS
Air Cooled Engine Technology. Roth 9 th Ch 6 Engine Performance Pages
 Roth 9 th Ch 6 Engine Performance Pages 95 112 1. Internal combustion engines belong to the engine category. Gasoline Diesel Heat 2. The heavy flywheel provides the necessary to keep the crankshaft spinning
Roth 9 th Ch 6 Engine Performance Pages 95 112 1. Internal combustion engines belong to the engine category. Gasoline Diesel Heat 2. The heavy flywheel provides the necessary to keep the crankshaft spinning
Handout Activity: HA170
 Basic diesel engine components Handout Activity: HA170 HA170-2 Basic diesel engine components Diesel engine parts are usually heavier or more rugged than those of similar output gasoline engines. Their
Basic diesel engine components Handout Activity: HA170 HA170-2 Basic diesel engine components Diesel engine parts are usually heavier or more rugged than those of similar output gasoline engines. Their
Internal Combustion Engine. Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST
 Internal Combustion Engine Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST What is an Engine? -a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy Two types of engines : 1. Internal
Internal Combustion Engine Prepared by- Md Ferdous Alam Lecturer, MEE, SUST What is an Engine? -a machine designed to convert one form of energy into mechanical energy Two types of engines : 1. Internal
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413)
 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413) Dr. Mohd Farid bin Muhamad Said Room : Block P21, Level 1, Automotive Development Centre (ADC) Tel : 07-5535449 Email: mfarid@fkm.utm.my HISTORY OF ICE History of
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE (SKMM 4413) Dr. Mohd Farid bin Muhamad Said Room : Block P21, Level 1, Automotive Development Centre (ADC) Tel : 07-5535449 Email: mfarid@fkm.utm.my HISTORY OF ICE History of
SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL
 IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Internal Combustion Engine GATE, IES & PSUs IC Engine - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T 1.
Internal Combustion Engines
 Introduction Lecture 1 1 Outline In this lecture we will learn about: Definition of internal combustion Development of the internal combustion engine Different engine classifications We will also draw
Introduction Lecture 1 1 Outline In this lecture we will learn about: Definition of internal combustion Development of the internal combustion engine Different engine classifications We will also draw
Topic Page: Internal Combustion Engine
 Topic Page: Internal Combustion Engine Definition: internal combustion engine from Dictionary of Energy Transportation. an engine in which the process of combustion takes place in a cylinder or cylinders
Topic Page: Internal Combustion Engine Definition: internal combustion engine from Dictionary of Energy Transportation. an engine in which the process of combustion takes place in a cylinder or cylinders
I.C ENGINES. CLASSIFICATION I.C Engines are classified according to:
 I.C ENGINES An internal combustion engine is most popularly known as I.C. engine, is a heat engine which converts the heat energy released by the combustion of the fuel taking place inside the engine cylinder
I.C ENGINES An internal combustion engine is most popularly known as I.C. engine, is a heat engine which converts the heat energy released by the combustion of the fuel taking place inside the engine cylinder
TKP3501 Farm Mechanization
 TKP3501 Farm Mechanization Topic 2: Internal Combustion Engines Ahmad Suhaizi, Mat Su Email: asuhaizi@upm.edu.my Outlines Internal vs external combustion engines Engine structure Combustion cycle 4 stroke
TKP3501 Farm Mechanization Topic 2: Internal Combustion Engines Ahmad Suhaizi, Mat Su Email: asuhaizi@upm.edu.my Outlines Internal vs external combustion engines Engine structure Combustion cycle 4 stroke
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
WEEK 4 Dynamics of Machinery
 WEEK 4 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J.Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2003 Prof.Dr.Hasan ÖZTÜRK 1 DYNAMICS OF RECIPROCATING ENGINES Prof.Dr.Hasan ÖZTÜRK The
WEEK 4 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J.Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2003 Prof.Dr.Hasan ÖZTÜRK 1 DYNAMICS OF RECIPROCATING ENGINES Prof.Dr.Hasan ÖZTÜRK The
California State University, Bakersfield. Signals and Systems. Kristin Koehler. California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 4 July 18 th, 2013
 Kristin Koehler California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 4 July 18 th, 2013 1 Outline Internal combustion engines 2 stroke combustion engines 4 stroke combustion engines Diesel engines 2 Consists
Kristin Koehler California State University, Bakersfield Lecture 4 July 18 th, 2013 1 Outline Internal combustion engines 2 stroke combustion engines 4 stroke combustion engines Diesel engines 2 Consists
Internal Combustion Engines.
 Internal Combustion Engines. Here's a quick description of a typical internal combustion engine, along with basic vocabularies that describe the components and their functions. This stuffs serve as a quick
Internal Combustion Engines. Here's a quick description of a typical internal combustion engine, along with basic vocabularies that describe the components and their functions. This stuffs serve as a quick
ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION IC Engine Fundamentals 2 Engine Systems An engine
2 Technical Background
 2 Technical Background Vibration In order to understand some of the most difficult R- 2800 development issues, we must first briefly digress for a quick vibration tutorial. The literature concerning engine
2 Technical Background Vibration In order to understand some of the most difficult R- 2800 development issues, we must first briefly digress for a quick vibration tutorial. The literature concerning engine
UNDERSTANDING ROD RATIOS
 UNDERSTANDING ROD RATIOS By Larry Carley, Technical Editor lcarley@babcox.com Performance engine builders are always looking at changes they can make that will give their engine an edge over the competition.
UNDERSTANDING ROD RATIOS By Larry Carley, Technical Editor lcarley@babcox.com Performance engine builders are always looking at changes they can make that will give their engine an edge over the competition.
InDesign template. Counterpoise Engine Technology. Better Geometry. Better Physics. A Better Internal Combustion Design.
 InDesign template Counterpoise Engine Technology Better Geometry. Better Physics. A Better Internal Combustion Design. tm 002 MOTORS TO POWER OUR FUTURE EIGHT CYLINDER COUNTERPOISE MODEL Shown is a Desk
InDesign template Counterpoise Engine Technology Better Geometry. Better Physics. A Better Internal Combustion Design. tm 002 MOTORS TO POWER OUR FUTURE EIGHT CYLINDER COUNTERPOISE MODEL Shown is a Desk
Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines
 Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mazlan Abdul Wahid Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia www.fkm.utm.my/~mazlan 1 Coverage Introduction Operation
Applied Thermodynamics Internal Combustion Engines Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mazlan Abdul Wahid Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia www.fkm.utm.my/~mazlan 1 Coverage Introduction Operation
Two Cycle and Four Cycle Engines
 Ch. 5 Two Cycle and Four Cycle Engines Feb 20 7:43 AM 1 Stroke of the piston is its movement in the cylinder from one end of its travel to the other Feb 20 7:44 AM 2 Four stroke cycle engine 4 strokes
Ch. 5 Two Cycle and Four Cycle Engines Feb 20 7:43 AM 1 Stroke of the piston is its movement in the cylinder from one end of its travel to the other Feb 20 7:44 AM 2 Four stroke cycle engine 4 strokes
The Basics of Four-Stroke Engines
 Youth Explore Trades Skills Description Students will be introduced to basic engine parts, theory and terminology. Understanding how an engine works and knowing some key related parts and terminology is
Youth Explore Trades Skills Description Students will be introduced to basic engine parts, theory and terminology. Understanding how an engine works and knowing some key related parts and terminology is
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
 UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
UNIT IV INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES Objectives After the completion of this chapter, Students 1. To know the different parts of IC engines and their functions. 2. To understand the working principle of
CHAPTER 1 MECHANICAL ARRANGEMENT
 CHAPTER 1 CHAPTER 1 MECHANICAL ARRANGEMENT CONTENTS PAGE Basic Principals 02 The Crankshaft 06 Piston Attachment 08 Major Assemblies 10 Valve Gear 12 Cam Drive 18 Mechanical Arrangement - Basic Principals
CHAPTER 1 CHAPTER 1 MECHANICAL ARRANGEMENT CONTENTS PAGE Basic Principals 02 The Crankshaft 06 Piston Attachment 08 Major Assemblies 10 Valve Gear 12 Cam Drive 18 Mechanical Arrangement - Basic Principals
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapter 11 Pages Engine Fundamentals 62 Points
 Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapter 11 Pages 145-161 Engine Fundamentals 62 Points 1. The is the area between the top of the piston & the cylinder head. Combustion Chamber Cylinder Chamber Chamber of
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapter 11 Pages 145-161 Engine Fundamentals 62 Points 1. The is the area between the top of the piston & the cylinder head. Combustion Chamber Cylinder Chamber Chamber of
Template for the Storyboard stage
 Template for the Storyboard stage Animation can be done in JAVA 2-D. Mention what will be your animation medium: 2D or 3D Mention the software to be used for animation development: JAVA, Flash, Blender,
Template for the Storyboard stage Animation can be done in JAVA 2-D. Mention what will be your animation medium: 2D or 3D Mention the software to be used for animation development: JAVA, Flash, Blender,
Singh Groove Concept Combustion Analysis using Ionization Current By: Garrett R. Herning AutoTronixs, LLC. October 2007
 Singh Groove Concept Combustion Analysis using Ionization Current By: Garrett R. Herning AutoTronixs, LLC. October 2007 Ionization Current: Ionization current is a method devised of using the spark plug
Singh Groove Concept Combustion Analysis using Ionization Current By: Garrett R. Herning AutoTronixs, LLC. October 2007 Ionization Current: Ionization current is a method devised of using the spark plug
THE STUDY of mechanical power
 The Internal Combustion Engine and Its Importance to Agriculture THE STUDY of mechanical power covers a broad area of learning. A basic understanding of engines is important if you are to keep pace with
The Internal Combustion Engine and Its Importance to Agriculture THE STUDY of mechanical power covers a broad area of learning. A basic understanding of engines is important if you are to keep pace with
Design and Development Of Opposite Piston Engine
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 3, Special Issue 3, March 2014 2014 IEEE International Conference
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 3, Special Issue 3, March 2014 2014 IEEE International Conference
Task 4: Read the texts, look at the illustrations and do the activities below.
 Task 4: Read the texts, look at the illustrations and do the activities below. 4 BASIC OPERATIONS The Induction Stroke On the induction stroke, the inlet valve opens and the piston, moving down, creates
Task 4: Read the texts, look at the illustrations and do the activities below. 4 BASIC OPERATIONS The Induction Stroke On the induction stroke, the inlet valve opens and the piston, moving down, creates
Service Advisor Customer Service Skills SERVICE ADVISOR. Technical for Non-technical - Engines INDUCTION
 Service Advisor Customer Service Skills SERVICE ADVISOR Technical for Non-technical - Engines INDUCTION Objectives Welcome to the technical for non-technical modules. We will discuss engines, transmissions
Service Advisor Customer Service Skills SERVICE ADVISOR Technical for Non-technical - Engines INDUCTION Objectives Welcome to the technical for non-technical modules. We will discuss engines, transmissions
Air Cooled Engine Technology. Roth 9 th Ch 5 2 & 4 Cycle Engines Pages 81 94
 Roth 9 th Ch 5 2 & 4 Cycle Engines Pages 81 94 1. The of the piston is its movement in the cylinder from one end of its travel to another. Either TDC to BDC (downstroke) or BDC to TDC (upstroke). Identified
Roth 9 th Ch 5 2 & 4 Cycle Engines Pages 81 94 1. The of the piston is its movement in the cylinder from one end of its travel to another. Either TDC to BDC (downstroke) or BDC to TDC (upstroke). Identified
Emission from gasoline powered vehicles are classified as 1. Exhaust emission 2. Crank case emission 3. Evaporative emission. Table 1.
 Introduction: Main three types of automotive vehicle being used 1. Passenger cars powered by four stroke gasoline engines 2. Motor cycles, scooters and auto rickshaws powered mostly by small two stroke
Introduction: Main three types of automotive vehicle being used 1. Passenger cars powered by four stroke gasoline engines 2. Motor cycles, scooters and auto rickshaws powered mostly by small two stroke
A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it.
 ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 1: ENGINE DESIGN LESSON 1: PRINCIPLES OF ENGINE DESIGN I. Terms and definitions A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it. B. Bearing A device that allows movement
ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 1: ENGINE DESIGN LESSON 1: PRINCIPLES OF ENGINE DESIGN I. Terms and definitions A. Aluminum alloy Aluminum that has other metals mixed with it. B. Bearing A device that allows movement
Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines
 Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines Use the Textbook Pages 321 349 to help answer the questions Why You Learn So Well in Tech & Engineering Classes 1. Internal combustion make heat by burning a fuel & air mixture
Chapter 14 Small Gas Engines Use the Textbook Pages 321 349 to help answer the questions Why You Learn So Well in Tech & Engineering Classes 1. Internal combustion make heat by burning a fuel & air mixture
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
 1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF MECHANICAL AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION By Desta Lemma (BSc, MSc) Introduction
1 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF MECHANICAL AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING DIVISON OF THERMAL AND ENERGY CONVERSION By Desta Lemma (BSc, MSc) Introduction
SIDEWINDER COURSE PREREQUISITE MANUAL
 SIDEWINDER COURSE PREREQUISITE MANUAL The S&S engine class is designed for the seasoned tech or shop owner. A certain level of knowledge and understanding is required for your success. We will be covering
SIDEWINDER COURSE PREREQUISITE MANUAL The S&S engine class is designed for the seasoned tech or shop owner. A certain level of knowledge and understanding is required for your success. We will be covering
Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01
 Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01 Notice Due to the wide range of vehicles makes and models, the information given during the class will be general in nature and
Learning Guide EMISSION SPECIALIST 5 GAS ANALYSIS COURSE NUMBER: E001-01 Notice Due to the wide range of vehicles makes and models, the information given during the class will be general in nature and
Unit IV. Marine Diesel Engine Read this article about the engines used in the marine industry
 Universidad Nacional Experimental Marítima del Caribe Vicerrectorado Académico Cátedra de Idiomas English VI. Maritime Engineering Marine facilities Unit IV. Marine Diesel Engine Read this article about
Universidad Nacional Experimental Marítima del Caribe Vicerrectorado Académico Cátedra de Idiomas English VI. Maritime Engineering Marine facilities Unit IV. Marine Diesel Engine Read this article about
How To Verify Your Valve/Crankshaft Timing & Set A Distributor.
 How To Verify Your Valve/Crankshaft Timing & Set A Distributor. If you don't have a good working knowledge of shop safety practices, DON'T ATTEMPT THIS! If you don't possess common sense or self preservation
How To Verify Your Valve/Crankshaft Timing & Set A Distributor. If you don't have a good working knowledge of shop safety practices, DON'T ATTEMPT THIS! If you don't possess common sense or self preservation
Rotary Internal Combustion Engine: Inventor: Gary Allen Schwartz
 Rotary Internal Combustion Engine: Inventor: Gary Allen Schwartz 1 The following is a design for a circular engine that can run on multiple fuels. It is much more efficient than traditional reciprocating
Rotary Internal Combustion Engine: Inventor: Gary Allen Schwartz 1 The following is a design for a circular engine that can run on multiple fuels. It is much more efficient than traditional reciprocating
Engine Construction and Principles of Operation
 Ch. 4 Engine Construction and Principles of Operation Gasoline Engine A gasoline fueled engine is a mechanism designed to transform chemical energy into mechanical energy It is an internal combustion engine.
Ch. 4 Engine Construction and Principles of Operation Gasoline Engine A gasoline fueled engine is a mechanism designed to transform chemical energy into mechanical energy It is an internal combustion engine.
Principles of Engine Operation. Information
 Internal Combustion Engines MAK 4070E Principles of Engine Operation Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Istanbul Technical University Information Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay İ.T.Ü. Makina Fakültesi Motorlar ve Taşıtlar Laboratuvarı
Internal Combustion Engines MAK 4070E Principles of Engine Operation Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay Istanbul Technical University Information Prof.Dr. Cem Soruşbay İ.T.Ü. Makina Fakültesi Motorlar ve Taşıtlar Laboratuvarı
THE FOUR STROKE CYCLE BUT HOW DOES IT WORK EXACTLY? LET S LOOK IN MORE DETAIL 1. INDUCTION SUCK 2. COMPRESSION 3. COMBUSTION 4.
 THE FOUR STROKE CYCLE BUT HOW DOES IT WORK EXACTLY? WE KNOW ABOUT:- WHICH WE KNOW AS:- LET S LOOK IN MORE DETAIL 1. INDUCTION SUCK 2. COMPRESSION 3. COMBUSTION 4. EXHAUST SQUEEZE BANG BLOW Inlet valve
THE FOUR STROKE CYCLE BUT HOW DOES IT WORK EXACTLY? WE KNOW ABOUT:- WHICH WE KNOW AS:- LET S LOOK IN MORE DETAIL 1. INDUCTION SUCK 2. COMPRESSION 3. COMBUSTION 4. EXHAUST SQUEEZE BANG BLOW Inlet valve
SHEILDED METAL ARC WELDING (SMAW) AT/AE MECHANICAL CONTEST
 SHEILDED METAL ARC WELDING (SMAW) AT/AE MECHANICAL CONTEST 1. Position two 3 x 6 x ¼ steel plates in the flat position for a butt weld. The weld joint should be 6 long. 2. Select to either bevel the metal
SHEILDED METAL ARC WELDING (SMAW) AT/AE MECHANICAL CONTEST 1. Position two 3 x 6 x ¼ steel plates in the flat position for a butt weld. The weld joint should be 6 long. 2. Select to either bevel the metal
Precision Degree Wheel Kit
 555-81621 Precision Degree Wheel Kit Instruction Booklet Instructions for 81621 Camshaft Degree Kit Thank you for purchasing the Jegs Camshaft Degree Kit. Please follow these detailed instructions to properly
555-81621 Precision Degree Wheel Kit Instruction Booklet Instructions for 81621 Camshaft Degree Kit Thank you for purchasing the Jegs Camshaft Degree Kit. Please follow these detailed instructions to properly
Dynamics of Machines. Prof. Amitabha Ghosh. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Module No.
 Dynamics of Machines Prof. Amitabha Ghosh Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module No. # 05 Lecture No. # 01 V & Radial Engine Balancing In the last session, you
Dynamics of Machines Prof. Amitabha Ghosh Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module No. # 05 Lecture No. # 01 V & Radial Engine Balancing In the last session, you
Handout Activity: HA185
 Cylinder heads Handout Activity: HA185 HA185-2 Cylinder head The cylinder head bolts onto the top of the cylinder block where it forms the top of the combustion chamber. It carries the valves and, in many
Cylinder heads Handout Activity: HA185 HA185-2 Cylinder head The cylinder head bolts onto the top of the cylinder block where it forms the top of the combustion chamber. It carries the valves and, in many
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES
 ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
ENGINE & WORKING PRINCIPLES A heat engine is a machine, which converts heat energy into mechanical energy. The combustion of fuel such as coal, petrol, diesel generates heat. This heat is supplied to a
CEE 452/652. Week 6, Lecture 1 Mobile Sources. Dr. Dave DuBois Division of Atmospheric Sciences, Desert Research Institute
 CEE 452/652 Week 6, Lecture 1 Mobile Sources Dr. Dave DuBois Division of Atmospheric Sciences, Desert Research Institute Today s topics Read chapter 18 Review of urban atmospheric chemistry What are mobile
CEE 452/652 Week 6, Lecture 1 Mobile Sources Dr. Dave DuBois Division of Atmospheric Sciences, Desert Research Institute Today s topics Read chapter 18 Review of urban atmospheric chemistry What are mobile
Automobile section, showing different parts in detail. and miscellaneous devices.
 SECTION VII Nos. 97 112 Automobile section, showing different parts in detail. and miscellaneous devices. Hydraulic jack MECHANICAL MODELS 43 Section VII 97. Automobile engine starter. This device known
SECTION VII Nos. 97 112 Automobile section, showing different parts in detail. and miscellaneous devices. Hydraulic jack MECHANICAL MODELS 43 Section VII 97. Automobile engine starter. This device known
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE
 VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR SI ENGINE VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM FOR CI ENGINE Page 1 of 13 EFFECT OF VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM ON VOLUMETRIC EFFICIENCY: Qu. 1:Why Inlet valve is closed after the Bottom Dead Centre
(v) Cylinder volume It is the volume of a gas inside the cylinder when the piston is at Bottom Dead Centre (B.D.C) and is denoted by V.
 UNIT II GAS POWER CYCLES AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard engines.
UNIT II GAS POWER CYCLES AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard engines.
Powertrain Efficiency Technologies. Turbochargers
 Powertrain Efficiency Technologies Turbochargers Turbochargers increasingly are being used by automakers to make it possible to use downsized gasoline engines that consume less fuel but still deliver the
Powertrain Efficiency Technologies Turbochargers Turbochargers increasingly are being used by automakers to make it possible to use downsized gasoline engines that consume less fuel but still deliver the
Combustion engines. Combustion
 Combustion engines Chemical energy in fuel converted to thermal energy by combustion or oxidation Heat engine converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Thermal energy raises temperature and pressure
Combustion engines Chemical energy in fuel converted to thermal energy by combustion or oxidation Heat engine converts chemical energy into mechanical energy Thermal energy raises temperature and pressure
Unit Plan SAFE Automotive (Survival Automotives For Everyone) Unit: Fundamental Operation of Vehicles
 Unit Plan SAFE Automotive (Survival Automotives For Everyone) Fundamental Operation of Vehicles Unit: Fundamental Operation of Vehicles Year:2012 Duration: 1 Week 1. List any special needs of students
Unit Plan SAFE Automotive (Survival Automotives For Everyone) Fundamental Operation of Vehicles Unit: Fundamental Operation of Vehicles Year:2012 Duration: 1 Week 1. List any special needs of students
CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
2. Engine Ignition Types. Worksheet: Engine Classification
 2. Engine Ignition Types Worksheet: Engine Classification There are types of ignition, based on how the fuel is ignited. Spark ignition the fuel mixture is ignited with an electrical spark. (spark plug)
2. Engine Ignition Types Worksheet: Engine Classification There are types of ignition, based on how the fuel is ignited. Spark ignition the fuel mixture is ignited with an electrical spark. (spark plug)
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE. On Industrial Automation and Control
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE On Industrial Automation and Control By Prof. S. Mukhopadhyay Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Kharagpur Topic Lecture
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE On Industrial Automation and Control By Prof. S. Mukhopadhyay Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Kharagpur Topic Lecture
NOVEL ENGINE DESIGN OF HIGHER EFFICIENCY
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol.14, No. 4 2007 NOVEL ENGINE DESIGN OF HIGHER EFFICIENCY Barbara Sieminska Institute of Aeronautics Al. Krakowska 110/114, 02-256 Warszawa, Poland tel.: +48
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol.14, No. 4 2007 NOVEL ENGINE DESIGN OF HIGHER EFFICIENCY Barbara Sieminska Institute of Aeronautics Al. Krakowska 110/114, 02-256 Warszawa, Poland tel.: +48
The Israeli revolution of the internal combustion engine
 GROUNDBREAKING INVENTION The Israeli revolution of the internal combustion engine Stand: 08:48 clock Reading time: 6 minutes By Gil Yaron Shaul Jaakobi presents the invented linear motor Source: AFP /
GROUNDBREAKING INVENTION The Israeli revolution of the internal combustion engine Stand: 08:48 clock Reading time: 6 minutes By Gil Yaron Shaul Jaakobi presents the invented linear motor Source: AFP /
Modern Automotive Technology Chapter 16. Engine Size and Performance Measurements
 Modern Automotive Technology Chapter 16 Engine Size and Performance Measurements 1 Learning Objectives Describe safety practices when making engine performance measurements Describe engine size measurements
Modern Automotive Technology Chapter 16 Engine Size and Performance Measurements 1 Learning Objectives Describe safety practices when making engine performance measurements Describe engine size measurements
Engine Systems. Basic Engine Operation. Firing Order. Four Stroke Cycle. Overhead Valves - OHV. Engine Design. AUMT Engine Systems 4/4/11
 Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Breakthrough in Linear Generator design
 Breakthrough in Linear Generator design Rotary Linear Generator (stroke-rotor generator) By Physicist Wolfhart Willimczik ABSTRACT The law of inductions demands high speed for the moveable electrical parts,
Breakthrough in Linear Generator design Rotary Linear Generator (stroke-rotor generator) By Physicist Wolfhart Willimczik ABSTRACT The law of inductions demands high speed for the moveable electrical parts,
Technical Support Note
 Title: Measuring Emissions from Diesel-Fueled Equipment TSN Number: 09 File:S:\Bridge_Analyzers\Customer_Service_Documentation\Technical_Support_Notes\ 09_Measuring_Emissions_from_Diesel_Fuel_Equipment.docx
Title: Measuring Emissions from Diesel-Fueled Equipment TSN Number: 09 File:S:\Bridge_Analyzers\Customer_Service_Documentation\Technical_Support_Notes\ 09_Measuring_Emissions_from_Diesel_Fuel_Equipment.docx
Dynamics of Machines. Prof. Amitabha Ghosh. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Module No.
 Dynamics of Machines Prof. Amitabha Ghosh Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module No. # 04 Lecture No. # 03 In-Line Engine Balancing In the last session, you
Dynamics of Machines Prof. Amitabha Ghosh Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module No. # 04 Lecture No. # 03 In-Line Engine Balancing In the last session, you
Car Engine Simulation Tool
 Car Engine Simulation Tool Final Bachelor Thesis Alejandro Victorio Ballestero INDEX I. Introduction -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Car Engine Simulation Tool Final Bachelor Thesis Alejandro Victorio Ballestero INDEX I. Introduction -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tips & Technology For Bosch business partners
 Tips & Technology For Bosch business partners Current topics for successful workshops No. 05 Trucks Starters and starter systems Part 2 Moderately heavy commercial vehicles with diesel engines having a
Tips & Technology For Bosch business partners Current topics for successful workshops No. 05 Trucks Starters and starter systems Part 2 Moderately heavy commercial vehicles with diesel engines having a
NONRESIDENT TRAINING COURSE
 NONRESIDENT TRAINING COURSE February 1994 Basic Machines NAVEDTRA 14037 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Although the words he, him, and his are used sparingly
NONRESIDENT TRAINING COURSE February 1994 Basic Machines NAVEDTRA 14037 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Although the words he, him, and his are used sparingly
Use these modules to gain valuable knowledge about STIHL policies, procedures and products that will be a benefit to you on the job immediately.
 Bronze Level Training Lesson 09 This is Bronze Level 09 of 10. Welcome to the Service Advantage Bronze Level Training on icademy. These modules are designed to enhance your knowledge base on topics such
Bronze Level Training Lesson 09 This is Bronze Level 09 of 10. Welcome to the Service Advantage Bronze Level Training on icademy. These modules are designed to enhance your knowledge base on topics such
In order to discuss powerplants in any depth, it is essential to understand the concepts of POWER and TORQUE.
 -Power and Torque - ESSENTIAL CONCEPTS: Torque is measured; Power is calculated In order to discuss powerplants in any depth, it is essential to understand the concepts of POWER and TORQUE. HOWEVER, in
-Power and Torque - ESSENTIAL CONCEPTS: Torque is measured; Power is calculated In order to discuss powerplants in any depth, it is essential to understand the concepts of POWER and TORQUE. HOWEVER, in
Math Geometry circle diameter Measurement length
 Topic Simple machines Key Question What simple machines are found in an internal combustion engine? Learning Goals Students will: construct a working model of an internal combustion engine that has a piston,
Topic Simple machines Key Question What simple machines are found in an internal combustion engine? Learning Goals Students will: construct a working model of an internal combustion engine that has a piston,
Sensors & Controls. Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask.
 Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
Roehrig Engineering, Inc.
 Roehrig Engineering, Inc. Home Contact Us Roehrig News New Products Products Software Downloads Technical Info Forums What Is a Shock Dynamometer? by Paul Haney, Sept. 9, 2004 Racers are beginning to realize
Roehrig Engineering, Inc. Home Contact Us Roehrig News New Products Products Software Downloads Technical Info Forums What Is a Shock Dynamometer? by Paul Haney, Sept. 9, 2004 Racers are beginning to realize
The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle
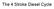 The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle Nickolaus Otto invented the 4 stroke cycle in 1862. More details of how the four stroke spark ignition cycle works, together with pictures of Otto's first engines can be found
The 4 Stroke Diesel Cycle Nickolaus Otto invented the 4 stroke cycle in 1862. More details of how the four stroke spark ignition cycle works, together with pictures of Otto's first engines can be found
Name Date Period. MATERIALS: Light bulb Battery Wires (2) Light socket Switch Penny
 Name Date Period Lab: Electricity and Circuits CHAPTER 34: CURRENT ELECTRICITY BACKGROUND: Just as water is the flow of H 2 O molecules, electric current is the flow of charged particles. In circuits of
Name Date Period Lab: Electricity and Circuits CHAPTER 34: CURRENT ELECTRICITY BACKGROUND: Just as water is the flow of H 2 O molecules, electric current is the flow of charged particles. In circuits of
Auto Tech 2 SEMESTER Exam Study Sheet
 Auto Tech 2 SEMESTER Exam Study Sheet 1. Safety 2. Are all brakes are self adjusting? 3. The front brakes do What % of the stopping. 4. The part of the disc brakes that turns or rotates with the wheel
Auto Tech 2 SEMESTER Exam Study Sheet 1. Safety 2. Are all brakes are self adjusting? 3. The front brakes do What % of the stopping. 4. The part of the disc brakes that turns or rotates with the wheel
Bthird, or power stroke by the expanding gases. As the
 third, or power stroke by the expanding gases. As the piston reaches DC it enters the fourth cycle. The exhaust valve opens and the piston rises forcing burned gases from the combustion chamber in what
third, or power stroke by the expanding gases. As the piston reaches DC it enters the fourth cycle. The exhaust valve opens and the piston rises forcing burned gases from the combustion chamber in what
NEW V FORCE REED CAGES FOR POLARIS ENGINES
 NEW V FORCE REED CAGES FOR POLARIS ENGINES Steve Tassinari of Moto Tassinari sent DTR new Vforce3 reed cages that fit the Polaris CFI twins, and asked us to do a back-to-back comparison of stock vs. new
NEW V FORCE REED CAGES FOR POLARIS ENGINES Steve Tassinari of Moto Tassinari sent DTR new Vforce3 reed cages that fit the Polaris CFI twins, and asked us to do a back-to-back comparison of stock vs. new
Diesel Engine Fundamentals Part 1 Course# ME4061
 Diesel Engine Fundamentals Part 1 Course# ME4061 EZpdh.com All Rights Reserved Diesel Engine Fundamentals DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF FIGURES... ii LIST OF TABLES...
Diesel Engine Fundamentals Part 1 Course# ME4061 EZpdh.com All Rights Reserved Diesel Engine Fundamentals DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF FIGURES... ii LIST OF TABLES...
CHECK OUT OUR WEBSITE SOME TIME FOR PLENTY OF ARTICES ABOUT SELF DEFENSE, SURVIVAL, FIREARMS AND MILITARY MANUALS.
 CHECK OUT OUR WEBSITE SOME TIME FOR PLENTY OF ARTICES ABOUT SELF DEFENSE, SURVIVAL, FIREARMS AND MILITARY MANUALS. http://www.survivalebooks.com/ Thank you for purchasing our ebook package. SUBCOURSE EDITION
CHECK OUT OUR WEBSITE SOME TIME FOR PLENTY OF ARTICES ABOUT SELF DEFENSE, SURVIVAL, FIREARMS AND MILITARY MANUALS. http://www.survivalebooks.com/ Thank you for purchasing our ebook package. SUBCOURSE EDITION
Wide Band EFIE Installation Instructions. Locate the wide band oxygen sensor current wire
 Wide Band EFIE Installation Instructions Install your fuel efficiency device The EFIE is not intended to be a fuel saver by itself. You should install a device that is designed to get more energy out of
Wide Band EFIE Installation Instructions Install your fuel efficiency device The EFIE is not intended to be a fuel saver by itself. You should install a device that is designed to get more energy out of
MECHANICAL SCIENCE Module 1 Diesel Engine Fundamentals
 Department of Energy Fundamentals Handbook MECHANICAL SCIENCE Module 1 Diesel Engine Fundamentals Diesel Engine Fundamentals DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF FIGURES... ii
Department of Energy Fundamentals Handbook MECHANICAL SCIENCE Module 1 Diesel Engine Fundamentals Diesel Engine Fundamentals DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF FIGURES... ii
Chapter 6. Supercharging
 SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
SHROFF S. R. ROTARY INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY (SRICT) DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Chapter 6. Supercharging Subject: Internal Combustion Engine 1 Outline Chapter 6. Supercharging 6.1 Need
