Theoretical investigation of the performance of an Alpha Stirling engine for low temperature applications
|
|
|
- Alisha Gilbert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Theoretical investigation of the performance of an Alpha Stirling engine for low temperature applications Benedikt HOEGEL a, *, Dirk PONS b, Michael GSCHWENDTNER c, Alan TUCKER d, Mathieu SELLIER e a University of Canterbury, Private Bag 48, 841 Christchurch, New Zealand, benedikt.hoegel@pg.canterbury.ac.nz b University of Canterbury, dirk.pons@canterbury.ac.nz c TS-dot Engineering Limited, michael.gschwendtner@ts-dot-engineering.com d University of Canterbury, alan.tucker@canterbury.ac.nz e University of Canterbury, mathieu.sellier@canterbury.ac.nz Keywords: Alpha type, performance mapping, mechanical efficiency, Sage simulation, waste heat, geothermal energy Abstract The purpose of this paper is to explore the applicability and peculiarities of Alpha engines at low heat source temperature levels of 1 to 2 C. A parameter study of an Alpha engine has been carried out using the commercial Stirling software Sage. The obtained results revealed some interesting insights into the peculiarities of low-temperature Alpha-SEs. A method for optimising the system design-parameters for a SE is described in this paper. The compact design of a double-acting Alpha engine helps to reduce not only engine size and complexity but also costs. At low temperature differences single-cylinder displacer-type (gamma) engines are well documented, while little is known about the performance of Alpha multi-cylinder engines. In order to achieve the highest possible power output not only the thermodynamic side but also the mechanical side of the engine has to be optimised. This is especially important at low temperature differentials, where the conversion efficiencies are inherently small and the driving force for heat absorption and rejection by the working gas is low. It is mandatory not only to convert as much heat as possible to indicated work but also to transfer as much of this hard gained work to usable power output by minimising internal friction, when trying to keep the engine size as small as possible. The indicated power output of an engine of a specific swept volume is dependent on the temperature and pressure levels, the frequency, the phase angle between the two pistons, the working fluid, and the design of the heat exchangers and the regenerator. A simple model of an Alpha engine was created using the commercial SE simulation tool Sage. In order to explore the relations between those parameters a model was developed, where the design parameters (temperature, mean pressure, frequency, and phase angle) were varied, and the heat exchangers and the regenerator were then optimised for each of the parameter combinations to reach the maximum power output. Temperature and mean pressure are shown to have the expected positive influence on the power output. For the frequency and the phase angle, optimum values can be found that differ significantly from those found for high temperature engines. Helium is used as the benchmark working gas. It can be shown that the use of Nitrogen instead cuts the power output in half, whereas Hydrogen doubles the achievable power output. The mechanical efficiency of a kinematic SE is largely dependent on the load that is transferred from the pistons to the crankshaft during expansion and vice versa during compression, as it increases frictional losses. In double-acting engines an identical pressure oscillation acts on the opposing faces of a piston, although it is out of phase. The resulting forces can balance each other to some extent depending on the phase, and thus the net force applied to the crankshaft can be reduced. For a four cylinder engine it is shown that the Siemens arrangement balances internal forces on the pistons to a larger extent than the Franchot arrangement, so that the mechanical losses are inherently smaller and thus the brake power is larger even though the indicated work is identical for both engine types. The contribution of this work is the provision of a modelling methodology, and the identification of a number of insights for system-design considerations for low-temperature applications. Nomenclature α = phase angle P = power * Corresponding author. Tel ; fax: address: benedikt.hoegel@gmail.com
2 θ = crank angle f = frequency m = gas mass p = pressure R = specific gas constant T = temperature V = volume W = work 1. Introduction Although at a thermodynamic unfavourable temperature level low exergy heat sources such as industrial waste heat and geothermal brine possess a large potential for power generation due to their large availability. As a consequence of increasing energy costs and demand the development of technology for the exploitation of low temperature heat sources becomes more and more viable. The idea to use double-acting pistons in Stirling engines of the Alpha type (engines that use only pistons to achieve volume and pressure variations) dates back to as early as 1853 when French engineer C. Franchot patented the concept [1]. A more detailed design of a double acting multi-cylinder was given by Englishman W. Siemens in 1863 [2] but was never realised. It took another eighty years for the first engine to actually be built at Philips in the Netherlands. Since then the four cylinder double-acting design was the design of choice for all following Alpha engines with power outputs larger than a few kilowatts. The great advantage of double-acting Alpha engines is their simplicity compared to displacer type engines and the economical use of the cylinders, as the whole space on both sides of the pistons acts as active swept volume. Figure 1 shows two possible arrangements for a four cylinder engine. According to Walker [2] engines with pistons having solely expansion or compression spaces on both sides of the pistons are referred to as Franchot arrangements (a). Where an expansion space is separated from a compression space by a piston it is referred to as Siemens arrangement (b). Fig. 1 Franchot (a) and Siemens (b) piston arrangement Until recently double-acting Alpha multi-cylinder engines were only used for high temperature heat sources. A prototype engine of the Franchot type for industrial waste-heat recovery was reported by Hoeg et al. [3]. The practical advantage of the Franchot arrangement over the Siemens arrangement is the fact that a minimum of two pistons is enough to create a working engine with a freely adjustable phase angle. In the Siemens arrangement with its interconnected cylinders the phase angle is always a result of the number of cylinders so that at least three cylinders are needed in a working engine. Because of the low heat source temperature it is possible to have pistons running in cylinders with expansion (hot) gas spaces on both sides as it is the case for the Franchot arrangement. This has the advantage of symmetric thermal expansion on both sides of the pistons and cylinders as well as omitted heat conduction. However, as the temperature difference is low these effects are much less pronounced than at high temperature differences. Although little is reported, double-acting Alpha engines seem to be an interesting option also at smaller temperature differences due to their inherent simplicity. The purpose of this paper is to explore the limitations of such engines in terms of the power and efficiency and to investigate the implications of the two different arrangements described above on performance and design.
3 2. Material and methods In order to optimise the power output of a Stirling engine two subsystems have to be understood and optimised: first, the thermodynamic and the fluid dynamic parts which involve the heat transfer to and from the gas as well as the transfer of the gas itself within the engine in order to maximise the indicated work; second, the minimisation of the mechanical losses when the generated indicated work is transferred into a usable power output. A meaningful optimisation of a Stirling engine relies on a detailed and validated model of the heat transfer mechanisms and the fluid dynamics. Thus a third order model should be used for any optimisation task of the heat exchangers and the regenerator. For this study the commercial SE simulation tool Sage is used [4]. Figure 2 shows the set-up of the main model on top and the corresponding sub-models for each component at the bottom. All gas flow path are indicated by the mass flow symbols (m Gt ) and matching numbers, the established heat transfer paths are indicated by the capital Qs. For all optimisation purposes, the set-up of this model was not modified; only the values of the different parameters within the components were. The key specifications of the model can be seen in Table 1. Note that the thickness of the regenerator walls changes according to the mean pressure and the regenerator inner diameter to compensate for the stress in the regenerator shell. The simulations performed with the described model are independent of the actual physical set-up; it is valid for single-acting Alpha engines as well as for double-acting engines of any arrangement as only the indicated power and efficiency is calculated. Little is known about the exact influence of frequency, phase angle, pressure level and working gas on engine performance at low temperature heat sources of 1-2⁰C. Therefore an experimental design was set-up to investigate the influence of these factors. In order to reduce the number of runs necessary for the simulation a centralcomposite design was chosen, after Montgomery [5]. For the engine of the given dimensions restrictions were made in the allowed regenerator diameter and in the maximum number of tubes to be used for the heat exchangers, according to Table 1. For each combination of parameters the geometry of the heat exchangers and the regenerator is optimised in order to receive the highest possible power output. The performance of each component is mapped in a separate model by varying its geometry with the geometry of the other two components unchanged. For the three components, this can be done simultaneously in three parallel running simulations. Then, the geometry that results in best performance is selected and implemented into the other two simulations. When all three models converge to the same power output, the simulation can be stopped as each component is now mapped with the other two optimized. Usually two or three iterations are enough to find the best overall performance possible with a set of parameters. Fig. 2 The used Sage model and corresponding sub-models
4 Table 1 Simulation parameters Value unit Bore m Stroke m Material steel - Heat source temperature 15 ⁰C Heat sink temperature 4 ⁰C Mean pressure 5 E6 Pa Max. regenerator diameter.5 m Max. number of tubes 1 - Wall thickness regenerator 7.5 E-1 p mean d reg m Gas model Redlich Kwong - For the comparison of the Siemens and the Franchot arrangement as well as for all the following efficiency and pressure considerations the much simplified isothermal model was used. In depth information on this analysis can be found for example in Walker s book [2], as well as in many others. The idea behind it is very basic and uses drastic simplifications but it allows a good insight in the Stirling cycle as long as heat transfer and fluid dynamics can be left aside, as it is possible when two thermodynamic identical setups are compared. The basic equations needed for the isothermal analysis are equations for the volume and pressure change in the engine. The volume is defined by the constant volume of the heat exchangers and the regenerator (V d ) and the variable volume in the expansion and compression space depending on the crank-angle (θ) and the phase angle between the two volumes (α). If sinusoidal piston motion is assumed the gas volume becomes: V(θ) = V e (θ) + V d + V c (θ) = V,e (1 - cos θ) + V d + V,c (1 - cos (θ - α)). With the constant dead volume chosen to a realistic size: V d = V,e + V,c There is no pressure drop within the engine, so that the pressure is identical in all parts of the engine but varies with the crank angle. The ideal gas law is applied to describe the reaction of the working fluid to volume and temperature changes: p V = m R T Considering the instantaneous gas mass distribution and the constancy of the gas mass in the engine the gas pressure can be found to be p gas (θ) = m gas R gas (V c (θ) / T c + V d / T d + V e (θ) / T e ) In order to gain a general formulation of the results pressure and volume are brought into the non-dimensional form. Thus: V* = V(θ) / V total and p* = p(θ) / p max with V total being the swept volume in the cylinders and the volume in the heat exchangers and the regenerator and p max being the maximum pressure in the cycle. The non-dimensional power output is then found to be P*= p* dv*. In order to find the mechanical efficiency of the engine a simple analysis similar to the one presented by Senft [6] is conducted. The mechanical efficiency of the engine (η mechanical ) is given by the ratio of the brake work to the indicated work: η mechanical = W brake / W indicated = W* brake / W* indicated Not all the work generated by the thermodynamic cycle can be used externally. In fact a large fraction of the generated work has to be recycled internally for the compression of the gas. Thus work is transferred from the pistons to the crankshaft and vice versa depending on the gas forces on the piston. In double-acting arrangements only the net
5 work of the two gas cycles acting on one piston is transferred to the crankshaft. A constant efficiency of the mechanism of the crankshaft is assumed regardless of the direction of the power transfer or the crank-angle. The brake work is then calculated by reducing the work transferred from the piston to the shaft (W - *) by the efficiency of the mechanism (η mechanism ) and increasing the work transferred back to the pistons (W + *) by the reciprocal value of that efficiency, as more work has to be supplied from the shaft to overcome the friction. W* brake = η mechanism W - * + 1 / η mechanism W + * With p eff being the difference of the two pressures acting on one piston the brake power can be calculated: W* brake = η mechanism - p* eff dv* + 1 / η mechanism + p* eff dv* 3. Results and Discussion First the results of the simulations with Sage are presented to show the thermodynamically achievable performance in terms of indicated power and efficiency followed by a comparison of the Siemens and Franchot arrangement using isothermal analysis to show the impact of the compounding on the brake power. Indicated power optimisation using Sage simulations It can be shown that the influence of the pressure level on the power output is linear. Thus the pressure level is set to a level of choice for all further optimisations. If a different pressure level has to be considered later the power output can be adjusted accordingly without further need for optimisation of the thermodynamic set-up. The temperature shows the expected strong influence on performance and efficiency. A detailed optimisation of the parameters frequency and phase angle is given in Figure 3 for Hydrogen (a, b), Helium (c, d), Nitrogen (e, f) as working gases at a heat source temperature of 15⁰C and 5 MPa mean pressure. It can be seen that the maximum achievable power output is doubled if Helium (~ 12 kw) is used instead of Nitrogen (~ 6 kw), and again if Hydrogen (~ 23 kw) is used instead of Helium. This is partly due to the decreasing molecule size (N2 > He > H2) which allows for higher frequency and thus more power, and partly due to the thermal properties of the different gases. At these low temperature differences, the heat transfer to and from the working fluid has a much smaller driving force than at higher temperatures as e.g. in fossil fired SEs. Therefore the achievable frequency is much lower than at high temperature differences. This has also an impact on the preferable phase angle. Iwabuchi et al. [7] showed experimentally that the heat transfer between the heat exchanger and the working gas in reciprocating flow improves when the phase angle between two opposed pistons is changed from 9 degrees to 18 degrees, so that the complete gas volume from one piston is swept to the other. In the case discussed here the 18 degree phase difference corresponds to a phase angle of zero degrees, as the backside of the piston is used as compression piston (see Figure 2). Depending on the used working fluid, the preferred phase angle lies in between 3 and 45 degrees which correspond to a 12, 1 or 8 cylinder engine in the case of a Siemens arrangement (the phase angle of an Alpha multi-cylinder engine can be calculated by: α piston = 36⁰/n, with n being the number of cylinders). These small phase angles lead to small volumetric changes as the pistons move very close to parallel motion, but the enhanced heat exchange with heat source and sink makes them the preferable choice. The West number (W n ) as a means to evaluate the power output of a SE relates the pressure level, the frequency, the volumetric change, and the temperature levels [8]: W n = P / (p f V (T hot -T cold ) / (T hot +T cold )) Typical values range from to 5. Not considering the mechanical efficiency, at maximum power, the simulation gives values between and 4 depending on the working fluid, which prove to be within the predicted range even though the temperature difference is very low. In the considered range the efficiency drops as the frequency rises. The higher the frequency the higher the temperature difference between the working gas and the heat exchangers and thus the smaller the temperature difference in the working gas and so the efficiency. As the optimisation of the heat exchanger components was done in order to achieve the highest possible power output, the efficiencies could be improved at the expense of power density. At the maximum power point the efficiency is independent of the working gas around 8%, which is 3% of the Carnot efficiency.
6 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Fig. 3 Power and efficiency for Hydrogen (a,b), Helium (c,d), and Nitrogen (e,f) at T hot =15⁰C and p mean = 5 MPa Brake power reduction as a result of the piston arrangement Low temperature differences between heat source and sink in Stirling engines result in an unfavourable ratio of compression work to expansion work. Figure 4 shows this relation clearly using pv-plots for the expansion, compression, and total gas volume for (~ 18 C) heat source and 3 K (~ 3 C) sink temperature. It can be seen that a large portion of the expansion work is consumed for compression. The net work (total) is largely diminished and the resulting pv-plot very narrow.
7 Non-dimensional Power / - Non-dimensional Power / - non-dimensional pressure / p expansion p compression non-dimensional volume / - Fig. 4 Pressure - volume variations for the expansion and compression space and the total gas volume In a double-acting Alpha arrangement two variable gas spaces are combined on the two sides of a piston. These can be a compression and an expansion space in the case of the Siemens arrangement or two gas spaces of the same kind in the case of the Franchot arrangement (expansion expansion; compression compression). Figure 5 shows the nondimensional power for each piston in a four cylinder engine. For each of the two different arrangements the power is given over one crankshaft revolution. In both cases the net indicated power of all four pistons (P ABCD ) is identical, which is not the case for the individual pistons. In the case of the Siemens arrangement (a) each piston shows the same characteristic. The combination of compression and expansion on one single piston leads to smaller power amplitudes and thus loads on the piston rods as parts of the power is directly transferred between the two gas cycles. In the case of the Franchot arrangement (b) two pistons supply the crankshaft with power (A, D) and two pistons consume power (B, C) most of the time. This results in larger power amplitudes and loads on the crankshaft as the generated power has to be transferred from the expansion pistons to the crankshaft first and then back to the compression pistons. p_total A B C D - ABCD -.3 Crank angle / rad -.3 Crank angle / rad (a) (b) Fig. 5 Non dimensional power (P*) Siemens (a) and Franchot (b) arrangement A B C D ABCD The magnitude of the load transferred from the pistons to the crankshaft and back has a direct influence on the mechanical efficiency of the engine. Applying the above explained analysis of the mechanical efficiency on the two arrangements, the benefits of internal balancing of expansion and compression forces can be seen clearly. Figure 6 shows the overall mechanical efficiency as a function of the efficiency of the crankshaft mechanism. As expected the overall mechanical efficiency drops as the efficiency of the crank mechanism drops. A less efficient crank mechanism proves to be less detrimental in the case of the Siemens arrangement. But even at high mechanism efficiencies of for example.95 the Siemens arrangement provides 18% more power or mechanical efficiency than the Franchot arrangement, a notable difference.
8 Non-dimensional pressure/ - Mechanical efficiency 1.8 SIEMENS FRANCHOT Crankshaft efficiency Fig. 6 Overall mechanical efficiency versus crankshaft efficiency The type of compounding also has an influence on the pressure difference between the gas spaces separated by the piston seal. A larger amplitude in pressure difference leads to increased leakage into the adjacent gas cycle. Even though there is no net loss of the working gas as the direction of the pressure difference changes there is a loss in power. Figure 7 shows the pressure difference acting on one piston for each of the two arrangements. For the Franchot arrangement the amplitude of this difference is almost 3% higher and leakage increases accordingly. For an identical piston diameter this pressure difference is also directly proportional to the force on the piston rod and the crankshaft. Although the indicated power is identical and both arrangements effectively reduce the engine size by using the double acting principle the Siemens arrangement shows a number of advantages. In addition to the above stated, the reduced load on the crankshaft has additional benefits. Having to sustain less stress, the piston rods can be made from less or lighter material. This reduction of mass reduces the inertial forces of the crank and thus side forces and piston ring friction (for slider crank assemblies). Reduced load on the bearings and reciprocating seals also increase longevity of the engine. A smaller rod diameter also decreases leakage to and from the crankcase as the sealed gap becomes smaller and the power output is increased p_eff_siemens p_eff_franchot Crank angle / rad Fig. 7 Effective pressure oscillation for the Siemens and the Franchot arrangement over one cycle So far the mechanical implications were discussed only for four cylinder engines. It could be shown that the combination of a compression space and an expansion space on one piston is favourable in terms of mechanical efficiency, seal leakage, and internal loads. The thermodynamic optimisation with Sage implies that phase angles between pistons of 3 45 degrees are favourable which correspond to piston numbers between 8 and 12 in the case of interconnected cylinders. In Figure 8 the above made analysis is expanded to higher piston numbers for the better balanced Siemens arrangement. The higher the number of interconnected pistons the higher the overall mechanical efficiency as the gas forces are balanced even better (Figure 8 (a)). The amplitude of the pressure difference on the piston seal decreases with the number of pistons as the pressure amplitude in each gas cycle decreases (Figure 8 (b)).
9 Mechanical efficiency / - non-dimensional pressure / cylinder.3 6-cylinder 8-cylinder 1-cylinder.1 12-cylinder cylinder - 6-cylinder cylinder 1-cylinder cylinder Crankshaft efficiency/ - Crank angle / rad (a) (b) Fig. 8 Mechanical efficiency and effective pressure for different cylinder numbers in a Siemens arrangement 4. Conclusion The results of the two different analyses to optimise the indicated power as well as the mechanical efficiency both indicate favourable working conditions in a similar region, thus no compromise has to be found to reach maximum performance, a well appreciated fact when dealing with low enthalpy heat sources. The simulation shows the possibility to reach high power outputs from Alpha Stirling engines operating at low temperature differentials if the operation conditions (phase angle, frequency, working fluid) are chosen appropriately and if the mechanical set-up is designed aptly. As discussed above the Siemens configuration is the superior double-acting set-up for a number of reasons. Acknowledgements The authors acknowledge the support received from Mighty River Power to carry out the research reported in this paper. References [1] Clifford M. Hargreaves. The Philips Stirling Engine. Elsevier, [2] Graham Walker. Stirling Engines. Clarendon Press, 198. [3] Arne Hoeg, Tor-Martin Tveit, and Trond-Atle Asphjell. The development of a double-acting Stirling lab engine for low temperature heat utilisation. In ISEC29 - The 14th International Stirling Engine Conference, Groningen, the Netherlands, 29. [4] Gedeon Associates, South Canaan Rd Athens, OH 4571 U.S.A., [5] Douglas C. Montgomery. Design and Analysis of Experiments. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 21. [6] J.R. Senft. Mechanical Efficiency of Heat Engines. Cambridge University Press, 27. [7] M. Iwabuchi and M. Kanzaka. Experimental investigation into heat transfer under the periodically reversing flow condition in heat tube. In Stirling engines - Progress towards reality, pages I Mech E, Mechanical engineering publications, [8] C.D. West. Principles and Applications of Stirling Engines. Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, 1986.
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 67 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 67 (2015 ) 518 523 25th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and the International Cryogenic Materials Conference in 2014,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 67 (2015 ) 518 523 25th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and the International Cryogenic Materials Conference in 2014,
Analysis of Parametric Studies on the Impact of Piston Velocity Profile On the Performance of a Single Cylinder Diesel Engine
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 12, Issue 2 Ver. II (Mar - Apr. 2015), PP 81-85 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of Parametric Studies
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 12, Issue 2 Ver. II (Mar - Apr. 2015), PP 81-85 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of Parametric Studies
FEASIBILITY STYDY OF CHAIN DRIVE IN WATER HYDRAULIC ROTARY JOINT
 FEASIBILITY STYDY OF CHAIN DRIVE IN WATER HYDRAULIC ROTARY JOINT Antti MAKELA, Jouni MATTILA, Mikko SIUKO, Matti VILENIUS Institute of Hydraulics and Automation, Tampere University of Technology P.O.Box
FEASIBILITY STYDY OF CHAIN DRIVE IN WATER HYDRAULIC ROTARY JOINT Antti MAKELA, Jouni MATTILA, Mikko SIUKO, Matti VILENIUS Institute of Hydraulics and Automation, Tampere University of Technology P.O.Box
Electromagnetic Fully Flexible Valve Actuator
 Electromagnetic Fully Flexible Valve Actuator A traditional cam drive train, shown in Figure 1, acts on the valve stems to open and close the valves. As the crankshaft drives the camshaft through gears
Electromagnetic Fully Flexible Valve Actuator A traditional cam drive train, shown in Figure 1, acts on the valve stems to open and close the valves. As the crankshaft drives the camshaft through gears
Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset
 Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset Vikas Kumar Agarwal Deputy Manager Mahindra Two Wheelers Ltd. MIDC Chinchwad Pune 411019 India Abbreviations:
Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset Vikas Kumar Agarwal Deputy Manager Mahindra Two Wheelers Ltd. MIDC Chinchwad Pune 411019 India Abbreviations:
Simulation Method of Hydraulic Confined Piston Engine
 5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Simulation Method of Hydraulic Confined Piston Engine JIAO Yuqin 1, a, ZHANG Hongxin 1,b * and XU Wei 1,c 1 Electromechanic
5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Simulation Method of Hydraulic Confined Piston Engine JIAO Yuqin 1, a, ZHANG Hongxin 1,b * and XU Wei 1,c 1 Electromechanic
National Conference on Recent Innovations in Science And Engineering (NCRISE)
 National Conference on Recent Innovations in Science And Engineering (NCRISE) International Journal of Scientific Research in Science, Engineering and Technology 2017 IJSRSET Volume 3 Issue 4 Design Fabrication
National Conference on Recent Innovations in Science And Engineering (NCRISE) International Journal of Scientific Research in Science, Engineering and Technology 2017 IJSRSET Volume 3 Issue 4 Design Fabrication
NOVEL DIAPHRAGM BASED STIRLING CRYOCOOLER. A.J. Caughley 1, A Tucker 2, M Gschwendtner 3, and M Sellier 2 ABSTRACT
 NOVEL DIAPHRAGM BASED STIRLING CRYOCOOLER A.J. Caughley 1, A Tucker 2, M Gschwendtner 3, and M Sellier 2 1 Industrial Research Ltd, Christchurch, New Zealand 2 University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New
NOVEL DIAPHRAGM BASED STIRLING CRYOCOOLER A.J. Caughley 1, A Tucker 2, M Gschwendtner 3, and M Sellier 2 1 Industrial Research Ltd, Christchurch, New Zealand 2 University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New
Design and Analysis of Stirling Engines. Justin Denno Advised by Dr. Raouf Selim
 Design and Analysis of Stirling Engines Justin Denno Advised by Dr. Raouf Selim Abstract The Stirling engines being researched here are the acoustic engines and the Alpha-V engine. The acoustic engine
Design and Analysis of Stirling Engines Justin Denno Advised by Dr. Raouf Selim Abstract The Stirling engines being researched here are the acoustic engines and the Alpha-V engine. The acoustic engine
ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 1260, Page 1 Patrice BONNEFOI 1, Philippe DUGAST 2, Jean de BERNARDI 3 1 Danfoss CC, Advanced Technology, Trévoux, France 33 (0)4 74 00 28 29, p.bonnefoi@danfoss.com 2 Danfoss CC, Advanced Technology,
1260, Page 1 Patrice BONNEFOI 1, Philippe DUGAST 2, Jean de BERNARDI 3 1 Danfoss CC, Advanced Technology, Trévoux, France 33 (0)4 74 00 28 29, p.bonnefoi@danfoss.com 2 Danfoss CC, Advanced Technology,
The Performance Optimization of Rolling Piston Compressors Based on CFD Simulation
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 The Performance Optimization of Rolling Piston Compressors Based on CFD Simulation
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 The Performance Optimization of Rolling Piston Compressors Based on CFD Simulation
A New Device to Measure Instantaneous Swept Volume of Reciprocating Machines/Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 A New Device to Measure Instantaneous Swept Volume of Reciprocating Machines/Compressors
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 A New Device to Measure Instantaneous Swept Volume of Reciprocating Machines/Compressors
Development, Implementation, and Validation of a Fuel Impingement Model for Direct Injected Fuels with High Enthalpy of Vaporization
 Development, Implementation, and Validation of a Fuel Impingement Model for Direct Injected Fuels with High Enthalpy of Vaporization (SAE Paper- 2009-01-0306) Craig D. Marriott PE, Matthew A. Wiles PE,
Development, Implementation, and Validation of a Fuel Impingement Model for Direct Injected Fuels with High Enthalpy of Vaporization (SAE Paper- 2009-01-0306) Craig D. Marriott PE, Matthew A. Wiles PE,
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE SPRING CONSTANT IMPACT ON THE WORK OF A STIRLING-RINGBOM ENGINE WITH AN ELASTIC ELEMENT
 FRI-9.3-1-THPE-06 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE SPRING CONSTANT IMPACT ON THE WORK OF A STIRLING-RINGBOM ENGINE WITH AN ELASTIC ELEMENT Assist. Prof. Tsvetelina Petrova, PhD College of Energy and Electronics
FRI-9.3-1-THPE-06 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE SPRING CONSTANT IMPACT ON THE WORK OF A STIRLING-RINGBOM ENGINE WITH AN ELASTIC ELEMENT Assist. Prof. Tsvetelina Petrova, PhD College of Energy and Electronics
(v) Cylinder volume It is the volume of a gas inside the cylinder when the piston is at Bottom Dead Centre (B.D.C) and is denoted by V.
 UNIT II GAS POWER CYCLES AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard engines.
UNIT II GAS POWER CYCLES AIR STANDARD CYCLES Air standard cycles are used for comparison of thermal efficiencies of I.C engines. Engines working with air standard cycles are known as air standard engines.
Structural Analysis Of Reciprocating Compressor Manifold
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Structural Analysis Of Reciprocating Compressor Manifold Marcos Giovani Dropa Bortoli
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Structural Analysis Of Reciprocating Compressor Manifold Marcos Giovani Dropa Bortoli
Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers
 Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers U. Bin-Nun FLIR Systems Inc. Boston, MA 01862 ABSTRACT Cryocooler self induced vibration is a major consideration in the design of IR
Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers U. Bin-Nun FLIR Systems Inc. Boston, MA 01862 ABSTRACT Cryocooler self induced vibration is a major consideration in the design of IR
A Novel Device to Measure Instantaneous Swept Volume of Internal Combustion Engines
 Global Journal of Researches in Engineering Vol. 10 Issue 7 (Ver1.0), December 2010 P a g e 47 A Novel Device to Measure Instantaneous Swept Volume of Internal Combustion Engines MURUGAN. R. GJRE -A Classification
Global Journal of Researches in Engineering Vol. 10 Issue 7 (Ver1.0), December 2010 P a g e 47 A Novel Device to Measure Instantaneous Swept Volume of Internal Combustion Engines MURUGAN. R. GJRE -A Classification
Development of Low-Exergy-Loss, High-Efficiency Chemical Engines
 Development of Low-Exergy-Loss, High-Efficiency Chemical Engines Investigators C. F., Associate Professor, Mechanical Engineering; Kwee-Yan Teh, Shannon L. Miller, Graduate Researchers Introduction The
Development of Low-Exergy-Loss, High-Efficiency Chemical Engines Investigators C. F., Associate Professor, Mechanical Engineering; Kwee-Yan Teh, Shannon L. Miller, Graduate Researchers Introduction The
Earlier Lecture. For an optimum design of a Stirling cryocooler, a compromise between the operating and the design parameters may be sought.
 29 1 Earlier Lecture For an optimum design of a Stirling cryocooler, a compromise between the operating and the design parameters may be sought. Based on Schmidt s analysis, the variation of Q E /(p max
29 1 Earlier Lecture For an optimum design of a Stirling cryocooler, a compromise between the operating and the design parameters may be sought. Based on Schmidt s analysis, the variation of Q E /(p max
THEORETICAL ASSESSMENT OF A STIRLING ENGINE 'AMAZON' BY USING PROSA AND MATHCAD
 THEORETICAL ASSESSMENT OF A STIRLING ENGINE 'AMAZON' BY USING PROSA AND MATHCAD R. B. Paula a, J. L. Goncalves b, V. R. M. Cobas c, and Electo E. S. Lora d Universidade Federal de Itajubá Instituto de
THEORETICAL ASSESSMENT OF A STIRLING ENGINE 'AMAZON' BY USING PROSA AND MATHCAD R. B. Paula a, J. L. Goncalves b, V. R. M. Cobas c, and Electo E. S. Lora d Universidade Federal de Itajubá Instituto de
Small Oil Free Piston Type Compressor For CO2
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2002 Small Oil Free Piston Type Compressor For CO2 H. Baumann Baumann Engineering M. Conzett
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2002 Small Oil Free Piston Type Compressor For CO2 H. Baumann Baumann Engineering M. Conzett
Turbo boost. ACTUS is ABB s new simulation software for large turbocharged combustion engines
 Turbo boost ACTUS is ABB s new simulation software for large turbocharged combustion engines THOMAS BÖHME, ROMAN MÖLLER, HERVÉ MARTIN The performance of turbocharged combustion engines depends heavily
Turbo boost ACTUS is ABB s new simulation software for large turbocharged combustion engines THOMAS BÖHME, ROMAN MÖLLER, HERVÉ MARTIN The performance of turbocharged combustion engines depends heavily
International Conference on Advances in Energy, Environment and Chemical Engineering (AEECE-2015)
 International Conference on Advances in Energy, Environment and Chemical Engineering (AEECE-2015) Supercritical CO2 Cycle System Optimization of Marine Diesel Engine Waste Heat Recovery Shengya Hou 1,
International Conference on Advances in Energy, Environment and Chemical Engineering (AEECE-2015) Supercritical CO2 Cycle System Optimization of Marine Diesel Engine Waste Heat Recovery Shengya Hou 1,
Clearance Loss Analysis in Linear Compressor with CFD Method
 Clearance Loss Analysis in Linear Compressor with CFD Method Wenjie Zhou, Zhihua Gan, Xiaobin Zhang, Limin Qiu, Yinzhe Wu Cryogenics Laboratory, Zhejiang University Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China, 310027 ABSTRACT
Clearance Loss Analysis in Linear Compressor with CFD Method Wenjie Zhou, Zhihua Gan, Xiaobin Zhang, Limin Qiu, Yinzhe Wu Cryogenics Laboratory, Zhejiang University Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China, 310027 ABSTRACT
Research of the Effectiveness of Use of New Mechanism in Reciprocating Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2000 Research of the Effectiveness of Use of New Mechanism in Reciprocating Compressors
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2000 Research of the Effectiveness of Use of New Mechanism in Reciprocating Compressors
INVESTIGATION OF SEAL PERFORMANCE IN A 4-α DOUBLE-ACTING STIRLING-CYCLE HEAT-PUMP/REFRIGERATOR. Abstract
 INVESTIGATION OF SEAL PERFORMANCE IN A 4-α DOUBLE-ACTING STIRLING-CYCLE HEAT-PUMP/REFRIGERATOR D. Haywood, Ph.D. student in Mechanical Engineering J.K. Raine, Professor in Mechanical Engineering M.A. Gschwendtner,
INVESTIGATION OF SEAL PERFORMANCE IN A 4-α DOUBLE-ACTING STIRLING-CYCLE HEAT-PUMP/REFRIGERATOR D. Haywood, Ph.D. student in Mechanical Engineering J.K. Raine, Professor in Mechanical Engineering M.A. Gschwendtner,
COMPRESSIBLE FLOW ANALYSIS IN A CLUTCH PISTON CHAMBER
 COMPRESSIBLE FLOW ANALYSIS IN A CLUTCH PISTON CHAMBER Masaru SHIMADA*, Hideharu YAMAMOTO* * Hardware System Development Department, R&D Division JATCO Ltd 7-1, Imaizumi, Fuji City, Shizuoka, 417-8585 Japan
COMPRESSIBLE FLOW ANALYSIS IN A CLUTCH PISTON CHAMBER Masaru SHIMADA*, Hideharu YAMAMOTO* * Hardware System Development Department, R&D Division JATCO Ltd 7-1, Imaizumi, Fuji City, Shizuoka, 417-8585 Japan
A REVIEW ON STIRLING ENGINES
 A REVIEW ON STIRLING ENGINES Neeraj Joshi UG Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sandip Foundation s Sandip Institute of Technology and Research Centre,Mahiravani, Nashik Savitribai Phule Pune
A REVIEW ON STIRLING ENGINES Neeraj Joshi UG Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sandip Foundation s Sandip Institute of Technology and Research Centre,Mahiravani, Nashik Savitribai Phule Pune
Comparing FEM Transfer Matrix Simulated Compressor Plenum Pressure Pulsations to Measured Pressure Pulsations and to CFD Results
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 Comparing FEM Transfer Matrix Simulated Compressor Plenum Pressure Pulsations to Measured
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 Comparing FEM Transfer Matrix Simulated Compressor Plenum Pressure Pulsations to Measured
Integrated Simulation of a Truck Diesel Engine with a Hydraulic Engine Braking System
 Integrated Simulation of a Truck Diesel Engine with a Hydraulic Engine Braking System N. Brinkert, K. Kanning GT-Suite Users Conference 2008 I want to give you a short presentation about a project we work
Integrated Simulation of a Truck Diesel Engine with a Hydraulic Engine Braking System N. Brinkert, K. Kanning GT-Suite Users Conference 2008 I want to give you a short presentation about a project we work
MODELING SUSPENSION DAMPER MODULES USING LS-DYNA
 MODELING SUSPENSION DAMPER MODULES USING LS-DYNA Jason J. Tao Delphi Automotive Systems Energy & Chassis Systems Division 435 Cincinnati Street Dayton, OH 4548 Telephone: (937) 455-6298 E-mail: Jason.J.Tao@Delphiauto.com
MODELING SUSPENSION DAMPER MODULES USING LS-DYNA Jason J. Tao Delphi Automotive Systems Energy & Chassis Systems Division 435 Cincinnati Street Dayton, OH 4548 Telephone: (937) 455-6298 E-mail: Jason.J.Tao@Delphiauto.com
Thermal Stress Analysis of Diesel Engine Piston
 International Conference on Challenges and Opportunities in Mechanical Engineering, Industrial Engineering and Management Studies 576 Thermal Stress Analysis of Diesel Engine Piston B.R. Ramesh and Kishan
International Conference on Challenges and Opportunities in Mechanical Engineering, Industrial Engineering and Management Studies 576 Thermal Stress Analysis of Diesel Engine Piston B.R. Ramesh and Kishan
Design and Development Of Opposite Piston Engine
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 3, Special Issue 3, March 2014 2014 IEEE International Conference
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 3, Special Issue 3, March 2014 2014 IEEE International Conference
Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep Copyright The McGraw-Hill
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep Copyright The McGraw-Hill
EFFICIENCY INCREASE IN SHIP'S PRIMAL ENERGY SYSTEM USING A MULTISTAGE COMPRESSION WITH INTERCOOLING
 THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2016, Vol. 20, No. 2, pp. 1399-1406 1399 EFFICIENCY INCREASE IN SHIP'S PRIMAL ENERGY SYSTEM USING A MULTISTAGE COMPRESSION WITH INTERCOOLING by Petar LANDEKA and Gojmir RADICA* Faculty
THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2016, Vol. 20, No. 2, pp. 1399-1406 1399 EFFICIENCY INCREASE IN SHIP'S PRIMAL ENERGY SYSTEM USING A MULTISTAGE COMPRESSION WITH INTERCOOLING by Petar LANDEKA and Gojmir RADICA* Faculty
Analysis of Torsional Vibration in Elliptical Gears
 The The rd rd International Conference on on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES Pilsen, Czech Pilsen, Republic, Czech August Republic, September -, Analysis of Torsional Vibration in Elliptical Gears
The The rd rd International Conference on on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES Pilsen, Czech Pilsen, Republic, Czech August Republic, September -, Analysis of Torsional Vibration in Elliptical Gears
Design and Stress Analysis of Crankshaft for Single Cylinder 4-Stroke Diesel Engine
 Design and Stress Analysis of Crankshaft for Single Cylinder 4-Stroke Diesel Engine Amit Solanki #1, Jaydeepsinh Dodiya #2, # Mechanical Engg.Deptt, C.U.Shah University, Wadhwan city, Gujarat, INDIA Abstract
Design and Stress Analysis of Crankshaft for Single Cylinder 4-Stroke Diesel Engine Amit Solanki #1, Jaydeepsinh Dodiya #2, # Mechanical Engg.Deptt, C.U.Shah University, Wadhwan city, Gujarat, INDIA Abstract
Influence of Cylinder Bore Volume on Pressure Pulsations in a Hermetic Reciprocating Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Influence of Cylinder Bore Volume on Pressure Pulsations in a Hermetic Reciprocating
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Influence of Cylinder Bore Volume on Pressure Pulsations in a Hermetic Reciprocating
THE IMPACT OF BATTERY OPERATING TEMPERATURE AND STATE OF CHARGE ON THE LITHIUM-ION BATTERY INTERNAL RESISTANCE
 Jurnal Mekanikal June 2017, Vol 40, 01-08 THE IMPACT OF BATTERY OPERATING TEMPERATURE AND STATE OF CHARGE ON THE LITHIUM-ION BATTERY INTERNAL RESISTANCE Amirul Haniff Mahmud, Zul Hilmi Che Daud, Zainab
Jurnal Mekanikal June 2017, Vol 40, 01-08 THE IMPACT OF BATTERY OPERATING TEMPERATURE AND STATE OF CHARGE ON THE LITHIUM-ION BATTERY INTERNAL RESISTANCE Amirul Haniff Mahmud, Zul Hilmi Che Daud, Zainab
Development of a High Frequency Pulse Tube
 1 Development of a High Frequency Pulse Tube N. Emery 1, A. Caughley 1, N. Glasson 1, A. Tucker 2, M. Gschwendtner 3 1 Industrial Research Ltd Christchurch, New Zealand 2 University of Canterbury Christchurch,
1 Development of a High Frequency Pulse Tube N. Emery 1, A. Caughley 1, N. Glasson 1, A. Tucker 2, M. Gschwendtner 3 1 Industrial Research Ltd Christchurch, New Zealand 2 University of Canterbury Christchurch,
Dynamic Behavior Analysis of Hydraulic Power Steering Systems
 Dynamic Behavior Analysis of Hydraulic Power Steering Systems Y. TOKUMOTO * *Research & Development Center, Control Devices Development Department Research regarding dynamic modeling of hydraulic power
Dynamic Behavior Analysis of Hydraulic Power Steering Systems Y. TOKUMOTO * *Research & Development Center, Control Devices Development Department Research regarding dynamic modeling of hydraulic power
Twin Screw Compressor Performance and Its Relationship with Rotor Cutter Blade Shape and Manufacturing Cost
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Twin Screw Compressor Performance and Its Relationship with Rotor Cutter Blade Shape
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Twin Screw Compressor Performance and Its Relationship with Rotor Cutter Blade Shape
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 67 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 67 (2015 ) 434 439 25th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and the International Cryogenic Materials Conference in 2014,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 67 (2015 ) 434 439 25th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and the International Cryogenic Materials Conference in 2014,
Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes
 8 CHAPTER Gas Power Cycles 8-1 Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes The analysis of many complex processes can be reduced to a manageable level by utilizing some idealizations (fig.
8 CHAPTER Gas Power Cycles 8-1 Idealizations Help Manage Analysis of Complex Processes The analysis of many complex processes can be reduced to a manageable level by utilizing some idealizations (fig.
Development of a High Frequency Pulse Tube
 Development of a High Frequency Pulse Tube N. Emery 1, A. Caughley 1, N. Glasson 1, A. Tucker 2, M. Gschwendtner 3 1 Industrial Research Ltd., Christchurch, New Zealand 2 University of Canterbury, Christchurch,
Development of a High Frequency Pulse Tube N. Emery 1, A. Caughley 1, N. Glasson 1, A. Tucker 2, M. Gschwendtner 3 1 Industrial Research Ltd., Christchurch, New Zealand 2 University of Canterbury, Christchurch,
Ambient Magnetic Field Compensation for the ARIEL (Advanced Rare IsotopE Laboratory) Electron Beamline. Gabriela Arias April 2014, TRIUMF
 Ambient Magnetic Field Compensation for the ARIEL (Advanced Rare IsotopE Laboratory) Electron Beamline Gabriela Arias April 2014, TRIUMF Summary TRIUMF s Advanced Rare IsotopE Laboratory (ARIEL) facility
Ambient Magnetic Field Compensation for the ARIEL (Advanced Rare IsotopE Laboratory) Electron Beamline Gabriela Arias April 2014, TRIUMF Summary TRIUMF s Advanced Rare IsotopE Laboratory (ARIEL) facility
Simulation of Performance Parameters of Spark Ignition Engine for Various Ignition Timings
 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology ISSN 2277-4106 2013 INPRESSCO. All Rights Reserved. Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Simulation of Performance
Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology ISSN 2277-4106 2013 INPRESSCO. All Rights Reserved. Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Simulation of Performance
Effect of Compressor Inlet Temperature on Cycle Performance for a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Brayton Cycle
 The 6th International Supercritical CO2 Power Cycles Symposium March 27-29, 2018, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Effect of Compressor Inlet Temperature on Cycle Performance for a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
The 6th International Supercritical CO2 Power Cycles Symposium March 27-29, 2018, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Effect of Compressor Inlet Temperature on Cycle Performance for a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Compression Loads in Twin Screw Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Compression Loads in Twin Screw Compressor
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Compression Loads in Twin Screw Compressor
Transmission Error in Screw Compressor Rotors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Transmission Error in Screw Compressor Rotors Jack Sauls Trane Follow this and additional
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Transmission Error in Screw Compressor Rotors Jack Sauls Trane Follow this and additional
Pressure Ratio Effect to Warm Displacer Type Pulse Tube Refrigerator
 227 1 Pressure Ratio Effect to Warm Displacer Type Pulse Tube Refrigerator S. Zhu 1,Y. Matsubara 2 1 School of Mechanical Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, 201804, China 2 Former professor of Nihon
227 1 Pressure Ratio Effect to Warm Displacer Type Pulse Tube Refrigerator S. Zhu 1,Y. Matsubara 2 1 School of Mechanical Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, 201804, China 2 Former professor of Nihon
Page 2. (a) (i) Show that during the change AB the gas undergoes an isothermal change.
 Q1.The Carnot cycle is the most efficient theoretical cycle of changes for a fixed mass of gas in a heat engine. The graph below shows the pressure volume (p V) diagram for a gas undergoing a Carnot cycle
Q1.The Carnot cycle is the most efficient theoretical cycle of changes for a fixed mass of gas in a heat engine. The graph below shows the pressure volume (p V) diagram for a gas undergoing a Carnot cycle
NEW CONCEPT OF A ROCKER ENGINE KINEMATIC ANALYSIS
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 19, No. 3 2012 NEW CONCEPT OF A ROCKER ENGINE KINEMATIC ANALYSIS Miros aw Szymkowiak Kochanowskiego Street 13, 64-100 Leszno, Poland e-mail: szymkowiak@op.pl
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 19, No. 3 2012 NEW CONCEPT OF A ROCKER ENGINE KINEMATIC ANALYSIS Miros aw Szymkowiak Kochanowskiego Street 13, 64-100 Leszno, Poland e-mail: szymkowiak@op.pl
Waste Heat Recovery from an Internal Combustion Engine
 Waste Heat Recovery from an Internal Combustion Engine Design Team Josh Freeman, Matt McGroarty, Rob McGroarty Greg Pellegrini, Ming Wood Design Advisor Professor Mohammed Taslim Abstract A substantial
Waste Heat Recovery from an Internal Combustion Engine Design Team Josh Freeman, Matt McGroarty, Rob McGroarty Greg Pellegrini, Ming Wood Design Advisor Professor Mohammed Taslim Abstract A substantial
K. Shiokawa & R. Takagi Department of Electrical Engineering, Kogakuin University, Japan. Abstract
 Computers in Railways XIII 583 Numerical optimisation of the charge/discharge characteristics of wayside energy storage systems by the embedded simulation technique using the railway power network simulator
Computers in Railways XIII 583 Numerical optimisation of the charge/discharge characteristics of wayside energy storage systems by the embedded simulation technique using the railway power network simulator
Discussion of Marine Stirling Engine Systems
 Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Marine Engineering Tokyo, October 24th to 28th, 2005 Discussion of Marine Stirling Engine Systems Koichi HIRATA* and Masakuni KAWADA** ABSTRACT Many kinds
Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Marine Engineering Tokyo, October 24th to 28th, 2005 Discussion of Marine Stirling Engine Systems Koichi HIRATA* and Masakuni KAWADA** ABSTRACT Many kinds
2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April/May 2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April/May 2013 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Development of a New Type Cylinder Head for Piston Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs nternational Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2 Development of a New Type Cylinder Head for Piston Compressors E. Ayder nstanbul Technical
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs nternational Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2 Development of a New Type Cylinder Head for Piston Compressors E. Ayder nstanbul Technical
CHAPTER 2 MODELLING OF SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTORS
 9 CHAPTER 2 MODELLING OF SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTORS 2.1 INTRODUCTION The Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM) has a simple design with a rotor without windings and a stator with windings located at the poles.
9 CHAPTER 2 MODELLING OF SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MOTORS 2.1 INTRODUCTION The Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM) has a simple design with a rotor without windings and a stator with windings located at the poles.
SONIC PROPULSION SYSTEM, AN OVERALL VIEW OF POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS
 SONIC PROPULSION SYSTEM, AN OVERALL VIEW OF POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS Horia Abaitancei *, Dan Abaitancei, Gheorghe-Alexandru Radu, Sebastian Radu, Mihaela Coldea, Alexandru Lupa Transilvania University of Brasov
SONIC PROPULSION SYSTEM, AN OVERALL VIEW OF POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS Horia Abaitancei *, Dan Abaitancei, Gheorghe-Alexandru Radu, Sebastian Radu, Mihaela Coldea, Alexandru Lupa Transilvania University of Brasov
Unit WorkBook 4 Level 4 ENG U13 Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 13: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines Unit Workbook 4 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 4 Internal Combustion
Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 13: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines Unit Workbook 4 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 4 Internal Combustion
White paper: Pneumatics or electrics important criteria when choosing technology
 White paper: Pneumatics or electrics important criteria when choosing technology The requirements for modern production plants are becoming increasingly complex. It is therefore essential that the drive
White paper: Pneumatics or electrics important criteria when choosing technology The requirements for modern production plants are becoming increasingly complex. It is therefore essential that the drive
The Internal combustion engine (Otto Cycle)
 The Internal combustion engine (Otto Cycle) The Otto cycle is a set of processes used by spark ignition internal combustion engines (2-stroke or 4-stroke cycles). These engines a) ingest a mixture of fuel
The Internal combustion engine (Otto Cycle) The Otto cycle is a set of processes used by spark ignition internal combustion engines (2-stroke or 4-stroke cycles). These engines a) ingest a mixture of fuel
NOVEL ENGINE DESIGN OF HIGHER EFFICIENCY
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol.14, No. 4 2007 NOVEL ENGINE DESIGN OF HIGHER EFFICIENCY Barbara Sieminska Institute of Aeronautics Al. Krakowska 110/114, 02-256 Warszawa, Poland tel.: +48
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol.14, No. 4 2007 NOVEL ENGINE DESIGN OF HIGHER EFFICIENCY Barbara Sieminska Institute of Aeronautics Al. Krakowska 110/114, 02-256 Warszawa, Poland tel.: +48
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S 2900 MIXER TO BE USED BY CNRL FOR BITUMEN VISCOSITY CONTROL Report R0. By Kimbal A.
 COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S 2900 MIXER TO BE USED BY CNRL FOR BITUMEN VISCOSITY CONTROL Report 412509-1R0 By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY May 2012 ALDEN RESEARCH
COMPUTATIONAL FLOW MODEL OF WESTFALL'S 2900 MIXER TO BE USED BY CNRL FOR BITUMEN VISCOSITY CONTROL Report 412509-1R0 By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY May 2012 ALDEN RESEARCH
Exhaust Gas Waste Heat Recovery and Utilization System in IC Engine
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Exhaust Gas Waste Heat Recovery and Utilization System in IC Engine Alvin
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Exhaust Gas Waste Heat Recovery and Utilization System in IC Engine Alvin
TECHNICAL PAPER FOR STUDENTS AND YOUNG ENGINEERS - FISITA WORLD AUTOMOTIVE CONGRESS, BARCELONA
 TECHNICAL PAPER FOR STUDENTS AND YOUNG ENGINEERS - FISITA WORLD AUTOMOTIVE CONGRESS, BARCELONA 2 - TITLE: Topic: INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECTS OF HYDROGEN ADDITION ON PERFORMANCE AND EXHAUST EMISSIONS OF
TECHNICAL PAPER FOR STUDENTS AND YOUNG ENGINEERS - FISITA WORLD AUTOMOTIVE CONGRESS, BARCELONA 2 - TITLE: Topic: INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECTS OF HYDROGEN ADDITION ON PERFORMANCE AND EXHAUST EMISSIONS OF
η th W = Q Gas Power Cycles: Working fluid remains in the gaseous state through the cycle.
 Gas Power Cycles: Gas Power Cycles: Working fluid remains in the gaseous state through the cycle. Sometimes useful to study an idealised cycle in which internal irreversibilities and complexities are
Gas Power Cycles: Gas Power Cycles: Working fluid remains in the gaseous state through the cycle. Sometimes useful to study an idealised cycle in which internal irreversibilities and complexities are
Noise Reduction in a Reciprocating Compressor by Optimizing the Suction Muffler
 Noise Reduction in a Reciprocating Compressor by Optimizing the Suction Muffler Katakama Nagarjuna ¹ K.Sreenivas² ¹ M.tech student, ²Professor, dept of mechanical engineering kits, markapur, A.P, INDIA
Noise Reduction in a Reciprocating Compressor by Optimizing the Suction Muffler Katakama Nagarjuna ¹ K.Sreenivas² ¹ M.tech student, ²Professor, dept of mechanical engineering kits, markapur, A.P, INDIA
Free-CHP: Free-Piston Reciprocating Joule Cycle Engine
 PRO-TEM Special Session on Power Generation and Polygeneration Systems Free-CHP: Free-Piston Reciprocating Joule Cycle Engine Rikard Mikalsen, Tony Roskilly Newcastle University, UK Background: micro-chp
PRO-TEM Special Session on Power Generation and Polygeneration Systems Free-CHP: Free-Piston Reciprocating Joule Cycle Engine Rikard Mikalsen, Tony Roskilly Newcastle University, UK Background: micro-chp
Long Transfer Lines Enabling Large Separations between Compressor and Coldhead for High- Frequency Acoustic-Stirling ( Pulse-Tube ) Coolers
 Long Transfer Lines Enabling Large Separations between Compressor and Coldhead for High- Frequency Acoustic-Stirling ( Pulse-Tube ) Coolers P. S. Spoor and J. A. Corey CFIC-Qdrive Troy, NY 12180 ABSTRACT
Long Transfer Lines Enabling Large Separations between Compressor and Coldhead for High- Frequency Acoustic-Stirling ( Pulse-Tube ) Coolers P. S. Spoor and J. A. Corey CFIC-Qdrive Troy, NY 12180 ABSTRACT
Numerical Investigation of the Gas Leakage through the Piston-Cylinder Clearance of Reciprocating Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Numerical Investigation of the Gas Leakage through the Piston-Cylinder Clearance of
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Numerical Investigation of the Gas Leakage through the Piston-Cylinder Clearance of
Designing and analysing the cooling of a medium speed engine piston using MPS method
 Designing and analysing the cooling of a medium speed engine piston using MPS method Sami Ojala Wärtsilä Finland Oy Vaasa, Finland Email: sami.ojala@wartsila.com Web: http://wartsila.com/ Summary In this
Designing and analysing the cooling of a medium speed engine piston using MPS method Sami Ojala Wärtsilä Finland Oy Vaasa, Finland Email: sami.ojala@wartsila.com Web: http://wartsila.com/ Summary In this
SUCCESSFUL DIESEL COLD START THROUGH PROPER PILOT INJECTION PARAMETERS SELECTION. Aleksey Marchuk, Georgiy Kuharenok, Aleksandr Petruchenko
 SUCCESSFUL DIESEL COLD START THROUGH PROPER PILOT INJECTION PARAMETERS SELECTION Aleksey Marchuk, Georgiy Kuharenok, Aleksandr Petruchenko Robert Bosch Company, Germany Belarussian National Technical Universitry,
SUCCESSFUL DIESEL COLD START THROUGH PROPER PILOT INJECTION PARAMETERS SELECTION Aleksey Marchuk, Georgiy Kuharenok, Aleksandr Petruchenko Robert Bosch Company, Germany Belarussian National Technical Universitry,
A FEASIBILITY STUDY ON WASTE HEAT RECOVERY IN AN IC ENGINE USING ELECTRO TURBO GENERATION
 A FEASIBILITY STUDY ON WASTE HEAT RECOVERY IN AN IC ENGINE USING ELECTRO TURBO GENERATION S.N.Srinivasa Dhaya Prasad 1 N.Parameshwari 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Automobile Engg., SACS MAVMM
A FEASIBILITY STUDY ON WASTE HEAT RECOVERY IN AN IC ENGINE USING ELECTRO TURBO GENERATION S.N.Srinivasa Dhaya Prasad 1 N.Parameshwari 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Automobile Engg., SACS MAVMM
Cooling Enhancement of Electric Motors
 Cooling Enhancement of Electric Motors Authors : Yasser G. Dessouky* and Barry W. Williams** Dept. of Computing & Electrical Engineering Heriot-Watt University Riccarton, Edinburgh EH14 4AS, U.K. Fax :
Cooling Enhancement of Electric Motors Authors : Yasser G. Dessouky* and Barry W. Williams** Dept. of Computing & Electrical Engineering Heriot-Watt University Riccarton, Edinburgh EH14 4AS, U.K. Fax :
ENERGY EXTRACTION FROM CONVENTIONAL BRAKING SYSTEM OF AUTOMOBILE
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 2009 (ICME2009) 26-28 December 2009, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME09- ENERGY EXTRACTION FROM CONVENTIONAL BRAKING SYSTEM OF AUTOMOBILE Aktaruzzaman
Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 2009 (ICME2009) 26-28 December 2009, Dhaka, Bangladesh ICME09- ENERGY EXTRACTION FROM CONVENTIONAL BRAKING SYSTEM OF AUTOMOBILE Aktaruzzaman
WEEK 4 Dynamics of Machinery
 WEEK 4 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J.Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2003 Prof.Dr.Hasan ÖZTÜRK 1 DYNAMICS OF RECIPROCATING ENGINES Prof.Dr.Hasan ÖZTÜRK The
WEEK 4 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J.Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2003 Prof.Dr.Hasan ÖZTÜRK 1 DYNAMICS OF RECIPROCATING ENGINES Prof.Dr.Hasan ÖZTÜRK The
Design & Development of Regenerative Braking System at Rear Axle
 International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 2250-3234 Volume 8, Number 2 (2018), pp. 165-172 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Design & Development of Regenerative
International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 2250-3234 Volume 8, Number 2 (2018), pp. 165-172 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Design & Development of Regenerative
A Sensitivity Analysis of a Miniature-Scale Linear Compressor for Electronics Cooling using a Comprehensive Model
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 A Sensitivity Analysis of a Miniature-Scale Linear Compressor for Electronics Cooling
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 A Sensitivity Analysis of a Miniature-Scale Linear Compressor for Electronics Cooling
(a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16]
![(a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16] (a) then mean effective pressure and the indicated power for each end ; (b) the total indicated power : [16]](/thumbs/79/80273804.jpg) Code No: R05220304 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
Code No: R05220304 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 THERMAL ENGINEERING-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering August 2000, Nice, FRANCE
 Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 7.6 ROLLING NOISE FROM
Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 7.6 ROLLING NOISE FROM
Numerical Simulation and Performance Analysis of Rotary Vane Compressors for Automobile Air Conditioner
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 24 Numerical Simulation and Performance Analysis of Rotary Vane Compressors for Automobile
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 24 Numerical Simulation and Performance Analysis of Rotary Vane Compressors for Automobile
NEW MODIFIED BETA TYPE STIRLING ENGINE COMPARISON WITH CLASSICAL STIRLING ENGINE LAYOUT
 NEW MODIFIED BETA TYPE STIRLING ENGINE COMPARISON WITH CLASSICAL STIRLING ENGINE LAYOUT Ilmars Blumbergs Riga Aeronautical Institute, Latvia ilmars-b@inbox.lv Abstract. In the paper the main aspects of
NEW MODIFIED BETA TYPE STIRLING ENGINE COMPARISON WITH CLASSICAL STIRLING ENGINE LAYOUT Ilmars Blumbergs Riga Aeronautical Institute, Latvia ilmars-b@inbox.lv Abstract. In the paper the main aspects of
CHAPTER 4 MODELING OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR BASED WIND ENERGY CONVERSION SYSTEM
 47 CHAPTER 4 MODELING OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR BASED WIND ENERGY CONVERSION SYSTEM 4.1 INTRODUCTION Wind energy has been the subject of much recent research and development. The only negative
47 CHAPTER 4 MODELING OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR BASED WIND ENERGY CONVERSION SYSTEM 4.1 INTRODUCTION Wind energy has been the subject of much recent research and development. The only negative
MARINE FOUR-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING OIL FILM LUBRICATION CHARACTERISTIC ANALYSIS
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH Special Issue 2018 S2 (98) 2018 Vol. 25; pp. 30-34 10.2478/pomr-2018-0070 MARINE FOUR-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING OIL FILM LUBRICATION CHARACTERISTIC ANALYSIS
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH Special Issue 2018 S2 (98) 2018 Vol. 25; pp. 30-34 10.2478/pomr-2018-0070 MARINE FOUR-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING OIL FILM LUBRICATION CHARACTERISTIC ANALYSIS
Plastic Ball Bearing Design Improvement Using Finite Element Method
 2017 Published in 5th International Symposium on Innovative Technologies in Engineering and Science 29-30 September 2017 (ISITES2017 Baku - Azerbaijan) Plastic Ball Bearing Design Improvement Using Finite
2017 Published in 5th International Symposium on Innovative Technologies in Engineering and Science 29-30 September 2017 (ISITES2017 Baku - Azerbaijan) Plastic Ball Bearing Design Improvement Using Finite
Modelling Automotive Hydraulic Systems using the Modelica ActuationHydraulics Library
 Modelling Automotive Hydraulic Systems using the Modelica ActuationHydraulics Library Peter Harman Ricardo UK Ltd. Leamington Spa, UK Peter.Harman@ricardo.com Abstract This paper describes applications
Modelling Automotive Hydraulic Systems using the Modelica ActuationHydraulics Library Peter Harman Ricardo UK Ltd. Leamington Spa, UK Peter.Harman@ricardo.com Abstract This paper describes applications
DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF GAMMA-TYPE STIRLING ENGINE WITH ROTARY DISPLACER
 DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF GAMMA-TYPE STIRLING ENGINE WITH ROTARY DISPLACER Ajay Ashok 1, Arundas S 2, Bestin Varghese 3, Ajithkumar.K.T 4 1 Student, Department Of Mechanical Engineering, B.T.C College
DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF GAMMA-TYPE STIRLING ENGINE WITH ROTARY DISPLACER Ajay Ashok 1, Arundas S 2, Bestin Varghese 3, Ajithkumar.K.T 4 1 Student, Department Of Mechanical Engineering, B.T.C College
The Effect of Spring Design as Return Cycle of Two Stroke Spark Ignition Linear Engine on the Combustion Process and Performance
 American J. of Engineering and Applied Sciences 3 (2): 412-417, 2010 ISSN 1941-7020 2010 Science Publications The Effect of Spring Design as Return Cycle of Two Stroke Spark Ignition Linear Engine on the
American J. of Engineering and Applied Sciences 3 (2): 412-417, 2010 ISSN 1941-7020 2010 Science Publications The Effect of Spring Design as Return Cycle of Two Stroke Spark Ignition Linear Engine on the
HERCULES-2 Project. Deliverable: D8.8
 HERCULES-2 Project Fuel Flexible, Near Zero Emissions, Adaptive Performance Marine Engine Deliverable: D8.8 Study an alternative urea decomposition and mixer / SCR configuration and / or study in extended
HERCULES-2 Project Fuel Flexible, Near Zero Emissions, Adaptive Performance Marine Engine Deliverable: D8.8 Study an alternative urea decomposition and mixer / SCR configuration and / or study in extended
Internal Combustion Engines
 Friction & Lubrication Lecture 1 1 Outline In this lecture we will discuss the following: Engine friction losses. Piston arrangement losses. Measurement of friction losses. Engine lubrication systems.
Friction & Lubrication Lecture 1 1 Outline In this lecture we will discuss the following: Engine friction losses. Piston arrangement losses. Measurement of friction losses. Engine lubrication systems.
Numerical Investigation of Diesel Engine Characteristics During Control System Development
 Numerical Investigation of Diesel Engine Characteristics During Control System Development Aleksandr Aleksandrovich Kudryavtsev, Aleksandr Gavriilovich Kuznetsov Sergey Viktorovich Kharitonov and Dmitriy
Numerical Investigation of Diesel Engine Characteristics During Control System Development Aleksandr Aleksandrovich Kudryavtsev, Aleksandr Gavriilovich Kuznetsov Sergey Viktorovich Kharitonov and Dmitriy
Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition
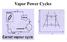 Vapor Power Cycles Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process from P1 to P2. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition process at constant temperature TH. Process 3-4: Reversible adiabatic
Vapor Power Cycles Process 1-2: Reversible adiabatic compression process from P1 to P2. Process 2-3: Reversible isothermal heat addition process at constant temperature TH. Process 3-4: Reversible adiabatic
INTERCONNECTION POSSIBILITIES FOR THE WORKING VOLUMES OF THE ALTERNATING HYDRAULIC MOTORS
 Scientific Bulletin of the Politehnica University of Timisoara Transactions on Mechanics Special issue The 6 th International Conference on Hydraulic Machinery and Hydrodynamics Timisoara, Romania, October
Scientific Bulletin of the Politehnica University of Timisoara Transactions on Mechanics Special issue The 6 th International Conference on Hydraulic Machinery and Hydrodynamics Timisoara, Romania, October
Simulation of Structural Latches in an Automotive Seat System Using LS-DYNA
 Simulation of Structural Latches in an Automotive Seat System Using LS-DYNA Tuhin Halder Lear Corporation, U152 Group 5200, Auto Club Drive Dearborn, MI 48126 USA. + 313 845 0492 thalder@ford.com Keywords:
Simulation of Structural Latches in an Automotive Seat System Using LS-DYNA Tuhin Halder Lear Corporation, U152 Group 5200, Auto Club Drive Dearborn, MI 48126 USA. + 313 845 0492 thalder@ford.com Keywords:
Extending the Operation Range of Dry Screw Compressors by Cooling Their Rotors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 Extending the Operation Range of Dry Screw Compressors by Cooling Their Rotors Nikola
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2004 Extending the Operation Range of Dry Screw Compressors by Cooling Their Rotors Nikola
A Large Modern High Speed Reciprocating Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 A Large Modern High Speed Reciprocating Compressor H. H. Van der Linden Grasso Products
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1998 A Large Modern High Speed Reciprocating Compressor H. H. Van der Linden Grasso Products
