(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,588,286 B1. Kudo et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2003
|
|
|
- Paulina Newman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 USOO B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,588,286 B1 Kudo et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2003 (54) NOFOAM SYSTEM FOR TESTING A FOAM (56) References Cited DELIVERY SYSTEM ON A VEHICLE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors: Rance Tetsuo Kudo, Oxnard, CA (US); O O 4,979, /1990 MacDonald /44 yet ENES, 5, A * 3/1999 Lee et al /15 Paula CA (US) s 6,357,532 B1 3/2002 Laskaris et al /43 sk - (73) Assignee: The United States of America as cited by examiner represented by the Secretary of the Navy, Washington, DC (US) Primary Examiner Edward Lefkowitz ASSistant Examiner Takisha S Miller (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-David Kalmbaugh patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by 0 days. (57) ABSTRACT A NoFoam system which permits the testing of the Aircraft (21) Appl. No.: 10/209,265 Rescue and Fire Fighting vehicle's foam delivery system. (22) Filed: Jul. 30, 2002 The NoFoam System includes the piping, valves, and con e a V3 necting elements to interface with the fire vehicle's foam (51) Int. Cl.... G01F1/05; A62C 35/00 delivery System, while minimizing the release of Aqueous (52) U.S. Cl /861.79; 169/15 Film Forming Foam (AFFF) to the environment. (58) Field of Search... 73/861.79; 169/54 70, 169/ Claims, 6 Drawing Sheets 1 O 81 nozzlese sy
2 U.S. Patent Jul. 8, 2003 Sheet 1 of 6 US 6,588,286 B1 WATER TANK (400 GALLONS) FIG. 1
3 U.S. Patent Jul. 8, 2003 Sheet 2 of 6 US 6,588,286 B1 1 O ) 90 NOZZLES O a WATER sy FIG 2 SUPPLY
4 U.S. Patent Jul. 8, 2003 Sheet 3 of 6 US 6,588,286 B1 1 O m N-2s BATTERY terr 12 MONITOR O O. O. O. O. O. O. O. O. O. O. O. 112 SOLAR PANEL 104 BATTERY FIG. 3
5
6
7 U.S. Patent Jul. 8, 2003 Sheet 6 of 6 US 6,588,286 B1
8 1 NOFOAM SYSTEM FOR TESTING A FOAM DELIVERY SYSTEM ON A VEHICLE BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention The present invent on relates generally to fire fighting Systems for use in fighting and extinguishing hydrocarbon and other flammable liquid fires. More particularly, the present invention relates to a foam free test System for the environmentally Safe testing the foam delivery Systems used on Aircraft Rescue and Fire Fighting (ARFF) vehicles. 2. Description of the Prior Art Currently, fire fighting guidelines and policies require quarterly and annual Aqueous Film Forming Foam (AFFF) discharge tests on all Aircraft Rescue and Fire Fighting (ARFF) vehicles. The foam discharge test verifies that the on-board foam delivery System is functioning properly, thereby ensuring a vehicle's fire fighting equipment is operational when called upon to Save lives and property. The method presently in use for determining fire fighting vehicle performance in the field is to discharge foam through each of the vehicle's nozzles and then collect foam Samples in accordance with the National Fire Protection ASSociation (NFPA) 412 Standard for Evaluating Aircraft; Rescue and Fire Fighting Foam Equipment. Each vehicle is equipped with at least two and up to five different types of nozzles, depending on the vehicle type. This procedure generates large amounts of AFFF wastewater. Depending on the type of vehicle, the generated AFFF wastewater volume may be anywhere from 850 gallons to more than 2,600 gallons per vehicle for each 30-second nozzle foam discharge test. This includes flushing the System with water as required under the guidelines of NFPA 412. At present, the Department of Defense (DOD) agencies have more than 1,200 ARFF vehicles in the fire fighting arsenal inventory at more than 240 activities. The net result is the testing of fire fighting vehicles generates a Substantial amount of AFFF wastewater annually. Fire fighting personnel often conduct routine daily, weekly or monthly AFFF discharge testing, in addition to the mandated requirements, due to low confidence in the per formance of the fire fighting vehicle's foam delivery System. The routine testing is a visual check of foam being emitted through the various nozzles of the vehicle. It is estimated that a minimum of 5 Seconds is required for the fire fighter to Verify that foam is being emitted through a single nozzle. Depending on the type of vehicle, these 5 Second routine checks, with system flush, generates 500 to 1,500 gallons of AFFF wastewater per ARFF vehicle. These routine foam delivery System tests generate Significant amounts of AFFF wastewater, which result in environmental damage. Despite its wide use and effectiveness for fire fighting, AFFF poses an environmental problem because of its resis tance to biodegradation, its toxicity due to constituents butyl carbitol (a glycol ether) and perfluorooctyl Sulfonates (PFOS), its high biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), and its chemical oxygen demand (COD). In addition to the environmental concerns with respect to AFFF wastewater discharges into the environment, the Sig nificant foaming capacity of AFFF makes the recovery and treatment of spent AFFF very difficult. In some regions, the military is no longer allowed to discharge AFFF wastewater to industrial waste treatment plant facilities because of Subsequent treatment plant fouling and damage. Hence, US 6,588,286 B when disposing of AFFF wastewater, the military incurs additional cost associated with hazardous waste handling, collection, disposal, and issues relating to liability for envi ronmental and other damage. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The NoFoam system for testing the foam delivery system on a fire fighting vehicle comprises a control panel having a flow meter, flow Sensor piping and valves, and a holding tank for the Surrogate fluid mounted on a portable trailer/ Stationary-pad. The fire fighter simply drives the vehicle to be tested to the.mobile/stationary pad NoFoam system and connects to the delivery System's fluid Supply line. At this point, the user continues through the fire fighting foam discharge procedures. A flow meter installed in the NoFoam System Senses the flow rate of the Surrogate fluid and allows the user to read a display for the flow meter. The firefighter Simply reads the monitor and quickly determines the vehi cle's foam delivery system performance. The flow that is monitored represents the flow rate of the AFFF concentrate into the vehicle's AFFF delivery system. The use of a dye-water Solution allows the user to visually inspect the vehicle's performance, although the NoFoam system still performs adequately without the dye concentrate. The dye concentrate Selected is an environmentally benign, biode gradable dye, certified by the National Sanitation Founda tion (NSF) International to NSF Standard 60 for the use in potable water (Drinking Water Treatment Chemicals Health Effects), and DOD adopted industry standard issued by the American National Standard Institute. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIGS. 1 and 2 illustrate a detailed fluid flow Schematic diagram of the NoFoam System for the testing of a foam delivery system on a P300 fire fighting vehicle; FIG. 3 illustrates a schematic diagram of the electrical circuit for the NoFoam system of FIGS. 1 and 2; FIG. 4 illustrates the stationary pad/trailer and the 400 gallon water tank mounted thereon for the NoFoam System of FIGS. 1 and 2; FIG. 5 illustrates the P300 fire fighting vehicle; and FIG. 6 illustrates the operation of the NoFoam system during a test of the P300 fire fighting vehicle's foam delivery System. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF A PREFERRED EMBODIMENT Referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, the NoFoam system, desig nated generally by the reference numeral 10, permits the testing of the Aircraft Rescue and Fire Fighting (ARFF) vehicle's foam delivery system, which includes the delivery System's piping, valves, pump, proportioner, eductor, and nozzles, while minimizing the release of Aqueous Film Forming Foam (AFFF) to the environment. An environmen tally benign Surrogate fluid is used for testing enabling a user to validate the readiness of the vehicle's fire fighting equip ment. NoFoam system complies with the NFPA 414 Stan dard for Aircraft Rescue and Fire Fighting Vehicles, which allows for the use of dye-water in Foam Distribution System Pump Testing and Flushing System Testing of ARFF vehicles. The NoFoam system 10 includes a trailer stationary-pad 12 which allows the user to transport the System to a location at a facility where fire fighting vehicles are normally tested. Trailer stationary-pad 12 has a 400 gallon water tank 14
9 3 mounted thereon. The water tank 14 is filled with approxi mately 400 gallons of water to test the fire fighting vehicle's foam delivery System. A fluorescent yellow/green dye or any other color dye is then. Addends to the water which results in a highly visible dye-water flowing from the water tank 14. The color of the dye added depends upon user requirements. The water tank 14 includes an opening or discharge port 16 at its bottom end. A 2 inch IPS (Iron Pipe Size) pipe 18 connects the opening 16 at the bottom of tank 14 to a first inlet/outlet port of a 2 inch IPS ball valve 20 which is manually opened and closed by a user of system 10. The second inlet/outlet port of ball valve includes a 2% inch IPS water fill and drain connector 22 which allows the user to connect an external water Source to ball valve 20 to fill tank 14. The user can also connect a drain hose to ball valve 20 to drain tank 14. Arrow 24 indicates that fluid flow through pipe 18 can be in either direction. Branching at angle of approximately 90 from pipe 18 is. a 1/4 inch IPS pipe 26 which includes the paddle wheel flow transmitter 28 of a fluid flow sensor 29. A flow indicator 30 for sensor 29, which is electrically connected to transmitter 28, allows the user to observe the flow rate of dye-water from tank 14. The direction of dye-water flow through the fluid flow meter is indicated by arrow 32. The open end of pipe 26 is connected to a 1% inch IPS ball valve 34 by a 1% inch IPSX1/4 inch IPS reducer 38. Valve 34 includes a hose connector 36 at its outlet port. One end of a flexible hose 40 is connected to the hose connector 36 for valve 34. The other end of flexible hose 40 is connected to the hose connector 47 for a ball valve 48 by a hose connector fitting 44 for the foam delivery system 46 currently being tested. When AFFF concentrate is being drained from foam delivery system 46 flexible hose is disconnected from the hose connector 36 for valve 34. Flexible hose terminates is then positioned above a 5% gallon polyethylene storage tank 90 allowing AFFF concen trate to drain into storage tank 90. A 1% inch IPS pipe 52 connects ball valve 48 to the AFFF concentrate's flow line pipe 60 which is a 2 inch IPS pipe. One end of pipe is thereof connected to the outlet port for a 2 inch IPS ball valve 53. A flexible hose 55 connects the inlet port of ball valve 53 to a ball valve with pneumatic operator 54 for AFFF concentrate tank 50. Tank 50 which is the Storage tank for AFFF concentrate on the fire fighting vehicle has at its bottom end an opening or discharge port 56 through which AFFF concentrate flows when ball valves 53 and 54 are open. An arrow 58 indicates that fluid flow through pipe 52 is in both directions. The 2 inch IPS pipe 60 has in its fluid flow path a ball valve 53, and a multi-metering manifold valve 62. Multi metering manifold valve 62 includes a 2% inch IPSx2 inch IPS reducer 64 at its inlet port and a 2% inch IPSx2 inch IPS reducer 66 at its discharge port. The direction of fluid flow through pipe 60 is indicated by arrow 70. Connected to the opposite end of pipe 60 is the first inlet port of eductor 72. A 2 inch IPS water supply line 74 Supplies water from a water Supply tank 75 through a water pump (not illustrated) to the eductor 72 which converts pressure to kinetic energy, creating a vacuum that Sucks the AFFF concentrate/surrogate fluid into the eductor 72. The eductor 72 mixes the AFFF concentrate/surrogate fluid with the pressurized water discharging the mixture through the discharge port of eductor 72 into a 2 inch IPS pipe 76. Pipe 76 connects the discharge port of educator 72 to the nozzles 81 for the fire fighting vehicle. The flow direction for the pressurized water Supplied to eductor 72 is indicated by US 6,588,286 B arrow 78, while the flow direction for the resulting water AFFF concentrate/surrogate fluid mixture is indicated by arrow 80. One end of 1% inch IPS pipe 82 branches from pipe 52, while the other end is connected to a ball/drain valve 84. The discharge port of ball valve 84 is connected to a manifold valve (not illustrated) by a flexible hose 86. A branch 1% inch IPS pipe 87 connects pipe 82 to a ball valve 87. Ball/drain valve 88 has one end of a flexible hose 89 connected to its discharge port. The other end of flexible hose 89 terminates in 5% gallon polyethylene storage tank 90. Opening ball valve 88 allows residual AFFF concentrate to drain into storage tank 90. Multi-metering manifold valve 62 allows for multiple flow rates of AFFF concentrate, water or fluorescent yellow/ green dye-water or any other color dye through the valve. When the user desires to test (for a 3% AFFF concentrate) the roof turret nozzle on the fire fighting vehicle at the high flow rate, the manifold valve 62 is set Such that the water flow rate is 1500 GPM which equates to flow rate of 45 GPM of AFFF concentrate through the valve 62. When the user desires to test (for a 3% AFFF concentrate) the roof turret nozzle at the low flow rate, the manifold valve 62 is set Such that the water flow rate is 750 GPM which equates to flow rate of 22.5 GPM of AFFF concentrate through the valve 62. Similarly, when the user desires to test (for a 3% AFFF concentrate) the bumper turret nozzle on the fire fighting vehicle, the manifold valve 62 is set Such that the water flow rate is 300 GPM which equates to flow rate of 9.0 GPM of AFFF concentrate through the valve 62. Further, when the user desires to test (for a 3% AFFF concentrate) the left handline nozzle of a pair of handline nozzles on the fire fighting vehicle, the manifold valve 62 is set such that the water flow rate is 90 GPM which equates to flow rate of 2.8 GPM of AFFF concentrate through the valve 62. When the user desires to test (for a 3% AFFF concentrate) the right handline nozzle of a pair of handline nozzles on the fire fighting vehicle, the manifold valve 62 is set such that the water flow rate is 90 GPM which equates to flow rate of 2.8 GPM of AFFF concentrate through the valve 62. Referring to. FIG. 1, 2 and 3, there is shown in FIG. 3 the electrical control panel 102 for the NoFoam system 10 of FIGS. 1 and 2. Fluid flow meter 29 of FIG. 1 includes paddle wheel flow transmitter 28 which is electrically connected to the flow indicator/rate meter 30 for fluid flow meter 29. Paddle wheel flow transmitter 28 transmits a 4 to 20 ma (milliamp) signal that is read by rate meter 30. Rate meter 30 is a digital meter located on control panel 102. The control panel include a Switch S1, a 12 Volt battery 104, and a voltage regulator 110. The positive terminal of the battery 104 is electrically connected to the positive terminal of the voltage regulator 110, while the negative terminal of the battery 104 is connected through switch S1 to the negative terminal of voltage regulator 110. There is a solar panel 112 mounted on control panel 102. The solar panel 112 is connected to the positive terminal of the Voltage regulator 110 and is connected through switch S1 to the negative terminal of voltage regulator 110. Panel 102 also includes a battery monitor 114 for monitoring battery output Voltage. Battery monitor 114 is connected to the positive and nega tive terminals of voltage regulator 110. Resistor R1 is a 10 K-ohm resistor. Referring to FIGS. 4, 5 and 6, FIG. 4 illustrates the stationary pad/trailer 12 and the 400 gallon water tank 14 mounted on the stationary pad/trailer 12 for the NoFoam
10 S System 10 depicted in FIGS. 1 and 2. FIG. 5 illustrates the P300 fire fighting vehicle, which is designated generally by the reference numeral 120. FIG. 6 illustrates the operation of the NoFoam system 10 during a test of the P300 fire fighting vehicle's foam delivery system 46. Positioned on the roof 122 of the driver's compartment 124 is the roof turret nozzle 126 for the fire fighting vehicle 120. Similarly, there is positioned on the front bumper 128 the bumper nozzle 130 for the fire fighting vehicle 120. When the foam delivery system 46 for fire fighting vehicle 120 is being tested a dye-water Solution discharge/spray 132 is generated by turret nozzle 126 and dye-water Solution discharge/spray 134 is generated by bumper nozzle 130. The sprays 132 and 134, which are yellow/green or another color, allow the user to visually inspect the operation of the foam delivery System 46, giving the firefighter confidence in the fire fighting vehicle's performance. Referring to FIGS. 1, 2 and 3, the user when operating the NoFoam system 10 utilizes the following procedure with respect to trailer/stationary-pad 12. The user first closes ball valve 34 and then fills 400 gallon water tank 14. In the alternative ball valve 20 could be open and the tank filled through ball valve 20. The user adds the fluorescent yellow/ green dye or any other color dye to the water and turns on the electrical panel 102 by closing Switch S1. With respect to the fire fighting vehicle and its fire fighting vehicle's foam delivery system 46, the user turns off the fire fighting vehicle and insures that the vehicle's air tanks are at their capacity of 120 PSI. The user attaches flexible 40 to the hose connector 47 for ball valve 48 using hose connector fitting 44. The user next closes ball valve 84, opens drain valve 88 and opens drain valve 48, which allows the AFFF concen trate in the AFFF delivery system 46 to drain through valves 48 and 88 into polyethylene storage tank 90. The user closes drain valve 88 and ball valve 53 after the user completely drain AFFF concentrate from foam delivery system 46. Draining the AFFF concentrate from delivery system 46 generally results in an accumulation of about 1/2 gallons of AFFF concentrate into storage tank 90. The user next attaches the other end of flexible hose 40 to the hose connector 36 for ball valve 34. Finally, the user opens 1% inch IPS ball valve 34, and is ready to begin the nozzle discharge test. To start the nozzle discharge test for the fire fighting vehicle the user Starts the vehicle, goes through normal foam delivery discharge tests and Sets the agent Selector valve for the fire fighting vehicle to the FOAM position. The user next opens the Station nozzle valve for the roof nozzle (high and low flow rates), bumper nozzle, left and right handline nozzle or any combination thereof to be tested. The user reads the flow indicator/rate meter 30 for fluid flow meter 29, a water pressure pump gage-which indicates water pressure of the foam delivery System 46 and the elapsed time. This information allows the user to determine the effectiveness of the foam delivery system 46 for the fire fighting vehicle. From the foregoing, it is readily apparent that the present invention comprises a new, unique, and exceedingly useful NoFoam System for testing an aqueous film forming foam delivery System on a fire fighting vehicle which constitutes a considerable improvement over the known prior art. Many modifications and variations of the present invention are possible in light of the above teachings. It is to be understood that within the Scope of the appended claims the invention may be practiced otherwise than as Specifically described. US 6,588,286 B What is claimed is: 1. A foam free System which provides for an environmen tally Safe testing of a foam delivery System on a fire fighting vehicle, comprising: a mobile platform adapted for movement to a location having Said fire fighting vehicle; a Surrogate fluid Storage tank mounted on Said mobile platform, said Surrogate fluid Storage tank containing an environmentally Safe Surrogate fluid, Said Surrogate fluid Storage tank having an inlet/outlet port; a flow Sensor located on Said mobile platform, Said flow Sensor including a paddle wheel flow transmitter con nected to the inlet/outlet port of Said Surrogate fluid Storage tank and a flow indicator electrically connected to said paddle wheel flow transmitter, said flow indi cator providing a measurement of a fluid flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through the paddle wheel flow transmitter of Said flow Sensor, a first ball valve located on said mobile platform, said first ball valve having an inlet port connected to the paddle wheel flow transmitter of said flow sensor and an outlet port, a flexible hose having one end connected to the outlet port of said first ball valve; a Second ball valve located on Said fire fighting vehicle, Said Secondball valve having an inlet port connected to the other end of said flexible hose and an outlet port, said first ball valve and said second ball valve being open when Said foam free System is testing the foam delivery System on Said fire fighting vehicle, Said first ball valve and said second ball valve when open allowing said Surrogate fluid to flow through said first ball valve and said second ball valve; a multi-metering manifold valve located on Said fire fighting vehicle, Said multi-metering manifold valve having an inlet port connected to the outlet port of Said Second ball valve and a discharge port, Said multi metering manifold valve controlling a flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through Said multi-metering manifold valve; a first reducer and a Second reducer, Said first reducer being affixed to the inlet port of Said multi-metering manifold valve and Said Second reducer being affixed to the outlet port of Said multi-metering manifold valve; a Supply tank for providing an environmentally Safe pressurized liquid, Said Supply tank having an outlet port, an eductor located on Said fire fighting vehicle, Said eductor having a first inlet port connected to the outlet port of Said Supply tank, a Second inlet port connected to the discharge port of Said multi-metering manifold Valve, Said eductor receiving Said pressurized liquid from Said Supply tank, said pressurized liquid creating a vacuum within Said eductor that draws said Surrogate fluid into Said eductor, Said eductor mixing Said Surro gate fluid with Said pressurized water to form a Surro gate fluid mixture under pressure discharging Said Surrogate fluid mixture through the discharge port of Said eductor; and a third reducer affixed to the discharge port of Said eductor. 2. The foam free System of claim 1 wherein Said Surrogate fluid mixture comprises a fluorescent yellow green dye which is an environmentally benign, biodegradable dye. 3. The foam free system of claim 1 further comprising:
11 7 a battery having a positive terminal and a negative ter minal; a Solar panel having an output; a normally open Switch having a first terminal connected to the negative terminal of Said battery and the output of Said Solar panel and a Second terminal; a Voltage regulator having a positive terminal connected to the positive terminal of Said battery and a negative terminal connected to the Second terminal of Said Voltage regulator and the flow indicator of Said flow Sensor; and a battery monitor connected to the positive terminal and the negative terminal of Said Voltage regulator. 4. The foam free system of claim 1 wherein the flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through Said multi-metering manifold valve is between about 2.8 GPM and 45 GPM, the flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through Said multi-metering manifold valve being set at approximately 45 GPM or 22.5 GPM when a user is testing a roof turret nozzle on Said fire fighting vehicle, the flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through Said multi-metering manifold valve being Set at approximately 9.0 GPM when a user is testing a bumper turret nozzle on Said fire fighting vehicle, and the flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through said multi-metering Valve being Set at approxi mately 2.8 GPM when the user is testing a left handline nozzle and a right handline nozzle on Said fire fighting vehicle. 5. The foam free system of claim 1 wherein said surrogate fluid Storage tank comprises a 400 gallon Storage tank. 6. A foam free System which provides for an environmen tally Safe testing of a foam delivery System on a fire fighting vehicle, comprising: a mobile platform adapted for movement to a location having Said fire fighting vehicle; a Surrogate fluid Storage tank mounted on Said mobile platform, Said Surrogate fluid Storage tank containing an environmentally Safe Surrogate fluid, Said Surrogate fluid Storage tank having an outlet port; a flow Sensor located on Said mobile platform, Said flow Sensor including a paddle wheel flow transmitter con nected to the outlet port of Said Surrogate fluid Storage tank and a flow indicator electrically connected to Said paddle wheel flow transmitter, Said flow indicator pro Viding a measurement of a fluid flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through the paddle wheel flow trans mitter of said flow sensor; a first ball valve located on said mobile platform, said first ball valve having an inlet port connected to the paddle wheel flow transmitter of said flow sensor and an outlet port, a first flexible hose having a first end connected to the outlet port of said first ball valve; a Second ball valve located on Said fire fighting vehicle, Said Second ball valve having a first inlet/outlet port connected to a Second end of Said first flexible hose and a Second inlet/outlet port, Said first ball valve and Said Second ball valve being open when Said foam free System is testing the foam delivery System on Said fire fighting vehicle, Said first ball valve and Said Second ball valve when open allowing Said Surrogate fluid to flow through said first ball valve and said second ball valve; a multi-metering manifold valve located on Said fire fighting vehicle, Said multi-metering manifold valve having an inlet port connected to the Second inlet/outlet US 6,588,286 B port of Said Secondball valve and a discharge port, Said multi-metering manifold valve controlling a flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through Said multi-metering manifold valve; a first reducer and a Second reducer, Said first reducer being affixed to the inlet port of Said multi-metering manifold valve and Said Second reducer being affixed to the outlet port of Said multi-metering manifold valve; Supply tank for providing an environmentally Safe pressurized liquid, Said Supply tank having an outlet port, an eductor located on Said fire fighting vehicle, Said eductor having a first inlet port connected to the outlet port of Said Supply tank, a Second inlet port connected to the discharge port of Said multi-metering manifold Valve, Said eductor receiving Said pressurized liquid from Said Supply tank, said pressurized liquid creating a vacuum within Said eductor that draws said Surrogate fluid into Said eductor, Said eductor mixing Said Surro gate fluid with Said pressurized water to form a Surro gate fluid mixture under pressure discharging Said Surrogate fluid mixture through the discharge port of Said eductor; third reducer affixed to the discharge port of Said eductor; and the second end of said first flexible hose being discon nected from the outlet port of said first ball valve prior to testing the foam delivery System on Said fire fighting vehicle; primary concentrate Storage tank positioned at the Second end of Said first flexible hose prior to testing the foam delivery System on Said fire fighting vehicle, Said primary concentrate storage tank receiving aqueous film forming foam concentrate drained from Said foam delivery System prior to testing Said foam delivery System, Said Secondball valve being open allowing Said aqueous film forming foam concentrate drained from Said foam delivery System to flow through said Second ball valve and said first flexible hose into said primary concentrate Storage tank. 7. The foam free system of claim 6 further comprising: a third ball valve having an inlet port connected to Said foam delivery System and an outlet port, a Second flexible hose having one end connected to the outlet port of said third ball valve and the other end positioned at Said primary concentrate Storage tank, and Said primary concentrate Storage tank receiving residual of Said aqueous film forming foam concentrate passing through when said third ball valve is open. 8. The foam free system of claim 7 further comprising: a fourth ball valve having an inlet port connected to Said foam delivery System and an outlet port, a third flexible hose having one end connected to the outlet port of said third ball valve; and Said fourth ball valve being closed when Said aqueous film forming foam concentrate is being drained from Said foam delivery System. 9. The foam free system of claim 6 wherein said primary Storage tank comprises a 5% gallon polyethylene Storage tank. 10. The foam free system of claim 6 wherein said surro gate fluid mixture comprises a fluorescent yellow green dye which is an environmentally benign, biodegradable dye. 11. The foam free system of claim 6 further comprising: a battery having a positive terminal and a negative ter minal;
12 9 a Solar panel having an output; a normally open Switch having a first terminal connected to the negative terminal of Said battery and the output of Said Solar panel and a Second terminal; a Voltage regulator having a positive terminal connected to the positive terminal of Said battery and a negative terminal connected to the Second terminal of Said Voltage regulator and the flow indicator of Said flow Sensor; and a battery monitor connected to the positive terminal and the negative terminal of Said Voltage regulator. 12. The foam free system of claim 6 wherein the flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through Said multi-metering manifold valve is between about 2.8 GPM and 45 GPM, the flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through Said multi-metering manifold valve being set at approximately 45 GPM or 22.5 GPM when a user is testing a roof turret nozzle on Said fire fighting vehicle, the flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through Said multi-metering manifold valve being Set at approximately 9.0 GPM when a user is testing a bumper turret nozzle on Said fire fighting vehicle, and the flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through said multi-metering Valve being Set at approxi mately 2.8 GPM when the user is testing a left handline nozzle and a right handline nozzle on Said fire fighting vehicle. 13. The foam free system of claim 6 wherein said surro gate fluid Storage tank comprises a 400 gallon Storage tank. 14. A foam free system which provides for an environ mentally Safe testing of a foam delivery System on a fire fighting vehicle, comprising: a mobile platform adapted for movement to a location having said fire fighting vehicle; a Surrogate fluid Storage tank mounted on Said mobile platform, Said Surrogate fluid Storage tank containing an environmentally Safe Surrogate fluid, Said Surrogate fluid Storage tank having an inlet/outlet port; a flow Sensor located on Said mobile platform, Said flow Sensor including a paddle wheel flow transmitter con nected to the outlet port of Said Surrogate fluid Storage tank and a flow indicator electrically connected to Said paddle wheel flow transmitter, Said flow indicator pro Viding a measurement of a fluid flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through the paddle wheel flow trans mitter of said flow sensor; a first ball valve located on said mobile platform, said first ball valve having an inlet port connected to the paddle wheel flow transmitter of said flow sensor and an outlet port, a first flexible hose having a first end connected to the outlet port of said first ball valve; a Second ball valve located on Said fire fighting vehicle, Said Second ball valve having a first inlet/outlet port connected to a Second end of Said first flexible hose and a Second inlet/outlet port, Said first ball valve and Said Second ball valve being open when Said foam free System is testing the foam delivery System on Said fire fighting vehicle, Said first ball valve and Said Second ball valve when open allowing Said. Surrogate fluid to flow through said first ball valve and said second ball valve; a multi-metering manifold valve located on Said fire fighting vehicle, Said multi-metering manifold valve having an inlet port connected to the Second inlet/outlet port of Said Secondball valve and a discharge port, Said multi-metering manifold valve controlling a flow rate US 6,588,286 B of Said Surrogate fluid through Said multi-metering manifold valve; a first reducer and a Second reducer, Said first reducer being affixed to the inlet port of Said multi-metering manifold valve and Said Second reducer being affixed to the outlet port of Said multi-metering manifold valve; Supply tank for providing an environmentally Safe pressurized liquid, Said Supply tank having an outlet port, an eductor located on Said fire fighting vehicle, Said eductor having a first inlet port connected to the outlet port of Said Supply tank, a Second inlet port connected to the discharge port of Said multi-metering manifold Valve, Said eductor receiving Said pressurized liquid from Said Supply tank, said pressurized liquid creating a vacuum within Said eductor that draws said Surrogate. fluid into Said eductor, Said eductor mixing Said Surro gate fluid with Said pressurized water to form a Surro gate fluid mixture under pressure discharging Said Surrogate fluid mixture through the discharge port of Said eductor; third reducer affixed to the discharge port of Said eductor; and the second end of said first flexible hose being discon nected from the outlet port of said first ball valve prior to testing the foam delivery System on Said fire fighting vehicle; primary concentrate Storage tank positioned at the Second end of Said first flexible hose prior to testing the foam delivery System on Said fire fighting vehicle, Said primary concentrate Storage tank receiving aqueous film forming foam concentrate drained from Said foam delivery System prior to testing Said foam delivery System, said secondball valve being open allowing said aqueous film forming foam concentrate drained from Said foam delivery System to flow through said Second ball valve and said first flexible hose into said primary concentrate Storage tank; a third ball valve located on said mobile platform, said third ball valve having an inlet/outlet port connected to the inlet/outlet port of Said Surrogate fluid Storage tank and a drain/fill connector for receiving Said Surrogate fluid, Said Surrogate fluid passing through Said third ball Valve to Said Surrogate fluid Storage tank filling Said Surrogate fluid Storage tank with Said Surrogate fluid, Said third ball valve being closed during Said environ mentally Safe testing of Said foam delivery System. 15. The foam free system of claim 14 further comprising: a fourth ball valve having an inlet port connected to Said foam delivery System and an outlet port, a Second flexible hose having one end connected to the outlet port of said fourth ball valve and the other end positioned at Said primary concentrate Storage tank, and Said primary concentrate Storage tank receiving residual of Said aqueous film forming foam concentrate passing through when said fourth ball valve is open. 16. The foam free system of claim 15 further comprising: a fifth ball valve having an inlet port connected to Said foam delivery System and an outlet port, a third flexible hose having one end connected to the outlet port of said fifth ball valve; and said fifth ball valve being closed when said aqueous film forming foam concentrate is being drained from Said foam delivery System. 17. The foam free system of claim 14 wherein said primary Storage tank comprises a 5% gallon polyethylene Storage tank.
13 The foam free system of claim 14 wherein said Surrogate fluid mixture comprises a fluorescent yellow green dye which is an environmentally benign, biodegradable dye. 19. The foam free system of claim 14 further comprising: a battery having a positive terminal and a negative ter minal; a Solar panel having an output; a normally open Switch having a first terminal connected to the negative terminal of Said battery and the output of Said Solar panel and a Second terminal; a Voltage regulator having a positive terminal connected to the positive terminal of Said battery and a negative terminal connected to the Second terminal of Said Voltage regulator and the flow indicator of Said flow Sensor; and a battery monitor connected to the positive terminal and the negative terminal of Said Voltage regulator. US 6,588,286 B The foam free system of claim 14 wherein the flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through Said multi-metering manifold valve is between about 2.8 GPM and 45 GPM, the flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through Said multi-metering manifold valve being set at approximately 45 GPM or 22.5 GPM when a user is testing a roof turret nozzle on said fire fighting vehicle, the flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through Said multi-metering manifold valve being Set at approxi mately 9.0 GPM when a user is testing a bumper turret nozzle on Said fire fighting vehicle, and the flow rate of Said Surrogate fluid through Said multi-metering valve being Set at approximately 2.8 GPM when the user is testing a left handline nozzle and a right handline nozzle on Said fire fighting vehicle.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1
 USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,055,613 B1. Bissen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2006
 US007055613B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,055,613 B1 Bissen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2006 (54) SELF LEVELING BOOM SYSTEM WITH (58) Field of Classification Search... 169/24,
US007055613B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,055,613 B1 Bissen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2006 (54) SELF LEVELING BOOM SYSTEM WITH (58) Field of Classification Search... 169/24,
United States Patent (19) Kim et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kim et al. 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR COATING AWAFER WITH A MINIMAL LAYER OF PHOTORESIST 75 Inventors: Moon-woo Kim, Kyungki-do; Byung-joo Youn, Seoul, both of Rep. of Korea
United States Patent (19) Kim et al. 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR COATING AWAFER WITH A MINIMAL LAYER OF PHOTORESIST 75 Inventors: Moon-woo Kim, Kyungki-do; Byung-joo Youn, Seoul, both of Rep. of Korea
United States Patent (19) Muranishi
 United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6989498B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,989,498 B1 Linder et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2006 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR LOCKING (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent USOO6989498B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,989,498 B1 Linder et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2006 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR LOCKING (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,080,888 B2. Hach (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006
 United States Patent US007080888B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,080,888 B2 Hach (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006 (54) DUAL NOZZLE HYDRO-DEMOLITION 6,049,580 A * 4/2000 Bodin et al.... 376/.316 SYSTEM 6,224,162
United States Patent US007080888B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,080,888 B2 Hach (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006 (54) DUAL NOZZLE HYDRO-DEMOLITION 6,049,580 A * 4/2000 Bodin et al.... 376/.316 SYSTEM 6,224,162
USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999
 USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999 54 SERIALLY CONNECTED CHARGER Primary Examiner Edward H. Tso Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Rosenberger,
USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999 54 SERIALLY CONNECTED CHARGER Primary Examiner Edward H. Tso Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Rosenberger,
NoFoam Unit Installation, Evaluation and Operations Manual
 AFRL-ML-TY-TR-03-4531 NoFoam Unit Installation, Evaluation and Operations Manual William Fischer Jennifer Kalberer AIR FORCE RESEARCH LABORATORY MATERIALS & MANUFACTURING DIRECTORATE AIRBASE TECHNOLOGIES
AFRL-ML-TY-TR-03-4531 NoFoam Unit Installation, Evaluation and Operations Manual William Fischer Jennifer Kalberer AIR FORCE RESEARCH LABORATORY MATERIALS & MANUFACTURING DIRECTORATE AIRBASE TECHNOLOGIES
(12) United States Patent
 US008998577B2 (12) United States Patent Gustafson et al. (10) Patent No.: US 8,998,577 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 7, 2015 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) TURBINE LAST STAGE FLOW PATH Inventors:
US008998577B2 (12) United States Patent Gustafson et al. (10) Patent No.: US 8,998,577 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 7, 2015 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) TURBINE LAST STAGE FLOW PATH Inventors:
3 23S Sé. -Né 33% (12) United States Patent US 6,742,409 B2. Jun. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: 6B M 2 O. (51) Int. Cl...
 (12) United States Patent Blanchard USOO6742409B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 2004 (54) DEVICE FORTRANSMISSION BETWEEN A PRIMARY MOTOR SHAFT AND AN OUTPUT SHAFT AND LAWN MOWER PROVIDED
(12) United States Patent Blanchard USOO6742409B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 2004 (54) DEVICE FORTRANSMISSION BETWEEN A PRIMARY MOTOR SHAFT AND AN OUTPUT SHAFT AND LAWN MOWER PROVIDED
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fujita 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,727,957 Mar. 1, 1988 (54) RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATOR FOR MUFFLER 75 Inventor: Akio Fujita, Fujisawa, Japan 73) Assignee: Bridgestone
United States Patent (19) Fujita 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,727,957 Mar. 1, 1988 (54) RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATOR FOR MUFFLER 75 Inventor: Akio Fujita, Fujisawa, Japan 73) Assignee: Bridgestone
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,205,840 B1
 USOO620584OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,205,840 B1 Thompson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) TIME CLOCK BREATHALYZER 4,749,553 * 6/1988 Lopez et al.... 73/23.3 X COMBINATION
USOO620584OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,205,840 B1 Thompson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) TIME CLOCK BREATHALYZER 4,749,553 * 6/1988 Lopez et al.... 73/23.3 X COMBINATION
US 7, B2. Loughrin et al. Jan. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: and/or the driven component. (12) United States Patent (54) (75)
 USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
Earl Sch yang y Lee, 5,457,342 10/1995 Herbst, II /712
 US005920264A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM PROTECTION 5,189,314 2/1993 Georgiou et al.... 307/271 DEVICE 5,287.292 2/1994
US005920264A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM PROTECTION 5,189,314 2/1993 Georgiou et al.... 307/271 DEVICE 5,287.292 2/1994
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Yenisey 54 FUSE OR CIRCUIT BREAKER STATUS INDICATOR 75) Inventor: 73) Assignee: Osman M. Yenisey, Manalapan, N.J. AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. (21) Appl. No.: 942,878
United States Patent (19) Yenisey 54 FUSE OR CIRCUIT BREAKER STATUS INDICATOR 75) Inventor: 73) Assignee: Osman M. Yenisey, Manalapan, N.J. AT&T Bell Laboratories, Murray Hill, N.J. (21) Appl. No.: 942,878
United States Patent (19) Ochi et al.
 United States Patent (19) Ochi et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,945,272 Jul. 31, 1990 54 ALTERNATOR FORMOTOR VEHICLES 75 Inventors: Daisuke Ochi; Yasuhiro Yoshida; Yoshiyuki Iwaki, all of
United States Patent (19) Ochi et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,945,272 Jul. 31, 1990 54 ALTERNATOR FORMOTOR VEHICLES 75 Inventors: Daisuke Ochi; Yasuhiro Yoshida; Yoshiyuki Iwaki, all of
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,446,482 B1. Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002
 USOO64.46482B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002 (54) BATTERY OPERATED HYDRAULIC D408.242 S 4/1999 Yamamoto... D8/61 COMPRESSION TOOL WITH RAPID
USOO64.46482B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002 (54) BATTERY OPERATED HYDRAULIC D408.242 S 4/1999 Yamamoto... D8/61 COMPRESSION TOOL WITH RAPID
United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 4,542,882 Choe [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 24, 1985
![United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 4,542,882 Choe [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 24, 1985 United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 4,542,882 Choe [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 24, 1985](/thumbs/74/69826496.jpg) United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 4,542,882 Choe [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 24, 1985 [54] AIR JACK FOR USE WITH A VEHICLE 4,222,549 9/1980 Lindgren..... 254/93 HP EXHAUST SYSTEM 4,294,141 10/1981
United States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 4,542,882 Choe [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 24, 1985 [54] AIR JACK FOR USE WITH A VEHICLE 4,222,549 9/1980 Lindgren..... 254/93 HP EXHAUST SYSTEM 4,294,141 10/1981
75 Inventors: William H. Robertson, Jr., Plantation; Primary Examiner-Peter S. Wong
 USOO592O178A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,920,178 Robertson, Jr. et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) BATTERY PACK HAVING INTEGRATED 56) References Cited CHARGING CIRCUIT AND CHARGING
USOO592O178A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,920,178 Robertson, Jr. et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) BATTERY PACK HAVING INTEGRATED 56) References Cited CHARGING CIRCUIT AND CHARGING
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,900,734 Munson (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 1999
 USOO5900734A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,900,734 Munson (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 1999 54) LOW BATTERY VOLTAGE DETECTION 5,444,378 8/1995 Rogers... 324/428 AND WARNING SYSTEM 5,610,525
USOO5900734A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,900,734 Munson (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 1999 54) LOW BATTERY VOLTAGE DETECTION 5,444,378 8/1995 Rogers... 324/428 AND WARNING SYSTEM 5,610,525
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,641,228 B2
 USOO6641228B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,641,228 B2 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) DETACHABLE FRONT WHEEL STRUCTURE (56) References Cited OF GOLF CART U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
USOO6641228B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,641,228 B2 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) DETACHABLE FRONT WHEEL STRUCTURE (56) References Cited OF GOLF CART U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,651,070 B2
 USOO8651070B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,651,070 B2 Lindner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 18, 2014 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS TO CONTROL USPC... 123/41.02, 41.08-41.1, 41.44, 198C
USOO8651070B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,651,070 B2 Lindner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 18, 2014 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS TO CONTROL USPC... 123/41.02, 41.08-41.1, 41.44, 198C
od f 11 (12) United States Patent US 7,080,599 B2 Taylor Jul. 25, 2006 (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.:
 US007080599B2 (12) United States Patent Taylor (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006 (54) RAILROAD HOPPER CAR TRANSVERSE DOOR ACTUATING MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Fred J. Taylor, 6485 Rogers
US007080599B2 (12) United States Patent Taylor (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006 (54) RAILROAD HOPPER CAR TRANSVERSE DOOR ACTUATING MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Fred J. Taylor, 6485 Rogers
USOO58065OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,806,500 Fargo et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 15, 1998
 USOO58065OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,806,500 Fargo et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 15, 1998 54 FUEL VAPOR RECOVERY SYSTEM 5,456,238 10/1995 Horiuchi et al.. 5,460,136 10/1995 Yamazaki
USOO58065OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,806,500 Fargo et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 15, 1998 54 FUEL VAPOR RECOVERY SYSTEM 5,456,238 10/1995 Horiuchi et al.. 5,460,136 10/1995 Yamazaki
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Swihla et al. USOO6287091B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,287,091 B1 Sep. 11, 2001 (54) TURBOCHARGER WITH NOZZLE RING COUPLNG (75) Inventors: Gary R Svihla, Clarendon
(12) United States Patent Swihla et al. USOO6287091B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,287,091 B1 Sep. 11, 2001 (54) TURBOCHARGER WITH NOZZLE RING COUPLNG (75) Inventors: Gary R Svihla, Clarendon
United States Patent (19) Kline et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kline et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 1990 54 BRAKING SYSTEMAND BREAK-AWAY BRAKNG SYSTEM 76 Inventors: Wayne K. Kline, R.D. 1, Box 340, Turbotville, Pa. 17772;
United States Patent (19) Kline et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 1990 54 BRAKING SYSTEMAND BREAK-AWAY BRAKNG SYSTEM 76 Inventors: Wayne K. Kline, R.D. 1, Box 340, Turbotville, Pa. 17772;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0157272 A1 Uhler et al. US 2009015.7272A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) FOUR-PASSAGE MULTIFUNCTION TOROUE CONVERTER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0157272 A1 Uhler et al. US 2009015.7272A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) FOUR-PASSAGE MULTIFUNCTION TOROUE CONVERTER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070231628A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0231628 A1 Lyle et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) FUEL CELL SYSTEM VENTILATION Related U.S. Application
US 20070231628A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0231628 A1 Lyle et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) FUEL CELL SYSTEM VENTILATION Related U.S. Application
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,820,200 Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
E. E. E.O.E. comprises a diverter valve downstream of the turbine, an
 USOO63056B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lui (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 2001 (54) INTEGRATED BLEED AIR AND ENGINE 5,363,641 11/1994 Dixon et al.. STARTING SYSTEM 5,414,992 5/1995 Glickstein.
USOO63056B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lui (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 2001 (54) INTEGRATED BLEED AIR AND ENGINE 5,363,641 11/1994 Dixon et al.. STARTING SYSTEM 5,414,992 5/1995 Glickstein.
(12) United States Patent
 US007307230B2 (12) United States Patent Chen (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,307,230 B2 Dec. 11, 2007 (54) MECHANISM FOR CONTROLLING CIRCUITCLOSINGAOPENING OF POWER RATCHET WRENCH (75) Inventor:
US007307230B2 (12) United States Patent Chen (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,307,230 B2 Dec. 11, 2007 (54) MECHANISM FOR CONTROLLING CIRCUITCLOSINGAOPENING OF POWER RATCHET WRENCH (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 USO09597628B2 (12) United States Patent Kummerer et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) OPTIMIZATION OF A VAPOR RECOVERY UNIT Applicant:
USO09597628B2 (12) United States Patent Kummerer et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) OPTIMIZATION OF A VAPOR RECOVERY UNIT Applicant:
United States Patent (19) Reid
 United States Patent (19) Reid 54 76) 21 22 (51) 52) 58 56) CONVENIENT DUAL FUELTANK SYSTEM Inventor: Richard M. Reid, 25474 State St., Loma Linda, Calif. 92354 Appl. No.: 638,377 Filed: Aug. 7, 1984 Int.
United States Patent (19) Reid 54 76) 21 22 (51) 52) 58 56) CONVENIENT DUAL FUELTANK SYSTEM Inventor: Richard M. Reid, 25474 State St., Loma Linda, Calif. 92354 Appl. No.: 638,377 Filed: Aug. 7, 1984 Int.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO698.1746B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,981,746 B2 Chung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 2006 (54) ROTATING CAR SEAT MECHANISM 4,844,543 A 7/1989 Ochiai... 297/344.26 4,925,227
(12) United States Patent USOO698.1746B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,981,746 B2 Chung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 2006 (54) ROTATING CAR SEAT MECHANISM 4,844,543 A 7/1989 Ochiai... 297/344.26 4,925,227
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O190837A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0190837 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2003 (54) BATTERY HOLDER HAVING MEANS FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 439/500 SECURELY
US 2003O190837A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0190837 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2003 (54) BATTERY HOLDER HAVING MEANS FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 439/500 SECURELY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
(19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0226455A1 Al-Anizi et al. US 2011 0226455A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SLOTTED IMPINGEMENT PLATES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0226455A1 Al-Anizi et al. US 2011 0226455A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SLOTTED IMPINGEMENT PLATES
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2
 US007592736 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2 Scott et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 2009 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ELECTRIC (56) References Cited GENERATOR WITH ROTOR CIRCUMIFERENTIALLY
US007592736 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2 Scott et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 2009 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ELECTRIC (56) References Cited GENERATOR WITH ROTOR CIRCUMIFERENTIALLY
(51) Int. Cl... B62D 25/00 flush with the end of the bed and the other edge overlapping
 USOO5904391A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,904.391 9 9 Lilienauest et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 18, 9 1999 54). TAILGATE GAP COVER 5,664,822 9/1997 Rosenfeld... 296/39.2 76 Inventors:
USOO5904391A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,904.391 9 9 Lilienauest et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 18, 9 1999 54). TAILGATE GAP COVER 5,664,822 9/1997 Rosenfeld... 296/39.2 76 Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Maloof
 United States Patent (19) Maloof 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 1984 54 CART WITH SEAT AND STORAGE COMPARTMENT 76 Inventor: John J. Maloof, 20 Greenwood St., East Hartford, Conn. 06118
United States Patent (19) Maloof 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 1984 54 CART WITH SEAT AND STORAGE COMPARTMENT 76 Inventor: John J. Maloof, 20 Greenwood St., East Hartford, Conn. 06118
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2
 US009 168973B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2 Offe (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2015 (54) MOTORCYCLE SUSPENSION SYSTEM (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Andrew Offe, Wilunga
US009 168973B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2 Offe (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2015 (54) MOTORCYCLE SUSPENSION SYSTEM (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Andrew Offe, Wilunga
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,805,593 B2
 USOO6805593B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,805,593 B2 Spaulding et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 2004 (54) QUICK CONNECT BATTERY TERMINAL 3,764,961. A 10/1973 Poltras... 439/759
USOO6805593B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,805,593 B2 Spaulding et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 2004 (54) QUICK CONNECT BATTERY TERMINAL 3,764,961. A 10/1973 Poltras... 439/759
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2. Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005
 United States Patent USOO6915721B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2 Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) CORDLESS RATCHET WRENCH 6,311,583 B1 11/2001 Izumisawa... 81/57.13 6,715,380
United States Patent USOO6915721B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2 Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) CORDLESS RATCHET WRENCH 6,311,583 B1 11/2001 Izumisawa... 81/57.13 6,715,380
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,840,124 B2
 USOO884O124B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Serhan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2014 (54) ROLLATOR HAVING ASITTO-LOCK BRAKE (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Michael Serhan, Arcadia,
USOO884O124B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Serhan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2014 (54) ROLLATOR HAVING ASITTO-LOCK BRAKE (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Michael Serhan, Arcadia,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8384329B2 (12) United States Patent Natsume (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) WIPER SYSTEMAND WIPER CONTROL METHOD Inventor: Takashi Natsume, Toyohashi (JP) Assignee: ASMO Co.,
USOO8384329B2 (12) United States Patent Natsume (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) WIPER SYSTEMAND WIPER CONTROL METHOD Inventor: Takashi Natsume, Toyohashi (JP) Assignee: ASMO Co.,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2
 US007125133B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2 Bilotti et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2006 (54) LED LIGHTING SYSTEM FOR PATIO 4.425,602 A 1/1984 Lansing UMBRELLA 5,053,931
US007125133B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2 Bilotti et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2006 (54) LED LIGHTING SYSTEM FOR PATIO 4.425,602 A 1/1984 Lansing UMBRELLA 5,053,931
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0091943 A1 Manor et al. US 2012009 1943A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (86) (60) SOLAR CELL CHARGING CONTROL Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0091943 A1 Manor et al. US 2012009 1943A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (86) (60) SOLAR CELL CHARGING CONTROL Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7654162B2 (12) United States Patent Braaten (54) DEVICE FOR INSTALLATION OF A PROBE AND PROBEACCOMMODATING ARRANGEMENT (75) Inventor: Nils A. Braaten, Trondheim (NO) (73) Assignee: Roxar ASA, Stavanger
USOO7654162B2 (12) United States Patent Braaten (54) DEVICE FOR INSTALLATION OF A PROBE AND PROBEACCOMMODATING ARRANGEMENT (75) Inventor: Nils A. Braaten, Trondheim (NO) (73) Assignee: Roxar ASA, Stavanger
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,603,073 B2
 USOO6603073B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,603,073 B2 Ferris (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003 (54) SNAP TOGETHER CABLE TROUGH FR 2 365 902 4/1978 SYSTEM GB 549840 12/1942 GB 612162
USOO6603073B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,603,073 B2 Ferris (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003 (54) SNAP TOGETHER CABLE TROUGH FR 2 365 902 4/1978 SYSTEM GB 549840 12/1942 GB 612162
United States Statutory Invention Registration (19)
 United States Statutory Invention Registration (19) P00rman 54 ELECTRO-HYDRAULIC STEERING SYSTEM FOR AN ARTICULATED VEHICLE 75 Inventor: Bryan G. Poorman, Princeton, Ill. 73 Assignee: Caterpillar Inc.,
United States Statutory Invention Registration (19) P00rman 54 ELECTRO-HYDRAULIC STEERING SYSTEM FOR AN ARTICULATED VEHICLE 75 Inventor: Bryan G. Poorman, Princeton, Ill. 73 Assignee: Caterpillar Inc.,
United States Patent (19) Dasa
 United States Patent (19) Dasa 54 MULTIPLE CONFIGURATION MODEL AIRCRAFT 76) Inventor: Madhava Dasa, P.O. Box 461, Kula, Hi. 96790-0461 (21) Appl. No.: 103,954 22 Filed: Oct. 2, 1987 51) Int. Cl.... A63H
United States Patent (19) Dasa 54 MULTIPLE CONFIGURATION MODEL AIRCRAFT 76) Inventor: Madhava Dasa, P.O. Box 461, Kula, Hi. 96790-0461 (21) Appl. No.: 103,954 22 Filed: Oct. 2, 1987 51) Int. Cl.... A63H
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2
 USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O00861 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0008610 A1 PetersOn (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2002 (54) KEY FOB WITH SLIDABLE COVER (75) Inventor: John Peterson,
(19) United States US 2002O00861 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0008610 A1 PetersOn (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2002 (54) KEY FOB WITH SLIDABLE COVER (75) Inventor: John Peterson,
United States Patent (19) 11) 4,324,219
 United States Patent (19) 11) 4,324,219 Hayashi 45) Apr. 13, 1982 54). SPARK INTENSIFIER IN GASOLINE 56) References Cited ENGINE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS s 703,759 7/1902 Brown... 123/169 PH 75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) 11) 4,324,219 Hayashi 45) Apr. 13, 1982 54). SPARK INTENSIFIER IN GASOLINE 56) References Cited ENGINE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS s 703,759 7/1902 Brown... 123/169 PH 75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,196,085 B1
 USOO6196085B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,196,085 B1 Chimonides et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) COUPLING AN ACCESSORY TO AN ENGINE 3,576,336 4/1971 Uhlig... 403/281 CRANKSHAFT
USOO6196085B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,196,085 B1 Chimonides et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) COUPLING AN ACCESSORY TO AN ENGINE 3,576,336 4/1971 Uhlig... 403/281 CRANKSHAFT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004.00431 O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0043102 A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2004 (54) ALIGNMENT COLLAR FOR A NOZZLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 425/567
US 2004.00431 O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0043102 A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2004 (54) ALIGNMENT COLLAR FOR A NOZZLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 425/567
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1. Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002
 USOO6435993B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1 Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) HYDRAULIC CHAIN TENSIONER WITH 5,707.309 A 1/1998 Simpson... 474/110 VENT DEVICE AND
USOO6435993B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1 Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) HYDRAULIC CHAIN TENSIONER WITH 5,707.309 A 1/1998 Simpson... 474/110 VENT DEVICE AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0119926 A1 LIN US 2013 0119926A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 16, 2013 (54) WIRELESS CHARGING SYSTEMAND METHOD (71) Applicant: ACER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0119926 A1 LIN US 2013 0119926A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 16, 2013 (54) WIRELESS CHARGING SYSTEMAND METHOD (71) Applicant: ACER
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Hozumi et al. 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,889,164 Dec. 26, 1989 54). SOLENOID CONTROLLED WALVE (75 Inventors: Kazuhiro Hozumi; Masaru Arai, both of Chiba; Yoshitane
United States Patent (19) Hozumi et al. 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,889,164 Dec. 26, 1989 54). SOLENOID CONTROLLED WALVE (75 Inventors: Kazuhiro Hozumi; Masaru Arai, both of Chiba; Yoshitane
Phillips (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 10, (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search
 (12) United States Patent US008747274B2 () Patent No.: Phillips () Date of Patent: Jun., 2014 (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search TRANSMISSION USPC... 74/3, 331; 475/207
(12) United States Patent US008747274B2 () Patent No.: Phillips () Date of Patent: Jun., 2014 (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search TRANSMISSION USPC... 74/3, 331; 475/207
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140208759A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0208759 A1 Ekanayake et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 31, 2014 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR REDUCING Publication
US 20140208759A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0208759 A1 Ekanayake et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 31, 2014 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR REDUCING Publication
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,511,619 B2
 USOO851 1619B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,511,619 B2 Mann (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2013 (54) SLAT DEPLOYMENT MECHANISM (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Alan Mann, Bristol
USOO851 1619B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,511,619 B2 Mann (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2013 (54) SLAT DEPLOYMENT MECHANISM (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Alan Mann, Bristol
United States Patent (19) Koitabashi
 United States Patent (19) Koitabashi 54 75 (73) 1 (51) (5) (58 56) ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH WITH AN IMPROVED MAGNETC ROTATABLE MEMBER Inventor: Takatoshi Koitabashi, Annaka, Japan Assignee: Sanden Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Koitabashi 54 75 (73) 1 (51) (5) (58 56) ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH WITH AN IMPROVED MAGNETC ROTATABLE MEMBER Inventor: Takatoshi Koitabashi, Annaka, Japan Assignee: Sanden Corporation,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1
 USOO648.4362B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1 Ku0 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) RETRACTABLE HANDLE ASSEMBLY WITH 5,692,266 A 12/1997 Tsai... 16/113.1 MULTIPLE ENGAGING
USOO648.4362B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1 Ku0 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) RETRACTABLE HANDLE ASSEMBLY WITH 5,692,266 A 12/1997 Tsai... 16/113.1 MULTIPLE ENGAGING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7357465B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,357.465 B2 Young et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2008 (54) BRAKE PEDAL FEEL SIMULATOR 3,719,123 A 3/1973 Cripe 3,720,447 A * 3/1973 Harned
(12) United States Patent USOO7357465B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,357.465 B2 Young et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2008 (54) BRAKE PEDAL FEEL SIMULATOR 3,719,123 A 3/1973 Cripe 3,720,447 A * 3/1973 Harned
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 20110283931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0283931 A1 Moldovanu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2011 (54) SUBMARINE RENEWABLE ENERGY GENERATION SYSTEMUSING
US 20110283931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0283931 A1 Moldovanu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2011 (54) SUBMARINE RENEWABLE ENERGY GENERATION SYSTEMUSING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,643,958 B1
 USOO6643958B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Krejci (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 11, 2003 (54) SNOW THROWING SHOVEL DEVICE 3,435,545. A 4/1969 Anderson... 37/223 3,512,279 A 5/1970 Benson... 37/244
USOO6643958B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Krejci (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 11, 2003 (54) SNOW THROWING SHOVEL DEVICE 3,435,545. A 4/1969 Anderson... 37/223 3,512,279 A 5/1970 Benson... 37/244
United States Patent (19) Kiba et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kiba et al. 54) VEHICLE BODY PAINTING ROBOT 75 Inventors: Hiroshi Kiba, Hiroshima; Yoshimasa Itoh, Yokohama; Kiyuji Kiryu, Kawasaki, all of Japan 73) Assignees: Mazda Motor Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Kiba et al. 54) VEHICLE BODY PAINTING ROBOT 75 Inventors: Hiroshi Kiba, Hiroshima; Yoshimasa Itoh, Yokohama; Kiyuji Kiryu, Kawasaki, all of Japan 73) Assignees: Mazda Motor Corporation,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
III III III. United States Patent 19 Justice. 11 Patent Number: position. The panels are under tension in their up position
 United States Patent 19 Justice (54) (76) (21) 22) (51) (52) 58 56) TRUCK BED LOAD ORGANIZER APPARATUS Inventor: 4,733,898 Kendall Justice, P.O. Box 20489, Wickenburg, Ariz. 85358 Appl. No.: 358,765 Filed:
United States Patent 19 Justice (54) (76) (21) 22) (51) (52) 58 56) TRUCK BED LOAD ORGANIZER APPARATUS Inventor: 4,733,898 Kendall Justice, P.O. Box 20489, Wickenburg, Ariz. 85358 Appl. No.: 358,765 Filed:
III. United States Patent (19) Hsu et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,330, Date of Patent: Jul. 19, electric power in addition to human force.
 United States Patent (19) Hsu et al. (54 REMOTE-CONTROLLED ELECTRIC SKATE-BOARD 76 Inventors: Chi-Hsueh Hsu, 4F, No. 144, Chu-Lin Rd., Yung-Ho Shih, Taipei Hsien; Shih-Hsin Chen, 4F, No. 35-1, Hsin-Ching,
United States Patent (19) Hsu et al. (54 REMOTE-CONTROLLED ELECTRIC SKATE-BOARD 76 Inventors: Chi-Hsueh Hsu, 4F, No. 144, Chu-Lin Rd., Yung-Ho Shih, Taipei Hsien; Shih-Hsin Chen, 4F, No. 35-1, Hsin-Ching,
United States Patent (19) Hormel et al.
 United States Patent (19) Hormel et al. 54 (75) (73) 21) 22) (51) 52) (58) 56) LAMP FAILURE INDICATING CIRCUIT Inventors: Ronald F. Hormel, Mt. Clemens; Frederick O. R. Miesterfeld, Troy, both of Mich.
United States Patent (19) Hormel et al. 54 (75) (73) 21) 22) (51) 52) (58) 56) LAMP FAILURE INDICATING CIRCUIT Inventors: Ronald F. Hormel, Mt. Clemens; Frederick O. R. Miesterfeld, Troy, both of Mich.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0121100A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0121100 A1 Feenstra (43) Pub. Date: May 26, 2011 (54) COVER FOR PROTECTINGA FUSIBLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2011 0121100A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0121100 A1 Feenstra (43) Pub. Date: May 26, 2011 (54) COVER FOR PROTECTINGA FUSIBLE Publication Classification
ESTCP Cost and Performance Report
 ESTCP Cost and Performance Report (PP-0026) Universal Stationary/Mobile NoFoam Unit (USNOFU) for Aircraft Rescue and Fire Fighting (ARFF) Vehicles January 2004 ENVIRONMENTAL SECURITY TECHNOLOGY CERTIFICATION
ESTCP Cost and Performance Report (PP-0026) Universal Stationary/Mobile NoFoam Unit (USNOFU) for Aircraft Rescue and Fire Fighting (ARFF) Vehicles January 2004 ENVIRONMENTAL SECURITY TECHNOLOGY CERTIFICATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,588,825 B1
 USOO6588825B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,588,825 B1 Wheatley (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2003 (54) RAIN DIVERTING DEVICE FOR A 6,024.402 A * 2/2000 Wheatley... 296/100.18 TONNEAU
USOO6588825B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,588,825 B1 Wheatley (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2003 (54) RAIN DIVERTING DEVICE FOR A 6,024.402 A * 2/2000 Wheatley... 296/100.18 TONNEAU
United States Patent (19) Woodburn
 United States Patent (19) Woodburn 54 (76) 21) 22 (51) 52 58 56 MOTOR VEHICLE AND BOAT TRALER Inventor: Clarence A. Woodburn, 43884 Pioneer Ave., Hemet, Calif. 92344 Appl. No.: 329,163 Filed: Mar. 17,
United States Patent (19) Woodburn 54 (76) 21) 22 (51) 52 58 56 MOTOR VEHICLE AND BOAT TRALER Inventor: Clarence A. Woodburn, 43884 Pioneer Ave., Hemet, Calif. 92344 Appl. No.: 329,163 Filed: Mar. 17,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,416,362 B1
 USOO6416362B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,416,362 B1 Conrad et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) PLUGADAPTER WITH SAFETY SWITCH 3,219,962 A 11/1965 Whalen 4,136,919 A * 1/1979
USOO6416362B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,416,362 B1 Conrad et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) PLUGADAPTER WITH SAFETY SWITCH 3,219,962 A 11/1965 Whalen 4,136,919 A * 1/1979
Kikuiri et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, (54) CAPACITIVE PRESSURE SENSOR 5, A 12, 1996 Ko /53
 (12) United States Patent USOO7382599B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,382,599 B2 Kikuiri et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, 2008 (54) CAPACITIVE PRESSURE SENSOR 5,585.311 A 12, 1996 Ko... 438/53 5,656,781 A *
(12) United States Patent USOO7382599B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,382,599 B2 Kikuiri et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, 2008 (54) CAPACITIVE PRESSURE SENSOR 5,585.311 A 12, 1996 Ko... 438/53 5,656,781 A *
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Imai USOO6581225B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,581,225 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2003 (54) MATTRESS USED FOR PREVENTING BEDSORES OR THE LIKE (76) Inventor: KaZumichi Imai, 7-29-1222,
(12) United States Patent Imai USOO6581225B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,581,225 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2003 (54) MATTRESS USED FOR PREVENTING BEDSORES OR THE LIKE (76) Inventor: KaZumichi Imai, 7-29-1222,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8905448B2 (12) United States Patent Vaz Coelho et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,905,448 B2 Dec. 9, 2014 (54) SIZE-ADJUSTABLE, PIVOTABLE TRIPLE CONNECTION DEVICE (75) Inventors: Joao
USOO8905448B2 (12) United States Patent Vaz Coelho et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,905,448 B2 Dec. 9, 2014 (54) SIZE-ADJUSTABLE, PIVOTABLE TRIPLE CONNECTION DEVICE (75) Inventors: Joao
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 Weimer 54 BUSWAY INSULATION SYSTEM (75) Inventor: Charles L. Weimer, Beaver Falls, Pa. 73) Assignee: Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Pittsburgh, Pa. 22 Filed: Feb. 22, 1974 21
United States Patent 19 Weimer 54 BUSWAY INSULATION SYSTEM (75) Inventor: Charles L. Weimer, Beaver Falls, Pa. 73) Assignee: Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Pittsburgh, Pa. 22 Filed: Feb. 22, 1974 21
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8545166 B2 (12) United States Patent Maruthamuthu et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 1, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING LEAK STEAM
USOO8545166 B2 (12) United States Patent Maruthamuthu et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 1, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING LEAK STEAM
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,668,685 B2
 USOO6668685B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,668,685 B2 Boston (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 30, 2003 (54) MULTI-LUG SOCKET TOOL 5,277,085 A * 1/1994 Tanimura et al.... 81/57.22 5,572,905
USOO6668685B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,668,685 B2 Boston (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 30, 2003 (54) MULTI-LUG SOCKET TOOL 5,277,085 A * 1/1994 Tanimura et al.... 81/57.22 5,572,905
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,047,956 B2. Masaoka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2006
 US007047956B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Masaoka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2006 (54) KICKBACK PREVENTING DEVICE FOR (56) References Cited ENGINE (75) Inventors: Akira Masaoka,
US007047956B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Masaoka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2006 (54) KICKBACK PREVENTING DEVICE FOR (56) References Cited ENGINE (75) Inventors: Akira Masaoka,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2
 US009035508B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2 Grosskopf et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 19, 2015 (54) ROTATING RESISTOR ASSEMBLY H02K II/042 (2013.01); H02K II/0057 (2013.01):
US009035508B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,035,508 B2 Grosskopf et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 19, 2015 (54) ROTATING RESISTOR ASSEMBLY H02K II/042 (2013.01); H02K II/0057 (2013.01):
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9284.05OB2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.284,050 B2 Bagai (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2016 (54) AIRFOIL FOR ROTOR BLADE WITH (56) References Cited REDUCED PITCHING MOMENT U.S. PATENT
(12) United States Patent USOO9284.05OB2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.284,050 B2 Bagai (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2016 (54) AIRFOIL FOR ROTOR BLADE WITH (56) References Cited REDUCED PITCHING MOMENT U.S. PATENT
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,994,308 B1. Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2006
 United States Patent USOO69943O8B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,994,308 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2006 (54) IN-TUBE SOLENOID GAS VALVE 4,520,227 A * 5/1985 Krimmer et al.... 251/129.21
United States Patent USOO69943O8B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,994,308 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2006 (54) IN-TUBE SOLENOID GAS VALVE 4,520,227 A * 5/1985 Krimmer et al.... 251/129.21
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,270 B2
 USOO654327OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,270 B2 Cmelik (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) AUTOBODY DENT REPAIR TOOL 4,461,192 A * 7/1984 Suligoy et al.... 81/177.7 4,502,317
USOO654327OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,270 B2 Cmelik (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) AUTOBODY DENT REPAIR TOOL 4,461,192 A * 7/1984 Suligoy et al.... 81/177.7 4,502,317
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201201.07098A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0107098 A1 Tirone, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 3, 2012 (54) GASTURBINE ENGINE ROTOR TIE SHAFT (52) U.S.
(19) United States US 201201.07098A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0107098 A1 Tirone, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 3, 2012 (54) GASTURBINE ENGINE ROTOR TIE SHAFT (52) U.S.
(12) United States Patent
 (1) United States Patent US007 1158B1 (10) Patent No.: US 7,115,8 B1 Day et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 006 (54) INDIRECT ENTRY CABLE GLAND (56) References Cited ASSEMBLY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75)
(1) United States Patent US007 1158B1 (10) Patent No.: US 7,115,8 B1 Day et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 006 (54) INDIRECT ENTRY CABLE GLAND (56) References Cited ASSEMBLY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75)
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Mayfield USOO6520521B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,520,521 B2 Feb. 18, 2003 (54) TILTING TRAILERSUSPENSION (76) Inventor: William Rodgers Mayfield, 1103 Collinwood
(12) United States Patent Mayfield USOO6520521B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,520,521 B2 Feb. 18, 2003 (54) TILTING TRAILERSUSPENSION (76) Inventor: William Rodgers Mayfield, 1103 Collinwood
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,531,492 Raskevicius (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 1996
 IIIHIIII US005531492A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,531,492 Raskevicius (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 1996 (54) RATCHETING LATCH MECHANISM FOR A 3,123,387 3/1964 Jackson et al.... 292/21
IIIHIIII US005531492A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,531,492 Raskevicius (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 1996 (54) RATCHETING LATCH MECHANISM FOR A 3,123,387 3/1964 Jackson et al.... 292/21
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,220,819 B1
 USOO6220819B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,220,819 B1 Chien et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 24, 2001 (54) CENTRIFUGAL PUMP IMPELLER 3.368,744 2/1968 Jenn... 416/237 4,236,871 12/1980
USOO6220819B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,220,819 B1 Chien et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 24, 2001 (54) CENTRIFUGAL PUMP IMPELLER 3.368,744 2/1968 Jenn... 416/237 4,236,871 12/1980
W. Hope. 15 Claims, 5 Drawing Figs. (52) U.S. Cl , 5ll int. Cl... F16k 43100, F16k 5/14
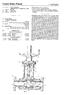 United States Patent (72 inventor Clyde H. Chronister 4 Kings Row, Rte. 14, Houston, Tex. 77040 (2) Appl. No. 823,103 (22 Filed May 8, 1969 45 Patented Jan. 26, 197i. 54) GATE WALVE 15 Claims, 5 Drawing
United States Patent (72 inventor Clyde H. Chronister 4 Kings Row, Rte. 14, Houston, Tex. 77040 (2) Appl. No. 823,103 (22 Filed May 8, 1969 45 Patented Jan. 26, 197i. 54) GATE WALVE 15 Claims, 5 Drawing
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
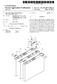 US 2011 01 17420A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0117420 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) BUS BAR AND BATTERY MODULE INCLUDING THE SAME (52)
US 2011 01 17420A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0117420 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) BUS BAR AND BATTERY MODULE INCLUDING THE SAME (52)
HO (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007
 (12) United States Patent US007191593B1 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,593 B1 HO (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) ELECTRO-HYDRAULIC ACTUATOR 5,072.584 A * 12/1991 Mauch et al.... 60/468 SYSTEM 5,351.914
(12) United States Patent US007191593B1 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,593 B1 HO (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) ELECTRO-HYDRAULIC ACTUATOR 5,072.584 A * 12/1991 Mauch et al.... 60/468 SYSTEM 5,351.914
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Ogasawara et al. (54) 75 RDING LAWN MOWER Inventors: Hiroyuki Ogasawara; Nobuyuki Yamashita; Akira Minoura, all of Osaka, Japan Assignee: Kubota Corporation, Osaka, Japan Appl.
United States Patent (19) Ogasawara et al. (54) 75 RDING LAWN MOWER Inventors: Hiroyuki Ogasawara; Nobuyuki Yamashita; Akira Minoura, all of Osaka, Japan Assignee: Kubota Corporation, Osaka, Japan Appl.
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Minnerop 54) DEVICE FOR WATER COOLING OF ROLLED STEEL SECTIONS 75 Inventor: Michael Minnerop, Ratingen, Germany 73 Assignee: SMS Schloemann-Siemag Aktiengesellschaft, Dusseldorf,
United States Patent (19) Minnerop 54) DEVICE FOR WATER COOLING OF ROLLED STEEL SECTIONS 75 Inventor: Michael Minnerop, Ratingen, Germany 73 Assignee: SMS Schloemann-Siemag Aktiengesellschaft, Dusseldorf,
