(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,083,631 B2. Shiohara (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 27, 2011
|
|
|
- Lillian Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 US B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Shiohara (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 27, 2011 (54) PLANETARY GEARTYPE GEARBOX (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Masaki Shiohara, Komatsu (JP) U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4, A 1/1977 Pearce et al. (73) Assignee: Komatsu Ltd., Tokyo (JP) 4,205,563 A 6, 1980 Gorrell 5,049,116 A 9/1991 Asada c - r - 5,823,9 A /1998 Park (*) Notice: Subject to any style the t 7.682,282 B2 * 3/20 Kamm et al /277 patent 1s extended or adjusted under 7,811,197 B2 * /20 Phillips et al.. 475/275 U.S.C. 4(b) by 220 days. 7,867,130 B2 * 1/2011 Carey et al / ,457 B2 * 2/2011 Wittkopp et al /277 (21) Appl. No.: 12/668,775 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (22) PCT Filed: Aug. 27, 2008 DE 2004 O23956 A1 12/ JP /1975 (86). PCT No.: PCT/UP2008/ JP JP O A 6, , 1993 S371 (c)(1) JP O A 11, 1997 (2), (4) Date: Jan. 12, 20 * cited by examiner (87) PCT Pub. No.: WO2009/ Primary Examiner Sherry Estremsky (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm Global IP Counselors PCT Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2009 (57) ABSTRACT (65) Prior Publication Data A planetary gear type gearbox includes a front-stage trans US 20/O A1 Jul. 22, 20 mission section and rear-stage transmission section. The front-stage transmission section is for transmitting power (30) Foreign Application Priority Data from an input shaft to an intermediate shaft. The front-stage transmission section includes first, second and third clutches, Sep. 25, 2007 (JP) two sets of planetary gear trains axially adjoining to each other. The first planetary gear train includes a Sun gear, a (51) Int. Cl. carrier, a ring gear and planet gears. The second planetary FI6H3/62 ( ) gear train includes a Sun gear, a carrier, a ring gear and two sets of planet gears. In the activation of second and third (52) U.S. Cl /282; 475/288 clutches, power is inputted into the carrier from the input shaft and is then outputted from the ring gear of the first planetary (58) Field of Classification Search /288, gear train. 475/282, 296 See application file for complete search history. Claims, 5 Drawing Sheets 1 1 O N 2O f 2nd Rev te' 12: 12g s c 14N 22c T A 13c 24, 25c 25c *= a 3rd S. Y e e 1 24b 25b. 25b : \- 5 ( H. - r H M 2nd Rev 1st 4b 24e- 25e2 : T -25e 1 " i 25, T, 24a -- INPUT H OUTPUT: it N.truly
2 U.S. Patent Dec. 27, 2011 Sheet 1 of 5
3 U.S. Patent Dec. 27, 2011 Sheet 2 of 5
4 U.S. Patent Dec. 27, 2011 Sheet 3 of 5 1 O Y 12b M12CH Sr. 12a L
5 U.S. Patent Dec. 27, Sheet 4 of 5 SPEED CLUTCH REDUCTION INTER EGF REVISTRATIO 5 F1 o O F2 O o O F4 o o F5 to to F6 O O HHPHEE F8 O O golf R A. R3 O 2541 His FIG. 4
6 U.S. Patent Dec. 27, 2011 Sheet 5 of 5
7 1. PLANETARY GEARTYPE GEARBOX CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This national phase application claims priority to Japanese Patent Application No , filed on Sep. 25, The entire disclosure of Japanese Patent Application No is hereby incorporated herein by reference. TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to a planetary gear type gear box, for instance, to be installed in a dump truck. BACKGROUND ART A transmission, including a plurality of planetary gear trains, has been recently installed in the construction vehicles Such the dump trucks. In the gearbox, engine torque is input- 20 ted into an input shaft and a plurality of speed stages are shifted back and forth depending on objects of driving a vehicle. For example, U.S. Pat. No. 4,205,563 (issued on Jun. 3, 1980) discloses a gearbox in which not only clutches and 25 brakes but also a torque converter and two sets of planetary gear trains are combined. According to the gearbox, a wide range of speed reduction can be realized by setting the inter stage ratios to be roughly the same. Note the inter-stage ratio is a ratio between speed change ratios of speed-change stages. 30 DISCLOSURE OF THE INVENTION The aforementioned conventional gearbox has the follow ing drawback. 35 In short, the gearbox, disclosed in the aforementioned patent document, has a drawback that a reduction ratio of a speed unit always exceeds 1. For example, as illustrated in FIG. 2 of the aforementioned patent document, the reduction ratio is set to be: 1.00 in engagement of a clutch 28 (L clutch): in engagement of a brake 24 (M clutch); and 1.84 in engagement of a brake 26 (H clutch). With the configuration, large torque is transmitted to the rear stage of the gearbox. In response to this, a variety of countermeasures are required. For example, torque is 45 required to be inhibited by installing a speedup gear in the front-stage side of the gears disposed in the rear stage. Alter natively, the gears to be disposed in the rear stage are required to beformed in a large size in consideration of their durability. It is an object of the present invention to provide a planetary 50 gear type gearbox for allowing a multi-stage gear train to keep a simple structure by inhibiting output-side torque without addition of an extra component such as a speedup gear or size increase of the gears to be disposed in the rear stage. A planetary gear type gearbox according to a first aspect of 55 the present invention includes a front-stage transmission sec tion and a rear-stage transmission section. The front-stage transmission section includes an input shaft that power is inputted thereto. The rear-stage transmission section includes an intermediate shaft coupled to the front-stage transmission 60 section and an output shaft for outputting power. The front stage transmission section includes a first planetary gear train, a second planetary gear train, a first clutch, a second clutch and a third clutch. The first planetary gear train includes a first Sun gear, a plurality of first planet gears, a first carrier and a 65 first ring gear. The first planet gears mesh with the first Sun gear. The first carrier is coupled to the input shaft, and rotat 2 ably supports the first planet gears. The first ring gear is connected to the intermediate shaft, and meshes with the first planet gears. The second planetary gear train includes a sec ond Sun gear, a plurality of inner peripheral side second planet gears, a plurality of outer peripheral side second planet gears, a second carrier and a second ring gear. The second Sun gear is integrally and rotatably coupled to the first Sun gear. The inner peripheral side second planet gears mesh with the sec ond Sun gear. The outer peripheral side second planet gears mesh with the inner peripheral side second planet gears. The second carrier is connected to the input shaft, and rotatably Supports the inner peripheral side second planetgears and the outer peripheral side second planet gears. The second ring gear meshes with the outer peripheral side second planet gears. The first clutch is configured to selectively couple? uncouple the input shaft and the intermediate shaft. The sec ond clutch is configured to selectively allow/prevent rotation of the second Sun gear. The third clutch is configured to selectively allow/prevent rotation of the second ring gear. The planetary gear type gearbox is installed in the con struction vehicles and the like (e.g., dump trucks), for instance. The planetary gear type gearbox includes the first and second planetary gear trains and the first to third clutches for shifting three speed-change stages back and forth. The second planetary gear train is so-called a double planetary type planetary gear train. Additionally, according to the plan etary gear type gearbox, power transmissions of the first and second planetary gear trains have a configuration that power is inputted into the first carrier and is outputted from the first ring gear in a speed-change stage in which a reduction ratio is gradually reduced. According to the configuration, the reduction ratios in the three stages can be all set to be equal to or less than by configuring power to be inputted into the carrier and to be outputted from the ring gear in the first planetary gear train. As a result, it is possible to compactly form the gears and the like on the rear-stage side without increasing their sizes just like the conventional gearboxes that the reduction ratios in three speed-change stages are all equal to or greater than Furthermore, with the adoption of the aforementioned structure, it is possible to appropriately set the reduction ratios of three speed-change stages so that the inter-stage ratios among three speed-change stages can be roughly the same. As a result, it is possible to compactly form a multi stage gearbox for providing nine forward stages and three reverse stages, for instance, by disposing the planetary gear type gearbox of the present invention in the input stage and disposing the conventional three-train gearbox in the output Stage. A planetary gear type gearbox according to a second aspect of the present invention is the planetary gear type gearbox of the first aspect. In the planetary gear type gearbox, an output side of the second planetary gear train is connected to the intermediate shaft through the first planetary gear train. According to the present invention, the size of the gearbox can be further reduced. A planetary gear type gearbox according to a third aspect of the present invention is the planetary gear type gearbox of the first aspect. In the planetary gear type gearbox, the rear-stage transmission section is a transmission for providing three forward stages and one reverse stage. The forward stages include a low-speed stage, a meddle-speed stage and a high speed stage. The rear-stage transmission section includes a third planetary gear train, a fourth planetary gear train, a fifth planetary gear train, a low-speed clutch, a middle-speed clutch, a high-speed clutch and a reverse clutch. The third planetary gear train includes a third Sun gear, a plurality of
8 3 third planet gears, a third carrier and a third ring gear. The third planet gears mesh with the third sun gear. The third carrier is coupled to the output shaft, and rotatably Supports the third planet gears. The third ring gear meshes with the third planet gears. The fourth planetary gear train includes a fourth Sun gear, a plurality of fourth planet gears, a fourth carrier and a fourth ring gear. The fourth planet gears mesh with the fourth sun gear. The fourth carrier rotatably supports the fourth planet gears. The fourth ring gear meshes with the fourth planet gears. The fifth planetary gear train includes a fifth Sun gear, a plurality of fifth planet gears, a fifth carrier and a fifth ring gear. The fifth planet gears mesh with the fifth sun gear. The fifth carrier rotatably supports the fifth planet gears. The fifth ring gear meshes with the fifth planet gears. The low-speed clutch is configured to selectively allow/pre vent rotation of the third ring gear. The middle-speed clutch is configured to selectively allow/prevent rotation of the fourth ring gear. The high-speed clutch is configured to selectively couple/uncouple the intermediate shaft and the fourth carrier, and is also configured to selectively couple?uncouple the intermediate shaft and the fifth carrier. The reverse clutch is configured to selectively allow/prevent rotation of the fifth ring gear. According to the present invention, the low-speed clutch and the third planetary gear train are disposed in the closest position to the outputside (i.e., the final stage) as output-side components of the gearbox, compared to the reverse clutch and the fifth planetary gear train that correspond to the reverse speed-change stage. When the reverse speed-change stage is normally disposed in the final stage side, power is inputted through a plurality of planetary gear trains. Therefore, a reduction ratio is increased and traction force thereby tends to be excessively increased. According to the present invention, however, such a con figuration can be avoided that a reduction ratio of the reverse first-speed stage is greater than that of the forward first-speed stage. As a result, it is possible to produce a gearbox for providing nine forward stages and three reverse stages, while Such as case is avoided that a less-usable gearbox is produced due to the reverse first-speed stage having low speed and quite large traction force. A planetary gear type gearbox according to a fourth aspect of the present invention is the planetary gear type gearbox of the third aspect. In the planetary gear type gearbox, the third Sun gear, the fourth Sun gear and the fifth Sun gear are all coupled to the intermediate shaft. A planetary gear type gearbox according to a fifth aspect of the present invention is the planetary gear type gearbox of the third aspect. In the planetary gear type gearbox, the fifth planet gear includes a plurality of inner peripheral side fifth planet gears and a plurality of outer peripheral side planet gears. The inner peripheral side fifth planet gears mesh with the fifth sun gear, whereas the outer peripheral side fifth planet gears mesh with the fifth ring gear. A planetary gear type gearbox according to a sixth aspect of the present invention is the planetary gear type gearbox of the third aspect. In the planetary gear type gearbox, the third ring gear, the fourth carrier and the fifth carrier are integrally and rotatably coupled to each other. A planetary gear type gearbox according to a seventh aspect of the present invention is the planetary gear type gearbox of the first aspect. In the planetary gear type gearbox, the rear-stage transmission section is a transmission for pro viding three forward stages and one reverse stage. The for ward stages include a low-speed stage, a meddle-speed stage and a high-speed stage. The rear-stage transmission section includes a third planetary gear train, a fourth planetary gear train, a fifth planetary gear train, a low-speed clutch, a middle speed clutch, a high-speed clutch, and a reverse clutch. The third planetary gear train includes a third Sun gear, a plurality of third planet gears, a third carrier, and a third ring gear. The third planet gears mesh with the third sun gear. The third carrier is coupled to the output shaft, and rotatably Supports the third planet gears. The third ring gear meshes with the third planet gears. The fourth planetary gear train includes a fourth Sun gear, a plurality of fourth planet gears, a fourth carrier, and a fourth ring gear. The fourth planet gears mesh with the fourth sun gear. The fourth carrier rotatably supports the fourth planet gears. The fourth ring gear meshes with the fourth planet gears. The fifth planetary gear train includes a fifth Sun gear, a plurality of fifth planet gears, a fifth carrier and a fifth ring gear. The fifth planet gears mesh with the fifth Sun gear. The fifth carrier is coupled to the output shaft, and rotatably Supports the fifth planet gears. The fifth ring gear meshes with the fifth planet gears. The low-speed clutch is configured to selectively allow/prevent rotation of the third ring gear. The middle-speed clutch is configured to selec tively allow/prevent rotation of the fourth ring gear. The high speed clutch is configured to selectively couple?uncouple the intermediate shaft and the fourth carrier. The reverse clutch is configured to selectively allow/prevent rotation of the fifth ring gear. According to the present invention, the reverse clutch and the fifth planetary gear train, which correspond to the reverse speed-change stage, are disposed in the closest position to the rear-stage side as output-side components of the gearbox. With the structure, it is possible to produce a gearbox for providing nine forward stages and three reverse stages while quite large traction force is achieved in the reverse first-speed stage by increasing a reduction ratio of the reverse first-speed Stage. A planetary gear type gearbox according to an eighth aspect of the present invention is the planetary gear type gearbox of the seventh aspect. In the planetary gear type gearbox, the third Sun gear and the fourth Sun gear are coupled to the intermediate shaft. A planetary gear type gearbox according to a ninth aspect of the present invention is the planetary gear type gearbox of the seventh aspect. In the planetary gear type gearbox, the third ring gear, the fourth carrier, and the fifth Sun gear are integrally and rotatatbly coupled to each other. BRIEF EXPLANATION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional diagram for illustrating a struc ture of a transmission according to an embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram for illustrating the transmis Sion of FIG. 1 FIGS. 3(a) to 3(c) are schematic diagrams for illustrating power transmission paths with respect to respective speed change stages in the front-stage transmission section. FIG. 4 is a chart for showing a relation between a reduction ratio and an inter-stage ratio for the respective speed-change stages in the transmission of FIG. 1. FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram for illustrating a configura tion of a transmission according to another embodiment of the present invention. DESCRIPTION OF EMBODIMENTS A configuration of a transmission (planetary gear type gearbox) 1, composed of a front-stage transmission section
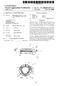
9 5 and a rear-stage transmission section 20, will be hereinaf ter explained with reference to FIGS. 1 to 4. Overall Structure of Transmission 1 As illustrated in FIGS. 1 and 2, the transmission 1 accord ing to the present embodiment includes a torque converter 2, the front-stage transmission section disposed on the rear stage side of the torque converter 2, and the rear-stage trans mission section 20. In the transmission 1, revolution of the torque converter 2 is transmitted to an input shaft 11. Revo lution speed of the input shaft 11 is shifted by the front-stage transmission section, and the shifted revolution is trans mitted to an intermediate shaft 21. Moreover, revolution speed of the intermediate shaft 21 is shafted by the rear-stage transmission section 20, and the shifted revolution is trans mitted to an output shaft 26. Specifically, the transmission 1 includes the front-stage transmission section and the rear-stage transmission sec tion 20. The front-stage transmission section is disposed between the input shaft 11 and the intermediate shaft 21, whereas the rear-stage transmission section 20 is disposed between the intermediate shaft 21 and the output shaft 26. The transmission 1 makes up speed-change stages including nine forward stages (F1 to F9) and three reverse stages (R1 to R3) by the combination of the front-stage transmission section (three stages) and the rear-stage transmission section 20 (three forward Stages and one reverse stage) (see FIG. 4). Front-Stage Transmission Section The front-stage transmission section is mainly com posed of the input shaft 11, an L clutch (first clutch) 12a, an M clutch (second clutch) 12b, an H clutch (third clutch) 12c, an M planetary gear train (first planetary gear train) 13 and an H planetary gear train (second planetary gear train) 14. In this case, the M planetary gear train 13 and the H planetary gear train 14 are coaxially disposed to each other. The input shaft 11 is disposed in the most upstream position of a power transmission path in the transmission 1. Power of the torque converter 2 is transmitted to the input shaft 11. The L clutch 12a is disposed in the closest position to the outputside in the front-stage transmission section. On the other hand, the M clutch 12b is disposed in the closest position to the inputside of the front-stage transmission section. The H clutch 12c is disposed between the L clutch 12a and the M clutch 12b. M-Planetary Gear Train 13 The M-planetary gear train 13 is a single planetary type planetary gear train. The M planetary gear train 13 is disposed on the output side in the front-stage transmission section. The M-planetary gear train 13 is mainly composed of a Sun gear 13a, a carrier 13b, a ring gear 13c and a plurality of planet gears 13e. The sun gear 13a is disposed on the outer peripheral side of the input shaft 11. The sun gear 13a is also disposed in the most radial inward position of the M planetary gear train 13. The carrier 13b rotatably supports the planet gears 13e roughly equally spaced apart from each other in the circum ferential direction. The respective planet gears 13e mesh with the sun gear 13a. In the present embodiment, the carrier 13b is fixed to the input shaft 11. In the M planetary gear train 13, revolution of the input shaft 11 is configured to be inputted into the carrier 13b. The ring gear 13c is disposed for meshing with the planet gears 13e whose axes are supported by the carrier 13b. In the present embodiment, the ring gear 13c is fixed with respect to the intermediate shaft 21. Revolution of the M planetary gear train 13 is thus outputted from the ring gear 13c. H Planetary Gear Train 14 The H planetary gear train 14 is a double planetary type planetary gear train. The H planetary gear train 14 is disposed in a closer position to the input side in the front-stage trans mission section than the M planetary gear train 13 is. The H planetary gear train 14 is mainly composed of a Sun gear 14a, a carrier 14b, a ring gear 14c., a plurality of inner periph eral side planetgears 14e1, and a plurality of outer peripheral side planet gears 14e2. In other words, the H planetary gear train 14 includes two groups of planet gears. The Sun gear 14a is disposed on the outer peripheral side of the input shaft 11. The Sun gear 14a is also disposed in the most radial inward position of the H planetary gear train 14. Additionally, the Sun gear 14a of the H planetary gear train 14 is configured to integrally rotate with the Sun gear 13a of the M planetary gear train 13. The carrier 14b rotatably supports the inner peripheral side planet gears 14e 1 roughly equally spaced apart from each other in the circumferential direction and the outer peripheral side planet gears 14e2 roughly equally spaced apart from each other in the circumferential direction. The inner periph eral side planet gears 14e 1 of the inner and outer peripheral side planet gears 14e 1, 14e2 herein mesh with the Sun gear 14a. In the present embodiment, the carrier 14b adjoins the carrier 13b included in the M planetary gear train 13 in the axial direction of the input shaft 11. The carrier 14b is also integrated with the carrier 13b. Therefore, revolution of the input shaft 11 can be inputted into the carrier 14b in the H planetary gear train 14, too. The ring gear 14c is disposed for meshing with the outer peripheral side planet gears 14e 1 of the planet gears 14e 1, 14e2 whose axes are supported by the carrier 14b. As described above, the inner peripheral side planet gears 14e1 mesh with the sun gear 14a whereas the outer peripheral side planet gears 14C2 mesh with the ring gear 14c. Addition ally, the inner peripheral side planet gears 14e 1 and the outer peripheral side planet gears 14e2 mesh with each other. In other words, each of the inner peripheral side planet gears 14e1 meshes with the sun gear 14a and one of the outer peripheral side planet gears 14e2. On the other hand, each of the outer peripheral planet gears 14e2 meshes with the ring gear 14c and one of the inner peripheral side planet gears 14e 1. As described above, the H planetary gear train 14 is a double planetary type planetary gear train composed of two groups of the planetgears 14e 1, 14e2. With the configuration, the output rotational direction can be reversed. Clutch and Power Transmission Path The L clutch 12a is configured to directly connect the input shaft 11 and the intermediate shaft 21. As illustrated in FIG. 3(a), power is thereby directly transmitted to the intermediate shaft 21 from the input shaft 11 via the L clutch 12a in the activation (i.e., clutch connection) of the L clutch 12a. In this case, the reduction ratio is set to be The M clutch 12b selectively joins the sun gear 13a of the M planetary gear train 13 and a casing (fixation part) of the front-stage transmission section. As illustrated in FIG. 3(b), after inputted into the carrier 13.b of the Mplanetary gear train 13 connected to the input shaft 11, power is transmitted to the intermediate shaft 21 from the ring gear 13c through the
10 7 planet gears 13e whose axes are supported by the carrier 13b in the activation (i.e., clutch connection) of the M clutch 12b. In other words, power is inputted into the carrier 13b and is then outputted from the ring gear 13c. With the configuration, the reduction ratio will be in the activation of the M clutch 12b. The reduction ratio is less than that in the activation of the L clutch 12a (L-M inter-stage ratio is 1.348). The H clutch 12c selectively joins the ring gear 14c of the H planetary gear train 14 and the casing (fixation part) of the front-stage transmission section. As illustrated in FIG. 3(c), after inputted into the carrier 13.b of the M planetary gear train 13 connected to the input shaft 11, power is partially transmitted to the intermediate shaft 21 from the ring gear 13c of the M planetary gear train 13 without any changes in the activation (clutch connection) of the H clutch 12c. On the other hand, rest of the power inputted into the carrier 13b is transmitted to the Sun gear 14a of the H planetary gear train 14 via the carrier 14b of the H planetary gear train 14 integrated with the carrier 13b of the Mplanetary gear train 13. Then, the power is transmitted to the sun gear 13a of the M planetary gear train 13. Subsequently, the power is transmitted to the intermediate shaft 21 from the ring gear 13c of the M plan etary gear train 13. In the activation of the H clutch 12c as described above, after inputted into the carrier 13b of the Mplanetary gear train 13, power is outputted from the ring gear 13c via the carrier 14b and the Sun gear 14a of the H planetary gear train 14 and the Sun gear 13a of the M planetary gear train 13 sequentially. Accordingly, the reduction ratio is set to be 0.556, which is less than that in the activation of the M clutch (M-H inter stage ratio is 1.335). Rear-Stage Transmission Section 20 The rear-stage transmission section 20 includes the inter mediate shaft 21, a first-speed clutch (low-speed clutch) 22a, a second-speed clutch (middle-speed clutch) 22b, a third speed clutch (high-speed clutch) 22c, a reverse clutch 22d, a first-speed planetary gear train (third planetary gear train) 23, a second-speed planetary gear train (fourth planetary gear train) 24, a reverse planetary gear train (fifth planetary gear train) 25 and the output shaft 26. The intermediate shaft 21 is interposed between the input shaft 11 and the output shaft 26. The intermediate shaft 21 transmits power, outputted from the front-stage transmission section, to the rear-stage transmission section 20. The first-speed clutch 22a is disposed in the closest position to the output side in the rear-stage transmission section 20. The second-speed clutch 22b is disposed between the third-speed clutch 22c and the reverse clutch 22d. The third-speed clutch 22c is disposed in the closest position to the input side in the rear-stage transmission section 20. The reverse clutch 22d is disposed between the first-speed clutch 22a and the second speed clutch 22b. The output shaft 26 is disposed in the most downstream position of the power transmission path in the transmission 1. The output shaft 26 outputs power, transmit ted thereto from the input shaft 11 via the intermediate shaft 21, to the downstream. First-Speed Planetary Gear Train 23 The first-speed planetary gear train (third planetary gear train) 23 is a single planetary type planetary gear train. The first-speed planetary gear train 23 is disposed in the closest position to the output side in the rear-stage transmission sec tion 20. The first-speed planetary gear train 23 is mainly composed of a Sun gear 23a, a carrier 23b, a ring gear 23c and a plurality of planet gears 23e. The sun gear 23a is disposed on the outer peripheral side of the intermediate shaft 21. The sun gear 23a is also disposed in the most radial inward position of the first-speed planetary gear train 23. The carrier 23b rotatably supports the planet gears 23e roughly equally spaced apart from each other in the circum ferential direction. The respective planet gears 23e mesh with the sun gear 23a. In the present embodiment, the carrier 23b is fixed to the output shaft 26. With the structure, power of the rear-stage transmission section 20 is outputted to the output shaft 26 from the carrier 23b. The ring gear 23c meshes with the planet gears 23e whose axes are supported by the carrier 23b. Second-Speed Planetary Gear Train 24 The second-speed planetary gear train (fourth planetary gear train) 24 is a single planetary type planetary gear train. The second-speed planetary gear train 24 is disposed in the closest position to the inputside of the rear-stage transmission section 20. The second-speed planetary gear train 24 is mainly composed of a Sun gear 24a, a carrier 24b, a ring gear 24c and a plurality of planet gears 24e. The Sun gear 24a is disposed on the outer peripheral side of the intermediate shaft 21. The Sun gear 24a is also disposed in the most radial inward position of the second-speed planetary gear train 24. The carrier 24b rotatably supports the planet gears 24e roughly equally spaced apart from each other in the circum ferential direction. The respective planet gears 24e mesh the Sun gear 24a. In the present embodiment, the carrier 24b adjoins a carrier 25b of the reverse planetary gear train 25 in the axial direction. The carrier 24b is also integrated with the carrier 25b. The ring gear 24c meshes with the planet gears 24e whose axes are supported by the carrier 24b. Reverse Planetary Gear Train 25 The reverse planetary gear train (fifth planetary gear train) 25 is a double planetary type planetary gear train. The reverse planetary gear train 25 is interposed between the first-speed planetary gear train 23 and the second-speed planetary gear train 24 in the rear-stage transmission section 20. The reverse gear train 25 is mainly composed of a Sun gear 25a, the carrier 25b, a ring gear 25c, a plurality of inner peripheral side planet gears 25e 1 and a plurality of outer peripheral side planetgears 25e2. The sun gear 25a is disposed on the outer peripheral side of the intermediate shaft 21. The sun gear 25a is also disposed in the most radial inward position of the reverse planetary gear train 25. The carrier 25b rotatably supports the inner peripheral side planet gears 25e 1 roughly equally spaced apart from each other in the circumferential direction and the outer peripheral side planet gears 25e2 roughly equally spaced apart from each other in the circumferential direction. The respective inner peripheral side planetgears 25e 1 mesh with the Sun gear 25a. In the present embodiment, the carrier 25b is integrated with and axially adjoins the carrier 24b of the second-speed planetary gear train 24 as described above. Furthermore, the carrier 25b is also integrally and rotatably coupled to the ring gear 23 of the first-speed planetary gear train 23.
11 9 The ring gear 25c meshes with the outer peripheral side planet gears 25e2 whose axes are Supported by the carrier 25b. As described above, the inner peripheral side planet gears 25e1 mesh with the sun gear 25a whereas the outer peripheral side planet gears 25e2 mesh with the ring gear 25c. Further more, the inner peripheral side planetgears 25e1 and the outer peripheral side planet gears 25e2 mesh with each other. In other words, each of the inner peripheral side planet gears 25e1 meshes with the sun gear 25a and one of the outer peripheral side planet gears 25e2. On the other hand, each of the outer peripheral side planet gears 25e2 meshes with the ring gear 25c and one of the inner peripheral side planetgears 25e1. As described above, the reverse planetary gear train 25 is a double planetary type planetary gear train composed of two groups of the planet gears 25e 1, 25e2. With the structure, power for reversely moving the vehicle can be transmitted by reversing the output rotational direction. Clutch and Power Transmission Path The first-speed clutch 22a selectively joins the ring gear 23c of the first-speed planetary gear train 23 and a casing (fixation part) of the rear-stage transmission section 20. In the activation (clutch connection) of the first-speed clutch 22a. power is transmitted to the carrier 23b from the sun gear 23a of the first-speed planetary gear train 23 connected to the intermediate shaft 21 via the planet gears 23e. The power, transmitted to the carrier 23b, is then transmitted to the output shaft 26. Note in the activation of the first-speed clutch 22a, forward first to third speed change stages (F1 to F3) can be achieved by the combination of the aforementioned activa tions of the L, M and H clutches 12a, 12b and 12c. FIG. 4 illustrates example speed change ratios of the case. Specifi cally, the speed change ratios of F1, F2 and F3 can be set to 5.091,3,780 and 2.830, respectively. As shown in FIG.4, the inter-stage ratio F1/F2 is herein whereas the inter-stage ratio F2/F3 is The second-speed clutch 22b selectively joins the ring gear 24c of the second-speed planetary gear train 24 to the casing (fixation part) of the rear-stage transmission section 20. In the activation (i.e., clutch connection) of the second-speed clutch 22b, the power inputted into the intermediate shaft 21 is partially transmitted from the Sun gear 24a of the second speed planetary gear train 24 to the carrier 25b integrated with the carrier 24b via the planet gears 24e. Then the partially transmitted power is transmitted to the carrier 23b of the first-speed planetary gear train 23 via the ring gear 23c and the planet gears 23e. Finally, the partially transmitted power is transmitted to the output shaft 26. Simultaneously, the rest of power is transmitted from the sun gear 23a of the first-speed planetary gear train 23 to the carrier 23b via the planet gears 23e. Thus transmitted power is then transmitted to the output shaft 26. In the activation of the second-speed clutch 22b, forward fourth to sixth speed change stages (F4 to F6) can beachieved by the combination of the aforementioned activations of the L, M and H clutches 12a, 12b and 12c. FIG. 4 shows example speed change ratios of the case. Specifically, the speed change ratios off4, F5 and F6 can be set to be 2.163, and 1.203, respectively. As shown in FIG. 4, the inter-stage ratios F3/F4. F4/F5 and F5/F6 are herein 1.308, and 1.335, respec tively. The third-speed clutch 22c selectively joins the intermedi ate shaft 21 and the carrier 24b of the second-speed planetary gear train 24. In the activation (i.e., clutch connection) of the third-speed clutch 22c, power inputted into the intermediate shaft 21 is partially transmitted from the carrier 25b inte grated with the carrier 24b of the second-speed planetary gear train 24 to the carrier 23b of the first-speed planetary gear train 23 via the ring gear 23c and the planet gears 23e. The partially transmitted power is then transmitted to the output shaft 26. Simultaneously, the rest of power is transmitted from the Sun gear 23a of the first-speed planetary gear train 23 to the carrier 23b via the planet gears 23e. Thus transmitted power is then transmitted to the output shaft 26. In the activation of the third-speed clutch 22c, forward seventh to ninth speed change stages (F7 to F9) can be achieved by the combination of the aforementioned L. Mand H clutches 12a, 12b and 12c. FIG. 4 shows example speed change ratios of the case. Specifically, the speed change ratios of F7, F8 and F9 can be set to be 1.000, and 0.556, respectively. As shown in FIG. 4, the inter-stage ratios F6/F7. F7/F8 and F8/F9 are herein 1.203, and 1.335, respec tively. The reverse clutch 22d selectively joins the ring gear 25c of the reverse planetary gear train 25 and the casing (fixation part) of the rear-stage transmission section 20. In the activa tion (i.e., clutch connection) of the reverse clutch 22d, power inputted into the intermediate shaft 21 is transmitted from the sun gear 25a of the reverse planetary gear train 25 to the carrier 25b via the planet gears 25e. The power is then trans mitted to the carrier 23b of the first-speed planetary gear train 23 via the ring gear 23c and the planet gears 23e. Thus transmitted power is then transmitted to the output shaft26. In the activation of the reverse clutch 22d, reverse first to third speed change stages (R1 to R3) can be achieved by the com bination of the aforementioned activations of the L, M and H clutches 12a, 12b and 12c. FIG. 4 shows example speed change ratios of the case. Specifically, the speed change ratios of R1,R2 and R3 can be set to be , and , respectively. As shown in FIG. 4, the inter-stage ratio R1/R2 is herein whereas the inter-stage ratio R2/R3 is Characteristics of Transmission 1 and Front-Stage Transmission Section (1) In the front-stage transmission section of the present embodiment, both of the carrier 13b of the M planetary gear train 13 and the carrier 14b of the H planetary gear train 14 are connected to the input shaft 11. Additionally, the ring gear 13c of the M planetary gear train 13 is connected to the interme diate shaft 21. With the structure, it is possible to achieve a configuration that power is inputted into the carrier 13b from the input shaft 11 and the inputted power is outputted from the ring gear 13e in the activation of the Mand H clutches 12b, 12c. Therefore, the reduction ratios can be all set to be equal to or less than with the combination of the aforementioned two plan etary gear trains in the activations of the L, M and H clutches 12a, 12b and 12c. Consequently, the large amount of torque is not transmitted to the intermediate shaft 21 on the outputside, and the structure of the transmission 1 can be simplified. Furthermore, the inter-stage ratios among H. M and L can be roughly the same using the structures of the M and H planetary gear trains 13, 14 and the relation between input power and output power, as described above. Accordingly, the speed change stages, composed of nine forward stages and three reverse stages, can be easily provided by the combina tion of the M and H planetary gear trains 13, 14 and the rear-stage transmission section 20 that is disposed on the rear-stage side and includes three forward Stages and one reverse stage.
12 11 (2) In the transmission 1 of the present embodiment, the rear-stage transmission section 20 is disposed on the output side of the aforementioned front-stage transmission section, as illustrated in FIGS. 1 and 2. The rear-stage transmission section 20 includes a clutch mechanism having the first speed, second-speed, third-speed and reverse clutches 22a. 22b. 22c and 22d, and the first-speed, the second-speed and reverse planetary gear trains 23, 24 and 25. With the structure, the inter-stage ratios among three speed change stages (L, M and H) can be set to be roughly the same in the front-stage transmission section. Consequently, it is possible to easily form the multi-stage (i.e., nine forward stages and three reverse stages) transmission 1 with equal inter-stage ratios in a compact size only by combining the front-stage transmission section with the rear-stage trans missions section 20 that provides three forward stages and one reverse stage. (3) In the transmission 1 of the present embodiment, the reverse clutch 22d and the reverse planetary gear train 25 are disposed closer to the input side than the first-speed clutch 22a and the first-speed planetary gear train 23 are. It is pos sible to prevent the reduction ratios of the speed change stages from having unduly large values in the reverse travel of the vehicle, compared to a transmission having a structure that the reverse clutch and the like are disposed in the closest position to the outputside. Consequently, the travel speed and the travel torque can be appropriately set when the vehicle reversely travels. Other Embodiments As described above, an embodiment of the present inven tion has been explained. However, the present invention is not limited to the aforementioned embodiment. A variety of changes are possible without departing from the scope of the present invention. (A) In the aforementioned embodiment, a configuration has been exemplified that the third speed clutch 22c, a col lection of the second-speed clutch 22b and the second-speed planetary gear train 24, a collection of the reverse clutch 22d and the reverse planetary gear train 25, and a collection of the first-speed clutch 22a and the first-speed planetary gear train 23 are disposed in this sequential order from the front-stage side as components forming the rear-stage transmission sec tion 20 disposed on the rear side of the front-stage transmis sion section. However, the present invention is not limited to the configuration. In short, a transmission section, having other configura tion, may be combined with the front-stage transmission sec tion as the rear-stage transmission section. For example, a transmission of the present invention may be a transmission 0 illustrated in FIG. 5. The transmission 0 is configured to transmit power from an intermediate shaft 31 to an output shaft 36. The transmission 0 includes a rear-stage transmission section 30. The rear-stage transmis sion section 30 has a configuration that a third-speed clutch 32c, a collection of a second-speed clutch 32b and a second speed planetary gear train 34, a collection of a first-speed clutch 32a and a first-speed planetary gear train 33, and a collection of a reverse clutch 32d and a reverse planetary gear train 35 are sequentially disposed in this order from the front stage side. In the transmission 0 illustrated in FIG. 5, the first-speed planetary gear train 33 is selectively joined to the first clutch 32a. The first-speed planetary gear train 33 includes a sun gear 33a, a carrier 33b, a plurality of planet gears 33e rotat ably supported by the carrier 33b, and a ring gear 33c On the other hand, the second-speed planetary gear train 34 is selectively joined to the second clutch 32b. The second speed planetary gear train34 includes a Sun gear 34a, a carrier 34b, a plurality of planet gears 34e rotatably supported by the carrier 34b, and a ring gear 34c. Further, the reverse planetary gear train 35 is selectively joined to the reverse clutch 32d. The reverse planetary gear train 35 includes a sun gear 35a, a carrier 35b, a plurality of planet gears 35e rotatably supported by the carrier 35b, and a ring gear 35c. Furthermore, the ring gear 33c, the carrier 34b and the sun gear 35a are coupled to the intermediate shaft 31 through the third-speed clutch 32c. On the other hand, the sun gears 33a, 34a are integrally and rotatably coupled to each other. The carriers 33b, 35b are coupled to the output shaft 36. Further, the first-speed clutch 32a couples/uncouples the ring gear 33c from a casing (fixation part). The second-speed clutch 32b couples/uncouples the ring gear 34c from the casing (fixation part). The third-speed clutch 32c couples the intermediate shaft 31 to the carrier 34b. The reverse clutch 32d couples the ring gear 35c to the case (fixation part). In this case, the reverse planetary gear train 35 and the like are positioned in the closest position to the rear-stage side. It is thereby possible to sufficiently ensure traction force by Substantially increasing the reduction ratio of the reverse first-speed Stage. As a result, the present example embodi ment can be applied to a type of vehicle that requires traction force in the reverse traveling. (B) In the aforementioned embodiment, the setting has been exemplified that the H, M and L reduction ratios of the front-stage transmission section are set to be 0.556, and 1.000, respectively. However, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, the reduction ratios can be set to be greater/ less than the above values as long as the inter-stage ratios H/M and M/L can be roughly the same based on the reduction ratios. (C) In the aforementioned embodiment, a configuration has been exemplified that the rear-stage transmission section 20 provides three forward stages and one reverse stage. How ever, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, a further multi-stage transmission section, providing four forward stages and one reverse stage, may be combined with the front-stage transmission section as the rear-stage transmission section. In this case, it is possible to obtain a further multi-stage gearbox that provides 12 forward stages and three reverse stages as a whole. (D) In the aforementioned embodiment, the transmission 1 of the present invention has been explained with an example case that it is installed in a dump truck. However, application of the present invention is not limited to this. For example, the transmission 1 may be installed in a construction vehicle such as a wheel loader. Alternatively, it may be installed in any other working vehicles. According to the planetary gear type gearbox of the above embodiments, a multi-stage gear train with a simple structure can be produced by inhibiting torque to be transmitted to a rear-stage transmission section without increasing the size of gears to be disposed in the rear stage or adding an extra component such as a speedup gear. Therefore, the planetary gear type gearbox of the above embodiments can be widely applied to the general vehicles configured to travel while the travel speed or the traction force are changed by shifting a plurality of speed change stages back and forth.
13 13 The invention claimed is: 1. A planetary gear type gearbox comprising: a front-stage transmission section including an input shaft to which power is inputted; and a rear-stage transmission section including an intermediate shaft coupled to the front-stage transmission section and an output shaft for outputting power, the front-stage transmission section including a first planetary gear train having a first Sun gear, a plurality of first planet gears meshing with the first Sun gear, a first carrier connected to the input shaft with the first carrier rotatably supporting the first planet gears, and a first ring gear connected to the intermediate shaft with the first ring gear meshing with the first planet gears, a second planetary gear train having a second Sun gear integrally and rotatably coupled to the first Sun gear, a plurality of inner peripheral side second planet gears meshing with the second Sun gear, a plurality of outer peripheral side second planet gears meshing with the inner peripheral side second planet gears, a second carrier connected to the input shaft with the second carrier rotatably supporting the inner peripheral side second planet gears and the outer peripheral side sec ond planetgears, and a second ring gear meshing with the outer peripheral side second planet gears, a first clutch configured to selectively couple?uncouple the input shaft and the intermediate shaft, a second clutch configured to selectively allow/prevent rotation of the second Sun gear, and a third clutch configured to selectively allow/prevent rotation of the second ring gear. 2. The planetary gear type gearbox according to claim 1, an output side of the second planetary gear train is con nected to the intermediate shaft through the first plan etary gear train. 3. The planetary gear type gearbox according to claim 1, a speedup ratio of the second planetary gear train is greater than that of the first planetary gear train. 4. The planetary gear type gearbox according to claim 1, the rear-stage transmission section is a transmission for providing three forward stages and one reverse stage, the forward stages including a low-speed stage, a middle speed stage and a high-speed stage, and the rear-stage transmission section including a third planetary gear train having a third Sun gear, a plurality of third planet gears meshing with the third Sun gear, a third carrier coupled to the output shaft with the third carrier rotatably supporting the third planet gears, and a third ring gear meshing with the third planet gears, a fourth planetary gear train having a fourth Sun gear, a plurality of fourth planet gears meshing with the fourth Sun gear, a fourth carrier rotatably supporting the fourth planetgears, and a fourth ring gear meshing with the fourth planet gears, a fifth planetary gear train having a fifth Sun gear, a plurality of fifth planet gears meshing with the fifth Sun gear, a fifth carrier rotatably supporting the fifth planet gears, and a fifth ring gear meshing with the fifth planet gears, a low-speed clutch configured to selectively allow/pre vent rotation of the third ring gear, a middle-speed clutch configured to selectively allow/ prevent rotation of the fourth ring gear, a high-speed clutch configured to selectively couple/ uncouple the intermediate shaft and the fourth carrier and selectively couple?uncouple the intermediate shaft and the fifth carrier, and a reverse clutch configured to selectively allow/prevent rotation of the fifth ring gear. 5. The planetary gear type gearbox according to claim 4. the third Sun gear, the fourth Sun gear and the fifth Sun gear are all coupled to the intermediate shaft. 6. The planetary gear type gearbox according to claim 4. the fifth planetgears includes a plurality of inner peripheral side fifth planet gears and a plurality of outer peripheral side planet gears, the inner peripheral side fifth planet gears meshing with the fifth Sun gear, and the outer peripheral side fifth planet gears meshing with the fifth ring gear. 7. The planetary gear type gearbox according to claim 4. the third ring gear, the fourth carrier and the fifth carrier are integrally and rotatably coupled to each other. 8. The planetary gear type gearbox according to claim 1, the rear-stage transmission section is a transmission for providing three forward stages and one reverse stage, the forward Stages including a low-speed stage, a middle speed stage and a high-speed stage, and the rear-stage transmission section including a third planetary gear train having a third sun gear, a plurality of third planet gears meshing with the third Sun gear, a third carrier coupled to the output shaft with the third carrier rotatably supporting the third planet gears, and a third ring gear meshing with the third planet gears, a fourth planetary gear train having a fourth Sun gear, a plurality of fourth planet gears meshing with the fourth Sun gear, a fourth carrier rotatably supporting the fourth planetgears, and a fourth ring gear meshing with the fourth planet gears, a fifth planetary gear train having a fifth Sun gear, a plurality of fifth planet gears meshing with the fifth sun gear, a fifth carrier coupled to the output shaft with the fifth carrier rotatably supporting the fifth planet gears, and a fifth ring gear meshing with the fifth planet gears, a low-speed clutch configured to selectively allow/pre vent rotation of the third ring gear, a middle-speed clutch configured to selectively allow/ prevent rotation of the fourth ring gear, a high-speed clutch configured to selectively couple/ uncouple the intermediate shaft and the fourth carrier, and a reverse clutch configured to selectively allow/prevent rotation of the fifth ring gear. 9. The planetary gear type gearbox according to claim 8. the third Sun gear and the fourth Sun gear are coupled to the intermediate shaft.. The planetary gear type gearbox according to claim 8. the third ring gear, the fourth carrier and the fifth Sun gear are integrally and rotatably coupled to each other. k k k k k
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O181130A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0181130 A1 Fukunaga (43) Pub. Date: Jul.19, 2012 (54) TORQUE CONVERTER Publication Classification 51) Int.
(19) United States US 2012O181130A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0181130 A1 Fukunaga (43) Pub. Date: Jul.19, 2012 (54) TORQUE CONVERTER Publication Classification 51) Int.
Phillips (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 10, (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search
 (12) United States Patent US008747274B2 () Patent No.: Phillips () Date of Patent: Jun., 2014 (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search TRANSMISSION USPC... 74/3, 331; 475/207
(12) United States Patent US008747274B2 () Patent No.: Phillips () Date of Patent: Jun., 2014 (54) TRIPLE CLUTCH MULTI-SPEED (58) Field of Classification Search TRANSMISSION USPC... 74/3, 331; 475/207
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0130234A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0130234 A1 Phillips (43) Pub. Date: (54) THREE-MODE HYBRID POWERTRAIN (52) U.S. Cl.... 475/5: 903/911 WITH
(19) United States US 2011 0130234A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0130234 A1 Phillips (43) Pub. Date: (54) THREE-MODE HYBRID POWERTRAIN (52) U.S. Cl.... 475/5: 903/911 WITH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0377323A1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0377323 A1 KOIKE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) GEARED MOTOR Publication Classification (71)
(19) United States US 2015.0377323A1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0377323 A1 KOIKE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) GEARED MOTOR Publication Classification (71)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0312869A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0312869 A1 WALTER (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016 (54) CVT DRIVE TRAIN Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2016.0312869A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0312869 A1 WALTER (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016 (54) CVT DRIVE TRAIN Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
IIIHIIII 5,509,863. United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. Apr. 23, Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent:
 United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. 54) TRANSMISSION DEVICE, ESPECIALLY FOR BOAT MOTORS 75 Inventors: Staffan Månsson, Hjalteby; Benny Hedlund, Hönö, both of Sweden 73 Assignee: AB Volvo Penta, Gothenburg,
United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. 54) TRANSMISSION DEVICE, ESPECIALLY FOR BOAT MOTORS 75 Inventors: Staffan Månsson, Hjalteby; Benny Hedlund, Hönö, both of Sweden 73 Assignee: AB Volvo Penta, Gothenburg,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070060439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0060439 A1 Kamada et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (75) Inventors: Shinya Kamada, Hiroshima
(19) United States US 20070060439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0060439 A1 Kamada et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (75) Inventors: Shinya Kamada, Hiroshima
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7246672B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,246,672 B2 Shirai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 24, 2007 (54) HYBRID-VEHICLE POWER TRAIN 6,007.443 A * 12/1999 Onimaru et al.... 475/5 6,344,008
(12) United States Patent USOO7246672B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,246,672 B2 Shirai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 24, 2007 (54) HYBRID-VEHICLE POWER TRAIN 6,007.443 A * 12/1999 Onimaru et al.... 475/5 6,344,008
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
United States Patent (19) Muranishi
 United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1. Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002
 USOO6435993B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1 Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) HYDRAULIC CHAIN TENSIONER WITH 5,707.309 A 1/1998 Simpson... 474/110 VENT DEVICE AND
USOO6435993B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1 Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) HYDRAULIC CHAIN TENSIONER WITH 5,707.309 A 1/1998 Simpson... 474/110 VENT DEVICE AND
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,215,503 B2. Appel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 10, 2012
 US008215503B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,215,503 B2 Appel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 10, 2012 (54) CRANE WITH TELESCOPIC BOOM 3,921,819 A * 1 1/1975 Spain... 212,349 4,394,108
US008215503B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,215,503 B2 Appel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 10, 2012 (54) CRANE WITH TELESCOPIC BOOM 3,921,819 A * 1 1/1975 Spain... 212,349 4,394,108
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 US 20170 1384.50A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0138450 A1 HART et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TWIN AXIS TWIN-MODE CONTINUOUSLY (52) U.S. Cl. VARABLE TRANSMISSION
US 20170 1384.50A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0138450 A1 HART et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TWIN AXIS TWIN-MODE CONTINUOUSLY (52) U.S. Cl. VARABLE TRANSMISSION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
(19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8384329B2 (12) United States Patent Natsume (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) WIPER SYSTEMAND WIPER CONTROL METHOD Inventor: Takashi Natsume, Toyohashi (JP) Assignee: ASMO Co.,
USOO8384329B2 (12) United States Patent Natsume (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) WIPER SYSTEMAND WIPER CONTROL METHOD Inventor: Takashi Natsume, Toyohashi (JP) Assignee: ASMO Co.,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0139355A1 Lee et al. US 2013 O1393.55A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) HINGEMECHANISMAND FOLDABLE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0139355A1 Lee et al. US 2013 O1393.55A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) HINGEMECHANISMAND FOLDABLE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US00893 1520B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,931,520 B2 Fernald (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 2015 (54) PIPE WITH INTEGRATED PROCESS USPC... 138/104 MONITORING (58) Field of Classification
(12) United States Patent US00893 1520B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,931,520 B2 Fernald (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 2015 (54) PIPE WITH INTEGRATED PROCESS USPC... 138/104 MONITORING (58) Field of Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO698.1746B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,981,746 B2 Chung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 2006 (54) ROTATING CAR SEAT MECHANISM 4,844,543 A 7/1989 Ochiai... 297/344.26 4,925,227
(12) United States Patent USOO698.1746B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,981,746 B2 Chung et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 3, 2006 (54) ROTATING CAR SEAT MECHANISM 4,844,543 A 7/1989 Ochiai... 297/344.26 4,925,227
US 7, B2. Loughrin et al. Jan. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: and/or the driven component. (12) United States Patent (54) (75)
 USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,511,619 B2
 USOO851 1619B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,511,619 B2 Mann (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2013 (54) SLAT DEPLOYMENT MECHANISM (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Alan Mann, Bristol
USOO851 1619B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,511,619 B2 Mann (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2013 (54) SLAT DEPLOYMENT MECHANISM (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Alan Mann, Bristol
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 201001 01228A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0101228A1 Bartosch et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) DRIVE TRAN COMPRISING AN EXPANDER
(19) United States US 201001 01228A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0101228A1 Bartosch et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) DRIVE TRAN COMPRISING AN EXPANDER
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Imai USOO6581225B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,581,225 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2003 (54) MATTRESS USED FOR PREVENTING BEDSORES OR THE LIKE (76) Inventor: KaZumichi Imai, 7-29-1222,
(12) United States Patent Imai USOO6581225B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,581,225 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2003 (54) MATTRESS USED FOR PREVENTING BEDSORES OR THE LIKE (76) Inventor: KaZumichi Imai, 7-29-1222,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0157272 A1 Uhler et al. US 2009015.7272A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) FOUR-PASSAGE MULTIFUNCTION TOROUE CONVERTER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0157272 A1 Uhler et al. US 2009015.7272A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) FOUR-PASSAGE MULTIFUNCTION TOROUE CONVERTER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080264.753A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0264753 A1 Rollion et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2008 (54) FRICTIONAL CLUTCH WITH O-RING Publication Classification
US 20080264.753A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0264753 A1 Rollion et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2008 (54) FRICTIONAL CLUTCH WITH O-RING Publication Classification
% Y 2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 30, Tanaka et al.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0216645 A1 Tanaka et al. US 20120216645A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 30, 2012 (54) WORM WHEEL (75) Inventors: Yosuke Tanaka, Saitama
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0216645 A1 Tanaka et al. US 20120216645A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 30, 2012 (54) WORM WHEEL (75) Inventors: Yosuke Tanaka, Saitama
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. Kobayashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009
 US 20090062784A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0062784 A1 Kobayashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) NEEDLEELECTRODE DEVICE FOR (30) Foreign Application
US 20090062784A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0062784 A1 Kobayashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) NEEDLEELECTRODE DEVICE FOR (30) Foreign Application
Patent Application Publication Nov. 27, 2014 Sheet 1 of 7 US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0346290 A1 YOSHIDA et al. US 20140346290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) SLIDING TYPE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0346290 A1 YOSHIDA et al. US 20140346290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) SLIDING TYPE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6989498B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,989,498 B1 Linder et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2006 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR LOCKING (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent USOO6989498B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,989,498 B1 Linder et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2006 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR LOCKING (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Hozumi et al. 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,889,164 Dec. 26, 1989 54). SOLENOID CONTROLLED WALVE (75 Inventors: Kazuhiro Hozumi; Masaru Arai, both of Chiba; Yoshitane
United States Patent (19) Hozumi et al. 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,889,164 Dec. 26, 1989 54). SOLENOID CONTROLLED WALVE (75 Inventors: Kazuhiro Hozumi; Masaru Arai, both of Chiba; Yoshitane
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2
 US007592736 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2 Scott et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 2009 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ELECTRIC (56) References Cited GENERATOR WITH ROTOR CIRCUMIFERENTIALLY
US007592736 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2 Scott et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 2009 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ELECTRIC (56) References Cited GENERATOR WITH ROTOR CIRCUMIFERENTIALLY
(12) United States Patent
 US007594759B2 (12) United States Patent Kawaguchi et al. (54) OBLIQUE CONTACT DOUBLE ROW BALL BEARING AND METHOD OF IMPARTING PRELOAD IN THE BALL BEARNG (75) Inventors: Toshihiro Kawaguchi, Osaka (JP);
US007594759B2 (12) United States Patent Kawaguchi et al. (54) OBLIQUE CONTACT DOUBLE ROW BALL BEARING AND METHOD OF IMPARTING PRELOAD IN THE BALL BEARNG (75) Inventors: Toshihiro Kawaguchi, Osaka (JP);
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2. Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005
 United States Patent USOO6915721B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2 Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) CORDLESS RATCHET WRENCH 6,311,583 B1 11/2001 Izumisawa... 81/57.13 6,715,380
United States Patent USOO6915721B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2 Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) CORDLESS RATCHET WRENCH 6,311,583 B1 11/2001 Izumisawa... 81/57.13 6,715,380
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007884512B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,884,512 B2 Horng et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 8, 2011 (54) FIXING STRUCTURE FOR PRINTED (56) References Cited CIRCUIT BOARD OF MICRO MOTOR
(12) United States Patent US007884512B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,884,512 B2 Horng et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 8, 2011 (54) FIXING STRUCTURE FOR PRINTED (56) References Cited CIRCUIT BOARD OF MICRO MOTOR
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fujita 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,727,957 Mar. 1, 1988 (54) RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATOR FOR MUFFLER 75 Inventor: Akio Fujita, Fujisawa, Japan 73) Assignee: Bridgestone
United States Patent (19) Fujita 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,727,957 Mar. 1, 1988 (54) RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATOR FOR MUFFLER 75 Inventor: Akio Fujita, Fujisawa, Japan 73) Assignee: Bridgestone
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (22) Filed: Jul. 16, 2010 rotatable relative to the stator.
 (19) United States US 0100 1311A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 01/001311 A1 Chamberlin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 01 (54) ELECTRIC MOTOR HAVING A SELECTIVELY ADJUSTABLE BASE
(19) United States US 0100 1311A1 (1) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 01/001311 A1 Chamberlin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 01 (54) ELECTRIC MOTOR HAVING A SELECTIVELY ADJUSTABLE BASE
United States Patent (19) Kitami et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kitami et al. 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,846,768 Jul. 11, 1989 (54) VARIABLE-SPEED DRIVING DEVICE 75) Inventors: Yasuo Kitami; Hidenori Tezuka; 73 Assignee: Syuji
United States Patent (19) Kitami et al. 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,846,768 Jul. 11, 1989 (54) VARIABLE-SPEED DRIVING DEVICE 75) Inventors: Yasuo Kitami; Hidenori Tezuka; 73 Assignee: Syuji
United States Patent (19) Koitabashi
 United States Patent (19) Koitabashi 54 75 (73) 1 (51) (5) (58 56) ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH WITH AN IMPROVED MAGNETC ROTATABLE MEMBER Inventor: Takatoshi Koitabashi, Annaka, Japan Assignee: Sanden Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Koitabashi 54 75 (73) 1 (51) (5) (58 56) ELECTROMAGNETIC CLUTCH WITH AN IMPROVED MAGNETC ROTATABLE MEMBER Inventor: Takatoshi Koitabashi, Annaka, Japan Assignee: Sanden Corporation,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
(12) United States Patent
 US007307230B2 (12) United States Patent Chen (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,307,230 B2 Dec. 11, 2007 (54) MECHANISM FOR CONTROLLING CIRCUITCLOSINGAOPENING OF POWER RATCHET WRENCH (75) Inventor:
US007307230B2 (12) United States Patent Chen (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,307,230 B2 Dec. 11, 2007 (54) MECHANISM FOR CONTROLLING CIRCUITCLOSINGAOPENING OF POWER RATCHET WRENCH (75) Inventor:
Earl Sch yang y Lee, 5,457,342 10/1995 Herbst, II /712
 US005920264A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM PROTECTION 5,189,314 2/1993 Georgiou et al.... 307/271 DEVICE 5,287.292 2/1994
US005920264A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM PROTECTION 5,189,314 2/1993 Georgiou et al.... 307/271 DEVICE 5,287.292 2/1994
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US B1
 USOO7628442B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Spencer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 2009 (54) QUICK RELEASE CLAMP FOR TONNEAU (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/100.04, COVER 296/100.07,
USOO7628442B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Spencer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 8, 2009 (54) QUICK RELEASE CLAMP FOR TONNEAU (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/100.04, COVER 296/100.07,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0041841 A1 Huazhao et al. US 20140041841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (62) (30) MICRO-CHANNEL HEAT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0041841 A1 Huazhao et al. US 20140041841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (62) (30) MICRO-CHANNEL HEAT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0340205 A1 CHUAH US 2013 0340205A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) BABY STROLLER FOLDING MECHANISM Inventor:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0340205 A1 CHUAH US 2013 0340205A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) BABY STROLLER FOLDING MECHANISM Inventor:
3 23S Sé. -Né 33% (12) United States Patent US 6,742,409 B2. Jun. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: 6B M 2 O. (51) Int. Cl...
 (12) United States Patent Blanchard USOO6742409B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 2004 (54) DEVICE FORTRANSMISSION BETWEEN A PRIMARY MOTOR SHAFT AND AN OUTPUT SHAFT AND LAWN MOWER PROVIDED
(12) United States Patent Blanchard USOO6742409B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 2004 (54) DEVICE FORTRANSMISSION BETWEEN A PRIMARY MOTOR SHAFT AND AN OUTPUT SHAFT AND LAWN MOWER PROVIDED
United States Patent (19) Ochi et al.
 United States Patent (19) Ochi et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,945,272 Jul. 31, 1990 54 ALTERNATOR FORMOTOR VEHICLES 75 Inventors: Daisuke Ochi; Yasuhiro Yoshida; Yoshiyuki Iwaki, all of
United States Patent (19) Ochi et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,945,272 Jul. 31, 1990 54 ALTERNATOR FORMOTOR VEHICLES 75 Inventors: Daisuke Ochi; Yasuhiro Yoshida; Yoshiyuki Iwaki, all of
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9671 011B2 (12) United States Patent Kimijima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,671,011 B2 Jun. 6, 2017 (54) WORM BIASING STRUCTURE (71) Applicant: Showa Corporation, Gyoda-shi (JP)
USOO9671 011B2 (12) United States Patent Kimijima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,671,011 B2 Jun. 6, 2017 (54) WORM BIASING STRUCTURE (71) Applicant: Showa Corporation, Gyoda-shi (JP)
USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999
 USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999 54 SERIALLY CONNECTED CHARGER Primary Examiner Edward H. Tso Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Rosenberger,
USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999 54 SERIALLY CONNECTED CHARGER Primary Examiner Edward H. Tso Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Rosenberger,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Ogasawara et al. (54) 75 RDING LAWN MOWER Inventors: Hiroyuki Ogasawara; Nobuyuki Yamashita; Akira Minoura, all of Osaka, Japan Assignee: Kubota Corporation, Osaka, Japan Appl.
United States Patent (19) Ogasawara et al. (54) 75 RDING LAWN MOWER Inventors: Hiroyuki Ogasawara; Nobuyuki Yamashita; Akira Minoura, all of Osaka, Japan Assignee: Kubota Corporation, Osaka, Japan Appl.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,840,124 B2
 USOO884O124B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Serhan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2014 (54) ROLLATOR HAVING ASITTO-LOCK BRAKE (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Michael Serhan, Arcadia,
USOO884O124B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Serhan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2014 (54) ROLLATOR HAVING ASITTO-LOCK BRAKE (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Michael Serhan, Arcadia,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2
 US0087.08325B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,708.325 B2 Hwang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2014 (54) PAPER CLAMPINGAPPARATUS FOR (56) References Cited OFFICE MACHINE (75) Inventors:
US0087.08325B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,708.325 B2 Hwang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2014 (54) PAPER CLAMPINGAPPARATUS FOR (56) References Cited OFFICE MACHINE (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,469,466 B1
 USOO6469466B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,469,466 B1 Suzuki (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2002 (54) AUTOMATIC GUIDED VEHICLE JP 7-2S1768 10/1995 JP 8-1553 1/1996 (75) Inventor: Takayuki
USOO6469466B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,469,466 B1 Suzuki (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2002 (54) AUTOMATIC GUIDED VEHICLE JP 7-2S1768 10/1995 JP 8-1553 1/1996 (75) Inventor: Takayuki
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8905448B2 (12) United States Patent Vaz Coelho et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,905,448 B2 Dec. 9, 2014 (54) SIZE-ADJUSTABLE, PIVOTABLE TRIPLE CONNECTION DEVICE (75) Inventors: Joao
USOO8905448B2 (12) United States Patent Vaz Coelho et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,905,448 B2 Dec. 9, 2014 (54) SIZE-ADJUSTABLE, PIVOTABLE TRIPLE CONNECTION DEVICE (75) Inventors: Joao
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9296.196B2 (12) United States Patent Castagna et al. (54) PRINTING UNITS FORVARIABLE-FORMAT OFFSET PRINTING PRESSES (71) Applicant: OMET S.r.l., Lecco (IT) (72) Inventors: Stefano Castagna, Civate
USOO9296.196B2 (12) United States Patent Castagna et al. (54) PRINTING UNITS FORVARIABLE-FORMAT OFFSET PRINTING PRESSES (71) Applicant: OMET S.r.l., Lecco (IT) (72) Inventors: Stefano Castagna, Civate
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070011840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0011840 A1 Gilli (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 18, 2007 (54) WINDSCREEN WIPER ARM (75) Inventor: Marco Gilli, Chieri
(19) United States US 20070011840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0011840 A1 Gilli (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 18, 2007 (54) WINDSCREEN WIPER ARM (75) Inventor: Marco Gilli, Chieri
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,695,581 B2
 USOO6695581B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,695,581 B2 Wass0n et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 2004 (54) COMBINATION FAN-FLYWHEEL-PULLEY JP 59-81.835 2/1984 ASSEMBLY AND METHOD OF
USOO6695581B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,695,581 B2 Wass0n et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 2004 (54) COMBINATION FAN-FLYWHEEL-PULLEY JP 59-81.835 2/1984 ASSEMBLY AND METHOD OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO64994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Matsumoto (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) STATIONARY BIKE (52) U.S. Cl.... 482/8 (76) Inventor: Masaaki Matsumoto,
(19) United States US 2005OO64994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Matsumoto (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) STATIONARY BIKE (52) U.S. Cl.... 482/8 (76) Inventor: Masaaki Matsumoto,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7654162B2 (12) United States Patent Braaten (54) DEVICE FOR INSTALLATION OF A PROBE AND PROBEACCOMMODATING ARRANGEMENT (75) Inventor: Nils A. Braaten, Trondheim (NO) (73) Assignee: Roxar ASA, Stavanger
USOO7654162B2 (12) United States Patent Braaten (54) DEVICE FOR INSTALLATION OF A PROBE AND PROBEACCOMMODATING ARRANGEMENT (75) Inventor: Nils A. Braaten, Trondheim (NO) (73) Assignee: Roxar ASA, Stavanger
United States Patent (19) Kim et al.
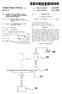 United States Patent (19) Kim et al. 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR COATING AWAFER WITH A MINIMAL LAYER OF PHOTORESIST 75 Inventors: Moon-woo Kim, Kyungki-do; Byung-joo Youn, Seoul, both of Rep. of Korea
United States Patent (19) Kim et al. 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR COATING AWAFER WITH A MINIMAL LAYER OF PHOTORESIST 75 Inventors: Moon-woo Kim, Kyungki-do; Byung-joo Youn, Seoul, both of Rep. of Korea
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Siltanen USOO6533006B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 18, 2003 (54) WINTER TIRE FOR VEHICLE, PARTICULARLY ATRACTION WINTER TIRE FOR HEAVY TRUCKS (75) Inventor: Teppo
(12) United States Patent Siltanen USOO6533006B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 18, 2003 (54) WINTER TIRE FOR VEHICLE, PARTICULARLY ATRACTION WINTER TIRE FOR HEAVY TRUCKS (75) Inventor: Teppo
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,967,934 Ishida et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 1999
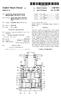 USOO5967934A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Ishida et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 1999 54 PLANETARY TRANSMISSION WITH 1,786,158 12/1930 Hawes... 475/338 X RELEASEABLE ONE WAY CLUTCH
USOO5967934A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Ishida et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 1999 54 PLANETARY TRANSMISSION WITH 1,786,158 12/1930 Hawes... 475/338 X RELEASEABLE ONE WAY CLUTCH
United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,598,045 Ohtake et al. 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 28, 1997
 US005598045A United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,598,045 Ohtake et al. 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 28, 1997 54 MINIATURE MOTOR 5,281,876 1/1994 Sato... 310/40 MM 5,294,852 3/1994 Straker... 310/68
US005598045A United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,598,045 Ohtake et al. 45) Date of Patent: Jan. 28, 1997 54 MINIATURE MOTOR 5,281,876 1/1994 Sato... 310/40 MM 5,294,852 3/1994 Straker... 310/68
United States Patent (19) Miller
 United States Patent (19) Miller 54 LAMPHOLDER FITTING WITH THREE-WAY BRIGHTNESS SOLD-STATE FLUORESCENT LAMP BALLAST 76) Inventor: Jack V. Miller, 700 N. Auburn Ave., Sierra Madre, Calif. 91024 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Miller 54 LAMPHOLDER FITTING WITH THREE-WAY BRIGHTNESS SOLD-STATE FLUORESCENT LAMP BALLAST 76) Inventor: Jack V. Miller, 700 N. Auburn Ave., Sierra Madre, Calif. 91024 21 Appl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
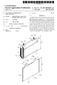 (19) United States US 2011 0183181A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0183181 A1 M00n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 28, 2011 (54) SECONDARY BATTERY HAVING NSULATION BAG (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2011 0183181A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0183181 A1 M00n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 28, 2011 (54) SECONDARY BATTERY HAVING NSULATION BAG (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7242106B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,242,106 B2 Kelly (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 10, 2007 (54) METHOD OF OPERATION FOR A (56) References Cited SE NYAVE ENERGY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent USOO7242106B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,242,106 B2 Kelly (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 10, 2007 (54) METHOD OF OPERATION FOR A (56) References Cited SE NYAVE ENERGY U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1
 USOO648.4362B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1 Ku0 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) RETRACTABLE HANDLE ASSEMBLY WITH 5,692,266 A 12/1997 Tsai... 16/113.1 MULTIPLE ENGAGING
USOO648.4362B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1 Ku0 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) RETRACTABLE HANDLE ASSEMBLY WITH 5,692,266 A 12/1997 Tsai... 16/113.1 MULTIPLE ENGAGING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,210,298 B1
 USOO6210298B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Baur et al. () Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) CONTINUOUSLY WARIABLE 4,864,889 9/1989 Sakakibara et al.... 475/211 TRANSMISSION 5,690,576 11/1997
USOO6210298B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Baur et al. () Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) CONTINUOUSLY WARIABLE 4,864,889 9/1989 Sakakibara et al.... 475/211 TRANSMISSION 5,690,576 11/1997
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Barbagli et al. (54) (75) TRACKED VEHICLE WITH AN EPICYCLIC STEERING DFFERENTIAL Inventors: Rino Oreste Barbagli; Giorgio De Castelli, both of Borgaretto, Italy (73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Barbagli et al. (54) (75) TRACKED VEHICLE WITH AN EPICYCLIC STEERING DFFERENTIAL Inventors: Rino Oreste Barbagli; Giorgio De Castelli, both of Borgaretto, Italy (73) Assignee:
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,092,999 Lilie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2000
 i & RS USOO6092999A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,092,999 Lilie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2000 54 RECIPROCATING COMPRESSOR WITH A 4,781,546 11/1988 Curwen... 417/417 LINEAR MOTOR
i & RS USOO6092999A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,092,999 Lilie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2000 54 RECIPROCATING COMPRESSOR WITH A 4,781,546 11/1988 Curwen... 417/417 LINEAR MOTOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,730,000 B1
 USOO673OOOOB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Leising et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) INTERACTIVE PROCESS DURING ENGINE 6,556,910 B2 4/2003 Suzuki et al.... 701/54 IDLE STOP MODE
USOO673OOOOB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Leising et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) INTERACTIVE PROCESS DURING ENGINE 6,556,910 B2 4/2003 Suzuki et al.... 701/54 IDLE STOP MODE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0119926 A1 LIN US 2013 0119926A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 16, 2013 (54) WIRELESS CHARGING SYSTEMAND METHOD (71) Applicant: ACER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0119926 A1 LIN US 2013 0119926A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 16, 2013 (54) WIRELESS CHARGING SYSTEMAND METHOD (71) Applicant: ACER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0226455A1 Al-Anizi et al. US 2011 0226455A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SLOTTED IMPINGEMENT PLATES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0226455A1 Al-Anizi et al. US 2011 0226455A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SLOTTED IMPINGEMENT PLATES
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.442,100 B2
 USOO74421 OOB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.442,100 B2 KOrhonen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS TO CONTROL A (58) Field of Classification Search...
USOO74421 OOB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.442,100 B2 KOrhonen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 2008 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS TO CONTROL A (58) Field of Classification Search...
1999. Feb. 3, 1998 (DE) (51) Int. Cl."... A47C 7/74 297/
 (12) United States Patent Faust et al. USOO6189966B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 20, 2001 (54) VEHICLE SEAT (75) Inventors: Eberhard Faust; Karl Pfahler, both of Stuttgart (DE) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent Faust et al. USOO6189966B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 20, 2001 (54) VEHICLE SEAT (75) Inventors: Eberhard Faust; Karl Pfahler, both of Stuttgart (DE) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.:
 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: USOO96371 64B2 Shavrnoch et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2017 (54) NYLON RESIN DRIVEN PULLEY (58) Field of Classification Search CPC... B62D 5700; B62D 5/04;
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: USOO96371 64B2 Shavrnoch et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2017 (54) NYLON RESIN DRIVEN PULLEY (58) Field of Classification Search CPC... B62D 5700; B62D 5/04;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O190837A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0190837 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2003 (54) BATTERY HOLDER HAVING MEANS FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 439/500 SECURELY
US 2003O190837A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0190837 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2003 (54) BATTERY HOLDER HAVING MEANS FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 439/500 SECURELY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2
 USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,626,061 B2. Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003
 USOO6626061B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) ACCELERATOR PEDAL DEVICE 6,276,229 B1 * 8/2001 Gohring et al... 74/513 6,289,762 B1 9/2001
USOO6626061B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) ACCELERATOR PEDAL DEVICE 6,276,229 B1 * 8/2001 Gohring et al... 74/513 6,289,762 B1 9/2001
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O124322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0124322 A1 Cimatti (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2014 (54) NORMALLY CLOSED AUTOMOTIVE (52) U.S. Cl. CLUTCH WITH HYDRAULC
(19) United States US 2014O124322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0124322 A1 Cimatti (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2014 (54) NORMALLY CLOSED AUTOMOTIVE (52) U.S. Cl. CLUTCH WITH HYDRAULC
(12) United States Patent
 USO0954.1209B2 (12) United States Patent Hayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,541,209 B2 Jan. 10, 2017 (54) STRUCTURE OF CHECK VALVE (71) Applicant: SANKEI GIKEN CO.,LTD., Kawaguchi-shi,
USO0954.1209B2 (12) United States Patent Hayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,541,209 B2 Jan. 10, 2017 (54) STRUCTURE OF CHECK VALVE (71) Applicant: SANKEI GIKEN CO.,LTD., Kawaguchi-shi,
WWWWWWWWVA IWWA. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1 IWW IWWIWWI IWWWWWW IWW IWWIYIVIVIVINNINWWWWWWIV
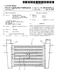 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0169926 A1 Watanabe et al. US 2007 O169926A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 >(54) HEAT EXCHANGER (75) Inventors: Haruhiko Watanabe,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0169926 A1 Watanabe et al. US 2007 O169926A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 >(54) HEAT EXCHANGER (75) Inventors: Haruhiko Watanabe,
(12) United States Patent Burkitt et a1.
 US008567174B2 (12) United States Patent Burkitt et a1. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,567,174 B2 Oct. 29, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) VALVE ASSEMBLY
US008567174B2 (12) United States Patent Burkitt et a1. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,567,174 B2 Oct. 29, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) VALVE ASSEMBLY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080056631A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0056631 A1 Beausoleil et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2008 (54) TUNGSTEN CARBIDE ENHANCED Publication Classification
US 20080056631A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0056631 A1 Beausoleil et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2008 (54) TUNGSTEN CARBIDE ENHANCED Publication Classification
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Minnerop 54) DEVICE FOR WATER COOLING OF ROLLED STEEL SECTIONS 75 Inventor: Michael Minnerop, Ratingen, Germany 73 Assignee: SMS Schloemann-Siemag Aktiengesellschaft, Dusseldorf,
United States Patent (19) Minnerop 54) DEVICE FOR WATER COOLING OF ROLLED STEEL SECTIONS 75 Inventor: Michael Minnerop, Ratingen, Germany 73 Assignee: SMS Schloemann-Siemag Aktiengesellschaft, Dusseldorf,
AN, (12) United States Patent. (10) Patent No.: US 6,443,131 B1. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, (54)
 (12) United States Patent BueSer USOO6443.131B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) FLAT PIPE PRESSURE DAMPER FOR DAMPING OSCILLATIONS IN LIQUID PRESSURE IN PIPES CARRYING LIQUIDS (75)
(12) United States Patent BueSer USOO6443.131B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) FLAT PIPE PRESSURE DAMPER FOR DAMPING OSCILLATIONS IN LIQUID PRESSURE IN PIPES CARRYING LIQUIDS (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
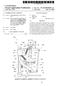 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0159457 A1 Saint-Marc et al. US 2016015.9457A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) RUDDER BAR FOR AN AIRCRAFT (71) Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0159457 A1 Saint-Marc et al. US 2016015.9457A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) RUDDER BAR FOR AN AIRCRAFT (71) Applicant:
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,580,324 Landry 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1996
 IIII USOO80324A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Landry ) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1996 54 DRIVEN PULLEY WITH ACLUTCH FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS 75 Inventor: Jean-Bernard Landry, 0222929 5/1987
IIII USOO80324A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Landry ) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1996 54 DRIVEN PULLEY WITH ACLUTCH FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS 75 Inventor: Jean-Bernard Landry, 0222929 5/1987
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,295,304
 O H USOO5295304A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,295,304 Ashley, Jr. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 22, 1994 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCING A FULL FACE Primary Examiner-P. W. Echols FABRICATED WHEEL
O H USOO5295304A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,295,304 Ashley, Jr. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 22, 1994 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCING A FULL FACE Primary Examiner-P. W. Echols FABRICATED WHEEL
United States Patent (19) Miller, Sr.
 United States Patent (19) Miller, Sr. 11 Patent Number: 5,056,448 (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 1991 (54) (76. (21) (22) 51 (52) (58) PVC BOAT Inventor: Terry L. Miller, Sr., P.O. Box 162, Afton, Okla.
United States Patent (19) Miller, Sr. 11 Patent Number: 5,056,448 (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 1991 (54) (76. (21) (22) 51 (52) (58) PVC BOAT Inventor: Terry L. Miller, Sr., P.O. Box 162, Afton, Okla.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. Durand (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2014 PUMP CPC... F04D 13/022 (2013.
 US 20140322042A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0322042 A1 Durand (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2014 (54) SWITCHABLE AUTOMOTIVE COOLANT (52) U.S. Cl. PUMP CPC...
US 20140322042A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0322042 A1 Durand (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2014 (54) SWITCHABLE AUTOMOTIVE COOLANT (52) U.S. Cl. PUMP CPC...
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,820,200 Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,446,482 B1. Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002
 USOO64.46482B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002 (54) BATTERY OPERATED HYDRAULIC D408.242 S 4/1999 Yamamoto... D8/61 COMPRESSION TOOL WITH RAPID
USOO64.46482B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002 (54) BATTERY OPERATED HYDRAULIC D408.242 S 4/1999 Yamamoto... D8/61 COMPRESSION TOOL WITH RAPID
(12) United States Patent
 USOO861 8656B2 (12) United States Patent Oh et al. (54) FLEXIBLE SEMICONDUCTOR PACKAGE APPARATUS HAVING ARESPONSIVE BENDABLE CONDUCTIVE WIRE MEMBER AND A MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Tac Keun.
USOO861 8656B2 (12) United States Patent Oh et al. (54) FLEXIBLE SEMICONDUCTOR PACKAGE APPARATUS HAVING ARESPONSIVE BENDABLE CONDUCTIVE WIRE MEMBER AND A MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Tac Keun.
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,892,675 Yatsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999
 USOO5892675A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Yatsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999 54 ACCURRENT SOURCE CIRCUIT FOR 4,876,635 10/1989 Park et al.... 363/17 CONVERTING DC VOLTAGE INTO
USOO5892675A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Yatsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999 54 ACCURRENT SOURCE CIRCUIT FOR 4,876,635 10/1989 Park et al.... 363/17 CONVERTING DC VOLTAGE INTO
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9284.05OB2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.284,050 B2 Bagai (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2016 (54) AIRFOIL FOR ROTOR BLADE WITH (56) References Cited REDUCED PITCHING MOMENT U.S. PATENT
(12) United States Patent USOO9284.05OB2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.284,050 B2 Bagai (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 15, 2016 (54) AIRFOIL FOR ROTOR BLADE WITH (56) References Cited REDUCED PITCHING MOMENT U.S. PATENT
Kikuiri et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, (54) CAPACITIVE PRESSURE SENSOR 5, A 12, 1996 Ko /53
 (12) United States Patent USOO7382599B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,382,599 B2 Kikuiri et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, 2008 (54) CAPACITIVE PRESSURE SENSOR 5,585.311 A 12, 1996 Ko... 438/53 5,656,781 A *
(12) United States Patent USOO7382599B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,382,599 B2 Kikuiri et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, 2008 (54) CAPACITIVE PRESSURE SENSOR 5,585.311 A 12, 1996 Ko... 438/53 5,656,781 A *
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120072180A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0072180 A1 Stuckey et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 22, 2012 (54) TIRE MOLD DESIGN METHOD TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 703/1
(19) United States US 20120072180A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0072180 A1 Stuckey et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 22, 2012 (54) TIRE MOLD DESIGN METHOD TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 703/1
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,080,888 B2. Hach (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006
 United States Patent US007080888B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,080,888 B2 Hach (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006 (54) DUAL NOZZLE HYDRO-DEMOLITION 6,049,580 A * 4/2000 Bodin et al.... 376/.316 SYSTEM 6,224,162
United States Patent US007080888B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,080,888 B2 Hach (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2006 (54) DUAL NOZZLE HYDRO-DEMOLITION 6,049,580 A * 4/2000 Bodin et al.... 376/.316 SYSTEM 6,224,162
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701.20388A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0120388 A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD FOR LASER Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201701.20388A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0120388 A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD FOR LASER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
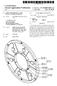 (19) United States US 2010O231027A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0231027 A1 SU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 16, 2010 (54) WHEEL WITH THERMOELECTRIC (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2010O231027A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0231027 A1 SU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 16, 2010 (54) WHEEL WITH THERMOELECTRIC (30) Foreign Application Priority
