The filling pressure of SUSPA gas springs depends on the extension force and the geometry and is between 10 and 230 bar.
|
|
|
- Cecilia Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FAQ s 1. Why is there a warning on the gas spring? Gas springs are filled with compressed nitrogen. The warning is intended to prevent unauthorized people from opening the gas spring or making other changes to the gas spring, which negatively impact the strength of the pressure pipe. 2. Can gas springs explode? No. The pressure pipes of all SUSPA pressure pipes have wall thicknesses and materials that are dimensioned so that there is a sufficient level of safety against bursting in all conceivable functional states. 3. What are SUSPA gas springs filled with? Only nitrogen is used as the pressure medium in SUSPA gas springs. About 75% of the air we breath consists of this gas. Nitrogen is absolutely safe and harmless to health. In addition, nitrogen does not burn. On the contrary, nitrogen is used in the chemical industry to prevent and extinguish fires. In addition, every SUSPA pneumatic spring contains flame-retardant oil to lubricate the seals and to achieve certain functions, such as damping or rigid locking. 4. How high is the pressure in a gas spring? The filling pressure of SUSPA gas springs depends on the extension force and the geometry and is between 10 and 230 bar. 5. How does a gas spring work? Inside a gas spring, the filling pressure acts on both surfaces of the piston. Once this is firmly bonded with the piston rod, the piston surface on the piston rod side is reduced by the cross-section of the piston rod. This results in a differential pressure on the piston, which acts in the extension direction. The size of the force [F] is equal to the product from the filling pressure [p] and the piston rod crosssection surface [A]. The following formula applies: F = p x A 6. What is "F1 force?" The "F1 force" is the designed force of SUSPA gas springs. This is measured when the piston rod of the gas spring is extended to 5 mm. It should be noted that the measured point of a significantly shorter position is approached with a defined speed and the value of the "F1 force" is read only about 3 seconds after the measurement devices comes to a standstill. The measurement must take place at 20 C gas spring and room temperature 7. Does the force of the gas spring change when displacing the piston rod? Yes. The inner volume of the gas spring is closed to the outside. This means that the filled gas volume can only occupy the free space in the pressure pipe that is not needed for components or oil. By pushing the piston rod in, this free space [V] is reduced by the inserted piston rod volume. Because the same gas volume has a smaller volume available, the pressure [p] in the gas spring increases. This formula applies: p2 = (V1 / V2) x p1 The index [1] corresponds to the piston rod position before moving
2 displacement and index [2] after displacement. The force [F] can also be used for the pressure [p] in this formula due to the correlation of the gas spring force with the filling pressure. 8. Does the force of a gas spring differ between retraction and extension? Yes. A friction force [FR] is created by the seal contacting the piston rod and the piston contacting the inside of the pressure pipe. This frictional force counteracts the movement direction of the piston rod. This means: During extension, the gas spring force [F = A x p] is reduced by the friction and a force increased by the amount of friction must be applied to push the piston rod in. This results in the following formula correlations: FOut = (A x p) - FOut; FIn = (A x p) + FIn Since the gas spring friction [FRGF] equals the difference of the insertion and extension force, the following applies: FRGF = FIn + FOut 9. Is it possible to manufacture a gas spring without friction? No. So that the gas filling does not escape from the pressure pipe, a hermetic seal of the gas spring interior must be created, even at the moving piston rods. To achieve a hermetic seal, the piston rods and the seal must be in contact with a sufficient surface pressure. The result of the contact of two bodies is always a frictional force. The sealing of SUSPA gas springs is designed so that the piston rods slide on the seal when displaced. The resulting friction is reduced to a minimum in SUSPA gas springs due to a careful selection of the materials and lubricants used. 10. What does the expression "damping" mean with a gas spring? Due to the gas spring structure, the interior of the gas spring is divided into two sub-spaces (chambers) by the piston, which is permanently connected with the piston rod. When the piston rod is displaced, the gas flows into a special connection channel through the piston from one chamber to the other. The structural design of this connection chamber has an effect on how big the resistance is that has to be overcome in order to press the gas through the piston. If the resistance is high, this is called a high "damping." The "damping" only occurs when the piston rod is moving and is used in gas springs above all to reduce the extension or insertion speed. In application, a pneumatic spring with a higher damping with all other installation conditions that are the same will insert and extend more slowly than a gas spring with a lower damping. 11. Can the damping of gas springs be changed? The damping of SUSPA gas springs can be preset by using different "damping discs." Furthermore, special "dampings" (e.g. end position damping or insertion damping) can be achieved by filling with larger oil quantities. Here, a larger resistance must be overcome to press the oil through the piston than if gas is flowing through the piston. 12. What is the difference between a gas spring and a damper? In general, a gas spring is an energy storage device and a damper is an energy absorber. The most common function of gas springs is to raise, lower and tilt or support doors, flaps or the like and to keep these in their end positions (opened/closed). The force of the gas spring thus acts against the weight force of the application so that the force expenditure of the operator is greatly reduced. Considered from a purely physical perspective, the gas spring stores some of the energy released while lowering a part, which is then released again when raising, which ultimately "helps" the operator. Dampers, on the other hand, are used in applications where the movement or vibration of a weight or body must be braked or reduced. Like a gas spring, a damper also has a piston that divides the interior of the damper pipe into two chambers. These chambers are usually filled with oil. When
3 displacing the piston rod, the oil has to be pressed through the piston via a special connection channel. Depending on the design of the connection channel, the oil can be pushed through more easily or with more difficulty. This resistance "results" in the damping force, which always counteracts the movement direction of the piston rod and increases with an increasing movement speed of the piston rod. Considered from a purely physical perspective, a damper absorbs the movement energy of an application or converts this into heat, thus ensuring for a higher level of comfort in the application. Of course there are many practical applications that require both the force-assisting and damping function in one product. SUSPA gas springs with various damping properties (damping in retraction or extension direction or in both directions or the end position damping) are designed in such cases. 13. What is a lockable gas spring? Like Liftline gas springs, Lockline gas springs have a piston that divides the interior of the pressure pipe into two chambers. Unlike the Liftline gas spring, there is a valve in the connection channel between the two chambers that can be opened and closed from the outside. The valve makes it possible to close the connection channel in any piston rod position. When the valve is closed, the gas can no longer flow between the two chambers. This means: The piston rod is locked in this position. If the two chambers are filled with gas, the locked piston rod can be displaced by high external forces. In this case, the gas is compressed in one of the two chambers and expanded in the other. If the external forces no longer act on the piston rod, then it very quickly moves back to the position in which the valve was previously closed. This is called elastic locking. Special structural designs make it possible to achieve a rigid locking of SUSPA gas springs. 14. How long is the service life of a gas spring? The general service life of SUSPA gas springs is between 10,000 and 100,000 double strokes (1x retraction and extension) depending on the type of gas spring. At SUSPA, the service life is tested according to internal test standards. These test standards provide for an optimal installation of gas springs. After the service life tests are completed, only a minimum power loss from escaped gas is tolerated at SUSPA. However, the actual service life of a pneumatic spring in application depends on many factors. That is why gas springs should be tested in the respective application under the actual conditions to be able to make a reliable statement about the service life of the gas spring. 15. What conditions affect the service life of gas springs? The most important criterion is the installation position of the gas spring with the piston rod facing down. This permanently ensures the lubrication of the piston rod seal. The frequency of the actuation also has a very decisive influence on the service life. The attachment of the pneumatic spring may not cause any lateral load on the piston rod. In the case of lateral forces, there is a unilateral, significantly higher wear on the piston rod, guide and seal. In addition, the piston rod may not become dirty or scratched. Extremely high or low temperatures and strong vibrations in the application also lead to a reduction of the service life of a gas spring. Due to these different influences, a careful review of all factors is necessary to achieve an optimal service life of the gas spring and thus the functional suitability of the entire application. 16. What properties of the gas spring change with its age? When a gas spring is optimally installed, the moving parts experience normal wear at the points of contact. This changes the surfaces, which allows the friction to rise slightly between the moving parts. To reduce the friction and wear, the gas springs are filled with a small amount of oil, which lubricates the sealing and sliding surfaces. Like any liquid, oil has the property that it can dissolve a larger amount
4 of gas in it under pressure than under atmospheric pressure without changing its volume. If the pressure in the liquid is reduced, this cannot dissolve as much gas and gas bubbles form in it, which rise to the surface. This effect can be seen particularly well when opening a bottle of mineral water. The oil saturated with gas inside the gas spring wets the surface of the piston rod. When sliding past the seal, a very thin film of saturated oil remains on the piston rod, which then releases the dissolved nitrogen outside of the gas spring into the atmosphere. In this way, some nitrogen molecules are "smuggled" out of the gas spring every time it extends and thus the gas volume and the pressure in the gas spring reduce, which ultimately results in a loss of power. If you omit the oil to prevent this effect, the wear on the seal increases so much that this no longer has a sealing effect already after a few load changes and the gas escapes. Even if the piston rod is not moved, gas springs lose pressure over time due to gas molecules that penetrate the seal. This effect is called permeation and can be reduced if the gas spring is installed and/or stored with the piston rod facing down so that the seal is not in direct contact with the gas filling, but rather is covered by the filled oil. 17. What needs to be taken into consideration when using gas springs? SUSPA gas springs should always be installed according to our installation instructions: 1. Install the gas spring with the piston rod facing down wards to ensure the optimal lubrication of the seal. 2. No lateral forces may act on the piston rod in order to avoid a unilateral and therefore higher wear. When using SUSPA gas springs of the Liftline model, lateral forces can be excluded by using ball joints to fasten the pneumatic springs. The centric force introduction must be structurally ensured when using other connection parts (e.g. eye or fork head). In the process, the axes of the eye holes and the middle axis of the pneumatic spring must intersect and the fastening bolts must be perpendicular to the middle axis of the gas spring in every position of the application. 3. The piston rod is to be protected from impacts, dirt and scratches. These factors increase the wear tremendously on the one hand, and on the other hand dirt particles and scratches on the sealing surfaces cause leaks. 4. The application temperature from -30 C to +80 C should not be exceeded or fallen below, because the sealing materials wear too quickly outside of this range on the one hand, and on the other hand no longer have the necessary elasticity. Within this temperature range, the change in the extension force must be taken into consideration in order to ensure the application function for all occurring temperatures. 5. Strong vibrations reduce the service life of pneumatic springs. Furthermore, the maximum possible extension force must be chosen during installation, because all pneumatic springs "lose" force during use. This can ensure that the application has a maximum functional duration. 18. Should gas springs be installed with the piston rod facing up or down? In general, gas springs should be installed with the piston rod facing down to ensure the piston rod seal is lubricated and to reduce the permeation of nitrogen through the seal. However, the opposite installation may be necessary in some special cases, for example if the gas spring requires a very specific damping characteristic. In such cases, the lubrication of the piston rod seal must be ensured by special measures (space mat). 19. Does a gas spring have to be maintained? No. SUSPA gas springs are equipped with a lubricant quantity during production that lasts a life time. 20. Can gas springs be repaired?
5 No. All SUSPA gas springs and dampers are by a plastic deformation of the external pipes during production. This makes it impossible to open the gas spring to replace individual components without destroying it. 21. How do you find the right gas spring for a specific application? The function of the entire application is always the focus at SUSPA. If you know the requirements profile of your application (e.g. opening a flap, holding the flap in both end positions, automatic opening, closing by a defined manual force at a defined handle, weight of the application), it still needs to be clarified in what area it is possible to fasten the gas spring. The exact mounting points must then be determined with this data and a suitable gas spring must be defined. This process, however, proves to be very complex and usually involves a tremendous amount of research and time. That is why we offer you the implementation and selection of a suitable gas spring for you to take over. Simply sketch us the application specifying the rotation point, the weight and the desired opening angle. Furthermore, the sketch should include the location of the center of gravity and the area in which a pneumatic spring attachment is possible. Our experienced employees will use special software to determine an optimal pneumatic spring for your application and make you a sketch with the installation dimensions. 22. How long can the gas springs be stored? The storage of SUSPA gas springs has no negative consequences on their function if it is ensured that the piston rods point down and no dirt accumulates on the piston rod. If gas springs are not actuated for a long time, they only have a slightly increased amount of friction during the first retraction. However, this effect is equalized after the first actuation and the gas spring then again exhibits the usual friction values. 23. Does the temperature affect the function of gas springs? Yes. However, three temperatures ranges must be distinguished between. Between -30 C and +80 C (operating range), the temperature only affects the pressure of the gas in the gas spring. The pressure increases / decreases in this range and therefore so too does the extension force of the gas spring by about 3.5% per 10 C of the temperature rise / fall. Below the operating range, the elasticity of the sealing materials used decreases so that the surface pressure distribution in the sealing points is no longer optimally adjusted. If the temperature rises significantly above the operating range, a higher wear results on the dynamically stressed sealing points, such as the piston rod seal, due to the softening of the sealing material. The temperature has an additional effect on the damping behavior of the gas springs. The temperature increase makes the oil be less viscous, which reduces the oil's resistance to the flow of the piston. This results in less damping. Likewise, the damping increases with a lowering temperature. 24. What is a soft-stop gas spring? Soft-stop gas springs do not have the same "damping" across the entire stroke like standard pneumatic springs (also see 10). With this gas spring type, the "damping" also continuously increases while the piston rod is being extended, whereby its extension speed reduces consistently. Unlike standard pneumatic springs, the connection channel between the two chambers in soft-stop pneumatic springs is not in the piston, but rather is formed by a groove in the inner surface of the pressure pipe. The gas then flows through this groove past the piston when the piston rod is displaced. The "damping" of the gas spring is determined by the cross-section of the groove at the respective piston position. The groove is designed so that its depth and therefore also the cross-section across the range of movement
6 of the piston is not the same, but rather reduces in the direction of extension. Applications that are equipped with soft-stop gas springs are characterized by a very convenient operation and high sense of value, because the movement is gently braked once the end position is reached. 25. What does Space-Mat mean? Space-Mat is a special lubrication system for gas springs developed by SUSPA. SUSPA gas springs equipped with Space-Mat can be mounted with the piston rod facing upwards without any problems without causing increased wear of the piston rod seal. in addition, the Space-Mat system greatly reduces the 'breakaway force" of the piston rod during the movement start, whereby the operating comfort and the sense of value of the entire application increases. Check out the collection of trailer hitches & towing we offer.
Every movement under control: individually adapted gas struts
 Specific design of gas struts increases service life and safety of moving components. Every movement under control: individually adapted gas struts Gas struts facilitate the lifting and lowering of machine
Specific design of gas struts increases service life and safety of moving components. Every movement under control: individually adapted gas struts Gas struts facilitate the lifting and lowering of machine
Development of an innovative diaphragm accumulator design and assembly process
 Group 7 - Hydraulic Components Paper 7-3 451 Development of an innovative diaphragm accumulator design and assembly process Dipl.-Ing. Thorsten Hillesheim Freudenberg Sealing Technologies GmbH & Co. KG,
Group 7 - Hydraulic Components Paper 7-3 451 Development of an innovative diaphragm accumulator design and assembly process Dipl.-Ing. Thorsten Hillesheim Freudenberg Sealing Technologies GmbH & Co. KG,
Seals Stretch Running Friction Friction Break-Out Friction. Build With The Best!
 squeeze, min. = 0.0035 with adverse tolerance build-up. If the O-ring is made in a compound that will shrink in the fluid, the minimum possible squeeze under adverse conditions then must be at least.076
squeeze, min. = 0.0035 with adverse tolerance build-up. If the O-ring is made in a compound that will shrink in the fluid, the minimum possible squeeze under adverse conditions then must be at least.076
Input, Control and Processing elements
 PNEUMATIC & HYDRAULIC SYSTEMS CHAPTER FIVE Input, Control and Processing elements Dr. Ibrahim Naimi Valves The function of valves is to control the fluid path or the pressure or the flow rate. Depending
PNEUMATIC & HYDRAULIC SYSTEMS CHAPTER FIVE Input, Control and Processing elements Dr. Ibrahim Naimi Valves The function of valves is to control the fluid path or the pressure or the flow rate. Depending
Shock Absorbers What is Ride Control Vehicle Dynamics Suspension System Shock Absorbers Struts Terminology
 Home Tech Support Shock Absorbers Shock Absorbers What is Ride Control Vehicle Dynamics Suspension System Shock Absorbers Struts Terminology A BRIEF HISTORY These first shock absorbers were simply two
Home Tech Support Shock Absorbers Shock Absorbers What is Ride Control Vehicle Dynamics Suspension System Shock Absorbers Struts Terminology A BRIEF HISTORY These first shock absorbers were simply two
Ball Rail Systems RE / The Drive & Control Company
 Ball Rail Systems RE 82 202/2002-12 The Drive & Control Company Rexroth Linear Motion Technology Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Standard Ball Rail Systems Super Ball Rail Systems Ball Rail Systems
Ball Rail Systems RE 82 202/2002-12 The Drive & Control Company Rexroth Linear Motion Technology Ball Rail Systems Roller Rail Systems Standard Ball Rail Systems Super Ball Rail Systems Ball Rail Systems
HPB Hydraulic Power Braking System
 HPB Hydraulic Power Braking System 4 th Edition This publication is not subject to any update service. New versions are available in INFORM at www.wabco-auto.com Copyright WABCO 2007 Vehicle Control Systems
HPB Hydraulic Power Braking System 4 th Edition This publication is not subject to any update service. New versions are available in INFORM at www.wabco-auto.com Copyright WABCO 2007 Vehicle Control Systems
Guide units. For toolmaking, fixture manufacturing and machine engineering
 Guide units For toolmaking, fixture manufacturing and machine engineering Guide units in compliance with DIN, ISO and STEINEL standards or according to your specifications Guide pillars Guide and pillar
Guide units For toolmaking, fixture manufacturing and machine engineering Guide units in compliance with DIN, ISO and STEINEL standards or according to your specifications Guide pillars Guide and pillar
White paper: Pneumatics or electrics important criteria when choosing technology
 White paper: Pneumatics or electrics important criteria when choosing technology The requirements for modern production plants are becoming increasingly complex. It is therefore essential that the drive
White paper: Pneumatics or electrics important criteria when choosing technology The requirements for modern production plants are becoming increasingly complex. It is therefore essential that the drive
Bearings. Rolling-contact Bearings
 Bearings A bearing is a mechanical element that limits relative motion to only the desired motion and at the same time it reduces the frictional resistance to the desired motion. Depending on the design
Bearings A bearing is a mechanical element that limits relative motion to only the desired motion and at the same time it reduces the frictional resistance to the desired motion. Depending on the design
Comparison between Fluid Viscous Dampers and Friction Damper Devices. Fluid Viscous Dampers (FVD) Friction Damper Device (FDD) Working principle:
 Fluid Viscous Dampers (FVD) Working principle: FVD is a central piston strokes through a fluid-filled chamber. As the piston moves it pushes fluid through orifices around and through the piston head. Fluid
Fluid Viscous Dampers (FVD) Working principle: FVD is a central piston strokes through a fluid-filled chamber. As the piston moves it pushes fluid through orifices around and through the piston head. Fluid
KUZMA STABI R TURNTABLE (supplied without arm ) S/N Instruction manual
 KUZMA STABI R TURNTABLE (supplied without arm ) S/N.. 2018-09 Instruction manual 1 KUZMA LTD INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR STABI R turntable The Stabi R turntable is a very precisely engineered piece of equipment.
KUZMA STABI R TURNTABLE (supplied without arm ) S/N.. 2018-09 Instruction manual 1 KUZMA LTD INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR STABI R turntable The Stabi R turntable is a very precisely engineered piece of equipment.
Special edition paper
 Efforts for Greater Ride Comfort Koji Asano* Yasushi Kajitani* Aiming to improve of ride comfort, we have worked to overcome issues increasing Shinkansen speed including control of vertical and lateral
Efforts for Greater Ride Comfort Koji Asano* Yasushi Kajitani* Aiming to improve of ride comfort, we have worked to overcome issues increasing Shinkansen speed including control of vertical and lateral
Optimization of Total Operating Costs Using Electric Linear Drives
 Optimization of Total Operating Costs Using Electric Linear Drives TCO analysis demonstrates high potential for savings, even for simple applications, by replacing pneumatic drives Electric linear drives
Optimization of Total Operating Costs Using Electric Linear Drives TCO analysis demonstrates high potential for savings, even for simple applications, by replacing pneumatic drives Electric linear drives
Industrial Gas Springs
 Industrial Gas Springs Function, Calculation and Mounting Tips Gas springs are universally accepted, wherever you want to push pull lift lower, or position covers, lids or other components by hand without
Industrial Gas Springs Function, Calculation and Mounting Tips Gas springs are universally accepted, wherever you want to push pull lift lower, or position covers, lids or other components by hand without
Name Date. True-False. Multiple Choice
 Name Date True-False T F 1. Oil film thickness increases with an increase in oil temperature. T F 2. Displacement is the volume that a piston displaces in an engine when it travels from top dead center
Name Date True-False T F 1. Oil film thickness increases with an increase in oil temperature. T F 2. Displacement is the volume that a piston displaces in an engine when it travels from top dead center
CHAPTER 4 MR DAMPER DESIGN. In this chapter, details of MR damper geometry and magnetic circuit design are provided.
 CHAPTER 4 MR DAMPER DESIGN In this chapter, details of MR damper geometry and magnetic circuit design are provided. Additional practical considerations for MR damper design, such as damper piston centering
CHAPTER 4 MR DAMPER DESIGN In this chapter, details of MR damper geometry and magnetic circuit design are provided. Additional practical considerations for MR damper design, such as damper piston centering
Heavy-Duty Rod Ends - Male with integral spherical plain bearing
 Heavy-Duty Rod Ends - Male with integral spherical plain bearing 65700 Order No. Thread (hand) d 1 l 1 d 2 d 3 d 4 l 2 l 3 X g H7 65700.W0005 Right 5 33 M 5 11,11 18 20 9 14 65700.W0006 Right 6 36 M 6
Heavy-Duty Rod Ends - Male with integral spherical plain bearing 65700 Order No. Thread (hand) d 1 l 1 d 2 d 3 d 4 l 2 l 3 X g H7 65700.W0005 Right 5 33 M 5 11,11 18 20 9 14 65700.W0006 Right 6 36 M 6
2.- HANDLING OF VALVES BEFORE ASSEMBLY 3.- FITTING THE VALVE TO THE REST OF THE ASSEMBLY 5.- PERIODICAL INSPECTION OF THE VALVE AND MAINTENANCE
 Page 1 of 16 CONTENTS 1.- INTRODUCTION 2.- HANDLING OF VALVES BEFORE ASSEMBLY 3.- FITTING THE VALVE TO THE REST OF THE ASSEMBLY 4.- OPERATION OF A BALL VALVE 5.- PERIODICAL INSPECTION OF THE VALVE AND
Page 1 of 16 CONTENTS 1.- INTRODUCTION 2.- HANDLING OF VALVES BEFORE ASSEMBLY 3.- FITTING THE VALVE TO THE REST OF THE ASSEMBLY 4.- OPERATION OF A BALL VALVE 5.- PERIODICAL INSPECTION OF THE VALVE AND
CH.4 Basic Components of Hydraulic and Pneumatic System/16 M HAP/17522/AE5G
 Content : 4.1 Hydraulic and Pneumatic actuators. 10 Marks Hydraulic Actuators - Hydraulic cylinders (single, double acting and telescopic) construction and working, Hydraulic motors (gear and piston type)
Content : 4.1 Hydraulic and Pneumatic actuators. 10 Marks Hydraulic Actuators - Hydraulic cylinders (single, double acting and telescopic) construction and working, Hydraulic motors (gear and piston type)
Table of Contents Industrial Shock Absorber
 Table of Contents Industrial Shock Absorber Page Technical informations 4 Survey 16 Non-adjustable Shock Absorber Type SA 10 N, SA 10 SN, SA 10 S2N 20 Type SA 12N, SA 12 SN, SA 12 S2N 22 Type SA 14, SA
Table of Contents Industrial Shock Absorber Page Technical informations 4 Survey 16 Non-adjustable Shock Absorber Type SA 10 N, SA 10 SN, SA 10 S2N 20 Type SA 12N, SA 12 SN, SA 12 S2N 22 Type SA 14, SA
SD Bendix E-10PR Retarder Control Brake Valve DESCRIPTION. OPERATION - Refer to Figure 2
 SD-03-832 Bendix E-10PR Retarder Control Brake Valve MOUNTING PLATE SUPPLY 4 PORTS ELECTRICAL AUXILIARY DESCRIPTION TREADLE RETARDER CONTROL SECTION EXHAUST DELIVERY 4 PORTS FIGURE 1 - E-10PR RETARDER
SD-03-832 Bendix E-10PR Retarder Control Brake Valve MOUNTING PLATE SUPPLY 4 PORTS ELECTRICAL AUXILIARY DESCRIPTION TREADLE RETARDER CONTROL SECTION EXHAUST DELIVERY 4 PORTS FIGURE 1 - E-10PR RETARDER
Workshop manual 5018 PDS Product Exploded View Disassembly & Assembling. Shock absorber 5018 PDS OEM Shock absorber 5018 PDS /2002
 Shock absorber 5018 PDS OEM 2000 Introduction 2 Exploded view 3 Disassembly shock absorber 4 Disassembly piston-rod 11 Disassembly adaptor DU-bush 15 Assembling adaptor DU-bush 17 Assembling piston-rod
Shock absorber 5018 PDS OEM 2000 Introduction 2 Exploded view 3 Disassembly shock absorber 4 Disassembly piston-rod 11 Disassembly adaptor DU-bush 15 Assembling adaptor DU-bush 17 Assembling piston-rod
M3 Design Product Teardown Ameda Purely Yours Breast Pump
 28 Sep, 2010 Why do the product teardowns? M3 Design Product Teardown Ameda Purely Yours Breast Pump Part of the product development process is to apply knowledge gained from prior experience during the
28 Sep, 2010 Why do the product teardowns? M3 Design Product Teardown Ameda Purely Yours Breast Pump Part of the product development process is to apply knowledge gained from prior experience during the
2. Hydraulic Valves, Actuators and Accessories. 24 Marks
 2. Hydraulic Valves, Actuators and Accessories 24 Marks Co related to chapter 602.2 Describe working principle of various components used in hydraulic & pneumatic systems. 602.3 Choose valves, actuators
2. Hydraulic Valves, Actuators and Accessories 24 Marks Co related to chapter 602.2 Describe working principle of various components used in hydraulic & pneumatic systems. 602.3 Choose valves, actuators
RE / STAR Tolerance Rings STAR Ball Knobs, Knob and Lever Type Handles
 RE 2 970/.99 STAR Tolerance Rings STAR Ball Knobs, Knob and Lever Type Handles STAR Tolerance Rings Product Overview Tolerance rings are made of hard, embossed spring steel strip and belong to the class
RE 2 970/.99 STAR Tolerance Rings STAR Ball Knobs, Knob and Lever Type Handles STAR Tolerance Rings Product Overview Tolerance rings are made of hard, embossed spring steel strip and belong to the class
Figure 1.1. From left to right: PVC, GRP and AISI 316L. Filter type Filter body material Max pressure Max temperature BSP PVC 150 psig 104 F, 40 C
 1. The filter body The filter bodies come in three different materials: PVC (PolyVinyl Chloride), AISI 316L (stainless steel) and GRP (Glass-fiber Reinforced Polyester). Filter bodies in PVC and GRP have
1. The filter body The filter bodies come in three different materials: PVC (PolyVinyl Chloride), AISI 316L (stainless steel) and GRP (Glass-fiber Reinforced Polyester). Filter bodies in PVC and GRP have
MEASURING INSTRUMENTS. Basic Electrical Engineering (REE-101) 1
 MEASURING INSTRUMENTS Basic Electrical Engineering (REE-101) 1 MEASURING INSTRUMENTS The device used for comparing the unknown quantity with the unit of measurement or standard quantity is called a Measuring
MEASURING INSTRUMENTS Basic Electrical Engineering (REE-101) 1 MEASURING INSTRUMENTS The device used for comparing the unknown quantity with the unit of measurement or standard quantity is called a Measuring
Profi le rail guides LLR
 Profi le rail guides LLR Content The SKF brand now stands for more than ever before, and means more to you as a valued customer. While SKF maintains its leadership as the hallmark of quality bearings throughout
Profi le rail guides LLR Content The SKF brand now stands for more than ever before, and means more to you as a valued customer. While SKF maintains its leadership as the hallmark of quality bearings throughout
Personal Restraint Hydraulic Lock "LE" for passenger restraint systems
 Personal Restraint Hydraulic Lock "LE" for passenger restraint systems Description The LE locking system was developed specifically for installation in seats in amusement park rides and mobile structures.
Personal Restraint Hydraulic Lock "LE" for passenger restraint systems Description The LE locking system was developed specifically for installation in seats in amusement park rides and mobile structures.
Testing Of Fluid Viscous Damper
 Testing Of Fluid Viscous Damper Feng Qian & Sunwei Ding, Jingjing Song Shanghai Research Institute of Materials, China Dr. Chien-Chih Chen US.VF Corp, Omni Device, China SUMMARY: The Fluid Viscous Damper
Testing Of Fluid Viscous Damper Feng Qian & Sunwei Ding, Jingjing Song Shanghai Research Institute of Materials, China Dr. Chien-Chih Chen US.VF Corp, Omni Device, China SUMMARY: The Fluid Viscous Damper
White paper More productivity with optimally cushioned pneumatic cylinders
 White paper More productivity with optimally cushioned pneumatic cylinders With the right end-position cushioning, you can significantly increase the efficiency of your entire pneumatic system. When used
White paper More productivity with optimally cushioned pneumatic cylinders With the right end-position cushioning, you can significantly increase the efficiency of your entire pneumatic system. When used
USE AN ENGINEERED APPROACH TO TAILOR A PERFECT STANDARD GAS SPRING FOR YOUR DESIGN A GUIDE TO GAS SPRING DESIGN AND CUSTOMIZATION WH ITE PA P E R
 WH ITE PA P E R USE AN ENGINEERED APPROACH TO TAILOR A PERFECT STANDARD GAS SPRING FOR YOUR DESIGN A GUIDE TO GAS SPRING DESIGN AND CUSTOMIZATION When your machine design calls for an industrial gas spring,
WH ITE PA P E R USE AN ENGINEERED APPROACH TO TAILOR A PERFECT STANDARD GAS SPRING FOR YOUR DESIGN A GUIDE TO GAS SPRING DESIGN AND CUSTOMIZATION When your machine design calls for an industrial gas spring,
Pull Type Gas Springs
 Pull Type Gas Springs ICTATOR pull type gas springs are the answer to your problems if you are unable to use normal push type gas springs due to a lack of space. They work in the opposite way to push type
Pull Type Gas Springs ICTATOR pull type gas springs are the answer to your problems if you are unable to use normal push type gas springs due to a lack of space. They work in the opposite way to push type
Vibration damping precision couplings
 Vibration damping precision couplings In light of the advantages of elasticity, strength, resilience, and damping effects, elastomer materials are now being used in most areas of mechanical engineering.
Vibration damping precision couplings In light of the advantages of elasticity, strength, resilience, and damping effects, elastomer materials are now being used in most areas of mechanical engineering.
Product information on Audi Genuine Accessories
 Audi Genuine Accessories Product information on Audi Genuine Accessories Audi A5 Coupé 27.02.2008 Information subject to change Page 1 Contents page Sport and design...3 Front spoiler with blade...3 Rear
Audi Genuine Accessories Product information on Audi Genuine Accessories Audi A5 Coupé 27.02.2008 Information subject to change Page 1 Contents page Sport and design...3 Front spoiler with blade...3 Rear
Chapter 2 Dynamic Analysis of a Heavy Vehicle Using Lumped Parameter Model
 Chapter 2 Dynamic Analysis of a Heavy Vehicle Using Lumped Parameter Model The interaction between a vehicle and the road is a very complicated dynamic process, which involves many fields such as vehicle
Chapter 2 Dynamic Analysis of a Heavy Vehicle Using Lumped Parameter Model The interaction between a vehicle and the road is a very complicated dynamic process, which involves many fields such as vehicle
Air-Oil Systems, Inc. Gas Springs AGS 15 - AGS 28
 Gas Springs GS 15 - GS 28 Gas Springs ontrols gas springs are reliable units designed to handle the demanding needs of the industrial and commercial markets. They are maintenance free and self-contained.
Gas Springs GS 15 - GS 28 Gas Springs ontrols gas springs are reliable units designed to handle the demanding needs of the industrial and commercial markets. They are maintenance free and self-contained.
AV INSTALLATION, OPERATION & MAINTENANCE MANUAL
 Rack & Pinion Pneumatic Actuators AV INSTALLATION, OPERATION & MAINTENANCE MANUAL AVCS PO Box 68172 Minneapolis, MN 55418 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: PRODUCT DESCRIPTION 3 CHAPTER 2: TECHNICAL FEATURES
Rack & Pinion Pneumatic Actuators AV INSTALLATION, OPERATION & MAINTENANCE MANUAL AVCS PO Box 68172 Minneapolis, MN 55418 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: PRODUCT DESCRIPTION 3 CHAPTER 2: TECHNICAL FEATURES
Steering unit LAGZ. Data sheet. Series 2 x
 Steering unit LAGZ Data sheet Nominal sizes 125 620 Series 2 x Maximum flow 50 l / min HE 11868 / 09.2017 2 LAGZ HE 11868 / 09.2017 Page Content 4 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Features Ordering details Function,
Steering unit LAGZ Data sheet Nominal sizes 125 620 Series 2 x Maximum flow 50 l / min HE 11868 / 09.2017 2 LAGZ HE 11868 / 09.2017 Page Content 4 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Features Ordering details Function,
Series 111 Accumulator Product Information
 Series 111 Accumulator Product Information l Model 111.11 Model 111.12 011-553-304 B Copyright information Trademark information Contact information Publication information 2000 MTS Systems Corporation.
Series 111 Accumulator Product Information l Model 111.11 Model 111.12 011-553-304 B Copyright information Trademark information Contact information Publication information 2000 MTS Systems Corporation.
Ball. Ball cage. Fig.1 Structure of Caged Ball LM Guide Actuator Model SKR
 Caged all LM Guide Actuator Model Inner block all screw shaft Grease nipple Outer rail all cage all Structure and Features Fig.1 Structure of Caged all LM Guide Actuator Model Caged all LM Guide Actuator
Caged all LM Guide Actuator Model Inner block all screw shaft Grease nipple Outer rail all cage all Structure and Features Fig.1 Structure of Caged all LM Guide Actuator Model Caged all LM Guide Actuator
TN1250 Technical note
 Technical note Press-fit ACEPACK power modules mounting instructions Introduction ST introduces the ACEPACK Power Module family, designed for easy mounting and reliable performance in rugged applications.
Technical note Press-fit ACEPACK power modules mounting instructions Introduction ST introduces the ACEPACK Power Module family, designed for easy mounting and reliable performance in rugged applications.
Operating Instructions for Elevator Buffers type LP
 Operating Instructions for Elevator Buffers type LP 1 Scope of application The Elevator Buffer type LP is an energy dissipation type buffer according to EN 81-1/2, EN 81-20, EN 81-50 5.5 and therefore
Operating Instructions for Elevator Buffers type LP 1 Scope of application The Elevator Buffer type LP is an energy dissipation type buffer according to EN 81-1/2, EN 81-20, EN 81-50 5.5 and therefore
EMC-HD. C 01_2 Subheadline_15pt/7.2mm
 C Electromechanical 01_1 Headline_36pt/14.4mm Cylinder EMC-HD C 01_2 Subheadline_15pt/7.2mm 2 Elektromechanischer Zylinder EMC-HD Short product name Example: EMC 085 HD 1 System = ElectroMechanical Cylinder
C Electromechanical 01_1 Headline_36pt/14.4mm Cylinder EMC-HD C 01_2 Subheadline_15pt/7.2mm 2 Elektromechanischer Zylinder EMC-HD Short product name Example: EMC 085 HD 1 System = ElectroMechanical Cylinder
1. General Description
 General Description 1. General Description A: SPECIFICATION Front Rear Model Wheel arch height (Tolerance: +12 mm 24 mm ( +0.47 in 0.94 in)) mm (in) 376 (14.8) Camber (Tolerance: 0 45 Differences between
General Description 1. General Description A: SPECIFICATION Front Rear Model Wheel arch height (Tolerance: +12 mm 24 mm ( +0.47 in 0.94 in)) mm (in) 376 (14.8) Camber (Tolerance: 0 45 Differences between
HYBRID LINEAR ACTUATORS BASICS
 HYBRID LINEAR ACTUATORS BASICS TECHNICAL OVERVIEW Converting the rotary motion of a stepping motor into linear motion can be accomplished by several mechanical means, including rack and pinion, belts and
HYBRID LINEAR ACTUATORS BASICS TECHNICAL OVERVIEW Converting the rotary motion of a stepping motor into linear motion can be accomplished by several mechanical means, including rack and pinion, belts and
Convertible with unique safety features
 PRESS INFORMATION The all new Volvo C70 Safety Convertible with unique safety features Volvo s Unique Side Impact Protection System (SIPS) interacts with world-first door-mounted inflatable curtain for
PRESS INFORMATION The all new Volvo C70 Safety Convertible with unique safety features Volvo s Unique Side Impact Protection System (SIPS) interacts with world-first door-mounted inflatable curtain for
Gas Springs AGS 15 - AGS 28
 Gas Springs GS 15 - GS 28 Gas Springs ontrols gas springs are reliable units designed to handle the demanding needs of the industrial and commercial markets. They are maintenance free and self-contained.
Gas Springs GS 15 - GS 28 Gas Springs ontrols gas springs are reliable units designed to handle the demanding needs of the industrial and commercial markets. They are maintenance free and self-contained.
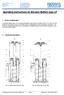
Service Kit
 Service Kit 753-05607 Date: Subject: Models Affected: April 17, 2009 (Revised 6/08/2009) Hydraulic Cylinder Seal Replacement XINGHUI 4.5 Cylinder 718-0769A Read through and understand these instructions
Service Kit 753-05607 Date: Subject: Models Affected: April 17, 2009 (Revised 6/08/2009) Hydraulic Cylinder Seal Replacement XINGHUI 4.5 Cylinder 718-0769A Read through and understand these instructions
> piston force up to 20,1 kn. > operating pressure 250/350 bar. > chemically nitrided body. > piston force up to 44,0 kn. > operating pressure 350 bar
 Vertical and link CLAMPS for DEMANDING TASKS vertical CLAMP > piston force up to 20,1 kn > operating pressure 250/350 bar > chemically nitrided body link CLAMP > piston force up to 44,0 kn > operating
Vertical and link CLAMPS for DEMANDING TASKS vertical CLAMP > piston force up to 20,1 kn > operating pressure 250/350 bar > chemically nitrided body link CLAMP > piston force up to 44,0 kn > operating
THE CARBURETOR: THE ADDITIONAL SYSTEMS
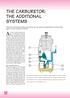 THE CARBURETOR: THE ADDITIONAL SYSTEMS From the acceleration pump to the power jet: the special configuration of circuits that apply to some carburetor models As stated in the previous article, a carburetor
THE CARBURETOR: THE ADDITIONAL SYSTEMS From the acceleration pump to the power jet: the special configuration of circuits that apply to some carburetor models As stated in the previous article, a carburetor
Commissioning & Maintenance Instructions. for. COBRA linear stepping motors
 Commissioning & Maintenance Instructions for COBRA linear stepping motors ACP&D Limited. 86 Rose Hill Road, Ashton-under-Lyne, Lancashire, OL6 8NS. Tel : +44 (0)161 343 1884 Fax: +44 (0)161 343 7773 e-mail:
Commissioning & Maintenance Instructions for COBRA linear stepping motors ACP&D Limited. 86 Rose Hill Road, Ashton-under-Lyne, Lancashire, OL6 8NS. Tel : +44 (0)161 343 1884 Fax: +44 (0)161 343 7773 e-mail:
Describe the function of a hydraulic power unit
 Chapter 7 Source of Hydraulic Power Power Units and Pumps 1 Objectives Describe the function of a hydraulic power unit and identify its primary components. Explain the purpose of a pump in a hydraulic
Chapter 7 Source of Hydraulic Power Power Units and Pumps 1 Objectives Describe the function of a hydraulic power unit and identify its primary components. Explain the purpose of a pump in a hydraulic
LOCKED SERIES. Machine Failures. General Information. set up. maintenance. reconditioning. repair 30.4%
 General Information LOCKED SERIES 2 Lowering machinery process costs is key in today s world. According to a recent study approximately a third of all machine stoppages result in unexpected damage and
General Information LOCKED SERIES 2 Lowering machinery process costs is key in today s world. According to a recent study approximately a third of all machine stoppages result in unexpected damage and
Operation and Maintenance Instructions
 Hydratight Limited Bentley Road South Darlaston West Midlands WS10 8LQ United Kingdom Tel: +44 121 50 50 600 Fax: +44 121 50 50 800 E-mail: enquiry@hydratight.com Website: www.hydratight.com HNOFC062490400
Hydratight Limited Bentley Road South Darlaston West Midlands WS10 8LQ United Kingdom Tel: +44 121 50 50 600 Fax: +44 121 50 50 800 E-mail: enquiry@hydratight.com Website: www.hydratight.com HNOFC062490400
Low-torque Deep-groove Ball Bearings for Transmissions
 New Product Low-torque Deep-groove Ball Bearings for Transmissions Katsuaki SASAKI To achieve low fuel consumption in response to environmental concerns, we have focused on reducing the friction of tapered
New Product Low-torque Deep-groove Ball Bearings for Transmissions Katsuaki SASAKI To achieve low fuel consumption in response to environmental concerns, we have focused on reducing the friction of tapered
TURCON STEPSEAL 2K. - Single Acting - Rubber Energised Plastic Faced Seal - Material - TurconR and ZurconR - Busak+ Shamban
 contents (catalogue) main menu product range fullscreen/variable R R TURCON STEPSEAL 2K - Single Acting - Rubber Energised Plastic Faced Seal - Material - TurconR and ZurconR - 19 20 Turcon R Stepseal
contents (catalogue) main menu product range fullscreen/variable R R TURCON STEPSEAL 2K - Single Acting - Rubber Energised Plastic Faced Seal - Material - TurconR and ZurconR - 19 20 Turcon R Stepseal
Finite Element Analysis of Clutch Piston Seal
 Finite Element Analysis of Clutch Piston Seal T. OYA * F. KASAHARA * *Research & Development Center Tribology Research Department Three-dimensional finite element analysis was used to simulate deformation
Finite Element Analysis of Clutch Piston Seal T. OYA * F. KASAHARA * *Research & Development Center Tribology Research Department Three-dimensional finite element analysis was used to simulate deformation
Inner block. Grease nipple. Fig.1 Structure of LM Guide Actuator Model KR
 LM Guide ctuator Model LM Guide + all Screw = Integral-structure ctuator Stopper Housing all screw Inner block Grease nipple Outer rail earing (supported side) Housing Stopper Double-row ball circuit earing
LM Guide ctuator Model LM Guide + all Screw = Integral-structure ctuator Stopper Housing all screw Inner block Grease nipple Outer rail earing (supported side) Housing Stopper Double-row ball circuit earing
...our linkages, your solution. Rod Ends
 ...our linkages, your solution Technical Information Introduction All of our rod ends incorporate either a plain spherical bearing, ball bearing, or roller bearing. Below is an overview of each type. Plain
...our linkages, your solution Technical Information Introduction All of our rod ends incorporate either a plain spherical bearing, ball bearing, or roller bearing. Below is an overview of each type. Plain
Maintenance Information
 45528270 Edition 1 June 2007 Barring Motor T480 Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions WARNING Always wear eye protection when operating or performing maintenance on this Barring Motor.
45528270 Edition 1 June 2007 Barring Motor T480 Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions WARNING Always wear eye protection when operating or performing maintenance on this Barring Motor.
The distinguishing features of the ServoRam and its performance advantages
 ADVANCED MOTION TECHNOLOGIES INC 1 The distinguishing features of the ServoRam and its performance advantages What is a Linear Motor? There are many suppliers of electrical machines that produce a linear
ADVANCED MOTION TECHNOLOGIES INC 1 The distinguishing features of the ServoRam and its performance advantages What is a Linear Motor? There are many suppliers of electrical machines that produce a linear
KLM. Application example. Linear modules Pneumatic Stroke module. 1 Single base support, SOE Adapter plate, APL 121
 KLM www.comoso.com Sizes 25.. 100 Mass 0.5 kg.. 5.18 kg Driving force 50 N.. 294 N Stroke 25 mm.. 225 mm Repeat accuracy ± 0.01 mm.. ± 0.015 mm Application example 4 5 3 3 6 7 2 2 8 1 1 Pneumatic two-axis
KLM www.comoso.com Sizes 25.. 100 Mass 0.5 kg.. 5.18 kg Driving force 50 N.. 294 N Stroke 25 mm.. 225 mm Repeat accuracy ± 0.01 mm.. ± 0.015 mm Application example 4 5 3 3 6 7 2 2 8 1 1 Pneumatic two-axis
OPERATION MANUAL NT50 NOMAD TRANS-FLO AIR-OPERATED DOUBLE DIAPHRAGM PUMPS. A JDA Global Company. 7/11 rev. 1
 OPERATION MANUAL NT50 NOMAD TRANS-FLO AIR-OPERATED DOUBLE DIAPHRAGM PUMPS A JDA Global Company 7/11 rev. 1 CAUTION SAFETY POINTS TEMPERATURE LIMITS: Neoprene -17.8 C to 93.3 C 0 F to 200 F Buna-N -12.2
OPERATION MANUAL NT50 NOMAD TRANS-FLO AIR-OPERATED DOUBLE DIAPHRAGM PUMPS A JDA Global Company 7/11 rev. 1 CAUTION SAFETY POINTS TEMPERATURE LIMITS: Neoprene -17.8 C to 93.3 C 0 F to 200 F Buna-N -12.2
ATM 322 PNEUMATICS MODULE 4
 ATM 322 PNEUMATICS MODULE 4 WARM UP VIDEO Explain the function of the one way flow control valve. Describe the main parts of the one way flow control valve. Adjust the one way flow control valve to the
ATM 322 PNEUMATICS MODULE 4 WARM UP VIDEO Explain the function of the one way flow control valve. Describe the main parts of the one way flow control valve. Adjust the one way flow control valve to the
OPERATION MANUAL. ALUMINUM Models. 316 S.S. Models NTG25 NOMAD TRANS-FLO AIR-OPERATED DOUBLE DIAPHRAGM PUMPS. A JDA Global Company. 1/14 rev.
 OPERATION MANUAL NTG25 NOMAD TRANS-FLO AIR-OPERATED DOUBLE DIAPHRAGM PUMPS ALUMINUM Models 316 S.S. Models A JDA Global Company 1/14 rev. 3 CAUTION SAFETY POINTS TEMPERATURE LIMITS: Neoprene -17.8 C to
OPERATION MANUAL NTG25 NOMAD TRANS-FLO AIR-OPERATED DOUBLE DIAPHRAGM PUMPS ALUMINUM Models 316 S.S. Models A JDA Global Company 1/14 rev. 3 CAUTION SAFETY POINTS TEMPERATURE LIMITS: Neoprene -17.8 C to
Series 16 Gas Springs. Lift, support, damping and adjustment devices
 Series 16 Gas Springs Lift, support, damping and adjustment devices Gas Springs: Series 16 For nearly 50 years, SUSPA has offered a proven, time-tested, highperformance gas spring line: SERIES 16. Conforming
Series 16 Gas Springs Lift, support, damping and adjustment devices Gas Springs: Series 16 For nearly 50 years, SUSPA has offered a proven, time-tested, highperformance gas spring line: SERIES 16. Conforming
Hydraulic Motors. Radial Piston Motors with fixed displacement Series RM...X Vg = 250 cm³/u cm³/u. Repair manual. Doc.-No.
 Hydraulic Motors Radial Piston Motors with fixed displacement Series RM...X Vg = 250 cm³/u - 900 cm³/u Doc.-No. HM3-005 UK Seite 2 Table of contents 1. General... 3 2. Dismantling the distributor unit...
Hydraulic Motors Radial Piston Motors with fixed displacement Series RM...X Vg = 250 cm³/u - 900 cm³/u Doc.-No. HM3-005 UK Seite 2 Table of contents 1. General... 3 2. Dismantling the distributor unit...
Servo-pneumatic drive solution for welding guns. Top quality welding!
 Servo-pneumatic drive solution for welding guns Sturdy and precise! Top quality welding! Highlights Extremely short cycle times High quality and outstanding reproducibility of the spot welds Excellent
Servo-pneumatic drive solution for welding guns Sturdy and precise! Top quality welding! Highlights Extremely short cycle times High quality and outstanding reproducibility of the spot welds Excellent
R10 Set No: 1 ''' ' '' '' '' Code No: R31033
 R10 Set No: 1 III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 2013 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks:
R10 Set No: 1 III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 2013 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks:
Chapter 2. Background
 Chapter 2 Background The purpose of this chapter is to provide the necessary background for this research. This chapter will first discuss the tradeoffs associated with typical passive single-degreeof-freedom
Chapter 2 Background The purpose of this chapter is to provide the necessary background for this research. This chapter will first discuss the tradeoffs associated with typical passive single-degreeof-freedom
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control. Basics of the damping system
 Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
Volkswagen DCC Adaptive Chassis Control - Design and Function DCC Adaptive Chassis Control The rule for suspension systems has always been that increasing sportiness compromises the ride. In this new system
Pneumatic actuator Assembly & maintenance procedures
 Pneumatic actuator Assembly & maintenance procedures SPRING RETURN ACTUATOR Fig.7901 DOUBLE ACTING ACTUATOR Fig.7902 - LCIE 05 AR 022 2 CONTENTS 1. Applicable Range... page 4-6 2. General Information...
Pneumatic actuator Assembly & maintenance procedures SPRING RETURN ACTUATOR Fig.7901 DOUBLE ACTING ACTUATOR Fig.7902 - LCIE 05 AR 022 2 CONTENTS 1. Applicable Range... page 4-6 2. General Information...
Self-Adjusting Clutch (SAC) Technology Special tools / User instructions
 Self-Adjusting Clutch (SAC) Technology Special tools / User instructions The content of this brochure shall not be legally binding and is for information purposes only. To the extent legally permissible,
Self-Adjusting Clutch (SAC) Technology Special tools / User instructions The content of this brochure shall not be legally binding and is for information purposes only. To the extent legally permissible,
KUZMA STABI XL TURNTABLE (with Air line tonearm) Instruction manual
 KUZMA STABI XL TURNTABLE (with Air line tonearm) Instruction manual 1 KUZMA LTD INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR STABI XL turntable The Stabi XL turntable is a very precisely engineered piece of equipment. However
KUZMA STABI XL TURNTABLE (with Air line tonearm) Instruction manual 1 KUZMA LTD INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR STABI XL turntable The Stabi XL turntable is a very precisely engineered piece of equipment. However
New Development of Highly Efficient Front-Wheel Drive Transmissions in the Compact Vehicle Segment
 New Development of Highly Efficient Front-Wheel Drive Transmissions in the Compact Vehicle Segment Introduction Dr. Ing. Ansgar Damm, Dipl.-Ing. Tobias Gödecke, Dr. Ing. Ralf Wörner, Dipl.-Ing. Gerhard
New Development of Highly Efficient Front-Wheel Drive Transmissions in the Compact Vehicle Segment Introduction Dr. Ing. Ansgar Damm, Dipl.-Ing. Tobias Gödecke, Dr. Ing. Ralf Wörner, Dipl.-Ing. Gerhard
2. Write the expression for estimation of the natural frequency of free torsional vibration of a shaft. (N/D 15)
 ME 6505 DYNAMICS OF MACHINES Fifth Semester Mechanical Engineering (Regulations 2013) Unit III PART A 1. Write the mathematical expression for a free vibration system with viscous damping. (N/D 15) Viscous
ME 6505 DYNAMICS OF MACHINES Fifth Semester Mechanical Engineering (Regulations 2013) Unit III PART A 1. Write the mathematical expression for a free vibration system with viscous damping. (N/D 15) Viscous
Axial Piston Fixed Pump A17FNO Series 10
 Axial Piston Fixed Pump A17FNO Series 10 RE 91510 Issue: 06.2012 Replaces: 03.2010 Size 125 Nominal pressure 250 bar Maximum pressure 300 bar For commercial vehicles Open circuit Features Fixed pump with
Axial Piston Fixed Pump A17FNO Series 10 RE 91510 Issue: 06.2012 Replaces: 03.2010 Size 125 Nominal pressure 250 bar Maximum pressure 300 bar For commercial vehicles Open circuit Features Fixed pump with
Variable Anti-roll Bars on the Touareg
 Service Training Self-Study Programme 331 Variable Anti-roll Bars on the Touareg Design and Function The running gear is a key component of the entire vehicle. It transmits all the forces acting between
Service Training Self-Study Programme 331 Variable Anti-roll Bars on the Touareg Design and Function The running gear is a key component of the entire vehicle. It transmits all the forces acting between
Isolators. F D = C Ẋ α. The concepts of isolation system can be best understood by presenting damper design first, followed by the isolation systems.
 Isolators The concepts of isolation system can be best understood by presenting damper design first, followed by the isolation systems. 1. DAMPER TYPES A conventional high performance fluid damper is depicted
Isolators The concepts of isolation system can be best understood by presenting damper design first, followed by the isolation systems. 1. DAMPER TYPES A conventional high performance fluid damper is depicted
PRECISMECA - MONTAN Gesellschaft für Fördertechnik mbh. Documentation Operating Instructions. Rollers
 PRECISMECA - Gesellschaft für Fördertechnik mbh Documentation Operating Instructions Rollers Operating Instructions Index No.: T311-00 Page: 1 of 1 Section Document No. Pages Preface Safety Technical data
PRECISMECA - Gesellschaft für Fördertechnik mbh Documentation Operating Instructions Rollers Operating Instructions Index No.: T311-00 Page: 1 of 1 Section Document No. Pages Preface Safety Technical data
FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES
 FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES Fundamental Principles The most important safety feature of an automobile is its brake system. The ability of a braking system to provide safe, repeatable stopping is the key to
FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES Fundamental Principles The most important safety feature of an automobile is its brake system. The ability of a braking system to provide safe, repeatable stopping is the key to
506E. LM Guide Actuator General Catalog
 LM Guide Actuator General Catalog A LM Guide Actuator General Catalog A Product Descriptions 506E Caged Ball LM Guide Actuator Model SKR.. A2-4 Structure and Features... A2-4 Caged Ball Technology... A2-6
LM Guide Actuator General Catalog A LM Guide Actuator General Catalog A Product Descriptions 506E Caged Ball LM Guide Actuator Model SKR.. A2-4 Structure and Features... A2-4 Caged Ball Technology... A2-6
Hydraulic Valves. Experience plus ideas
 Hydraulic Valves Experience plus ideas Contents Type/Page Product information Hydraulic valves Function description Non-return valves Pg. 271 Non-return valves Pg. 272-273 RHD RHDI RHV RHZ Function description
Hydraulic Valves Experience plus ideas Contents Type/Page Product information Hydraulic valves Function description Non-return valves Pg. 271 Non-return valves Pg. 272-273 RHD RHDI RHV RHZ Function description
Product information Damage symptoms - brake discs
 Product information Damage symptoms - brake discs Table of contents Purpose... p. 02 1.0 Mounting errors 2.0 Driving conditions 1.1... p. 03 1.2... p. 03 1.3... p. 03 1.4... p. 04 2.1... p. 04 2.2... p.
Product information Damage symptoms - brake discs Table of contents Purpose... p. 02 1.0 Mounting errors 2.0 Driving conditions 1.1... p. 03 1.2... p. 03 1.3... p. 03 1.4... p. 04 2.1... p. 04 2.2... p.
USER MANUAL FOR AREX DIGI+ SYSTEMS
 USER MANUAL FOR AREX DIGI+ SYSTEMS Arex Test Systems bv, Vennestraat 4b, 2161 LE Lisse, Holland Property of: Arex Test Systems bv Vennestraat 4b 2161 LE Lisse Tel: +31 (0) 252 419151 Fax: +31 (0) 252 420510
USER MANUAL FOR AREX DIGI+ SYSTEMS Arex Test Systems bv, Vennestraat 4b, 2161 LE Lisse, Holland Property of: Arex Test Systems bv Vennestraat 4b 2161 LE Lisse Tel: +31 (0) 252 419151 Fax: +31 (0) 252 420510
Lesson 5: Directional Control Valves
 : Directional Control Valves Basic Hydraulic Systems Hydraulic Fluids Hydraulic Tank Hydraulic Pumps and Motors Pressure Control Valves Directional Control Valves Flow Control Valves Cylinders : Directional
: Directional Control Valves Basic Hydraulic Systems Hydraulic Fluids Hydraulic Tank Hydraulic Pumps and Motors Pressure Control Valves Directional Control Valves Flow Control Valves Cylinders : Directional
I) Clamping the work piece II) Drilling the work piece. III) Unclamping the work piece. 10
 Seventh Semester B.E. III IA Test, 2014 USN 1 P E M E PES INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (Bangalore South Campus) (Hosur Road, 1KM before Electronic City, Bangalore-560 100) Department of Mechanical Engineering
Seventh Semester B.E. III IA Test, 2014 USN 1 P E M E PES INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (Bangalore South Campus) (Hosur Road, 1KM before Electronic City, Bangalore-560 100) Department of Mechanical Engineering
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE. On Industrial Automation and Control
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE On Industrial Automation and Control By Prof. S. Mukhopadhyay Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Kharagpur Topic Lecture
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE On Industrial Automation and Control By Prof. S. Mukhopadhyay Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Kharagpur Topic Lecture
Gated and assembled in one moulding cycle
 Customer information from EWIKON Heißkanalsysteme GmbH Gated and assembled in one moulding cycle Tailored hot runner solution for a demanding -component mould concept Pages - 5 Processing of sensitive
Customer information from EWIKON Heißkanalsysteme GmbH Gated and assembled in one moulding cycle Tailored hot runner solution for a demanding -component mould concept Pages - 5 Processing of sensitive
ORIGA Pneumatic Linear Drives OSP-L
 ORIGA Pneumatic Linear Drives OSP-L Very long lifetime and lowest leakage A NEW Modular Linear Drive System With this second generation linear drive Parker Origa offers design engineers complete flexibility.
ORIGA Pneumatic Linear Drives OSP-L Very long lifetime and lowest leakage A NEW Modular Linear Drive System With this second generation linear drive Parker Origa offers design engineers complete flexibility.
Six keys to achieving better precision in linear motion control applications
 profile Drive & Control Six keys to achieving better precision in linear motion control applications Achieving precise linear motion Consider these factors when specifying linear motion systems: Equipped
profile Drive & Control Six keys to achieving better precision in linear motion control applications Achieving precise linear motion Consider these factors when specifying linear motion systems: Equipped
LECTURE 30 to 31 ACCESSORIES USED IN FLUID POWER SYSTEMS FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 LECTURE 30 to 31 ACCESSORIES USED IN FLUID POWER SYSTEMS FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1. Explain the two types of the leakages in hydraulic system. In what way do they affect the performance of a fluid system?
LECTURE 30 to 31 ACCESSORIES USED IN FLUID POWER SYSTEMS FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1. Explain the two types of the leakages in hydraulic system. In what way do they affect the performance of a fluid system?
SHOCK DYNAMOMETER: WHERE THE GRAPHS COME FROM
 SHOCK DYNAMOMETER: WHERE THE GRAPHS COME FROM Dampers are the hot race car component of the 90s. The two racing topics that were hot in the 80s, suspension geometry and data acquisition, have been absorbed
SHOCK DYNAMOMETER: WHERE THE GRAPHS COME FROM Dampers are the hot race car component of the 90s. The two racing topics that were hot in the 80s, suspension geometry and data acquisition, have been absorbed
New Reliability Assessment Methods for MEMS. Prof. Mervi Paulasto-Kröckel Electronics Integration and Reliability
 New Reliability Assessment Methods for MEMS Prof. Mervi Paulasto-Kröckel Electronics Integration and Reliability Aalto University A merger of leading Finnish universities in 2010: Helsinki School of Economics
New Reliability Assessment Methods for MEMS Prof. Mervi Paulasto-Kröckel Electronics Integration and Reliability Aalto University A merger of leading Finnish universities in 2010: Helsinki School of Economics
Aircraft Maintenance Prof. A.K Ghosh Prof. Vipul Mathur Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Aircraft Maintenance Prof. A.K Ghosh Prof. Vipul Mathur Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 05 Aircraft Landing Gear System Now, coming to the next aircraft
Aircraft Maintenance Prof. A.K Ghosh Prof. Vipul Mathur Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 05 Aircraft Landing Gear System Now, coming to the next aircraft
Telescopic slides 603
 603 Technical information for telescopic slides Construction: consist of two or more ball-bearing supported guide rails mounted one inside another that can be pulled out like a telescope. The load rating
603 Technical information for telescopic slides Construction: consist of two or more ball-bearing supported guide rails mounted one inside another that can be pulled out like a telescope. The load rating
Spring hangers, spring supports
 Spring hangers, spring supports 2 spring Spring hangers, supports PRODUCT 2 GROUP Spring hangers, spring supports Contents Page Field of application...2.1 Overview of spring hangers and spring supports...2.3
Spring hangers, spring supports 2 spring Spring hangers, supports PRODUCT 2 GROUP Spring hangers, spring supports Contents Page Field of application...2.1 Overview of spring hangers and spring supports...2.3
Roehrig Engineering, Inc.
 Roehrig Engineering, Inc. Home Contact Us Roehrig News New Products Products Software Downloads Technical Info Forums What Is a Shock Dynamometer? by Paul Haney, Sept. 9, 2004 Racers are beginning to realize
Roehrig Engineering, Inc. Home Contact Us Roehrig News New Products Products Software Downloads Technical Info Forums What Is a Shock Dynamometer? by Paul Haney, Sept. 9, 2004 Racers are beginning to realize
