2. Power Steering System
|
|
|
- Dulcie Henry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 W1860BE.book Page 5 Tuesday, January 28, :01 PM 2. Power Steering System A: HYDRAULIC SYSTEM The fluid pump is directly driven by the engine through a belt. The fluid flow is maintained almost constant regardless of change in the engine speed by the function of the flow control valve. The flow-regulated fluid is delivered to the control valve through hose A. When the steering wheel is turned, the rotary control valve connected to the pinion shaft opens the hydraulic circuit corresponding to the direction in which the steering wheel is turned. The fluid then flows into chamber A or B via pipe A or B. The fluid pressure in chamber A or B acts on the rack piston in the same direction as that in which the rack shaft is moved by rotation of the steering wheel. This helps reduce the effort required of the driver to operate the steering wheel. Movement of the rack piston causes the fluid in the other chamber to return to the reservoir tank via pipe A or B, control valve, and hose B. As the steering shaft is connected to the pinion shaft mechanically via the rotary control valve, the steering system can operate as a manual system even if the hydraulic system becomes inoperative. To control the maximum fluid pressure, a relief valve is built into the fluid pump to prevent buildup of an excessive fluid pressure. PS-5
2 W1860BE.book Page 6 Tuesday, January 28, :01 PM (5) (6) (12) (13) (10) (11) (14) (16) (17) (19) (18) (15) PS Power cylinder (11) Steering wheel Rack piston (12) Tank Rack shaft (13) Vane pump Pinion shaft (14) Relief valve (5) Chamber A (15) Hose A (6) Chamber B (16) Hose B Pipe A (17) Pump control valve Pipe B (18) Fluid pump Control valve (19) Engine (10) Steering shaft PS-6
3 W1860BE.book Page 7 Tuesday, January 28, :01 PM B: GEARBOX ASSEMBLY 1. POWER CYLINDER The gearbox integrates the control valve and power cylinder into a single unit. The rack shaft serves as a power cylinder piston. The rotary control valve is located around the pinion shaft. The rotary control valve and power cylinder are connected to each other by two pipes through which hydraulic fluid flows. (5) (6) PS Piston Power cylinder Rack shaft (5) Pinion shaft Cylinder (6) Control valve 2. ROTARY CONTROL VALVE The rotary control valve consists of a rotor (which rotates together with the steering shaft), a pinion (which is connected to the rotor and torsion bar), and a sleeve (which rotates together with the pinion). The rotor and sleeve have grooves C and D, respectively, which form fluid passages V 1 through V 4. The pinion is in mesh with the rotor with adequate clearance, which enable the rack to be moved manually by rotating the steering shaft (fail-safe feature). PS-7
4 W1860BE.book Page 8 Tuesday, January 28, :01 PM (B) (A) (5) (A) (B) (17) (10) (11) (6) (11) (16) (18) (10) (10) (12) (13) (15) (14) PS Torsion bar (12) Torsion bar Sleeve (13) Rotor Rotor (14) Sleeve Pinion (15) Fluid return line (to reservoir tank) (5) Pinion-to-rotor engagement (fail-safe feature) (16) Pinion (6) Fluid passage V 1 (17) Torsion bar Fluid passage V 2 (18) Rotor Fluid passage V 3 Fluid passage V 4 (A) Cross-sectional view A (fluid passage switching circuit) (10) Groove C (B) Cross-sectional view B (pinion-to-rotor engagement) (11) Groove D PS-8
5 W1860BE.book Page 9 Tuesday, January 28, :01 PM Principle of operation When the torsion bar is twisted by a rotational force applied to the steering wheel, the relative position between the rotor and sleeve changes. This changes the cross-sectional area of fluid passages V 1, V 2, V 3 and V 4. The fluid passages are thus switched and the fluid pressure is controlled in accordance with the operation of the steering wheel. When no steering force is applied: The rotor and sleeve are held at the neutral position. Fluid passages V 1, V 2, V 3 and V 4, which are formed by grooves C and D are open equally. Under this condition, the fluid from the pump returns to the reservoir tank so that neither fluid pressure builds up nor the rack piston moves in the power cylinder. (5) (6) PS Chamber A V 2 From fluid pump Chamber B (5) V 3 To A V 1 (6) V 4 To B PS-9
6 W1860BE.book Page 10 Tuesday, January 28, :01 PM When steering force is applied: When the steering wheel is turned to the right, for example, fluid passages V 1 and V 3 are opened while fluid passages V 2 and V 4 are nearly closed. At this point, the fluid pressure in chamber A of the power cylinder increases depending on the degree of closure of fluid passages V 2 and V 4 so that the rack piston moves to the right. The fluid in chamber B, on the other hand, is drained through fluid passage V 3 into the reservoir tank. (5) (6) PS Chamber A V 2 From fluid pump Chamber B (5) V 3 To A V 1 (6) V 4 From B Fail-safe function If fluid pressure fails to build up due to, for example, a broken fluid pump drive belt, the steering wheel rotating torque is transmitted from the valve rotor to the pinion through mechanical engagement between them. PS-10
7 W1860BE.book Page 11 Tuesday, January 28, :01 PM C: FLUID PUMP AND RESERVOIR TANK The fluid pump is a vane type driven by the engine via belt. The reservoir tank is mounted on the vehicle body. The fluid pump incorporates the flow control valve and relief valve, each performing the following functions: The flow control valve regulates the flow rate of discharged fluid to a constant level irrespective of the engine speed. The relief valve protects the system from an excessively high pressure which may occur, for example, when the steering wheel is turned all the way. PS Fluid pump Reservoir tank PS-11
8 W1860BE.book Page 12 Tuesday, January 28, :01 PM (5) PS Reservoir tank Fluid pump assembly Flow control and relief valve assembly (5) Steering gearbox Vane pump PS-12
9 W1860BE.book Page 13 Tuesday, January 28, :01 PM The fluid pump is belt-driven by the engine. The fluid flow is controlled according to the engine speed so that an adequate steering resistance is given during high-speed operation. The fluid pump is a variable capacity type vane pump whose delivery rate per rotation decreases as the engine speed increases. The pump is integral with a pump control valve and relief valve. The vane pump consists of a rotor, a cam ring, and eleven vanes. When the rotor rotates, the vane in each slot of the rotor is radially moved out by centrifugal force and pressed against the cam ring. The fluid from the suction port is confined in chambers formed between two adjacent vanes and carried to the discharge port. Since the cam ring is movable in relation to the rotor, the volume of each chamber is variable. This enables the delivery rate per rotation of the pump to be changed. (5) PS Suction Vane Rotor Cam ring (5) Discharge PS-13
10 W1860BE.book Page 14 Tuesday, January 28, :01 PM Flow control The variable capacity pump changes its delivery rate per rotation by changing the degree of eccentricity of the cam ring according to its rotating speed (engine speed). On turbo models, a constant flow as shown with the broken line in the drawing below is maintained. C D B A (5) (6) PS Fluid flow (6) High-speed Pump speed Delivery rate per unit time Idling Delivery rate per rotation of pump Low-speed Turbo models (5) Mid-speed NOTE: In the following description, pump speed ranges will be indicated using the speed points A through D shown in the drawing above. PS-14
11 W1860BE.book Page 15 Tuesday, January 28, :01 PM Low-range-speed operation (A B range) In this speed range, as well as in all the other speed ranges, two different pump discharge pressures are always applied to the control valve; one is directly led from the discharge port to the left end of the valve and the other is led through an orifice (variable orifice) to the right end of the valve. Since the orifice has a pressure reducing effect, the latter pressure is lower than the former. When the pump is operating at a low speed, its discharge pressure is also low, resulting in only small difference between the two pressures. In this condition, the valve stays pushed leftward by the spring, allowing the non-pressurized tank fluid to enter chamber A. To chamber B, on the other hand, the orifice-reduced discharge pressure is applied, so the cam ring is pushed leftward by the cam ring spring. This makes the eccentricity of the cam ring a maximum and, therefore, the delivery rate per rotation of the pump become a maximum. (5) (6) PS Control valve (6) Variable orifice Reservoir tank fluid Pressure chamber A Control valve spring Pressure chamber B Gear box Cam ring (5) Cam ring spring PS-15
12 W1860BE.book Page 16 Tuesday, January 28, :01 PM Mid- to high-range-speed operation (B D range) During mid-range speed operation, the pump increases its delivery rate. Since the pressure before passing through the variable orifice increases, the control valve moves rightward, overcoming the tension of the control valve spring. This movement of the control valve allows the pressure upstream of the variable orifice to be directed to chamber A after being adjusted to a necessary pressure* by the port opening area created by the control valve. On the other hand, chamber B receives the reservoir pressure (suction pressure). This means that the pressure in chamber A is higher than that in chamber B. As a result, the cam ring moves rightward against the tension of the cam spring. This causes the delivery rate per rotation of the pump to be reduced, so that the flow rate of the fluid to the steering gear box decreases accordingly. The above control is performed when the pump is operating at a speed in the B - D range. * The "necessary pressure" for chamber A is a pressure required to move the cam ring to the position corresponding to each predetermined flow rate (pump delivery rate). The pressure is obtained by changing the port opening area appropriately through displacement of the control valve. The displacement of the control valve is determined by how much the pressure before the variable orifice is different from that after the orifice. (10) (5) (6) PS Control valve (6) Variable orifice Reservoir tank fluid Pressure chamber A Control valve spring Pressure chamber B Gear box Cam ring (5) Cam ring spring (10) Opening PS-16
13 W1860BE.book Page 17 Tuesday, January 28, :01 PM Maximum pressure control When the overall delivery rate of the pump exceeds a preset value, the relief valve opens to allow part of the discharged fluid to flow toward the suction side of the pump, thereby controlling the maximum pressure. PS Reservoir tank fluid Relief valve Gear box Relief spring PS-17
14 W1860BE.book Page 18 Tuesday, January 28, :01 PM MEMO PS-18
2. Power Steering System
 2. Power Steering System A: HYDRAULIC SYSTEM POWER STEERING SYSTEM The fluid pump is directly driven by the engine through a belt. The fluid flow is maintained almost constant regardless of change in the
2. Power Steering System A: HYDRAULIC SYSTEM POWER STEERING SYSTEM The fluid pump is directly driven by the engine through a belt. The fluid flow is maintained almost constant regardless of change in the
POWER ASSISTED SYSTEM (POWER STEERING)
 POWER ASSISTED SYSTEM (POWER STEERING) TILT STEERING COLUMN 1. Tilt Steering Column A: TILT MECHANISM The steering wheel vertical position can be adjusted within a 38 mm (1.50 in) range by using the tilt
POWER ASSISTED SYSTEM (POWER STEERING) TILT STEERING COLUMN 1. Tilt Steering Column A: TILT MECHANISM The steering wheel vertical position can be adjusted within a 38 mm (1.50 in) range by using the tilt
2. Reverse Check Mechanism
 W1860BE.book Page 4 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM REVERSE CHECK MECHNISM MNUL TRNSMISSION ND DIFFERENTIL 2. Reverse Check Mechanism Located in the transfer case, the reverse check mechanism prevents
W1860BE.book Page 4 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM REVERSE CHECK MECHNISM MNUL TRNSMISSION ND DIFFERENTIL 2. Reverse Check Mechanism Located in the transfer case, the reverse check mechanism prevents
3. Fuel System FUEL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-7
 W1860BE.book Page 7 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter.
W1860BE.book Page 7 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter.
2. Air Line AIR LINE FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL B: MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR FU(H4DOTC)-3
 W1860BE.book Page 3 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 2. Air Line A: GENERAL The air filtered by the air cleaner enters the throttle body where it is regulated in the volume by the throttle valve and
W1860BE.book Page 3 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 2. Air Line A: GENERAL The air filtered by the air cleaner enters the throttle body where it is regulated in the volume by the throttle valve and
11.AWD Transfer System
 W1860BE.book Page 54 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 11.AWD Transfer System A: MPT MODELS 1. GENERAL This all-wheel-drive (AWD) transfer system uses an electronically controlled multi-plate type transfer
W1860BE.book Page 54 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 11.AWD Transfer System A: MPT MODELS 1. GENERAL This all-wheel-drive (AWD) transfer system uses an electronically controlled multi-plate type transfer
Chapter. Steering System Technology
 Chapter 78 Steering System Technology Objectives After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Explain the operating principles of steering systems. Identify the major parts of a steering system. Compare
Chapter 78 Steering System Technology Objectives After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Explain the operating principles of steering systems. Identify the major parts of a steering system. Compare
Module 13: Mechanical Fuel Injection Diagnosis and Repair
 Terms and Definitions Parts of Injection Nozzles Types of Nozzle Valves Operation of an Injection Nozzle Fuel Flow Through the Unit Injector Optional Features on Fuel Injection Pumps Main Parts of a Distributor-Type
Terms and Definitions Parts of Injection Nozzles Types of Nozzle Valves Operation of an Injection Nozzle Fuel Flow Through the Unit Injector Optional Features on Fuel Injection Pumps Main Parts of a Distributor-Type
POWER STEERING SYSTEM
 14-3 POWER SYSTEM GENERAL 1. POWER SYSTEM OVERVIEW The power steering has been designed to make the wheel move more easily than in a manual steering system. The hydraulic power assists the process utilizing
14-3 POWER SYSTEM GENERAL 1. POWER SYSTEM OVERVIEW The power steering has been designed to make the wheel move more easily than in a manual steering system. The hydraulic power assists the process utilizing
1. Cruise Control CRUISE CONTROL A: OPERATION CC-2
 W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Cruise Control A: OPERATION The cruise system automatically s the vehicle speed. It allows the vehicle to run at a constant speed without need
W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Cruise Control A: OPERATION The cruise system automatically s the vehicle speed. It allows the vehicle to run at a constant speed without need
2. Hydraulic Valves, Actuators and Accessories. 24 Marks
 2. Hydraulic Valves, Actuators and Accessories 24 Marks Co related to chapter 602.2 Describe working principle of various components used in hydraulic & pneumatic systems. 602.3 Choose valves, actuators
2. Hydraulic Valves, Actuators and Accessories 24 Marks Co related to chapter 602.2 Describe working principle of various components used in hydraulic & pneumatic systems. 602.3 Choose valves, actuators
Test Which component has the highest Energy Density? A. Accumulator. B. Battery. C. Capacitor. D. Spring.
 Test 1 1. Which statement is True? A. Pneumatic systems are more suitable than hydraulic systems to drive powerful machines. B. Mechanical systems transfer energy for longer distances than hydraulic systems.
Test 1 1. Which statement is True? A. Pneumatic systems are more suitable than hydraulic systems to drive powerful machines. B. Mechanical systems transfer energy for longer distances than hydraulic systems.
1. Anti-lock Brake System (ABS)
 W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Anti-lock Brake System () A: FEATURE The 5.3i type used in the Impreza has a hydraulic control unit, an control module, a valve relay and a motor
W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Anti-lock Brake System () A: FEATURE The 5.3i type used in the Impreza has a hydraulic control unit, an control module, a valve relay and a motor
CHAPTER 30 Power-Assisted Steering Operation and Service
 CHAPTER 30 Power-Assisted Steering Operation and Service OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 30, the reader will be able to: 1. Prepare for ASE Suspension and Steering (A4) certification test content area
CHAPTER 30 Power-Assisted Steering Operation and Service OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 30, the reader will be able to: 1. Prepare for ASE Suspension and Steering (A4) certification test content area
Development of Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS) System for Large Vehicles
 TECHNICAL REPORT Development of Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS) System for Large Vehicles T. SUGIMOTO I. UNO H. ISHIHARA S. URANO T. OHHASHI T. IKEDA In accordance with recent increases in crude oil prices
TECHNICAL REPORT Development of Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS) System for Large Vehicles T. SUGIMOTO I. UNO H. ISHIHARA S. URANO T. OHHASHI T. IKEDA In accordance with recent increases in crude oil prices
CH.4 Basic Components of Hydraulic and Pneumatic System/16 M HAP/17522/AE5G
 Content : 4.1 Hydraulic and Pneumatic actuators. 10 Marks Hydraulic Actuators - Hydraulic cylinders (single, double acting and telescopic) construction and working, Hydraulic motors (gear and piston type)
Content : 4.1 Hydraulic and Pneumatic actuators. 10 Marks Hydraulic Actuators - Hydraulic cylinders (single, double acting and telescopic) construction and working, Hydraulic motors (gear and piston type)
1. General Description
 1. General Description A: SPECIFICATIONS Whole system Gearbox Pump (Power steering system) Working fluid (Power steering system) NON-TURBO TURBO Model SEDAN and Others OUTBACK WRX STi Minimum turning radius
1. General Description A: SPECIFICATIONS Whole system Gearbox Pump (Power steering system) Working fluid (Power steering system) NON-TURBO TURBO Model SEDAN and Others OUTBACK WRX STi Minimum turning radius
Marine Engineering Exam Resource Review of Hydraulics
 1. What is Pascal s law? Pressure confined on a confined fluid will transmit the pressure in all directions and act with equal force on all areas at right angles. 2. How does the law pertain to hydraulics?
1. What is Pascal s law? Pressure confined on a confined fluid will transmit the pressure in all directions and act with equal force on all areas at right angles. 2. How does the law pertain to hydraulics?
Introduction. General Information. Systems Operation
 Systems Operation Introduction Reference: For illustrated Specifications, refer to the Specifications For 416, 426, 428, 436, 438, & Series II Backhoe Loaders Transmission, Form No. SENR3131. If the specifications
Systems Operation Introduction Reference: For illustrated Specifications, refer to the Specifications For 416, 426, 428, 436, 438, & Series II Backhoe Loaders Transmission, Form No. SENR3131. If the specifications
INTRODUCTION: Rotary pumps are positive displacement pumps. The rate of flow (discharge) of rotary pump remains constant irrespective of the
 INTRODUCTION: Rotary pumps are positive displacement pumps. The rate of flow (discharge) of rotary pump remains constant irrespective of the pressure. That is, even at very high pressure, these pumps can
INTRODUCTION: Rotary pumps are positive displacement pumps. The rate of flow (discharge) of rotary pump remains constant irrespective of the pressure. That is, even at very high pressure, these pumps can
LogSplitterPlans.Com
 Hydraulic Pump Basics LogSplitterPlans.Com Hydraulic Pump Purpose : Provide the Flow needed to transmit power from a prime mover to a hydraulic actuator. Hydraulic Pump Basics Types of Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic Pump Basics LogSplitterPlans.Com Hydraulic Pump Purpose : Provide the Flow needed to transmit power from a prime mover to a hydraulic actuator. Hydraulic Pump Basics Types of Hydraulic Pumps
ESCONDIDO FIRE DEPT TRAINING MANUAL Section DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 Pumps and Accessory Equipment Revised
 DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 PUMPS AND ACCESSORY EQUIPMENT Pumps are designed for many different purposes. In order to understand the proper application and operation of a pump in a given situation, firefighters
DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 PUMPS AND ACCESSORY EQUIPMENT Pumps are designed for many different purposes. In order to understand the proper application and operation of a pump in a given situation, firefighters
Table 6-1. Problems and solutions with pump operations. No Fluid Delivery
 Table 6-1. and solutions with pump operations No Fluid Delivery Fluid level in the reservoir is low. Oil intake pipe or inlet filter is plugged. Air leak in the inlet line prevents priming or causes noise
Table 6-1. and solutions with pump operations No Fluid Delivery Fluid level in the reservoir is low. Oil intake pipe or inlet filter is plugged. Air leak in the inlet line prevents priming or causes noise
Torque Converter, Transmission Pump, Screen And Filter
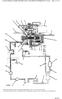 Page 13 of 27 Transmission Hydraulic System In Forward (Engine Running - Type 2 & 3 Control Valve Shown) (4) Transmission control valve. (5) Neutralizer valve. (6) Neutralizer solenoid. (7) Flow control
Page 13 of 27 Transmission Hydraulic System In Forward (Engine Running - Type 2 & 3 Control Valve Shown) (4) Transmission control valve. (5) Neutralizer valve. (6) Neutralizer solenoid. (7) Flow control
7. Evaporative Emission Control System
 W1860BE.book Page 10 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 7. Evaporative Emission Control System A: GENERAL The evaporative emission control system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into atmosphere. This
W1860BE.book Page 10 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 7. Evaporative Emission Control System A: GENERAL The evaporative emission control system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into atmosphere. This
GEAR PUMP. Mohammud Hanif Dewan, Lecturer, Malaysian Maritime Academy, Malaysia.
 GEAR PUMP Mohammud Hanif Dewan, Lecturer, Malaysian Maritime Academy, Malaysia. Introduction Learning Objective: - Operation and maintenance of a Gear Pump. Specific Learning Objective: - Describe the
GEAR PUMP Mohammud Hanif Dewan, Lecturer, Malaysian Maritime Academy, Malaysia. Introduction Learning Objective: - Operation and maintenance of a Gear Pump. Specific Learning Objective: - Describe the
3. Center Differential
 W1860BE.book Page 9 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 3. Center Differential A: CONSTRUCTION The center differential consists of a set of bevel gears and a viscous coupling. The center differential has
W1860BE.book Page 9 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 3. Center Differential A: CONSTRUCTION The center differential consists of a set of bevel gears and a viscous coupling. The center differential has
Section 6.1. Implement Circuit - General System. General: TF Configuration TB Configurations Implement Control Valve:
 Section 6.1 Implement Circuit - General System General: TF Configuration... 6.1.3 TB Configurations... 6.1.5 Implement Pump Breakdown... 6.1.6 Operational Description: General... 6.1.7 Compensator Control...
Section 6.1 Implement Circuit - General System General: TF Configuration... 6.1.3 TB Configurations... 6.1.5 Implement Pump Breakdown... 6.1.6 Operational Description: General... 6.1.7 Compensator Control...
application and are used in chemical injection systems (water
 Mechanical Equipment - Course 430.1 POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT PUMPS In the previous lesson it was explained that although centrifugal pumps have many operational and maintenance adva.ntages over positive displacement
Mechanical Equipment - Course 430.1 POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT PUMPS In the previous lesson it was explained that although centrifugal pumps have many operational and maintenance adva.ntages over positive displacement
Definitions of Technical Terms
 Definitions of Technical Terms ABSOLUTE A measure having as it s zero point of base the complete absence of the entity being measured. ABSOLUTE PRESSURE A pressure scale with zero point at a perfect vacuum.
Definitions of Technical Terms ABSOLUTE A measure having as it s zero point of base the complete absence of the entity being measured. ABSOLUTE PRESSURE A pressure scale with zero point at a perfect vacuum.
CHASSIS STEERING. A rack and pinion type steering is used. The EHPS (Electro-Hydraulic Power Steering) is standard equipment on all models.
 60 STEERING DESCRIPTION The stepless tilt steering is used. The steering column has adopted an energy absorbing mechanism that uses energy absorbing plate. The basic construction and operation are the
60 STEERING DESCRIPTION The stepless tilt steering is used. The steering column has adopted an energy absorbing mechanism that uses energy absorbing plate. The basic construction and operation are the
Automotive Technology
 Louisiana curriculum: Automotive Technology Steering and Suspension Systems Student Reference written by Larry Rains revised by Robin Ferguson technical advisor Fred Smith project coordinator Richard Branton
Louisiana curriculum: Automotive Technology Steering and Suspension Systems Student Reference written by Larry Rains revised by Robin Ferguson technical advisor Fred Smith project coordinator Richard Branton
Section 6.1. Implement Circuit - General System. General: TF Configuration TB Configurations Implement Control Valve:
 Section 6.1 Implement Circuit - General System General: TF Configuration... 6.1.3 TB Configurations... 6.1.5 Implement Pump Breakdown... 6.1.6 Operational Description: General... 6.1.7 Compensator Control...
Section 6.1 Implement Circuit - General System General: TF Configuration... 6.1.3 TB Configurations... 6.1.5 Implement Pump Breakdown... 6.1.6 Operational Description: General... 6.1.7 Compensator Control...
1. Seat Belt SEAT BELT A: ADJUSTABLE SHOULDER BELT ANCHOR SB-2
 W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM SYSTEM 1. Seat Belt A: ADJUSTABLE SHOULDER BELT ANCHOR 1. FRONT Each front seat belt system has an adjustable shoulder belt anchor which allows the
W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM SYSTEM 1. Seat Belt A: ADJUSTABLE SHOULDER BELT ANCHOR 1. FRONT Each front seat belt system has an adjustable shoulder belt anchor which allows the
Section 6.1. Implement Circuit - General System. General: Implement Control Valve: Implement Circuit
 Section 6.1 Implement Circuit - General System General: Implement Circuit... 6.1.3 Implement Pump Breakdown... 6.1.4 Operational Description: General... 6.1.5 Compensator Control... 6.1.6 Standby Condition...
Section 6.1 Implement Circuit - General System General: Implement Circuit... 6.1.3 Implement Pump Breakdown... 6.1.4 Operational Description: General... 6.1.5 Compensator Control... 6.1.6 Standby Condition...
A 1 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
 A1 A2 Clutch CLUTCH Specifications Pedal height (from asphalt sheet) Release point (from pedal stroke end position) Push rod play at pedal top Pedal freeplay Disc rivet head depth Disc runout Diaphragm
A1 A2 Clutch CLUTCH Specifications Pedal height (from asphalt sheet) Release point (from pedal stroke end position) Push rod play at pedal top Pedal freeplay Disc rivet head depth Disc runout Diaphragm
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
 F01B MACHINES OR ENGINES, IN GENERAL OR OF POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT TYPE, e.g. STEAM ENGINES (of rotary-piston or oscillating-piston type F01C; of non-positive-displacement type F01D; internal-combustion
F01B MACHINES OR ENGINES, IN GENERAL OR OF POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT TYPE, e.g. STEAM ENGINES (of rotary-piston or oscillating-piston type F01C; of non-positive-displacement type F01D; internal-combustion
MODULE- 5 : INTRODUCTION TO HYDROSTATIC UNITS (PUMPS AND MOTORS)
 MODULE- 5 : INTRODUCTION TO HYDROSTATIC UNITS (PUMPS AND MOTORS) LECTURE- 18 : BASIC FEATURES OF SOME Hydraulic Pumps & Motors Introduction In this section we shall discuss the working principles and fundamental
MODULE- 5 : INTRODUCTION TO HYDROSTATIC UNITS (PUMPS AND MOTORS) LECTURE- 18 : BASIC FEATURES OF SOME Hydraulic Pumps & Motors Introduction In this section we shall discuss the working principles and fundamental
Section 6.1. Implement Circuit - General System. General: TF Configuration TB Configurations Implement Control Valve:
 Section 6.1 Implement Circuit - General System General: TF Configuration... 6.1.3 TB Configurations... 6.1.5 Implement Pump Breakdown... 6.1.6 Operational Description: General... 6.1.7 Compensator Control...
Section 6.1 Implement Circuit - General System General: TF Configuration... 6.1.3 TB Configurations... 6.1.5 Implement Pump Breakdown... 6.1.6 Operational Description: General... 6.1.7 Compensator Control...
Steering Fundamentals
 CHAPTER 65 Fundamentals OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to: List the parts of steering systems. Describe the principles of operation of steering systems. Compare linkage
CHAPTER 65 Fundamentals OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to: List the parts of steering systems. Describe the principles of operation of steering systems. Compare linkage
SECTION steering mechanism
 07-302.01/ 1 2011MR17 SECTION 07-302.01 GENERAL Description See Figure 1. The includes the steering wheel (1), the steering column, the miter box (3), the steering shafts (2 and 4), and the drag link (7).
07-302.01/ 1 2011MR17 SECTION 07-302.01 GENERAL Description See Figure 1. The includes the steering wheel (1), the steering column, the miter box (3), the steering shafts (2 and 4), and the drag link (7).
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION
 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION BRAKE BOOSTER Delco-Moraine Single Diaphragm A combined vacuum-hydraulic unit which uses a combination of intake manifold vacuum and atmospheric pressure to provide power assist.
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION BRAKE BOOSTER Delco-Moraine Single Diaphragm A combined vacuum-hydraulic unit which uses a combination of intake manifold vacuum and atmospheric pressure to provide power assist.
FLUID POWER FLUID POWER EQUIPMENT TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC MOTORS. This work covers part of outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module:
 FLUID POWER FLUID POWER EQUIPMENT TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC MOTORS This work covers part of outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module: UNIT 21746P APPLIED PNEUMATICS AND HYDRAULICS The material needed
FLUID POWER FLUID POWER EQUIPMENT TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC MOTORS This work covers part of outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module: UNIT 21746P APPLIED PNEUMATICS AND HYDRAULICS The material needed
(3) (4) (6) (5) (10) (9) (8) (7)
 3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter. Fuel injection pressure is regulated to an optimum
3. Fuel System A: GENERAL The fuel pressurized by the fuel tank inside pump is delivered to each fuel injector by way of the fuel pipe and fuel filter. Fuel injection pressure is regulated to an optimum
STEERING 19-1 STEERING CONTENTS
 PL STEERING 19-1 STEERING CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 POWER STEERING PUMP... 9 page STEERING COLUMN... 35 STEERING GEAR... 26 GENERAL INFORMATION INDEX page GENERAL INFORMATION STEERING SYSTEM
PL STEERING 19-1 STEERING CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION... 1 POWER STEERING PUMP... 9 page STEERING COLUMN... 35 STEERING GEAR... 26 GENERAL INFORMATION INDEX page GENERAL INFORMATION STEERING SYSTEM
Hydraulic Pumps Classification of Pumps
 Fluidsys Training Centre, Bangalore offers an extensive range of skill-based and industry-relevant courses in the field of Pneumatics and Hydraulics. For more details, please visit the website: https://fluidsys.org
Fluidsys Training Centre, Bangalore offers an extensive range of skill-based and industry-relevant courses in the field of Pneumatics and Hydraulics. For more details, please visit the website: https://fluidsys.org
FLUID POWER TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC PUMPS APPLIED PNEUMATICS AND HYDRAULICS H1
 FLUID POWER TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC PUMPS This work covers outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module: APPLIED PNEUMATICS AND HYDRAULICS H1 The material needed for outcome 2 is very extensive so the tutorial
FLUID POWER TUTORIAL HYDRAULIC PUMPS This work covers outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module: APPLIED PNEUMATICS AND HYDRAULICS H1 The material needed for outcome 2 is very extensive so the tutorial
Removing and installing parts of the lubrication system Removing and installing parts of the lubrication system
 Side 1 av 15 Removing and parts of the lubrication system Removing and parts of the lubrication system Notes: If large quantities of metal particles or other deposits (caused, for example, by partial seizure
Side 1 av 15 Removing and parts of the lubrication system Removing and parts of the lubrication system Notes: If large quantities of metal particles or other deposits (caused, for example, by partial seizure
Section 6.1. Implement Circuit - General System. General: Implement Control Valve:
 Section 6.1 Implement Circuit - General System General: Implement Circuit... 6.1.3 Implement Pump Breakdown... 6.1.4 Operational Description: General... 6.1.5 Compensator Control... 6.1.6 Standby Condition...
Section 6.1 Implement Circuit - General System General: Implement Circuit... 6.1.3 Implement Pump Breakdown... 6.1.4 Operational Description: General... 6.1.5 Compensator Control... 6.1.6 Standby Condition...
Vickers 45. VMQ Series 30 Vane Pumps. Fixed Displacement, For Industrial and Mobile Applications (4.188)
 [ (4.188) 49,4 (1.94) /21,8 /.86) 174,7/172,3 (6.88/6.78) 332,9/33,5 (13.11/13.1) "M" is marked if metric port threads No marking if inch port threads AS-568-152 O-ring Vickers 45 65,3 (2.57) 13 (5.1 VMQ
[ (4.188) 49,4 (1.94) /21,8 /.86) 174,7/172,3 (6.88/6.78) 332,9/33,5 (13.11/13.1) "M" is marked if metric port threads No marking if inch port threads AS-568-152 O-ring Vickers 45 65,3 (2.57) 13 (5.1 VMQ
Experiments on Hydraulic and Pneumatic circuit trainers HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS:
 Experiments on Hydraulic and Pneumatic circuit trainers HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS: Hydraulic circuits are used in high power and high load applications such as earth moving equipment. The pressure used in industrial
Experiments on Hydraulic and Pneumatic circuit trainers HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS: Hydraulic circuits are used in high power and high load applications such as earth moving equipment. The pressure used in industrial
A pump is a machine used to move liquid through a piping system and to raise the pressure of the liquid.
 What is a pump A pump is a machine used to move liquid through a piping system and to raise the pressure of the liquid. Why increase a liquid s pressure? Static elevation a liquid s pressure must be increased
What is a pump A pump is a machine used to move liquid through a piping system and to raise the pressure of the liquid. Why increase a liquid s pressure? Static elevation a liquid s pressure must be increased
Syslog Technologies Innovative Thoughts
 AUTOMATIC PNEUMATIC WATER PUMPING SYSTEM SYNOPSIS The aim of the project is pneumatic operated water pumping system. Radial plunger Pneumatic Water pumping system are reciprocating pump in which the piston
AUTOMATIC PNEUMATIC WATER PUMPING SYSTEM SYNOPSIS The aim of the project is pneumatic operated water pumping system. Radial plunger Pneumatic Water pumping system are reciprocating pump in which the piston
V-Series. Oil-less Rotary Vane
 V-Series Oil-less Rotary Vane Oil-less rotary vane vacuum pumps, compressors and pressure-vacuum pumps The compact V-VTE vacuum pumps and V-DTE compressors are each available in four sizes. Low noise and
V-Series Oil-less Rotary Vane Oil-less rotary vane vacuum pumps, compressors and pressure-vacuum pumps The compact V-VTE vacuum pumps and V-DTE compressors are each available in four sizes. Low noise and
Infinitely Variable Capacity Control
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1972 Infinitely Variable Capacity Control K. H. White Ingersoll-Rand Company Follow this
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1972 Infinitely Variable Capacity Control K. H. White Ingersoll-Rand Company Follow this
speed hydraulic motors. Permission granted to reproduce for educational use only. Contrast the operation of fixed- and variable-
 Chapter 9 Actuators Workhorses of the System 1 Objectives Describe the construction and operation of basic hydraulic cylinders, limited-rotation actuators, and motors. Compare the design and operation
Chapter 9 Actuators Workhorses of the System 1 Objectives Describe the construction and operation of basic hydraulic cylinders, limited-rotation actuators, and motors. Compare the design and operation
Hopkinsons Fig 9052 VALVE ACTUATOR
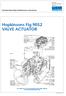 Excellent Power & Industrial Solutions Standard Operating & Maintenance Instructions Hopkinsons Fig 9052 VALVE ACTUATOR CUT-AWAY OF FIG. 9052 GEAR BOX, WITH LIMIT SWITCH & VALVE POSITION INDICATOR HOP
Excellent Power & Industrial Solutions Standard Operating & Maintenance Instructions Hopkinsons Fig 9052 VALVE ACTUATOR CUT-AWAY OF FIG. 9052 GEAR BOX, WITH LIMIT SWITCH & VALVE POSITION INDICATOR HOP
NECO Pumping Systems
 INSTALLATION OPERATION & MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS For Your NECO Pumping Systems Fuel Oil Transfer System THIS COMPLETELY ASSEMBLED, TESTED, PACKAGED SYSTEM IS OF THE HIGHEST QUALITY AND DESIGN. TO OBTAIN
INSTALLATION OPERATION & MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS For Your NECO Pumping Systems Fuel Oil Transfer System THIS COMPLETELY ASSEMBLED, TESTED, PACKAGED SYSTEM IS OF THE HIGHEST QUALITY AND DESIGN. TO OBTAIN
Topic 1. Basics of Oil Hydraulic Systems
 Topic 1. Basics of Oil Hydraulic Systems Fluid power Fluid power is the technology that deals with the generation, control and transmission of forces and movement of mechanical element or system with the
Topic 1. Basics of Oil Hydraulic Systems Fluid power Fluid power is the technology that deals with the generation, control and transmission of forces and movement of mechanical element or system with the
ENGINEERING STANDARD FOR MACHINERY PIPING
 ENGINEERING STANDARD FOR MACHINERY PIPING CONTENTS : PAGE No. 0. INTRODUCTION... 2 1. SCOPE... 3 2. REFERENCES... 3 3. UNITS... 4 4. PIPING DESIGN FOR MACHINERIES... 4 4.1 General... 4 4.2 Pumps... 5 4.3
ENGINEERING STANDARD FOR MACHINERY PIPING CONTENTS : PAGE No. 0. INTRODUCTION... 2 1. SCOPE... 3 2. REFERENCES... 3 3. UNITS... 4 4. PIPING DESIGN FOR MACHINERIES... 4 4.1 General... 4 4.2 Pumps... 5 4.3
LESSON 2 BASIC CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION OF HYDRAULIC ACTUATING DEVICES, FLOW CONTROL, AND DIRECTIONAL DEVICES. STP Tasks:
 LESSON 2 BASIC CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION OF HYDRAULIC ACTUATING DEVICES, FLOW CONTROL, AND DIRECTIONAL DEVICES STP Tasks: 552-758-1003 552-758-1071 OVERVIEW LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this lesson you will
LESSON 2 BASIC CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION OF HYDRAULIC ACTUATING DEVICES, FLOW CONTROL, AND DIRECTIONAL DEVICES STP Tasks: 552-758-1003 552-758-1071 OVERVIEW LESSON DESCRIPTION: In this lesson you will
Section 35 Chapter 2 HYDRAULIC SYSTEM HOW IT WORKS AND TROUBLESHOOTING NH
 Section 35 Chapter HYDRAULIC SYSTEM HOW IT WORKS AND TROUBLESHOOTING 6-80NH TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INTRODUCTION... 35-3 Hydraulic Pumps... 35-3 Standard Flow PFC Pump Layout... 35-5 MegaFlow PFC Pump
Section 35 Chapter HYDRAULIC SYSTEM HOW IT WORKS AND TROUBLESHOOTING 6-80NH TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INTRODUCTION... 35-3 Hydraulic Pumps... 35-3 Standard Flow PFC Pump Layout... 35-5 MegaFlow PFC Pump
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
CENTAC Inlet and Bypass Valve Positioners
 CENTAC Inlet and Bypass Valve Positioners INGERSOLL-RAND AIR COMPRESSORS INLET AND BYPASS VALVE POSITIONERS Copyright Notice Copyright 1992, 1999 Ingersoll-Rand Company THIS CONTENTS OF THIS MANUAL ARE
CENTAC Inlet and Bypass Valve Positioners INGERSOLL-RAND AIR COMPRESSORS INLET AND BYPASS VALVE POSITIONERS Copyright Notice Copyright 1992, 1999 Ingersoll-Rand Company THIS CONTENTS OF THIS MANUAL ARE
MultiPort II Lubricator
 MultiPort II Lubricator Mobile, Progressive, Grease General The MultiPort II Lubricator is an electrically driven multiple outlet lubrication unit designed primarily for use with progressive divider valve
MultiPort II Lubricator Mobile, Progressive, Grease General The MultiPort II Lubricator is an electrically driven multiple outlet lubrication unit designed primarily for use with progressive divider valve
Chapter Thirteen. Nose Wheel Steering Systems. A. Small Aircraft. B. Large Aircraft. C. Shimmy Dampers
 Chapter Thirteen Nose Wheel Steering Systems A. Small Aircraft Almost all airplanes with tricycle landing gear have some provisions for steering on the ground by controlling the nose wheel. Some of the
Chapter Thirteen Nose Wheel Steering Systems A. Small Aircraft Almost all airplanes with tricycle landing gear have some provisions for steering on the ground by controlling the nose wheel. Some of the
Oil Hydraulics Basic Technology Textbook
 Technical education document Oil Hydraulics Basic Technology Textbook DAIKIN INDUSTRIES, LTD. Training Dept. Chapter 1 Basis of Oil Hydraulics CONTENTS 1. Overview of oil hydraulics...1 2. Basic structure
Technical education document Oil Hydraulics Basic Technology Textbook DAIKIN INDUSTRIES, LTD. Training Dept. Chapter 1 Basis of Oil Hydraulics CONTENTS 1. Overview of oil hydraulics...1 2. Basic structure
Pumps. Pumps GoTo Europe
 Pumps GoTo Europe 7 Pumps Axial piston pumps Axial piston pumps in swash plate and bent axis design are intended for the medium and high pressure range. Variations in the designs, in the performance ranges
Pumps GoTo Europe 7 Pumps Axial piston pumps Axial piston pumps in swash plate and bent axis design are intended for the medium and high pressure range. Variations in the designs, in the performance ranges
1. Cruise Control CRUISE CONTROL A: OPERATION B: LOCATION OF COMPONENTS. CC(STi)-2
 W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Cruise Control A: OPERATION The cruise control system automatically controls the vehicle speed. It allows the vehicle to run at a constant speed
W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Cruise Control A: OPERATION The cruise control system automatically controls the vehicle speed. It allows the vehicle to run at a constant speed
MultiPort II Lubricator
 MultiPort II Lubricator Mobile, PDI, Grease General The MultiPort II Lubricator is an electrically driven multiple outlet lubrication unit designed primarily for use with positive displacement injector(pdi)
MultiPort II Lubricator Mobile, PDI, Grease General The MultiPort II Lubricator is an electrically driven multiple outlet lubrication unit designed primarily for use with positive displacement injector(pdi)
TORQUE CONVERTER. Section 2. Lesson Objectives. 6 TOYOTA Technical Training
 Section 2 TORQUE CONVERTER Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the function of the torque converter. 2. Identify the three major components of the torque converter that contribute to the multiplication of torque.
Section 2 TORQUE CONVERTER Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the function of the torque converter. 2. Identify the three major components of the torque converter that contribute to the multiplication of torque.
CHAPTER 11 BASIC ACTUATING SYSTEMS
 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 11 BASIC ACTUATING SYSTEMS The actuating systems consist of the hydraulic components used to direct and control the flow of pressurized fluid as well as the components used to perform
INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 11 BASIC ACTUATING SYSTEMS The actuating systems consist of the hydraulic components used to direct and control the flow of pressurized fluid as well as the components used to perform
Describe the function of a hydraulic power unit
 Chapter 7 Source of Hydraulic Power Power Units and Pumps 1 Objectives Describe the function of a hydraulic power unit and identify its primary components. Explain the purpose of a pump in a hydraulic
Chapter 7 Source of Hydraulic Power Power Units and Pumps 1 Objectives Describe the function of a hydraulic power unit and identify its primary components. Explain the purpose of a pump in a hydraulic
9.1 Assembled Planetary Gearbox
 SEC. 9 GEARBOX 9.1 Assembled Planetary Gearbox SEC. 9 GEARBOX Page 1 9.1 Assembley Gearbox Drawing 9.1.1. Drawing #11236 - Gearbox, Planetary SEC. 9 GEARBOX Page 2 9.2. Assembly Lower Output Shaft and
SEC. 9 GEARBOX 9.1 Assembled Planetary Gearbox SEC. 9 GEARBOX Page 1 9.1 Assembley Gearbox Drawing 9.1.1. Drawing #11236 - Gearbox, Planetary SEC. 9 GEARBOX Page 2 9.2. Assembly Lower Output Shaft and
Actuator Control Manual with ESD Valve
 ActCont Manual with ESD Actuator Control Manual with ESD Valve Replacement Procedure on a Rotary Vane Actuator with a System using Power Gas The purpose of this procedure is to guide the replacement of
ActCont Manual with ESD Actuator Control Manual with ESD Valve Replacement Procedure on a Rotary Vane Actuator with a System using Power Gas The purpose of this procedure is to guide the replacement of
INTEGRAL POWER STEERING GEAR FORD Applies to F-100 F-350 (4X2), F-150 F-250 (4X4) And Bronco
 Rockcrawler Steering Shop Manual page1 The following is from the Ford 1978 Truck Shop Manual, Volume 1 Chassis. It is provided here as a courtesy to classic Ford owners who would like to perform their
Rockcrawler Steering Shop Manual page1 The following is from the Ford 1978 Truck Shop Manual, Volume 1 Chassis. It is provided here as a courtesy to classic Ford owners who would like to perform their
Principals of Operation... 1 Rotary Vane Priming Pump VPE and VPES... 2 Rotary Vane Priming Pump VPO and VPOS Priming Valve...
 Priming Systems Installation Priming Systems Operation & Maintenance Form No. F 1031 Section 2312 Issue Date 10/07/94 Rev. Date 02/27/06 Table of Contents Illustrations Principals of Operation...........................
Priming Systems Installation Priming Systems Operation & Maintenance Form No. F 1031 Section 2312 Issue Date 10/07/94 Rev. Date 02/27/06 Table of Contents Illustrations Principals of Operation...........................
Triro Pump Range TRIPLE SCREW PUMPS. T-Range C-Range E-Range H-Range
 Triro Pump Range TRIPLE SCREW PUMPS T-Range C-Range E-Range H-Range With decades of experience in designing and manufacturing rotary positive displacement pumps, SPX FLOW s Plenty Pumps have built an excellent
Triro Pump Range TRIPLE SCREW PUMPS T-Range C-Range E-Range H-Range With decades of experience in designing and manufacturing rotary positive displacement pumps, SPX FLOW s Plenty Pumps have built an excellent
Automatic Transmission Basics
 Section 1 Automatic Transmission Basics Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the function of the torque converter. 2. Identify the three major components of the torque converter that contribute to the multiplication
Section 1 Automatic Transmission Basics Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the function of the torque converter. 2. Identify the three major components of the torque converter that contribute to the multiplication
TROUBLESHOOTING TABLE
 TROUBLESHOOTING TABLE TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE GLOSARY OF TERMS VANE PUMPS NO FLOW, NO PRESSURE A) Is the pump rotating? a-1) Check if the coupling is rotating. If not, check the rotation of the electric
TROUBLESHOOTING TABLE TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE GLOSARY OF TERMS VANE PUMPS NO FLOW, NO PRESSURE A) Is the pump rotating? a-1) Check if the coupling is rotating. If not, check the rotation of the electric
Operating Principle. Rotary Vane Compressor
 Operating Principle Rotary Vane Compressor Vane Compressor The vane compressor is a volumetric rotary compressor. It consists of a cylinder (stator), of a rotor mounted eccentrically inside the stator,
Operating Principle Rotary Vane Compressor Vane Compressor The vane compressor is a volumetric rotary compressor. It consists of a cylinder (stator), of a rotor mounted eccentrically inside the stator,
ENGINE MECHANICAL <134>
 11A-1 GROUP 11A ENGINE MECHANICAL CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 11A-2.................. 11A-3 11A-2 The newly developed 1.1L 134910 engine features 3-cylinder, 12-valve, and double overhead
11A-1 GROUP 11A ENGINE MECHANICAL CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 11A-2.................. 11A-3 11A-2 The newly developed 1.1L 134910 engine features 3-cylinder, 12-valve, and double overhead
SECTION 6C POWER STEERING GEAR TABLE OF CONTENTS
 SECTION 6C POWER STEERING GEAR TABLE OF CONTENTS Description and Operation... 6C2 Power Rack and Pinion... 6C2 Component Locator... 6C3 Diagnostic Information and Procedures... 6C4 Power Steering Rack
SECTION 6C POWER STEERING GEAR TABLE OF CONTENTS Description and Operation... 6C2 Power Rack and Pinion... 6C2 Component Locator... 6C3 Diagnostic Information and Procedures... 6C4 Power Steering Rack
GENESIS COUPE(BK) > 2010 > G 3.8 DOHC > Steering System
 GENESIS COUPE(BK) > 2010 > G 3.8 DOHC > Steering System Steering System > General Information > Specifications Specifications Steering gear Oil pump Steering angle Power steering oil Item Specification
GENESIS COUPE(BK) > 2010 > G 3.8 DOHC > Steering System Steering System > General Information > Specifications Specifications Steering gear Oil pump Steering angle Power steering oil Item Specification
Triro Pump Range. T-Range C-Range E-Range H-Range
 Triro Pump Range triple screw pumps T-Range C-Range E-Range H-Range With decades of experience in designing and manufacturing rotary positive displacement pumps, SPX s Plenty Pumps have built an excellent
Triro Pump Range triple screw pumps T-Range C-Range E-Range H-Range With decades of experience in designing and manufacturing rotary positive displacement pumps, SPX s Plenty Pumps have built an excellent
DIESEL ENGINES AND FUEL SYSTEMS
 TRAINING COURSE 6 DIESEL ENGINES AND FUEL SYSTEMS VOLUME 1 Course Program GENERAL The purpose of this course is to introduce the characteristics of diesel fuel systems. This discussion will include a description
TRAINING COURSE 6 DIESEL ENGINES AND FUEL SYSTEMS VOLUME 1 Course Program GENERAL The purpose of this course is to introduce the characteristics of diesel fuel systems. This discussion will include a description
AGE 222. Introduction to Farm Machinery Dr. O. U. Dairo. Farm Machinery and Power
 AGE 222 Introduction to Farm Machinery Dr. O. U. Dairo Farm Machinery and Power Equipment in the farm are classified as farm power and farm machinery Power provides pull/force required tom operate implements
AGE 222 Introduction to Farm Machinery Dr. O. U. Dairo Farm Machinery and Power Equipment in the farm are classified as farm power and farm machinery Power provides pull/force required tom operate implements
Hopkinsons Fig 9051 VALVE ACTUATOR
 Excellent Power & Industrial Solutions Standard Operating & Maintenance Instructions Hopkinsons Fig 9051 VALVE ACTUATOR TERMINAL BOX TERMINAL BOX COVER SPINDLE COVER SEAL BEARING HOUSING MOTOR TAPERED
Excellent Power & Industrial Solutions Standard Operating & Maintenance Instructions Hopkinsons Fig 9051 VALVE ACTUATOR TERMINAL BOX TERMINAL BOX COVER SPINDLE COVER SEAL BEARING HOUSING MOTOR TAPERED
Service Manual for Hydraulic Vane Pumps Subplate Mounted
 Industrial Hydraulics Electric Drives and Controls Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Pneumatics Service Automation Mobile Hydraulics Service Manual for Hydraulic Vane Pumps Subplate Mounted SM PSSF/07.03
Industrial Hydraulics Electric Drives and Controls Linear Motion and Assembly Technologies Pneumatics Service Automation Mobile Hydraulics Service Manual for Hydraulic Vane Pumps Subplate Mounted SM PSSF/07.03
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
 CPC - F04B - 2017.08 F04B POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS (machines for liquids, or pumps, of rotary piston or oscillating piston type F04C; non-positive displacement pumps F04D; pumping
CPC - F04B - 2017.08 F04B POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS (machines for liquids, or pumps, of rotary piston or oscillating piston type F04C; non-positive displacement pumps F04D; pumping
Changes in direction.! Using pulleys with belts
 Mechanisms Changes in direction! Using pulleys with belts Changes in direction! Using friction wheels Changes in direction! Using gears Worm drive! Reduces the speed! It is non-reversible Worm drive! Multiple
Mechanisms Changes in direction! Using pulleys with belts Changes in direction! Using friction wheels Changes in direction! Using gears Worm drive! Reduces the speed! It is non-reversible Worm drive! Multiple
SUBJECT: PUMP TYPES & OPERATIONS
 SUBJECT: PUMP TYPES & OPERATIONS ABOUT THE SESSION This session will highlight different types of pumps and its working. INTRODUCTION In Hydraulic system, the pump converts mechanical energy (hydraulic
SUBJECT: PUMP TYPES & OPERATIONS ABOUT THE SESSION This session will highlight different types of pumps and its working. INTRODUCTION In Hydraulic system, the pump converts mechanical energy (hydraulic
AERZEN BULK VEHICLE BLOWER
 AERZEN BULK VEHICLE BLOWER A E R Z E N E R M A S C H I N E N F A B R I K GMBH G1-071 05 EN 250 11.2012 Fields of application and principle of operation Aerzen bulk vehicle blowers have been specifically
AERZEN BULK VEHICLE BLOWER A E R Z E N E R M A S C H I N E N F A B R I K GMBH G1-071 05 EN 250 11.2012 Fields of application and principle of operation Aerzen bulk vehicle blowers have been specifically
MECHANISM: TRANSMISSION THE TYPE OF INPUT MOVEMENT IS THE SAME AS THE OUTPUT TRANSFORMATION THE MECHANISM TRANSFORMS THE TYPE OF MOVEMENT
 MECHANISM: The mechanisms are elements intended to transmit and transform forces and movements from an INPUT element (motor) to an OUTPUT element. Types of movements: Rotary Motion -this is motion in a
MECHANISM: The mechanisms are elements intended to transmit and transform forces and movements from an INPUT element (motor) to an OUTPUT element. Types of movements: Rotary Motion -this is motion in a
CYCLICALLY OPERATING VALVES FOR MACHINES OR ENGINES (valves in general F16K)
 F01L CYCLICALLY OPERATING VALVES FOR MACHINES OR ENGINES (valves in general F16K) Valve-gear or valve arrangements, e.g. lift-valve gear; Lift-valve, i.e. cut-off apparatus with closure members having
F01L CYCLICALLY OPERATING VALVES FOR MACHINES OR ENGINES (valves in general F16K) Valve-gear or valve arrangements, e.g. lift-valve gear; Lift-valve, i.e. cut-off apparatus with closure members having
FIXED DISPLACEMENT HYDRAULIC VANE PUMPS SERIE BQ
 FIXED DISPLACEMENT HYDRAULIC VANE PUMPS SERIE BQ BQ FIXED DISPLACEMENT HYDRAULIC VANE PUMPS BQ SERIES Versatility, power, compactness and low running costs are the main characteristics of B&C vane pumps.
FIXED DISPLACEMENT HYDRAULIC VANE PUMPS SERIE BQ BQ FIXED DISPLACEMENT HYDRAULIC VANE PUMPS BQ SERIES Versatility, power, compactness and low running costs are the main characteristics of B&C vane pumps.
Vane Pumps. Single Stage Single and Double Vane Pumps. Vickers. Overhaul Manual
 Vickers Vane Pumps Overhaul Manual Single Stage Single and Double Vane Pumps V14, 124, 134,144 V19, 129, 139, 149 V15, 125, 135, 145 V35*, 36*, 45*, 46* V18, 128, 138, 148 (V)VF-**-**, (V)VG-**-** Reprinted
Vickers Vane Pumps Overhaul Manual Single Stage Single and Double Vane Pumps V14, 124, 134,144 V19, 129, 139, 149 V15, 125, 135, 145 V35*, 36*, 45*, 46* V18, 128, 138, 148 (V)VF-**-**, (V)VG-**-** Reprinted
Table of Contents. E70 Lateral Dynamics Systems
 Table of Contents Subject Page Lateral Dynamics..............................................3 Active Steering (AS)............................................3 Active Front Steering (AFS)......................................4
Table of Contents Subject Page Lateral Dynamics..............................................3 Active Steering (AS)............................................3 Active Front Steering (AFS)......................................4
STEERING STEERING SR 1
 SR1 SR2 Precautions PRECAUTIONS Care must be taken to replace parts properly because they could affect the performance of the steering system and result in a driving hazard. TROUBLESHOOTING Problem Hard
SR1 SR2 Precautions PRECAUTIONS Care must be taken to replace parts properly because they could affect the performance of the steering system and result in a driving hazard. TROUBLESHOOTING Problem Hard
POWER ASSISTED SYSTEM (POWER STEERING) PS
 POWER ASSISTED SYSTEM (POWER STEERING) PS Page 1. General Description...2 2. Steering Wheel...23 3. Universal Joint...24 4. Tilt Steering Column...26 5. Steering Gearbox [LHD MODEL]...29 6. Steering Gearbox
POWER ASSISTED SYSTEM (POWER STEERING) PS Page 1. General Description...2 2. Steering Wheel...23 3. Universal Joint...24 4. Tilt Steering Column...26 5. Steering Gearbox [LHD MODEL]...29 6. Steering Gearbox
