|
|
|
- Gary Ray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 1 of : Brake control system V70 (00-08), 2004, B5244S2, M56, L.H.D, YV1SW65S , /7/2018 PRINT 593: Brake control system ABS control ABS function Active yaw control Active yaw control system Electronic brake force distribution (EBD) Stability Control STC (stability and traction control) system Traction Control Traction Control Function ABS function While driving, the brake control module (BCM) (1) registers the acceleration and deceleration of the wheels. The 4 wheel sensors (3) (one on each wheel) give the brake control module (BCM) information about the rotation speed of the wheels. The brake control module (BCM)
2 Page 2 of 23 calculates the speed of the car using this information and puts it out on the Control area network (CAN). There the signal is accessible for other systems. During braking, the brake control module (BCM) receives a signal from the brake lamp switch (2) indicating braking. The brake control module (BCM) then goes into standby mode for ABS control. The signal from the brake lamp switch is not required for ABS control, but does give softer control at the beginning of ABS control. If the brake control module (BCM) detects that there is a risk of wheel lock-up, the ABS hydraulic modulator (4) is affected and the hydraulic pressure for the relevant wheel is adapted so that wheel lock up is avoided. The pressure in the circuit is controlled so that the maximum possible braking force is transferred to the road surface. This occurs when the wheel rotates with 12-20% slippage on the surface. ABS is first activated when the speed of the car exceeds approximately 7 km/h, which means that at speeds below approximately 7 km/h the wheels can lock up. This has no practical effect on the function of the system or from the
3 Page 3 of 23 driver's point of view. ABS control can be divided into three stages: 1. Open position. (Pressure increase). This is the normal condition during braking. The inlet valve is open and the outlet valve is closed. This permits the brake pressure to pass from the master cylinder to the wheel 2. Pressure retention phase. (Constant pressure). If the brake control module (BCM) detects that one of the wheels is rotating too slowly, the brake control module (BCM) will close the inlet valve. This stops the brake pressure to the wheel from increasing, even if the driver increases the pressure on the brake pedal. If the rotation speed of the wheel continues to fall the control moves into the pressure reduction phase 3. Pressure reduction phase. (Pressure release). The inlet valve remains closed. The brake control module
4 Page 4 of 23 (BCM) opens the outlet valve and starts the pump which transfers brake fluid from the wheel, this reduces the brake pressure. When the rotation speed has increased sufficiently the control module closes the exhaust valve, opens the inlet valve and control returns to the open position. Steps 1, 2 or 3 are repeated until braking finishes or the ABS system stops. ABS control No braking When the driver is not braking, the brake system is unaffected (i.e. the master cylinder is in the rest position and the connections between the brake fluid reservoir and the rest of the hydraulic system is open). There is no pressure in the system. In the ABS hydraulic modulator valve block, the hydraulic valves are
5 Page 5 of 23 in their rest position. In other words, the inlet valves are open and the outlet valves closed. Braking without ABS When the brake pedal is depressed, the movement of the pedal is transmitted via the servo unit to the master cylinder pistons and the brake lamp switch trips. When the primary and secondary pistons move forwards in the master cylinder, the openings for the brake fluid reservoir are closed. The hydraulic pressure in the two brake circuits increases and affects the pistons in the brake callipers which press the brake pads against the brake discs. When the brake pedal is released, the pistons revert to the rest position in the master cylinder. The connection to the brake fluid reservoir opens and the brake system pressure falls. The brake calliper pistons return to their rest positions with the aid of the sealing rings.
6 Page 6 of 23 Braking with ABS When a wheel locks-up under braking, the brake control module (BCM) begins to close the inlet valve for the relevant brake circuit so that the supply of brake fluid from the master cylinder is interrupted. This means that the hydraulic pressure cannot increase irrespective of the pressure in the master cylinder (constant pressure, see the righthand front wheel - FR). The hydraulic pump starts at the same time. If the wheel locks anyway, the outlet valve opens and the brake fluid is allowed back to the accumulators resulting in a reduction in the brake circuit pressure (pressure release, see the left front wheel - FL). This reduces the hydraulic pressure and braking effect, allowing the wheel to accelerate. The hydraulic pump returns the brake fluid from the accumulators
7 Page 7 of 23 to the master cylinder. When the acceleration is sufficient, the brake control module (BCM) closes the outlet valve and opens the inlet valve, so that the hydraulic pressure in the circuit increases. During the pressure increase phase the required fluid volume is supplied by the master cylinder and the pump if the accumulators contain brake fluid. As the volume of fluid supplied to the brake circuit is greater than the volume released back into the accumulators from the brake circuits, the accumulators only compensate for the volume peaks on the pump suction side. The pump returns the brake fluid from the low pressure accumulators to the master cylinder or brake circuits depending on the position of the inlet valves. When the pump operates the brake pedal is raised and lowered (pulses). This is normal and is also a warning to the driver that ABS control is active. The hydraulic pump is operational for approximately 1 second after the ABS control has finished to ensure that the accumulators are empty.
8 Page 8 of 23 Electronic brake force distribution (EBD) Electronic brake force distribution (EBD) is integrated in the ABS system and controls the braking forces to the rear wheel brakes. Electronic brake force distribution (EBD) replaces the relief valve, which otherwise reduces the pressure in the brake circuit for the rear wheels and prevents premature activation of rear ABS control. Electronic brake force distribution controls the hydraulic pressure in the brake circuit for the rear wheels the rear wheels slip considerably less than the front wheels under braking. This ensures optimal and stable braking. The brake control module (BCM) controls the brake pressure by controlling the inlet and outlet valves in the rear wheel brake circuits.
9 Page 9 of 23 The brake pressure in the rear wheel circuits varies, depending on how much the rear wheels slip in relation to the front wheels. This functions tries to keep the rear wheel slippage 0-2 % lower than front wheel slippage. The function is load sensitive. Generally, the difference between the rear wheel and front wheel slippage under braking is dependent on how hard the brakes are applied and on the load of the car. Hard braking /light loads cause more slippage, light braking/heavy loads cause less slippage. Therefore the requirement for brake fluid when the hydraulic pump is not activated during electronic brake force distribution (EBD) control is less than during stability and traction control. The fluid volume returned from the brake circuits is taken up by the accumulators. STC (stability and traction control) system The STC (stability and traction control) system consists of two functions, stability control and traction
10 Page 10 of 23 control. The stability function is controlled by the engine control module (ECM). The traction control function and TRACS (TRAction Control System) operate in the same way. See the Traction control section. Stability Control Stability control occurs when the brake control module (BCM) transmits a signal to the engine control module (ECM) to lower the engine torque if any of the wheels loose traction. Stability control is available between 0 km/h and top speed. For information about traction control, see the Traction control section. Traction Control Components 1. Separation valve, normally open 2. Electronic shuttle valve, normally closed
11 Page 11 of Hydraulic pump 4. Outlet valve, normally closed 5. Inlet valve, normally open 6. Pressure equalizer 7. By-pass valve 8. Non-return valve. Traction control is integrated in the steering wheel bracket. The system is mainly designed to assist with moving off on slippery surfaces at speeds up to approximately 60 km/h. Traction control has only a very limited effect at speeds over 60 km/h. The traction control function is always engaged when the ignition is switched on. The function can be disengaged (model years only) using the STC/DSTC switch, which is located on the lower section of the climate control module (CCM). If the brake control module (BCM) registers, via the front wheel sensors, that one of the driven wheels is spinning faster than the other, the separation valve (1) closes and the hydraulic pump (3) starts so that the brake fluid is pumped to the brake calliper of the slipping wheel. Pressure builds up in the brake circuit and the brakes are applied as much as required so that the drive force is distributed between the driven wheels. The wheel which has the best traction receives the
12 Page 12 of 23 most driven force against the surface. This process is independent of engine output. On cars with traction control, the brake control module (BCM) continually registers brake usage and calculates the temperatures of the front wheel brake discs. If traction control is engaged and the calculated temperature is too high (approximately 450 C), traction control cuts out and the wheel spin warning indicator lights (applies to model year ). From model year 2003, the general warning lamp (yellow) lights, and a text is displayed in the combined instrument panel. A diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is stored in the brake control module (BCM). Traction control is blocked to prevent the brakes from overheating. The light goes out once the calculated temperature falls below approximately 300 C and traction control is engaged again. However, the ABS function is always available. Information about the calculated temperature of the brake discs is in the brake control module (BCM) as long as the 30-supply is connected. If the brake system has been used too hard, this
13 Page 13 of 23 may also cause high brake temperatures. Traction Control No traction control When the driven wheels are not spinning the brake system is unaffected (i.e. the master cylinder is in the rest position and the connections between the brake fluid reservoir and the rest of the hydraulic system are open). There is no pressure in the system. In the ABS hydraulic modulator valve block, the hydraulic valves are in their rest position. In other words, the inlet valves and the separation valves are open and the outlet valves closed. Traction control when one or both driven wheels spin
14 Page 14 of 23 If the car moves off and one or both driven wheels are threatening to slip, the brake control module (BCM) detects this by comparing the signals from the wheel sensors with a calculated reference speed. The control module closes one or both separation valves and the hydraulic pump starts. The separation valve blocks the connection between the pump pressure side and the master cylinder primary circuit /secondary circuit. The inlet valve for the non-spinning wheel closes so that the brake is not applied on that wheel. The hydraulic pump draws brake fluid from the brake fluid reservoir via the electronic shuttle valve and increases the pressure until the bypass valve opens. The hydraulic pressure reaches the spinning wheel and slows down the wheel so that the driven force is
15 Page 15 of 23 distributed between the driven wheels so that the wheel with the best traction receives the most driven force. As the pump supplies a greater flow than required by traction control, the excess brake fluid is drained off by the by-pass valve for the master cylinder or is drawn directly up by the pump. If traction control is manually disengaged (model tears ) it can be reengaged using the switch whilst the wheels are spinning. The function then starts more softly than normal. The inlet valve closes as soon as the spinning wheel has been slowed down by the brake to a relatively normal speed. Depending on the acceleration of the wheel, the outlet valve opens (brake fluid flows back to the suction side of the pump) so that the pressure in the brake circuit drops or the outlet valve remains closed to maintain the pressure (constant pressure). The outlet valve closes to increase the pressure in the brake circuit, the inlet valve opens and the pressure rises in the brake circuit. This control brakes the wheel in proportion to optimum slippage until
16 Page 16 of 23 one of the following occurs: As friction against the surface becomes greater wheel spin stops The process is stopped by the brake control module (BCM) to prevent the brakes from overheating Braking occurs The function is disengaged using the switch on the climate control module (CCM) (applies to model years ) The car reaches the speed where traction control ceases. If the rear wheels lock during traction control (for example the handbrake is applied), the brake control module (BCM) stops traction control to allow ABS to cut-in. The traction control lamp lights (applies to model years ). The separation valve is activated during traction control. Activating the brakes, which is registered by the brake control module (BCM) via the signal from the brake lamp switch, enables the traction control to be interrupted and the separation valve to open. The electronic shuttle valve closes, so that the pump is unable to draw brake fluid from
17 Page 17 of 23 the master cylinder. The hydraulic modulator now operates as a normal ABS hydraulic modulator. A difference in speed between the driven wheels requires traction control. This difference varies with the speed of the car. When the vehicle speed is 0 km/h, a difference in speed of 8 km/h between the driven wheels is required for traction control to function. At a vehicle speed of 20 km/h, a difference of 18 km/h, and at 40 km/h a difference of 25 km/h are required. At higher speeds the differences required between the driven wheel speeds is so great that in practice traction control does not function above 60 km/h. Active yaw control system
18 Page 18 of 23 The brake control module (BCM) with DSTC (dynamic stability and traction control) uses continuous information from the different sensors in the system to calculate the positions of the steering wheel and car. The brake control module (BCM) calculates the driving manner of the driver by measuring the steering wheel angle, the engine torque, the speed of the car and brake pressure. The brake control module (BCM) also calculates the behaviour of the car by monitoring the steering wheel angle, steering wheel angle speed, yaw rate speed and lateral acceleration. When the differences between the movements of the driver and the behaviour of the car exceed a certain point, Active Yaw Control limits the engine torque to maintain lateral stability in all driving conditions. Active Yaw Function also activates the servo unit and the individual brake control to control the hydraulic modulator separation valves and electronic shuttle valves and the inlet and outlet valves which correct the car in the event of a skid. Active yaw control
19 Page 19 of Inlet valve, normally open 2. Outlet valve, normally closed 3. Electronic shuttle valve, normally closed 4. Separation valve, normally open 5. Brake pressure sensor 6. Pedal pressure sensor 7. By-pass valve 8. Hydraulic pump 9. Pressure absorber 10. Non-return valve 11. Pressure build-up valve. During Active Yaw Control, when the car skids, a vacuum valve opens on the servo unit. The servo unit then quickly builds up pressure without the driver activating the brake pedal. At the same time the hydraulic pump (8) starts and builds up brake pressure. The hydraulic pump takes over braking after the initial phase. The brake control module (BCM) then activates the
20 Page 20 of 23 valves in the hydraulic modulator and checks the individual wheel brake forces by raising, maintaining or lowering the pressure individually to stabilize the car. The brake pedal moves up and down during activation. If the driver presses the brake pedal during stability control, the control module, through the pedal pressure sensor (6) in the servo unit, will take account of the pressure exerted by the driver in the stability control. Active yaw control oversteer Oversteer is a very dangerous condition which is difficult for the average driver to control. Oversteer is when the car turns more than the steering wheel has been turned. If not corrected, oversteer can lead to the car spinning uncontrollably. In the example above the car turns to the
21 Page 21 of 23 right and the car oversteers. To counter this the DSTC system has closed the separation valve, opened the electronic shuttle valve and started the pump. The inlet valve (C1) has been left open, while the other inlet valves are closed. This causes brakes the left front wheel, which causes the wheel to lose grip and reduces oversteer. Active yaw control understeer Understeer is when the car continues straight forward even though the steering wheel has been turned. Understeer is caused by too much acceleration. When the car understeers the brake control module (BCM) transmits a request for torque reduction to the engine control module (ECM) via the Controller area network (CAN). In the example above, the steering wheel has
22 Page 22 of 23 been turned to the right, but the car continues straight on. The separation valve closes, the electronic shuttle valve opens and the pump starts. The DSTC system applies the brakes to the right rear wheel by leaving inlet valve C2 open and closing and closing the other inlet valves (C1, C3 and C4). In the event that braking the right rear wheel is not sufficient to get the car back on course, the brake control module (BCM) opens inlet valve C4 and brakes the right front wheel. Dynamic stability control When the driver brakes during Active Yaw Control, the brake control module (BCM) releases the active servo unit and increases the brake pressure for a short time as priority is given to the lateral stability of the car. Included in the calculations are the driver's desired brake pressure and functions
23 Page 23 of 23 for: Active yaw control ABS EBD Stability control. In the event of a hand brake turn, the anti-yaw control function is activated if the speed exceeds approximately 40 km/h. At lower speeds the AYC is decreased successively, and at km/h will not be noticeable. The self diagnostic function, for valves and pump motors, occurs at speeds exceeding 20 km/h after a new drive cycle. The self diagnostic function for the active servo unit takes place when the speed exceeds 11 km/h. The self diagnostics are carried out at each new drive cycle. If the driver presses the brake pedal during stability control, the control module, through the pedal pressure sensor in the servo unit, will take account of the pressure exerted by driver in the stability control. 16/7/2018 PRINT
System overview. Introduction. Copyright 2004 Volvo Car Corporation. All rights reserved.
 "VCC141172 EN 20090206" 1(40) System overview Introduction The Mark25 brake control system The Mark 25 brake control system with the brake control module (BCM) is an electronic control system which prevents
"VCC141172 EN 20090206" 1(40) System overview Introduction The Mark25 brake control system The Mark 25 brake control system with the brake control module (BCM) is an electronic control system which prevents
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC)
 VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM 1. Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) System A: GENERAL The vehicle dynamics control (VDC) system is a driver assist system which enhances vehicle s running stability
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) SYSTEM 1. Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) System A: GENERAL The vehicle dynamics control (VDC) system is a driver assist system which enhances vehicle s running stability
capacity due to increased traction; particularly advantageous on road surfaces
 42-800 Design and function of acceleration slip control (ASR I) A. General B. Driving with ASR I C. Overall function of ASR I D. Location of components E. Individual functions A. General The acceleration
42-800 Design and function of acceleration slip control (ASR I) A. General B. Driving with ASR I C. Overall function of ASR I D. Location of components E. Individual functions A. General The acceleration
1. INTRODUCTION. Anti-lock Braking System
 1. INTRODUCTION Car manufacturers world wide are vying with each other to invent more reliable gadgets there by coming closer to the dream of the Advanced safety vehicle or Ultimate safety vehicle, on
1. INTRODUCTION Car manufacturers world wide are vying with each other to invent more reliable gadgets there by coming closer to the dream of the Advanced safety vehicle or Ultimate safety vehicle, on
35C-1 GROUP 35C CONTENTS FEATURES... 35C-2 SYSTEM OPERATION... 35C-16 CONSTRUCTION DESCRIPTION... 35C-5
 35C-1 GROUP 35C CONTENTS FEATURES.................... 35C-2 SYSTEM OPERATION............ 35C-16... 35C-5 35C-2 FEATURES Anti-skid Brake System/Active Stability System (ABS/active stability system) is available
35C-1 GROUP 35C CONTENTS FEATURES.................... 35C-2 SYSTEM OPERATION............ 35C-16... 35C-5 35C-2 FEATURES Anti-skid Brake System/Active Stability System (ABS/active stability system) is available
HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice. Operating temperature - 40 C to 150 C - 40 C to 150 C
 489000 113 1. SPECIFICATION Unit Description Specification ABS ESP HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice Wheel speed sensor ABS / ESP CBS Operating temperature
489000 113 1. SPECIFICATION Unit Description Specification ABS ESP HECU Clock frequency 32 MHz 50 MHz Memory 128 KB 512 KB Switch Orifice Orifice Wheel speed sensor ABS / ESP CBS Operating temperature
2006 Mercedes-Benz USA, LLC. Chassis and Drivetrain 42
 Page 1 of 5 Chassis and Drivetrain 42 Brakes Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) 4-Wheel Electronic Traction Control System (4-ETS) Electronic Brake Proportioning (EBP) System Description The hydraulic pressure
Page 1 of 5 Chassis and Drivetrain 42 Brakes Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) 4-Wheel Electronic Traction Control System (4-ETS) Electronic Brake Proportioning (EBP) System Description The hydraulic pressure
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART
 50 DTC chart of ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: If a malfunction code is displayed during the DTC check, check the circuit indicated by the DTC. For details of each code, refer to the respective
50 DTC chart of ABS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: If a malfunction code is displayed during the DTC check, check the circuit indicated by the DTC. For details of each code, refer to the respective
SUBJECT: Automatic Stability Control with Traction Control System (ASC+T)
 Group 34 34 01 90 (2105) Woodcliff Lake, NJ October 1990 Brakes Service Engineering -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SUBJECT: Automatic
Group 34 34 01 90 (2105) Woodcliff Lake, NJ October 1990 Brakes Service Engineering -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- SUBJECT: Automatic
1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION
 4890-01 08-3 1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION Front Disc 1) FRONT BRAKE For the front brake system, the ventilated disc type is applied regardless of the ABS/ system installation. Two 43 mm diameter
4890-01 08-3 1. BRAKE SYSTEM GENERAL INFORMATION Front Disc 1) FRONT BRAKE For the front brake system, the ventilated disc type is applied regardless of the ABS/ system installation. Two 43 mm diameter
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 71 & 73 Pages Brake Systems 49 Points. Automotive Service
 Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 71 & 73 Pages 1369 1444 Brake Systems 49 Points 1. Automotive systems use to stop, slow or to hold the wheels from turning. Brake, Friction Brake, Fraction Brake,
Modern Auto Tech Study Guide Chapters 71 & 73 Pages 1369 1444 Brake Systems 49 Points 1. Automotive systems use to stop, slow or to hold the wheels from turning. Brake, Friction Brake, Fraction Brake,
The following rear differential is provided for the off-road package models. BD20B (with Differential Lock Actuator)
 6 4RUNNER NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES DIFFERENTIAL (OFF-ROAD PACKAGE MODELS) 1. General The following rear differential is provided for the off-road package models. Rear Differential Lock Actuator 233CH46
6 4RUNNER NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES DIFFERENTIAL (OFF-ROAD PACKAGE MODELS) 1. General The following rear differential is provided for the off-road package models. Rear Differential Lock Actuator 233CH46
DESCRIPTION. Chrysler NCV3 Service Info Section 08 > Electronic Modules > MODULE, Transmission Control Information
 DESCRIPTION The transmission control module (TCM) receives, processes and sends various digital and analog signals related to the automatic transmission. In addition, it processes information received
DESCRIPTION The transmission control module (TCM) receives, processes and sends various digital and analog signals related to the automatic transmission. In addition, it processes information received
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION
 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION ANTI-LOCK BRAKING 1998-99 BRAKES Anti-Lock/TCS - Corvette The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Traction Control System (TCS) increases vehicle control during severe deceleration
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION ANTI-LOCK BRAKING 1998-99 BRAKES Anti-Lock/TCS - Corvette The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Traction Control System (TCS) increases vehicle control during severe deceleration
 TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM 1996 Toyota Supra 1995-96 BRAKES Traction Control Supra DESCRIPTION Toyota Traction Control (TRAC) system controls engine torque and braking of the driving wheels. TRAC system is
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM 1996 Toyota Supra 1995-96 BRAKES Traction Control Supra DESCRIPTION Toyota Traction Control (TRAC) system controls engine torque and braking of the driving wheels. TRAC system is
MASTER CYLINDER. Section 2. Lesson Objectives
 MASTER CYLINDER Lesson Objectives 1. Explain the difference between conventional and diagonal split piping system and their application. 2. Describe the function of the compensating port of the master
MASTER CYLINDER Lesson Objectives 1. Explain the difference between conventional and diagonal split piping system and their application. 2. Describe the function of the compensating port of the master
ABS keeps the vehicle steerable, even during an emergency braking
 ABS keeps the vehicle steerable, even during an emergency braking under all road conditions 1 Contents! Safety systems in vehicles! Why do you need ABS?! How does ABS work?! What are the benefits of ABS?!
ABS keeps the vehicle steerable, even during an emergency braking under all road conditions 1 Contents! Safety systems in vehicles! Why do you need ABS?! How does ABS work?! What are the benefits of ABS?!
Read on to find out more about each component of the Star Safety System and how it can be of benefit to you.
 All 2011 Toyota models come standard with the Star Safety System. This integration of active safety features is designed to protect occupants by helping drivers avoid accidents in the first place. The
All 2011 Toyota models come standard with the Star Safety System. This integration of active safety features is designed to protect occupants by helping drivers avoid accidents in the first place. The
ANTI-LOCK BRAKES. Section 9. Fundamental ABS Systems. ABS System Diagram
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKES Fundamental ABS Systems Toyota Antilock Brake Systems (ABS) are integrated with the conventional braking system. They use a computer controlled actuator unit, between the brake master
ANTI-LOCK BRAKES Fundamental ABS Systems Toyota Antilock Brake Systems (ABS) are integrated with the conventional braking system. They use a computer controlled actuator unit, between the brake master
Module 11: Antilock Brakes Systems
 ÂÂ ABS Brake System Antilock Brake System Operation Principles of ABS Braking ABS Master Cylinder Hydraulic Control Unit Wheel Speed Sensors ABS Electronic Control Unit Terms and Definitions Purposes for
ÂÂ ABS Brake System Antilock Brake System Operation Principles of ABS Braking ABS Master Cylinder Hydraulic Control Unit Wheel Speed Sensors ABS Electronic Control Unit Terms and Definitions Purposes for
FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 35B-2 35B-6 SENSOR 35B-6 ACTUATORS 35B-6 ABS-ECU 35B-7 35B-2 The ABS that ensures directional stability and controllability
35B-1 GROUP 35B FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 35B-2 35B-6 SENSOR 35B-6 ACTUATORS 35B-6 ABS-ECU 35B-7 35B-2 The ABS that ensures directional stability and controllability
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW. 1) Terms and Definition. 2) Functions
 485000 093 1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1) Terms and Definition CBS: Conventional Brake System ABS: AntiLock Brake System EBD: Electronic brakeforce Distribution ESP: Electronic Stability Program ABD: Automatic
485000 093 1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1) Terms and Definition CBS: Conventional Brake System ABS: AntiLock Brake System EBD: Electronic brakeforce Distribution ESP: Electronic Stability Program ABD: Automatic
ABS, 4-ETS and EBP BRAKES ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) 4-WHEEL ELECTRONIC TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (4-ETS) ELECTRONIC BRAKE PROPORTIONING (EBP)
 1 of 9 4/27/2008 7:52 AM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: METRO TOYOTA OK 2002 Mercedes Benz Truck ML 320 (163.154) V6-3.2L (112.942)
1 of 9 4/27/2008 7:52 AM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: METRO TOYOTA OK 2002 Mercedes Benz Truck ML 320 (163.154) V6-3.2L (112.942)
35A-1 SERVICE BRAKES CONTENTS BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) <2WD> ACTIVE STABILITY CONTOROL (ASC) SYSTEM
 35A-1 SERVICE BRAKES CONTENTS BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM... 35A ANTI-SKID BRAKI SYSTEM (ABS) ... 35B ACTIVE STABILITY CONTOROL (ASC) SYSTEM... 35C 35A-2 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM General/On-vehicle Service GENERAL
35A-1 SERVICE BRAKES CONTENTS BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM... 35A ANTI-SKID BRAKI SYSTEM (ABS) ... 35B ACTIVE STABILITY CONTOROL (ASC) SYSTEM... 35C 35A-2 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM General/On-vehicle Service GENERAL
ESCONDIDO FIRE DEPT TRAINING MANUAL Section DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 Pumps and Accessory Equipment Revised
 DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 PUMPS AND ACCESSORY EQUIPMENT Pumps are designed for many different purposes. In order to understand the proper application and operation of a pump in a given situation, firefighters
DRIVER OPERATOR Page 1 of 13 PUMPS AND ACCESSORY EQUIPMENT Pumps are designed for many different purposes. In order to understand the proper application and operation of a pump in a given situation, firefighters
ENRESO.WORLD. Traction Control System. Created by Istas René - enreso.world. Graduated in Autmotomotiv Technolgogys
 ENRESO.WORLD Traction Control System Created by Istas René - enreso.world Graduated in Autmotomotiv Technolgogys Traction Control (TCS) is an option that is often found on vehicles equipped with antilock
ENRESO.WORLD Traction Control System Created by Istas René - enreso.world Graduated in Autmotomotiv Technolgogys Traction Control (TCS) is an option that is often found on vehicles equipped with antilock
Driving dynamics GENERAL INFORMATION WINTER MODE. JaguarDrive Control
 Driving dynamics GENERAL INFORMATION It remains the driver's responsibility to drive safely, according to the prevailing conditions and within the law. JaguarDrive Control JaguarDrive Control is a selectable
Driving dynamics GENERAL INFORMATION It remains the driver's responsibility to drive safely, according to the prevailing conditions and within the law. JaguarDrive Control JaguarDrive Control is a selectable
BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM SECTION BRC CONTENTS BRAKES BRC-1 WITH VDC PRECAUTION... 5 PREPARATION... 9 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION...10
 BRAKES SECTION BRC A BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM B C D CONTENTS E WITH VDC PRECAUTION... 5 PRECAUTIONS... 5 Precaution for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) "AIR BAG" and "SEAT BELT PRE-TEN- SIONER"...5 Precaution
BRAKES SECTION BRC A BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM B C D CONTENTS E WITH VDC PRECAUTION... 5 PRECAUTIONS... 5 Precaution for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) "AIR BAG" and "SEAT BELT PRE-TEN- SIONER"...5 Precaution
GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function
 GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function 14.1.13 MODEL 212 (except 212.095/098/298) as of model year 2014 Function requirements, general the engine is running or has been switched off by the ECO
GF42.47-P-0001FLM Adaptive brake (ABR), function 14.1.13 MODEL 212 (except 212.095/098/298) as of model year 2014 Function requirements, general the engine is running or has been switched off by the ECO
1. Anti-lock Brake System (ABS)
 W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Anti-lock Brake System () A: FEATURE The 5.3i type used in the Impreza has a hydraulic control unit, an control module, a valve relay and a motor
W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Anti-lock Brake System () A: FEATURE The 5.3i type used in the Impreza has a hydraulic control unit, an control module, a valve relay and a motor
SECTION 1-6 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS 05 HIGHLANDER_U (L/O 0409) Gauges, Meters and Service reminder indicators
 SECTION 1-6 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Gauges, Meters and Service reminder indicators Fuel gauge................................................ 132 Engine coolant temperature gauge...........................
SECTION 1-6 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Gauges, Meters and Service reminder indicators Fuel gauge................................................ 132 Engine coolant temperature gauge...........................
PRE-CHECK USA: DI-224 DLC1 E 1 ABS WITH EBD & BA & TRAC & VSC SYSTEM 2WD: CANADA: 4WD:
 DI224 2WD: 4WD: USA: CANADA: F14323 PRECHECK DI8XO02 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Inspect the battery positive voltage. Battery positive voltage: 10 14 V (b) Check the warning lights and buzzer. (1) Release
DI224 2WD: 4WD: USA: CANADA: F14323 PRECHECK DI8XO02 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Inspect the battery positive voltage. Battery positive voltage: 10 14 V (b) Check the warning lights and buzzer. (1) Release
POWER TRAIN 2-1 CONTENTS AYC SYSTEM... 9 CLUTCH... 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS... 4 FRONT AXLE... 5 REAR AXLE... 6
 2-1 POWER TRAIN CONTENTS CLUTCH................................ 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION............... 3 Transmission Control....................... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS................... 4 FRONT AXLE...........................
2-1 POWER TRAIN CONTENTS CLUTCH................................ 2 MANUAL TRANSMISSION............... 3 Transmission Control....................... 3 PROPELLER SHAFTS................... 4 FRONT AXLE...........................
8. Other system and brake theories
 8. Other system and brake theories Objective To understand the limiting valve, proportioning valve, load sensing proportioning valve and brake theories, which were used immediately before the development
8. Other system and brake theories Objective To understand the limiting valve, proportioning valve, load sensing proportioning valve and brake theories, which were used immediately before the development
SECTION 1 7 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake
 SECTION 1 7 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake Ignition switch.............................................. 114 Automatic transmission.....................................
SECTION 1 7 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake Ignition switch.............................................. 114 Automatic transmission.....................................
Continuously Variable Transaxle Specification. Forward/Reverse Switching Mechanism Double Pinion Type Planetary Gear
 CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41B Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1nr-fe engine models. 2. The K41B CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41B Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1nr-fe engine models. 2. The K41B CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
 Page 1 of 13 437: Transmission control module (TCM), TF-80SC AWD XC90, 2007, D5244T4, TF-80SC AWD, L.H.D, YV1CM714671338226, 338226 7/7/2016 PRINT 437: Transmission control module (TCM), TF-80SC AWD Adaptation
Page 1 of 13 437: Transmission control module (TCM), TF-80SC AWD XC90, 2007, D5244T4, TF-80SC AWD, L.H.D, YV1CM714671338226, 338226 7/7/2016 PRINT 437: Transmission control module (TCM), TF-80SC AWD Adaptation
Traction Control and Assist Systems Design and function
 SERVICE TRAINING Self-study Programme 374 Traction Control and Assist Systems Design and function Commercial Vehicles Increasing speed and road traffic density are increasing the need for vehicle dynamics
SERVICE TRAINING Self-study Programme 374 Traction Control and Assist Systems Design and function Commercial Vehicles Increasing speed and road traffic density are increasing the need for vehicle dynamics
Braking System Layout
 The Braking System The energy used to accelerate or move a vehicle from rest to a certain speed is called Kinetic i (moving) energy. To slow the vehicle down, this kinetic energy must be converted or changed,
The Braking System The energy used to accelerate or move a vehicle from rest to a certain speed is called Kinetic i (moving) energy. To slow the vehicle down, this kinetic energy must be converted or changed,
Continuously Variable Transaxle Specification. Forward/Reverse Switching Mechanism Double Pinion Type Planetary Gear
 CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41A Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1kr-fe engine models. 2. The K41A CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
CVT SYSTEM > GENERAL OUTLINE 1. A newly developed K41A Continuously Variable Transaxle (CVT) is used for the1kr-fe engine models. 2. The K41A CVT, including a pair of the pulleys and the belt in the shift
Ride and Handling Optimization
 Page 1 of 6 Published: Feb 23, 2009 Ride and Handling Optimization COMPONENT LOCATION Item Part Number Description 1 Terrain Response rotary control OVERVIEW The Terrain Response system allows the driver
Page 1 of 6 Published: Feb 23, 2009 Ride and Handling Optimization COMPONENT LOCATION Item Part Number Description 1 Terrain Response rotary control OVERVIEW The Terrain Response system allows the driver
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION
 DESCRIPTION & OPERATION BRAKE BOOSTER Delco-Moraine Single Diaphragm A combined vacuum-hydraulic unit which uses a combination of intake manifold vacuum and atmospheric pressure to provide power assist.
DESCRIPTION & OPERATION BRAKE BOOSTER Delco-Moraine Single Diaphragm A combined vacuum-hydraulic unit which uses a combination of intake manifold vacuum and atmospheric pressure to provide power assist.
ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS)
 GROUP 35B ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 35B-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS....... 35B-4 SPECIAL TOOLS................ 35B-5............ 35B-6 STANDARD FLOW OF DIAGNOSTIC................
GROUP 35B ANTI-SKID BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION........ 35B-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS....... 35B-4 SPECIAL TOOLS................ 35B-5............ 35B-6 STANDARD FLOW OF DIAGNOSTIC................
Brake System Fundamentals Chapter 71 Name Date Period
 Brake System Fundamentals Chapter 71 Name Date Period Basic Brake System Matching 1. Metal tubing and rubber hose that transmit pressure to the wheel brake assemblies. 2. Mechanical system for applying
Brake System Fundamentals Chapter 71 Name Date Period Basic Brake System Matching 1. Metal tubing and rubber hose that transmit pressure to the wheel brake assemblies. 2. Mechanical system for applying
Adaptive cruise control (ACC)
 Adaptive cruise control (ACC) PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION E94163 It is the drivers responsibility to stay alert, drive safely and be in control of the vehicle at all times. Keep the front of the vehicle free
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION E94163 It is the drivers responsibility to stay alert, drive safely and be in control of the vehicle at all times. Keep the front of the vehicle free
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
RIDE AND HANDLING OPTIMIZATION
 PUBLISHED: 26-JAN-2015 2013.0 RANGE ROVER SPORT (LS), 204-06 RIDE AND HANDLING OPTIMIZATION DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Terrain Response - Component Location ITEM DESCRIPTION 1 Terrain Response control and
PUBLISHED: 26-JAN-2015 2013.0 RANGE ROVER SPORT (LS), 204-06 RIDE AND HANDLING OPTIMIZATION DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Terrain Response - Component Location ITEM DESCRIPTION 1 Terrain Response control and
05/01/06 1er mai 2006 Cruise Control - Diagnostic Updates General Service Procedure Service Procedure Speed Control Diagnostic Tips Additional
 05/01/06 1er mai 2006 General Service Procedure Service Procedure Speed Control Diagnostic Tips Additional Reference Information SPEED CONTROL DIAGNOSTICS - W/O SCP FORD: 2000-2003 Escort 2000-2004 Crown
05/01/06 1er mai 2006 General Service Procedure Service Procedure Speed Control Diagnostic Tips Additional Reference Information SPEED CONTROL DIAGNOSTICS - W/O SCP FORD: 2000-2003 Escort 2000-2004 Crown
PRE CHECK DI 211 2WD: DLC3 CG F09750 ABS & BA & TRAC & VSC SYSTEM. VSC warning light circuit
 2WD: F13414 PRECHECK DI211 DI84M02 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Check the warning lights. (1) Release the parking break pedal. (2) When the ignition switch is turned, check that the ABS warning light, VSC warning
2WD: F13414 PRECHECK DI211 DI84M02 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Check the warning lights. (1) Release the parking break pedal. (2) When the ignition switch is turned, check that the ABS warning light, VSC warning
Chapter 33 Fundamentals of Hydraulic and Air-Over-Hydraulic Braking Systems
 Chapter 33 Fundamentals of Hydraulic and Air-Over-Hydraulic Braking Systems Introduction Vehicle s braking system must meet the following requirements: To adequately and safely reduce a vehicle s speed,
Chapter 33 Fundamentals of Hydraulic and Air-Over-Hydraulic Braking Systems Introduction Vehicle s braking system must meet the following requirements: To adequately and safely reduce a vehicle s speed,
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL 1994 Nissan Pickup 1994 BRAKES Nissan - Rear Anti-Lock Pathfinder, Pickup DESCRIPTION In 2WD mode, Rear Anti-Lock Brake System (RABS) helps the driver to maintain steering
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM - REAR WHEEL 1994 Nissan Pickup 1994 BRAKES Nissan - Rear Anti-Lock Pathfinder, Pickup DESCRIPTION In 2WD mode, Rear Anti-Lock Brake System (RABS) helps the driver to maintain steering
Technical Service Bulletin
 Number 02-36-030 Subject OBD-II READINESS TEST DRIVE CYCLE FOR 1996-1998 SONATA Date Model DECEMBER, 2002 1996-1998 SONATA DESCRIPTION: This TSB describes Drive Cycles which may assist the vehicle s OBD-II
Number 02-36-030 Subject OBD-II READINESS TEST DRIVE CYCLE FOR 1996-1998 SONATA Date Model DECEMBER, 2002 1996-1998 SONATA DESCRIPTION: This TSB describes Drive Cycles which may assist the vehicle s OBD-II
Adaptive cruise control (ACC)
 Adaptive cruise control (ACC) PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION WARNING Adaptive Cruise Control is not a collision warning or avoidance system. Additionally, Adaptive Cruise Control will not detect: stationary or
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION WARNING Adaptive Cruise Control is not a collision warning or avoidance system. Additionally, Adaptive Cruise Control will not detect: stationary or
Text in Illustration
 ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION If using a dropper to adjust the fluid amount, make sure that the dropper has not been used with mineral oils, water or deteriorated brake fluid. Sealed areas may deteriorate and
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION If using a dropper to adjust the fluid amount, make sure that the dropper has not been used with mineral oils, water or deteriorated brake fluid. Sealed areas may deteriorate and
To study about various types of braking system.
 To study about various types of braking system INTRODUCTION The system is purely mechanical means & is independent of the hydraulic system which controls the brake normally. A brake commonly referred to
To study about various types of braking system INTRODUCTION The system is purely mechanical means & is independent of the hydraulic system which controls the brake normally. A brake commonly referred to
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
 206-09-1 Vehicle Dynamic Systems 206-09-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Anti-Lock Control Traction Control and Stability Assist Special Tool(s) Principles of Operation 73III Automotive Meter 105-R0057 or equivalent
206-09-1 Vehicle Dynamic Systems 206-09-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Anti-Lock Control Traction Control and Stability Assist Special Tool(s) Principles of Operation 73III Automotive Meter 105-R0057 or equivalent
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (5AT)
 (5AT) GENERAL 1. General To improve the dynamic performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle, a new 5-speed automatic transmission is developed. The features of this new automatic transmission are as
(5AT) GENERAL 1. General To improve the dynamic performance and fuel efficiency of the vehicle, a new 5-speed automatic transmission is developed. The features of this new automatic transmission are as
Part 1 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS
 Part 1 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Chapter 1-6 Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake Ignition switch with steering lock Automatic transmission Manual transmission Four-wheel drive system
Part 1 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Chapter 1-6 Ignition switch, Transmission and Parking brake Ignition switch with steering lock Automatic transmission Manual transmission Four-wheel drive system
The electromechanical parking brake
 Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Service Training Self-study programme 346 The electromechanical parking brake Design and function To make absolutely sure that the vehicle could not roll away when parked up, the driver had to pull up
Driving dynamics GENERAL INFORMATION WINTER MODE. JaguarDrive Control
 GENERAL INFORMATION Driving dynamics It remains the driver's responsibility to drive safely, according to the prevailing conditions and within the law. JaguarDrive Control JaguarDrive Control is a selectable
GENERAL INFORMATION Driving dynamics It remains the driver's responsibility to drive safely, according to the prevailing conditions and within the law. JaguarDrive Control JaguarDrive Control is a selectable
Cruise control. Introduction WARNING. Indicator lights Cruise control operation. More information: In this section you ll find information about:
 Cruise control Introduction In this section you ll find information about: Indicator lights Cruise control operation The cruise control helps maintain an individually stored constant speed when driving
Cruise control Introduction In this section you ll find information about: Indicator lights Cruise control operation The cruise control helps maintain an individually stored constant speed when driving
PRE-CHECK ABS Warning Light BRAKE Warning Light USA: USA: Canada: Canada: VSC Warning Light SLIP Indicator Light. TRAC OFF Indicator Light
 ABS Warning Light BRAKE Warning Light USA: Canada: USA: Canada: VSC Warning Light SLIP Indicator Light TRAC Indicator Light F45096 PRECHECK 05765 05H3Y02 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Check the warning lights.
ABS Warning Light BRAKE Warning Light USA: Canada: USA: Canada: VSC Warning Light SLIP Indicator Light TRAC Indicator Light F45096 PRECHECK 05765 05H3Y02 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Check the warning lights.
ABS LOCATION OF COMPONENTS - ABS UP TO 99MY. 4. Front and rear sensors/exciter rings 5. Pressure Conscious Reducing Valve (PCRV) 6.
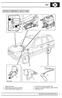 ABS LOCATION OF COMPONENTS - ABS UP TO 99MY 1. Relays and fuses 2. ABS Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 3. Brake booster/abs modulator unit 4. Front and rear sensors/exciter rings 5. Pressure Conscious Reducing
ABS LOCATION OF COMPONENTS - ABS UP TO 99MY 1. Relays and fuses 2. ABS Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 3. Brake booster/abs modulator unit 4. Front and rear sensors/exciter rings 5. Pressure Conscious Reducing
Part 1 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS
 Part 1 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Chapter 1-5 Gauges, Meters and Service reminder indicators Fuel gauge Engine coolant temperature gauge Tachometer Odometer and two trip meters Service reminder
Part 1 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Chapter 1-5 Gauges, Meters and Service reminder indicators Fuel gauge Engine coolant temperature gauge Tachometer Odometer and two trip meters Service reminder
Road Safety Factsheet
 Road Safety Factsheet Electronic Braking Systems Factsheet August 2017 Brake Assist Brake Assist (BA) is a technology that ensures that the maximum pressure is applied by the brakes to stop a vehicle in
Road Safety Factsheet Electronic Braking Systems Factsheet August 2017 Brake Assist Brake Assist (BA) is a technology that ensures that the maximum pressure is applied by the brakes to stop a vehicle in
SECTION 2 5 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS. Gauges, Meters and Service reminder indicators
 SECTION 2 5 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Gauges, Meters and Service reminder indicators Fuel gauge................................................ 122 Odometer and two trip meters................................
SECTION 2 5 OPERATION OF INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Gauges, Meters and Service reminder indicators Fuel gauge................................................ 122 Odometer and two trip meters................................
10.1 Electronic Stability Program (ESP) and Speed-sensitive Power Steering (SPS) Contents
 10.1 lectronic Stability Program (SP) and Speed-sensitive Power Steering (SPS) Contents 10.1 Models 129 (with engine 104, 119) up to M.Y. 1999, Model 129 (with engine 120), 140, 210 as of M.Y. 1996 Page
10.1 lectronic Stability Program (SP) and Speed-sensitive Power Steering (SPS) Contents 10.1 Models 129 (with engine 104, 119) up to M.Y. 1999, Model 129 (with engine 120), 140, 210 as of M.Y. 1996 Page
Adaptive cruise control (ACC)
 Adaptive cruise control (ACC) PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION The Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) system is designed to aid the driver to maintain a gap from the vehicle ahead or a set road speed if there is no slower
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION The Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) system is designed to aid the driver to maintain a gap from the vehicle ahead or a set road speed if there is no slower
Active On demand Coupling (AOC) Clutch unit and control module Signals
 Page 1 of 5 09: Differential Electronic Module (DEM) XC90, 2007, D5244T4, TF-80SC AWD, L.H.D, YV1CM714671338226, 338226 26/3/2013 PRINT 09: Differential Electronic Module (DEM) Active On demand Clutch
Page 1 of 5 09: Differential Electronic Module (DEM) XC90, 2007, D5244T4, TF-80SC AWD, L.H.D, YV1CM714671338226, 338226 26/3/2013 PRINT 09: Differential Electronic Module (DEM) Active On demand Clutch
Safe Braking on the School Bus Advanced BrakingTechniques and Practices. Reference Guide and Test by Video Communications
 Safe Braking on the School Bus Advanced BrakingTechniques and Practices Reference Guide and Test by Video Communications Introduction Brakes are considered one of the most important items for school bus
Safe Braking on the School Bus Advanced BrakingTechniques and Practices Reference Guide and Test by Video Communications Introduction Brakes are considered one of the most important items for school bus
Active & passive safety systems on Hyundai vehicles; Development & strategy. Road Safety conference, Belgrade April 27 th 29 th 2011
 Active & passive safety systems on Hyundai vehicles; Development & strategy Road Safety conference, Belgrade April 27 th 29 th 2011 Hyundai Auto Beograd, Since 2002 3 HISTORY 1997 ~ 1967 HISTORY 1996 Completion
Active & passive safety systems on Hyundai vehicles; Development & strategy Road Safety conference, Belgrade April 27 th 29 th 2011 Hyundai Auto Beograd, Since 2002 3 HISTORY 1997 ~ 1967 HISTORY 1996 Completion
The parking brake is an electrically actuated system that operates drum brakes integrated into the rear brake discs. The
 Page 1 of 15 Published: Oct 22, 2004 Parking Brake COMPONENT LOCATIONS Item Part Number Description 1 Clutch pedal position sensor (manual transmission models only) 2 Parking brake indicators (all except
Page 1 of 15 Published: Oct 22, 2004 Parking Brake COMPONENT LOCATIONS Item Part Number Description 1 Clutch pedal position sensor (manual transmission models only) 2 Parking brake indicators (all except
9.1 Traction Systems (ASR, ETS) and Speed-sensitive Power Steering (SPS) Contents
 9.1 Traction Systems (ASR, TS) and Speed-sensitive Power Steering (SPS) Contents 9.1 Models 129, 140 as of 06/94 up to 08/95 Page Diagnosis Function Test (ASR only).......................... 11/1 Diagnostic
9.1 Traction Systems (ASR, TS) and Speed-sensitive Power Steering (SPS) Contents 9.1 Models 129, 140 as of 06/94 up to 08/95 Page Diagnosis Function Test (ASR only).......................... 11/1 Diagnostic
Electronic Engine Power Control (EPC) (E-Gas), checking
 Page 1 of 51 24-113 Electronic Engine Power Control (EPC) (E-Gas), checking E-Gas system, function For E-Gas, the throttle valve is not operated by a cable from the accelerator pedal. There is no mechanical
Page 1 of 51 24-113 Electronic Engine Power Control (EPC) (E-Gas), checking E-Gas system, function For E-Gas, the throttle valve is not operated by a cable from the accelerator pedal. There is no mechanical
HOW TO PROCEED WITH TROUBLESHOOTING
 2005 BRAKES Anti-Lock Brake System With Electronic Brake Force Distribution (EBD) - Diagnostics - RAV4 HOW TO PROCEED WITH TROUBLESHOOTING Troubleshoot in accordance with the following procedures. Fig.
2005 BRAKES Anti-Lock Brake System With Electronic Brake Force Distribution (EBD) - Diagnostics - RAV4 HOW TO PROCEED WITH TROUBLESHOOTING Troubleshoot in accordance with the following procedures. Fig.
Conventional Cruise Control
 About Conventional Cruise Control Conventional Cruise Control Conventional Cruise Control is a driving support system intended to allow more comfortable driving on expressways, freeways and interstate
About Conventional Cruise Control Conventional Cruise Control Conventional Cruise Control is a driving support system intended to allow more comfortable driving on expressways, freeways and interstate
Driver Instructions. Hydraulic Launch Assist (HLA ) TRDR1200
 Driver Instructions Hydraulic Launch Assist (HLA ) TRDR1200 September 2011 Table of Contents Warnings and Cautions Definitions... 1 Driver Display Module... 7 Operation... 9 Service and Maintenance...
Driver Instructions Hydraulic Launch Assist (HLA ) TRDR1200 September 2011 Table of Contents Warnings and Cautions Definitions... 1 Driver Display Module... 7 Operation... 9 Service and Maintenance...
Document ID# Chevrolet/Geo Corvette
 Page 1 of 10 Document ID# 426762 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Corvette Print ABS Description Brake Pressure Modulator Valve (BPMV) FIGURE EBTCM/BPMV(c) (1) Electronic Brake and Traction Control
Page 1 of 10 Document ID# 426762 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Corvette Print ABS Description Brake Pressure Modulator Valve (BPMV) FIGURE EBTCM/BPMV(c) (1) Electronic Brake and Traction Control
SERVICE BRAKES GROUP 35A 35A-1 CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 35A-2 FRONT DISC BRAKE... 35A-5 MASTER CYLINDER... 35A-4 REAR DISC BRAKE...
 35A-1 GROUP 35A CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-2 MASTER CYLINDER............. 35A-4 FRONT DISC BRAKE............. 35A-5 REAR DISC BRAKE.............. 35A-6 BRAKE BOOSTER ASSEMBLY.... 35A-4 35A-2
35A-1 GROUP 35A CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-2 MASTER CYLINDER............. 35A-4 FRONT DISC BRAKE............. 35A-5 REAR DISC BRAKE.............. 35A-6 BRAKE BOOSTER ASSEMBLY.... 35A-4 35A-2
There are 2 ways of brake fluid replacement: using the Techstream or not using the Techstream.
 REPLACEMENT HINT: There are 2 ways of brake fluid replacement: using the Techstream or not using the Techstream. Perform fluid replacement with park (P) selected and the parking brake applied. As brake
REPLACEMENT HINT: There are 2 ways of brake fluid replacement: using the Techstream or not using the Techstream. Perform fluid replacement with park (P) selected and the parking brake applied. As brake
ABS Operator s Manual
 ABS Operator s Manual Bendix Antilock Brake Systems With optional advanced antilock braking features: Automatic Traction Control (ATC) and RSP Roll Stability System Read, understand and follow the information
ABS Operator s Manual Bendix Antilock Brake Systems With optional advanced antilock braking features: Automatic Traction Control (ATC) and RSP Roll Stability System Read, understand and follow the information
AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION IS FOR DRIVERS WHO DRIVE VEHICLES WITH AIR BRAKES
 Section 5 AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION IS FOR DRIVERS WHO DRIVE VEHICLES WITH AIR BRAKES AIR BRAKES/Section 5 SECTION 5: AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION COVERS Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting
Section 5 AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION IS FOR DRIVERS WHO DRIVE VEHICLES WITH AIR BRAKES AIR BRAKES/Section 5 SECTION 5: AIR BRAKES THIS SECTION COVERS Air Brake System Parts Dual Air Brake Systems Inspecting
FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS)
 35B-1 GROUP 35B FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35B-2 SENSORS..................... 35B-6 BRAKE MODULATOR (ABS-ECU).. 35B-9 SYSTEM OPERATION............ 35B-10
35B-1 GROUP 35B FOUR-WHEEL ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (4ABS) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35B-2 SENSORS..................... 35B-6 BRAKE MODULATOR (ABS-ECU).. 35B-9 SYSTEM OPERATION............ 35B-10
200C II BRAKE SYSTEM
 200C II BRAKE SYSTEM The braking system on the 200C II Kress Coal Hauler uses hydraulic oil pressure from both the System and Steering accumulator circuits. Using oil from both circuits provides braking
200C II BRAKE SYSTEM The braking system on the 200C II Kress Coal Hauler uses hydraulic oil pressure from both the System and Steering accumulator circuits. Using oil from both circuits provides braking
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM GROUP 35A 35A-1 CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 35A-3 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35A-6
 35A-1 GROUP 35A BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-3 DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 INTRODUCTION..................... 35A-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY......................... 35A-6
35A-1 GROUP 35A BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-3 DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 INTRODUCTION..................... 35A-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY......................... 35A-6
GF1A TRANSFER / 4WD / AWD: DYNAMIC TORQUE CONTROL AWD SYSTEM: SYSTEM DESCRIPTION; 2016 MY RAV4 [10/ /2016]
![GF1A TRANSFER / 4WD / AWD: DYNAMIC TORQUE CONTROL AWD SYSTEM: SYSTEM DESCRIPTION; 2016 MY RAV4 [10/ /2016] GF1A TRANSFER / 4WD / AWD: DYNAMIC TORQUE CONTROL AWD SYSTEM: SYSTEM DESCRIPTION; 2016 MY RAV4 [10/ /2016]](/thumbs/92/109878214.jpg) 11/29/2017 Dynamic Torque System - System Description - [10/2015-08/2016] (Transfer Case) - ALLDATA 2016 Toyota Truck RAV4 4WD L4-2.5L (2AR-FE) Vehicle > Transmission and Drivetrain > Transfer Case > Description
11/29/2017 Dynamic Torque System - System Description - [10/2015-08/2016] (Transfer Case) - ALLDATA 2016 Toyota Truck RAV4 4WD L4-2.5L (2AR-FE) Vehicle > Transmission and Drivetrain > Transfer Case > Description
Electrical Braking System Simulation and Control based on Force to Voltage Conversion using Servo Motor
 Electrical Braking System Simulation and Control based on Force to Voltage Conversion using Servo Motor Mohammad A Obeidat Abstract In this paper an electrical braking system is proposed. The force on
Electrical Braking System Simulation and Control based on Force to Voltage Conversion using Servo Motor Mohammad A Obeidat Abstract In this paper an electrical braking system is proposed. The force on
P0733 DTC P0733 A/T 3RD GEAR FUNCTION
 2003 Nissan-Datsun Altima L4-2.5L (QR25DE) Vehicle > ALL Diagnostic Trouble Codes ( DTC ) > Testing and Inspection > P Code Charts P0733 DTC P0733 A/T 3RD GEAR FUNCTION Description - This is an OBD-II
2003 Nissan-Datsun Altima L4-2.5L (QR25DE) Vehicle > ALL Diagnostic Trouble Codes ( DTC ) > Testing and Inspection > P Code Charts P0733 DTC P0733 A/T 3RD GEAR FUNCTION Description - This is an OBD-II
GROUP 35A 35A-1 CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 35A-3 BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 HYDRAULIC BRAKE BOOSTER (HBB) DIAGNOSIS...
 35A-1 GROUP 35A CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-3 DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 INTRODUCTION..................... 35A-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY......................... 35A-6 SYMPTOM CHART...................
35A-1 GROUP 35A CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 35A-3 DIAGNOSIS 35A-6 INTRODUCTION..................... 35A-6 DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY......................... 35A-6 SYMPTOM CHART...................
Inspection and Basic Maintenance of Brake Systems
 Inspection and Basic Maintenance of Brake Systems 11-1 Types Air brakes Hydraulic brakes Secondary braking systems 11-2 Air Brake System Most large, modern fire apparatus are equipped with air-operated
Inspection and Basic Maintenance of Brake Systems 11-1 Types Air brakes Hydraulic brakes Secondary braking systems 11-2 Air Brake System Most large, modern fire apparatus are equipped with air-operated
4.4. Forces Applied to Automotive Technology. The Physics of Car Tires
 Forces Applied to Automotive Technology Throughout this unit we have addressed automotive safety features such as seat belts and headrests. In this section, you will learn how forces apply to other safety
Forces Applied to Automotive Technology Throughout this unit we have addressed automotive safety features such as seat belts and headrests. In this section, you will learn how forces apply to other safety
TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION CIRCUIT ACTYON
 311001 017 311001 TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION 018 311001 (3) DESCRIPTION A. ION (BTRA) M74 4WD AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION The ION (BTR) Four Speed
311001 017 311001 TCU 1) CONNECTOR INFORMATION 2) CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION SYMBOL & PIN NUMBER POSITION 018 311001 (3) DESCRIPTION A. ION (BTRA) M74 4WD AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION The ION (BTR) Four Speed
16 Introduction to DSC
 Lateral Acceleration Sensor (Bosch 5.3) This new sensor is a major contributor of the expanded capabilities of DSC III. It is located under the drivers seat but mounted on the vertical surface of the inner
Lateral Acceleration Sensor (Bosch 5.3) This new sensor is a major contributor of the expanded capabilities of DSC III. It is located under the drivers seat but mounted on the vertical surface of the inner
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM. Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD
 ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD INTRODUCTION An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM Seminar by K.JAYAKISHORE GRIET HYDERABAD INTRODUCTION An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety system on motor vehicles which prevents the wheels from locking while braking.
Cooling System Description and Operation
 Page 1 of 5 2008 Holden VE Sedan VE, WM, Caprice, Statesman, Lumina, Omega, VXR8 Service Manual Engine Engine Cooling Description and Operation Document ID: 1990377 Cooling System Description and Operation
Page 1 of 5 2008 Holden VE Sedan VE, WM, Caprice, Statesman, Lumina, Omega, VXR8 Service Manual Engine Engine Cooling Description and Operation Document ID: 1990377 Cooling System Description and Operation
From the Lohner-Porsche to the 911 Turbo
 newsroom History Mar 14, 2018 From the Lohner-Porsche to the 911 Turbo One of the first cars to feature all-wheel drive was a Porsche, and it was a sports car: Ferdinand Porsche designed and built the
newsroom History Mar 14, 2018 From the Lohner-Porsche to the 911 Turbo One of the first cars to feature all-wheel drive was a Porsche, and it was a sports car: Ferdinand Porsche designed and built the
BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES
 BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES AUTOMOTIVE BRAKING SYSTEMS How brakes manufacturing industry is different then rest of the automotive
BRAKE SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS KARAN BHARDIYA ASSISTANT MANAGER -R&D ENDURANCE TECHNOLOGIES PVT.LTD. DISC BRAKES AUTOMOTIVE BRAKING SYSTEMS How brakes manufacturing industry is different then rest of the automotive
Transmission and Brake
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Gear selector lever in automatic transmission*...-2 Driving tips for automatic transmission...-3 Gear selector lever positions...-5 Winter (W) / standard (S) mode... -11 Safety mode (automatic
TABLE OF CONTENTS Gear selector lever in automatic transmission*...-2 Driving tips for automatic transmission...-3 Gear selector lever positions...-5 Winter (W) / standard (S) mode... -11 Safety mode (automatic
V8 Vantage Sportshift Driving Guide
 LG/GE/10/03/2011 The V8 Vantage incorporates a 6-speed Sportshift automated manual transmission. There are two driving modes for V8 Vantage Sportshift. The first is Paddle Shift Mode This is the mode where
LG/GE/10/03/2011 The V8 Vantage incorporates a 6-speed Sportshift automated manual transmission. There are two driving modes for V8 Vantage Sportshift. The first is Paddle Shift Mode This is the mode where
SECTION 1 3 INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS. Gauges, meters and service reminder indicators
 SECTION 1 3 INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Gauges, meters and service reminder indicators Fuel gauge............................................... 26 Engine coolant temperature gauge..........................
SECTION 1 3 INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS Gauges, meters and service reminder indicators Fuel gauge............................................... 26 Engine coolant temperature gauge..........................
