The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points:
|
|
|
- Valentine Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
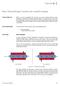
1 Exercise 2 Float Switch EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Learn the working principle of float switches and how to use the float switch, Model DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points: Introduction Reed-switch-type float switches Industrial applications Advantages and limitations Description of the supplied float switch Commissioning the float switch Installing the float switch DISCUSSION Instrument symbol Float switch Introduction A float switch is a point-level detection device used to actuate another device when the level in a vessel rises above, or drops below, a set point. Like all pointlevel sensors, float switches allow level detection of a single discrete level. A float switch that stops a pump when a tank is full is an example of a typical float switch application. Figure 9 shows a point-level detection mechanism that uses a simple float switch. Figure 9. Float switch application. In this example, the float of a float switch is displaced when its buoyancy makes it move upward when it comes in contact with the liquid. The float can be linked mechanically to an actuator, such as in the example of Figure 9, or via another mechanism, such as a reed switch and magnet mechanism, like the one on the float switch of the Instrumentation and Process Control System. The working principle of float switches using this type of mechanism is described in the section below. Festo Didactic
2 Exercise 2 Float Switch Discussion Reed-switch-type float switches Reed-switch-type float switches have two main components: a reed switch and a float with an encased magnet. Depending on its position along a stem, the float actuates (or not) the reed switch. The reed switches used in float switches usually have a single-pole single-throw (SPST) or a single-pole double-throw (SPDT) contact configuration. The reed switch in the float switch of the Instrumentation and Process Control System is of the SPST type. How a reed switch works The reed switch was invented in 1936 by Walter B. Ellwood from the Bell Telephone Laboratories. As stated in the original patent application, this device eliminates the complicated mechanical and magnetic structures of the usual electromagnetic relays. Figure 10 shows a typical reed switch diagram. This type of switch is named after the thin metal reeds enclosed in its glass capsule. The capsule is filled with an inert gas to prevent the reeds from rusting. The portions of the reeds that come in contact when the switch closes are plated with precious metal to ensure good conductivity. Glass capsule Reed Inert gas Terminal Gap Contact plating Figure 10. Reed switch. The working principle of a reed switch is simple. The reed switch is normally open. The gap between the two reeds isolates them and no current can flow through the switch. If a permanent magnet is placed close to the switch, the magnetic flux generated by the magnet draws the two reeds together. As shown in Figure 11, the plated tip of one of the reeds becomes a magnetic north pole, while the tip of the other reed becomes a magnetic south pole 2. Since the tips of the reeds have opposite magnetic poles, they attract each other and the two reeds snap together to close the electric circuit. When the magnet is removed from the proximity of the switch, the stiffness of the reeds brings them apart and the electrical circuit is open again. 2 Note that each reed also has an opposite pole at its other extremity. Magnetic poles always come in pairs; a magnetic monopole has never been observed. 18 Festo Didactic
3 Exercise 2 Float Switch Discussion Permanent magnet Magnetic flux S N N S N S Contact closed Figure 11. Actuated reed switch. The float and the stem In a float switch, the reed switch described above is located in the stem, a nonmagnetic tube. The stem is waterproof and protects the reed switch from water. The float has a cylindrical shape and the stem passes through a hole along its axis. The float is made of a material of a lesser density than water so that it floats. A permanent magnet is embedded in the float and, when the float moves along the stem, the magnet changes the state of the reed contact. Construction and operation The working principle of the float switch can be summarized as follows. The float is made of a material that is lighter than water and incorporates a permanent magnet. As the float rises and falls with the changes in the water level, it moves the magnet along the stem, thereby opening and closing the reed switch contact, which consists of two thin moveable blades of ferromagnetic metal. The free ends of the reeds are the contact points and form the actual reed contact. Float switches can be normally-open or normally-closed switches. For example, the factory default configuration for the float switch, Model 46935, is with the reed contact acting as a normally-closed contact. With this configuration, the magnet in the float closes the reed contact when the level is below the float. When the level rises above the float, the magnet rises with the float and, because it is too far from the reed switch, its magnetic field is too weak to keep the reed switch contact closed. Thus, the two reeds separate from each other and the circuit opens. Figure 12 shows how a float switch operates in NC configuration. The configuration of most float switches can be reversed to transform them into normally-open switches. This is generally done by inverting the position of the float. Festo Didactic
4 Exercise 2 Float Switch Discussion Stem Contact open Contact closed Float Lower stop Figure 12. Float switch (NC configuration). Industrial applications Float switches are mainly used to perform on/off control and to start sequential operations in batch processes. They are also used to trigger alarms when high or low liquid levels are detected in vessels. High levels can indicate unusual change in normal load demand, due to clogged pipes or valves accidentally closing, while low levels can indicate pump or liquid supply failure. Advantages and limitations Float switches are relatively inexpensive, reliable, and require minimum maintenance. However, they are limited in their use as on/off control devices or alarm switches. They do not provide continuous measurement of the liquid level. Moreover, some types of float switches are not recommended for processes where dirty liquids are handled. For example, liquids that contain particles of ferrous metal can cause malfunction of magnetically-operated float switches. Description of the supplied float switch The float switch, Model 46935, designed for the Instrumentation and Process Control Training System is shown in Figure 13. A connection box at the top of the float switch gives access to the switch contacts. 20 Festo Didactic
5 Exercise 2 Float Switch Discussion Figure 13. Float switch, Model Table 6. Components of the float switch. Component Contact connectors Non-magnetic tube Mounting screw Stem Float Fault panel Description Connectors for the contact points of the reed switch. Tube holding the float switch in place in the column. The tube can slide in the mounting screw. This allows the float switch to be positioned at different heights. Secures the float switch in the installation hole of the column flange. The stem contains the reed switch and allows the float to slide. The float has an embedded magnet that actuates (or not) the reed switch, depending on its position along the stem. The float can be reversed to switch between a NC and a NO float switch. Contains one switch used to simulate a fault with the apparatus. Commissioning the float switch The float of the float switch, Model 46935, can be reversed to transform the NC float switch into a NO float switch and vice versa. Before installing the float switch at the top of the column, you must make sure that the switch configuration is correct for your needs. The float switch has a NC factory default configuration. Float switches with this configuration are frequently used to cut power to pumps in case of high level alarms. However, for the exercise that follows, the switch is used differently and the float switch must be configured as a NO switch. To check if your float switch is configured as a NC or NO switch, follow the steps below: a. Hold the float switch vertically so that the tip with the float is pointing downward. b. Connect a multimeter (set to the continuity measurement mode) to the jacks on the float switch connection box. c. If the float switch is configured as a NC switch, it should conduct current when pointing downward. If not, it is configured as a NO switch. Festo Didactic
6 Exercise 2 Float Switch Discussion If your switch is not configured as a NO switch, you must reverse the float to be able to use it to complete the following exercise. Follow the steps below to reverse the float switch contact configuration. a. Remove the lower stop (i.e., the retaining ring). b. Remove the float from the stem and flip it 180 degrees. c. Put the float back on the stem. d. Put the lower stop back in place. (a) (b) (c) (d) Figure 14. Changing the float switch configuration (from NC to NO). Installing the float switch The float switch is not designed to operate in a pressurized column. To avoid damage to the equipment, be sure the column is open to atmosphere when using the float switch. The float switch is designed to be installed at the top of the column, on the flange. Use Figure 15 and the instructions below to install the float switch on your system. a. First, secure the flange at the top of the column. b. Once the flange is secured, remove the brass hexagonal-head plug using a wrench. 22 Festo Didactic
7 Exercise 2 Float Switch Procedure Outline c. Insert the float switch in the installation hole and screw the mounting screw in place. You can slide the float switch up and down to adjust the height of the float. a) b) c) Figure 15. Installing the float switch. PROCEDURE OUTLINE The Procedure is divided into the following sections: Setup and connections Testing the float switch PROCEDURE Setup and connections 1. Connect the equipment according to the piping and instrumentation diagram (P&ID) shown in Figure 16 and use Figure 17 to position the equipment correctly on the frame of the training system. To set up your system for this exercise, start with the basic setup presented in the Familiarization with the Instrumentation and Process Control Training System manual and add the equipment listed in Table 7. Before installing the float switch on the flange, be sure it is configured as a normally-open switch. Refer to the Commissioning the float switch section for details. Table 7. Material to add to the basic setup for this exercise. Name Model Identification Float switch LSH 1 Electrical unit Pneumatic unit Accessories Festo Didactic
8 Exercise 2 Float Switch Procedure Figure 16. P&ID. 24 Festo Didactic
9 Exercise 2 Float Switch Procedure Air from the pneumatic unit (140 kpa (20 psi)) Figure 17. Setup. 2. In this exercise, the float switch is used to open the solenoid valve to provide additional drainage to the column if the level of water is too high. Water exits the column only under the effect of gravity. Therefore, the column drains slowly relative to the input flow. To avoid an accidental overflow, you must limit the input flow by reducing the speed of the pump or by restricting the flow using the control valve. 3. Connect the control valve to the pneumatic unit. Details about the installation and operation of the control valve are available in the Familiarization with the Instrumentation and Process Control Training System manual. Festo Didactic
10 Exercise 2 Float Switch Procedure 4. Connect the pneumatic unit to a dry-air source with an output pressure of at least 700 kpa (100 psi). 5. Wire the emergency push-button so that you can cut power in case of emergency. The Familiarization with the Instrumentation and Process Control Training System manual covers the security issues related to the use of electricity with the system as well as the wiring of the emergency pushbutton. 6. Do not power up the instrumentation workstation yet. Do not turn the electrical panel on before your instructor has validated your setup that is, not before step Wire the float switch and the solenoid valve so that a voltage of 24 V dc actuates the solenoid valve when the contact of the float switch closes. 8. Before proceeding further, complete the following checklist to make sure you have set up the system properly. The points on this checklist are crucial elements to the proper completion of this exercise. This checklist is not exhaustive, so be sure to follow the instructions in the Familiarization with the Instrumentation and Process Control Training System manual as well. f All unused male adapters on the column are capped and the flange is properly tightened. The ball valves are in the positions shown in the P&ID. The three-way valve at the suction of the pump (HV1) is set so that the flow is directed toward the pump inlet. The control valve is fully open. The pneumatic connections are correct. The solenoid valve is wired so that the valve opens when the contact of the float switch closes. The vent tube is correctly installed. 9. Ask your instructor to check and approve your setup. 10. Make sure it is safe to energize the system for you and for the team working on the other side of the system, if any. When ready, turn on the main power. Testing the float switch 11. Press the S1 button to power all the devices not already active on the station (i.e., the drive, the pneumatic devices, etc.). 26 Festo Didactic
11 Exercise 2 Float Switch Conclusion 12. Test your system for leaks. Use the drive to make the pump run at low speed to produce a low flow rate. Gradually increase the flow rate, up to 50% of the maximum flow rate that the pumping unit can deliver (i.e., set the drive speed to 30 Hz). Repair any leaks. 13. Stop the drive and let the column drain. 14. Start the pump and set the flow rate at about 36 L/min (9.5 gal/min). This flow rate should be obtained by setting the pump to 65% of the maximum flow rate that the pumping unit can deliver (i.e., set the drive speed to 40 Hz, approximately). Do not set the drive speed higher to avoid overflow. You can also use the control valve to adjust the flow rate instead of adjusting the drive speed. 15. Watch the level rise in the column up to the float switch. 16. What happens when the level reaches the float switch? 17. Is this a good way to control the level in a vessel? Why? 18. Stop the pump, open HV4, and turn off the power to the system. CONCLUSION You should now be able to install and use the float switch, Model You should also be able to change the float switch configuration so that it operates as a NO switch instead of a NC switch. REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. What is the contact configuration of the reed switch in the float switch, Model 46935? Festo Didactic
12 Exercise 2 Float Switch Review Questions 2. Name one advantage of using a reed switch. 3. Explain how a reed switch works. 4. Why is the reed-switch glass capsule filled with an inert gas? 5. Name one advantage and one limitation of float switches. 28 Festo Didactic
Exercise 4-1. Flowmeters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Rotameters. How do rotameter tubes work?
 Exercise 4-1 Flowmeters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Learn the basics of differential pressure flowmeters via the use of a Venturi tube and learn how to safely connect (and disconnect) a differential pressure flowmeter
Exercise 4-1 Flowmeters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Learn the basics of differential pressure flowmeters via the use of a Venturi tube and learn how to safely connect (and disconnect) a differential pressure flowmeter
Familiarize yourself with the pressure loss phenomenon. The Discussion of this exercise covers the following point:
 Exercise 3-2 Pressure Loss EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Familiarize yourself with the pressure loss phenomenon. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion of this exercise covers the following point: Pressure loss Major
Exercise 3-2 Pressure Loss EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Familiarize yourself with the pressure loss phenomenon. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion of this exercise covers the following point: Pressure loss Major
Basic Thermal Energy Transfer with a Heat Exchanger
 Exercise 4-1 Basic Thermal Energy Transfer with a Heat Exchanger EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the basic principles of operation of a typical heat
Exercise 4-1 Basic Thermal Energy Transfer with a Heat Exchanger EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the basic principles of operation of a typical heat
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points: Centrifugal pumps in series Centrifugal pumps in parallel. Centrifugal pumps in series
 Exercise 2-4 Centrifugal Pumps in Series and in Parallel (Optional Exercise) EXERCISE OBJECTIVE In this exercise, you will observe the effects that connecting two centrifugal pumps in series or parallel
Exercise 2-4 Centrifugal Pumps in Series and in Parallel (Optional Exercise) EXERCISE OBJECTIVE In this exercise, you will observe the effects that connecting two centrifugal pumps in series or parallel
Exercise 3-1. Basic Hydraulic Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Complete hydraulic circuit
 Exercise 3-1 Basic Hydraulic Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the hydraulic schematic and components of the nacelle trainer. You will identify
Exercise 3-1 Basic Hydraulic Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the hydraulic schematic and components of the nacelle trainer. You will identify
Exercise 3-1. Basic Hydraulic Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Complete hydraulic circuit
 Exercise 3-1 Basic Hydraulic Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the hydraulic schematic and components of the nacelle trainer. You will identify
Exercise 3-1 Basic Hydraulic Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the hydraulic schematic and components of the nacelle trainer. You will identify
Exercise 7. Thyristor Three-Phase Rectifier/Inverter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Thyristor three-phase rectifier/inverter
 Exercise 7 Thyristor Three-Phase Rectifier/Inverter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will know what a thyristor threephase rectifier/limiter (thyristor three-phase bridge)
Exercise 7 Thyristor Three-Phase Rectifier/Inverter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will know what a thyristor threephase rectifier/limiter (thyristor three-phase bridge)
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points:
 Exercise 3-2 Hydraulic Brakes EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the hydraulic circuits of the yaw and the rotor brakes. You will control brakes by changing
Exercise 3-2 Hydraulic Brakes EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the hydraulic circuits of the yaw and the rotor brakes. You will control brakes by changing
Fundamentals of the Ultrasonic Flowmeter
 Exercise 1 Fundamentals of the Ultrasonic Flowmeter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Learn the working principle of ultrasonic flowmeters, familiarize yourself with the ultrasonic flow transmitter of the Instrumentation
Exercise 1 Fundamentals of the Ultrasonic Flowmeter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Learn the working principle of ultrasonic flowmeters, familiarize yourself with the ultrasonic flow transmitter of the Instrumentation
Permanent Magnet DC Motor Operating as a Generator
 Exercise 2 Permanent Magnet DC Motor Operating as a Generator EXERCIE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the construction of permanent magnet dc motors as well as
Exercise 2 Permanent Magnet DC Motor Operating as a Generator EXERCIE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the construction of permanent magnet dc motors as well as
FLUID POWER FLUID POWER EQUIPMENT TUTORIAL PNEUMATIC CIRCUTS. This work covers part of outcome 3 of the Edexcel standard module:
 FLUID POWER FLUID POWER EQUIPMENT TUTORIAL PNEUMATIC CIRCUTS This work covers part of outcome 3 of the Edexcel standard module: UNIT 21746P APPLIED PNEUMATICS AND HYDRAULICS The material needed for outcome
FLUID POWER FLUID POWER EQUIPMENT TUTORIAL PNEUMATIC CIRCUTS This work covers part of outcome 3 of the Edexcel standard module: UNIT 21746P APPLIED PNEUMATICS AND HYDRAULICS The material needed for outcome
Exercise 1-3. Manual Starters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Direct-on-line (DOL) starters. Reversing starters
 Exercise 1-3 Manual Starters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Examine and describe the operation of manual motor starters. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points: Direct-on-line
Exercise 1-3 Manual Starters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Examine and describe the operation of manual motor starters. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points: Direct-on-line
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points:
 Exercise 3-3 Venturi Tubes EXERCISE OBJECTIVE In this exercise, you will study the relationship between the flow rate and the pressure drop produced by a venturi tube. You will describe the behavior of
Exercise 3-3 Venturi Tubes EXERCISE OBJECTIVE In this exercise, you will study the relationship between the flow rate and the pressure drop produced by a venturi tube. You will describe the behavior of
Exercise 1-1. Lockout/Tagout Procedure EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION. Become familiar with the Industrial Controls Training System.
 Exercise 1-1 Lockout/Tagout Procedure EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Become familiar with the Industrial Controls Training System. Understand and perform proper lockout/tagout procedures during industrial servicing
Exercise 1-1 Lockout/Tagout Procedure EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Become familiar with the Industrial Controls Training System. Understand and perform proper lockout/tagout procedures during industrial servicing
The Electromagnet. Electromagnetism
 The Electromagnet When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to explain the operation of an electromagnet by using a coil of wire. You will verify your results with a compass and an iron nail.
The Electromagnet When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to explain the operation of an electromagnet by using a coil of wire. You will verify your results with a compass and an iron nail.
Electromagnetic Induction (approx. 1.5 h) (11/9/15)
 (approx. 1.5 h) (11/9/15) Introduction In 1819, during a lecture demonstration, the Danish scientist Hans Christian Oersted noticed that the needle of a compass was deflected when placed near a current-carrying
(approx. 1.5 h) (11/9/15) Introduction In 1819, during a lecture demonstration, the Danish scientist Hans Christian Oersted noticed that the needle of a compass was deflected when placed near a current-carrying
Exercise 4-1. Friction Brakes EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION. Understand the construction and operation of friction brakes.
 Exercise 4-1 Friction Brakes EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Understand the construction and operation of friction brakes. DISCUSSION Friction brakes, or magnetic brakes, are used to secure (hold) the position of a
Exercise 4-1 Friction Brakes EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Understand the construction and operation of friction brakes. DISCUSSION Friction brakes, or magnetic brakes, are used to secure (hold) the position of a
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
 Renewable Energy Permanent Magnet DC Motor Courseware Sample 86357-F0 A RENEWABLE ENERGY PERMANENT MAGNET DC MOTOR Courseware Sample by the staff of Lab-Volt Ltd. Copyright 2011 Lab-Volt Ltd. All rights
Renewable Energy Permanent Magnet DC Motor Courseware Sample 86357-F0 A RENEWABLE ENERGY PERMANENT MAGNET DC MOTOR Courseware Sample by the staff of Lab-Volt Ltd. Copyright 2011 Lab-Volt Ltd. All rights
Ex. 1-1 Nacelle Familiarization and Safety Discussion
 Exercise 1-1 Nacelle Familiarization and Safety EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with key components and safety aspects of the nacelle trainer. You will be
Exercise 1-1 Nacelle Familiarization and Safety EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with key components and safety aspects of the nacelle trainer. You will be
Exercise 6. Three-Phase AC Power Control EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Introduction to three-phase ac power control
 Exercise 6 Three-Phase AC Power Control EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will know how to perform ac power control in three-phase ac circuits, using thyristors. You will know
Exercise 6 Three-Phase AC Power Control EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will know how to perform ac power control in three-phase ac circuits, using thyristors. You will know
Lesson 5: Directional Control Valves
 : Directional Control Valves Basic Hydraulic Systems Hydraulic Fluids Hydraulic Tank Hydraulic Pumps and Motors Pressure Control Valves Directional Control Valves Flow Control Valves Cylinders : Directional
: Directional Control Valves Basic Hydraulic Systems Hydraulic Fluids Hydraulic Tank Hydraulic Pumps and Motors Pressure Control Valves Directional Control Valves Flow Control Valves Cylinders : Directional
Understand how soft starters operate.
 Exercise 5-2 Soft Starters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Understand how soft starters operate. DISCUSSION Soft starters are solid-state devices providing gradual voltage increase, for the purpose of starting a motor
Exercise 5-2 Soft Starters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Understand how soft starters operate. DISCUSSION Soft starters are solid-state devices providing gradual voltage increase, for the purpose of starting a motor
DISCUSSION OF FUNDAMENTALS. A hydraulic system can be controlled either manually or automatically:
 Unit 1 Introduction to Electrical Control of Hydraulic Systems UNIT OBJECTIVE When you have completed this unit, you will be able to identify the components used for electrical control of the Hydraulics
Unit 1 Introduction to Electrical Control of Hydraulic Systems UNIT OBJECTIVE When you have completed this unit, you will be able to identify the components used for electrical control of the Hydraulics
KOBOLD VKA FLOWMETER/SWITCH. User Instructions. Manual-VKA_03-04
 KOBOLD VKA FLOWMETER/SWITCH User Instructions Manual-VKA_03-04 VKA Table of Contents 1.0 General............................................. 1 Specifications..........................................
KOBOLD VKA FLOWMETER/SWITCH User Instructions Manual-VKA_03-04 VKA Table of Contents 1.0 General............................................. 1 Specifications..........................................
Electropneumatics Basic Level Set of Overhead Transparencies TP 201
 Electropneumatics Basic Level Set of Overhead Transparencies TP 0 Festo Didactic 0950 en Order No.: 0950 Description: EL-PN.FOLIEN-GS Designation: D:OT-TP0-GB Edition: 0/000 Author: Frank Ebel Graphics:
Electropneumatics Basic Level Set of Overhead Transparencies TP 0 Festo Didactic 0950 en Order No.: 0950 Description: EL-PN.FOLIEN-GS Designation: D:OT-TP0-GB Edition: 0/000 Author: Frank Ebel Graphics:
GraspIT AQA GCSE Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Questions
 A. Permanent and Induced Magnetism, Magnetic Forces and Fields 1. The following question is about magnets. a. Iron is a magnetic material. Name two other magnetic elements. (2) b. Describe the effect a
A. Permanent and Induced Magnetism, Magnetic Forces and Fields 1. The following question is about magnets. a. Iron is a magnetic material. Name two other magnetic elements. (2) b. Describe the effect a
FLUID POWER P&IDs. IDENTIFY the symbols used on engineering fluid power drawings for the following components:
 FLUID POWER P&IDs Fluid power diagrams and schematics require an independent review because they use a unique set of symbols and conventions. EO 1.11 IDENTIFY the symbols used on engineering fluid power
FLUID POWER P&IDs Fluid power diagrams and schematics require an independent review because they use a unique set of symbols and conventions. EO 1.11 IDENTIFY the symbols used on engineering fluid power
Button Bounce. Fryad M. Rashid and Pei-Lin Chung
 Button Bounce Fryad M. Rashid and Pei-Lin Chung 1 Outline The purpose of this presentation What is a button? Button States Switch Bounce Definition Basic Types of Switch Switch Applications How does bounce
Button Bounce Fryad M. Rashid and Pei-Lin Chung 1 Outline The purpose of this presentation What is a button? Button States Switch Bounce Definition Basic Types of Switch Switch Applications How does bounce
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points:
 Exercise 1 Battery Fundamentals EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with various types of lead-acid batteries and their features. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion
Exercise 1 Battery Fundamentals EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with various types of lead-acid batteries and their features. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion
Ch 4 Motor Control Devices
 Ch 4 Motor Control Devices Part 1 Manually Operated Switches 1. List three examples of primary motor control devices. (P 66) Answer: Motor contactor, starter, and controller or anything that control the
Ch 4 Motor Control Devices Part 1 Manually Operated Switches 1. List three examples of primary motor control devices. (P 66) Answer: Motor contactor, starter, and controller or anything that control the
6081 Pneumatics Training System
 6081 Pneumatics Training System LabVolt Series Datasheet Festo Didactic en 220 V - 50 Hz 03/2018 Table of Contents General Description 2 Innovative design 3 Virtual Laboratory Equipment 3 Courseware 3
6081 Pneumatics Training System LabVolt Series Datasheet Festo Didactic en 220 V - 50 Hz 03/2018 Table of Contents General Description 2 Innovative design 3 Virtual Laboratory Equipment 3 Courseware 3
LEVEL SWITCH INTRODUCTION APPLICATIONS
 LEVEL SWITCH LEVEL SWITCH INTRODUCTION Kimray pneumatic and electric switches give customers dependable service in all types of environments. Both can be used for high or low level control, and the 316
LEVEL SWITCH LEVEL SWITCH INTRODUCTION Kimray pneumatic and electric switches give customers dependable service in all types of environments. Both can be used for high or low level control, and the 316
NHP SAFETY REFERENCE GUIDE
 4 NHP SAFETY REFERENCE GUIDE CONTENTS SAFETY TECHNOLOGY Risk Reduction Options Permanent Fixed Guard 4-02 Interlocked Guard: 4-03 Limit Switches 4-08 Presence Sensing Technology 4-09 Safety Laser Scanners
4 NHP SAFETY REFERENCE GUIDE CONTENTS SAFETY TECHNOLOGY Risk Reduction Options Permanent Fixed Guard 4-02 Interlocked Guard: 4-03 Limit Switches 4-08 Presence Sensing Technology 4-09 Safety Laser Scanners
BELT-DRIVEN ALTERNATORS
 CHAPTER 13 BELT-DRIVEN ALTERNATORS INTRODUCTION A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy using the principle of magnetic induction. This principle is based on the
CHAPTER 13 BELT-DRIVEN ALTERNATORS INTRODUCTION A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy using the principle of magnetic induction. This principle is based on the
Exercise 5-1. Primary Resistor Starters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION. Understand how primary resistor starters operate.
 Exercise 5-1 Primary Resistor Starters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Understand how primary resistor starters operate. DISCUSSION High starting torque can result in sudden acceleration and damage to the driven machinery.
Exercise 5-1 Primary Resistor Starters EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Understand how primary resistor starters operate. DISCUSSION High starting torque can result in sudden acceleration and damage to the driven machinery.
8036-A0 Motor Drives Training System (Stand-Alone)
 8036-A0 Motor Drives Training System (Stand-Alone) LabVolt Series Datasheet Festo Didactic en 120 V - 60 Hz 04/2018 Table of Contents General Description 2 List of Equipment 2 List of Manuals 2 Table of
8036-A0 Motor Drives Training System (Stand-Alone) LabVolt Series Datasheet Festo Didactic en 120 V - 60 Hz 04/2018 Table of Contents General Description 2 List of Equipment 2 List of Manuals 2 Table of
Learning System for Automation and Communications. Electropneumatics. Workbook Basic Level S1 K1 K1 Y1
 Learning System for Automation and Communications Electropneumatics Workbook Basic Level 1 2 3 S1 K1 K1 S2 K1 094005 Order no. 094005 Description: TEACHW.E-PNEUM. Designation: D.S201-C-GB Edition: 08/1993
Learning System for Automation and Communications Electropneumatics Workbook Basic Level 1 2 3 S1 K1 K1 S2 K1 094005 Order no. 094005 Description: TEACHW.E-PNEUM. Designation: D.S201-C-GB Edition: 08/1993
6080 Hydraulics Training System
 6080 Hydraulics Training System LabVolt Series Datasheet Festo Didactic en 240 V - 50 Hz 03/2018 Table of Contents General Description 2 Innovative Design 3 Virtual Laboratory Equipment 3 Courseware 3
6080 Hydraulics Training System LabVolt Series Datasheet Festo Didactic en 240 V - 50 Hz 03/2018 Table of Contents General Description 2 Innovative Design 3 Virtual Laboratory Equipment 3 Courseware 3
Experiment 6: Induction
 Experiment 6: Induction Part 1. Faraday s Law. You will send a current which changes at a known rate through a solenoid. From this and the solenoid s dimensions you can determine the rate the flux through
Experiment 6: Induction Part 1. Faraday s Law. You will send a current which changes at a known rate through a solenoid. From this and the solenoid s dimensions you can determine the rate the flux through
Basic Electrically-Controlled Hydraulic System
 Exercise 2-3 EXERCISE OBJECIVE o describe the function and operation of a magnetic proximity switch; o describe the purpose of a holding relay contact; o assemble and test a one-cycle reciprocation system.
Exercise 2-3 EXERCISE OBJECIVE o describe the function and operation of a magnetic proximity switch; o describe the purpose of a holding relay contact; o assemble and test a one-cycle reciprocation system.
C. Figure 1. CA-16 Front View Figure 2. CA-16 Rear View
 Figure 1. CA-16 Front View Figure 2. CA-16 Rear View 2 2.1. Restraint Elements Each restraint element consists of an E laminated electromagnet with two primary coils and a secondary coil on its center
Figure 1. CA-16 Front View Figure 2. CA-16 Rear View 2 2.1. Restraint Elements Each restraint element consists of an E laminated electromagnet with two primary coils and a secondary coil on its center
VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE
 Electromagnetism Observation sheet Name VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE http://studentorgs.vanderbilt.edu/vsvs Electromagnetism Spring 2016 (Adapted from Student Guide for Electric Snap Circuits
Electromagnetism Observation sheet Name VANDERBILT STUDENT VOLUNTEERS FOR SCIENCE http://studentorgs.vanderbilt.edu/vsvs Electromagnetism Spring 2016 (Adapted from Student Guide for Electric Snap Circuits
5-2 FUEL SYSTEM AND THROTTLE BODY FUEL SYSTEM FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM The fuel delivery system consists of the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filters, fuel f
 FUEL SYSTEM AND THROTTLE BODY 5-1 FUEL SYSTEM AND THROTTLE BODY I CONTENTS FUEL SYSTEM 5-2 FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM 5-2 FUEL PUMP 5-3 FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR 5-4 FUEL INJECTOR 5-4 FUEL PUMP CONTROL SYSTEM
FUEL SYSTEM AND THROTTLE BODY 5-1 FUEL SYSTEM AND THROTTLE BODY I CONTENTS FUEL SYSTEM 5-2 FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM 5-2 FUEL PUMP 5-3 FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR 5-4 FUEL INJECTOR 5-4 FUEL PUMP CONTROL SYSTEM
Solenoid valve. Solenoid Coil
 Solenoid valve Solenoid valve Solenoid Coil Plunger Valve body A simple solenoid valve consists ofi: Valve body with a plunger the plunger is made of metal Coil an electrical coil if the coil is given
Solenoid valve Solenoid valve Solenoid Coil Plunger Valve body A simple solenoid valve consists ofi: Valve body with a plunger the plunger is made of metal Coil an electrical coil if the coil is given
16000SIII Automatic Grease System
 Manual # 99905495 16000SIII Automatic Grease System Effective 20120716 IOWA MOLD TOOLING CO., INC. PO Box 189 Garner, IA 50438 Tel: 641-923-3711 FAX: 641-923-2424 Website: http://www.imt.com Copyright
Manual # 99905495 16000SIII Automatic Grease System Effective 20120716 IOWA MOLD TOOLING CO., INC. PO Box 189 Garner, IA 50438 Tel: 641-923-3711 FAX: 641-923-2424 Website: http://www.imt.com Copyright
Exercise 4-1. Nacelle Control System EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Control and simulation of environmental conditions
 Exercise 4-1 Nacelle Control System EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will know more about the logic behind the control system. In particular, you will understand alarm management
Exercise 4-1 Nacelle Control System EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will know more about the logic behind the control system. In particular, you will understand alarm management
PTEX extruder pumps Pneumatic extruder pump for drums of grease up to NLGI grade 2
 1-4009-EN PTEX extruder pumps Pneumatic extruder pump for drums of grease up to NLGI grade 2 The PTEX extruder pumps are pneumatically actuated pumps designed to deliver lubricant under pressure to lubrication
1-4009-EN PTEX extruder pumps Pneumatic extruder pump for drums of grease up to NLGI grade 2 The PTEX extruder pumps are pneumatically actuated pumps designed to deliver lubricant under pressure to lubrication
Level Switches. Level Float Switch. Visual/Electrical Low Level. LEN Series RL Series. LV/E1 Series. S e c t i o n
 Level Switches Level Float Switch LEN Series RL Series Visual/Electrical Low Level LV/E1 Series S e c t i o n 5 Level Float Switch - LEN Series The electromagnetic level indicator activates an electric
Level Switches Level Float Switch LEN Series RL Series Visual/Electrical Low Level LV/E1 Series S e c t i o n 5 Level Float Switch - LEN Series The electromagnetic level indicator activates an electric
SPECIFICATIONS. Installation arrow must point downward Vertical Valve For top mounting.
 PNEUMATIC FLOAT VALVE DESCRIPTION The Magnetic is an air sensor for detecting liquid level inside a vessel. The float mechanism mounted within the vessel operates a ceramic coated magnet. As the float
PNEUMATIC FLOAT VALVE DESCRIPTION The Magnetic is an air sensor for detecting liquid level inside a vessel. The float mechanism mounted within the vessel operates a ceramic coated magnet. As the float
FHM Series. Magnetic Separator. RoHS FH HOW
 Magnetic Separator FHM Series RoHS These magnetic separators protect machinery from malfunctions, reduced precision, and burnout by adsorbing and eliminating contaminants in the fluid by means of magnetism.
Magnetic Separator FHM Series RoHS These magnetic separators protect machinery from malfunctions, reduced precision, and burnout by adsorbing and eliminating contaminants in the fluid by means of magnetism.
Check Valves Check Valves are the simplest form of directional control valves, but they can also be used as pressure controls.
 Check Valves Check Valves are the simplest form of directional control valves, but they can also be used as pressure controls. Standard Check Valve The standard check valve permits free flow in one direction
Check Valves Check Valves are the simplest form of directional control valves, but they can also be used as pressure controls. Standard Check Valve The standard check valve permits free flow in one direction
Familiarization with voltage and current measurements. 1. Disconnect your training system from the wall outlet.
 Job Sheet 6 Geothermal Heat Pumps OBJECTIVE In this job sheet, you will determine the coefficient of performance (COP) and the energy efficiency ratio (EER) using measured temperature, humidity, voltage,
Job Sheet 6 Geothermal Heat Pumps OBJECTIVE In this job sheet, you will determine the coefficient of performance (COP) and the energy efficiency ratio (EER) using measured temperature, humidity, voltage,
Volumetric Measuring Devices Issued: Revision Number: 2
 Field Inspection Manual Part: 4-STP Section: 29 Page: 1 of 5 APPLICATION This procedure is used when performing accuracy tests on any measuring systems that incorporate an air eliminator or deaerator of
Field Inspection Manual Part: 4-STP Section: 29 Page: 1 of 5 APPLICATION This procedure is used when performing accuracy tests on any measuring systems that incorporate an air eliminator or deaerator of
1. Anti-lock Brake System (ABS)
 W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Anti-lock Brake System () A: FEATURE The 5.3i type used in the Impreza has a hydraulic control unit, an control module, a valve relay and a motor
W1860BE.book Page 2 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 1. Anti-lock Brake System () A: FEATURE The 5.3i type used in the Impreza has a hydraulic control unit, an control module, a valve relay and a motor
Reed Technology. standexmeder.com
 Reed Technology standexmeder.com How Reed Switches are used with a Permanent Magnet Using Reed Switches in a sensing environment, one generally uses a magnet for actuation. It is important to understand
Reed Technology standexmeder.com How Reed Switches are used with a Permanent Magnet Using Reed Switches in a sensing environment, one generally uses a magnet for actuation. It is important to understand
Exercise 2. Discharge Characteristics EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Cutoff voltage versus discharge rate
 Exercise 2 Discharge Characteristics EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the discharge characteristics of lead-acid batteries. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion
Exercise 2 Discharge Characteristics EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the discharge characteristics of lead-acid batteries. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion
Installation, Series 1200 Magnetic Level Gauges and Switches. Engineered Performance. Series 1200
 Installation, OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL Series 1200 Engineered Performance TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 2.0.0. Magnetic Level Gauges 2.1.0. Description 1 2.1.1. Introduction 1 2.1.2. Components 1 2.1.3.
Installation, OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL Series 1200 Engineered Performance TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 2.0.0. Magnetic Level Gauges 2.1.0. Description 1 2.1.1. Introduction 1 2.1.2. Components 1 2.1.3.
Figure 1: Relative Directions as Defined for Faraday s Law
 Faraday s Law INTRODUCTION This experiment examines Faraday s law of electromagnetic induction. The phenomenon involves induced voltages and currents due to changing magnetic fields. (Do not confuse this
Faraday s Law INTRODUCTION This experiment examines Faraday s law of electromagnetic induction. The phenomenon involves induced voltages and currents due to changing magnetic fields. (Do not confuse this
KOBOLD SV FLOWMETER/SWITCH. User Instructions
 KOBOLD SV FLOWMETER/SWITCH User Instructions KOBOLD Instruments Inc. 1801 Parkway View Drive Pittsburgh PA 15205 Phone (412) 788-2830 Fax (412)-788-4890 www.koboldusa.com R2_4-13 SV Table Of Contents
KOBOLD SV FLOWMETER/SWITCH User Instructions KOBOLD Instruments Inc. 1801 Parkway View Drive Pittsburgh PA 15205 Phone (412) 788-2830 Fax (412)-788-4890 www.koboldusa.com R2_4-13 SV Table Of Contents
NCP/NCB/NCS. Magnetic Float Switches. for Liquids
 Magnetic Float Switches for Liquids measuring monitoring analyzing NCP/NCB/NCS Available Materials: Brass, SS, NBR, Polypropylene, and PVC Maximum Pressure: 400 PSIG Maximum Temperature: 300 F Single Point
Magnetic Float Switches for Liquids measuring monitoring analyzing NCP/NCB/NCS Available Materials: Brass, SS, NBR, Polypropylene, and PVC Maximum Pressure: 400 PSIG Maximum Temperature: 300 F Single Point
M-50/55 Series. Fixed setting flow switch with in-line flow
 M-50/55 Series Fixed setting flow switch with in-line flow Features Very accurate custom flow settings For corrosive and non-corrosive liquids or gases All-Teflon switch available Senses increasing or
M-50/55 Series Fixed setting flow switch with in-line flow Features Very accurate custom flow settings For corrosive and non-corrosive liquids or gases All-Teflon switch available Senses increasing or
Hermetically Sealed Power Contact
 Hermetically Sealed Power Contact What is Bestact? Sealed switches in glass tube with inert gas Q: What is Bestact? A : Briefly, it is a hermetically sealed contact in a glass tube that can be used in
Hermetically Sealed Power Contact What is Bestact? Sealed switches in glass tube with inert gas Q: What is Bestact? A : Briefly, it is a hermetically sealed contact in a glass tube that can be used in
DELUGE VALVE MODEL: SD-DVA TECHNICAL DATA : VALVE OPERATION TRIM DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION PRESSURE THREADED OPENING
 DELUGE VALVE MODEL: SD-DVA TECHNICAL DATA : NOMINAL SIZE MATERIAL MAXIMUM SERVICE PRESSURE 200, 150, 100, 80 & 50NB Cast Iron 12 Bar (175 PSI) THREADED OPENING MOUNTING FACTORY HYDROSTATIC TEST PRESSURE
DELUGE VALVE MODEL: SD-DVA TECHNICAL DATA : NOMINAL SIZE MATERIAL MAXIMUM SERVICE PRESSURE 200, 150, 100, 80 & 50NB Cast Iron 12 Bar (175 PSI) THREADED OPENING MOUNTING FACTORY HYDROSTATIC TEST PRESSURE
ELECTRICAL. Contents - Wiring Diagrams
 Contents - Wiring Diagrams T-Bar (Floating Deck - Hydro)............................................ 8-16 T-Bar (Fixed Deck - Gear)............................................... 8-17 T-Bar (Fixed Deck
Contents - Wiring Diagrams T-Bar (Floating Deck - Hydro)............................................ 8-16 T-Bar (Fixed Deck - Gear)............................................... 8-17 T-Bar (Fixed Deck
UNIQUE SCIENCE ACADEMY
 1 UIQUE IEE EMY Test (Unit 21) ame :... Paper: Physics ate :... ode: 5054 lass: II Time llowed: 40Minutes This document consists of 6 printed pages. Maximum Marks: 25 T [Total 15 Marks] heory ection: Fig.
1 UIQUE IEE EMY Test (Unit 21) ame :... Paper: Physics ate :... ode: 5054 lass: II Time llowed: 40Minutes This document consists of 6 printed pages. Maximum Marks: 25 T [Total 15 Marks] heory ection: Fig.
BUCHHOLZ RELAYS EE Series
 BUCHHOLZ RELAYS EE Series The newest Buchholz relay release for use in oil-immersed power transformers www.cedaspe.com 1. General Features 1.1 Characteristics The gas-actuated protective relay is designed
BUCHHOLZ RELAYS EE Series The newest Buchholz relay release for use in oil-immersed power transformers www.cedaspe.com 1. General Features 1.1 Characteristics The gas-actuated protective relay is designed
The Starter motor. Student booklet
 The Starter motor Student booklet The Starter motor - INDEX - 2006-04-07-13:20 The Starter motor The starter motor is an electrical motor and the electric motor is all about magnets and magnetism: A motor
The Starter motor Student booklet The Starter motor - INDEX - 2006-04-07-13:20 The Starter motor The starter motor is an electrical motor and the electric motor is all about magnets and magnetism: A motor
7.9.8 Elctromagnetism
 7.9.8 Elctromagnetism 71 minutes 86 marks Page 1 of 25 Q1. The diagram shows an electromagnet used in a door lock. (a) The push switch is closed and the door unlocks. Explain in detail how this happens.
7.9.8 Elctromagnetism 71 minutes 86 marks Page 1 of 25 Q1. The diagram shows an electromagnet used in a door lock. (a) The push switch is closed and the door unlocks. Explain in detail how this happens.
M-100 Adjustable flow switch with right-angle flow
 M-100 Adjustable flow switch with right-angle flow Operating Instructions and Quick Start Guide Table of Contents Introduction 03 Operation 03 Storage and Handling 03 Installation Instruction 03 Specification
M-100 Adjustable flow switch with right-angle flow Operating Instructions and Quick Start Guide Table of Contents Introduction 03 Operation 03 Storage and Handling 03 Installation Instruction 03 Specification
Exercise 2-1. The Separately-Excited DC Motor N S EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Simplified equivalent circuit of a dc motor
 Exercise 2-1 The Separately-Excited DC Motor EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to demonstrate the main operating characteristics of a separately-excited dc motor
Exercise 2-1 The Separately-Excited DC Motor EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to demonstrate the main operating characteristics of a separately-excited dc motor
Motor Drives Training System (Stand-Alone, 120 V Version) (8036-C0)
 Motor Drives Training System (Stand-Alone, 120 V Version) 581526 (8036-C0) LabVolt Series Datasheet Festo Didactic en 120 V - 60 Hz 11/2018 Table of Contents General Description 2 List of Equipment 2 List
Motor Drives Training System (Stand-Alone, 120 V Version) 581526 (8036-C0) LabVolt Series Datasheet Festo Didactic en 120 V - 60 Hz 11/2018 Table of Contents General Description 2 List of Equipment 2 List
Model 5000 Level Controller
 Features Multiple Configurations The 5000 level controller is easily configured for either reverse or direct actions for both pneumatic and electric pilot options. The pneumatic pilot is available in snap
Features Multiple Configurations The 5000 level controller is easily configured for either reverse or direct actions for both pneumatic and electric pilot options. The pneumatic pilot is available in snap
Model 3200 Liquid Level Controller
 Model 3200 Liquid Level Controller The Model 3200 Liquid Level Controller is ideal for oilfield scrubber and separator applications. Its rugged and versatile design make it the preferred choice of production
Model 3200 Liquid Level Controller The Model 3200 Liquid Level Controller is ideal for oilfield scrubber and separator applications. Its rugged and versatile design make it the preferred choice of production
Mini Magnetic Float Type Level Switch
 33 Mini Magnetic Float Type Level Switch Hydraulic Equipment. Lubricating Oils. and Coolant Tanks Introduction SFM series float type liquid level Switch made by Seojin Instech is intended for mounting
33 Mini Magnetic Float Type Level Switch Hydraulic Equipment. Lubricating Oils. and Coolant Tanks Introduction SFM series float type liquid level Switch made by Seojin Instech is intended for mounting
Armature Reaction and Saturation Effect
 Exercise 3-1 Armature Reaction and Saturation Effect EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to demonstrate some of the effects of armature reaction and saturation in
Exercise 3-1 Armature Reaction and Saturation Effect EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to demonstrate some of the effects of armature reaction and saturation in
HPB Hydraulic Power Braking System
 HPB Hydraulic Power Braking System 4 th Edition This publication is not subject to any update service. New versions are available in INFORM at www.wabco-auto.com Copyright WABCO 2007 Vehicle Control Systems
HPB Hydraulic Power Braking System 4 th Edition This publication is not subject to any update service. New versions are available in INFORM at www.wabco-auto.com Copyright WABCO 2007 Vehicle Control Systems
2012 FIRST Robotics Competition Pneumatics Manual
 2012 FIRST Robotics Competition Pneumatics Manual The 2012 FIRST Robotics Competition (FRC) pneumatic components are outlined in this document. It is being provided as a courtesy, and therefore does not
2012 FIRST Robotics Competition Pneumatics Manual The 2012 FIRST Robotics Competition (FRC) pneumatic components are outlined in this document. It is being provided as a courtesy, and therefore does not
Exercise 2-1. Hub and Low-Speed Shaft EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION. Blade pitch in the nacelle system
 Exercise 2-1 Hub and Low-Speed Shaft EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the portion of the nacelle that extracts mechanical power from the wind and transfers
Exercise 2-1 Hub and Low-Speed Shaft EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the portion of the nacelle that extracts mechanical power from the wind and transfers
Float switch For horizontal installation, miniature design Model HLS-M
 Level switch For horizontal installation, miniature design Model HLS-M WIKA data sheet LM 30.06 Applications For level monitoring and level indication of liquids Level detection for almost all liquid media
Level switch For horizontal installation, miniature design Model HLS-M WIKA data sheet LM 30.06 Applications For level monitoring and level indication of liquids Level detection for almost all liquid media
ENVIROMUX Series E-LLS-SF-10/25CM. Stainless Steel Vertical Liquid Level Float Switch. Installation Instruction. Description.
 ENVIROMUX Series E-LLS-SF-10/25CM Stainless Steel Vertical Liquid Level Float Switch Installation Instruction Description The action of the E-LLS-SF-xxCM Float Switch is straight forward and simple. Mount
ENVIROMUX Series E-LLS-SF-10/25CM Stainless Steel Vertical Liquid Level Float Switch Installation Instruction Description The action of the E-LLS-SF-xxCM Float Switch is straight forward and simple. Mount
Contents. Pressure measurement technology Pressure calibrators 18 Exercises 19-20
 1 Pressure Contents Topics: Slide No: Pressure measurement technology 03-17 Pressure calibrators 18 Exercises 19-20 2 Pressure Gauges Barometer Used to measure Barometric Pressure Reference is 0 psia,
1 Pressure Contents Topics: Slide No: Pressure measurement technology 03-17 Pressure calibrators 18 Exercises 19-20 2 Pressure Gauges Barometer Used to measure Barometric Pressure Reference is 0 psia,
Fig There is a current in each wire in a downward direction (into the page).
 1 (a) Two straight, vertical wires X and Y pass through holes in a horizontal card. Fig. 8.1 shows the card viewed from above. card wire in hole X Y wire in hole Fig. 8.1 There is a current in each wire
1 (a) Two straight, vertical wires X and Y pass through holes in a horizontal card. Fig. 8.1 shows the card viewed from above. card wire in hole X Y wire in hole Fig. 8.1 There is a current in each wire
Chapter 7: DC Motors and Transmissions. 7.1: Basic Definitions and Concepts
 Chapter 7: DC Motors and Transmissions Electric motors are one of the most common types of actuators found in robotics. Using them effectively will allow your robot to take action based on the direction
Chapter 7: DC Motors and Transmissions Electric motors are one of the most common types of actuators found in robotics. Using them effectively will allow your robot to take action based on the direction
Didactic and technological innovation at the service of training in pneumatics and electro-pneumatics have resulted in the creation of the
 Didactic and technological innovation at the service of training in pneumatics and electro-pneumatics have resulted in the creation of the PNEUTRAINER-200 system. A fully modular system designed for the
Didactic and technological innovation at the service of training in pneumatics and electro-pneumatics have resulted in the creation of the PNEUTRAINER-200 system. A fully modular system designed for the
4 x 0-10Vdc Channels Fused 24V o/p terminals for actuator power Direct or buffered output signals
 IO Input/Output Modules IO-ABM4 Analogue Override Module Description IO-ABM4 Analogue Override Module Intended for applications which require independent manual override of analogue output channels from
IO Input/Output Modules IO-ABM4 Analogue Override Module Description IO-ABM4 Analogue Override Module Intended for applications which require independent manual override of analogue output channels from
Deep Well Pump Control Valve
 MODEL 61-02 661-02 Deep Well Pump Control Valve Prevent Surges in Pipelines Simple Hydraulic Operation Adjustable Opening & Closing Speeds Solenoid Control Can Be Operated Manually Proven Reliable Design
MODEL 61-02 661-02 Deep Well Pump Control Valve Prevent Surges in Pipelines Simple Hydraulic Operation Adjustable Opening & Closing Speeds Solenoid Control Can Be Operated Manually Proven Reliable Design
Model 3201 Liquid Level Controller
 Model 3201 Liquid Level Controller The Model 3201 Liquid Level Controller is ideal for oilfield scrubber and separator applications. Its rugged and versatile design make it the preferred choice of production
Model 3201 Liquid Level Controller The Model 3201 Liquid Level Controller is ideal for oilfield scrubber and separator applications. Its rugged and versatile design make it the preferred choice of production
 PHP-C Pressureless Expansion System Overview Description: The PHP-C balanced pressure expansion equipment is sized according to the total system volume and the boiler or chiller load. The PHP-C vessel
PHP-C Pressureless Expansion System Overview Description: The PHP-C balanced pressure expansion equipment is sized according to the total system volume and the boiler or chiller load. The PHP-C vessel
Basics of Control Components
 Basics of Control Components Table of Contents Introduction...2 Electrical Symbols...6 Line Diagrams...16 Overload Protection...22 Overload Relays...26 Manual Control...35 Magnetic Contactors and Starters...41
Basics of Control Components Table of Contents Introduction...2 Electrical Symbols...6 Line Diagrams...16 Overload Protection...22 Overload Relays...26 Manual Control...35 Magnetic Contactors and Starters...41
Job Sheet 5 Hydraulic Unit Circuit
 Job Sheet 5 Hydraulic Unit Circuit The key components involved in the cylinder piston rod actuation (solenoid valves SV1, SV2, SV3A, and SV3B) are within the core components of the hydraulic unit of the
Job Sheet 5 Hydraulic Unit Circuit The key components involved in the cylinder piston rod actuation (solenoid valves SV1, SV2, SV3A, and SV3B) are within the core components of the hydraulic unit of the
DG 023 DG 024 DG 025 DG 041 DG 042. Clogging Indicators
 Clogging Indicators DG 03 DG 04 DG 05 DG 041 DG 04 For Pressure and High Pressure Filters Operating pressure up to 657 psi Response/Switching pressure up to 73 psi 60.30-4us Description Application Monitoring
Clogging Indicators DG 03 DG 04 DG 05 DG 041 DG 04 For Pressure and High Pressure Filters Operating pressure up to 657 psi Response/Switching pressure up to 73 psi 60.30-4us Description Application Monitoring
GAS ACTUATED RELAYS FOR OIL FILLED TRANSFORMERS EN
 GAS ACTUATED RELAYS FOR OIL FILLED TRANSFORMERS EN 50216-2 Nome file : RELE EN50216 REV 04 DTD 23/04/2007 Pagina 1 di 22 1. General Features 1.1 Characteristics The gas-actuated protective relay is designed
GAS ACTUATED RELAYS FOR OIL FILLED TRANSFORMERS EN 50216-2 Nome file : RELE EN50216 REV 04 DTD 23/04/2007 Pagina 1 di 22 1. General Features 1.1 Characteristics The gas-actuated protective relay is designed
Pneumatic Manual 2008
 Pneumatic Manual 2008 The Advantages of Using Pneumatics in 2008 Fluid power technology encompasses both hydraulics and pneumatics. Hydraulic applications use pressurized fluids, mostly oil, while pneumatic
Pneumatic Manual 2008 The Advantages of Using Pneumatics in 2008 Fluid power technology encompasses both hydraulics and pneumatics. Hydraulic applications use pressurized fluids, mostly oil, while pneumatic
The Basic Reed Switch
 REED SWITCH CHARACTERISTICS The Basic Reed Switch MEDER electronic Shown below in Figure # 1, Throw (DPST)), 3 Form A (three normally open switches), etc. A normally closed (N.C.) switch is described as
REED SWITCH CHARACTERISTICS The Basic Reed Switch MEDER electronic Shown below in Figure # 1, Throw (DPST)), 3 Form A (three normally open switches), etc. A normally closed (N.C.) switch is described as
PHYS 2212L - Principles of Physics Laboratory II
 PHYS 2212L - Principles of Physics Laboratory II Laboratory Advanced Sheet Faraday's Law 1. Objectives. The objectives of this laboratory are a. to verify the dependence of the induced emf in a coil on
PHYS 2212L - Principles of Physics Laboratory II Laboratory Advanced Sheet Faraday's Law 1. Objectives. The objectives of this laboratory are a. to verify the dependence of the induced emf in a coil on
Jo-Bell Products. DIVISION OF DALNOR SYSTEMS, INC Sierra Vista Drive Carlsbad NM, Phone: Fax:
 Jo-Bell Products DIVISION OF DALNOR SYSTEMS, INC. 5325 Sierra Vista Drive Carlsbad NM, 88220 Phone: 575-628-0675 Fax: 575-628-0679 Jo-Bell Products has been producing liquid level controls since 1947,
Jo-Bell Products DIVISION OF DALNOR SYSTEMS, INC. 5325 Sierra Vista Drive Carlsbad NM, 88220 Phone: 575-628-0675 Fax: 575-628-0679 Jo-Bell Products has been producing liquid level controls since 1947,
LS200, LS200N, LS200NDVOR Series and L1100 Liquid Level Switches
 LS200, LS200N, LS200NDVOR Series and L1100 Liquid Level Switches Installation and Operations Manual CALL MURCAL TO PLACE YOUR ORDER P:(661)272-4700 F:(661)947-7570 www.murcal.com e-mail: sales@murcal.com
LS200, LS200N, LS200NDVOR Series and L1100 Liquid Level Switches Installation and Operations Manual CALL MURCAL TO PLACE YOUR ORDER P:(661)272-4700 F:(661)947-7570 www.murcal.com e-mail: sales@murcal.com
Day Tank Controller Design Details by David Lynn s/y Nine of Cups
 Day Tank Controller Design Details by David Lynn s/y Nine of Cups A day tank controller is a pretty simple device. It should sense when the level of fuel in the day tank drops to somewhere around ¼ full
Day Tank Controller Design Details by David Lynn s/y Nine of Cups A day tank controller is a pretty simple device. It should sense when the level of fuel in the day tank drops to somewhere around ¼ full
Table of Contents.
 3551 Table of Contents Operating Information...2 Hydraulic Information Diagrams...7 Hydraulic and Electrical Installation...10 Parts List...11 Troubleshooting...15 Page 1 M3551 M3551 Operating Information
3551 Table of Contents Operating Information...2 Hydraulic Information Diagrams...7 Hydraulic and Electrical Installation...10 Parts List...11 Troubleshooting...15 Page 1 M3551 M3551 Operating Information
MAGNETIC MOTOR STARTERS
 Chapter 6 MAGNETIC MOTOR STARTERS 1 The basic use for the magnetic contactor is for switching power in resistance heating elements, lighting, magnetic brakes, or heavy industrial solenoids. Contactors
Chapter 6 MAGNETIC MOTOR STARTERS 1 The basic use for the magnetic contactor is for switching power in resistance heating elements, lighting, magnetic brakes, or heavy industrial solenoids. Contactors
