Power Train Transmission
|
|
|
- Julianna Hines
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SB4264E00 May Transmission D35S-5, D40S-5, D45S-5, D50C-5, D55C-5 D40SC-5, D45SC-5, D50SC-5, D55SC-5 G35S-5, G40S-5, G45S-5, G50C-5, G55C-5 G40SC-5, G45SC-5, G50SC-5, G55SC-5 GC35S-5, GC40S-5, GC45S-5 GC50C-5, GC55C-5
2 Important Safety Information Most accidents involving product operation, maintenance and repair are caused by failure to observe basic safety rules or precautions. An accident can often be avoided by recognizing potentially hazardous situations before an accident occurs. A person must be alert to potential hazards. This person should also have the necessary training, skills and tools to perform these functions properly. Read and understand all safety precautions and warnings before operating or performing lubrication, maintenance and repair on this product. Basic safety precautions are listed in the Safety section of the Service or Technical Manual. Additional safety precautions are listed in the Safety section of the owner/operation/maintenance publication. Specific safety warnings for all these publications are provided in the description of operations where hazards exist. WARNING labels have also been put on the product to provide instructions and to identify specific hazards. If these hazard warnings are not heeded, bodily injury or death could occur to you or other persons. Warnings in this publication and on the product labels are identified by the following symbol. WARNING Improper operation, lubrication, maintenance or repair of this product can be dangerous and could result in injury or death. Do not operate or perform any lubrication, maintenance or repair on this product, until you have read and understood the operation, lubrication, maintenance and repair information. Operations that may cause product damage are identified by NOTICE labels on the product and in this publication. DOOSAN cannot anticipate every possible circumstance that might involve a potential hazard. The warnings in this publication and on the product are therefore not all inclusive. If a tool, procedure, work method or operating technique not specifically recommended by DOOSAN is used, you must satisfy yourself that it is safe for you and others. You should also ensure that the product will not be damaged or made unsafe by the operation, lubrication, maintenance or repair procedures you choose. The information, specifications, and illustrations in this publication are on the basis of information available at the time it was written. The specifications, torques, pressures, measurements, adjustments, illustrations, and other items can change at any time. These changes can affect the service given to the product. Obtain the complete and most current information before starting any job. DOOSAN dealers have the most current information available. 1
3
4 Index Specification General Tightening Torque... 5 System Operation General Information... 6 Torque Converter... 7 Power Shift Transmission... 8 Tightening Torque for Transmission... 9 Torque Converter Transmission Pump Power Flow of Transmission Power Flow at Low Speed Reverse...11 Power Flow at High Speed Reverse...12 Power Flow at Low Speed Forward...13 Power Flow at High Speed Forward...14 Transmission Control Valve Cross-Sectional View...15 Hydraulic Schematic...16 Testing, Adjusting & Trouble shooting Trouble shooting Transmission Pressure Test Converter Stall Test Shimming of Transmission Shaft Assembly Inching Pedal Adjustment Transmission Electrical System Troubleshooting Disassembly & Assembly Transmission Control Valve Transmission Index
5
6 Specification General Tightening Torque 5 Specification
7 System Operation General Information Power Flow (1) Drive axle. (2) U-joint. (3) Transmission. (4) Engine. The basic components of the power train are engine (4), Transmission (3), U-Joint (2), Drive axle (1) and the final drives and wheels. Two axle shafts connect the differential to two final drives. The drive wheels are mounted to the final drives. Power from the engine goes through the flywheel into the torque converter. Power then flows through a transmission (3) and U-joint (2) to the yoke of drive axle (1). The transmission has two hydraulically operated clutch packs that are released by spring. The transmission has one speed in forward and one speed in reverse. Power from the yoke of drive axle is sent through a spiral bevel gear set to the differential. The differential sends power out through the axle shafts to the final drives and wheels. CAUTION Damage can be caused to the transmission if the truck is moved with the engine not running. There will be no lubrication to the transmission components. 6 System Operation
8 Torque Converter The torque converter has four main parts; housing (4), impeller (pump) (3), turbine (1) and stator (2). The housing is connected to the engine flywheel through flex plate (6). Impeller (3) and housing (4) are connected and turn with the engine flywheel at engine speed. Turbine (1) turns the transmission input shaft. Stator (2) is installed stationary on stator support (5). Impeller (3), which turns with housing (4) at engine speed, directs the oil toward the outside of the impeller and against the blades, of turbine (1). When the oil hits the turbine blades, it causes turbine (1) and the input shaft to turn. This sends torque to the transmission. Oil returns through the stator vanes to the impeller. The stator anes direct the oil back to the impeller that causes a torque increase. When the speed of turbine (1) is the same as the speed of impeller (3) stator clutch (7) permits the stator to turn freely with engine rotation but it locks (holds), to prevent opposite rotation to engine rotation. The free rotation of the stator helps also to decrease the sudden or fast movement of the oil which can cause aeration (air bubles) in the hydraulic system. Torque Converter (1) Turbine. (2) Stator. (3) Impeller. (4) Housing. (5) Stator support. (6) Flex plate. (7) Stator clutch. When the turbine speed is less than the speed of impller (3), stator (2) holds in place. Torque is multiplied only when the stator is held in place. The torque converter hydraulically connects the engine to the transmission. There is no direct mechanical connection between the engine and the transmission. When the machine works against a load, the torque converter can multiply the torque from the engine and send a higher torque to the transmission. The oil for the operation of the torque converter comes from the transmission oil pump. The oil flows through a small passage in stator support (5) around the shaft of the stator support and into the converter. Outlet oil from the converter flows through the transmission oil cooler and into the lubrication system. 7 System Operation
9 Power Shift Transmission The transmission is a constant mesh power shift transmission and has four clutches that are engaged hydraulically and released by spring force. The direction and speed are changed electrically. Illustration A (1) PLUG. (2) O-RING. (3) SPRING. (4) REG.VALVE. (5) ELBOW. (6) RUBBER HOSE. (7) PLUG. (8) O-RING. (9) SPRING CLIP. (10) DIPSTICK ASS'Y. (11) DIPSTICK TUBE. (12) BOLT.SOCKET. (13) BOLT.SOCKET. (14) BOLT. (15) WASHER. (16) PLUG. (17) O-RING. (18) SPRING. (19) OIL STRAINER. (20) STEEL BALL. (21) SPRING. (22) ADAPTER-FILTER. (23) FILTER-T/C. (24) PLATSTIC PLUG. (25) O-RING. (26) PLATSTIC PLUG. (27) BRACKET. (28) DOWEL PIN. (29) HEX HEAD BOLT. Most components inside the transmission turn when the control is in either of the FORWARD or REVERSE speed. Power Shift Transmission (1) CONVERTER SUB ASS'Y. (2) T/C HOUSING. (3) OIL SEAL. (4) BOLT.HEX. (5) PIN-IDLE GEAR. (6) NEEDLE BEARING. (7) GEAR-PTO. (8) T/WASHER. (9) BOLT,SOC HEAD. (10) PTO FLANGE SUB ASS'Y. (11) GASKET. (12) CHARGING PUMP ASS'Y. (13) INPUT SHAFT. (14) T/M CASE. (15) OIL SEAL. (16) OUTPUT SHAFT ASS'Y. (17) BAFFLE-OIL. (18) MAGNET. (19) BOLT.HEX. (20) S/WASHER. (21) BEARING PLATE ASS'Y. (22) BOLT.HEX. (23) WASHER-HARD. In the power flow diagrams that follow, the components are shown in a position to make it easier to follow the power flow through the transmission. ILLUSTRATION A shows the transmission from the drive axle end with the correct location of the components. 8 System Operation
10 Tightening Torque for Transmission 9 System Operation
11 Torque Converter Transmission Pump (1) Clearance between outside of drive gear and crescent 0.36 to 0.43 mm (0.014 to in) (1) Torque for bolts (plate to torque converter)...45 ± 7 N m (33 ± 5 lb ft) Apply LOCTITE NO. 277 sealant to threads of bolts. (2) Torque for bolts (plate to flywheel)...25 ± 7 N m (18 ± 5 lb ft) (3) End play of turbine hub (new)...0 to 0.99mm (0 to in) Maximum end play of turbine hub (worn) mm (0.065 in) (2) Clearance between inside of driven gear and crescent 0.25 to 0.33 mm (0.010 to in) (4) Torque for bolts (torque converter to PTO gear)...20 ± 3 N m (15 ± 2 lb ft) Apply LOCTITE NO. 277 sealant to threads of bolts. NOTE : For Torque values not given, see the page of specifications for general tightening torques. (3) Gear end play to mm ( to in) 10 System Operation
12 Power Flow of Transmission Power Flow at Low Speed Reverse Power Flow in Low Speed Reverse. (1) Input shaft. (2) Cylinder clutch(reverse). (3) Cylinder clutch (Forward). (4) Counter shaft. (5) Gear(Reverse low). (6) Clutch(Reverse low). (7) Piston. (8) Clutch(Reverse high). (9) Gear(Reverse high). (10) Output shaft. (11) Output gear(low). (12) Output gear(high). (13) Gear(Forward high). (14) Gear(Forward low). (15) Clutch(Forward low). (16) Clutch(Forward high). (17) Valve ass y Input shaft (1) of the transmission is turned by the turbine of the torque converter. The clutch cylinder (2) for the reverse clutches is connected to the input shaft by rivets. When REVERSE low clutch (6) is engaged, gear (5) is turned through the clutch. Gear (5) is engaged with gear (11) and turns gear (11) [gear (11) is connected to output shaft (10) by splines]. Output shaft (10) sends the power to the drive axle. 11 System Operation
13 Power Flow at High Speed Reverse Power Flow in High Speed Reverse (1) Input shaft. (2) Cylinder clutch (reverse). (3) Cylinder clutch (Forward). (4) Counter shaft. (5) Gear (Reverse low). (6) Clutch (Reverse low). (7) Piston. (8) Clutch (Reverse high). (9) Gear (Reverse high). (10) Output shaft. (11) Output gear (low). (12) Output gear (high). (13) Gear (Forward high). (14) Gear (Forward low). (15) Clutch (Forward low). (16) Clutch (Forward high). (17) Valve ass'y. Input shaft (1) of the transmission is turned by the turbine of the torque converter. The clutch cylinder (2) for the reverse clutches is connected to the input shaft by rivets. When REVERSE high clutch (8) is engaged, gear (9) is turned through the clutch. Gear (9) is engaged with gear (12) and turns gear (12). [gear (12) is connected to output shaft (10) by splines]. Output shaft (10) sends the power to the drive axle. 12 System Operation
14 Power Flow at Low Speed Forward Power Flow in Low Speed Forward (1) Input shaft. (2) Cylinder clutch(reverse). (3) Cylinder clutch (Forward). (4) Counter shaft. (5) Gear(Reverse low). (6) Clutch(Reverse low). (7) Piston. (8) Clutch(Reverse high). (9) Gear(Reverse high). (10) Output shaft. (11) Output gear(low). (12) Output gear(high). (13) Gear(Forward high). (14) Gear(Forward low). (15) Clutch(Forward low). (16) Clutch(Forward high). (17) Valve ass'y. Input shaft (1) of the transmission is turned by the turbine of the torque converter. The clutch cylinder (2) for the reverse clutches is connected to the input shaft by rivets. Clutch cylinder (2) is engaged with and turns clutch cylinder (3). When FORWARD low clutch (15) is engaged, gear (14) is turned through the clutch. Gear (14) is engaged with gear (11) and turns gear (11). [gear (11) is connected to output shaft (10) by splines]. Output shaft (10) sends the power to the drive axle. 13 System Operation
15 Power Flow at High Speed Forward Power Flow in High Speed Forward (1) Input shaft. (2) Cylinder clutch (reverse). (3) Cylinder clutch (Forward). (4) Counter shaft. (5) Gear (Reverse low). (6) Clutch (Reverse low). (7) Piston. (8) Clutch (Reverse high). (9) Gear (Reverse high). (10) Output shaft. (11) Output gear (low). (12) Output gear (high). (13) Gear (Forward high). (14) Gear (Forward low). (15) Clutch (Forward low). (16) Clutch (Forward high). (17) Valve ass'y. Input shaft (1) of the transmission is turned by the turbine of the torque converter. The clutch cylinder (2) for the reverse clutches is connected to the input shaft by rivets. Clutch cylinder (2) is engaged with and turns clutch cylinder (3). When FORWARD high clutch (16) is engaged, gear (13) is turned through the clutch. Gear (13) is engaged with gear (12) and turns gear (12). [gear (12) is connected to output shaft (10) by splines]. Output shaft (10) sends the power to the drive axle. 14 System Operation
16 Transmission Control Valve Cross-Sectional View (1) BODY. (2) SPOOL. (3) SPRING. (4) PLUG. (5) O-RING. (6) ORIFICE. (7) STOPPER. (8) O-RING. (9) SPRING. (10) PISTON. (11) PLUG. (12) FILTER ASS'Y. (13) O-RING. (14) SPOOL. (15) SPRING. (16) SPRING. (17) PLUNGER. (18) PIN. (19) STOP BOLT. (20) OIL SEAL. (21) PLUG. (22) O-RING. (23) PLUG. (24) O-RING. (25) SOLENOIDE VALVE ASS'Y. (26) PLUG. (27) O-RING. (28) BS CONNECTOR ASS'Y. (29) GASKET. (30) O-RING. (31) SPRING. (32) PLATE. (33) PISTON. (34) GASKET 15 System Operation
17 Hydraulic Schematic (1) RELIEF VALVE. (2) INCHING VALVE. (3) ACCUMULATOR VALVE. (4) SOLENOID VALVE. (1) RELIEF VALVE FUNCTION The function of relief valve is to keep the pressure of control valve properly within the limited value and, pass the oil to torque converter. OPERATION The oil from the pump flows to relief valve through A. As the oil pressure increases, the oil from A pushes the spool left side against the spring force. Then, the oil flows to torque converter through B. As the oil pressure decreases, the spool returns. This process takes place repeatedly so that the pressure in the control valve keeps the required pressure although the oil flows to the control valve. If the pressure reaches the set pressure, the oil drains through C. 16 System Operation
18 (2) INCHING VALVE FUNCTION The function of inching valve lets the operator control the oil pressure to the directional selector valve, which permits a gradual engagement of the clutches. Through the use of the inching valve, the lift truck can move slowly while the engine is at higher speeds. This lets the operator move the lift truck slowly up to a load while the mast is raised rapidly. installed prior to piston. So, this filter needs to be cleaned at the maintenance interval of transmission oil. (4) SOLENIOD VALVE FUNCTION Solenoid valve functions to open the circuit for providing the oil to the selected clutch. OPERATION When the operator does not use the inching pedal, the oil through A flows to the accumulator valve through D. When the operator pushes the inching pedal part of the way down, the plunger (17) shifts left so as to block A line. Then, the oil from A is shut down and, the oil in accumulator returns to E through D. By this operation, the pressure in clutch is decreased. As a result of the slippage of the discs and plates of the engaged clutch, the truck will have operator controlled movement (inching). The amount of decreasing oil pressure depends on the position of inching plunger. As the plunger is pulled out completely, the clutch pressure drops to zero which completely stops the lift truck after some time. (3) ACCUMULATOR VALVE FUNCTION The function of accumulator valve is to make the engagement smooth by increasing the pressure-up time just after the clutch starts to slip. OPERATION When releasing the inching pedal, the oil from inching valve passes into the accumulator valve through orifice F. Then, the piston shifts right. As the pressure in accumulator valve increases, the second orifice G opens. To protect the solenoid valves from the contaminants, a screen filter is 17 OPERATION When engaing F/R-S/W, the spool inside solenoid valve moves to the oil direction by the electric force. Then, the oil from the accumulator comes through H and flows to the clutch through I. When F/R-S/W is in neutral, the spools returns by spring force so that the oil drains to J. System Operation
19 Testing, Adjusting & Trouble shooting Trouble shooting Troubleshooting can be difficult. A list of possible problems and corrections is on the pages that follow. Use this as a reference for the location and correction of problems in the transmission. When more testing and adjusting is necessary. Use the procedures that are given in Transmission Pressure Tests, Inching Pedal Adjustments and Converter Stall Tests, Always make visual checks first, operation checks second and then make checks on the transmission with instruments. WARNING When testing and adjusting the power train, move the machine to an area clear of obstructions, and with safe ventilation for the exhaust. To prevent personal injury when drive wheels are off the ground for testing, keep away from wheels that are in rotation. Operate the machine in each direction. Make note of all noises that are not normal and find their source. If the operation is not correct, make reference to the troubleshooting chart for problems and probable causes Visual Check 1. Check the oil level in the transmission with the engine running and with the transmission in NEUTRAL. 2. Check all oil lines, hoses and connections for leaks and damage. Look for oil on the ground under the machine. 3. Move and turn the lever for the speed control and the direction control to all REVERSE and FORWARD positions. The detents must be felt in each position. 4. Check the strainer behind the transmission oil plug and the filter foreign material. a. Particles of friction paper material give an indication of a clutch failure. 18 b. Metallic (metal) particles in the filter give an indication of wear or mechanical failure in the transmission. c. Rubber particles give an indication of seal or hose failure. d. Aluminum particles give an indication of a torque converter or control valve failure. If metal or rubber particles are found, all components of the transmission hydraulic system must be flushed. Make a replacement of all parts that show damage. Checks During Operation NOTICE Before these checks are started, fill the transmission with oil to the correct level. Improper oil level can cause damage to the transmission components. With the engine running and brakes on, move the selector lever for transmission speeds to all positions. The detents must be felt in each position. Operate the machine in each direction and in all speeds. Make note of all noises that are not normal and find their sources. If the operation is not correct, make reference to the CHECK LIST DURING OPERATION for problems and probable causes. Check List during Operation Problem : Transmission does not operate in any speed or does not engage(slips) in all speeds. 1. Low oil pressure or no oil pressure caused by : a. Low oil, no oil, or thick oil. b. Inching control valve linkage loose, broken or adjustment is not correct. c. Inching valve spool stuck (held) open. d. Failure of the oil pump or a defect in the oil pump e. Converter drive tangs worn off or not engaged into pump. f. Main regulator valve stuck open. g. Restriction in the oil flow circuit such as dirty oil screen. Testing, Adjusting & Troubleshooting
20 h. Leakage inside the transmission. - Damaged control valve gasket. - Worn or broken metal seal rings on clutch shaft. - Worn or broken seals around clutch piston. i. Control valve gasket is worn that causes leakage. 2. Cooler external lines are not connected correctly. 3. Mechanical failure in the transmission. Problem : Transmission does not shift. 1. Low oil pressure. 2. Main regulator valve will not move (stuck). 3. Solenoids or related electric components are out of order. Problem : Transmission gets hot. 1. Restriction in cooling circuit. 2. Oil level too high or too low. 3. Low pump pressure -worn or damaged pump. 4. Converter one way clutch worn and slipping. 5. Air mixed in the oil. Air leaks on the intake side of the pump. 6. Low oil flow through converter. 7. Wrong application for vehicle, (loads are too heavy for the lift truck). 8. Too much inching operation (slipping the clutch plates and discs). 9. Too much stalling of torque converter. 10. Cooler bypass valve stuck (held) open, full oil flow does not go through oil cooler. Problem : Clutch engagement is slow or loss of power during engagement. 1. Low oil pressure. 2. Low converter pressure. 3. Air mixed in the oil. a. Air leaks on suction side of pump. b. Low oil level also causes aeration. 4. Inching valve linkage adjustment is not correct. Problem : Transmission operates in forward speeds only. 1. Discs and plates have too much wear in reverse direction clutches. 2. Leakage at the seals. 3. Reverse clutch components have damage. a. Leakage caused by worn or broken metal sealing rings. b. Leakage caused by worn or broken seal around clutch piston. c. Failure of other components. 4. Solenoids or related electric components are out of order. Problem : Transmission operates in reverse speeds only 1. Discs and plates have too much wear in forward direction clutches. 2. Leakage at the seals. 3. Forward clutch components have damage. a. Leakage caused by worn or broken seal around metal sealing rings. b. Leakage caused by worn or broken seal around clutch piston. 19 Testing, Adjusting & Troubleshooting
21 c. Failure of other components. 4. Solenoids or related electric components are out of order. Problem : Low stall speed. 1. Engine performance is not correct. 2. The one-way clutch of the torque converter does not hold. Problem : High stall speed in all transmission speeds and directions. 1. Low oil level. 2. Air in the oil. 3. Clutches slip(clutch plates slide in relation to one another). 4. Torque converter failure. Problem : High stall speed in one speed or one direction. 1. There is a leak in that clutch circuit. 2. There is a failure of the clutch in that speed or direction. Problem : Clutch engagement is slow and makes rough shifts. 1. Inching valve adjustment is not correct. 2. Inching valve is not completely closed or orifice has dirt(plugged). 3. Low main pressure. 4. Low directional clutch pressure. 5. Internal oil leaks. 6. Valve spool springs are weak or have damage. Problem : Vehicle operates in one direction and creeps in that direction in NEUTRAL. Engine stalls when shifted to the other direction. 1. Failure of clutch in the direction the lift truck moves. Clutch discs or plates are warped (damaged) or held together because of too much heat. 2. Failure of the valve spool in the direction the lift truck moves. The spool stuck (held) in the engaged position possibly caused by metal burrs (particles) or dirt. Check List from Operation Noise Problem : Noise in NEUTRAL only. 1. Worn bushing in pump assembly. 2. Worn one-way clutch in torque converter. 3. Oil level low. 4. Converter housing or converter tangs not in alignment with engine or transmission pump. Problem : Pump noise not normal. 1. A loud sound at short time periods gives an indication that foreign material is in the transmission hydraulic system. 2. A constant loud noise is an indication of pump failure. Problem : Noise in the transmission that is not normal. 1. Converter housing or converter tangs not in alignment with engine or transmission pump. 2. Transmission components have wear or damage. a. Damaged gears. b. Worn teeth or clutch plates and/or clutch discs. 20 c. Slipping clutch plates and discs noise. Testing, Adjusting & Troubleshooting
22 d. Failure of the thrust washers. e. Other component parts have wear or damage. Problem : Noise in the control valve. 1. Air in the hydraulic system. a. Air leakage on suction side of the pump. b. Low oil level that causes aeration. 2. Restrictions in oil passage. 3. Valve spools movement has restriction. Check List from Pressure Test Problem : Low pressure to FORWARD and REVERSE clutches. 1. Inching valve linkage adjustment is not correct. 2. Inching valve spool held (stuck) open. 3. Clutch piston seals cause leakages. 4. A defective regulator valve spring. 5. Low oil pressure, see Probable Cause for Low Oil Pressure. 6. Cooler external lines are not connected correctly. Problem : Clutch pressure and main pressure are high. 1. Pressure regulator valve is not free to move (stuck). 2. A restriction in the hydraulic circuit. 2. Seal rings on shaft or clutch piston seals are broken or worn. 3. Control valve surface not flat or gasket has damage. Problem : Low main line pressure. 1. Low oil level. 2. Main regulator valve movement is restricted. 3. Transmission pump is worn. 4. Inner oil leakage. 5. Low oil pressure. Problem : Low lubrication pressure or no lubrication pressure 1. Low oil pressure or no oil pressure caused by : a. Failure of the oil pump or a defect in the oil pump b. Restriction in the oil flow circuit such as a dirt, oil screen. c. Converter drive tangs worn off or not engaged in pump. d. Main regulator valve spool stuck closed. e. Leakage inside of the transmission caused by component defect. 2. Oil cooler has restriction to oil flow. Problem : Low converter pressure. 1. Main regulator valve movement is restricted. Problem : Pressure to one clutch is low. 1. Clutch piston seal alignment is not correct, oil leaks through. 21 Testing, Adjusting & Troubleshooting
23 Problem : Converter outlet pressure or cooler inlet pressure is low. 1. Low oil pressure. 2. Cooler bypass valve stuck open. Problem : Converter outlet pressure or cooler inlet pressure too high. 1. Restriction in oil cooler lines or a plugged oil cooler. Transmission Pressure Test Raise the front of the lift truck off of the floor. Put wood blocks or jack stands of the correct capacity under it to hold it in this position while pressure tests are performed. WARNING When the transmission is tested, move the truck to a clear area that is level. Keep all other personnel away from the lift truck. Make sure the drive wheels do not touch the floor. To prevent personal injury, keep feet and hands away from the turning drive wheels. When the transmission tests are made, the transmission oil must be at the correct level. The pressures given in the chart are taken with transmission oil at the normal temperature for operation, 82 ± 6 C (180 ± 10 F). If the temperature is lower than 77 C (170 F), the pressure will be higher than that shown. If the temperature is higher than 88 C (190 F), the pressure will be lower than that shown. A problem in the hydraulic circuit to the clutches can normally be found when the main line pressure is checked. If more information is necessary, gauges can be installed at each pressure tap. WARNING Before any pressure tap plugs or connections are removed, the engine must be stopped with the transmission controls in neutral. This will release hydraulic pressure in the transmission. Check the transmission pressure at the pressure taps shown. Check main line pressure in both transmission speeds and both directions. If the pressure in one speed or one direction drops 70 to 140 kpa (10 to 20 psi), there is a leak in that clutch circuit. EXAMPLE : If the pressure drops when in low speed forward, the low speed forward clutch circuit has a leak. Also check clutches in both directions and speeds. Check the converter inlet and lubrication pressures with the transmission in neutral. Leaks in the clutch circuit can be caused by : seal rings on shaft or clutch piston are broken or worn, control valve plate or transmission face not flat. 22 Testing, Adjusting & Troubleshooting
24 Transmission Pressure Taps (1) Reverse high clutch pressure tap. (2) Reverse low clutch pressure tap. (3) Forward low clutch pressure tap. (4) Forward high clutch pressure tap. (6) Main line pressure tap. (7) Converter pressure tap. Transmission Pressure Engine RPM Unit Main Line (Neutral) Converter (Neutal) Forwaed Low Clutch Forwaed High Clutch Reverse Low Clutch Reverse Low Clutch MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX MIN MAX ldle psi ,300 psi ,500 psi ldle Kpa 426 1, ,300 KPa 709 1, , , , , ,175 2,500 KPa 709 1, , , , , , Testing, Adjusting & Troubleshooting
25 Converter Stall Test The converter stall test is a test to check engine power. It can also be used to locate a problem in the transmission when the condition of the engine is known. An engine which does not have correct performance will give an indication of a stall speed that is not correct. If the engine performance is correct, and the stall speed is not correct, the problem in the converter or transmission can be found with this test. The test checks the maximum RPM that the engine, at full throttle, can turn the converter with the turbine held stationary. To hold the converter turbine, engage the brakes with the transmission in either FORWARD or REVERSE and in HIGH speed. The drive wheels must not turn during the stall test. Put a heavy load on the forks and put the truck in position against a solid object that will not move (such as a loading dock). Engage the parking brake. When the tests are made, the wheel brakes must be engaged with the left foot ; the accelerator pedal can be operated with the right foot. Make sure that the transmission oil is at the correct temperature for operation before tests are made. Check the high idle setting before the stall test is made. The high idle on the LP and diesel engines is shown in the chart below. Engine High Idle Setting High Idle RPM DB58S Diesel 2,370±50 G643(E) 2,500±50 WARNING Make tests in a clear, level area only, There must be one operator. Keep all other personnel away from the lift truck. Check to be sure the operation of the brakes is correct before the tests are made. 1. Connect a tachometer to the engine. Start the engine and move the control levers to the FORWARD direction and HIGH speed. 2. Engage the wheel brakes and push the accelerator pedal down completely. Read the RPM on the tachometer, then release the accelerator pedal. Turn the speed control lever to LOW. Push the accelerator pedal down completely and read the RPM again. Release the accelerator pedal. NOTICE To make sure that the transmission oil does not get hot, do not hold the transmission in a stall condition for more than ten seconds. After the transmission is stalled, put the controls in NEUTRAL and run the engine at 1200 to 1500 RPM to cool the oil. 3. Repeat the procedure above for both REVERSE speeds. 4. The stall speeds for the different trucks are in the chart below. Engine Stall Speed RPM±75 without power Brakes Applied RPM±75 With power Brakes Applied DB58S Diesel 1,600 1,550 G643(E) 1,500 1,450 Stall speeds that are low are an indication that the engine performance is not correct or the one-way clutch of the torque converter does not hold in reverse direction. If the one-way clutch has a defect, the stall speed will probably be more than 800 RPM low. The stall speed must be the same in all forward and reverse speeds, If the stall speed is high in all forward and reverse speeds, one or more of the problems that follow can be present ; low oil level, air in the oil, a torque converter failure, or low oil pressure to all clutches. If the stall speed is high in both speeds in one direction, check the clutch operation for that direction. If the stall speed is high in one speed only, both forward and reverse, check the clutch operation for that speed. 24 Testing, Adjusting & Troubleshooting
26 Shimming of Transmission Shaft Assembly 1. Assemble shaft assembly (including taper bearing cone and cup). 2. Insert shaft assembly into transmission case. 9. If you reshim input shaft or counter shaft, turn transmission input shaft by hand. It should be turned smoothly. If you reshim output shaft, turn output shaft by hand. It should be turned smoothly. 10. If the input shaft or output shaft does not turn smoothly, remove shims about 0.1mm. 3. Measure the dimension X from the surface of transmission case to surface of bearing cup. NOTE : Use depth gage and block gage because the height of bearing cup is higher than surface of transmission case. 4. Measure the dimension Y from the surface of transmission cover to bottom of bore where bearing cup is installed. 5. Calculate required shim thickness as following formula. Required shim thickness Z = Y - X - (0.04~0.11) mm 6. Select shims to have 0.04 to 0.11mm (0.001 to in) of end-play. 7. Assemble transmission case and cover. 8. Set up transmission assembly vertically. 25 Testing, Adjusting & Troubleshooting
27 Inching Pedal Adjustment To check the inching valve adjustment and operation, do the procedure that follows : WARNING When this procedure is used, the lift truck must be in an area clear of obstructions. There must be one operator with all other personnel away from the lift truck. Check the operation of the brakes before the test is made. 1. With the engine at idle speed, put the transmission in FORWARD. WARNING To prevent personal injury, when the inching pedal is adjusted, move the truck to a clear area that is level. Keep all other personnel away from the lift truck. Use lifting equipment or a safe method to lift the front of the lift truck until the drive wheels are off the floor. Put wood blocks or jack stands of the correct capacity under it to hold it in this position while the inching pedal is adjusted. 2. Raise the front of the lift truck off the floor. Put wood blocks or jack stands of the correct capacity under it while the inching pedal is adjusted Inching Operation Test (1) Inching pedal. 2. Slowly push down on inching pedal (1) until the movement of the brake pedal causes the brake discs to make contact (small drag) with the brake plates. 3. Increase the engine speed to high idle. The truck must not move. If the operation of the inching valve is not correct, do the procedure that follows. 1. Adjust and bleed the wheel brakes as shown in the Vehicle Systems module. Inching Pedal Adjustment (1) Lug. (2) Bolt. (3) Nut. 3. Start the engine and put the transmission FORWARD. 4. With the drive wheels turning, depress inching pedal until the drive wheels stop. 5. Now depress the brake pedal until disc contact is felt. 6. Loosen nut (3) and adjust bolt (2) to contact lug (1) that rotates the brake control cross shaft. Tighten nut (3). 7. Check the inching valve operation again. a. If something is wrong, inspect all points again one by one very carefully. 26 Testing, Adjusting & Troubleshooting
28 The adjusting procedure is as follows. Be sure that the air bleeding of brake system should be done in advance. < OCDB > mm (A) 2. Adjust the length (B) of rod by fixing the nuts at both ends. (B) should be 212 ± 1 mm. < Shoe Brake > 1. Adjust the length (A) from the spool to the connection point of yoke. Be sure that 1mm of gap between the piston and the rod should exist. In case of no gap, it would result in brake drag or overheating of axle oil. In case of too loose, the performance of service brake become lowered. 3. Adjust the height (C) of inching pedal and brake pedal. (C) should be 110mm at the same level. 4. Adjust the gap (D) for engaging brake pedal by inching pedal. (D) is about 9.5 mm. 27 Testing, Adjusting & Troubleshooting
29 82.5 mm (E) 5. The distance (E) between the shaft center and its mounting bracket should be about 82.5 mm. 6. The stroke of inching spool should be 5 ± 1 mm. 7. Before doing the truck test, inspect again all relevant dimensions. 8. Inspect the service brake and then, inching operation. 28 Testing, Adjusting & Troubleshooting
30 Transmission Electrical System Troubleshooting Transmission Control Schematic (1) Connector A. Neutral Start Function D(G)35/40/45S-5 Forward 1 Pin 1 (VE) D(G)40/45/50SC-5 Reverse 2 Pin 7 (WH/BR) 2nd Speed (Forward 2/Reverse 2) Back-Up Signal Conn A Pin 5(WHBK) and Pin 6(WH/BU) Pin 2(BR) Pin 7(WH/BR) and Pin 8(LGN) If the connections are not made properly, they can cause either continuous or intermittent problems. Make sure all connectors in a problem circuit are fastened correctly before tests are performed. The chart gives the pin numbers across which a continuity measurement should be taken when the gear selector is in the gear shown. 29 Testing, Adjusting & Troubleshooting
31 Solenoid Voltage Check (1) Forward 1 solenoid. (2) Forward 2 solenoid (3) Reverse 1 solenoid. (4) Reverse 2 solenoid. Wiring Harness From Transmission Selector Lever Connector A. Reverse 1 : System voltage between reverse 1 solenoid (BU wire) and battery negative. Reverse 2 : System voltage between reverse 2 solenoid (BU/YL wire) and battery negative. Forward 1 : System voltage between forward 1 solenoid (RD wire) and battery negative. Forward 1 : System voltage between forward 1 solenoid (RD/YL wire) and battery negative. 30 Testing, Adjusting & Troubleshooting
32 Additional Checks System Voltage Check If the transmission will not operate, one of the first checks that should be performed is a check of the system voltage. The control solenoids require a minimum of 18 volts to energize for diesel trucks (9 volts for gasoline trucks). If the system voltage is below this, the solenoids will not energize and the transmission will not engage. Neutral Start This check is to be performed on the nine pin connector coming from the shift control. With the shift control lever in NEUTRAL, there must be continuity between pin 5 and pin 6. This indicates the ability to start the vehicle. If there is no continuity, the vehicle will not start and the shift control must be replaced. Back-Up Alarm This check is to be performed on the nine pin connector coming from the shaft control. With the shift control lever in REVERSE, there must be continuity between pin 7 and pin 8. This activates the back-up alarm. If there is no continuity, the backup alarm will not work and the shift control must be replaced. Solenoid Test This test will determine if the solenoid coil is energizing and the plunger is shifting to permit oil flow. Hearing a solenoid click or checking to see if the coil is energized by checking magnetically with a screw driver. If the screwdriver indicates that the coil is energized, the problem is in the solenoid. The problem could be a bent stem, dirty or clogged screen. If the screwdrive does not indicate that the coil is energized, the problem is in the electrical circuit. Possible problems include a bad solenoid coil, a bad connection in a connector, a broken wire or a faulty shift control group. Measure the resistance value of solenoids with multimeter. SPEC : 40 ± 0.1 (25ºC) for diesel trucks. SPEC : 9.7 ± 0.1 (25ºC) for gasoline trucks. Input Voltage To Shift Control This check to be performed on the eight pin connector coming from the vehicle harness. Input voltage to the shift control can be checked on the vehicle side of the eight pin connector between pin 4 or pin 5 or pin 8 and battery negative. The voltage measured should be equal to the vehicle system voltage. 31 Testing, Adjusting & Troubleshooting
33 Disassembly & Assembly Transmission Control Valve Disassembly of Control Valve 3. Disassemble Accumulator Valve - Disassemble PLUG (11) with filter, O-rings (13) (30), and SPRING (9) from the main body. - Disassemble STOPPER (7) and O-RING (8) from the main body. 1. Disassemble Solenoid Valve - Unscrew NUT (C), remove COIL (B), disassemble SOLENOID VALVE body (A). 4. Disassemble RELIEF VALVE - Disassemble ORIFICE (6), PLUG (4), SPRING (3), O-RING (5) and SPOOL (2) in the said order. 2. Disassemble INCHING VALVE - Disassemble PLUG (21) and O-RING (5) (22) from the main body - Unscrew STOP BOLT (19), remove PIN (18). - Disassemble SPOOL (14), SPRING (31) (15) (16), and PLUNGER (17) from the main body Disassemble BODY SUB - Remove PLUG (26), O-RING (27), PLUG (23), and O-RING (24) from the main body. Disassembly & Assembly
34 Assembly of Control Valve 1. Preparation for Assembling - Refer to the valve disassembling/assembling procedure in advance. - Arrange the work area. - Prepare assembling tools. - Prepare necessary parts according to the number of valves to be assembled. - Wash the parts, put in separate boxes and mark names and part numbers. WARNING When handling the parts, take care not to be injured by sharp edges of body and spool. Fix the main body when assembling the parts. Otherwise, your hands may hurt). Take care that wash fluid does not enter eyes when washing the parts. Keep the working area clean to prevent foreign matter. Seals have to be applied with grease or oil to prevent damage. 3. Assemble RELIEF VALVE - Assemble SPOOL (2) and SPRING (3) in the said order - Assemble O-RING (5) with PLUG (4), and assemble them with the main body (torque : 50 N m) - Apply Loctite #603 to ORIFICE (6), and assemble with the main body (check looseness. Conduct caulking when necessary) 4. Assemble ACCUMULATOR VALVE - Apply Loctite #609 to FILTER (12), and assemble it with PLUG (11). 2. Assemble BODY SUB - Assemble PLUG (23) with O-RING (24), and assemble them with the main body (3 points; torque : 27 N m) - Assemble PLUG (26) with O-RING (27), and assemble them with the 5 pressure detecting points on the main body (torque: 10 N m) - Assemble STOPPER (7) with O-RING (8), and assemble them with the main body (torque: 68 N m) - Assemble SPRING (9) and PISTON (11) with the main body. - Assemble PLUG (11) fitted with filter with O- RING (13) and O-RING (31), and assemble them with the main body. (torque : 100 N m) 33 Disassembly & Assembly
35 5. Assemble INCHING VALVE - Assemble BODY with SPOOL (14), SPRING (31), SPRING (15), and SPRING (16) in the said order. Insert PLUNGER and push it down, insert PIN (18) and tighten with STOP BOLT (19). (STOP BOLT must not project from the bottom surface). - Assemble PLUG (21) with O-RING (5) and O- RING (23), tighten with the main body (torque : 50 N m) 6. Assemble SOLENOID VALVE - Assemble BODY with SOLENOID VALVE body (A) (at 4 points) (torque : 27 N m) - Insert COIL (B) to the SOLENOID VALVE body(a), which is assembled with the main body, tighten with NUT (C) (torque : 6.8 N m) CAUTION The voltage marking on the COIL has to face outwards. Check the voltage. 34 Disassembly & Assembly
36 Transmission Disassembly of Transmission 4. Isolate plug (20), O-ring, spring (21) and ball (22) from cover. 1. Isolate torque converter from housing. Remove 6 bolts (3) from the torque converter, isolate plate (2) and flexible plate (1). 5. Disassemble plug (18), O-ring, spring (17) and spool (16). 6. Disassemble plug (15). 2. From the torque converter (4), unscrew 6 socket bolts (6), disassemble Gear P.T.O Input (5). WARNING The bearing cup and shim (64) are in the cover or transmission case. Mark their correct positions on the cover or case. 3. From the housing (7), disassemble oil seal (10), 4 bolts (8), 4 bolts (9) and washer. 35 Disassembly & Assembly
37 7. Unscrew the 5 bolts (11) from the Stator Hub (12) fixed on the Bearing Plate (14), and isolate them from the plate. Use rubber hammer to protect Stator Hub from damage. 10. Disassemble 2 bolts (35), 9 bolts (36), and valve gasket (34). 8. Isolate 4 socket bolts (26) from the bearing plate (14), disassemble flange pump (25). 11. Unscrew 8 bolts (37) and 5 socket bolts (38) from transmission. Isolate valve plate (69) slowly. Isolate socket bolt (28) and 4 socket bolts (30) from the flange pump. Isolate charging pump (29) and gasket (27). Disassemble Gear-P.T.O Output (23) and ball bearing, and isolate elbow (24). 12. Isolate plug (41) and O-ring. Disassemble spring (39) and oil screen (40) from the case. 9. From the bearing plate (14), isolate 2 thrust washers (31), needle bearing (32), and Gear- P.T.O Idle (33). 36 Disassembly & Assembly
38 13. Use plastic hammer when pushing-out the tube (45) from transmission case. 14. Disassemble output shaft assembly (43), input shaft assembly (44), and counter shaft assembly (42). 17. Disassemble 2 thrust washers (48) and gear(49). 18. Disassemble needle bearing and washer from front axle of the high speed clutch face. 15. Disassemble Output Gear (46) from the transmission case 19. Using a screw driver, disassemble snap ring (50) from cylinder. 16. Disassemble the bearing cone (47) for high speed, in front of the clutch assemble, using gear puller. 20. Disassemble pressure plate, 7 clutch discs (51), 8 clutch plates, and band plate (67) from the cylinder. 37 Disassembly & Assembly
39 21. Push down the retainer (53) with pressure. Isolate snap ring (52) with a screw driver. Remove the tension force on the assembly slowly. 22. Disassemble retainer (53) and spring assembly from cylinder. 23. Disassemble piston (54) using compressed air. Disassemble O-ring from shaft. 26. Disassemble 2 thrust washers (59) and pin (57) 27. Push retainer (53) down with press and remove snap ring (52). Slowly release the tension force of spring assemble, and remove retainer and spring. 28. Using compressed air, isolate piston (54), and remove O-ring from the axle. CAUTION The disassembling procedure of the input shaft assembly is the same as that of the counter shaft assembly. 24. Isolate sealing from the low speed forward clutch assembly. Remove bearing (56), thrust washer (57), gear (58), needle bearing, and spacer. 29. Disassemble input power shaft assembly 30. Remove bearing (60) and gear (61) from the output shaft assembly. 25. Remove snap ring (50), then remove compression plate, 7 clutch discs, 8 clutch plates, and band plate from the cylinder. 38 Disassembly & Assembly
40 31. Disassemble bearing (62) from the transmission case. 3. Assemble bearing cup (62) at its correct position. CAUTION Mark the bearing for identification. 4. Assemble gear (61) and bearing (60) on the output shaft. 32. Remove 2 lip-shaped oil seals (63) from the transmission. Assembly of Transmission 5. Assemble seal ring with the piston (54). Apply transmission oil on the seal ring, 6. In the cylinder, assemble piston with seal ring. CAUTION Take care not to damage seal ring when assembling the piston. 1. Wash all the parts clean. Apply transmission oil on all the parts. 2. The lip part of the seals both inside and outside of the transmission case - have to face inwards. 39 Disassembly & Assembly
41 - Then, assemble the clutch disc having toothed surface on the inner diameter. - Repeat above procedures (1) and (2) to complete the assembling of the clutch discs and plates. - Assemble the bending plate (67) with the bended part facing downwards. 12. Install the pressure plate at its place in the cylinder. 7. Install spring assembly and retainer (53) in the cylinder. 8. Place the shaft assembly on press. Press down the retainer, and assemble snap ring (52) using a screw driver. 9. Assemble pin (57) and 2 thrust washers (59) in the counter shaft of the low speed clutch. 13. Assemble the pressure plate at its place in the cylinder, mount the snap ring (50) using a screw driver. 14. Assemble 3 seal rings on the shaft. CAUTION Take care not to damage the seal ring in the counter shaft. 10. Assemble needle bearing, spacer, needle bearing, gear (58), thrust washer (59) and bearing (56). 15. Refer clauses 5 through 8 for the opposite side of the shaft assembly. 11. Apply clean transmission oil on the clutch discs and plates. Assemble the 7 discs and 8 plates in following order. - First, install the clutch plate having toothed surface on its outer diameter. 16. Apply clean transmission oil on the clutch plates and discs. Assemble clutch disc plates in following procedures. - First, assemble the plate having teeth on outer diameter. - Next, assemble the clutch disc having teeth on inner diameter. - Repeat procedures (1) and (2) until all the discs and plates are assembled. - Assemble the bending plate (67) with its bended part downward. 40 Disassembly & Assembly
42 17. Install the pressure plate in the cylinder. 18. Assemble the snap ring (50) which sets the pressure plate in the cylinder, using a screw driver. 19. Assemble thrust washer and needle bearing on the counter shaft of the high speed clutch. 21. Assembling procedures of input shaft assembly are same as those of the counter shaft assembly. 22. Assemble the gear assembly (46) in the transmission. 20. Assemble gear (46), thrust washer (45). Adjust bearing cone (44) using assembling jig. CAUTION Do not exert excessive force when assembling gears. Move the gear forward/backward in to the clutch assembly, until the gear spline aligns with the teeth of the disc. 23. Place the transmission case at correct position, install counter shaft assembly (42) carefully. 24. Install input shaft (44) at correct position on the transmission case, carefully. Install output shaft assembly (43) in the output shaft gear assembly (46), and turn the gear until their teeth aligns with the gears of other shaft assembly. 25. Install tube (45) on the transmission case with plastic hammer. 26. Assemble strainer (40), spring (39) and plug (41) in the transmission case. 41 Disassembly & Assembly
43 27. Assemble oil screen (40), spring (39), plug (41) and O-ring in the transmission case. 30. For the bearing plate (14), assemble thrust 2 washers (31), needle bearing (32), and Gear- P.T.O Idle (33). 28. Apply Loctite #5172 on the gasket surface of the case, and fix it. Assemble the valve plate (69) with 11 bolts (37) and 5 socket bolts (38) 31. Assemble flange pump (25) with Gear-P.T.O Output (23) and 2 ball bearings using jigs. Assemble 4 bolts (26) with the bearing plate. Assemble flange pump (25) with charging pump (29) and gasket (27) with bolt (28) and 4 bolts (30). Assemble elbow (24). 29. Place gasket (34), assemble 2 bolts (36) and 9 bolts (35) with the control valve. 32. Assemble Stator Hub assembly (12), bush (13), piston ring, and 6 bolts (11), and assemble them with the bearing plate (14). 42 Disassembly & Assembly
44 Caution Since depth gauge and block gauge are used, the height of the bearing cup must be higher than the transmission case surface. Measuring method of Shim on Shaft : Transmission cover depth from transmission case to bearing step rise on shaft assembly 33. Assemble plug (15) and O-ring on the transmission cover. 34. Assemble valve (16), spring (17), plug (18) and O-ring in the transmission cover. 35. Assemble the plug (19). 36. In the transmission cover, assemble ball (22), spring (21), plug (20), and O-ring. 37. Mount bearing cup and shim on the transmission cover. CAUTION The bearing cup and shim have to be installed at the original positions on the transmission cover, in order to be aligned with shaft in the transmission case. Name Thickness of Shims Input Shaft Y X 0.01 Counter Shaft Y X 0.05 Output Shaft Y X ) Select the shim of which thickness (0~0.05 mm ) fits with the shaft. 7) Assemble cover on the transmission case. 8) Set the transmission assembly vertically. 9) Check the shim adjustment on the input and counter shafts. The input shaft of the transmission must be able to rotate freely. 10) If the input or output shaft does not rotate freely, remove 0.025~0.05 mm shim. CAUTION Do not tilt the cover while assembling. Otherwise, the seal ring on the input power shaft may be damaged. 38. When using a new part, calculate the shim thickness shown in the table below. 1) Assemble shaft assembly (including taper bearing cone and cup) 39. With the housing (7), assemble oil seal (10), 4 bolts (8), 4 bolts (9) and washer. 2) Install shaft assembly on the transmission case. 43 Disassembly & Assembly
45 40. Mount Gear P.T.O Input (5) on the torque converter (4), assemble with 6 socket bolts (6). 41. On the torque converter, assemble plate (2) and flexible plate (1) with 6 bolts (3). Then, assemble torque converter and housing. 44 Disassembly & Assembly
Troubleshooting the Transmission Hydraulic System
 Testing and Adjusting IT28F INTEGRATED TOOLCARRIER POWER TRAIN Testing And Adjusting Introduction Reference: For Specifications with illustrations, refer to SENR5974, IT28F Integrated Toolcarrier Power
Testing and Adjusting IT28F INTEGRATED TOOLCARRIER POWER TRAIN Testing And Adjusting Introduction Reference: For Specifications with illustrations, refer to SENR5974, IT28F Integrated Toolcarrier Power
Troubleshooting The Transmission Hydraulic System
 416B, 426B, 428B, 436B, & 438B BACKHOE LOADERS TRANSMISSION Testing And Adjusting Troubleshooting The Transmission Hydraulic System Make reference to the following warning and pressure tap locations for
416B, 426B, 428B, 436B, & 438B BACKHOE LOADERS TRANSMISSION Testing And Adjusting Troubleshooting The Transmission Hydraulic System Make reference to the following warning and pressure tap locations for
Disassembly and Assembly
 SENR9973-01 September 2007 Disassembly and Assembly 400C Industrial Engine HB (Engine) HD (Engine) HH (Engine) HL (Engine) HM (Engine) HN (Engine) HP (Engine) HR (Engine) Important Safety Information Most
SENR9973-01 September 2007 Disassembly and Assembly 400C Industrial Engine HB (Engine) HD (Engine) HH (Engine) HL (Engine) HM (Engine) HN (Engine) HP (Engine) HR (Engine) Important Safety Information Most
RELEASING PRESSURE IN THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM,
 Testing And Adjusting Introduction NOTE: For Specifications with illustrations, make reference to SPECIFICATIONS for 225 EXCAVATOR HYDRAULIC SYSTEM, Form No. SENR7734. If the Specifications are not the
Testing And Adjusting Introduction NOTE: For Specifications with illustrations, make reference to SPECIFICATIONS for 225 EXCAVATOR HYDRAULIC SYSTEM, Form No. SENR7734. If the Specifications are not the
Introduction. General Information. Systems Operation
 Systems Operation Introduction Reference: For illustrated Specifications, refer to the Specifications For 416, 426, 428, 436, 438, & Series II Backhoe Loaders Transmission, Form No. SENR3131. If the specifications
Systems Operation Introduction Reference: For illustrated Specifications, refer to the Specifications For 416, 426, 428, 436, 438, & Series II Backhoe Loaders Transmission, Form No. SENR3131. If the specifications
MANUAL TRANSAXLE Return to Main Table of Contents
 MANUAL TRANSAXLE Return to Main Table of Contents GENERAL... 2 MANUAL TRANSAXLE CONTROL... 12 SHIFT LEVER ASSEMBLY... 14 MANUAL TRANSAXLE... 15 MANUAL TRANSAXLE ASSEMBLY... 17 FIFTH SPEED SYNCHRONIZER
MANUAL TRANSAXLE Return to Main Table of Contents GENERAL... 2 MANUAL TRANSAXLE CONTROL... 12 SHIFT LEVER ASSEMBLY... 14 MANUAL TRANSAXLE... 15 MANUAL TRANSAXLE ASSEMBLY... 17 FIFTH SPEED SYNCHRONIZER
K EN R A ugu st Specifications Industrial Engine. M G D (Engine) MGB (Engine)
 K EN R 623 0-00 A ugu st 200 6 Specifications 2506-15 Industrial Engine M G A (Engine) MGB (Engine) M G D (Engine) Important Safety Information i01658146 Most accidents that involve product operation,
K EN R 623 0-00 A ugu st 200 6 Specifications 2506-15 Industrial Engine M G A (Engine) MGB (Engine) M G D (Engine) Important Safety Information i01658146 Most accidents that involve product operation,
Disassembly and Assembly
 K EN R 623 2-00 August 2006 Disassembly and Assembly 2506-15 Industrial Engine M G A (Engine) MGB (Engine) M G D (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance
K EN R 623 2-00 August 2006 Disassembly and Assembly 2506-15 Industrial Engine M G A (Engine) MGB (Engine) M G D (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance
RF80C-76G9 RF80M-77K5
 Publication No. W561-0201E 01 Torque converter Transmission Model RF80C-76G9 RF80M-77K5 Foreword Foreword This service manual gives the disassembly and reassembly procedures for torque converters and transmissions
Publication No. W561-0201E 01 Torque converter Transmission Model RF80C-76G9 RF80M-77K5 Foreword Foreword This service manual gives the disassembly and reassembly procedures for torque converters and transmissions
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS Mitsubishi F3A20 Series TRANSMISSION APPLICATION TABLE
 Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS Mitsubishi F3A20 Series APPLICATION TRANSMISSION APPLICATION TABLE Vehicle Application Transmission Model Colt 3-Speed (1990-94)... F3A21 Colt Vista
Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS Mitsubishi F3A20 Series APPLICATION TRANSMISSION APPLICATION TABLE Vehicle Application Transmission Model Colt 3-Speed (1990-94)... F3A21 Colt Vista
Brake System H TX, H2.0TXS [B475]; H TX [B466] Safety Precautions Maintenance and Repair
![Brake System H TX, H2.0TXS [B475]; H TX [B466] Safety Precautions Maintenance and Repair Brake System H TX, H2.0TXS [B475]; H TX [B466] Safety Precautions Maintenance and Repair](/thumbs/86/93834005.jpg) HMM180001 Brake System H1.5-1.8TX, H2.0TXS [B475]; H2.5-3.5TX [B466] Safety Precautions Maintenance and Repair When lifting parts or assemblies, make sure all slings, chains, or cables are correctly fastened,
HMM180001 Brake System H1.5-1.8TX, H2.0TXS [B475]; H2.5-3.5TX [B466] Safety Precautions Maintenance and Repair When lifting parts or assemblies, make sure all slings, chains, or cables are correctly fastened,
Geo Prizm ( LSi) Toyota Celica 1.8L (1994)
 Page 1 of 140 ARTICLE BEGINNING APPLICATION TRANSMISSION APPLICATIONS Application Geo Prizm (1993-94 LSi) Toyota Celica 1.6L (1993) Celica 1.8L (1994) Celica 2.2L (1993) Corolla 1.8L MR2 Paseo Transaxle
Page 1 of 140 ARTICLE BEGINNING APPLICATION TRANSMISSION APPLICATIONS Application Geo Prizm (1993-94 LSi) Toyota Celica 1.6L (1993) Celica 1.8L (1994) Celica 2.2L (1993) Corolla 1.8L MR2 Paseo Transaxle
Maintenance Information
 04581245 Edition 2 May 2014 Air Grinder, Die Grinder and Sander Series G2 (Angle) Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings,
04581245 Edition 2 May 2014 Air Grinder, Die Grinder and Sander Series G2 (Angle) Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings,
Maintenance Information
 16573370 Edition 2 February 2014 Air Grinder 99V Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
16573370 Edition 2 February 2014 Air Grinder 99V Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
MANUAL TRANS OVERHAUL - BORG-WARNER - T56 6-SPEED MANUAL TRANSMISSIONS Borg-Warner T56 (MM6) 6-Speed
 IDENTIFICATION MANUAL TRANS OVERHAUL - BORG-WARNER - T56 6-SPEED 1998 MANUAL TRANSMISSIONS Borg-Warner T56 (MM6) 6-Speed Transmission has 2 identification labels, located on lower left side of case. One
IDENTIFICATION MANUAL TRANS OVERHAUL - BORG-WARNER - T56 6-SPEED 1998 MANUAL TRANSMISSIONS Borg-Warner T56 (MM6) 6-Speed Transmission has 2 identification labels, located on lower left side of case. One
Troubleshooting, Service Tips, And Major Improvements For Hydrostatic Transmissions (Special Edition){3200}
 Page 1 of 75 Troubleshooting, Service Tips, And Major Improvements For Hydrostatic Transmissions (Special Edition){3200} 943, 953, 963, 973 Loaders Introduction The hydrostatic transmissions used in 943,
Page 1 of 75 Troubleshooting, Service Tips, And Major Improvements For Hydrostatic Transmissions (Special Edition){3200} 943, 953, 963, 973 Loaders Introduction The hydrostatic transmissions used in 943,
Implement and Steering/Hydraulic System Testing and Adjusting
 Page 1 of 64 Testing And Adjusting Introduction Reference: This supplement contains the Specifications, Systems Operation, and Testing And Adjusting for the components and systems that are different than
Page 1 of 64 Testing And Adjusting Introduction Reference: This supplement contains the Specifications, Systems Operation, and Testing And Adjusting for the components and systems that are different than
POWERSHIFT TRANSMISSION
 1. Specifications... 5-3 2. Structure... 5-4 2.1 Torque converter... 5-4 2.2 Transmission... 5-5 2.3 Power Train Line... 5-6 2.4 Control Valve... 5-7 2.5 Main Regulator Valve... 5-7 2.6 Torque Converter
1. Specifications... 5-3 2. Structure... 5-4 2.1 Torque converter... 5-4 2.2 Transmission... 5-5 2.3 Power Train Line... 5-6 2.4 Control Valve... 5-7 2.5 Main Regulator Valve... 5-7 2.6 Torque Converter
SECTION 5B MANUAL TRANSMISSION TABLE OF CONTENTS
 SECTION 5B MANUAL TRANSMISSION TABLE OF CONTENTS General Description and Operation... 5B-2 Shift Lever... 5B-2 Transmission Assembly... 5B-2 Specifications... 5B-3 Diagnostic Information and Procedures...
SECTION 5B MANUAL TRANSMISSION TABLE OF CONTENTS General Description and Operation... 5B-2 Shift Lever... 5B-2 Transmission Assembly... 5B-2 Specifications... 5B-3 Diagnostic Information and Procedures...
BRAKE E
 8-1 GENERAL...8-2 SPECIFICATIONS...8-6 COMPONENTS...8-7 FRONT BRAKE...8-12 DISASSEMBLY INSPECTION REASSEMBLY (Pn1, Cu2 3 TON SERIES)...8-12 DISASSEMBLY INSPECTION REASSEMBLY (Pn2 3 TON SERIES)...8-17 BRAKE
8-1 GENERAL...8-2 SPECIFICATIONS...8-6 COMPONENTS...8-7 FRONT BRAKE...8-12 DISASSEMBLY INSPECTION REASSEMBLY (Pn1, Cu2 3 TON SERIES)...8-12 DISASSEMBLY INSPECTION REASSEMBLY (Pn2 3 TON SERIES)...8-17 BRAKE
PowerSynchro Transmission Systems Operation Testing & Adjusting
 PowerSynchro Transmission Systems Operation Testing & Adjusting Models TH336, TH337, TH406, TH407, TH414, TH514, TH417 S/N TDE00100 & After S/N TDF00100 & After S/N TBX00100 & After S/N TBY00100 & After
PowerSynchro Transmission Systems Operation Testing & Adjusting Models TH336, TH337, TH406, TH407, TH414, TH514, TH417 S/N TDE00100 & After S/N TDF00100 & After S/N TBX00100 & After S/N TBY00100 & After
Transaxle. 1. Mount the transaxle to Bench Mounted Holding Fixture T57L-500-B.
 «1997 Aspire Table of Contents» «Group 07: TRANSAXLE» «Section 07-01: Transaxle, Automatic» «DISASSEMBLY» Transaxle CAUTION: To prevent dirt from entering the transaxle, it should be disassembled and kept
«1997 Aspire Table of Contents» «Group 07: TRANSAXLE» «Section 07-01: Transaxle, Automatic» «DISASSEMBLY» Transaxle CAUTION: To prevent dirt from entering the transaxle, it should be disassembled and kept
Maintenance Information
 80234313 Edition 2 May 2014 Air Grinder, Die Grinder, Sander and Belt Sander Series G1 (Angle) Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the
80234313 Edition 2 May 2014 Air Grinder, Die Grinder, Sander and Belt Sander Series G1 (Angle) Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the
Media Number -SENR Publication Date -01/10/1977 Date Updated -12/10/2001
 - - 55, 56, 57, 58 & 59 TOWING WINCHES Page 1 of 21 Testing and Adjusting 55, 56, 57, 58 & 59 TOWING WINCHES Media Number -SENR7217-01 Publication Date -01/10/1977 Date Updated -12/10/2001 Testing And
- - 55, 56, 57, 58 & 59 TOWING WINCHES Page 1 of 21 Testing and Adjusting 55, 56, 57, 58 & 59 TOWING WINCHES Media Number -SENR7217-01 Publication Date -01/10/1977 Date Updated -12/10/2001 Testing And
Maintenance Information
 80234313 Edition 1 June 2006 Air Grinder, Die Grinder, Sander and Belt Sander Series G1 (Angle) Maintenance Information Save These Instructions WARNING Always wear eye protection when operating or performing
80234313 Edition 1 June 2006 Air Grinder, Die Grinder, Sander and Belt Sander Series G1 (Angle) Maintenance Information Save These Instructions WARNING Always wear eye protection when operating or performing
1. General Description
 1. General Description A: SPECIFICATION 1. MANUAL TRANSMISSION AND FRONT DIFFERENTIAL Type Transmission gear ratio Front reduction gear Rear reduction gear Front differential Center differential Final
1. General Description A: SPECIFICATION 1. MANUAL TRANSMISSION AND FRONT DIFFERENTIAL Type Transmission gear ratio Front reduction gear Rear reduction gear Front differential Center differential Final
Maintenance Information
 16573347 Edition 2 February 2014 Air Grinder Series 88H Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
16573347 Edition 2 February 2014 Air Grinder Series 88H Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
MANUAL TRANSMISSION SECTION MT CONTENTS TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE MT-1 SERVICE INFORMATION POSITION SWITCH...13 Checking...13
 TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE SECTION MT A B MANUAL TRANSMISSION MT D CONTENTS E SERVICE INFORMATION... 2 PRECAUTIONS... 2 Service Notice or Precaution...2 PREPARATION... 3 Special Service Tool...3 Commercial
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE SECTION MT A B MANUAL TRANSMISSION MT D CONTENTS E SERVICE INFORMATION... 2 PRECAUTIONS... 2 Service Notice or Precaution...2 PREPARATION... 3 Special Service Tool...3 Commercial
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS. General Motors Corp. Hydra-Matic 4L60-E Overhaul
 1997-98 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS General Motors Corp. Hydra-Matic 4L60-E Overhaul APPLICATION TRANSMISSION APPLICATIONS Application Corvette Transaxle 4L60-E IDENTIFICATION The 4L60-E transmission can be
1997-98 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS General Motors Corp. Hydra-Matic 4L60-E Overhaul APPLICATION TRANSMISSION APPLICATIONS Application Corvette Transaxle 4L60-E IDENTIFICATION The 4L60-E transmission can be
Diagnostic Procedures
 Section 6 Diagnostic Procedures Learning Objectives: 1. Describe manual transmission, transaxle and transfer case component inspection and diagnostic procedures 2. Identify clutch component inspection
Section 6 Diagnostic Procedures Learning Objectives: 1. Describe manual transmission, transaxle and transfer case component inspection and diagnostic procedures 2. Identify clutch component inspection
DC MOTOR MAINTENANCE ALL ELECTRIC LIFT TRUCKS PART NO SRM 294
 DC MOTOR MAINTENANCE ALL ELECTRIC LIFT TRUCKS PART NO. 897076 620 SRM 294 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR When lifting parts or assemblies, make sure all slings, chains, or cables are correctly
DC MOTOR MAINTENANCE ALL ELECTRIC LIFT TRUCKS PART NO. 897076 620 SRM 294 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR When lifting parts or assemblies, make sure all slings, chains, or cables are correctly
TURBOCHARGER Toyota Celica DESCRIPTION OPERATION TURBOCHARGING SYSTEMS All Models
 TURBOCHARGER 1988 Toyota Celica 1988 TURBOCHARGING SYSTEMS All Models DESCRIPTION Most models use a water-cooled turbocharger, mounted directly to the exhaust manifold with a wastegate assembly attached
TURBOCHARGER 1988 Toyota Celica 1988 TURBOCHARGING SYSTEMS All Models DESCRIPTION Most models use a water-cooled turbocharger, mounted directly to the exhaust manifold with a wastegate assembly attached
Disassembly and Assembly
 SENR9779-03 January 2007 Disassembly and Assembly 1103 and 1104 Industrial Engines DC (Engine) DD (Engine) DJ (Engine) DK (Engine) RE (Engine) RG (Engine) RJ (Engine) RR (Engine) RS (Engine) DF (Engine)
SENR9779-03 January 2007 Disassembly and Assembly 1103 and 1104 Industrial Engines DC (Engine) DD (Engine) DJ (Engine) DK (Engine) RE (Engine) RG (Engine) RJ (Engine) RR (Engine) RS (Engine) DF (Engine)
2002 F-Super Duty /Excursion Workshop Manual
 Page 1 of 25 SECTION 307-01: Automatic Transaxle/Transmission 2002 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion Workshop Manual ASSEMBLY Procedure revision date: 05/23/2001 Transmission Special Tool(s) Remover, O-Ring
Page 1 of 25 SECTION 307-01: Automatic Transaxle/Transmission 2002 F-Super Duty 250-550/Excursion Workshop Manual ASSEMBLY Procedure revision date: 05/23/2001 Transmission Special Tool(s) Remover, O-Ring
Maintenance Information
 16573321 Edition 3 February 2014 Air Grinder Series 61H Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
16573321 Edition 3 February 2014 Air Grinder Series 61H Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
TCI Turbo 400 Full Manual Valve Body. Shift Pattern: Park Reverse Neutral First Second Third. NOTE: You must reuse stock manual control valve.
 TCI 221100 Turbo 400 Full Manual Valve Body Shift Pattern: Park Reverse Neutral First Second Third This Kit Contains: (1) Turbo 400 Full Manual Valve Body (1) Separator Plate & Gaskets (1) Pressure Regulator
TCI 221100 Turbo 400 Full Manual Valve Body Shift Pattern: Park Reverse Neutral First Second Third This Kit Contains: (1) Turbo 400 Full Manual Valve Body (1) Separator Plate & Gaskets (1) Pressure Regulator
WALKIE HIGH LIFT HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
 WALKIE HIGH LIFT HYDRAULIC SYSTEM W30-40ZA [B453]; W20-30ZR [B455]; W25-30-40ZC [B454] PART NO. 1524251 2000 SRM 1025 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR When lifting parts or assemblies, make sure
WALKIE HIGH LIFT HYDRAULIC SYSTEM W30-40ZA [B453]; W20-30ZR [B455]; W25-30-40ZC [B454] PART NO. 1524251 2000 SRM 1025 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR When lifting parts or assemblies, make sure
2005 Toyota RAV AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS U240E & U241E Overhaul
 2001-05 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS U240E & U241E Overhaul APPLICATION CAUTION: Flush oil cooler and oil cooler lines prior to transaxle installation. Oil cooling system contamination may cause premature transaxle
2001-05 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS U240E & U241E Overhaul APPLICATION CAUTION: Flush oil cooler and oil cooler lines prior to transaxle installation. Oil cooling system contamination may cause premature transaxle
SPECIAL TOOLS Dodge Pickup 5.9L Eng R3500. Fig 1: Identifying Remover C-3985-B (Special Tool) 9/6/13 Printer Friendly View
 Procedures 2003 Dodge Pickup 5.9L Eng R3500 manual transmission SPECIAL TOOLS Fig 1: Identifying Remover C-3985-B (Special Tool) www2.prodemand.com/print/index?content=tabs&module=true&tab=true&terms=true&ymms=false&classname=
Procedures 2003 Dodge Pickup 5.9L Eng R3500 manual transmission SPECIAL TOOLS Fig 1: Identifying Remover C-3985-B (Special Tool) www2.prodemand.com/print/index?content=tabs&module=true&tab=true&terms=true&ymms=false&classname=
CHAPTER 7 TRANSMISSION (MFO6S)
 1 page INDEX1 Model SG1J (MF06S) TRANSMISSION 7-1 7-142E-07 CHAPTER 7 TRANSMISSION (MFO6S) Model SG1J 1 Models FE, FF and SG2J 1 Model FD 7 TROUBLESHOOTING...7-2 SPECIAL TOOLS...7-5 REMOVAL...7-7 GEAR
1 page INDEX1 Model SG1J (MF06S) TRANSMISSION 7-1 7-142E-07 CHAPTER 7 TRANSMISSION (MFO6S) Model SG1J 1 Models FE, FF and SG2J 1 Model FD 7 TROUBLESHOOTING...7-2 SPECIAL TOOLS...7-5 REMOVAL...7-7 GEAR
Maintenance Information
 16572679 Edition 2 May 2014 Air Drill QP Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these potentially
16572679 Edition 2 May 2014 Air Drill QP Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these potentially
SUZUKI SQ 416/420/625 M.Y TRANSMISSION SERVICE MANUAL - MANUAL - AUTOMATIC - TRANSFER - DIFFERENTIALS
 SUZUKI SQ 416/420/625 M.Y 1998-2005 TRANSMISSION SERVICE MANUAL - MANUAL - AUTOMATIC - TRANSFER - DIFFERENTIALS WARNING/CAUTION/NOTE IMPORTANT Please read this manual and follow its instructions carefully.
SUZUKI SQ 416/420/625 M.Y 1998-2005 TRANSMISSION SERVICE MANUAL - MANUAL - AUTOMATIC - TRANSFER - DIFFERENTIALS WARNING/CAUTION/NOTE IMPORTANT Please read this manual and follow its instructions carefully.
Media Number -SENR Publication Date -01/07/1992 Date Updated -11/10/2001
 518 GRAPPLE SKIDDER--SERIES II 95U03200-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY 330 Page 1 of 16 Model: 518 WHEEL SKIDDER 95U Configuration: 518 GRAPPLE SKIDDER--SERIES II 95U03200-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY 3304 ENGINE
518 GRAPPLE SKIDDER--SERIES II 95U03200-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY 330 Page 1 of 16 Model: 518 WHEEL SKIDDER 95U Configuration: 518 GRAPPLE SKIDDER--SERIES II 95U03200-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY 3304 ENGINE
Maintenance Information
 16575243 Edition 2 October 2013 Air Screwdrivers 1R Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
16575243 Edition 2 October 2013 Air Screwdrivers 1R Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
DIFFERENTIALS & AXLE SHAFTS
 DIFFERENTIALS & AXLE SHAFTS 2001 Chevrolet Camaro 2000-01 DRIVE AXLES General Motors Differentials & Axle Shafts Chevrolet; Camaro Pontiac; Firebird DESCRIPTION & OPERATION Drive axle is a semi-floating,
DIFFERENTIALS & AXLE SHAFTS 2001 Chevrolet Camaro 2000-01 DRIVE AXLES General Motors Differentials & Axle Shafts Chevrolet; Camaro Pontiac; Firebird DESCRIPTION & OPERATION Drive axle is a semi-floating,
TSM54/52 MANUAL TRANSMISSION
 3B-1 SECTION 00 3B TSM54/52 MANUAL TRANSMISSION Table of Contents GENERAL INFORMATION... 3B-3 Overview... 3B-3 Specifications... 3B-4 System components... 3B-5 Shifting mechanism... 3B-17 Diagnostic information
3B-1 SECTION 00 3B TSM54/52 MANUAL TRANSMISSION Table of Contents GENERAL INFORMATION... 3B-3 Overview... 3B-3 Specifications... 3B-4 System components... 3B-5 Shifting mechanism... 3B-17 Diagnostic information
BRAKE SYSTEM Return To Main Table of Contents
 BRAKE SYSTEM Return To Main Table of Contents GENERAL... 2 BRAKE PEDAL... 10 MASTER CYLINDER... 13 BRAKE BOOSTER... 16 BRAKE LINE... 18 PROPORTIONING VALVE... 19 FRONT DISC BRAKE... 20 REAR DRUM BRAKE...
BRAKE SYSTEM Return To Main Table of Contents GENERAL... 2 BRAKE PEDAL... 10 MASTER CYLINDER... 13 BRAKE BOOSTER... 16 BRAKE LINE... 18 PROPORTIONING VALVE... 19 FRONT DISC BRAKE... 20 REAR DRUM BRAKE...
Table 6-1. Problems and solutions with pump operations. No Fluid Delivery
 Table 6-1. and solutions with pump operations No Fluid Delivery Fluid level in the reservoir is low. Oil intake pipe or inlet filter is plugged. Air leak in the inlet line prevents priming or causes noise
Table 6-1. and solutions with pump operations No Fluid Delivery Fluid level in the reservoir is low. Oil intake pipe or inlet filter is plugged. Air leak in the inlet line prevents priming or causes noise
Maintenance Information
 16606022 Edition 3 May 2014 Air Drill 728 Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these potentially
16606022 Edition 3 May 2014 Air Drill 728 Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these potentially
HIGH PERFORMANCE TRANSMISSION PARTS Instructions. Line Pressure Booster Kit. TCC Control Plunger Valve Kit. Line Pressure Modulator Plunger Valve Kit
 Performance Pack Ford 4R100 Part No. HP-4R100-01 Line Pressure Booster Kit Line-to-Lube Pressure Regulator Valve Line Pressure Booster Kit Valve Sleeve O-Rings (2) TCC Control Plunger Valve Kit Front Lube/Drainback
Performance Pack Ford 4R100 Part No. HP-4R100-01 Line Pressure Booster Kit Line-to-Lube Pressure Regulator Valve Line Pressure Booster Kit Valve Sleeve O-Rings (2) TCC Control Plunger Valve Kit Front Lube/Drainback
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
 205-03-1 Front Drive Axle/Differential Ford 8.8-Inch Ring Gear 205-03-1 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Axle Front Drive Special Tool(s) 2-Jaw Puller 205-D072 (D97L-4221-A) Special Tool(s) Carrier Bearing Replacer
205-03-1 Front Drive Axle/Differential Ford 8.8-Inch Ring Gear 205-03-1 DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Axle Front Drive Special Tool(s) 2-Jaw Puller 205-D072 (D97L-4221-A) Special Tool(s) Carrier Bearing Replacer
1. General Description
 1. General Description A: SPECIFICATIONS 1. Type Transmission gear ratio Front reduction gear Rear reduction gear 2. TRANSMISSION GEAR OIL Recommended oil Final Transfer 5-forward speeds with synchromesh
1. General Description A: SPECIFICATIONS 1. Type Transmission gear ratio Front reduction gear Rear reduction gear 2. TRANSMISSION GEAR OIL Recommended oil Final Transfer 5-forward speeds with synchromesh
1992 Clutch. Eclipse, Expo/Expo LRV, Galant, Mirage, Precis, 3000GT
 Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1992 Clutch Eclipse, Expo/Expo LRV, Galant, Mirage, Precis, 3000GT DESCRIPTION All clutches are single disc type. Pressure plate assembly uses a diaphragm spring to engage
Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1992 Clutch Eclipse, Expo/Expo LRV, Galant, Mirage, Precis, 3000GT DESCRIPTION All clutches are single disc type. Pressure plate assembly uses a diaphragm spring to engage
SPECIFICATIONS TEST AND ADJUSTMENT SPECIFICATIONS SPECIFICATIONS ENGINE FD620D, K SERIES
 ENGINE FD620D, K SERIES SPECIFICATIONS SPECIFICATIONS TEST AND ADJUSTMENT SPECIFICATIONS Engine Oil Pressure Sensor Activates............................... 98 kpa (14.2 psi) Oil Pressure While Cranking
ENGINE FD620D, K SERIES SPECIFICATIONS SPECIFICATIONS TEST AND ADJUSTMENT SPECIFICATIONS Engine Oil Pressure Sensor Activates............................... 98 kpa (14.2 psi) Oil Pressure While Cranking
HIGH PERFORMANCE TRANSMISSION PARTS Instructions. Line Pressure Booster Kit. TCC Control Plunger Valve Kit. Line Pressure Modulator Plunger Valve Kit
 Performance Pack Ford 4R100 Part No. HP-4R100-01 Line Pressure Booster Kit Line-to-Lube Pressure Regulator Valve Line Pressure Booster Kit Valve Sleeve O-Rings (2) TCC Control Plunger Valve Kit Front Lube/Drainback
Performance Pack Ford 4R100 Part No. HP-4R100-01 Line Pressure Booster Kit Line-to-Lube Pressure Regulator Valve Line Pressure Booster Kit Valve Sleeve O-Rings (2) TCC Control Plunger Valve Kit Front Lube/Drainback
ABBREVIATIONS USED IN THIS
 IN10 INTRODUCTION ABBREVIATIONS USED IN THIS MANUAL ABBREVIATIONS USED IN THIS MANUAL ATF Automatic Transmission Fluid B 0 Overdrive Brake B 2 Second Brake B 3 No. 3 Brake C 0 Overdrive Direct Clutch C
IN10 INTRODUCTION ABBREVIATIONS USED IN THIS MANUAL ABBREVIATIONS USED IN THIS MANUAL ATF Automatic Transmission Fluid B 0 Overdrive Brake B 2 Second Brake B 3 No. 3 Brake C 0 Overdrive Direct Clutch C
Torque Converter, Transmission Pump, Screen And Filter
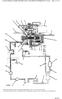 Page 13 of 27 Transmission Hydraulic System In Forward (Engine Running - Type 2 & 3 Control Valve Shown) (4) Transmission control valve. (5) Neutralizer valve. (6) Neutralizer solenoid. (7) Flow control
Page 13 of 27 Transmission Hydraulic System In Forward (Engine Running - Type 2 & 3 Control Valve Shown) (4) Transmission control valve. (5) Neutralizer valve. (6) Neutralizer solenoid. (7) Flow control
CLUTCH 6-1 CLUTCH TABLE OF CONTENTS
 PL CLUTCH 6-1 CLUTCH TABLE OF CONTENTS page DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY....1 CLUTCH CABLE...1 CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH....1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING CLUTCH SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS...2
PL CLUTCH 6-1 CLUTCH TABLE OF CONTENTS page DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY....1 CLUTCH CABLE...1 CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH....1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING CLUTCH SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS...2
Items Vehicles with 4G63 engine Vehicles with 4D56 engine. Type 4-speed full automatic 4-speed full automatic. 2nd rd
 23-2 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION General Information/ Service Specifications GENERAL INFORMATION 23100010141 Items Vehicles with 4G63 engine Vehicles with 4D56 engine Transmission model R4AW2-6 V4AW2-6 Type
23-2 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION General Information/ Service Specifications GENERAL INFORMATION 23100010141 Items Vehicles with 4G63 engine Vehicles with 4D56 engine Transmission model R4AW2-6 V4AW2-6 Type
Transmission Overhaul Procedures-Bench Service
 How to Assemble the Lower Reverse Idler Gear Assembly Special Instructions In 1996 Eaton changed the reverse idler system design. In the nut design, the reverse idler bearing was lubricated through a hole
How to Assemble the Lower Reverse Idler Gear Assembly Special Instructions In 1996 Eaton changed the reverse idler system design. In the nut design, the reverse idler bearing was lubricated through a hole
Maintenance Information
 16575128 Edition 2 May 2014 Air Grinder, Sander or Polisher 77A Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid
16575128 Edition 2 May 2014 Air Grinder, Sander or Polisher 77A Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid
Maintenance Information
 45528270 Edition 1 June 2007 Barring Motor T480 Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions WARNING Always wear eye protection when operating or performing maintenance on this Barring Motor.
45528270 Edition 1 June 2007 Barring Motor T480 Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions WARNING Always wear eye protection when operating or performing maintenance on this Barring Motor.
Maintenance Information
 Form 16573321 Edition 1 July 2004 Air Grinder Series 61H Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Always wear eye protection when operating or performing maintenance on this tool. Always turn off
Form 16573321 Edition 1 July 2004 Air Grinder Series 61H Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Always wear eye protection when operating or performing maintenance on this tool. Always turn off
SERVICE MANUAL STEERING AND RIGID DRIVE AXLES SERIES 068. Date Revision Description Owner 06/10/ Document emission PM
 SERVICE MANUAL STEERING AND RIGID DRIVE AXLES SERIES 068 Date Revision Description Owner 06/10/09 1.0 Document emission PM COMER INDUSTRIES Axles & Wheel Drive Units Via Magellano, 37-42046 Reggiolo (RE)
SERVICE MANUAL STEERING AND RIGID DRIVE AXLES SERIES 068 Date Revision Description Owner 06/10/09 1.0 Document emission PM COMER INDUSTRIES Axles & Wheel Drive Units Via Magellano, 37-42046 Reggiolo (RE)
Part Name. TOYOTA electrical tester. Engine sling device. Crankshaft pulley replacer. Belt tension gage. Connecting rod bushing remover & replacer
 16-2 SST LIST Illustration Part No. Part Name Section : Newly adopted SST 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 11 12 13 14 15 09082-76002-71 (09082-00050) TOYOTA electrical tester 09090-76002-71 (09090-04020) Engine sling device
16-2 SST LIST Illustration Part No. Part Name Section : Newly adopted SST 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 11 12 13 14 15 09082-76002-71 (09082-00050) TOYOTA electrical tester 09090-76002-71 (09090-04020) Engine sling device
Vickers. Overhaul Manual. Vane Pumps. Small and Large Series Combination Pumps VC(K)(S)-**-(*)*D*-6(1) VC(K)(S)-**-(*)-*-*D*-5(1)
 Overhaul Manual Vickers Vane Pumps Small and Large Series Combination Pumps VC(K)(S)-**-(*)*D*-6(1) VC(K)(S)-**-(*)-*-*D*-5(1) Revised 12/1/86 I-3150-S Table of Contents Section I. Introduction................................................................................
Overhaul Manual Vickers Vane Pumps Small and Large Series Combination Pumps VC(K)(S)-**-(*)*D*-6(1) VC(K)(S)-**-(*)-*-*D*-5(1) Revised 12/1/86 I-3150-S Table of Contents Section I. Introduction................................................................................
OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
 WREN IBT SERIES HYDRAULIC TORQUE WRENCHES IBT SQUARE DRIVE SERIES OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR WREN Products: POINT 75, 1IBT, 3IBT, 5IBT, 8IBT, 10IBT, 20IBT, 25IBT, 35IBT, 50IBT SQUARE DRIVE HYDRAULIC
WREN IBT SERIES HYDRAULIC TORQUE WRENCHES IBT SQUARE DRIVE SERIES OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR WREN Products: POINT 75, 1IBT, 3IBT, 5IBT, 8IBT, 10IBT, 20IBT, 25IBT, 35IBT, 50IBT SQUARE DRIVE HYDRAULIC
Maintenance Manual MM Transfer Cases. MTC-4208X/XL/XP/XLEV, MTC-4210X/XL/XP/XLEV and MTC-4213X Series Revised 09-16
 Maintenance Manual MM-0861 Transfer Cases MTC-4208X/XL/XP/XLEV, MTC-4210X/XL/XP/XLEV and MTC-4213X Series Revised 09-16 Service Notes About This Manual This manual provides maintenance and service procedures
Maintenance Manual MM-0861 Transfer Cases MTC-4208X/XL/XP/XLEV, MTC-4210X/XL/XP/XLEV and MTC-4213X Series Revised 09-16 Service Notes About This Manual This manual provides maintenance and service procedures
980 B Wheel Loader S/n 89P1 & Up Volume 1 of 2
 Caterpillar Service Manual 980 B Wheel Loader S/n 89P1 & Up Volume 1 of 2 Service Manual THIS IS A MANUAL PRODUCED BY JENSALES INC. WITHOUT THE AUTHORIZATION OF CATERPILLAR OR IT S SUCCESSORS. CATERPILLAR
Caterpillar Service Manual 980 B Wheel Loader S/n 89P1 & Up Volume 1 of 2 Service Manual THIS IS A MANUAL PRODUCED BY JENSALES INC. WITHOUT THE AUTHORIZATION OF CATERPILLAR OR IT S SUCCESSORS. CATERPILLAR
3.2 DRIVE TORQUE HUB. Roll, Leak and Brake Testing SECTION 3 - CHASSIS & TURNTABLE. 3-2 JLG Lift
 3.2 DRIVE TORQUE HUB Roll, Leak and Brake Testing 10 LUG PATTERN Torque-Hub units should always be roll and leak tested before disassembly and after assembly to make sure that the unit's gears, bearings
3.2 DRIVE TORQUE HUB Roll, Leak and Brake Testing 10 LUG PATTERN Torque-Hub units should always be roll and leak tested before disassembly and after assembly to make sure that the unit's gears, bearings
Power Train. Chapter 5
 Chapter Power Train Spefications................................................................. -3 Test Spefications........................................................ -3 Repair Spefications.......................................................
Chapter Power Train Spefications................................................................. -3 Test Spefications........................................................ -3 Repair Spefications.......................................................
MANUAL TRANSMISSION MUA 5C (4X2, 4X4) AND TREMEC T5R(4X2)
 MANUAL TRANSMISSION 7B 1 RODEO TRANSMISSION MANUAL TRANSMISSION MUA 5C (4X2, 4X4) AND TREMEC T5R(4X2) CONTENTS Service Precaution...................... 7B 2 General Description..................... 7B
MANUAL TRANSMISSION 7B 1 RODEO TRANSMISSION MANUAL TRANSMISSION MUA 5C (4X2, 4X4) AND TREMEC T5R(4X2) CONTENTS Service Precaution...................... 7B 2 General Description..................... 7B
Maintenance Instructions
 General Note These instructions contain information common to more than one model of Bevel Gear Drive. To simplify reading, similar models have been grouped as follows: GROUP 1 Models 11, 0, 1,, (illustrated),,
General Note These instructions contain information common to more than one model of Bevel Gear Drive. To simplify reading, similar models have been grouped as follows: GROUP 1 Models 11, 0, 1,, (illustrated),,
Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting
 M0064276 (en-us) December 2015 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 4008-30 Industrial Engine SD8 (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and
M0064276 (en-us) December 2015 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 4008-30 Industrial Engine SD8 (Engine) Important Safety Information Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and
1999 F-150/250 Workshop Manual
 Page 1 of 30 SECTION 205-03: Front Drive Axle/Differential Ford 8.8-Inch Ring Gear 1999 F-150/250 Workshop Manual DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Procedure revision date: 01/08/2003 Axle Front Drive Special Tool(s)
Page 1 of 30 SECTION 205-03: Front Drive Axle/Differential Ford 8.8-Inch Ring Gear 1999 F-150/250 Workshop Manual DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY Procedure revision date: 01/08/2003 Axle Front Drive Special Tool(s)
2001 Dodge RAM 3500 PICKUP
 1 of 76 9/14/2012 7:02 PM 2001 Dodge RAM 3500 PICKUP Submodel: Engine Type: L6 Liters: 5.9 Fuel Delivery: FI Fuel: DIESEL Subarticles MANUAL- NV3500 - DISASSEMBLY MANUAL- NV3500 - DISASSEMBLY MANUAL -
1 of 76 9/14/2012 7:02 PM 2001 Dodge RAM 3500 PICKUP Submodel: Engine Type: L6 Liters: 5.9 Fuel Delivery: FI Fuel: DIESEL Subarticles MANUAL- NV3500 - DISASSEMBLY MANUAL- NV3500 - DISASSEMBLY MANUAL -
Clutches for Automobiles and Light Trucks
 Clutches for Automobiles and Light Trucks What does the Clutch do? Connects the engine torque to transmission when ENGAGED Unhooks engine from transmission when DISENGAGED Where is the driver s foot when
Clutches for Automobiles and Light Trucks What does the Clutch do? Connects the engine torque to transmission when ENGAGED Unhooks engine from transmission when DISENGAGED Where is the driver s foot when
22-1 GROUP 22 MANUAL TRANSAXLE CONTENTS MANUAL TRANSAXLE... 22A MANUAL TRANSAXLE OVERHAUL... 22B
 22-1 GROUP 22 MANUAL TRANSAXLE CONTENTS............................... 22A OVERHAUL..................... 22B 22A-2 GROUP 22A MANUAL TRANSAXLE CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 22A-3 DIAGNOSIS 22A-6
22-1 GROUP 22 MANUAL TRANSAXLE CONTENTS............................... 22A OVERHAUL..................... 22B 22A-2 GROUP 22A MANUAL TRANSAXLE CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION......... 22A-3 DIAGNOSIS 22A-6
John Deere. MODEL: 8430 & 8630 Volume 1 of 2 JD-S-TM1143
 John Deere MODEL: 8430 & 8630 Volume 1 of 2 THIS IS A MANUAL PRODUCED BY JENSALES INC. WITHOUT THE AUTHORIZATION OF JOHN DEERE OR IT'S SUCCESSORS. JOHN DEERE AND IT'S SUCCESSORS ARE NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR
John Deere MODEL: 8430 & 8630 Volume 1 of 2 THIS IS A MANUAL PRODUCED BY JENSALES INC. WITHOUT THE AUTHORIZATION OF JOHN DEERE OR IT'S SUCCESSORS. JOHN DEERE AND IT'S SUCCESSORS ARE NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR
Maintenance Information
 Form 16575334 Edition 1 April 2005 Electric Screwdrivers EL, EP and ET 34V DC Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions WARNING Maintenance procedures have the potential for severe shock hazard
Form 16575334 Edition 1 April 2005 Electric Screwdrivers EL, EP and ET 34V DC Series Maintenance Information Save These Instructions WARNING Maintenance procedures have the potential for severe shock hazard
Transmission Disassembly
 TRANSMISSION SYSTEM F8B( 800 CC Car) Transmission system Components Name Transmission Disassembly Shifting Shaft & Fork TRANSMISSION ASSY: M/T The transmission provides four forward speeds and one reverse
TRANSMISSION SYSTEM F8B( 800 CC Car) Transmission system Components Name Transmission Disassembly Shifting Shaft & Fork TRANSMISSION ASSY: M/T The transmission provides four forward speeds and one reverse
ENGINE TUNE-UP INSPECTION OF ENGINE COOLANT INSPECTION OF ENGINE OIL INSPECTION OF BATTERY. INSPECTION OF AIR FILTER (Paper Filter Type)
 ENGINE MECHANICAL - Engine Tune-Up EM-17 ENGINE TUNE-UP INSPECTION OF ENGINE COOLANT (See steps 1 and 2 on page CO-4) INSPECTION OF ENGINE OIL (See steps 1 and 2 on page LU-5) INSPECTION OF BATTERY (See
ENGINE MECHANICAL - Engine Tune-Up EM-17 ENGINE TUNE-UP INSPECTION OF ENGINE COOLANT (See steps 1 and 2 on page CO-4) INSPECTION OF ENGINE OIL (See steps 1 and 2 on page LU-5) INSPECTION OF BATTERY (See
CLUTCH CONTENTS SERVICE DIAGNOSIS. (a) Worn or damaged disc assembly. (b) Grease or oil on disc facings. (c) Improperly adjusted cover assembly.
 CLUTCH CONTENTS -GROUP 6 Page CLUTCH HOUSING ALIGNMENT... 6 CLUTCH PEDAL FREE PLAY 1 CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING 5 CLUTCH RELEASE FORK... 5 CLUTCH SERVICING 2 PILOT BUSHING CRANKSHAFT TO TRANSMISSION DRIVE
CLUTCH CONTENTS -GROUP 6 Page CLUTCH HOUSING ALIGNMENT... 6 CLUTCH PEDAL FREE PLAY 1 CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING 5 CLUTCH RELEASE FORK... 5 CLUTCH SERVICING 2 PILOT BUSHING CRANKSHAFT TO TRANSMISSION DRIVE
Turbo 400 Trans Brake Valve Body Shift Pattern: Park Reverse Neutral 1st 2nd 3rd
 TCI 221500 Turbo 400 Trans Brake Valve Body Shift Pattern: Park Reverse Neutral 1st 2nd 3rd This Valve Body will neutralize at shut-down by putting shifter In 2nd gear position This Kit Contains: (1) Turbo
TCI 221500 Turbo 400 Trans Brake Valve Body Shift Pattern: Park Reverse Neutral 1st 2nd 3rd This Valve Body will neutralize at shut-down by putting shifter In 2nd gear position This Kit Contains: (1) Turbo
Maintenance Information
 51984144 Edition 6 May 2014 Air Paving Breaker MX60 & MX90 Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
51984144 Edition 6 May 2014 Air Paving Breaker MX60 & MX90 Maintenance Information Save These Instructions Product Safety Information WARNING Failure to observe the following warnings, and to avoid these
Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting
 KENR6225-01 April 2008 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 402D-403D-404D Industrial Engine GG (Engine) GH (Engine) GJ (Engine) GK (Engine) GL (Engine) GM (Engine) GN (Engine) GP (Engine) GQ (Engine)
KENR6225-01 April 2008 Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting 402D-403D-404D Industrial Engine GG (Engine) GH (Engine) GJ (Engine) GK (Engine) GL (Engine) GM (Engine) GN (Engine) GP (Engine) GQ (Engine)
Kysor On/Off Rear Air Fan Drive
 . Proper precautions must be taken to prevent personal injury from contact with moving parts, unintended engine start, or other hazards present when working with powered equipment. Refer to the vehicle
. Proper precautions must be taken to prevent personal injury from contact with moving parts, unintended engine start, or other hazards present when working with powered equipment. Refer to the vehicle
12. FRONT WHEEL/FRONT BRAKE/
 12 4.5kgm 0.9kg-m 4.5kg-m 12-0 SERVICE INFORMATION... 12-1 HYDRAULIC BRAKE... 12-10 TROUBLESHOOTING... 12-2 FRONT SHOCK ABSORBER... 12-16 FRONT WHEEL... 12-3 STEERING HANDLEBAR... 12-19 FRONT BRAKE...
12 4.5kgm 0.9kg-m 4.5kg-m 12-0 SERVICE INFORMATION... 12-1 HYDRAULIC BRAKE... 12-10 TROUBLESHOOTING... 12-2 FRONT SHOCK ABSORBER... 12-16 FRONT WHEEL... 12-3 STEERING HANDLEBAR... 12-19 FRONT BRAKE...
WEBER CARBURETOR TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
 This guide is to help pinpoint problems by diagnosing engine symptoms associated with specific vehicle operating conditions. The chart will guide you step by step to help correct these problems. For successful
This guide is to help pinpoint problems by diagnosing engine symptoms associated with specific vehicle operating conditions. The chart will guide you step by step to help correct these problems. For successful
GENESIS COUPE(BK) > 2010 > G 3.8 DOHC > Steering System
 GENESIS COUPE(BK) > 2010 > G 3.8 DOHC > Steering System Steering System > General Information > Specifications Specifications Steering gear Oil pump Steering angle Power steering oil Item Specification
GENESIS COUPE(BK) > 2010 > G 3.8 DOHC > Steering System Steering System > General Information > Specifications Specifications Steering gear Oil pump Steering angle Power steering oil Item Specification
Technical Bulletin # 1251
 Transmission: Subject: Application: Issue Date: CD4E TCC Slip Code Diagnosis Ford, Mercury and Mazda May 2009 CD4E TCC Slip Code Diagnosis Once the check engine light illuminates, the transmission will
Transmission: Subject: Application: Issue Date: CD4E TCC Slip Code Diagnosis Ford, Mercury and Mazda May 2009 CD4E TCC Slip Code Diagnosis Once the check engine light illuminates, the transmission will
CLUTCH Nissan 240SX DESCRIPTION PEDAL HEIGHT & FREE PLAY ADJUST CLUTCH ASSEMBLY R & I Clutch. Pathfinder, Pickup, 240SX, 300ZX
 CLUTCH 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 Clutch Pathfinder, Pickup, 240SX, 300ZX DESCRIPTION Clutch is of dry, single disc type, with a diaphragm spring type pressure plate. Clutch release bearing is prelubricated.
CLUTCH 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 Clutch Pathfinder, Pickup, 240SX, 300ZX DESCRIPTION Clutch is of dry, single disc type, with a diaphragm spring type pressure plate. Clutch release bearing is prelubricated.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
 307-01B-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Special Testing Procedures The special tests are designed to aid the technician in diagnosing the hydraulic and mechanical portion of the transmission. Engine Idle speed
307-01B-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Special Testing Procedures The special tests are designed to aid the technician in diagnosing the hydraulic and mechanical portion of the transmission. Engine Idle speed
Copper Sleeve, Unit Injector, Replacement
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA This service bulletin replaces SB 237-46, Copper Sleeve, Unit Injector, Replacement dated 6.2007, publication no. PV776-20177417. DService Bulletin Trucks
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA This service bulletin replaces SB 237-46, Copper Sleeve, Unit Injector, Replacement dated 6.2007, publication no. PV776-20177417. DService Bulletin Trucks
SECTION 4 - FUEL/LUBRICATION/COOLING
 For Arctic Cat Discount Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983 SECTION 4 - FUEL/LUBRICATION/COOLING 4 TABLE OF CONTENTS Carburetor Specifications... 4-2 Carburetor Schematic... 4-2 Carburetor... 4-3 Cleaning
For Arctic Cat Discount Parts Call 606-678-9623 or 606-561-4983 SECTION 4 - FUEL/LUBRICATION/COOLING 4 TABLE OF CONTENTS Carburetor Specifications... 4-2 Carburetor Schematic... 4-2 Carburetor... 4-3 Cleaning
SUPERCHARGER. ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION 1. INSPECT SUPERCHARGER OIL LEVEL HINT: With the engine cold, check the oil level on the dipstick.
 EG45 ONVEHICLE INSPECTION 1. INSPECT OIL LEVEL HINT: With the engine cold, check the oil level on the dipstick. (a) Park the vehicle on a level spot and turn the engine off. (b) 4WD: Remove the LH front
EG45 ONVEHICLE INSPECTION 1. INSPECT OIL LEVEL HINT: With the engine cold, check the oil level on the dipstick. (a) Park the vehicle on a level spot and turn the engine off. (b) 4WD: Remove the LH front
HYDRAULICS. TX420 & & lower. Hydraulic Tandem Pump Removal. 4. Remove the LH side panel (Fig. 0388).
 TX420 & 425 240000299 & lower 4. Remove the LH side panel (Fig. 0388). Hydraulic Tandem Pump Removal Note: Cleanliness is a key factor in a successful repair of any hydraulic system. Thoroughly clean all
TX420 & 425 240000299 & lower 4. Remove the LH side panel (Fig. 0388). Hydraulic Tandem Pump Removal Note: Cleanliness is a key factor in a successful repair of any hydraulic system. Thoroughly clean all
15.Main Shaft Assembly
 15.Main Shaft Assembly A: REMOVAL 1) Remove the manual transmission assembly from vehicle. 2) Remove the transfer case with extension case assembly.
15.Main Shaft Assembly A: REMOVAL 1) Remove the manual transmission assembly from vehicle. 2) Remove the transfer case with extension case assembly.
IBT Series Square Drive Torque Wrenches
 IBT Series Square Drive Torque Wrenches Operation and Maintenance Manual Model.75, 1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 20, 25, 35, 50 http://www.torsionx.com Use the IBT Series Square Drive Torque Wrenches Model.75, 1, 3,
IBT Series Square Drive Torque Wrenches Operation and Maintenance Manual Model.75, 1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 20, 25, 35, 50 http://www.torsionx.com Use the IBT Series Square Drive Torque Wrenches Model.75, 1, 3,
B&M / INTRODUCTION
 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR B&M AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS REPLACING GM TH350, TH400, and TH700R4 / 4L60 (not including 4L60E / electronic shift models) B&M part numbers: 102002-103005 - 107101-107104 107105-107106
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR B&M AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS REPLACING GM TH350, TH400, and TH700R4 / 4L60 (not including 4L60E / electronic shift models) B&M part numbers: 102002-103005 - 107101-107104 107105-107106
