(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
|
|
|
- Charlotte Cooper
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1 Han et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 22, 2007 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE PACKAGE AND (30) Foreign Application Priority Data LIGHT EMITTING DODE SYSTEMI HAVING AT LEAST TWO HEAT SINKS May 28, 2003 (KR) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) Inventors: Kwan Young Han, Seoul (KR); Kwang Il Park, Seoul (KR); Jae Ho Cho, Seoul (KR); Jung Hoo Seo, Seoul (KR); Seong Ryeol Ryu, Gyeonggi-do (KR) Correspondence Address: MCDERMOTT WILL & EMERY LLP TH STREET, N.W. WASHINGTON, DC (US) Assignee: SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR CO., LTD., Seoul (KR) Appl. No.: 10/557,820 PCT Filed: May 14, 2004 PCT No.: PCT/KRO4/O1153 S 371(c)(1), (2), (4) Date: Nov. 23, 2005 Sep. 30, 2003 (KR) OO67949 Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. HOIL 23/2495 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /675 (57) ABSTRACT There is provided a light emitting diode package having at least two heat sinks. The light emitting diode package includes a main body, at least two lead terminals fixed to the main body, and at least two heat sinks of electrically and thermally conductive materials, the heat sinks being fixed to the main body. The at least two heat sinks are separated from each other. Thus, high luminous power can be obtained mounting a plurality of light emitting diode dies in one LED package. Further, it is possible to embody polychromatic lights mounting LED dies emitting different wavelengths of light each other in the LED package.
2 Patent Application Publication Mar. 22, 2007 Sheet 1 of 6 US 2007/ A1 Fig.1
3 Patent Application Publication Mar. 22, 2007 Sheet 2 of 6 Fig.2 US 2007/ A1 Fig.3 Fig.4
4 Patent Application Publication Mar. 22, 2007 Sheet 3 of 6 Fig.5 US 2007/ A1 Fig.6
5 Patent Application Publication Mar. 22, 2007 Sheet 4 of 6 Fig.7 US 2007/ A1
6 Patent Application Publication Mar. 22, 2007 Sheet 5 of 6 Fig.9 US 2007/ A1 Fig.10 2Se: 2XSS As (EHCitéS)+... ZEx t
7 Patent Application Publication Mar. 22, 2007 Sheet 6 of 6 Fig.11 US 2007/ A1
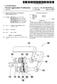
8 US 2007/ A1 Mar. 22, 2007 LIGHT EMITTING DODE PACKAGE AND LIGHT EMITTING DODE SYSTEMI HAVING AT LEAST TWO HEAT SINKS TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to a light emitting diode package and a light emitting diode system, and more particularly, to a high power light emitting diode package using a light emitting diode die as a light source, and a light emitting diode system having the high power light emitting diode package. BACKGROUND ART 0002 Recently, it is on the rise to use a light emitting diode (LED) as a light source. More than several thousands lumina of luminous power are, generally, required to use the light emitting diode as a light source for specific applications Such as illumination. The luminous power of the light emitting diode is substantially proportional to input power. Therefore, high luminous power is obtained by increasing the electric power inputted to the light emitting diode. However, the increase of the input power raises also the junction temperature of the light emitting diode. The increase of the junction temperature of the light emitting diode causes the loss of photometric efficiency which rep resents the conversion rate of input energy into visible light. As a result, power consumption increases considerably. Therefore, it is required to prevent the increase of the junction temperature of the light emitting diode due to the increase of input power. For the purpose, it is proposed a light emitting diode package in which the light emitting diode is attached on a heat sink, and the heat generated from the light emitting diode is dissipated through the heat sink The light emitting diode package (hereinafter, LED package) employing the heat sink is disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 6,274,924 B1, entitled Surface Mountable LED Pack age' from Carey et al FIG. 1 is a perspective view illustrating the LED package 100 disclosed in the U.S. Pat. No ,924 B Referring to FIG. 1, a heat sink 103 is placed into an insert-molded lead frame 101. The lead frame 101 is a plastic material molded around a metal frame. The heat sink 103 may include a reflector cup 113. A light emitting diode (LED) die 105 is mounted directly or indirectly via a thermally conducting submount 109 to the heat sink 103. Bonding wires(not shown) extend to the metal lead termi nals 111 on the lead frame 101 from the LED die 105 and the submount 109. The lead frame 101 is electrically and thermally isolated from the heat sink 103. In addition, an optical lens 107 may be added to the package As a result, the LED die 105 is maintained at a low junction temperature because the LED die 105 is thermally coupled on the heat sink 103. Therefore, it is possible to obtain high luminous power since relatively high input power can be supplied to the LED die However, using only one LED die limits the increase of the luminous power. To overcome Such a limi tation, it is necessary for a plurality of LED dies to be mounted in one LED package. However, mounting a plu rality of LED dies to one heat sink 103 limits an electrical connecting scheme. That is, the electrical connecting scheme of the plurality of LED dies with the heat sink 103 and the lead terminals is limited. Further, in order to assure uniformity of emitted light, it is necessary for the plurality of LED dies, which have the same structure and emit the same wavelength of light, to be mounted on the LED package. However, in the case that the plurality of LED dies, which have the same structure and emit the same wave length of light, are mounted on one heat sink 103, the input current for driving the LED dies considerably increases since all the LED dies are connected in parallel An additional submount may be used for prevent ing the increase of the input current and emitting uniform light. However, use of the submount complicates fabrication processes of the LED package and increases manufacturing cost thereof Meantime, it is required to provide a high power LED package capable of embodying polychromatic lights adapted to meet a variety of applications. An LED die, generally, emits a single wavelength of light. Therefore, LED dies emitting a variety of wavelengths of light should be mounted in one LED package in order to embody the polychromatic lights. Also, the LED dies emitting the vari ous wavelengths of light should be driven respectively. For the purpose, it is needed to control the power Supplied to each of the LED dies. DISCLOSURE OF THE INVENTION 0010) Therefore, an object of the present invention is to provide an LED package in which a plurality of LED dies are mounted and which can secure high luminous power, without a Submount It is another object of this invention to provide an LED package capable of mounting LED dies having the same structure and emitting the same wavelength of light, and capable of emitting uniform light It is a further object of this invention to provide a high power LED package capable of embodying polychro matic lights It is still another object of this invention to provide a high power LED system capable of embodying polychro matic lights In order to achieve the above objects, an embodi ment of the present invention provides an LED package having at least two heat sinks. The LED package according to the embodiment of the present invention comprises a main body, at least two lead terminals fixed to the main body, and at least two heat sinks of electrically and thermally conductive materials. The at least two heat sinks are sepa rated from each other and fixed to the main body. Thus, at least one LED die can be mounted on upper surfaces of the at least two heat sinks. As a result, a plurality of LED dies can be mounted in one LED package, thereby making Sure of high luminous power The main body may be formed of a thermoplastic material using a injection molding technique. And, the main body may be formed along with the lead terminals and the heat sinks in a single body using a insert molding technique Each of the at least two heat sinks may also have a reflective surface extended from the upper surface thereof. The at least two heat sinks having the reflective surfaces are
9 US 2007/ A1 Mar. 22, 2007 appropriately arranged to reflect the light emitted from the LED die out of the LED package. As a result, the luminous power emitted toward specific direction is increased According to another embodiment of the present invention, the at least two lead terminals comprise a pair of lead terminals to be electrically connected to an external power source. Further, the at least two heat sinks may be a pair of heat sinks. At least one LED die is mounted on upper surfaces of the at least two heat sinks. The at least one LED die is electrically and directly connected to the heat sinks via a surface of the die. The LED dies may be arranged such that at least one LED die is located on each of the at least two heat sinks. In addition, a lens attached to the main body encloses the at least one LED die. Further, the lens may include an optically transparent material contacted with the at least one LED die. The optically transparent material may be an optically transparent epoxy or silicone. The optically transparent material protects the at least one LED die. The optically transparent material may contain a light diffusing material Meantime, a fluorescent material converting the wavelength of light emitted from the at least one LED die, may be distributed over the at least one LED die. The fluorescent material may be distributed directly on the at least one LED die, or distributed within the optically trans parent material. Thus, it is possible to change the light emitted from the at least one LED die into another light having predetermined wavelengths, in particular, white light In addition, bonding wires may electrically connect the at least two lead terminals, the at least two heat sinks and the at least one LED die. Then, the at least one LED die is electrically and directly connected to at least one of the bonding wires through another surface of the LED die. As a result, the at least one LED die is electrically connected to the at least one bonding wire and the heat sink to which the die is mounted. Thus, as a power source is coupled to the at least two lead terminals, the electric power can be supplied to the at least one LED die According to another embodiment of the present invention, at least one LED die is located on each of the at least two heat sinks. The LED dies comprise LED dies emitting different wavelengths of light each other Further, the lead terminals may include lead ter minals electrically connected to the at least two heat sinks respectively, and a common lead terminal electrically con nected to all of the at least two heat sinks. Accordingly, it is possible for power sources to be placed between the com mon lead terminal and each of the lead terminals which are electrically connected to the at least two heat sinks respec tively. Thus, the LED dies mounted on the at least two heat sinks can be separately driven by turning on or off the respective power Sources. Thus, it is possible to embody polychromatic lights Further, the LED dies may include LED dies emitting a first wavelength of light, a second wavelength of light and a third wavelength of light, respectively. The first, the second and the third wavelengths may be red, green and blue wavelengths, respectively. Thus, it is possible to embody seven colors of light by turning on or off the respective power sources connected to the LED dies. Fur ther, by controlling the power inputted to each of the LED dies, instead of turning on or off the power source, it is possible to embody even more colors of light Meantime, an additional heat sink may be arranged along with the at least two heat sinks. A Zener diode is mounted on the additional heat sink. The Zener diode allows the LED package to be maintained in a constant Voltage, thereby protecting the LED package from static electricity or OVer Current. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The above objects, other features and advantages of the present invention will become more apparent by describing the preferred embodiment thereof with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which: FIG. 1 is a perspective view illustrating the LED package of the prior art FIG. 2 is a perspective view illustrating the LED package according to a first embodiment of the present invention FIG. 3 is a plan view illustrating the LED package of FIG FIG. 4 is a cross sectional view illustrating the LED package of FIG FIG. 5 is a perspective view illustrating the LED package mounting LED dies according to the first embodi ment of the present invention FIG. 6 is a perspective view illustrating the LED package according to a second embodiment of the present invention FIG. 7 is an exploded perspective view illustrating the LED package of FIG FIG. 8 is a cross sectional view illustrating the LED package of FIG FIG. 9 is a bottom perspective view illustrating a main body of the LED package of FIG FIG. 10 is a plan view illustrating an LED package according to the second embodiment of the present inven tion FIG. 11 is a perspective view illustrating an LED package according to a third embodiment according to the present invention. A LIST OF REFERENCE NUMERALS 0036) 1, 31, 71: main body, 3, 35: septum or septa, 0037) 5, 51, 111: lead terminals, 7, 7a, 7b, 41, 81, 103: heat sink(s) ) ) ) 9, 43: reflective surfaces, 11, 49: bonding wires, 13, 47a, 47b, 47c, 105: LED die(s), 15, 23, 63, 107: lens, 21, 61, 100: LED package, 33: heat-sink receiving recesses, 37: lead-terminal receiving grooves, 38: heat-sink binding grooves,
10 US 2007/ A1 Mar. 22, ) 39: lead terminal holes, : lower portions of heat sinks, : inner portions of lead terminals, : Outer portions of lead terminals, 0048) 83: additional heat sink, : Zener diode, : lead frame, 0051) 109: submount, : reflector cup Best Mode for Carrying Out the Invention 0053) Reference will now be made in detail to preferred embodiments of the present invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings. First Embodiment 0054 FIG. 2 is a perspective view illustrating the LED package according to the first embodiment of the present invention, and FIG.3 and FIG. 4 are a plan view and a cross sectional view illustrating the LED package of FIG. 2, respectively Referring to FIG. 2 to FIG. 4, at least two lead terminals 5 and at least two heat sinks 7 are fixed to a main body 1. The at least two lead terminals 5 comprise a pair of lead terminals 5 electrically coupled to a power source. And the at least two heat sinks 7 may be a pair The main body 1 may be formed by injection molding a plastic resin such as poly carbonate(pc), PCABS, PPA, nylon, polyethyleneterephthalate(pet), polybutylene terephthalate(pbt), or a model. The main body 1 may be formed in a single body along with at least a septum 3 which electrically isolate the at least two heat sinks 7. In addition, the main body 1 may be attached to the lead terminals 5 and the at least two heat sinks 7 using an insert-molding tech nique The at least two heat sinks 7 may be slugs, and each having an upper Surface for mounting LED dies. Each of the at least two heat sinks 7 may also have a reflective surface 9 extended from the upper surface thereof. The at least two heat sinks 7 having the reflective surface 9 are appropriately arranged to gather the light emitted from the LED dies efficiently. The at least two heat sinks 7 are formed of electrically and thermally conductive materials. For example, the at least two heat sinks 7 may be formed of copper(cu), gold, silver(ag), silicon carbide(sic) or alumi num(al). Since each of the at least two heat sinks 7 is conductive, each of the heat sinks 7 may be used as an electrode of the LED die and electrically connected to the lead terminals 5 through bonding wires. The at least two heat sinks 7 are separated from each other. The at least two heat sinks 7 may be separated by the at least a septum 3 formed in a single body along with the main body 1. Although the two heat sinks 7a, 7b separated from each other are shown in FIG. 2 to FIG. 4, the heat sinks 7 may include much more number of heat sinks. In addition, the lower surface of each of the heat sinks 7 may have a relatively wide width compared with the upper surface thereof to promote thermal relief A pair of the lead terminals 5 is electrically con nected to an external power source. Therefore, each of the lead terminals 5 may have a curved shape suitable to be mounted on a printed circuit board (PCB) and others, as shown in FIG. 2 to FIG. 4. Although FIG. 2 to FIG. 4 show a pair of lead terminals 5, additional lead terminals (not shown) may be fixed to the main body 1. The additional lead terminals may be thermally connected to the at least two heat sinks 7 to promote thermal relief. Also, the additional lead terminals may be connected to the printed circuit board and others to support the LED package safely FIG. 5 is a perspective view illustrating the LED package in which the LED dies are mounted Referring to FIG. 5, LED dies 13 are mounted on each of the at least two heat sinks 7a, 7b. Each of the LED dies 13 is electrically and directly connected to the heat sinks 7 via a surface of the LED die. That is, the surface of each of the LED dies 13 is contacted with the upper surface of the heat sink 7 without any submount. The number of the LED dies attached on each of the at least two heat sinks 7 may be varied with a desired purpose. And, various kinds of the LED dies 13 may be selected according to the desired purpose. However, it is preferable that the LED dies 13 having the same structure are mounted in one package to make sure of uniformity of emitted light and simplify fabrication processes of the LED package. Also, the LED dies 13 may be arranged symmetrically each other to make sure of uniformity of emitted light Bonding wires 11 electrically connect the pair of lead terminals 5, the at least two heat sinks 7 and the LED dies 13. Then, each of the LED dies 13 may be electrically connected to at least one of the bonding wires 13 through another surface of the LED die. As a result, each of the LED dies 13 is electrically connected to the at least one bonding wire 11 and the heat sink 7 mounting it. Thus, a power Source may be coupled to the pair of lead terminals to Supply electric power to the LED dies. Meantime, the LED dies 13 mounted on the same heat sinks 7 are connected in parallel, while the LED dies 13 mounted on different heat sinks 7 respectively are connected in series. As a result, the con nection of the LED dies 13 may be constituted in combi nation with in parallel and series between the pair of the lead terminals. A variety of manners connecting the bonding wires 11 are possible, and it is possible to connect the bonding wires 11 such that the input current driving the LED dies 13 can be decreased relatively Meantime, a lens 15 is attached to the main body 1 to enclose the LED dies 13. The lens 15 may have a variety of shapes according to its applications. Further, the lens 15 may include an optically transparent material directly con tacted with the LED dies 13. The optically transparent material may be an transparent epoxy or silicone, and contain an additive such as an diffusing material, an fluo rescent material and so on. The diffusing material prevents the bonding wires 11 and LED dies 13 from appearing on the outside, while the fluorescent material converts a wave length of light emitted from the LED dies 13. And the fluorescent material may be distributed directly on the LED dies 13. The desired wavelengths of light is emitted to outside by appropriately selecting the fluorescent material. For example, the fluorescent material may be a material including at least one element selected from the group
11 US 2007/ A1 Mar. 22, 2007 consisting of Ca, Sr. Ba and O, and at least one element selected from the group consisting of Al, O and Si, and activated by an element (Eu) of cerium group According to the first embodiment of the present invention, the LED package having high luminous power is provided employing at least two heat sinks 7 and mounting a plurality of LED dies 13 in one LED package. Second Embodiment 0064 FIG. 6 is a perspective view illustrating an LED package 21 according to the second embodiment of the present invention. And FIG. 7 and FIG. 8 are an exploded perspective view of the FIG. 6 and a cross sectional view of FIG. 6 without lens, respectively. Also, FIG. 9 is a bottom perspective view illustrating a main body of FIG. 6. In the second embodiment, it is described in detail the LED package 21 having three heat sinks and four lead terminals. However, the numbers of the heat sinks and the lead terminals are not limited by the above. That is, it is possible for the LED package 21 to have two heat sinks and three lead terminals, and also the LED package 21 may have much more numbers of heat sinks and lead terminals In FIG. 6 to FIG.9, lead terminals 51 and heat sinks 41 are fixed to a main body 31, as described referring to FIG. 2 to FIG The main body 31 may be formed by injection molding a plastic resin, as described referring to FIG. 2 to FIG. 4. The main body 31 is formed in a single body along with septa 35 which electrically isolate the heat sinks 41. In addition, the main body 31 is attached to the lead terminals 51 and the heat sinks 41 using an insert-molding technique. The main body 31 may have heat-sink receiving recesses 33, and the heat-sink receiving recesses 33 may be separated by the septa 35. The receiving recesses 33 may be holes passing through the main body 31, as shown in drawings Lead-terminal receiving grooves 37 may be placed onto upper surface of the main body 31. The lead-terminal receiving grooves 37 may be arranged along the circumfer ence direction of the main body 31, as shown in drawings. The lead terminals 51 are mounted to the lead-terminal receiving grooves 37, respectively. Lead terminal holes 39 passing through the side wall of the main body 31 may be connected to the lead-terminal receiving grooves 37, respec tively. The lead terminals 51 mounted to the lead-terminal receiving grooves 37 project outside through the lead terminal holes As shown in FIG. 9, recessed heat-sink binding grooves 38 are placed onto the lower surface of the main body 31. The heat-sink binding grooves 38 may be arranged along the circumference direction of the main body 31. And, the heat-sink binding grooves 38 may be separated by the septa 35 from each other. Further, the heat-sink binding grooves 38 are connected to the heat-sink receiving recesses 33, respectively The heat sinks 41 are bound to the heat-sink binding grooves 38, and exposed toward the upper potion of the main body 31 through the heat-sink receiving recesses 33. In this case, lower portions 45 of the heat sinks 41 are bound to the heat-sink binding grooves 38. As described referring to FIG. 2 to FIG. 4, the heat sinks 41 may be slugs, each of which has upper surface for mounting LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c. Further, each of the heat sinks 41 may have a reflective surface 43 extended from the upper surface thereof, and is formed of an electrically and thermally conductive material, as described referring to FIG. 2 to FIG. 4. The lower surfaces of the heat sinks 41 have relatively wide widths compared with the upper surfaces on which the LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c are mounted, thereby promoting thermal relief. Also, the lower surfaces of the heat sinks 41 may be exposed outside, as shown in FIG. 8, to promote thermal relief. Meantime, as described above, the heat sinks 41 are insert-molded using a molding technique, while forming the main body ). Each of the lead terminals 51 includes an inner portion 52 and an outer portion 54. The inner portions 52 of the lead terminals 51 are mounted to the respective lead terminal receiving grooves 37 of the main body 31, and may have hook shapes so as not to be detached from the main body 31. Compared to the inner portions 52, the outer portions 54 of the lead terminals 51 may have curved shapes suitable to be mounted on a printed circuit board and others. The outer portions 54 of the lead terminals 51 are exposed outside passing through the lead-terminal holes 39 of the main body 31. Meantime, as described above, the lead terminals 51 are insert-molded using a molding technique, while forming the main body ) The LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c are mounted on the heat sinks 41. As shown in FIG. 6 to FIG. 8, the LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c may be one by one mounted on the heat sinks 41. However, the number of the LED dies mounted on each of the heat sinks 41 is not limited by the above, and much more number of the LED dies may be mounted on each of the heat sinks 41. The LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c include LED dies emitting the different wavelengths of light each other. That is, the LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c may include a first group emitting a first wavelength of light, a second group emitting a second wavelength of light and a third group emitting a third wavelength of light. The first, second and third wavelengths may be red, green and blue wavelengths, respectively. In addition, the first, second and third groups may be mounted on the heat sinks 41, respec tively. For the convenience of description, the heat sinks 41 on which the first, second and third groups are mounted, are defined as a first heat sink, a second heat sink and a third heat sink, respectively. The LED package embodying polychro matic light using the LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c, are described referring to FIG FIG. 10 is a plan view illustrating the LED package 21 with bonding wires connected according to the second embodiment of the present invention. 0073) Referring to FIG. 10, the heat sinks 41, the lead terminals 51 and the LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c are connected by bonding wires 49. In this case, the first, second and third heat sinks 41 are electrically connected to the lead terminals 51, respectively. For convenience of description, the lead terminals 51 connected to the first, second and third heat sinks 41 are defined as a first lead terminal, a second lead terminal and a third lead terminal, respectively. Mean time, the lead terminals 51 include a common lead terminal electrically connected to all of the first, second and third heat sinks 41, in addition to the first, second and third lead terminals. More concretely, a negative common lead termi nal (-) is connected to the first, second and third heat sinks
12 US 2007/ A1 Mar. 22, through the bonding wires 49, while positive lead termi nals (+) are connected to the respective LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c through the bonding wires 49, as shown in FIG. 10. Thus, the LED dies mounted on one heat sink may be connected to a power source different from that which is connected to the LED dies mounted on another heat sink. That is, three power sources may be connected between the common lead terminal and each of the first, second and third lead terminals. As a result, polychromatic lights from the LED package 21 may be embodied by controlling ON/OFF of the power Sources. For example, when a power Source between the first lead terminal and the common lead termi nal is turned on, and the other power sources are turned off the first group of light can be emitted. If the three power Sources are turned on, all of the first, second and third groups of light can be emitted to embody white light. Meantime, much more number of colors can be embodied by control ling the amount of electric power Supplied to the respective LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c, instead of controlling ON/OFF of the power sources. The amount of electric power supplied to the respective LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c can be controlled by controlling the amount of currents or Voltages supplied to the respective LED dies. A controller (not shown) may be connected to the LED package 21 to control ON/OFF of the power sources or control the electric power. Meantime, the heat sinks 41, the lead terminals 51 and the LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c can be connected by the bonding wires 49 in various connecting manners Turning to FIG. 6 and FIG. 7, a lens 23 is attached to the main body 31 to enclose the LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c, as described referring to FIG. 5. The lens 23 may have various shapes according to its applications, and include a transparent material directly contacted with the LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c, as described referring to FIG According to the second embodiment of the present invention, the polychromatic LED package having high luminous power is provided employing the at least two heat sinks 41 and mounting the plurality of LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c which are capable of emitting mutually different wavelengths of light in one LED package. Third Embodiment FIG. 11 is a perspective view illustrating an LED package 61 according to the third embodiment according to the present invention Referring to FIG. 11, the lead terminals 51 and heat sinks 81 are fixed to a main body 71, and the LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c are mounted on the heat sinks 81, as described referring to FIG. 6 to FIG.9. However, the LED package 61 includes an additional heat sink 83, different from the LED package 21 of the second embodiment. Thus, heat-sink receiving recesses, heat-sink binding grooves and septa 75 of the main body 71 are arranged different from those shown in FIG. 6 to FIG. 9. That is, there are provided a receiving recess for receiving the additional heat sink 83 and a binding groove for binding the additional heat sink A Zener diode 85 is mounted on the additional heat sink 83. The Zener diode 85 allows the LED package 61 to be maintained in a constant Voltage. Meantime, polychro matic lights from the LED package 61 may be embodied by appropriately connecting the lead terminals 51, the heat sinks 81, the LED dies 47a, 47b and 47c, and the Zener diode 85 through bonding wires(not shown). As a result, by means of the Zener diode 85, it is possible to protect the LED package 61 from static electricity or a Sudden change in current, thereby increasing the reliability of the products. INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY 0079 According to the embodiments of the present invention, the LED package having high luminous power is provided employing at least two heat sinks 7 and mounting the plurality of LED dies in one LED package without a submount Further, by employing heat sinks of electrically conductive materials, there is provided an LED package which can be made by simplified fabrication processes. And further, it is possible to provide an LED package having high luminous power at relatively low input current since the heat sinks are separated from each other and thus the LED dies are connected each other in various connecting manners. Still further, it is possible to provide a high luminous power LED package which embodies polychromatic lights by mounting LED dies emitting different wavelengths of light each other in one LED package. 1. A high power light emitting diode package comprising: a main body; at least two lead terminals fixed to the main body; and at least two heat sinks of electrically and thermally conductive materials, the heat sinks being separated from each other and fixed to the main body. 2. The package of claim 1, wherein each of the at least two heat sinks has a reflective Surface extended from an upper surface thereof. 3. The package of claim 1, wherein the at least two heat sinks are a pair. 4. The package of claim 3, further comprising: at least one light emitting diode die mounted on upper Surfaces of the at least two heat sinks, the die being directly and electrically connected to the heat sinks through a surface of the die. 5. The package of claim 4, further comprising: bonding wires electrically connecting the at least two lead terminals, the at least two heat sinks and the at least one light emitting diode die. 6. The package of claim 4, further comprising: a lens attached to the main body, the lens enclosing the at least one light emitting diode die. 7. The package of claim 6, wherein the lens includes an optically transparent material which is directly contacted with the at least one light emitting diode die. 8. The package of claim 4, further comprising: a fluorescent material converting the wavelength of light emitted from the at least one light emitting diode die. 9. The package of claim 1, further comprising: light emitting diode dies mounted on the respective heat sinks, the light emitting diode dies emitting different wavelengths of light. 10. The package of claim 9, wherein the at least two lead terminals include: lead terminals electrically connected to the at least two heat sinks respectively; and
13 US 2007/ A1 Mar. 22, 2007 a common lead terminal electrically connected to all of the at least two heat sinks. 11. The package of claim 10, further comprising: an additional heat sink; and a Zener diode mounted on the additional heat sink. 12. The package of claim 9, wherein the light emitting diode dies include light emitting diode dies emitting a first wavelength of light, a second wavelength of light and a third wavelength of light, respectively. 13. The package of claim 13, wherein the first wave length, the second wavelength and the third wavelength are red wavelength, green wavelength and blue wavelength, respectively. 14. A light emitting diode system comprising: the light emitting diode package according to claim 10 or claim 11; and a controller for controlling the electric power supplied to the light emitting diode package, wherein the controller controls the amount of the current Supplied to the respective heat sinks. k k k k k
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004.00431 O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0043102 A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2004 (54) ALIGNMENT COLLAR FOR A NOZZLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 425/567
US 2004.00431 O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0043102 A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2004 (54) ALIGNMENT COLLAR FOR A NOZZLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 425/567
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 01 17420A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0117420 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) BUS BAR AND BATTERY MODULE INCLUDING THE SAME (52)
US 2011 01 17420A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0117420 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) BUS BAR AND BATTERY MODULE INCLUDING THE SAME (52)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
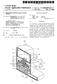
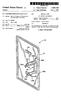
 (19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
(19) United States US 20080000052A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000052 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) REFRIGERATOR (75) Inventors: Dae Jin Hong, Jangseong-gun
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O231027A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0231027 A1 SU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 16, 2010 (54) WHEEL WITH THERMOELECTRIC (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2010O231027A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0231027 A1 SU (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 16, 2010 (54) WHEEL WITH THERMOELECTRIC (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160064308A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0064308A1 YAMADA (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) SEMICONDUCTORMODULE HOIL23/00 (2006.01) HOIL 25/8 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 20160064308A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0064308A1 YAMADA (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 3, 2016 (54) SEMICONDUCTORMODULE HOIL23/00 (2006.01) HOIL 25/8 (2006.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO64994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Matsumoto (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) STATIONARY BIKE (52) U.S. Cl.... 482/8 (76) Inventor: Masaaki Matsumoto,
(19) United States US 2005OO64994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Matsumoto (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) STATIONARY BIKE (52) U.S. Cl.... 482/8 (76) Inventor: Masaaki Matsumoto,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130075499A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0075499 A1 JEON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 28, 2013 (54) NOZZLE FOR A BURNER BOOM WATER SPRAY SYSTEM OF AN
(19) United States US 20130075499A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0075499 A1 JEON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 28, 2013 (54) NOZZLE FOR A BURNER BOOM WATER SPRAY SYSTEM OF AN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O190837A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0190837 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2003 (54) BATTERY HOLDER HAVING MEANS FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 439/500 SECURELY
US 2003O190837A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0190837 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2003 (54) BATTERY HOLDER HAVING MEANS FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 439/500 SECURELY
(12) United States Patent
 US009113558B2 (12) United States Patent Baik (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,113,558 B2 Aug. 18, 2015 (54) LED MOUNT BAR CAPABLE OF FREELY FORMING CURVED SURFACES THEREON (76) Inventor: Seong
US009113558B2 (12) United States Patent Baik (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,113,558 B2 Aug. 18, 2015 (54) LED MOUNT BAR CAPABLE OF FREELY FORMING CURVED SURFACES THEREON (76) Inventor: Seong
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 2010O293805A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0293805 A1 Chang (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 25, 2010 (54) NAIL GEL SOLIDIFICATION APPARATUS Publication Classification
US 2010O293805A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0293805 A1 Chang (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 25, 2010 (54) NAIL GEL SOLIDIFICATION APPARATUS Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006
 US 2006005 1222A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0051222 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) MINIATURE PUMP FOR LIQUID COOLING Publication Classification
US 2006005 1222A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0051222 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2006 (54) MINIATURE PUMP FOR LIQUID COOLING Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO861 8656B2 (12) United States Patent Oh et al. (54) FLEXIBLE SEMICONDUCTOR PACKAGE APPARATUS HAVING ARESPONSIVE BENDABLE CONDUCTIVE WIRE MEMBER AND A MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Tac Keun.
USOO861 8656B2 (12) United States Patent Oh et al. (54) FLEXIBLE SEMICONDUCTOR PACKAGE APPARATUS HAVING ARESPONSIVE BENDABLE CONDUCTIVE WIRE MEMBER AND A MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Tac Keun.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 200700.74941A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0074941 A1 Liang (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 5, 2007 (54) EXPANDABLE LUGGAGE (52) U.S. Cl.... 190/107; 190/18 A
US 200700.74941A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0074941 A1 Liang (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 5, 2007 (54) EXPANDABLE LUGGAGE (52) U.S. Cl.... 190/107; 190/18 A
USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999
 USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999 54 SERIALLY CONNECTED CHARGER Primary Examiner Edward H. Tso Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Rosenberger,
USOO5963O14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,963,014 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 1999 54 SERIALLY CONNECTED CHARGER Primary Examiner Edward H. Tso Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Rosenberger,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2
 US007125133B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2 Bilotti et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2006 (54) LED LIGHTING SYSTEM FOR PATIO 4.425,602 A 1/1984 Lansing UMBRELLA 5,053,931
US007125133B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,125,133 B2 Bilotti et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2006 (54) LED LIGHTING SYSTEM FOR PATIO 4.425,602 A 1/1984 Lansing UMBRELLA 5,053,931
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080209237A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0209237 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: (54) COMPUTER APPARATUS AND POWER SUPPLY METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Dae-hyeon
(19) United States US 20080209237A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0209237 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: (54) COMPUTER APPARATUS AND POWER SUPPLY METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventor: Dae-hyeon
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. Kobayashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009
 US 20090062784A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0062784 A1 Kobayashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) NEEDLEELECTRODE DEVICE FOR (30) Foreign Application
US 20090062784A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0062784 A1 Kobayashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) NEEDLEELECTRODE DEVICE FOR (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 US007307230B2 (12) United States Patent Chen (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,307,230 B2 Dec. 11, 2007 (54) MECHANISM FOR CONTROLLING CIRCUITCLOSINGAOPENING OF POWER RATCHET WRENCH (75) Inventor:
US007307230B2 (12) United States Patent Chen (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,307,230 B2 Dec. 11, 2007 (54) MECHANISM FOR CONTROLLING CIRCUITCLOSINGAOPENING OF POWER RATCHET WRENCH (75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Hozumi et al. 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,889,164 Dec. 26, 1989 54). SOLENOID CONTROLLED WALVE (75 Inventors: Kazuhiro Hozumi; Masaru Arai, both of Chiba; Yoshitane
United States Patent (19) Hozumi et al. 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,889,164 Dec. 26, 1989 54). SOLENOID CONTROLLED WALVE (75 Inventors: Kazuhiro Hozumi; Masaru Arai, both of Chiba; Yoshitane
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0018203A1 HUANG et al. US 20140018203A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 16, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) TWO-STAGE DIFFERENTIAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0068960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0068960 A1 Kopecek (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2006 (54) DRIVE ASSEMBLIES Publication Classification (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2006.0068960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0068960 A1 Kopecek (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2006 (54) DRIVE ASSEMBLIES Publication Classification (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
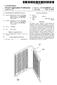 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0041841 A1 Huazhao et al. US 20140041841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (62) (30) MICRO-CHANNEL HEAT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0041841 A1 Huazhao et al. US 20140041841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (62) (30) MICRO-CHANNEL HEAT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0226455A1 Al-Anizi et al. US 2011 0226455A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SLOTTED IMPINGEMENT PLATES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0226455A1 Al-Anizi et al. US 2011 0226455A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SLOTTED IMPINGEMENT PLATES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O131873A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Klingbail et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 22, 2006 (54) HIGH PRESSURE SWIVEL JOINT Publication Classification (76) Inventors:
US 2006O131873A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Klingbail et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 22, 2006 (54) HIGH PRESSURE SWIVEL JOINT Publication Classification (76) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Miller
 United States Patent (19) Miller 54 LAMPHOLDER FITTING WITH THREE-WAY BRIGHTNESS SOLD-STATE FLUORESCENT LAMP BALLAST 76) Inventor: Jack V. Miller, 700 N. Auburn Ave., Sierra Madre, Calif. 91024 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Miller 54 LAMPHOLDER FITTING WITH THREE-WAY BRIGHTNESS SOLD-STATE FLUORESCENT LAMP BALLAST 76) Inventor: Jack V. Miller, 700 N. Auburn Ave., Sierra Madre, Calif. 91024 21 Appl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0041248A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0041248 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2011 (54) BEDSORE PREVENTION MATTRESS (76) Inventor: Ju Young KIM,
(19) United States US 2011 0041248A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0041248 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2011 (54) BEDSORE PREVENTION MATTRESS (76) Inventor: Ju Young KIM,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007218212B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,218,212 B2 HL (45) Date of Patent: May 15, 2007 (54) TWO-STEPCONTROL SIGNAL DEVICE 5,281,950 A 1/1994 Le... 340/475 WITH A U-TURN SIGNAL 5,663,708
(12) United States Patent US007218212B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,218,212 B2 HL (45) Date of Patent: May 15, 2007 (54) TWO-STEPCONTROL SIGNAL DEVICE 5,281,950 A 1/1994 Le... 340/475 WITH A U-TURN SIGNAL 5,663,708
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2
 US0087.08325B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,708.325 B2 Hwang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2014 (54) PAPER CLAMPINGAPPARATUS FOR (56) References Cited OFFICE MACHINE (75) Inventors:
US0087.08325B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,708.325 B2 Hwang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2014 (54) PAPER CLAMPINGAPPARATUS FOR (56) References Cited OFFICE MACHINE (75) Inventors:
Patent Application Publication Nov. 27, 2014 Sheet 1 of 7 US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0346290 A1 YOSHIDA et al. US 20140346290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) SLIDING TYPE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0346290 A1 YOSHIDA et al. US 20140346290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 27, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) SLIDING TYPE
Earl Sch yang y Lee, 5,457,342 10/1995 Herbst, II /712
 US005920264A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM PROTECTION 5,189,314 2/1993 Georgiou et al.... 307/271 DEVICE 5,287.292 2/1994
US005920264A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM PROTECTION 5,189,314 2/1993 Georgiou et al.... 307/271 DEVICE 5,287.292 2/1994
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2. Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005
 United States Patent USOO6915721B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2 Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) CORDLESS RATCHET WRENCH 6,311,583 B1 11/2001 Izumisawa... 81/57.13 6,715,380
United States Patent USOO6915721B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2 Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) CORDLESS RATCHET WRENCH 6,311,583 B1 11/2001 Izumisawa... 81/57.13 6,715,380
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070247877A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0247877 A1 KWON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2007 54) ACTIVE-CLAMP CURRENTSOURCE 3O Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20070247877A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0247877 A1 KWON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2007 54) ACTIVE-CLAMP CURRENTSOURCE 3O Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150214458A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0214458 A1 Nandigama et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 30, 2015 (54) THERMOELECTRIC GENERATORSYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 20150214458A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0214458 A1 Nandigama et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 30, 2015 (54) THERMOELECTRIC GENERATORSYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1
 USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
USOO6429647B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,429,647 B1 Nicholson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2002 (54) ANGULAR POSITION SENSOR AND 5,444,369 A 8/1995 Luetzow... 324/207.2 METHOD OF MAKING
(21) Appl.No.: 14/288,967
 US 20150075332Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0075332 A1 CHEN (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2015 (54) PASS-THRU RATCHET WRENCH (71) Applicant: Chia-Yu CHEN,
US 20150075332Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0075332 A1 CHEN (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2015 (54) PASS-THRU RATCHET WRENCH (71) Applicant: Chia-Yu CHEN,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US00893 1520B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,931,520 B2 Fernald (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 2015 (54) PIPE WITH INTEGRATED PROCESS USPC... 138/104 MONITORING (58) Field of Classification
(12) United States Patent US00893 1520B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,931,520 B2 Fernald (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 2015 (54) PIPE WITH INTEGRATED PROCESS USPC... 138/104 MONITORING (58) Field of Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O00861 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0008610 A1 PetersOn (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2002 (54) KEY FOB WITH SLIDABLE COVER (75) Inventor: John Peterson,
(19) United States US 2002O00861 OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0008610 A1 PetersOn (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2002 (54) KEY FOB WITH SLIDABLE COVER (75) Inventor: John Peterson,
of a quadratic function f(x)=aox+box+co whose con
 US005624250A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,624,250 Son 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 1997 54 TOOTH PROFILE FOR COMPRESSOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS SCREW ROTORS 1197432 7/1970 United Kingdom.
US005624250A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,624,250 Son 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 1997 54 TOOTH PROFILE FOR COMPRESSOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS SCREW ROTORS 1197432 7/1970 United Kingdom.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1
 USOO648.4362B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1 Ku0 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) RETRACTABLE HANDLE ASSEMBLY WITH 5,692,266 A 12/1997 Tsai... 16/113.1 MULTIPLE ENGAGING
USOO648.4362B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,484,362 B1 Ku0 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) RETRACTABLE HANDLE ASSEMBLY WITH 5,692,266 A 12/1997 Tsai... 16/113.1 MULTIPLE ENGAGING
Šá4% & -S. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States SSS. Ryu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec.
 (19) United States US 200702949.15A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0294.915 A1 Ryu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) SHOE SOLE (76) Inventors: Jeung hyun Ryu, Busan
(19) United States US 200702949.15A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0294.915 A1 Ryu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) SHOE SOLE (76) Inventors: Jeung hyun Ryu, Busan
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120072180A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0072180 A1 Stuckey et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 22, 2012 (54) TIRE MOLD DESIGN METHOD TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 703/1
(19) United States US 20120072180A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0072180 A1 Stuckey et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 22, 2012 (54) TIRE MOLD DESIGN METHOD TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 703/1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060066075A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0066075A1 Zlotkowski (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2006 (54) TOWING TRAILER FOR TWO OR THREE Publication Classification
US 20060066075A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0066075A1 Zlotkowski (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 30, 2006 (54) TOWING TRAILER FOR TWO OR THREE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150224968A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0224968 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) CONTROL METHOD FOR HILL START ASSIST CONTROL SYSTEM (71)
(19) United States US 20150224968A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0224968 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) CONTROL METHOD FOR HILL START ASSIST CONTROL SYSTEM (71)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
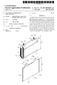 (19) United States US 2011 0183181A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0183181 A1 M00n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 28, 2011 (54) SECONDARY BATTERY HAVING NSULATION BAG (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2011 0183181A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0183181 A1 M00n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 28, 2011 (54) SECONDARY BATTERY HAVING NSULATION BAG (76) Inventors:
WWWWWWWWVA IWWA. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1 IWW IWWIWWI IWWWWWW IWW IWWIYIVIVIVINNINWWWWWWIV
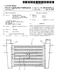 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0169926 A1 Watanabe et al. US 2007 O169926A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 >(54) HEAT EXCHANGER (75) Inventors: Haruhiko Watanabe,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0169926 A1 Watanabe et al. US 2007 O169926A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 >(54) HEAT EXCHANGER (75) Inventors: Haruhiko Watanabe,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O152831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0152831 A1 Sakamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2002 (54) ACCELERATOR PEDAL DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazunori
(19) United States US 2002O152831A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0152831 A1 Sakamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2002 (54) ACCELERATOR PEDAL DEVICE (76) Inventors: Kazunori
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007026 1863A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0261863 A1 MACLEOD et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2007 (54) SEALING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 166/387: 166/202
(19) United States US 2007026 1863A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0261863 A1 MACLEOD et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2007 (54) SEALING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 166/387: 166/202
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Ogasawara et al. (54) 75 RDING LAWN MOWER Inventors: Hiroyuki Ogasawara; Nobuyuki Yamashita; Akira Minoura, all of Osaka, Japan Assignee: Kubota Corporation, Osaka, Japan Appl.
United States Patent (19) Ogasawara et al. (54) 75 RDING LAWN MOWER Inventors: Hiroyuki Ogasawara; Nobuyuki Yamashita; Akira Minoura, all of Osaka, Japan Assignee: Kubota Corporation, Osaka, Japan Appl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0139355A1 Lee et al. US 2013 O1393.55A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) HINGEMECHANISMAND FOLDABLE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0139355A1 Lee et al. US 2013 O1393.55A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) HINGEMECHANISMAND FOLDABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0251883 A1 WANG US 2016O251883A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2016 (54) LOCKING AND UNLOCKING MECHANISM FOR ADOOR LOCK (71) Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0251883 A1 WANG US 2016O251883A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2016 (54) LOCKING AND UNLOCKING MECHANISM FOR ADOOR LOCK (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,626,061 B2. Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003
 USOO6626061B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) ACCELERATOR PEDAL DEVICE 6,276,229 B1 * 8/2001 Gohring et al... 74/513 6,289,762 B1 9/2001
USOO6626061B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Sakamoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 30, 2003 (54) ACCELERATOR PEDAL DEVICE 6,276,229 B1 * 8/2001 Gohring et al... 74/513 6,289,762 B1 9/2001
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014.0034628A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0034628A1 CHEN (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 6, 2014 (54) TEMPERATURE CONTROL MODULE FOR (52) U.S. Cl. ELECTRICBLANKETS
(19) United States US 2014.0034628A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0034628A1 CHEN (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 6, 2014 (54) TEMPERATURE CONTROL MODULE FOR (52) U.S. Cl. ELECTRICBLANKETS
-10 III. United States Patent to. 39a. 39b. 21 Claims, 3 Drawing Sheets. Appl. No.: 643,492 Fied: May 6, 1996 Int. Cla.m.
 United States Patent to Lutzker III US005683166A 11 Patent Number: 5,683,166 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997 54 (76 21 22) 51 52 (58) ELECTROLUMNESCENT WALLPLATE Inventor: Robert S. Lutzker, Woodstone
United States Patent to Lutzker III US005683166A 11 Patent Number: 5,683,166 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997 54 (76 21 22) 51 52 (58) ELECTROLUMNESCENT WALLPLATE Inventor: Robert S. Lutzker, Woodstone
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Nelson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005
 US 2005O189800A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0189800 A1 Nelson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) ENERGY ABSORBING SEAT AND SEAT Publication Classification
US 2005O189800A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0189800 A1 Nelson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) ENERGY ABSORBING SEAT AND SEAT Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2
 US007592736 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2 Scott et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 2009 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ELECTRIC (56) References Cited GENERATOR WITH ROTOR CIRCUMIFERENTIALLY
US007592736 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,592,736 B2 Scott et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 22, 2009 (54) PERMANENT MAGNET ELECTRIC (56) References Cited GENERATOR WITH ROTOR CIRCUMIFERENTIALLY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015 0084494A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084494 A1 Tonthat et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 (54) SLIDING RACK-MOUNTABLE RAILS FOR H05K 5/02 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 2015 0084494A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0084494 A1 Tonthat et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2015 (54) SLIDING RACK-MOUNTABLE RAILS FOR H05K 5/02 (2006.01)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2008/04
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 880 821 A1 (43) Date of publication: 23.01.2008 Bulletin 2008/04 (51) Int Cl.: B29C 45/14 (2006.01) H04M 1/02 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 07008807.5
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 880 821 A1 (43) Date of publication: 23.01.2008 Bulletin 2008/04 (51) Int Cl.: B29C 45/14 (2006.01) H04M 1/02 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 07008807.5
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
USOO7324657B2 (12) United States Patent Kobayashi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,324,657 B2 Jan. 29, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Mar.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201700.96035A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0096035 A1 NUGER et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TREAD COMPRISING VOIDS FOR CIVIL (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 201700.96035A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0096035 A1 NUGER et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) TREAD COMPRISING VOIDS FOR CIVIL (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Imai USOO6581225B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,581,225 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2003 (54) MATTRESS USED FOR PREVENTING BEDSORES OR THE LIKE (76) Inventor: KaZumichi Imai, 7-29-1222,
(12) United States Patent Imai USOO6581225B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,581,225 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2003 (54) MATTRESS USED FOR PREVENTING BEDSORES OR THE LIKE (76) Inventor: KaZumichi Imai, 7-29-1222,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6989498B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,989,498 B1 Linder et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2006 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR LOCKING (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent USOO6989498B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,989,498 B1 Linder et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 24, 2006 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR LOCKING (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US009277323B2 (10) Patent No.: L0cke et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2016 (54) COMPACT AUDIO SPEAKER (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA (US) U.S.
(12) United States Patent US009277323B2 (10) Patent No.: L0cke et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2016 (54) COMPACT AUDIO SPEAKER (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA (US) U.S.
conductance to references and provide outputs. Output cir
 USOO5757192A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: McShane et al. 45) Date of Patent: May 26, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 4.881,038 11/1989 Champlin. DETECTING A BAD CELL IN A STORAGE 4,912,416
USOO5757192A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: McShane et al. 45) Date of Patent: May 26, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 4.881,038 11/1989 Champlin. DETECTING A BAD CELL IN A STORAGE 4,912,416
United States Patent (19) Kitami et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kitami et al. 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,846,768 Jul. 11, 1989 (54) VARIABLE-SPEED DRIVING DEVICE 75) Inventors: Yasuo Kitami; Hidenori Tezuka; 73 Assignee: Syuji
United States Patent (19) Kitami et al. 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 4,846,768 Jul. 11, 1989 (54) VARIABLE-SPEED DRIVING DEVICE 75) Inventors: Yasuo Kitami; Hidenori Tezuka; 73 Assignee: Syuji
Kikuiri et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, (54) CAPACITIVE PRESSURE SENSOR 5, A 12, 1996 Ko /53
 (12) United States Patent USOO7382599B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,382,599 B2 Kikuiri et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, 2008 (54) CAPACITIVE PRESSURE SENSOR 5,585.311 A 12, 1996 Ko... 438/53 5,656,781 A *
(12) United States Patent USOO7382599B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,382,599 B2 Kikuiri et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 3, 2008 (54) CAPACITIVE PRESSURE SENSOR 5,585.311 A 12, 1996 Ko... 438/53 5,656,781 A *
22 Š. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1 SSSNS. (19) United States Z SN a. (43) Pub.
 (19) United States US 200801 05234A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0105234 A1 Yoshizumi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FUEL INJECTION PUMP EQUIPPED WITH ROTARY DEFLECTOR (76)
(19) United States US 200801 05234A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0105234 A1 Yoshizumi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FUEL INJECTION PUMP EQUIPPED WITH ROTARY DEFLECTOR (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040085703A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0085703 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) MULTI-PULSE HVDC SYSTEM USING AUXILARY CIRCUIT (76)
(19) United States US 20040085703A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0085703 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) MULTI-PULSE HVDC SYSTEM USING AUXILARY CIRCUIT (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070011840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0011840 A1 Gilli (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 18, 2007 (54) WINDSCREEN WIPER ARM (75) Inventor: Marco Gilli, Chieri
(19) United States US 20070011840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0011840 A1 Gilli (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 18, 2007 (54) WINDSCREEN WIPER ARM (75) Inventor: Marco Gilli, Chieri
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Glance et al. US 20040183344A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) (51) SEAT ENERGY ABSORBER Inventors: Patrick
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Glance et al. US 20040183344A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 23, 2004 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) (51) SEAT ENERGY ABSORBER Inventors: Patrick
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 201200 13216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0013216 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) CORELESS PERMANENT MAGNET MOTOR (76) Inventors:
Y-Né Š I/? S - - (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States 2S) (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 20, 2003 (54) (75)
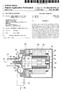 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0035740 A1 Knoll et al. US 2003.0035740A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 20, 2003 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) WET TYPE ROTOR PUMP Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0035740 A1 Knoll et al. US 2003.0035740A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 20, 2003 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) WET TYPE ROTOR PUMP Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,215,503 B2. Appel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 10, 2012
 US008215503B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,215,503 B2 Appel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 10, 2012 (54) CRANE WITH TELESCOPIC BOOM 3,921,819 A * 1 1/1975 Spain... 212,349 4,394,108
US008215503B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,215,503 B2 Appel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 10, 2012 (54) CRANE WITH TELESCOPIC BOOM 3,921,819 A * 1 1/1975 Spain... 212,349 4,394,108
United States Patent (19) Harrod et al.
 United States Patent (19) Harrod et al. 54 (75) STORAGE BATTERY WITH BUILT-N FUSE Inventors: Lawrence R. Harrod; Lucio C. Perego, both of Ft. Wayne, Ind. 73) Assignee: Pines of America, Inc., Fort Wayne,
United States Patent (19) Harrod et al. 54 (75) STORAGE BATTERY WITH BUILT-N FUSE Inventors: Lawrence R. Harrod; Lucio C. Perego, both of Ft. Wayne, Ind. 73) Assignee: Pines of America, Inc., Fort Wayne,
US 7, B2. Loughrin et al. Jan. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: and/or the driven component. (12) United States Patent (54) (75)
 USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
USOO7314416B2 (12) United States Patent Loughrin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,314.416 B2 Jan. 1, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) DRIVE SHAFT COUPLNG Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.448,812 B2
 USOO8448812B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.448,812 B2 Gruber et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 28, 2013 (54) WASTE CONTAINER WITH BASE MEMBER 3,394,832 A * 7/1968 McAllister et. al....
USOO8448812B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.448,812 B2 Gruber et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 28, 2013 (54) WASTE CONTAINER WITH BASE MEMBER 3,394,832 A * 7/1968 McAllister et. al....
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,820,200 Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
United States Patent (19) Muranishi
 United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
United States Patent (19) Muranishi (54) DEVICE OF PREVENTING REVERSE TRANSMISSION OF MOTION IN A GEAR TRAIN 75) Inventor: Kenichi Muranishi, Ena, Japan 73) Assignee: Ricoh Watch Co., Ltd., Nagoya, Japan
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,603,073 B2
 USOO6603073B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,603,073 B2 Ferris (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003 (54) SNAP TOGETHER CABLE TROUGH FR 2 365 902 4/1978 SYSTEM GB 549840 12/1942 GB 612162
USOO6603073B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,603,073 B2 Ferris (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2003 (54) SNAP TOGETHER CABLE TROUGH FR 2 365 902 4/1978 SYSTEM GB 549840 12/1942 GB 612162
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080056631A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0056631 A1 Beausoleil et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2008 (54) TUNGSTEN CARBIDE ENHANCED Publication Classification
US 20080056631A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0056631 A1 Beausoleil et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2008 (54) TUNGSTEN CARBIDE ENHANCED Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O150479A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0150479 A1 Saunders et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) POWERED GARDEN OR LAWN EDGING ASSEMBLY (75)
(19) United States US 2006O150479A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0150479 A1 Saunders et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) POWERED GARDEN OR LAWN EDGING ASSEMBLY (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011
 US 20110081573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0081573 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) RECHARGEABLE BATTERY Publication Classification (76)
US 20110081573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0081573 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 7, 2011 (54) RECHARGEABLE BATTERY Publication Classification (76)
United States Patent (19) 11) 4,324,219
 United States Patent (19) 11) 4,324,219 Hayashi 45) Apr. 13, 1982 54). SPARK INTENSIFIER IN GASOLINE 56) References Cited ENGINE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS s 703,759 7/1902 Brown... 123/169 PH 75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) 11) 4,324,219 Hayashi 45) Apr. 13, 1982 54). SPARK INTENSIFIER IN GASOLINE 56) References Cited ENGINE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS s 703,759 7/1902 Brown... 123/169 PH 75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008O141971 A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/014 1971 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 19, 2008 (54) CYLINDER HEAD AND EXHAUST SYSTEM (30) Foreign
US 2008O141971 A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/014 1971 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 19, 2008 (54) CYLINDER HEAD AND EXHAUST SYSTEM (30) Foreign
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012
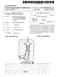 US 2012O163742A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0163742 A1 Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) AXIAL GAS THRUST BEARING FOR (30) Foreign
US 2012O163742A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0163742 A1 Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) AXIAL GAS THRUST BEARING FOR (30) Foreign
and Crew LLP Mar. 4, 1999 (DE) Int. Cl."... GO2N 11/06
 (1) United States Patent Raffer USOO64O77OB1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 5, 001 (54) ROTARY VISCOSIMETER (75) Inventor: Gerhard Raffer, Graz (AT) (73) Assignee: Anton Paar GmbH, Graz (AT)
(1) United States Patent Raffer USOO64O77OB1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 5, 001 (54) ROTARY VISCOSIMETER (75) Inventor: Gerhard Raffer, Graz (AT) (73) Assignee: Anton Paar GmbH, Graz (AT)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fujita 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,727,957 Mar. 1, 1988 (54) RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATOR FOR MUFFLER 75 Inventor: Akio Fujita, Fujisawa, Japan 73) Assignee: Bridgestone
United States Patent (19) Fujita 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,727,957 Mar. 1, 1988 (54) RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATOR FOR MUFFLER 75 Inventor: Akio Fujita, Fujisawa, Japan 73) Assignee: Bridgestone
United States Patent (19) Kim et al.
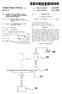 United States Patent (19) Kim et al. 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR COATING AWAFER WITH A MINIMAL LAYER OF PHOTORESIST 75 Inventors: Moon-woo Kim, Kyungki-do; Byung-joo Youn, Seoul, both of Rep. of Korea
United States Patent (19) Kim et al. 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR COATING AWAFER WITH A MINIMAL LAYER OF PHOTORESIST 75 Inventors: Moon-woo Kim, Kyungki-do; Byung-joo Youn, Seoul, both of Rep. of Korea
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O124322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0124322 A1 Cimatti (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2014 (54) NORMALLY CLOSED AUTOMOTIVE (52) U.S. Cl. CLUTCH WITH HYDRAULC
(19) United States US 2014O124322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0124322 A1 Cimatti (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2014 (54) NORMALLY CLOSED AUTOMOTIVE (52) U.S. Cl. CLUTCH WITH HYDRAULC
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
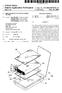 (19) United States US 2004OO38.125A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0038.125 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2004 (54) REINFORCED POUCH TYPE SECONDARY BATTERY (75) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2004OO38.125A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0038.125 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2004 (54) REINFORCED POUCH TYPE SECONDARY BATTERY (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Nishiyama et al. USOO6174618B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 16, 2001 (54) BATTERY HOLDER (75) Inventors: Koichi Nishiyama; Yoshinori Tanaka; Takehito Matsubara,
(12) United States Patent Nishiyama et al. USOO6174618B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 16, 2001 (54) BATTERY HOLDER (75) Inventors: Koichi Nishiyama; Yoshinori Tanaka; Takehito Matsubara,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O225192A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0225192 A1 Jeung (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 9, 2010 (54) PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD AND METHOD Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2010O225192A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0225192 A1 Jeung (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 9, 2010 (54) PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD AND METHOD Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2
 USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
USOO9624044B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,624,044 B2 Wright et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2017 (54) SHIPPING/STORAGE RACK FOR BUCKETS (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: CWS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O181130A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0181130 A1 Fukunaga (43) Pub. Date: Jul.19, 2012 (54) TORQUE CONVERTER Publication Classification 51) Int.
(19) United States US 2012O181130A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0181130 A1 Fukunaga (43) Pub. Date: Jul.19, 2012 (54) TORQUE CONVERTER Publication Classification 51) Int.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
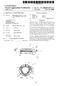 US 20080264.753A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0264753 A1 Rollion et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2008 (54) FRICTIONAL CLUTCH WITH O-RING Publication Classification
US 20080264.753A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0264753 A1 Rollion et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2008 (54) FRICTIONAL CLUTCH WITH O-RING Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,695,581 B2
 USOO6695581B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,695,581 B2 Wass0n et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 2004 (54) COMBINATION FAN-FLYWHEEL-PULLEY JP 59-81.835 2/1984 ASSEMBLY AND METHOD OF
USOO6695581B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,695,581 B2 Wass0n et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 2004 (54) COMBINATION FAN-FLYWHEEL-PULLEY JP 59-81.835 2/1984 ASSEMBLY AND METHOD OF
United States Patent (19) Hormel et al.
 United States Patent (19) Hormel et al. 54 (75) (73) 21) 22) (51) 52) (58) 56) LAMP FAILURE INDICATING CIRCUIT Inventors: Ronald F. Hormel, Mt. Clemens; Frederick O. R. Miesterfeld, Troy, both of Mich.
United States Patent (19) Hormel et al. 54 (75) (73) 21) 22) (51) 52) (58) 56) LAMP FAILURE INDICATING CIRCUIT Inventors: Ronald F. Hormel, Mt. Clemens; Frederick O. R. Miesterfeld, Troy, both of Mich.
(12) United States Patent
 USO0971 0014B2 (12) United States Patent Lee et al. (54) MOBILE TERMINAL (75) Inventors: Jang Won Lee, Seoul (KR); Chu Young Yoon, Seoul (KR) (73) Assignee: BLUEBIRD SOFT INC. (KR) (*) Notice: Subject
USO0971 0014B2 (12) United States Patent Lee et al. (54) MOBILE TERMINAL (75) Inventors: Jang Won Lee, Seoul (KR); Chu Young Yoon, Seoul (KR) (73) Assignee: BLUEBIRD SOFT INC. (KR) (*) Notice: Subject
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O240592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0240592 A1 Keny et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) COMBUSTOR WITH FUEL NOZZLE LINER HAVING CHEVRON
(19) United States US 2012O240592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0240592 A1 Keny et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2012 (54) COMBUSTOR WITH FUEL NOZZLE LINER HAVING CHEVRON
Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) J (12) Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 774 824 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: ition: (51) IntCI.6: H02K 3/52, H02K
(19) J (12) Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 774 824 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: ition: (51) IntCI.6: H02K 3/52, H02K
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 20090314114A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0314114A1 Grosberg (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 24, 2009 (54) BACKLASH ELIMINATION MECHANISM (22) Filed: Jun. 15,
US 20090314114A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0314114A1 Grosberg (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 24, 2009 (54) BACKLASH ELIMINATION MECHANISM (22) Filed: Jun. 15,
