51. absolute pressure sensor
|
|
|
- Victoria George
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
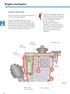
1 51. absolute pressure sensor Function The absolute pressure sensor measures the atmospheric pressure. Specifications supply voltage: 5 V output voltage sea level: V output voltage at 2000m: V WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands
2 Adjustment Data MAZDA i 8V - FE Engine (general) Item Values Units Engine code FE Capacity 1998 (cc) Idle speed (rpm) Automatic (rpm) Valve clearance Hot Inlet 0.30 (mm) Exhaust 0.30 (mm) Compression pressure Normal 13.0 (bar) Minimum 9.1 (bar) Oil pressure /1000 (bar / rpm) Fuel system (make & type) EGI Fuel system (make & type) EGI Adjustment screws (A = idle speed B = CO) Firing order Timing stroboscopic (before TDC) Start End Start End ± 1/850 0 ± 2/ /300 0 ± 2/ /5800 ( / rpm) ( / mmhg) ( / mmhg) ( / rpm) ( / rpm)
3 Ignition-coil resistance, primary (ohms) Ignition-coil resistance, secondary (ohms) Spark plugs (make & type) NGK/BPR6E-11 Spark-plug gap (mm) Fuel-pump pressure (bar) Injection pressure / system pressure (bar) CO exhaust gas < 0.5 (%) CO (%) HC 300 (ppm) O (%) Lambda Lambda change (Delta Lambda) 0.02 Oil temperature during test 60 ( C) Fast-idle speed (rpm) CO at fast-idle speed < 0.3 (%) Closed-loop test at: (rpm) (rpm) Cooling system Item Cap pressure Thermostat opens at Fan on at Values Units (bar) ( C) ( C) Belt layout Item Drawing Values Units Electrical Item Battery Alternator Values Units (Ah) (A) Brakes Item Values Units
4 Disc thickness, front, min. Drum diameter, rear, max (mm) (mm) Steering and wheel alignment Item Values Units Toe-in, front 18' ± 18' ( ) Camber, front 17' ± 45' ( ) Castor, front 1 13' ± 45' ( ) K.P.I., front 12 47' ( ) Toe-in, rear 0 ± 18' ( ) Camber, rear -30' ± 45' ( ) Wheels and tyres Item Values Units Tyre size 185/70R14 Front tyre pressure 2.0 (bar) Rear tyre pressure 2.0 (bar) Capacities Item Values Units Engine sump, incl. filter 3.8 (l) Manual transmission Gearbox refill 3.35 (l) Automatic transmission Gearbox refill (l) Cooling system 7.5 (l) Torque settings Item Cylinder head Values Units Stage (Nm) Stage (Nm) Stage (Nm) Front hub (Nm) Rear hub (Nm) Wheel nuts (Nm) Spark plugs (Nm)
5 30. airflow meter Function The airflow meter uses an air temperature sensor and a movable vane connected to a potentiometer, which return a signal to the control unit, proportional to the temperature and volume of air entering the engine. When air enters the engine, the airflow meter closes the fuel-pump contact, activating the fuel pump. Specifications supply voltage: 12 V output voltage: 0-12 V resistance air temperature sensor: 2,000-3,000 ohms / 20 C waveform information: output signal during acceleration Scope image 1 WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands Pins to ground: 2E
6 9. auxiliary valve Extra Info Function The auxiliary air valve supplies additional air to the inlet system, which increases engine rpm during a cold start. The valve consists of an electrically heated bi-metallic strip, which closes the by-pass airflow as temperature rises. Specifications supply voltage: 12 V resistance heater element: ohms WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands
7 AUXILAIRY AIR VALVE Function The auxiliary air valve supplies the engine with an addition amount of air during the warm up phase. The auxiliary air valve is located in a tube bypassing the throttle. The valve consists of an electrically heated bi-metallic strip which closes an air by-pass. The air by-pass closes as the temperature rises. The bi-metallic strip is heated up by an electrical heating element and by the engine temperature. Specifications resistance heating element supply voltage ± ohms 12 Volts Electrical control The auxiliary air valve has a connector with two terminals. One of those terminals is continuously connected with ground. The other terminal is connected with a relay switching the power to the heating element. Electrical diagnosis STATIC
8 disconnect the connector. check the if the supply voltage exists on one of the two terminals of the connector. check if continuity exists between the other terminal of the connector and ground. check the resistance of the heating element. Mechanical diagnosis Remove the auxiliary air valve without disconnecting the connector. Turn the ignition on and make sure that the valve closes as the heating element heats-up the bi-metallic strip.
9 Description Values Units Note 1/1 Engine code FE 8V MAZDA - FE 8V Compression Compression ratio 8.6 : 1 Compression pressure 11.5 bar Idle speed /min Exhaust gas emissions CO content at idle speed vol. % Thermostat opening temperature 86 * C Valve timing Intake opens 16 before TDC Intake closes 54 after BDC Outlet opens 54 before BDC Outlet closes 16 after TDC Valve clearance Condition hot Intake 0.30 mm Outlet 0.30 mm Firing order Ignition timing, static / dynamic 6 ± 1 before TDC Data from secondary source; No manufacturer's information Copyright, Wessels + Mьller AG
10 2. canister purge solenoid Extra Info Function The evaporative canister is equipped with a purge solenoid valve. The control unit switches the solenoid on or off. This controls the amount of vapour purged into the inlet manifold. Specifications supply voltage: 12 V resistance: ohms Diagnosis Check connector(s): Inspect the connector(s) and if necessary clean or fix them to make sure the connection is good. Check resistance: Turn ignition off. Remove connector from solenoid. Measure resistance between the two pins of the solenoid. Compare with specified resistance. Alternatively, check solenoid function by applying battery voltage to its pins. The solenoid should "click". Check supply voltage: Turn ignition off. Remove connector from solenoid. Start the engine and measure voltage between one connector terminal and the negative terminal of the battery. Check the second terminal. One of the two should equal battery voltage. If not check wiring and, if present, fuse(s) and relay. Check connection to ECU: Turn ignition off. Remove connector from solenoid and ECU. Measure the resistance between one of the two connector terminals and the corresponding terminal in the ECU connector. Check the other terminal. One of the two should be < 1 ohm. If not check wiring. WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands
11 CANISTER PURGE SOLENOID Function The evaporative gases produced in the fuel tank are absorbed by the activated charcoal in the carbon canister. As The purge control solenoid valve opens these gases are delivered to the intake manifold for combustion purposes. The purge control solenoid valve is controlled by the control unit. The control unit operates this valve during the time the lambda control loop is active. Specifications RESISTANCE: resistance: supply voltage: current: ± 50 ohms 12 Volts ± 250 ma Electrical control Most solenoids are normally closed. This means that the connection between the canister and the intake manifold is closed. The solenoid has a connector with two terminals. On one of those terminals is connected to the battery voltage. This supply-voltage is often switched with a relay. The other terminal leads directly to the control unit. The current through the solenoid is switched on during the time the control unit connects this terminal to ground. The voltage on this terminal is during this time 0 Volts. During the time the solenoid is switched off, the voltage on this terminal is 12 Volts. Some motormanagement systems control the amount gases delivered to the intake manifold switching the solenoid on and of with a certain duty cycle. In this case the duty-cycle depends on engine RPM and engine load. Electrical diagnosis STATIC
12 General To perform this measurements the relay switching the power to the solenoid should be closed. Short circuit the switch in the relay if necessary. Measurements Measure the voltage on the control unit. Use the pin which switches the solenoid. result: 12 V solenoid and wiring are electrically OK 0 V check the relay switching the power to the solenoid check the wiring between the relay and the solenoid check the solenoid resistance check the wiring between the solenoid and the control unit check the control unit
13 Capacities MAZDA i 8V - FE Item Engine sump, incl. filter Manual transmission Gearbox refill Automatic transmission Gearbox refill Cooling system Values Units (l) (l) (l) (l) Copyright, Wessels + Mьller AG
14 100. control unit Function The control unit receives signals from sensors that monitor various engine operating parameters. The control unit generates output signals to provide optimal air/fuel ratio and idle speed control. Diagnosis Check connector(s): Inspect the connector(s) and if necessary clean or fix them to make sure the connection is good. When you suspect the control unit is faulty, make sure all sensors and actuators function properly, and that signals from other control unit(s) are received properly. Next check the supply voltage and ground connections of the control unit: Turn ignition off. Remove ECU connector. Locate the supply voltage connections. Turn ignition on. Measure voltage between corresponding connector terminal(s) and the negative terminal of the battery. They should equal battery voltage. If not check wiring and fuse. Turn ignition off. Locate the ground connections. Measure resistance between corresponding connector terminal(s) and the negative terminal of the battery. They should be < 1 ohm. WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands
15 42. coolant temperature sensor Function The coolant temperature sensor is a temperature-sensitive resistor. Low temperature causes high resistance while high temperature causes low resistance. The control unit determines the temperature by monitoring the voltage across the sensor. Specifications supply voltage: 5 V (connector disconnected) resistance: 2,000-3,000 ohms / 20 C resistance: ohms / 90 C Diagnosis Check connector(s): Inspect the connector(s) and if necessary clean or fix them to make sure the connection is good. Check resistance: Turn ignition off. Remove connector from sensor. Measure resistance between both pins of the sensor. Compare with specified resistance. Check supply voltage: Turn ignition off. Remove connector from sensor. Turn ignition on and measure voltage between both connector terminals and the negative terminal of the battery. One should be 5 V. If not check wiring then check ECU. Check connection to ECU: Turn ignition off. Remove connectors from sensor and ECU. Measure the resistance between supply voltage connector terminal and the corresponding terminal in the ECU connector. It should be < 1 ohm. If not check wiring. Check ground: Check in schematic if ground connection is connected to a direct ground or to the ECU. When it is connected directly to ground: Turn ignition off. Remove connector from sensor and measure resistance between ground connector terminal and the negative terminal of the battery. It should be < 1 ohm. If not check wiring. When it is connected to the ECU: Turn ignition off. Remove connector from sensor and ECU. Measure resistance between ground connector terminal and the corresponding terminal in the ECU connector. It should be < 1 ohm. If not check wiring. WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands
16 190. coolant temperature switch Function The coolant temperature switch returns a signal to the control unit at temperatures above 17 C. Specifications the temperature switch closes at 17 C. WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands
17 83. diagnostic connector Function This connector is used to communicate with the control unit. WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands
18 Environmental Data MAZDA i 8V - FE Item Values Engine code FE Idle speed Automatic Fuel system (make & type) EGI Fuel system (make & type) EGI Adjustment screws (A = idle speed B = CO) Units (rpm) (rpm) Timing stroboscopic (before TDC) 6 ± 1/850 ( / rpm) Start 0 ± 2/125 ( / mmhg) End 18-22/300 ( / mmhg) Start 0 ± 2/1000 ( / rpm) End 16-20/5800 ( / rpm) Fuel-pump pressure (bar) Injection pressure / system pressure (bar) CO exhaust gas < 0.5 (%) CO (%) HC 300 (ppm) O (%) Lambda Lambda change (Delta Lambda) 0.02 Oil temperature during test 60 ( C) Fast-idle speed (rpm) CO at fast-idle speed < 0.3 (%)
19 Closed-loop test at: (rpm) (rpm) Copyright, Wessels + Mьller AG
20 Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug (green, 6-pin): 1 = Datalink LED tester (green/black wire) 2 = positive battery terminal (+B, red/brown wire) Diagnostic plug (green, 1-pin): 3 = activation error codes Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery terminal (+B) and diagnostic-plug terminal 1. -Connect terminal 3 (diagnostic plug, green, 1-pin) to ground. -Turn ignition on. -LED will light for 3 to 5 seconds. -Error codes will appear on LED tester. Reset -Turn ignition off. -Disconnect negative terminal of the battery. -Depress brake pedal for at least 2 seconds. -Connect negative terminal of the battery. -Turn ignition on and wait at least 6 seconds. -Start and warm up the engine. Let the engine run for 3 minutes at rpm. -Verify that no error codes are displayed. Signal -Digit 1 (tens position): Light pulse 1.2 seconds long, 0.4 seconds pause in-between. -Pause 1.6 seconds light-off. -Digit 2 (units position): Light pulse 0.4 seconds long, 0.4 seconds pause in-between. -Pause 4.0 seconds light-off. Error codes 01 Ignition pulse no signal. 08 Airflow meter, open or short circuit. 09 Coolant temperature sensor, open or short circuit. 10 Air temperature sensor, open or short circuit. 12 Throttle position sensor, open or short circuit. 14 Absolute pressure sensor (inside ECU), open or short circuit. 15 Oxygen sensor, lean signal for longer than 120 seconds, engine speed is higher than 1500 rpm, warm engine. 17 Oxygen sensor signal does not change for 20 seconds, engine speed is higher than 1500 rpm. 25 Increased fuel pressure solenoid, open or short circuit. 26 Canister purge solenoid, open or short circuit. 28 EGR purge solenoid. 34 Idle speed control solenoid (C) open or short circuit. 35 Idle speed control solenoid (B) open or short circuit. WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands
21 ID Location MAZDA i 8V - FE 1/1 1 Identification plate 2 VIN 3 Engine code B3 / B5 / B6 / PN 4 Engine code BP / FP / FS 5 Engine code 6-cylinder 6 Manual transmission code Copyright, Wessels + Mьller AG
22 6. idle speed control valve Extra Info Function The idle speed control valve regulates the by-pass airflow. Specifications supply voltage: 12 V resistance coil with red wires: ohms resistance coil with blue wires: ohms resistance coil with yellow wires: ohms WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands
23 IDLE SPEED CONTROL VALVE Function The idle control valve is located in a tube bypassing the throttle. The control unit controls this device to ensure stable idling in all operating conditions. Specifications resistance coil(s): supply voltage: ± 20 ohms 12 Volts A rotary slide valve attached to the armature is turned to open the air bypass until the desired idle speed is obtained. The position of the armature is controlled by the force of an internal spring opposing the force of a solenoid (types with to terminals) or controlled by two solenoids energised alternately which exerts opposing forces on the armature (types with three terminals). Electrical control Types with two terminals As a current flows through the coil the armature is turned against the spring force. As the current increases the airflow and the idle speed increases. If the current through the coil is switched off due to a mall functioning system, the valve is forced into a position which results in a (too) high idle speed. The idle control valve has a connector with two terminals. On one of those terminals is connected to the battery voltage. This supply-voltage is often switched with a relay. The other terminal leads directly to the control unit. The current through the coil is switched on during the time the control unit connects this terminal to ground. The voltage on this terminal is during this time 0 Volts. During the time the current through the coil is switched off, the voltage on this terminal is 12 Volts.
24 The control unit controls the current through the coil switching the current on and off with a certain duty cycle. The current increases as the duty-cycle increases. The duty cycle varies between approx. 35% (valve closed) and 85% (valve opened). Nominal idle speed is obtained when slightly open. Three terminal types The two coils inside this type of idle speed control valve are connected with the supply voltage using one common terminal. The other two terminals lead directly to the control unit. The control unit switches the current through the solenoid on and off alternately with a duty cycle between 35 and 85%. Electrical diagnosis STATIC DYNAMIC TESTS THREE TERMINAL TYPES To perform this measurements the relay switching the power to the idle control valve should be closed. Short circuit the switch in the relay if necessary. Measurements: Remove the idle control valve but leave the electrical connections in place. Fully open or close the rotating plunger. Switch on the ignition. Disconnect the connector and
25 measure the resistance of the coil(s). The nominal value is app. 20 ohms. Check the relay switching the power result: Switch on the ignition. The to the idle control valve rotating plunger must move Check the wiring between the relay to a position equivalent to and the idle control valve app. 50% opening, and Check the wiring between the idle control valve and the control unit Check the control unit remain there. Mechanical diagnosis Check the air chamber on air leakage. Check engine on air leaks into the intake system. Remove the idle control valve. The plunger should rotate or move easily. Clean if necessary.
26 11. ignition coil Extra Info Function The ignition coil stores energy when current is passed through the coil primary. When the current is switched off a high voltage is induced in the coil secondary. Specifications supply voltage: 12 V resistance primary coil: ohms resistance secondary coil: 7,000-10,000 ohms waveform information: engine running at idle Scope image 1 Diagnosis Check connector(s): Inspect the connector(s) and if necessary clean or fix them to make sure the connection is good. Check resistance primary coil: Turn ignition off. Remove connectors from ignition coil. Measure resistance between supply voltage connector pin and primary switching connector pin of the ignition coil. Compare with specified resistance. Check resistance secondary coil: Turn ignition off. Remove connectors from ignition coil. Measure resistance between central lead terminal and primary switching connector pin. Compare with specified resistance. Check supply voltage: Turn ignition off. Remove connectors from ignition coil. Turn ignition on and measure voltage between supply voltage connector terminal and the negative terminal of the battery. It should equal battery voltage. If not check wiring and, if present, fuse(s) and relay. Check connection to ignition module: Turn ignition off. Remove connector from ignition coil and ignition module. Turn ignition on and measure resistance between primary switching connector terminal and corresponding terminal in ignition module connector. It should be < 1 ohm. If not check wiring. Check ignition signal: Connect oscilloscope to the ignition module pin corresponding to the primary switching wire of the ignition coil and ground. Start the engine and compare to the scope image shown.
27 IGNITION COIL Function The ignition coil transforms the battery voltage into the high voltage needed to create a spark. The ignition coil consists of an electromagnet (the primary coil) and a high voltage coil (secondary coil). By switching the current through the primary coil on, a magnetic field is induced. The moment the current is switched of, the magnetic field suddenly disappears. This change of magnetic field creates an induction voltage in the secondary coil, high enough to ionise the mixture. The ionised mixture is a conductor and a current flows through the spark plug. Specifications RESISTANCE: primary: secondary supply voltage: current limited at: ± 0,3-2 ohms ± 5k - 20k ohms 12 V ± 7A Systems with a distributor Ignition coils used in combination with a distributor consists of one primary and one secondary coil. The high voltage, induced in the secondary coil is connected to one of the spark plugs selected by the distributor.
28 Wasted spark ignition coils The secondary coil has two ends. In a normal ignition coil one of those ends delivers the high The other end is connected to either the positive (15) or the negative (1) terminal of the prim In a wasted spark ignition coil both ends are connected to a spark plug. Therefore both spark will spark at the same time. wasted spark ignition coil on 2- cylinder 4-stroke engine a wasted spark ignition coil on a 4- cylinder 4-str To supply the four spark plugs of an 4 cylinder engine, two ignition coils are needed. The pict below (left) shows an ignition coil for two spark plugs. The ignition coil in the right picture incorporates two of those. This ignition coil supplies four spark plugs. Sequential ignition Sequential ignition systems are distributor less ignition systems using one ignition coil per cylinder. Each ignition coil is controlled by the control unit individually.
29 Electrical control A current through the primary coil induces a magnetic field. The moment the current is switched of, the magnetic field suddenly disappears. This change of magnetic field induces an induction voltage and causes a spark. The amperage before switching the current off should be high enough to create a high change of magnetic field the moment the current is switched off. Therefore the current through the primary coil is controlled electronically. The ignition module is supplied with a current limited circuit. Using this in combination with a low resistance ignition coil the amperage does not depend on the battery voltage. During the time the current is switched off, the voltage over the ignition module is 12 Volts. The moment the current is switched on, the voltage drops to 0 Volts. From this moment on the current increases until the limiting value is reached. The oscilloscope images A and B gives you an example of the primary voltage measured on two different current limiting circuits. By increasing the voltage over the ignition module, the voltage over the primary coil decreases. This causes a limited current in oscilloscope image A. The ignition module in oscilloscope image B switches the current on and off to limit the current.
30 Electrical diagnosis STATIC DYNAMIC To perform this measurements the ignition should be switched on. Measurements: Start the engine and measure the primary voltage using an oscilloscope. Measure the primary and secondary resistance of the ignition coil. Measure the voltage on the positive terminal of the ignition module. The voltage should be equal to the battery voltage. result: Voltage is lower than battery result: 0 V voltage. disconnect positive terminal and repeat measurement 12 V check power supply. result: Voltage is equal to battery voltage. check ignition module result check primary resistance of the ignition coil check ignition module check wiring between ignition module and ignition module. Voltage is still lower than battery voltage. check ignition lock check wiring between ignition lock and ignition coil Mechanical diagnosis Not available for this subject!
31 10. ignition module Extra Info Function The ignition module receives its input signal from the magnetic pickup sensor and switches the current through the coil primary circuit on and off. Specifications supply voltage: 12 V WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands
32 IGNITION MODULE Function The ignition module switches the current through the primary ignition coil on and off. The ignition module charges the ignition coil during the time the current is switched on. The moment the ignition module switches the current 'off' the ignition coil induces an induction voltage which causes the spark. An ignition module switches the current on and off according to an input signal. This input is delivered by the control unit. On older systems the input signal is delivered by an inductive, Hall or opto-coupled sensor mounted in the distributor. Specifications resistance supply voltage - - Electrical control The connector of the ignition module has several terminals. The following terminals are used on common ignition modules. a terminal connected with the ignition coil. By this terminal the current through the ignition coil is switched on and of. a terminal connected with the supply voltage ( 12 Volts) a terminal connected with ground. terminal(s) to receive the input signal. If the input signal is delivered by an inductive sensor two terminals are needed. The output voltage of an inductive sensor is delivered by an internal coil. This coil induces an almost sine wave output voltage. If the input signal is delivered by an Hall-sensor or opto-coupler three terminals are needed. Two of those three terminals are used to supply the sensor. The supply voltage is either 5 or 12 Volts. The third terminal receives the output signal from the sensor. The output voltage of these sensors is a square wave signal.
33 Addition terminals are possible. For example to send out a RPM signal to the revolution counter. Sometimes the input signal is delivered by a sensor while the ignition timing is controlled by the control unit. In this case the received input signal from the sensor is converted into a square wave signal by the ignition module and send out to the control unit. The control unit receiving this signal computes this input information and other input information from various engine parameters and sends out a new square wave signal to the ignition module. This signal is used by the ignition module to switch the current through the primary ignition coil on and off. During the time the input signal for the ignition module is 'high' the current is switched 'on'. The moments this input signals falls to 'low' the current is switched 'off'. This moment the spark will appear Electrical diagnosis Start the engine and measure (using an oscilloscope) the input signal delivered by the control unit or input sensor. The square wave signal or sine wave signal from a inductive sensor should be visible. signal not OK: Disconnect the ignition module's connector and check the wiring between the ignition module and the control unit or input sensor. replace the ignition module if the signal appears on the disconnected connector and disappears on the connected connector. If the output signal remains invisible the failure is not in the component. signal OK: check the power supply of the ignition module. check the primary voltage using an ignition oscilloscope or normal oscilloscope with a suitable probe. check the wiring between the ignition module and the ignition coil. The voltage should be nearly 0 Volt during the period the ignition module receives an 'high' input voltage from the sensor or control unit. Mechanical diagnosis Remove the auxiliary air valve without disconnecting the connector. Turn the ignition on and make sure that the valve closes as the heating element heats-up the bi-metallic strip.
34 167. increased fuel pressure solenoid Function The vacuum solenoid (P.R.C.) regulates the connection between the fuel pressure regulator and the inlet manifold vacuum. The vacuum solenoid is activated by the control unit at air temperatures above 20 C, at engine speeds below 1500 rpm, and with the idle switch closed. Specifications supply voltage: 12 V resistance: ohms WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands
35 1. injector Extra Info Function A fuel injector is an electrically operated solenoid valve which is powered by the control unit. The fuel injector injects fuel into the inlet manifold. Specifications supply voltage: 12 V resistance: ohms waveform information: engine running at idle Scope image 1 Pins to ground: 3C, 3E Diagnosis Check connector(s): Inspect the connector(s) and if necessary clean or fix them to make sure the connection is good. Check resistance: Turn ignition off. Remove connector(s) from injector(s). Measure resistance between the two pins of the injector. Compare with specified resistance. Check supply voltage: Turn ignition off. Remove connector(s) from injector(s). Crank the engine and measure voltage between one connector terminal and the negative terminal of the battery. Check the second terminal, one of the two should equal battery voltage. If not check wiring and, if present, fuse(s) and relay or power supply control unit. Check connection to ECU: Turn ignition off. Remove connector(s) from injector(s) and ECU. Measure the resistance between one of the two connector terminals and the corresponding terminal in the ECU connector. Check the other terminal. One of the two should be < 1 ohm. If not check wiring. Check injector activation: Connect oscilloscope to one of the signal wire pin(s) of the ECU and ground. Start or crank the engine and compare to the scope image shown. WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands
36 INJECTOR Function Injectors are electronically operated electromagnetic valves. Using the injectors the control unit is able to inject an exact quantity of fuel. Adding this quantity of fuel to the air, a mixture with the demanded air/fuel ratio is created. Depending on the kind of motormanagement system either one injector per cylinder (multipoint systems) or one injector for all cylinders (singlepoint systems) are used. Specifications RESISTANCE: high impedance: low impedance: flow: gr/minsupply voltage: current: ± 15 ohms ± 0,5-2,5 ohm ± Volts ± 0,75Amps Single-point systems Single-point fuel injection systems use one central placed injector to create the required air/fuel ratio. The injector is mounted in the throttle-body and injects the fuel on top of the throttle. The fuel is delivered by a fuel pump and kept at a constant level by the fuel pressure regulator mounted on the throttle body. The fuel pressure on single-point systems is usually between 0,6 and 1,2 bars. Multipoint systems Multipoint fuel injection systems use one injector for each cylinder. The injectors are mounted in the intake manifold. The fuel is injected in the direction of the inlet valves. The fuel is delivered by a fuel pump. The pressure difference between the air pressure in the intake manifold and the fuel pressure is kept at a constant level by the fuel pressure regulator. Therefore the fuel pressure regulator increases the fuel pressure as the intake manifold pressure increases. The fuel pressure on multipoint systems is usually between 2 and 3 bars. The fuel pressure regulator is mounted on the fuel rail. Sequential fuel injection Sequential fuel injection is a method used by multipoint systems to control the air/fuel ratio and the injection timing per cylinder. Each injector of a sequential injection system is controlled by the control unit individually.. Bottom- and top-feed injectors The injector fuel inlet can be at the
37 top or at the bottom. Bottom-feed injectors are often used on singlepoint injection systems while top-feed injectors more often are used as multipoint injectors. Electrical control The electrical behaviour of an injector is determined by the coil inside. As a current flows through the coil the injector needle is pulled up against the spring force which courses the fuel to be injected. Two types of injector coils are used. The resistance of a normal coil is approximate 15 ohms. Other injection systems use low resistance coils (approximate 1-2,5 ohms). Low impedance injector can be switched on in two different ways: using an extra external resistance to limit the current using a current limiting circuit inside the control unit. An injector has an electrical connector with two pins. On one of those pins is connected with the battery voltage. This supply-voltage is often switched to the injector using a relay. The other pin leads directly to the control unit. The current through the injector is switched on during the period the control unit connects this pin to ground. The voltage on this pin is during this time 0 Volts. During the period the injector is not switched on, the voltage on the pin is 12 Volts Oscilloscope image A shows the voltage signal measured on an high impedance injector or low impedance injector with external resistance.
38 Oscilloscope images B and C show two different current limiting circuits used on low impedance injectors. Electrical diagnosis STATIC DYNAMIC To perform this measurements the relay switching the power to the injector(s) should be closed. Short circuit the switch in the relay if necessary. Perform the tests on one injector at the time. Disconnect parallel switched injectors. Connect all injectors. Start the engine and measure using an oscilloscope the voltage on the control unit's pin switching the injector current. Measurements Measure the voltage on the control unit. Use the pin which switches the injector current. result: 12 V result: 0 V 0 V injector and wiring are electrically OK check the relay switching the power to the injector(s) check the wiring between the relay and the injector check the injector resistance check the wiring between the injector and the control unit check the control unit 12 V perform static tests. control unit does not switch the injector(s). Mechanical diagnosis check fuel system pressure check injectors on leakage and pollution bottom-feed injectors: check the seal between the injector and the throttle body multipoint systems: disconnect the hose between the fuel pressure regulator and the intake manifold. No fuel should leak out of the fuel pressure regulator.
39 Lubricants and Fluids MAZDA i 8V - FE 1/1 Engine Motor oil API SG Below 0 C SAE 5W-30 Motor oil API SG Above -25 C SAE 10W-30 Cooling system Coolant All temperatures Manual transmission Gear oil API GL-4 All temperatures SAE 75W-90 Gear oil API GL-5 All temperatures SAE 75W-90 Gear oil API GL-4 Above 5 C SAE 80W-90 Gear oil API GL-5 Above 5 C SAE 80W-90 Automatic transmission ATF Dexron II ATF M-III All temperatures All temperatures Transfer box Gear oil API GL-5 Above -20 C SAE 90 Gear oil API GL-5 Below -20 C SAE 80W Differential, rear (4x4) Gear oil API GL-5 Above -20 C SAE 90 Gear oil API GL-5 Below -20 C SAE 80W Power steering ATF Dexron II ATF M-III All temperatures All temperatures Brakes system Brake fluid DOT 3 All temperatures Copyright, Wessels + Mьller AG
40 37. oxygen sensor Function The oxygen sensor is exposed to exhaust gas flow. It monitors the oxygen content of the exhaust gases. A low oxygen content (rich mixture) increases the output voltage of the sensor. In this way a constantly updated air/fuel ratio is returned to the control unit. Specifications output voltage: mv waveform information: hot engine running at idle Scope image 1 WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands Pins to ground: 2D
41 47. power-steering pressure switch Function The power-steering pressure switch detects reduced pressure in the steering circuit and returns a signal to the control unit, which increases the idle speed. Specifications switch is normally open WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands
42 Timing MAZDA i 8V - FE General Item Always check the timing marks before timing belt removal Note Before disconnecting the battery cable, check the audio system security code Removal Item Disconnect the battery Disconnect the spark-plug leads Remove the spark plugs Remove the lower cover Note Remove the ancillary drive belt Remove the crankshaft pulley
43 Remove the timing-belt covers Remove the guide plates Align the timing marks
44 Loosen the tensioner Push the tensioner pulley away from the timing belt Tighten the tensioner Remove the timing belt Installation Item Check the timing marks Note
45 Fit the timing belt Turn the engine 2 rotations by hand Check the timing marks Loosen the tensioner Tighten the tensioner Turn the engine 2 rotations by hand Check the timing marks again Measure the timing belt deflection Nm 98 N The tension is set at a deflection of: Refit the timing belt guide plates mm
46 Refit the timing belt covers Refit the crankshaft pulley Fit the ancillary drive belt Refit the engine lower covers
47 Refit the spark plugs Refit the spark plug leads Reconnect the battery earth cable Torque settings Item Tensioner Crankshaft pulley: Spark plugs: Note Nm Nm Nm Special tools Item Special tools are not required Note Copyright, Wessels + Mьller AG
48 34. throttle position sensor with idle switch Function The throttle position sensor measures the angle of the throttle shaft using a potentiometer. The idle switch in the position sensor is closed when the throttle is fully closed. Specifications supply voltage: 5 V output voltage: 0-5 V waveform information: output signal while opening throttle. Scope image 1 WorkshopCD Electude NL, The Netherlands Pins to ground: 2G
Error codes Diagnostic plug Read-out Reset Signal Error codes
 Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
Error codes Diagnostic plug Diagnostic plug: 1 = Datalink LED tester (FEN) 3 = activation error codes (TEN) 4 = positive battery terminal (+B) 5 = ground Read-out -Connect LED tester to positive battery
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO
 E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
E - THEORY/OPERATION - TURBO 1995 Volvo 850 1995 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo - Theory & Operation 850 - Turbo INTRODUCTION This article covers basic description and operation of engine performance-related
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL FU(H4DOTC)-29
 W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 29 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT
 FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 Electronic Fuel Injection JEEP MULTI-POINT 4.0L Cherokee, Comanche, Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The Multi-Point Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - MULTI-POINT 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 Electronic Fuel Injection JEEP MULTI-POINT 4.0L Cherokee, Comanche, Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The Multi-Point Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G9>
 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) 13C-1 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL................................. 2 Outline of Changes............................ 2 GENERAL INFORMATION...................
4.0L CEC SYSTEM Jeep Cherokee DESCRIPTION OPERATION FUEL CONTROL DATA SENSORS & SWITCHES
 4.0L CEC SYSTEM 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 COMPUTERIZED ENGINE Controls ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM JEEP 4.0L MPFI 6-CYLINDER Cherokee, Comanche & Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The 4.0L engine control system controls engine
4.0L CEC SYSTEM 1988 Jeep Cherokee 1988 COMPUTERIZED ENGINE Controls ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM JEEP 4.0L MPFI 6-CYLINDER Cherokee, Comanche & Wagoneer DESCRIPTION The 4.0L engine control system controls engine
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM........ 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATION............... 3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.................. 3 Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment... 3 ACCELERATOR
17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM........ 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATION............... 3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.................. 3 Accelerator Cable Check and Adjustment... 3 ACCELERATOR
13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) FUEL SUPPLY... 13B
 13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI)... 13A FUEL SUPPLY... 13B 13A-2 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 6 SEALANT... 6 SPECIAL TOOLS...
13A-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI)... 13A FUEL SUPPLY... 13B 13A-2 MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION... 3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 6 SEALANT... 6 SPECIAL TOOLS...
5. Control System CONTROL SYSTEM FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL. FU(STi)-27
 W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
W1860BE.book Page 27 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 5. Control System A: GENERAL The ECM receives signals from various sensors, switches, and other control modules. Using these signals, it determines
There are predominantly two reasons for excessive fuelling: increased fuel pressure and extended injector duration. Figure 1.0
 In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
In this tutorial we look at the actuators and components that affect the vehicles exhaust emissions when the electronically controlled fuel injection system is found to be over fuelling. There are predominantly
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L
 G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection
 4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Contents Accelerator cable - removal and..................... 11 Air cleaner element - renewal..............................
4D 1 Chapter 4 Part D: Fuel and exhaust systems - Magneti Marelli injection Contents Accelerator cable - removal and..................... 11 Air cleaner element - renewal..............................
Technical Note 3676A CB1N
 Technical Note 3676A CB1N Basic manual: Workshop Repair Manual 345 and Technical Note 3286A Features of Renault Clio Sport SPL lighter version (see manufacturer's plate) For parts not dealt with in this
Technical Note 3676A CB1N Basic manual: Workshop Repair Manual 345 and Technical Note 3286A Features of Renault Clio Sport SPL lighter version (see manufacturer's plate) For parts not dealt with in this
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) <2.4L ENGINE>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI) CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION 13B-2 CONTROL UNIT 13B-5 SENSOR 13B-7 ACTUATOR 13B-24 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL 13B-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR
Fuel Metering System Component Description
 1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
1999 Chevrolet/Geo Tahoe - 4WD Fuel Metering System Component Description Purpose The function of the fuel metering system is to deliver the correct amount of fuel to the engine under all operating conditions.
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4DOTC SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Lotus Service Notes Section EMR
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMR Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMR.1 3 Component Function EMR.2 7 Component Location EMR.3 9 Diagnostic Guide EMR.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMR Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMR.1 3 Component Function EMR.2 7 Component Location EMR.3 9 Diagnostic Guide EMR.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE. 1. Description 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES
 12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
12 TERCEL NEW FEATURES NEW FEATURES 3E E ENGINE 1. Description The 3E E engine is based on the 1.5 liter, 12 valve, OHC 3E engine, but with fuel injection, ignition timing and other engine functions controlled
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL........... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION....... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.......... 17-3 ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL........... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION....... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE.......... 17-3 ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK
FUEL 13-1 CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)... 2 GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 3 SEALANT... 3 SPECIAL TOOLS...
 13-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)....... 2 GENERAL INFORMATION................ 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS.............. 3 SEALANT............................... 3 SPECIAL TOOLS........................
13-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)....... 2 GENERAL INFORMATION................ 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS.............. 3 SEALANT............................... 3 SPECIAL TOOLS........................
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H6DO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
Internal Combustion Engines
 Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Internal Combustion Engines The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the burning of a fuel occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an
Lotus Service Notes Section EMD
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMD Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMD.1 3 Component Function EMD.2 8 Component Location EMD.3 10 Diagnostic Guide EMD.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMD Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMD.1 3 Component Function EMD.2 8 Component Location EMD.3 10 Diagnostic Guide EMD.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM... 2 GENERAL... 2 Outline of Changes... 2 GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATION... 2 VACUUM HOSE... 3 Vacuum Hose Piping Diagram...
17-1 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM... 2 GENERAL... 2 Outline of Changes... 2 GENERAL INFORMATION... 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATION... 2 VACUUM HOSE... 3 Vacuum Hose Piping Diagram...
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (continued) SAE Defined Codes
 78 SAE Defined Codes P01XX Fuel and Air Metering P0100 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Problem P0101 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Range or Performance Problem P0102 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Low
78 SAE Defined Codes P01XX Fuel and Air Metering P0100 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Problem P0101 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Range or Performance Problem P0102 Mass or Volume Airflow Circuit Low
Honda Accord/Prelude
 Honda Accord/Prelude 1984-1995 In Tank Fuel Pumps TEST 1. Turn the ignition OFF. 2. On the Accord, remove the screws securing the underdash fuse box to its mount. Remove the fuel cut off relay from the
Honda Accord/Prelude 1984-1995 In Tank Fuel Pumps TEST 1. Turn the ignition OFF. 2. On the Accord, remove the screws securing the underdash fuse box to its mount. Remove the fuel cut off relay from the
Motronic September 1998
 The Motronic 1.8 engine management system was introduced with the 1992 Volvo 960. The primary difference between this Motronic system and the previous generation of Volvo LH-Jetronic engine management
The Motronic 1.8 engine management system was introduced with the 1992 Volvo 960. The primary difference between this Motronic system and the previous generation of Volvo LH-Jetronic engine management
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO
 EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
EMISSION CONTROL (AUX. EMISSION CONTROL DEVICES) H4SO SYSTEM OVERVIEW 1. System Overview There are three emission control systems, which are as follows: Crankcase emission control system Exhaust emission
DESCRIPTION Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20. Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI
 Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI DESCRIPTION 1989 Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20 The throttle body fuel injection system consists of 7 major sub-assemblies: fuel supply system, throttle body
Service Manual: FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM - TBI DESCRIPTION 1989 Chevrolet Chevy Van 5.7L Eng G20 The throttle body fuel injection system consists of 7 major sub-assemblies: fuel supply system, throttle body
Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition
 Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
Page 1 of 16 Audi A4 Current Flow Diagram No. 44 / 1 Edition 05.2003 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (110 kw - Motronic - 4 cylinder), engine code AVJ from model year 2002 1.8 l - Fuel injection engine (120
1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE TOYOTA SYSTEM & COMPONENT TESTING
 1 of 65 12/5/2014 1:13 PM 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE TOYOTA SYSTEM & COMPONENT TESTING INTRODUCTION Before testing separate components or systems, perform procedures in articles listed below: BASIC TESTING
1 of 65 12/5/2014 1:13 PM 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE TOYOTA SYSTEM & COMPONENT TESTING INTRODUCTION Before testing separate components or systems, perform procedures in articles listed below: BASIC TESTING
3. At sea level, the atmosphere exerts psi of pressure on everything.
 41 Chapter Gasoline Injection Fundamentals Name Instructor Date Score Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to explain the construction, operation, and classifications of modern gasoline
41 Chapter Gasoline Injection Fundamentals Name Instructor Date Score Objective: After studying this chapter, you will be able to explain the construction, operation, and classifications of modern gasoline
FUEL 13-1 CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)... 2 FUEL SUPPLY ON-VEHICLE SERVICE GENERAL SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS... 4 SEALANT...
 13-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)....... 2 GENERAL............................... 2 Outline of Change......................... 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS.............. 4 SEALANT...............................
13-1 FUEL CONTENTS MULTIPOINT INJECTION (MPI)....... 2 GENERAL............................... 2 Outline of Change......................... 2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS.............. 4 SEALANT...............................
2002 Buick Rendezvous - AWD
 2002 Buick Rendezvous - AWD DTC P0410 Description The control module activates the secondary air injection (AIR) system by grounding both the pump relay and the vacuum control solenoid control circuits.
2002 Buick Rendezvous - AWD DTC P0410 Description The control module activates the secondary air injection (AIR) system by grounding both the pump relay and the vacuum control solenoid control circuits.
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM. 1. General ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE
 ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE 69 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 3VZ FE engine has the same basic construction and operation as for the 2VZ FE engine. However, the sequential
ENGINE 3VZ FE ENGINE 69 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General The engine control system for the 3VZ FE engine has the same basic construction and operation as for the 2VZ FE engine. However, the sequential
5. Engine Control Module (ECM) I/O Signal
 5. A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION B134 B135 B136 B137 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 35 34 33 32 31
5. A: ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION B134 B135 B136 B137 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 35 34 33 32 31
MULTIPORT FUEL SYSTEM (MFI)
 13A-1 GROUP 13A CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION...13A-2 CONTROL UNIT...13A-7 SENSOR...13A-9 ACTUATOR...13A-26 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL...13A-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME...13A-36
13A-1 GROUP 13A CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION...13A-2 CONTROL UNIT...13A-7 SENSOR...13A-9 ACTUATOR...13A-26 FUEL INJECTION CONTROL...13A-31 IGNITION TIMING AND CONTROL FOR CURRENT CARRYING TIME...13A-36
Test and adjustment values. DTC memory DTC text Possible cause/note Remedy
 AD07.51-P-4000A Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) diagnosis, DTC memory 27.2.97 ENGINE 111 a b c d e a b c a b c d Check and adjust engine Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) - diagnosis,
AD07.51-P-4000A Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) diagnosis, DTC memory 27.2.97 ENGINE 111 a b c d e a b c a b c d Check and adjust engine Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) - diagnosis,
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 -1 ENGINE CONTROL.......... GENERAL INFORMATION...... SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... ON-VEHICLE SERVICE......... ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK AND ADJUSTMENT.................... ACCELERATOR CABLE AND PEDAL......................
-1 ENGINE CONTROL.......... GENERAL INFORMATION...... SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... ON-VEHICLE SERVICE......... ACCELERATOR CABLE CHECK AND ADJUSTMENT.................... ACCELERATOR CABLE AND PEDAL......................
Lotus Service Notes Section EMQ
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SECTION EMQ Lotus Techcentre Sub-Section Page Component Function EMQ.1 3 Component Location EMQ.2 5 Diagnostic Trouble Code List EMQ.3 7 Diagnostic Guide EMQ.4 11 CAN Bus Diagnostics;
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine
 1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
1,9 ltr-tdi-industrial Engine Technical Status: 4/1999 Contents Combustion process................3 Injectors.........................4 Needle Lift Sender.................5 Air-mass Flow Meter...............6
The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain
 Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
Service. Self study programme 296 The 1.4 ltr. and 1.6 ltr. FSI engine with timing chain Design and function For Volkswagen, new and further development of engines with direct petrol injection is an important
1993 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Basic Diagnostic Procedures. Cabriolet, Corrado SLC, EuroVan, Fox, Golf, GTI, Jetta, Passat GL, Passat GLX
 Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1993 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Basic Diagnostic Procedures Cabriolet, Corrado SLC, EuroVan, Fox, Golf, GTI, Jetta, Passat GL, Passat GLX INTRODUCTION The following diagnostic
Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1993 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volkswagen Basic Diagnostic Procedures Cabriolet, Corrado SLC, EuroVan, Fox, Golf, GTI, Jetta, Passat GL, Passat GLX INTRODUCTION The following diagnostic
1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE. General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L
 INTRODUCTION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem. This is also where to begin
INTRODUCTION 1998 ENGINE PERFORMANCE General Motors Corp. - Basic Diagnostic Procedures - 5.7L The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem. This is also where to begin
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION...... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 TROUBLESHOOTING.......... 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL.......... 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION...... 17-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS..... 17-3 TROUBLESHOOTING.......... 17-3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINE CONTROL
WARNING: ALWAYS relieve fuel pressure before disconnecting any fuel related component. DO NOT allow fuel to contact engine or electrical components.
 4.0L V8 - VINS [K,U] Selected Block 1990 Lexus LS 400 For Lextreme Powertrain 2020 S. Hacienda Blvd. # D Hacienda Heights California 91745 Copyright 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC Friday,
4.0L V8 - VINS [K,U] Selected Block 1990 Lexus LS 400 For Lextreme Powertrain 2020 S. Hacienda Blvd. # D Hacienda Heights California 91745 Copyright 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC Friday,
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21
 Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
Fuel and exhaust systems 4A 21 15.40 Unscrew the union nuts and disconnect the fuel feed and return hoses from the manifold 41 Disconnect the injector wiring harness connector and the vacuum hose from
A. Perform a vacuum gauge test to determine engine condition and performance.
 ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSIS, REMOVAL, AND INSTALLATION LESSON 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC TESTS NOTE: Testing the engine s mechanical condition is required when the cause of a problem is not located
ENGINE REPAIR UNIT 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSIS, REMOVAL, AND INSTALLATION LESSON 2: ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC TESTS NOTE: Testing the engine s mechanical condition is required when the cause of a problem is not located
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT:
 DIAGNOSTICS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: SFI SYSTEM (1MZFE) 05241 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a
DIAGNOSTICS DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE CHART HINT: SFI SYSTEM (1MZFE) 05241 Parameters listed in the chart may not be exactly the same as your reading due to the type of instrument or other factors. If a
F - BASIC TESTING Article Text 1992 Dodge Colt For a a a a a Copyright 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC Saturday, April 27, :48PM
 Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1992 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Chrysler Motors/Mitsubishi Basic Diagnostic Procedures Chrysler Motors: Colt, Colt 200, Summit Mitsubishi: Mirage INTRODUCTION The following diagnostic
Article Text ARTICLE BEGINNING 1992 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Chrysler Motors/Mitsubishi Basic Diagnostic Procedures Chrysler Motors: Colt, Colt 200, Summit Mitsubishi: Mirage INTRODUCTION The following diagnostic
Engine Systems. Basic Engine Operation. Firing Order. Four Stroke Cycle. Overhead Valves - OHV. Engine Design. AUMT Engine Systems 4/4/11
 Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
Advanced Introduction Brake to Automotive Systems Diagnosis Service and Service Basic Engine Operation Engine Systems Donald Jones Brookhaven College The internal combustion process consists of: admitting
H - TESTS W/O CODES Nissan 240SX INTRODUCTION TROUBLE SHOOTING SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS WILL NOT START
 H - TESTS W/O CODES 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Trouble Shooting - No Codes Nissan; 240SX, Axxess, Maxima, Pathfinder, Pickup, Pulsar, Sentra, Van, INTRODUCTION Before diagnosing symptoms
H - TESTS W/O CODES 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Trouble Shooting - No Codes Nissan; 240SX, Axxess, Maxima, Pathfinder, Pickup, Pulsar, Sentra, Van, INTRODUCTION Before diagnosing symptoms
Swirl Flaps. A = Non swirl not active. B = Swirl active
 Swirl Flaps A = Non swirl not active B = Swirl active 35 Swirl Flaps 36 Swirl Flap Operating Parameters 37 Swirl Flap Functional Diagram 12 Intake manifold 1 Swirl flap 22/9 Aneroid capsule swirl flap
Swirl Flaps A = Non swirl not active B = Swirl active 35 Swirl Flaps 36 Swirl Flap Operating Parameters 37 Swirl Flap Functional Diagram 12 Intake manifold 1 Swirl flap 22/9 Aneroid capsule swirl flap
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS II SYSTEM. 5. Specified Data. Signal (V) Ignition SW ON (Engine OFF)
 1. ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL OBD0092A Crankshaft Camshaft Mass air flow Throttle Signal (+) 8 0 7 +7 Sensor output waveform Signal ( ) 29 0 0 Shield 54 0 0 Signal (+) 7 0 7 +7 Sensor output
1. ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) I/O SIGNAL OBD0092A Crankshaft Camshaft Mass air flow Throttle Signal (+) 8 0 7 +7 Sensor output waveform Signal ( ) 29 0 0 Shield 54 0 0 Signal (+) 7 0 7 +7 Sensor output
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G63-Non-Turbo>
 13A-1 GROUP 13A MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13A-2 FUEL INJECTI CTROL...... 13A-6 IDLE SPEED CTROL (ISC)..... 13A-7 IGNITI TIMING AND DISTRIBUTI CTROL........
13A-1 GROUP 13A MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13A-2 FUEL INJECTI CTROL...... 13A-6 IDLE SPEED CTROL (ISC)..... 13A-7 IGNITI TIMING AND DISTRIBUTI CTROL........
MONO - MOTRONIC 0309 En
 02.1992 MONO - MOTRONIC 0309 En Published by: Robert Bosch GmbH Division KH After-Sales-Service Department for Training and Technology (KH/VSK) Please direct questions and comments concerning the contents
02.1992 MONO - MOTRONIC 0309 En Published by: Robert Bosch GmbH Division KH After-Sales-Service Department for Training and Technology (KH/VSK) Please direct questions and comments concerning the contents
Yes Minimum octane rating RON 95. Cam/ Crankshaft Fuel System. Trigger location. Air metering Combined ignition and fuel ECM. Yes Diagnostic socket
 Vehicle identification No. of cylinders Type 4/DOHC Capacity (Fiscal) cc 1998 Compression ratio :1 11,0 Suitable for unleaded petrol Minimum octane rating RON 95 Ignition system Description Map-DI Trigger
Vehicle identification No. of cylinders Type 4/DOHC Capacity (Fiscal) cc 1998 Compression ratio :1 11,0 Suitable for unleaded petrol Minimum octane rating RON 95 Ignition system Description Map-DI Trigger
Bosch Motronic 2.5 Copyright Equiptech
 1 Motronic 2.5 operation Motronic 2.5 is an enhancement of the Motronic 4.1 EMS fitted to earlier Vauxhall and Opel vehicles. It was first fitted in the 1990 model year (late 1989) and is a fully integrated
1 Motronic 2.5 operation Motronic 2.5 is an enhancement of the Motronic 4.1 EMS fitted to earlier Vauxhall and Opel vehicles. It was first fitted in the 1990 model year (late 1989) and is a fully integrated
1999 E-Series Workshop Manual
 http://www.fordservicecontent.com/pubs/content/~wsxm/~mus~len/21/sxm31c16.h... Page 1 of 3 SECTION 303-01C: Engine 6.8L 1999 E-Series Workshop Manual IN-VEHICLE REPAIR Procedure revision date: 06/30/1998
http://www.fordservicecontent.com/pubs/content/~wsxm/~mus~len/21/sxm31c16.h... Page 1 of 3 SECTION 303-01C: Engine 6.8L 1999 E-Series Workshop Manual IN-VEHICLE REPAIR Procedure revision date: 06/30/1998
MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTION (MPI) <4G63-Turbo>
 13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13B-2 SENSOR....................... 13B-8 THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CTROL.............. 13B-9 FUEL INJECTI
13B-1 GROUP 13B MULTIPOINT FUEL INJECTI (MPI) CTENTS GENERAL INFORMATI........ 13B-2 SENSOR....................... 13B-8 THROTTLE VALVE OPENING ANGLE CTROL.............. 13B-9 FUEL INJECTI
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM. System Sensors
 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM System Sensors Throttle position sensor - Used to relay throttle position information to the ECU. Throttle opening angle is used by the ECU to determine fuelling and ignition requirements
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM System Sensors Throttle position sensor - Used to relay throttle position information to the ECU. Throttle opening angle is used by the ECU to determine fuelling and ignition requirements
A L L Diagnostic Trouble Codes ( DTC ): P Code Charts General Information
 P0133 O2-Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 / Sensor 1) - The linear O2 sensor is mounted on the front side of the Catalytic Converter (warm-up catalytic converter) or in the front exhaust pipe. It detects
P0133 O2-Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 / Sensor 1) - The linear O2 sensor is mounted on the front side of the Catalytic Converter (warm-up catalytic converter) or in the front exhaust pipe. It detects
Engine mechanics. Crankcase ventilation outlet
 Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
Engine mechanics Crankcase ventilation outlet The gases are drawn out of the crankcase by the vacuum in the intake manifold. The oil is separated from the gases in the labyrinth and in the cyclone oil
2.8 Liter VR6 2V Fuel Injection & Ignition, Engine Code(s): AAA m.y
 2.8 Liter VR6 2V Fuel Injection & Ignition, Engine Code(s): AAA m.y. 1996-1997 01 - On Board Diagnostic (OBD) On Board Diagnostic (OBD II) Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) On Board Diagnostic (OBD II),
2.8 Liter VR6 2V Fuel Injection & Ignition, Engine Code(s): AAA m.y. 1996-1997 01 - On Board Diagnostic (OBD) On Board Diagnostic (OBD II) Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) On Board Diagnostic (OBD II),
Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace
 Assessment Requirements Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace Content: Basic electrical principles a. Explain the direction of current flow
Assessment Requirements Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace Content: Basic electrical principles a. Explain the direction of current flow
Common rail injection system
 Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Common rail injection system Pressure limiting valve The pressure limiting valve is located directly on the high-pressure fuel rail. Its function is to limit maximum pressure in the high-pressure fuel
Fig.11 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
 2003 Dodge or Ram Truck Caravan V6-3.3L VIN R Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Relays and Modules - Powertrain Management > Relays and Modules - Computers and Control Systems > Engine Control Module >
2003 Dodge or Ram Truck Caravan V6-3.3L VIN R Vehicle > Powertrain Management > Relays and Modules - Powertrain Management > Relays and Modules - Computers and Control Systems > Engine Control Module >
Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review
 Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your own hand written notes may be used for the 1 st 10 minutes of the test Based on Chapters 25, 26, 32, 33, 34 and Lab Demonstrations Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your
Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your own hand written notes may be used for the 1 st 10 minutes of the test Based on Chapters 25, 26, 32, 33, 34 and Lab Demonstrations Auto Diagnosis Test #7 Review Your
Malfunction Criteria and Threshold Value Adaptive value. Secondary Parameters with Enable Conditions. >50.8 S Engine load 9-45% Delta fuel adaptation
 DTC Error Message P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1) Diagnostic Procedure Check fuel pump delivery and quantity. Refer to page 126. Check Fuel pressure regulator and residual pressure. Refer to Fuel Injection
DTC Error Message P0171 System Too Lean (Bank 1) Diagnostic Procedure Check fuel pump delivery and quantity. Refer to page 126. Check Fuel pressure regulator and residual pressure. Refer to Fuel Injection
2. Air Line AIR LINE FUEL INJECTION (FUEL SYSTEM) A: GENERAL B: MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR FU(H4DOTC)-3
 W1860BE.book Page 3 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 2. Air Line A: GENERAL The air filtered by the air cleaner enters the throttle body where it is regulated in the volume by the throttle valve and
W1860BE.book Page 3 Tuesday, January 28, 2003 11:01 PM 2. Air Line A: GENERAL The air filtered by the air cleaner enters the throttle body where it is regulated in the volume by the throttle valve and
PIERBURG. Carburetor: 2E3
 PIERBURG Carburetor: 2E3 1 fast idle adjusting screw 2 throttle lever 3 fuel mixture adjusting screw 4 main body 5 idle cut off valve 6 stop screw 7 accelerator pump cover 8 diaphragm 9 spring 10 valve
PIERBURG Carburetor: 2E3 1 fast idle adjusting screw 2 throttle lever 3 fuel mixture adjusting screw 4 main body 5 idle cut off valve 6 stop screw 7 accelerator pump cover 8 diaphragm 9 spring 10 valve
Fuel control. The fuel injection system tasks. Starting fuel pump (FP)
 1 Fuel control The fuel injection system tasks - To provide fuel - To distribute the fuel between the cylinders - To provide the correct quantity of fuel Starting fuel pump (FP) The control module (1)
1 Fuel control The fuel injection system tasks - To provide fuel - To distribute the fuel between the cylinders - To provide the correct quantity of fuel Starting fuel pump (FP) The control module (1)
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
 EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES 1992 Infiniti G20 1983-98 GENERAL INFORMATION Emission Control Visual Inspection Procedures All Models * PLEASE READ THIS FIRST * This article is provided
Truck and Transport IP Red Seal Practice Exam PRACTICE EXAM 4
 Truck and Transport IP Red Seal Practice Exam PRACTICE EXAM 4 1. Which of these sensors directly measures engine load? a. Manifold absolute pressure sensor. b. Coolant sensor (ECT). c. Vehicle speed sensor.
Truck and Transport IP Red Seal Practice Exam PRACTICE EXAM 4 1. Which of these sensors directly measures engine load? a. Manifold absolute pressure sensor. b. Coolant sensor (ECT). c. Vehicle speed sensor.
Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish
 Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish 1. COMBUSTION ENGINES IN 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. COMBUSTION 1.2.1. IDEAL COMBUSTION 1.2.2. FIRING TRIGGER 1.2.3. Precombustion OR 1.3. FACTORS AFFECTING ON THE COMBUSTION
Engine Auxiliary Systems-Spanish 1. COMBUSTION ENGINES IN 1.1. INTRODUCTION 1.2. COMBUSTION 1.2.1. IDEAL COMBUSTION 1.2.2. FIRING TRIGGER 1.2.3. Precombustion OR 1.3. FACTORS AFFECTING ON THE COMBUSTION
Propane and Gasoline Electronic Fuel Injection
 Zenith Electronic Engine Management System Propane and Gasoline Electronic Fuel Injection 1 Slide 1 2 Slide 2 Home Page System Advantages Block Diagram, Electronic Control Unit Inputs Output Controls System
Zenith Electronic Engine Management System Propane and Gasoline Electronic Fuel Injection 1 Slide 1 2 Slide 2 Home Page System Advantages Block Diagram, Electronic Control Unit Inputs Output Controls System
D. Functions in the KE control unit. a) General
 D. Functions in the KE control unit a) General The KE control unit (N3) analyzes the data regarding the operating state of the engine supplied by the sensors. It forms from these data a control current
D. Functions in the KE control unit a) General The KE control unit (N3) analyzes the data regarding the operating state of the engine supplied by the sensors. It forms from these data a control current
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS
 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS (3SFE) EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS EC1 EC2 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS (3SFE) System Purpose System SYSTEM PURPOSE Abbreviation Purpose Positive crankcase ventilation Fuel evaporative
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS (3SFE) EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS EC1 EC2 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS (3SFE) System Purpose System SYSTEM PURPOSE Abbreviation Purpose Positive crankcase ventilation Fuel evaporative
The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control
 The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control actuators. The PCM has various memories within it. These
The PCM is the on-board computer which receives input from various sensors and, with this information, controls various engine & emissions control actuators. The PCM has various memories within it. These
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine
 The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
The 2.3-ltr. V5 Engine Design and Function Self-Study Programme No. 195 195_118 The new 2.3-ltr. V5 engine is related to the VR6 engine as regards design. For this reason this Self-Study Programme will
GROUP 13Aa. 13Aa-5 CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION... SPECIAL TOOLS... ON-VEHICLE SERVICE... INJECTOR... 13Aa-25. THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY...
 13Aa-1 GROUP 13Aa CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION SPECIAL TOOLS 13Aa-2 13Aa-4 13Aa-5 COMPONENT LOCATION 13Aa-5 THROTTLE BODY CLEANING 13Aa-11 ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION ADJUSTMENT 13Aa-12 FUEL PRESSURE TEST
13Aa-1 GROUP 13Aa CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION SPECIAL TOOLS 13Aa-2 13Aa-4 13Aa-5 COMPONENT LOCATION 13Aa-5 THROTTLE BODY CLEANING 13Aa-11 ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION ADJUSTMENT 13Aa-12 FUEL PRESSURE TEST
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL
 17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL 17-2 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-2 AUTO-CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-3 CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION 17-5 17-7 GENERAL INFORMATION
17-1 GROUP 17 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL CONTENTS ENGINE CONTROL 17-2 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-2 AUTO-CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM 17-3 GENERAL INFORMATION 17-3 CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION 17-5 17-7 GENERAL INFORMATION
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle
 Document ID# 850406 2002 Pontiac Firebird Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle DTC DTC 021 and/or 031 DTC 022 and/or 032 DTC 023 or 033 DTC 24/34 DTC 025 and/or 035 DTC 041 DTC 042 DTC 043 DTC
Document ID# 850406 2002 Pontiac Firebird Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle DTC DTC 021 and/or 031 DTC 022 and/or 032 DTC 023 or 033 DTC 24/34 DTC 025 and/or 035 DTC 041 DTC 042 DTC 043 DTC
TROUBLESHOOTING FOR EFI ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT WITH VOLT/OHMMETER
 FI118 TROUBLESHOOTING FOR EFI ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT WITH VOLT/OHMMETER HINT: Because the following troubleshooting procedures are designed for inspection of each separate system, the actual troubleshooting
FI118 TROUBLESHOOTING FOR EFI ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT WITH VOLT/OHMMETER HINT: Because the following troubleshooting procedures are designed for inspection of each separate system, the actual troubleshooting
VACUUM MODULATOR COMPOSITION. Layout. EGR valve. Turbocharger actuator. Vacuum pump hose Vacuum pump. Turbocharger vacuum modulator
 42 04 VACUUM MODULATOR COMPOSITION Layout Turbocharger actuator EGR valve Vacuum pump hose Vacuum pump Turbocharger vacuum modulator EGR vacuum modulator Vacuum Modulator for VGT Turbocharger Actuator
42 04 VACUUM MODULATOR COMPOSITION Layout Turbocharger actuator EGR valve Vacuum pump hose Vacuum pump Turbocharger vacuum modulator EGR vacuum modulator Vacuum Modulator for VGT Turbocharger Actuator
D - ADJUSTMENTS Nissan 240SX ENGINE COMPRESSION VALVE CLEARANCE IGNITION TIMING ENGINE PERFORMANCE On-Vehicle Adjustments
 D - ADJUSTMENTS 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 ENGINE PERFORMANCE On-Vehicle Adjustments Nissan; Axxess, Stanza, 240SX ENGINE COMPRESSION 1) Start engine and warm to normal operating temperature. Disconnect distributor
D - ADJUSTMENTS 1990 Nissan 240SX 1990 ENGINE PERFORMANCE On-Vehicle Adjustments Nissan; Axxess, Stanza, 240SX ENGINE COMPRESSION 1) Start engine and warm to normal operating temperature. Disconnect distributor
1.2 HFM Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection/Ignition System (HFM-SFI) Engine 111
 Diagnosis - Diagnostic Trouble Code () Memory Preliminary work:........................ Engine Test, djustment, Engines, Volume 1 Note regarding diagnostic trouble code () readout: The engine control module
Diagnosis - Diagnostic Trouble Code () Memory Preliminary work:........................ Engine Test, djustment, Engines, Volume 1 Note regarding diagnostic trouble code () readout: The engine control module
Sensors & Controls. Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask.
 Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
Everything you wanted to know about gas engine ignition technology but were too afraid to ask. Contents 1. Introducing Electronic Ignition 2. Inductive Ignition 3. Capacitor Discharge Ignition 4. CDI vs
3. Engine Control System Diagram
 ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 59 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Pump Resister Circuit Opening Fuel Relay Filter Intake Temp. Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Fuel Pump
ENGINE - 2UZ-FE ENGINE 59 3. Engine Control System Diagram Ignition Switch Fuel Pump Relay Fuel Pump Resister Circuit Opening Fuel Relay Filter Intake Temp. Mass Air Flow Meter Throttle Position Fuel Pump
SERVICE MANUAL. Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation. For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only
 For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
For DENSO Authorized ECD Service Dealer Only Diesel Injection Pump No. E-03-03 SERVICE MANUAL Common Rail System for HINO J08C/J05C Type Engine Operation June, 2003-1 00400024 GENERAL The ECD-U2 was designed
G - TESTS W/CODES Volvo 960 INTRODUCTION SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo Self-Diagnostics
 G - TESTS W/CODES 1994 Volvo 960 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo Self-Diagnostics 960 INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing BASIC DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES, proceed with SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM.
G - TESTS W/CODES 1994 Volvo 960 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Volvo Self-Diagnostics 960 INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing BASIC DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES, proceed with SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM.
Simple Carburettor Fuel System for a Piston Engine. And how it works
 Simple Carburettor Fuel System for a Piston Engine And how it works Inlet Exhaust Tank PISTON ENGINE Carburettor Fuel System Filler Cap COCKPIT FUEL GAUGE E FUEL 1/2 F Filler Neck Tank Cavity FUEL LEVEL
Simple Carburettor Fuel System for a Piston Engine And how it works Inlet Exhaust Tank PISTON ENGINE Carburettor Fuel System Filler Cap COCKPIT FUEL GAUGE E FUEL 1/2 F Filler Neck Tank Cavity FUEL LEVEL
DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION CHECK ENGINE WARNING LIGHT CHECK
 FI146 EFI SYSTEM (3VZE) DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The engine (engine and ECT) ECU contains a builtin, selfdiagnosis system which detects troubles within the engine signal network and flashes the warning
FI146 EFI SYSTEM (3VZE) DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM DESCRIPTION The engine (engine and ECT) ECU contains a builtin, selfdiagnosis system which detects troubles within the engine signal network and flashes the warning
Evaporative Emissions
 Page 1 of 6 Published : Apr 8, 2005 Evaporative Emissions 4.4L V8 Evaporative Emissions Component Layout Item Part Number 1 - Fuel filler head 2 - DMTL pump filter (NAS only) 3 - Fuel tank vent hose to
Page 1 of 6 Published : Apr 8, 2005 Evaporative Emissions 4.4L V8 Evaporative Emissions Component Layout Item Part Number 1 - Fuel filler head 2 - DMTL pump filter (NAS only) 3 - Fuel tank vent hose to
TECHNICAL MANUAL L-JETRONIC FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM PORSCHE 912E
 TECHNICAL MANUAL L-JETRONIC FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM PORSCHE 912E 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Introduction to L-Jetronic Fuel Injection 2.0 L-Jetronic Fuel Injection Theory of Operation 3.0 L-Jetronic Component
TECHNICAL MANUAL L-JETRONIC FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM PORSCHE 912E 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 Introduction to L-Jetronic Fuel Injection 2.0 L-Jetronic Fuel Injection Theory of Operation 3.0 L-Jetronic Component
ENGINE 6G74 3.5L-SOHC-24 VALVE
 11A ENGINE General Information/Service Specifications ENGINE 6G74 3.5L-SOHC-24 VALVE GENERAL INFORMATION Items Specifications Type V-type, Over Head Camshaft Number of cylinders 6 Bore mm 93.0 Stroke mm
11A ENGINE General Information/Service Specifications ENGINE 6G74 3.5L-SOHC-24 VALVE GENERAL INFORMATION Items Specifications Type V-type, Over Head Camshaft Number of cylinders 6 Bore mm 93.0 Stroke mm
CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
CHAPTER 6 CHAPTER 6 IGNITION SYSTEM CONTENTS PAGE Faraday s Law 02 The magneto System 04 Dynamo/Alternator System 06 Distributor 08 Electronic System 10 Spark Plugs 12 IGNITION SYSTEM Faraday s Law The
On Board Diagnostics II PCED
 Page 1 of 5 1999 PCED On Board Diagnostics II SECTION 5: Pinpoint Tests HD: Misfire Detection Monitor HD: Introduction HD1 DTC P0301-P0310: CHECK FOR NO LOW FUEL te: Running out of fuel can turn on the
Page 1 of 5 1999 PCED On Board Diagnostics II SECTION 5: Pinpoint Tests HD: Misfire Detection Monitor HD: Introduction HD1 DTC P0301-P0310: CHECK FOR NO LOW FUEL te: Running out of fuel can turn on the
F - BASIC TESTING Infiniti G20 INTRODUCTION PRELIMINARY INSPECTION & ADJUSTMENTS VISUAL INSPECTION MECHANICAL INSPECTION
 F - BASIC TESTING 1992 Infiniti G20 1992 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Infiniti Basic Diagnostic Procedures G20, M30, Q45 INTRODUCTION The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem.
F - BASIC TESTING 1992 Infiniti G20 1992 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Infiniti Basic Diagnostic Procedures G20, M30, Q45 INTRODUCTION The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem.
STARTING SYSTEMS 8B - 1 STARTING SYSTEMS CONTENTS
 TJ STARTING SYSTEMS 8B - 1 STARTING SYSTEMS CONTENTS page DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION STARTER MOTOR... 2 STARTER RELAY... 3 STARTING SYSTEM... 1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING STARTER MOTOR... 8 STARTER MOTOR NOISE
TJ STARTING SYSTEMS 8B - 1 STARTING SYSTEMS CONTENTS page DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION STARTER MOTOR... 2 STARTER RELAY... 3 STARTING SYSTEM... 1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING STARTER MOTOR... 8 STARTER MOTOR NOISE
