TEPZZ 7 97_5B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
|
|
|
- Gerald Gilbert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) TEPZZ 7 97_B_T (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: Bulletin 16/1 (21) Application number: (22) Date of filing: (1) Int Cl.: F16F 9/36 (06.01) F16F 9/34 (06.01) F16F 9/43 (06.01) F16F 9/44 (06.01) F16F 9/02 (06.01) F16F 9/48 (06.01) F16F 9/12 (06.01) F16F 9/32 (06.01) (86) International application number: PCT/CZ12/ (87) International publication number: WO 13/ ( Gazette 13/03) (4) GAS SPRING WITH DAMPENING GASFEDER MIT DÄMPFUNG RESSORT À GAZ AVEC AMORTISSEMENT (84) Designated Contracting States: AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR () Priority: CZ U (43) Date of publication of application: Bulletin 14/ (73) Proprietors: Krislo, Michal 1 00 Praha 4 (CZ) Knobloch, Rafael Praha 6 (CZ) (72) Inventor: KNOBLOCH, Rafael Praha 6 (CZ) (74) Representative: Svorcik, Otakar Vsetecka Zeleny Svorcik Kalensky & Partners Associated Law Offices Hálkova Praha 2 (CZ) (6) References cited: EP-A DE-A US-A US-A EP B1 Note: Within nine months of the publication of the mention of the grant of the European patent in the European Patent Bulletin, any person may give notice to the European Patent Office of opposition to that patent, in accordance with the Implementing Regulations. Notice of opposition shall not be deemed to have been filed until the opposition fee has been paid. (Art. 99(1) European Patent Convention). Printed by Jouve, 7001 PARIS (FR)
2 1 EP B1 2 Description Field of the invention [0001] This invention concerns gas (pneumatic) spring with dampening, in which working gas can optionally be transferred between the working cylinder and a reservoir (or transfer cylinder) in order to provide springing and dampening of the return. Background of the invention [0002] In the prior art, and the automotive industry in particular, a variety of solutions for gas springs with dampening is known. [0003] Firstly, document GB describes a lockable pneumatic (or hydro-pneumatic) spring, in which dampening occurs based on the transfer through the piston body. However, the chamber into which it is transferred is not located in the piston rod. The hollow piston rod is only used here to fill such a spring. As a result of this, such a spring not only lacks compaction but, more importantly, the working length of such a spring is significantly reduced. [0004] Document US describes an air shock absorber for a vehicle - i.e. air damper - with regulation capable of adapting its characteristics according to the load of the vehicle. The transfer chamber is located externally in this case. [000] Another gas spring is described in document GB Here, the whole transferring is conceived solely to set the length of the spring (more specifically the rise of a suspended chair); the spring is not damped here. The solution described in document US works similarly, too. [0006] Document DE describes a device for springing and/or dampening, provided with a chamber with an additional volume of the medium. However, this device is of a totally different construction for a very specific use. [0007] Document WO 94/19619 introduces a shock absorber - damper, comprising a working cylinder with a piston and a piston rod. The piston and the piston rod have a through bore aligned with their axis, in which bore, rotatably placed, is a regulating pipe, and in this regulating pipe, rotatably placed, is a controlling rod. On the free end of the piston rod, the regulating pipe and the controlling rod protrude in the axial direction out of the bore of the piston rod, and they are provided with means for angular setting. Axial through openings are provided in the piston for flow through of the medium from the space above the piston to the space bellow the piston and vice versa. On the opposite side of the piston from the piston rod side, vis-à-vis with respect to the mentioned axial through openings, there are axially movable damping discs provided with axial through openings arranged in a ring coaxially with the piston axis. Two disc valves are inserted between the damping discs; these disc valves alternately abutting to one of the opposite front surfaces of the damping discs. In case of one-directional flow through of the working medium, one disc valve closes the flow through axial openings of one damping disc and the second disc valve draws away from the second damping disc and releases flow through its openings. The rotatably arranged regulating discs abut against the other front sides of the damping discs, these regulating discs having their peripheral cut outs arranged against axial through openings of the damping discs. By means of angular setting of the regulating discs, it is possible to cover openings of the axial through openings of the damping discs and to throttle the flow through of the working medium through the damping discs and piston. One regulating disc is connected with the end of the regulating pipe and the second regulating disc is connected with the end of the controlling rod. Angular setting of the regulating discs and regulating the stiffness of the shock absorber - damper - can be implemented by means of regulating means of the regulating pipe and of the controlling rod, without a necessity to disassemble the shock absorber - damper. Such a shock absorber - damper - according to WO 94/19619 is however very complex and labor intensive. [0008] Document US describes a solution having three air chambers, wherein the medium flows between two chambers (chambers 17 and 18 in this document) and the chambers together provide for a damping function, whereas the third air chamber (chamber 16) is an air cushion and has a springing function only. This solution integrates an air spring (cushion) and an air damper into a single device with relative success. It can be anticipated that thanks to the arrangement one after another (one above another) in a single body, there might be certain savings of production costs; however, as a matter of fact, these are still two independent air units, namely an air spring and an air damper, which might be separated as well, since each of them has a completely different function. [0009] Another gas spring is described in document US This gas spring does not fulfil the requirements imposed on the solution according to this invention. [00] Furthermore, combined air/hydraulic solutions are known. Such a solution can be found for example in high end dampers for the automotive industry produced by the company KONI, Netherlands. The company s hydraulic damper damps based on transferring the liquid medium (oil) from the space above the piston to the space bellow the piston. Hence, this solution works on a totally different basis. Moreover, such transfer systems and regulation systems are very complex. [0011] A hydraulic damper is described for example in document US Moreover, in this document, the transferring is realized externally (which means in a complicated and not sufficiently robust manner); again, it is the hydraulic liquid that is transferred. [0012] Another solution is described in document US 2
3 3 EP B Again, this solution is too complex from the constructional point of view, requires steel helical springs or other separate springs, and is not compact enough. [0013] Another complicated combined oil spring is described in document DE This oil spring is designed for use on a bicycle. [0014] More combined solutions are described for example in documents DE , US and GB These solutions do not fulfil the requirement imposed on the solution according to this invention either. [001] A gas spring according to the preamble of Claim 1 is known from the document US Another gas spring according to the state of the art is described in the document DE Examples of shock absorbers known from the state of the art are described in the documents US and EP Summary of the invention [0016] All of the above-mentioned solutions according to the state of the art are complex from the constructional point of view and involve many individual elements; in many cases they combine a gas spring (generally air spring) or a steel spring with an oil damper. Hence, these solutions are complicated to produce and their cost of production is high. [0017] This invention aims to eliminate the deficiencies of the prior art and to provide a gas spring, simple from the constructional point of view, with dampening of the return of the piston which, by using the same simple elements, works as an air spring during compression and as an air damper during the extension. Another aim of this invention is to ensure, by using simple means, an external regulation of springing characteristics as well as damping characteristics, also continuously under working conditions of the damping spring. The invention also aims to provide a facultative function of the so-called throttle dashpot which, in case of extreme shocks (vibrations), causes an immediate closing of the transfer openings between the working cylinder and the transfer reservoir. Another aim of the invention is to provide a spring of the above-mentioned art having high reliability, simple construction, easy mounting and disassembling, a spring that can be produced in a very broad range of dimensions. [0018] The disadvantages of the prior art are significantly eliminated and the aim of the invention is achieved by a pneumatic spring having a working cylinder and therein slidably arranged piston, whereas in order to provide springing and/or dampening optionally (i.e. in case that the dampening is requested) the working gas is transferable between the working cylinder and a reservoir, wherein the reservoir is arranged in the piston rod. The reservoir is made up by a hollow cylinder constituting the piston rod, one end of which is closed up by the piston. Such an arrangement is particularly compact (at the maximum extension), it is very simple from the constructional point of view, has low construction costs and, at the same time, is very reliable, and this at almost arbitrary dimensions. [0019] In order to provide regulation, there is at least one transfer opening in the piston, provided with at least one gas flow control element (i.e. actually a throttle element for controlling the flow through of the working gas between the working cylinder and the reservoir), which is axially slidable with respect to the transfer opening (like a valve) and, for instance, it can be a regulation cone or a ring, or a combination of both. In this way, by using simple means, we get a compact gas spring with a gas damper integrated in a single unit. [00] According to the invention, the regulation is enabled from outside by means of the controlling rod for axially adjusting the gas flow control element or elements, said controlling rod being preferably provided with back stops for gas flow control element on both side, that is to say the controlling rod has an upper back stop for gas flow control element and a lower back stop for gas flow control element. In a particularly simple embodiment, the upper back stop may be constituted by a shoulder on the controlling rod and the lower back stop may be constituted for example by the so-called Seeger circlip ring provided on this controlling rod. [0021] Preferably, on the controlling rod, there are springing means for returning of the gas flow control element, and also sealing means for providing sealing of the through going controlling rod with respect to the reservoir, which the controlling rod goes through, whereas preferably both these means are constituted by a single flexible tube, for example a silicon tube; by its springing, the tube returns the gas flow control element to its release position and thereby seals the reservoir with respect to the passage through of this controlling rod. [0022] Such an arrangement makes it therefore possible by simple and cheap means to externally adjust both springing as well as damping characteristics at any time, even under working conditions of the gas spring according to this invention. [0023] Preferably at least one so-called throttle dashpot may be arranged for closing the transfer opening in case of sharp stroke at least in one direction, whereas this throttle dashpot is preferably constituted by a suspended cone or by a suspended plate ("planchette"). Thanks to such a simple throttle dashpot, the gas spring according to this invention further gets the advantage of an instantaneous closing (or possibly partial closing) of the transfer openings between the working cylinder and the transfer reservoir in case of extreme shocks (vibrations); therefore we call this element the "throttle dashpot". [0024] It is of advantage that these elements, i.e. gas flow control elements (for example regulation cones and/or rings) and possibly throttle dashpots might be arranged from one or the other side of the piston or even from both sides of the piston; this way allows providing 3
4 EP B1 6 for adjustable dampening and counter shock protection in both working directions of the piston, thereby not losing the advantage of a simple and compact construction. [002] Between the sealing of the piston with respect to the working cylinder and the sealing of the upper cover of the working cylinder, through which the hollow cylinder protrudes constituting the piston rod, there may be, in the space between this hollow cylinder and the mantle of the working cylinder, gas contained, constituting a flexible cushioning in the case of the piston approaching the upper cover of the working cylinder at the maximum extension of the piston. At the return of the piston, the pressure in this space increases, providing a kind of a gas silent-block preventing a sharp impact of the piston onto the upper cover, for example in the case of no dampening due to closing of the transfer opening, regardless if by the gas flow control element or by the throttle dashpot. [0026] Preferably, a spacer may be arranged between the gas flow control element and the transfer opening for preventing the total closing of the transfer opening (by virtue of the transferred working gas or by virtue of springing means for returning of the gas flow control element) at the normal functioning of the spring. Preferably, however, this spacer of the dampening is deformable and thus allows even a total closing of the transfer opening if needed. [0027] The individual stiffnesses of the respective flexible elements are only restricted by their mutual proportions that are unambiguously predetermined by the function of the individual elements, namely: - on one side, the stiffness of the flexible tube must be overcome by the transferred gas under working conditions, and - on the other side, the stiffness of the spacer of the dampening must not be overcome either by the flexible tube or by the transferred gas, but it should be possible to compress it, if needed, for example by tightening the controlling rod, see above. [0028] The working gas in the gas spring according to this invention preferably is the air. An air gas spring is of advantage above all from the economic point of view. [0029] The gas spring according to this invention might be filled with the working gas by any suitable way, for example by means of the filling valve in the bottom of the working cylinder. [00] It is also of advantage that such a gas spring can be, depending on its use, constituted either as a compression spring, where the working gas in both chambers, i.e. in the working cylinder as well as in the reservoir, is under a pressure that is higher than the pressure of the surroundings, or as an extension spring, where there is a negative pressure in both chambers. [0031] Such a compression spring with a positive pressure working gas has a reservoir, which in the release state of the spring preferably takes up approximately to 0 % of the total volume of the working gas, even more preferably approximately %. [0032] In one particular preferred embodiment of this invention an opening and/or valve is arranged in the upper sealing between the hollow cylinder and a mantle of the working cylinder for allowing filling and discharging, respectively, of the pressurized air (or gas) into/from the space above the piston between the hollow cylinder constituting the hollow piston rod and the mantle of the working cylinder in order to compress the spring and to return the spring back, respectively. It is therefore possible to introduce pressurized air (or gas) through the aforementioned opening or valve into the space above the piston around the hollow piston rod, and thereby to compress the spring. By releasing the air (or gas), the spring returns back. Such a solution is in particular suitable for different air brakes, but it can also be used as a so-called air cylinder ("pneumotor") or as a lifting jack for passenger cars and trucks etc. [0033] The air or gas spring according to this invention is self-dampening in both directions, i.e. at compression as well as at the extension. At compression, it behaves as an air spring with dampening; at the extension, it also behaves as an air spring with dampening, whereas both these damping effects can be, as regards the magnitude of the dampening, controlled independently from each other. Brief description of the drawings [0034] Embodiments of this invention will now be described in more detail based on specific exemplary embodiments shown on the drawings, where: Fig. 1a Fig. 1b Fig. 2 Fig. 3 Fig. 4 Fig. Fig. 6 Fig. 7 illustrates one embodiment of the gas spring according to this invention, partially in a longitudinal cross section, illustrates another embodiment of the gas spring according to this invention in the same view as in fig. 1a, illustrates an exemplary arrangement of the individual elements in a mode of so-called hard springing, illustrates an exemplary arrangement of the individual elements in a mode of springing with dampening of the return of the piston, illustrates an exemplary arrangement of the individual elements in a mode of springing without dampening of the return of the piston, illustrates one embodiment of the throttle dashpot, illustrates another embodiment of the throttle dashpot, illustrates an exemplary embodiment of the spacers of the dampening. Detailed description of the preferred embodiments [003] The device in fig. 1 consists of the working cyl- 4
5 7 EP B1 8 inder and the reservoir (or transfer cylinder) constituted by the storage cylinder 21, which constitutes the piston rod, a piston 2 being arranged on its lower end, this piston at the same time closing up the storage cylinder 21 on the lower end. On the upper end, the reservoir being closed up by a cover, with which cover an attachment of the gas spring for coupling with the piece, for which a suspension has to be provided, is connected. An opposite attachment is arranged on the lower cover of the working cylinder, in which cover at the same time a filling valve 80 is established. Hence, the working cylinder is positioned outside of the storage cylinder and between both these cylinders a transfer opening is created. All the expressions such as upper, lower, or up and down, and others, as being used throughout this text, refer only to the illustration of the exemplary embodiment as shown on the attached drawings, and they do not limit in any way the working position of the gas spring according to this invention at its use. [0036] The working gas can be the air; therefore, in one embodiment, the gas spring can be an air spring. In the embodiment shown, the spring is a compression spring, where the working gas is under a pressure that is higher than the atmospheric pressure. As already mentioned above, the spring according to this invention might also be arranged as an extension spring, where the working gas is under a pressure that is lower than the atmospheric pressure. [0037] In order to control the transferring of the working gas through the opening, a controlling rod 1 is provided, which protrudes through the upper cover of the storage cylinder 21, in which it is sealed by means of a silicon tube, and ends in the area of the transfer opening in the piston 2, whereas on this controlling rod 1 there are provided a regulation cone 42 and a ring 60, which can be constituted for example as a Seeger circlip ring. On the upper end, above the cover of the storage cylinder, the controlling rod 1 is provided with an externally accessible adjusting element 0 for adjusting dampening of the return of the piston and/or for adjusting dampening of the springing, for example manually. [0038] The regulation cone 42 (similarly to the socalled valve plug) can be moved in the axial direction relatively with respect to the controlling rod 1 and at the same time relatively with respect to the transfer opening downwards to the contact with the transfer opening, and upwards against the effect of the flexible silicon tube to the so-called upper back stop 2 constituted by the shoulder on the controlling rod 1. [0039] The ring 60 (for example the Seeger circlip ring) is arranged on the controlling rod 1, under the cone 42, and in this embodiment it can be moved, together with the controlling rod 1 on which it is stationary fixed, relatively to the transfer opening between the upper position, in which it closes the transfer opening, and a second position, in which the transfer opening is opened to the maximum and therefore the dampening of the gas spring is minimal [00] When the air spring - damper is compressed, the pressure in the working cylinder increases, thereby pushing away the regulation cone 42 (throttling regulation valve plug), allowing for transferring of the medium into the storage cylinder. The medium struggles through the transfer opening or openings to the transfer reservoir. At releasing at the extension, the regulation cone 42 prevents from a fast return of the medium and therefore prevents also a fast returning of the air spring (it performs the function of an air damper). The returning of the spring (dampening) can be controlled externally by means of the external adjusting element 0 of the regulation of the springing and dampening, by means of the controlling rod 1 (for example a regulation screw) and by means of the upper back stop 2, and this according to the requested level of dampening. A silicon tube is arranged in the storage cylinder 21 around the spacer screw, this silicon tube having sealing and spring function, i.e. it seals the reservoir and pushes the regulation cone 42 to the transfer opening. The cone 42 fits to the conical depression in the bottom of the storage cylinder 21 constituting the piston 2, closes the transfer opening and at the same time ensures the centering of the controlling rod, on which it is slidably arranged. Cone 42 with the controlling rod 1 has the function of the external control of the springing and damping characteristics. In case of the maximum tightening of the controlling rod, the shoulder of the rod enables total closing of the transfer opening, so that if needed an exponential increase of the pressure in the working cylinder occurs with no dampening function. In case of untightening of the spacer screw, the pressure does not increase exponentially and a dampening function occurs. However, thanks to the small flow through of the medium, the springing is very hard. In an intermediate position, the space between the shoulder of the rod (upper back stop) and the Seeger circlip ring (lower back stop) enables a free movement of the regulation cone. The flexible silicon tube forces the regulation cone, so that it works as one way valve. At the compression of the spring it allows a free transfer of the medium from the space of the working cylinder to the space of the storage cylinder 21, but at the returning of the spring to its original state the cone 42 closes the transfer opening and prevents the transfer of the medium from the storage cylinder 21 back into the working cylinder. Theoretically, the spring remains compressed. With even further untightening of the screw of the controlling rod 1, the ring 60 (Seeger circlip ring) raises the cone 42, so that it enables the re-entry of the medium into the working cylinder. Proportionally to the distance of the cone 42 from the conical depression, the medium "struggles" more or less through the opening, and the spring is more or less damped on its returning. [0041] Such a gas spring enables three basic regimes of functioning: not only springing with dampening of the return of the piston (fig. 3) (so-called soft springing), but also a hard springing (fig. 2), and finally also springing
6 9 EP B without dampening (fig. 4). [0042] In fig. 2, so-called hard springing is shown, i.e. springing, when the gas at the compression is not transferred from the working cylinder into the reservoir, because the cone 42 is, by means of the upper back stop 2 of the controlling rod 1 (based on the setting of the adjusting element 0), pushed into the transfer opening, and this transfer opening is therefore blocked. The spring therefore springs solely based on the compressibility of the working gas in the working cylinder. [0043] At the springing, or soft springing (as it is not the hard springing that has just been described) with dampening of the return of the piston (for which the gas spring according to this invention is primarily intended), as illustrated in fig. 3, a transfer of the working gas from the working cylinder into the reservoir occurs. The cone 42 can be axially moved between the upper back stop 2 and the lower back stop, in this exemplary embodiment constituted by the ring 60 (for example so called Seeger circlip ring). When compressing the spring, the flow of the working gas passing through the transfer opening overcomes the force of the flexible tube, for example a silicon tube, pushing the cone 42 away from the upper back stop, and pushes this cone 42 up to the upper back stop. In this position, the transfer opening is opened to the most, whereby this opening is given by the position of the upper back stop. At the returning of the spring, the flexible tube pushes the cone 42 down to the ring 60 (i.e. to the lower back stop). Based on the setting of this lower back stop, the minimum level of the transferring through the transfer opening is set - and thereby also the level of the dampening of the return of the spring is set. [0044] Between the cone 42 and the transfer opening a spacer 0 can be arranged for preventing a total closure of the transfer opening at the normal functioning of the spring based on the influence of the transferred working gas or of the silicon tube, see fig. 7. Preferably, however, this spacer 0 is deformable (it can be for example a silicon separator) and it allows a total closing of the transfer opening if needed (for example by means of tightening the controlling means, for example the controlling rod 1, into extreme position, if not hindered by the position of the ring 60) in order to get an extra hard springing, as shown in fig. 2. [004] In fig. 4, the lower back stop is set by means of the ring 60 so that the working gas can pass through the transfer opening at the compression of the spring as well as at the return of the piston. Hence, a springing without dampening occurs (or almost without dampening, in case of a very intense vehement compression of the spring, the cone 42 can be pushed even further). [0046] As shown in fig., in a preferred embodiment the whole device can be completed with a throttle dashpot 91 in the form of a cone with suspension 911 (constituted for example by a silicon tube). This throttle dashpot 91 closes in case of a sharp increase in pressure (for example when used in a car in case of running over an unexpected hump). This throttle dashpot 91 causes the pressure in the spring to increase exponentially, it inactivates the dampening, so that after passing over the hump the wheel returns back without slowdown, and the car does not fall down. [0047] In yet another embodiment, a steel plate 92, for example steel plate 92 suspended by the helical springs, or any other suitable element, may constitute the throttle dashpot (see fig. 6). Between the sealing of the upper cover of the working cylinder with the storage cylinder 21 and the sealing of the piston 2, there is a space 70, wherein the pressure in this space 70 increases at the return of the piston 2, providing a kind of a gas silentblock, preventing a sharp impact of the piston 2 onto the upper cover in the case of no dampening at all due to closing of the transfer opening by the cone 42 or by means of the throttle dashpot 91, 92, or possibly by means of tightening the controlling rod 1. Thanks to the storage (transfer) cylinder 21, the pressure increase bellow the piston is not as dramatic as, for example, in case of a common air spring. In this embodiment, the storage cylinder 21 takes up approximately % of the total volume of the cavity of the spring (of the medium). The extension of the spring in that case is approximately %. [0048] In an alternative embodiment, the silicon tube can be replaced by a helical spring. In such a case however, the cone with the controlling rod, as well as the controlling rod with the cover of the storage cylinder, must be sealed by other means (for example by means of an o-ring seal or by a gasket). With this embodiment, high friction and uneasy moving are a disadvantage, above all in case of the cone. [0049] A throttling ring, or a bullet, or other sealing element can also replace the cone. [000] In yet another alternative embodiment, as shown in fig. 1b, the adjusting element 0 can be constituted by a pinion 0 for adjusting by means of servo mechanism, for example changing servo motor. Adjusting of the dampening and/or springing might than be controlled automatically, especially electronically. [001] Fig. 1b also illustrates an alternative filling opening 80 that, in contrast to the filling valve 80, does not only serve to a single action filling of the gas spring, but can also be connected to a continuous regulation of the pressure in the spring (for example by means of a compressor). In this way, it is possible to adapt the overall amount of the gas and thereby change the nominal pressure in the gas spring according to this invention on the go. [002] Both above-mentioned alternative embodiments, allowing for controlling the dampening and/or springing, or allowing for regulating the pressure in the spring, can preferably be used for example for a car suspension variable depending on the running conditions, especially based on the load or roadway surface. [003] The main advantages of this invention are: - Gas spring at compression and gas damper at the 6
7 11 EP B1 12 extension both in a single integrated body. - Reservoir (transfer cylinder) provides for an advantage of a slow pressure increase at compression (comfort springing). - Slow extension without sharp bounce-back (comfort dampening). - External control of the springing characteristics of the gas spring. - External control of the damping characteristics of the gas damper. - A facultative throttle dashpot. - Pneumatic spring according to this invention is constituted by simple, easy-to-produce parts of standard design, it is very simple from the constructional point of view, and its mounting and disassembling is easy. The pneumatic spring according to this invention is also highly reliable thanks to the use of standard constructional parts, providing good results in the field of dampers. The pneumatic spring according to this invention can be produced and used in a very broad spectrum of dimensions, with the diameter of the working cylinder from a very few centimeters to more than one meter. The pneumatic spring according to this invention does not suffer from any fatigue of the material, its damping elements practically do not suffer from any wear, the hardness of the springing can be widely regulated by setting the initial pressure in the working cylinder. The compressibility of the pneumatic damping spring is up to 60 % of the initial length. The weight of the pneumatic spring according to this invention is low; it can be manufactured from light aluminium alloys or plastic materials and with far lower production costs if compared to the known pneumatic springs and helical steel springs. [004] The gas spring according to this invention can preferably be used especially for providing suspension for shoes (men s, ladies, sport), for springing with dampening for a bike, for passenger cars, for trucks and for railway cars, for providing suspension of the bridge structures and building constructions, as an anti-vibration device for stabilization of machines, as a door closer, and many more... [00] An embodiment with the opening and/or valve 111 in the upper sealing between the hollow cylinder 21 and a mantle of the working cylinder for allowing filling and discharging, respectively, of the pressurized air into/from the space 70 above the piston between the hollow cylinder 21 constituting the hollow piston rod and the mantle of the working cylinder in order to compress the spring and to return the spring back, respectively, can preferably be used for different air brakes, as socalled air cylinder ("pneumotor") or as a lifting jack for passenger cars and trucks etc. [006] The air or gas spring according to this invention is self-dampening in both directions, i.e. at compression as well as at the extension. At compression it behaves as an air spring with dampening and at the extension it also behaves as an air spring with dampening, whereas both these damping effects can be, as regards the magnitude of the dampening, controlled independently from each other. Claims 1. Compression gas spring having a working cylinder () and therein slidably arranged piston (2), whereas the working gas is, in order to provide for springing and dampening, transferable between the working cylinder () and a reservoir (), the reservoir () being made up by a closed hollow cylinder (21) constituting the piston rod, one end of which is closed up by the piston (2), in the piston (2), there is at least one transfer opening (), characterized in that the transfer opening () is provided with at least one gas flow control element which is slidable axially with respect to the transfer opening () between an upper back stop (2) and a lower back stop, whereby a controlling rod (1) goes through the piston rod in order to axially adjust the gas flow control element from outside by means of adjusting the upper back stop (2) and the lower back stop, both being preferably arranged on this controlling rod (1). 2. Gas spring according to claim 1, characterized in that the gas flow control element is a regulation cone (42) or a ring or a combination of both. 3. Gas spring according to any of the preceding claims, characterized in that the lower back stop is a ring (60), e.g. circlip ring. 4. Gas spring according to any of the preceding claims, characterized in that on the controlling rod (1), there are arranged springing means for returning of the gas flow control element, and sealing means for providing sealing of the through going controlling rod (1) with respect to the reservoir (), whereas the means for returning of the gas flow control element and at the same time the means for sealing of the through going controlling rod are preferably constituted by a single flexible tube (), e.g. a silicon tube ().. Gas spring according to any of the preceding claims, characterized in that at least one throttle dashpot (91, 92) is arranged for closing the transfer opening () in case of sharp stroke at least in one direction, whereas this throttle dashpot is preferably constituted by a suspended cone (91) or by a suspended plate (92). 6. Gas spring according to any of the preceding claims, 7
8 13 EP B1 14 characterized in that between the sealing of the piston (2) with respect to the working cylinder () and the sealing of the upper cover of the working cylinder (), through which the hollow cylinder (21) protrudes constituting the piston rod, there is, in the space (70) between the hollow cylinder (21) and the mantle of the working cylinder (), gas contained, constituting a cushioning in case of approaching of the piston (2) to the upper cover of the working cylinder at the maximum extension of the piston (2). 7. Gas spring according to any of the preceding claims, characterized in that a spacer (0) is arranged between the gas flow control element and the transfer opening () for preventing total closing of the transfer opening () at the normal functioning of the spring, whereas preferably the spacer (0) of the dampening is deformable and allows in this way a total closing of the transfer opening () if needed. 8. Gas spring according to any of the preceding claims, characterized in that in the release state of the spring, the reservoir () takes up approximately to 0 % of the total volume of the working gas, preferably approximately %. 9. Gas spring according to any of the preceding claims, characterized in that the working gas is air.. Gas spring according to any of the preceding claims, characterized in that an opening and/or valve (111) is arranged in the upper sealing between the hollow cylinder (21) and a mantle of the working cylinder () for allowing filling and discharging, respectively, of the pressurized air into/from the space (70) above the piston between the hollow cylinder (21) constituting the hollow piston rod and the mantle of the working cylinder () in order to compress the spring and to return the spring, respectively. Patentansprüche zwischen dem oberen Anschlag (2) und dem unteren Anschlag axial verschiebbar ist, wobei durch die Kolbenstange eine Regulationsstange (1) für die axiale Einstellung des Elements zur Regulierung des Gasdurchflusses von außen mittels Einstellung des oberen Anschlags (2) und des unteren Anschlags durchgeht, die beide vorteilhaft an dieser Regulationsstange (1) angeordnet sind. 2. Gasfeder gemäß dem Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Element zur Regulierung des Gasdurchflusses ein Regulationskegel (42) oder ein Ring oder die Kombination der beiden ist. 3. Gasfeder gemäß einem beliebigen der vorausgehenden dass der untere Anschlag ein Ring (60), z. B. ein Sicherungsring ist. 4. Gasfeder gemäß einem beliebigen der vorausgehenden dass an der Regulationsstange (1) ein federndes Mittel zur Rückführung des Elements zur Regulierung des Gasdurchflusses und ein Mittel zur Abdichtung der durchgehenden Regulationsstange (1) gegenüber der Vorratskammer () angeordnet ist, wobei das Mittel zur Rückführung des Elements zur Regulierung des Gasdurchflusses und gleichzeitig das Mittel zur Abdichtung der durchgehenden Regulationsstange vorteilhaft durch ein einziges flexibles Röhrchen (), z. B. durch ein Silikonröhrchen (), gebildet sind.. Gasfeder gemäß einem beliebigen der vorausgehenden dass mindestens eine Schockklappe (91, 92) zum Verschließen der Überlauföffnung () im Falle eines heftigen Schlags mindestens in einer Richtung angeordnet ist, wobei diese Schockklappe vorteilhaft durch einen federgelagerten Kegel (91) oder eine federgelagerte Planchette (92) gebildet ist. 1. Druckgasfeder umfassend einen Arbeitszylinder () und einen darin verschiebbar angeordneten Kolben (2), wobei das Arbeitsgas zum Zweck der Federung und Dämpfung zwischen dem Arbeitszylinder () und der Vorratskammer () transferierbar ist, wobei die Vorratskammer () durch einen die Kolbenstange bildenden verschlossenen hohlen Zylinder (21) gebildet ist, dessen ein Ende mit dem Kolben (2) geschlossen ist, wobei es im Kolben (2) mindestens eine Überlauföffnung () gibt, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Überlauföffnung () mit mindestens einem Element zur Regulierung des Gasdurchflusses versehen ist, das bezogen auf die Überlauföffnung () Gasfeder gemäß einem beliebigen der vorausgehenden dass zwischen der Abdichtung des Kolbens (2) gegenüber dem Arbeitszylinder () und der Abdichtung des oberen Deckels des Arbeitszylinders (), durch den der die Kolbenstange bildende hohle Zylinder (21) durchgeht, im Raum (70) zwischen dem hohlen Zylinder (21) und dem Mantel des Arbeitszylinders () das Gas geschlossen ist, dass einen Kissen im Falle der Näherung des Kolbens (2) zum oberen Deckel des Arbeitszylinders bei maximalem Hochziehen des Kolbens (2) bildet. 7. Gasfeder gemäß einem beliebigen der vorausgehenden 8
9 1 EP B1 16 dass zwischen dem Element zur Regulierung des Gasdurchflusses und der Überlauföffnung () eine Distanzeinlage (0) zum Verhindern des vollständigen Schließens der Überlauföffnung () beim gewöhnlichen Betrieb der Feder angeordnet ist, wobei die Distanzeinlage (0) der Dämpfung vorteilhaft deformierbar ist und so das vollständige Schließen der Überlauföffnung () im Bedarfsfalle ermöglicht. 8. Gasfeder gemäß einem beliebigen der vorausgehenden dass in Ruhelage der Feder die Vorratskammer () ungefähr bis 0 % des Gesamtvolumens des Arbeitsgases, vorteilhaft ungefähr % darstellt. 9. Gasfeder gemäß einem beliebigen der vorausgehenden dass das Arbeitsgas die Luft ist.. Gasfeder gemäß einem beliebigen der vorausgehenden dass eine Öffnung und/oder ein Ventil (111) in der oberen Dichtung zwischen dem hohlen Zylinder (21) und dem Mantel des Arbeitszylinders () zur Ermöglichung des Einlassens bzw. Auslassens der Druckluft in den/aus dem Raum (70) über dem Kolben zwischen dem die hohle Kolbenstange bildenden hohlen Zylinder (21) und dem Mantel des Arbeitszylinders () zum Zweck der Verdrückung der Feder bzw. der Rückführung der Feder angeordnet ist. Revendications 1. Ressort à gaz de poussée comprenant un cylindre de travail () logeant un piston (2) agencé de façon coulissant, le gaz de travail, afin de permettre faire ressort et amortir, étant transférable entre ledit cylindre de travail () et le réservoir (), ledit réservoir () étant formé d un cylindre creux fermé (21) qui représente une tige de piston, et dont une extrémité est obturée par ledit piston (2), ledit piston (2) comprenant au moins un orifice de transfert () caractérisé en ce que ledit orifice de transfert () est pourvu d au moins un élément de réglage de débit de gaz apte à être déplacé axialement par rapport à ledit orifice de transfert () entre une butée supérieure (2) et une butée inférieure, ladite tige de piston étant traversée par une tige de contrôle (1) pour un ajustement axial de l élément de réglage de débit de gaz depuis l extérieur en ajustant la butée supérieure (2) et la butée inférieure, les deux avantageusement agencées sur cette tige de contrôle (1). 2. Ressort à gaz selon la revendication 1 caractérisé en ce que ledit élément de réglage de débit de gaz est un cône de réglage (42) ou un anneau ou la combinaison des deux. 3. Ressort à gaz selon l une quelconque des revendications précédentes caractérisé en ce que la butée inférieure est un anneau (60), par exemple l anneau de sûreté. 4. Ressort à gaz selon l une quelconque des revendications précédentes caractérisé en ce que sur la tige de contrôle (1), un moyen de ressort pour ramener l élément de réglage de débit de gaz et un moyen d étanchéité pour étancher la tige de contrôle traversante (1) à l égard du réservoir () sont agencés, le moyen pour ramener l élément de réglage de débit de gaz et le moyen d étanchéité de la tige de contrôle traversante étant avantageusement formés d un seul tube souple (), p. ex. d un tube de silicone ().. Ressort à gaz selon l une quelconque des revendications précédentes caractérisé en ce que au moins un clapet d étranglement (91, 92) est agencé pour fermer l orifice de transfert () en cas d un choc violent au moins dans une direction, ledit clapet d étranglement étant avantageusement formé d un cône de suspension (91) ou d une lame de suspension (92). 6. Ressort à gaz selon l une quelconque des revendications précédentes caractérisé en ce qu entre joint d étanchéité du piston (2) à l égard du cylindre de travail () et joint d étanchéité du couvercle supérieur de cylindre de travail (), traversé par le cylindre creux (21) formant la tige de piston, dans l espace (70) entre le cylindre creux (21) et l enveloppe du cylindre de travail (), est enfermé le gaz formant un amortisseur en cas de l approchement du piston au couvercle supérieur du cylindre de travail lors du levage maximal du piston (2). 7. Ressort à gaz selon l une quelconque des revendications précédentes caractérisé en ce qu entre l élément de réglage de débit de gaz et l orifice de transfert (), une entretoise (0) est agencée pour empêcher la fermeture totale de l orifice de transfert () en fonctionnement normal du ressort, l entretoise (0) d amortissement étant avantageusement déformable et ainsi permettant la fermeture totale de l orifice de transfert () en cas de besoin. 8. Ressort à gaz selon l une quelconque des revendications précédentes caractérisé en ce qu à l état de repos de ressort, le réservoir () présente d environ à 0% du volume total de gaz de travail, avantageusement environ %. 9. Ressort à gaz selon l une quelconque des revendi- 9
10 17 EP B1 18 cations précédentes caractérisé en ce que le gaz de travail est de l air.. Ressort à gaz selon l une quelconque des revendications précédentes caractérisé en ce que l orifice et/ou valve (111) sont agencés dans le joint supérieur entre le cylindre creux (21) et l enveloppe de cylindre de travail () pour permettre le remplissage respectivement la vidange de l air de compression dans/de l espace au-dessus de piston entre le cylindre creux (21), représentant une tige de piston creuse, et l enveloppe de cylindre de travail () afin de comprimer le ressort respectivement de ramener le ressort à la position initiale
11 EP B1 11
12 EP B1 12
13 EP B1 13
14 EP B1 REFERENCES CITED IN THE DESCRIPTION This list of references cited by the applicant is for the reader s convenience only. It does not form part of the European patent document. Even though great care has been taken in compiling the references, errors or omissions cannot be excluded and the EPO disclaims all liability in this regard. Patent documents cited in the description GB 1028 A [0003] US 9916 A [0004] GB A [000] US A [000] DE [0006] WO A [0007] US A [0008] US A [0009] US A [0011] US A [0012] DE [0013] DE [0014] US 4696 A [0014] GB A [0014] US A [001] DE [001] US A [001] EP A [001] 14
TEPZZ 6Z7 _6A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2013/26
 (19) TEPZZ 6Z7 _6A_T (11) EP 2 607 216 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (51) Int Cl.: B62D 55/21 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13160462.1 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 6Z7 _6A_T (11) EP 2 607 216 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (51) Int Cl.: B62D 55/21 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13160462.1 (22)
TEPZZ 5 59 A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 5 59 A T (11) EP 2 535 922 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 19.12.2012 Bulletin 2012/51 (21) Application number: 12172230.0 (51) Int Cl.: H01J 61/26 (2006.01) H01J
(19) TEPZZ 5 59 A T (11) EP 2 535 922 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 19.12.2012 Bulletin 2012/51 (21) Application number: 12172230.0 (51) Int Cl.: H01J 61/26 (2006.01) H01J
(51) Int Cl.: B66C 13/14 ( ) B66C 3/00 ( ) A01G 23/08 ( ) E02F 9/22 ( ) E02F 3/36 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 8 4Z59A_T (11) EP 2 824 059 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.01.2015 Bulletin 2015/03 (21) Application number: 13181144.0 (51) Int Cl.: B66C 13/14 (2006.01) B66C
(19) TEPZZ 8 4Z59A_T (11) EP 2 824 059 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.01.2015 Bulletin 2015/03 (21) Application number: 13181144.0 (51) Int Cl.: B66C 13/14 (2006.01) B66C
TEPZZ Z Z 85A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ Z Z 8A_T (11) EP 3 0 38 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 18.0.16 Bulletin 16/ (21) Application number: 1482271.7 (22)
(19) TEPZZ Z Z 8A_T (11) EP 3 0 38 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 18.0.16 Bulletin 16/ (21) Application number: 1482271.7 (22)
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/42
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 512 002 A2 (43) Date of publication: 17.10.2012 Bulletin 2012/42 (51) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 (2006.01) H02J 7/35 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11250613.4
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 512 002 A2 (43) Date of publication: 17.10.2012 Bulletin 2012/42 (51) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 (2006.01) H02J 7/35 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11250613.4
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2009/04
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 017 118 A1 (43) Date of publication: 21.01.2009 Bulletin 2009/04 (51) Int Cl.: B60M 1/06 (2006.01) B60M 3/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 08159353.5
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 017 118 A1 (43) Date of publication: 21.01.2009 Bulletin 2009/04 (51) Int Cl.: B60M 1/06 (2006.01) B60M 3/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 08159353.5
TEPZZ 6 6 8_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ 6 6 8_A_T (11) EP 2 626 281 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.2013 Bulletin 2013/33 (1) Int Cl.: B62D 3/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1214679.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 6 6 8_A_T (11) EP 2 626 281 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.2013 Bulletin 2013/33 (1) Int Cl.: B62D 3/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1214679.0 (22)
TEPZZ ZZ9 78A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B65D 85/804 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ ZZ9 78A_T (11) EP 3 009 378 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.04.16 Bulletin 16/16 (1) Int Cl.: B6D 8/804 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1189391.4 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ ZZ9 78A_T (11) EP 3 009 378 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.04.16 Bulletin 16/16 (1) Int Cl.: B6D 8/804 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1189391.4 (22) Date of
(51) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 ( ) H02K 1/32 ( ) H02K 1/20 ( ) H02K 7/18 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 4ZZ6 4B_T (11) EP 2 400 634 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 02.10.2013 Bulletin 2013/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 (2006.01)
(19) TEPZZ 4ZZ6 4B_T (11) EP 2 400 634 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 02.10.2013 Bulletin 2013/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 (2006.01)
(51) Int Cl.: B61F 5/38 ( ) (54) Two- axle bogie for railway vehicle with radially adjustable wheelsets with cross coupling
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 157 007 A1 (43) Date of publication: 24.02.2010 Bulletin 2010/08 (51) Int Cl.: B61F 5/38 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09475002.3 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 157 007 A1 (43) Date of publication: 24.02.2010 Bulletin 2010/08 (51) Int Cl.: B61F 5/38 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09475002.3 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: F16H 47/04 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 6774A T (11) EP 2 67 74 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.10.2013 Bulletin 2013/44 (1) Int Cl.: F16H 47/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1316271.1 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 6774A T (11) EP 2 67 74 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.10.2013 Bulletin 2013/44 (1) Int Cl.: F16H 47/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1316271.1 (22) Date
(51) Int Cl.: B41F 31/30 ( ) B41F 31/34 ( ) B41F 31/36 ( ) B41F 13/20 ( ) B41F 7/04 ( ) B41F 7/12 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 7ZZ5Z4A T (11) EP 2 700 504 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.02.2014 Bulletin 2014/09 (21) Application number: 13179814.2 (51) Int Cl.: B41F 31/30 (2006.01) B41F
(19) TEPZZ 7ZZ5Z4A T (11) EP 2 700 504 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.02.2014 Bulletin 2014/09 (21) Application number: 13179814.2 (51) Int Cl.: B41F 31/30 (2006.01) B41F
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/41
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001585051A1* (11) EP 1 585 051 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 12.10.2005 Bulletin 2005/41
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001585051A1* (11) EP 1 585 051 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 12.10.2005 Bulletin 2005/41
(51) Int Cl.: A47C 7/44 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 66_986B_T (11) EP 2 661 986 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (51) Int Cl.: A47C 7/44 (2006.01)
(19) TEPZZ 66_986B_T (11) EP 2 661 986 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (51) Int Cl.: A47C 7/44 (2006.01)
TEPZZ 7 Z4_ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2014/20
 (19) TEPZZ 7 Z4_ZA_T (11) EP 2 730 410 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.05.2014 Bulletin 2014/20 (21) Application number: 13191611.6 (22) Date of filing: 05.11.2013 (51)
(19) TEPZZ 7 Z4_ZA_T (11) EP 2 730 410 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.05.2014 Bulletin 2014/20 (21) Application number: 13191611.6 (22) Date of filing: 05.11.2013 (51)
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2001/43
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001147979A1* (11) EP 1 147 979 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.10.2001 Bulletin 2001/43
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001147979A1* (11) EP 1 147 979 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.10.2001 Bulletin 2001/43
TEPZZ 7 Z88A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 7 Z88A_T (11) EP 2 722 088 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 23.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/17 (21) Application number: 12799927.4
(19) TEPZZ 7 Z88A_T (11) EP 2 722 088 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 23.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/17 (21) Application number: 12799927.4
(51) Int Cl.: F16C 17/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 47 749B_T (11) EP 2 473 749 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.12.2015 Bulletin 2015/52 (21) Application number: 09848790.3
(19) TEPZZ 47 749B_T (11) EP 2 473 749 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.12.2015 Bulletin 2015/52 (21) Application number: 09848790.3
TEPZZ 57847_B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 57847_B_T (11) EP 2 578 471 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 16.03.2016 Bulletin 2016/11 (21) Application number: 11789623.3
(19) TEPZZ 57847_B_T (11) EP 2 578 471 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 16.03.2016 Bulletin 2016/11 (21) Application number: 11789623.3
TEPZZ _84894A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: F23N 5/12 ( ) F23N 5/24 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ _84894A_T (11) EP 3 184 894 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.06.17 Bulletin 17/26 (1) Int Cl.: F23N /12 (06.01) F23N /24 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1681.0
(19) TEPZZ _84894A_T (11) EP 3 184 894 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.06.17 Bulletin 17/26 (1) Int Cl.: F23N /12 (06.01) F23N /24 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1681.0
TEPZZ 67_744A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B60K 6/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 67_744A_T (11) EP 2 671 744 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/50 (51) Int Cl.: B60K 6/10 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13169502.5 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 67_744A_T (11) EP 2 671 744 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/50 (51) Int Cl.: B60K 6/10 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13169502.5 (22)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2006/42
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 712 388 A1 (43) Date of publication: 18.10.2006 Bulletin 2006/42 (51) Int Cl.:
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 712 388 A1 (43) Date of publication: 18.10.2006 Bulletin 2006/42 (51) Int Cl.:
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2008/04
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 880 821 A1 (43) Date of publication: 23.01.2008 Bulletin 2008/04 (51) Int Cl.: B29C 45/14 (2006.01) H04M 1/02 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 07008807.5
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 880 821 A1 (43) Date of publication: 23.01.2008 Bulletin 2008/04 (51) Int Cl.: B29C 45/14 (2006.01) H04M 1/02 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 07008807.5
TEPZZ 7 8Z6ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 7 8Z6ZA_T (11) EP 2 738 060 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.06.2014 Bulletin 2014/23 (21) Application number: 12194849.1 (51) Int Cl.: B61D 41/04 (2006.01) B60N
(19) TEPZZ 7 8Z6ZA_T (11) EP 2 738 060 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.06.2014 Bulletin 2014/23 (21) Application number: 12194849.1 (51) Int Cl.: B61D 41/04 (2006.01) B60N
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: A61F 5/01 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 86 47A_T (11) EP 2 862 47 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 22.04.201 Bulletin 201/17 (1) Int Cl.: A61F /01 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 14167197.4 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 86 47A_T (11) EP 2 862 47 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 22.04.201 Bulletin 201/17 (1) Int Cl.: A61F /01 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 14167197.4 (22) Date
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/09
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 159 888 A2 (43) Date of publication: 03.03.2010 Bulletin 2010/09 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 13/53 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09167901.9 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 159 888 A2 (43) Date of publication: 03.03.2010 Bulletin 2010/09 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 13/53 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09167901.9 (22) Date of filing:
(51) Int Cl.: H05F 3/02 ( ) F16K 1/22 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 1 637 016 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 13.02.08 Bulletin 08/07 (21) Application number: 047769.3 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (11) EP 1 637 016 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 13.02.08 Bulletin 08/07 (21) Application number: 047769.3 (22) Date of filing:
(51) Int Cl.: F01D 5/08 ( ) F01D 5/30 ( ) F01D 11/00 ( ) F01D 25/12 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _46ZB_T (11) EP 2 146 0 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28.11.2012 Bulletin 2012/48 (1) Int Cl.: F01D /08 (2006.01) F01D
(19) TEPZZ _46ZB_T (11) EP 2 146 0 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28.11.2012 Bulletin 2012/48 (1) Int Cl.: F01D /08 (2006.01) F01D
(51) Int Cl.: F03D 11/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9 66B_T (11) EP 2 92 266 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 2.06.2014 Bulletin 2014/26 (1) Int Cl.: F03D 11/02 (2006.01) (21)
(19) TEPZZ 9 66B_T (11) EP 2 92 266 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 2.06.2014 Bulletin 2014/26 (1) Int Cl.: F03D 11/02 (2006.01) (21)
TEPZZ 9 Z79A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 9 Z79A_T (11) EP 2 922 079 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.09.2015 Bulletin 2015/39 (21) Application number: 151573.2 (51) Int Cl.: H01H 31/12 (2006.01) H01H
(19) TEPZZ 9 Z79A_T (11) EP 2 922 079 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.09.2015 Bulletin 2015/39 (21) Application number: 151573.2 (51) Int Cl.: H01H 31/12 (2006.01) H01H
(51) Int Cl.: F16L 3/205 ( ) F16F 7/14 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9 8 6B_T (11) EP 2 392 836 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.03.2013 Bulletin 2013/ (51) Int Cl.: F16L 3/205 (2006.01)
(19) TEPZZ 9 8 6B_T (11) EP 2 392 836 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.03.2013 Bulletin 2013/ (51) Int Cl.: F16L 3/205 (2006.01)
TEPZZ 55_5Z6A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2013/05
 (19) TEPZZ _Z6A T (11) EP 2 1 06 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/0 (1) Int Cl.: F02K 1/72 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1217601.0 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ _Z6A T (11) EP 2 1 06 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/0 (1) Int Cl.: F02K 1/72 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1217601.0 (22) Date of
TEPZZ 7_ Z6ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 ( ) H02K 7/18 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 7_ Z6ZA_T (11) EP 2 712 060 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.03.2014 Bulletin 2014/13 (51) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 (2006.01) H02K 7/18 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ 7_ Z6ZA_T (11) EP 2 712 060 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.03.2014 Bulletin 2014/13 (51) Int Cl.: H02K 1/27 (2006.01) H02K 7/18 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
TEPZZ 557 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 557 A_T (11) EP 3 115 573 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/02 (21) Application number: 16176199.4 (51) Int Cl.: F02B 25/20 (2006.01) F02M
(19) TEPZZ 557 A_T (11) EP 3 115 573 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/02 (21) Application number: 16176199.4 (51) Int Cl.: F02B 25/20 (2006.01) F02M
(51) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 ( ) H02J 7/02 ( ) A61B 17/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_684 96B_T (11) EP 1 684 396 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 29.04. Bulletin /18 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 (06.01) H02J 7/02
(19) TEPZZ_684 96B_T (11) EP 1 684 396 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 29.04. Bulletin /18 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 7/00 (06.01) H02J 7/02
TEPZZ Z6 Z79A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01L 19/14 ( ) G01L 19/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ Z6 Z79A_T (11) EP 3 062 079 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.08.2016 Bulletin 2016/3 (1) Int Cl.: G01L 19/14 (2006.01) G01L 19/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ Z6 Z79A_T (11) EP 3 062 079 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.08.2016 Bulletin 2016/3 (1) Int Cl.: G01L 19/14 (2006.01) G01L 19/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2009/31
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 083 6 A2 (43) Date of publication: 29.07.09 Bulletin 09/31 (1) Int Cl.: H0K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 08172.9 (22) Date of filing: 0.02.08 (84)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 083 6 A2 (43) Date of publication: 29.07.09 Bulletin 09/31 (1) Int Cl.: H0K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 08172.9 (22) Date of filing: 0.02.08 (84)
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2003/49
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001366948A1* (11) EP 1 366 948 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.12.2003 Bulletin 2003/49
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001366948A1* (11) EP 1 366 948 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.12.2003 Bulletin 2003/49
(51) Int Cl. 7 : B60B 33/04. (56) References cited:
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP000958150B1* (11) EP 0 958 150 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP000958150B1* (11) EP 0 958 150 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant
TEPZZ 4_8Z84B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 4_8Z84B_T (11) EP 2 418 084 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.09.13 Bulletin 13/36 (21) Application number: 0984.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 4_8Z84B_T (11) EP 2 418 084 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.09.13 Bulletin 13/36 (21) Application number: 0984.0 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: B62J 17/00 ( ) B62J 17/02 ( ) B62J 23/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 6_ 8Z6B_T (11) EP 2 612 806 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 05.11.2014 Bulletin 2014/45 (51) Int Cl.: B62J 17/00 (2006.01)
(19) TEPZZ 6_ 8Z6B_T (11) EP 2 612 806 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 05.11.2014 Bulletin 2014/45 (51) Int Cl.: B62J 17/00 (2006.01)
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2007/47
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 88 077 A2 (43) Date of publication: 21.11.2007 Bulletin 2007/47 (1) Int Cl.: H01L 23/367 (2006.01) H01L 2/06 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 070731.2
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 88 077 A2 (43) Date of publication: 21.11.2007 Bulletin 2007/47 (1) Int Cl.: H01L 23/367 (2006.01) H01L 2/06 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 070731.2
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 9778 A_T (11) EP 2 977 82 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.01.16 Bulletin 16/04 (21) Application number: 1417804.4 (1) Int Cl.: F02B 19/ (06.01) F02B 19/12 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 9778 A_T (11) EP 2 977 82 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.01.16 Bulletin 16/04 (21) Application number: 1417804.4 (1) Int Cl.: F02B 19/ (06.01) F02B 19/12 (06.01)
TEPZZ 9 4 7A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 9 4 7A_T (11) EP 2 924 237 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 143822.3 (1) Int Cl.: F01D /08 (06.01) F01D 11/00 (06.01) F01D
(19) TEPZZ 9 4 7A_T (11) EP 2 924 237 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 143822.3 (1) Int Cl.: F01D /08 (06.01) F01D 11/00 (06.01) F01D
(51) Int Cl.: B62K 19/30 ( ) B62K 11/00 ( ) B62M 6/90 ( ) B62K 19/40 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _ 49 B_T (11) EP 2 134 92 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.02.2013 Bulletin 2013/09 (21) Application number: 08717.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ _ 49 B_T (11) EP 2 134 92 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.02.2013 Bulletin 2013/09 (21) Application number: 08717.0 (22)
TEPZZ Z85967A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ Z8967A_T (11) EP 3 08 967 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26..16 Bulletin 16/43 (21) Application number: 14871329.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ Z8967A_T (11) EP 3 08 967 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26..16 Bulletin 16/43 (21) Application number: 14871329.0 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: B66F 9/08 ( ) B66F 17/00 ( ) B66F 9/20 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _ 96B_T (11) EP 2 123 96 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 17..12 Bulletin 12/42 (1) Int Cl.: B66F 9/08 (06.01) B66F 17/00
(19) TEPZZ _ 96B_T (11) EP 2 123 96 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 17..12 Bulletin 12/42 (1) Int Cl.: B66F 9/08 (06.01) B66F 17/00
Europaisches Patentamt (1 9) Qjl) European Patent Office. Office eurodeen des brevets (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 Europaisches Patentamt (1 9) Qjl) European Patent Office Office eurodeen des brevets (11) EP 0 702 165 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) int. CI.6: F16F7/09, D06F 37/20
Europaisches Patentamt (1 9) Qjl) European Patent Office Office eurodeen des brevets (11) EP 0 702 165 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) int. CI.6: F16F7/09, D06F 37/20
(54) LITHIUM SECONDARY BATTERY PACK HAVING ENBLOC CLIP FORM COMBINED TO COINCIDE WITH TWO OR FOUR BATTERY COMPARTMENTS OF ELECTRONIC DEVICE
 (19) TEPZZ Z79_8ZA_T (11) EP 3 079 180 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 12..16 Bulletin 16/41 (21) Application number: 14867926.9
(19) TEPZZ Z79_8ZA_T (11) EP 3 079 180 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 12..16 Bulletin 16/41 (21) Application number: 14867926.9
(51) Int Cl.: B60R 19/00 ( ) E01F 15/14 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 725 435 B1 (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 18.07.2007 Bulletin 2007/29 (21) Application number: 05711175.9 (22) Date of
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 725 435 B1 (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 18.07.2007 Bulletin 2007/29 (21) Application number: 05711175.9 (22) Date of
Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) J (12) Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 810 112 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) nt. CI.6: B60H 1/34 03.12.1997
(19) J (12) Europaisches Patentamt 1 1 1 1 European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 810 112 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) nt. CI.6: B60H 1/34 03.12.1997
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/20
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001531305A1* (11) EP 1 531 305 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.05.2005 Bulletin 2005/20
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001531305A1* (11) EP 1 531 305 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.05.2005 Bulletin 2005/20
3 23S Sé. -Né 33% (12) United States Patent US 6,742,409 B2. Jun. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: 6B M 2 O. (51) Int. Cl...
 (12) United States Patent Blanchard USOO6742409B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 2004 (54) DEVICE FORTRANSMISSION BETWEEN A PRIMARY MOTOR SHAFT AND AN OUTPUT SHAFT AND LAWN MOWER PROVIDED
(12) United States Patent Blanchard USOO6742409B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 2004 (54) DEVICE FORTRANSMISSION BETWEEN A PRIMARY MOTOR SHAFT AND AN OUTPUT SHAFT AND LAWN MOWER PROVIDED
(51) Int Cl.: B62K 19/32 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 1 16 807 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 13.06.07 Bulletin 07/24 (1) Int Cl.: B62K 19/32 (06.01) (21) Application number:
(19) (11) EP 1 16 807 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 13.06.07 Bulletin 07/24 (1) Int Cl.: B62K 19/32 (06.01) (21) Application number:
~ mi mi ii mi ii imiii i ii ii i ii European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) J (12) ~ mi mi ii mi ii imiii i ii ii i ii European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 770 762 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) Int. CI.6: F01 L 1/14,
(19) J (12) ~ mi mi ii mi ii imiii i ii ii i ii European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 770 762 A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) Int. CI.6: F01 L 1/14,
(51) Int Cl.: F02M 51/06 ( ) F02M 61/12 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ ZZ968B_T (11) EP 3 009 68 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.09.17 Bulletin 17/36 (1) Int Cl.: F02M 1/06 (06.01) F02M 61/12
(19) TEPZZ ZZ968B_T (11) EP 3 009 68 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.09.17 Bulletin 17/36 (1) Int Cl.: F02M 1/06 (06.01) F02M 61/12
(51) Int Cl.: B04B 11/02 ( ) B04B 13/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 6 7797B_T (11) EP 2 637 797 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.04.2016 Bulletin 2016/14 (21) Application number: 11784932.3
(19) TEPZZ 6 7797B_T (11) EP 2 637 797 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.04.2016 Bulletin 2016/14 (21) Application number: 11784932.3
(51) Int Cl.: H02J 7/35 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 2 0 12 B1 (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.02.12 Bulletin 12/0 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 7/3 (06.01) (21) Application number: 08172418.9
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 2 0 12 B1 (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.02.12 Bulletin 12/0 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 7/3 (06.01) (21) Application number: 08172418.9
TEPZZ 68 A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2014/02
 (19) TEPZZ 68 A T (11) EP 2 682 333 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.01.2014 Bulletin 2014/02 (21) Application number: 13174817.0 (51) Int Cl.: B62K 25/08 (2006.01) F16F
(19) TEPZZ 68 A T (11) EP 2 682 333 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.01.2014 Bulletin 2014/02 (21) Application number: 13174817.0 (51) Int Cl.: B62K 25/08 (2006.01) F16F
TEPZZ Z56 96A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2016/33
 (19) TEPZZ Z6 96A_T (11) EP 3 06 396 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 17.08.16 Bulletin 16/33 (21) Application number: 161074.4 (1) Int Cl.: B60T 8/17 (06.01) B60T 8/88 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ Z6 96A_T (11) EP 3 06 396 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 17.08.16 Bulletin 16/33 (21) Application number: 161074.4 (1) Int Cl.: B60T 8/17 (06.01) B60T 8/88 (06.01)
Europaisches Patentamt (19) J. European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) J Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 885 802 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) int. CI.6: B62M 23/02 23.12.1998 Bulletin
(19) J Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets (11) EP 0 885 802 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) int. CI.6: B62M 23/02 23.12.1998 Bulletin
TEPZZ Z4Z 75A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ Z4Z 7A_T (11) EP 3 0 27 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.07.16 Bulletin 16/27 (21) Application number: 1161787. (1) Int Cl.: B64D 13/06 (06.01) B64D 37/32 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ Z4Z 7A_T (11) EP 3 0 27 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.07.16 Bulletin 16/27 (21) Application number: 1161787. (1) Int Cl.: B64D 13/06 (06.01) B64D 37/32 (06.01)
TEPZZ Z 44Z8A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B64D 33/02 ( ) B64D 41/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ Z 44Z8A_T (11) EP 3 034 8 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 22.06.16 Bulletin 16/2 (1) Int Cl.: B64D 33/02 (06.01) B64D 41/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1199431.6
(19) TEPZZ Z 44Z8A_T (11) EP 3 034 8 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 22.06.16 Bulletin 16/2 (1) Int Cl.: B64D 33/02 (06.01) B64D 41/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1199431.6
(51) Int Cl.: F16H 63/06 ( ) F16H 9/18 ( ) F16H 55/56 ( ) (56) References cited:
 (19) TEPZZ 784 8B_T (11) EP 2 784 38 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.01.2016 Bulletin 2016/01 (1) Int Cl.: F16H 63/06 (2006.01)
(19) TEPZZ 784 8B_T (11) EP 2 784 38 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.01.2016 Bulletin 2016/01 (1) Int Cl.: F16H 63/06 (2006.01)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1. Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002
 USOO6435993B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1 Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) HYDRAULIC CHAIN TENSIONER WITH 5,707.309 A 1/1998 Simpson... 474/110 VENT DEVICE AND
USOO6435993B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,435,993 B1 Tada (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) HYDRAULIC CHAIN TENSIONER WITH 5,707.309 A 1/1998 Simpson... 474/110 VENT DEVICE AND
TEPZZ 8998 ZB_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8998 ZB_T (11) EP 2 899 8 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.08.17 Bulletin 17/3 (21) Application number: 11018.7 (1) Int Cl.:
(19) TEPZZ 8998 ZB_T (11) EP 2 899 8 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.08.17 Bulletin 17/3 (21) Application number: 11018.7 (1) Int Cl.:
(51) Int Cl.: H02K 51/00 ( ) H02K 49/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z8_59B_T (11) EP 2 308 159 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.09.2017 Bulletin 2017/39 (21) Application number: 09776927.7
(19) TEPZZ Z8_59B_T (11) EP 2 308 159 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.09.2017 Bulletin 2017/39 (21) Application number: 09776927.7
TEPZZ 9_8945A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: F24J 3/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9_894A_T (11) EP 2 918 94 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.09.1 Bulletin 1/38 (1) Int Cl.: F24J 3/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1416093.1 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ 9_894A_T (11) EP 2 918 94 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.09.1 Bulletin 1/38 (1) Int Cl.: F24J 3/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1416093.1 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ Z874Z7B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ Z874Z7B_T (11) EP 2 087 407 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 17.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/29 (21) Application number: 07860559.9
(19) TEPZZ Z874Z7B_T (11) EP 2 087 407 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 17.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/29 (21) Application number: 07860559.9
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B60T 8/17 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9445 6A_T (11) EP 2 944 526 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.11.2015 Bulletin 2015/47 (51) Int Cl.: B60T 8/17 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 15166035.4 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 9445 6A_T (11) EP 2 944 526 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.11.2015 Bulletin 2015/47 (51) Int Cl.: B60T 8/17 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 15166035.4 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: B62K 21/00 ( ) B62K 25/16 ( ) B62K 25/28 ( ) B62J 15/00 ( ) B62K 21/20 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 1 910 159 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.01.2010 Bulletin 2010/04 (21) Application number: 05764546.7 (22) Date of
(19) (11) EP 1 910 159 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.01.2010 Bulletin 2010/04 (21) Application number: 05764546.7 (22) Date of
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001 0023637A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0023637 A1 Klitmose et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2001 (54) FLEXIBLE PISTON ROD (76) Inventors: Lars Peter
(19) United States US 2001 0023637A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0023637 A1 Klitmose et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 27, 2001 (54) FLEXIBLE PISTON ROD (76) Inventors: Lars Peter
TEPZZ ZZ _A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: F28F 3/10 ( ) F28F 3/08 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ ZZ _A_T (11) EP 3 001 131 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.03.16 Bulletin 16/13 (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/ (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1418664.2
(19) TEPZZ ZZ _A_T (11) EP 3 001 131 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.03.16 Bulletin 16/13 (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/ (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1418664.2
(51) Int Cl.: E05F 3/22 ( ) E05F 3/10 ( ) E05F 3/20 ( ) E05D 7/04 ( ) E05D 5/02 ( ) E05D 7/081 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 68 55 B_T (11) EP 2 682 553 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 22.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/12 (21) Application number: 12180603.8
(19) TEPZZ 68 55 B_T (11) EP 2 682 553 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 22.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/12 (21) Application number: 12180603.8
Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office. Publication number: Office europeen des brevets EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 Europaisches Patentamt J t European Patent Office Publication number: 0 265 682 Office europeen des brevets A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 87114152.9 Date of filing: 28.09.87 int. ci*
Europaisches Patentamt J t European Patent Office Publication number: 0 265 682 Office europeen des brevets A1 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 87114152.9 Date of filing: 28.09.87 int. ci*
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,994,308 B1. Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2006
 United States Patent USOO69943O8B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,994,308 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2006 (54) IN-TUBE SOLENOID GAS VALVE 4,520,227 A * 5/1985 Krimmer et al.... 251/129.21
United States Patent USOO69943O8B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,994,308 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2006 (54) IN-TUBE SOLENOID GAS VALVE 4,520,227 A * 5/1985 Krimmer et al.... 251/129.21
(51) Int Cl.: H01J 61/34 ( ) F21V 17/04 ( ) H01J 61/70 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 683 184 B1 (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.12.2007 Bulletin 2007/0 (21) Application number: 0477493.2 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 683 184 B1 (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.12.2007 Bulletin 2007/0 (21) Application number: 0477493.2 (22) Date of filing:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
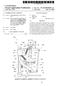 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0159457 A1 Saint-Marc et al. US 2016015.9457A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) RUDDER BAR FOR AN AIRCRAFT (71) Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0159457 A1 Saint-Marc et al. US 2016015.9457A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) RUDDER BAR FOR AN AIRCRAFT (71) Applicant:
IIIHIIII 5,509,863. United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. Apr. 23, Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent:
 United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. 54) TRANSMISSION DEVICE, ESPECIALLY FOR BOAT MOTORS 75 Inventors: Staffan Månsson, Hjalteby; Benny Hedlund, Hönö, both of Sweden 73 Assignee: AB Volvo Penta, Gothenburg,
United States Patent (19) Månsson et al. 54) TRANSMISSION DEVICE, ESPECIALLY FOR BOAT MOTORS 75 Inventors: Staffan Månsson, Hjalteby; Benny Hedlund, Hönö, both of Sweden 73 Assignee: AB Volvo Penta, Gothenburg,
(51) Int Cl.: C10L 1/02 ( ) F02B 77/04 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _8_66 A_T (11) EP 3 181 663 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.06.17 Bulletin 17/2 (1) Int Cl.: CL 1/02 (06.01) F02B 77/04 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1382628.4
(19) TEPZZ _8_66 A_T (11) EP 3 181 663 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.06.17 Bulletin 17/2 (1) Int Cl.: CL 1/02 (06.01) F02B 77/04 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1382628.4
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,820,200 Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998
 USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
USOO582O2OOA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Zubillaga et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 1998 54 RETRACTABLE MOTORCYCLE COVERING 4,171,145 10/1979 Pearson, Sr.... 296/78.1 SYSTEM 5,052,738
(51) Int Cl.: F16L 33/04 ( ) F16L 21/00 ( ) F16L 21/06 ( ) F16L 55/172 ( ) F01N 13/18 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_7_4Z6B_T (11) EP 1 714 06 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 17.12.14 Bulletin 14/1 (21) Application number: 0713378.7 (22)
(19) TEPZZ_7_4Z6B_T (11) EP 1 714 06 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 17.12.14 Bulletin 14/1 (21) Application number: 0713378.7 (22)
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,988,655 Sakai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999
 USOO5988655A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Sakai et al. () Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54) VEHICULAR HEIGHT ADJUSTING DEVICE 3,554,5 1/1971 De Koning et al.... 267/64.17 3,593,978 7/1971
USOO5988655A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Sakai et al. () Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54) VEHICULAR HEIGHT ADJUSTING DEVICE 3,554,5 1/1971 De Koning et al.... 267/64.17 3,593,978 7/1971
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O124322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0124322 A1 Cimatti (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2014 (54) NORMALLY CLOSED AUTOMOTIVE (52) U.S. Cl. CLUTCH WITH HYDRAULC
(19) United States US 2014O124322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0124322 A1 Cimatti (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2014 (54) NORMALLY CLOSED AUTOMOTIVE (52) U.S. Cl. CLUTCH WITH HYDRAULC
(51) Int Cl.: F01N 1/02 ( ) F01N 13/02 ( ) F01N 1/00 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 1 789 660 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.05.2010 Bulletin 2010/19 (21) Application number: 05815839.5 (22) Date of
(19) (11) EP 1 789 660 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.05.2010 Bulletin 2010/19 (21) Application number: 05815839.5 (22) Date of
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO64994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Matsumoto (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) STATIONARY BIKE (52) U.S. Cl.... 482/8 (76) Inventor: Masaaki Matsumoto,
(19) United States US 2005OO64994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Matsumoto (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) STATIONARY BIKE (52) U.S. Cl.... 482/8 (76) Inventor: Masaaki Matsumoto,
(51) Int Cl.: F03D 3/06 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z47_4 B_T (11) EP 3 047 142 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21.06.2017 Bulletin 2017/25 (21) Application number: 14786540.6
(19) TEPZZ Z47_4 B_T (11) EP 3 047 142 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21.06.2017 Bulletin 2017/25 (21) Application number: 14786540.6
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Imai USOO6581225B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,581,225 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2003 (54) MATTRESS USED FOR PREVENTING BEDSORES OR THE LIKE (76) Inventor: KaZumichi Imai, 7-29-1222,
(12) United States Patent Imai USOO6581225B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,581,225 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 24, 2003 (54) MATTRESS USED FOR PREVENTING BEDSORES OR THE LIKE (76) Inventor: KaZumichi Imai, 7-29-1222,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,791,205 B2
 USOO6791205B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Woodbridge (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2004 (54) RECIPROCATING GENERATOR WAVE 5,347,186 A 9/1994 Konotchick... 310/17 POWER BUOY 5,696,413 A 12/1997
USOO6791205B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Woodbridge (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2004 (54) RECIPROCATING GENERATOR WAVE 5,347,186 A 9/1994 Konotchick... 310/17 POWER BUOY 5,696,413 A 12/1997
TEPZZ_99 5 ZB_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ_99 ZB_T (11) EP 1 992 20 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 31.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/31 (1) Int Cl.: B60N 2/60 (2006.01) B60N
(19) TEPZZ_99 ZB_T (11) EP 1 992 20 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 31.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/31 (1) Int Cl.: B60N 2/60 (2006.01) B60N
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070011840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0011840 A1 Gilli (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 18, 2007 (54) WINDSCREEN WIPER ARM (75) Inventor: Marco Gilli, Chieri
(19) United States US 20070011840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0011840 A1 Gilli (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 18, 2007 (54) WINDSCREEN WIPER ARM (75) Inventor: Marco Gilli, Chieri
(51) Int Cl.: A61M 5/24 ( ) A61M 5/32 ( ) A61M 5/20 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 6548 8B_T (11) EP 2 654 838 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.08.2017 Bulletin 2017/34 (21) Application number: 11802724.2
(19) TEPZZ 6548 8B_T (11) EP 2 654 838 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.08.2017 Bulletin 2017/34 (21) Application number: 11802724.2
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,446,482 B1. Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002
 USOO64.46482B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002 (54) BATTERY OPERATED HYDRAULIC D408.242 S 4/1999 Yamamoto... D8/61 COMPRESSION TOOL WITH RAPID
USOO64.46482B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Heskey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 2002 (54) BATTERY OPERATED HYDRAULIC D408.242 S 4/1999 Yamamoto... D8/61 COMPRESSION TOOL WITH RAPID
(51) Int Cl.: D01D 5/00 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 673 493 B1 (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 08.07.09 Bulletin 09/28 (21) Application number: 047628.7 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (11) EP 1 673 493 B1 (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 08.07.09 Bulletin 09/28 (21) Application number: 047628.7 (22) Date of filing:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7654162B2 (12) United States Patent Braaten (54) DEVICE FOR INSTALLATION OF A PROBE AND PROBEACCOMMODATING ARRANGEMENT (75) Inventor: Nils A. Braaten, Trondheim (NO) (73) Assignee: Roxar ASA, Stavanger
USOO7654162B2 (12) United States Patent Braaten (54) DEVICE FOR INSTALLATION OF A PROBE AND PROBEACCOMMODATING ARRANGEMENT (75) Inventor: Nils A. Braaten, Trondheim (NO) (73) Assignee: Roxar ASA, Stavanger
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2. Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005
 United States Patent USOO6915721B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2 Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) CORDLESS RATCHET WRENCH 6,311,583 B1 11/2001 Izumisawa... 81/57.13 6,715,380
United States Patent USOO6915721B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,721 B2 Hsu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) CORDLESS RATCHET WRENCH 6,311,583 B1 11/2001 Izumisawa... 81/57.13 6,715,380
(51) Int Cl.: F23D 1/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z_ZZB_T (11) EP 2 01 00 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.06.2017 Bulletin 2017/24 (1) Int Cl.: F23D 1/02 (2006.01) (21)
(19) TEPZZ Z_ZZB_T (11) EP 2 01 00 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.06.2017 Bulletin 2017/24 (1) Int Cl.: F23D 1/02 (2006.01) (21)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2
 US009 168973B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2 Offe (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2015 (54) MOTORCYCLE SUSPENSION SYSTEM (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Andrew Offe, Wilunga
US009 168973B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,168,973 B2 Offe (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 27, 2015 (54) MOTORCYCLE SUSPENSION SYSTEM (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Andrew Offe, Wilunga
TEPZZ 55_ZZ9A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B01D 53/94 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _ZZ9A_T (11) EP 2 1 009 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.01.13 Bulletin 13/0 (1) Int Cl.: B01D 3/94 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1217.7 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ _ZZ9A_T (11) EP 2 1 009 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.01.13 Bulletin 13/0 (1) Int Cl.: B01D 3/94 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1217.7 (22) Date of filing:
AN, (12) United States Patent. (10) Patent No.: US 6,443,131 B1. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, (54)
 (12) United States Patent BueSer USOO6443.131B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) FLAT PIPE PRESSURE DAMPER FOR DAMPING OSCILLATIONS IN LIQUID PRESSURE IN PIPES CARRYING LIQUIDS (75)
(12) United States Patent BueSer USOO6443.131B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) FLAT PIPE PRESSURE DAMPER FOR DAMPING OSCILLATIONS IN LIQUID PRESSURE IN PIPES CARRYING LIQUIDS (75)
