Modeling Filter Bypass: Impact on Filter Efficiency
|
|
|
- Dinah Barnett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modeling Filter Bypass: Impact on Filter Efficiency Matthew Ward Jeffrey Siegel, Ph.D. Member ASHRAE ABSTRACT Current models and test methods for determining filter efficiency ignore filter bypass, the air that circumvents filter media because of gaps around the filter or filter housing. In this paper, we develop a general model to estimate the size-resolved particle removal efficiency, including bypass, of HVAC filters. The model applies the measured pressure drop of the filter to determine the airflow through the bypass cracks and accounts for particle loss in the bypass cracks. We consider a particle size range of 1 to 10 µm, nine typical commercial and residential filters in clean and dust-loaded configurations, and a wide range of bypass gaps typical of those found in real filter installations. The model suggests that gaps on the order of around well-seated filters have little effect on the performance of most filters. For high pressure drop filters, small gaps decrease filter performance and large gaps substantially decrease filter performance. Because higher efficiency filters also typically have a larger pressure drop, bypass tends to have a larger effect on high performance filters. The results provided here suggest that bypass can dramatically affect filter performance. INTRODUCTION Filtration in HVAC systems is the most widely used method for protecting people and equipment from airborne particulate matter. To aid in filter selection, there are several standards that address HVAC filtration efficacy including ASHRAE Standard 52.2: Method of Testing General Ventilation Air-Cleaning Devices for Removal Efficiency by Particle Size (ASHRAE 1999) and ASHRAE Standard 52.1: Gravimetric and Dust-Spot Procedures for Testing Air-Cleaning Devices Used in General Ventilation for Removing Particulate Matter (ASHRAE 1992). The result of an ASHRAE Standard 52.2 test includes the Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value (MERV), which classifies filters according to their efficiency. Standard 52.2, as well as most other filter test methodologies, are tests of the filter media, rather than the installed filter system. When applied to real systems, filter test results implicitly assume that no bypass exists around filters. Examination of most residential and commercial HVAC systems suggests that this is not a good assumption: both small and large gaps are common. The purpose of this paper is to simulate the effect of filter bypass on common filters. HVAC filtration has been widely studied, and several studies have measured particle-size resolved efficiencies for a variety of filters (e.g. Hanley et al. 1994; Raynor and Chae 2003). Filter efficiency curves are typically U- shaped with very small particles (<5 µm) removed by Brownian diffusion and very large particles (>5 µm) removed by inertial mechanisms. Although most measurements have been made with filter bypass intentionally sealed, there are numerous anecdotal reports of particle bypass. Braun (1986) reported that catastrophic filter bypass led to fouling of an evaporator coil. Ottney (1993) and several others suggest that eliminating filter bypass is an important component of achieving acceptable indoor air quality. Siegel (2002) simulated filter bypass and suggested that even moderate amounts of filter bypass could dramatically increase HVAC heat exchanger fouling. Despite its obvious importance, we know of no existing mathematical models for filter bypass and decisionmakers have limited information available on the effect of bypass. In this paper we present a model of filter bypass that predicts the amount of air that will bypass a filter, and the effect on overall filter efficiency. The most important independent parameters are the size (i.e. gap width) and geometry of the gaps around the filter and the efficiency and pressure drop of the filter. We report several parameters including the volumetric airflow that bypasses the filter (Q B ) and the effective filter efficiency as a function of particle diameter (η eff ) for the filter system (filter + bypass). We apply our model to a variety of commonly used HVAC filters in order to understand the interplay between filter efficiency, pressure drop, and bypass. From these simulations, we calculate the effective MERV (MERV eff ) that accounts for bypass. The results are intended to provide additional assistance when selecting filters and to quantify the benefits associated with eliminating bypass.
2 METHODOLOGY An effective filtration efficiency that includes bypass can be derived by differentiating bypass flow from filtered flow. Knowledge of both the bypass flow rate and the removal of particles in the gap, as well as the flow through the filter and the particle removal by the filter, are needed to implement the model. In order to quantify bypass flow, a quadratic relationship is employed to relate flow to pressure drop in a rectangular sharp-edged crack such as are present in HVAC filter holders or slots. Flow through the filter and filter efficiency are determined from measured data in the literature. The flow through an HVAC filter system (Q) can be considered as the sum of the flow passing through the filter media (Q F ) and the flow bypassing the filter (Q B ). The effective particle removal efficiency of the filter can then be written in terms of the penetration fraction of particles passing through the filter (P F ) and the penetration fraction of particles bypassing the filter (P B ) as shown in Equation 1. PF QF + PB QB η eff = 1 (1) Q P F is equal to one minus the measured particle removal efficiency, η F, of a filter with the gap sealed (Q B = 0). Hanley et al. (1994) measured P F and Q for various filters with different dust loadings and pressure drops. They eliminated bypass in their experiments, so Q equals Q F for their work. The results of Hanley et al. (1994) and the measurements of filters from a major manufacturer by an independent laboratory provide values of P F and Q F for our model. We estimated Q B by using an expression, derived by Baker et al. (1987), that relates airflow to pressure drop through a rectangular-shaped crack in terms of the crack dimensions. Equation 2 is the Baker et al. (1987) expression applied to a bypass crack around a filter. This expression accounts for both laminar and turbulent flow and is directly applicable to the sharp-edged, rectangular gap between a filter and the filter frame or slot that holds the filter in place. 12µ L (1.5 + n) ρ 2 P = Q 3 B + Q 2 2 B (2) WH 2W H where P is the pressure drop across the filter, Q B is the flow rate of air bypassing the filter, L is the length of the crack longitudinal to the flow, W is the width of the crack perpendicular to flow, H is the height of the crack, n is the number of right angle bends (n < 3 for Equation 2 to be valid) in the path of bypass flow, µ is the dynamic viscosity of air, and ρ is the density of the air. Baker et al. (1987) experimentally validated their model for P between and 100 Pa, and they demonstrated that, for P up to 200 Pa, their model is superior to the power law relationship between pressure drop and flow. The results of Baker et al. (1987) show strongest agreement with measured data for higher Reynolds numbers and large gaps, conditions typical of those around HVAC filters. Equation 2 can be solved for Q B, as shown in Equation 3: Q B 12µ L + 3 WH = 2 12µ L 2(1.5 + n) ρ P WH W H (1.5 + n) ρ 2 2 W H (3) Several researchers have studied deposition of particles traveling through cracks (Liu and Nazaroff 2001; Mosley et al. 2001; Carrie and Modera 2002). To account for P B, we adapted the model of Liu and Nazaroff (2001) for particle penetration efficiency through a building envelope crack. As shown in Equation 4, Liu and Nazaroff (2001) modeled particle penetration through a rectangular crack as the product of penetration due to individual particle removal mechanisms.
3 P P P P P P B = (4) g d i g d P g, particle penetration due to gravitational settling, is assumed to be independent of P d, particle penetration due to diffusion, since these two particle removal mechanisms are significant for different sized particles. P i, particle penetration due to impaction, and P g are not independent, and particles with enough inertia to be removed by impaction usually are removed by gravitational settling. Therefore, we have neglected P i in order to avoid overestimating the removal of larger particles in the gaps. The model of Liu and Nazaroff was intended for cracks in buildings where P is less than 10 Pa, whereas the P across an HVAC filter can be greater than 100 Pa. However, Liu and Nazaroff s reasoning should extend to HVAC filter gaps because it is based on the Baker et al. (1987) relationship between Q B and P, which was validated for P up to 100 Pa and applies theoretically for higher P. Liu and Nazaroff (2003) later experimentally validated their model. Model Parameters The model was applied to ten different HVAC filters with particle size, pressure drop, and gap shape varied. The face velocity (and hence Q F ) was held constant for each filter. Table 1 summarizes the descriptions of each filter. Table 1: Filter characteristics Filter Face Area (m 2 ) Face velocity (m/s) Display Element Filter Depth Filter Name (m) Furnace Filter a Fig. 2 Self-Charging Panel Filter a Fig. 3 Pleated Panel Filter a Fig. 4 Panel Electronic Filter a Fig. 5 Pleated Paper-Media Filter a Fig. 6 Pocket Filter a Fig. 7 MERV 6 b Fig. 8 MERV 11 b Fig. 9 MERV 15 b Fig. 10 a: Data from Hanley et al.. (1994) b: Data from independent test lab Effective particle removal efficiency, η eff, was compared for each filter with five gap shapes while P and Q F were held constant. The gap configurations were characterized as follows: the first was the no bypass case; the second, H = and n = 2, was chosen to represent the lower bound on Q B in which a filter is well seated around its perimeter in a U-shaped slot; the third, H = and n = 0, was chosen to represent a well-seated filter with a straight-through crack; the fourth gap configuration, H = and n = 2, was chosen to represent a poorly seated filter with a U-shaped gap; the final, H = and n = 0, was chosen to represent the upper bound on Q B in which the filter is poorly seated against a flange with no bends in the path of the air bypassing the filter. For all gap configurations, W is equal to the distance around the perimeter of the filter, and L (the distance a particle travels as it bypasses the filter) is equal to the depth (short dimension) of the filter plus 20 mm added for each bend (each flange adds 20mm to L.). Table 2 summarizes the bypass gap dimensions for each case considered. Table 2: Bypass gap descriptions Dimension U-shaped gap 2 bends Straight-through gap 0 bends U-shaped gap 2 bends Straight-through gap 0 bends H 0 L 0 Filter depth mm Filter depth Filter depth mm Filter depth W 0 Filter perimeter Filter perimeter Filter perimeter Filter perimeter
4 RESULTS This section presents model simulation results for each of the nine filters described in Table 1. Crack height (H), pressure drop ( P), and, to a lesser extent, the number of bends (n) significantly affected the bypass flow rate (Q B ). The Penetration fraction (P F ) and Q B significantly affected the effective filtration efficiency (η eff ), but the bypass penetration fraction (P B ) only slightly affected η eff. Impact of bypass on flow Model simulations indicate that Q B increases significantly as gap size (H) or pressure drop ( P) increase. Further, effective fractional particle removal efficiency (η eff ) decreases significantly with Q B and increases with the number of bends (n) for every particle size. To illustrate the relationship between bypass flow, pressure drop, and gap shape, Q B /Q has been plotted as a function of P for a 1 m 1 m 25 m filter with a 1.87 m/s face velocity for several gap shapes. Figure 1 shows that Q B /Q increases parabolically with P and that both gap size (H) and the number of bends (n) are important. Bypass flows are small (i.e. less than 5% of total flow) for a gap and increase to 25-35% for a gap. For a given gap size, increasing the number of bends decreases the bypass flow, and thus decreases the bypass flow ratio. Bypass flow ratio 2 bends 5 mm 5 mm 2 bends 2 bends Pressure Drop (Pa) Figure 1: Relationship between pressure drop and bypass flow Another factor that affects P, and hence Q B /Q, is the age or the amount of dust built up on the filter. A clean filter will have a lower pressure drop than at any other time during its life. Hence, the smallest bypass flow occurs when a filter is clean. Table 3, which presents Q B /Q for each combination of clean filter and gap shape, shows that the ratio of bypass flow to total flow for clean filters ranges from 1-27%.
5 Table 3: Ratio of initial bypass flow to total flow rate for each clean filter U-shaped Straight-through U-shaped gap gap gap 2 bends 0 bends 2 bends Straight-through gap 0 bends Clean P Q F Filter (Pa) (m 3 /s) Furnace Filter % % 9.8% 14.3% Self-Charging Panel Filter % 1.9% 17.0% 23.8% Pleated Panel Filter % 2.5% 19.2% 26.7% Panel Electronic Filter % 2.5% 19.6% 27.2% Pleated Paper-Media Filter % % 17.7% 24.7% Pocket Filter % % 18.8% 25.6% MERV % % 14.1% 2% MERV % % 15.2% 21.5% MERV % 1.5% 14.7% 2% Table 4, which presents Q B /Q for each combination of dust-loaded filter and gap shape, shows that the ratio of bypass flow to total flow ranges from 1-38% for dirty filters. Filter Table 4: Ratio of bypass flow to total flow rate for each dust-loaded filter U-shaped Straight-through U-shaped Dirty P Q F gap gap gap (Pa) (m 3 /s) 2 bends 0 bends 2 bends Straight-through gap 0 bends Furnace Filter % 4.4% 27.9% 37.2% Self-Charging Panel Filter % 4.4% 27.9% 37.2% Pleated Panel Filter % 3.7% 24.4% 33.1% Panel Electronic Filter % 4.4% 27.9% 37.2% Pleated Paper-Media Filter % 1.7% 27.8% 36.9% Pocket Filter % % 27.2% 36.0% MERV % 2.2% 28.5% 37.8% MERV % 1.3% 17.8% 24.9% MERV % 2.2% 18.4% 25.6% Impact of bypass on filter efficiency The effective efficiency, η eff is plotted as a function of particle size for each clean (Figures 2a-10a) and dustloaded (Figures 2b-10b) filter. The five gap configurations discussed above are presented in each figure. The nobypass case comes from measured data of Hanley et al. (1994) and from an independent test lab. The lines represent simulated effective filter efficiencies for each gap. These figures delineate the bounds of the influence of bypass on efficiency for a range of typical filters. In general, a gap slightly lowered the fractional efficiency for every particle size, and a gap significantly lowered fractional efficiency. Gaps with two bends lowered fractional efficiency less than gaps with no bends. Fractional efficiency was lowered by about the same amount for particles less than 1 µm. For particles larger than 1µm, fractional efficiency was lowered less as particle size increased. This indicates that particles larger than 1µm deposit in the gap but particles smaller than 1 µm are not appreciably removed in the gap. For most of the filters, a gap completely negates the added efficiency from dust loading, and a clean filter with no gap performs better than a loaded filter with a gap. For relatively low pressure drop filters, such as the clean Furnace Filter (Figure 2a), the bypass flow, Q B, is quite small. For the gaps, the effective efficiency, η eff, is very close to the filter efficiency, η F. For the larger gaps, the effective efficiency is close to zero for all submicron particles. Figure 2b shows the same filter when loaded with test dust to 125 Pa. The larger pressure drop causes more bypass flow, which in turn causes an increased reduction in η eff. Overall efficiency reductions are 2-5 percentage points for gaps and percentage points for gaps.
6 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends Figure 2: Effective particle removal efficiency for a clean and dust-loaded Furnace Filter with pressure drops of 10 and 125 Pa, respectively Figure 3 shows η eff for a Self-Charging Panel Filter. Bypass decreases η eff by about one percentage point for a gap to about 20 percentage points for a gap. For the Self-Charging Panel Filter with a large gap, η eff is zero for the most respirable range of particle size. This observation indicates that bypass could negate most protection to indoor air quality afforded by this filter. 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends Figure 3: Effective particle removal efficiency for a clean and dust-loaded Self-Charging Panel Filter with pressure drops of 35 and 125 Pa, respectively Like the Furnace Filter (Figure 2) and the Self-Charging Filter (Figure 3), the Pleated Panel Filter (Figure 4) offers no protection from most respirable particles when large bypass gaps are present. Bends begin to play a significant role in this filter with a difference of five percentage points for 2 µm particles.
7 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends Figure 4: Effective particle removal efficiency for a clean and dust-loaded Pleated Panel Filter with pressure drops of 68 and 125 Pa, respectively The number of bends in the bypass gap is important for the Panel Electronic Filter (Figure 5). Two bends decrease efficiency by two to three percentage points for a clean filter with small gaps to about six percentage points for large gaps. Bypass decreases efficiency much more for the smallest and largest particles than for the middle range for this filter. 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends Figure 5: Effective particle removal efficiency for a clean and dust-loaded Panel Electronic Filter with pressure drops of 50 and 125 Pa, respectively Figures 6 and 7 show the effective efficiency of the Pleated Paper-Media Filter and the Pocket Filter, respectively. Bypass has a similar impact on both of these filters. The gap causes almost no change in the effective efficiency, and the number of bends is unimportant. For the gaps, the effective efficiency degrades by percentage points for the clean Pleated Paper-Media Filter and percentage points for the Pocket Filter. When loaded to 125 Pa, the effective efficiency of the Pleated Paper-Media Filter decreases by percentage points and the Pocket Filter shows a similar degradation of percentage points. Note that when loaded, and with no bypass, the Pocket Filter has a measured efficiency of over 90% for the entire particle size range
8 measured by Hanley et al. (1994). With a bypass crack, the effective efficiency drops to between 50 and 60% over the same range. Another interesting observation about the Pleated Paper Media Filter and the Pocket Filter is that decreased efficiency is fairly uniform over the range of particle sizes. 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends Figure 6: Effective particle removal efficiency for a clean and dust-loaded Pleated Paper-Media Filter with pressure drops of 40 and 125 Pa, respectively 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends Figure 7: Effective particle removal efficiency for a clean and dust-loaded Pocket Filter with pressure drops of 50 and 125 Pa, respectively The MERV rated filters show data for a particles ranging from 10 µm as opposed to the range used in Figures 2 7. The different range is representative of the fact that this data was produced as part of an ASHRAE Standard 52.2 test. This particle size range shows that bypass has a greater influence on efficiency as particle size increases. The MERV filters should not be compared to the other filters in this study without noting differences in face velocity, flow rate, filter area, and filter depth. For most of the filters, a gap completely negates the added efficiency from dust loading, and the clean filter with no gap performed better than the loaded filter with a gap. However, for the MERV 6 (Figure 8)
9 filter dust loading increases efficiency by more than the gap lowers efficiency, and this dust-loaded filter with a gap performs better than the clean filter with no gap. 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends Figure 8: Effective particle removal efficiency for a clean and dust-loaded MERV 6 filter with pressure drops of 26 and 150 Pa, respectively For the MERV 11 filter (Figure 9), the importance of bends increases as particles increase in size up to 2 µm, after which, the number of bends no longer increases in importance. Also, for the MERV 11 filter, a gap height of 1 mm makes almost no effect on efficiency. 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends Figure 9: Effective particle removal efficiency for a clean and dust-loaded MERV 11 filter with pressure drops of 88 and 125 Pa, respectively The MERV 15 filter (Figure 10) has the largest clean pressure drop, P, of any of the other filters and, not surprisingly, it has the least difference in efficiency between clean and dust loaded. Bypass lowers efficiency by percentage points for gaps with 2 bends to percentage points for gaps with no bends.
10 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends 2 bends Figure 10: Effective particle removal efficiency for a clean and dust-loaded MERV 15 filter with pressure drops of 92 and 156 Pa, respectively Impact of bypass on MERV rating Effective MERV ratings (MERV eff ) that include the effect of bypass were calculated for the three MERV rated filters. For the MERV 15 filter, a small gap (H = ) caused the MERV eff rating to decrease by one point. A small gap did not decrease the rating of the MERV 11 or the MERV 6 filter. A large gap decreased the rating of the MERV 15 filter by seven points, the MERV 11 filter by three points, and the MERV 6 filter by one point. Except for the MERV 6 filter, bends did not make large enough differences to change the MERV eff rating. Table 5 summarizes these results. Table 5: Effective MERV ratings with bypass included Filter gap, 2 bends gap, 0 bends gap, 2 bends gap, 0 bends MERV <5 MERV MERV DISSCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS The results have important implications for the understanding filter performance. They suggest that most HVAC filters with sizeable bypass gaps actually perform worse with age, which is opposite to the assumption of conventional knowledge. Moreover, high efficiency filters may not justify their expense if they have sizable gaps. For example the loaded Pleated Paper-Media Filter with no gap performs better than the loaded Pocket Filter with a gap. In other words any economic analysis seeking to optimize the cost effectiveness of filtration must either include costs for minimizing bypass or account for reduced efficiency caused by bypass. The data presented in this paper can provide a basis for such analyses. The results also show that respirable particles are not appreciably removed in the gap, which means that bypass is significantly detrimental to indoor air quality. An HVAC design that employs high efficiency filters to prevent health problems associated with indoor fine particles may fail to perform as intended due to bypass. The results presented in this paper can provide a basis to quantify the effect of bypass on indoor air quality. For all of the simulations, we assumed that volumetric flow through the filter (Q F ) was constant. In some HVAC systems, it would be more correct to hold the total flow (Q) constant. The analysis of bypass would thus involve an iterative procedure where the flow is allocated between the filter and the bypass crack until the pressure drop through both flow paths was equal. We did not complete this procedure because we did not have efficiency data for the reduced filter face velocities that would result, but this effect should be included in future measurements of bypass.
11 While the model simulations presented in this paper provide a quantitative account of bypass, they do not substitute for experimental data and the results should be verified experimentally both in a laboratory apparatus with controlled parameters and in real HVAC systems. Also, the bypass results coupled with full HVAC deposition models can provide a comprehensive accounting of HVAC systems influence on indoor particulate matter with an ability to relax the usual assumption that the particle removal efficiency is equal to the rated filter efficiency. Finally, the authors hope that this work will motivate methods to detect bypass in the field and to create HVAC designs that reduce bypass. REFERENCES ASHRAE Standard Gravimetric and Dust-Spot Procedures for Testing Air-Cleaning Devices Used in General Ventilation for Removing Particulate Matter. Atlanta, GA: American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers. ASHRAE Standard Method of Testing General Ventilation Air-Cleaning Devices for Removal Efficiency by Particle Size. Atlanta, GA: American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers. Baker, P. H., Sharples, S., and Ward, I. C Air flow through cracks. Building and Environment, Vol. 22, pp Braun, R. H Problem and solution to plugging of a finned-tube cooling coil in an air handler. ASHRAE Transactions, Vol. 92, pp Carrie, F. R. and Modera, M. P Experimental investigation of aerosol deposition on slot- and joint-type leaks. Journal of Aerosol Science, Vol. 33, pp Hanley, J. T., Ensor, D. S., Smith, D. D., and Sparks, L. E Fractional aerosol filtration efficiency of in-duct ventilation air cleaners. Indoor Air-International Journal of Indoor Air Quality and Climate, Vol. 4, pp Liu, D. L. and Nazaroff, W. W Modeling pollutant penetration across building envelopes. Atmospheric Environment, Vol. 35, pp Liu, D.-L. and Nazaroff, W. W Particle penetration through building cracks. Aerosol Science and Technology, Vol. 37, pp Mosley, R. B., Greenwell, D. J., Sparks, L. E., Guo, Z., Tucker, W. G., Fortmann, R., and Whitfield, C Penetration of ambient fine particles into the indoor environment. Aerosol Science and Technology, Vol. 34, pp Ottney, T. C Particle management for HVAC systems. ASHRAE Journal, Vol. 35, pp. 6. Raynor, P. C. and Chae, S. J Dust loading on electrostatically charged filters in a standard test and a real HVAC system. Filtration and Separation, Vol. 40, pp Siegel, J Particle Deposition on HVAC Heat Exchangers. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of California, Berkeley.
...And Watch Your Grow!
 Break The One-Inch Cycle! With the 5 MERV 10 High Performance...And Watch Your Grow! No More Retro-Fitting! Because of the 1-inch restriction combined with a limited allocation for pressure, homeowners
Break The One-Inch Cycle! With the 5 MERV 10 High Performance...And Watch Your Grow! No More Retro-Fitting! Because of the 1-inch restriction combined with a limited allocation for pressure, homeowners
MERV Filter Models for Aerobiological Applications. W.J. Kowalski, PE, PhD W.P. Bahnfleth, PE, PhD The Pennsylvania State University
 MERV Filter Models for Aerobiological Applications W.J. Kowalski, PE, PhD W.P. Bahnfleth, PE, PhD The Pennsylvania State University Recent concerns about bioterrorism and existing concerns about indoor
MERV Filter Models for Aerobiological Applications W.J. Kowalski, PE, PhD W.P. Bahnfleth, PE, PhD The Pennsylvania State University Recent concerns about bioterrorism and existing concerns about indoor
CFD Investigation of Influence of Tube Bundle Cross-Section over Pressure Drop and Heat Transfer Rate
 CFD Investigation of Influence of Tube Bundle Cross-Section over Pressure Drop and Heat Transfer Rate Sandeep M, U Sathishkumar Abstract In this paper, a study of different cross section bundle arrangements
CFD Investigation of Influence of Tube Bundle Cross-Section over Pressure Drop and Heat Transfer Rate Sandeep M, U Sathishkumar Abstract In this paper, a study of different cross section bundle arrangements
Performance of VAV Parallel Fan-Powered Terminal Units: Experimental Results and Models
 NY-08-013 (RP-1292) Performance of VAV Parallel Fan-Powered Terminal Units: Experimental Results and Models James C. Furr Dennis L. O Neal, PhD, PE Michael A. Davis Fellow ASHRAE John A. Bryant, PhD, PE
NY-08-013 (RP-1292) Performance of VAV Parallel Fan-Powered Terminal Units: Experimental Results and Models James C. Furr Dennis L. O Neal, PhD, PE Michael A. Davis Fellow ASHRAE John A. Bryant, PhD, PE
Development of Power-head Based Fan Airflow Station
 ESL-IC-5-1- Development of Power-head Based Fan Airflow Station Gang ang Research associate University of Nebraska, Lincoln Mingsheng Liu Professor University of Nebraska, Lincoln Abstract Fan airflow
ESL-IC-5-1- Development of Power-head Based Fan Airflow Station Gang ang Research associate University of Nebraska, Lincoln Mingsheng Liu Professor University of Nebraska, Lincoln Abstract Fan airflow
nivia utilities Why Air Filters???
 Why Air Filters??? Protection to Air Handler components like coil, fan etc. To get minimum required indoor air quality. To act as guard filters to high efficiency filters. To attain required cleanliness
Why Air Filters??? Protection to Air Handler components like coil, fan etc. To get minimum required indoor air quality. To act as guard filters to high efficiency filters. To attain required cleanliness
STUDY OF THE INFLUENCE OF THE TYPE OF FUEL USED IN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES OVER THE RHEOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF LUBRICANTS
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 9 (58) No. 2 - Special Issue 2016 Series I: Engineering Sciences STUDY OF THE INFLUENCE OF THE TYPE OF FUEL USED IN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES OVER
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 9 (58) No. 2 - Special Issue 2016 Series I: Engineering Sciences STUDY OF THE INFLUENCE OF THE TYPE OF FUEL USED IN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES OVER
Heat Transfer Enhancement for Double Pipe Heat Exchanger Using Twisted Wire Brush Inserts
 Heat Transfer Enhancement for Double Pipe Heat Exchanger Using Twisted Wire Brush Inserts Deepali Gaikwad 1, Kundlik Mali 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sinhgad College of
Heat Transfer Enhancement for Double Pipe Heat Exchanger Using Twisted Wire Brush Inserts Deepali Gaikwad 1, Kundlik Mali 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sinhgad College of
Numerical Study on the Flow Characteristics of a Solenoid Valve for Industrial Applications
 Numerical Study on the Flow Characteristics of a Solenoid Valve for Industrial Applications TAEWOO KIM 1, SULMIN YANG 2, SANGMO KANG 3 1,2,4 Mechanical Engineering Dong-A University 840 Hadan 2 Dong, Saha-Gu,
Numerical Study on the Flow Characteristics of a Solenoid Valve for Industrial Applications TAEWOO KIM 1, SULMIN YANG 2, SANGMO KANG 3 1,2,4 Mechanical Engineering Dong-A University 840 Hadan 2 Dong, Saha-Gu,
A STUDY OF HYDRAULIC RESISTANCE OF VISCOUS BYPASS GAP IN MAGNETORHEOLOGICAL DAMPER
 ACTA UNIVERSITATIS AGRICULTURAE ET SILVICULTURAE MENDELIANAE BRUNENSIS Volume 64 134 Number 4, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.11118/actaun201664041199 A STUDY OF HYDRAULIC RESISTANCE OF VISCOUS BYPASS GAP IN
ACTA UNIVERSITATIS AGRICULTURAE ET SILVICULTURAE MENDELIANAE BRUNENSIS Volume 64 134 Number 4, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.11118/actaun201664041199 A STUDY OF HYDRAULIC RESISTANCE OF VISCOUS BYPASS GAP IN
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Wind tunnel investigation of waste air re-entry with wall ventilation P. Broas Technical Research Centre of Finland, Ship Laboratory, Tekniikantie 12, SF-02150, Espoo, Finland ABSTRACT A wind tunnel investigation
Wind tunnel investigation of waste air re-entry with wall ventilation P. Broas Technical Research Centre of Finland, Ship Laboratory, Tekniikantie 12, SF-02150, Espoo, Finland ABSTRACT A wind tunnel investigation
Filter and Particle Simulation for Hydraulic Systems
 1 Filter and Particle Simulation for Hydraulic Systems Karl Wartlick Argo-Hytos GmbH, Kraichtal-Menzingen, Germany René von Dombrowski RWTH Aachen University, Germany, Institute for Fluid Power Drives
1 Filter and Particle Simulation for Hydraulic Systems Karl Wartlick Argo-Hytos GmbH, Kraichtal-Menzingen, Germany René von Dombrowski RWTH Aachen University, Germany, Institute for Fluid Power Drives
China. Keywords: Electronically controled Braking System, Proportional Relay Valve, Simulation, HIL Test
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2013-10-11 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vol. 437, pp 418-422 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.437.418 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Simulation and HIL Test for
Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2013-10-11 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vol. 437, pp 418-422 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.437.418 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Simulation and HIL Test for
REMOVAL OF FINE AND ULTRAFINE COMBUSTION DERIVED PARTICLES IN A WET ELECTROSTATIC SCRUBBER
 REMOVAL OF FINE AND ULTRAFINE COMBUSTION DERIVED PARTICLES IN A WET ELECTROSTATIC SCRUBBER L. D Addio, F. Di Natale, C. Carotenuto, G. Scoppa, V. Dessy, A. Lancia francesco.dinatale@unina.it Dipartimento
REMOVAL OF FINE AND ULTRAFINE COMBUSTION DERIVED PARTICLES IN A WET ELECTROSTATIC SCRUBBER L. D Addio, F. Di Natale, C. Carotenuto, G. Scoppa, V. Dessy, A. Lancia francesco.dinatale@unina.it Dipartimento
Enhance the Performance of Heat Exchanger with Twisted Tape Insert: A Review
 Enhance the Performance of Heat Exchanger with Twisted Tape Insert: A Review M.J.Patel 1, K.S.Parmar 2, Umang R. Soni 3 1,2. M.E. Student, department of mechanical engineering, SPIT,Basna, Gujarat, India,
Enhance the Performance of Heat Exchanger with Twisted Tape Insert: A Review M.J.Patel 1, K.S.Parmar 2, Umang R. Soni 3 1,2. M.E. Student, department of mechanical engineering, SPIT,Basna, Gujarat, India,
Investigation of Direct-Injection via Micro-Porous Injector Nozzle
 Investigation of Direct-Injection via Micro-Porous Injector Nozzle J.J.E. Reijnders, M.D. Boot, C.C.M. Luijten, L.P.H. de Goey Department of Mechanical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology,
Investigation of Direct-Injection via Micro-Porous Injector Nozzle J.J.E. Reijnders, M.D. Boot, C.C.M. Luijten, L.P.H. de Goey Department of Mechanical Engineering, Eindhoven University of Technology,
6. Acoustical simulation of straight and side inlet/outlet rectangular plenums using the FEM method
 Research Signpost 37/661 (2), Fort P.O. Trivandrum-695 023 Kerala, India Noise Control: Theory, Application and Optimization in Engineering, 2014: 119-144 ISBN: 978-81-308-0552-8 Editors: Min-Chie Chiu
Research Signpost 37/661 (2), Fort P.O. Trivandrum-695 023 Kerala, India Noise Control: Theory, Application and Optimization in Engineering, 2014: 119-144 ISBN: 978-81-308-0552-8 Editors: Min-Chie Chiu
Numerical Investigation of the Gas Leakage through the Piston-Cylinder Clearance of Reciprocating Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Numerical Investigation of the Gas Leakage through the Piston-Cylinder Clearance of
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Numerical Investigation of the Gas Leakage through the Piston-Cylinder Clearance of
Original. M. Pang-Ngam 1, N. Soponpongpipat 1. Keywords: Optimum pipe diameter, Total cost, Engineering economic
 Original On the Optimum Pipe Diameter of Water Pumping System by Using Engineering Economic Approach in Case of Being the Installer for Consuming Water M. Pang-Ngam 1, N. Soponpongpipat 1 Abstract The
Original On the Optimum Pipe Diameter of Water Pumping System by Using Engineering Economic Approach in Case of Being the Installer for Consuming Water M. Pang-Ngam 1, N. Soponpongpipat 1 Abstract The
LESSON Transmission of Power Introduction
 LESSON 3 3.0 Transmission of Power 3.0.1 Introduction Earlier in our previous course units in Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering, we introduced ourselves to the concept of support and process systems
LESSON 3 3.0 Transmission of Power 3.0.1 Introduction Earlier in our previous course units in Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering, we introduced ourselves to the concept of support and process systems
A Review on Experimental Investigation of U-Tube Heat Exchanger using Plain Tube and Corrugated Tube
 A Review on Experimental Investigation of U-Tube Heat Exchanger using Plain Tube and Corrugated Tube 1 Dhavalkumar A. Maheshwari, 2 Kartik M. Trivedi 1 ME Student, 2 Assistant Professor 1 Mechanical Engineering
A Review on Experimental Investigation of U-Tube Heat Exchanger using Plain Tube and Corrugated Tube 1 Dhavalkumar A. Maheshwari, 2 Kartik M. Trivedi 1 ME Student, 2 Assistant Professor 1 Mechanical Engineering
EFFECT OF SURFACE ROUGHNESS ON PERFORMANCE OF WIND TURBINE
 Chapter-5 EFFECT OF SURFACE ROUGHNESS ON PERFORMANCE OF WIND TURBINE 5.1 Introduction The development of modern airfoil, for their use in wind turbines was initiated in the year 1980. The requirements
Chapter-5 EFFECT OF SURFACE ROUGHNESS ON PERFORMANCE OF WIND TURBINE 5.1 Introduction The development of modern airfoil, for their use in wind turbines was initiated in the year 1980. The requirements
THE INFLUENCE OF THE MICROGROOVES ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION AND LOAD CARRYING CAPACITY OF THE CONICAL SLIDE BEARING
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 19, No. 3 2012 THE INFLUENCE OF THE MICROGROOVES ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION AND LOAD CARRYING CAPACITY OF THE CONICAL SLIDE BEARING Adam Czaban
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 19, No. 3 2012 THE INFLUENCE OF THE MICROGROOVES ON THE HYDRODYNAMIC PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION AND LOAD CARRYING CAPACITY OF THE CONICAL SLIDE BEARING Adam Czaban
Simulation Studies on the Effect of Porous Twisted Plate Inserts on the Performance of Fire Tube Steam Packaged Boiler
 Simulation Studies on the Effect of Porous Twisted Plate Inserts on the Performance of Fire Tube Steam Packaged Boiler S. Hassan *,a, M. K. Roslim b and R. M. Zain c Mechanical Engineering Department,
Simulation Studies on the Effect of Porous Twisted Plate Inserts on the Performance of Fire Tube Steam Packaged Boiler S. Hassan *,a, M. K. Roslim b and R. M. Zain c Mechanical Engineering Department,
Comparing Total Mine Airflow Requirements using a comprehensive new approach vs. traditional method(s)
 Comparing Total Mine Airflow Requirements using a comprehensive new approach vs. traditional method(s) J. Daniel Stinnette, PE Overview In an effort to improve overall air quality, the U.S. EPA mandated
Comparing Total Mine Airflow Requirements using a comprehensive new approach vs. traditional method(s) J. Daniel Stinnette, PE Overview In an effort to improve overall air quality, the U.S. EPA mandated
On the potential application of a numerical optimization of fatigue life with DoE and FEM
 On the potential application of a numerical optimization of fatigue life with DoE and FEM H.Y. Miao and M. Lévesque Département de Génie Mécanique, École Polytechnique de Montréal, Canada Abstract Shot
On the potential application of a numerical optimization of fatigue life with DoE and FEM H.Y. Miao and M. Lévesque Département de Génie Mécanique, École Polytechnique de Montréal, Canada Abstract Shot
MARINE FOUR-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING OIL FILM LUBRICATION CHARACTERISTIC ANALYSIS
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH Special Issue 2018 S2 (98) 2018 Vol. 25; pp. 30-34 10.2478/pomr-2018-0070 MARINE FOUR-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING OIL FILM LUBRICATION CHARACTERISTIC ANALYSIS
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH Special Issue 2018 S2 (98) 2018 Vol. 25; pp. 30-34 10.2478/pomr-2018-0070 MARINE FOUR-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING OIL FILM LUBRICATION CHARACTERISTIC ANALYSIS
Data envelopment analysis with missing values: an approach using neural network
 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.17 No.2, February 2017 29 Data envelopment analysis with missing values: an approach using neural network B. Dalvand, F. Hosseinzadeh
IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.17 No.2, February 2017 29 Data envelopment analysis with missing values: an approach using neural network B. Dalvand, F. Hosseinzadeh
STIFFNESS CHARACTERISTICS OF MAIN BEARINGS FOUNDATION OF MARINE ENGINE
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 23, No. 1 2016 STIFFNESS CHARACTERISTICS OF MAIN BEARINGS FOUNDATION OF MARINE ENGINE Lech Murawski Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 23, No. 1 2016 STIFFNESS CHARACTERISTICS OF MAIN BEARINGS FOUNDATION OF MARINE ENGINE Lech Murawski Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering August 2000, Nice, FRANCE
 Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 0.0 EFFECTS OF TRANSVERSE
Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 0.0 EFFECTS OF TRANSVERSE
CFD Analysis and Comparison of Fluid Flow Through A Single Hole And Multi Hole Orifice Plate
 CFD Analysis and Comparison of Fluid Flow Through A Single Hole And Multi Hole Orifice Plate Malatesh Barki. 1, Ganesha T. 2, Dr. M. C. Math³ 1, 2, 3, Department of Thermal Power Engineering 1, 2, 3 VTU
CFD Analysis and Comparison of Fluid Flow Through A Single Hole And Multi Hole Orifice Plate Malatesh Barki. 1, Ganesha T. 2, Dr. M. C. Math³ 1, 2, 3, Department of Thermal Power Engineering 1, 2, 3 VTU
microns microns 70% 85%
 For over 30 years the KETCHaire Filter has been recognized regionally for its premium high efficiency multi pleat and disposable panel air filtration products and its support of the ASHRAE Standard 52.2
For over 30 years the KETCHaire Filter has been recognized regionally for its premium high efficiency multi pleat and disposable panel air filtration products and its support of the ASHRAE Standard 52.2
Cost-Efficiency by Arash Method in DEA
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 104, 5179-5184 Cost-Efficiency by Arash Method in DEA Dariush Khezrimotlagh*, Zahra Mohsenpour and Shaharuddin Salleh Department of Mathematics, Faculty
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 104, 5179-5184 Cost-Efficiency by Arash Method in DEA Dariush Khezrimotlagh*, Zahra Mohsenpour and Shaharuddin Salleh Department of Mathematics, Faculty
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DOUBLE PIPE HEAT EXCHANGER WITH TRIANGULAR BAFFLES
 International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-issn: 2395-56 Volume: 3 Issue: 8 Aug-216 www.irjet.net p-issn: 2395-72 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DOUBLE PIPE HEAT EXCHANGER WITH
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-issn: 2395-56 Volume: 3 Issue: 8 Aug-216 www.irjet.net p-issn: 2395-72 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DOUBLE PIPE HEAT EXCHANGER WITH
Enhanced Heat Transfer Surface Development for Exterior Tube Surfaces
 511 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 2013 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
511 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 2013 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
FLUID FLOW. Introduction
 FLUID FLOW Introduction Fluid flow is an important part of many processes, including transporting materials from one point to another, mixing of materials, and chemical reactions. In this experiment, you
FLUID FLOW Introduction Fluid flow is an important part of many processes, including transporting materials from one point to another, mixing of materials, and chemical reactions. In this experiment, you
Use of Flow Network Modeling for the Design of an Intricate Cooling Manifold
 Use of Flow Network Modeling for the Design of an Intricate Cooling Manifold Neeta Verma Teradyne, Inc. 880 Fox Lane San Jose, CA 94086 neeta.verma@teradyne.com ABSTRACT The automatic test equipment designed
Use of Flow Network Modeling for the Design of an Intricate Cooling Manifold Neeta Verma Teradyne, Inc. 880 Fox Lane San Jose, CA 94086 neeta.verma@teradyne.com ABSTRACT The automatic test equipment designed
Numerical Simulation of the Thermoelectric Model on Vehicle Turbocharged Diesel Engine Intercooler
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 6(16): 3054-3059, 013 ISSN: 040-7459; e-issn: 040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 013 Submitted: January 1, 013 Accepted: January
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 6(16): 3054-3059, 013 ISSN: 040-7459; e-issn: 040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 013 Submitted: January 1, 013 Accepted: January
Design of closing electromagnet of high power spring operating mechanism
 Abstract Design of closing electromagnet of high power spring operating mechanism Pengpeng Li a, Xiangqiang Meng, Cheng Guo Mechanical and Electronic Engineering Institute, Shandong University of Science
Abstract Design of closing electromagnet of high power spring operating mechanism Pengpeng Li a, Xiangqiang Meng, Cheng Guo Mechanical and Electronic Engineering Institute, Shandong University of Science
Determination of power loss of combine harvester travel gear
 Agronomy Research 13(1), 5 3, 015 Determination of power loss of combine harvester travel gear L. Beneš *, P. Heřmánek and P. Novák Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Faculty of Engineering, Department
Agronomy Research 13(1), 5 3, 015 Determination of power loss of combine harvester travel gear L. Beneš *, P. Heřmánek and P. Novák Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Faculty of Engineering, Department
Flanging and Hemming of Auto Body Panels using the Electro Magnetic Forming technology
 Flanging and Hemming of Auto Body Panels using the Electro Magnetic Forming technology P. Jimbert 1, I Eguia 1, M. A. Gutierrez 1, B. Gonzalez 1, G. S. Daehn 2, Y. Zhang 2, R. Anderson 3, H. Sundberg 4,
Flanging and Hemming of Auto Body Panels using the Electro Magnetic Forming technology P. Jimbert 1, I Eguia 1, M. A. Gutierrez 1, B. Gonzalez 1, G. S. Daehn 2, Y. Zhang 2, R. Anderson 3, H. Sundberg 4,
Numerical Simulation on Erosion of Drain Valve Liangliang Xu1,a, Zhengdong Wang2,b, Xinhai Yu3,c, Cong Zeng4,d
 3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Information Technology (ICMIT 2016) Numerical Simulation on Erosion of Drain Valve Liangliang Xu1,a, Zhengdong Wang2,b, Xinhai Yu3,c, Cong Zeng4,d 1 2 3
3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Information Technology (ICMIT 2016) Numerical Simulation on Erosion of Drain Valve Liangliang Xu1,a, Zhengdong Wang2,b, Xinhai Yu3,c, Cong Zeng4,d 1 2 3
A Study on the Optimum Shape of Automobile Air Cleaner Diffuser
 A Study on the Optimum Shape of Automobile Air Cleaner Diffuser HoseopSong 1, Byungmo Yang 2 and Haengmuk Cho 1,* 1 Division of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, Kongju National University, Chungnam,
A Study on the Optimum Shape of Automobile Air Cleaner Diffuser HoseopSong 1, Byungmo Yang 2 and Haengmuk Cho 1,* 1 Division of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, Kongju National University, Chungnam,
Effect of Stator Shape on the Performance of Torque Converter
 16 th International Conference on AEROSPACE SCIENCES & AVIATION TECHNOLOGY, ASAT - 16 May 26-28, 2015, E-Mail: asat@mtc.edu.eg Military Technical College, Kobry Elkobbah, Cairo, Egypt Tel : +(202) 24025292
16 th International Conference on AEROSPACE SCIENCES & AVIATION TECHNOLOGY, ASAT - 16 May 26-28, 2015, E-Mail: asat@mtc.edu.eg Military Technical College, Kobry Elkobbah, Cairo, Egypt Tel : +(202) 24025292
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 10, October ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 0, October-205 97 The Effect of Pitch and Fins on Enhancement of Heat Transfer in Double Pipe Helical Heat Exchanger 2 Abdulhassan
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 0, October-205 97 The Effect of Pitch and Fins on Enhancement of Heat Transfer in Double Pipe Helical Heat Exchanger 2 Abdulhassan
Smart Automated Vent Register Using an SMA Spring Actuated Rotary Ratchet
 Smart Automated Vent Register Using an SMA Spring Actuated Rotary Ratchet Mary Molepske, Victor Braciszewski, James Butler, Gregory Caputo, Fan-Ning Cheng, WonHee Kim, Jonathan Luntz, Diann Brei ABSTRACT
Smart Automated Vent Register Using an SMA Spring Actuated Rotary Ratchet Mary Molepske, Victor Braciszewski, James Butler, Gregory Caputo, Fan-Ning Cheng, WonHee Kim, Jonathan Luntz, Diann Brei ABSTRACT
Impacts of Short Tube Orifice Flow and Geometrical Parameters on Flow Discharge Coefficient Characteristics
 Impacts of Short Tube Orifice Flow and Geometrical Parameters on Flow Discharge Coefficient Characteristics M. Metwally Lecturer, Ph.D., MTC, Cairo, Egypt Abstract Modern offset printing machine, paper
Impacts of Short Tube Orifice Flow and Geometrical Parameters on Flow Discharge Coefficient Characteristics M. Metwally Lecturer, Ph.D., MTC, Cairo, Egypt Abstract Modern offset printing machine, paper
A LES/RANS HYBRID SIMULATION OF CANOPY FLOWS
 BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics & Applications Milano, Italy, July, - 8 A ES/RANS HYBRID SIMUATION OF CANOPY FOWS Satoru Iizuka and Hiroaki Kondo Nagoya University Furo-cho,
BBAA VI International Colloquium on: Bluff Bodies Aerodynamics & Applications Milano, Italy, July, - 8 A ES/RANS HYBRID SIMUATION OF CANOPY FOWS Satoru Iizuka and Hiroaki Kondo Nagoya University Furo-cho,
EFFECTS OF LOCAL AND GENERAL EXHAUST VENTILATION ON CONTROL OF CONTAMINANTS
 Ventilation 1 EFFECTS OF LOCAL AND GENERAL EXHAUST VENTILATION ON CONTROL OF CONTAMINANTS A. Kelsey, R. Batt Health and Safety Laboratory, Buxton, UK British Crown copyright (1) Abstract Many industrial
Ventilation 1 EFFECTS OF LOCAL AND GENERAL EXHAUST VENTILATION ON CONTROL OF CONTAMINANTS A. Kelsey, R. Batt Health and Safety Laboratory, Buxton, UK British Crown copyright (1) Abstract Many industrial
Perodua Myvi engine fuel consumption map and fuel economy vehicle simulation on the drive cycles based on Malaysian roads
 Perodua Myvi engine fuel consumption map and fuel economy vehicle simulation on the drive cycles based on Malaysian roads Muhammad Iftishah Ramdan 1,* 1 School of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Sains
Perodua Myvi engine fuel consumption map and fuel economy vehicle simulation on the drive cycles based on Malaysian roads Muhammad Iftishah Ramdan 1,* 1 School of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Sains
DEVELOPMENT OF A 3D MODEL OF TUBE BUNDLE OF VVER REACTOR STEAM GENERATOR
 DEVELOPMENT OF A 3D MODEL OF TUBE BUNDLE OF VVER REACTOR STEAM GENERATOR V.F. Strizhov, M.A. Bykov, A.Ye. Kiselev A.V. Shishov, A.A. Krutikov, D.A. Posysaev, D.A. Mustafina IBRAE RAN, Moscow, Russia Abstract
DEVELOPMENT OF A 3D MODEL OF TUBE BUNDLE OF VVER REACTOR STEAM GENERATOR V.F. Strizhov, M.A. Bykov, A.Ye. Kiselev A.V. Shishov, A.A. Krutikov, D.A. Posysaev, D.A. Mustafina IBRAE RAN, Moscow, Russia Abstract
Comparison Between Different Arrangements of Bypass Valves in Scroll Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Comparison Between Different Arrangements of Bypass Valves in Scroll Compressors Yangguang
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2008 Comparison Between Different Arrangements of Bypass Valves in Scroll Compressors Yangguang
Leadership in Filtration. High Efficiency Oil Separator for Crankcase Ventilation in Passenger Car Applications
 Leadership in Filtration High Efficiency Oil Separator for Crankcase Ventilation in Passenger Car Applications 2 MANN+HUMMEL HIGH EFFICIENCY OIL SEPARATOR FOR CRANKCASE VENTILATION IN PASSENGER CAR APPLICATIONS
Leadership in Filtration High Efficiency Oil Separator for Crankcase Ventilation in Passenger Car Applications 2 MANN+HUMMEL HIGH EFFICIENCY OIL SEPARATOR FOR CRANKCASE VENTILATION IN PASSENGER CAR APPLICATIONS
Heat Transfer in Rectangular Duct with Inserts of Triangular Duct Plate Fin Array
 Heat Transfer in Rectangular Duct with Inserts of Triangular Duct Plate Fin Array Deepak Kumar Gupta M. E. Scholar, Raipur Institute of Technology, Raipur (C.G.) Abstract: In compact plate fin heat exchanger
Heat Transfer in Rectangular Duct with Inserts of Triangular Duct Plate Fin Array Deepak Kumar Gupta M. E. Scholar, Raipur Institute of Technology, Raipur (C.G.) Abstract: In compact plate fin heat exchanger
Case Study: Design of a Calibration Reference Device for ANSI/ASHRAE Standard ME 4054W November 16, 2010 T. H. Kuehn SCREEN CONCEPTS
 Case Study: Design of a Calibration Reference Device for ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 52.2 2007 ME 4054W November 16, 2010 T. H. Kuehn IDENT OPP GATHER INFO DEFINE PROBLEM GEN CONCEPTS SCREEN CONCEPTS IMPLEMENT
Case Study: Design of a Calibration Reference Device for ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 52.2 2007 ME 4054W November 16, 2010 T. H. Kuehn IDENT OPP GATHER INFO DEFINE PROBLEM GEN CONCEPTS SCREEN CONCEPTS IMPLEMENT
Particle size and distribution of oil mist from cooking equipments in electrical commercial kitchens
 Indoor Air 8, 7- August 8, Copenhagen, Denmark - Paper ID: 4 Particle size and distribution of oil mist from cooking equipments in electrical commercial kitchens Ryohei oshida, asushi Kondo, Hajime oshino,,
Indoor Air 8, 7- August 8, Copenhagen, Denmark - Paper ID: 4 Particle size and distribution of oil mist from cooking equipments in electrical commercial kitchens Ryohei oshida, asushi Kondo, Hajime oshino,,
Figure 1: Forces Are Equal When Both Their Magnitudes and Directions Are the Same
 Moving and Maneuvering 1 Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics III (Notes primarily from Underwater Robotics Science Design and Fabrication, an excellent book for the design, fabrication, and
Moving and Maneuvering 1 Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics III (Notes primarily from Underwater Robotics Science Design and Fabrication, an excellent book for the design, fabrication, and
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF DYNAMIC THERMAL BEHAVIOUR OF AN 11 KV DISTRIBUTION TRANSFORMER
 Paper 110 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF DYNAMIC THERMAL BEHAVIOUR OF AN 11 KV DISTRIBUTION TRANSFORMER Rafael VILLARROEL Qiang LIU Zhongdong WANG The University of Manchester - UK The University of Manchester
Paper 110 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF DYNAMIC THERMAL BEHAVIOUR OF AN 11 KV DISTRIBUTION TRANSFORMER Rafael VILLARROEL Qiang LIU Zhongdong WANG The University of Manchester - UK The University of Manchester
IMPACT OF SKIN EFFECT FOR THE DESIGN OF A SQUIRREL CAGE INDUCTION MOTOR ON ITS STARTING PERFORMANCES
 IMPACT OF SKIN EFFECT FOR THE DESIGN OF A SQUIRREL CAGE INDUCTION MOTOR ON ITS STARTING PERFORMANCES Md. Shamimul Haque Choudhury* 1,2, Muhammad Athar Uddin 1,2, Md. Nazmul Hasan 1,2, M. Shafiul Alam 1,2
IMPACT OF SKIN EFFECT FOR THE DESIGN OF A SQUIRREL CAGE INDUCTION MOTOR ON ITS STARTING PERFORMANCES Md. Shamimul Haque Choudhury* 1,2, Muhammad Athar Uddin 1,2, Md. Nazmul Hasan 1,2, M. Shafiul Alam 1,2
Part C: Electronics Cooling Methods in Industry
 Part C: Electronics Cooling Methods in Industry Indicative Contents Heat Sinks Heat Pipes Heat Pipes in Electronics Cooling (1) Heat Pipes in Electronics Cooling (2) Thermoelectric Cooling Immersion Cooling
Part C: Electronics Cooling Methods in Industry Indicative Contents Heat Sinks Heat Pipes Heat Pipes in Electronics Cooling (1) Heat Pipes in Electronics Cooling (2) Thermoelectric Cooling Immersion Cooling
Clearance Loss Analysis in Linear Compressor with CFD Method
 Clearance Loss Analysis in Linear Compressor with CFD Method Wenjie Zhou, Zhihua Gan, Xiaobin Zhang, Limin Qiu, Yinzhe Wu Cryogenics Laboratory, Zhejiang University Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China, 310027 ABSTRACT
Clearance Loss Analysis in Linear Compressor with CFD Method Wenjie Zhou, Zhihua Gan, Xiaobin Zhang, Limin Qiu, Yinzhe Wu Cryogenics Laboratory, Zhejiang University Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China, 310027 ABSTRACT
Twin Screw Compressor Performance and Its Relationship with Rotor Cutter Blade Shape and Manufacturing Cost
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Twin Screw Compressor Performance and Its Relationship with Rotor Cutter Blade Shape
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Twin Screw Compressor Performance and Its Relationship with Rotor Cutter Blade Shape
DESIGN OF THROTTLE BODY: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF DIFFERENT SHAFT PROFILES USING CFD ANALYSIS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 14(S2), 2016, 681-686 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN OF TROTTLE BODY: A COMARATIVE STUDY OF DIFFERENT SAFT ROFILES USING CFD ANALYSIS M. BALAJI *, K. AMAL SATEES,
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 14(S2), 2016, 681-686 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN OF TROTTLE BODY: A COMARATIVE STUDY OF DIFFERENT SAFT ROFILES USING CFD ANALYSIS M. BALAJI *, K. AMAL SATEES,
Pump Control Ball Valve for Energy Savings
 VM PCBVES/WP White Paper Pump Control Ball Valve for Energy Savings Table of Contents Introduction............................... Pump Control Valves........................ Headloss..................................
VM PCBVES/WP White Paper Pump Control Ball Valve for Energy Savings Table of Contents Introduction............................... Pump Control Valves........................ Headloss..................................
Cost Benefit Analysis of Faster Transmission System Protection Systems
 Cost Benefit Analysis of Faster Transmission System Protection Systems Presented at the 71st Annual Conference for Protective Engineers Brian Ehsani, Black & Veatch Jason Hulme, Black & Veatch Abstract
Cost Benefit Analysis of Faster Transmission System Protection Systems Presented at the 71st Annual Conference for Protective Engineers Brian Ehsani, Black & Veatch Jason Hulme, Black & Veatch Abstract
Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset
 Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset Vikas Kumar Agarwal Deputy Manager Mahindra Two Wheelers Ltd. MIDC Chinchwad Pune 411019 India Abbreviations:
Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset Vikas Kumar Agarwal Deputy Manager Mahindra Two Wheelers Ltd. MIDC Chinchwad Pune 411019 India Abbreviations:
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF PISTON COOLING USING SINGLE CIRCULAR OIL JET IMPINGEMENT
 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF PISTON COOLING USING SINGLE CIRCULAR OIL JET IMPINGEMENT BALAKRISHNAN RAJU, CFD ANALYSIS ENGINEER, TATA CONSULTANCY SERVICES LTD., BANGALORE ABSTRACT Thermal loading of piston
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF PISTON COOLING USING SINGLE CIRCULAR OIL JET IMPINGEMENT BALAKRISHNAN RAJU, CFD ANALYSIS ENGINEER, TATA CONSULTANCY SERVICES LTD., BANGALORE ABSTRACT Thermal loading of piston
CHAPTER THREE DC MOTOR OVERVIEW AND MATHEMATICAL MODEL
 CHAPTER THREE DC MOTOR OVERVIEW AND MATHEMATICAL MODEL 3.1 Introduction Almost every mechanical movement that we see around us is accomplished by an electric motor. Electric machines are a means of converting
CHAPTER THREE DC MOTOR OVERVIEW AND MATHEMATICAL MODEL 3.1 Introduction Almost every mechanical movement that we see around us is accomplished by an electric motor. Electric machines are a means of converting
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOWFIELD OF DUCT FLOW WITH AN INCLINED JET INJECTION DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FLOWFIELDS WITH AND WITHOUT A GUIDE VANE
 Proceedings of the 3rd ASME/JSME Joint Fluids Engineering Conference July 8-23, 999, San Francisco, California FEDSM99-694 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOWFIELD OF DUCT FLOW WITH AN INCLINED JET
Proceedings of the 3rd ASME/JSME Joint Fluids Engineering Conference July 8-23, 999, San Francisco, California FEDSM99-694 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOWFIELD OF DUCT FLOW WITH AN INCLINED JET
Design and Performance Analysis of Louvered Fin Automotive Radiator using CAE Tools
 Design and Performance Analysis of Louvered Fin Automotive Radiator using CAE Tools Vishwa Deepak Dwivedi Scholar of Master of Technology, Mechanical Engineering Department, UCER, Allahabad, India Ranjeet
Design and Performance Analysis of Louvered Fin Automotive Radiator using CAE Tools Vishwa Deepak Dwivedi Scholar of Master of Technology, Mechanical Engineering Department, UCER, Allahabad, India Ranjeet
Analysis of Torsional Vibration in Elliptical Gears
 The The rd rd International Conference on on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES Pilsen, Czech Pilsen, Republic, Czech August Republic, September -, Analysis of Torsional Vibration in Elliptical Gears
The The rd rd International Conference on on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES Pilsen, Czech Pilsen, Republic, Czech August Republic, September -, Analysis of Torsional Vibration in Elliptical Gears
Bandmill Strain System Response
 Bandmill Strain System Response Bruce Lehmann, Ph.D., P.Eng, Sr. Engineer, Thin Kerf Technologies Inc. The responsiveness of the strain system of a bandmill is a critical factor for bandsaw performance
Bandmill Strain System Response Bruce Lehmann, Ph.D., P.Eng, Sr. Engineer, Thin Kerf Technologies Inc. The responsiveness of the strain system of a bandmill is a critical factor for bandsaw performance
Improvement of Vehicle Dynamics by Right-and-Left Torque Vectoring System in Various Drivetrains x
 Improvement of Vehicle Dynamics by Right-and-Left Torque Vectoring System in Various Drivetrains x Kaoru SAWASE* Yuichi USHIRODA* Abstract This paper describes the verification by calculation of vehicle
Improvement of Vehicle Dynamics by Right-and-Left Torque Vectoring System in Various Drivetrains x Kaoru SAWASE* Yuichi USHIRODA* Abstract This paper describes the verification by calculation of vehicle
Compact Finedust / HEPA Filter
 Compact Finedust / HEPA Filter Type G7 Overview The G7 filter is designed and tested to extract the smallest particles out of the air. The G7 series contains a fibreglass media pack in five (5) different
Compact Finedust / HEPA Filter Type G7 Overview The G7 filter is designed and tested to extract the smallest particles out of the air. The G7 series contains a fibreglass media pack in five (5) different
Design Makes All The Difference...
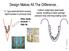 CAMFIL FARR 13-09-19 Design Makes All The Difference... V type pleat will blind causing rapid increase in pressure drop. Filter media blocked = high Δp Uniform radial style pleat loads evenly, resulting
CAMFIL FARR 13-09-19 Design Makes All The Difference... V type pleat will blind causing rapid increase in pressure drop. Filter media blocked = high Δp Uniform radial style pleat loads evenly, resulting
A Cost Benefit Analysis of Faster Transmission System Protection Schemes and Ground Grid Design
 A Cost Benefit Analysis of Faster Transmission System Protection Schemes and Ground Grid Design Presented at the 2018 Transmission and Substation Design and Operation Symposium Revision presented at the
A Cost Benefit Analysis of Faster Transmission System Protection Schemes and Ground Grid Design Presented at the 2018 Transmission and Substation Design and Operation Symposium Revision presented at the
EQUIPMENT FOR FILTRATION OFAIR
 EQUIPMENT FOR FILTRATION OFAIR PRESENTED BY SWAPNA.M M. Pharm 2 nd semester Department of pharmaceutics University College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kakatiya University, Warangal-506009. CONTENTS INTRODUCTION
EQUIPMENT FOR FILTRATION OFAIR PRESENTED BY SWAPNA.M M. Pharm 2 nd semester Department of pharmaceutics University College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kakatiya University, Warangal-506009. CONTENTS INTRODUCTION
An easy and inexpensive way to estimate the trapping efficiency of a two stroke engine
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 82 (2015 ) 17 22 ATI 2015-70th Conference of the ATI Engineering Association An easy and inexpensive way to estimate the trapping
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 82 (2015 ) 17 22 ATI 2015-70th Conference of the ATI Engineering Association An easy and inexpensive way to estimate the trapping
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF UNDERTRAY DIFFUSER FOR A FORMULA STYLE RACECAR
 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF UNDERTRAY DIFFUSER FOR A FORMULA STYLE RACECAR Ali Asgar S. Khokhar 1, Suhas S. Shirolkar 2 1 Graduate in Mechanical Engineering, KJ Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai, India.
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF UNDERTRAY DIFFUSER FOR A FORMULA STYLE RACECAR Ali Asgar S. Khokhar 1, Suhas S. Shirolkar 2 1 Graduate in Mechanical Engineering, KJ Somaiya College of Engineering, Mumbai, India.
CHAPTER 3: THE CHARACTERISATION OF MAGNETIC PARTICLE TYPE (GRADE) WITH RESPECT TO OIL PICK-UP
 CHAPTE 3: THE CHAACTEISATION OF MAGNETIC PATICLE TYPE (GADE) WITH ESPECT TO OIL PICK-UP 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Characterisation of oil pick-up from a glass substrate 3.2.1 The effect of particle size distribution
CHAPTE 3: THE CHAACTEISATION OF MAGNETIC PATICLE TYPE (GADE) WITH ESPECT TO OIL PICK-UP 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Characterisation of oil pick-up from a glass substrate 3.2.1 The effect of particle size distribution
Comparison of Swirl, Turbulence Generating Devices in Compression ignition Engine
 Available online atwww.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2016, 8 (7):31-40 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Comparison
Available online atwww.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2016, 8 (7):31-40 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Comparison
ANALYSIS ON MECHANICAL PARAMETERS OF LUNAR ROVER WHEEL
 ANALYSIS ON MECHANICAL PARAMETERS OF LUNAR ROVER WHEEL 1,2 DAWEI JIN, 1 JIANQIAO LI, 3 JIANXIN ZHU, 3 CHUNHUA ZHANG 1 Key laboratary of Bionic Engineering (Ministry of Education), Jilin University, Changchu
ANALYSIS ON MECHANICAL PARAMETERS OF LUNAR ROVER WHEEL 1,2 DAWEI JIN, 1 JIANQIAO LI, 3 JIANXIN ZHU, 3 CHUNHUA ZHANG 1 Key laboratary of Bionic Engineering (Ministry of Education), Jilin University, Changchu
Performance Rating of Airto-Air Heat Exchangers for Energy Recovery Ventilation Equipment
 AHRI Standard 1060 (I-P) 2011 Standard for Performance Rating of Airto-Air Heat Exchangers for Energy Recovery Ventilation Equipment IMPORTANT SAFETY DISCLAIMER AHRI does not set safety standards and does
AHRI Standard 1060 (I-P) 2011 Standard for Performance Rating of Airto-Air Heat Exchangers for Energy Recovery Ventilation Equipment IMPORTANT SAFETY DISCLAIMER AHRI does not set safety standards and does
Noise Reduction in a Reciprocating Compressor by Optimizing the Suction Muffler
 Noise Reduction in a Reciprocating Compressor by Optimizing the Suction Muffler Katakama Nagarjuna ¹ K.Sreenivas² ¹ M.tech student, ²Professor, dept of mechanical engineering kits, markapur, A.P, INDIA
Noise Reduction in a Reciprocating Compressor by Optimizing the Suction Muffler Katakama Nagarjuna ¹ K.Sreenivas² ¹ M.tech student, ²Professor, dept of mechanical engineering kits, markapur, A.P, INDIA
Aerodynamic Characteristics of Sedan with the Rolling Road Ground Effect Simulation System
 Vehicle Engineering (VE) Volume 2, 2014 www.seipub.org/ve Aerodynamic Characteristics of Sedan with the Rolling Road Ground Effect Simulation System Yingchao Zhang 1, Linlin Ren 1, Kecheng Pan 2, Zhe Zhang*
Vehicle Engineering (VE) Volume 2, 2014 www.seipub.org/ve Aerodynamic Characteristics of Sedan with the Rolling Road Ground Effect Simulation System Yingchao Zhang 1, Linlin Ren 1, Kecheng Pan 2, Zhe Zhang*
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD20: Last updated: 26th September 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD20: Last updated: 26th September 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
Analysis and evaluation of a tyre model through test data obtained using the IMMa tyre test bench
 Vehicle System Dynamics Vol. 43, Supplement, 2005, 241 252 Analysis and evaluation of a tyre model through test data obtained using the IMMa tyre test bench A. ORTIZ*, J.A. CABRERA, J. CASTILLO and A.
Vehicle System Dynamics Vol. 43, Supplement, 2005, 241 252 Analysis and evaluation of a tyre model through test data obtained using the IMMa tyre test bench A. ORTIZ*, J.A. CABRERA, J. CASTILLO and A.
Prediction of Thermal Deflection at Spindle Nose-tool Holder Interface in HSM
 Prediction of Thermal Deflection at Spindle Nose-tool Holder Interface in HSM V Prabhu Raja, J Kanchana, K Ramachandra, P Radhakrishnan PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641004 Abstract Loss of machining
Prediction of Thermal Deflection at Spindle Nose-tool Holder Interface in HSM V Prabhu Raja, J Kanchana, K Ramachandra, P Radhakrishnan PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641004 Abstract Loss of machining
Technical Report Lotus Elan Rear Suspension The Effect of Halfshaft Rubber Couplings. T. L. Duell. Prepared for The Elan Factory.
 Technical Report - 9 Lotus Elan Rear Suspension The Effect of Halfshaft Rubber Couplings by T. L. Duell Prepared for The Elan Factory May 24 Terry Duell consulting 19 Rylandes Drive, Gladstone Park Victoria
Technical Report - 9 Lotus Elan Rear Suspension The Effect of Halfshaft Rubber Couplings by T. L. Duell Prepared for The Elan Factory May 24 Terry Duell consulting 19 Rylandes Drive, Gladstone Park Victoria
Redesign of exhaust protection cover for high air flow levelling valve
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 2 Ver. II (Mar- Apr. 2014), PP 90-96 Redesign of exhaust protection cover for high air
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 2 Ver. II (Mar- Apr. 2014), PP 90-96 Redesign of exhaust protection cover for high air
Optimal design of a double coil magnetorheological fluid damper with various piston profiles
 11 th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimisation 07 th -12 th, June 2015, Sydney Australia Optimal design of a double coil magnetorheological fluid damper with various piston profiles
11 th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimisation 07 th -12 th, June 2015, Sydney Australia Optimal design of a double coil magnetorheological fluid damper with various piston profiles
Experimental Investigation of Hot Surface Ignition of Hydrocarbon-Air Mixtures
 Paper # 2D-09 7th US National Technical Meeting of the Combustion Institute Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA Mar 20-23, 2011. Topic: Laminar Flames Experimental Investigation of Hot Surface
Paper # 2D-09 7th US National Technical Meeting of the Combustion Institute Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA Mar 20-23, 2011. Topic: Laminar Flames Experimental Investigation of Hot Surface
Application Notes. Calculating Mechanical Power Requirements. P rot = T x W
 Application Notes Motor Calculations Calculating Mechanical Power Requirements Torque - Speed Curves Numerical Calculation Sample Calculation Thermal Calculations Motor Data Sheet Analysis Search Site
Application Notes Motor Calculations Calculating Mechanical Power Requirements Torque - Speed Curves Numerical Calculation Sample Calculation Thermal Calculations Motor Data Sheet Analysis Search Site
FINAL REPORT MARCH 2008
 AIRFLOW ASSESSMENT OF NOVEL VENTILATION AND MOISTURE DRAINAGE HOLES FINAL REPORT MARCH 2008 Daniel James, Richard Adamec Centre for Wireless Monitoring and Applications Griffith University CWMA WEEPA Ventilation
AIRFLOW ASSESSMENT OF NOVEL VENTILATION AND MOISTURE DRAINAGE HOLES FINAL REPORT MARCH 2008 Daniel James, Richard Adamec Centre for Wireless Monitoring and Applications Griffith University CWMA WEEPA Ventilation
Research on Skid Control of Small Electric Vehicle (Effect of Velocity Prediction by Observer System)
 Proc. Schl. Eng. Tokai Univ., Ser. E (17) 15-1 Proc. Schl. Eng. Tokai Univ., Ser. E (17) - Research on Skid Control of Small Electric Vehicle (Effect of Prediction by Observer System) by Sean RITHY *1
Proc. Schl. Eng. Tokai Univ., Ser. E (17) 15-1 Proc. Schl. Eng. Tokai Univ., Ser. E (17) - Research on Skid Control of Small Electric Vehicle (Effect of Prediction by Observer System) by Sean RITHY *1
ANALYSIS OF THE INFLUENCE OF HYDRAULIC CYLINDER DIAMETER TO THE TOTAL DAMPING FORCE AND THE GENERATED ELECTRICITY OF REGENERATIVE SHOCK ABSORBER
 ANALYSIS OF THE INFLUENCE OF HYDRAULIC CYLINDER DIAMETER TO THE TOTAL DAMPING FORCE AND THE GENERATED ELECTRICITY OF REGENERATIVE SHOCK ABSORBER Harus Laksana Guntur Dynamic System and Vibration Laboratory,
ANALYSIS OF THE INFLUENCE OF HYDRAULIC CYLINDER DIAMETER TO THE TOTAL DAMPING FORCE AND THE GENERATED ELECTRICITY OF REGENERATIVE SHOCK ABSORBER Harus Laksana Guntur Dynamic System and Vibration Laboratory,
Experimental Investigation of Damping Coefficient for Compressor Reed Valves
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Experimental Investigation of Damping Coefficient for Compressor Reed Valves Sergio
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Experimental Investigation of Damping Coefficient for Compressor Reed Valves Sergio
Ultipleat SRT Filters
 Lenntech info@lenntech.com www.lenntech.com Tel. +31-15-261.09.00 Fax. +31-15-261.62.89 Ultipleat SRT Filters Stress Resistant Technology The Ultimate in Filter Design Ultipleat SRT Filters Pall s Ultipleat
Lenntech info@lenntech.com www.lenntech.com Tel. +31-15-261.09.00 Fax. +31-15-261.62.89 Ultipleat SRT Filters Stress Resistant Technology The Ultimate in Filter Design Ultipleat SRT Filters Pall s Ultipleat
Influence of Cylinder Bore Volume on Pressure Pulsations in a Hermetic Reciprocating Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Influence of Cylinder Bore Volume on Pressure Pulsations in a Hermetic Reciprocating
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2014 Influence of Cylinder Bore Volume on Pressure Pulsations in a Hermetic Reciprocating
The Effect of Spring Pressure on Carbon Brush Wear Rate
 The Effect of Spring Pressure on Carbon Brush Wear Rate By Jeff D. Koenitzer, P.E. Milwaukee, Wisconsin, USA Preface 2008 For decades there was extensive testing of countless different carbon brush contact
The Effect of Spring Pressure on Carbon Brush Wear Rate By Jeff D. Koenitzer, P.E. Milwaukee, Wisconsin, USA Preface 2008 For decades there was extensive testing of countless different carbon brush contact
