1 Variable spring supports Design Instructions
|
|
|
- Philomena Barnett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Design Instructions 1.1 Application Rigid supporting structures are not capable to accommodate vertical displacement or large horizontal forced travels of piping. This nodes should be supported by spring hangers and spring supports. Variable spring supports are recommended for vertical displacements of piping up to mm. Application of constant supports needs to be considered for higher values. Springs supports are designed for application in assemblies comprising hangers or piping supports according to the summary shown in pages B.5 B.7. The MPS Gradior s.r.o. standard series of variable spring supports are designed for the load range between 0.2 kn to 108 kn. Higher loads require multi-spring supports with capacity up to 432 kn. Standard range of springs is designed in three nominal travel ranges of 50, 100 and 200 mm. Requirements for larger travel may be met by coupling several springs into a series to obtain the total nominal travel of 300 to 400 mm. The operating temperature range for springs is -40 C to +80 C or even up to +150 C for short-term exposure. Any lower or higher temperature would result in change of spring force due to the change in shrear modulus with the dispersion of +1.6 / -1.6 %. Change of spring force is proportional to the values above lower or higher temperature range. The spring service life for cyclic stress within the range of load change of 25 % higher than 1E5 full load amplitudes. The tolerance of spring rate is less than 5 % compared to the theoretical value. Spring supports are covered to ensure operation safety, when the tube casing and plates prevent potential injuries on touch. However, the spring unit is not sealed off completely and is not secured against ingress and deposits of dust. That is why very dusty environments, i.e. ceilings of coal burning boilers, require cleaning of spring support interior using compressed air. Under such circumstances, the relevant purchase order shall include a literal specific requirement for cleaning options. The unit surface is galvanized as standard, outdoor applications in highly corrosive environment or primary circuits of nuclear power plants, where galvanized surfaces are not acceptable, can be treated by means of additional surface finishing using epoxy coating. 1.2 Design The spring unit is designed with a pre-compressed springs inside a cylindrical casing, elements for indication of elevation (force) and turnbuckles for adjustment of spring force settings. Compensation of angular tolerances of spring and corrections of tolerances is enabled by the spherical bearing of in-built threaded rod, to ensure alignment of the rods without any additional bending. Spring units are delivered blocked to required set load. This blocking is ensured by means of shim device inserted into spring shell apertures and embraced with a safety tape. The device needs to be removed from the spring unit after piping pressure test, before the operation start up! The load capacity of spring unit lock during pressure test is double the nominal spring load. Spring plate (travel indication) Safety tape Locking device Spring Turnbuckle 1.3 Materials and Technologies Helical coil springs for all variable spring supports are manufactured from SH grade materials acc. to EN for cold-coiled spring and grade 51CrV-4 compliant with EN for hot-coiled springs. Springs are quenched to the required level and pre-compressed to the block length prior to their insertion into units to achieve the spring presetting, when the creep yielding will be stabilized and pre-torsioning develops in the wire surface. Further loading will not cause any significant relaxation and the spring force will remain within the range under 2.5 % of the operating force. Springs have been designed using the non-linear elasto-plastic calculation model derived by the company MPS Gradior s.r.o. 1.1
2 Design Instructions 1.4 Review of Spring Support Types Specific type version of a spring unit is designated by the last character of the three digits specifying type number. To simplify identification, so that the second character does not have to cover all travel versions, the designation of type is written as simple as 1x2 (the second character is replaced with the x symbol). Spring units are supplied as single-spring (types and ) or multi-spring (types 1.5 and 1.8). Particular design versions divided according to integration methods are described further below. Type 1x1 Range: kn Travel: 50, 100, 200 mm Type 1x2 Range: kn Travel: 50, 100, 200 mm Type 1x3 Range: kn Travel: 50, 100, 200 mm Type 1x4 Range: kn Travel: 50, 100, 200 mm Type 1x5 Range: kn Travel: 50, 100 mm Type 1x6 Range: kn Travel: 50, 100 mm Type 1x7 Range: kn Travel: 50, 100, (200) mm Type 1x8 Range: kn Travel: 50, 100 mm Selection of spring size: required load under any piping operation and occasional conditions shall be within the range of selected spring operating characteristics. Further, the travel reserve is required to min. 5 mm or 20 % of the pipe displacement value. The selection of spring size shall also accommodate changes to the set load of spring by 10 %. Spring units also feature the so called hidden travel allowances, i.e. 5 mm above the rated minimum or maximum. However, this allowance may not be relied upon during spring selection. Caution: Displacement of the pipe above the lowest value of operating travel of spring support may impose the risk of complete spring alleviation! Additional load is determined by the so called dead forces that are equal to the sum of loads on those parts of hanger or support assembly, which perform a displacement together with pipe. Those include mainly clamps, beams, supports and parts of rods below the spring support. It shall be added to the values of set load, obtained from piping flexibility analysis, when the dead forces exceed the approximate value of 0.01 to 0.02 multiple of calculation forces. The design load of spring is then determined by the formula F zn = F an + ΣG i, where F an refers to the force obtained through analysis of pipe for n-th load condition and ΣG i is the sum of weights of moving assembly parts. The additional force is usually calculated with the accuracy to multiple of the calculation force. Selection of nominal travel is defined by the condition of load change between hot and cold condition respectively. The load change condition is determined using the following formula: df = (F h - F c ) / F h < 25 % where F h refers to hot load and F c is the cold or set load respectively. Springs with lower travel show greater load changes due to higher stiffness, yet their application is more economical for their lower weight. Higher values of load change are acceptable if confirmed by the piping flexibility analysis. Correction of design displacement is performed in case of the total displacement comprising the result of vertical and horizontal displacement exceeds 2.5 mm, or, if the travel reserve is below 10 mm. These values occur with approximately 4 deviation of rods exceeding 1 m per hanger length. The total design displacement of spring support is given by the formula: s r = u z + u v * tan (a/2), where u z refers to the vertical displacement obtained through pipe analysis, u v is the resultant horizontal displacement of pipe at the particular node, and a is the angular deviation of hanger rod. However, some software would calculate the combined displacement when the length of hanger rod is entered, such situation does not require any further correction. 1.5 Declination of Hanger Rod Standards applicable to piping design require the assurance of the hanger rod declination to 4 from its vertical position in every direction. Spring units types 1x1 1x4 shall be therefore considered with respect to its characteristics described in the text below. 1.2
3 Design Instructions a/ Spring Supports Type 1x1 and 1x2 These are used for assemblies SH1, SH2, SH4, SH5, SH8 and other. These are integrated into hanger rod between two joints. Horizontal displacement of pipe declines the full rod with spring unit, where the rod remains theoretically direct when passing through spring support. In this case, the angular deviation is limited only by parameters of swing joints in pipe clamps and attachment to structure, that is why spring cages do not require any check or specifications of special designs. The weight of spring support obviously results in slight cranking of link between both end points of the rod resulting in tilt inside the spring unit that is, however, balanced by the spherical pad on the interior spring plate. b/ Spring Supports Type 1x3 and 1x5 These are used for assemblies SH3, SH6, SH10, SH13, SH21 and other. These are located on the auxiliary structure and the hanger rod is fitted in the joint cradle above spring support. The rod is passing through the inner diameter of spring as well as the space determined by planes of girders below the spring support. Horizontal displacement of pipe declines the rod passing through the spring; its deviation therefore requires consistent checking. That also depends on rated spring travel, as springs with high travel are long and the cathetus of the imaginary triangle developed is short. Springs with travel of 200 mm are applicable for rod declinations up to 2.5 only. Higher values require use of type 133A, see the relevant catalogue sheet for details. Another parameter to be checked is the collision of rod with girder webs under the spring support. PTFE slide plate in head is recommended for higher displacement levels. The support in pair requires polished slide surface made of stainless steel (design T ). Further checks shall be focused on displacement allowances. Axial and lateral displacements require the allowance determined by distance between the spring support head and the edge of support base. Lateral displacement of clamp supports further require verification of assembly stability against spinning of clamps and pipe (cranking of support). That occurs approximately after lateral displacement of 0.4 D1, where D1 refers to the diameter of spring support head. When higher displacement required, the clamp support shall be secured against spinning by means of attachment and shape joint. b/ Spring Supports Type 1x6 These are equipped with rod ends that enable tilt by 6. These are used in assemblies that require minimum resistance to horizontal movement. However, the analysis of piping flexibility requires verification, whether the node cannot develop any higher horizontal displacement of pipe, exceeding the anticipated level; that is due to various inaccuracies or very low flexibility of the piping or kinematic uncertainty of certain section. It is recommended to stabilise the piping using guides in adjacent nodes, i.e. to force nodal displacement of rigid strut at a single specific and possible direction required. c/ Spring Supports Type 1x4 These are used for assemblies SH7 and SH15. They are fitted to the beam, when the hanger rod extends out of the spring support up to the top swing joint. Inside the spring, this rod is attached to the central unit plate via the spherical pad representing the second swing joint. Displacement of pipes results in declination of rod passing through the spring, its deviation therefore shall be checked. It depends on the nominal spring travel, as springs with high travel are long and the cathetus of imaginary triangle developed is short. Supports with travel of 200 mm are applicable for rod deviations of up to 2.5 only. Higher deviations require installation of type 134A, see the relevant catalogue sheet for details. 1.6 Displacement on Spring Supports Standards applicable to piping design require assurance that the horizontal force developed by displacement of pipe does not exceed multiple of the vertical load, depending on displacement. This condition can be met by suitable selection of elements in pipe support assembly. The assembly further requires verification of stability, as described further below. a/ Spring Supports Type 1x7 and 1x8 Weld-on or clamped support is placed onto the flat head of spring unit with diameter D1, as specified in catalogue sheet. Horizontal displacement of pipe develops friction forces. The friction surface of metal-metal type may be used for horizontal displacement of up to 0.1 nominal spring travel. The use of spring supports with 1.3
4 Design 1.7 Design of Particular Spring Unit Types Eye Rod Spring Unit Type 1x1 Spring unit for attachment to the structure via welding eye and connection of rod to the turnbuckle. It is suitable for assembly with short assembly length. It may be also used in assemblies for seismic applicatioons, when the spring in the rod centre is not secured against oscillation. Rod Rod Spring Unit Type 1x2 Spring unit for the most common applications, attached into the threaded rod. The spring support may be located at any point on the rod, the only restriction is the option for adjustment of rod length by means of built-in turnbuckle. Its position on the rod shall be selected in such manner to prevent the spring support from collisions, spring unit shall be visible and accessible for adjustment purposes. Beam top attachment Spring Unit Type 1x3 Spring unit for installation on a pair of beams using a securing sheet featuring slots for bolting. The rod passes through the spring centre and it is attached to the top of spring support via a nut and lock nut set onto a spherical washer to enable tilting. Beam to rod Spring Unit Type 1x4 Spring unit for attachment to threaded rod and beam to set the support. Used for double-rod hangers of horizontal pipes. Attachment to the beam type 334 using bolts and pivot. The assembly is applied in restricted areas that require low construction height of hangers. Higher displacements of pipe need to be checked for compliance of rod declination values as specified in the relevant catalogue sheet. Rod end Spring Unit Type 1x6 Spring supports for attachment on structure and clamp support via rod ends. Suitable for assemblies with horizontal pipe displacement that require elimination of the effect of friction. The maximum deviation of support from its vertical axis shall be limited to 6. The design of this support also enables additional height adjustment. Spring Support Type 1x7 Spring support for attachments on structure using bolts and mounted to slide under pipe support. It is suitable for any regular assembly without the need for stabilisation. For horizontal displacement of pipe set on, exceeding 10 mm, the spring support of type 1x7T shall be used, fitted with a sliding head PTFE plate. 1.4
5 Marking 1.8 Marking Spring supports are marked by two different means: 1. Shortened labels used for code marking of assemblies only. This marking specifies the size and nominal travel of spring but it does not differentiate between various types. Size (1 16) Travel (1, 2, 3) Number designating spring size as shown in Table 1.2, pg Number designating spring travel as shown in type number marking. Marking example: Designation of spring with load capacity of N and nominal travel of 100 mm: the code No Marking with type number is used for specification in purchase orders. Type number comprises the size and travel code, as well as specification of the spring support type. 1 Travel Type FN 1 variable spring support product group 1 nominal travel of 50 mm 2 nominal travel of 100 mm 3 nominal travel of 200 mm nominal load in (N), see table on pg spring unit for hangers, eye-rod attachment type 2 spring unit for hangers, rod-rod attachment type 3 spring unit for hangers, beam-rod attachment type 4 spring unit for beam for double-rod hangers of horizontal pipe 5 multi-spring unit, beam-rod attachment type 6 spring support, attachment with two joint lugs 7 spring support, slide surface beam attachment type 8 multi-spring support, slide surface beam type For marking examples see catalogue sheets for particular spring types. 1.5
6 Spring Characteristics 1.9 Spring Characteristics Single-spring units for hangers and supports are divided into twelve basic nominal load sizes ranging from 0.2 to 108 kn. Nominal load is defined by spring maximum operating load of spring in N and the operating travel. Size of spring marked with a number 1 12 corresponds with its nominal load. Characteristics of load-travel values for all spring sizes and spring rates relevant to particular nominal travel values are shown in the table below. The table with spring characteristics relates to cage types 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 7. Each of these cages is provided with a single spring only. For bearing capacity classes that determine the joining dimension of rod (see summary on pg. A.11) refer to the bottom line. Table 1.1 Summary of Nominal Loads Spring size Nominal load FN (kn) Load group Table 1.2 Summary of Spring Rates Operating travel Spring size mm mm mm Load (kn) Spring rate (N/mm) Every spring is pre-set into the unit to the basic preload (with the label displacement value of 0 mm), which is equal to one half of the nominal travel. That means the default preload for nominal travel of 50 mm is 25 mm, the default pre-load for rated travel of 100 mm is 50 mm and the value for rated travel of 200 is 100 mm. 1.6
7 Spring Characteristics Multi-spring units for hangers and supports are divided into four nominal load sizes ranging from 48 and 432 kn. Spring sizes marked with number corresponds with its nominal load. Characteristics of load-travel values for all spring sizes and spring rates relevant to particular nominal travel values are shown in the table below. Table 1.3 Summary of Spring Characteristics Spring size Rated load FN (kn) Load group Multi-spring units are produced for nominal travel of 50 and 100 mm only. These springs are used for suspension of walls and boiler parts, supporting of duct systems, condensers, furnaces, cooling water supply pipes and various machinery or devices. The multi spring units manufactured by MPS Gradior s.r.o. are equipped with locking mechanisms and sufficient load settings after installation. Multi-spring units are usually used for balancing of small thermal displacements or installation inaccuracies, beam flexures, different setting-down of foundations, etc. The table with spring characteristics relates to cage types 5 and 8 formed by multiple springs each. Bearing capacity classes to determine the joining dimension of rod (see the summary in introduction and data sheets for product group 800 joining parts), see the bottom line. Table 1.4 Summary of Spring Characteristics Travel Spring size mm Load (kn) Spring rate (N/mm) Design Multi spring support comprise of four springs, these are arranged in circular pattern around the central tube. Springs are inserted onto dowels. When in the set position, the moving centre plate is blocked by means of thread bars that need to be removed prior to commissioning. Spring supports type 1x8 shall be always provided with PTFE sliding surfaces for horizontal displacement of pipe exceeding 5 mm. The counterpart (base of support) shall be then provided with polished stainless surface. Supports are adjusted by loosening four heads of hexagonal shape to accommodate spanner designed with axial bearings to enable their easy loosening. Cross-section of multi-spring unit 1.7
8 Installation Instructions Installation of spring hangers is guided by assembly drawings supplied by the manufacturer. Spring hangers/supports are delivered blocked with preset cold set load as required. Hanger rods shall be shortened to the required length at suspension points prior to hanger installation Deblocking Unlocking is always done after completion of pressure test and all works on piping, i.e. connecting of all equipment at the start and end of the route, branches and full erection. Locking devices are removed at any order, e.g. from the start of branch along the flow direction. However, it is essential that this process is performed without any excessive force: inability to remove the locking element is due to imbalance of load in spring and the pipe weight. The differential force is then transferred to the spring unit body via locking element. At first, the release of locking device shall be done by straining or releasing the rod using the turnbuckle on hanger or the adjustment nut on support. Further verification focuses on the subsequent hangers in branch, whether it transfers the load properly strained rod or spring hanger; and whether the sliding supports sits tight on the base. Spring supports type 1x7 and 1x8 are inserted under sliding supports of piping. Supports shall be checked for correct position, so that the sliding support base always lies on the plate of spring support head. Additional load adjustments are performed by turning the centre bolt moving support tube. The spring unit shall be secured against horizontal displacement using the bottom contact plate. Spring setting check unlocking of all springs will be followed by position check and processing of report with assessment of deviations from theoretical/installation position. Permissible deviations in vertical direction are: branch-intermediate hangers: +/-10 % of the nominal spring travel, max. 25 mm, branch-end hangers: +/-5 % of the nominal spring travel, max. 10 mm. Checks shall be conducted to verify the actual travel reserves, which shall be within the following ranges: The reserve for constant supports in cold or hot condition to the end position shall be at least 10 % of the calculation displacement; however the minimum value is 25 mm. The reserve for variable springs in cold or hot condition to the end position shall be at least 10 % of to the calculation displacement; however the minimum value is 5 mm. Checks of travel allowance shall be done considering the assumed end position during operation as well! Unlocking of all hangers and the position check result shall be stated in report. The depth for rod screwing into built-in turnbuckle should be equal to approximately 0.5 rate spring travel. When the additional adjustment of load completed, the minimum length of screwing overlap shall be 0.5 M (see figure below). For spring supportss type 1x2 the top rod shall be screwed into the top plate to the depth M and secured by means of locking nut. M/2 M M Removal of locking device Left locking device in shop default condition Right ejection of locking device after removal of the safety tape Type 1x2 Type 1x3 Spring supports type 1x2 and 1x4 are attached to rods using a turnbuckle integrated into the spring unit. The steel safety tape securing the locking devices shall be removed first. If the spring load is set-up properly, i.e. the pipe weight equals to the set spring load, locking device can be removed from spring shell slots freely. Potential modifications of settings are done by means of reducing the rod length (increasing the load) or extending the rod length (decreasing the load) by turning the turnbuckle. Once unlocked, the locking devices are secured to the hanger rod using a binding wire for future use. Spring supports type 1x3 and 1x5 are set on a pair of beams. The hanger rod passes through spring unit to be secured with two nuts on the top bearing pad; these nuts are also used for additional adjustments. Horizontal displacement of hanger shall be prevented by means of contact plate. M/2 Type 1x4 Types 1x7, 1x8 Springs adjustment corrections after deblocking are conducted progressively, from the node with greatest deviation from the installation position required to the node with lowest deviation. A deviation of position is defined as a drop or lift of pipe compared to the mark on spring support label or position defined in the design specification of springs (the piping cold position might differ from the set position). Negative deviation of position would raise the set load, whereas positive deviation will reduce it. Adjustment 1.8
9 Installation Instructions of one node might result in spontaneous alignment of adjacent hangers. Load on one node should be reset by the maximum of 5 % of the set value and if the position is not aligned to reach the tolerance range required, the spring on adjacent hanger will be reset. In case such unsatisfactory condition prevails, the procedure will be repeated up to reset values of +/-10 % for particular springs compared to initial settings. Higher re-adjustment values shall be considered by the pipe design engineer, same as the permissible value of deviation from the vertical position in mm (permissible drop or lift). New values of spring load settings shall be recorded and saved prior to commissioning. The check of cold position is repeated after commissioning and first shutdown. Load deviations in the newly established condition should not exceed 5 % compared to the previous settings. 1.9
Spring hangers, spring supports
 Spring hangers, spring supports 2 spring Spring hangers, supports PRODUCT 2 GROUP Spring hangers, spring supports Contents Page Field of application...2.1 Overview of spring hangers and spring supports...2.3
Spring hangers, spring supports 2 spring Spring hangers, supports PRODUCT 2 GROUP Spring hangers, spring supports Contents Page Field of application...2.1 Overview of spring hangers and spring supports...2.3
SPRING HANGERS, SPRING SUPPORTS PRODUCT GROUP
 SPRING HANGERS, SPRING SUPPORTS PRODUCT GROUP VARIABLE SPRING ELEMENTS CONTENTS PAGE 0 Spring hangers, spring supports, sway braces.1 Load table for spring hangers, spring supports and other spring elements.3
SPRING HANGERS, SPRING SUPPORTS PRODUCT GROUP VARIABLE SPRING ELEMENTS CONTENTS PAGE 0 Spring hangers, spring supports, sway braces.1 Load table for spring hangers, spring supports and other spring elements.3
DIN EN : (E)
 DIN EN 13480-3:2017-12 (E) Metallic industrial piping - Part 3: Design and calculation Contents Page European foreword... 10 1 Scope... 12 2 Normative references... 12 3 Terms, definitions, symbols and
DIN EN 13480-3:2017-12 (E) Metallic industrial piping - Part 3: Design and calculation Contents Page European foreword... 10 1 Scope... 12 2 Normative references... 12 3 Terms, definitions, symbols and
CLASSIFICATION OF ROLLING-ELEMENT BEARINGS
 CLASSIFICATION OF ROLLING-ELEMENT BEARINGS Ball bearings can operate at higher speed in comparison to roller bearings because they have lower friction. In particular, the balls have less viscous resistance
CLASSIFICATION OF ROLLING-ELEMENT BEARINGS Ball bearings can operate at higher speed in comparison to roller bearings because they have lower friction. In particular, the balls have less viscous resistance
Heavy-Duty Rod Ends - Male with integral spherical plain bearing
 Heavy-Duty Rod Ends - Male with integral spherical plain bearing 65700 Order No. Thread (hand) d 1 l 1 d 2 d 3 d 4 l 2 l 3 X g H7 65700.W0005 Right 5 33 M 5 11,11 18 20 9 14 65700.W0006 Right 6 36 M 6
Heavy-Duty Rod Ends - Male with integral spherical plain bearing 65700 Order No. Thread (hand) d 1 l 1 d 2 d 3 d 4 l 2 l 3 X g H7 65700.W0005 Right 5 33 M 5 11,11 18 20 9 14 65700.W0006 Right 6 36 M 6
...our linkages, your solution. Rod Ends
 ...our linkages, your solution Technical Information Introduction All of our rod ends incorporate either a plain spherical bearing, ball bearing, or roller bearing. Below is an overview of each type. Plain
...our linkages, your solution Technical Information Introduction All of our rod ends incorporate either a plain spherical bearing, ball bearing, or roller bearing. Below is an overview of each type. Plain
PIPE HANGERS & SUPPORTS PRIVATE LIMITED Plot No 29 Industrial Estate Perungudi Chennai, Tamilnadu India
 PIPE HANGERS & SUPPORTS PRIVATE LIMITED Plot No 29 Industrial Estate Perungudi Chennai, Tamilnadu India-600096 Telephone +91 (0) 44-24962668, 24961003 Fax: +44 (0) 44-24961395 E mail: mengg@pipehangers.in
PIPE HANGERS & SUPPORTS PRIVATE LIMITED Plot No 29 Industrial Estate Perungudi Chennai, Tamilnadu India-600096 Telephone +91 (0) 44-24962668, 24961003 Fax: +44 (0) 44-24961395 E mail: mengg@pipehangers.in
Riverhawk Company 215 Clinton Road New Hartford NY (315) Free-Flex Flexural Pivot Engineering Data
 Riverhawk Company 215 Clinton Road New Hartford NY (315)768-4937 Free-Flex Flexural Pivot Engineering Data PREFACE Patented Flexural Pivot A unique bearing concept for applications with limited angular
Riverhawk Company 215 Clinton Road New Hartford NY (315)768-4937 Free-Flex Flexural Pivot Engineering Data PREFACE Patented Flexural Pivot A unique bearing concept for applications with limited angular
VARIABLE SPRING SUPPORTS BV35, BV70, BV140, BV210
 SUPPORTS 35, 70, 140, 210 GENERAL Variable spring supports are used for supporting pipework, vessels, columns and pipe connections to large tanks, that are subject to thermal movement and/or subsidence.
SUPPORTS 35, 70, 140, 210 GENERAL Variable spring supports are used for supporting pipework, vessels, columns and pipe connections to large tanks, that are subject to thermal movement and/or subsidence.
PIPINGSOLUTIONS, INC.
 Piping Stress Analysis Where do I start? The following information will take you step-by-step through the logic of the data collection effort that should occur prior to beginning to model a piping system
Piping Stress Analysis Where do I start? The following information will take you step-by-step through the logic of the data collection effort that should occur prior to beginning to model a piping system
10 Thrust ball bearings
 10 Thrust ball bearings Designs and variants.............. 1010 Single direction thrust ball bearings... 1010 Double direction thrust ball bearings.. 1010 Cages............................ 1010 Bearings
10 Thrust ball bearings Designs and variants.............. 1010 Single direction thrust ball bearings... 1010 Double direction thrust ball bearings.. 1010 Cages............................ 1010 Bearings
Mounting Overlap Shield. Face Clamps. Gap. Seat Depth. Lead In Chamfer. Loose Fit.
 Mounting Introduction: Reali-Slim thin section ball bearings have a crosssection thickness that is much thinner than standard bearings of the same diameter, and are therefore more sensitive to shaft and
Mounting Introduction: Reali-Slim thin section ball bearings have a crosssection thickness that is much thinner than standard bearings of the same diameter, and are therefore more sensitive to shaft and
INDEX EASY RAIL: THE SOLUTION IS EASY...D4 EXAMPLES OF LOAD CAPACITIES...D5 ORDER CODES...D6 MOUNTING EXAMPLES...D7 TECHNICAL DATA...
 INDEX EASY RAIL: THE SOLUTION IS EASY...D4 EXAMPLES OF LOAD CAPACITIES...D5 ORDER CODES...D6 MOUNTING EXAMPLES...D7 TECHNICAL DATA...D8 STANDARD CONFIGURATIONS...D10 VERIFICATION UNDER STATIC LOAD...D12
INDEX EASY RAIL: THE SOLUTION IS EASY...D4 EXAMPLES OF LOAD CAPACITIES...D5 ORDER CODES...D6 MOUNTING EXAMPLES...D7 TECHNICAL DATA...D8 STANDARD CONFIGURATIONS...D10 VERIFICATION UNDER STATIC LOAD...D12
SECTION 11 INTERMODAL EQUIPMENT
 SECTION 11 INTERMODAL EQUIPMENT ROA MANUAL SCHEDULE OF AMENDMENTS SECTION 11 AMENDMENT NUMBER PAGES AMENDED AMENDMENT SUMMARY DATE ISSUED TABLE OF CONTENTS Section Description Page No. 11.1 SCOPE... 11-1
SECTION 11 INTERMODAL EQUIPMENT ROA MANUAL SCHEDULE OF AMENDMENTS SECTION 11 AMENDMENT NUMBER PAGES AMENDED AMENDMENT SUMMARY DATE ISSUED TABLE OF CONTENTS Section Description Page No. 11.1 SCOPE... 11-1
ORDERING: Specify size, figure number, description, nominal pipe size or special O.D. and C-to-C dimension. C - C LOAD lb.
 Fig. 2110 www.pipingtech.com/fig2110 Sway Strut with 4 of Adjustment Engineered spring supports option 1 option 2 ORDERING: Specify size, figure number, description, nominal pipe size or special O.D. and
Fig. 2110 www.pipingtech.com/fig2110 Sway Strut with 4 of Adjustment Engineered spring supports option 1 option 2 ORDERING: Specify size, figure number, description, nominal pipe size or special O.D. and
R10 Set No: 1 ''' ' '' '' '' Code No: R31033
 R10 Set No: 1 III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 2013 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks:
R10 Set No: 1 III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 2013 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY (Common to Mechanical Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks:
INSTALLATION & MAINTENANCE MANUAL
 A Subsidiary of Dynamic Instruments INSTALLATION & MAINTENANCE MANUAL A Subsidiary of Dynamic Instruments 3860 Calle Fortunada San Diego, CA 92123-1825 Phone: 1-(800) 821-5831 Web Site: hardyinst.com (858)
A Subsidiary of Dynamic Instruments INSTALLATION & MAINTENANCE MANUAL A Subsidiary of Dynamic Instruments 3860 Calle Fortunada San Diego, CA 92123-1825 Phone: 1-(800) 821-5831 Web Site: hardyinst.com (858)
DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS - I
 R10 Set No: 1 III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 2013 DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS - I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions
R10 Set No: 1 III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 2013 DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS - I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions
Axial-radial cylindrical roller bearings
 Axial-radial cylindrical roller bearings Designs and variants.............. 320 Bearing data..................... 321 (Boundary dimensions, tolerances) Product table 5.1 Axial-radial cylindrical roller
Axial-radial cylindrical roller bearings Designs and variants.............. 320 Bearing data..................... 321 (Boundary dimensions, tolerances) Product table 5.1 Axial-radial cylindrical roller
Operating Instruction
 Operating Instruction Drive element LEWA - ecosmart type LCA with manual stroke adjustment, motor mounted vertically Table of contents 1 General information / safety 1.1 Important preliminary information
Operating Instruction Drive element LEWA - ecosmart type LCA with manual stroke adjustment, motor mounted vertically Table of contents 1 General information / safety 1.1 Important preliminary information
Kaydon white paper. The importance of properly mounting thin section bearings. an SKF Group brand. by Rob Roos, Senior Product Engineer
 The importance of properly mounting thin section by Rob Roos, Senior Product Engineer an SKF Group brand Figure 1 Radial Load Reversing Thrust Overturning Moment Thin section ball have a much thinner cross-section
The importance of properly mounting thin section by Rob Roos, Senior Product Engineer an SKF Group brand Figure 1 Radial Load Reversing Thrust Overturning Moment Thin section ball have a much thinner cross-section
The GK units differ from the LK units in that the springs of the GK units have a spring eye at the front.
 01 09 Installation guidelines Mechanical suspension units GK LK GN0032-0 Mechanical suspension units GK LK The GK units differ from the LK units in that the springs of the GK units have a spring eye at
01 09 Installation guidelines Mechanical suspension units GK LK GN0032-0 Mechanical suspension units GK LK The GK units differ from the LK units in that the springs of the GK units have a spring eye at
Installation and Operational Instructions for EAS -Compact overload clutch, Type 49_. 4._ Sizes 4 and 5
 Please read these Operational Instructions carefully and follow them accordingly! Ignoring these Instructions may lead to malfunctions or to clutch failure, resulting in damage to other parts. Contents:
Please read these Operational Instructions carefully and follow them accordingly! Ignoring these Instructions may lead to malfunctions or to clutch failure, resulting in damage to other parts. Contents:
Profi le rail guides LLR
 Profi le rail guides LLR Content The SKF brand now stands for more than ever before, and means more to you as a valued customer. While SKF maintains its leadership as the hallmark of quality bearings throughout
Profi le rail guides LLR Content The SKF brand now stands for more than ever before, and means more to you as a valued customer. While SKF maintains its leadership as the hallmark of quality bearings throughout
Discipline: Engineering (Track & Civil) Category: Code of Practice. Clearances. Section 7. Applicability. ARTC Network wide.
 Discipline: Engineering (Track & Civil) Category: Code Practice Clearances Section 7 Applicability ARTC Network wide Primary Source Document Status Version Date Reviewed Prepared by Reviewed by Endorsed
Discipline: Engineering (Track & Civil) Category: Code Practice Clearances Section 7 Applicability ARTC Network wide Primary Source Document Status Version Date Reviewed Prepared by Reviewed by Endorsed
Shaft-Hub-Connections
 Stand: 14.01.2010 Shaft-Hub-Connections Shrink Discs Cone Clamping Elements Star Discs 36 Edition 2012/2013 RINGSPANN Eingetragenes Warenzeichen der RINGSPANN GmbH, Bad Homburg Table of Contents Introduction
Stand: 14.01.2010 Shaft-Hub-Connections Shrink Discs Cone Clamping Elements Star Discs 36 Edition 2012/2013 RINGSPANN Eingetragenes Warenzeichen der RINGSPANN GmbH, Bad Homburg Table of Contents Introduction
TAPE EXTENSOMETER Model CONVEX-D. Roctest Limited, All rights reserved.
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL TAPE EXTENSOMETER Model Roctest Limited, 2013. All rights reserved. This product should be installed and operated only by qualified personnel. Its misuse is potentially dangerous. The
INSTRUCTION MANUAL TAPE EXTENSOMETER Model Roctest Limited, 2013. All rights reserved. This product should be installed and operated only by qualified personnel. Its misuse is potentially dangerous. The
Company Introduction. History and Progress
 Company Introduction The company Gradior s.r.o. was founded in the year 1996 under its former name GDV Energo, spol. s r.o. The company started as a technical bureau for designing of pipeline routings
Company Introduction The company Gradior s.r.o. was founded in the year 1996 under its former name GDV Energo, spol. s r.o. The company started as a technical bureau for designing of pipeline routings
BoWex FLE-PA. BoWex FLE-PAC. KTR-N Sheet: Edition: EN 1 of BoWex FLE-PA / FLE-PAC Operating/Assembly instructions
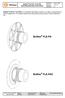 1 of 17 is a torsionally rigid flange coupling. It is able to compensate for shaft misalignment, for example caused by manufacturing inaccuracies, thermal expansion, etc. BoWex FLE-PA BoWex FLE-PAC Drawn:
1 of 17 is a torsionally rigid flange coupling. It is able to compensate for shaft misalignment, for example caused by manufacturing inaccuracies, thermal expansion, etc. BoWex FLE-PA BoWex FLE-PAC Drawn:
Lightweight. Geislinger Gesilco
 Lightweight Geislinger Gesilco The Geislinger Gesilco product range is based on more than 20 years of experience in developing fibre composite couplings and shafts. The maintenance-free composite membranes
Lightweight Geislinger Gesilco The Geislinger Gesilco product range is based on more than 20 years of experience in developing fibre composite couplings and shafts. The maintenance-free composite membranes
Submitted by: Sr. Engineer. Sr. Product Engineer. Product Engineer. Director Power Market Sales. Approved by: Director of Engineering
 Modeling Victaulic Couplings in Piping System Stress Analysis Programs By David Hudson, BSME Gary Trinker, BSME Osama AlMasri, BSME Dan Christian, BSMC Victaulic Engineering Services Department May 2012
Modeling Victaulic Couplings in Piping System Stress Analysis Programs By David Hudson, BSME Gary Trinker, BSME Osama AlMasri, BSME Dan Christian, BSMC Victaulic Engineering Services Department May 2012
Introduction to Bellows Why bellows are used in Piping System?
 Introduction to BELLOWS http://www.sigmaflexeng.com http://www.sigmaflexeng.com Manufacturers of Expansion Joints & Flexible Metal Hose Assemblies Reg. Office & Factory: 865/2 GIDC INDUSTRIAL ESTATE, MAKARPURA,
Introduction to BELLOWS http://www.sigmaflexeng.com http://www.sigmaflexeng.com Manufacturers of Expansion Joints & Flexible Metal Hose Assemblies Reg. Office & Factory: 865/2 GIDC INDUSTRIAL ESTATE, MAKARPURA,
NME-501 : MACHINE DESIGN-I
 Syllabus NME-501 : MACHINE DESIGN-I UNIT I Introduction Definition, Design requirements of machine elements, Design procedure, Standards in design, Selection of preferred sizes, Indian Standards designation
Syllabus NME-501 : MACHINE DESIGN-I UNIT I Introduction Definition, Design requirements of machine elements, Design procedure, Standards in design, Selection of preferred sizes, Indian Standards designation
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF IMPACT BETWEEN SHUNTING LOCOMOTIVE AND SELECTED ROAD VEHICLE
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 21, No. 4 2014 ISSN: 1231-4005 e-issn: 2354-0133 ICID: 1130437 DOI: 10.5604/12314005.1130437 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF IMPACT BETWEEN SHUNTING LOCOMOTIVE AND
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 21, No. 4 2014 ISSN: 1231-4005 e-issn: 2354-0133 ICID: 1130437 DOI: 10.5604/12314005.1130437 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF IMPACT BETWEEN SHUNTING LOCOMOTIVE AND
Huco Dynatork Flexible Couplings
 Huco Dynatork Flexible Couplings Flexible Couplings The Company & Its Products Huco products are manufactured in Hertford, England, in a modern plant equipped with all necessary design, development, toolroom
Huco Dynatork Flexible Couplings Flexible Couplings The Company & Its Products Huco products are manufactured in Hertford, England, in a modern plant equipped with all necessary design, development, toolroom
Pipe clamps, clamp bases, connecting parts
 Pipe clamps, clamp bases, pipe connecting parts 4 pipe Pipe clamps, clamp bases, connecting parts PRODUT 4 GROUP Pipe clamps, clamp bases, pipe connections ontents Page Field of application... 4.1 Product
Pipe clamps, clamp bases, pipe connecting parts 4 pipe Pipe clamps, clamp bases, connecting parts PRODUT 4 GROUP Pipe clamps, clamp bases, pipe connections ontents Page Field of application... 4.1 Product
TECHNICAL INFORMATION
 General Nomenclature Spherical Roller Bearings The spherical roller bearing is a combination radial and thrust bearing designed for taking misalignment under load When loads are heavy, alignment of housings
General Nomenclature Spherical Roller Bearings The spherical roller bearing is a combination radial and thrust bearing designed for taking misalignment under load When loads are heavy, alignment of housings
CERTIFICATES OF COMPETENCY IN THE MERCHANT NAVY MARINE ENGINEER OFFICER
 CERTIFICATES OF COMPETENCY IN THE MERCHANT NAVY MARINE ENGINEER OFFICER EXAMINATIONS ADMINISTERED BY THE SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF THE MARITIME AND COASTGUARD AGENCY STCW 95 CHIEF
CERTIFICATES OF COMPETENCY IN THE MERCHANT NAVY MARINE ENGINEER OFFICER EXAMINATIONS ADMINISTERED BY THE SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF THE MARITIME AND COASTGUARD AGENCY STCW 95 CHIEF
Expansion Joints Guide Module 2a - Axial Expansion Joints General - Standard Program (EFB) - Installation Instructions
 Expansion Joints Guide Module 2a - Axial Expansion Joints General - Standard Program (EFB) - Installation Instructions BOA Expansion Joints Guide Expansion Joints Guide Summary Module 2a 1 AXIAL EXPANSION
Expansion Joints Guide Module 2a - Axial Expansion Joints General - Standard Program (EFB) - Installation Instructions BOA Expansion Joints Guide Expansion Joints Guide Summary Module 2a 1 AXIAL EXPANSION
For advanced drive technology CLAMPEX. Shaft-Hub-Connection. KTR Precision Joints CLAMPEX
 technology CLAMPEX Shaft-Hub-Connection CLAMPEX KTR Precision Joints 07 technology Table of contents Page Brief information 09 Selection and calculation -5 CLAMPEX -Selection Shaft diameter = d 0 10 0
technology CLAMPEX Shaft-Hub-Connection CLAMPEX KTR Precision Joints 07 technology Table of contents Page Brief information 09 Selection and calculation -5 CLAMPEX -Selection Shaft diameter = d 0 10 0
NEW. Cone Clamping Elements Trantorque Keyless Locking Devices for very small diameters from 3 mm. E03.050e
 Cone Clamping Elements Trantorque Keyless Locking Devices for very small diameters from 3 mm NEW E03.050e Backlash free positioning Excellent concentricity Quick mounting by central clamping nut Issue
Cone Clamping Elements Trantorque Keyless Locking Devices for very small diameters from 3 mm NEW E03.050e Backlash free positioning Excellent concentricity Quick mounting by central clamping nut Issue
Please read and observe
 Please read and observe these operating instructions carefully! Non-observation of the information it contains may lead to coupling malfunction or failure and consequential damage. Danger and information
Please read and observe these operating instructions carefully! Non-observation of the information it contains may lead to coupling malfunction or failure and consequential damage. Danger and information
Load Cell for Manually Operated Presses Model 8451
 w Technical Product Information Load Cell for Manually Operated Presses 1. Introduction... 2 2. Preparing for use... 2 2.1 Unpacking... 2 2.2 Using the instrument for the first time... 2 2.3 Grounding
w Technical Product Information Load Cell for Manually Operated Presses 1. Introduction... 2 2. Preparing for use... 2 2.1 Unpacking... 2 2.2 Using the instrument for the first time... 2 2.3 Grounding
MÜPRO. One-piece pipe clamps. Sprinkler pipe clamps. Refrigerant pipe clamps. Two-piece pipe clamps. Heavy-duty pipe support/din pipe clamps
 0. MÜPRO 1. Vibration control 2. Fire protection 3. Pipe clamps 4. Support channels 5. Accessories 6. Anchor points/expansion points 7. Heavy-duty pipe support 8. MPT-Support system 9. Ventilation 10.
0. MÜPRO 1. Vibration control 2. Fire protection 3. Pipe clamps 4. Support channels 5. Accessories 6. Anchor points/expansion points 7. Heavy-duty pipe support 8. MPT-Support system 9. Ventilation 10.
 heet: 1 of 22 Backlash-free, torsionally stiff and maintenance-free coupling Type with setscrew Type with clamping hubs Type KN (Taper hubs) Type M with setscrew Type M with clamping hubs Type PI 11-3379-883
heet: 1 of 22 Backlash-free, torsionally stiff and maintenance-free coupling Type with setscrew Type with clamping hubs Type KN (Taper hubs) Type M with setscrew Type M with clamping hubs Type PI 11-3379-883
TEKNISK RIKTLINJE TR05-10E
 Notes Change notes Date 1 (A) Revision of standards and new template 09 / 07 2010 2 Template changed.clause. 10.5.1.4 support clamp inserted. Clause 10.5.4.2 creepage text revised. Clause 10.6.7 Dry inserted
Notes Change notes Date 1 (A) Revision of standards and new template 09 / 07 2010 2 Template changed.clause. 10.5.1.4 support clamp inserted. Clause 10.5.4.2 creepage text revised. Clause 10.6.7 Dry inserted
ORIGA Pneumatic Linear Drives OSP-L
 ORIGA Pneumatic Linear Drives OSP-L Very long lifetime and lowest leakage A NEW Modular Linear Drive System With this second generation linear drive Parker Origa offers design engineers complete flexibility.
ORIGA Pneumatic Linear Drives OSP-L Very long lifetime and lowest leakage A NEW Modular Linear Drive System With this second generation linear drive Parker Origa offers design engineers complete flexibility.
Installation Procedures
 For the precision ball and roller bearings supplied by MRC Bearings, skill and cleanliness while handling, mounting and dismounting are necessary to ensure satisfactory bearing performance. As precision
For the precision ball and roller bearings supplied by MRC Bearings, skill and cleanliness while handling, mounting and dismounting are necessary to ensure satisfactory bearing performance. As precision
Coaxial Joining (6-axis) FUS
 Original Manual Coaxial Joining (6-axis) FUS Assembly and Operating Manual Superior Clamping and Gripping Imprint Imprint Copyright: This manual remains the copyrighted property of SCHUNK GmbH & Co. KG.
Original Manual Coaxial Joining (6-axis) FUS Assembly and Operating Manual Superior Clamping and Gripping Imprint Imprint Copyright: This manual remains the copyrighted property of SCHUNK GmbH & Co. KG.
Bevel gearboxes. Catalogue
 Bevel gearboxes Catalogue INDEX Bevel gearbox description... page 2 Manufacturing features... page 2 Materials and components... page 4 Bevel gearbox selection... page 5 Thermal power limit... page 7
Bevel gearboxes Catalogue INDEX Bevel gearbox description... page 2 Manufacturing features... page 2 Materials and components... page 4 Bevel gearbox selection... page 5 Thermal power limit... page 7
SCHMIDT-KUPPLUNG GmbH
 Schmidt-Kupplung SCHMIDT-KUPPLUNG GmbH Schmidt-Kupplung About us About us In the early 1960s Richard Schmidt developed of propulsion systems for rockets in a zero-gravity environment. Among the possible
Schmidt-Kupplung SCHMIDT-KUPPLUNG GmbH Schmidt-Kupplung About us About us In the early 1960s Richard Schmidt developed of propulsion systems for rockets in a zero-gravity environment. Among the possible
DYWIDAG Marine Tie Rods Smooth Bars & Walings
 DYWIDAG Marine Tie Rods Smooth Bars & Walings 2 Contents General Information... 4 Fields of Applications... 4 Overview of Steel Grades... 5 Steel Properties... 5 Thread Creation... 6 Key Advantages of
DYWIDAG Marine Tie Rods Smooth Bars & Walings 2 Contents General Information... 4 Fields of Applications... 4 Overview of Steel Grades... 5 Steel Properties... 5 Thread Creation... 6 Key Advantages of
Ch# 11. Rolling Contact Bearings 28/06/1438. Rolling Contact Bearings. Bearing specialist consider matters such as
 Ch# 11 Rolling Contact Bearings The terms rolling-contact bearings, antifriction bearings, and rolling bearings are all used to describe the class of bearing in which the main load is transferred through
Ch# 11 Rolling Contact Bearings The terms rolling-contact bearings, antifriction bearings, and rolling bearings are all used to describe the class of bearing in which the main load is transferred through
Translation of the Original operating instructions Lifting device Z 70 /...
 Translation of the Original operating instructions Lifting device Z 70 /... Content 1. Lifting device / Correct use according to regulations 2. Basic principles 3. General information 4. Special remarks
Translation of the Original operating instructions Lifting device Z 70 /... Content 1. Lifting device / Correct use according to regulations 2. Basic principles 3. General information 4. Special remarks
Features of the LM Guide
 Features of the Functions Required for Linear Guide Surface Large permissible load Highly rigid in all directions High positioning repeatability Running accuracy can be obtained easily High accuracy can
Features of the Functions Required for Linear Guide Surface Large permissible load Highly rigid in all directions High positioning repeatability Running accuracy can be obtained easily High accuracy can
argco.com
 800-854-1015 argco.com STRUT SUPORT SYSTEM STRUT SUPPORT CHANNEL US Strut Support Channel Quick, strong attachment of single or multiple pipes horizontally or vertically Unlimited applications - range
800-854-1015 argco.com STRUT SUPORT SYSTEM STRUT SUPPORT CHANNEL US Strut Support Channel Quick, strong attachment of single or multiple pipes horizontally or vertically Unlimited applications - range
Six keys to achieving better precision in linear motion control applications
 profile Drive & Control Six keys to achieving better precision in linear motion control applications Achieving precise linear motion Consider these factors when specifying linear motion systems: Equipped
profile Drive & Control Six keys to achieving better precision in linear motion control applications Achieving precise linear motion Consider these factors when specifying linear motion systems: Equipped
Classification and Characteristics of Rolling Bearings
 1. Classification Characteristics of Rolling Beas 1.1 Rolling bea construction Most rolling consist of s with raceway (inner outer ), rolling elements (either balls or rollers) cage. The cage separates
1. Classification Characteristics of Rolling Beas 1.1 Rolling bea construction Most rolling consist of s with raceway (inner outer ), rolling elements (either balls or rollers) cage. The cage separates
2. Write the expression for estimation of the natural frequency of free torsional vibration of a shaft. (N/D 15)
 ME 6505 DYNAMICS OF MACHINES Fifth Semester Mechanical Engineering (Regulations 2013) Unit III PART A 1. Write the mathematical expression for a free vibration system with viscous damping. (N/D 15) Viscous
ME 6505 DYNAMICS OF MACHINES Fifth Semester Mechanical Engineering (Regulations 2013) Unit III PART A 1. Write the mathematical expression for a free vibration system with viscous damping. (N/D 15) Viscous
TOOLFLEX Operating-/Assembly Instructions
 D-807 Rheine heet: 5810 EN 1 of 19 Backlash-free, torsionally stiff and maintenance-free coupling is a backlash-free, torsionally stiff and maintenance-free metal bellow-type coupling designed to be used
D-807 Rheine heet: 5810 EN 1 of 19 Backlash-free, torsionally stiff and maintenance-free coupling is a backlash-free, torsionally stiff and maintenance-free metal bellow-type coupling designed to be used
Shaft Couplings Flange-Couplings Rigid Shaft Couplings Flexible Couplings
 Shaft Couplings Flange-Couplings Rigid Shaft Couplings Flexible Couplings 44 Edition 2013/2014 RINGSPANN Registered Trademark of RINGSPANN GmbH, Bad Homburg 2 Table of Contents Flange-Couplings Page Flange-Couplings
Shaft Couplings Flange-Couplings Rigid Shaft Couplings Flexible Couplings 44 Edition 2013/2014 RINGSPANN Registered Trademark of RINGSPANN GmbH, Bad Homburg 2 Table of Contents Flange-Couplings Page Flange-Couplings
Plate Girder and Stiffener
 Plate Girder and Stiffener (Gelagar Pelat dan Pengaku) Dr. AZ Department of Civil Engineering Brawijaya University Introduction These girders are usually fabricated from welded plates and thus are called
Plate Girder and Stiffener (Gelagar Pelat dan Pengaku) Dr. AZ Department of Civil Engineering Brawijaya University Introduction These girders are usually fabricated from welded plates and thus are called
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 14691 First edition 1999-11-01 Petroleum and natural gas industries Flexible couplings for mechanical power transmission General purpose applications Industries du pétrole et
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 14691 First edition 1999-11-01 Petroleum and natural gas industries Flexible couplings for mechanical power transmission General purpose applications Industries du pétrole et
Simulating Rotary Draw Bending and Tube Hydroforming
 Abstract: Simulating Rotary Draw Bending and Tube Hydroforming Dilip K Mahanty, Narendran M. Balan Engineering Services Group, Tata Consultancy Services Tube hydroforming is currently an active area of
Abstract: Simulating Rotary Draw Bending and Tube Hydroforming Dilip K Mahanty, Narendran M. Balan Engineering Services Group, Tata Consultancy Services Tube hydroforming is currently an active area of
 1 TAMCO ALUMINUM CONTROL DAMPER Installation Guidelines For Series 1000, 1400, 1500, 9000, 9000 BF FOR TAMCO JACK SHAFTS REFER TO INSTRUCTIONS PROVIDED IN PARTS BOX. FOR TAMCO JUMPERS REFER TO INSTRUCTIONS
1 TAMCO ALUMINUM CONTROL DAMPER Installation Guidelines For Series 1000, 1400, 1500, 9000, 9000 BF FOR TAMCO JACK SHAFTS REFER TO INSTRUCTIONS PROVIDED IN PARTS BOX. FOR TAMCO JUMPERS REFER TO INSTRUCTIONS
Instruction manual. EK6 Earthing switch 36/40.5 kv
 Instruction manual EK6 Earthing switch 36/40.5 kv Your safety first always! That s why our instruction manual begins with these recommendations: Only install switchgear and/or switchboards in enclosed
Instruction manual EK6 Earthing switch 36/40.5 kv Your safety first always! That s why our instruction manual begins with these recommendations: Only install switchgear and/or switchboards in enclosed
Expansion & contraction
 Expansion & contraction All materials expand & contract with thermal change & pressure change. In case of piping systems, this dimension change can produce excessive stresses throughout the piping system
Expansion & contraction All materials expand & contract with thermal change & pressure change. In case of piping systems, this dimension change can produce excessive stresses throughout the piping system
The economical machinery mounting solution
 The universal adjustable chock The economical machinery mounting solution Why use? is a self leveling, height adjustable and re-usable chock Easy and accurate mounting of all types of rotating equipment
The universal adjustable chock The economical machinery mounting solution Why use? is a self leveling, height adjustable and re-usable chock Easy and accurate mounting of all types of rotating equipment
SIT-LOCK self locking elements
 self locking elements Advantages of on the shaft-hub connection compared with traditional systems Easy assembly and disassembly Both actions take place by locking and unlocking the clamping screws with
self locking elements Advantages of on the shaft-hub connection compared with traditional systems Easy assembly and disassembly Both actions take place by locking and unlocking the clamping screws with
Reli-a-Flex TM Reliance
 Reli-a-Flex TM Reliance Precision Mechatronics LLP www.myostat.ca Reli-a-Flex - Accurate transfer of motion between two shafts Patented: - UK No. 2316735 - US No. 6,203,437 B1 - European No. EP 0922168
Reli-a-Flex TM Reliance Precision Mechatronics LLP www.myostat.ca Reli-a-Flex - Accurate transfer of motion between two shafts Patented: - UK No. 2316735 - US No. 6,203,437 B1 - European No. EP 0922168
12.1 SINGLE ROW BALL BEARINGS
 12.1 SINGLE ROW BALL BEARINGS Due to the versatility of applications, single row ball bearings are among the most frequently used types of rolling bearings. They are made as non-separable without a filling
12.1 SINGLE ROW BALL BEARINGS Due to the versatility of applications, single row ball bearings are among the most frequently used types of rolling bearings. They are made as non-separable without a filling
PIPE SUPPORTS INDIA PRIVATELIMITED Plot No 29 Industrial Estate Perungudi Chennai, Tamilnadu India
 PIPE SUPPORTS INDIA PRIVATELIMITED Plot No 29 Industrial Estate Perungudi Chennai, Tamilnadu India-600096 Telephone +91 (0) 44-24952668, 24961003 Fax: +44 (0) 44-24961395 E mail: psindia@vsnl.com www.pipesupports.com
PIPE SUPPORTS INDIA PRIVATELIMITED Plot No 29 Industrial Estate Perungudi Chennai, Tamilnadu India-600096 Telephone +91 (0) 44-24952668, 24961003 Fax: +44 (0) 44-24961395 E mail: psindia@vsnl.com www.pipesupports.com
Crane. Bridge. Crane Control. Crane. Force, breakaway. hook device. hook device. Friction-type pressure gripping lifters. Below. hook device.
 Fail-safe General A provision designed to automatically stop or safely Control any motion in which a malfunction occurs. (CMAA Spec. 70) Field wiring General The wiring required after erection of the crane.
Fail-safe General A provision designed to automatically stop or safely Control any motion in which a malfunction occurs. (CMAA Spec. 70) Field wiring General The wiring required after erection of the crane.
For advanced drive technology CLAMPEX. Shaft-hub-connection. KTR Precision joints CLAMPEX
 technology CLAMPEX Shaft-hub-connection CLAMPEX KTR Precision joints 227 technology Table of contents Page Brief information 228 Selection and calculation 25-255 CLAMPEX -Selection Shaft diameter = d 0
technology CLAMPEX Shaft-hub-connection CLAMPEX KTR Precision joints 227 technology Table of contents Page Brief information 228 Selection and calculation 25-255 CLAMPEX -Selection Shaft diameter = d 0
NTN Ball Screw Support Bearings
 Ball Screw Support Bearings 1. Ball Screw Support Bearings CONTENTS 1. Ball Screw Support Bearings q Angular contact thrust ball bearing A-BST w Duplex angular contact ball bearing HT 1 e Needle roller
Ball Screw Support Bearings 1. Ball Screw Support Bearings CONTENTS 1. Ball Screw Support Bearings q Angular contact thrust ball bearing A-BST w Duplex angular contact ball bearing HT 1 e Needle roller
3. BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN
 3. BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN 3.1 GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ROLLING BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN Rotating shaft or another component arranged in rolling bearings is guided by them in radial as well as in axial
3. BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN 3.1 GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ROLLING BEARING ARRANGEMENT DESIGN Rotating shaft or another component arranged in rolling bearings is guided by them in radial as well as in axial
SSC Case Study V Container Ship Recurring Failure of Side Longitudinal Passing through a Web Frame
 SSC Case Study V Container Ship Recurring Failure of Side Longitudinal Passing through a Web Frame Contents: Vessel Particulars Summary of Structural Failure Background Detailed Description of Structural
SSC Case Study V Container Ship Recurring Failure of Side Longitudinal Passing through a Web Frame Contents: Vessel Particulars Summary of Structural Failure Background Detailed Description of Structural
RADEX -N Composite Operating/Assembly instructions
 1 of 14 RADEX -N is a torsionally stiff flexible steel lamina coupling. It is able to compensate for shaft misalignment, for example caused by thermal expansion, etc. note ISO 101. Drawn: 0.05.15 Kb/Wig
1 of 14 RADEX -N is a torsionally stiff flexible steel lamina coupling. It is able to compensate for shaft misalignment, for example caused by thermal expansion, etc. note ISO 101. Drawn: 0.05.15 Kb/Wig
1. SPECIFICATION. Altitude of motor installation. Information: Resistance and temperature specifications of the PTC thermistor / posistor/.
 1. SPECIFICATION 5 GENERAL INFORMATION Motors with parameters according to the data sheet comply with the requirements of the IEC 60034-1 standard, and IEC 60034-30 class efficiency IE2 Motor versions:
1. SPECIFICATION 5 GENERAL INFORMATION Motors with parameters according to the data sheet comply with the requirements of the IEC 60034-1 standard, and IEC 60034-30 class efficiency IE2 Motor versions:
01 09 Installation guidelines Air suspension units GL70 GL70HD GL70L GN Air suspension units GL70 GL70HD GL70L
 01 09 Installation guidelines Air suspension units GL70 GL70HD GL70L GN0031-1 Air suspension units GL70 GL70HD GL70L can be identified by the hanger brackets with a welded-on support for the eccentric
01 09 Installation guidelines Air suspension units GL70 GL70HD GL70L GN0031-1 Air suspension units GL70 GL70HD GL70L can be identified by the hanger brackets with a welded-on support for the eccentric
Toothed belt axis ELGC-TB-KF. Operating instruction [ ]
![Toothed belt axis ELGC-TB-KF. Operating instruction [ ] Toothed belt axis ELGC-TB-KF. Operating instruction [ ]](/thumbs/83/87984161.jpg) Toothed belt axis ELGC-TB-KF en Operating instruction 8068220 2017-02 [8068222] Original instructions Identification of hazards and instructions on how to prevent them: Danger Immediate dangers which can
Toothed belt axis ELGC-TB-KF en Operating instruction 8068220 2017-02 [8068222] Original instructions Identification of hazards and instructions on how to prevent them: Danger Immediate dangers which can
Finite Element Analysis of Clutch Piston Seal
 Finite Element Analysis of Clutch Piston Seal T. OYA * F. KASAHARA * *Research & Development Center Tribology Research Department Three-dimensional finite element analysis was used to simulate deformation
Finite Element Analysis of Clutch Piston Seal T. OYA * F. KASAHARA * *Research & Development Center Tribology Research Department Three-dimensional finite element analysis was used to simulate deformation
SECTION PIPE HANGERS AND SUPPORTS
 Part I - GENERAL 1.01 SECTION INCLUDES A. The work covered under this section consists of the furnishing of all necessary labor, supervision, materials, equipment, and services to completely execute the
Part I - GENERAL 1.01 SECTION INCLUDES A. The work covered under this section consists of the furnishing of all necessary labor, supervision, materials, equipment, and services to completely execute the
Analysis Methods for Skewed Structures. Analysis Types: Line girder model Crossframe Effects Ignored
 Analysis Methods for Skewed Structures D Finite Element Model Analysis Types: Line girder model Crossframe Effects Ignored MDX Merlin Dash BSDI StlBridge PC-BARS Others Refined model Crossframe Effects
Analysis Methods for Skewed Structures D Finite Element Model Analysis Types: Line girder model Crossframe Effects Ignored MDX Merlin Dash BSDI StlBridge PC-BARS Others Refined model Crossframe Effects
Bearing preload. Preload considerations
 Bearing preload There may be some applications where the bearing arrangement needs to be preloaded i.e. requires a negative operating clearance. In applications such as machine tool spindles, automotive
Bearing preload There may be some applications where the bearing arrangement needs to be preloaded i.e. requires a negative operating clearance. In applications such as machine tool spindles, automotive
MIL-STD-883G METHOD LEAD INTEGRITY
 LEAD INTEGRITY 1. PURPOSE. This method provides various tests for determining the integrity of microelectronic device leads (terminals), welds, and seals. Test condition A provides for straight tensile
LEAD INTEGRITY 1. PURPOSE. This method provides various tests for determining the integrity of microelectronic device leads (terminals), welds, and seals. Test condition A provides for straight tensile
Proportional directional valves, pilot operated, with electrical position feedback and integrated electronics (OBE)
 Proportional directional valves, pilot operated, with electrical position feedback and integrated electronics (OE) RE 29075/08.13 Replaces: 08.04 1/22 Type 4WRKE Size 10 to 35 Component series 3X Maximum
Proportional directional valves, pilot operated, with electrical position feedback and integrated electronics (OE) RE 29075/08.13 Replaces: 08.04 1/22 Type 4WRKE Size 10 to 35 Component series 3X Maximum
MANUAL INSTALLATION. Active Chilled Beam Linear. ACBL Series. v101 Issue Date: 04/10/ Price Industries Limited. All rights reserved.
 MANUAL INSTALLATION Active Chilled Beam Linear ACBL Series v11 Issue Date: 4/1/18 218 Price Industries Limited. All rights reserved. TABLE OF CONTENTS Product Overview Before You Start...1 Maintenance...1
MANUAL INSTALLATION Active Chilled Beam Linear ACBL Series v11 Issue Date: 4/1/18 218 Price Industries Limited. All rights reserved. TABLE OF CONTENTS Product Overview Before You Start...1 Maintenance...1
Is Low Friction Efficient?
 Is Low Friction Efficient? Assessment of Bearing Concepts During the Design Phase Dipl.-Wirtsch.-Ing. Mark Dudziak; Schaeffler Trading (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China Dipl.-Ing. (TH) Andreas Krome,
Is Low Friction Efficient? Assessment of Bearing Concepts During the Design Phase Dipl.-Wirtsch.-Ing. Mark Dudziak; Schaeffler Trading (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China Dipl.-Ing. (TH) Andreas Krome,
Slotted nut NMG. Housing nut GWR. Bosch Rexroth AG. for economical constructions. a min. 0,3. M A = tightening torque of slotted nut.
 R310EN 3301 (2009.08) Precision Ball Screw Assemblies Bosch Rexroth AG 113 Slotted nut NMG for economical constructions B D d d1 b M A = tightening torque of slotted nut a min. 0,3 Polyamide insert Designation
R310EN 3301 (2009.08) Precision Ball Screw Assemblies Bosch Rexroth AG 113 Slotted nut NMG for economical constructions B D d d1 b M A = tightening torque of slotted nut a min. 0,3 Polyamide insert Designation
产品技术规范. Product Name: Product Technical Specification SMARTSTONE. No.: CPFL0002 Version: A Issued date: Page 1 of 16
 Product Name: TMAP Part Number: CPF00002 Drawing Number: CPFJ0002 Page 1 of 16 CONTENTS 1. General Data 1.1. Description 1.2. Installation Guide 1.3. Maximum ratings of pressure sensor 1.4. Operating characteristics
Product Name: TMAP Part Number: CPF00002 Drawing Number: CPFJ0002 Page 1 of 16 CONTENTS 1. General Data 1.1. Description 1.2. Installation Guide 1.3. Maximum ratings of pressure sensor 1.4. Operating characteristics
126 Ridge Road Tel: (607) PO Box 187 Fax: (607)
 1. Summary Finite element modeling has been used to determine deflections and stress levels within the SRC planar undulator. Of principal concern is the shift in the magnetic centerline and the rotation
1. Summary Finite element modeling has been used to determine deflections and stress levels within the SRC planar undulator. Of principal concern is the shift in the magnetic centerline and the rotation
Interlocks 325 Series
 rd 12070 43 St. NE, St. Michael, MN 55376 763-497-7000 www.tcamerican.com sales@tcamerican.com Installation Instructions Interlocks 325 Series 3I-615; 3I-430 3I-613; 3I-450 Crane Interlock and Operating
rd 12070 43 St. NE, St. Michael, MN 55376 763-497-7000 www.tcamerican.com sales@tcamerican.com Installation Instructions Interlocks 325 Series 3I-615; 3I-430 3I-613; 3I-450 Crane Interlock and Operating
Inner block. Grease nipple. Fig.1 Structure of LM Guide Actuator Model KR
 LM Guide ctuator Model LM Guide + all Screw = Integral-structure ctuator Stopper Housing all screw Inner block Grease nipple Outer rail earing (supported side) Housing Stopper Double-row ball circuit earing
LM Guide ctuator Model LM Guide + all Screw = Integral-structure ctuator Stopper Housing all screw Inner block Grease nipple Outer rail earing (supported side) Housing Stopper Double-row ball circuit earing
CABLE MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS CATALOGUE2003/04 A COMPLETE CABLE MANAGEMENT SOLUTION FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS.
 CABLE MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS CATALOGUE03/04 A COMPLETE CABLE MANAGEMENT SOLUTION FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS www.legrand.co.uk CHANNEL SUPPORT THE BACKBONE OF ALL YOUR SUPPORT NEEDS Swifts
CABLE MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS CATALOGUE03/04 A COMPLETE CABLE MANAGEMENT SOLUTION FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS www.legrand.co.uk CHANNEL SUPPORT THE BACKBONE OF ALL YOUR SUPPORT NEEDS Swifts
FREE STANDING WORK STATION JIB CRANE
 SECTION 14661 FREE STANDING WORK STATION JIB CRANE ***** Gorbel, Inc. manufacturers a broad range of material handling cranes including monorail, bridge, gantry, and jib cranes. Numerous work station and
SECTION 14661 FREE STANDING WORK STATION JIB CRANE ***** Gorbel, Inc. manufacturers a broad range of material handling cranes including monorail, bridge, gantry, and jib cranes. Numerous work station and
Steering Column. Steering Column Component Layout.
 Page 1 of 9 Published : May 5, 2004 Steering Column Steering Column Component Layout Item Part Number Description 1 - Screw (3 off) 2 - Steering angle sensor 3 - Upper steering column assembly 4 - Cowl
Page 1 of 9 Published : May 5, 2004 Steering Column Steering Column Component Layout Item Part Number Description 1 - Screw (3 off) 2 - Steering angle sensor 3 - Upper steering column assembly 4 - Cowl
SECTION ENCLOSED SWITCHES AND CIRCUIT BREAKERS
 SECTION 26 28 16 ENCLOSED SWITCHES AND PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 SUMMARY A. Section includes the following individually mounted, enclosed switches and circuit breakers rated 600V AC and less: 1. Fusible switches.
SECTION 26 28 16 ENCLOSED SWITCHES AND PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 SUMMARY A. Section includes the following individually mounted, enclosed switches and circuit breakers rated 600V AC and less: 1. Fusible switches.
4.5 COMPOSITE STEEL AND CONCRETE
 4.5 COMPOSITE STEEL AND CONCRETE 4.5.1 RULES OF THUMB 4.5 Composite Steel and Concrete (1/11) Typical starting point Overall concrete depth 130mm (Grade 30) Depth of profiled decking 60mm Size beam with
4.5 COMPOSITE STEEL AND CONCRETE 4.5.1 RULES OF THUMB 4.5 Composite Steel and Concrete (1/11) Typical starting point Overall concrete depth 130mm (Grade 30) Depth of profiled decking 60mm Size beam with
Features of the LM Guide
 Features of the Functions Required for Linear Guide Surface Large permissible load Highly rigid in all directions High positioning repeatability Running accuracy can be obtained easily High accuracy can
Features of the Functions Required for Linear Guide Surface Large permissible load Highly rigid in all directions High positioning repeatability Running accuracy can be obtained easily High accuracy can
