Popravilo / zamenjava alternatorja. Volvo V50, 2.0D, letnik 2005
|
|
|
- Mitchell Daniels
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Popravilo / zamenjava alternatorja Volvo V50, 2.0D, letnik 2005 Splošno: 1. Alternator funkcija in delovanje 2. Alternator kosovnica Navodila: 3. Odklop in priklop akumulatorja 4. Zamenjava alternatorja 5. Zamenjava pomožnega jermena 6. Zamenjava regulatorja, krtačk ali diodnih plošč 7. Polnenje sistema z nafto 8. Sile pri zategovanju matic in vijakov Postopki v domači delavnici 9. Razstavljanje 10. Servis 11. Sestavljanje Aljaž Ogrin - Aly, p 1
2 1. Alternator funkcija in delovanje System overview This document describes the basic principles of the design and function of the generator, irrespective of the make. The generator provides power consuming components with current whilst the engine is running and maintains battery charge. The generator is on the front of the engine and is driven from the crankshaft by a Poly V- belt. An automatic belt tensioner is used to adjust the belt tension. First of all the generator creates an alternating current (AC) which is converted to a direct current (DC) in the rectifier bridge. A charge regulator is welded to the rear of the generator. For 5 cylinder engines, the charge regulator is also known as the alternator control module (ACM). The regulator can be replaced. The carbon brushes are screwed to the slip rings on the rotor on the regulator. The carbon brushes can be replaced separately from the regulator. The output of the generator depends on engine speed. When the engine is idling, the generator operates at approximately half of maximum output. When the engine is idling with many power consuming components engaged, the generator may be unable to maintain full battery charge. In cold conditions the capacity of the battery to receive charge is lower than at room temperature. This means that, when the engine is idling for a long period with a large number of power consuming components connected, the battery may discharge. If the generator charge is cut, the power consuming components of the vehicle are only supplied with energy from the battery, which means that the battery will eventually run flat. The charge indicator lamp in the combined instrument panel is controlled by the driver information module (DIM) via signals from the controller area network (CAN). The generator and charge regulator is diagnosed by both the central electronic module (CEM) and the engine control module (ECM). Generator design The main components of the generator consist of: 1. Stator 2. Rotor with slip rings 3. Integrated cooling fans 4. DC bridge 5. Charge regulator 6. Carbon brushes 7. Pulley with freewheel. The 150 A generator has double stator windings and diodes. p 2
3 Generator terminals Generator terminals, 5 cylinder engine: 1. Screw terminal. B+ to the battery via the starter motor 2. Upper terminal #1. Not used 3. Center terminal #2. To the engine control module (ECM) 4. Lower terminal #3. Not used. Generator terminals, 4 cylinder engine: 1. Screw terminal. B+ to the battery via the starter motor 2. Upper terminal #1. To the engine control module (ECM) 3. Center terminal #2. To the engine control module (ECM) 4. Lower terminal #3. Reference voltage from the battery. Freewheel Certain generators are equipped with a freewheel between the rotor shaft and the pulley. The freewheel on the pulley can be seen on the internal hexagonal section of the center of the pulley. Using the freewheel, the generator rotor shaft can only rotate freely in one direction. This minimizes any jerking in the belt transmission. Stator The stator is fixed and consists of grooved plates which are insulated internally and pressed together onto a fixed plate unit. The stator winding coils are positioned in the grooves. They are delta connected at 120 and p rovide a three phase alternating current to the rectifier bridge. The 150 A generator has double stator windings in one unit to maintain a constant high current. p 3
4 Rotor with slip rings The rotor consists of two halves (claw-poles) which interlock. The halves are pressed on the rotor shaft. There are 16 claws on the rotor, i.e. 16 poles. One half has 8 north poles and the other half 8 south poles. The excitation winding is secured on the rotor shaft between the claw-pole halves. The excitation winding (also known as rotor winding) consists of a circular coil surrounded by the clawpoles and connected to the slip rings. The charge regulator supplies a magnetic current through carbon brushes positioned against the slip rings. The higher the current in the rotor the stronger the magnet field of the rotor, and therefore the higher the current generated in the windings of the stator. Cooling fans The heat generated in the generator is, in principle, proportional to the current generated and must be directed away to prevent damage to the insulation and diodes. The generator is therefore air cooled and equipped with two integrated cooling fans on the rotor shaft. Rectifier Alternating current (AC) is created in the generator stator windings. This must be converted to direct current (DC) before it can be used in the electrical system of the car. This conversion is made using a rectifier bridge which consists of six diodes, two diodes per phase winding. The 150 A generator has twice the number of diodes due to its double stator windings, in other words it has 12 diodes. The diodes are pressed into a diode holder. Charge regulator with carbon brushes A charge regulator is welded to the rear of the generator. For 5 cylinder engines, the charge regulator is also known as the alternator control module (ACM). The regulator can be replaced. The carbon brushes are screwed to the slip rings on the rotor on the regulator. The carbon brushes can be replaced separately from the regulator. p 4
5 Charge voltage At room temperature a fully charged battery cell produces 2.12 V. A 12 V battery has 6 cells and therefore produces V when the battery is fully charged. The battery has an internal resistance which must be exceeded before charging can take place. At room temperature 0.2 V is required per cell, or 1.2 V for the entire battery. Therefore to charge a battery at room temperature, V (12.72 V+1.2 V) is required. In cold conditions, the chemical reactions take place at a slower rate and the internal resistance increases. This requires a higher voltage during charging to exceed the internal resistance. The charge regulator, depending on how it is controlled by the engine control module (ECM)/central electronic module (CEM), regulates the output voltage so that the battery receives optimal charge. Charge regulator, 5 cylinder engines For 5 cylinder engines the charge regulator (also known as the alternator control module (ACM) is connected to the engine control module (ECM) and communicates via LIN communication. The engine control module (ECM) then communicates with the central electronic module (CEM) via the controller area network (CAN) to regulate the generator. The central electronic module (CEM) has internal functions to regulate the voltage level and the power consumption in the vehicle. The central electronic module (CEM) controls the charge regulator via the engine control module (ECM) and therefore the current/voltage generated by the generator. The generator does not initially charge when the engine is started. When the engine is started, the engine control module (ECM) increases the charge successively. When there is an increase in load at the generator, the increase from 0 100% takes place over the course of a few seconds (this time varies slightly depending on the operating mode the engine management system is in). This is to gradually increase the load on the engine during the start-up phase and to ensure the engine starts. If the engine speed (RPM) exceeds idle speed (the exact engine speed varies slightly depending on the mode the engine management system is in) during this delay, or if the progressive increase is interrupted, full charge is obtained immediately. If there is no communication with the charge regulator, the charge regulator will not start charging on start-up. The charge regulator can however self magnetize the rotor and start charging. This occurs at engine speeds greater than approximately 2100 rpm. There is no charge engagement by stages with self magnetization, the generator operates at full charge immediately. When self magnetizing has begun, the generator also charges at engine speeds below 2100 rpm. p 5
6 Charge regulator, 4 cylinder engines On 4 cylinder engines the charge regulator is connected to both the engine control module (ECM) and the battery. The engine control module (ECM) then communicates with the central electronic module (CEM) via the controller area network (CAN) to regulate the generator. The central electronic module (CEM) has internal functions to regulate the voltage level and the power consumption in the vehicle. The central electronic module (CEM) controls the charge regulator via the engine control module (ECM) and therefore the current/voltage generated by the generator. The communication between the charge regulator and the engine control module (ECM) occurs across two cables using pulse width modulated (PWM) signals. One cable is used to transmit information about the requested voltage (desired value) to the regulator from the central electronic module (CEM) via the engine control module (ECM). The second cable is used to transmit information about the generator load from the regulator to the central electronic module (CEM) via the engine control module (ECM). This cable is also used to transmit any fault information. A direct connection to the battery measures the drop in voltage between the generator and battery so that any such drop can be compensated for. If the generated voltage exceeds or is below the pre-determined desired value, the regulator controls the current to the rotor so that its magnetic field increases or is reduced, thus raising or lowering the voltage from the stator windings as necessary. This process is repeated continually. The generator does not initially charge when the engine is started. The charge increases successively when the engine has been started. When there is an increase in load at the generator, the increase from 0 100% takes place over the course of a few seconds (this time varies slightly depending on the engine management system in the car). This is to gradually increase the load on the engine during the start-up phase and to ensure the engine starts. If the engine speed (RPM) exceeds idle speed (the exact engine speed varies slightly depending on the engine management system in the car) during this delay, or if the progressive increase is interrupted, full charge is created immediately. If the communication with the charge regulator is missing, the regulator will not start charging on start-up. The charge regulator can however self magnetize the rotor and start charging. This begins however at engine speeds above approximately 2000 rpm (the exact engine speed varies slightly depending on the engine management system in the vehicle). There is no charge engagement by stages with self magnetization, the generator operates at full charge immediately. Function Output voltage from the generator is calculated from the battery temperature in order to charge the battery fully. To determine the temperature of the battery, a battery temperature gauge is connected to the central electronic module (CEM). See Design and Function, central electronic module (CEM). p 6
7 Charging, 5 cylinder engines When the ignition key is turned to position II (and III), information is transmitted from the central electronic module (CEM) to the charge regulator (alternator control module (ACM)) via the engine control module (ECM). The regulator directs current to the excitation winding rotor and is then grounded via the regulator. When the current travels through the rotor a magnetic field is formed around the rotor. When the engine is started and the rotor begins to rotate, the magnetic field also rotates and then produces alternating current in the stator windings. Alternating current is rectified when it passes the diodes and is then fed to the electrical system of the vehicle. The voltage obtained from the stator winding also passes to the regulator via the rectifier and affects the control functions. The desired value for charge voltage is transmitted from the central electronic module (CEM) to the charge regulator via the engine control module (ECM). This value is based on factors such as the calculated battery temperature. The regulator then operates so that the desired voltage is maintained at the battery. The charge indicator lamp in the combined instrument panel is controlled by the driver information module (DIM) via signals from the controller area network (CAN). Charging, 4 cylinder, engines When the ignition key is turned to position II (and III), information is transmitted from the central electronic module (CEM) to the charge regulator via the engine control module (ECM). The regulator directs current to the excitation winding rotor and is then grounded via the regulator. When the current travels through the rotor a magnetic field is formed around the rotor. When the engine is started and the rotor begins to rotate, the magnetic field also rotates and then produces alternating current in the stator windings. Alternating current is rectified when it passes the diodes and is then fed to the electrical system of the vehicle. The voltage obtained from the stator winding also passes to the regulator via the rectifier and affects the control functions. The desired charge voltage is transmitted from the central electronic module (CEM) to the charge regulator via the engine control module (ECM). The regulator then operates so that the desired voltage is maintained at the battery. A direct connection to the battery provides a reference so that the voltage of the battery can be determined. This is to measure the drop in voltage between the generator and battery so that any such drop can be compensated for. The charge indicator lamp in the combined instrument panel is controlled by the driver information module (DIM) via signals from the controller area network (CAN). 2. Alternator kosovnica Alternator. DSL Part No. Qty PS Description Notes EU Alternator, exch A EU Alternator, exch A 120A 150A p 7
8 3. Navodila Odklop in priklop akumulatorja Note when disconnecting/connecting the battery lead Note! The illustrations in this service information are used for different model years and/or models. Some variation may occur. However, the essential information in the illustrations is always correct. Note before disconnecting the battery lead If the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) lights, read off the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) for the engine management system. If necessary, remedy any faults before cutting the power to the vehicle. When the ignition has been switched off, wait at least 1 minute before cutting the power to the vehicle. This is so that there is sufficient time for information to be stored in the control modules. Warning! The SRS (supplemental restraint system) is active for a certain time after the power is cut. Therefore wait 3 minutes before starting work. If the vehicle has a heater with remote starting, the personal code is reset to the factory default (1234) if the battery is disconnected or the power is cut. Caution! Always disconnect the battery negative lead. Note before connecting the battery lead Warning! The key must be in position 2. No one must be in the vehicle when the battery is connected. This is a safety precaution in case an airbag module activates when the power is connected. Central locking Initialize the central locking and the courtesy lighting by unlocking the vehicle using the remote control, the key or via VIDA vehicle communication. Engine When the battery has been disconnected, the car may have to be driven for a few minutes before the engine runs normally. p 8
9 4. Zamenjava alternatorja Generator, replacing Note! The illustrations in this service information are used for different model years and/or models. Some variation may occur. However, the essential information in the illustrations is always correct. Ignition off. Disconnect the battery negative lead. See section 3. Remove the engine cover. Removing the auxiliaries belt and intake manifold Remove the auxiliaries belt. See section 5. Disconnect intake manifold and push to one side. Removing the drip pan cover: Remove 2x the bolts, the cover. Removing the generator Remove: the nut for the battery positive lead the connector the M6 screw and the bracket the 3 M10 screws. Lift out the generator. p 9
10 5. Zamenjava (snemanje) pomožnega jermena Auxiliaries belt / belt tensioner, replacing Remove the upper engine cover by pulling it straight up. Raise the vehicle. Remove the lower engine cover. Relieving the load on the belt tensioner Relieve the load from the belt tensioner. Turn the tensioner clockwise as far as it will go. Lock the belt tensioner using a 5 mm pin. p 10
11 Remove the auxiliaries belt. Removing the belt tensioner Remove: the torx screw for the belt tensioner. Installation Installing the belt tensioner Note! Ensure that the tensioner is correctly positioned against the bracket. Install the belt tensioner. Tighten the screw. Installing the auxiliaries belt Install as illustrated: 1. the auxiliaries belt and the crankshaft 2. the A/C compressor 3. the generator 4. the tensioner. p 11
12 Relieve the load from the belt tensioner and remove the lock pin. Finishing Install: the lower engine cover. Lower the vehicle the upper engine cover. Start the vehicle. Check the function. p 12
13 6. Zamenjava regulatorja, krtačk ali diodnih plošč Removing the carbon brush set Remove: the generator. See section 4. the 3 x M6 nuts on the cover the cover the 2 x M4 screws for the carbon brush set the carbon brush set. p 13
14 Installing the carbon brush set Hint: In order to keep the brushes out when installing, press out the brushes using a finger. Then insert a 1.5 mm Allen key in the hole on the top of the brush holder. Install: the carbon brush set the 2 x M4 screws for the carbon brush set the cover the 3 x M6 nuts on the cover the generator. See section Polnenje sistema z nafto Bleed the fuel injection system Note! Put paper over the generator to avoid fuel spillage. Remove the hose together with the quick-release connector from the fuel pump. Place the hose in a container. Remove the hose together with the quick-release connector from the fuel filter. Install the pump ( ). Ensure that the arrow on the rubber bellows is pointing towards the fuel filter. Using the rubber bellows, pump until there is a continuous flow of fuel into the container. Connect the hose together p 14
15 with the quick-release connector to the fuel pump. Pump until the rubber bellows become hard. Remove the paper. Note! The starter motor must not run for longer than 10 seconds. After 10 seconds, switch off the ignition and wait 30 seconds. Try to start the engine again as above. Run the engine until it reaches operating temperature. Put paper on the generator again. Remove the pump. Install the hose together with the quick-release connector. 8. sile pri zategovanju matic in vijakov General tightening torque Note! Screws coated with a locking fluid or self locking nuts must be replaced with new when reinstalled. See the table below to find the tightening torques for components not included in the summary. Nuts and screws which are not self locking can be reused provided that they are in good condition. Applies to screwed joint with strength class 8.8. Thread Tightening torque (Nm) M5 5 M6 10 M7 17 M8 24 M10 50 M12 80 M p 15
16 Postopki v domači delavnici 9. Razstavljanje Postopek je bil malo drugačen od navodil, ker delo v servisni jami ni bilo možno. Pogled v motor z odstranjenim pokrovom Filter za nafto odvij vijake (ključ 10) odstrani zaščitni pokrov p 16
17 Filter za nafto (1) z nosilcem (2) in zaščitnim pokrovom (3). Odstranjevanje filtra za nafto odsvetujem, kajti ko filter odklopiš, pride v sistem zrak in je težko sistem zopet napolniti z nafto (glej poglavje 7. Polnenje sistema z nafto in poglevje 11. Sestavljanje ). vhod izhod konektor za predgretje Odvij ta vijak (na levi) in snemi vertikalno ven. Na zadnji strani je profil, v katerega je vstavljeno. p 17
18 Odmontiran filter in nosilci Spodnji nosilec filtra Odvij 3 vijake (ključ 8) Filter Zaščitni pokrov p 18
19 Odstranjen alternator Alternator je pritrjen z: 3 vijaki (ključ 16) os v nosilcu z inbusom Najprej se odvije zgornja dva vijaka. Spodnji vijak se malo odpusti. Alternator se potegne dol (se obrne na spodnji osi) in sname jermen. Z veliko potrpljenja se odvije spodnji levi vijak. Alternator se gunca gor in dol ter z vzvodom potiska levo, da je inbus dostopen. Nato se odpusti inbus (ni potrebno sneti nosilca). Sedaj je možno sneti alternator. p 19
20 10. Servis Alternator sam se zelo težko pokvari. Lahko crknejo ležaji ali diodna plošča ali regulator. Priklop alternatorja na vrtalni stroj ali kak drug hitro vrteči motor, da se preveri ležaje. Če ne cvili, je v redu. Snemanje pokrova (ključ 8). Snemanje regulatorja in krtačk (križni izvijač). Izgled usmerniške plošče p 20
21 Alternator z odstranjeno elektroniko Skurjene diode na spodnji plošči p 21
22 Napačen način snemanja usmerniške plošče spoj na ploščo (to odreži) žice iz alternatorja odžagano (napačno) Pravilno je rezanje (ali cvikanje ali brušenje) zgornjega dela žic. Sedaj bo potrebno prekratke žice iz alternatorja podaljšati (s srebrovim visokotemperaturnim lotom). Oznaka alternatorja Fo Mo Co 3M5T-103D0-PC C DENSO V-120A RGZCC Na servisu se sedaj vgrajuje 150A modele alternatorjev. p 22
23 Nadomestno diodno ploščo je zelo težko dobiti. Edini avtoelektričar, ki bi lahko dobavil novo (nadomestno, od drugega proizvajalca) je: Cena nove bi bila 55 (z vključenim DDV). Za zamenjavo plošče se nisem odločil, ker bi bila enako poddimenzionirana kot originalna (35A). Zato sem kupil set novih, močnejših diod, in sicer Schottky, ki imajo manjši padec napetosti (boljši izkoristek - se manj grejejo). Izbral sem MBR A, 60V, cena 1,8 na komad, dostava iz Anglije naslednji delavni dan (poštnina 5 ). Alternator ima tri statorska navitja, katerih priključki so zadaj speljani ven. Priklop je standardni trifazni usmerniški mostiček pri trikot vezavi generatorja. Shema povezav na alternatorju: p 23
24 Originalna nosilna plošča za diode po dimenzijah ni bila primerna, zato sem iz aluminija izrezkal dve novi, večji, in za boljše hlajenje z večimi luknjami. Vseh 6 diod je pritrjenih na spodnje plošče, zgornja je le za + kontakt. Izgled zmontirane nove plošče: Pred montažo regulatorja je potrebno preveriti, če sta krtački v normalnem stanju in dovolj dolgi. Vse diode morajo biti montirane na izolacijsko termalno folijo. Detalj priključitve diod in detajl priključitve ene faze na regulator: p 24
25 Stranski pogled na»sendvič konstrukcijo«. Pritrdilni vijaki (M3) za diode so visoki, zato je potrebno zgornjo ploščo ponekod odbrusiti, da ni stika z vijakom. Ob morebitnem kratkem stiku zgornje in spodnje plošče lahko stečejo ogromni tokovi, zato je potrebno ves čas paziti na dovolj velike razdalje, da tudi ob vibracijah zanesljivo ni stikov. p 25
26 11. Sestavljanje Sestavljanje je v približno obratnem vrstnem redu kot razstavljanje. Najprej se alternator namesti na pozicijo in zategne držalo na desni (imbus vijak kasneje ni več dosegljiv). Z vijakom spodaj levo (ključ 16) se alternator potisne desno na pozicijo. Vijaka se ne sme zategnit, ker se potem alternatorja ne da več premikati. vijak spodaj levo držalo Alternator je sedaj v»spodnji«poziciji potisnjen navzdol. Sledi nameščanje pomožnega jermena pomagamo si lahko s tanko palico, da dosežemo spodnje jermenice, ali pa snamemo spodnji pokrov motorja. Za nameščanje pomožnega jermena glej poglavje 5. Napenjalnik jermena je praktično nedostopen, zato lahko za napenjanje uporabimo kar alternator, napenjalnika pa se sploh ne dotikamo. Ko je jermen na poziciji, alternator obrnemo oz. dvignemo v ležišče in vstavimo vijak levo zgoraj. Pri premikanju alternatorja je potrebno preseči silo napenjalnika jermena in paziti, da nam alternator ne uide iz rok in useka nazaj. Ko je na poziciji, privijemo vse tri vijake. Ne pozabimo na raztezmo pušo pri vijaku desno zgoraj. p 26
27 Za odvitje in privitje vijaka levo spodaj je potrebno posebno orodje ustrezno skrajšan natični ključ 16, da ga lahko vrtimo spodaj pod nosilcem motorja. Ke je alternator na mestu, priključimo kabel do akumulatorja, signalni kabel in zmontiramo nazaj nosilec za filter nafte. vijak filtra 3 vijaki (ključ 8) nosilec filtra p 27
28 Filter na mestu, cevi za nafto priključene. Spodaj se vidi alternator. Če je bil naftni filter odklopljen (kar odsvetujem), potem je potrebno iz cevi izčrpati zrak. Zračni mehurji se pojavijo na teh mestih: priklop na motor Rešitev po servisnih navodilih (glej poglavje 7) je z vstavitvijo ročne gumijaste črpalke pred filter nafte. p 28
29 Druga rešitev (če nimamo ročne črpalke) je, da odklopimo medeninasti priključek na motorju in s podtlakom do te točke potegnemo nafto. Nato filter nafte vzamemo iz ležišča, ga obrnemo na glavo, dvignemo višje od motorja, iztaknemo medeninasti priključek ter na filtru za 1 obrat odvijemo spodnji odzračevalni ventil (ki je sedaj najvišja točka napeljave). Ko nafta priteče iz cevi, priključek nataknemo nazaj na motor in zapremo oddušnik. Filter še vedno držimo v zrako kot prej. Sedaj je potrebno izčrpati zrak ven iz filtra to naredimo s podtlakom skozi oddušni ventil. Nato namestimo filter, priključimo akumulator in poskušano zagnati motor. Ko vžge, ga parkrat spravimo v višje obrate, da povsem izčrpa zrak iz sistema za nafto. Priključek dovodne cevi za nafto na motorju. Medeninasti priključek je pritrjen s plastično objemko. Pozor pri snemanju in nameščanju le te, ker se lahko polomi. Sedaj pomerimo napetost na akumulatorju. Napetost mora biti vmes med 14V in 15V in ne sme preveč nihati. Tudi med dodajanjem plina mora ostati dokaj konstantna. Motor pustimo teči mekaj minut ter pozorno spremljamo napetost. Priporočljivo je pomeriti temperaturo diod oziroma zadnjega dela alternatorja. Maksimalna delovna temperatura diod je 125 C, kar pomeni da je maksimalna temperatura alternatorja cca C na vroč sončen dan ob segretem motorju. p 29
30 Temperatura, pomerjena z infrardečim merilcem, je v tem primeru 30 C višja od tempera ture zraka. Ne pozabimo namestiti še zgornje zaščite naftnega filtra (zaščita pri čelnem trku). Pritrdimo še vse cevi in kable, preverimo priključek za predgretje nafte v filtru ter se odpeljemo na testno vožnjo. Po testni vožnji pustimo motor teči in ponovimo meritve napetosti in temperature. Če je vse v mejah normale, je servis zaključen. Potreben material: natični ključ 16 (8 eur) diode in izolacija (16 eur) aluminijasta plošča vijaki M3 bakrena žica 1,5 ali 2,5 mm 2 Delo: 5 do 8 ur. p 30
Battery Operation. Battery Construction. Battery State Of Charge. Battery Load Test. Battery Rating Systems 2/14/12
 Battery Operation Batteries, Charging and Donald Jones Brookhaven College Batteries convert chemical energy into electrical energy During discharge the battery s plate composition is changed During charging
Battery Operation Batteries, Charging and Donald Jones Brookhaven College Batteries convert chemical energy into electrical energy During discharge the battery s plate composition is changed During charging
Just what is an alternator?
 Just what is an alternator? An alternator is the device used to produce the electricity the car needs to run and to keep the battery charged. The battery is the heart of your electrical system. But you
Just what is an alternator? An alternator is the device used to produce the electricity the car needs to run and to keep the battery charged. The battery is the heart of your electrical system. But you
ALTERNATOR PRECAUTIONS. Some precautions should be taken when working on this, or any other, AC charging system.
 The alternator charging system is a negative (-) ground system which consists of an alternator, a regulator, a charge indicator, a storage battery and wiring connecting the components, and fuse link wire.
The alternator charging system is a negative (-) ground system which consists of an alternator, a regulator, a charge indicator, a storage battery and wiring connecting the components, and fuse link wire.
Motronic ignition system, servicing
 Page 1 of 25 28-2 Motronic ignition system, servicing Note: Motronic Engine Control Module (ECM) J220* with connector page 24-9, item 16. 1 - Highvoltage ignition cable Ignition secondary circuit Check
Page 1 of 25 28-2 Motronic ignition system, servicing Note: Motronic Engine Control Module (ECM) J220* with connector page 24-9, item 16. 1 - Highvoltage ignition cable Ignition secondary circuit Check
CHARGING SYSTEM ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
 CHARGING (2UZFE) CHARGING SYSTEM CHARGING SYSTEM ONVEHICLE INSPECTION CH1 CH0J603 CAUTION: Check that the battery cables are connected to the correct terminals. Disconnect the battery cables when the battery
CHARGING (2UZFE) CHARGING SYSTEM CHARGING SYSTEM ONVEHICLE INSPECTION CH1 CH0J603 CAUTION: Check that the battery cables are connected to the correct terminals. Disconnect the battery cables when the battery
1. SPECIFICATION
 000000 093 1. SPECIFICATION Specification HPS EPS Alternator Crankshaft pulley : Alternator Pulley 1 : 2.94 Normal output (idling/2200 rpm) 70/120 A 70/140A Regulator voltage 14.6 V Brush Length 12.5 mm
000000 093 1. SPECIFICATION Specification HPS EPS Alternator Crankshaft pulley : Alternator Pulley 1 : 2.94 Normal output (idling/2200 rpm) 70/120 A 70/140A Regulator voltage 14.6 V Brush Length 12.5 mm
N1240/N1243 Series Troubleshooting Guide for N1240-3/N Alternators
 N1240/N1243 Series Troubleshooting Guide for N1240-3/N1243-2 Alternators Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information
N1240/N1243 Series Troubleshooting Guide for N1240-3/N1243-2 Alternators Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information
STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM
 K ELECTRICAL SECTION SC A STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM B C D CONTENTS E PRECAUTIONS... 2 Precautions for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) AIR BAG and SEAT BELT PRE-TEN- SIONER... 2 Precautions for Power
K ELECTRICAL SECTION SC A STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM B C D CONTENTS E PRECAUTIONS... 2 Precautions for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) AIR BAG and SEAT BELT PRE-TEN- SIONER... 2 Precautions for Power
C.E. Niehoff & Co. C653/C653A and C625 Alternators Troubleshooting Guide NOTICE. Hazard Definitions. Battery Charge Volt and Amp Values
 C.E. Niehoff & Co. C653/C653A and C625 Alternators Troubleshooting Guide Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information
C.E. Niehoff & Co. C653/C653A and C625 Alternators Troubleshooting Guide Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information
Replacing the camshaft seals / variable valve timing (VVT) unit
 "VCC097794 EN 20100918" 1(10) Replacing the camshaft seals / variable valve timing (VVT) unit Special tools: 951 2050, 999 5450, 999 5451, 999 5452, 999 5651, 999 5718, 999 5719, 999 5919 Note! As the
"VCC097794 EN 20100918" 1(10) Replacing the camshaft seals / variable valve timing (VVT) unit Special tools: 951 2050, 999 5450, 999 5451, 999 5452, 999 5651, 999 5718, 999 5719, 999 5919 Note! As the
Replacing the camshaft seals / variable valve timing (VVT) unit
 "VCC097794 EN 20110521" 1(10) Replacing the camshaft seals / variable valve timing (VVT) unit Special tools: 951 2050, 999 5450, 999 5451, 999 5452, 999 5651, 999 5718, 999 5719, 999 5919 Note! As the
"VCC097794 EN 20110521" 1(10) Replacing the camshaft seals / variable valve timing (VVT) unit Special tools: 951 2050, 999 5450, 999 5451, 999 5452, 999 5651, 999 5718, 999 5719, 999 5919 Note! As the
Charging Systems. ATASA 5 th. ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 19 Pages Charging Systems 42 Points. Please Read The Summary
 ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 19 Pages 571 595 42 Points Please Read The Summary 1. The primary purpose of the charging system is to the battery with a constant and relatively low charge after it has
ATASA 5 TH Study Guide Chapter 19 Pages 571 595 42 Points Please Read The Summary 1. The primary purpose of the charging system is to the battery with a constant and relatively low charge after it has
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
 414-00-1 Charging System General Information 414-00-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Charging System The charging system voltage is controlled by the PCM. The generator charges the battery, and at the Special Tool(s)
414-00-1 Charging System General Information 414-00-1 DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING Charging System The charging system voltage is controlled by the PCM. The generator charges the battery, and at the Special Tool(s)
TIMING BELT COMPONENTS EM 15
 ENGINE MECHANICAL COMPONENTS EM15 EM16 ENGINE MECHANICAL COMPONENTS (Cont d) ENGINE MECHANICAL EM17 REMOVAL OF (See pages EM15 and 16) 1. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE TERMINAL OF BATTERY CAUTION: Work
ENGINE MECHANICAL COMPONENTS EM15 EM16 ENGINE MECHANICAL COMPONENTS (Cont d) ENGINE MECHANICAL EM17 REMOVAL OF (See pages EM15 and 16) 1. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE TERMINAL OF BATTERY CAUTION: Work
A/C Generator Systems
 A/C Generator Systems What is the function of the charging system? Provide power for all electrical loads Recharge the starting battery What happens if the charging systems puts out too much power? Voltage
A/C Generator Systems What is the function of the charging system? Provide power for all electrical loads Recharge the starting battery What happens if the charging systems puts out too much power? Voltage
ENGINE ELECTRICAL GROUP CONTENTS CHARGING SYSTEM IGNITION SYSTEM STARTING SYSTEM
 16-1 GROUP 16 ENGINE ELECTRICAL CONTENTS 16-2 GENERAL INFORMATION 16-2 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 16-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 16-3 DIAGNOSIS 16-3 SPECIAL TOOL 16-6 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 16-7 GENERATOR OUTPUT
16-1 GROUP 16 ENGINE ELECTRICAL CONTENTS 16-2 GENERAL INFORMATION 16-2 GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS 16-3 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 16-3 DIAGNOSIS 16-3 SPECIAL TOOL 16-6 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 16-7 GENERATOR OUTPUT
PART 1. Function. Alarm See Design and Function, Alarm. Central locking See Design and Function, Central locking.
 2009 Volvo S60 2.5T AWD L5-2.5L Turbo VIN 59 B5254T2 Vehicle > Body and Frame > Body Control Systems > Description and Operation > Components > Central Electronic Module (CEM) > Function PART 1 Function
2009 Volvo S60 2.5T AWD L5-2.5L Turbo VIN 59 B5254T2 Vehicle > Body and Frame > Body Control Systems > Description and Operation > Components > Central Electronic Module (CEM) > Function PART 1 Function
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L
 G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
G - TESTS W/CODES - 2.2L 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 2.2L Self-Diagnostics Celica INTRODUCTION If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING, proceed with self-diagnostics.
Copper Sleeve, Unit Injector, Replacement
 Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA This service bulletin replaces SB 237-46, Copper Sleeve, Unit Injector, Replacement dated 6.2007, publication no. PV776-20177417. DService Bulletin Trucks
Volvo Trucks North America Greensboro, NC USA This service bulletin replaces SB 237-46, Copper Sleeve, Unit Injector, Replacement dated 6.2007, publication no. PV776-20177417. DService Bulletin Trucks
500 Series Troubleshooting Guide for C520 Alternators
 500 Series Troubleshooting Guide for C520 Alternators Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information concerning product
500 Series Troubleshooting Guide for C520 Alternators Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information concerning product
Atim - izvlečni mehanizmi
 Atim - izvlečni mehanizmi - Tehnični opisi in mere v tem katalogu, tudi tiste s slikami in risbami niso zavezujoče. - Pridružujemo si pravico do oblikovnih izboljšav. - Ne prevzemamo odgovornosti za morebitne
Atim - izvlečni mehanizmi - Tehnični opisi in mere v tem katalogu, tudi tiste s slikami in risbami niso zavezujoče. - Pridružujemo si pravico do oblikovnih izboljšav. - Ne prevzemamo odgovornosti za morebitne
LIQUID COOLED ALTERNATORS AAN AAP
 T Y P E AAL AAN AAP MAIN TECHNICAL DATA Type Nominal voltage AAL AAN AAP 14 V Nominal current 150 A 190 A 350 A Current at 1800 rpm / 6000 rpm (At 23 C Air / 40 Coolant) 90 A / 150 A 120 A / 190 A Current
T Y P E AAL AAN AAP MAIN TECHNICAL DATA Type Nominal voltage AAL AAN AAP 14 V Nominal current 150 A 190 A 350 A Current at 1800 rpm / 6000 rpm (At 23 C Air / 40 Coolant) 90 A / 150 A 120 A / 190 A Current
REMOVAL OF ALTERNATOR
 CH6 CHARGING SYSTEM ALTERNATOR REMOVAL OF ALTERNATOR 1. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE TERMINAL OF BATTERY CAUTION: Work must be started after approx. 20 seconds or longer from the time the ignition switch
CH6 CHARGING SYSTEM ALTERNATOR REMOVAL OF ALTERNATOR 1. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE TERMINAL OF BATTERY CAUTION: Work must be started after approx. 20 seconds or longer from the time the ignition switch
STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM SECTIONSC CONTENTS IDX
 STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM SECTIONSC GI MA EM LC EC CONTENTS FE PRECAUTIONS...2 Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) AIR BAG and SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER...2 Wiring Diagrams and Trouble Diagnosis...2 BATTERY...3
STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM SECTIONSC GI MA EM LC EC CONTENTS FE PRECAUTIONS...2 Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) AIR BAG and SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER...2 Wiring Diagrams and Trouble Diagnosis...2 BATTERY...3
Starting and Charging
 The Starting and Charging System is a critical system in your vehicle. The Starting system provides the ability to crank the engine electrically from the drivers position. The first car with electric starting
The Starting and Charging System is a critical system in your vehicle. The Starting system provides the ability to crank the engine electrically from the drivers position. The first car with electric starting
GENERATOR CH-9 COMPONENTS FOR REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
 CH9 COMPONENTS FOR REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION CH10 REMOVAL (See Components for Removal and Installation) 1. DISCONNECT NEGATIVE TERMINAL CABLE FROM BATTERY CAUTION: Work must be started after 90 seconds
CH9 COMPONENTS FOR REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION CH10 REMOVAL (See Components for Removal and Installation) 1. DISCONNECT NEGATIVE TERMINAL CABLE FROM BATTERY CAUTION: Work must be started after 90 seconds
14-6. TSB Revision ENGINE COOLING ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
 14-6 RADIATOR CAP DRAIN PLUG ENGINE COOLING ON-VEHICLE SERVICE When removing the radiator cap, use care to avoid contact with hot coolant or steam Place a shop towel over the cap and turn the cap counterclockwise
14-6 RADIATOR CAP DRAIN PLUG ENGINE COOLING ON-VEHICLE SERVICE When removing the radiator cap, use care to avoid contact with hot coolant or steam Place a shop towel over the cap and turn the cap counterclockwise
1999 Toyota RAV ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Cruise Control Systems - RAV4
 1999 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Cruise Control Systems - RAV4 DESCRIPTION WARNING: Deactivate air bag system before performing any service operation. See AIR BAG RESTRAINT SYSTEMS article. DO NOT apply electrical
1999 ACCESSORIES & EQUIPMENT Cruise Control Systems - RAV4 DESCRIPTION WARNING: Deactivate air bag system before performing any service operation. See AIR BAG RESTRAINT SYSTEMS article. DO NOT apply electrical
Troubleshooting Guide for N1225-1/N1237-1/N Alternators
 Troubleshooting Guide for N1225-1/N1237-1/N1505-1 Alternators Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information concerning
Troubleshooting Guide for N1225-1/N1237-1/N1505-1 Alternators Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information concerning
Handout Activity: HA773
 Charging system HA773-2 Handout Activity: HA773 Charging system The charging system allows for a means to recharge the battery and allow for electrical usage of components in the vehicle. The charging
Charging system HA773-2 Handout Activity: HA773 Charging system The charging system allows for a means to recharge the battery and allow for electrical usage of components in the vehicle. The charging
ENGINE ELECTRICAL GROUP CONTENTS CHARGING SYSTEM IGNITION SYSTEM STARTING SYSTEM
 16-1 GROUP 16 ENGINE ELECTRICAL CONTENTS CHARGING SYSTEM 16-3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 16-3 CHARGING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 16-4 SPECIAL TOOL 16-6 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 16-7 GENERATOR OUTPUT LINE VOLTAGE DROP TEST 16-7
16-1 GROUP 16 ENGINE ELECTRICAL CONTENTS CHARGING SYSTEM 16-3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 16-3 CHARGING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS 16-4 SPECIAL TOOL 16-6 ON-VEHICLE SERVICE 16-7 GENERATOR OUTPUT LINE VOLTAGE DROP TEST 16-7
2008 Toyota RAV ELECTRICAL Charging (2AZ-FE) - RAV4
 2008 ELECTRICAL Charging (2AZ-FE) - RAV4 CHARGING SYSTEM PRECAUTION 1. Check that the battery cables are connected to the correct terminals. 2. Disconnect the battery cables if a quick charge is given
2008 ELECTRICAL Charging (2AZ-FE) - RAV4 CHARGING SYSTEM PRECAUTION 1. Check that the battery cables are connected to the correct terminals. 2. Disconnect the battery cables if a quick charge is given
IGNITION SYSTEM ON VEHICLE INSPECTION NOTICE:
 SYSTEM ONVEHICLE INSPECTION NOTICE: SPARK TEST NO CHECK CONNECTION OF COIL, IGNITER AND DISTRIBUTOR CONNECTOR OK CHECK RESISTANCE OF HIGHTENSION CORD (See step 2) Maximum resistance: 25 kω per cord OK
SYSTEM ONVEHICLE INSPECTION NOTICE: SPARK TEST NO CHECK CONNECTION OF COIL, IGNITER AND DISTRIBUTOR CONNECTOR OK CHECK RESISTANCE OF HIGHTENSION CORD (See step 2) Maximum resistance: 25 kω per cord OK
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
 REMOVAL & INSTALLATION TIMING BELT Removal 1. Disconnect negative battery cable. Remove air cleaner assembly. Remove upper fan shroud. Remove cooling fan assembly. Remove all accessory drive belts. 2.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION TIMING BELT Removal 1. Disconnect negative battery cable. Remove air cleaner assembly. Remove upper fan shroud. Remove cooling fan assembly. Remove all accessory drive belts. 2.
Before disconnecting battery Ground (GND) strap obtain security code for radio with antitheft
 Page 1 of 14 Volkswagen > New Beetle > 1998-2005 Body Interior 70 - Interior trim Instrument panel, removing and installing WARNING! Disconnect battery Ground (GND) strap before working on electrical system,
Page 1 of 14 Volkswagen > New Beetle > 1998-2005 Body Interior 70 - Interior trim Instrument panel, removing and installing WARNING! Disconnect battery Ground (GND) strap before working on electrical system,
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
 REMOVAL & INSTALLATION TIMING BELT Removal 1. Disconnect negative battery cable. Rotate engine clockwise and position cylinder No. 1 on TDC of compression stroke. Ensure "O" mark on crankshaft pulley aligns
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION TIMING BELT Removal 1. Disconnect negative battery cable. Rotate engine clockwise and position cylinder No. 1 on TDC of compression stroke. Ensure "O" mark on crankshaft pulley aligns
ALTERNATOR REQUESTED INFORMATION. Vehicles With Dual Generator [ Engine Mount - LH ] 2007 Ford Pickup 6.0L Eng F350 Super Duty
![ALTERNATOR REQUESTED INFORMATION. Vehicles With Dual Generator [ Engine Mount - LH ] 2007 Ford Pickup 6.0L Eng F350 Super Duty ALTERNATOR REQUESTED INFORMATION. Vehicles With Dual Generator [ Engine Mount - LH ] 2007 Ford Pickup 6.0L Eng F350 Super Duty](/thumbs/72/66590437.jpg) ALTERNATOR 2007 Ford Pickup 6.0L Eng F350 Super Duty REQUESTED INFORMATION Vehicles With Dual Generator [ Engine Mount - LH ] Fig 1: Rotating Drive Belt Tensioner Clockwise 1. Remove the accessory drive
ALTERNATOR 2007 Ford Pickup 6.0L Eng F350 Super Duty REQUESTED INFORMATION Vehicles With Dual Generator [ Engine Mount - LH ] Fig 1: Rotating Drive Belt Tensioner Clockwise 1. Remove the accessory drive
CHARGING SYSTEM SECTION CHG CONTENTS ELECTRICAL & POWER CONTROL CHG-1 PRECAUTION... 3 WIRING DIAGRAM... 9 BASIC INSPECTION...13 PREPARATION...
 ELECTRICAL & POWER CONTROL SECTION CHG A CHARGING SYSTEM B C D CONTENTS E PRECAUTION... 3 PRECAUTIONS... 3 Precaution for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) "AIR BAG" and "SEAT BELT PRE-TEN- SIONER"...3
ELECTRICAL & POWER CONTROL SECTION CHG A CHARGING SYSTEM B C D CONTENTS E PRECAUTION... 3 PRECAUTIONS... 3 Precaution for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) "AIR BAG" and "SEAT BELT PRE-TEN- SIONER"...3
UNIT 2. INTRODUCTION TO DC GENERATOR (Part 1) OBJECTIVES. General Objective
 DC GENERATOR (Part 1) E2063/ Unit 2/ 1 UNIT 2 INTRODUCTION TO DC GENERATOR (Part 1) OBJECTIVES General Objective : To apply the basic principle of DC generator, construction principle and types of DC generator.
DC GENERATOR (Part 1) E2063/ Unit 2/ 1 UNIT 2 INTRODUCTION TO DC GENERATOR (Part 1) OBJECTIVES General Objective : To apply the basic principle of DC generator, construction principle and types of DC generator.
STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM
 K ELECTRICAL A SECTION STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM B C D CONTENTS E PRECAUTIONS... 2 Precautions for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) AIR BAG and SEAT BELT PRE-TEN- SIONER... 2 Wiring Diagrams and Trouble
K ELECTRICAL A SECTION STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM B C D CONTENTS E PRECAUTIONS... 2 Precautions for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) AIR BAG and SEAT BELT PRE-TEN- SIONER... 2 Wiring Diagrams and Trouble
F - BASIC TESTING Toyota Celica INTRODUCTION PRELIMINARY INSPECTION & ADJUSTMENTS VISUAL INSPECTION MECHANICAL INSPECTION
 F - BASIC TESTING 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 4-Cylinder Basic Diagnostic Procedures Celica INTRODUCTION The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem.
F - BASIC TESTING 1994 Toyota Celica 1994 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Toyota 4-Cylinder Basic Diagnostic Procedures Celica INTRODUCTION The following diagnostic steps will help prevent overlooking a simple problem.
CHARGING SYSTEM PRECAUTION CH 1
 1NZ-FE ARGING ARGING SYSTEM ARGING SYSTEM PRECAUTION 1 1. Check that the battery cables are connected to the correct terminals. 2. Disconnect the battery cables when the battery is given a quick charge.
1NZ-FE ARGING ARGING SYSTEM ARGING SYSTEM PRECAUTION 1 1. Check that the battery cables are connected to the correct terminals. 2. Disconnect the battery cables when the battery is given a quick charge.
Batteries, Alternators, and Chargers
 FAMA BUYER S GUIDE TC035 Batteries, Alternators, and Chargers Prepared by the FAMA Electrical Subcommittee This guide does not endorse any manufacturer or product Page 1 of 8 Contents Introduction...3
FAMA BUYER S GUIDE TC035 Batteries, Alternators, and Chargers Prepared by the FAMA Electrical Subcommittee This guide does not endorse any manufacturer or product Page 1 of 8 Contents Introduction...3
THREE PHASE RECHARGING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
 THREE PHASE RECHARGING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS INDEX 1. Foreword 2. Battery Voltage 3. Recharging System Connections 4. Stator Three Phase Continuity 5. Alternator Phase Insulation 6. Checking Absorption with
THREE PHASE RECHARGING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS INDEX 1. Foreword 2. Battery Voltage 3. Recharging System Connections 4. Stator Three Phase Continuity 5. Alternator Phase Insulation 6. Checking Absorption with
GENERATOR REMOVAL OF GENERATOR (4A FE) CH 6
 CH6 GENERATOR REMOVAL OF GENERATOR (4AFE) 1. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE TERMINAL OF BATTERY CAUTION: Work must be started after approx. 20 seconds or longer from the time the ignition switch is turned
CH6 GENERATOR REMOVAL OF GENERATOR (4AFE) 1. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE TERMINAL OF BATTERY CAUTION: Work must be started after approx. 20 seconds or longer from the time the ignition switch is turned
STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM
 K ELECTRICAL A SECTION STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM B C D CONTENTS E PRECAUTIONS... 2 Precautions for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) AIR BAG and SEAT BELT PRE-TEN- SIONER... 2 Precautions for Power
K ELECTRICAL A SECTION STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM B C D CONTENTS E PRECAUTIONS... 2 Precautions for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) AIR BAG and SEAT BELT PRE-TEN- SIONER... 2 Precautions for Power
CHARGING SYSTEM 8C - 1 CHARGING SYSTEM CONTENTS
 ZG CHARGING SYSTEM 8C - 1 CHARGING SYSTEM CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION OVERVIEW... 1 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR... 2 CHARGING SYSTEM OPERATION... 1 ELECTRONIC VOLTAGE REGULATOR...
ZG CHARGING SYSTEM 8C - 1 CHARGING SYSTEM CONTENTS page GENERAL INFORMATION OVERVIEW... 1 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR... 2 CHARGING SYSTEM OPERATION... 1 ELECTRONIC VOLTAGE REGULATOR...
Service and Repair REPLACING TIMING BELT/IDLER PULLEY/BELT TENSIONER. Special Tools:
 1 of 9 6/18/2008 8:48 AM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: METRO TOYOTA OK 1999 Volvo V70 XC AWD L5-2.4L Turbo VIN 56 B5254T Vehicle
1 of 9 6/18/2008 8:48 AM Home Account Contact ALLDATA Log Out Help Select Vehicle New TSBs Technician's Reference Component Search: METRO TOYOTA OK 1999 Volvo V70 XC AWD L5-2.4L Turbo VIN 56 B5254T Vehicle
ALTERNATOR - HITACHI
 ALTERNATOR - HITACHI 1986 Isuzu Trooper II 1986 Alternators & Regulators HITACHI ALTERNATORS Isuzu DESCRIPTION Hitachi alternators are conventional 3-phase, self-rectifying alternators. Three positive
ALTERNATOR - HITACHI 1986 Isuzu Trooper II 1986 Alternators & Regulators HITACHI ALTERNATORS Isuzu DESCRIPTION Hitachi alternators are conventional 3-phase, self-rectifying alternators. Three positive
1996 Aerostar/Ranger/Explorer
 Page 1 of 11 Section 03-01B: Engine, 3.0L V-6 IN-VEHICLE SERVICE 1996 Aerostar and Ranger Vehicles Workshop Manual Water Pump SPECIAL SERVICE TOOL(S) REQUIRED Description Tool Number Fan Clutch Holding
Page 1 of 11 Section 03-01B: Engine, 3.0L V-6 IN-VEHICLE SERVICE 1996 Aerostar and Ranger Vehicles Workshop Manual Water Pump SPECIAL SERVICE TOOL(S) REQUIRED Description Tool Number Fan Clutch Holding
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
 CH2 P11586 CHARGING CHARGING SYSTEM ONVEHICLE INSPECTION 1. CHECK BATTERY ELECTROLYTE LEVEL Check the electrolyte quantity of each cell. MaintenanceFree Battery: CH03L01 If under the lower level, replace
CH2 P11586 CHARGING CHARGING SYSTEM ONVEHICLE INSPECTION 1. CHECK BATTERY ELECTROLYTE LEVEL Check the electrolyte quantity of each cell. MaintenanceFree Battery: CH03L01 If under the lower level, replace
CHARGING SYSTEM CHARGING SYSTEM CH 1
 CH1 CH2 Precautions PRECAUTIONS 1. Check that the battery cables are connected to the correct terminals. 2. Disconnect the battery cables when the battery is given a quick charge. 3. Do not perform tests
CH1 CH2 Precautions PRECAUTIONS 1. Check that the battery cables are connected to the correct terminals. 2. Disconnect the battery cables when the battery is given a quick charge. 3. Do not perform tests
CHARGING SYSTEM 8C - 1 CHARGING SYSTEM CONTENTS
 TJ CHARGING SYSTEM 8C - 1 CHARGING SYSTEM CONTENTS page DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR... 2 CHARGING SYSTEM OPERATION... 1 ELECTRONIC VOLTAGE REGULATOR... 2 GENERATOR... 1 DIAGNOSIS
TJ CHARGING SYSTEM 8C - 1 CHARGING SYSTEM CONTENTS page DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR... 2 CHARGING SYSTEM OPERATION... 1 ELECTRONIC VOLTAGE REGULATOR... 2 GENERATOR... 1 DIAGNOSIS
Installation AC B22 Install the ignition switch in the bearing housing
 Installation AC B22 Install the ignition switch in the bearing housing Lubricate contact areas of bearing housing with bearing grease. AC B23 Installing as applies to cars with ignition switch interlock
Installation AC B22 Install the ignition switch in the bearing housing Lubricate contact areas of bearing housing with bearing grease. AC B23 Installing as applies to cars with ignition switch interlock
Reproduction. Not for ADVANCE PRODUCT SERVICE INFORMATION INFORMATION BULLETIN NO: 36 DATE: 11/27/02 SUBJECT: POWERLINK SYSTEM
 ADVANCE PRODUCT SERVICE INFORMATION INFORMATION BULLETIN NO: 36 DATE: 11/27/02 SUBJECT: POWERLINK SYSTEM FILE IN: INTEK & VANGUARD REPAIR MANUAL GFCI Inverter Stator POWERLINK Harness Reset ON OFF Switch
ADVANCE PRODUCT SERVICE INFORMATION INFORMATION BULLETIN NO: 36 DATE: 11/27/02 SUBJECT: POWERLINK SYSTEM FILE IN: INTEK & VANGUARD REPAIR MANUAL GFCI Inverter Stator POWERLINK Harness Reset ON OFF Switch
ON VEHICLE INSPECTION
 IG 18 IGNITION SYSTEM (3VZ E) ON VEHICLE INSPECTION SPARK TEST CHECK THAT SPARK OCCURS (a) Disconnect high tension cord from the distributor. (b) Hold the end approx. 12.5 mm (0.50 in.) from engine ground
IG 18 IGNITION SYSTEM (3VZ E) ON VEHICLE INSPECTION SPARK TEST CHECK THAT SPARK OCCURS (a) Disconnect high tension cord from the distributor. (b) Hold the end approx. 12.5 mm (0.50 in.) from engine ground
STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM
 K ELECTRICAL SECTION SC A STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM B C D CONTENTS E PRECAUTIONS... 2 Precautions for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) AIR BAG and SEAT BELT PRE-TEN- SIONER... 2 Precautions for Power
K ELECTRICAL SECTION SC A STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM B C D CONTENTS E PRECAUTIONS... 2 Precautions for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) AIR BAG and SEAT BELT PRE-TEN- SIONER... 2 Precautions for Power
1. Disconnect negative battery cable. 2. Remove upper and lower front timing belt covers..
 BELT AND SPROCKETS-TIMING REMOVAL TIMING BELT Zoom 1. Disconnect negative battery cable. 2. Remove upper and lower front timing belt covers.. CAUTION: When aligning crankshaft and camshaft timing marks
BELT AND SPROCKETS-TIMING REMOVAL TIMING BELT Zoom 1. Disconnect negative battery cable. 2. Remove upper and lower front timing belt covers.. CAUTION: When aligning crankshaft and camshaft timing marks
Use Installation Procedure 1 when the crankshaft has NOT been rotated from the original position.
 2001 Blazer 4WD Applies to: 4.3L Report a problem with this article Removal Procedure Notice: There are two procedures available to install the distributor. Use Installation Procedure 1 when the crankshaft
2001 Blazer 4WD Applies to: 4.3L Report a problem with this article Removal Procedure Notice: There are two procedures available to install the distributor. Use Installation Procedure 1 when the crankshaft
SHORT-STOP. Electronic Motor Brake Type G. Instructions and Setup Manual
 Electronic Motor Brake Type G Instructions and Setup Manual Table of Contents Table of Contents Electronic Motor Brake Type G... 1 1. INTRODUCTION... 2 2. DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS... 2 3. SAFETY NOTES...
Electronic Motor Brake Type G Instructions and Setup Manual Table of Contents Table of Contents Electronic Motor Brake Type G... 1 1. INTRODUCTION... 2 2. DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS... 2 3. SAFETY NOTES...
Welcome VA School Bus Technicians From
 1 Welcome VA School Bus Technicians From Agenda Leece Neville Company Overview & Product Offering Understanding the Charging System Goal of the system testing The System Components Testing Maintenance
1 Welcome VA School Bus Technicians From Agenda Leece Neville Company Overview & Product Offering Understanding the Charging System Goal of the system testing The System Components Testing Maintenance
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
 REMOVAL & INSTALLATION TIMING BELT Removal (Esteem) 1. Disconnect negative battery cable. Remove right side engine under cover. Remove power steering and A/C compressor drive belts. 2. Remove A/C compressor
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION TIMING BELT Removal (Esteem) 1. Disconnect negative battery cable. Remove right side engine under cover. Remove power steering and A/C compressor drive belts. 2. Remove A/C compressor
N1387 Series Troubleshooting Guide for N Alternators
 N1387 Series Troubleshooting Guide for N1387-1 Alternators Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information concerning
N1387 Series Troubleshooting Guide for N1387-1 Alternators Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information concerning
Replacing timing belt
 "VCC001207 EN 20100809" 1(5) Replacing timing belt Special tools: 998 8500, 999 5456 spark plugs cover two fuel lines clamps lift up expansion tank and place over engine to one side front timing cover
"VCC001207 EN 20100809" 1(5) Replacing timing belt Special tools: 998 8500, 999 5456 spark plugs cover two fuel lines clamps lift up expansion tank and place over engine to one side front timing cover
16A. STARTING - CHARGING Starter: Removal - Refitting REFITTING 16A-11 K4M II - REMOVAL OPERATION III - FINAL OPERATION
 STARTING - CHARGING Starter: Removal - Refitting 16A K4M II - REMOVAL OPERATION III - FINAL OPERATION JR5 a Clip: -the gearbox control cable sleeve stops on the gearbox, - the control cables onto the gearbox.
STARTING - CHARGING Starter: Removal - Refitting 16A K4M II - REMOVAL OPERATION III - FINAL OPERATION JR5 a Clip: -the gearbox control cable sleeve stops on the gearbox, - the control cables onto the gearbox.
C.E. Niehoff & Co. N1601, N1602, N1603, and N1604 Alternator Troubleshooting Guide NOTICE. Hazard Definitions. Battery Charge Volt and Amp Values
 C.E. Niehoff & Co. N1601, N1602, N1603, and N1604 Alternator Troubleshooting Guide Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazard(s) of various risk levels or to important
C.E. Niehoff & Co. N1601, N1602, N1603, and N1604 Alternator Troubleshooting Guide Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazard(s) of various risk levels or to important
Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace
 Assessment Requirements Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace Content: Basic electrical principles a. Explain the direction of current flow
Assessment Requirements Unit AE01K Knowledge of Locating and Correcting Simple Electrical Faults in the Automotive Workplace Content: Basic electrical principles a. Explain the direction of current flow
ENGINE COOLING GROUP CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS COOLANT SEALANT THERMOSTAT...
 14-1 GROUP 14 CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 14-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 14-2 COOLANT 14-3 SEALANT 14-3 DIAGNOSIS 14-3 INTRODUCTION 14-3 TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 14-3 SYMPTOM CHART 14-3 SYMPTOM PROCEDURES
14-1 GROUP 14 CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 14-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 14-2 COOLANT 14-3 SEALANT 14-3 DIAGNOSIS 14-3 INTRODUCTION 14-3 TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 14-3 SYMPTOM CHART 14-3 SYMPTOM PROCEDURES
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
 REMOVAL & INSTALLATION CAUTION: This application is an interference engine. Do not rotate camshaft or crankshaft when timing belt is removed, or engine damage may occur. TIMING BELT Removal 1. Disconnect
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION CAUTION: This application is an interference engine. Do not rotate camshaft or crankshaft when timing belt is removed, or engine damage may occur. TIMING BELT Removal 1. Disconnect
Sized for Print. Timing belt, replacing. Special tools: COUNTERHOLD See: Tools and Equipment\ Counterhold
 Timing belt, replacing Special tools: 999 5433 COUNTERHOLD See: Tools and Equipment\999 5433 Counterhold Note! Since the illustrations in this service information are used for different model years and/or
Timing belt, replacing Special tools: 999 5433 COUNTERHOLD See: Tools and Equipment\999 5433 Counterhold Note! Since the illustrations in this service information are used for different model years and/or
Tech Talk. Timing Belt 6VD1/6VE1
 Holden DOHC V6 Frontera 6VD1 3.2L 1999 2004 Jackaroo 6VE1 3.5L 1998 2004 Rodeo TF 6VD1 3.2L 1998 2003 Rodeo RA 6VE1 3.5L 2003 2005 Important: Read through all the instructions before proceeding with the
Holden DOHC V6 Frontera 6VD1 3.2L 1999 2004 Jackaroo 6VE1 3.5L 1998 2004 Rodeo TF 6VD1 3.2L 1998 2003 Rodeo RA 6VE1 3.5L 2003 2005 Important: Read through all the instructions before proceeding with the
Understanding the Modern Automotive Air Conditioning System. Trainer: Grant Hand
 Understanding the Modern Automotive Air Conditioning System Trainer: Grant Hand AUTOMOTIVE TRAINING SOLUTIONS PTY LTD Training for the future... Automotive Training Solutions IMPORTANT NOTE Copyright The
Understanding the Modern Automotive Air Conditioning System Trainer: Grant Hand AUTOMOTIVE TRAINING SOLUTIONS PTY LTD Training for the future... Automotive Training Solutions IMPORTANT NOTE Copyright The
ENGINE COOLING GROUP CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS COOLANT SEALANT THERMOSTAT...
 14-1 GROUP 14 CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 14-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 14-2 COOLANT 14-3 SEALANT 14-3 DIAGNOSIS 14-3 INTRODUCTION 14-3 TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 14-3 SYMPTOM CHART 14-3 SYMPTOM PROCEDURES
14-1 GROUP 14 CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 14-2 SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS 14-2 COOLANT 14-3 SEALANT 14-3 DIAGNOSIS 14-3 INTRODUCTION 14-3 TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY 14-3 SYMPTOM CHART 14-3 SYMPTOM PROCEDURES
600 Series Troubleshooting Guide for C651 and C654 Alternators
 600 Series Troubleshooting Guide for C651 and C654 Alternators Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information concerning
600 Series Troubleshooting Guide for C651 and C654 Alternators Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information concerning
CHARGING SYSTEM. Page PRECAUTIONS... CH-2 TROUBLESHOOTING... CH-2 ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION... CH-2 ALTERNATOR... CH-6
 CHARGING SYSTEM Page PRECAUTIONS... CH-2 TROUBLESHOOTING... CH-2 ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION... CH-2 ALTERNATOR... CH-6 CH-2 CHARGING SYSTEM - Precautions, Troubleshooting,On-Vehicle Inspection PRECAUTIONS 1.
CHARGING SYSTEM Page PRECAUTIONS... CH-2 TROUBLESHOOTING... CH-2 ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION... CH-2 ALTERNATOR... CH-6 CH-2 CHARGING SYSTEM - Precautions, Troubleshooting,On-Vehicle Inspection PRECAUTIONS 1.
STARTING SYSTEM (1ZZ FE) (April, 2003)
 STARTING & CHARGING STARTING SYSTEM (1ZZ FE) (April, 2003) STARTING SYSTEM (1ZZ FE) (April, 2003) INSPECTION 19 1 190QO 02 1. INSPECT STARTER ASSY NOTICE: These tests must be performed within 3 to 5 seconds
STARTING & CHARGING STARTING SYSTEM (1ZZ FE) (April, 2003) STARTING SYSTEM (1ZZ FE) (April, 2003) INSPECTION 19 1 190QO 02 1. INSPECT STARTER ASSY NOTICE: These tests must be performed within 3 to 5 seconds
N1233 Series Troubleshooting Guide for N Alternator
 N1233 Series Troubleshooting Guide for N1233-2 Alternator Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information concerning
N1233 Series Troubleshooting Guide for N1233-2 Alternator Hazard Definitions These terms are used to bring attention to presence of hazards of various risk levels or to important information concerning
Replacing the timing belt
 "VCC116740 EN 20091209" 1(5) Replacing the timing belt Special tools: 999 5433, 999 5456 Removing the timing belt Note! As the illustrations in this service information are used for different model years
"VCC116740 EN 20091209" 1(5) Replacing the timing belt Special tools: 999 5433, 999 5456 Removing the timing belt Note! As the illustrations in this service information are used for different model years
ALTERNATOR - BOSCH 35/75-AMP & 40/90-AMP
 ALTERNATOR - BOSCH 35/75-AMP & 40/90-AMP 1988 Chrysler LeBaron Convert/Coupe 1988 ALTERNATORS & REGULATORS Chrysler Motors - Bosch 35/75 & 40/90 Amp Alternator All Models DESCRIPTION The charging system
ALTERNATOR - BOSCH 35/75-AMP & 40/90-AMP 1988 Chrysler LeBaron Convert/Coupe 1988 ALTERNATORS & REGULATORS Chrysler Motors - Bosch 35/75 & 40/90 Amp Alternator All Models DESCRIPTION The charging system
2014 Volkswagen Golf
 Fig. 2: Identifying Airbag Component Location Overview (2 Of 2) Courtesy of VOLKSWAGEN GROUP OF AMERICA, INC. 1. 10 - Front passenger side curtain airbag Removing, refer to DRIVER AND PASSENGER SIDE CURTAIN
Fig. 2: Identifying Airbag Component Location Overview (2 Of 2) Courtesy of VOLKSWAGEN GROUP OF AMERICA, INC. 1. 10 - Front passenger side curtain airbag Removing, refer to DRIVER AND PASSENGER SIDE CURTAIN
SECTION 1E ENGINE ELECTRICAL
 SECTION 1E ENGINE ELECTRICAL CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical
SECTION 1E ENGINE ELECTRICAL CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical
2012 Kia Soul L4 2.0L
 2012 Kia Soul L4 2.0L Vehicle» Engine, Cooling and Exhaust» Engine» Timing Chain» Service and Repair» Repair Procedures» Part 2 Installation 1. The TDC marks of the intake and exhaust CVVT sprockets are
2012 Kia Soul L4 2.0L Vehicle» Engine, Cooling and Exhaust» Engine» Timing Chain» Service and Repair» Repair Procedures» Part 2 Installation 1. The TDC marks of the intake and exhaust CVVT sprockets are
SECTION ZF TRANSMISSION
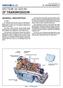 10-103.04/ 1 2009JL16 SECTION 10-103.04 GENERAL DESCRIPTION See Figure 1. The ZF-Ecomat transmission consists of a hydrodynamic torque converter, with a lock-up clutch for direct drive, a hydrodynamic
10-103.04/ 1 2009JL16 SECTION 10-103.04 GENERAL DESCRIPTION See Figure 1. The ZF-Ecomat transmission consists of a hydrodynamic torque converter, with a lock-up clutch for direct drive, a hydrodynamic
TSI Date Group No. Supp. Page
 Volvo Trucks North America, Inc. Greensboro, NC USA This TSI Service Bulletin and others in Groups 21 and 33 replace TSI Service Manual 210 600, Basic Engine, D12, D12A, D12B, D12C (8.2000), publication
Volvo Trucks North America, Inc. Greensboro, NC USA This TSI Service Bulletin and others in Groups 21 and 33 replace TSI Service Manual 210 600, Basic Engine, D12, D12A, D12B, D12C (8.2000), publication
A rotary solenoid type ISC system is used, which controls the fast idle and idle speeds.
 44 ENGINE 5S FE ENGINE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General Basic functions of the engine control system of the new 5S FE engine for the new Camry are the same as those in the 5S FE engine for the 90 model
44 ENGINE 5S FE ENGINE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM 1. General Basic functions of the engine control system of the new 5S FE engine for the new Camry are the same as those in the 5S FE engine for the 90 model
Starting of Induction Motors
 1- Star Delta Starter The method achieved low starting current by first connecting the stator winding in star configuration, and then after the motor reaches a certain speed, throw switch changes the winding
1- Star Delta Starter The method achieved low starting current by first connecting the stator winding in star configuration, and then after the motor reaches a certain speed, throw switch changes the winding
CH 10 ALTERNATOR COMPONENTS FOR REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (3S GTE)
 CH10 CHARGING SYSTEM COMPONENTS FOR REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (3SGTE) CHARGING SYSTEM CH11 REMOVAL (3SGTE) (See Components for Removal and Installation) 1. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE TERMINAL OF BATTERY
CH10 CHARGING SYSTEM COMPONENTS FOR REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (3SGTE) CHARGING SYSTEM CH11 REMOVAL (3SGTE) (See Components for Removal and Installation) 1. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE TERMINAL OF BATTERY
1999 Chevrolet Tahoe - 4WD. DTC P1345 Crankshaft Position (CKP)-Camshaft Position (CMP) Correlation
 1999 Chevrolet Tahoe - 4WD DTC P1345 Crankshaft Position (CKP)-Camshaft Position (CMP) Correlation Circuit Description This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) monitors the crankshaft position (CKP) and the
1999 Chevrolet Tahoe - 4WD DTC P1345 Crankshaft Position (CKP)-Camshaft Position (CMP) Correlation Circuit Description This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) monitors the crankshaft position (CKP) and the
Replacing the oil pump / front crankshaft seal
 "VCC097797 EN 20100518" 1(5) Replacing the oil pump / front crankshaft seal Special tools: 998 6187, 999 5433, 999 5455, 999 5919, 999 5747, 951 2050 Note! As the illustrations in the information are used
"VCC097797 EN 20100518" 1(5) Replacing the oil pump / front crankshaft seal Special tools: 998 6187, 999 5433, 999 5455, 999 5919, 999 5747, 951 2050 Note! As the illustrations in the information are used
Timing Belt: Service and Repair
 Timing Belt: Service and Repair REPLACING TIMING BELT/IDLER PULLEY/BELT TENSIONER B 52X4 S Removing timing belt Remove components Caution! Note! Remove the ignition key from the ignition switch before
Timing Belt: Service and Repair REPLACING TIMING BELT/IDLER PULLEY/BELT TENSIONER B 52X4 S Removing timing belt Remove components Caution! Note! Remove the ignition key from the ignition switch before
Throttle Body (4A FE)
 Air Induction System (Throttle Body (4AFE)) FI185 Throttle Body (4AFE) Throttle Position Sensor PSW E2 IDL ower oint oving oint F10451 P03147 F15040 F10452 Throttle Position Sensor Idle Point Guide Cam
Air Induction System (Throttle Body (4AFE)) FI185 Throttle Body (4AFE) Throttle Position Sensor PSW E2 IDL ower oint oving oint F10451 P03147 F15040 F10452 Throttle Position Sensor Idle Point Guide Cam
TECHNICAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR SAFETY RECALL ALE VALVE SPRING AND LASH ADJUSTER REPLACEMENT GS 350: IS 350:
 TECHNICAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR SAFETY RECALL ALE VALVE SPRING AND LASH ADJUSTER REPLACEMENT GS 350: 2007 2008 IS 350: 2006 2008 I. OPERATION FLOWCHART Verify Vehicle Eligibility 1. Check the VIN range. 2.
TECHNICAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR SAFETY RECALL ALE VALVE SPRING AND LASH ADJUSTER REPLACEMENT GS 350: 2007 2008 IS 350: 2006 2008 I. OPERATION FLOWCHART Verify Vehicle Eligibility 1. Check the VIN range. 2.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
 REMOVAL & INSTALLATION CAUTION: This application is an interference engine. Do not rotate camshaft or crankshaft when timing belt is removed, or engine damage may occur. TIMING BELT Removal 1. Raise and
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION CAUTION: This application is an interference engine. Do not rotate camshaft or crankshaft when timing belt is removed, or engine damage may occur. TIMING BELT Removal 1. Raise and
VS403 INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM AND PRESSURE TEST / BRAKE BLEEDING UNIT MODEL: SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS INTRODUCTION & CONTENTS. fig.1
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM AND PRESSURE TEST / BRAKE BLEEDING UNIT MODEL: VS403 Thank you for purchasing a Sealey product. Manufactured to a high standard this product will, if used according to these instructions
INSTRUCTIONS FOR: VACUUM AND PRESSURE TEST / BRAKE BLEEDING UNIT MODEL: VS403 Thank you for purchasing a Sealey product. Manufactured to a high standard this product will, if used according to these instructions
SECTION M. ELECTRICAL. Section Description Page No.
 SECTION M. ELECTRICAL. Section Description Page No. M.1 General Page 2 M.2 Alternator Page 2 M.3 Battery Page 7 M.4 Hazard Warning System Page 7 M.5 Brake Fail Warning System Page 8 M.6 Seat Belt Warning
SECTION M. ELECTRICAL. Section Description Page No. M.1 General Page 2 M.2 Alternator Page 2 M.3 Battery Page 7 M.4 Hazard Warning System Page 7 M.5 Brake Fail Warning System Page 8 M.6 Seat Belt Warning
1992 Mitsubishi 3000GT VR-4
 TIMING BELT Removal (Diamante SOHC) 1. Remove left front and left side splash shields. Using engine hoist, lift engine just enough to remove weight from engine mounts. Remove drive belts. Remove A/C tensioner
TIMING BELT Removal (Diamante SOHC) 1. Remove left front and left side splash shields. Using engine hoist, lift engine just enough to remove weight from engine mounts. Remove drive belts. Remove A/C tensioner
EG2 173 EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
 5SFE ENGINE EG2173 EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM EG2174 5SFE ENGINE EGR SYSTEM INSPECTION 1. INSPECT AND CLEAN FILTER IN EGR VACUUM MODULATOR (a) Remove the cap and filter. (b) Check the filter
5SFE ENGINE EG2173 EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM EG2174 5SFE ENGINE EGR SYSTEM INSPECTION 1. INSPECT AND CLEAN FILTER IN EGR VACUUM MODULATOR (a) Remove the cap and filter. (b) Check the filter
Test and adjustment values. DTC memory DTC text Possible cause/note Remedy
 AD07.51-P-4000A Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) diagnosis, DTC memory 27.2.97 ENGINE 111 a b c d e a b c a b c d Check and adjust engine Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) - diagnosis,
AD07.51-P-4000A Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) diagnosis, DTC memory 27.2.97 ENGINE 111 a b c d e a b c a b c d Check and adjust engine Fuel injection and ignition system (HFM-SFI) - diagnosis,
DI 3 ENGINE DIAGNOSTICS DI PRE CHECK
 FI0534 PRECHECK DI3 DI09603 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Description When troubleshooting OBD II vehicles, the only difference from the usual troubleshooting procedure is that you connect to the vehicle the
FI0534 PRECHECK DI3 DI09603 1. DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM (a) Description When troubleshooting OBD II vehicles, the only difference from the usual troubleshooting procedure is that you connect to the vehicle the
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
 Table of Contents IMPORTANT INFORMATION Section 1B - Maintenance MAINTENANCE 1 B Specifications........................... 1B-1 Special Tools........................... 1B-2 Mercury/Quicksilver Lubricants
Table of Contents IMPORTANT INFORMATION Section 1B - Maintenance MAINTENANCE 1 B Specifications........................... 1B-1 Special Tools........................... 1B-2 Mercury/Quicksilver Lubricants
