ENHANCED ROTORDYNAMICS FOR HIGH POWER CRYOGENIC TURBINE GENERATORS
|
|
|
- Loraine Bridges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
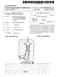
1 The 9th International Symposium on Transport Phenomena and Dynamics of Rotating Machinery Honolulu, Hawaii, February -1, ENHANCED ROTORDYNAMICS FOR HIGH POWER CRYOGENIC TURBINE GENERATORS Joel V. Madison Ebara International Corporation 35 Salomon Circle Sparks, NV 93 Telephone: (775) Fax: (775) ABSTRACT This paper presents novel generator and thrust balancing configurations to enhance the rotordynamic behavior of Vertical Cryogenic Turbine Generators. The LNG production plants currently in the design stages are utilizing economy of scale to increase production with lower capital costs, which has the effect of increasing the power ratings of the critical rotating equipment being supplied. The higher power ratings of the variable speed hydraulic turbine generators implicitly require larger physical sizes, however the possible loss of generator load demands critical speed separation below minimum continuous speed and above maximum "breakaway" speed. The limitations on bearing design, shaft size and overall diameter of machines of this type impose certain restrictions on the design, which entail unique fabrication techniques to produce a robust, reliable machine. INTRODUCTION Figure 1 shows a conventional vertical cryogenic turbine generator that is rated at 115 kw power output. It can be seen that the turbine, consisting of three hydraulic stages, and generator share a common shaft. The turbine generator is mounted in a stainless steel pressure containment vessel, suspended by a flanged connection with a flexible gasket at the headplate. The LNG flows in from the top and expands through three radial inflow runners, which are mounted on a common shaft with the submerged generator. A small percentage of the high pressure inlet flow is routed through the thrust equalizing mechanism to balance the axial thrust load, then fed through the generator air gap to dissipate any heat production. The shaft is supported by three ball bearings, one each at the upper and lower ends of the generator and one at the turbine end of the shaft. Each bearing is lubricated by a controlled flow of process fluid, and is supported by the turbine casings. Circumferentially grooved seals are located between each stage and at the front shroud of each runner. The fluid routed through the generator air gap behaves as a hydrodynamic bearing due to the low pressure difference in the axial direction. The rotordynamic performance of this machine has been proven through analysis and performance testing data in the past (Habets and Kimmel; Smalley, Hollingsworth, Habets and Kimmel). However, as the power requirements increase with the demands for the next generation of liquefaction plants, the generator size must increase physically. As the generator is the dominant component in terms of rotordynamic stability, the increased size has negative ramifications to the machine reliability. As described in detail in previous work (Madison), the possible loss of generator load demands critical speed separation below minimum continuous speed and above maximum "breakaway" speed. For the turbine hydraulic combinations used in these applications the normal breakaway speed is on the order of 3 rpm. The calculated critical speed of the machine should have a Figure 1: Vertical Cryogenic Turbine Generator 1
2 nominal 15% margin above the maximum expected speed to ensure that no assumptions regarding the speed or the calculations will result in an inadequate design. This yields a minimum acceptable critical speed of 95 rpm. There are several unique aspects related to the design of this machine that are required as a result of operating while submerged in a cryogenic fluid (Weisser and Madison). These include limitations on bearing size, shaft diameter and generator diameter, all of which make it difficult to increase the physical size of the generator without detracting from the rotordynamic integrity. This paper presents solutions for increasing the generator size in small and large increments while still maintaining acceptable rotordynamic characteristics. PROPOSED INCREMENTAL ENHANCEMENTS For generator power increases of up to % simply reducing the span between the main bearings can offset the reduction in the critical speed resulting from the increased generator size. Referring again to Figure 1, it can be noted that this is not readily accomplished. The upper bearing needs to be located outside of the generator end turns to avoid any possible electrical effects associated from the variable speed electrical control system of the generator, and the lower bearing is integral to the thrust balancing system. One distinctive feature of these machines is that the deep groove ball bearings are cooled and lubricated by the product fluid. Due to the low viscosity of liquefied hydrocarbon gases the thrust generated by the hydraulic components must be totally eliminated for the bearing to achieve adequate running time between overhauls. While a device employing a combination of fixed and variable orifices has been utilized in the past, it has limitations with regards to location, length and resultant variable orifice gap size. variable orifice gap to increase to such as degree that the device would be rendered inoperable. The solution to this problem is to integrate another component within the device composed of a material that shrinks less than the shaft. The individual heights of the thrust plate and compensator portion are selected to produce the desired variable orifice gap at the actual operating temperature that will result in the most effective thrust balancing and highest machine efficiency. The rotordynamic performance of the original configuration and the modified machine were calculated using the methodology described in references 3, 5 and and compared to the original results. The analytical model geometry for the original configuration is shown in figure 3. The runner and generator masses are depicted by the attached weights, and the hydrodynamic and ball bearing supports are depicted by the spring symbols. Details on the hydrodynamic bearing stiffness and damping calculations can be found in the previous references. The ball bearings are located at 1.3, 37.9 and 9.5 inches from the left end of the shaft in the original model, yielding a bearing span of 5. inches for the generator and 3. inches for the turbine. The damped resonance frequency of the generator for this configuration was calculated to be 579 rpm, as indicated in the unbalance response plot taken at the center of the generator rotor, Figure. The deflected shape at the resonant frequency shown in Figure 5 confirms that the generator rotor first mode is causing the resonance. The revised geometry shown in Figure was employed for the second analysis case. As shown in Figure, the bearings for this geometry are located at 1.3,. and 9.5 inches respectively. This results in a reduction in the critical bearing span of.5 inches, or 5%. The span between the bottom guide bearing and the lower generator bearing is increased from 3. to 39.1 inches, however this segment of the rotor assembly has a second order effect on the critical speed as it has small masses that are well supported. As expected from the unbalance response results shown in Figure 7, the resultant critical speed was increased by % from 553 rpm to 55 rpm. The deflected shape at the resonant speed is shown in Figure, where it can be easily noted again that the generator is the source of the resonance. Increases in generator power cause a nearly linear increase in the physical length, which will result in a corresponding linear reduction in the critical speed. The revised configuration for the thrust balancing geometry can effectively compensate for an increase in generator size of up to approximately %, which will be acceptable for a large proportion of new projects. Figure : Comparison of Original and Modified Thrust Balancing Configurations Relocating the lower bearing by the requisite amount would entail a dramatic increase in the length of the thrust balancing device, as shown in Figure. The resultant differential shrink between the thrust plate material and the shaft would cause the NON-INCREMENTAL ENHANCEMENTS For increases in capacity beyond the % incremental limit demonstrated above, more novel techniques must be employed. One primary factor that drives a more concrete change in the configuration is that the generator frame size will necessarily increase in addition to the length. When the frame size increases, the rotor diameter will also increase, and centrifugal forces on the rotor itself become a concern in addition to the impact on the
3 35 Rotordynamic Response Plot Sta. No. : ROTOR CENTER Excitation = 1x 1 Figure : Unbalance Response for Original Configuration < > Shaft Radius, inches Axial Location, inches Figure 5: Deflected Shape for Original Configuration Rotordynamic Deflected Shape Plot, mils pk 3
4 Rotordynamic Response Plot Sta. No. : ROTOR1 CENTER 1 Figure 7: Unbalance Response for Revised Configuration 1, Modified Thrust Balancing Device 3.9 Shaft Radius, inches Axial Location, inches Figure : Deflected Shape for Revised Configuration 1, Modified Thrust Balancing Device Rotordynamic Deflected Shape Plot, mils pk
5 critical speed. Fortunately, the variable speed controller allows for multiple generators to be controlled from the same source. This allows the single large submerged generator to be replaced with two smaller generators on a common shaft that are driven by the same set of hydraulics. The generators can be configured at either end of the hydraulic components or at the same end. The analytical model for the case with two generators located on the upper end of the machine with the turbine at the lower end is depicted in Figure 9. Each of the generators in this configuration is rated at exactly half the output power of the original single generator used in the baseline case. The actual length of each generator stack is 5% of the original single generator length for this duty. Figure 9 demonstrates that the three ball bearing system employed in configurations 1 and is replaced by a four bearing system, a guide bearing at the bottom of the shaft, a main bearing between the turbine and the first generator, a main bearing between the two generators and a main bearing at the upper end of the shaft. The revised configuration 3 now consists of three important bearing spans; 3.5 inches for the turbine hydraulics, 7.9 for the first generator and 35. for the second generator. While the overall length of the system has increased from 9.5 to 1.9 inches, the rotating masses have been more evenly distributed over shorter bearing spans, which will result in a more stable system. The unbalance response for configuration 3 taken at the center of the first rotor, shown in Figure 9, indicates that the critical speed has been raised to 75 rpm. This dramatic increase is to be expected considering the distribution of the masses and the shorter critical bearing spans. The resonance at 75 rpm is clearly attributed to the first rotor in this case, as a second resonance is also noted at 975 rpm, which is due to the second generator rotor, as depicted in Figure. Figure 11 shows the deflected shape of the rotor assembly at the first resonance, which indicates that the mode is being driven by the first generator, or middle mass element. Again, this result is to be expected considering that this element has the largest bearing span with the highest mass. The third alternate configuration being considered places a generator on either side of the turbine, as shown in Figure 1. As in the previous configuration the combination of the two generators gives the identical power rating to the original single generator configuration. This revised configuration also uses a four bearing system, but in this case all four bearings can be considered as main generator support bearings with the turbine connected between the two generators. The bearing spans for this configuration are 37 inches for the first generator, 31. inches for the turbine hydraulics and 3. inches for the second generator. With this configuration the end turns of the two generators were not located adjacent to each other so the overall shaft length only increased to 1.9 inches. The unbalance response results for configuration are shown in Figure 11, which indicate the critical speed to be approximately rpm. This increase is to be expected due to the reduced bearing span over the first generator as compared to configuration 3. The deflected mode shape for this case shows that both generators appear to be resonating at nearly the same frequency, which is an expected result given the similar bearing span over the two components. Again, as expected this configuration offers the most stability due to the more compact bearing spans and the resultant higher critical speed. SUMMARY The proposed changes to the configuration of the turbine generators show that increased capacity can be realized without sacrificing the rotordynamic integrity of the machine. Table 1 summarizes the resultant critical speeds and separation margins with respect to the expected maximum breakaway speed. Considering that there is a 9% separation margin built in to the baseline configuration, capacity increases of % over the baseline configuration can be accommodated through modifications to the thrust balancing system. This implies that the original design will be stable for power requirements of up to 13 kw. An additional benefit that can be realized with the revised thrust balancing system is the ability to tune the variable orifice gap to maximize the efficiency and stability of the machine. Configuration Critical Speed % Increase Over Baseline Separation Margin Baseline 553 rpm N/A 9% Revised Thrust 55 rpm % 3% Balancing System Two Generators 75 rpm % 3% Located Adjacently Two generators Located on Opposite Ends rpm 59% % Table 1. Comparison of Calculated Critical Speeds and Separation Margins for Each of the Four Analyzed Configurations For power outputs beyond % a two generator system is proposed. This could reasonably double the power output of the machine to ratings of 3 kw or higher while maintaining rotordynamic and mechanical integrity. The control and operation of the machine would not be complicated as the variable speed controller is fully capable of operating two generators in series. The modification to the trhust balancing system described in configuration is applicable to the two generator system also. An additional benefit to this configuration would be the ability to shut one generator down while operating at part load conditions, thereby operating the remaining generator closer to the rated point where peak efficiency and stability are attained. Of the systems proposed the preferred solution for higher powered units for future application is the configuration employing a generator on either side of the turbine. This will provide the most stability and will result in the highest reliability over the lifetime of the machine. 5
6 Rotordynamic Response Plot 1 Sta. No. : ROTOR1 Center Figure 9: Unbalance Response for Revised Configuration, Two Generators on Same Side of Turbine, Center of Rotor 1 1 Rotordynamic Response Plot Sta. No.5 : ROTOR1 Center Figure : Unbalance Response for Revised Configuration, Two Generators on Same Side of Turbine, Center of Rotor
7 Shaft Radius, inches Axial Location, inches Figure 11: Deflected Shape for Revised Configuration, Two Generators on Same Side of Turbine Rotordynamic Deflected Shape Mils pk 1 Rotordynam ic Res ponse Plot Sta. No.11 : ROTOR1 CENTER 1 1 Figure 13: Unbalance Response for Revised Configuration 3, Two Generators on Opposite Sides of Turbine, Center of Rotor 1 7
8 1 Rotordynamic Response Plot Sta. No.5 : ROTOR CENTER REFERENCES Habets, G.L.G.M., and Kimmel, H. E., April 1999, 1 Figure 13: Unbalance Response for Revised Configuration 3, Two Generators on Opposite Sides of Turbine, Center of Rotor Shaft Radius, inches Axial Location, inches Figure 1: Deflected Shape for Revised Configuration 3, Two Generators on Opposite Sides of Turbine Development of a Hydraulic Turbine in Liquefied Natural Gas, Proceedings of the 7th International Fluid Machinery Conference, IMechE, The Hague, The Netherlands. Rotordynamic Deflected Shape Plot, mils pk Weisser, G. L. and Madison, J.V., Application of Aerospace research on Cryogenic Fuel technology, AIAA 9-, 3th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, January 199. Smalley, A. J., Hollingsworth, J. R., Habets, G.L.G.M., and Kimmel, H. E., September 199, Rotor Dynamic Analysis of a Submerged Turbine Generator Driven by Liquefied Natural Gas, Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Rotor Dynamics, IFToMM, Darmstadt University of Technology, Darmstadt, Germany, pp Madison, J., March, Torque Dependent Vibrations for a Vertical Cryogenic Turbine Generator, Proceedings of the th International Symposium on Transport Phenomena and Dynamics of Rotating Machinery, ISROMAC, Vol. I. Guo, S., and Tano, M., Analysis on the Coupled Vibration of Rotor and Casing of a Vertical Shaft Pump by Using the Substructure Synthesis Method, Proceedings of the th International Symposium on Transport Phenomena and Dynamics of Rotating Machinery, Vol. 1, 199. Harris, R. E., and Bates, L. C., Southwest Research Institute Technical Memorandum --, June 199.
Investigations of Oil Free Support Systems to Improve the Reliability of ORC Hermetic High Speed Turbomachinery
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 15, No. 3 (2011) 355 365 c Technical University of Lodz Investigations of Oil Free Support Systems to Improve the Reliability of ORC Hermetic High Speed Turbomachinery
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 15, No. 3 (2011) 355 365 c Technical University of Lodz Investigations of Oil Free Support Systems to Improve the Reliability of ORC Hermetic High Speed Turbomachinery
PNEUMATIC HIGH SPEED SPINDLE WITH AIR BEARINGS
 PNEUMATIC HIGH SPEED SPINDLE WITH AIR BEARINGS Terenziano RAPARELLI, Federico COLOMBO and Rodrigo VILLAVICENCIO Department of Mechanics, Politecnico di Torino Corso Duca degli Abruzzi 24, Torino, 10129
PNEUMATIC HIGH SPEED SPINDLE WITH AIR BEARINGS Terenziano RAPARELLI, Federico COLOMBO and Rodrigo VILLAVICENCIO Department of Mechanics, Politecnico di Torino Corso Duca degli Abruzzi 24, Torino, 10129
ROTATING MACHINERY DYNAMICS
 Pepperdam Industrial Park Phone 800-343-0803 7261 Investment Drive Fax 843-552-4790 N. Charleston, SC 29418 www.wheeler-ind.com ROTATING MACHINERY DYNAMICS SOFTWARE MODULE LIST Fluid Film Bearings Featuring
Pepperdam Industrial Park Phone 800-343-0803 7261 Investment Drive Fax 843-552-4790 N. Charleston, SC 29418 www.wheeler-ind.com ROTATING MACHINERY DYNAMICS SOFTWARE MODULE LIST Fluid Film Bearings Featuring
Evaluating and Correcting Subsynchronous Vibration in Vertical Pumps
 Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software https://dyrobes.com Evaluating and Correcting Subsynchronous Vibration in Vertical Pumps Abstract By Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Co. Kelly J. Conner
Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software https://dyrobes.com Evaluating and Correcting Subsynchronous Vibration in Vertical Pumps Abstract By Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Co. Kelly J. Conner
Effect of Compressor Inlet Temperature on Cycle Performance for a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Brayton Cycle
 The 6th International Supercritical CO2 Power Cycles Symposium March 27-29, 2018, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Effect of Compressor Inlet Temperature on Cycle Performance for a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
The 6th International Supercritical CO2 Power Cycles Symposium March 27-29, 2018, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Effect of Compressor Inlet Temperature on Cycle Performance for a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
Dynamic Coefficients in Hydrodynamic Bearing Analysis Steven Pasternak C.O. Engineering Sleeve and Sleevoil Bearings 8/10/18 WP0281
 Dynamic Coefficients in Hydrodynamic Bearing Analysis Steven Pasternak C.O. Engineering Sleeve and Sleevoil Bearings 8/10/18 WP0281 Hydrodynamic Bearing Basics Hydrodynamic journal bearings operate by
Dynamic Coefficients in Hydrodynamic Bearing Analysis Steven Pasternak C.O. Engineering Sleeve and Sleevoil Bearings 8/10/18 WP0281 Hydrodynamic Bearing Basics Hydrodynamic journal bearings operate by
CHAPTER 1. Introduction and Literature Review
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction and Literature Review 1.1 Introduction The Active Magnetic Bearing (AMB) is a device that uses electromagnetic forces to support a rotor without mechanical contact. The AMB offers
CHAPTER 1 Introduction and Literature Review 1.1 Introduction The Active Magnetic Bearing (AMB) is a device that uses electromagnetic forces to support a rotor without mechanical contact. The AMB offers
Design and Test of Transonic Compressor Rotor with Tandem Cascade
 Proceedings of the International Gas Turbine Congress 2003 Tokyo November 2-7, 2003 IGTC2003Tokyo TS-108 Design and Test of Transonic Compressor Rotor with Tandem Cascade Yusuke SAKAI, Akinori MATSUOKA,
Proceedings of the International Gas Turbine Congress 2003 Tokyo November 2-7, 2003 IGTC2003Tokyo TS-108 Design and Test of Transonic Compressor Rotor with Tandem Cascade Yusuke SAKAI, Akinori MATSUOKA,
ISCORMA-3, Cleveland, Ohio, September 2005
 Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software https://dyrobes.com ISCORMA-3, Cleveland, Ohio, 19-23 September 2005 APPLICATION OF ROTOR DYNAMIC ANALYSIS FOR EVALUATION OF SYNCHRONOUS SPEED INSTABILITY AND AMPLITUDE HYSTERESIS
Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software https://dyrobes.com ISCORMA-3, Cleveland, Ohio, 19-23 September 2005 APPLICATION OF ROTOR DYNAMIC ANALYSIS FOR EVALUATION OF SYNCHRONOUS SPEED INSTABILITY AND AMPLITUDE HYSTERESIS
Study on Flow Fields in Variable Area Nozzles for Radial Turbines
 Vol. 4 No. 2 August 27 Study on Fields in Variable Area Nozzles for Radial Turbines TAMAKI Hideaki : Doctor of Engineering, P. E. Jp, Manager, Turbo Machinery Department, Product Development Center, Corporate
Vol. 4 No. 2 August 27 Study on Fields in Variable Area Nozzles for Radial Turbines TAMAKI Hideaki : Doctor of Engineering, P. E. Jp, Manager, Turbo Machinery Department, Product Development Center, Corporate
Effect Of Bearing Faults On Dynamic Behavior And Electric Power Consumption Of Pumps
 Effect Of Bearing Faults On Dynamic Behavior And Electric Power Consumption Of Pumps Abstract Samir M. Abdel-Rahman Dalia M. Al-Gazar M. A. Helal Associate Professor Engineer Professor Mechanical & Electrical
Effect Of Bearing Faults On Dynamic Behavior And Electric Power Consumption Of Pumps Abstract Samir M. Abdel-Rahman Dalia M. Al-Gazar M. A. Helal Associate Professor Engineer Professor Mechanical & Electrical
719. Diagnostic research of rotor systems with variable inertia moment
 719. Diagnostic research of rotor systems with variable inertia moment Valentinas Kartašovas 1, Vytautas Barzdaitis 2, Pranas Mažeika 3, Marius Vasylius 4 1, 2 Kaunas University of Technology, Mickevičiaus
719. Diagnostic research of rotor systems with variable inertia moment Valentinas Kartašovas 1, Vytautas Barzdaitis 2, Pranas Mažeika 3, Marius Vasylius 4 1, 2 Kaunas University of Technology, Mickevičiaus
EXPERIMENTAL VERIFICATION OF INDUCED VOLTAGE SELF- EXCITATION OF A SWITCHED RELUCTANCE GENERATOR
 EXPERIMENTAL VERIFICATION OF INDUCED VOLTAGE SELF- EXCITATION OF A SWITCHED RELUCTANCE GENERATOR Velimir Nedic Thomas A. Lipo Wisconsin Power Electronic Research Center University of Wisconsin Madison
EXPERIMENTAL VERIFICATION OF INDUCED VOLTAGE SELF- EXCITATION OF A SWITCHED RELUCTANCE GENERATOR Velimir Nedic Thomas A. Lipo Wisconsin Power Electronic Research Center University of Wisconsin Madison
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012
 US 2012O163742A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0163742 A1 Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) AXIAL GAS THRUST BEARING FOR (30) Foreign
US 2012O163742A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0163742 A1 Underbakke et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) AXIAL GAS THRUST BEARING FOR (30) Foreign
Analysis and control of vehicle steering wheel angular vibrations
 Analysis and control of vehicle steering wheel angular vibrations T. LANDREAU - V. GILLET Auto Chassis International Chassis Engineering Department Summary : The steering wheel vibration is analyzed through
Analysis and control of vehicle steering wheel angular vibrations T. LANDREAU - V. GILLET Auto Chassis International Chassis Engineering Department Summary : The steering wheel vibration is analyzed through
FEDSM NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL FLOW ANALYSIS OF A CRYOGENIC POWER RECOVERY TURBINE
 Proceedings of FEDSM 98 1998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 1-5, 1998, Washington, DC FEDSM98-4988 NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL FLOW ANALYSIS OF A CRYOGENIC POWER RECOVERY TURBINE Nick
Proceedings of FEDSM 98 1998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 1-5, 1998, Washington, DC FEDSM98-4988 NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL FLOW ANALYSIS OF A CRYOGENIC POWER RECOVERY TURBINE Nick
EVALUATION OF THE ELLIPTICAL FLANGE CONFIGURATIONS FOR 24-INCH AND 30-INCH HEATER/COOLER UNITS
 Proceedings of the ASME PVP 2007/CREEP 8 Conference July 22-26, 2007, San Antonio, Texas USA Paper No. PVP2007-26080 EVALUATION OF THE ELLIPTICAL FLANGE CONFIGURATIONS FOR 24-INCH AND 30-INCH HEATER/COOLER
Proceedings of the ASME PVP 2007/CREEP 8 Conference July 22-26, 2007, San Antonio, Texas USA Paper No. PVP2007-26080 EVALUATION OF THE ELLIPTICAL FLANGE CONFIGURATIONS FOR 24-INCH AND 30-INCH HEATER/COOLER
Cage Bearing Concept for Large-scale Gear Systems
 Cage Bearing Concept for Large-scale Gear Systems Roland Lippert and Bruno Scherb INA reprint from Der Konstrukteur Vol. No. S 4, April 1999 Verlag für Technik und Wirtschaft, Mainz Cage Bearing Concept
Cage Bearing Concept for Large-scale Gear Systems Roland Lippert and Bruno Scherb INA reprint from Der Konstrukteur Vol. No. S 4, April 1999 Verlag für Technik und Wirtschaft, Mainz Cage Bearing Concept
20th. SOLUTIONS for FLUID MOVEMENT, MEASUREMENT & CONTAINMENT. Do You Need a Booster Pump? Is Repeatability or Accuracy More Important?
 Do You Need a Booster Pump? Secrets to Flowmeter Selection Success Is Repeatability or Accuracy More Important? 20th 1995-2015 SOLUTIONS for FLUID MOVEMENT, MEASUREMENT & CONTAINMENT Special Section Inside!
Do You Need a Booster Pump? Secrets to Flowmeter Selection Success Is Repeatability or Accuracy More Important? 20th 1995-2015 SOLUTIONS for FLUID MOVEMENT, MEASUREMENT & CONTAINMENT Special Section Inside!
Weight Reduction Finite Element Study of Selected Power Train Components for Heavy Duty Vehicles
 Phase II Progress Report No. F/MAE/NG/-2016-02 Weight Reduction Finite Element Study of Selected Power Train Components for Heavy Duty Vehicles Submitted to FIERF and AISI By James Lowrie, Research Assistant
Phase II Progress Report No. F/MAE/NG/-2016-02 Weight Reduction Finite Element Study of Selected Power Train Components for Heavy Duty Vehicles Submitted to FIERF and AISI By James Lowrie, Research Assistant
Piezoelectric Direct Drive Servovalve
 Piezoelectric Direct Drive Servovalve Jason E. Lindler, Eric H. Anderson CSA Engineering 2565 Leghorn Street, Mountain View, California Industrial and Commercial Applications of Smart Structures Technologies
Piezoelectric Direct Drive Servovalve Jason E. Lindler, Eric H. Anderson CSA Engineering 2565 Leghorn Street, Mountain View, California Industrial and Commercial Applications of Smart Structures Technologies
Comparison of different 600 kw designs of a new permanent magnet generator for wind power applications
 Comparison of different 600 kw designs of a new permanent magnet generator for wind power applications E. Peeters, Vito, Boeretang 200, 2400 Mol, Belgium, eefje.peeters@vito.be, tel +32 14 33 59 23, fax
Comparison of different 600 kw designs of a new permanent magnet generator for wind power applications E. Peeters, Vito, Boeretang 200, 2400 Mol, Belgium, eefje.peeters@vito.be, tel +32 14 33 59 23, fax
Copyright Notice. Small Motor, Gearmotor and Control Handbook Copyright Bodine Electric Company. All rights reserved.
 Copyright Notice Small Motor, Gearmotor and Control Handbook Copyright 1993-2003 Bodine Electric Company. All rights reserved. Unauthorized duplication, distribution, or modification of this publication,
Copyright Notice Small Motor, Gearmotor and Control Handbook Copyright 1993-2003 Bodine Electric Company. All rights reserved. Unauthorized duplication, distribution, or modification of this publication,
Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers
 Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers U. Bin-Nun FLIR Systems Inc. Boston, MA 01862 ABSTRACT Cryocooler self induced vibration is a major consideration in the design of IR
Reduction of Self Induced Vibration in Rotary Stirling Cycle Coolers U. Bin-Nun FLIR Systems Inc. Boston, MA 01862 ABSTRACT Cryocooler self induced vibration is a major consideration in the design of IR
Comparing the Lateral Behaviour of a Boil off Gas Compressor with Dry and Wet Seals
 International Journal of Science and Technology Volume 2 No. 2, February, 2013 Comparing the Lateral Behaviour of a Boil off Gas Compressor with Dry and Wet Seals Aimikhe, V.J and Akpabio, E.J 1 Petroleum
International Journal of Science and Technology Volume 2 No. 2, February, 2013 Comparing the Lateral Behaviour of a Boil off Gas Compressor with Dry and Wet Seals Aimikhe, V.J and Akpabio, E.J 1 Petroleum
MAIN SHAFT SUPPORT FOR WIND TURBINE WITH A FIXED AND FLOATING BEARING CONFIGURATION
 Technical Paper MAIN SHAFT SUPPORT FOR WIND TURBINE WITH A FIXED AND FLOATING BEARING CONFIGURATION Tapered Double Inner Row Bearing Vs. Spherical Roller Bearing On The Fixed Position Laurentiu Ionescu,
Technical Paper MAIN SHAFT SUPPORT FOR WIND TURBINE WITH A FIXED AND FLOATING BEARING CONFIGURATION Tapered Double Inner Row Bearing Vs. Spherical Roller Bearing On The Fixed Position Laurentiu Ionescu,
Experimental research on dynamic characteristics of gas bearing-rotor with different radial clearances
 Experimental research on dynamic characteristics of gas bearing-rotor with different radial clearances Long Hao 1, Jinfu Yang 2, Dongjiang Han 3, Changliang Tang 4 Institute of Engineering Thermophysics,
Experimental research on dynamic characteristics of gas bearing-rotor with different radial clearances Long Hao 1, Jinfu Yang 2, Dongjiang Han 3, Changliang Tang 4 Institute of Engineering Thermophysics,
Is Low Friction Efficient?
 Is Low Friction Efficient? Assessment of Bearing Concepts During the Design Phase Dipl.-Wirtsch.-Ing. Mark Dudziak; Schaeffler Trading (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China Dipl.-Ing. (TH) Andreas Krome,
Is Low Friction Efficient? Assessment of Bearing Concepts During the Design Phase Dipl.-Wirtsch.-Ing. Mark Dudziak; Schaeffler Trading (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China Dipl.-Ing. (TH) Andreas Krome,
CRITICAL SPEED ANALYSIS FOR DUAL ROTOR SYSTEM USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 CRITICAL SPEED ANALYSIS FOR DUAL ROTOR SYSTEM USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Kai Sun, Zhao Wan, Huiying Song, Shaohui Wang AVIC Commercial Aircraft Engine Co. Ltd, 3998 South Lianhua Road, 201108 Shanghai,
CRITICAL SPEED ANALYSIS FOR DUAL ROTOR SYSTEM USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Kai Sun, Zhao Wan, Huiying Song, Shaohui Wang AVIC Commercial Aircraft Engine Co. Ltd, 3998 South Lianhua Road, 201108 Shanghai,
Six keys to achieving better precision in linear motion control applications
 profile Drive & Control Six keys to achieving better precision in linear motion control applications Achieving precise linear motion Consider these factors when specifying linear motion systems: Equipped
profile Drive & Control Six keys to achieving better precision in linear motion control applications Achieving precise linear motion Consider these factors when specifying linear motion systems: Equipped
Research on the Structure of Linear Oscillation Motor and the Corresponding Applications on Piston Type Refrigeration Compressor
 International Conference on Informatization in Education, Management and Business (IEMB 2015) Research on the Structure of Linear Oscillation Motor and the Corresponding Applications on Piston Type Refrigeration
International Conference on Informatization in Education, Management and Business (IEMB 2015) Research on the Structure of Linear Oscillation Motor and the Corresponding Applications on Piston Type Refrigeration
Balancing with the presence of a rub
 Balancing with the presence of a rub Nicolas Péton 1 1 GE Measurement & Control, 14 rue de la Haltinière, CS 10356, 44303 Nantes, Cedex 3, France Abstract During commissioning of a cogeneration plant the
Balancing with the presence of a rub Nicolas Péton 1 1 GE Measurement & Control, 14 rue de la Haltinière, CS 10356, 44303 Nantes, Cedex 3, France Abstract During commissioning of a cogeneration plant the
Pearls from Martin J. King Quarter Wave Design
 Pearls from Martin J. King Quarter Wave Design An introduction by Bjorn Johannesen, Denmark. September the 1 st 2005. The first time you visit http://www.quarter-wave.com/, you might get overwhelmed by
Pearls from Martin J. King Quarter Wave Design An introduction by Bjorn Johannesen, Denmark. September the 1 st 2005. The first time you visit http://www.quarter-wave.com/, you might get overwhelmed by
IDENTIFICATION OF ABNORMAL ROTOR DYNAMIC STIFFNESS USING MEASURED VIBRATION INFORMATION AND ANALYTICAL MODELING
 Proceedings of PWR2009 ASME Power July 21-23, 2009, Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA Power2009-81019 IDENTIFICATION OF ABNORMAL ROTOR DYNAMIC STIFFNESS USING MEASURED VIBRATION INFORMATION AND ANALYTICAL MODELING
Proceedings of PWR2009 ASME Power July 21-23, 2009, Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA Power2009-81019 IDENTIFICATION OF ABNORMAL ROTOR DYNAMIC STIFFNESS USING MEASURED VIBRATION INFORMATION AND ANALYTICAL MODELING
Improvement of Vehicle Dynamics by Right-and-Left Torque Vectoring System in Various Drivetrains x
 Improvement of Vehicle Dynamics by Right-and-Left Torque Vectoring System in Various Drivetrains x Kaoru SAWASE* Yuichi USHIRODA* Abstract This paper describes the verification by calculation of vehicle
Improvement of Vehicle Dynamics by Right-and-Left Torque Vectoring System in Various Drivetrains x Kaoru SAWASE* Yuichi USHIRODA* Abstract This paper describes the verification by calculation of vehicle
Cooling Enhancement of Electric Motors
 Cooling Enhancement of Electric Motors Authors : Yasser G. Dessouky* and Barry W. Williams** Dept. of Computing & Electrical Engineering Heriot-Watt University Riccarton, Edinburgh EH14 4AS, U.K. Fax :
Cooling Enhancement of Electric Motors Authors : Yasser G. Dessouky* and Barry W. Williams** Dept. of Computing & Electrical Engineering Heriot-Watt University Riccarton, Edinburgh EH14 4AS, U.K. Fax :
CFD on Cavitation around Marine Propellers with Energy-Saving Devices
 63 CFD on Cavitation around Marine Propellers with Energy-Saving Devices CHIHARU KAWAKITA *1 REIKO TAKASHIMA *2 KEI SATO *2 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (MHI) has developed energy-saving devices that
63 CFD on Cavitation around Marine Propellers with Energy-Saving Devices CHIHARU KAWAKITA *1 REIKO TAKASHIMA *2 KEI SATO *2 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (MHI) has developed energy-saving devices that
ME High Pressure Stage Casing Pump
 Sulzer Pumps ME High Pressure Stage Casing Pump The Heart of Your Process Sulzer Pumps Your Partner for Pumping Solutions Sulzer Pumps is one of the world leaders in state-of-the-art pumping solutions.
Sulzer Pumps ME High Pressure Stage Casing Pump The Heart of Your Process Sulzer Pumps Your Partner for Pumping Solutions Sulzer Pumps is one of the world leaders in state-of-the-art pumping solutions.
Subsynchronous Shaft Vibration in an Integrally Geared Expander-Compressor due to Vortex Flow in an Expander
 Subsynchronous Shaft Vibration in an Integrally Geared Expander-Compressor due to Vortex Flow in an Expander Daisuke Hirata cting Manager, Engineering & Design Division Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Compressor
Subsynchronous Shaft Vibration in an Integrally Geared Expander-Compressor due to Vortex Flow in an Expander Daisuke Hirata cting Manager, Engineering & Design Division Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Compressor
ROTORDYNAMICS OF SEMI-RIGID AND OVERHUNG TURBOMACHINERY
 ROTORDYNAMICS OF SEMI-RIGID AND OVERHUNG TURBOMACHINERY Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Co. P.O. BOX 157 Dickinson, TX 77539 MLeader@RotorBearingDynamics.COM Abstract: This paper continues
ROTORDYNAMICS OF SEMI-RIGID AND OVERHUNG TURBOMACHINERY Malcolm E. Leader, P.E. Applied Machinery Dynamics Co. P.O. BOX 157 Dickinson, TX 77539 MLeader@RotorBearingDynamics.COM Abstract: This paper continues
APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE
 Colloquium DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 2012 Prague, February 7 8, 2011 CzechNC APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE Jiří Šimek Abstract: New type of aerodynamic
Colloquium DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 2012 Prague, February 7 8, 2011 CzechNC APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE Jiří Šimek Abstract: New type of aerodynamic
New Way Porous Gas Bearings as Seals. Bearings Seals
 New Way Porous Gas Bearings as Seals Bearings Seals New Way Overview TM Founded January 1994. Aston, Pa. 15 miles south of Philadelphia 54 employees 35,000 sq ft facility, Environmentally Controlled Precision
New Way Porous Gas Bearings as Seals Bearings Seals New Way Overview TM Founded January 1994. Aston, Pa. 15 miles south of Philadelphia 54 employees 35,000 sq ft facility, Environmentally Controlled Precision
Low-torque Deep-groove Ball Bearings for Transmissions
 New Product Low-torque Deep-groove Ball Bearings for Transmissions Katsuaki SASAKI To achieve low fuel consumption in response to environmental concerns, we have focused on reducing the friction of tapered
New Product Low-torque Deep-groove Ball Bearings for Transmissions Katsuaki SASAKI To achieve low fuel consumption in response to environmental concerns, we have focused on reducing the friction of tapered
Chapter 2. Background
 Chapter 2 Background The purpose of this chapter is to provide the necessary background for this research. This chapter will first discuss the tradeoffs associated with typical passive single-degreeof-freedom
Chapter 2 Background The purpose of this chapter is to provide the necessary background for this research. This chapter will first discuss the tradeoffs associated with typical passive single-degreeof-freedom
IMECE DESIGN OF A VARIABLE RADIUS PISTON PROFILE GENERATING ALGORITHM
 Proceedings of the ASME 2009 International Mechanical Engineering Conference and Exposition ASME/IMECE 2009 November 13-19, 2009, Buena Vista, USA IMECE2009-11364 DESIGN OF A VARIABLE RADIUS PISTON PROFILE
Proceedings of the ASME 2009 International Mechanical Engineering Conference and Exposition ASME/IMECE 2009 November 13-19, 2009, Buena Vista, USA IMECE2009-11364 DESIGN OF A VARIABLE RADIUS PISTON PROFILE
Computer Model for a Parallel Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) with CVT
 Proceedings of the American Control Conference Chicago, Illinois June 2000 Computer Model for a Parallel Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) with CVT Barry Powell, Xianjie Zhang, Robert Baraszu Scientific Research
Proceedings of the American Control Conference Chicago, Illinois June 2000 Computer Model for a Parallel Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) with CVT Barry Powell, Xianjie Zhang, Robert Baraszu Scientific Research
Development of TPL and TPS Series Marine Turbocharger
 Development of TPL and TPS Series Marine Turbocharger IWAKI Fuminori : MITSUBORI Ken : General Machinery Engineering Department, Rotating Machinery Division, Industrial Machinery Chief Engineer, General
Development of TPL and TPS Series Marine Turbocharger IWAKI Fuminori : MITSUBORI Ken : General Machinery Engineering Department, Rotating Machinery Division, Industrial Machinery Chief Engineer, General
Improvements for Ver November 23, 2017
 Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software dyrobes.com Improvements for Ver 20.00 November 23, 2017 Add new features in BePerf for fixed-lobe and tilting pad journal bearing design: 1) Parametric study 2) Design Comparison.
Dyrobes Rotordynamics Software dyrobes.com Improvements for Ver 20.00 November 23, 2017 Add new features in BePerf for fixed-lobe and tilting pad journal bearing design: 1) Parametric study 2) Design Comparison.
NEW CONCEPT OF A ROCKER ENGINE KINEMATIC ANALYSIS
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 19, No. 3 2012 NEW CONCEPT OF A ROCKER ENGINE KINEMATIC ANALYSIS Miros aw Szymkowiak Kochanowskiego Street 13, 64-100 Leszno, Poland e-mail: szymkowiak@op.pl
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 19, No. 3 2012 NEW CONCEPT OF A ROCKER ENGINE KINEMATIC ANALYSIS Miros aw Szymkowiak Kochanowskiego Street 13, 64-100 Leszno, Poland e-mail: szymkowiak@op.pl
Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset
 Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset Vikas Kumar Agarwal Deputy Manager Mahindra Two Wheelers Ltd. MIDC Chinchwad Pune 411019 India Abbreviations:
Multi Body Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank Mechanism to Study the effect of Cylinder Offset Vikas Kumar Agarwal Deputy Manager Mahindra Two Wheelers Ltd. MIDC Chinchwad Pune 411019 India Abbreviations:
TURBOLINK BEARINGS L U I D I L M E A R I N G S. Manufcturing Engineering Consulting Service & Retrofit
 TURBOLINK BEARINGS Manufcturing Engineering Consulting Service & Retrofit L U I D I L M E A R I N G S 제작 : 2012. 10 #111 5th Standard Factory, 41-3 Paryongdong, Changwon, 641-847 Korea Tel : +82-55-267-3715
TURBOLINK BEARINGS Manufcturing Engineering Consulting Service & Retrofit L U I D I L M E A R I N G S 제작 : 2012. 10 #111 5th Standard Factory, 41-3 Paryongdong, Changwon, 641-847 Korea Tel : +82-55-267-3715
A Recommended Approach to Pipe Stress Analysis to Avoid Compressor Piping Integrity Risk
 A Recommended Approach to Pipe Stress Analysis to Avoid Compressor Piping Integrity Risk by: Kelly Eberle, P.Eng. Beta Machinery Analysis Calgary, AB Canada keberle@betamachinery.com keywords: reciprocating
A Recommended Approach to Pipe Stress Analysis to Avoid Compressor Piping Integrity Risk by: Kelly Eberle, P.Eng. Beta Machinery Analysis Calgary, AB Canada keberle@betamachinery.com keywords: reciprocating
Case Study #8. 26 th Texas A&M International Pump Users Symposium March, Malcolm E. Leader Kelly J Conner Jamie D. Lucas
 Evaluating and Correcting Subsynchronous Vibration In Vertical Pumps Case Study #8 26 th Texas A&M International Pump Users Symposium March, 2010 Malcolm E. Leader Kelly J Conner Jamie D. Lucas Case Study
Evaluating and Correcting Subsynchronous Vibration In Vertical Pumps Case Study #8 26 th Texas A&M International Pump Users Symposium March, 2010 Malcolm E. Leader Kelly J Conner Jamie D. Lucas Case Study
Oscillating Mountings
 Type HS for hanging screens H B F E HS 7 38 D A HS 45 50 HS 50- Z C G M L M L M L Art. o. Type Load capacity Gmin. G [] A unloaded A* load B unloaded B* load C D E F H L M Weight [kg] 07 311 001 HS 7 500
Type HS for hanging screens H B F E HS 7 38 D A HS 45 50 HS 50- Z C G M L M L M L Art. o. Type Load capacity Gmin. G [] A unloaded A* load B unloaded B* load C D E F H L M Weight [kg] 07 311 001 HS 7 500
High Speed Reciprocating Compressors The Importance of Interactive Modeling
 High Speed Reciprocating Compressors The Importance of Interactive Modeling Christine M. Gehri Ralph E. Harris, Ph.D. Southwest Research Institute ABSTRACT Cost-effective, reliable operation of reciprocating
High Speed Reciprocating Compressors The Importance of Interactive Modeling Christine M. Gehri Ralph E. Harris, Ph.D. Southwest Research Institute ABSTRACT Cost-effective, reliable operation of reciprocating
Magnetic Bearings for Supercritical CO2 Turbomachinery
 The 6 th International Supercritical CO 2 Power Cycles Symposium March 27-29, 2018, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Magnetic Bearings for Supercritical CO2 Turbomachinery Richard Shultz Chief Engineer Waukesha
The 6 th International Supercritical CO 2 Power Cycles Symposium March 27-29, 2018, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Magnetic Bearings for Supercritical CO2 Turbomachinery Richard Shultz Chief Engineer Waukesha
APS 420 ELECTRO-SEIS Long Stroke Shaker with Linear Ball Bearings Page 1 of 5
 Long Stroke Shaker with Linear Ball Bearings Page 1 of 5 The APS 420 ELECTRO-SEIS shaker is a long stroke, electrodynamic force generator specifically designed to be used alone or in arrays for studying
Long Stroke Shaker with Linear Ball Bearings Page 1 of 5 The APS 420 ELECTRO-SEIS shaker is a long stroke, electrodynamic force generator specifically designed to be used alone or in arrays for studying
Effects of Large Bending Deflections on Blade Flutter Limits. UpWind Deliverable D2.3. Bjarne Skovmose Kallesøe Morten Hartvig Hansen.
 Effects of Large Bending Deflections on Blade Flutter Limits UpWind Deliverable D2.3 Bjarne Skovmose Kallesøe Morten Hartvig Hansen Risø R 1642(EN) Risø National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy Technical
Effects of Large Bending Deflections on Blade Flutter Limits UpWind Deliverable D2.3 Bjarne Skovmose Kallesøe Morten Hartvig Hansen Risø R 1642(EN) Risø National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy Technical
The Design Aspects of Metal- Polymer Bushings in Compressor Applications
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 The Design Aspects of Metal- Polymer Bushings in Compressor Applications Christopher
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 The Design Aspects of Metal- Polymer Bushings in Compressor Applications Christopher
MARINE FOUR-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING OIL FILM LUBRICATION CHARACTERISTIC ANALYSIS
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH Special Issue 2018 S2 (98) 2018 Vol. 25; pp. 30-34 10.2478/pomr-2018-0070 MARINE FOUR-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING OIL FILM LUBRICATION CHARACTERISTIC ANALYSIS
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH Special Issue 2018 S2 (98) 2018 Vol. 25; pp. 30-34 10.2478/pomr-2018-0070 MARINE FOUR-STROKE DIESEL ENGINE CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING OIL FILM LUBRICATION CHARACTERISTIC ANALYSIS
Research on vibration reduction of multiple parallel gear shafts with ISFD
 Research on vibration reduction of multiple parallel gear shafts with ISFD Kaihua Lu 1, Lidong He 2, Wei Yan 3 Beijing Key Laboratory of Health Monitoring and Self-Recovery for High-End Mechanical Equipment,
Research on vibration reduction of multiple parallel gear shafts with ISFD Kaihua Lu 1, Lidong He 2, Wei Yan 3 Beijing Key Laboratory of Health Monitoring and Self-Recovery for High-End Mechanical Equipment,
VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT OIL PUMP IMPROVES TRACKED VEHICLE TRANSMISSION EFFICIENCY
 2018 NDIA GROUND VEHICLE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SYMPOSIUM POWER & MOBILITY (P&M) TECHNICAL SESSION AUGUST 7-9, 2018 NOVI, MICHIGAN VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT OIL PUMP IMPROVES TRACKED VEHICLE TRANSMISSION
2018 NDIA GROUND VEHICLE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SYMPOSIUM POWER & MOBILITY (P&M) TECHNICAL SESSION AUGUST 7-9, 2018 NOVI, MICHIGAN VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT OIL PUMP IMPROVES TRACKED VEHICLE TRANSMISSION
OBSERVATIONS ABOUT ROTATING AND RECIPROCATING EQUIPMENT
 OBSERVATIONS ABOUT ROTATING AND RECIPROCATING EQUIPMENT Brian Howes Beta Machinery Analysis, Calgary, AB, Canada, T3C 0J7 ABSTRACT This paper discusses several small issues that have occurred in the last
OBSERVATIONS ABOUT ROTATING AND RECIPROCATING EQUIPMENT Brian Howes Beta Machinery Analysis, Calgary, AB, Canada, T3C 0J7 ABSTRACT This paper discusses several small issues that have occurred in the last
Externally Pressurized Bearings and Machinery Diagnostics
 D23 Externally Pressurized MD.qxd 9/1/22 11:17 AM Page 499 499 Chapter 23 Externally Pressurized Bearings and Machinery Diagnostics IN PREVIOUS SECTIONS OF THIS BOOK, we have discussed machinery diagnostics
D23 Externally Pressurized MD.qxd 9/1/22 11:17 AM Page 499 499 Chapter 23 Externally Pressurized Bearings and Machinery Diagnostics IN PREVIOUS SECTIONS OF THIS BOOK, we have discussed machinery diagnostics
Compressor Noise Control
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1972 Compressor Noise Control G. M. Diehl Ingersoll-Rand Research Follow this and additional
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1972 Compressor Noise Control G. M. Diehl Ingersoll-Rand Research Follow this and additional
DAVINCH Lite Chamber Design By Analysis and Full-Scale Testing CWD 2014 London, United Kingdom June 4-6, 2014
 DAVINCH Lite Chamber Design By Analysis and Full-Scale Testing CWD 2014 London, United Kingdom June 4-6, 2014 Robert E. Nickell, Consultant, San Diego, CA, USA Takao Shirakura, Transnuclear, Ltd., Tokyo,
DAVINCH Lite Chamber Design By Analysis and Full-Scale Testing CWD 2014 London, United Kingdom June 4-6, 2014 Robert E. Nickell, Consultant, San Diego, CA, USA Takao Shirakura, Transnuclear, Ltd., Tokyo,
SOME INTERESTING ESTING FEATURES OF TURBOCHARGER ROTOR DYNAMICS
 Colloquium DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 2013 Prague, February 5 6, 2013 CzechNC 1. I SOME INTERESTING ESTING FEATURES OF TURBOCHARGER ROTOR DYNAMICS Jiří Šimek Abstract: Turbochargers for combustion engines are
Colloquium DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 2013 Prague, February 5 6, 2013 CzechNC 1. I SOME INTERESTING ESTING FEATURES OF TURBOCHARGER ROTOR DYNAMICS Jiří Šimek Abstract: Turbochargers for combustion engines are
5 kw Multilevel DC-DC Converter for Hybrid Electric and Fuel Cell Automotive Applications
 1 5 kw Multilevel DC-DC Converter for Hybrid Electric and Fuel Cell Automotive Applications Faisal H. Khan 1,2 Leon M. Tolbert 2 fkhan3@utk.edu tolbert@utk.edu 2 Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI)
1 5 kw Multilevel DC-DC Converter for Hybrid Electric and Fuel Cell Automotive Applications Faisal H. Khan 1,2 Leon M. Tolbert 2 fkhan3@utk.edu tolbert@utk.edu 2 Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI)
INDUCTION motors are widely used in various industries
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 44, NO. 6, DECEMBER 1997 809 Minimum-Time Minimum-Loss Speed Control of Induction Motors Under Field-Oriented Control Jae Ho Chang and Byung Kook Kim,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 44, NO. 6, DECEMBER 1997 809 Minimum-Time Minimum-Loss Speed Control of Induction Motors Under Field-Oriented Control Jae Ho Chang and Byung Kook Kim,
The Effects of Magnetic Circuit Geometry on Torque Generation of 8/14 Switched Reluctance Machine
 213 XXIV International Conference on Information, Communication and Automation Technologies (ICAT) October 3 November 1, 213, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina The Effects of Magnetic Circuit Geometry on
213 XXIV International Conference on Information, Communication and Automation Technologies (ICAT) October 3 November 1, 213, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina The Effects of Magnetic Circuit Geometry on
Design and Field Test of a Full Scale Performance Augmentation Network (PAN) 2014 GMRC Research Project
 2014 GMRC Gas Machinery Conference Nashville, TN October 6-8, 2014 Design and Field Test of a Full Scale Performance Augmentation Network (PAN) 2014 GMRC Research Project W. Norman Shade, PE & John J.
2014 GMRC Gas Machinery Conference Nashville, TN October 6-8, 2014 Design and Field Test of a Full Scale Performance Augmentation Network (PAN) 2014 GMRC Research Project W. Norman Shade, PE & John J.
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial Number 09/652.303 Filing Date 28 August 2000 Inventor Antoniko M. Amaral Stanley J. Olson NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should
Serial Number 09/652.303 Filing Date 28 August 2000 Inventor Antoniko M. Amaral Stanley J. Olson NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should
ONLINE NON-CONTACT TORSION SENSING METHOD USING FIBER BRAGG GRATING SENSORS AND OPTICAL COUPLING METHOD. Yoha Hwang and Jong Min Lee
 ICSV14 Cairns Australia 9-1 July, 007 ONLINE NON-CONTACT TORSION SENSING METHOD USING FIBER BRAGG GRATING SENSORS AND OPTICAL COUPLING METHOD Yoha Hwang and Jong Min Lee Intelligent System Research Division,
ICSV14 Cairns Australia 9-1 July, 007 ONLINE NON-CONTACT TORSION SENSING METHOD USING FIBER BRAGG GRATING SENSORS AND OPTICAL COUPLING METHOD Yoha Hwang and Jong Min Lee Intelligent System Research Division,
A Magneto-rheological Fluid Squeeze Film Damper for Rotor Vibration Control
 A Magneto-rheological Fluid Squeeze Film Damper for Rotor Vibration Control Changsheng Zhu Department of Electrical Engineering, Zhejiang University Hangzhou, 310027, Zhejiang, P. R. of China David A.
A Magneto-rheological Fluid Squeeze Film Damper for Rotor Vibration Control Changsheng Zhu Department of Electrical Engineering, Zhejiang University Hangzhou, 310027, Zhejiang, P. R. of China David A.
White paper: Originally published in ISA InTech Magazine Page 1
 Page 1 Improving Differential Pressure Diaphragm Seal System Performance and Installed Cost Tuned-Systems ; Deliver the Best Practice Diaphragm Seal Installation To Compensate Errors Caused by Temperature
Page 1 Improving Differential Pressure Diaphragm Seal System Performance and Installed Cost Tuned-Systems ; Deliver the Best Practice Diaphragm Seal Installation To Compensate Errors Caused by Temperature
Introduction. Lubrication Related Failures. Gear Couplings. Failure Analysis All Types (Page 1 of 7)
 All Types (Page 1 of 7) Introduction A gear coupling serves as a mechanical device which connects shafts of two separate machines and accommodates small amounts of shaft misalignment. Commercial gear couplings
All Types (Page 1 of 7) Introduction A gear coupling serves as a mechanical device which connects shafts of two separate machines and accommodates small amounts of shaft misalignment. Commercial gear couplings
Revision 4 May 23, 2018
 Kalsi Seals Handbook Chapter C16 Plastic lined Kalsi Seals Revision 4 May 23, 2018 Individual chapters of the Kalsi Seals Handbook are periodically updated. To determine if a newer revision of this chapter
Kalsi Seals Handbook Chapter C16 Plastic lined Kalsi Seals Revision 4 May 23, 2018 Individual chapters of the Kalsi Seals Handbook are periodically updated. To determine if a newer revision of this chapter
TURBOGENERATOR DYNAMIC ANALYSIS TO IDENTIFY CRITICAL SPEED AND VIBRATION SEVERITY
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series D, Vol. 77, Iss. 3, 2015 ISSN 1454-2358 TURBOGENERATOR DYNAMIC ANALYSIS TO IDENTIFY CRITICAL SPEED AND VIBRATION SEVERITY Claudiu BISU 1, Florian ISTRATE 2, Marin ANICA 3 Vibration
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series D, Vol. 77, Iss. 3, 2015 ISSN 1454-2358 TURBOGENERATOR DYNAMIC ANALYSIS TO IDENTIFY CRITICAL SPEED AND VIBRATION SEVERITY Claudiu BISU 1, Florian ISTRATE 2, Marin ANICA 3 Vibration
Pulsation dampers for combustion engines
 ICLASS 2012, 12 th Triennial International Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Heidelberg, Germany, September 2-6, 2012 Pulsation dampers for combustion engines F.Durst, V. Madila, A.Handtmann,
ICLASS 2012, 12 th Triennial International Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Heidelberg, Germany, September 2-6, 2012 Pulsation dampers for combustion engines F.Durst, V. Madila, A.Handtmann,
APS 113 ELECTRO-SEIS Long Stroke Shaker with Linear Ball Bearings Page 1 of 5
 Long Stroke Shaker with Linear Ball Bearings Page 1 of 5 The ELECTRO-SEIS shaker is a long stroke, electrodynamic force generator specifically designed to be used alone or in arrays for studying dynamic
Long Stroke Shaker with Linear Ball Bearings Page 1 of 5 The ELECTRO-SEIS shaker is a long stroke, electrodynamic force generator specifically designed to be used alone or in arrays for studying dynamic
Components of Hydronic Systems
 Valve and Actuator Manual 977 Hydronic System Basics Section Engineering Bulletin H111 Issue Date 0789 Components of Hydronic Systems The performance of a hydronic system depends upon many factors. Because
Valve and Actuator Manual 977 Hydronic System Basics Section Engineering Bulletin H111 Issue Date 0789 Components of Hydronic Systems The performance of a hydronic system depends upon many factors. Because
PRECISION BELLOWS COUPLINGS
 PRECISION BELLOWS COUPLINGS Bellows couplings are used where precise rotation, high speeds, and dynamic motion must be transmitted. They exhibit zero backlash and a high level of torsional stiffness, offering
PRECISION BELLOWS COUPLINGS Bellows couplings are used where precise rotation, high speeds, and dynamic motion must be transmitted. They exhibit zero backlash and a high level of torsional stiffness, offering
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD20: Last updated: 26th September 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD20: Last updated: 26th September 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
Relative ride vibration of off-road vehicles with front-, rear- and both axles torsio-elastic suspension
 Relative ride vibration of off-road vehicles with front-, rear- and both axles torsio-elastic suspension Mu Chai 1, Subhash Rakheja 2, Wen Bin Shangguan 3 1, 2, 3 School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,
Relative ride vibration of off-road vehicles with front-, rear- and both axles torsio-elastic suspension Mu Chai 1, Subhash Rakheja 2, Wen Bin Shangguan 3 1, 2, 3 School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,
Linear Shaft Motors in Parallel Applications
 Linear Shaft Motors in Parallel Applications Nippon Pulse s Linear Shaft Motor (LSM) has been successfully used in parallel motor applications. Parallel applications are ones in which there are two or
Linear Shaft Motors in Parallel Applications Nippon Pulse s Linear Shaft Motor (LSM) has been successfully used in parallel motor applications. Parallel applications are ones in which there are two or
APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE
 Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 19, 2012, No. 5, p. 359 368 359 APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE Jiří Šimek* New type of aerodynamic tilting pad journal
Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 19, 2012, No. 5, p. 359 368 359 APPLICATION OF A NEW TYPE OF AERODYNAMIC TILTING PAD JOURNAL BEARING IN POWER GYROSCOPE Jiří Šimek* New type of aerodynamic tilting pad journal
CO 2 Transportation and Injection Pumps
 CO 2 Transportation and Injection Pumps DMX WIK/WIKO DVSR Experience In Motion The Preferred Choice for CO 2 Pumps and Seals Whether for pipeline or injection service, Flowserve boasts unrivaled expertise
CO 2 Transportation and Injection Pumps DMX WIK/WIKO DVSR Experience In Motion The Preferred Choice for CO 2 Pumps and Seals Whether for pipeline or injection service, Flowserve boasts unrivaled expertise
AN INVESTIGATION IN RADIAL GAP AIR-RIDING SEALS FOR AERO-ENGINES
 AN INVESTIGATION IN RADIAL GAP AIR-RIDING SEALS FOR AERO-ENGINES Shubham Kumar, Seamus Garvey and Hervé Morvan The University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom E-Mail: Shubham.Kumar@nottingham.ac.uk
AN INVESTIGATION IN RADIAL GAP AIR-RIDING SEALS FOR AERO-ENGINES Shubham Kumar, Seamus Garvey and Hervé Morvan The University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom E-Mail: Shubham.Kumar@nottingham.ac.uk
Forced vibration frequency response for a permanent magnetic planetary gear
 Forced vibration frequency response for a permanent magnetic planetary gear Xuejun Zhu 1, Xiuhong Hao 2, Minggui Qu 3 1 Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Parallel Robot and Mechatronic System, Yanshan
Forced vibration frequency response for a permanent magnetic planetary gear Xuejun Zhu 1, Xiuhong Hao 2, Minggui Qu 3 1 Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Parallel Robot and Mechatronic System, Yanshan
T E C H N I C A L P A P E R
 Wheeler Industries, Inc. An ISO9002 Certified Supplier 7261 Investment Drive N. Charleston, SC 29418 Tel: 843-552-1251 Fax: 843-552-4790 Website: www.wheeler-ind.com T E C H N I C A L P A P E R Design
Wheeler Industries, Inc. An ISO9002 Certified Supplier 7261 Investment Drive N. Charleston, SC 29418 Tel: 843-552-1251 Fax: 843-552-4790 Website: www.wheeler-ind.com T E C H N I C A L P A P E R Design
VALVE-INDUCED PIPING VIBRATION
 Proceedings of the ASME 2011 Pressure Vessel and Piping Division Conference PVP2011 July 17-21, 2011, Baltimore, Maryland PVP2011-57391 VALVE-INDUCED PIPING VIBRATION Michael A. Porter Porter McGuffie,
Proceedings of the ASME 2011 Pressure Vessel and Piping Division Conference PVP2011 July 17-21, 2011, Baltimore, Maryland PVP2011-57391 VALVE-INDUCED PIPING VIBRATION Michael A. Porter Porter McGuffie,
Design Modification and Optimization of Trolley in an Off-Bearer Mechanism Present In Concrete Block Making Machines
 Design Modification and Optimization of Trolley in an Off-Bearer Mechanism Present In Concrete Block Making Machines Aravindhan. V 1, Anantha Krishnan. P 2 1,2Final Year UG Students, Dept. of Mechanical
Design Modification and Optimization of Trolley in an Off-Bearer Mechanism Present In Concrete Block Making Machines Aravindhan. V 1, Anantha Krishnan. P 2 1,2Final Year UG Students, Dept. of Mechanical
Figure1: Kone EcoDisc electric elevator drive [2]
![Figure1: Kone EcoDisc electric elevator drive [2] Figure1: Kone EcoDisc electric elevator drive [2]](/thumbs/77/75088735.jpg) Implementation of an Elevator s Position-Controlled Electric Drive 1 Ihedioha Ahmed C. and 2 Anyanwu A.M 1 Enugu State University of Science and Technology Enugu, Nigeria 2 Transmission Company of Nigeria
Implementation of an Elevator s Position-Controlled Electric Drive 1 Ihedioha Ahmed C. and 2 Anyanwu A.M 1 Enugu State University of Science and Technology Enugu, Nigeria 2 Transmission Company of Nigeria
Development of a Superconducting High-Speed Flywheel Energy Storage System
 Juni 2015 Development of a Superconducting High-Speed Flywheel Energy Storage System W. Walter 8. Braunschweiger Supraleiterseminar 2015 Outline Background SC bearing prototype Technology demonstrator
Juni 2015 Development of a Superconducting High-Speed Flywheel Energy Storage System W. Walter 8. Braunschweiger Supraleiterseminar 2015 Outline Background SC bearing prototype Technology demonstrator
MIKLOS Cristina Carmen, MIKLOS Imre Zsolt UNIVERSITY POLITEHNICA TIMISOARA FACULTY OF ENGINEERING HUNEDOARA ABSTRACT:
 1 2 THEORETICAL ASPECTS ABOUT THE ACTUAL RESEARCH CONCERNING THE PHYSICAL AND MATHEMATICAL MODELING CATENARY SUSPENSION AND PANTOGRAPH IN ELECTRIC RAILWAY TRACTION MIKLOS Cristina Carmen, MIKLOS Imre Zsolt
1 2 THEORETICAL ASPECTS ABOUT THE ACTUAL RESEARCH CONCERNING THE PHYSICAL AND MATHEMATICAL MODELING CATENARY SUSPENSION AND PANTOGRAPH IN ELECTRIC RAILWAY TRACTION MIKLOS Cristina Carmen, MIKLOS Imre Zsolt
Development of Integrated Vehicle Dynamics Control System S-AWC
 Development of Integrated Vehicle Dynamics Control System S-AWC Takami MIURA* Yuichi USHIRODA* Kaoru SAWASE* Naoki TAKAHASHI* Kazufumi HAYASHIKAWA** Abstract The Super All Wheel Control (S-AWC) for LANCER
Development of Integrated Vehicle Dynamics Control System S-AWC Takami MIURA* Yuichi USHIRODA* Kaoru SAWASE* Naoki TAKAHASHI* Kazufumi HAYASHIKAWA** Abstract The Super All Wheel Control (S-AWC) for LANCER
High-voltage Direct Inverter Applied to Induced Draft Fan Motor at Takehara Thermal Power Station No. 3 of Electric Power Development Co., Ltd.
 Hitachi Review Vol. 53 (2004), No. 3 121 High-voltage Direct Inverter Applied to Induced Draft Fan Motor at Takehara Thermal Power Station No. 3 of Electric Power Development Co., Ltd. Hiroaki Yamada Kiyoshi
Hitachi Review Vol. 53 (2004), No. 3 121 High-voltage Direct Inverter Applied to Induced Draft Fan Motor at Takehara Thermal Power Station No. 3 of Electric Power Development Co., Ltd. Hiroaki Yamada Kiyoshi
The Development of a New Generation of Miniature Long-Life Linear Coolers
 The Development of a New Generation of Miniature Long-Life Linear Coolers W. van de Groep, J. Mullié, D. Willems, F. van Wordragen, T. Benschop Thales Cryogenics Eindhoven, The Netherlands ABSTRACT Thales
The Development of a New Generation of Miniature Long-Life Linear Coolers W. van de Groep, J. Mullié, D. Willems, F. van Wordragen, T. Benschop Thales Cryogenics Eindhoven, The Netherlands ABSTRACT Thales
Electric Drive - Magnetic Suspension Rotorcraft Technologies
 Electric Drive - Suspension Rotorcraft Technologies William Nunnally Chief Scientist SunLase, Inc. Sapulpa, OK 74066-6032 wcn.sunlase@gmail.com ABSTRACT The recent advances in electromagnetic technologies
Electric Drive - Suspension Rotorcraft Technologies William Nunnally Chief Scientist SunLase, Inc. Sapulpa, OK 74066-6032 wcn.sunlase@gmail.com ABSTRACT The recent advances in electromagnetic technologies
Extremely High Load Capacity Tapered Roller Bearings
 New Product Extremely High Load Capacity Tapered Roller Bearings Takashi UENO Tomoki MATSUSHITA Standard tapered roller bearing Extreme high load capacity bearing NTN developed a tapered roller bearing
New Product Extremely High Load Capacity Tapered Roller Bearings Takashi UENO Tomoki MATSUSHITA Standard tapered roller bearing Extreme high load capacity bearing NTN developed a tapered roller bearing
